| Styphelia mutica | |
|---|---|

| |
| In the Australian National Botanic Gardens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Styphelia |
| Species: | S. mutica |
| Binomial name | |
| Styphelia mutica (R.Br.) F.Muell. | |
| |
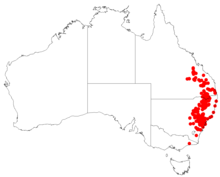
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms | |
Styphelia mutica, commonly known as blunt beard-heath, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is an erect, straggling shrub with egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and small numbers of white, tube-shaped flowers that are densely bearded inside.
Description
Styphelia mutica is an erect, straggling shrub that typically grows to a height of up to 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in), and has softly-hairy branchlets. Its leaves are egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, 9.6–23 mm (0.38–0.91 in) long and 2.5–5.8 mm (0.098–0.228 in) wide on a petiole 1.5–2.0 mm (0.059–0.079 in) long. The leaves are flat with 3 to 5 parallel veins. The flowers are arranged in spikes of 4 to 10 up to 9 mm (0.35 in) long in leaf axils on a peduncle about 2 mm (0.079 in) long with bracteoles 0.9–1.2 mm (0.035–0.047 in) long at the base. The sepals are 0.9–2.4 mm (0.035–0.094 in) long, the petals joined at the base to form a tube 2.0–2.5 mm (0.079–0.098 in) long with lobes 1.4–2.0 mm (0.055–0.079 in) long and densely bearded inside. Flowering mainly occurs from September to October and the fruit is a bristly, black, elliptic drupe 3.0–4.5 mm (0.12–0.18 in) long.
Taxonomy
This species was first formally described in 1810 by Robert Brown, who gave it the name Leucopogon muticus in his Prodromus Florae Novae Hollandiae et Insulae Van Diemen. In 1867, Ferdinand von Mueller transferred the species to Styphelia as S. mutica. The specific epithet (mutica) means "blunt".
Distribution and habitat
Blunt beard-heath grows in heath and forest on slopes and ridges from sea level to an altitude of 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in south-east Queensland and in eastern New South Wales as far south as Cooma.
References
- ^ "Styphelia mutica". Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 17 March 2024.
- ^ Powell, Jocelyn M. "Leucopogon muticus". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ Benson, Doug; McDougall, Lyn (1995). "Ecology of Sydney Plants 3: families Cabombaceae to Eupomatiaceae". Cunninghamia. 4 (2): 374. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- "Leucopogon muticus". APNI. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- Brown, Robert (1810). Prodromus florae Novae Hollandiae et Insulae Van-Diemen, exhibens characteres plantarum. London. p. 543. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- Sharr, Francis Aubi; George, Alex (2019). Western Australian Plant Names and Their Meanings (3rd ed.). Kardinya, WA: Four Gables Press. p. 257. ISBN 9780958034180.
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Styphelia mutica | |
| Leucopogon muticus | |