| Revision as of 08:25, 9 January 2006 editLa goutte de pluie (talk | contribs)22,509 edits fix link← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 10:48, 17 October 2024 edit undoDocWatson42 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers217,141 edits →Community Development Council districts: Cleaned up references and other matters.Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit | ||
| (129 intermediate revisions by 75 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|none}} <!-- "none" is preferred when the title is sufficiently descriptive; see ] --> | |||
| While the small physical size of ] does not justify the creation of national subdivisions in the form of ]s, ]s, and other national political divisions found in larger countries, '''the city-state is nonetheless subdivided''' in various ways throughout its history for the purpose of local administration and urban planning. | |||
| {{use Singapore English|date=August 2019}} | |||
| {{use dmy dates|date=August 2019}} | |||
| {{multiple image|perrow=2|total_width=300|caption_align=center | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | direction =vertical | |||
| | header=Administrative divisions of Singapore | |||
| | image1 = SubzonesOfSingapore.png | |||
| | caption1 = Subzones of Singapore, one of the many ways Singapore is locally divided | |||
| }} | |||
| ] is governed as a ] without ]s or ]. However, for the purposes of administration and urban planning, it has been subdivided in various ways throughout its history. | |||
| As of 2022, Singapore has a total land area of about {{convert|753|km2|abbr=on}}, not including its sea area. | |||
| Historically, these subdivisions have been based on postal districts especially during the colonial era. When local elections neccesited the setting up of electorial districts, however, it began to supplement postal districts as an alternative form of local governence, since each electorial district is headed by a member of parliament who represents and speaks for the respective electoriates. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| In the ], the ] carved up the country into 55 planning areas. These boundaries became increasingly accepted as an alternative method of subdividing the country, made all the more popular as the boundaries do not change compared to the more fluid nature of electorical boundaries. The Singapore ] adopted these boundaries for the latest ] nationwide population census, and the ] uses them as an approximate guide when demarcating boundaries for its ]s, as opposed to the former ] system which was also based on electorial divisions. | |||
| Historically, these subdivisions have been based on postal districts, especially during the colonial era. When local elections necessitated the setting up of electoral districts, however, it began to supplement postal districts as an alternative form of local governance, since each electoral district is headed by a member of parliament who represents and speaks for the respective electorates. | |||
| ==Administrative and electoral divisions== | |||
| ==Postal Districts== | |||
| Postal districts were numbered from 01 to 83 under the new system implemented in ] ]. Census data and most forms of internal boundaries had been based on postal districts until the introduction of new ] in the 1990s. | |||
| ===Community Development Council districts=== | |||
| ==Electorial Districts== | |||
| {{main|Community Development Council}} | |||
| The electorial boundaries of Singapore are relatively fluid, and are reviewed prior to each general election. The following districts were in force since the 2001 General Elections: | |||
| {{Infobox subdivision type | |||
| | name = Community Development Council districts of Singapore | |||
| | map = CDC_map_of_Singapore_2020.svg | |||
| | imagesize = 300px | |||
| | category = ] | |||
| | territory = ] | |||
| | start_date = February 1997<ref name=PAact1997>{{cite web|url= http://eresources.nlb.gov.sg/newspapers/Digitised/Article/straitstimes19970821-1.2.39.1.aspx|title=Full map of CDCs released for first time. |date= 21 August 1997 |work=The Straits Times |page=25 |access-date=19 August 2016}} (Retrieved from Newspaper SG.)</ref> | |||
| | start_date1 = 11 November 2001 (Finalized) | |||
| | legislation_begin = PA Act 1997 | |||
| | current_number = Five districts | |||
| | number_date = 2015 | |||
| | population_range = | |||
| | area_range = | |||
| | government = ] | |||
| | government1 = ] | |||
| | subdivision = ] | |||
| }} | |||
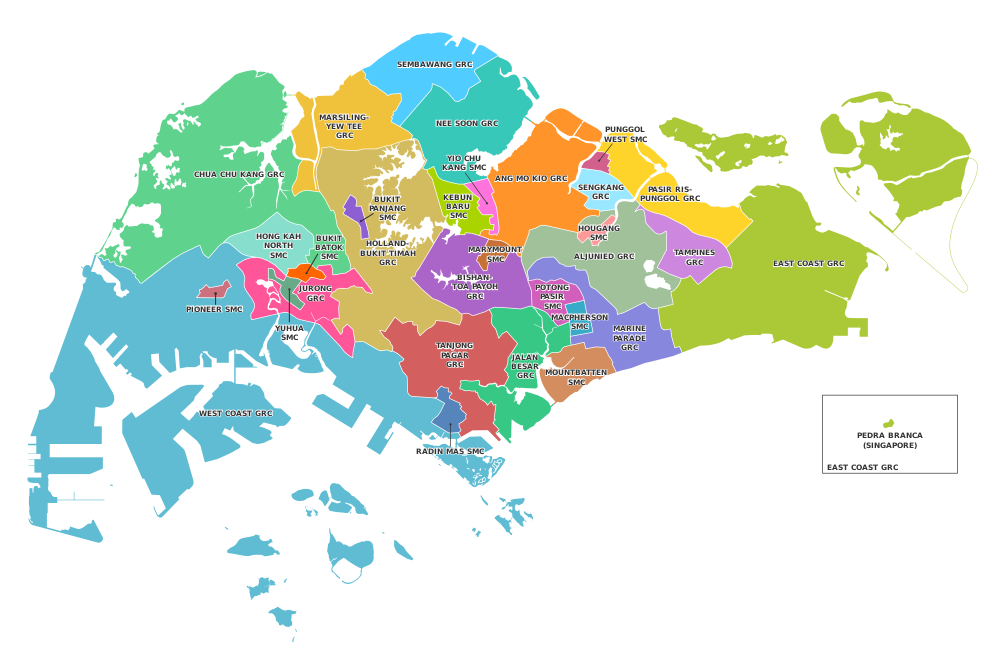
| Established in 1997 by the PA Act, there were nine districts formerly, governed by nine different ]s (CDCs). In 2001, the nine districts and CDCs were then reformed into five, namely the ], ], ], ] and ].<ref name=PAact1997/><ref>{{cite web|url=http://eresources.nlb.gov.sg/newspapers/Digitised/Article/straitstimes19970217-1.2.34.13.aspx|title= First 2 CDCs preparing for launch. |date=17 February 1997 |work=The Straits Times |page=27 |access-date=19 August 2016}} Retrieved from Newspaper SG.</ref> Each district is then further divided into ] and ]. | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Aljunied-Hougang Division | |||
| **Aljunied-Kembangan Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **Kembangan-Punggol Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **Nee Soon South Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *] - ] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Bishan East Division | |||
| **Bishan-Toa Payoh North Division | |||
| **Thomson Division | |||
| **Toa Payoh Central Division | |||
| **Toa Payoh East Division | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *East Coast Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **]-] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *Holland-Bukit Panjang Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| **Cashew | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **Hong Kah North Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **]-] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **Bukit Batok East Division | |||
| **Jurong Central Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *Nee Soon Central Single Member Constituency | |||
| *Nee Soon East Single Member Constituency | |||
| *]-] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Pasir Ris East Division | |||
| **Pasir Ris West Division | |||
| **Punggol Central Division | |||
| **Punggol North Division | |||
| **Punggol South Division | |||
| *] Single Member Constituency | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **Canberra Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **Tampines Central Division | |||
| **Tampines East Division | |||
| **Tampines North Division | |||
| **Tampines West Division | |||
| *] Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **]-] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| *West Coast Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **] Division | |||
| **West Coast Division | |||
| The council boundaries follow that of the existing political divisions, with each handling between four and six ] and ] and roughly dividing the country's population into equal parts. Each CDC is managed by a Council, which in turn is headed by a ] and has between 12 and 80 members. The members are appointed by the Chairman or Deputy Chairman of the ]. | |||
| ==Community Development Council Districts== | |||
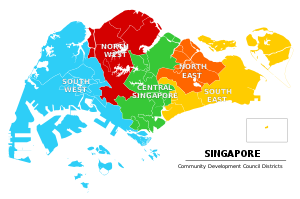
| Community Development Councils are regional organisations with the main aim of organising community-based programmes, projects, and other activities which are aimed at promoting communal bonding. There are 5 CDCs at present, with their districts divided by electorial boundaries as follows: | |||
| The role of the CDCs is to initiate, plan and manage community programmes to promote community bonding and social cohesion within local communities.<ref>Fernandez, W. (19 August 1996). . ''The Straits Times'', p. 1. Retrieved from NewspaperSG; ''The Straits Times'', 19 August 1996, p. 24.</ref> The electoral boundaries of Singapore are relatively fluid, and are reviewed prior to each general election. The districts are composed of the constituencies and electoral districts (the latter as of the 2015 General Elections). | |||
| *Central Singapore Community Development Council | |||
| **Ang Mo Kio Group Representation Constituency | |||
| **Bishan-Toa Payoh Group Representation Constituency | |||
| **Jalan Besar Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Tanjong Pagar Group Representative Constituency | |||
| *North East Community Development Council | |||
| **Aljunied Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Hougang Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Pasir Ris-Punggol Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Tampines Group Representative Constituency | |||
| *North West Community Development Council | |||
| **Holland-Bukit Panjang Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Nee Soon Central Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Nee Soon East Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Sembawang Group Representative Constituency | |||
| *South East Community Development Council | |||
| **East Coast Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Joo Chiat Single Member Constituency | |||
| **MacPherson Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Marine Parade Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Potong Pasir Single Member Constituency | |||
| *South West Community Development Council | |||
| **Ayer Rajah Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Bukit Timah Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Choa Chu Kang Single Member Constituency | |||
| **Hong Kah Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **Jurong Group Representative Constituency | |||
| **West Coast Group Representative Constituency | |||
| There are currently five CDCs, namely the | |||
| ==Urban Planning Areas== | |||
| {{main|Urban planning areas in Singapore}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| Singapore is divided into into 5 Regions by the ] of Singapore, and further organised into 55 areas. A ] is then drawn up for each planning area, providing for detailed planning guidelines for every individual plot of land throughout the country. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ===Town councils=== | |||
| *] | |||
| {{main|List of Singaporean town councils}} | |||
| **] | |||
| The first town councils were set up in September 1986 by the Town Councils Act, with the main purpose of ].<ref>Low, A. (1 September 1986). .The Straits Times, p. 8. Retrieved from NewspaperSG.</ref> Prior to the introduction of town councils, housing estates were managed by the ].<ref name=MyKindOfTown>Ngoo, I., et al. (7 April 1987). The Straits Times, Retrieved from NewspaperSG; Koh, T., et al.</ref> As the estates were centrally managed, the standardised rules that the board had set for all housing estates made HDB towns monotonous in appearance and problems faced by residents in the different estates were not addressed fast enough.<ref name=MyKindOfTown/> | |||
| **] | |||
| **] | |||
| Town councils boundaries are drawn based on electoral district boundaries. A town council area can consist of a ] (GRC), a Single Member Constituency (SMC), or a collection of neighbouring GRCs and SMCs controlled by the same political party. The Members of ] head the town councils of their constituencies. Town councils boundaries do not correspond to ] boundaries; different parts of the same HDB town may be managed by different town councils.<ref>{{Singapore legislation|title=Town Councils Act|titlelink=|cap=329A|ed=2000}}</ref> | |||
| **] | |||
| ] | |||
| **] | |||
| There are currently 17 town councils as of 2020:<ref>{{Cite web|date=29 July 2020|title=Town Councils (Declaration) Order 2020|url=https://sso.agc.gov.sg/SL-Supp/S641-2020/Published/20200730?DocDate=20200730|website=Singapore Statues Online}}</ref> | |||
| **] | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| **] | |||
| !Town Council | |||
| **] | |||
| !Constituency | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| | rowspan=2|Aljunied–Hougang | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| ***] | |||
| | rowspan="3" |Ang Mo Kio | |||
| ***] | |||
| |] | |||
| ***] | |||
| |- | |||
| ***] | |||
| |] | |||
| ***] | |||
| |- | |||
| ***] | |||
| |] | |||
| ***] | |||
| |- | |||
| ***] | |||
| | rowspan="2" |Bishan–Toa Payoh | |||
| ***] | |||
| |] | |||
| ***] | |||
| |- | |||
| *] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| | rowspan="2" |Chua Chu Kang | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| *] | |||
| |East Coast | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| | rowspan="2" |Holland–Bukit Panjang | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| | rowspan="2" |Jalan Besar | |||
| *] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| | rowspan="3" |Jurong–Clementi | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| *] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| | rowspan="3" |Marine Parade | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| **] | |||
| |Marsiling–Yew Tee | |||
| **] | |||
| |] | |||
| **] | |||
| |- | |||
| |Nee Soon | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| | rowspan="2" |Pasir Ris–Punggol | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |Sembawang | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |Sengkang | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |Tampines | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| | rowspan="2" |Tanjong Pagar | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| | rowspan="2" |West Coast | |||
| |] | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Constituencies=== | |||
| {{main|Constituencies of Singapore}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Town councils are then further subdivided into different constituencies, which are classified as either Single Member Constituencies (SMCs) or Group Representation Constituencies (GRCs). The boundaries of the electoral constituencies are decided by the Elections Department, which is under the control of the Prime Minister's Office.<ref>Alex Au Waipang, 'The Ardour of Tokens: Opposition Parties' Struggle to Make a Difference', in T.Chong (eds), '' Management of Success: Singapore Revisited ''(Singapore, 2010), p. 106.</ref> | |||
| ==Other administrative subdivisions== | |||
| ===URA Master Plan boundaries=== | |||
| ====Regions==== | |||
| {{main|Regions of Singapore}} | |||
| The five regions of Singapore are groupings of the planning areas. | |||
| ====Planning areas==== | |||
| {{main|Planning areas of Singapore}} | |||
| In the 1990s, the ] carved up the country into 55 of planning areas. The Singapore ] adopted these boundaries for the latest 2000 nationwide population census, and the ] uses them as an approximate guide when demarcating boundaries for its ]s. | |||
| ===Survey districts=== | |||
| Singapore is divided into 64 survey districts, of which 34 are ]s (originally, rural districts) and 30 are town subdivisions.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.sla.gov.sg/Services/PropertyOwnership/LandTitlesSearch.aspx|title=Land Titles Search|website=Singapore Land Authority|access-date=2016-04-23|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151101010449/http://www.sla.gov.sg/Services/PropertyOwnership/LandTitlesSearch.aspx|archive-date=2015-11-01|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ===Postal districts=== | |||
| Postal districts were numbered from 01 to 83 under the new system implemented on 1 September 1995. Census data and most forms of internal boundaries had been based on postal districts until the introduction of new ] in the 1990s.{{Citation needed|reason=Whether census data used postal districts is questionable|date=May 2016}} | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200723104915/https://www.cdc.org.sg/ |date=23 July 2020 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090823115220/http://www.sla.gov.sg/what_we_do/what_we_do_land_registry.html |date=23 August 2009 }} | |||
| {{Singapore}} | {{Places in Singapore}} | ||
| {{Singapore topics}} | |||
| {{Articles on first-level administrative divisions of Asian countries}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:48, 17 October 2024
Administrative divisions of Singapore
 Subzones of Singapore, one of the many ways Singapore is locally divided
Subzones of Singapore, one of the many ways Singapore is locally divided
Singapore is governed as a unitary state without provinces or states. However, for the purposes of administration and urban planning, it has been subdivided in various ways throughout its history.
As of 2022, Singapore has a total land area of about 753 km (291 sq mi), not including its sea area.
History
Historically, these subdivisions have been based on postal districts, especially during the colonial era. When local elections necessitated the setting up of electoral districts, however, it began to supplement postal districts as an alternative form of local governance, since each electoral district is headed by a member of parliament who represents and speaks for the respective electorates.
Administrative and electoral divisions
Community Development Council districts
Main article: Community Development Council| Community Development Council districts of Singapore | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Singapore |
| Created by | PA Act 1997 |
| Created |
|
| Number | Five districts (as of 2015) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
Established in 1997 by the PA Act, there were nine districts formerly, governed by nine different Community Development Councils (CDCs). In 2001, the nine districts and CDCs were then reformed into five, namely the North East CDC, North West CDC, South East CDC, South West CDC and Central Singapore CDC. Each district is then further divided into electoral constituencies and town councils.
The council boundaries follow that of the existing political divisions, with each handling between four and six GRCs and SMCs and roughly dividing the country's population into equal parts. Each CDC is managed by a Council, which in turn is headed by a mayor and has between 12 and 80 members. The members are appointed by the Chairman or Deputy Chairman of the People's Association.
The role of the CDCs is to initiate, plan and manage community programmes to promote community bonding and social cohesion within local communities. The electoral boundaries of Singapore are relatively fluid, and are reviewed prior to each general election. The districts are composed of the constituencies and electoral districts (the latter as of the 2015 General Elections).
There are currently five CDCs, namely the
- Central Singapore Community Development Council
- North East Community Development Council
- North West Community Development Council
- South East Community Development Council
- South West Community Development Council
Town councils
Main article: List of Singaporean town councilsThe first town councils were set up in September 1986 by the Town Councils Act, with the main purpose of estate management. Prior to the introduction of town councils, housing estates were managed by the Housing Development Board. As the estates were centrally managed, the standardised rules that the board had set for all housing estates made HDB towns monotonous in appearance and problems faced by residents in the different estates were not addressed fast enough.
Town councils boundaries are drawn based on electoral district boundaries. A town council area can consist of a Group Representation Constituency (GRC), a Single Member Constituency (SMC), or a collection of neighbouring GRCs and SMCs controlled by the same political party. The Members of Parliament head the town councils of their constituencies. Town councils boundaries do not correspond to new town boundaries; different parts of the same HDB town may be managed by different town councils.

There are currently 17 town councils as of 2020:
| Town Council | Constituency |
|---|---|
| Aljunied–Hougang | Aljunied GRC |
| Hougang SMC | |
| Ang Mo Kio | Ang Mo Kio GRC |
| Kebun Baru SMC | |
| Yio Chu Kang SMC | |
| Bishan–Toa Payoh | Bishan–Toa Payoh GRC |
| Marymount SMC | |
| Chua Chu Kang | Chua Chu Kang GRC |
| Hong Kah North SMC | |
| East Coast | East Coast GRC |
| Holland–Bukit Panjang | Holland–Bukit Timah GRC |
| Bukit Panjang SMC | |
| Jalan Besar | Jalan Besar GRC |
| Potong Pasir SMC | |
| Jurong–Clementi | Jurong GRC |
| Bukit Batok SMC | |
| Yuhua SMC | |
| Marine Parade | Marine Parade GRC |
| MacPherson SMC | |
| Mountbatten SMC | |
| Marsiling–Yew Tee | Marsiling–Yew Tee GRC |
| Nee Soon | Nee Soon GRC |
| Pasir Ris–Punggol | Pasir Ris–Punggol GRC |
| Punggol West SMC | |
| Sembawang | Sembawang GRC |
| Sengkang | Sengkang GRC |
| Tampines | Tampines GRC |
| Tanjong Pagar | Tanjong Pagar GRC |
| Radin Mas SMC | |
| West Coast | West Coast GRC |
| Pioneer SMC |
Constituencies
Main article: Constituencies of SingaporeTown councils are then further subdivided into different constituencies, which are classified as either Single Member Constituencies (SMCs) or Group Representation Constituencies (GRCs). The boundaries of the electoral constituencies are decided by the Elections Department, which is under the control of the Prime Minister's Office.
Other administrative subdivisions
URA Master Plan boundaries
Regions
Main article: Regions of SingaporeThe five regions of Singapore are groupings of the planning areas.
Planning areas
Main article: Planning areas of SingaporeIn the 1990s, the Urban Redevelopment Authority carved up the country into 55 of planning areas. The Singapore Department of Statistics adopted these boundaries for the latest 2000 nationwide population census, and the Singapore Police Force uses them as an approximate guide when demarcating boundaries for its Neighbourhood Police Centres.
Survey districts
Singapore is divided into 64 survey districts, of which 34 are mukims (originally, rural districts) and 30 are town subdivisions.
Postal districts
Postal districts were numbered from 01 to 83 under the new system implemented on 1 September 1995. Census data and most forms of internal boundaries had been based on postal districts until the introduction of new planning boundaries in the 1990s.
See also
References
- ^ "Full map of CDCs released for first time". The Straits Times. 21 August 1997. p. 25. Retrieved 19 August 2016. (Retrieved from Newspaper SG.)
- "First 2 CDCs preparing for launch". The Straits Times. 17 February 1997. p. 27. Retrieved 19 August 2016. Retrieved from Newspaper SG.
- Fernandez, W. (19 August 1996). "PM Goh urges young to rally behind him". The Straits Times, p. 1. Retrieved from NewspaperSG; The Straits Times, 19 August 1996, p. 24.
- Low, A. (1 September 1986). Town councils take over from HDB. .The Straits Times, p. 8. Retrieved from NewspaperSG.
- ^ Ngoo, I., et al. (7 April 1987). My kind of town. The Straits Times, Retrieved from NewspaperSG; Koh, T., et al.
- Town Councils Act (Cap. 329A, 2000 Rev. Ed.)
- "Town Councils (Declaration) Order 2020". Singapore Statues Online. 29 July 2020.
- Alex Au Waipang, 'The Ardour of Tokens: Opposition Parties' Struggle to Make a Difference', in T.Chong (eds), Management of Success: Singapore Revisited (Singapore, 2010), p. 106.
- "Land Titles Search". Singapore Land Authority. Archived from the original on 1 November 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
External links
- CDC Districts Archived 23 July 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Singapore Land Registry Archived 23 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine
| Places in Singapore by region | |
|---|---|
| Listed by planning areas | |
| Central | |
| East | |
| North | |
| North-East | |
| West | |
| Articles on first-level administrative divisions of Asian countries | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
Table of administrative divisions by country
| |