 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
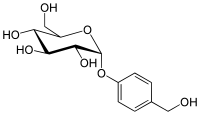
| IUPAC name 4-(Hydroxymethyl)phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names
Gastrodine 4-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)benzyl alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.712 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C13H18O7 |
| Molar mass | 286.280 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Gastrodin is a chemical compound which is the glucoside of gastrodigenin. It has been isolated from the orchid Gastrodia elata and from the rhizome of Galeola faberi. It can also be produced by biotransformation of 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde by Datura tatula cell cultures.
G. elata is a herb used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat headache, and it is standardized in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia by gastrodin and gastrodigenin content. In line with this traditional use, gastrodin and its acetyl derivative are used in China as an over-the-counter drug to treat neurasthenia, headache, and migraine. It is available as a dietary supplement in other countries.
A Chinese literature review considers it useful for a range of central nervous system disorders, with the evidence coming from mostly Chinese researches.
References
- Li, Y. M.; Zhou, Z. L.; Hong, Y. F. (1993). "Studies on the phenolic derivatives from Galeola faberi Rolfe". Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 28 (10): 766–71. PMID 8009989.
- Gong, J.; Ma, W.; Pu, J.; Xu, S.; Zheng, S.; Xiao, C. (2006). "Production of Gastrodin Through Biotransformation of p-hydroxybenzaldehyde Using Cell Suspension Cultures of Datura tatula L". Chinese Journal of Biotechnology. 22 (5): 800–804. doi:10.1016/S1872-2075(06)60056-3. PMID 17037205.
- 国家药典委员会 (2015). "天麻 / GASTRODIAE RHIZOMA". 中国药典 (in Chinese). Vol. 1. p. 58. ISBN 978-7-5067-7337-9.
- "Gastrodin Tablets (天麻素片) Monograph". drugs.dxy.cn.
- Liu, Y; Gao, J; Peng, M; Meng, H; Ma, H; Cai, P; Xu, Y; Zhao, Q; Si, G (2018). "A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 9: 24. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00024. PMC 5801292. PMID 29456504.