 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 69% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3 to 8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
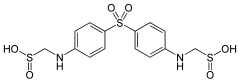
| Formula | C14H16N2Na2O6S3 |
| Molar mass | 450.45 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Sulfoxone or aldesulfone sodium is an anti-leprosy drug. It is also known as diasone. Sulfoxone sodium was introduced in Japan in 1948. Ernest Muir introduced it to Western use while serving as superintendent of the Chacachacare Leprosarium on Trinidad in the Caribbean.
References
- "Sulfoxone".
- Ozawa H, Maruyama Y (2002). "". Yakushigaku Zasshi. 37 (1): 76–83. PMID 12412600.
- Browne, Stanley George (1974), "Ernest Muir, C.M.G., C.I.E., M.D. (Edin.), F.R.C.S., LL.D. 1880–1974" (PDF), International Journal of Leprosy, vol. 42, no. 4, Bauru: International Leprosy Association, pp. 457–458, PMID 4617724.
| Antimycobacterials, including tuberculosis treatment and leprostatic agents (J04) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleic acid inhibitor |
| ||||||||
| Protein synthesis inhibitor |
| ||||||||
| Cell envelope antibiotic |
| ||||||||
| Other/unknown | |||||||||
| Combinations | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Antibacterials that inhibit nucleic acid (J01E, J01M) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antifolates (inhibit bacterial purine metabolism, thereby inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Quinolones (inhibit bacterial topoisomerase and/or DNA gyrase, thereby inhibiting DNA replication) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Anaerobic DNA inhibitors |
| ||||||||||||||||
| RNA synthesis |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||