

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to water:
Water – chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state (water vapor or steam). Under nomenclature used to name chemical compounds, Dihydrogen monoxide is the scientific name for water, though it is almost never used.
History
Chemical properties and use


- Properties of water – Physical and chemical properties of pure water
- Electrolysis of water – Electricity-induced chemical reaction
- Water of crystallization – Water molecules present inside crystals
- Dealkalization of water – Removal of alkalinity ions from water
- Drinking water quality standards – Quality parameters set for drinking water
- Portable water purification – Self-contained, easily transported units used to purify water from untreated sources
- Self-ionization of water – Autoprotolysis or exchange of a proton between two water molecules
- Water-in-water emulsion
- Water purification – Process of removing impurities from water
- Water treatment – Process that improves the quality of water
- Water (data page) – Chemical data page for water
- Hard water – Water that has a high mineral content
- Soft water – Water that has a high mineral contentPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water softening – Removing positive ions from hard water
- Water absorption
- Heavy water – Form of water
- Distilled water – Water that has had many of its impurities removed through distillation
- Salinity – Proportion of salt dissolved in water
- Saline water – Water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts
- Seawater – Water from a sea or an ocean
- Hydrate – Substance containing water or its constituent elements
- Boiling – Rapid phase transition from liquid to gas or vapour
Physical properties

- Properties of water – Physical and chemical properties of pure water
- Color of water – Water color in different conditions
- Water vapor – Gaseous phase of water
- Vapour pressure of water – Pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor in gaseous form
- Steam – Water in the gas phase
- Ice – Frozen water: the solid state of water
- Optical properties of water and ice
- Water quality – Assessment against standards for use
- Water (data page) – Chemical data page for water
- Mineral water – Drinking water from a mineral spring
Geography


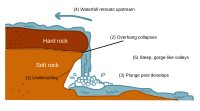 Formation of a waterfall
Formation of a waterfall Victoria Falls
Victoria Falls
- Origin of water on Earth – Hypotheses for the possible sources of the water on Earth
- Extraterrestrial liquid water – Liquid water naturally occurring outside Earth
- Water on terrestrial planets of the Solar System
- Lunar water – Presence of water on the Moon
- Water on Mars – Study of past and present water on Mars
- List of extrasolar candidates for liquid water – Possible existence of liquid water beyond Earth
- Water on terrestrial planets of the Solar System
- Hydrosphere – Total amount of water on a planet
- Hydrology – Science of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth
- Water distribution on Earth – Overview of the distribution of water on planet Earth
- Water cycle – Biogeochemical cycle for movement of water on Earth
- Groundwater – Water located beneath the ground surface
- Hydrology – Science of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth
- Body of water – Any significant accumulation of water, generally on a planet's surface
- Salt water – Water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts
- Seawater – Water from a sea or an ocean
- Ocean – Body of salt water covering most of Earth
- Sea – Large body of salt water
- Tide – Rise and fall of the sea level under astronomical gravitational influences
- Brine – Concentrated solution of salt in water
- Brackish water – Water with salinity between freshwater and seawater
- Fresh water – Naturally occurring water with low amounts of dissolved salts
- Aquifer – Underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock
- River – Natural flowing freshwater stream
- Drainage – Removal of water from an area of land
- Drainage divide – Elevated terrain that separates neighbouring drainage basins
- Drainage basin – Land area where water converges to a common outlet
- Lake – Large inland body of relatively still water
- Salt water – Water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts
- Glacier – Persistent body of ice that moves downhill under its own weight
- Geyser – Natural explosive eruption of hot water
- Spring – A point at which water emenges from an aquifer to the surface
- Waterfall – A point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop
Weather


- Precipitation (meteorology) – Product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravityPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Rain – Precipitation in the form of water droplets
- Freezing rain – Rain maintained at temperatures below freezing
- Drizzle – Light liquid precipitation
- Snow – Precipitation in the form of ice crystal flakes
- Snow pellets – Precipitation that forms when supercooled droplets of water freeze on a falling snowflakePages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Snow grains – very small particles of ice, the solid equivalent of drizzlePages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Ice pellets – Precipitation consisting of small, translucent balls of ice
- Hail – Form of solid precipitation
- Ice crystals – Water ice in symmetrical shapesPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Dew – Water in the form of droplets that appears on thin, exposed objects in the morning or evening
- Frost – Coating or deposit of ice
- Hoarfrost – Coating or deposit of icePages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Atmospheric icing – Weather condition in which water droplets freeze onto objects they come in contact with
- Glaze ice – Coating of ice on objectsPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Cloud – Visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals suspended in the atmospheres
- Fog – Atmospheric phenomenon
- Mist – Phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in air
- Spindrift – Spray blown from cresting waves in gales
- Flood – Water overflow submerging usually-dry land
- Wave – Repeated oscillation around equilibrium
- Drought – Period with less precipitation than normal
In nature and life
- Origin of water on Earth – Hypotheses for the possible sources of the water on Earth
- Water intoxication – Potentially fatal overhydration
- Drinking water – Water safe for consumption
- Drowning – Respiratory impairment caused by submersion in liquid
- Dehydration – Deficit of total body water
Marine and aquatic life
- Underwater – Aquatic or submarine environment
- Marine biology – Scientific study of organisms that live in the ocean
- Marine life – Organisms that live in salt water
- Hydrobiology – Science of life and life processes in water
- Aquatic ecosystem – Ecosystem in a body of water
Politics and issues
- Human right to water and sanitation
- Water politics – Politics affected by the availability of water and water resources
- Water politics in the Middle East
- Water politics in the Jordan River basin – Political issues arising from or related to the water of the Jordan River
- Water law – Law and regulations that relate to water resourcesPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water right – Right of a user to use water from a water source
- Water resources – Sources of water that are potentially useful for humans
- Water resources of the People's Republic of China – Geography, cleanliness, and access to waterPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water resources of Singapore
- Reuse of water bottles – Waste managementPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water crisis (disambiguation) – a type of crises focused on access to waterPages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Water conservation – Policies for sustainable development of water use
- Water efficiency – gallons per capita per dayPages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Water footprint – Extent of water use in relation to consumption by people
- Water conservation – Policies for sustainable development of water use
- Water industry – Drinking and wastewater services
- Water privatization – Private sector participation in the provision of water services and sanitation
- Water management – Sources of water that are potentially useful for humansPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water conflicts – Conflict over an access to water resourcesPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water export – Outbound trade involving freshwater
- Water pollution – Contamination of water bodies
Supply and sanitation

- Water supply – Provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations or others
- Water supply network – System of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components providing water
- Reservoir – Storage space for water
- Dam – Barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface or underground streams
- Water tower – Elevated structure supporting a tank
- Aqueduct – Structure constructed to convey waterPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Pump – Device that imparts energy to the fluids by mechanical action
- Water well – Excavation or structure to provide access to groundwater
- Drinking Fountain – Architecture which pours water into a basin or jets it into the air
- Water pipe – Systems for conveying fluidsPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Plumbing – Systems for conveying fluids
- Tap (valve) – Valve controlling the release of a liquid or gas
- Water supply network – System of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components providing water
- Sanitation – Public health conditions related to clean water and proper excreta and sewage disposal
- Drinking water – Water safe for consumption
- Water fluoridation – Addition of fluoride to a water supply to reduce tooth decay
- Opposition to water fluoridation – Debate over the anti-tooth-decay measure
In culture and sport

- Water deity
- Water (classical element) – One of four primary substances in antiquity
- Holy water – Water blessed by a religious figure
- Adam's ale – Colloquial allusion to water
- Water sports )
- List of water sports
- Swimming – Water-based sport
- Water polo – Competitive team sport played in water
- Underwater sports – Competitive underwater recreational activities
- List of water sports
- Winter sports – Sports or recreational activities which are played on snow or ice
- Water gun – Type of toy gun designed to shoot water
- Water fight – A type of mock combat
- Fountain – Architecture which pours water into a basin or jets it into the air
- Underwater diving – Descending below the surface of the water to interact with the environment
Uses
- Bathing – Washing of the body with a liquid
- Drinking – Ingestion of water or other liquids
- Drinking water – Water safe for consumption
- Tap water – Water supplied through a pipe and tap combination
- Bottled water – Water sold as a bottled product
- Drinking vessel – Small container for drinksPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Use of water in fire fighting – Actions to prevent damage from firePages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Irrigation – Agricultural artificial application of water to land
- Professional diving – Underwater diving where divers are paid for their work
- Naval warfare – Combat involving sea-going ships
- Washing – Method of cleaning
- Pressure washing – Use of high-pressure water jet for cleaning hard surfaces
- Water transport – Transport of people or goods via waterwaysPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Water clock – Time-piece in which time is measured by the flow of liquid into or out of a vessel
- Water-based sources of power
- Water wheel – Machine that converts the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power
- Hydroelectricity – Electricity generated by hydropower
- Hydropower – Power generation via movement of water
- Marine current power – Extraction of power from ocean currents
- Marine energy – Energy available from oceans
- Osmotic power – Energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water
- Tidal power – Technology to convert the energy from tides into useful forms of power
- Wave power – Transport of energy by wind waves, and the capture of that energy to do useful work
- Water turbine – Type of turbine
- Steam engine – Engine that uses steam to perform mechanical work
- Tidal stream generator – Type of tidal power generation technology
See also
References
- Bramer, Scott. "Chemical Nomenclature". Widener University, Department of Chemistry. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
External links
- OECD Water statistics
- The World's Water Data Page
- FAO Comprehensive Water Database, AQUASTAT
- The Water Conflict Chronology: Water Conflict Database
- US Geological Survey Water for Schools information
- Portal to The World Bank's strategy, work and associated publications on water resources
- America Water Resources Association
- America Water Resources Association
- Water structure and science
| Misplaced Pages outlines | |
|---|---|