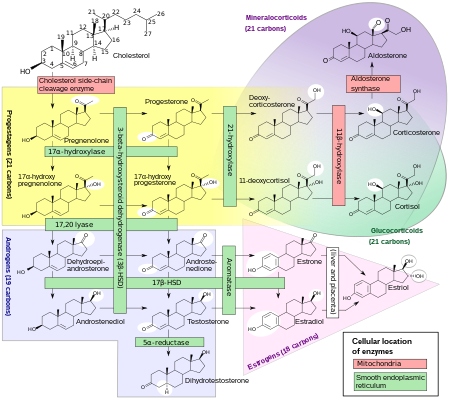
Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis. They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids (androgens, estrogens, and progestogens) and corticosteroids (glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids), as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol. Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body.
List of steroidogenic enzymes
- Steroid desmolases
- Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (20,22-desmolase) – steroid synthesis
- 17,20-Lyase (17,20-desmolase) – androgen synthesis
- Steroid hydroxylases
- 11β-Hydroxylase – corticosteroid synthesis
- 17α-Hydroxylase – androgen and glucocorticoid synthesis
- 18-Hydroxylase (aldosterone synthase) – mineralocorticoid synthesis
- 21-Hydroxylase – corticosteroid synthesis
- Cytochrome P450 (CYP1, 2, 3) – estrogen metabolism
- Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (and ketosteroid reductases)
- 3α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase – androgen, progestogen, and neurosteroid synthesis and metabolism
- 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ-isomerase (1, 2) – androgen, progestogen, and neurosteroid synthesis
- 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (1, 2) – corticosteroid synthesis and metabolism
- 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (1–15) – androgen, estrogen, and progestogen synthesis and metabolism
- 20α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase – progestogen synthesis and metabolism
- 20β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase – progestogen synthesis and metabolism

- Steroid reductases
- 5α-Reductase (1, 2, 3) – androgen and neurosteroid synthesis, progestogen metabolism
- 5β-Reductase – androgen and progestogen metabolism, neurosteroid synthesis
- Conjugation (and deconjugation)
- Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT2Bs) – steroid metabolism
- Glucuronidase (β-glucuronidase) – steroid synthesis
- Steroid sulfotransferase (SULT1A1, 1E1, 2A1, 2B1a, 2B1b) – steroid metabolism, neurosteroid synthesis
- Steroid sulfatase – steroid synthesis, neurosteroid metabolism
- Others
- Aromatase (estrogen synthetase) – estrogen synthesis
See also
References
- Häggström, Mikael; Richfield, David (2014). "Diagram of the pathways of human steroidogenesis". WikiJournal of Medicine. 1 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.005.
- Hanukoglu I (Dec 1992). "Steroidogenic enzymes: structure, function, and role in regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 43 (8): 779–804. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90307-5. PMID 22217824. S2CID 112729.
- ^ Payne AH, Hales DB (2004). "Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones". Endocr. Rev. 25 (6): 947–70. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0030. PMID 15583024.
- ^ Luu-The V, Labrie F (2010). "The Intracrine Sex Steroid Biosynthesis Pathways". Neuroendocrinology: The Normal Neuroendocrine System. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 181. pp. 177–92. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)81010-2. ISBN 9780444536174. PMID 20478438.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Honour JW (2009). "Diagnosis of diseases of steroid hormone production, metabolism and action". J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 1 (5): 209–26. doi:10.4274/jcrpe.v1i5.209. PMC 3005746. PMID 21274298.
- Guillemette C, Lévesque E, Harvey M, Bellemare J, Menard V (2010). "UGT genomic diversity: beyond gene duplication". Drug Metab. Rev. 42 (1): 24–44. doi:10.3109/03602530903210682. hdl:20.500.11794/10528. PMID 19857043. S2CID 32737680.
- William Fishman (2 December 2012). Metabolic Conjugation and Metabolic Hydrolysis, Volume II. Elsevier. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-323-14308-0.
- ^ Mueller JW, Gilligan LC, Idkowiak J, Arlt W, Foster PA (2015). "The Regulation of Steroid Action by Sulfation and Desulfation". Endocr. Rev. 36 (5): 526–63. doi:10.1210/er.2015-1036. PMC 4591525. PMID 26213785.
| Metabolism: lipid metabolism – ketones/cholesterol synthesis enzymes/steroid metabolism | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mevalonate pathway |
| ||||||||||||
| To cholesterol |
| ||||||||||||
| To Bile acids | |||||||||||||
| Steroidogenesis |
| ||||||||||||