| Revision as of 06:34, 18 February 2015 editGimliDotNet (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers14,019 editsm Reverted edits by GimliDotNet (talk) to last version by 65.126.152.254← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:43, 2 December 2024 edit undoAadirulez8 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users43,495 editsm v2.05 - auto / Fix errors for CW project (Link equal to linktext)Tag: WPCleaner | ||
| (41 intermediate revisions by 31 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{refimprove|date=December 2021}} | |||
| {{Infobox video game | {{Infobox video game | ||
| | title = |
| title = GemStone IV | ||
| | image = ] | | image = ] | ||
| | developer = ] | | developer = ] | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
| | platforms = ], ] | | platforms = ], ] | ||
| | released = 1988 | | released = 1988 | ||
| | genre = Fantasy ] | | genre = Fantasy ] | ||
| | modes = ] | | modes = ] | ||
| | media = ] | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''''GemStone IV''''' is a multiplayer text-based online ] (often known as a ]) produced by ]. |
'''''GemStone IV''''' is a multiplayer text-based online ] (often known as a ]) produced by ]. Players control characters in a ] game world named "Elanthia".{{R|olivetti}} The first playable version of the game was known as ''GemStone ]].{{R|bartle2}} It was one of the first ]s and is one of the longest running ] games still active.{{R|dunin}} Access to the game is subscription-based (monthly fee) through its website, with three additional subscriptions levels available, "Premium", "Platinum" and "Shattered", in addition to a free-to-play model introduced in early March 2015. | ||
| ==Technical |
==Technical information== | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone IV'' is a text-based game built on Simutronics' proprietary engine, the IFE (Interactive Fiction Engine). This engine is capable of changing nearly any aspect of the game ] which allows updates without the necessity for ]. Due to the use of the IFE, ''GemStone'' is rarely taken offline, giving a 24-hour uptime cycle aside from the occasional game ]. | ||
| ⚫ | The ''GemStone'' interface is simply a text stream, and the game can be played with a ] interface after authentication. There are several official interfaces to the game, as well as several unofficial ones. The oldest interface for ] is called the "Wizard Front End" and offers several useful features such as status readouts, macros, and limited scripting abilities. The Wizard has since been superseded with the "StormFront" Front End introduced in 2003, which itself has been rebranded as "Wrayth" in 2022. Wrayth offers several additional extensions to the game, including a "point and click" interface that allows one to click on text within the game and bring up action menus applicable to that portion of text. The Java FE and a browser-based version named "eScape" are less popular alternatives. A Wizard (similar to the Windows version) also exists for ], while a Front End named "Avalon" is available for ]. No official ] client exists. | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone IV'' is a text-based game built on Simutronics' proprietary engine, the IFE (Interactive Fiction Engine). |
||
| ⚫ | The ''GemStone'' interface is simply a text stream, and the game can be played with a ] interface after authentication. |
||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone'' was first demonstrated to GEnie in 1987 before Simutronics was officially incorporated. It was only used as a demonstration model and was never available to the general subscribers. ''GemStone ][" to "III" maintained significant portions of the environment, but not all, and character records were not maintained over the transition, requiring all players to begin anew. ''GemStone III'' evolved into ''GemStone IV'' in November 2003, but the game world and character records were maintained over the transition. ''GemStone III'' was promoted on GEnie by promising players the opportunity to receive real-life versions of gems found in-game, something that persisted for many years. | ||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone'' originally operated with a license to use the Rolemaster game mechanics and ] environment from ] (ICE). In 1995, Simutronics and ICE agreed to let the business relationship expire, necessitating the removal of all ICE intellectual property from ''GemStone''. Many of the game changes were simply renaming ICE names, such as changing the world name from ] to Elanthia, and renaming the deities while keeping their previous characteristics. | ||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone'' was first demonstrated to GEnie in 1987 before Simutronics was officially incorporated. |
||
| ⚫ | Game mechanics were greatly changed with the de-ICEing (as the period is colloquially named), which required every game character to undergo significant changes. Character racial and class choices were also changed, making any direct translation between the two systems difficult. The end result was that every character was required to "re-roll" their character with the option to change race and skills, but maintaining their old experience level, class, and equipment. | ||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone'' originally operated with a license to use the Rolemaster game mechanics and ] environment from ] (ICE). |
||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone'' became available on ]{{R|bartle3}} in September, 1995, just after the de-ICEing process. It had already become available on ] and ] before that. When AOL switched to flat-rate pricing, ''GemStone'' did over 1.4 million customer-hours in a single month{{R|netpreneur}} and was attracting 2,000-2,500 simultaneous players.{{R|bartle4}} Simutronics launched a web portal in 1997, and started phasing customers off of the online services and onto the web interface, although it would take several years before the last of the online service portals were closed. | ||
| ⚫ | Game mechanics were greatly changed with the de-ICEing (as the period is colloquially named), which required every game character to undergo significant changes. |
||
| ⚫ | ''GemStone'' became available on ]{{R|bartle3}} in September, 1995, just after the de-ICEing process. |
||
| ==Reception== | ==Reception== | ||
| '']'' in 1991 stated that ''Gemstone III'' was a good example of the best and worst aspects of online play. The reviewer liked the game's community aspect and well-written prose, but criticized the poor parser, "surprisingly empty" game environment and—given the per-minute charge—lack of a free tutorial, and concluded that "the present incarnation of on-line games doesn't quite work for him".<ref name="wilson199102">{{cite |
'']'' in 1991 stated that ''Gemstone III'' was a good example of the best and worst aspects of online play. The reviewer liked the game's community aspect and well-written prose, but criticized the poor parser, "surprisingly empty" game environment and—given the per-minute charge—lack of a free tutorial, and concluded that "the present incarnation of on-line games doesn't quite work for him".<ref name="wilson199102">{{cite magazine | url=http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1991&pub=2&id=79 | title=On-Line Gaming Viewed by a Skeptic / Gemstone III, for Example | magazine=Computer Gaming World | date=February 1991 | accessdate=17 November 2013 | author=Wilson, Johnny L. | pages=53 | issue=79}}</ref> In a follow-up 1993 review, the reviewer wrote that his sojourn in Kulthea was a rewarding experience. He reported receiving help from both built-in commands and other characters and the ability and opportunity for his bard character to sing. The reviewer concluded that "at last, I know why" the game was so popular.<ref name="wilson199301">{{cite magazine | url=http://www.cgwmuseum.org/galleries/index.php?year=1993&pub=2&id=102 | title=Genie's GemStone III | magazine=Computer Gaming World | date=January 1993 | accessdate=5 July 2014 | author=Wilson, Johnny L. | pages=124}}</ref> In 1997 '']'' named it as number seven on their "Top 10 Online Game Picks".<ref>{{cite magazine |title=Next Generation's Top 10 Online Game Picks |magazine=]|issue=27|publisher=] |date=March 1997|page=42}}</ref> At its peak (1996), ''GemStone III'' had over 2,000 simultaneous users and 1 million play hours per month, large numbers for its era.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Landau |first1=Elizabeth |title=I Had My First Kiss in GemStone III |url=https://gizmodo.com/i-had-my-first-kiss-in-gemstone-iii-1845229020 |website=Gizmodo |date=30 September 2020 |language=en-us}}</ref> | ||
| In 2020 and 2021, ''GemStone III'' inspired retrospectives by ] in ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Ep. 20: Text Adventure Gemstone III with Liz Landau |url=https://gamehistory.org/ep-20-text-adventure-gemstone-iii-with-liz-landau/ |website=Video Game History Foundation |date=24 February 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite magazine|url=https://www.wired.com/story/multiplayer-text-games-mud-mmo-social-media/|author=Landau, Liz|date=January 14, 2021|magazine=]|title=How old-school text adventures inspired our virtual spaces}}</ref> She noted its ability to facilitate human communication and its similar nature to later ]s and ]. | |||
| ⚫ | * 1998 Finalist, Online Game of the Year, Academy of Interactive Arts and Sciences{{R|aias}} | ||
| ⚫ | * ] Finalist, "]", ]{{R|aias}} | ||
| * December 1996, AOL Members' Choice Award{{R|aolchoice}} | * December 1996, AOL Members' Choice Award{{R|aolchoice}} | ||
| ==GemStone IV - Shattered== | ==''GemStone IV - Shattered''== | ||
| ⚫ | In May 2010, ''GemStone IV - Shattered'' was released by Simutronics. It allows unrestricted player-vs-player combat and has no policy against automated play. | ||
| ⚫ | In May 2010, ''GemStone IV - Shattered'' was released by Simutronics. |
||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|colwidth=40em|refs= | {{Reflist|colwidth=40em|refs= | ||
| <ref name="aolchoice"></ref> | <ref name="aolchoice"> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070928042615/http://www.washingtontechnology.com/print/12_23/13829-1.html |date=2007-09-28}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name="dunin"> Interview: Elonka Dunin</ref> | <ref name="dunin"> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927213317/http://www.gignews.com/goddess/dunin.htm |date=September 27, 2007}} Interview: Elonka Dunin</ref> | ||
| <ref name="washtech"></ref> | <ref name="washtech"> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070928042615/http://www.washingtontechnology.com/print/12_23/13829-1.html |date=2007-09-28}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name="netpreneur"></ref> | <ref name="netpreneur"></ref> | ||
| <ref name="aias"></ref> | <ref name="aias">{{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name="bartle1">{{cite web | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | url = http://mud.co.uk/dvw/errata.html | title = Designing Virtual Worlds, Errata | date = 2003-07-17 | quote = The second version was "GemStone ][" (rather than "Gemstone II"); Roman numerals were used for the third and fourth versions.}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="bartle1">{{cite web | |||
| ⚫ | <ref name="bartle2">{{cite book | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | title = ] | publisher = New Riders | year = 2003 | isbn = 0-13-101816-7 | pages = 14 | quote = GEnie was the launch point for many classic online games, including two very important virtual worlds: ''Gemstone II'' in 1988 and ''Dragon's Gate'' in 1990.}}</ref> | ||
| | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | |||
| <ref name="bartle3">{{cite book | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | title = ] | publisher = New Riders | year = 2003 | isbn = 0-13-101816-7 | pages = 15 | quote = AOL went for the throat and signed up ''Gemstone III'', ''Dragon's Gate'', and ''Federation II'' (it already had ''Neverwinter Nights'').}}</ref> | |||
| | url = http://mud.co.uk/dvw/errata.html | |||
| <ref name="bartle4">{{cite book | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | title = ] | publisher = New Riders | year = 2003 | isbn = 0-13-101816-7 | pages = 17 | quote = At its peak, ''Gemstone III'' on AOL was attracting 2,000-2,500 players simultaneously.}}</ref> | |||
| | title = Designing Virtual Worlds, Errata | |||
| <ref name="olivetti">{{cite web | last = Olivetti | first = Justin | title = The Game Archaeologist plays with MUDs: The games | work = Massively | date = 2011-04-19 | url = http://massively.joystiq.com/2011/04/19/the-game-archaeologist-plays-with-muds-the-games/ | accessdate = 2011-04-25 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110507224055/http://massively.joystiq.com/2011/04/19/the-game-archaeologist-plays-with-muds-the-games/ | archive-date = 2011-05-07 | url-status = dead}}</ref> | |||
| | date = 2003-07-17 | |||
| | quote = The second version was "GemStone ][" (rather than "Gemstone II"); Roman numerals were used for the third and fourth versions. | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="bartle2">{{cite book | |||
| | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| | publisher = New Riders | |||
| | year = 2003 | |||
| | isbn = 0-13-101816-7 | |||
| | pages = 14 | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="bartle3">{{cite book | |||
| | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| | publisher = New Riders | |||
| | year = 2003 | |||
| | isbn = 0-13-101816-7 | |||
| | pages = 15 | |||
| | quote = AOL went for the throat and signed up Gemstone III, Dragon's Gate, and Federation II (it already had Neverwinter Nights). | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="bartle4">{{cite book | |||
| | last = Bartle | first = Richard | authorlink = Richard Bartle | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| | publisher = New Riders | |||
| | year = 2003 | |||
| | isbn = 0-13-101816-7 | |||
| | pages = 17 | |||
| | quote = At its peak, Gemstone III on AOL was attracting 2,000-2,500 players simultaneously. | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="olivetti">{{cite web | |||
| | last = Olivetti | first = Justin | |||
| | title = The Game Archaeologist plays with MUDs: The games | |||
| | work = Massively | |||
| | date = 2011-04-19 | |||
| | url = http://massively.joystiq.com/2011/04/19/the-game-archaeologist-plays-with-muds-the-games/ | |||
| | accessdate = 2011-04-25 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{MUDs}} | {{MUDs}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:43, 2 December 2024
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "GemStone IV" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| GemStone IV | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Developer(s) | Simutronics |
| Publisher(s) | GEnie, AOL, independent |
| Platform(s) | Windows, Macintosh |
| Release | 1988 |
| Genre(s) | Fantasy MUD |
| Mode(s) | Multiplayer |
GemStone IV is a multiplayer text-based online role-playing video game (often known as a MUD) produced by Simutronics. Players control characters in a high fantasy game world named "Elanthia". The first playable version of the game was known as GemStone ][ and was launched in April 1988 on GEnie. It was one of the first MMORPGs and is one of the longest running online games still active. Access to the game is subscription-based (monthly fee) through its website, with three additional subscriptions levels available, "Premium", "Platinum" and "Shattered", in addition to a free-to-play model introduced in early March 2015.
Technical information
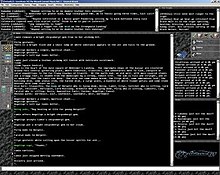
GemStone IV is a text-based game built on Simutronics' proprietary engine, the IFE (Interactive Fiction Engine). This engine is capable of changing nearly any aspect of the game on the fly which allows updates without the necessity for downtime. Due to the use of the IFE, GemStone is rarely taken offline, giving a 24-hour uptime cycle aside from the occasional game crash.
The GemStone interface is simply a text stream, and the game can be played with a Telnet interface after authentication. There are several official interfaces to the game, as well as several unofficial ones. The oldest interface for Windows is called the "Wizard Front End" and offers several useful features such as status readouts, macros, and limited scripting abilities. The Wizard has since been superseded with the "StormFront" Front End introduced in 2003, which itself has been rebranded as "Wrayth" in 2022. Wrayth offers several additional extensions to the game, including a "point and click" interface that allows one to click on text within the game and bring up action menus applicable to that portion of text. The Java FE and a browser-based version named "eScape" are less popular alternatives. A Wizard (similar to the Windows version) also exists for Macintosh Classic, while a Front End named "Avalon" is available for Mac OS X. No official Linux client exists.
History
GemStone was first demonstrated to GEnie in 1987 before Simutronics was officially incorporated. It was only used as a demonstration model and was never available to the general subscribers. GemStone ][" to "III" maintained significant portions of the environment, but not all, and character records were not maintained over the transition, requiring all players to begin anew. GemStone III evolved into GemStone IV in November 2003, but the game world and character records were maintained over the transition. GemStone III was promoted on GEnie by promising players the opportunity to receive real-life versions of gems found in-game, something that persisted for many years.
GemStone originally operated with a license to use the Rolemaster game mechanics and Shadow World environment from Iron Crown Enterprises (ICE). In 1995, Simutronics and ICE agreed to let the business relationship expire, necessitating the removal of all ICE intellectual property from GemStone. Many of the game changes were simply renaming ICE names, such as changing the world name from Kulthea to Elanthia, and renaming the deities while keeping their previous characteristics.
Game mechanics were greatly changed with the de-ICEing (as the period is colloquially named), which required every game character to undergo significant changes. Character racial and class choices were also changed, making any direct translation between the two systems difficult. The end result was that every character was required to "re-roll" their character with the option to change race and skills, but maintaining their old experience level, class, and equipment.
GemStone became available on AOL in September, 1995, just after the de-ICEing process. It had already become available on CompuServe and Prodigy before that. When AOL switched to flat-rate pricing, GemStone did over 1.4 million customer-hours in a single month and was attracting 2,000-2,500 simultaneous players. Simutronics launched a web portal in 1997, and started phasing customers off of the online services and onto the web interface, although it would take several years before the last of the online service portals were closed.
Reception
Computer Gaming World in 1991 stated that Gemstone III was a good example of the best and worst aspects of online play. The reviewer liked the game's community aspect and well-written prose, but criticized the poor parser, "surprisingly empty" game environment and—given the per-minute charge—lack of a free tutorial, and concluded that "the present incarnation of on-line games doesn't quite work for him". In a follow-up 1993 review, the reviewer wrote that his sojourn in Kulthea was a rewarding experience. He reported receiving help from both built-in commands and other characters and the ability and opportunity for his bard character to sing. The reviewer concluded that "at last, I know why" the game was so popular. In 1997 Next Generation named it as number seven on their "Top 10 Online Game Picks". At its peak (1996), GemStone III had over 2,000 simultaneous users and 1 million play hours per month, large numbers for its era.
In 2020 and 2021, GemStone III inspired retrospectives by Elizabeth Landau in Wired and Gizmodo. She noted its ability to facilitate human communication and its similar nature to later MMORPGs and social media.
- 1998 Finalist, "Online Game of the Year", Academy of Interactive Arts and Sciences
- December 1996, AOL Members' Choice Award
GemStone IV - Shattered
In May 2010, GemStone IV - Shattered was released by Simutronics. It allows unrestricted player-vs-player combat and has no policy against automated play.
References
- Olivetti, Justin (2011-04-19). "The Game Archaeologist plays with MUDs: The games". Massively. Archived from the original on 2011-05-07. Retrieved 2011-04-25.
- Bartle, Richard (2003-07-17). "Designing Virtual Worlds, Errata".
The second version was "GemStone ][" (rather than "Gemstone II"); Roman numerals were used for the third and fourth versions.
- Bartle, Richard (2003). Designing Virtual Worlds. New Riders. p. 14. ISBN 0-13-101816-7.
GEnie was the launch point for many classic online games, including two very important virtual worlds: Gemstone II in 1988 and Dragon's Gate in 1990.
- Gignews.com May 2002 Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Interview: Elonka Dunin
- Online Gaming Firm Attracts Fans Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine
- Bartle, Richard (2003). Designing Virtual Worlds. New Riders. p. 15. ISBN 0-13-101816-7.
AOL went for the throat and signed up Gemstone III, Dragon's Gate, and Federation II (it already had Neverwinter Nights).
- NPNEWS archives - 1997/02/06
- Bartle, Richard (2003). Designing Virtual Worlds. New Riders. p. 17. ISBN 0-13-101816-7.
At its peak, Gemstone III on AOL was attracting 2,000-2,500 players simultaneously.
- Wilson, Johnny L. (February 1991). "On-Line Gaming Viewed by a Skeptic / Gemstone III, for Example". Computer Gaming World. No. 79. p. 53. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- Wilson, Johnny L. (January 1993). "Genie's GemStone III". Computer Gaming World. p. 124. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- "Next Generation's Top 10 Online Game Picks". Next Generation. No. 27. Imagine Media. March 1997. p. 42.
- Landau, Elizabeth (30 September 2020). "I Had My First Kiss in GemStone III". Gizmodo.
- "Ep. 20: Text Adventure Gemstone III with Liz Landau". Video Game History Foundation. 24 February 2021.
- Landau, Liz (January 14, 2021). "How old-school text adventures inspired our virtual spaces". Wired.
- AIAS awards
- Washington Technology 1998-03-05 Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine
External links
| Multi-user dungeons (MUDs) | |
|---|---|
| Major branches | |
| Minor branches, codebases, libraries | |
| Concepts, terminology |
|
| Publications | |
| Companies, organizations | |