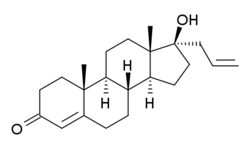
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 17α-Allyltestosterone; 17α-Allylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H32O2 |
| Molar mass | 328.496 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Allyltestosterone, or 17α-allyltestosterone, also known as 17α-allylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a steroid derived from testosterone that was first synthesized in 1936 and was never marketed. Along with propyltestosterone (topterone), it has been patented as a topical antiandrogen and hair growth inhibitor. Allyltestosterone is the parent structure of two marketed 19-nortestosterone progestins, allylestrenol and altrenogest. These progestins are unique among testosterone derivatives in that they appear to be associated with few or no androgenic effects.
See also
- Steroidal antiandrogen
- List of steroidal antiandrogens
- Allylnortestosterone
- Ethinyltestosterone
- Vinyltestosterone
References
- Josephy E, Radt F (1 December 2013). "Allyltestosterone". Elsevier's Encyclopaedia of Organic Chemistry: Series III: Carboisocyclic Condensed Compounds. Springer. pp. 2653–. ISBN 978-3-662-25863-7.
- ^ Ahluwalia GS (16 December 2008). "Management of unwanted hair". In Ahluwalia G (ed.). Cosmetics Applications of Laser and Light-Based Systems. William Andrew. pp. 239–252 (248). ISBN 978-0-8155-1967-6.
- US 4885289, Breuer MM, Kaszynski EG, Shander D, Usdin VR, van der Lee H, "Alteration of character of male beard growth", issued 5 December 1989, assigned to Gillette Co LLC.
- Zeelen FJ (1990). Medicinal chemistry of steroids. Elsevier Science Limited. pp. 108–109. ISBN 978-0-444-88727-6.
Other examples are allylestrenol (42), a pro-drug converted to the 3-keto analogue (43), which is used in the treatment of threatened abortion and altrenogest (44), used in sows and mares to suppress ovulation and estrus behaviour . Progestins with a 17a-allyl side chain: (42) allylestrenol, (43), (44) altrenogest.
- Bergink EW, Loonen PB, Kloosterboer HJ (August 1985). "Receptor binding of allylestrenol, a progestagen of the 19-nortestosterone series without androgenic properties". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry. 23 (2): 165–168. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(85)90232-8. PMID 3928974.
- Madjerek Z, De Visser J, Van Der Vies J, Overbeek GA (September 1960). "Allylestrenol, a pregnancy maintaining oral gestagen". Acta Endocrinologica. 35 (I): 8–19. doi:10.1530/acta.0.XXXV0008. PMID 13765069.
- Bain FT (5 July 2011). "Infectious arthritis and osteomyelitis". In McKinnon AO, Squires EL, Vaala WE, Varner DD (eds.). Equine Reproduction. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 457–462. ISBN 978-0-470-96187-2.
- Committee to Review the Bureau of Land Management Wild Horse and Burro Management Program; Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources; Division on Earth and Life Studies; National Research Council (4 October 2013). "Methods and Effects of Fertility Management". Using Science to Improve the BLM Wild Horse and Burro Program: A Way Forward. National Academies Press. pp. 93–142 (120). ISBN 978-0-309-26494-5.
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |