 Nor'easter just past its initial peak intensity moving into North Carolina Nor'easter just past its initial peak intensity moving into North Carolina | |
| Type | Extratropical cyclone Nor'easter |
|---|---|
| Formed | November 20, 2006 |
| Dissipated | December 1, 2006 |
| Lowest pressure | 944 mbar (hPa) |
| Maximum snowfall or ice accretion | 5 inches (13 cm) |
| Fatalities | 1 |
| Damage | Not yet known |
| Areas affected | East Coast of the United States, Southern Greenland, Iceland, Ireland, United Kingdom |
| Part of the 2006–07 North American winter storms | |
The November 2006 nor'easter was a powerful extratropical cyclone that formed offshore of the Southeastern United States on November 20, bringing heavy rains, high winds, beach erosion, and coastal flooding to the Carolinas and southern New England. In addition, the earliest snowfall ever noted in both Charleston, South Carolina and Savannah, Georgia occurred on the southwest side of this cyclone. Over 10,000 were without power during the storm. No longer a nor'easter, the extratropical cyclone accelerated rapidly across the North Atlantic while rapidly strengthening, becoming a cyclonic storm again by November 25, but this time with hurricane-force sustained winds. The intense low made a cyclonic loop west of Iceland, before being absorbed by another strengthening extratropical cyclone to the west of Great Britain, late on December 1.
Meteorological synopsis
A shortwave moved through the southern stream of the polar jetstream of the Westerlies, dropping temperatures in its wake across the southeast United States. Cyclogenesis spurred a developing surface cyclone which quickly occluded on November 20. Surface pressure gradient between this cyclone and a sprawling high stretching around its periphery from New England into the Deep South led to strong winds in the Carolinas. The cyclone deepened to a central pressure of 999 hectopascals (29.5 inHg) before swinging westward into the Outer Banks of North Carolina on November 22. At this time, a trio of upper-level shortwaves were rotating around the main closed cyclone aloft, which spurred development of a new, weaker low pressure center offshore North Carolina. This cyclone was weaker after its interaction with North Carolina until it reached New England, when renewed strengthening led to significant impacts across Long Island and southern New England. The system then began accelerating east-northeast while continuing to slowly strengthen, passing offshore Atlantic Canada on November 24. The cyclone subsequently bombed, or strengthened quite rapidly, and accelerated east-northeast, becoming a hurricane-force storm in the far north Atlantic with a central pressure of 967 hectopascals (28.6 inHg) by the afternoon of November 25 and peaking at 944 hectopascals (27.9 inHg) by the morning of November 26. Slow weakening occurred soon afterward as the system slowed down and turned towards Iceland. By the evening of November 27, its central pressure had increased to 957 hectopascals (28.3 inHg) while located a couple hundred miles south of Iceland. The cyclone continued to loop cyclonically west of Iceland, absorbing a cyclone along the way as it passed southwest off the southern tip of Greenland, before a developing gale approaching Great Britain absorbed this cyclone late on December 1.
Preparations

There had been indications in the forecast model guidance as early as the first week of November that weather would be unsettled/rainy across the eastern United States around November 23. Within seven days of the event, medium range forecasts generally maintained the idea of a coastal storm offshore the Southeast, though its progression out to sea remained uncertain until November 21, after the cyclone actually formed offshore the Southeast United States and began edging northeast.
Virginia
On the Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel, officials restricted the types of vehicles that could cross the span between Virginia Beach and the Eastern Shore to cars and pickup trucks. Poquoson Public Schools were closed, and the Midtown Tunnel between Norfolk and Portsmouth was shut down because of the possibility of flooding. Sandbags surrounded buildings at Langley Air Force Base, which lies 11 feet (3.4 m) above sea level, and all computers and electrical equipment were waterproofed.
Maryland
The Maryland State Highway Administration worked to clear storm drains of branches and leaves and called in more patrollers to assist motorists in the event of an accident or stranded vehicle. The administration also prepared for falling branches, by making sure the department's chain saws had enough gas.
Effects
Florida
Snow flurries fell as far south as central Florida on the backside of this system. Snow flurries were reported in Orange, Seminole, and Volusia Counties. It was the earliest snow had ever fallen this far south, and only the second time on record snow had fallen in Florida in November.
Georgia
Snow mixed in with rain around noon on November 21, which led to the earliest trace of snow on record in Savannah. Just inland, 5–7 inches of snow fell across extreme southeast Georgia.
South Carolina
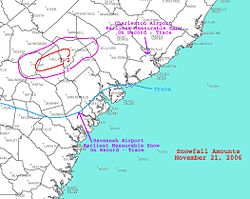
Heavy rains fell across northern portions of the state, with 4.13 inches (105 mm) measured at Chester. Snow mixed in with rain during the morning of November 21, leading to the earliest trace of snow on record in Charleston. Also, as the snow mixed in, thunder was heard, which is the first report of thundersnow in the history of Charleston. An inch of snow was reported just inland. Winds gusted to 44 mph (38 kn) at Folly Beach. The combination of pounding surf and high winds led to moderate to heavy beach erosion at Hunting Island, Folly Beach, Isle of Palms, Wild Dunes, and Sullivan's Island.
North Carolina
Heavy rainfall fell throughout central and eastern North Carolina, with the maximum amount of 7.68 inches (195 mm) measured at Sandy Run. This precipitation combined with high tides led to river flooding across the eastern half of the state, and led to Raleigh-Durham International Airport setting a record for its wettest November on record, breaking the record from 1948. The combination of wind and rain led to the downing of numerous trees. Winds gusted to 70 knots (80 mph) at Alligator River, with numerous gusts above 50 knots (60 mph) throughout the Outer Banks, leading to beach erosion and coastal flooding, with Highway 12 being overwashed by the surge south of Oregon Inlet. Power went out to 1,250 in northeastern sections of the state. The combination of coastal flooding and heavy rains led to the Lumber River rising to 3.5 feet (1.1 m) above flood stage. In Nags Head, 54 homes were condemned due to damage from this cyclone. At sea, the container ship Courtney L lost four containers on November 22 or 23 due to the storm. One of them, which contained Doritos bound for Costa Rica, was eventually washed ashore near Cape Hatteras.
Virginia
High winds lashed extreme southeast sections of the state. The highest wind gust reported was 66 mph (57 kn) from the first island on the Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel at 9:45 a.m. EST. In southeast sections of the state, over 9000 went without power. Moderate to heavy rain fell across the tidewater, with 1.97 inches (50 mm). One person perished when the car he was driving hydroplaned and subsequently crashed.
A brief period of sleet was experienced across Northern Virginia on the morning of November 22 as moisture from the storm moved in from a northeast-to-southwest track. This form of precipitation is rare for the area in mid-November, but was quickly replaced by driving rainfall as warmer air from the Atlantic pushed inland. Steady rain persisted throughout the afternoon and evening of the 22nd, with a mix of showers and moderate-to-heavy mist occurring throughout Thanksgiving Day, November 23.
Maryland
Winds as high as 54 mph (47 kn) lashed Assateague Island. The highest rainfall amount reported was 2.12 inches (54 mm) from Ocean City.
Delaware
Georgetown reported a record rainfall for November 22, when 1.93 inches (49 mm) was measured; a total of 2.50 inches (64 mm) fell.
Pennsylvania

Rainfall amounts ranged at high as 1.21 inches (31 mm) at Lehighton.
New Jersey
Winds peaked at 57 mph (50 kn) at both Cape May Harbor and Ocean City. At Newark, the 1.26 inches (32 mm) that fell on November 23 set a daily precipitation record for the date. The highest amount noted was 2.57 inches (65 mm) at the United States Coast Guard site in Atlantic City.
An oak tree toppled onto a house located in West Deptford Township. A tree also got caught in a power line in Vivian Court, so the electric power had to be cut, so the power line could be cleared of the tree. A traffic light and some trees were also damaged in Northfield. Minor flooding was also reported in some back-bays, which forced some intersections to be closed.
New York
Low level wind shear led to moderate delays of an hour or more at major airports within the megalopolis on the morning of November 22, the day before Thanksgiving in the United States. At Kennedy Airport, 1.56 inches (40 mm) of rainfall set a daily precipitation record for November 23. The highest amount reported was 2.83 inches (72 mm) at Shoreham. Around Binghamton, a light coating of ice covered surfaces as a slight amount of freezing rain fell.
Connecticut
At Bridgeport, rainfall of 1.84 inches (47 mm) fell on November 23, setting a daily rainfall record. The highest amount reported was 3.27 inches (83 mm) at Norwich.
Rhode Island
High winds downed a telephone pole in Warwick, and numerous tree limbs throughout the state. Downtown Providence reported 3.91 inches (99 mm) of rainfall on November 23 and November 24. This rain led to minor flooding of the Pawtuxet River in Cranston, an area hard-hit by the flooding in October, 2005.
Massachusetts
High winds downed numerous tree limbs throughout the state. A total of 2.09 inches (53 mm) of rainfall fell in Boston as of the morning of November 24. The highest amount reported was 4.76 inches (121 mm) at Hingham.
See also
References
- Ocean Prediction Center. Weather Map of the North Atlantic. Archived November 17, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1408 UTC on 2006-11-26.
- Ocean Prediction Center. Unified Surface Analysis: 14 Day Loop. Archived September 20, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2006-12-09.
- Associated Press. Winds, rain make messy driving conditions on Virginia coast. Retrieved at 2254 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- Alia Malik. Travelers Might Not Be Thankful For Holiday Weather. Archived June 10, 2010, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 2301 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- Local6.com. Snow Falls In Central Florida. Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2006-11-26.
- National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: South Carolina. Archived October 25, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 0313 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: North Carolina. Archived November 15, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 0303 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- ^ Steve Stone. Storm brings high winds, heavy flooding. Archived September 26, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 2236 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- Associated Press.Storm leaves condemned homes in Nags Head, rivers still rising. Retrieved on 2006-11-24.
- CATHERINE KOZAK. Doritos junkies hit jackpot as beached cargo container spills the goods. Archived February 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2007-07-02.
- CATHERINE KOZAK. Beached Doritos in N.C. were in 1 of 4 lost containers. Archived September 26, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2007-07-02.
- Jim Washington. The forecast is tough for travelers, perfect for feasting, relaxing inside. Archived September 26, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 2243 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- ^ National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: Virginia. Archived October 25, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1240 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: Delaware. Archived September 29, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1246 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- ^ National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: Pennsylvania. Archived October 25, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1321 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- ^ National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: New York. Archived October 25, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1249 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- 2006 NBC Weather Plus: NBC10. Nor'easter Causes High Tides, Flooding Beach Erosion Retrieved at 0150 UTC on 2006-11-26.
- ^ National Weather Service Forecast Office, Upton, New York. Public Information Statement. Retrieved at 2217 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- National Weather Service. Public Information Statements: Massachusetts. Archived November 12, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1349 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- National Weather Service Forecast Office, Boston, Massachusetts. Public Information Statement. Retrieved at 2208 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- Associated Press. Pawtuxet River crests above flood stage, homes flooded. Retrieved on 2006-11-26.
- National Weather Service. Selected Cities Forecast. Archived December 1, 2006, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved at 1303 UTC on 2006-11-24.
- "HinghamWeather.com". Archived from the original on September 7, 2008. Retrieved August 28, 2008.
| Major snow and ice events in the United States | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18th–19th century | |||||||
| 20th century |
| ||||||
| 21st century |
| ||||||
| Related | |||||||
- Natural disasters in North Carolina
- Natural disasters in South Carolina
- Natural disasters in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Natural disasters in Virginia
- Natural disasters in Maryland
- Natural disasters in Delaware
- Natural disasters in Pennsylvania
- Natural disasters in New Jersey
- Natural disasters in New York (state)
- Natural disasters in Connecticut
- Natural disasters in Rhode Island
- Natural disasters in Massachusetts
- 2006 meteorology
- Nor'easters
- 2006 natural disasters in the United States
- November 2006 events in the United States
- December 2006 events in the United States
- November 2006 events in Europe
- December 2006 events in Europe
- 2000s in Greenland
- 2006 in Iceland
- 2006 in the United Kingdom
- 2006 in the Republic of Ireland
- 2006 in Georgia (U.S. state)
- 2006 in North Carolina