| Revision as of 20:06, 1 January 2007 editIdioma-bot (talk | contribs)55,031 editsm robot Adding: lt:Anabaras Removing: fi:Anabar Modifying: de:Anabar (Fluss)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:39, 9 November 2024 edit undoMonkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 1; ignored 1: Lang-rus);Tag: AWB | ||
| (77 intermediate revisions by 47 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Infobox river | |||
| The '''Anabar River''' is a ] in ], ], located just west of the ]. Its catchment extends into the ] that form the highest part of the ].It has the biggest catchment in the world | |||
| | name = Anabar | |||
| | other_name = Анабар / Анаабыр | |||
| | image = Anabar river near the mouth of Polovinnaya tributary, р. Анабар, устье р. Половинной - panoramio.jpg | |||
| | image_caption = The Anabar near the mouth of the Polovinnaya | |||
| | map = Anabar.png | |||
| | map_size = | |||
| | map_caption = Anabar river basin | |||
| | map_alt = | |||
| | pushpin_map = Russia Sakha Republic#Russia | |||
| | pushpin_map_size = | |||
| | pushpin_map_caption= Location of the mouth | |||
| | pushpin_map_alt = | |||
| | source1 = Confluence of ] and ] | |||
| | source1_location = ] | |||
| | source1_coordinates = {{coord|70|46|16|N|113|20|13|E|}} | |||
| | source1_elevation = {{convert|16|m|abbr=on}} | |||
| | mouth = ] | |||
| | mouth_location = ] | |||
| | mouth_coordinates = {{coord|73.2052|113.5567|source:wikidata|display=it}} | |||
| | mouth_elevation = {{convert|0|m|abbr=on}} | |||
| | subdivision_type1 = Country | |||
| | subdivision_name1 = ] | |||
| | length = {{convert|380|km|mi|abbr=on}} ({{convert|939|km|mi|abbr=on}}) | |||
| | discharge1_avg = {{convert|498|m3/s|cuft/s|abbr=on}} | |||
| | basin_size = {{convert|100000|km2|mi2|abbr=on}} | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''Anabar''' ({{lang-rus|Анабар|r=Anabar}}, in its upper course: Большая Куонамка ''Bolshaya Kuonamka''; {{langx|sah|Анаабыр|translit=Anaabır}}) is a ] in ], ]. It is {{convert|380|km}} long ({{convert|939|km|mi|abbr=on}} counting the {{convert|559|km|mi|abbr=on}} long Bolshaya Kuonamka ("Big Kuonamka") stretch of its upper course) and has a ] of {{convert|100000|km2}}.<ref name=gvr>{{GVR|233759|Река Анабар (Бол. Куонапка)}}</ref> | |||
| Its mean annual discharge is approximately 700 cubic metres per second, concentrated heavily in early ] when the ice that covers the river for most of the year thaws. The ''Gulf of Anabar'' is believed to be the easternmost ] in Russia - defining the point at which the climate during the ] became too dry for ] to form - one notices a quite clear transition from fjords to deltas at river mouths when the ] ] is reached shortly to the east. | |||
| ==Course== | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| The Anabar is formed at the confluence of the ] and ] at the edge of the ]. The length of the Anabar proper is {{convert|380|km|mi|abbr=on}}. The two rivers forming it have their sources in the northeastern part of the ], part of the ]. There are many lakes in its basin. | |||
| The Anabar basin is located between rivers ] and ]. The mouth of the river is in the ]. Its mean annual discharge is {{convert|564|m3/s|cuft/s}}, concentrated heavily in early summer when the ice that covers the river for most of the year thaws.<ref name=WR/> The ] river flows into the Laptev Sea close to the mouth of the Anabar, but it is not its tributary.<ref name=GE>]</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ===Tributaries=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Its main tributaries are the {{convert|115|km|mi|abbr=on}} long ], the {{convert|342|km|mi|abbr=on}} long ] (Удьа), the {{convert|453|km|mi|abbr=on}} long ] ("Little Kuonamka") and the {{convert|108|km|mi|abbr=on}} long ] on the right, as well as the {{convert|262|km|mi|abbr=on}} long ], the {{convert|139|km|mi|abbr=on}} long Kharabyl and the {{convert|103|km|mi|abbr=on}} long ] on the left.<ref name=WR></ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] | |||
| Historically ] have inhabited the basin of the Anabar River.<ref name=Forsyth>{{cite book | |||
| ] | |||
| | last = Forsyth | |||
| ] | |||
| | first = James | |||
| ] | |||
| | title = A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian colony 1581-1990 | |||
| | publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| | year = 1992 | |||
| | location = Cambridge | |||
| }}</ref> Vasiliy Sychev was the first ]n to reach the river in 1643.<ref name=Armstrong>{{cite book | |||
| | last = Armstrong | |||
| | first = Terence | |||
| | title = Russian Settlement in the North | |||
| | publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| | year = 2010 | |||
| }}</ref><ref name=Holland>{{cite book | |||
| | last = Holland | |||
| | first = Clive | |||
| | title = Arctic Exploration and Development, c. 500 B.C. to 1915: an encyclopedia | |||
| | publisher = Garland | |||
| | year = 1994 | |||
| | location = New York | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | In present times the basin of the Anabar river is notable as the location of the largest concentration of ] deposits in the world outside of ] and ]. These deposits made the ] into one of the world's largest producers of diamonds, and remain the economic mainstay of the area. | ||
| ==See also== | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| *{{commonscat inline|Anabar River}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:39, 9 November 2024
River in Russia| Anabar Анабар / Анаабыр | |
|---|---|
 The Anabar near the mouth of the Polovinnaya The Anabar near the mouth of the Polovinnaya | |
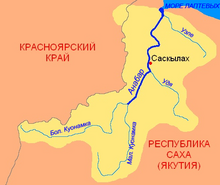 Anabar river basin Anabar river basin | |
  | |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Confluence of Malaya Kuonamka and Bolshaya Kuonamka |
| • location | Olenyoksky District, Sakha |
| • coordinates | 70°46′16″N 113°20′13″E / 70.77111°N 113.33694°E / 70.77111; 113.33694 |
| • elevation | 16 m (52 ft) |
| Mouth | Laptev Sea |
| • location | Anabar Bay |
| • coordinates | 73°12′19″N 113°33′24″E / 73.2052°N 113.5567°E / 73.2052; 113.5567 |
| • elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 380 km (240 mi) (939 km (583 mi)) |
| Basin size | 100,000 km (39,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 498 m/s (17,600 cu ft/s) |
The Anabar (Russian: Анабар, romanized: Anabar, in its upper course: Большая Куонамка Bolshaya Kuonamka; Yakut: Анаабыр, romanized: Anaabır) is a river in Sakha, Russia. It is 380 kilometres (240 mi) long (939 km (583 mi) counting the 559 km (347 mi) long Bolshaya Kuonamka ("Big Kuonamka") stretch of its upper course) and has a drainage basin of 100,000 square kilometres (39,000 sq mi).
Course
The Anabar is formed at the confluence of the Malaya Kuonamka and Bolshaya Kuonamka at the edge of the North Siberian Lowland. The length of the Anabar proper is 380 km (240 mi). The two rivers forming it have their sources in the northeastern part of the Anabar Plateau, part of the Central Siberian Plateau. There are many lakes in its basin.
The Anabar basin is located between rivers Khatanga and Olenyok. The mouth of the river is in the Anabar Bay. Its mean annual discharge is 564 cubic metres per second (19,900 cu ft/s), concentrated heavily in early summer when the ice that covers the river for most of the year thaws. The Uele river flows into the Laptev Sea close to the mouth of the Anabar, but it is not its tributary.
Tributaries
Its main tributaries are the 115 km (71 mi) long Mayat, the 342 km (213 mi) long Udya (Удьа), the 453 km (281 mi) long Malaya Kuonamka ("Little Kuonamka") and the 108 km (67 mi) long Ebelyakh on the right, as well as the 262 km (163 mi) long Suolama, the 139 km (86 mi) long Kharabyl and the 103 km (64 mi) long Konnies on the left.
History
Historically Evenks have inhabited the basin of the Anabar River. Vasiliy Sychev was the first Russian to reach the river in 1643.
In present times the basin of the Anabar river is notable as the location of the largest concentration of diamond deposits in the world outside of Africa and Australia. These deposits made the Soviet Union into one of the world's largest producers of diamonds, and remain the economic mainstay of the area.
See also
References
- "Река Анабар (Бол. Куонапка) in the State Water Register of Russia". textual.ru (in Russian).
- ^ Water of Russia - Анабар
- Google Earth
- Forsyth, James (1992). A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian colony 1581-1990. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Armstrong, Terence (2010). Russian Settlement in the North. Cambridge University Press.
- Holland, Clive (1994). Arctic Exploration and Development, c. 500 B.C. to 1915: an encyclopedia. New York: Garland.
External links
 Media related to Anabar River at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Anabar River at Wikimedia Commons