| Olivocerebellar tract | |
|---|---|
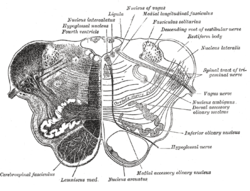 Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. (Cerebello-olivary fibers visible at center right.) Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. (Cerebello-olivary fibers visible at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus olivocerebellaris |
| NeuroNames | 804 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1579 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.118 |
| TA2 | 5853 |
| FMA | 72638 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The olivocerebellar tract, also known as olivocerebellar fibers, are neural fibers which originate at the olivary nucleus and pass out through the hilum and decussate with those from the opposite olive in the raphe nucleus, then as internal arcuate fibers they pass partly through and partly around the opposite olive and enter the inferior peduncle to be distributed to the cerebellar hemisphere of the opposite side from which they arise.
They terminate directly on Purkinje cells as the climbing fiber input system.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Eccles J.C, Llinas R, and Sasaki. Excitation of cerebellar Purkinje cells by the climbing fibers. Nature 203: 245-246, 1964
External links
- Illustration and text: cere/text/p3/olivo.htm at the University of Wisconsin-Madison Medical school
| Anatomy of the medulla | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grey matter |
| ||||||||||
| White matter |
| ||||||||||
| Surface |
| ||||||||||
| Grey | |||||||||||
| Anatomy of the cerebellum | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface |
| ||||
| Grey matter |
| ||||
| White matter | |||||
This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |