For other uses, see Eternity (disambiguation). "Sempiternal" redirects here. For the album by Bring Me the Horizon, see Sempiternal (album).

| Time |
|---|
 |
| Major concepts |
| Fields of study |
| Philosophy |
|
|
| Related topics |
Eternity, in common parlance, is an infinite amount of time that never ends or the quality, condition or fact of being everlasting or eternal. Classical philosophy, however, defines eternity as what is timeless or exists outside time, whereas sempiternity corresponds to infinite duration.
Philosophy
See also: Eternalism (philosophy of time) and Philosophy of space and timeClassical philosophy defines eternity as what exists outside time, as in describing timeless supernatural beings and forces, distinguished from sempiternity which corresponds to infinite time, as described in requiem prayers for the dead. Some thinkers, such as Aristotle, suggest the eternity of the natural cosmos in regard to both past and future eternal duration. Boethius defined eternity as "simultaneously full and perfect possession of interminable life". Thomas Aquinas believed that God's eternity does not cease, as it is without either a beginning or an end; the concept of eternity is of divine simplicity, thus incapable of being defined or fully understood by humankind.
Thomas Hobbes (1588–1679) and many others in the Age of Enlightenment drew on the classical distinction to put forward metaphysical hypotheses such as "eternity is a permanent now".
Contemporary philosophy and physics
Today cosmologists, philosophers, and others look towards analyses of the concept from across cultures and history. They debate, among other things, whether an absolute concept of eternity has real application for fundamental laws of physics; compare the issue of entropy as an arrow of time.
Religion
See also: God and eternity and Unto the ages of agesEternity as infinite duration is an important concept in many lives and religions. God or gods are often said to endure eternally, or exist for all time, forever, without beginning or end. Religious views of an afterlife may speak of it in terms of eternity or eternal life. Christian theologians may regard immutability, like the eternal Platonic forms, as essential to eternity.
Symbolism
See also: Alpha and Omega, Armenian eternity sign, Engagement ring, and Eternity ringEternity is often symbolized by the endless snake, swallowing its own tail, the ouroboros. The circle, band, or ring is also commonly used as a symbol for eternity, as is the mathematical symbol of infinity, . Symbolically these are reminders that eternity has no beginning or end.
-
 The ouroboros
The ouroboros
-
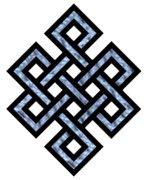 The "endless knot," a symbol of eternity used in Tibetan Buddhism.
The "endless knot," a symbol of eternity used in Tibetan Buddhism.
-
 Infinity symbol variations
Infinity symbol variations
-
 Folk art allegorical map "The 3 Roads to Eternity" from Matthew 7:13–14 by the woodcutter Georgin François (1801–1863) in 1825.
Folk art allegorical map "The 3 Roads to Eternity" from Matthew 7:13–14 by the woodcutter Georgin François (1801–1863) in 1825.
-
 Jacopo da Sellaio, Triumph of Eternity, 1485–1490
Jacopo da Sellaio, Triumph of Eternity, 1485–1490
-
 An allegorical classical woman c. 1670s, representing eternity.
An allegorical classical woman c. 1670s, representing eternity.
See also
- Aeon
- Akal (Sikh term)
- Chronology of the universe
- Eternal now
- Eternal return
- Everlasting life
- Eviternity
- Kalpa
- Philosophical presentism
- Planck epoch
- Time perception
- Temporal finitism
- Wheel of time
Notes
- Boethius (523), book 5, prose §. 6, quote: "Aeternitas igitur est interminabilis vitae tota simul et perfecta possessio."
- For examples: Bassali (2008), p. 138, quote: "In the next life, there will be two places only - heaven and hell. ... In heaven, you will spend an eternity of bliss, light, and glory with God. In hell, you will spend an eternity of woe, darkness and torment apart from God. Which of these two places would you prefer to spend your eternity?"
- Deng (2018), quote: "Augustine connects God's timeless eternity to God's being the cause of all times and God's immutability."
- She holds up an hourglass, her elbow above a human skull and in her lower hand two flowers in maturity, one of which is a dandelion blowball or clock (seed head), reminders of transience. An Ouroboros, snake swallowing its own tail, floats above her head as a halo - symbols of eternity.
References
- "eternity". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Boedder (1902), book 2, ch. 2, "The Eternity of God".
- Helm (2010), §. 6, "Medieval thinkers".
- Hobbes (1662), p. 50.
- Deng (2018), §. 3.1, "The Loci Classici".
Works cited
- Bassali, Maurice (2008). Where Will You Spend Eternity?. Xulon Press. ISBN 9781606473276. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- Boedder, Bernard (1902). Natural Theology. Longmans, Green, and Co. Archived from the original on March 26, 2023. Retrieved July 29, 2022 – via University of Notre Dame.
- Boethius, Anicius Manlius Torquatus Severinus. De philosophiae consolatione Boethius (in Latin) – via Wikisource.
- Deng, Natalja. "Eternity in Christian Thought". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2018 ed.).
- Helm, Paul. "Eternity". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2010 ed.).
- Hobbes, Thomas (1662). Mr. Hobbes considered in his loyalty, religion, reputation, and manners, by way of a letter to Dr. Wallis.
Further reading
- Yu, Jiyuan (2003). The Structure of Being in Aristotle's Metaphysics. Springer. pp. 188–. ISBN 9781402015373.
External links
- Entry in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy on Eternity.
- Entry in the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy on the relationship between God and Time.
| Time | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key concepts | |||||||||
| Measurement and standards |
| ||||||||
| Philosophy of time | |||||||||
| Human experience and use of time | |||||||||
| Time in science |
| ||||||||
| Related | |||||||||
| Time in religion and mythology | |
|---|---|
| Philosophy of time | |
|---|---|
| Concepts in time | |
| Theories of time | |
| Related articles | |
| Infinity (∞) | |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Branches of mathematics | |
| Formalizations of infinity |
|
| Geometries | |
| Mathematicians | |
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote
 . Symbolically these are reminders that eternity has no beginning or end.
. Symbolically these are reminders that eternity has no beginning or end.