| Revision as of 16:23, 13 November 2010 editHorkana (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users12,299 edits Cite web and Cite news. Be generous use that extra space.← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:02, 5 December 2024 edit undoIznoRepeat (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users50,076 editsm add WP:TEMPLATECAT to remove from template; genfixesTag: AWB | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Small planetary-mass object}} | |||
| : ''Not to be confused with ].'' | |||
| {{Distinguish|minor planet}} | |||
| {{Featured article}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=September 2024}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | header = Nine likeliest{{efn|The ] criterion of a dwarf planet cannot be confirmed unless a spacecraft directly visits the object.}} dwarf planets<br/>and dates of discovery | |||
| | perrow = 2/3/4 | |||
| | total_width = 315 | |||
| | caption_align = center | |||
| | image1 = Ceres - RC3 - Haulani Crater (22381131691).jpg | |||
| | caption1 = ] (1801) | |||
| | image2 = Pluto in True Color - High-Res.jpg | |||
| | caption2 = ] (1930) | |||
| | image3 = Quaoar-weywot hst.jpg | |||
| | caption3 = ] (2002) | |||
| | image4 = Sedna PRC2004-14d.jpg | |||
| | caption4 = ] (2003) | |||
| | image5 = Orcus-Vanth 10801.jpg | |||
| | caption5 = ] (2004)<!--- Feb 2004 ---> | |||
| | image6 = Haumea Hubble.png | |||
| | caption6 = ] (2004)<!--- Dec 2004 ---> | |||
| | image7 = Eris and dysnomia2.jpg | |||
| | caption7 = ] (2005)<!--- Jan 2005 ---> | |||
| | image8 = Makemake and its moon.jpg | |||
| | caption8 = ] (2005)<!--- Mar 2005 ---> | |||
| | image9 = 225088 Gonggong and Xiangliu by Hubble (clean).png | |||
| | caption9 = ] (2007) | |||
| }} | |||
| A '''dwarf planet''' is a small ] that is in direct orbit around the ], ]ive enough to be ], but insufficient to achieve ] like the eight classical ]s of the ]. The prototypical dwarf planet is ], which for decades was regarded as a planet before the "dwarf" concept was adopted in 2006. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| A '''dwarf planet''', as defined by the ] (IAU), is a ] ]ing a ] that is massive enough to be spherical as a result of its own ] but has not ] of ]s and is not a ].<ref name=iau>{{cite news|publisher=International Astronomical Union|title=IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes|url=http://www.iau.org/iau0603.414.0.html|year=2006|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url= http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/profile.cfm?Object=Dwarf&Display=OverviewLong|title=Dwarf Planets|publisher=NASA|accessdate=2008-01-22}}</ref> More explicitly, it has to have sufficient ] to overcome its ] and achieve ]. | |||
| Dwarf planets are capable of being geologically active, an expectation that was borne out in 2015 by the '']'' mission to {{dp|Ceres}} and the '']'' mission to Pluto. ] are therefore particularly interested in them. | |||
| The term ''dwarf planet'' was adopted in 2006 as part of a ] of bodies orbiting the Sun,<ref name=finalresolution/> brought about by an increase in discoveries of ]s that rivaled ] in size, and finally precipitated by the discovery of an even larger object, ].<ref>"The Outer Planets", 2007, The Universe program (rebroadcast 2008-09-29, 18-19:00 hrs EDST) The History Channel.</ref> This classification states that bodies large enough to have cleared the neighbourhood of their orbit are defined as '']s'', while those that are not massive enough to be rounded by their own gravity are defined as ''].'' Dwarf planets come in between. The definition officially adopted by the IAU in 2006 has been both praised and criticized, and has been disputed by scientists such as Alan Stern.<ref name="Stern">{{cite web|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5283956.stm|title=Pluto vote 'hijacked' in revolt|publisher=BBC News|first=Paul|last=Rincon|date=2006-08-25|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref><ref name="Stern2009">{{cite web | |||
| |date=2009-11-30 | |||
| |title=Alan Stern: ‘A Chihuahua is still a dog, and Pluto is still a planet' | |||
| |publisher=EarthSky (Earthsky Interviews) | |||
| |author=Jorge Salazar | |||
| |url=http://www.earthsky.org/interviewpost/space/alan-stern-%E2%80%98a-chihuahua-is-still-a-dog-and-pluto-is-still-a-planet | |||
| |accessdate=2009-12-08}}</ref> | |||
| Astronomers are in general agreement that at least the ] are dwarf planets – in rough order of size, {{dp|Pluto}}, {{dp|Eris}}, {{dp|Haumea}}, {{dp|Makemake}}, {{dp|Gonggong}}, {{dp|Quaoar}}, {{dp|Ceres}}, {{dp|Orcus}}, and {{dp|Sedna}}. Considerable uncertainty remains over the tenth largest candidate {{dp|Salacia}}, which may thus be considered a borderline case. Of these ten, two have been visited by spacecraft (Pluto and Ceres) and seven others have at least one known moon (Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Salacia), which allows their masses and thus an estimate of their densities to be determined. Mass and density in turn can be fit into geophysical models in an attempt to determine the nature of these worlds. Only one, Sedna, has neither been visited nor has any known moons, making an accurate estimate of mass difficult. Some astronomers include many smaller bodies as well,<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210627154315/https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/plutosystem2019/pdf/7016.pdf |date=June 27, 2021 }}.</ref> but there is no consensus that these are likely to be dwarf planets. | |||
| The IAU currently recognizes five dwarf planets—{{dp|Ceres}}, ], {{dp|Haumea}}, {{dp|Makemake}}, and {{dp|Eris}}.<ref name=WGPSN/> However, only two of these bodies, Ceres and Pluto, have been observed in enough detail to demonstrate that they fit the definition. Eris has been accepted as a dwarf planet because it is more massive than Pluto. The IAU subsequently decided that unnamed trans-Neptunian objects with an ] brighter than +1 (and hence a mathematically delimited minimum diameter of 838 km<ref name=bruton>{{cite web | |||
| |title=Conversion of Absolute Magnitude to Diameter for Minor Planets | |||
| |publisher=Department of Physics & Astronomy (Stephen F. Austin State University) | |||
| |author=Dan Bruton | |||
| |url=http://www.physics.sfasu.edu/astro/asteroids/sizemagnitude.html | |||
| |accessdate=2008-06-13}}</ref>) are to be named under the assumption that they are dwarf planets. The only two such objects known at the time, Makemake and Haumea, went through this naming procedure and were declared to be dwarf planets. | |||
| The term ''dwarf planet'' was coined by planetary scientist ] as part of a three-way categorization of planetary-mass objects in the Solar System: classical planets, dwarf planets, and ]s. Dwarf planets were thus conceived of as a category of planet. In 2006, however, the concept was adopted by the ] (IAU) as a category of ''sub''-planetary objects, part of a ] of bodies orbiting the Sun: planets, dwarf planets, and ].<ref name="finalresolution"/> Thus Stern and other planetary geologists consider dwarf planets and large satellites to be planets,<ref>{{Cite journal |first1=Philip T. |last1=Metzger |author-link1=Philip T. Metzger |first2=W. M. |last2=Grundy |first3=Mark V. |last3=Sykes |first4=Alan |last4=Stern |author-link4=Alan Stern |first5=James F. |last5=Bell III |author-link5=James F. Bell III |first6=Charlene E. |last6=Detelich |first7=Kirby |last7=Runyon |first8=Michael |last8=Summers |display-authors=3 |date=March 1, 2022 |title=Moons Are Planets: Scientific Usefulness Versus Cultural Teleology in the Taxonomy of Planetary Science |url=https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2021.114768 |doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2021.114768 |s2cid=240071005 |journal=] |volume=374 |page=114768 |arxiv=2110.15285 |bibcode=2022Icar..37414768M |access-date=May 30, 2022}}</ref> but since 2006, the IAU and perhaps the majority of astronomers have excluded them from the roster of planets. | |||
| It is suspected that at least another 40 known objects in the ] are dwarf planets,<ref name=Brown/> and estimates are that up to 200 dwarf planets may be found when the entire region known as the ] is explored, and that the number might be as high as 2,000 when objects scattered outside the Kuiper belt are considered.<ref name=Brown/> | |||
| == History of the concept == | |||
| The classification of bodies in other ]s with the characteristics of dwarf planets has not been addressed,<ref name="Draft Resolution 5"/> although if they were detectable they would not be considered planets.<ref name=WSGESP>{{cite web|year=2001|title=Working Group on Extrasolar Planets of the International Astronomical Union|publisher=International Astronomical Union|url=http://www.dtm.ciw.edu/boss/definition.html|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Geophysical definition of planet|IAU definition of planet}} | |||
| ] and its moon ]. Separation not to scale]] | |||
| ], an asteroid that was once a dwarf planet<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/asteroids-comets-and-meteors/asteroids/4-vesta/in-depth|title=In Depth | 4 Vesta|website=NASA Solar System Exploration|access-date=February 29, 2020|archive-date=February 29, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200229050949/https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/asteroids-comets-and-meteors/asteroids/4-vesta/in-depth/|url-status=live}}</ref>]] | |||
| Starting in 1801, astronomers discovered ] and other bodies between ] and Jupiter that for decades were considered to be planets. Between then and around 1851, when the number of planets had reached 23, astronomers started using the word ] (from Greek, meaning 'star-like' or 'star-shaped') for the smaller bodies and began to distinguish them as ''minor planets'' rather than ''major planets''.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/3418/ |author=Mauro Murzi |title=Changes in a scientific concept: what is a planet? |date=2007 |access-date=April 6, 2013 |journal=Preprints in Philosophy of Science |type=Preprint |publisher=University of Pittsburgh |archive-date=June 11, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190611023948/http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/3418/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| With the discovery of Pluto in 1930, most astronomers considered the Solar System to have nine major planets, along with thousands of significantly smaller bodies (]s and ]s). For almost 50 years, ] was thought to be larger than ],<ref>{{cite web |title=Pluto Revealed |url=http://www.discoveryofpluto.com/pluto06.html |first=Brad |last=Mager |access-date=January 26, 2008 |publisher=discoveryofpluto.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110722004610/http://www.discoveryofpluto.com/pluto06.html |archive-date=July 22, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Is Pluto a planet? |url=http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/question.php?number=624 |date=September 14, 2007 |author1=Cuk, Matija |author2=Masters, Karen |publisher=Cornell University, Astronomy Department |access-date=January 26, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071012225232/http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/question.php?number=624 |archive-date=October 12, 2007 }}</ref> but with the discovery in 1978 of Pluto's moon ], it became possible to measure Pluto's mass accurately and to determine that it was much smaller than initial estimates.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Orbits and Photometry of Pluto's Satellites: Charon, S/2005 P1, and S/2005 P2 |journal=The Astronomical Journal |date=2006 |issue=1 |pages=290–298 |doi=10.1086/504422 |first=Marc W. |last=Buie |author2=Grundy, William M. |author3=Young, Eliot F. |author4=Young, Leslie A. |author5=Stern, S. Alan |volume=132 |bibcode=2006AJ....132..290B |arxiv=astro-ph/0512491|s2cid=119386667 }}</ref> It was roughly one-twentieth the mass of Mercury, which made Pluto by far the smallest planet. Although it was still more than ten times as massive as the largest object in the ], Ceres, it had only one-fifth the mass of Earth's ].<ref>{{cite book |first=David |last=Jewitt |author2=Delsanti, Audrey |title=The Solar System Beyond The Planets in Solar System Update : Topical and Timely Reviews in Solar System Sciences |publisher=Springer |doi=10.1007/3-540-37683-6 |isbn=978-3-540-37683-5 |date=2006 |url=http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/faculty/jewitt/papers/2006/DJ06.pdf |access-date=February 10, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060525051103/http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/faculty/jewitt/papers/2006/DJ06.pdf |archive-date=May 25, 2006 }}</ref> Furthermore, having some unusual characteristics, such as large ] and a high ], it became evident that it was a different kind of body from any of the other planets.<ref>{{cite book |title=Is Pluto a Planet? A Historical Journey through the Solar System |first=David A. |last=Weintraub |date=2006 |pages= |isbn=978-0-691-12348-6 |publisher=Princeton Univ. Press |location=Princeton, N.J. |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/isplutoplanethis00wein/page/1 }}</ref> | |||
| ==History of the concept== | |||
| {{main|2006 definition of planet}} | |||
| Before the discoveries of the early 21st century, astronomers had no strong need for a formal definition of a planet. With the discovery of Pluto in 1930, astronomers considered the Solar System to have nine planets, along with thousands of significantly smaller bodies such as ]s and ]s. For almost 50 years Pluto was thought to be larger than ],<ref>{{cite web|title=Pluto Revealed|url=http://www.discoveryofpluto.com/pluto06.html|first=Brad|last=Mager|accessdate=2008-01-26|publisher=discoveryofpluto.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Is Pluto a planet?|url=http://curious.astro.cornell.edu/question.php?number=624|date=2007-09-14|author=Cuk, Matija; Masters, Karen |publisher=Cornell University, Astronomy Department|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> but with the discovery in 1978 of Pluto's moon ], it became possible to measure the mass of Pluto accurately and it was determined that its actual mass was much smaller than the initial estimates.<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.iop.org/EJ/abstract/1538-3881/132/1/290|title=Orbits and Photometry of Pluto's Satellites: Charon, S/2005 P1, and S/2005 P2|journal=The Astronomical Journal|year=2006|issue=132|pages=290–98|doi= 10.1086/504422 |first=Marc W.|last=Buie|coauthors=William M. Grundy, Eliot F. Young, Leslie A. Young and S. Alan Stern|accessdate=2008-02-10|volume=132|format=abstract page}}</ref> It was roughly one-twentieth the mass of Mercury, which made Pluto by far the smallest planet. Although it was still more than ten times as massive as the largest object in the ], Ceres, it was one-fifth that of Earth's ].<ref>{{citebook|first=David |last=Jewitt|coauthors=Delsanti, Audrey|title=The Solar System Beyond The Planets in Solar System Update : Topical and Timely Reviews in Solar System Sciences (PDF)|publisher=Springer|doi=10.1007/3-540-37683-6|isbn=978-3-540-37683-5 |year=2006|url= http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/faculty/jewitt/papers/2006/DJ06.pdf|accessdate=2008-02-10|format=PDF}}</ref> Furthermore, having some unusual characteristics such as large ] and a high ], it became evident it was a completely different kind of body from any of the other planets.<ref>{{citebook|title=Is Pluto a Planet? A Historical Journey through the Solar System|first=David A.|last=Weintraub|year=2006|pages=1–272|isbn=978-0-691-12348-6|publisher=Princeton Univ. Press|location=Princeton, N.J.}}</ref> | |||
| In the 1990s, astronomers began to find objects in the same region of space as Pluto (now known as the ]), and some even farther away.<ref>{{cite web |title=Much Ado about Pluto |publisher=PlutoPetition.com |first=Tony |last=Phillips |author2=Phillips, Amelia |date=September 4, 2006 |url=http://www.plutopetition.com/unplanet.php |access-date=January 26, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080125225956/http://www.plutopetition.com/unplanet.php |archive-date=January 25, 2008 }}</ref> | |||
| In the 1990s, astronomers began to find objects in the same region of space as Pluto (now known as the ]), and some even farther away.<ref>{{cite web|title=Much Ado about Pluto|publisher=PlutoPetition.com|first=Tony|last=Phillips|coauthors=Phillips, Amelia|date=2006-09-04|url=http://www.plutopetition.com/unplanet.php |accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> Many of these shared some of the key orbital characteristics of Pluto, and Pluto started being seen as the largest member of a new class of objects, ]s. This led some astronomers to stop referring to Pluto as a planet. Several terms including ''], subplanet,'' and ''planetoid'' started to be used for the bodies now known as ''dwarf planets.''<ref>{{cite web|title=Planetoids Beyond Pluto|url=http://www.astrobio.net/news/modules.php?op=modload&name=News&file=article&sid=1366|publisher=Astrobiology Magazine|date=2004-12-30|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2004/14/|date=2004-04-14|title=Hubble Observes Planetoid Sedna, Mystery Deepens|publisher=NASA's Hubble Space Telescope home site|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> By 2005, three other bodies comparable to Pluto in terms of size and orbit (], ], and Eris) had been reported in the scientific literature.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/planetlila/|title=The Discovery of Eris, the Largest Known Dwarf Planet|first=Michael E.|last=Brown|publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> It became clear that either they would also have to be classified as planets, or Pluto would have to be reclassified.<ref>{{cite web|title=What is the definition of a planet?|year=2004|url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/sedna/index.html#planets|first=Michael E.|last=Brown|publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> Astronomers were also confident that more objects as large as Pluto would be discovered, and the number of planets would start growing quickly if Pluto were to remain a planet.<ref>{{cite news|title=War of the Worlds|publisher=New York Times|author=Brown, Mike|date=2006-08-16|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/08/16/opinion/16brown.html|accessdate=2008-02-20}}</ref> | |||
| Many of these shared several of Pluto's key orbital characteristics, and Pluto started being seen as the largest member of a new class of objects, the ]s. It became clear that either the larger of these bodies would also have to be classified as planets, or Pluto would have to be reclassified, much as Ceres had been reclassified after the discovery of additional asteroids.<ref>{{cite web |title=What is the definition of a planet? |date=2004 |url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/sedna/index.html#planets |first=Michael E. |last=Brown |publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110719160217/http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/sedna/index.html#planets |archive-date=July 19, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| This led some astronomers to stop referring to Pluto as a planet. Several terms, including ''subplanet'' and ''planetoid'', started to be used for the bodies now known as dwarf planets.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Eicher |first1=David J. |author1-link=David J. Eicher |title=Should Pluto Be Considered a Planet? |url=https://astronomy.com/magazine/greatest-mysteries/2007/07/32-should-pluto-be-considered-a-planet |website=] |access-date=November 28, 2022 |language=en |date=July 21, 2007 |archive-date=November 28, 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221128115033/https://astronomy.com/magazine/greatest-mysteries/2007/07/32-should-pluto-be-considered-a-planet |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2004/news-2004-14.html/ |date=April 14, 2004 |title=Hubble Observes Planetoid Sedna, Mystery Deepens |publisher=NASA's Hubble Space Telescope home site |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210113110507/https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2004/news-2004-14.html |archive-date=January 13, 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Astronomers were also confident that more objects as large as Pluto would be discovered, and the number of planets would start growing quickly if Pluto were to remain classified as a planet.<ref>{{cite news |title=War of the Worlds |work=] |author=Brown, Mike |date=August 16, 2006 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2006/08/16/opinion/16brown.html |access-date=February 20, 2008 |archive-date=February 13, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170213193022/http://www.nytimes.com/2006/08/16/opinion/16brown.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] (then known as {{mp|2003 UB|313}}) was discovered in January 2005;<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/planetlila/ |title=California Institute of Technology, Retrieved 4-12-2015 |access-date=April 12, 2015 |archive-date=May 17, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120517130215/http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/planetlila/ |url-status=live }}</ref> it was thought to be slightly larger than Pluto, and some reports informally referred to it as the '']''.<ref>{{cite news |title=Astronomers Measure Mass of Largest Dwarf Planet |publisher=NASA's Hubble Space Telescope home site |url=http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2007/24/full/ |date=June 14, 2007 |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-date=August 7, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110807132150/http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2007/24/full/ |url-status=live }}</ref> As a consequence, the issue became a matter of intense debate during the ] in August 2006.<ref>{{cite web |title=What makes a planet? |url=http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/whatsaplanet/ |first=Michael E. |last=Brown |publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-date=May 16, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120516023200/http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/whatsaplanet/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The IAU's initial draft proposal included Charon, Eris, and Ceres in the list of planets. After many astronomers objected to this proposal, an alternative was drawn up by the Uruguayan astronomers ] and ]: They proposed an intermediate category for objects large enough to be round but that had not cleared their orbits of ]s. Beside dropping Charon from the list, the new proposal also removed Pluto, Ceres, and Eris, because they have not cleared their orbits.<ref name="19aug">{{cite web |date=August 19, 2006 |first=Robert Roy |last=Britt |title=Details Emerge on Plan to Demote Pluto |publisher=Space.com |access-date=August 18, 2006 |url=http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/060819_new_proposal.html |archive-date=June 28, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110628232939/http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/060819_new_proposal.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Although concerns were raised about the classification of planets orbiting other stars,<ref name="Draft Resolution 5">{{cite web |title=The IAU draft definition of "planet" and "plutons" |url=http://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau0601/ |publisher=] |date=August 16, 2006 |access-date=May 17, 2008 |archive-date=April 29, 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140429050716/http://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau0601/ |url-status=live }}</ref> the issue was not resolved; it was proposed instead to decide this only when dwarf-planet-size objects start to be observed.<ref name=19aug/> | |||
| The IAU's final resolution preserved this three-category system for the celestial bodies orbiting the Sun. Fernández suggested calling these median objects ''planetoids,''<ref> | |||
| {{cite web|title=Comments & discussions on Resolution 5: The definition of a planet - Planets Galore|first=Mark E.|last=Bailey|url=http://astro.cas.cz/nuncius/appendix.html|work=Dissertatio cum Nuncio Sidereo, Series Tertia - official newspaper of the IAU General Assembly 2006|publisher=Astronomical Institute Prague|accessdate=2008-02-09}}</ref><ref> | |||
| {{cite web|title=Dos uruguayos, Julio Fernández y Gonzalo Tancredi en la historia de la astronomía:reducen la cantidad de planetas de 9 a 8 ...&Anotaciones de Tancredi|language=Spanish|publisher=Science and Research Institute, Mercedes, Uruguay|url=http://www.ici.edu.uy/perfilASTRO.htm|accessdate=2008-02-11| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20071220063342/http://www.ici.edu.uy/perfilASTRO.htm| archivedate = December 20, 2007}} | |||
| </ref> but the IAU's division III plenary session voted unanimously to call them ''dwarf planets.''<ref name=finalresolution> | |||
| {{cite news|url=http://www.iau.org/static/resolutions/Resolution_GA26-5-6.pdf|format=PDF|title=Definition of a Planet in the Solar System: Resolutions 5 and 6|date=2006-08-24|work=IAU 2006 General Assembly|publisher=International Astronomical Union|accessdate=2008-01-26}} | |||
| </ref> The resolution read, in full: | |||
| {{cquote|The IAU ... resolves that planets and other bodies, except satellites, in our Solar System be defined into three distinct categories in the following way:<br /> | |||
| (1) A planet<sup>1</sup> is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has ] around its orbit.<br /> | |||
| (2) A “''dwarf planet''” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape<sup>2</sup>, (c) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit, and (d) is not a ].<br /> | |||
| (3) All other objects<sup>3</sup>, except satellites, orbiting the Sun shall be referred to collectively as “].”<br /> | |||
| :<small>Footnotes: | |||
| :<sup>1</sup> The ] are: ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| :<sup>2</sup> An IAU process will be established to assign borderline objects either dwarf planet or other status. | |||
| :<sup>3</sup> These currently include most of the Solar System asteroids, most Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs), comets, and other small bodies.}} | |||
| Although there were concerns about the classification of planets in other solar systems,<ref name="Draft Resolution 5"/> this issue was not resolved; it was proposed instead to decide this only when such objects will start being observed.<ref name=19aug/> | |||
| In the immediate aftermath of the IAU definition of dwarf planet, some scientists expressed their disagreement with the IAU resolution.<ref name="Stern"/> Campaigns included car bumper stickers and T-shirts.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.usatoday.com/tech/science/space/2006-08-25-pluto-memorabilia_x.htm |title=Online merchants see green in Pluto news |first=Alicia |last=Chang |agency=Associated Press |publisher=USA Today |date=August 25, 2006 |access-date=January 25, 2008 |archive-date=May 11, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080511172619/http://www.usatoday.com/tech/science/space/2006-08-25-pluto-memorabilia_x.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> ] (the discoverer of Eris) agrees with the reduction of the number of planets to eight.<ref>{{cite web |title=The Eight Planets |first=Michael E. |last=Brown |url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/eightplanets/ |publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110719162512/http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/eightplanets/ |archive-date=July 19, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| The 2006 IAU's Resolution 6a<ref name="Resolution Result"> | |||
| {{cite web | title=IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes| url= http://www.iau.org/public_press/news/release/iau0603}} | |||
| </ref> recognizes Pluto as "the prototype of a new category of trans-Neptunian objects". The name and precise nature of this category were not specified but left for the IAU to establish at a later date; in the debate leading up to the resolution, the members of the category were variously referred to as '']s'' and ''plutonian objects'' but neither name was carried forward.<ref name=finalresolution/> On June 11, 2008, the IAU Executive Committee announced a name, '']'', and a definition: all trans-Neptunian dwarf planets are plutoids.<ref>{{cite press release|url=http://www.iau.org/public_press/news/release/iau0804/|title=Plutoid chosen as name for Solar System objects like Pluto}}</ref> On July 18, 2008, the ] reclassified the object then known as ''(136472) 2005 FY<sub>9</sub>'' as a dwarf planet, and renamed it ].<ref>{{cite web |title= Minor Planets, Dwarf Planets |publisher = IAU| url= http://cbat.eps.harvard.edu/Headlines.html| accessdate= 2010-10-24}}</ref> | |||
| NASA announced in 2006 that it would use the new guidelines established by the IAU.<ref>{{cite press release|title= {{Sic|hide=y|Hotly|-}}Debated Solar System Object Gets a Name|publisher=]|url= http://www.nasa.gov/vision/universe/solarsystem/erisf-20060914.html|date= September 14, 2006|access-date= January 26, 2008|archive-date= June 29, 2011|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110629155731/http://www.nasa.gov/vision/universe/solarsystem/erisf-20060914.html|url-status= dead}}</ref> ], the director of ], rejects the current IAU definition of planet, both in terms of defining dwarf planets as something other than a type of planet, and in using orbital characteristics (rather than intrinsic characteristics) of objects to define them as dwarf planets.<ref>{{cite web |title=Unabashedly Onward to the Ninth Planet |first=Alan |last=Stern |date=September 6, 2006 |publisher=New Horizons Web Site |url=http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/overview/piPerspectives/piPerspective_09_06_2006.php |access-date=January 26, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131207024954/http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/overview/piPerspectives/piPerspective_09_06_2006.php |archive-date=December 7, 2013 }}</ref> Thus, in 2011, he still referred to Pluto as a planet,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.space.com/12710-pluto-defender-alan-stern-dwarf-planet-interview.html |first=Mike |last=Wall |publisher=Space.com |title=Pluto's Planet Title Defender: Q & A With Planetary Scientist Alan Stern |date=August 24, 2011 |access-date=December 3, 2012 |archive-date=August 14, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120814212232/http://www.space.com/12710-pluto-defender-alan-stern-dwarf-planet-interview.html |url-status=live }}</ref> and accepted other likely dwarf planets such as Ceres and Eris, as well as the ], as additional planets.<ref name="News.discovery.com"/> Several years before the IAU definition, he used orbital characteristics to separate "überplanets" (the dominant eight) from "unterplanets" (the dwarf planets), considering both types "planets".<ref name="Stern 2002"/> | |||
| ==Characteristics== | |||
| <div style="float: right; margin: 5px;"> | |||
| == Name == | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
| ] showing the IAU Executive Committee conception of the types of bodies in the Solar System (except the Sun)]] | |||
| Names for large subplanetary bodies include ''dwarf planet'', ''planetoid'' (more general term), '']'' (narrowly used for sizes between Mercury and Ceres), ''quasi-planet'', and (in the transneptunian region) ''plutoid''. ''Dwarf planet'', however, was originally coined as a term for the smallest planets, not the largest sub-planets, and is still used that way by many planetary astronomers. | |||
| Alan Stern coined the term ''dwarf planet'', analogous to the term '']'', as part of a three-fold classification of planets, and he and many of his colleagues continue to classify dwarf planets as a class of planets. The IAU decided that dwarf planets are not to be considered planets, but kept Stern's term for them. Other terms for the IAU definition of the largest subplanetary bodies that do not have such conflicting connotations or usage include ''quasi-planet''<ref>{{cite news |first=Tom |last=Service |title=Sounds of the solar system: probing Pluto's predicted score |newspaper=The Guardian |date=July 15, 2015 |url=https://www.theguardian.com/music/tomserviceblog/2015/jul/15/sounds-pluto-new-horizons-colin-matthews-holst |access-date=December 26, 2019 |archive-date=December 26, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191226002852/https://www.theguardian.com/music/tomserviceblog/2015/jul/15/sounds-pluto-new-horizons-colin-matthews-holst |url-status=live }}</ref> and the older term ''planetoid'' ("having the form of a planet").<ref>{{cite book |editor=Karttunen |display-editors=etal |title=Fundamental Astronomy |publisher=Springer |date=2007 |edition=5 |title-link=Fundamental Astronomy (book)}}</ref> ] stated that ''planetoid'' is "a perfectly good word" that has been used for these bodies for years, and that the use of the term ''dwarf planet'' for a non-planet is "dumb", but that it was motivated by an attempt by the IAU division III plenary session to reinstate Pluto as a planet in a second resolution.<ref name=killed>{{cite book |first=Mike |last=Brown |title=How I Killed Pluto and Why It Had It Coming |page= |publisher=Spiegel & Grau |date=2010 |title-link=How I Killed Pluto and Why It Had It Coming}}</ref> Indeed, the draft of Resolution 5A had called these median bodies ''planetoids,''<ref>{{cite web |title=Comments & discussions on Resolution 5: The definition of a planet – Planets Galore |first=Mark E. |last=Bailey |url=http://astro.cas.cz/nuncius/appendix.html |work=Dissertatio cum Nuncio Sidereo, Series Tertia – official newspaper of the IAU General Assembly 2006 |publisher=Astronomical Institute Prague |access-date=February 9, 2008 |archive-date=July 20, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110720030946/http://astro.cas.cz/nuncius/appendix.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Dos uruguayos, Julio Fernández y Gonzalo Tancredi en la historia de la astronomía:reducen la cantidad de planetas de 9 a 8 ...&Anotaciones de Tancredi |language=es |publisher=Science and Research Institute, Mercedes, Uruguay |url=http://www.ici.edu.uy/perfilASTRO.htm |access-date=February 11, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071220063342/http://www.ici.edu.uy/perfilASTRO.htm |archive-date=December 20, 2007}}</ref> but the plenary session voted unanimously to change the name to ''dwarf planet.''<ref name="finalresolution">{{cite news |url=http://www.iau.org/static/resolutions/Resolution_GA26-5-6.pdf |title=Definition of a Planet in the Solar System: Resolutions 5 and 6 |date=August 24, 2006 |work=IAU 2006 General Assembly |publisher=] |access-date=January 26, 2008 |author=IAU |archive-date=June 20, 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090620102000/http://www.iau.org/static/resolutions/Resolution_GA26-5-6.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> The second resolution, 5B, defined ''dwarf planets'' as a subtype of ''planet'', as Stern had originally intended, distinguished from the other eight that were to be called "classical planets". Under this arrangement, the twelve planets of the rejected proposal were to be preserved in a distinction between eight ''classical planets'' and four ''dwarf planets''. Resolution 5B was defeated in the same session that 5A was passed.<ref name=killed/> Because of the semantic inconsistency of a ''dwarf planet'' not being a planet due to the failure of Resolution 5B, alternative terms such as ''nanoplanet'' and ''subplanet'' were discussed, but there was no consensus among the CSBN to change it.<ref name=D3-PSS-Cambridge/> | |||
| In most languages equivalent terms have been created by translating ''dwarf planet'' more-or-less literally: French ''{{lang|fr|planète ]}}'', Spanish ''{{lang|es|planeta enano}}'', German ''{{lang|de|]}}'', Russian ''karlikovaya planeta'' ({{lang|ru|] планета}}), Arabic ''kaukab qazm'' ({{lang|ar|كوكب ]}}), Chinese ''ǎixíngxīng'' ({{lang|cmn|]行星}}), Korean ''waesohangseong'' ({{lang|ko|왜소행성 / 矮小行星}}) or ''waehangseong'' ({{lang|ko|왜행성 / 矮行星}}), but in Japanese they are called ''junwakusei'' ({{lang|ja|準惑星}}), meaning "quasi-planets" or "peneplanets" (] meaning "almost"). | |||
| IAU Resolution 6a of 2006<ref name="Resolution Result">{{Cite web|date=August 24, 2006|url=https://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau0603/|title=International Astronomical Union 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes|website=]|access-date=August 10, 2021|archive-date=April 29, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140429212224/https://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau0603/|url-status=live}}</ref> recognizes Pluto as "the prototype of a new category of trans-Neptunian objects". The name and precise nature of this category were not specified but left for the IAU to establish at a later date; in the debate leading up to the resolution, the members of the category were variously referred to as ''plutons'' and ''plutonian objects'' but neither name was carried forward, perhaps due to objections from geologists that this would create confusion with their '']''.<ref name="finalresolution" /> | |||
| On June 11, 2008, the IAU Executive Committee announced a new term, ''plutoid'', and a definition: all trans-Neptunian dwarf planets are plutoids.<ref name=IAU2008>{{Cite web |date=June 11, 2008|url=https://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau0804/|title=Plutoid chosen as name for Solar System objects like Pluto|website=]|access-date=August 10, 2021|archive-date=November 23, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201123162642/https://www.iau.org/news/pressreleases/detail/iau0804/|url-status=live|location=Paris}}</ref> Other departments of the IAU have rejected the term: {{blockquote|...in part because of an email miscommunication, the ]] was not involved in choosing the word plutoid. ... In fact, a vote taken by the WG-PSN subsequent to the Executive Committee meeting has rejected the use of that specific term..."<ref name=D3-PSS-Cambridge>{{cite journal |last1=Bowell |first1=Edward L.G. |author-link1=Edward L. G. Bowell |last2=Meech |first2=Karen J. |author-link2=Karen Jean Meech |last3=Williams |first3=Iwan P. |author-link3=:fr:Iwan Williams |last4=Boss |first4=Alan P. |author-link4=Alan Boss |last5=Consolmagno |first5=Guy J. |author-link5=Guy Consolmagno |last6=Courtin |first6=Régis |last7=Fernández |first7=Julio A. |author-link7=Julio Ángel Fernández |last8=Gustafson |first8=Bo Å. S. |last9=Huebner |first9=Walter F. |author-link9=Walter F. Huebner |last10=Levasseur-Regourd |first10=Anny-Chantal |author-link10=Anny-Chantal Levasseur-Regourd |last11=Marov |first11=Mikhail Ya. |author-link11=Mikhail Marov |last12=Mayor |first12=Michel |author-link12=Michel Mayor |last13=Schulz |first13=Rita M. |author-link13=:de:Rita Schulz |last14=Spurný |first14=Pavel |author-link14=:cs:Pavel Spurný |last15=Valsecchi |first15=Giovanni B. |last16=Watanabe |first16=Jun-ichi |author-link16=:ja:渡部潤一 |last17=Witt |first17=Adolf N. |display-authors=3 |date=2008-12-01 |title=Division III: Planetary Systems Sciences |journal=] |volume=4 |issue=T27A |pages=149–153 |publisher=] |doi=10.1017/S1743921308025398 |doi-access=free}}</ref>}} | |||
| The category of 'plutoid' captured an earlier distinction between the 'terrestrial dwarf' Ceres and the 'ice dwarfs' of the outer Solar system,<ref>{{cite book |last=Carson |first=Mary Kay |date=2011 |title=Far-Out Guide to the Icy Dwarf Planets |url=https://archive.org/details/faroutguidetoicy0000cars/mode/2up |url-access=registration |publisher=] |isbn=9780766031876 |oclc=441945398 |via=]}}</ref> part of a conception of a threefold division of the Solar System into inner '']s'', central '']s'', and outer ''ice dwarfs'', of which Pluto was the principal member.<ref>{{cite book |last=Lew |first=Kristi |date=2010 |title=Space! The Dwarf Planet Pluto |url=https://archive.org/details/dwarfplanetpluto0000lewk |url-access=registration |publisher=] |place=New York |page=10 |isbn=9780761445531 |oclc=562529871 |via=]}}</ref> 'Ice dwarf' also saw some use as an umbrella term for all trans-Neptunian ]s, or for the ice ]s of the outer Solar System; one attempted definition was that an ice dwarf "is larger than the ] of a normal ] and icier than a typical asteroid."<ref name=darling>{{cite web | |||
| |title=Ice dwarf |website=Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy and Spaceflight |editor-last=Darling |editor-first=David |editor-link=David J. Darling |url=http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/I/icedwarf.html |access-date=June 22, 2008 |url-status =dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080706143614/http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/I/icedwarf.html |archive-date=July 6, 2008 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| Since the '']'' mission, it has been recognized that Ceres is a geologically icy body that may have originated from the outer Solar System.<ref>{{Cite web|url = https://www.space.com/33934-dwarf-planet-ceres-ice-volcano-discoveries.html|title = Ice Volcanoes and More: Dwarf Planet Ceres Continues to Surprise|website = ]|date = September 2016|access-date = December 19, 2019|archive-date = October 12, 2019|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20191012004925/https://www.space.com/33934-dwarf-planet-ceres-ice-volcano-discoveries.html|url-status = live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Dawn at Ceres: What Have we Learned?|display-authors=etal|first1=J. C.|last1=Castillo-Rogez|first2=C. A.|last2=Raymond|first3=C. T.|last3=Russell|url=http://sites.nationalacademies.org/cs/groups/ssbsite/documents/webpage/ssb_183286.pdf|publisher=Committee on Astrobiology and Planetary Science|date=September 12, 2017|access-date=October 12, 2019|archive-date=October 8, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181008123813/http://sites.nationalacademies.org/cs/groups/ssbsite/documents/webpage/ssb_183286.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Ceres has since been called an ice dwarf as well.<ref>{{Cite book|chapter=Ceres: The First Known Ice Dwarf Planet |title=Ice Worlds of the Solar System: Their Tortured Landscapes and Biological Potential |first=Michael |last=Carroll|author-link=Michael Carroll (space artist) |date=October 23, 2019 |doi=10.1007/978-3-030-28120-5 |publisher=Springer Cham |isbn=978-3-030-28120-5}}</ref> | |||
| == Criteria == | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable floatright" style="text-align:center; width: 330px;" | |||
| |+ Planetary discriminants<ref name=soter/> | |+ Planetary discriminants<ref name=soter/> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! Body | ! scope=col | Body | ||
| ! scope=col style="font-weight: normal;" | {{nobr| '''{{sfrac|{{mvar|m}}|{{Earth mass}} }}''' {{sup|}} }} | |||
| ! Mass (''M''<sub>E</sub><sup>*</sup>)<br /> | |||
| ! scope=col style="font-weight: normal;" | '''{{math|Λ}}''' {{sup|}} | |||
| ! ''Λ''/''Λ''<sub>E</sub><sup>**</sup><br /> | |||
| ! scope=col style="font-weight: normal;" | '''{{mvar|µ}}''' {{sup|}} | |||
| ! '' µ''<sup>***</sup> | |||
| ! scope=col style="font-weight: normal;" | '''{{math|Π}}''' {{sup|}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| | ] | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.055|0.055}} | |||
| | 0.055 | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.012|0.012 6}} | |||
| | {{val|1.95e3}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|009100|9.1{{esp|4}}}} | |||
| | {{val|9.1e4}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{val|1.3e2}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.815|0.815}} | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.815 | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|135000|1.35{{esp|6}}}} | |||
| | {{val|1.66e5}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{val|1.35e6}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{val|9.5e2}} | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0001|1.00}} | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|170000|1.7{{esp|6}}}} | |||
| | |
| 1 | ||
| | {{val|1.53e5}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{val|1.7e6}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.107|0.107}} | |||
| | {{val|8.1e2}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.0006|0.006 1}} | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|018000|1.8{{esp|5}}}} | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.107 | |||
| | {{val|9.42e2}} | |||
| | {{val|1.8e5}} | |||
| | {{val|5.4e1}} | |||
| |- style="background: #E8E0FF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.00016 | |||
| | {{val|8.32e−4}} | |||
| | {{val|0.33}} | |||
| | {{val|4.0e−2}} | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 317.7 | |||
| | {{val|1.30e9}} | |||
| | {{val|6.25e5}} | |||
| | {{val|4.0e4}} | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 95.2 | |||
| | {{val|4.68e7}} | |||
| | {{val|1.9e5}} | |||
| | {{val|6.1e3}} | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 14.5 | |||
| | {{val|3.85e5}} | |||
| | {{val|2.9e4}} | |||
| | {{val|4.2e2}} | |||
| |- style="background: #FFF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 17.1 | |||
| | {{val|2.73e5}} | |||
| | {{val|2.4e4}} | |||
| | {{val|3.0e2}} | |||
| |- style="background: #E8E0FF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.0022 | |||
| | {{val|2.95e−3}} | |||
| | {{val|0.077}} | |||
| | {{val|2.8e−2}} | |||
| <!-- | |||
| |- style="background: #E8E0FF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.00067 | |||
| | {{val|2.68e–4}} | |||
| | {{val|0.02}} | |||
| | {{val|7.8e−3}} | |||
| |- style="background: #E8E0FF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.00067 | |||
| | {{val|2.22e–4}} | |||
| | {{val|0.02}}{{efn|Calculated using the estimate for the mass of the Kuiper belt found by Iorio (2007)<ref>{{cite journal |last=Iorio |first=Lorenzo |date=March 2007 |orig-date=February 5, 2007 |title=Dynamical determination of the mass of the Kuiper Belt from motions of the inner planets of the Solar system |journal=] |volume=375 |issue=4 |pages=1,311–1,314 |bibcode=2007MNRAS.375.1311I |arxiv=gr-qc/0609023 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11384.x |doi-access=free |url=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2007MNRAS.tmp...24I}}</ref> of 0.033 Earth masses.}} | |||
| | {{val|7.3e−3}} | |||
| --> | |||
| |- style="background: #E8E0FF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.0028 | |||
| | {{val|2.13e−3}} | |||
| | {{val|0.10}} | |||
| | {{val|2.0e−2}} | |||
| |- style="background: #E8E0FF;" | |||
| !scope=row align=left | ] | |||
| | 0.0002 | |||
| | {{val|3.64e−7}} | |||
| | {{val|0.07|p= < }}{{efn|Calculated using the minimum estimate from 15 objects in its region with at least Sedna's mass, as estimated by Schwamb, Brown, & Rabinowitz (2009).<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Schwamb |first1=Megan E. |author-link1=Megan Schwamb |last2=Brown |first2=Michael E. |author-link2=Michael E. Brown |last3=Rabinowitz |first3=David L. |author-link3=David L. Rabinowitz |year=2009 |title=A search for distant solar system bodies in the region of Sedna |journal=] |volume=694 |issue=1 |pages=L45–L48 |arxiv=0901.4173 |doi=10.1088/0004-637X/694/1/L45 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2009ApJ...694L..45S|s2cid=15072103 }}</ref>}} | |||
| | {{val|1.6e−4}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! colspan=5 style="font-size: 0.8em; font-weight: normal; text-align: center; padding: 4px;" |<!-- note --> | |||
| |- style="background: #CCF;" | |||
| Planetary discriminants of the planets ({{background color|#FFF;"| white }}), and of the largest known dwarf planet ({{background color|#E8E0FF;"| light purple }}) in each orbital population (], ], ], ]s). All other known objects in these populations have smaller discriminants than the one shown. | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.00015|0.000 15}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.0000000087|8.7{{esp|−9}}}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000000.33|0.33}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! colspan=5 |<!-- legend --> | |||
| | ] | |||
| {| style="font-size: 0.9em; font-weight: normal; text-align: left; padding: 4px" | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|317.7|317.7}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|8510|8,510}} | |||
| | valign=top | || Mass in ], the unit of mass equal to that of Earth {{nobr| ( {{math|5.97 × {{10^|24}} kg}} ).}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|062500|6.25{{esp|5}}}} | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | valign=top | || {{math| Λ }} is the capacity to ] (greater than 1 for planets) by Stern & Levison (2002):<ref name="Stern 2002"/> {{nobr| {{math|Λ {{=}} ''k'' ''m''{{sup|2}} ''a''{{sup|{{sup|{{sfrac|− | 3 |2}}}} }} }} ,}} where {{nobr| {{math| ''k'' {{=}} 0.0043 }} }} for {{mvar| m }} in units of ]s ({{10^|18}} ]s) and {{mvar| a }} in ]s ({{sc|AU}}), where {{mvar| a }} is the body's semi-major axis.<ref name="Stern 2002"/> | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|095.2|95.2}} | |||
| | valign=top | || {{mvar| µ }} is Soter's planetary discriminant, which he finds greater than 100 for planets. {{nobr| {{math| ''µ'' {{=}} {{sfrac|''m''| ''M'' − ''m'' }} }} ,}} where {{mvar| m }} is the mass of the body, and {{mvar| M }} is the aggregate mass of ''all'' the bodies that occupy its orbital zone.<ref name=soter/> | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0308|308}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|019000|1.9{{esp|5}}}} | |||
| | valign=top | || {{math| Π }} is the capacity to ] (greater than 1 for planets) by Margot. {{nobr| {{math| Π {{=}} ''k'' ''m'' ''a''{{sup| {{sup|{{sfrac|− | 9 |8}}}} }} }},}} where {{nobr| {{math| ''k'' {{=}} 807 }} }} for units of ]es and ].<ref name="Margot 2015">{{cite journal |first=Jean-Luc |last=Margot |author-link=Jean-Luc Margot |date=October 15, 2015 |title=A quantitative criterion for defining planets |journal=] |volume=150 |issue=6 |page=185 |doi=10.1088/0004-6256/150/6/185 |arxiv=1507.06300 |bibcode=2015AJ....150..185M |s2cid=51684830 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|014.5|14.5}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0002.51|2.51}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|002900|2.9{{esp|4}}}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|017.1|17.1}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0001.79|1.79}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|002400|2.4{{esp|4}}}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |- style="background: #CCF;" | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.002|0.002 2}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.0000000195|1.95{{esp|−8}}}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000000.077|0.077}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |- style="background: #CCF;" | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.00067|0.000 67}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.00000000172|1.72{{esp|–9}}}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000000.02|0.02}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |- style="background: #CCF;" | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.00067|0.000 67}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.00000000145|1.45{{esp|–9}}}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000000.02|0.02<ref>Calculated using the estimate for the mass of the Kuiper belt found in of 0.033 Earth masses</ref>}} | |||
| |- | |||
| |- style="background: #CCF;" | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000.002|0.002 8}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|0000.000000035|3.5{{esp|−8}}}} | |||
| | align="center" | {{sort|000000.1|0.10}} | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| <small>*''M''<sub>E</sub> in Earth masses.</small><br /> | |||
| The category ''dwarf planet'' arose from a conflict between dynamical and geophysical ideas of what a useful conception of a planet would be. In terms of the dynamics of the Solar System, the major distinction is between bodies that gravitationally dominate their neighbourhood (Mercury through Neptune) and those that do not (such as the asteroids and Kuiper belt objects). A celestial body may have a dynamic (planetary) geology at approximately the mass required for its mantle to become plastic under its own weight, which results in the body acquiring a round shape. Because this requires a much lower mass than gravitationally dominating the region of space near their orbit, there are a population of objects that are massive enough to have a world-like appearance and planetary geology, but not massive enough to clear their neighborhood. Examples are Ceres in the asteroid belt and Pluto in the Kuiper belt.<ref name=planetarysociety/> | |||
| <small>**''Λ''/''Λ''<sub>E</sub> = ''M''<sup>2</sup>/''P'' × ''P<sub>E</sub>''/M<sup>2</sup><sub>E</sub>.</small><br /> | |||
| <small>***''µ'' = ''M''/''m'', where ''M'' is the mass of the body,<br /> and ''m'' is the aggregate mass of all the other bodies<br /> that share its orbital zone.</small> | |||
| Dynamicists usually prefer using gravitational dominance as the threshold for planethood, because from their perspective smaller bodies are better grouped with their neighbours, e.g. Ceres as simply a large asteroid and Pluto as a large Kuiper belt object.<ref>{{cite web |first=Mike |last=Brown |title=The eight planets |website=gps.caltech.edu |publisher=] |url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/eightplanets/ |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-date=July 19, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110719162512/http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/eightplanets/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |first=David |last=Jewitt |title=Classification of Pluto |website=ess.ucla.edu |publisher=] |url=http://www2.ess.ucla.edu/~jewitt/kb/pluto_classification.html |access-date=August 19, 2021 |archive-date=August 19, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210819074719/http://www2.ess.ucla.edu/~jewitt/kb/pluto_classification.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Geoscientists usually prefer roundness as the threshold, because from their perspective the internally driven geology of a body like Ceres makes it more similar to a classical planet like Mars, than to a small asteroid that lacks internally driven geology. This necessitated the creation of the category of ''dwarf planets'' to describe this intermediate class.<ref name=planetarysociety>{{cite web |first1=Emily |last1=Lakdawalla |author-link1=Emily Lakdawalla|display-authors=etal |date=April 21, 2020 |title=What is a planet? |website=planetary.org |publisher=] |url=https://www.planetary.org/worlds/what-is-a-planet |access-date=August 19, 2021 |archive-date=January 22, 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220122142140/https://www.planetary.org/worlds/what-is-a-planet |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| </div> | |||
| ===Orbital dominance=== | === Orbital dominance === | ||
| {{Main|Clearing the neighbourhood}} | {{Main|Clearing the neighbourhood}} | ||
| ] and ] introduced a parameter Λ (]), expressing the probability of an encounter resulting in a given deflection of orbit.<ref name=Stern/> The value of this parameter in Stern's model is proportional to the square of the mass and inversely proportional to the period. Following the authors, this value can be used to estimate the capacity of a body to clear the neighbourhood of its orbit. A gap of five orders of magnitude in Λ was found between the smallest ]s and the largest asteroids and Kuiper belt objects (third column of the planetary discriminants table to the right).<ref name=soter/> | |||
| Alan Stern and ] introduced a parameter {{math|Λ}} (upper case ]) in 2000, expressing the likelihood of an encounter resulting in a given deflection of orbit.<ref name="Stern 2002">{{cite conference |last1=Stern |first1=S.A. |author1-link=Alan Stern |last2=Levison |first2=H.F. |author2-link=Harold F. Levison |date=August 7–18, 2000 |publication-date=2002 |title=Regarding the criteria for planethood and proposed planetary classification schemes |journal=Highlights of Astronomy |volume=12 |pages=205–213 |conference=XXIVth General Assembly of the IAU – 2000 |place=Manchester, UK |bibcode=2002HiA....12..205S |doi=10.1017/S1539299600013289 |doi-access=free |url=http://www.boulder.swri.edu/~hal/PDF/planet_def.pdf |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-date=September 23, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923220319/http://www.boulder.swri.edu/~hal/PDF/planet_def.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> The value of this parameter in Stern's model is proportional to the square of the mass and inversely proportional to the period. This value can be used to estimate the capacity of a body to ] of its orbit, where {{math| Λ > 1 }} will eventually clear it. A gap of five orders of magnitude in {{math|Λ}} was found between the smallest ]s and the largest asteroids and Kuiper belt objects.<ref name=soter/> | |||
| Using this parameter, ] and other astronomers argued for a distinction between dwarf planets and the other eight planets based on their inability to "clear the neighbourhood around their orbits": planets are able to remove smaller bodies near their orbits by collision, capture, or gravitational disturbance, (or establish orbital resonances that prevent collisions), while dwarf planets lack the mass to do so.<ref name=Stern>{{cite journal|last=Stern|first=S. Alan|coauthors=Levison, Harold F.|year=2002|title=Regarding the criteria for planethood and proposed planetary classification schemes|url=http://www.boulder.swri.edu/~hal/PDF/planet_def.pdf|format=PDF|journal=Highlights of Astronomy|volume=12|pages=205–13, as presented at the XXIVth General Assembly of the IAU–2000 Manchester, UK, 7–18 August 2000|accessdate=2008-01-22}}</ref> Soter went on to propose a parameter he called the ''planetary discriminant'', designated with the symbol µ (]), that represents an experimental measure of the actual degree of cleanliness of the orbital zone (where µ is calculated by dividing the mass of the candidate body by the total mass of the other objects that share its orbital zone).<ref name=soter>{{cite journal|id={{arxiv|astro-ph/0608359}}|title=What is a Planet?|journal=The Astronomical Journal|first=Steven|last=Soter|date=2006-08-16|volume=132|pages=2513–19|accessdate=2008-01-22|doi=10.1086/508861}}</ref> There are several other schemes that try to differentiate between planets and dwarf planets,<ref name=Stern/> but the 2006 definition uses this concept.<ref name=finalresolution/> | |||
| Using this parameter, ] and other astronomers argued for a distinction between planets and dwarf planets based on the inability of the latter to "clear the neighbourhood around their orbits": planets are able to remove smaller bodies near their orbits by collision, capture, or gravitational disturbance (or establish orbital resonances that prevent collisions), whereas dwarf planets lack the mass to do so.<ref name="Stern 2002"/> Soter went on to propose a parameter he called the ''planetary discriminant'', designated with the symbol {{mvar|µ}} (]), that represents an experimental measure of the actual degree of cleanliness of the orbital zone (where {{mvar|µ}} is calculated by dividing the mass of the candidate body by the total mass of the other objects that share its orbital zone), where {{nobr| {{math| ''µ'' > 100 }} }} is deemed to be cleared.<ref name=soter>{{cite journal |first=S. |last=Soter |author-link=Steven Soter |date=August 16, 2006 |title=What is a Planet? |journal=] |volume=132 |issue=6 |pages=2513–2519 |doi=10.1086/508861 |bibcode=2006AJ....132.2513S |s2cid=14676169 |arxiv=astro-ph/0608359 }}</ref> | |||
| ] refined Stern and Levison's concept to produce a similar parameter {{math|Π}} (upper case ]).<ref name="Margot 2015"/> It is based on theory, avoiding the empirical data used by {{math|Λ .}} {{nobr| {{math| Π > 1 }} }} indicates a planet, and there is again a gap of several orders of magnitude between planets and dwarf planets. | |||
| There are several other schemes that try to differentiate between planets and dwarf planets,<ref name="Stern">{{cite news |first=Paul |last=Rincon |date=August 25, 2006 |title=Pluto vote 'hijacked' in revolt |agency=] |publisher=] |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5283956.stm |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-date=July 23, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110723033823/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5283956.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> but the 2006 definition uses this concept.<ref name=finalresolution/> | |||
| === |
=== Hydrostatic equilibrium === | ||
| {{Main|Hydrostatic equilibrium}} | {{Main|Hydrostatic equilibrium}} | ||
| {{Image frame | |||
| When an object achieves hydrostatic equilibrium, also known as gravitational relaxation, there are no gravitational imbalances in its surface. A global layer of liquid placed on this surface (assuming for argument's sake it would remain a liquid) would form a liquid surface of the same shape, apart from small-scale surface features such as craters and fissures. This does not mean the body is a sphere; the faster a body rotates, the more ] or even ] it becomes, but such forces affect a liquid surface as well. The extreme example of a non-spherical body in hydrostatic equilibrium is {{dp|Haumea}}, which is twice as long along its major axis as it is at the poles. | |||
| |content={{Graph:Chart | |||
| | width=200 | |||
| | height=200 | |||
| | type=rect | |||
| | x = Eris, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Charon, Quaoar, Ceres, Orcus, Salacia | |||
| | y1 = 16.6, 13.03, 4.01, 3.1, 1.75, 1.586, 1.4, 0.938, 0.61, 0.492 | |||
| | showValues=offset:1,format:.2 | |||
| | xAxisAngle = 45 | |||
| }} | |||
| |width=240 | |||
| |caption=Comparative masses of the likeliest dwarf planets, with ] for comparison. The unit of mass is ~{{10^|21}} kg. ] and Pluto dominate. Unmeasured ] is excluded, but is likely on the order of Ceres. The Moon in contrast is 73.5×{{10^|21}}, over four times more massive than Eris. | |||
| |border=no | |||
| }} | |||
| Enough internal pressure, caused by the body's gravitation, will turn a body ], and enough plasticity will allow high elevations to sink and hollows to fill in, a process known as gravitational relaxation. Bodies smaller than a few kilometers are dominated by non-gravitational forces and tend to have an irregular shape and may be rubble piles. Larger objects, where gravity is significant but not dominant, are potato-shaped; the more massive the body, the higher its internal pressure, the more solid it is and the more rounded its shape, until the pressure is enough to overcome its ] and it achieves ]. Then, a body is as round as it is possible to be, given its rotation and tidal effects, and is an ] in shape. This is the defining limit of a dwarf planet.<ref>{{cite conference |first1=Charles H. |last1=Lineweaver |first2=Marc |last2=Norman |date=September 28–30, 2009 |publication-date=2010 |title=The potato radius: A lower minimum size for dwarf planets |editor-last1=Short |editor-first1=W. |editor-last2=Cairns |editor-first2=I. |conference=9th Australian Space Science Conference |book-title=Proceedings of 2009 Australian Space Science Conference |pages=67–78 |publisher=] |arxiv=1004.1091 |isbn=9780977574032 |url=https://www.mso.anu.edu.au/~charley/papers/Potato%20Radiusv8.pdf |access-date=August 11, 2023 |archive-date=March 10, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230310103945/https://www.mso.anu.edu.au/~charley/papers/Potato%20Radiusv8.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The upper and lower size and mass limits of dwarf planets have not been specified by the IAU. There is no defined upper limit, and an object larger or more massive than ] that has not "cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit" would be classified as a dwarf planet.<ref>Indeed, Mike Brown has set out to find such an object. ({{cite web|title= Julia Sweeney and Michael E. Brown|work= Hammer Conversations: KCET podcast|url=http://www.pluggd.tv/audio/channels/kcet_podcast__hammer_conversations/episodes/2h10l|year=2007|accessdate=2008-06-28}})</ref> The lower limit is determined by the requirements of achieving a hydrostatic equilibrium shape, but the size or mass at which an object attains this shape depends on its composition and thermal history. The original draft of the 2006 IAU resolution redefined hydrostatic equilibrium shape as applying "to objects with mass above 5{{e|20}} kg and diameter greater than 800 km",<ref name="Draft Resolution 5">{{cite web|title=The IAU draft definition of "planet" and "plutons"|url=http://www.iau.org/public_press/news/release/iau0601/|publisher=International Astronomical Union|date=2006-08-16|accessdate=2008-05-17}}</ref> but this was not retained in the final draft.<ref name=finalresolution/> | |||
| If an object is in hydrostatic equilibrium, a global layer of liquid on its surface would form a surface of the same shape as the body, apart from small-scale surface features such as craters and fissures. The body will have a spherical shape if it does not rotate and an ellipsoidal one if it does. The faster it rotates, the more ] or even ] it becomes. If such a rotating body were heated until it melts, its shape would not change. The extreme example of a body that may be scalene due to rapid rotation is {{dp|Haumea}}, which is twice as long on its major axis as it is at the poles. If the body has a massive nearby companion, then tidal forces gradually slow its rotation until it is tidally locked; that is, it always presents the same face to its companion. Tidally locked bodies are also scalene, though sometimes only slightly so. Earth's ] is tidally locked, as are all the rounded satellites of the gas giants. Pluto and Charon are tidally locked to each other, as are Eris and ], and probably also Orcus and ]. | |||
| Empirical observations suggest that the lower limit may vary according to the composition of the object. For example, in the asteroid belt, Ceres, with a diameter of 975 km, is the only object presently known to be self-rounded, while ] at approximately 600 km appears to be partially but incompletely differentiated. Therefore, it has been suggested that the limit where other rocky-ice bodies like Ceres become rounded might be somewhere around 900 km.<ref name=Brown/> The rocky body Vesta, at 530 km appears to have achieved equilibrium, only to have it disrupted by a massive impact after it solidified. More icy bodies like ]s have less rigid interiors and therefore more easily relax under their self-gravity into a rounded shape.<ref name=Brown/> The smallest icy body known to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium is ], while the largest irregular one is ]; both average slightly more than 400 km (250 mi) in diameter. ] (a leading researcher in this field and discoverer of Eris) suggests that the lower limit for an icy dwarf planet is therefore likely to be somewhere under 400 km.<ref name=Brown/> | |||
| There are no specific size or mass limits of dwarf planets, as those are not defining features. There is no clear upper limit: an object very far out in the Solar System that is more massive than ] might not have had time to clear its neighbourhood, and such a body would fit the definition of dwarf planet rather than planet. Indeed, Mike Brown set out to find such an object.<ref>{{cite AV media |people=] (interviewer & host), ] (interviewed astronomer) |date=June 28, 2007 |title=Julia Sweeney and Michael E. Brown |series=Hammer Conversations |publisher=] |medium=podcast |quote=Actress and comedienne ] (''God Said Ha!'') discusses the discovery that dwarfed Pluto with ] astronomer ]. |url=http://www.pluggd.tv/audio/channels/kcet_podcast__hammer_conversations/episodes/2h10l |access-date=June 28, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080626220548/http://www.pluggd.tv/audio/channels/kcet_podcast__hammer_conversations/episodes/2h10l <!--Added by H3llBot--> |archive-date=June 26, 2008}}</ref> The lower limit is determined by the requirements of achieving and retaining hydrostatic equilibrium, but the size or mass at which an object attains and retains equilibrium depends on its composition and thermal history, not simply its mass. An ] 2006 press release<ref name="Q&A"/> question-and-answer section estimated that objects with mass above {{val|0.5|e=21|u=kg}} and ] would "normally" be in hydrostatic equilibrium (''the shape ... would normally be determined by self-gravity''), but that ''all borderline cases would need to be determined by observation''.<ref name="Q&A">{{cite press release |title='Planet definition' questions & answers sheet |publisher=] |date=August 24, 2006 |url=https://www.iau.org/static/archives/releases/doc/iau0601_q_answers.doc |access-date=October 16, 2021 |archive-date=May 7, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210507125920/https://www.iau.org/static/archives/releases/doc/iau0601_q_answers.doc |url-status=live }}</ref> This is close to what as of 2019 is believed to be roughly the limit for objects beyond Neptune that are fully compact, solid bodies, with {{dp|Salacia}} {{nobr|( {{mvar|r}} {{=}} {{val|423|11|u=km}} ,}} {{nobr| {{mvar|m}} {{=}} {{val|0.492|0.007|e=21|u=kg}} )}} being a borderline case both for the 2006 Q&A expectations and in more recent evaluations, and with {{dp|Orcus}} being just above the expected limit.<ref name=Grundy2019/> No other body with a measured mass is close to the expected mass limit, though ] approach the expected size limit. | |||
| It is also not clear to what extent deviations from perfect equilibrium are to be tolerated, or whether ''having'' achieved equilibrium is sufficient for inclusion. All solid bodies in the solar system, such as ] with its equatorial ridge and ] with its shield volcanoes, deviate to some extent. This may be a critical for the consideration of the asteroid ], which may deviate from equilibrium due to a large impact that removed part of one hemisphere. | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| == Population of dwarf planets == | |||
| ==Current members== | |||
| {{Main|List of possible dwarf planets}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Though the definition of a dwarf planet is clear, evidence about whether a given trans-Neptunian object is large and malleable enough to be shaped by its own gravitational field is often inconclusive. There are also outstanding questions relating to the interpretation of the IAU criterion in certain instances. Consequently the number of currently conformed TNOs which meet the hydrostatic equilibrium criterion is uncertain. | |||
| {{FixBunching|beg}} | |||
| ] with its moons, Hiʻiaka and Namaka (artist's conception)]] | |||
| ] (artist's conception)]] | |||
| ] (through the ])]] | |||
| {{FixBunching|end}} | |||
| {{FixBunching|beg}} | |||
| ] (through the Hubble Space Telescope)]] | |||
| ] (approximate true color)]] | |||
| {{FixBunching|end}} | |||
| The three objects under consideration during the debates leading up to the 2006 IAU acceptance of the category of dwarf planet – Ceres, Pluto and Eris – are generally accepted as dwarf planets, including by those astronomers who continue to classify dwarf planets as planets. Only one of them – Pluto – has been observed in enough detail to verify that its current shape fits what would be expected from hydrostatic equilibrium.<ref name="Nimmo2017"> | |||
| As of 2008, the IAU has classified five celestial bodies as dwarf planets. Two of these, Ceres and Pluto, are known to qualify as dwarf planets through direct observation. The other three, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake, are thought to be dwarf planets from mathematical modeling—or in the case of Eris, because it is larger than Pluto—and qualify for the classification under IAU naming rules based on their magnitudes.<ref name=WGPSN>{{cite web |date= 2008-07-11 <!--11:42:58 -->|title=Dwarf Planets and their Systems |publisher= Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN) |url=http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/append7.html#DwarfPlanets |accessdate=2008-07-13}}</ref><ref name="Resolution Result">{{cite web|title=IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes|url=http://www.iau2006.org/mirror/www.iau.org/iau0603/index.html|publisher=International Astronomical Union|date=2006-08-26|accessdate=2008-01-26| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20071025051134/http://www.iau2006.org/mirror/www.iau.org/iau0603/index.html| archivedate = October 25, 2007}}</ref> | |||
| {{cite journal |last1=Nimmo |first1=Francis |display-authors=etal |title=Mean radius and shape of Pluto and Charon from New Horizons images|journal=Icarus |date=2017 |volume=287 |pages=12–29 |doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2016.06.027|bibcode=2017Icar..287...12N |arxiv=1603.00821|s2cid=44935431 }}</ref> Ceres is close to equilibrium, but some gravitational anomalies remain unexplained.<ref name=EPSC>{{cite book|chapter-url=https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EPSC2018/EPSC2018-645-1.pdf|display-authors=4|author1=Raymond, C.|author2=Castillo-Rogez, J.C.|author3=Park, R.S.|author4=Ermakov, A.|author5=Bland, M.T.|author6=Marchi, S.|author7=Prettyman, T.|author8=Ammannito, E.|author9=De Sanctis, M.C.|author10=Russell, C.T.|date=September 2018|chapter=Dawn Data Reveal Ceres' Complex Crustal Evolution|title=European Planetary Science Congress|volume=12|access-date=July 19, 2020|archive-date=January 30, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200130111631/https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EPSC2018/EPSC2018-645-1.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> Eris is generally assumed to be a dwarf planet because it is more massive than Pluto. | |||
| In order of discovery, these three bodies are: | |||
| #{{dp|Ceres}} ] – discovered on January 1, 1801 (45 years before ]), considered a planet for half a century before reclassification as an asteroid. Classified as a dwarf planet on September 13, 2006. | |||
| #{{dp| |
# {{dp|Ceres}} – discovered January 1, 1801, and announced January 24, 45 years before ]. Considered a planet for half a century before reclassification as an asteroid. Considered a dwarf planet by the IAU since the adoption of Resolution 5A on August 24, 2006. | ||
| # {{dp|Pluto}} – discovered February 18, 1930, and announced March 13. Considered a planet for 76 years. Explicitly reclassified as a dwarf planet by the IAU with Resolution 6A on August 24, 2006.<ref>'Pluto is a "dwarf planet" by the above definition and is recognized as the prototype of a new category of trans-Neptunian objects'</ref> Five known moons. | |||
| #{{dp|Eris}} – discovered on January 5, 2005. Called the "]" in media reports. Accepted as a dwarf planet on September 13, 2006. | |||
| # {{dp|Eris}} ({{mp|2003 UB|313}}) – discovered January 5, 2005, and announced July 29. Called the "]" in media reports. Considered a dwarf planet by the IAU since the adoption of Resolution 5A on August 24, 2006, and named by the IAU dwarf-planet naming committee on September 13 of that year. One known moon. | |||
| #{{dp|Makemake}} – discovered on March 31, 2005. Accepted as a dwarf planet on July 11, 2008. | |||
| #{{dp|Haumea}} – discovered on December 28, 2004. Accepted as a dwarf planet on September 17, 2008. | |||
| The IAU only established guidelines for which committee would oversee the naming of likely dwarf planets: any unnamed trans-Neptunian object with an ] brighter than +1 (and hence a minimum diameter of 838 km at the maximum ] of 1)<ref name="bruton">{{cite web |title=Conversion of Absolute Magnitude to Diameter for Minor Planets |publisher=Department of Physics & Astronomy (Stephen F. Austin State University) |author=Dan Bruton |url=http://www.physics.sfasu.edu/astro/asteroids/sizemagnitude.html |access-date=June 13, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100323180835/http://www.physics.sfasu.edu/astro/asteroids/sizemagnitude.html |archive-date=March 23, 2010 }}</ref> was to be named by a joint committee consisting of the ] and the planetary working group of the IAU.<ref name=IAU2008/> At the time (and still as of 2023), the only bodies to meet this threshold were {{dp|Haumea}} and {{dp|Makemake}}. These bodies are generally assumed to be dwarf planets, although they have not yet been demonstrated to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, and there is some disagreement for Haumea:<ref name="Ortiz2017">{{cite journal | |||
| No ]s have ] any of the dwarf planets. This will change if ]'s '']'' and '']'' missions reach Ceres and Pluto, respectively, as planned in 2015.<ref name=Russel2006>{{cite journal|last=Russel|first=C.T.|coauthors=Capaccioni, F.; Coradini, A.; et al.|title=Dawn Discovery mission to Vesta and Ceres: Present status|journal=Advances in Space Research|volume=38|pages=2043–48|year=2006|doi=10.1016/j.asr.2004.12.041| bibcode=2006AdSpR..38.2043R| accessdate=2007-12-08}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Pluto Mission a Go! Initial Funding Secured|first=Robert Roy|last=Britt|publisher=Space.com| url=http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/pluto_horizons_030225.html| year=2003|accessdate=2007-04-13}}</ref> ''Dawn'' is also slated to orbit and observe another potential dwarf planet, ], in 2011. | |||
| | display-authors = etal | |||
| | last1 = Ortiz | |||
| | first1 = J. L. | |||
| | last2 = Santos-Sanz | |||
| | first2 = P. | |||
| | last3 = Sicardy | |||
| | first3 = B. | |||
| | last4 = Benedetti-Rossi | |||
| | first4 = G. | |||
| | last5 = Bérard | |||
| | first5 = D. | |||
| | last6 = Morales | |||
| | first6 = N. | |||
| | title = The size, shape, density and ring of the dwarf planet Haumea from a stellar occultation | |||
| | url = http://www.astrosurf.com/sogorb/occultations/nature24051.pdf | |||
| | journal = Nature | |||
| | volume = 550 | |||
| | issue = 7675 | |||
| | year = 2017 | |||
| | pages = 219–223 | |||
| | doi = 10.1038/nature24051 | |||
| | pmid = 29022593 | |||
| | bibcode = 2017Natur.550..219O | |||
| | arxiv = 2006.03113 | |||
| | hdl = 10045/70230 | |||
| | s2cid = 205260767 | |||
| | hdl-access = free | |||
| | access-date = January 14, 2022 | |||
| | archive-date = November 7, 2020 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20201107052958/http://www.astrosurf.com/sogorb/occultations/nature24051.pdf | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref><ref name="Dunham2019"> | |||
| {{cite journal | |||
| | title = Haumea's Shape, Composition, and Internal Structure | |||
| | author1 = Dunham, E. T. | |||
| | author2 = Desch, S. J. | |||
| | author3 = Probst, L. | |||
| | date = April 2019 | |||
| | journal = The Astrophysical Journal | |||
| | volume = 877 | |||
| | issue = 1 | |||
| | pages = 11 | |||
| | doi = 10.3847/1538-4357/ab13b3 | |||
| | bibcode = 2019ApJ...877...41D | |||
| | arxiv = 1904.00522 | |||
| | s2cid = 90262114 | |||
| | doi-access = free | |||
| }} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| {{ordered list|start=4 | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto" | |||
| | {{dp|Haumea}} ({{mp|2003 EL|61}}) – discovered by Brown et al. December 28, 2004, and announced by Ortiz et al. on July 27, 2005. Named by the IAU dwarf-planet naming committee on September 17, 2008. Two known moons and one known ring. | |||
| |- bgcolor=#ccccff | |||
| | {{dp|Makemake}} ({{mp|2005 FY|9}}) – discovered March 31, 2005, and announced July 29. Named by the IAU dwarf-planet naming committee on July 11, 2008. One known moon. | |||
| ! colspan=12 style="background:#dddddd;" | Orbital attributes of dwarf planets<ref name=asteroidorbit>{{cite web|url=ftp://ftp.lowell.edu/pub/elgb/astorb.html| title=The Asteroid Orbital Elements Database|first=Ted|last=Bowell|publisher=]|accessdate=2008-02-12}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| |- style="font-size: smaller;" | |||
| !Name | |||
| These five bodies – the three under consideration in 2006 (Pluto, Ceres and Eris) plus the two named in 2008 (Haumea and Makemake) – are commonly presented as the dwarf planets of the Solar System, though the limiting factor (albedo) is not what defines an object as a dwarf planet.<ref name="WGPSN">{{cite web |date=July 11, 2008 <!--11:42:58 --> |title=Dwarf Planets and their Systems |publisher=Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN) |url=http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/append7.html#DwarfPlanets |access-date=September 12, 2019 |archive-date=July 14, 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070714225312/http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/append7.html#DwarfPlanets |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| !Region of<br />Solar System | |||
| !Orbital<br />radius (]) | |||
| The astronomical community commonly refers to other larger TNOs as dwarf planets as well.<ref name=Pinilla-Alonso>{{cite book |last1=Pinilla-Alonso |first1= Noemi |last2=Stansberry |first2= John A. |last3= Holler |first3= Bryan J. |date=November 22, 2019 |chapter=Surface properties of large TNOs: Expanding the study to longer wavelengths with the James Webb Space Telescope |arxiv=1905.12320 |title= The Transneptunian Solar System |editor= Dina Prialnik |editor2=Maria Antonietta Barucci |editor3=Leslie Young |publisher= Elsevier}}</ref> At least four additional bodies meet the preliminary criteria of Brown, of Tancredi et al., of Grundy et al., and of Emery et al. for identifying dwarf planets, and are generally called dwarf planets by astronomers as well: | |||
| !]<br />(years) | |||
| !Mean orbital<br />speed (km/s) | |||
| {{ordered list|start=6 | |||
| !] (°) | |||
| | {{dp|Quaoar}} ({{mp|2002 LM|60}}) – discovered June 5, 2002, and announced October 7 of that year.<!--per Govert Schilling, ''The Hunt for Planet X: New Worlds and the Fate of Pluto'', p. 289, autocorrected? to "Quasar"--> One known moon and two known rings. | |||
| !] | |||
| | {{dp|Sedna}} ({{mp|2003 VB|12}}) – discovered November 14, 2003, and announced March 15, 2004.<!--per Govert Schilling, ''The Hunt for Planet X: New Worlds and the Fate of Pluto'', p. 289--> | |||
| !] | |||
| | {{dp|Orcus}} ({{mp|2004 DW}}) – discovered February 17, 2004, and announced two days later.<!--per Govert Schilling, ''The Hunt for Planet X: New Worlds and the Fate of Pluto'', p. 289--> One known moon. | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| | {{dp|Gonggong}} ({{mp|2007 OR|10}}) – discovered July 17, 2007, and announced January 2009. One known moon. | |||
| ! align="left" | ] | |||
| }} | |||
| For instance, JPL/NASA called ] a dwarf planet after observations in 2016,<ref name=OR10>{{cite web |url=https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=6509 |title=2007 OR10: Largest Unnamed World in the Solar System |website=Jet Propulsion Laboratory |first=Preston |last=Dyches |date=May 11, 2016 |access-date=September 12, 2019 |archive-date=November 23, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201123155324/https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=6509 |url-status=live }}</ref> and Simon Porter of the Southwest Research Institute spoke of "the big eight dwarf planets" in 2018, referring to Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, {{dp|Quaoar}}, {{dp|Sedna}} and {{dp|Orcus}}.<ref name="PorterTwitter">{{cite web | |||
| | first = Simon | |||
| | last = Porter | |||
| | url = https://twitter.com/AscendingNode/status/978592143626375169 | |||
| | title = #TNO2018 | |||
| | publisher = Twitter | |||
| | date = March 27, 2018 | |||
| | access-date = March 27, 2018 | |||
| | archive-date = October 2, 2018 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20181002133130/https://twitter.com/AscendingNode/status/978592143626375169 | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref> The IAU itself has called Quaoar a dwarf planet in a 2022–2023 annual report.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.iau.org/static/science/scientific_bodies/divisions/f/division-f-annual-report-2022-2023.pdf |title=Report of Division F "Planetary Systems and Astrobiology": Annual Report 2022-23 |last= |first= |date=2022–2023 |website= |publisher=International Astronomical Union |access-date=December 8, 2023 |quote= |archive-date=December 8, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231208112824/https://www.iau.org/static/science/scientific_bodies/divisions/f/division-f-annual-report-2022-2023.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| More bodies have been proposed, such as {{dp|Salacia}} and {{mpl|(307261) 2002 MS|4}} by Brown; {{dp|Varuna}} and {{dp|Ixion}} by Tancredi et al., and {{mpl|(532037) 2013 FY|27}} by ] et al.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sheppard |first1=Scott S. |last2=Fernandez |first2=Yanga R. |first3=Arielle |last3=Moullet |date=November 16, 2018 |title=The Albedos, Sizes, Colors, and Satellites of Dwarf Planets Compared with Newly Measured Dwarf Planet 2013 FY27 |journal=The Astronomical Journal |volume=156 |issue=6 |page=270 |doi=10.3847/1538-3881/aae92a |arxiv=1809.02184 |bibcode=2018AJ....156..270S |s2cid=119522310 |doi-access=free }}</ref> Most of the larger bodies have moons, which enables a determination of their mass and thus their density, which inform estimates of whether they could be dwarf planets. The largest TNOs that are not known to have moons are Sedna, {{mpl|(307261) 2002 MS|4}}, {{mpl|(55565) 2002 AW|197}} and Ixion. In particular, Salacia has a known mass and diameter, putting it as a borderline case by the IAU's 2006 Q&A. | |||
| {{ordered list|start=10 | |||
| | {{dp|Salacia}} ({{mp|2004 SB|60}}) – discovered September 22, 2004. One known moon. | |||
| }} | |||
| At the time Makemake and Haumea were named, it was thought that ]s (TNOs) with icy cores would require a diameter of only about 400 km (250 mi), or 3% the size of Earth{{snd}}the size of the moons ], the smallest moon that is round, and ], the largest that is not{{snd}}to relax into gravitational equilibrium.<ref name="Brown" /> Researchers thought that the number of such bodies could prove to be around 200 in the ], with thousands more beyond.<ref name="Brown">{{cite web |author-link=Michael E. Brown |title=The Dwarf Planets |first=Michael E. |last=Brown |publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences |url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dwarfplanets/ |access-date=January 26, 2008 |archive-date=July 19, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110719164447/http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dwarfplanets/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="BrownList">{{cite web |last=Brown |first=Mike |author-link=Michael E. Brown |title=How many dwarf planets are there in the outer solar system? |url=http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dps.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111018154917/http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dps.html |archive-date=October 18, 2011 |url-status=live |access-date=November 15, 2013 |website=CalTech}}</ref><ref name=Stern2012>{{cite web |last=Stern |first=Alan |author-link=Alan Stern |date=August 24, 2012 |title=The PI's Perspective. |url=https://pluto.jhuapl.edu/overview/piPerspective.php?page=piPerspective_08_24_2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141113225430/http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/overview/piPerspective.php?page=piPerspective_08_24_2012 |archive-date=November 13, 2014 |access-date=August 24, 2012}}</ref> | |||
| This was one of the reasons (keeping the roster of 'planets' to a reasonable number) that Pluto was reclassified in the first place. | |||
| Research since then has cast doubt on the idea that bodies that small could have achieved or maintained equilibrium under the typical conditions of the Kuiper belt and beyond. | |||
| Individual astronomers have recognized a number of objects as dwarf planets or as likely to prove to be dwarf planets. In 2008, ] et al. advised the IAU to officially accept Orcus, Sedna and Quaoar as dwarf planets (Gonggong was not yet known), though the IAU did not address the issue then and has not since. Tancredi also considered the five TNOs {{dp|Varuna}}, {{dp|Ixion}}, {{mpl-|208996|2003 AZ|84}}, {{mpl-|90568|2004 GV|9}}, and {{mpl-|55565|2002 AW|197}} to most likely be dwarf planets as well.<ref name=Tancredi2008>{{Cite journal |last1=Tancredi |first1=G. |last2=Favre |first2=S. A. |doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2007.12.020 |title=Which are the dwarfs in the Solar System? |journal=] |volume=195 |issue=2 |pages=851–862 |year=2008 |bibcode=2008Icar..195..851T}}</ref> | |||
| Since 2011, Brown has maintained a list of hundreds of candidate objects, ranging from "nearly certain" to "possible" dwarf planets, based solely on estimated size.<ref name=free>{{cite web |last=Brown |first=Michael |author-link=Michael E. Brown |date=August 23, 2011 |title=Free the Dwarf Planets! |url=http://www.mikebrownsplanets.com/2011/08/free-dwarf-planets.html |website=Mike Brown's Planets |access-date=August 24, 2011 |archive-date=October 5, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111005064654/http://www.mikebrownsplanets.com/2011/08/free-dwarf-planets.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| As of September 13, 2019, Brown's list identifies ten ]s with diameters then thought to be greater than 900 km (the four named by the IAU plus {{dp|Gonggong}}, {{dp|Quaoar}}, {{dp|Sedna}}, {{dp|Orcus}}, {{mpl|(307261) 2002 MS|4}}, and {{dp|Salacia}}) as "near certain" to be dwarf planets, and another 16, with diameter greater than 600 km, as "highly likely".<ref name="BrownList"/> Notably, Gonggong may have a larger diameter ({{val|1230|50|u=km}}) than Pluto's round moon Charon (1212 km). | |||
| But in 2019 Grundy et al. proposed, based on their studies of ], that dark, low-density bodies smaller than about 900–1000 km in diameter, such as Salacia and {{dp|Varda}}, never fully collapsed into solid planetary bodies and retain internal porosity from their formation (in which case they could not be dwarf planets). They accept that brighter (albedo > ≈0.2)<ref>Of bodies smaller than 900 km in diameter, the only ones thought to have albedos much greater than this are fragments in the ] and possibly {{mpl|2005 QU|182}} (albedo between 0.2 and 0.5).</ref> or denser (> ≈1.4 g/cc) Orcus and Quaoar probably were fully solid:<ref name=Grundy2019>{{cite journal | |||
| |first1=W.M. |last1=Grundy | |||
| |first2=K.S. |last2=Noll | |||
| |first3=M.W. |last3=Buie | |||
| |first4=S.D. |last4=Benecchi | |||
| |first5=D. |last5=Ragozzine | |||
| |first6=H.G. |last6=Roe | |||
| |title=The Mutual Orbit, Mass, and Density of Transneptunian Binary Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà ({{mp|(229762) 2007 UK|126}}) | |||
| |url=http://www2.lowell.edu/users/grundy/abstracts/2019.G-G.html | |||
| |journal=Icarus | |||
| |doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2018.12.037 | |||
| |year= 2019 | |||
| |volume=334 | |||
| |pages=30–38 | |||
| |bibcode=2019Icar..334...30G | |||
| |s2cid=126574999 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190407045339/http://www2.lowell.edu/~grundy/abstracts/preprints/2019.G-G.pdf | |||
| |url-status=live | |||
| |archive-date=April 7, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| {{blockquote|Orcus and Charon probably melted and differentiated, considering their higher densities and spectra indicating surfaces made of relatively clean H<sub>2</sub>O ice. But the lower albedos and densities of ], ], Varda, and Salacia suggest that they never did differentiate, or if they did, it was only in their deep interiors, not a complete melting and overturning that involved the surface. Their surfaces could remain quite cold and uncompressed even as the interior becomes warm and collapses. The liberation of volatiles could further help transport heat out of their interiors, limiting the extent of their internal collapse. An object with a cold, relatively pristine surface and a partially collapsed interior should exhibit very distinctive surface geology, with abundant thrust faults indicative of the reduction in total surface area as the interior compresses and shrinks.<ref name=Grundy2019/>}} | |||
| Salacia was later found to have a somewhat higher density, comparable within uncertainties to that of Orcus, though still with a very dark surface. Despite this determination, Grundy et al. call it "dwarf-planet sized", while calling Orcus a dwarf planet.<ref name="Grundy-orbits">{{cite journal | |||
| |title=Mutual Orbit Orientations of Transneptunian Binaries | |||
| |url=http://www2.lowell.edu/users/grundy/abstracts/preprints/2019.TNB_orbits.pdf | |||
| |first1=W. M. | |||
| |last1=Grundy | |||
| |first2=K. S. | |||
| |last2=Noll | |||
| |first3=H. G. | |||
| |last3=Roe | |||
| |first4=M. W. | |||
| |last4=Buie | |||
| |first5=S. B. | |||
| |last5=Porter | |||
| |first6=A. H. | |||
| |last6=Parker | |||
| |first7=D. | |||
| |last7=Nesvorný | |||
| |first8=S. D. | |||
| |last8=Benecchi | |||
| |first9=D. C. | |||
| |last9=Stephens | |||
| |first10=C. A. | |||
| |last10=Trujillo | |||
| |journal=Icarus | |||
| |volume=334 | |||
| |pages=62–78 | |||
| |year=2019 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2019.03.035 | |||
| |bibcode=2019Icar..334...62G | |||
| |s2cid=133585837 | |||
| |issn=0019-1035 | |||
| |access-date=October 26, 2019 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200115091416/http://www2.lowell.edu/~grundy/abstracts/preprints/2019.TNB_orbits.pdf | |||
| |archive-date=January 15, 2020 | |||
| |url-status=dead | |||
| }}</ref> Later studies on Varda suggest that its density may also be high, though a low density could not be excluded.<ref name="Souami2020">{{cite journal | |||
| |display-authors = etal | |||
| |first1 = D. |last1 = Souami | |||
| |first2 = F. |last2 = Braga-Ribas | |||
| |first3 = B. |last3 = Sicardy | |||
| |first4 = B. |last4 = Morgado | |||
| |first5 = J. L. |last5 = Ortiz | |||
| |first6 = J. |last6 = Desmars | |||
| |date = August 2020 | |||
| |title = A multi-chord stellar occultation by the large trans-Neptunian object (174567) Varda | |||
| |journal = Astronomy & Astrophysics |volume = 643 |pages = A125 |doi = 10.1051/0004-6361/202038526 |arxiv = 2008.04818 | |||
| |bibcode = 2020A&A...643A.125S |s2cid = 221095753 }}</ref> | |||
| In 2023, Emery et al. wrote that ] ] by the ] (JWST) in 2022 suggests that Sedna, Gonggong, and Quaoar underwent internal melting, differentiation, and chemical evolution, like the larger dwarf planets Pluto, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake, but unlike "all smaller KBOs". This is because light hydrocarbons are present on their surfaces (e.g. ], ], and ]), which implies that methane is continuously being resupplied, and that methane would likely come from internal geochemistry. On the other hand, the surfaces of Sedna, Gonggong, and Quaoar have low abundances of CO and CO<sub>2</sub>, similar to Pluto, Eris, and Makemake, but in contrast to smaller bodies. This suggests that the threshold for dwarf planethood in the trans-Neptunian region is a diameter of ~900 km (thus including only Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Sedna), and that even Salacia may not be a dwarf planet.<ref name=JWST>{{cite journal|last1=Emery|first1=J. P. |first2=I. |last2=Wong |first3=R. |last3=Brunetto |first4=J. C. |last4=Cook |first5=N. |last5=Pinilla-Alonso |first6=J. A. |last6=Stansberry |first7=B. J. |last7=Holler |first8=W. M. |last8=Grundy |first9=S. |last9=Protopapa |first10=A. C. |last10=Souza-Feliciano |first11=E. |last11=Fernández-Valenzuela |first12=J. I. |last12=Lunine |first13=D. C. |last13=Hines |author-link=|date=2024|title=A Tale of 3 Dwarf Planets: Ices and Organics on Sedna, Gonggong, and Quaoar from JWST Spectroscopy|journal=Icarus |volume=414 |doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2024.116017 |arxiv=2309.15230|bibcode=2024Icar..41416017E }}</ref> A 2023 study of {{mp|(307261) 2002 MS|4}} shows that it probably has an extremely large crater, whose depth takes up 5.7% of its diameter: this is proportionally larger than the Rheasilvia crater on Vesta, which is the reason Vesta is not usually considered a dwarf planet today.<ref name="Rommel2023">{{cite journal | |||
| |display-authors = etal | |||
| |first1 = F. L. |last1 = Rommel | |||
| |first2 = F. |last2 = Braga-Ribas | |||
| |first3 = J. L. |last3 = Ortiz | |||
| |first4 = B. |last4 = Sicardy | |||
| |first5 = P. |last5 = Santos-Sanz | |||
| |first6 = J. |last6 = Desmars | |||
| |title = A large topographic feature on the surface of the trans-Neptunian object (307261) 2002 MS4 measured from stellar occultations | |||
| |journal = Astronomy & Astrophysics | |||
| |date = October 2023 | |||
| |volume = 678 | |||
| |id = A167 | |||
| |pages = 25 | |||
| |doi-access = free | |||
| |doi = 10.1051/0004-6361/202346892 | |||
| |arxiv = 2308.08062 | |||
| |bibcode = 2023A&A...678A.167R | |||
| |s2cid = 260926329}}</ref> | |||
| In 2024, Kiss et al. found that Quaoar has an ellipsoidal shape incompatible with hydrostatic equilibrium for its current spin. They hypothesised that Quaoar originally had a rapid rotation and was in hydrostatic equilibrium, but that its shape became "frozen in" and did not change as it spun down due to tidal forces from its moon ].<ref name="Kiss2024">{{cite journal | |||
| |display-authors = etal | |||
| |first1 = C. |last1 = Kiss | |||
| |first2 = T. G. |last2 = Müller | |||
| |first3 = G. |last3 = Marton | |||
| |first4 = R. |last4 = Szakáts | |||
| |first5 = A. |last5 = Pál | |||
| |first6 = L. |last6 = Molnár | |||
| |title = The visible and thermal light curve of the large Kuiper belt object (50000) Quaoar | |||
| |journal = Astronomy & Astrophysics | |||
| |date = March 2024 | |||
| |volume = 684 | |||
| |issue = | |||
| |pages = A50 |doi = 10.1051/0004-6361/202348054 | |||
| |arxiv = 2401.12679 | |||
| |bibcode = 2024A&A...684A..50K}}</ref> If so, this would resemble the situation of Saturn's moon ], which is too oblate for its current spin.<ref name="Science News">Cowen, R. (2007). Idiosyncratic Iapetus, ''Science News'' vol. 172, pp. 104–106. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071013165655/http://www.sciencenews.org/articles/20070818/bob8ref.asp |date=October 13, 2007 }}</ref><ref name="Thomas2010">{{cite journal| doi = 10.1016/j.icarus.2010.01.025| last1 = Thomas| first1 = P. C.| date = July 2010| title = Sizes, shapes, and derived properties of the saturnian satellites after the Cassini nominal mission| journal = Icarus| volume = 208| issue = 1| pages = 395–401| url = http://www.ciclops.org/media/sp/2011/6794_16344_0.pdf| bibcode = 2010Icar..208..395T| access-date = September 25, 2015| archive-date = December 23, 2018| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20181223003125/http://www.ciclops.org/media/sp/2011/6794_16344_0.pdf| url-status = dead}}</ref> Iapetus is generally still considered a ] nonetheless,<ref name=planetarysociety/> though not always.<ref name=ChenKipping>{{cite journal |last1=Chen |first1=Jingjing |last2=Kipping |first2=David |date=2016 |title=Probabilistic Forecasting of the Masses and Radii of Other Worlds |journal=The Astrophysical Journal |volume=834 |issue=1 |page=17 |doi= 10.3847/1538-4357/834/1/17|arxiv=1603.08614 |s2cid=119114880 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2017ApJ...834...17C }}</ref> | |||
| ===Most likely dwarf planets=== | |||
| {{main|List of possible dwarf planets}} | |||
| The trans-Neptunian objects in the following tables, except Salacia, are agreed by Brown, Tancredi et al., Grundy et al., and Emery et al. to be probable dwarf planets, or close to it. Salacia has been included as the largest TNO not generally agreed to be a dwarf planet; it is a borderline body by many criteria, and is therefore italicized. Charon, a moon of Pluto that was proposed as a dwarf planet by the IAU in 2006, is included for comparison. Those objects that have absolute magnitude greater than +1, and so meet the threshold of the joint planet–minor planet naming committee of the IAU, are highlighted, as is Ceres, which the IAU has assumed is a dwarf planet since they first debated the concept. | |||
| The masses of given dwarf planets are listed for their systems (if they have satellites) with exceptions for Pluto and Orcus. | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align: center" | |||
| |+ Orbital attributes | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope=col | Name | |||
| ! scope=col | Region of the<br /> Solar System | |||
| ! scope=col | Semi-major <br /> axis (]) | |||
| ! scope=col | ] <br /> (years) | |||
| ! scope=col | Mean orbital <br /> speed (km/s) | |||
| ! scope=col | ] | |||
| ! scope=col | ] | |||
| ! scope=col | ] | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | ] | |||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | 2. |
| 2.768 | ||
| | 4. |
| 4.604 | ||
| | 17. |
| 17.90 | ||
| | 10.59 | | 10.59° | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.079 | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.3 | ||
| |- | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| {{dp|Orcus}} | |||
| ! align=left| ] | |||
| | ] | | ] (] – ]) | ||
| | 39.40 | |||
| | 247.3 | |||
| | 4.75 | |||
| | 20.58° | |||
| | 0.220 | |||
| | 0.003 | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| ] | |||
| | ] (] – ]) | |||
| | 39.48 | | 39.48 | ||
| | |
| 247.9 | ||
| | 4. |
| 4.74 | ||
| | 17. |
| 17.16° | ||
| | 0.249 | | 0.249 | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.08 | ||
| |- align= |
|- align=center | ||
| ! |
! scope=row style="text-align: left"| ''{{dp|Salacia}}'' | ||
| | ] | | ] (]) | ||
| | |
| 42.18 | ||
| | |
| 274.0 | ||
| | 4. |
| 4.57 | ||
| | |
| 23.92° | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.106 | ||
| | |
| 0.003 | ||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | {{dp|Haumea}} | |||
| ! align="left" | ] | |||
| | ] | | ] (]) | ||
| | |
| 43.22 | ||
| | |
| 284.1 | ||
| | 4. |
| 4.53 | ||
| | 28. |
| 28.19° | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.191 | ||
| | |
| 0.02 | ||
| |- | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| {{dp|Quaoar}} | |||
| ! align="left" | ] | |||
| | ] (]) | |||
| | 43.69 | |||
| | 288.8 | |||
| | 4.51 | |||
| | 7.99° | |||
| | 0.040 | |||
| | 0.007 | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | ] | |||
| | ] (]) | |||
| | 45.56 | |||
| | 307.5 | |||
| | 4.41 | |||
| | 28.98° | |||
| | 0.158 | |||
| | 0.02 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| ] | |||
| | ] (]) | |||
| | 67.49 | |||
| | 554.4 | |||
| | 3.63 | |||
| | 30.74° | |||
| | 0.503 | |||
| | 0.01<!--per Eris--> | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | ] | |||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | 67. |
| 67.86 | ||
| | |
| 559.1 | ||
| | 3. |
| 3.62 | ||
| | 44. |
| 44.04° | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.441 | ||
| | 0. |
| 0.1 | ||
| |- | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| {{dp|Sedna}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 506.8 | |||
| |data-sort-value="11400"| ≈ 11,400 | |||
| |data-sort-value="1.3"| ≈ 1.3 | |||
| | 11.93° | |||
| | 0.855 | |||
| |data-sort-value="0.06"| < 0.07 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style=" |
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align: center" | ||
| |+ Other attributes | |||
| |- bgcolor=#ccccff | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan=14 style="background:#dddddd;" | Physical attributes of dwarf planets | |||
| ! scope=col width=54 |Name | |||
| |- style="font-size: smaller;" | |||
| ! scope=col | Diameter <br /> relative to <br /> the ] | |||
| !Name | |||
| ! scope=col | Diameter <br /> (km) | |||
| !Equatorial<br>diameter<br>relative to<br>the ] | |||
| ! |
! scope=col | Mass <br /> relative to <br /> the ] | ||
| ! scope=col | Mass <br /> ({{e|21}} kg) | |||
| !Mass<br> relative to<br> the ] | |||
| ! scope=col | ] <br /> (g/cm<sup>3</sup>) | |||
| !Mass<br />({{e|21}} kg) | |||
| ! scope=col | ] <br /> (hours) | |||
| !]<br />({{e|3}}g/m<sup>3</sup>) | |||
| ! scope=col | ] | |||
| !Surface<br />]<br />(]) | |||
| ! scope=col | ] | |||
| !]<br />(]) | |||
| ! scope=col | ] | |||
| !] | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| !]<br />(days) | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | ] | |||
| !] | |||
| | 27% | |||
| !Surface<br />]<br />(]) | |||
| | {{val|939.4|0.2}} | |||
| !] | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| ! align="left" | ]<ref>{{cite journal|first=P.C|last=Thomas|coauthors=Parker J.Wm.; McFadden, L.A.; et al.|title=Differentiation of the asteroid Ceres as revealed by its shape|year=2005|journal=Nature|volume=437|pages=224–26|doi=10.1038/nature03938| bibcode=2005Natur.437..224T|accessdate=2008-02-16|pmid=16148926|issue=7056}}</ref><ref>Calculated based on the known parameters. APmag and AngSize generated with (Ephemeris: Observer Table: Quantities = 9,13,20,29)</ref> | |||
| | 28% | |||
| | 974.6±3.2 | |||
| | 1.3% | | 1.3% | ||
| | {{val|0.93835|0.00001}} | |||
| | 0.95 | |||
| | 2. |
| {{val|2.16}} | ||
| | |
| {{val|9.1}} | ||
| | 0.51 | |||
| | ~3° | |||
| | 0.38 | |||
| | 0 | | 0 | ||
| | {{val|0.09}} | |||
| | 167 | |||
| | |
| 3.33 | ||
| |- | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | {{dp|Orcus}} | |||
| ! align=left| ]<ref>{{cite web|first=D.R.|last=Williams|title=Pluto Fact Sheet|publisher=NASA|date=2006-09-07|url=http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/factsheet/plutofact.html|accessdate=2007-03-24}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|first=M. W.|last=Buie|coauthors=Grundy, W.M.; Young, E.F.; Young, L.A.; Stern, S.A.|title = Orbits and photometry of Pluto's satellites: Charon, S/2005 P1, and S/2005 P2|journal=Astronomical Journal|year=2006|volume=132|pages=290|url=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-bib_query?bibcode=2006AJ....132..290B&db_key=AST&data_type=HTML&format=&high=444b66a47d27727|id={{Arxiv|archive=astro-ph|id=0512491}}|doi = 10.1086/504422}}</ref> | |||
| | |
| 26% | ||
| | {{val|910|50|40}} | |||
| | 2306±10 | |||
| | |
| 0.8% | ||
| | {{val|0.55|0.01}} | |||
| | 13.05 | |||
| | |
| {{val|1.4|0.2}} | ||
| | {{val|13|4}} | |||
| | 0.58 | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 1.2 | |||
| | {{val|0.23|0.02|0.01}} | |||
| | 119.59° | |||
| | |
| 2.19 | ||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| | ] | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| ] | |||
| | 44 | |||
| | 68% | |||
| | transient | |||
| | {{val|2377|3}} | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| | 17.7% | |||
| ! align=left| {{Dp|Haumea}}<ref name=Stansberry/><ref name="Rabinowitz2006">{{cite journal|first=David L.|last=Rabinowitz|coauthors=Barkume, K.M.; Brown, E.M. et al.|title=Photometric Observations Constraining the Size, Shape, and Albedo of {{mp|2003 EL|61}}, a Rapidly Rotating, Pluto-Sized Object in the Kuiper Belt''|journal=The Astrophysical Journal|year=2006|volume=639|issue=2|pages=1238–1251|id={{arxiv|astro-ph/0509401}}|doi=10.1086/499575}}</ref> | |||
| | {{val|13.03|0.03}} | |||
| | 33% | |||
| | |
| {{val|1.85}} | ||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|153.3}}"| 6d 9.3h | |||
| | 5.7% | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 4.2 ± 0.1 | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|0.575}}"| {{val|0.49|to|0.66}} | |||
| | 2.6–3.3 | |||
| | |
| −0.45 | ||
| |- | |||
| | ~0.84 | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" data-sort-value="Charon"| (]) | |||
| | | |||
| | | | 35% | ||
| | {{val|1212|1}} | |||
| | 2.2% | |||
| | {{val|1.59|0.02}} | |||
| | {{val|1.70|0.02}} | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|153.3}}"| 6d 9.3h | |||
| | – | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|0.35}}"| {{val|0.2|to|0.5}} | |||
| | 1 | |||
| |- align=center | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| ''{{dp|Salacia}}'' | |||
| | 24% | |||
| | {{val|846|21}} | |||
| | 0.7% | |||
| | {{val|.49|0.01}} | |||
| | {{val|1.50|0.12}} | |||
| | {{val|6.1}} | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 0.04 | |||
| | 4.27 | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| {{dp|Haumea}} | |||
| |data-sort-value="45%"| ≈ 45% | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|1560}}"| ≈ 1560<ref name="Dunham2019" /> | |||
| | 5.5% | |||
| | {{val|4.01|0.04}} | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|2.02}}"| ≈ 2.02<ref name="Dunham2019" /> | |||
| | {{val|3.9}} | |||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|0.66}}"| ≈ 0.66 | |||
| | 32 ± 3 | |||
| | |
| 0.23 | ||
| |- | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | {{dp|Quaoar}} | |||
| ! align=left| ]<ref name=Stansberry>{{cite journal| last=Stansberry| first=J.| coauthors=Grundy, W.; Brown, M.; et al.| title=Physical Properties of Kuiper Belt and Centaur Objects: Constraints from Spitzer Space Telescope|id={{arxiv|astro-ph/0702538}}| year=2007| format=abstract| publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title=The methane ice rich surface of large TNO 2005 FY9: a Pluto-twin in the trans-neptunian belt?|author=J. Licandro, N. Pinilla-Alonso, M. Pedani, et al.|journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics|year=2006|volume= 445 |doi= 10.1051/0004-6361:200500219|url=http://www.aanda.org/index.php?option=article&access=doi&doi=10.1051/0004-6361:200500219 | |||
| | 32% | |||
| |accessdate=2008-07-14|pages=L35|issue= L35-L38}}</ref> | |||
| | {{val|1086|4}} | |||
| | 43% | |||
| | 1.9% | |||
| | 1500{{±|400|200}} | |||
| | {{val|1.2|0.05}} | |||
| | ~5%? | |||
| | {{val|1.7|0.1}} | |||
| | ~4? | |||
| | {{val|17.7}} | |||
| | ~2? | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ~0.5 | |||
| | |
| {{val|0.11|0.01}} | ||
| | | | 2.42 | ||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| | | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left"| ] | |||
| | 0 | |||
| | |
| 41% | ||
| | {{val|1430|38|22}} | |||
| | transient? | |||
| |data-sort-value="4.2%"| ≈ 4.2% | |||
| |- align="center" | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|3.1}}"| ≈ 3.1 | |||
| ! align="left" | ]<ref name=Stansberry/><ref>{{cite journal|title=The Mass of Dwarf Planet Eris|first=Michael E.|last=Brown|coauthors=Schaller, Emily L.|journal=Science|year=2007 |volume=316|issue =5831|pages=1585| doi=10.1126/science.1139415 |url=http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/316/5831/1585|pmid=17569855}}</ref> | |||
| | {{val|1.9|0.2}} | |||
| | 75% | |||
| | {{val|22.8}} | |||
| | <2340 | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 22.7% | |||
| | {{val|0.81|0.03|0.05}} | |||
| | 16.7 | |||
| | |
| −0.20 | ||
| |- | |||
| | ~0.8 | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | ] | |||
| | 1.3 | |||
| | 35% | |||
| | | |||
| | {{val|1230|50}} | |||
| | ~0.3 | |||
| | 2.4% | |||
| | {{val|1.75|0.07}} | |||
| | {{val|1.74|0.16}} | |||
| | {{val|22.4|0.2}}? | |||
| | ] | |||
| | {{val|0.14|0.01}} | |||
| | 1.86 | |||
| |-style="background: #E5E5FF;" | |||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | ] | |||
| | 67% | |||
| | {{val|2326|12}} | |||
| | 22.4% | |||
| | {{val|16.47|0.09}} | |||
| | {{val|2.43|0.05}} | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|378.864}}"| 15d 18.9h | |||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | {{val|0.96|0.04}} | |||
| | 42 | |||
| | −1.21 | |||
| | transient? | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! scope=row style="text-align: left" | {{dp|Sedna}} | |||
| |colspan=14 style="background: #FFFFFF; border-right:1px solid white; border-bottom:1px solid white; border-left:1px solid white;"|<div class="references-small" style="margin-bottom: 0em;"> | |||
| | 26% | |||
| </div> | |||
| | {{val|906|314|258}} | |||
| |data-sort-value="1%"| ≈ 1%? | |||
| |data-sort-value="{{val|1}}"| ≈ 1? | |||
| | ? | |||
| | {{val|10|3}} | |||
| | 0? | |||
| | {{val|0.41|0.393|0.186}} | |||
| | 1.52 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| == |
=== Symbols === | ||
| {{Main|Astronomical symbol#Symbols for trans-Neptunian objects}} | |||
| {{main|List of dwarf planet candidates}} | |||
| Ceres ]<ref name=bode-1801>{{cite book | |||
| After Ceres, the next most massive body in the asteroid belt, ], might also be classified as a dwarf planet, as its shape appears to deviate from hydrostatic equilibrium only because of a large impact that occurred after it solidified;<ref>{{cite journal|first=Peter C.|last=Thomas|coauthors=Binzelb, Richard P.; Gaffeyc, Michael J.; Zellnerd, Benjamin H.; Storrse, Alex D.; Wells, Eddie|title=Vesta: Spin Pole, Size, and Shape from HST Images|journal=Icarus|volume=128|pages=88–94|year=1997|issue=1|doi=10.1006/icar.1997.5736}}</ref> the definition of dwarf planet does not specifically address this issue. The ] probe scheduled to enter orbit around Vesta in 2011 may help clarify matters.<ref name=Russel2006/> | |||
| | editor-last = Bode | |||
| | editor-first = J.E. | |||
| | date = 1801 | |||
| | title = Berliner astronomisches Jahrbuch führ das Jahr 1804 | |||
| | trans-title = The Berlin Astronomical Yearbook for 1804 | |||
| | pages = 97–98 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=6GElAQAAIAAJ&pg=RA2-PA98 | |||
| | access-date = October 19, 2022 | |||
| | archive-date = December 14, 2023 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20231214145307/https://books.google.com/books?id=6GElAQAAIAAJ&pg=RA2-PA98#v=onepage&q&f=false | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref> and Pluto ]<ref name=popular-astronomy>{{cite magazine | |||
| | last = Slipher | |||
| | first = V.M. | |||
| | date = 1930 | |||
| | title = The trans-Neptunian planet | |||
| | magazine = Popular Astronomy | |||
| | volume = 38 | |||
| | page = 415 | |||
| | url = http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-journal_query?volume=38&plate_select=NO&page=415&plate=&cover=&journal=PA... | |||
| | access-date = October 19, 2022 | |||
| | archive-date = December 11, 2021 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211211143952/http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-journal_query?volume=38&plate_select=NO&page=415&plate=&cover=&journal=PA... | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref> received planetary symbols, as they were considered to be planets when they were discovered. By the time the others were discovered, ]s had mostly fallen out of use among astronomers. ] includes symbols for Quaoar ], Sedna ], Orcus ], Haumea ], Eris ], Makemake ], and Gonggong ] that are primarily used by astrologers: they were devised by Denis Moskowitz, a software engineer in Massachusetts.<ref name=anderson>{{cite web |url=http://blog.unicode.org/2022/05/out-of-this-world-new-astronomy-symbols.html |title=Out of this World: New Astronomy Symbols Approved for the Unicode Standard |last=Anderson |first=Deborah |date=May 4, 2022 |website=unicode.org |publisher=The Unicode Consortium |access-date=August 6, 2022 |archive-date=August 6, 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220806075352/http://blog.unicode.org/2022/05/out-of-this-world-new-astronomy-symbols.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=DPU>{{cite web|url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2021/21224-dwarf-planet-syms.pdf|title=Unicode request for dwarf-planet symbols|last=Miller|first=Kirk|date=October 26, 2021|website=unicode.org|access-date=October 19, 2022|archive-date=March 23, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220323174107/https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2021/21224-dwarf-planet-syms.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Unicode-1F700">{{cite web | |||
| | title = Alchemical Symbols | |||
| | date = 2022 | |||
| | website = unicode.org | |||
| | publisher = The Unicode Consortium | |||
| | url = https://www.unicode.org/charts/PDF/U1F700.pdf | |||
| | access-date = October 19, 2022 | |||
| | archive-date = April 2, 2020 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200402042357/http://www.unicode.org/charts/PDF/U1F700.pdf | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| }}</ref> NASA has used his Haumea, Eris, and Makemake symbols, as well as the traditional astrological symbol for Pluto ]<ref name=DP>{{cite web |url= https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/infographics/what-is-a-dwarf-planet |date= April 22, 2015 |website= Jet Propulsion Laboratory |publisher=] |title= What is a Dwarf Planet? |access-date= September 24, 2021 |archive-date= December 8, 2021 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20211208181916/https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/infographics/what-is-a-dwarf-planet |url-status= live }}</ref> when referring to it as a dwarf planet.<ref name=DPU/> Symbols have been proposed for the next-largest named candidates, but do not have consistent usage among astrologers.<ref name=DPU/> The Unicode proposal for Quaoar, Orcus, Haumea, Makemake, and Gonggong mentions the following symbols for named objects over 600 km diameter: Salacia ], Varda ], Ixion ], Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà ] and Varuna ].<ref name=DPU/><ref name=constellations>{{cite web |url=https://www.unicode.org/L2/L2024/24235-constellation-symbols.pdf |title=Preliminary presentation of constellation symbols |last=Miller |first=Kirk |date=18 October 2024 |website=unicode.org |publisher=The Unicode Consortium |access-date=22 October 2024 |quote=}}</ref> | |||
| == Exploration == | |||
| The status of ] (currently regarded as a satellite of Pluto) remains uncertain, as there is currently no clear definition of what distinguishes a satellite system from a binary (]) system. The original draft resolution (5)<ref name="Draft Resolution 5"/> presented to the IAU stated that Charon could be considered a planet because: | |||
| ]'' spacecraft]] | |||
| #Charon independently would satisfy the size and shape criteria for a dwarf planet status (in the terms of the final resolution); | |||
| #Charon revolves with Pluto around a common ] located between the two bodies (rather than within one of the bodies) because Charon's mass is not insignificant relative to that of Pluto.<ref>the footnote in the original text reads: ''For two or more objects comprising a multiple object system.... A secondary object satisfying these conditions i.e. that of ], ] is also designated a planet if the system barycentre resides outside the primary. Secondary objects not satisfying these criteria are "satellites". Under this definition, Pluto's companion Charon is a planet, making Pluto-Charon a double planet.''</ref> | |||
| As of 2024, only two missions have targeted and explored dwarf planets up close. On March 6, 2015, the '']'' spacecraft entered orbit around ], becoming the first spacecraft to visit a dwarf planet.<ref name="NASA-20150306">{{cite web |last1=Landau |first1=Elizabeth |last2=Brown |first2=Dwayne |title=NASA Spacecraft Becomes First to Orbit a Dwarf Planet |url=http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4503 |date=March 6, 2015 |work=] |access-date=March 6, 2015 |archive-date=March 7, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150307062258/http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4503 |url-status=live }}</ref> On July 14, 2015, the '']'' space probe flew by ] and its five moons. | |||
| This definition was not preserved in the IAU's final resolution and it is unknown if it will be included in future debates. | |||
| Ceres displays such evidence of an active geology as salt deposits and ]s, while Pluto has water-ice mountains drifting in nitrogen-ice glaciers, as well as a significant atmosphere. | |||
| ]s, and colours of the largest Trans-Neptunian objects]] | |||
| Ceres evidently has brine percolating through its subsurface, while there is evidence that Pluto has an actual subsurface ocean. | |||
| Many ]s (TNOs) are thought to have icy cores and therefore would require a diameter of perhaps 400 km (250 mi) – only about 3% of that of Earth – to relax into gravitational equilibrium, making them dwarf planets of the plutoid class.<ref name=Brown/> Although only rough estimates of the diameters of these objects are available, as of August 2006, it was believed that another 42 bodies beyond Neptune (besides Pluto and Eris) were likely dwarf planets.<ref name=Brown/><ref name="Space.com">{{cite web|title=Nine Planets Become 12 with Controversial New Definition|publisher=]|first=Robert Roy|last=Britt|date=2006-08-16|url= http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/060816_planet_definition.html| accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> A team is investigating another 30 such objects, and believe that the total number will eventually prove to be about 200 in the Kuiper belt, and many more beyond it.<ref name=Brown>{{cite web|authorlink=Michael E. Brown|title=The Dwarf Planets|first=Michael E.|last=Brown |publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences|url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dwarfplanets/|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> | |||
| ''Dawn'' had previously orbited the asteroid Vesta. Saturn's moon ] has been imaged by Cassini and before that by Voyager 2, which also encountered Neptune's moon ]. All three bodies show evidence of once being dwarf planets, and their exploration helps clarify the evolution of dwarf planets. | |||
| Tancredi & Favre (2008) attempt to estimate which TNOs are likely to qualify, based on both direct measurements and lightcurve data. They propose that nine of the candidates be considered dwarf planets.<ref>{{cite web|author=Tancredi & Favre|title=Which are the dwarfs in the Solar system?|publisher=Asteroids, Comets, Meteors|url=http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/acm2008/pdf/8261.pdf |accessdate=2008-09-20}}</ref> Six of these have been estimated by one researcher or another to be at least 900 km in diameter, the size of the smallest known dwarf planet, {{dp|Ceres}}, as has a tenth candidate, {{mp|2002 AW|197}}. These ten prime candidates are: | |||
| ''New Horizons'' has captured distant images of Triton, Quaoar, Haumea, Eris, and Makemake, as well as the smaller candidates Ixion, {{mp|2002 MS|4}}, and {{mpl-|556416|2014 OE|394}}.<ref name="Verbiscer2022">{{cite journal | |||
| {{TNO dwarf planet candidates}} | |||
| |display-authors = etal | |||
| |first1 = Anne J. |last1 = Verbiscer | |||
| |first2 = Paul |last2 = Helfenstein | |||
| |first3 = Simon B. |last3 = Porter | |||
| |first4 = Susan D. |last4 = Benecchi | |||
| |first5 = J. J. |last5 = Kavelaars | |||
| |first6 = Tod R. |last6 = Lauer | |||
| |title = The Diverse Shapes of Dwarf Planet and Large KBO Phase Curves Observed from New Horizons | |||
| |journal = The Planetary Science Journal | |||
| |date = April 2022 | |||
| |volume = 3 | |||
| |issue = 4 | |||
| |id = 95 | |||
| |pages = 31 | |||
| |doi-access = free | |||
| |doi = 10.3847/PSJ/ac63a6 | |||
| |bibcode = 2022PSJ.....3...95V}}</ref> | |||
| One of the ]'s two '']'' probes has been proposed to visit Quaoar in 2040.<ref name="SpaceNews">{{cite news |last1=Jones |first1=Andrew |title=China to launch a pair of spacecraft towards the edge of the solar system |url=https://spacenews.com/china-to-launch-a-pair-of-spacecraft-towards-the-edge-of-the-solar-system/ |access-date=April 29, 2021 |work=SpaceNews |publisher=SpaceNews |date=April 16, 2021 |archive-date=September 29, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210929080320/https://spacenews.com/china-to-launch-a-pair-of-spacecraft-towards-the-edge-of-the-solar-system/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==Similar objects== | |||
| Additionally, more-recently discovered ] should probably be seen as a prime candidate, as Mike Brown estimates its size to be between that of Sedna and Quaoar.<ref name=SnowWhite>{{cite web|authorlink=Michael E. Brown|title=Snow White Needs A Bailout|first=Michael E.|last=Brown |publisher=Mike Brown's Planets|url=http://www.mikebrownsplanets.com/2009/03/snow-white-needs-bailout.html|accessdate=2009-05-19}}</ref> | |||
| A number of bodies physically resemble dwarf planets. These include former dwarf planets, which may still have equilibrium shape or evidence of active geology; planetary-mass moons, which meet the physical but not the orbital definition for dwarf planet; and Charon in the Pluto–Charon system, which is arguably a binary dwarf planet. The categories may overlap: Triton, for example, is both a former dwarf planet and a planetary-mass moon. | |||
| === Former dwarf planets === | |||
| ===Ellipsoidal moons=== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{seealso|List of moons by diameter}} | |||
| ], the next-most-massive body in the asteroid belt after Ceres, was once in hydrostatic equilibrium and is roughly spheroidal, deviating mainly due to massive impacts that formed the ] and ] craters after it solidified.<ref>{{cite journal |first=Peter C. |last=Thomas |author2=Binzelb, Richard P. |author3=Gaffeyc, Michael J. |author4=Zellnerd, Benjamin H. |author5=Storrse, Alex D. |author6=Wells, Eddie |title=Vesta: Spin Pole, Size, and Shape from HST Images |journal=Icarus |volume=128 |pages=88–94 |date=1997 |issue=1 |doi=10.1006/icar.1997.5736 |bibcode=1997Icar..128...88T|doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| A total of 19 known ] are massive enough to have relaxed into a rounded shape under their own gravity. These bodies have no significant physical differences from the dwarf planets, but are not considered members of that class because they do not directly orbit the Sun. They are ], the four ] of Jupiter (], ], ], and ]), seven moons of Saturn (], ], ], ], ], ], and ]), five moons of Uranus (], ], ], ], and ]), one moon of Neptune (]), and one moon of Pluto (]). | |||
| Its dimensions are not consistent with it currently being in ].<ref name="Asmar 2012">{{cite journal |last=Asmar |first=S. W. |author2=Konopliv, A. S. |author3=Park, R. S. |author4=Bills, B. G. |author5=Gaskell, R. |author6=Raymond, C. A. |author7=Russell, C. T. |author8=Smith, D. E. |author9=Toplis, M. J. |author10=Zuber, M. T. |title=The Gravity Field of Vesta and Implications for Interior Structure |journal=43rd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference |issue=1659 |date=2012 |page=2600 |url=http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2012/pdf/2600.pdf |bibcode=2012LPI....43.2600A |access-date=July 15, 2015 |archive-date=October 20, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131020181320/http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2012/pdf/2600.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Russel 2012">{{cite journal |last=Russel |first=C. T. |title=Dawn at Vesta: Testing the Protoplanetary Paradigm |journal=Science |date=2012 |volume=336 |issue=6082 |pages=684–686 |doi=10.1126/science.1219381 |url=http://www.phyast.pitt.edu/~wmwv/Classes/A1122/Literature/Science-2012-Russell-684-6.pdf |bibcode=2012Sci...336..684R |display-authors=etal |pmid=22582253 |s2cid=206540168 |access-date=July 15, 2015 |archive-date=July 15, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150715181221/http://www.phyast.pitt.edu/~wmwv/Classes/A1122/Literature/Science-2012-Russell-684-6.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] is more massive than Eris or Pluto, has an equilibrium shape, and is thought to be a captured dwarf planet (likely a member of a binary system), but no longer directly orbits the sun.<ref name="Agnor06">{{Cite journal |doi=10.1038/nature04792 |url=http://extranet.on.br/rodney/curso2010/aula9/tritoncapt_hamilton.pdf |title=Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary–planet gravitational encounter |journal=Nature |volume=441 |issue=7090 |pages=192–194 |year=2006 |last1=Agnor |first1=C. B. |last2=Hamilton |first2=D. P. |pmid=16688170 |bibcode=2006Natur.441..192A |s2cid=4420518 |access-date=August 29, 2015 |archive-date=October 14, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161014134243/http://extranet.on.br/rodney/curso2010/aula9/tritoncapt_hamilton.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ] is a captured ] that, like Vesta, is no longer in hydrostatic equilibrium, but is thought to have been so early in its history due to ].<ref>{{cite news |last1=Cook |first1=Jia-Rui C. |last2=Brown |first2=Dwayne |date=April 26, 2012 |url=http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/news/newsreleases/newsrelease20120426/ |url-status=dead |title=Cassini Finds Saturn Moon Has Planet-Like Qualities |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150713125236/http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/news/newsreleases/newsrelease20120426/ |archive-date=July 13, 2015 |location=Pasadena, California|work=Jey Propoulsion Laboratory |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| === Planetary-mass moons === | |||
| ==Contention== | |||
| {{Main|Planetary-mass moon}} | |||
| In the immediate aftermath of the IAU definition of dwarf planet, a number of scientists expressed their disagreement with the IAU resolution.<ref name="Stern" /> Campaigns included car bumper stickers and T-shirts.<ref>{{cite news|url= http://www.usatoday.com/tech/science/space/2006-08-25-pluto-memorabilia_x.htm|title=Online merchants see green in Pluto news|first=Alicia|last=Chang|work=Associated Press|publisher=USA Today|date=2006-08-25|accessdate=2008-01-25}}</ref> ] (the discoverer of Eris) agrees with the reduction of the number of planets to eight.<ref>{{cite web|title=The Eight Planets|first=Michael E.|last=Brown|url=http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/eightplanets/|publisher=California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> | |||
| At least nineteen ] have equilibrium shape from having relaxed under self-gravity at some point, though some have since frozen solid and are no longer in equilibrium. Seven are more massive than either Eris or Pluto. These moons are not physically distinct from the dwarf planets, but do not fit the IAU definition because they do not directly orbit the Sun. (Indeed, Neptune's moon Triton is a captured dwarf planet, and Ceres formed in the same region of the Solar System as the moons of Jupiter and Saturn.) Alan Stern calls planetary-mass moons "]s", one of three categories of planet, together with dwarf planets and classical planets.<ref name="News.discovery.com">{{cite web |url=http://news.discovery.com/space/should-large-moons-be-called-satellite-planets.html |title=Should Large Moons Be Called 'Satellite Planets'? |publisher=News.discovery.com |date=May 14, 2010 |access-date=November 4, 2011 |archive-date=May 5, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120505221146/http://news.discovery.com/space/should-large-moons-be-called-satellite-planets.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> The term '']'' ("planetary-mass object") also covers all three populations.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Basri |first1=Gibor |last2=Brown |first2=Michael E. |date=2006 |title=Planetesimals to Brown Dwarfs: What is a Planet? |url=http://siba.unipv.it/fisica/articoli/A/Annual%20Review%20Earth%20Planetary%20Sciences_vol.34_2006_pp.193-216.pdf |journal=Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences |volume=34 |pages=193–216 |doi=10.1146/annurev.earth.34.031405.125058 |arxiv=astro-ph/0608417 |bibcode=2006AREPS..34..193B |s2cid=119338327 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130731133553/http://siba.unipv.it/fisica/articoli/A/Annual%20Review%20Earth%20Planetary%20Sciences_vol.34_2006_pp.193-216.pdf |archive-date=July 31, 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| NASA has announced that it will use the new guidelines established by the IAU.<ref>{{cite web|title= Hotly-Debated Solar System Object Gets a Name|publisher=NASA press release|url= http://www.nasa.gov/vision/universe/solarsystem/erisf-20060914.html |date= 2006-09-14|accessdate= 2008-01-26}}</ref> However, ], the director of ], rejects the current IAU definition of planet, both in terms of defining dwarf planets as something other than a type of planet, and in using orbital characteristics (rather than intrinsic characteristics) of objects to define them as dwarf planets.<ref>{{cite web|title=Unabashedly Onward to the Ninth Planet|first=Alan|last=Stern|date=2006-09-06|publisher=New Horizons Web Site|url=http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/overview/piPerspectives/piPerspective_09_06_2006.php|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> Thus, as of January 2008, he and his team still referred to Pluto as the ninth planet,<ref>{{cite web|url =http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/overview/piPerspectives/piPerspective_01_17_2008.php|first=Alan|last=Stern |publisher=New Horizons Web Site|title=Happy Birthday New Horizons! Two Years on the Road to the Ninth Planet|date=2008-01-17|accessdate=2008-01-26}}</ref> | |||
| while accepting the characterization of dwarf planet for Ceres and Eris. | |||
| == |
==== Charon ==== | ||
| There has been some debate as to whether the Pluto–] system should be considered a ]. | |||
| {{Misplaced Pages-Books|Solar System}} | |||
| In a draft resolution for the ], both Pluto and Charon were considered planets in a binary system.<ref name="Draft Resolution 5"/>{{efn| The footnote in the original text reads: "For two or more objects comprising a multiple object system. ... A secondary object satisfying these conditions i.e. that of mass, shape is also designated a planet if the system barycentre resides outside the primary. Secondary objects not satisfying these criteria are "satellites". Under this definition, Pluto's companion Charon is a planet, making Pluto–Charon a double planet."<ref name="Draft Resolution 5"/>}} The IAU currently says Charon is not considered a dwarf planet but rather a satellite of Pluto, though the idea that Charon might qualify as a dwarf planet may be considered at a later date.<ref>{{cite web |title=Pluto and the Solar System |website=iau.org |publisher=] |url=http://www.iau.org/public/themes/pluto/ |access-date=July 10, 2013 |archive-date=April 17, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200417193151/https://www.iau.org/public/themes/pluto/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Nonetheless, it is no longer clear that Charon is in hydrostatic equilibrium. Also, the location of the ] depends not only on the relative masses of the bodies, but also on the distance between them; the barycenter of the Sun–Jupiter orbit, for example, lies outside the Sun, but they are not considered a binary object. Thus, a formal definition of what constitutes a binary (dwarf) planet must be established before Pluto and Charon are formally defined as binary dwarf planets. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == |
== See also == | ||
| {{portal|Solar System|Outer Space|Astronomy | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=20em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| == |
== Notes == | ||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| {{wiktionary|Dwarf planet}} | |||
| * NPR: (David Kestenbaum) | |||
| * BBC News: , August 16, 2006 | |||
| * ]: (P. Surdas Mohit) August 24, 2006 | |||
| *], | |||
| {{Solar System}} | |||
| * NASA: | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{featured article}} | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Wiktionary}} | |||
| ] | |||
| * (Anshool Deshmukh, ''Visual Capitalist,'' October 8, 2021, graphics by Mark Belan) | |||
| * ]: (David Kestenbaum, '']'') | |||
| * ]: , August 16, 2006 | |||
| * '']'': (P. Surdas Mohit) August 24, 2006 | |||
| * ]: | |||
| * NASA: | |||
| {{ |
{{Dwarf planets}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Solar System}} | ||
| {{Portal bar|Astronomy|Stars|Spaceflight|Outer space|Solar System}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Dwarf Planet}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:02, 5 December 2024
Small planetary-mass object Not to be confused with minor planet.Nine likeliest dwarf planets
and dates of discovery
 Ceres (1801)
Ceres (1801) Pluto (1930)
Pluto (1930) Quaoar (2002)
Quaoar (2002) Sedna (2003)
Sedna (2003) Orcus (2004)
Orcus (2004) Haumea (2004)
Haumea (2004) Eris (2005)
Eris (2005) Makemake (2005)
Makemake (2005) Gonggong (2007)
Gonggong (2007)
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve orbital dominance like the eight classical planets of the Solar System. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto, which for decades was regarded as a planet before the "dwarf" concept was adopted in 2006.
Dwarf planets are capable of being geologically active, an expectation that was borne out in 2015 by the Dawn mission to Ceres and the New Horizons mission to Pluto. Planetary geologists are therefore particularly interested in them.
Astronomers are in general agreement that at least the nine largest candidates are dwarf planets – in rough order of size, Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Ceres, Orcus, and Sedna. Considerable uncertainty remains over the tenth largest candidate Salacia, which may thus be considered a borderline case. Of these ten, two have been visited by spacecraft (Pluto and Ceres) and seven others have at least one known moon (Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Salacia), which allows their masses and thus an estimate of their densities to be determined. Mass and density in turn can be fit into geophysical models in an attempt to determine the nature of these worlds. Only one, Sedna, has neither been visited nor has any known moons, making an accurate estimate of mass difficult. Some astronomers include many smaller bodies as well, but there is no consensus that these are likely to be dwarf planets.
The term dwarf planet was coined by planetary scientist Alan Stern as part of a three-way categorization of planetary-mass objects in the Solar System: classical planets, dwarf planets, and satellite planets. Dwarf planets were thus conceived of as a category of planet. In 2006, however, the concept was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) as a category of sub-planetary objects, part of a three-way recategorization of bodies orbiting the Sun: planets, dwarf planets, and small Solar System bodies. Thus Stern and other planetary geologists consider dwarf planets and large satellites to be planets, but since 2006, the IAU and perhaps the majority of astronomers have excluded them from the roster of planets.
History of the concept
Main articles: Geophysical definition of planet and IAU definition of planet

Starting in 1801, astronomers discovered Ceres and other bodies between Mars and Jupiter that for decades were considered to be planets. Between then and around 1851, when the number of planets had reached 23, astronomers started using the word asteroid (from Greek, meaning 'star-like' or 'star-shaped') for the smaller bodies and began to distinguish them as minor planets rather than major planets.
With the discovery of Pluto in 1930, most astronomers considered the Solar System to have nine major planets, along with thousands of significantly smaller bodies (asteroids and comets). For almost 50 years, Pluto was thought to be larger than Mercury, but with the discovery in 1978 of Pluto's moon Charon, it became possible to measure Pluto's mass accurately and to determine that it was much smaller than initial estimates. It was roughly one-twentieth the mass of Mercury, which made Pluto by far the smallest planet. Although it was still more than ten times as massive as the largest object in the asteroid belt, Ceres, it had only one-fifth the mass of Earth's Moon. Furthermore, having some unusual characteristics, such as large orbital eccentricity and a high orbital inclination, it became evident that it was a different kind of body from any of the other planets.
In the 1990s, astronomers began to find objects in the same region of space as Pluto (now known as the Kuiper belt), and some even farther away. Many of these shared several of Pluto's key orbital characteristics, and Pluto started being seen as the largest member of a new class of objects, the plutinos. It became clear that either the larger of these bodies would also have to be classified as planets, or Pluto would have to be reclassified, much as Ceres had been reclassified after the discovery of additional asteroids. This led some astronomers to stop referring to Pluto as a planet. Several terms, including subplanet and planetoid, started to be used for the bodies now known as dwarf planets. Astronomers were also confident that more objects as large as Pluto would be discovered, and the number of planets would start growing quickly if Pluto were to remain classified as a planet.
Eris (then known as 2003 UB313) was discovered in January 2005; it was thought to be slightly larger than Pluto, and some reports informally referred to it as the tenth planet. As a consequence, the issue became a matter of intense debate during the IAU General Assembly in August 2006. The IAU's initial draft proposal included Charon, Eris, and Ceres in the list of planets. After many astronomers objected to this proposal, an alternative was drawn up by the Uruguayan astronomers Julio Ángel Fernández and Gonzalo Tancredi: They proposed an intermediate category for objects large enough to be round but that had not cleared their orbits of planetesimals. Beside dropping Charon from the list, the new proposal also removed Pluto, Ceres, and Eris, because they have not cleared their orbits.
Although concerns were raised about the classification of planets orbiting other stars, the issue was not resolved; it was proposed instead to decide this only when dwarf-planet-size objects start to be observed.
In the immediate aftermath of the IAU definition of dwarf planet, some scientists expressed their disagreement with the IAU resolution. Campaigns included car bumper stickers and T-shirts. Mike Brown (the discoverer of Eris) agrees with the reduction of the number of planets to eight.
NASA announced in 2006 that it would use the new guidelines established by the IAU. Alan Stern, the director of NASA's mission to Pluto, rejects the current IAU definition of planet, both in terms of defining dwarf planets as something other than a type of planet, and in using orbital characteristics (rather than intrinsic characteristics) of objects to define them as dwarf planets. Thus, in 2011, he still referred to Pluto as a planet, and accepted other likely dwarf planets such as Ceres and Eris, as well as the larger moons, as additional planets. Several years before the IAU definition, he used orbital characteristics to separate "überplanets" (the dominant eight) from "unterplanets" (the dwarf planets), considering both types "planets".
Name
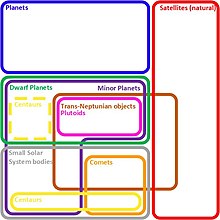
Names for large subplanetary bodies include dwarf planet, planetoid (more general term), meso-planet (narrowly used for sizes between Mercury and Ceres), quasi-planet, and (in the transneptunian region) plutoid. Dwarf planet, however, was originally coined as a term for the smallest planets, not the largest sub-planets, and is still used that way by many planetary astronomers.
Alan Stern coined the term dwarf planet, analogous to the term dwarf star, as part of a three-fold classification of planets, and he and many of his colleagues continue to classify dwarf planets as a class of planets. The IAU decided that dwarf planets are not to be considered planets, but kept Stern's term for them. Other terms for the IAU definition of the largest subplanetary bodies that do not have such conflicting connotations or usage include quasi-planet and the older term planetoid ("having the form of a planet"). Michael E. Brown stated that planetoid is "a perfectly good word" that has been used for these bodies for years, and that the use of the term dwarf planet for a non-planet is "dumb", but that it was motivated by an attempt by the IAU division III plenary session to reinstate Pluto as a planet in a second resolution. Indeed, the draft of Resolution 5A had called these median bodies planetoids, but the plenary session voted unanimously to change the name to dwarf planet. The second resolution, 5B, defined dwarf planets as a subtype of planet, as Stern had originally intended, distinguished from the other eight that were to be called "classical planets". Under this arrangement, the twelve planets of the rejected proposal were to be preserved in a distinction between eight classical planets and four dwarf planets. Resolution 5B was defeated in the same session that 5A was passed. Because of the semantic inconsistency of a dwarf planet not being a planet due to the failure of Resolution 5B, alternative terms such as nanoplanet and subplanet were discussed, but there was no consensus among the CSBN to change it.
In most languages equivalent terms have been created by translating dwarf planet more-or-less literally: French planète naine, Spanish planeta enano, German Zwergplanet, Russian karlikovaya planeta (карликовая планета), Arabic kaukab qazm (كوكب قزم), Chinese ǎixíngxīng (矮行星), Korean waesohangseong (왜소행성 / 矮小行星) or waehangseong (왜행성 / 矮行星), but in Japanese they are called junwakusei (準惑星), meaning "quasi-planets" or "peneplanets" (pene- meaning "almost").
IAU Resolution 6a of 2006 recognizes Pluto as "the prototype of a new category of trans-Neptunian objects". The name and precise nature of this category were not specified but left for the IAU to establish at a later date; in the debate leading up to the resolution, the members of the category were variously referred to as plutons and plutonian objects but neither name was carried forward, perhaps due to objections from geologists that this would create confusion with their pluton.
On June 11, 2008, the IAU Executive Committee announced a new term, plutoid, and a definition: all trans-Neptunian dwarf planets are plutoids. Other departments of the IAU have rejected the term:
...in part because of an email miscommunication, the WG-PSN was not involved in choosing the word plutoid. ... In fact, a vote taken by the WG-PSN subsequent to the Executive Committee meeting has rejected the use of that specific term..."
The category of 'plutoid' captured an earlier distinction between the 'terrestrial dwarf' Ceres and the 'ice dwarfs' of the outer Solar system, part of a conception of a threefold division of the Solar System into inner terrestrial planets, central giant planets, and outer ice dwarfs, of which Pluto was the principal member. 'Ice dwarf' also saw some use as an umbrella term for all trans-Neptunian minor planets, or for the ice asteroids of the outer Solar System; one attempted definition was that an ice dwarf "is larger than the nucleus of a normal comet and icier than a typical asteroid."
Since the Dawn mission, it has been recognized that Ceres is a geologically icy body that may have originated from the outer Solar System. Ceres has since been called an ice dwarf as well.
Criteria
| Body | m/ME | Λ | µ | Π | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 0.055 | 1.95×10 | 9.1×10 | 1.3×10 | ||||||||
| Venus | 0.815 | 1.66×10 | 1.35×10 | 9.5×10 | ||||||||
| Earth | 1 | 1.53×10 | 1.7×10 | 8.1×10 | ||||||||
| Mars | 0.107 | 9.42×10 | 1.8×10 | 5.4×10 | ||||||||
| Ceres | 0.00016 | 8.32×10 | 0.33 | 4.0×10 | ||||||||
| Jupiter | 317.7 | 1.30×10 | 6.25×10 | 4.0×10 | ||||||||
| Saturn | 95.2 | 4.68×10 | 1.9×10 | 6.1×10 | ||||||||
| Uranus | 14.5 | 3.85×10 | 2.9×10 | 4.2×10 | ||||||||
| Neptune | 17.1 | 2.73×10 | 2.4×10 | 3.0×10 | ||||||||
| Pluto | 0.0022 | 2.95×10 | 0.077 | 2.8×10 | ||||||||
| Eris | 0.0028 | 2.13×10 | 0.10 | 2.0×10 | ||||||||
| Sedna | 0.0002 | 3.64×10 | < 0.07 | 1.6×10 | ||||||||
|
Planetary discriminants of the planets ( white ), and of the largest known dwarf planet ( light purple ) in each orbital population (asteroid belt, Kuiper belt, scattered disc, sednoids). All other known objects in these populations have smaller discriminants than the one shown. | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
The category dwarf planet arose from a conflict between dynamical and geophysical ideas of what a useful conception of a planet would be. In terms of the dynamics of the Solar System, the major distinction is between bodies that gravitationally dominate their neighbourhood (Mercury through Neptune) and those that do not (such as the asteroids and Kuiper belt objects). A celestial body may have a dynamic (planetary) geology at approximately the mass required for its mantle to become plastic under its own weight, which results in the body acquiring a round shape. Because this requires a much lower mass than gravitationally dominating the region of space near their orbit, there are a population of objects that are massive enough to have a world-like appearance and planetary geology, but not massive enough to clear their neighborhood. Examples are Ceres in the asteroid belt and Pluto in the Kuiper belt.
Dynamicists usually prefer using gravitational dominance as the threshold for planethood, because from their perspective smaller bodies are better grouped with their neighbours, e.g. Ceres as simply a large asteroid and Pluto as a large Kuiper belt object. Geoscientists usually prefer roundness as the threshold, because from their perspective the internally driven geology of a body like Ceres makes it more similar to a classical planet like Mars, than to a small asteroid that lacks internally driven geology. This necessitated the creation of the category of dwarf planets to describe this intermediate class.
Orbital dominance
Main article: Clearing the neighbourhoodAlan Stern and Harold F. Levison introduced a parameter Λ (upper case lambda) in 2000, expressing the likelihood of an encounter resulting in a given deflection of orbit. The value of this parameter in Stern's model is proportional to the square of the mass and inversely proportional to the period. This value can be used to estimate the capacity of a body to clear the neighbourhood of its orbit, where Λ > 1 will eventually clear it. A gap of five orders of magnitude in Λ was found between the smallest terrestrial planets and the largest asteroids and Kuiper belt objects.
Using this parameter, Steven Soter and other astronomers argued for a distinction between planets and dwarf planets based on the inability of the latter to "clear the neighbourhood around their orbits": planets are able to remove smaller bodies near their orbits by collision, capture, or gravitational disturbance (or establish orbital resonances that prevent collisions), whereas dwarf planets lack the mass to do so. Soter went on to propose a parameter he called the planetary discriminant, designated with the symbol µ (mu), that represents an experimental measure of the actual degree of cleanliness of the orbital zone (where µ is calculated by dividing the mass of the candidate body by the total mass of the other objects that share its orbital zone), where µ > 100 is deemed to be cleared.
Jean-Luc Margot refined Stern and Levison's concept to produce a similar parameter Π (upper case Pi). It is based on theory, avoiding the empirical data used by Λ . Π > 1 indicates a planet, and there is again a gap of several orders of magnitude between planets and dwarf planets.
There are several other schemes that try to differentiate between planets and dwarf planets, but the 2006 definition uses this concept.
Hydrostatic equilibrium
Main article: Hydrostatic equilibrium| Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Enough internal pressure, caused by the body's gravitation, will turn a body plastic, and enough plasticity will allow high elevations to sink and hollows to fill in, a process known as gravitational relaxation. Bodies smaller than a few kilometers are dominated by non-gravitational forces and tend to have an irregular shape and may be rubble piles. Larger objects, where gravity is significant but not dominant, are potato-shaped; the more massive the body, the higher its internal pressure, the more solid it is and the more rounded its shape, until the pressure is enough to overcome its compressive strength and it achieves hydrostatic equilibrium. Then, a body is as round as it is possible to be, given its rotation and tidal effects, and is an ellipsoid in shape. This is the defining limit of a dwarf planet.
If an object is in hydrostatic equilibrium, a global layer of liquid on its surface would form a surface of the same shape as the body, apart from small-scale surface features such as craters and fissures. The body will have a spherical shape if it does not rotate and an ellipsoidal one if it does. The faster it rotates, the more oblate or even scalene it becomes. If such a rotating body were heated until it melts, its shape would not change. The extreme example of a body that may be scalene due to rapid rotation is Haumea, which is twice as long on its major axis as it is at the poles. If the body has a massive nearby companion, then tidal forces gradually slow its rotation until it is tidally locked; that is, it always presents the same face to its companion. Tidally locked bodies are also scalene, though sometimes only slightly so. Earth's Moon is tidally locked, as are all the rounded satellites of the gas giants. Pluto and Charon are tidally locked to each other, as are Eris and Dysnomia, and probably also Orcus and Vanth.
There are no specific size or mass limits of dwarf planets, as those are not defining features. There is no clear upper limit: an object very far out in the Solar System that is more massive than Mercury might not have had time to clear its neighbourhood, and such a body would fit the definition of dwarf planet rather than planet. Indeed, Mike Brown set out to find such an object. The lower limit is determined by the requirements of achieving and retaining hydrostatic equilibrium, but the size or mass at which an object attains and retains equilibrium depends on its composition and thermal history, not simply its mass. An IAU 2006 press release question-and-answer section estimated that objects with mass above 0.5×10 kg and radius greater than 400 km would "normally" be in hydrostatic equilibrium (the shape ... would normally be determined by self-gravity), but that all borderline cases would need to be determined by observation. This is close to what as of 2019 is believed to be roughly the limit for objects beyond Neptune that are fully compact, solid bodies, with Salacia ( r = 423±11 km , m = (0.492±0.007)×10 kg ) being a borderline case both for the 2006 Q&A expectations and in more recent evaluations, and with Orcus being just above the expected limit. No other body with a measured mass is close to the expected mass limit, though several without a measured mass approach the expected size limit.
Population of dwarf planets
Main article: List of possible dwarf planets
Though the definition of a dwarf planet is clear, evidence about whether a given trans-Neptunian object is large and malleable enough to be shaped by its own gravitational field is often inconclusive. There are also outstanding questions relating to the interpretation of the IAU criterion in certain instances. Consequently the number of currently conformed TNOs which meet the hydrostatic equilibrium criterion is uncertain.
The three objects under consideration during the debates leading up to the 2006 IAU acceptance of the category of dwarf planet – Ceres, Pluto and Eris – are generally accepted as dwarf planets, including by those astronomers who continue to classify dwarf planets as planets. Only one of them – Pluto – has been observed in enough detail to verify that its current shape fits what would be expected from hydrostatic equilibrium. Ceres is close to equilibrium, but some gravitational anomalies remain unexplained. Eris is generally assumed to be a dwarf planet because it is more massive than Pluto.
In order of discovery, these three bodies are:
- Ceres – discovered January 1, 1801, and announced January 24, 45 years before Neptune. Considered a planet for half a century before reclassification as an asteroid. Considered a dwarf planet by the IAU since the adoption of Resolution 5A on August 24, 2006.
- Pluto – discovered February 18, 1930, and announced March 13. Considered a planet for 76 years. Explicitly reclassified as a dwarf planet by the IAU with Resolution 6A on August 24, 2006. Five known moons.
- Eris (2003 UB313) – discovered January 5, 2005, and announced July 29. Called the "tenth planet" in media reports. Considered a dwarf planet by the IAU since the adoption of Resolution 5A on August 24, 2006, and named by the IAU dwarf-planet naming committee on September 13 of that year. One known moon.
The IAU only established guidelines for which committee would oversee the naming of likely dwarf planets: any unnamed trans-Neptunian object with an absolute magnitude brighter than +1 (and hence a minimum diameter of 838 km at the maximum geometric albedo of 1) was to be named by a joint committee consisting of the Minor Planet Center and the planetary working group of the IAU. At the time (and still as of 2023), the only bodies to meet this threshold were Haumea and Makemake. These bodies are generally assumed to be dwarf planets, although they have not yet been demonstrated to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, and there is some disagreement for Haumea:
- Haumea (2003 EL61) – discovered by Brown et al. December 28, 2004, and announced by Ortiz et al. on July 27, 2005. Named by the IAU dwarf-planet naming committee on September 17, 2008. Two known moons and one known ring.
- Makemake (2005 FY9) – discovered March 31, 2005, and announced July 29. Named by the IAU dwarf-planet naming committee on July 11, 2008. One known moon.
These five bodies – the three under consideration in 2006 (Pluto, Ceres and Eris) plus the two named in 2008 (Haumea and Makemake) – are commonly presented as the dwarf planets of the Solar System, though the limiting factor (albedo) is not what defines an object as a dwarf planet.
The astronomical community commonly refers to other larger TNOs as dwarf planets as well. At least four additional bodies meet the preliminary criteria of Brown, of Tancredi et al., of Grundy et al., and of Emery et al. for identifying dwarf planets, and are generally called dwarf planets by astronomers as well:
- Quaoar (2002 LM60) – discovered June 5, 2002, and announced October 7 of that year. One known moon and two known rings.
- Sedna (2003 VB12) – discovered November 14, 2003, and announced March 15, 2004.
- Orcus (2004 DW) – discovered February 17, 2004, and announced two days later. One known moon.
- Gonggong (2007 OR10) – discovered July 17, 2007, and announced January 2009. One known moon.
For instance, JPL/NASA called Gonggong a dwarf planet after observations in 2016, and Simon Porter of the Southwest Research Institute spoke of "the big eight dwarf planets" in 2018, referring to Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Sedna and Orcus. The IAU itself has called Quaoar a dwarf planet in a 2022–2023 annual report.
More bodies have been proposed, such as Salacia and (307261) 2002 MS4 by Brown; Varuna and Ixion by Tancredi et al., and (532037) 2013 FY27 by Sheppard et al. Most of the larger bodies have moons, which enables a determination of their mass and thus their density, which inform estimates of whether they could be dwarf planets. The largest TNOs that are not known to have moons are Sedna, (307261) 2002 MS4, (55565) 2002 AW197 and Ixion. In particular, Salacia has a known mass and diameter, putting it as a borderline case by the IAU's 2006 Q&A.
- Salacia (2004 SB60) – discovered September 22, 2004. One known moon.
At the time Makemake and Haumea were named, it was thought that trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) with icy cores would require a diameter of only about 400 km (250 mi), or 3% the size of Earth – the size of the moons Mimas, the smallest moon that is round, and Proteus, the largest that is not – to relax into gravitational equilibrium. Researchers thought that the number of such bodies could prove to be around 200 in the Kuiper belt, with thousands more beyond. This was one of the reasons (keeping the roster of 'planets' to a reasonable number) that Pluto was reclassified in the first place. Research since then has cast doubt on the idea that bodies that small could have achieved or maintained equilibrium under the typical conditions of the Kuiper belt and beyond.
Individual astronomers have recognized a number of objects as dwarf planets or as likely to prove to be dwarf planets. In 2008, Tancredi et al. advised the IAU to officially accept Orcus, Sedna and Quaoar as dwarf planets (Gonggong was not yet known), though the IAU did not address the issue then and has not since. Tancredi also considered the five TNOs Varuna, Ixion, 2003 AZ84, 2004 GV9, and 2002 AW197 to most likely be dwarf planets as well. Since 2011, Brown has maintained a list of hundreds of candidate objects, ranging from "nearly certain" to "possible" dwarf planets, based solely on estimated size. As of September 13, 2019, Brown's list identifies ten trans-Neptunian objects with diameters then thought to be greater than 900 km (the four named by the IAU plus Gonggong, Quaoar, Sedna, Orcus, (307261) 2002 MS4, and Salacia) as "near certain" to be dwarf planets, and another 16, with diameter greater than 600 km, as "highly likely". Notably, Gonggong may have a larger diameter (1230±50 km) than Pluto's round moon Charon (1212 km).
But in 2019 Grundy et al. proposed, based on their studies of Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà, that dark, low-density bodies smaller than about 900–1000 km in diameter, such as Salacia and Varda, never fully collapsed into solid planetary bodies and retain internal porosity from their formation (in which case they could not be dwarf planets). They accept that brighter (albedo > ≈0.2) or denser (> ≈1.4 g/cc) Orcus and Quaoar probably were fully solid:
Orcus and Charon probably melted and differentiated, considering their higher densities and spectra indicating surfaces made of relatively clean H2O ice. But the lower albedos and densities of Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà, 55637, Varda, and Salacia suggest that they never did differentiate, or if they did, it was only in their deep interiors, not a complete melting and overturning that involved the surface. Their surfaces could remain quite cold and uncompressed even as the interior becomes warm and collapses. The liberation of volatiles could further help transport heat out of their interiors, limiting the extent of their internal collapse. An object with a cold, relatively pristine surface and a partially collapsed interior should exhibit very distinctive surface geology, with abundant thrust faults indicative of the reduction in total surface area as the interior compresses and shrinks.
Salacia was later found to have a somewhat higher density, comparable within uncertainties to that of Orcus, though still with a very dark surface. Despite this determination, Grundy et al. call it "dwarf-planet sized", while calling Orcus a dwarf planet. Later studies on Varda suggest that its density may also be high, though a low density could not be excluded.
In 2023, Emery et al. wrote that near-infrared spectroscopy by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) in 2022 suggests that Sedna, Gonggong, and Quaoar underwent internal melting, differentiation, and chemical evolution, like the larger dwarf planets Pluto, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake, but unlike "all smaller KBOs". This is because light hydrocarbons are present on their surfaces (e.g. ethane, acetylene, and ethylene), which implies that methane is continuously being resupplied, and that methane would likely come from internal geochemistry. On the other hand, the surfaces of Sedna, Gonggong, and Quaoar have low abundances of CO and CO2, similar to Pluto, Eris, and Makemake, but in contrast to smaller bodies. This suggests that the threshold for dwarf planethood in the trans-Neptunian region is a diameter of ~900 km (thus including only Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Sedna), and that even Salacia may not be a dwarf planet. A 2023 study of (307261) 2002 MS4 shows that it probably has an extremely large crater, whose depth takes up 5.7% of its diameter: this is proportionally larger than the Rheasilvia crater on Vesta, which is the reason Vesta is not usually considered a dwarf planet today.
In 2024, Kiss et al. found that Quaoar has an ellipsoidal shape incompatible with hydrostatic equilibrium for its current spin. They hypothesised that Quaoar originally had a rapid rotation and was in hydrostatic equilibrium, but that its shape became "frozen in" and did not change as it spun down due to tidal forces from its moon Weywot. If so, this would resemble the situation of Saturn's moon Iapetus, which is too oblate for its current spin. Iapetus is generally still considered a planetary-mass moon nonetheless, though not always.
Most likely dwarf planets
Main article: List of possible dwarf planetsThe trans-Neptunian objects in the following tables, except Salacia, are agreed by Brown, Tancredi et al., Grundy et al., and Emery et al. to be probable dwarf planets, or close to it. Salacia has been included as the largest TNO not generally agreed to be a dwarf planet; it is a borderline body by many criteria, and is therefore italicized. Charon, a moon of Pluto that was proposed as a dwarf planet by the IAU in 2006, is included for comparison. Those objects that have absolute magnitude greater than +1, and so meet the threshold of the joint planet–minor planet naming committee of the IAU, are highlighted, as is Ceres, which the IAU has assumed is a dwarf planet since they first debated the concept.
The masses of given dwarf planets are listed for their systems (if they have satellites) with exceptions for Pluto and Orcus.
| Name | Region of the Solar System |
Semi-major axis (AU) |
Orbital period (years) |
Mean orbital speed (km/s) |
Inclination to ecliptic |
Orbital eccentricity |
Planetary discriminant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceres | Asteroid belt | 2.768 | 4.604 | 17.90 | 10.59° | 0.079 | 0.3 |
| Orcus | Kuiper belt (resonant – 2:3) | 39.40 | 247.3 | 4.75 | 20.58° | 0.220 | 0.003 |
| Pluto | Kuiper belt (resonant – 2:3) | 39.48 | 247.9 | 4.74 | 17.16° | 0.249 | 0.08 |
| Salacia | Kuiper belt (cubewano) | 42.18 | 274.0 | 4.57 | 23.92° | 0.106 | 0.003 |
| Haumea | Kuiper belt (resonant – 7:12) | 43.22 | 284.1 | 4.53 | 28.19° | 0.191 | 0.02 |
| Quaoar | Kuiper belt (cubewano) | 43.69 | 288.8 | 4.51 | 7.99° | 0.040 | 0.007 |
| Makemake | Kuiper belt (cubewano) | 45.56 | 307.5 | 4.41 | 28.98° | 0.158 | 0.02 |
| Gonggong | Scattered disc (resonant – 3:10) | 67.49 | 554.4 | 3.63 | 30.74° | 0.503 | 0.01 |
| Eris | Scattered disc | 67.86 | 559.1 | 3.62 | 44.04° | 0.441 | 0.1 |
| Sedna | Detached | 506.8 | ≈ 11,400 | ≈ 1.3 | 11.93° | 0.855 | < 0.07 |
| Name | Diameter relative to the Moon |
Diameter (km) |
Mass relative to the Moon |
Mass (×10 kg) |
Density (g/cm) |
Rotation period (hours) |
Moons | Albedo | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceres | 27% | 939.4±0.2 | 1.3% | 0.93835±0.00001 | 2.16 | 9.1 | 0 | 0.09 | 3.33 |
| Orcus | 26% | 910+50 −40 |
0.8% | 0.55±0.01 | 1.4±0.2 | 13±4 | 1 | 0.23+0.02 −0.01 |
2.19 |
| Pluto | 68% | 2377±3 | 17.7% | 13.03±0.03 | 1.85 | 6d 9.3h | 5 | 0.49 to 0.66 | −0.45 |
| (Charon) | 35% | 1212±1 | 2.2% | 1.59±0.02 | 1.70±0.02 | 6d 9.3h | – | 0.2 to 0.5 | 1 |
| Salacia | 24% | 846±21 | 0.7% | 0.49±0.01 | 1.50±0.12 | 6.1 | 1 | 0.04 | 4.27 |
| Haumea | ≈ 45% | ≈ 1560 | 5.5% | 4.01±0.04 | ≈ 2.02 | 3.9 | 2 | ≈ 0.66 | 0.23 |
| Quaoar | 32% | 1086±4 | 1.9% | 1.2±0.05 | 1.7±0.1 | 17.7 | 1 | 0.11±0.01 | 2.42 |
| Makemake | 41% | 1430+38 −22 |
≈ 4.2% | ≈ 3.1 | 1.9±0.2 | 22.8 | 1 | 0.81+0.03 −0.05 |
−0.20 |
| Gonggong | 35% | 1230±50 | 2.4% | 1.75±0.07 | 1.74±0.16 | 22.4±0.2? | 1 | 0.14±0.01 | 1.86 |
| Eris | 67% | 2326±12 | 22.4% | 16.47±0.09 | 2.43±0.05 | 15d 18.9h | 1 | 0.96±0.04 | −1.21 |
| Sedna | 26% | 906+314 −258 |
≈ 1%? | ≈ 1? | ? | 10±3 | 0? | 0.41+0.393 −0.186 |
1.52 |
Symbols
Main article: Astronomical symbol § Symbols for trans-Neptunian objectsCeres ![]() and Pluto
and Pluto ![]() received planetary symbols, as they were considered to be planets when they were discovered. By the time the others were discovered, planetary symbols had mostly fallen out of use among astronomers. Unicode includes symbols for Quaoar
received planetary symbols, as they were considered to be planets when they were discovered. By the time the others were discovered, planetary symbols had mostly fallen out of use among astronomers. Unicode includes symbols for Quaoar ![]() , Sedna
, Sedna ![]() , Orcus
, Orcus ![]() , Haumea
, Haumea ![]() , Eris
, Eris ![]() , Makemake
, Makemake ![]() , and Gonggong
, and Gonggong ![]() that are primarily used by astrologers: they were devised by Denis Moskowitz, a software engineer in Massachusetts. NASA has used his Haumea, Eris, and Makemake symbols, as well as the traditional astrological symbol for Pluto
that are primarily used by astrologers: they were devised by Denis Moskowitz, a software engineer in Massachusetts. NASA has used his Haumea, Eris, and Makemake symbols, as well as the traditional astrological symbol for Pluto ![]() when referring to it as a dwarf planet. Symbols have been proposed for the next-largest named candidates, but do not have consistent usage among astrologers. The Unicode proposal for Quaoar, Orcus, Haumea, Makemake, and Gonggong mentions the following symbols for named objects over 600 km diameter: Salacia
when referring to it as a dwarf planet. Symbols have been proposed for the next-largest named candidates, but do not have consistent usage among astrologers. The Unicode proposal for Quaoar, Orcus, Haumea, Makemake, and Gonggong mentions the following symbols for named objects over 600 km diameter: Salacia ![]() , Varda
, Varda ![]() , Ixion
, Ixion ![]() , Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà
, Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà ![]() and Varuna
and Varuna ![]() .
.
Exploration

As of 2024, only two missions have targeted and explored dwarf planets up close. On March 6, 2015, the Dawn spacecraft entered orbit around Ceres, becoming the first spacecraft to visit a dwarf planet. On July 14, 2015, the New Horizons space probe flew by Pluto and its five moons.
Ceres displays such evidence of an active geology as salt deposits and cryovolcanos, while Pluto has water-ice mountains drifting in nitrogen-ice glaciers, as well as a significant atmosphere. Ceres evidently has brine percolating through its subsurface, while there is evidence that Pluto has an actual subsurface ocean.
Dawn had previously orbited the asteroid Vesta. Saturn's moon Phoebe has been imaged by Cassini and before that by Voyager 2, which also encountered Neptune's moon Triton. All three bodies show evidence of once being dwarf planets, and their exploration helps clarify the evolution of dwarf planets.
New Horizons has captured distant images of Triton, Quaoar, Haumea, Eris, and Makemake, as well as the smaller candidates Ixion, 2002 MS4, and 2014 OE394. One of the China National Space Administration's two Shensuo probes has been proposed to visit Quaoar in 2040.
Similar objects
A number of bodies physically resemble dwarf planets. These include former dwarf planets, which may still have equilibrium shape or evidence of active geology; planetary-mass moons, which meet the physical but not the orbital definition for dwarf planet; and Charon in the Pluto–Charon system, which is arguably a binary dwarf planet. The categories may overlap: Triton, for example, is both a former dwarf planet and a planetary-mass moon.
Former dwarf planets
Vesta, the next-most-massive body in the asteroid belt after Ceres, was once in hydrostatic equilibrium and is roughly spheroidal, deviating mainly due to massive impacts that formed the Rheasilvia and Veneneia craters after it solidified. Its dimensions are not consistent with it currently being in hydrostatic equilibrium. Triton is more massive than Eris or Pluto, has an equilibrium shape, and is thought to be a captured dwarf planet (likely a member of a binary system), but no longer directly orbits the sun. Phoebe is a captured centaur that, like Vesta, is no longer in hydrostatic equilibrium, but is thought to have been so early in its history due to radiogenic heating.
Planetary-mass moons
Main article: Planetary-mass moonAt least nineteen moons have equilibrium shape from having relaxed under self-gravity at some point, though some have since frozen solid and are no longer in equilibrium. Seven are more massive than either Eris or Pluto. These moons are not physically distinct from the dwarf planets, but do not fit the IAU definition because they do not directly orbit the Sun. (Indeed, Neptune's moon Triton is a captured dwarf planet, and Ceres formed in the same region of the Solar System as the moons of Jupiter and Saturn.) Alan Stern calls planetary-mass moons "satellite planets", one of three categories of planet, together with dwarf planets and classical planets. The term planemo ("planetary-mass object") also covers all three populations.
Charon
There has been some debate as to whether the Pluto–Charon system should be considered a double dwarf planet. In a draft resolution for the IAU definition of planet, both Pluto and Charon were considered planets in a binary system. The IAU currently says Charon is not considered a dwarf planet but rather a satellite of Pluto, though the idea that Charon might qualify as a dwarf planet may be considered at a later date. Nonetheless, it is no longer clear that Charon is in hydrostatic equilibrium. Also, the location of the barycenter depends not only on the relative masses of the bodies, but also on the distance between them; the barycenter of the Sun–Jupiter orbit, for example, lies outside the Sun, but they are not considered a binary object. Thus, a formal definition of what constitutes a binary (dwarf) planet must be established before Pluto and Charon are formally defined as binary dwarf planets.
See also
- Centaur
- Lists of astronomical objects
- List of former planets
- List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
- List of planetary bodies
- List of possible dwarf planets
- Lists of small Solar System bodies
- Solar System belts
Notes
- The hydrostatic equilibrium criterion of a dwarf planet cannot be confirmed unless a spacecraft directly visits the object.
- Calculated using the minimum estimate from 15 objects in its region with at least Sedna's mass, as estimated by Schwamb, Brown, & Rabinowitz (2009).
- The footnote in the original text reads: "For two or more objects comprising a multiple object system. ... A secondary object satisfying these conditions i.e. that of mass, shape is also designated a planet if the system barycentre resides outside the primary. Secondary objects not satisfying these criteria are "satellites". Under this definition, Pluto's companion Charon is a planet, making Pluto–Charon a double planet."
References
- "Dwarf planets are planets, too: Planetary pedagogy after New Horizons" Archived June 27, 2021, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ IAU (August 24, 2006). "Definition of a Planet in the Solar System: Resolutions 5 and 6" (PDF). IAU 2006 General Assembly. International Astronomical Union. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 20, 2009. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Metzger, Philip T.; Grundy, W. M.; Sykes, Mark V.; et al. (March 1, 2022). "Moons Are Planets: Scientific Usefulness Versus Cultural Teleology in the Taxonomy of Planetary Science". Icarus. 374: 114768. arXiv:2110.15285. Bibcode:2022Icar..37414768M. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2021.114768. S2CID 240071005. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- "In Depth | 4 Vesta". NASA Solar System Exploration. Archived from the original on February 29, 2020. Retrieved February 29, 2020.
- Mauro Murzi (2007). "Changes in a scientific concept: what is a planet?". Preprints in Philosophy of Science (Preprint). University of Pittsburgh. Archived from the original on June 11, 2019. Retrieved April 6, 2013.
- Mager, Brad. "Pluto Revealed". discoveryofpluto.com. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Cuk, Matija; Masters, Karen (September 14, 2007). "Is Pluto a planet?". Cornell University, Astronomy Department. Archived from the original on October 12, 2007. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Buie, Marc W.; Grundy, William M.; Young, Eliot F.; Young, Leslie A.; Stern, S. Alan (2006). "Orbits and Photometry of Pluto's Satellites: Charon, S/2005 P1, and S/2005 P2". The Astronomical Journal. 132 (1): 290–298. arXiv:astro-ph/0512491. Bibcode:2006AJ....132..290B. doi:10.1086/504422. S2CID 119386667.
- Jewitt, David; Delsanti, Audrey (2006). The Solar System Beyond The Planets in Solar System Update : Topical and Timely Reviews in Solar System Sciences (PDF). Springer. doi:10.1007/3-540-37683-6. ISBN 978-3-540-37683-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 25, 2006. Retrieved February 10, 2008.
- Weintraub, David A. (2006). Is Pluto a Planet? A Historical Journey through the Solar System. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton Univ. Press. pp. 1–272. ISBN 978-0-691-12348-6.
- Phillips, Tony; Phillips, Amelia (September 4, 2006). "Much Ado about Pluto". PlutoPetition.com. Archived from the original on January 25, 2008. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Brown, Michael E. (2004). "What is the definition of a planet?". California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Eicher, David J. (July 21, 2007). "Should Pluto Be Considered a Planet?". Astronomy. Archived from the original on November 28, 2022. Retrieved November 28, 2022.
- "Hubble Observes Planetoid Sedna, Mystery Deepens". NASA's Hubble Space Telescope home site. April 14, 2004. Archived from the original on January 13, 2021. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Brown, Mike (August 16, 2006). "War of the Worlds". The New York Times. Archived from the original on February 13, 2017. Retrieved February 20, 2008.
- "California Institute of Technology, Retrieved 4-12-2015". Archived from the original on May 17, 2012. Retrieved April 12, 2015.
- "Astronomers Measure Mass of Largest Dwarf Planet". NASA's Hubble Space Telescope home site. June 14, 2007. Archived from the original on August 7, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Brown, Michael E. "What makes a planet?". California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences. Archived from the original on May 16, 2012. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- ^ Britt, Robert Roy (August 19, 2006). "Details Emerge on Plan to Demote Pluto". Space.com. Archived from the original on June 28, 2011. Retrieved August 18, 2006.
- ^ "The IAU draft definition of "planet" and "plutons"". International Astronomical Union. August 16, 2006. Archived from the original on April 29, 2014. Retrieved May 17, 2008.
- ^ Rincon, Paul (August 25, 2006). "Pluto vote 'hijacked' in revolt". British Broadcasting Corporation. BBC News. Archived from the original on July 23, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Chang, Alicia (August 25, 2006). "Online merchants see green in Pluto news". USA Today. Associated Press. Archived from the original on May 11, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2008.
- Brown, Michael E. "The Eight Planets". California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- "Hotly-Debated Solar System Object Gets a Name" (Press release). NASA. September 14, 2006. Archived from the original on June 29, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Stern, Alan (September 6, 2006). "Unabashedly Onward to the Ninth Planet". New Horizons Web Site. Archived from the original on December 7, 2013. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Wall, Mike (August 24, 2011). "Pluto's Planet Title Defender: Q & A With Planetary Scientist Alan Stern". Space.com. Archived from the original on August 14, 2012. Retrieved December 3, 2012.
- ^ "Should Large Moons Be Called 'Satellite Planets'?". News.discovery.com. May 14, 2010. Archived from the original on May 5, 2012. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
- ^ Stern, S.A.; Levison, H.F. (August 7–18, 2000). Regarding the criteria for planethood and proposed planetary classification schemes (PDF). XXIVth General Assembly of the IAU – 2000. Highlights of Astronomy. Vol. 12. Manchester, UK (published 2002). pp. 205–213. Bibcode:2002HiA....12..205S. doi:10.1017/S1539299600013289. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 23, 2015. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Service, Tom (July 15, 2015). "Sounds of the solar system: probing Pluto's predicted score". The Guardian. Archived from the original on December 26, 2019. Retrieved December 26, 2019.
- Karttunen; et al., eds. (2007). Fundamental Astronomy (5 ed.). Springer.
- ^ Brown, Mike (2010). How I Killed Pluto and Why It Had It Coming. Spiegel & Grau. p. 223.
- Bailey, Mark E. "Comments & discussions on Resolution 5: The definition of a planet – Planets Galore". Dissertatio cum Nuncio Sidereo, Series Tertia – official newspaper of the IAU General Assembly 2006. Astronomical Institute Prague. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved February 9, 2008.
- "Dos uruguayos, Julio Fernández y Gonzalo Tancredi en la historia de la astronomía:reducen la cantidad de planetas de 9 a 8 ...&Anotaciones de Tancredi" (in Spanish). Science and Research Institute, Mercedes, Uruguay. Archived from the original on December 20, 2007. Retrieved February 11, 2008.
- ^ Bowell, Edward L.G.; Meech, Karen J.; Williams, Iwan P. ; et al. (December 1, 2008). "Division III: Planetary Systems Sciences". Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. 4 (T27A). Cambridge University Press: 149–153. doi:10.1017/S1743921308025398.
- "International Astronomical Union 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes". IAU. August 24, 2006. Archived from the original on April 29, 2014. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- ^ "Plutoid chosen as name for Solar System objects like Pluto". IAU. Paris. June 11, 2008. Archived from the original on November 23, 2020. Retrieved August 10, 2021.
- Carson, Mary Kay (2011). Far-Out Guide to the Icy Dwarf Planets. Enslow Publishers. ISBN 9780766031876. OCLC 441945398 – via Internet Archive.
- Lew, Kristi (2010). Space! The Dwarf Planet Pluto. New York: Marshall Cavendish Benchmark. p. 10. ISBN 9780761445531. OCLC 562529871 – via Internet Archive.
- Darling, David (ed.). "Ice dwarf". Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy and Spaceflight. Archived from the original on July 6, 2008. Retrieved June 22, 2008.
- "Ice Volcanoes and More: Dwarf Planet Ceres Continues to Surprise". Space.com. September 2016. Archived from the original on October 12, 2019. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
- Castillo-Rogez, J. C.; Raymond, C. A.; Russell, C. T.; et al. (September 12, 2017). "Dawn at Ceres: What Have we Learned?" (PDF). Committee on Astrobiology and Planetary Science. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 12, 2019.
- Carroll, Michael (October 23, 2019). "Ceres: The First Known Ice Dwarf Planet". Ice Worlds of the Solar System: Their Tortured Landscapes and Biological Potential. Springer Cham. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-28120-5. ISBN 978-3-030-28120-5.
- ^ Soter, S. (August 16, 2006). "What is a Planet?". The Astronomical Journal. 132 (6): 2513–2519. arXiv:astro-ph/0608359. Bibcode:2006AJ....132.2513S. doi:10.1086/508861. S2CID 14676169.
- Schwamb, Megan E.; Brown, Michael E.; Rabinowitz, David L. (2009). "A search for distant solar system bodies in the region of Sedna". The Astrophysical Journal. 694 (1): L45–L48. arXiv:0901.4173. Bibcode:2009ApJ...694L..45S. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/694/1/L45. S2CID 15072103.
- ^ Margot, Jean-Luc (October 15, 2015). "A quantitative criterion for defining planets". The Astronomical Journal. 150 (6): 185. arXiv:1507.06300. Bibcode:2015AJ....150..185M. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/6/185. S2CID 51684830.
- ^ Lakdawalla, Emily; et al. (April 21, 2020). "What is a planet?". planetary.org. The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on January 22, 2022. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- Brown, Mike. "The eight planets". gps.caltech.edu. Caltech. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- Jewitt, David. "Classification of Pluto". ess.ucla.edu. UCLA. Archived from the original on August 19, 2021. Retrieved August 19, 2021.
- Lineweaver, Charles H.; Norman, Marc (September 28–30, 2009). "The potato radius: A lower minimum size for dwarf planets" (PDF). In Short, W.; Cairns, I. (eds.). Proceedings of 2009 Australian Space Science Conference. 9th Australian Space Science Conference. National Space Society of Australia (published 2010). pp. 67–78. arXiv:1004.1091. ISBN 9780977574032. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 10, 2023. Retrieved August 11, 2023.
- Julia Sweeney (interviewer & host), M.E. Brown (interviewed astronomer) (June 28, 2007). Julia Sweeney and Michael E. Brown (podcast). Hammer Conversations. KCET. Archived from the original on June 26, 2008. Retrieved June 28, 2008.
Actress and comedienne Julia Sweeney (God Said Ha!) discusses the discovery that dwarfed Pluto with Caltech astronomer Michael E. Brown.
- ^ "'Planet definition' questions & answers sheet" (Press release). International Astronomical Union. August 24, 2006. Archived from the original on May 7, 2021. Retrieved October 16, 2021.
- ^ Grundy, W.M.; Noll, K.S.; Buie, M.W.; Benecchi, S.D.; Ragozzine, D.; Roe, H.G. (2019). "The Mutual Orbit, Mass, and Density of Transneptunian Binary Gǃkúnǁʼhòmdímà ((229762) 2007 UK126)". Icarus. 334: 30–38. Bibcode:2019Icar..334...30G. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2018.12.037. S2CID 126574999. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 7, 2019.
- Nimmo, Francis; et al. (2017). "Mean radius and shape of Pluto and Charon from New Horizons images". Icarus. 287: 12–29. arXiv:1603.00821. Bibcode:2017Icar..287...12N. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2016.06.027. S2CID 44935431.
- Raymond, C.; Castillo-Rogez, J.C.; Park, R.S.; Ermakov, A.; et al. (September 2018). "Dawn Data Reveal Ceres' Complex Crustal Evolution" (PDF). European Planetary Science Congress. Vol. 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 30, 2020. Retrieved July 19, 2020.
- 'Pluto is a "dwarf planet" by the above definition and is recognized as the prototype of a new category of trans-Neptunian objects'
- Dan Bruton. "Conversion of Absolute Magnitude to Diameter for Minor Planets". Department of Physics & Astronomy (Stephen F. Austin State University). Archived from the original on March 23, 2010. Retrieved June 13, 2008.
- Ortiz, J. L.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Sicardy, B.; Benedetti-Rossi, G.; Bérard, D.; Morales, N.; et al. (2017). "The size, shape, density and ring of the dwarf planet Haumea from a stellar occultation" (PDF). Nature. 550 (7675): 219–223. arXiv:2006.03113. Bibcode:2017Natur.550..219O. doi:10.1038/nature24051. hdl:10045/70230. PMID 29022593. S2CID 205260767. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 7, 2020. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ Dunham, E. T.; Desch, S. J.; Probst, L. (April 2019). "Haumea's Shape, Composition, and Internal Structure". The Astrophysical Journal. 877 (1): 11. arXiv:1904.00522. Bibcode:2019ApJ...877...41D. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab13b3. S2CID 90262114.
- "Dwarf Planets and their Systems". Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). July 11, 2008. Archived from the original on July 14, 2007. Retrieved September 12, 2019.
- Pinilla-Alonso, Noemi; Stansberry, John A.; Holler, Bryan J. (November 22, 2019). "Surface properties of large TNOs: Expanding the study to longer wavelengths with the James Webb Space Telescope". In Dina Prialnik; Maria Antonietta Barucci; Leslie Young (eds.). The Transneptunian Solar System. Elsevier. arXiv:1905.12320.
- Dyches, Preston (May 11, 2016). "2007 OR10: Largest Unnamed World in the Solar System". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Archived from the original on November 23, 2020. Retrieved September 12, 2019.
- Porter, Simon (March 27, 2018). "#TNO2018". Twitter. Archived from the original on October 2, 2018. Retrieved March 27, 2018.
- "Report of Division F "Planetary Systems and Astrobiology": Annual Report 2022-23" (PDF). International Astronomical Union. 2022–2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 8, 2023. Retrieved December 8, 2023.
- Sheppard, Scott S.; Fernandez, Yanga R.; Moullet, Arielle (November 16, 2018). "The Albedos, Sizes, Colors, and Satellites of Dwarf Planets Compared with Newly Measured Dwarf Planet 2013 FY27". The Astronomical Journal. 156 (6): 270. arXiv:1809.02184. Bibcode:2018AJ....156..270S. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aae92a. S2CID 119522310.
- ^ Brown, Michael E. "The Dwarf Planets". California Institute of Technology, Department of Geological Sciences. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- ^ Brown, Mike. "How many dwarf planets are there in the outer solar system?". CalTech. Archived from the original on October 18, 2011. Retrieved November 15, 2013.
- Stern, Alan (August 24, 2012). "The PI's Perspective". Archived from the original on November 13, 2014. Retrieved August 24, 2012.
- Tancredi, G.; Favre, S. A. (2008). "Which are the dwarfs in the Solar System?". Icarus. 195 (2): 851–862. Bibcode:2008Icar..195..851T. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.12.020.
- Brown, Michael (August 23, 2011). "Free the Dwarf Planets!". Mike Brown's Planets. Archived from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved August 24, 2011.
- Of bodies smaller than 900 km in diameter, the only ones thought to have albedos much greater than this are fragments in the Haumea collisional family and possibly 2005 QU182 (albedo between 0.2 and 0.5).
- Grundy, W. M.; Noll, K. S.; Roe, H. G.; Buie, M. W.; Porter, S. B.; Parker, A. H.; Nesvorný, D.; Benecchi, S. D.; Stephens, D. C.; Trujillo, C. A. (2019). "Mutual Orbit Orientations of Transneptunian Binaries" (PDF). Icarus. 334: 62–78. Bibcode:2019Icar..334...62G. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2019.03.035. ISSN 0019-1035. S2CID 133585837. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 15, 2020. Retrieved October 26, 2019.
- Souami, D.; Braga-Ribas, F.; Sicardy, B.; Morgado, B.; Ortiz, J. L.; Desmars, J.; et al. (August 2020). "A multi-chord stellar occultation by the large trans-Neptunian object (174567) Varda". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 643: A125. arXiv:2008.04818. Bibcode:2020A&A...643A.125S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202038526. S2CID 221095753.
- Emery, J. P.; Wong, I.; Brunetto, R.; Cook, J. C.; Pinilla-Alonso, N.; Stansberry, J. A.; Holler, B. J.; Grundy, W. M.; Protopapa, S.; Souza-Feliciano, A. C.; Fernández-Valenzuela, E.; Lunine, J. I.; Hines, D. C. (2024). "A Tale of 3 Dwarf Planets: Ices and Organics on Sedna, Gonggong, and Quaoar from JWST Spectroscopy". Icarus. 414. arXiv:2309.15230. Bibcode:2024Icar..41416017E. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2024.116017.
- Rommel, F. L.; Braga-Ribas, F.; Ortiz, J. L.; Sicardy, B.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Desmars, J.; et al. (October 2023). "A large topographic feature on the surface of the trans-Neptunian object (307261) 2002 MS4 measured from stellar occultations". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 678: 25. arXiv:2308.08062. Bibcode:2023A&A...678A.167R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346892. S2CID 260926329. A167.
- Kiss, C.; Müller, T. G.; Marton, G.; Szakáts, R.; Pál, A.; Molnár, L.; et al. (March 2024). "The visible and thermal light curve of the large Kuiper belt object (50000) Quaoar". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 684: A50. arXiv:2401.12679. Bibcode:2024A&A...684A..50K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202348054.
- Cowen, R. (2007). Idiosyncratic Iapetus, Science News vol. 172, pp. 104–106. references Archived October 13, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- Thomas, P. C. (July 2010). "Sizes, shapes, and derived properties of the saturnian satellites after the Cassini nominal mission" (PDF). Icarus. 208 (1): 395–401. Bibcode:2010Icar..208..395T. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2010.01.025. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 23, 2018. Retrieved September 25, 2015.
- Chen, Jingjing; Kipping, David (2016). "Probabilistic Forecasting of the Masses and Radii of Other Worlds". The Astrophysical Journal. 834 (1): 17. arXiv:1603.08614. Bibcode:2017ApJ...834...17C. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/834/1/17. S2CID 119114880.
- Bode, J.E., ed. (1801). Berliner astronomisches Jahrbuch führ das Jahr 1804 [The Berlin Astronomical Yearbook for 1804]. pp. 97–98. Archived from the original on December 14, 2023. Retrieved October 19, 2022.
- Slipher, V.M. (1930). "The trans-Neptunian planet". Popular Astronomy. Vol. 38. p. 415. Archived from the original on December 11, 2021. Retrieved October 19, 2022.
- Anderson, Deborah (May 4, 2022). "Out of this World: New Astronomy Symbols Approved for the Unicode Standard". unicode.org. The Unicode Consortium. Archived from the original on August 6, 2022. Retrieved August 6, 2022.
- ^ Miller, Kirk (October 26, 2021). "Unicode request for dwarf-planet symbols" (PDF). unicode.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 23, 2022. Retrieved October 19, 2022.
- "Alchemical Symbols" (PDF). unicode.org. The Unicode Consortium. 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 2, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2022.
- "What is a Dwarf Planet?". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NASA. April 22, 2015. Archived from the original on December 8, 2021. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- Miller, Kirk (October 18, 2024). "Preliminary presentation of constellation symbols" (PDF). unicode.org. The Unicode Consortium. Retrieved October 22, 2024.
- Landau, Elizabeth; Brown, Dwayne (March 6, 2015). "NASA Spacecraft Becomes First to Orbit a Dwarf Planet". NASA. Archived from the original on March 7, 2015. Retrieved March 6, 2015.
- Verbiscer, Anne J.; Helfenstein, Paul; Porter, Simon B.; Benecchi, Susan D.; Kavelaars, J. J.; Lauer, Tod R.; et al. (April 2022). "The Diverse Shapes of Dwarf Planet and Large KBO Phase Curves Observed from New Horizons". The Planetary Science Journal. 3 (4): 31. Bibcode:2022PSJ.....3...95V. doi:10.3847/PSJ/ac63a6. 95.
- Jones, Andrew (April 16, 2021). "China to launch a pair of spacecraft towards the edge of the solar system". SpaceNews. SpaceNews. Archived from the original on September 29, 2021. Retrieved April 29, 2021.
- Thomas, Peter C.; Binzelb, Richard P.; Gaffeyc, Michael J.; Zellnerd, Benjamin H.; Storrse, Alex D.; Wells, Eddie (1997). "Vesta: Spin Pole, Size, and Shape from HST Images". Icarus. 128 (1): 88–94. Bibcode:1997Icar..128...88T. doi:10.1006/icar.1997.5736.
- Asmar, S. W.; Konopliv, A. S.; Park, R. S.; Bills, B. G.; Gaskell, R.; Raymond, C. A.; Russell, C. T.; Smith, D. E.; Toplis, M. J.; Zuber, M. T. (2012). "The Gravity Field of Vesta and Implications for Interior Structure" (PDF). 43rd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (1659): 2600. Bibcode:2012LPI....43.2600A. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- Russel, C. T.; et al. (2012). "Dawn at Vesta: Testing the Protoplanetary Paradigm" (PDF). Science. 336 (6082): 684–686. Bibcode:2012Sci...336..684R. doi:10.1126/science.1219381. PMID 22582253. S2CID 206540168. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 15, 2015. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- Agnor, C. B.; Hamilton, D. P. (2006). "Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary–planet gravitational encounter" (PDF). Nature. 441 (7090): 192–194. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..192A. doi:10.1038/nature04792. PMID 16688170. S2CID 4420518. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 14, 2016. Retrieved August 29, 2015.
- Cook, Jia-Rui C.; Brown, Dwayne (April 26, 2012). "Cassini Finds Saturn Moon Has Planet-Like Qualities". Jey Propoulsion Laboratory. Pasadena, California: NASA. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015.
- Basri, Gibor; Brown, Michael E. (2006). "Planetesimals to Brown Dwarfs: What is a Planet?" (PDF). Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. 34: 193–216. arXiv:astro-ph/0608417. Bibcode:2006AREPS..34..193B. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.34.031405.125058. S2CID 119338327. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 31, 2013.
- "Pluto and the Solar System". iau.org. International Astronomical Union. Archived from the original on April 17, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2013.
External links
- A Visual Introduction to the Dwarf Planets in our Solar System (Anshool Deshmukh, Visual Capitalist, October 8, 2021, graphics by Mark Belan)
- NPR: Dwarf Planets May Finally Get Respect (David Kestenbaum, Morning Edition)
- BBC News: Q&A New planets proposal, August 16, 2006
- Ottawa Citizen: The case against Pluto (P. Surdas Mohit) August 24, 2006
- James L. Hilton: When Did the Asteroids Become Minor Planets?
- NASA: IYA 2009 Dwarf Planets
| Solar System | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Solar System → Local Interstellar Cloud → Local Bubble → Gould Belt → Orion Arm → Milky Way → Milky Way subgroup → Local Group → Local Sheet → Virgo Supercluster → Laniakea Supercluster → Local Hole → Observable universe → Universe | |||||||||||||||||||||


