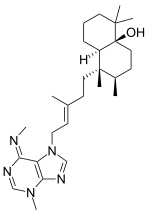
Agelasimines are a group of adenine-related bicyclic diterpenoids isolated from the orange sponge Agelas mauritania. Their chemical structures are closely related to the agelasines.
Both groups of compounds display a range of biological activities, such as cytotoxicity, inhibition of adenosine transfer into rabbit erythrocytes (red blood cells), Ca channel antagonistic action, α1 adrenergic blockade and others.
Both compounds have been reproduced in the laboratory by organic synthesis.
References
- Ohba, Masashi; Iizuka, Kazuaki; Ishibashi, Hiroyuki; Fujii, Tozo (December 1997). "Syntheses and absolute configurations of the marine sponge purines (+)-agelasimine-A and (+)-agelasimine-B". Tetrahedron. 53 (50): 16977–16986. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(97)10120-X.
- Fathi-Afshar, R.; Allen, T. M. (January 1988). "Biologically active metabolites from". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 66 (1): 45–50. doi:10.1139/v88-006.
- Fathi-Afshar, R.; Allen, T. M.; Krueger, C. A.; Cook, D. A.; Clanachan, A. S.; Vriend, R.; Baer, H. P.; Cass, C. E. (April 1989). "Some pharmacological activities of novel adenine-related compounds isolated from a marine sponge". Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 67 (4): 276–281. doi:10.1139/y89-045.
This article about an alkaloid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |