| Revision as of 10:10, 28 October 2004 edit80.181.111.248 (talk) →Kuznets' Law← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 23:59, 14 November 2024 edit undoIljhgtn (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users35,907 edits →Recent lead rewrite: ReplyTag: Reply | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{skip to talk}} | |||
| == ''Read'' Smith before you quote him == and even then, do him justice; and even then, opinions and personal or political interpretations are not encyclopedic - they are political and belong on this ''discussion'' page, or on a politics site. | |||
| {{Talk header}} | |||
| I come just short of advocating a complete removal of all the Smith material, | |||
| {{WikiProject banner shell|class=C|1= | |||
| except that these sorts of argument have been made for two decades in mainstream politics. | |||
| {{WikiProject Economics |importance=mid}} | |||
| It is relevant because of the politics, not because of any ''genuine'' intimate connection between Nations and trickle-down. | |||
| {{WikiProject Conservatism |importance=mid}} | |||
| A genuine connection to Kurzets and Keynes is actually less problematic, but that's not how the politics fall. | |||
| {{WikiProject Politics |importance=mid |American=yes |American-importance=mid}} | |||
| * "lowest ranks of the people" is completely misrepresented. It has ''nothing'' to do with trickle-down. It is in the very next sentence that Smith writes about laborers - not rich people. And it is in this entire chapter that Smith writes about laborers dividing and combining their labor. There is absolutely ''no'' "trickling down". Regardless of the merits of trickle-down, chapter one is ''not'' about trickle down. Quite the contrary; Nations embraces a free market for ''everyone'' and as the lower classes are more numerous, and more motivated by the mother of invention than the liesure class, it is they who will account for the lion's share of a powerful and lively economy. This is not communism, as they are entitled to the fruits of their labor in proportion the quality and quantity of that labor - Smith was a strong advocate of such a meritocracy, and "well governed society" is a reference to that entitlement. Nor is it trickle-down; to abolish apprenticeships would increase the supply of tradesmen, lower prices and improve the economy - but at the unquestionable immediate expense of the '''''upper''''' classes. It is far more accurate to say that Nations is Trickle-up. Because the lower economic classes are more numerous, and because they are ''exactly'' those laborers/owners who will benefit the most from abolition of the collusion (fetters) of Smith's day, Nations is ''actually'' quite the counter-example to trickle-down. Further more, dividing supply side from demand side is anachronistic. To Smith, supply and demand two faces of the same coin. There will be an increase in laborers (supply) only if there is demand to motivate such. In fact, Smith is one of the most influencial authors to use and demonstrate the relativity of supply verses demand. Your supply is my demand, and visa versa. Money like all other things is a commodity, and if I want a lot of gold I can purchase it with my labor or other goods. | |||
| {{WikiProject United States |importance=mid |USGov=yes |USGov-importance=mid}} | |||
| {{WikiProject Taxation |importance=Mid}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{page views}} | |||
| {{User:ClueBot III/ArchiveThis | |||
| | age =2160 | |||
| | archiveprefix =Talk:Trickle-down economics/Archive | |||
| | numberstart =1 | |||
| | maxarchsize =75000 | |||
| | header ={{Automatic archive navigator}} | |||
| | minkeepthreads =5 | |||
| | format = %%i | |||
| }} | |||
| == |
== Citations for contested content == | ||
| The concept was also discussed by ]. For example, | |||
| Per above, i will use this section as a discussion of the contested lines above. ] (]) 14:32, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| :* . '''Does not support either claim.''' The article neither mentions any other study nor the laffer curve at all. Therefore, it does not directly support the contested claims. ] (]) 14:34, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| Capital can multiply itself only by exchanging itself for labor-power, by calling wage-labor into life. The labor-power of the wage-laborer can exchange itself for capital only by increasing capital, by strengthening that very power whose slave it is. Increase of capital, therefore, is increase of the proletariat, i.e., of the working class. | |||
| :*:Incorrect. It's not cited for the Laffer curve claim. But it does support the claim that, {{tq|Last week two British scholars released a study (PDF) concluding that trickle-down economics doesn’t work. Trickle-down theory says cutting taxes on rich people will encourage them to work and invest more, ultimately creating jobs and benefiting everyone. In reality, it increases inequality while not having “any significant effect on economic growth and unemployment,” wrote David Hope, a visiting fellow at the London School of Economics}} ''']'''<span style="border:2px solid #073642;background:rgb(255,156,0);background:linear-gradient(90deg, rgba(255,156,0,1) 0%, rgba(147,0,255,1) 45%, rgba(4,123,134,1) 87%);">]</span> 14:37, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| ::Sure, but that is not a line to which im objecting. ] (]) 14:41, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| :* . '''Does not support either claim.''' ] (]) 14:40, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| :*:I don't understand your point. It's not cited for the Laffer curve, and it supports the claim that studies have shown that trickle-down doesn't work. Your arguments are invalid. ''']'''<span style="border:2px solid #073642;background:rgb(255,156,0);background:linear-gradient(90deg, rgba(255,156,0,1) 0%, rgba(147,0,255,1) 45%, rgba(4,123,134,1) 87%);">]</span> 14:42, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| ::My point is that you need a citation for the claim that "As of 2023, a number of studies have shown that there is no obvious link between reducing tax burdens on the upper end and economic growth." You cant simply cite some studies and then draw broad conclusions not stated in the sources themselves for the same reason I could not say that "As of 2023, a number of studies have shown that there is positive relationship between reducing tax burdens on the upper end and economic growth." and then cite a bunch of studies. You can cite the studies, if relevant and consistent with the other rules of Misplaced Pages, but not to support the broad conclusion that I object to. ] (]) 14:49, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| :::Actually, no, it's a summary. We absolutely can if there's a consensus that this is an accurate summary, that due to the copious secondary sources interpreting that trickle-down is a myth, it's a myth and no study has shown any evidence of it. We can change the wording, but your argument is a bunch of bunk and unproductive and ]. ''']'''<span style="border:2px solid #073642;background:rgb(255,156,0);background:linear-gradient(90deg, rgba(255,156,0,1) 0%, rgba(147,0,255,1) 45%, rgba(4,123,134,1) 87%);">]</span> 14:50, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| :::Looking at the archive (2), I noticed another citation which was discussed that seems relevant to this discussion.<ref>{{Cite web |last=widworld_admin |date=2021-10-20 |title=The World #InequalityReport 2022 presents the most up-to-date & complete data on inequality worldwide: |url=https://wir2022.wid.world/chapter-10/ |access-date=2023-12-20 |website=World Inequality Report 2022 |language=fr-FR}}</ref> ] (]) 20:16, 20 December 2023 (UTC) | |||
| {{reflist-talk}} | |||
| == "Despite the lack of practical evidence of the Laffer curve"? Excuse me? == | |||
| And so, the bourgeoisie and its economists maintain that the interest of the capitalist and of the laborer is the same. And in fact, so they are! The worker perishes if capital does not keep him busy. Capital perishes if it does not exploit labor-power, which, in order to exploit, it must buy. The more quickly the capital destined for production -- the productive capital -- increases, the more prosperous industry is, the more the bourgeoisie enriches itself, the better business gets, so many more workers does the capitalist need, so much the dearer does the worker sell himself. The fastest possible growth of productive capital is, therefore, the indispensable condition for a tolerable life to the laborer. | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| '''I removed this section from the main article because I don't see the ''direct'' relevance'''. The only direct relevance of Marx is that anti-communist rhetoric is often used in advocacy of trickle-down. However, this is rhetoric, not reason. And this is actually relevant to the Soviet style of communism, not Marxism. | |||
| What about Estonia and Jamaica? What about New Hampshire? What about the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017? Taxes went down and revenue went up. ] (]) 02:52, 8 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| '''I originally added it to the text because it supports the economic thesis. When even your ideological enemies agree with you then you should give them a little room. Did Adam Smith vote for Ronald Reagan!!! Of course he did not. If there is no discuss on this within the next week I'll put the text back. TERJE 26-JUNE-2004. ''' | |||
| : You seem to think that short term changes prove a long-term point. Track changes over several business cycles and think again.] (]) 10:16, 8 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::The claim that there is some kind of 'lack of practical evidence of the Laffer Curve' is OR. The LC is a concept that can be found in any modern Econ textbook and we should defer to what those RS's say, not a few cherry picked newspaper articles. ] (]) 15:32, 8 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Didn't either of you bother to read ]? May you missed this in the lead? | |||
| :::{{blockquote|One implication of the Laffer curve is that increasing tax rates beyond a certain point is counter-productive for raising further tax revenue. Particularly in the United States, ] have used the Laffer curve to argue that lower taxes may increase tax revenue. However, the hypothetical maximum revenue point of the Laffer curve for any given market cannot be observed directly and can only be estimated—such estimates are often controversial. According to '']'', estimates of revenue-maximizing income tax rates have varied widely, with a mid-range of around 70%.<ref name="dictionaryofeconomics">{{cite book |doi=10.1057/9780230226203.0922 |chapter=Laffer curve |title=The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics |year=2008 |last1=Fullerton |first1=Don |editor1-first=Steven N. |editor1-last=Durlauf |editor2-first=Lawrence E. |editor2-last=Blume |edition=2nd |isbn=978-0-333-78676-5 |page=839 }}</ref>}} | |||
| :::That clear enough for you? --] (]) 17:07, 8 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Im not sure who the 'either of you' is supposed to be, but i would argue that the section you quoted supports my argument. High quality RS's dont make the kind of claims being made here about the LC. Most everything ive read from actual Econ reliable sources say that the LC is correct, but its not always possible to know where a tax is on the Laffer Curve. In other words, as a practical matter, lowering taxes might raise revenue, or it might lower it, but its difficult to know for sure beforehand. ] (]) 20:48, 8 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::If it has no testable predictive ability, it is essentially ]. Practical evidence for it would include predictive ability. Otherwise, saying "A tax increase may either raise or lower revenue" isn't really saying anything at all; of course it might do one of those two things. An actual predictive ability would be to say "Under X circumstances, tax increases are likely to lower revenues, and under circumstances opposite those it will likely raise them." Then that claim could be tested to see if it's actually borne out in practice. That principle of ] is critical to any theory. ] <small><sup>]</sup></small> 22:08, 8 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::Doesnt matter what you think of the Laffer Curve or it falsifiability, only what the best Reliable sources say. ] (]) 16:49, 11 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::''You'' are the one who stated that the best available sources state that it lacks predictive ability: {{tq|Most everything ive read from actual Econ reliable sources say that the LC is correct, but its not always possible to know where a tax is on the Laffer Curve}}. So, I was going by what you claim they say. ] <small><sup>]</sup></small> 16:55, 11 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::Except that the reliable sources i quoted did not say anything about pseudoscience or falsifiability, you did. ] (]) 17:00, 11 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| {{od}}Of course, just like if a source says someone "was killed", we can conclude that they are dead, without the source explicitly saying "dead". If what you're asking for is sources which explicitly state that a theory must be testable and falsifiable in order to have validity, I can certainly provide those. ] <small><sup>]</sup></small> 17:10, 11 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :If it is explicitly about the Laffer Curve or TDE, then sure, provide away. If its some inference that you think is relevant, then not so much so. ] (]) 17:26, 11 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Furthermore, the texts say (and the Laffer curve says) that the effect of a tax regime is imprecise, that nobody knows where the Goldilocks spot is. It the equivalent of the ]s debating how many angels could dance on the head of a pin: it is a thought experiment with no expectation of real-world application. But it is also superficially attractive answer beloved of populists of left and right. It is not deterministic but that doesn't make it pseudoscience. --] (]) 17:28, 11 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| === There was no context supplied with the quote, === and it seams to me that this very quote is a '''counter-argument''' to trickle-down. Are you saying Marx's position was that the capitalists (owners) weren't getting a fair deal. The idea of trickle-down is relief for the upper classes. This is the ''first'' time I have ''ever'' heard someone say Marx wasn't saying the opposite: that the working class wasn't getting a fair deal - that he was advocating relief for the ''lower'' classes. This article has a lot on politics, but is sorely lacking in facts and theories. For example, improvements have historically manifested in the upperclasses before manifesting in the lower classes. P.S. ''"When even your ideological enemies agree with you then..."'' implies that your point is a point of debate, not a point of theory or fact. So if you're going to reintroduce the work are you going to give it context? and if that context is as a point of debate, will you label it as such? I'm not saying don't put it in, just it should be relevant. And maybe you should spell it out - for those of us who don't yet see Marx as a proponent of the idea that the upper classes (owners) aren't getting a fair deal. | |||
| ::Is there something you would like to see changed in this article? If, so, can you specify what that is? ] (]) 14:44, 12 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| Just as evidence that a reliable source agrees: | |||
| I don't think the Marx quote makes any comment on who is getting what deal. It is first and formost an economic observation. Namely that an abundance of capital leads to a better wage deal for workers. As such it is a quote that supports the trickle down argument. Would you be happy for me to put the quote back in if I added some more context around it? '''TERJE 28-JUN-2004.''' | |||
| * {{cite news |title=Searching in vain for the Laffer curve boost |work=] |author=Chris Giles |date=14 March 2024 |url=https://www.ft.com/content/7c023708-76ad-4f8e-b8b1-e4f426f0483d | quote=Perhaps because Arthur Laffer is extraordinarily rightwing, the curve he drew on a napkin in 1974, suggesting lower tax rates increase revenues, has become a weapon of Conservative thinkers. This is far from ideal. If any government can find tax reductions that change behaviour sufficiently to raise receipts, everyone should be in favour. The problem is that genuine examples of the phenomenon are vanishingly rare.}} | |||
| "Chris Giles is the FT’s economics commentator. He writes a fortnightly column and the weekly newsletter, Chris Giles on Central Banks (sign up here). Previously, he was economics editor and served as a leader writer. | |||
| He is an Honorary Professor of Practice at the UCL Policy Lab. Before joining the FT, he worked for the BBC, Ofcom and the Institute for Fiscal Studies. Chris loves numbers." (https://www.ft.com/chris-giles) That good enough? --] (]) 21:27, 14 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Good enough for what? Are you hoping to include that quote? ] (]) 12:01, 15 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::No, just affirming that the article does not need to change, that the OP's challenge is baseless. ] (]) 17:59, 15 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::]'s views only appeal to a minority of economists. As explained in the main article on Laffer: | |||
| *"Numerous leading economists have rejected the view that a tax rate cut of current federal ] can lead to increased tax revenue. When asked in a 2012 ] survey whether a "cut in federal income tax rates in the US right now would raise taxable income enough so that the annual total tax revenue would be higher within five years than without the tax cut", none of the economists surveyed agreed and 71% disagreed.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Popp Berman |first1=Elizabeth |title=Trump is giving Arthur Laffer the Presidential Medal of Freedom. Economists aren't smiling |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2019/06/01/trump-is-giving-arthur-laffer-presidential-medal-freedom-economists-arent-laughing/ |newspaper=] |date=June 1, 2019 |access-date=July 7, 2021 |archive-date=February 6, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210206133554/https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2019/06/01/trump-is-giving-arthur-laffer-presidential-medal-freedom-economists-arent-laughing/ |url-status=live }}</ref> According to ], most economists have been very skeptical of Laffer's contention that decreases in tax rates could increase tax revenue, at least in the United States. In his textbook, Mankiw states, "there was little evidence for Laffer's view that U.S. tax rates had in fact reached such extreme levels."<ref name="mankiw">{{cite book | title=Principles of Economics | publisher=Cengage | author=Mankiw, Greg | author-link=Greg Mankiw | year=2014 | pages=164–165}}</ref> Under the direction of conservative economist ], the ] conducted a 2005 study on the fiscal effects of a 10% cut in federal income tax rates, finding that it resulted in a significant net revenue loss." ] (]) 12:08, 15 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::This is not an article on the Laffer curve. ] (]) 12:52, 15 March 2024 (UTC) | |||
| {{reflist talk}} | |||
| == Recent lead rewrite == | |||
| === Yes, I would be happy if you explained it. === | |||
| The idea that something can be good for everyone is not the question though. Trickle-down is very specific - that, ''by a process'' benefits to the upperclasses ''trickle-down'' to the lower classes. So if you could explain how Marx demonstrated ''trickling-down'', that would make the quote a ''much'' stronger addition to the article. This quote seems to be saying that the relationship between labor (lower classes) and capital (upper classes) is reciprical - that there is no argument leaning trickle-up, nor trickle-down. Until the last sentence; to improve the working condition of the ''working classes'' is the fastest (I presume best) way of stimulating the entire economy. That sounds like trickle-up in that the capital will be more productive and profitable ''after'' an improvement to the conditions of the working classes. That, by a process, benefit trickles up from the masses into the upper classes. So if you could explain how this quote translates into the idea that incentives for the wealthy, by a process, trickle down to the masses, that would be great. Also, where is this quote from? | |||
| The lead was recently rewritten in series of edits to say that "trickle-down economics" is another term for "supply-side economics", a statement that obviously contradicts the body and numerous sources describing its usage as something that predates supply-side economics entirely. When I reverted it, it was reverted back in with the statement that it had been discussed; however, I can see no such discussion (nor can I imagine that such a ] rewrite would have withstood any serious scrutiny, because, again, it directly contradicts the body of the article and most high-quality sources, relying entirely on lower-quality news sources.) As far as I can tell, the rewrite had no discussion at all. In fact, the only discussion around the time of the rewrite focused solely on the Laffer curve. The proposed rewrite to the lead contradicts most sources, severely damaged the quality of the lead, and fails to accurately summarize the entire article or the relevant sources per ]. --] (]) 17:26, 5 April 2024 (UTC) | |||
| Many major economists have said that to improve the lowest ranks of the economy is the best and fastest way to improve the economy as a whole; that to benefit the economy is to benefit everyone. For example Smith in Nations said that apprenticeships were a drag on the economy; that labor would be more motivated to enter a trade and to work hard and often if only they were free to do so and paid in direct reward for the quality and quantity of their labor. Keynes is credited with "demand-side" economics, that more money in the pockets of the masses will stimulate capitalist growth in the economy as a whole. And here, in this quote by Marx, Marx advises us to improve the working condition of the laborer. But this is all trickle-up. What is the theoretical body of trickle-down? Who has said it? and what is the merits of this theory? | |||
| :The core problem i have with your rewrite is that it does not clearly state that TDE is a pejorative and not used by economists. I agree that the term predates Supply side econ and so the lead should reflect that. I think your edits are superior to what we had, but, again, i think we need to emphasize what the sources actually say, that TDE isnt an economic term and never has been. Ill revert my reversion and offer some tweaks to address my concerns. Thanks ] (]) 16:06, 8 April 2024 (UTC) | |||
|   - For example, the quote of Smith; who said this is an advocation of trickle-down? did Reagan say it? and if so, when and where? | |||
| ::Will fix. That one word should certainly be in the lead on this and the majority of editors on this section here seem to agree. ] (]) 23:59, 14 November 2024 (UTC) | |||
| As I said 18 months ago, "Did someone forget that “trickle down” is a journalistic expression, and as such, entirely appropriate in a Guardian article? Please stop debating “trickle down” as if it were some kind of economic theory; it isn’t." ] (]) 16:33, 8 April 2024 (UTC) | |||
| P.S. Kuznets was added back in by someone with the addition of that which made Kuznets relevant to this article - improvements have hit the upper classes before the lower classes. | |||
| :I agree. I have no problem with the lede rewrite, save that it does not spell this out, and, frankly, the last line is doing exactly what ] is saying. Which is, acting as if some study or whatever 'disproves' something that isnt an economic theory in the first place. ] (]) 15:38, 9 April 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == US politics in the New Zealand section == | |||
| == Horse and Sparrow Economics == I removed this from the article | |||
| :] has summarized trickle-down theory as economics: "if you feed enough oats to the horse, some will pass through to feed the sparrows." | |||
| Why are the 2016 candidates Trump and Clinton mentioned in the New Zealand section?? That should be in the U.S section instead. ] (]) 16:28, 11 August 2024 (UTC) | |||
| I think it is humerous and has a point, but I don't think its encyclopedic - at least, not in ''this'' article. I have put a link to ] because it is relevant to trickle-down, just not ''central''. P.S. a web search for "Horse and Sparrow" finds a lot of articles on trickle-down. | |||
| == Bit of History? == | |||
| === inappropriately credited to Galbraith? === | |||
| In my coastal town of 100 thousand people we had naval bases and a boatmaker and a sailmaker and schools and solicitors and pubs, tattoo artists, shops, government departments, national and local, light engineering works etc, etc. | |||
| The link you see above links to someone else's writing; while Galbraith is quoted in it, and I'll presume that Galbraith really did make the analogy, I think there is a better source of that information than the link above. I'm going to remove the link in the article. | |||
| External Income was from taxes, yachtsmen, outside shoppers, customers of the engineering companies (e.g. Rolls Royce Aerospace) etc. | |||
| If you disagree, please tell me why and go ahead and readd the link to the article. | |||
| The sailmakers and sailors and solicitors and teachers etc bought food and clothes and beer from the relevant places. The barmen too. The butchers shopped at the greengrocers', the greengrocers shopped at the butchers' and so on. | |||
| Eventually all the money in town diffused out in this manner and reached equilibrium and in theory you could calculate how much there was and how much of it went where and what everyone ended up with. | |||
| == NPOV == | |||
| This was explained to me as trickle down theory in school in the early 1970s. | |||
| I think supadawg pruned a little too much. It now seems less balanced, and less NPOV than before. The points made to refute Adam Smith's endorsement are basically correct, and to compleatly remove them instead of improving them seem counter-productive to NPOV. | |||
| Then someone 30-odd years ago defined it as "if we give as much money as possible to rich people, we'll all end up benefitting" | |||
| Therefore I added these points back in, and I will make efforts to clean them up and improve them. | |||
| That's not even a theory, it's just an assertion. ] (]) 15:21, 3 October 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :From your description, the person explaining it in this way did not understand the trickle-down concept. What you have described is closer in theory to a closed economy. ] (]) 20:14, 3 October 2024 (UTC) | |||
| I think a better approach to improving NPOV of this article is to clean up and improve the position of both sides. | |||
| I did leave out the section "criticisms of the reaganite pitch". This part seemed redundant and less well written. I invite people to look at the history and read that part and add it back and clean it up. It is not entirely without merit. | |||
| Is the blockquote in the middle the source of NPOV problems? Who is this attributed to? Can someone point to or reproduce David Stockman's speach? | |||
| == Kuznets' Law == | |||
| Is this really relevant to trickle down economics. Is it accurate to imply that he is anti-Keynes? | |||
| I removed this from the article: | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| Other variants include ]' "Law", which says that increases in income inequality that occur in the early stages of ] are followed by increases in income equality. Ironically, this is close to some of ]'s theories. A more general version argues that increases in ] are almost always good for the poor. | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| I doubt that Kuznets is directly relevant to trickle down theory and I doubt the characterizations here. Marx? A far more common characterization of Kuznets is that his work helped the "Keynesian Revolution". Yet, trickle down and supply side are anti-Keynes. A more appropriate place to mention Kuznets may be in the article on ]. Also, I think the wikipedia article on Kuznets is more 'encyclopedic'. | |||
| === . . more kuznets' law === there is now relevant content form kuznets in the article: improvements occur first in the upper classes, then in the lower classes. | |||
| However, the history of kuznets in this article is a good illustration of a lack of differentiation; Kuznets has been repeatedly used as an argument for trickle-down. However, | |||
| * '''Incentive to Invest:''' Supply side Economics is billed by advocates as a means of increasing investment. However, it is not the ''only'' means, nor the most direct or effective means of increasing investment and to equate ''supply side'' with ''inducement to invest'' is erroneous and unencyclopedic. Supply side is a subset of inducement to invest - if it is such an inducement. | |||
| ** in fact, while many economic indicators improved during the reagan era, savings and investment by wealthy individuals and businesses did not significantly increase. They pocketed the money. Therefore - ironically - if these tax cuts ''were'' the cause of improvement in the economy, then it was the result of increased "aggregate demand" - straight out of ]' ]. That is, the economic effect was the same as in Roosevelt's programs; more money in consumer's pockets translates into increased demand - which is a market regulated incentive to invest for producers. | |||
| ** '''Other Incentives:''' state initiated incentives to investment are far more successful if they ''directly'' impact investment. For example, tax breaks on the interests of home loans increases demand for homes and for loans - for investment. | |||
| P.S. Tell me how the average joe was induced to invest by Reaganomics. If you can do that you can ''validly'' cite Adam Smith as an advocate of trickle-down. | |||
| == From the Ministry of Truth == | |||
| This is an interesting sentence, and I've seen similar sentiments for two decades: | |||
| <blockquote>To Smith, the "well-governed society" is one in which free markets replace state command as the main method of resource allocation. Smith's argument is that increased division of labor (specialization) raises labor productivity. This in turn leads to lower costs, which are passed on to consumers in the form of lower prices (correcting for inflation). | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| This blockquote may seem uninformed, but I believe its inacuracies are intentional and politically motivated. | |||
| * '''"replaces state command"''' - ] was written before ]. Using the term "The state" instead of ''Nobility'' or ''Aristrocracy'' comes off as awkwardly anachronistic. "state command" is the language normally and appropriately used in describing controlled economies - communism. The rhetoric of the McCarthy Era. A more accurate portrait of ''Nations'' is that Smith made a solid case against corruption - as imbodied by feudal corporations, apprenticeships, monopolies, tarrifs, exclusive rights etcetera. For example, the nobility favored apprenticeships because the nobility was being paid royalties. The commerce that Smith witnessed and wrote about was a market economy, the complaint he made was that it was corrupted by special interest. Nobility (the state) - ''which was feudalistic, not communist'' - had their fingers in it along with many players outside of nobility and royalty. Any such arrangements in modern day U.S. would be illegal, and scandalous. As for "state command of resource allocation": Eisenhauer's Highway program was a state project which improved the transportation network of the United States, very much in accord with ''Nations'', Chapter III, "the division of labor is limited by the extent of the market", wherein Smith explains how water carriage (boats) extend the market and therefore support improved productivity and dexterity of the labor force. Smith made one exception to controls / incentives in the economy: incentives to the military. And the phrase "tolerable degree of security" is frequent in the work. The U.S. military is quite impressive and it is state controlled. Further, Reagan increased military spending. On the other hand Eisenhauer warned of the 'military-industrial complex'. | |||
| * '''"well-governed society"''' - this, and "a tolerable degree of security" are qualifications. They are not central to his themes. For example, the free market economy he describes is wonderful ''assuming'' goods aren't stolen in transport. | |||
| * '''"correcting inflation"''' - costs were unnaturally high, ''not'' costs unnaturally rose. Whether or not inflation was a problem on top of an unfair market is a completely separate issue. Stagflation was a political hot button when supply-side economics came about, and to tack on 'inflation' to Smith's work for political points is manipulative - ''as is citing Smith in the first place.'' Quite the contrary to this orwellian interpretation, free markets often overheat and are characterized by rapid growth, heavy borrowing and inflation. In fact the Fed is currently keeping its eye on inflation due to very attractive interest rates. | |||
| == More from the Ministry of Truth == I pasted the following sentence from the article. It follows a line of reasoning that Smith advocated Supply-Side Economics. | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| A major variant of trickle-down theory would say that tax cuts for the rich, special benefits for them, subsidies for corporations, and in general, government/business cooperation would not simply provide direct benefits to business but would also help the middle classes and even the poor. In effect, it says that "what's good for business is good for the country." | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| Read the book! Incentives like these are ''EXACTLY'' what smith was critical of. It's the major theme of ''Nations''. If an incentive benefits one group of producers over another, it's not a free market, and that's exactly what Smith's postion is. | |||
Latest revision as of 23:59, 14 November 2024
| Skip to table of contents |
| This is the talk page for discussing improvements to the Trickle-down economics article. This is not a forum for general discussion of the article's subject. |
|
| Find sources: Google (books · news · scholar · free images · WP refs) · FENS · JSTOR · TWL |
| Archives: Index, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5Auto-archiving period: 3 months |
| This article is rated C-class on Misplaced Pages's content assessment scale. It is of interest to the following WikiProjects: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Citations for contested content
Per above, i will use this section as a discussion of the contested lines above. Bonewah (talk) 14:32, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- archive copy of bloomberg article. Does not support either claim. The article neither mentions any other study nor the laffer curve at all. Therefore, it does not directly support the contested claims. Bonewah (talk) 14:34, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- Incorrect. It's not cited for the Laffer curve claim. But it does support the claim that,
Last week two British scholars released a study (PDF) concluding that trickle-down economics doesn’t work. Trickle-down theory says cutting taxes on rich people will encourage them to work and invest more, ultimately creating jobs and benefiting everyone. In reality, it increases inequality while not having “any significant effect on economic growth and unemployment,” wrote David Hope, a visiting fellow at the London School of Economics
Andre🚐 14:37, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- Incorrect. It's not cited for the Laffer curve claim. But it does support the claim that,
- Sure, but that is not a line to which im objecting. Bonewah (talk) 14:41, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- CBS new article covering the same study as bloomberg article above. Does not support either claim. Bonewah (talk) 14:40, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- I don't understand your point. It's not cited for the Laffer curve, and it supports the claim that studies have shown that trickle-down doesn't work. Your arguments are invalid. Andre🚐 14:42, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- My point is that you need a citation for the claim that "As of 2023, a number of studies have shown that there is no obvious link between reducing tax burdens on the upper end and economic growth." You cant simply cite some studies and then draw broad conclusions not stated in the sources themselves for the same reason I could not say that "As of 2023, a number of studies have shown that there is positive relationship between reducing tax burdens on the upper end and economic growth." and then cite a bunch of studies. You can cite the studies, if relevant and consistent with the other rules of Misplaced Pages, but not to support the broad conclusion that I object to. Bonewah (talk) 14:49, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- Actually, no, it's a summary. We absolutely can if there's a consensus that this is an accurate summary, that due to the copious secondary sources interpreting that trickle-down is a myth, it's a myth and no study has shown any evidence of it. We can change the wording, but your argument is a bunch of bunk and unproductive and WP:1AM. Andre🚐 14:50, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- Looking at the archive (2), I noticed another citation which was discussed that seems relevant to this discussion. DN (talk) 20:16, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
- archive copy of bloomberg article. Does not support either claim. The article neither mentions any other study nor the laffer curve at all. Therefore, it does not directly support the contested claims. Bonewah (talk) 14:34, 20 December 2023 (UTC)
References
- widworld_admin (2021-10-20). "The World #InequalityReport 2022 presents the most up-to-date & complete data on inequality worldwide:". World Inequality Report 2022 (in French). Retrieved 2023-12-20.
"Despite the lack of practical evidence of the Laffer curve"? Excuse me?
What about Estonia and Jamaica? What about New Hampshire? What about the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017? Taxes went down and revenue went up. 181.194.252.59 (talk) 02:52, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- You seem to think that short term changes prove a long-term point. Track changes over several business cycles and think again.DOR (ex-HK) (talk) 10:16, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- The claim that there is some kind of 'lack of practical evidence of the Laffer Curve' is OR. The LC is a concept that can be found in any modern Econ textbook and we should defer to what those RS's say, not a few cherry picked newspaper articles. Bonewah (talk) 15:32, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- Didn't either of you bother to read Laffer curve? May you missed this in the lead?
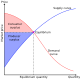
One implication of the Laffer curve is that increasing tax rates beyond a certain point is counter-productive for raising further tax revenue. Particularly in the United States, conservatives have used the Laffer curve to argue that lower taxes may increase tax revenue. However, the hypothetical maximum revenue point of the Laffer curve for any given market cannot be observed directly and can only be estimated—such estimates are often controversial. According to The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, estimates of revenue-maximizing income tax rates have varied widely, with a mid-range of around 70%.
- That clear enough for you? --𝕁𝕄𝔽 (talk) 17:07, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- Im not sure who the 'either of you' is supposed to be, but i would argue that the section you quoted supports my argument. High quality RS's dont make the kind of claims being made here about the LC. Most everything ive read from actual Econ reliable sources say that the LC is correct, but its not always possible to know where a tax is on the Laffer Curve. In other words, as a practical matter, lowering taxes might raise revenue, or it might lower it, but its difficult to know for sure beforehand. Bonewah (talk) 20:48, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- If it has no testable predictive ability, it is essentially pseudoscience. Practical evidence for it would include predictive ability. Otherwise, saying "A tax increase may either raise or lower revenue" isn't really saying anything at all; of course it might do one of those two things. An actual predictive ability would be to say "Under X circumstances, tax increases are likely to lower revenues, and under circumstances opposite those it will likely raise them." Then that claim could be tested to see if it's actually borne out in practice. That principle of falsifiability is critical to any theory. Seraphimblade 22:08, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- Doesnt matter what you think of the Laffer Curve or it falsifiability, only what the best Reliable sources say. Bonewah (talk) 16:49, 11 March 2024 (UTC)
- You are the one who stated that the best available sources state that it lacks predictive ability:
Most everything ive read from actual Econ reliable sources say that the LC is correct, but its not always possible to know where a tax is on the Laffer Curve
. So, I was going by what you claim they say. Seraphimblade 16:55, 11 March 2024 (UTC)- Except that the reliable sources i quoted did not say anything about pseudoscience or falsifiability, you did. Bonewah (talk) 17:00, 11 March 2024 (UTC)
- You are the one who stated that the best available sources state that it lacks predictive ability:
- Doesnt matter what you think of the Laffer Curve or it falsifiability, only what the best Reliable sources say. Bonewah (talk) 16:49, 11 March 2024 (UTC)
- If it has no testable predictive ability, it is essentially pseudoscience. Practical evidence for it would include predictive ability. Otherwise, saying "A tax increase may either raise or lower revenue" isn't really saying anything at all; of course it might do one of those two things. An actual predictive ability would be to say "Under X circumstances, tax increases are likely to lower revenues, and under circumstances opposite those it will likely raise them." Then that claim could be tested to see if it's actually borne out in practice. That principle of falsifiability is critical to any theory. Seraphimblade 22:08, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- Im not sure who the 'either of you' is supposed to be, but i would argue that the section you quoted supports my argument. High quality RS's dont make the kind of claims being made here about the LC. Most everything ive read from actual Econ reliable sources say that the LC is correct, but its not always possible to know where a tax is on the Laffer Curve. In other words, as a practical matter, lowering taxes might raise revenue, or it might lower it, but its difficult to know for sure beforehand. Bonewah (talk) 20:48, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
- The claim that there is some kind of 'lack of practical evidence of the Laffer Curve' is OR. The LC is a concept that can be found in any modern Econ textbook and we should defer to what those RS's say, not a few cherry picked newspaper articles. Bonewah (talk) 15:32, 8 March 2024 (UTC)
Of course, just like if a source says someone "was killed", we can conclude that they are dead, without the source explicitly saying "dead". If what you're asking for is sources which explicitly state that a theory must be testable and falsifiable in order to have validity, I can certainly provide those. Seraphimblade 17:10, 11 March 2024 (UTC)
- If it is explicitly about the Laffer Curve or TDE, then sure, provide away. If its some inference that you think is relevant, then not so much so. Bonewah (talk) 17:26, 11 March 2024 (UTC)
- Furthermore, the texts say (and the Laffer curve says) that the effect of a tax regime is imprecise, that nobody knows where the Goldilocks spot is. It the equivalent of the medieval scholastics debating how many angels could dance on the head of a pin: it is a thought experiment with no expectation of real-world application. But it is also superficially attractive answer beloved of populists of left and right. It is not deterministic but that doesn't make it pseudoscience. --𝕁𝕄𝔽 (talk) 17:28, 11 March 2024 (UTC)
- Is there something you would like to see changed in this article? If, so, can you specify what that is? Bonewah (talk) 14:44, 12 March 2024 (UTC)
Just as evidence that a reliable source agrees:
- Chris Giles (14 March 2024). "Searching in vain for the Laffer curve boost". Financial Times.
Perhaps because Arthur Laffer is extraordinarily rightwing, the curve he drew on a napkin in 1974, suggesting lower tax rates increase revenues, has become a weapon of Conservative thinkers. This is far from ideal. If any government can find tax reductions that change behaviour sufficiently to raise receipts, everyone should be in favour. The problem is that genuine examples of the phenomenon are vanishingly rare.
"Chris Giles is the FT’s economics commentator. He writes a fortnightly column and the weekly newsletter, Chris Giles on Central Banks (sign up here). Previously, he was economics editor and served as a leader writer. He is an Honorary Professor of Practice at the UCL Policy Lab. Before joining the FT, he worked for the BBC, Ofcom and the Institute for Fiscal Studies. Chris loves numbers." (https://www.ft.com/chris-giles) That good enough? --𝕁𝕄𝔽 (talk) 21:27, 14 March 2024 (UTC)
- Good enough for what? Are you hoping to include that quote? Bonewah (talk) 12:01, 15 March 2024 (UTC)
- No, just affirming that the article does not need to change, that the OP's challenge is baseless. 𝕁𝕄𝔽 (talk) 17:59, 15 March 2024 (UTC)
- Arthur Laffer's views only appeal to a minority of economists. As explained in the main article on Laffer:
- "Numerous leading economists have rejected the view that a tax rate cut of current federal U.S. income taxes can lead to increased tax revenue. When asked in a 2012 University of Chicago business school survey whether a "cut in federal income tax rates in the US right now would raise taxable income enough so that the annual total tax revenue would be higher within five years than without the tax cut", none of the economists surveyed agreed and 71% disagreed. According to Greg Mankiw, most economists have been very skeptical of Laffer's contention that decreases in tax rates could increase tax revenue, at least in the United States. In his textbook, Mankiw states, "there was little evidence for Laffer's view that U.S. tax rates had in fact reached such extreme levels." Under the direction of conservative economist Douglas Holtz-Eakin, the Congressional Budget Office conducted a 2005 study on the fiscal effects of a 10% cut in federal income tax rates, finding that it resulted in a significant net revenue loss." Dimadick (talk) 12:08, 15 March 2024 (UTC)
- This is not an article on the Laffer curve. Bonewah (talk) 12:52, 15 March 2024 (UTC)
References
- Fullerton, Don (2008). "Laffer curve". In Durlauf, Steven N.; Blume, Lawrence E. (eds.). The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics (2nd ed.). p. 839. doi:10.1057/9780230226203.0922. ISBN 978-0-333-78676-5.
- Popp Berman, Elizabeth (June 1, 2019). "Trump is giving Arthur Laffer the Presidential Medal of Freedom. Economists aren't smiling". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on February 6, 2021. Retrieved July 7, 2021.
- Mankiw, Greg (2014). Principles of Economics. Cengage. pp. 164–165.
Recent lead rewrite
The lead was recently rewritten in this series of edits to say that "trickle-down economics" is another term for "supply-side economics", a statement that obviously contradicts the body and numerous sources describing its usage as something that predates supply-side economics entirely. When I reverted it, it was reverted back in with the statement that it had been discussed; however, I can see no such discussion (nor can I imagine that such a WP:BOLD rewrite would have withstood any serious scrutiny, because, again, it directly contradicts the body of the article and most high-quality sources, relying entirely on lower-quality news sources.) As far as I can tell, the rewrite had no discussion at all. In fact, the only discussion around the time of the rewrite focused solely on the Laffer curve. The proposed rewrite to the lead contradicts most sources, severely damaged the quality of the lead, and fails to accurately summarize the entire article or the relevant sources per WP:LEAD. --Aquillion (talk) 17:26, 5 April 2024 (UTC)
- The core problem i have with your rewrite is that it does not clearly state that TDE is a pejorative and not used by economists. I agree that the term predates Supply side econ and so the lead should reflect that. I think your edits are superior to what we had, but, again, i think we need to emphasize what the sources actually say, that TDE isnt an economic term and never has been. Ill revert my reversion and offer some tweaks to address my concerns. Thanks Bonewah (talk) 16:06, 8 April 2024 (UTC)
- Will fix. That one word should certainly be in the lead on this and the majority of editors on this section here seem to agree. Iljhgtn (talk) 23:59, 14 November 2024 (UTC)
As I said 18 months ago, "Did someone forget that “trickle down” is a journalistic expression, and as such, entirely appropriate in a Guardian article? Please stop debating “trickle down” as if it were some kind of economic theory; it isn’t." DOR (ex-HK) (talk) 16:33, 8 April 2024 (UTC)
- I agree. I have no problem with the lede rewrite, save that it does not spell this out, and, frankly, the last line is doing exactly what DOR (ex-HK) is saying. Which is, acting as if some study or whatever 'disproves' something that isnt an economic theory in the first place. Bonewah (talk) 15:38, 9 April 2024 (UTC)
US politics in the New Zealand section
Why are the 2016 candidates Trump and Clinton mentioned in the New Zealand section?? That should be in the U.S section instead. UniFanNumOne (talk) 16:28, 11 August 2024 (UTC)
Bit of History?
In my coastal town of 100 thousand people we had naval bases and a boatmaker and a sailmaker and schools and solicitors and pubs, tattoo artists, shops, government departments, national and local, light engineering works etc, etc. External Income was from taxes, yachtsmen, outside shoppers, customers of the engineering companies (e.g. Rolls Royce Aerospace) etc. The sailmakers and sailors and solicitors and teachers etc bought food and clothes and beer from the relevant places. The barmen too. The butchers shopped at the greengrocers', the greengrocers shopped at the butchers' and so on. Eventually all the money in town diffused out in this manner and reached equilibrium and in theory you could calculate how much there was and how much of it went where and what everyone ended up with. This was explained to me as trickle down theory in school in the early 1970s. Then someone 30-odd years ago defined it as "if we give as much money as possible to rich people, we'll all end up benefitting" That's not even a theory, it's just an assertion. FangoFuficius (talk) 15:21, 3 October 2024 (UTC)
- From your description, the person explaining it in this way did not understand the trickle-down concept. What you have described is closer in theory to a closed economy. DOR (ex-HK) (talk) 20:14, 3 October 2024 (UTC)
- C-Class Economics articles
- Mid-importance Economics articles
- WikiProject Economics articles
- C-Class Conservatism articles
- Mid-importance Conservatism articles
- WikiProject Conservatism articles
- C-Class politics articles
- Mid-importance politics articles
- C-Class American politics articles
- Mid-importance American politics articles
- American politics task force articles
- WikiProject Politics articles
- C-Class United States articles
- Mid-importance United States articles
- C-Class United States articles of Mid-importance
- C-Class United States Government articles
- Mid-importance United States Government articles
- WikiProject United States Government articles
- WikiProject United States articles