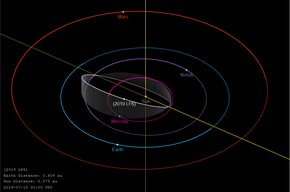
 Highly inclined orbit of 2019 LF6 passing within Mercury's orbit, and slightly outside Venus's orbit Highly inclined orbit of 2019 LF6 passing within Mercury's orbit, and slightly outside Venus's orbit | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Zwicky Transient Facility |
| Discovery site | Palomar Obs. |
| Discovery date | 10 June 2019 (first observed only) |
| Designations | |
| MPC designation | 2019 LF6 |
| Minor planet category | NEO · Atira |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch 31 May 2020 (JD 2459000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 3 | |
| Observation arc | 358 days |
| Aphelion | 0.7938 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.3170 AU |
| Semi-major axis | 0.5554 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.42928 |
| Orbital period (sidereal) | 0.41 yr (151.2 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 347.653° |
| Mean motion | 2° 22 51.74 / day |
| Inclination | 29.506° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 179.029° |
| Argument of perihelion | 213.779° |
| Earth MOID | 0.2608 AU |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | 1–2 km (est. at 0.05–0.15) |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 17.200±0.398 |
2019 LF6 is a near-Earth object of the Atira group. After 2021 PH27, it has the second-smallest semi-major axis among the known asteroids (0.555 AU), beating the previously-held record of 2019 AQ3. It orbits the Sun in 151 days. Discovered at only 19th magnitude, it is very difficult to see, never getting far from the sun and twilight. It only occasionally brightens above 16th magnitude. Discovery was made using the Zwicky Transient Facility.
2019 LF6 orbits the Sun at a distance of 0.3–0.8 AU once every 5 months (151 days; semi-major axis of 0.56 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.43 and an unusually high inclination of 30° with respect to the ecliptic. The asteroids 594913 ꞌAylóꞌchaxnim and 2019 AQ3 are the only known asteroids with closer aphelions. The orbital evolution of 2019 AQ3 is similar to that of 2019 LF6.
References
- ^ "2019 LF6". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2019 LF6)" (2019-07-05 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: a > 0 (au) and a < 0.7 (au) and data-arc span > 3 (d)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (1 August 2019). "Understanding the evolution of Atira-class asteroid 2019 AQ3, a major step towards the future discovery of the Vatira population". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 487 (2): 2742–2752. arXiv:1905.08695. Bibcode:2019MNRAS.487.2742D. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1437.
- Hop Aboard 2019 LF6, The Asteroid With The Shortest Year Known Astrobob, 7/10/2019
- ^ Young, Monica (10 July 2019). "Sky-surveying Telescopes Sweep Up Near-Earth Asteroids". Sky & Telescope. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- de la Fuente Marcos, Carlos; de la Fuente Marcos, Raúl (25 July 2019). "Hot and Eccentric: The Discovery of 2019 LF6 as a New Step in the Quest for the Vatira Population". Research Notes of the American Astronomical Society. 3 (7): 106. Bibcode:2019RNAAS...3g.106D. doi:10.3847/2515-5172/ab346c. S2CID 201405666.
External links
- 2019 LF6 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- 2019 LF6 at the JPL Small-Body Database
| Asteroids | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main | |||||||||
| Distribution |
| ||||||||
| Classification |
| ||||||||
| Exploration | |||||||||
| Lists | |||||||||
| Related | |||||||||
This near-Earth asteroid-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |