| Revision as of 19:24, 8 August 2012 editXqbot (talk | contribs)Bots, Template editors2,325,690 editsm r2.7.3) (Robot: Adding el:Πρίλεπ-Μοναστηρίου διάλεκτος← Previous edit |
Latest revision as of 20:39, 8 November 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1);Tag: AWB |
| (40 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
|
|
{{Short description|Dialect of Macedonian}} |
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
{{Listen |
|
|
|
|
|
| header = Дијалектни примери |
|
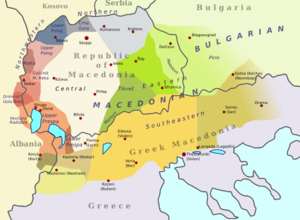
The '''Prilep-Bitola dialect''' ({{lang-mk|Прилепско-битолски дијалект}}, ''Prilepsko-bitolski dijalekt'') is a member of the central subgroup of the western group of ] of the ]. This dialect is spoken in much of the ] (more specifically, the ], ], ] and ]), as well as by the ] population in and around ] (Lerin)<ref>'''author missing'''. Леринскиот говор. Македонски jазик, 1983, ХХХIV, стр. 23-49.</ref><ref>Hill, Peter. The Dialect of Gorno Kalenik 1991, Columbus, OH</ref> in neighbouring ]. The Prilep-Bitola dialect, along with other peripheral west-central dialects, provides much of the basis for modern ].<ref>Makedonska gramatika by Krume Kepeski |
|
|
|
| filename = Prilep-Bitola dialect speech - Topolčani.ogg |
|
Language, Vol. 27, No. 2 (Apr–Jun, 1951), pp. 180–187</ref> ] dialects have developed in the cities of ] and ]. |
|
|
|
| title = Peter's Mourning |
|
|
| description = Folk epic told by a resident of ], ] region |
|
|
| filename2 = Prilep-Bitola dialect speech - Bitola.ogg |
|
|
| title2 = The Pebble Stew |
|
|
| description2 = Tale told by a woman from the city of ] |
|
|
}} |
|
|
The '''Prilep-Bitola dialect''' ({{langx|mk|Прилепско-битолски дијалект}}, ''Prilepsko-bitolski dijalekt'') is a member of the central subgroup of the western group of ]. This dialect is spoken in much of the ] (more specifically, the ], ], ] and ] municipalities), as well as by the ] population in and around ] (Lerin)<ref>{{Cite book |last=Vidoeski|first=Božidar (Божидар Видоески) |title=Lerinskiot govor. |date=1983|pages=23–49 |language=mk |script-title=mk:Леринскиот говор}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Hill |first=Peter |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ibxiAAAAMAAJ |title=The Dialect of Gorno Kalenik |date=1991 |publisher=Slavica Publishers |location=Columbus, OH |isbn=9780893572174 |language=en |via=Google Books}}</ref> in neighbouring ]. The Prilep-Bitola dialect, along with other peripheral west-central dialects, provides much of the basis for modern ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Lunt |first=Horace G. |date=1951 |title=Makedonska gramatika by Krume Kepeski |journal=Language |language=en |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=180–187 |doi=10.2307/410435 |jstor=410435}}</ref> ] dialects have developed in the cities of ] and ]. |
|
|
|
|
|
==Phonological characteristics== |
|
==Phonological characteristics== |
|
|
|
|
|
The phonological characteristics of the Bitola-Prilep dialect which also can also be found in the other peripheral dialects are: |
|
The phonological characteristics of the Bitola-Prilep dialect which can also be found in the other peripheral dialects are: |
|
*mostly ] word stress (see ]) |
|
*mostly ] word stress (see ]); |
|
*the ] has reflexed into {{IPA|/ɛ/}} |
|
*] *ǫ has reflexed into {{IPA|/a/}}: |
|
|
::rǫka > ''рака'' {{IPA|/ˈraka/}} ('hand') |
|
*as in most South(-Western) dialects, the central vowel {{IPA|/a/}} is more fronted (i.e. a cardinal {{IPA|}}) rather than the more central {{IPA|}} typical of other dialect groups |
|
|
|
*except for the Prilep sub-dialects, Bitola sub-dialects have two phonemic ]s ({{IPA|/ɫ/}} and {{IPA|/l/}}, continuants of Proto-Slavic *l and *ĺ): |
|
*the palatal affricates are typically prepalatalized: {{IPA|/ˈsvɛca/}} is realized {{IPA|}}, {{IPA|/ˈmɛɟa/}} is realized {{IPA|}} |
|
|
|
::ex. Proto-Slavic *kĺučь > {{IPA|}} in Bitola sub-dialects, {{IPA|}} in Prilep sub-dialects |
|
*similarly, the palatal nasal is also prepalatalized: {{IPA|/ˈjadɛɲɛ/}} is realized {{IPA|}} |
|
|
|
*while most Macedonian dialects have a phonemic {{IPA|/f/}} (in loanwords), many sub-dialects of the Prilep-Bitola dialect—with the exception of urban prestige dialects—instead have {{IPA|/v/}}: |
|
* consonant ] is typical of this dialect and occurs in the following environments: |
|
|
|
::] ''fustan'' {{IPA|/ˈfustan/}} > ''вустан'' {{IPA|/ˈvustan/}} ('ladies' dress') |
|
**the etymological {{IPA|/v/}} in initial position has been lost in a number of instances: |
|
|
|
::] فوطة {{IPA|/ˈfuta/}} > ''вута'' {{IPA|/ˈvuta/}} ('apron') |
|
***in the sequences ''*vs-'' and ''*vz-''; e.g. ''*vse'' > {{IPA|/sɛ/}} (''сè'', "all"), ''*vzema'' > {{IPA|/ˈzɛma/}} (''зема'', "to take") as is the case in the standard |
|
|
|
::Ottoman Turkish فرنا {{IPA|/ˈfuɾna/}} > ''вурна'' {{IPA|/ˈvurna/}} ('], ]') |
|
***in a handful of other words: {{IPA|/ˈtɔrnik/}} for standard {{IPA|/ˈftɔrnik/}} (''вторник'', "Tuesday"), {{IPA|/ˈnatrɛ/}} for standard {{IPA|/ˈvnatrɛ/}} (''внатре'', "inside") |
|
|
|
*the palatal affricates are typically prepalatalized: ''свеќа'' {{IPA|/ˈsvɛca/}} ('candle') is realized as {{IPA|}}, ''меѓа'' {{IPA|/ˈmɛɟa/}} ('border, frontier') is realized as {{IPA|}} and in Prilep, especially in younger speakers as {{IPA|}} and {{IPA|}}; |
|
****the same process (bringing the pronunciation closer to their antonyms) also occurred with {{IPA|/ˈmnɔɡu/}} (''многу'', "much", "a lot") → {{IPA|/ˈnɔɡu/}} |
|
|
|
**a similar features occurs with the palatal nasal: ''јадење'' {{IPA|/ˈjadɛɲɛ/}} ('food') is realized as {{IPA|}}; |
|
**absence of the intervocalic {{IPA|/v/}} |
|
|
|
*the etymological {{IPA|/v/}} in initial position has been lost in a number of instances: |
|
*** in the plural forms of monosyllabic nouns, e.g. лебо(в)и:<ref>Граматика на македонскиот литературен јазик, Блаже Конески, Култура, Скопје 1967, стр.68</ref> |
|
|
|
**in the sequences ''*vs-'' and ''*vz-'', as is the case in the standard; e.g. ''сè'' {{IPA|/sɛ/}} ('all') from the earlier *''все'', ''зема'' {{IPA|/ˈzɛma/}} ('to take') from the earlier *''взема''; |
|
****{{IPA|/ˈlɛbɔvi/}} → {{IPA|/ˈlɛbɔi/}} (realized {{IPA|}}) |
|
|
|
**in a handful of words where the pronunciation was "evened up" with that of their antonyms: ''натре'' {{IPA|/ˈnatrɛ/}} from the earlier ''внатре'' {{IPA|/ˈvnatrɛ/}} ('inside') as per ''надвор'' {{IPA|/ˈnadvɔr/}} ('outside'), ''ногу'' {{IPA|/ˈnɔɡu/}} from the earlier ''многу'' {{IPA|/ˈmnɔɡu/}} ('much, a lot') as per ''малку'' {{IPA|/ˈmalku/}} ('a little'); |
|
*** and in most other positions, e.g. то(в)ар:<ref>Историја на македонскиот јазик, Блаже Конески, Култура, Скопје 1986, стр. 21</ref> |
|
|
|
*intervocalic consonant ] is typical of this dialect, and elided forms are in ] with non-elided forms: |
|
****{{IPA|/ˈtɔvar/}} → {{IPA|/ˈtɔar/}} (realized {{IPA|}}) |
|
|
|
**elision of the intervocalic {{IPA|/v/}}: |
|
** certain short words (conjunctions, pronouns, adverbs, determiners, etc.) have undergone further elision, ex.: |
|
|
|
***in the plural forms of monosyllabic nouns, e.g. ''лебо(в)и'':<ref>{{Cite book |last=Koneski |first=Blaže (Блаже Конески) |title=Gramatika na makedonskiot literaturen jazik |date=1967 |publisher=Kultura <!--Култура--> |location=Skopje <!--Скопје--> |pages=68 |language=mk |script-title=mk:Граматика на македонскиот литературен јазик |author-link=Blaže Koneski}}</ref> |
|
*** ''sega'' → ''sea'' → {{IPA|/sa/}} ("now") |
|
|
|
::::{{IPA|/ˈlɛbɔvi/}} → {{IPA|/ˈlɛbɔi/}} (realized as {{IPA|}} ~ {{IPA|}}) |
|
*** ''tova'' → ''toa'' → {{IPA|/tɔ/}} ("that") |
|
|
|
::* and in most other positions, e.g. ''то(в)ар'':<ref>{{Cite book |last=Koneski |first=Blaže (Блаже Конески) |title=Istorija na makedonskiot jazik |date=1986 |publisher=Kultura <!--Култура--> |location=Skopje <!--Скопје--> |pages=21 |language=mk |script-title=mk:Историја на македонскиот јазик }}</ref> |
|
*** ''koga'' → ''koa'' → {{IPA|/kɔ/}} ("when") |
|
|
|
::::{{IPA|/ˈtɔvar/}} → {{IPA|/ˈtɔar/}} (realized as {{IPA|}}) |
|
*insertion of {{IPA|/t/}} and {{IPA|/d/}} into consonant clusters {{IPA|/sr/}}- and {{IPA|/zr/}}-, respectively; for example, {{IPA|/stram/}} for the standard {{IPA|/sram/}} (''срам'', "shame") and {{IPA|/zdrɛl/}} for the standard {{IPA|/zrɛl/}} (''зрел'', "ripe") |
|
|
|
:* certain short words (conjunctions, pronouns, determiners, etc.) have undergone further elision, ex.: |
|
|
::: {{IPA|/ˈsɛɡa/}} (→ {{IPA|/ˈsɛa/}}) → {{IPA|}} ('now') |
|
|
::: *{{IPA|/ˈtɔva/}} (→ {{IPA|/ˈtɔa/}}) → {{IPA|}} (''indic. pron.'' 'that') |
|
|
::: {{IPA|/ˈkɔɡa/}} (→ {{IPA|/ˈkɔa/}}) → {{IPA|}} (''interr. pron.'' 'when') |
|
|
*insertion of {{IPA|/t/}} and {{IPA|/d/}} into consonant clusters -{{IPA|/sr/}}- and -{{IPA|/zr/}}-, respectively; for example, {{IPA|/stram/}} from the earlier {{IPA|/sram/}} (''срам'', 'shame') and {{IPA|/zdrɛl/}} from the earlier {{IPA|/zrɛl/}} (''зрел'', 'ripe'). |
|
|
*use of /v/ instead of the archaic /x/: страх (strah) > страв ({{transl|mk|italic=no|strav}}; fear); |
|
*In the sub-dialect of ]-], especially among the oldest generations: |
|
*In the sub-dialect of ]-], especially among the oldest generations: |
|
**while {{IPA|}} is an allophone of {{IPA|/l/}} in most dialects (occurring in all positions except before front vowels and {{IPA|/j/}}, in this dialect {{IPA|}} is used instead: e.g. {{IPA|}} for {{IPA|}} (''глава'', "head") and {{IPA|}} for {{IPA|}} (''слама'', "straw")) |
|
**while {{IPA|}} is an allophone of {{IPA|/l/}} in most dialects (occurring in all positions except before front vowels and {{IPA|/j/}}), in this dialect {{IPA|}} is used instead; ex.: |
|
|
:::{{IPA|}} for {{IPA|}} (''глава'', 'head') and {{IPA|}} for {{IPA|}} (''слама'', 'straw') |
|
**the etymological {{IPA|/a/}} mutates (is raised) to {{IPA|}} ({{IPA|}} ~ {{IPA|}}) when preceding an ] or ] consonant, e.g. {{IPA|}} for {{IPA|/ˈt͡ʃaʃa/}} (''чаша'', "cup") |
|
**the phoneme {{IPA|/a/}} mutates (is raised) to {{IPA|}} ({{IPA|}} ~ {{IPA|}}) when preceding an ] or ] consonant with the exception of suffixes; ex.: |
|
|
:::''чаша'' {{IPA|/ˈt͡ʃaʃa/}} ('cup') is realized as {{IPA|}} |
|
**the ] syllabic ''*l̥'' has reflexed into {{IPA|/ə/}}, e.g. {{IPA|/ˈsənt͡sɛ/}} ("sun") for the standard {{IPA|/ˈsɔnt͡sɛ/}} and {{IPA|/vək/}} ("wolf") for the standard {{IPA|/vɔlk/}} |
|
|
|
:::''жаба'' {{IPA|/ˈʒaba/}} ('frog') is realized as {{IPA|}} |
|
|
**the ] syllabic *l̥ has reflexed into {{IPA|/ə/}}, e.g. *sъlnьce > {{IPA|/ˈsənt͡sɛ/}} ('sun'), *vьlkъ > {{IPA|/vək/}} ('wolf'). |
|
|
|
|
|
==Morphological characteristics== |
|
==Morphological characteristics== |
|
|
|
|
|
*three ]s pertaining to the position of the object (see ]) |
|
*tripartite ] pertaining to the position of the object (see ]); |
|
|
*use of the preposition во (vo) or в (v); |
|
*the third-person personal pronouns: тој, та/таа/таја, то, тие/тија (he, she, it, they) |
|
|
|
*use of the grammatical construction have + past participle: имам работено (imam raboteno; I have worked); |
|
**some of the outermost dialects of the Lerin subdialect have он, она, то, они |
|
|
|
*merger of ] ''е''-group verbs to ''и''-group verbs; e.g. ''јаде'' {{IPA|/ˈjade/}} → ''јади'' {{IPA|/ˈjadi/}} (] ] ] of 'to eat'); |
|
*] verbs are typically derived from ] verbs by means of the suffix –ва (e.g. зборва and боледва) |
|
|
|
*the third-person personal pronouns: ''тој, та/таа/таја, то(а), тие/тија'' (he, she, it, they); |
|
*'expansion' where other dialects have palatalization: ''падина'' ("to fall", sing. present third-person) versus the standard ''паѓа'' |
|
|
|
**some of the outermost dialects of the Lerin subdialect have ''он, она, то, они''; |
|
*the use of the inflectional suffix ''-и'' in third-person singular verbs (e.g. ''можи'' and ''биди'' versus the standard ''може'' and ''биде'') |
|
|
|
*] verbs are typically derived from ] verbs by means of the suffix –ва (e.g. ''зборва'' and ''боледва'') in Bitola dialects, but standard -ува in Prilep dialects; |
|
*use of the ] for proper names<ref>Friedman, Victor (1998), Macedonian: Comparative Grammar, Slavic and East European Language Research Center (SEELRC): p. 22</ref> |
|
|
|
*'expansion' where other dialects have palatalization: ''падина'' ("to fall", sing. present third-person) versus the standard ''паѓа''; |
|
*no distinction between masculine and feminine short possessive pronouns, i.e. consistent use of ''му'' and ''го'' for both genders and also the plural third person |
|
|
|
*use of the ] for proper names;<ref>{{Citation |last=Friedman |first=Victor |title=Macedonian: Comparative Grammar |date=1998 |pages=22 |publisher=Slavic and East European Language Research Center (SEELRC)}}</ref> |
|
|
*no distinction between masculine and feminine short possessive pronouns, i.e. consistent use of ''му'' and ''го'' for both genders, in Bitola dialects, but they are used in the plural third person in Prilep; |
|
|
*use of -јќум and -јким instead of the standard -јќи for the gerund, in older speakers, e.g. одејќум (while walking). |
|
|
|
|
|
==Typical Words== |
|
==Typical words== |
|
|
*чупе ({{IPA|/ˈt͡ʃupɛ/}}) 'girl' |
|
|
|
|
|
*преѓе ({{IPA|/ˈprɛɟɛ/}}), преѓеска ({{IPA|/ˈprɛɟɛska/}}) 'recently, lately' |
|
*'''Чупе''' – girl |
|
|
|
*модистра ({{IPA|/ˈmɔdistra/}}) 'seamstress' |
|
*'''Преѓе(ска)''' – recently, lately |
|
|
|
*бендиса ({{IPA|/ˈbɛndisa/}}) 'to have a liking for something or someone', 'to fancy' |
|
*'''Модистра''' – seamstress |
|
|
|
*сурат ({{IPA|/ˈsurat/}}) 'face' |
|
*'''Бендиса''' – to have a liking for something or someone, to fancy |
|
|
|
*плусне ({{IPA|/ˈplusnɛ/}}) 'to fire (a rifle)' |
|
*'''Сурат''' – face |
|
|
|
*капнат ({{IPA|/ˈkapnat/}}) 'exhausted' |
|
|
|
|
|
*греда ({{IPA|/ˈɡrɛda/}}) 'plank', 'beam (of wood)' |
|
===Typical words from the Lerin sub-dialect=== |
|
|
|
|
|
*'''Пл'усна''' – fire a rifle |
|
|
*'''Капнат''' – thirsty |
|
|
*'''Гренди''' – timber |
|
|
|
|
|
|
==Notes== |
|
==Notes== |
| Line 61: |
Line 77: |
|
|
|
|
|
==External links== |
|
==External links== |
|
* |
|
* |
|
|
|
|
|
{{Macedonian dialects}} |
|
{{Macedonian dialects}} |
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
The phonological characteristics of the Bitola-Prilep dialect which can also be found in the other peripheral dialects are: