| Revision as of 22:54, 25 June 2006 view sourceAntiVandalBot (talk | contribs)258,750 editsm BOT - rv 202.37.173.10 (talk) to last version by Ohnoitsjamie← Previous edit | Revision as of 06:14, 8 December 2024 view source Citation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,403,233 edits Altered url. URLs might have been anonymized. Added date. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Pack animals | #UCB_Category 1/11Next edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Domesticated equine}} | |||
| {{cleanup-date|June 2006}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=November 2024}} | |||
| {{otheruses}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| {{pp|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Taxobox | |||
| {{Good article}} | |||
| | color = pink | |||
| {{Subspeciesbox | |||
| | name = Domestic Horse | |||
| | name = Horse | |||
| | status = {{StatusDomesticated}} | |||
| | |
| status = DOM | ||
| | image = Nokota Horses cropped.jpg | |||
| | image_width = 225px | |||
| | image_caption = <!-- Caption intentionally left blank per consensus to avoid promoting one breed. --> | |||
| | regnum = ]ia | |||
| | image_alt = Two Nokota horses standing in open grassland with rolling hills and trees visible in the background. | |||
| | phylum = ] | |||
| | |
| genus = Equus | ||
| | species = ferus | |||
| | ordo = ] | |||
| | species_link = Wild horse | |||
| | familia = ] | |||
| | subspecies = caballus | |||
| | genus = '']'' | |||
| | authority = ], ]<ref name="Linn1758">{{cite book | last = Linnaeus | first = Carolus | author-link = Carl Linnaeus | title = Systema naturae per regna tria naturae :secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis | publisher = Holmiae (Laurentii Salvii) | year = 1758 | page = 73 | url = https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726976 | access-date = 2008-09-08 | volume = 1 | edition = 10th | archive-date = 2018-10-12 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20181012203414/https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726976 | url-status = live }}</ref> | |||
| | subgenus = ''Equus'' | |||
| | synonyms = at least 48 published | |||
| | species = '''''E. caballus''''' | |||
| | synonyms_ref = <ref name=MSW3/> | |||
| | binomial = ''Equus caballus'' | |||
| | binomial_authority = ], 1758 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''horse''' ('''''Equus ferus caballus''''')<ref name=MSW3>{{MSW3 Perissodactyla | id = 14100016 | pages = 630–631}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature|year=2003|title=Usage of 17 specific names based on wild species which are pre-dated by or contemporary with those based on domestic animals (Lepidoptera, Osteichthyes, Mammalia): conserved. Opinion 2027 (Case 3010)|journal=Bull. Zool. Nomencl.|volume=60|issue=1|pages=81–84|url=http://www.nhm.ac.uk/hosted_sites/iczn/BZNMar2003opinions.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070821235959/http://www.nhm.ac.uk/hosted_sites/iczn/BZNMar2003opinions.htm|archive-date=2007-08-21}}</ref> is a ], ], ]. It belongs to the taxonomic family ] and is one of two ] ] of ]. The horse has ] over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, '']'', into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 ], and their ] is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies ''caballus'' are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as ]s. These feral populations are not true ]s, which are horses that never have been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from ] to life stages, size, ], ], ], ], and behavior. | |||
| The '''horse''' (''Equus caballus'' or ''Equus ferus caballus'') is a large ] ], one of ten modern species of the genus '']''. Horses have long been one of the most economically important ] animals, and have played an important role in the ] of people and ] for thousands of years. While isolated ] may have occurred as early as 10,000 years ago, clear evidence of widespread horse use by humans dates to around ]. | |||
| Horses are ], allowing them to quickly escape predators, and possess a good ] and a strong ]. Related to this need to flee from predators in the wild is an unusual trait: horses are able to sleep both standing up and lying down, with younger horses tending to sleep significantly more than adults.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.thespruce.com/learn-how-all-horses-sleep-1887328|title=Do You Know How Horses Sleep?|access-date=12 September 2018|archive-date=22 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180122181803/https://www.thespruce.com/learn-how-all-horses-sleep-1887328|url-status=live}}</ref> Female horses, called ]s, carry their young for approximately 11 months and a young horse, called a ], can stand and run shortly following birth. Most domesticated horses begin training under a ] or in a ] between the ages of two and four. They reach full adult development by age five, and have an average lifespan of between 25 and 30 years. | |||
| Horses have been carefully bred so that they can be ], usually with a ]. They can also be ] to pull objects like ]s or ]s. In some cultures, horses are a source of food, including ] and sometimes ]; in other cultures it is taboo to eat them. | |||
| Horse breeds are loosely divided into three categories based on general temperament: spirited "hot bloods" with speed and endurance; "cold bloods", such as ]s and some ], suitable for slow, heavy work; and "]s", developed from crosses between hot bloods and cold bloods, often focusing on creating breeds for specific riding purposes, particularly in Europe. There are more than 300 breeds of horse in the world today, developed for many different uses. | |||
| Today, in wealthy countries, horses are predominently kept for leisure and sporting pursuits. However, around the world they continue to fulfill a wide range of economic functions. | |||
| Horses and humans interact in a wide variety of sport competitions and non-competitive recreational pursuits as well as in working activities such as ], ], entertainment, and ]. Horses were historically used in warfare, from which a wide variety of ] and ] techniques developed, using many different styles of ] and methods of control. Many products are derived from horses, including ], ], ], ], bone, and ]. Humans provide domesticated horses with food, water, and shelter, as well as attention from specialists such as ]s and ]s. | |||
| Humans have bred horses for millennia, resulting in many different ]. As with ] breeding, horses have been bred in order to develop particular, specialised qualities and abilities; for example, ]s were developed for the speed required in ]. | |||
| ==Biology |
==Biology== | ||
| {{Main|Equine anatomy}} | |||
| Depending on breed, management, and environment, the domestic horse today has an average life expectancy of 25 to 30 years, though there are many exceptions in both directions. | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Lifespan and life stages=== | |||
| The ] is pregnant for 11 months and usually gives birth to one ] (male: ], female: ]). Twins are rare, but do occur on occasion. Horses may sometimes be physically capable of reproduction at approximately 18 months, particularly colts, but in practice rarely are allowed to breed until the age of 2 or 3 years at the earliest. Fillies are rarely bred until they are at least 3 years old. Horses are not considered completely grown until an average age of 4 years, though age of achieving full growth also varies by breed and by individual genetics. In the strenuous sport of ], horses are not allowed to compete until they are a full 60 months (5 years) old. | |||
| Depending on breed, ] and environment, the modern domestic horse has a life expectancy of 25 to 30 years.<ref name=Ensminger46/> Uncommonly, a few animals live into their 40s and, occasionally, beyond.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/livestock/horses/facts/info_age.htm|title=The Age of a Horse|publisher=Government of Ontario|website=Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs|author=Wright, B.|date=March 29, 1999|access-date=2009-10-21|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100120031232/http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/livestock/horses/facts/info_age.htm|archive-date=January 20, 2010}}</ref> The oldest verifiable record was "]", a 19th-century horse that lived to the age of 62.<ref name=Ensminger46/> In modern times, Sugar Puff, who had been listed in '']'' as the world's oldest living pony, died in 2007 at age 56.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.thehorse.com/viewarticle.aspx?ID=9708|title= World's Oldest Living Pony Dies at 56|access-date= 2007-05-31|author= Ryder, Erin|website= The Horse|archive-date= 2014-01-24|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20140124211019/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/18956/worlds-oldest-living-pony-dies-at-56|url-status= live}}</ref> | |||
| Regardless of a horse or pony's actual birth date, for most competition purposes a year is added to its age each January 1 of each year in the Northern Hemisphere<ref name=Ensminger46/><ref>{{cite book |title= The Manual of Horsemanship of the British Horse Society and the Pony Club |url= https://archive.org/details/manualofhorseman00pony |url-access= registration |author=British Horse Society |year=1966|edition=6th edition, reprinted 1970 |publisher= British Horse Society |location= Kenilworth, UK |isbn= 0-9548863-1-3|page= }}</ref> and each August 1 in the Southern Hemisphere.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.studbook.org.au/DisplayPDF.aspx?ty=RULES |format= PDF |title= Rules of the Australian Stud Book |access-date= 2008-07-09 |year= 2007 |publisher= Australian Jockey Club |page= 7 |archive-date= 2013-04-24 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130424221902/http://www.studbook.org.au/DisplayPDF.aspx?ty=RULES |url-status= live }}</ref> The exception is in ], where the minimum age to compete is based on the animal's actual calendar age.<ref name=Endurance>{{cite web|url= http://www.aerc.org/HorseAge.aspx|title= Equine Age Requirements for AERC Rides|access-date= 2011-07-25|publisher= American Endurance Riding Conference|url-status=dead|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110811110201/http://aerc.org/HorseAge.aspx|archive-date= 2011-08-11}}</ref> | |||
| The size of horses varies, depending on the breed. The cutoff in height between what is considered a horse and a pony is generally 14.2 ] (58 inches, 145 cm), though some smaller horse breeds are considered "horses" regardless of height. Light horses such as ]s, ], ]s, ] and ]s usually range in height from 14.0 to 17.0 hands, and can weigh up to 1300lbs (about 595kg). Heavy or ]s such as the ], ], ], and ] are usually at least 16.0 hands tall and can weigh up to 2000lbs (about 907kg). Ponies are no taller than 14.2 hands, but can be much smaller, down to the ] which can be the size of a large dog. | |||
| The following terminology is used to describe horses of various ages: | |||
| ==Evolution of the horse== | |||
| ; ] | |||
| ]''<!-- Eohippus is a synonym, refer to correct name-->, is the oldest known ancestor of all modern horses, was only about 8 inches (20 cm) high at the shoulder.]] | |||
| : A horse of either sex less than one year old. A nursing foal is sometimes called a ''suckling'', and a foal that has been weaned is called a ''weanling''.<ref name=Ensminger418>], p. 418</ref> Most domesticated foals are weaned at five to seven months of age, although foals can be weaned at four months with no adverse physical effects.<ref>], p. 431</ref> | |||
| {{main|Evolution of the horse}} | |||
| ; ] | |||
| : A horse of either sex that is between one and two years old.<ref>], p. 430</ref> | |||
| ; ] | |||
| : A male horse under the age of four.<ref>], p. 415</ref> A common terminology error is to call any young horse a "colt", when the term actually only refers to young male horses.<ref>{{cite book|author1=Becker, Marty|author2=Pavia, Audrey|author3=Spadafori, Gina|author4=Becker, Teresa|title=Why Do Horses Sleep Standing Up?: 101 of the Most Perplexing Questions Answered About Equine Enigmas, Medical Mysteries, and Befuddling Behaviors|publisher=HCI|year=2007|isbn=978-0-7573-0608-2|url=https://archive.org/details/whydohorsessleep0000unse/page/23|page=}}</ref> | |||
| ; ] | |||
| : A female horse under the age of four.<ref name=Ensminger418/> | |||
| ; ] | |||
| : A female horse four years old and older.<ref>], p. 422</ref> | |||
| ; ] | |||
| : A non-castrated male horse four years old and older.<ref>], p. 427</ref> The term "horse" is sometimes used colloquially to refer specifically to a stallion.<ref name=Ensminger420>], p. 420</ref> | |||
| ; ] | |||
| : A ] male horse of any age.<ref name=Ensminger418/> | |||
| In ], these definitions may differ: For example, in the British Isles, ] horse racing defines colts and fillies as less than five years old.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.equibase.com/newfan/glossary-full.cfm|title= Glossary of Horse Racing Terms|access-date= 2008-04-03|website= Equibase.com|publisher= Equibase Company, LLC|archive-date= 2008-05-12|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080512170317/http://www.equibase.com/newfan/glossary-full.cfm|url-status= live}}</ref> However, Australian Thoroughbred racing defines colts and fillies as less than four years old.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.studbook.org.au/DisplayPDF.aspx?ty=RULES|title=Rules of the Australian Stud Book|access-date=2010-02-05|page=9|date=July 2008|publisher=Australian Jockey Club Ltd and Victoria Racing Club Ltd|archive-date=2013-04-24|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130424221902/http://www.studbook.org.au/DisplayPDF.aspx?ty=RULES|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Horses and other equids are ]s of the ] Perissodactyla, a relatively ancient group of browsing and grazing animals that first arose less than 10 million years after the ]s became extinct. In the past, this order contained twelve families, but only three ]—the ], ]s and ]—have survived till today. The earliest equids (belonging to the genus '']'') were found approximately 54 million years to the ] period. The ]s were the dominant group of large terrestrial browsing animals until the ] (about 20 million years ago), when ], with stomachs better adapted to digesting ], began to outcompete them. | |||
| ===Size and measurement=== | |||
| The horse as it is known today adapted by evolution to survive in areas of wide-open terrain with sparse vegetation, surviving in an ] where other large grazing animals, especially ]s, could not. <ref name="Budiansky">Budiansky, Stephen. ''The Nature of Horses.'' Free Press, 1997. ISBN 0684827689</ref> | |||
| The height of horses is measured at the highest point of the ], where the neck meets the ].<ref name=Whitaker77>], p. 77</ref> This point is used because it is a stable point of the anatomy, unlike the head or neck, which move up and down in relation to the body of the horse. | |||
| ] | |||
| Horse evolution was characterized by a reduction in the number of toes, from five per foot, to three per foot, to only one toe per foot (late ] 5.3 million years ago); essentially, the animal was standing on tiptoe. One of the first true horse species was the tiny ''Hyracotherium'', which had 4 toes on each front foot (missing the ]) and 3 toes on each back foot (missing toes 1 and 5). Over about five million years, this early equids evolved into the '']''. The 5th fingers vanished, and new grinding teeth evolved. This was significant in that it signalled a transition to improved ] of tougher plant material, allowing grazing of not just leafy plants but also tougher plains ]es. Thus the proto-horses changed from leaf-eating forest-dwellers to grass-eating inhabitants of the ]. | |||
| In English-speaking countries, the height of horses is often stated in units of ] and inches: one hand is equal to {{convert|101.6|mm|in|0|order=flip}}. The height is expressed as the number of full hands, followed by a ], then the number of additional inches, and ending with the abbreviation "h" or "hh" (for "hands high"). Thus, a horse described as "15.2 h" is 15 hands plus 2 inches, for a total of {{convert|62|in|cm|1}} in height.<ref name=Ensminger51>], p. 51</ref> | |||
| The size of horses varies by breed, but also is influenced by ]. Light-riding horses usually range in height from {{hands|14|to|16|lk=off}} and can weigh from {{convert|380|to|550|kg}}.<ref>], entries 1, 68, 69</ref> Larger-riding horses usually start at about {{hands|15.2|lk=off}} and often are as tall as {{hands|17|lk=off}}, weighing from {{convert|500|to|600|kg|sigfig=3}}.<ref>], entries 12, 30, 31, 32, 75</ref> Heavy or ]s are usually at least {{hands|16|lk=off}} high and can be as tall as {{hands|18|lk=off}} high. They can weigh from about {{convert|700|to|1000|kg|sigfig=3}}.<ref>], entries 86, 96, 97</ref> | |||
| More recently the 2nd and 4th toes disappeared on all feet, and horses became bigger. This may be because horses' feet developed ]s, making the extra toes unnecessary. These side toes were shrinking in '']'' and have vanished in modern horses (but they occasionally reappear as a ]). | |||
| The largest horse in recorded history was probably a ] named ], who was born in 1848. He stood {{hands|21.2+1/4|lk=off}} high and his peak weight was estimated at {{convert|1524|kg}}.<ref name=Whitaker60>], p. 60</ref> The record holder for the smallest horse ever is ], a fully mature ] affected by ]. She was {{convert|17|in|cm hand|lk=off|order=flip}} tall and weighed {{convert|57|lb|kg|abbr=on|order=flip}}.<ref>{{cite news | title = World's smallest horse has tall order | url = https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/03/19/AR2007031901754.html | date = 2007-03-19 | newspaper = ] | agency = ] | author = Douglas, Jeff | access-date = 2017-03-14 | archive-date = 2017-03-15 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170315174315/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/03/19/AR2007031901754.html | url-status = live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=2019-09-05|title=Meet the smallest horse in the world that's shorter than a greyhound|url=https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/news/2019/9/meet-the-smallest-horse-in-the-world-thats-shorter-than-a-greyhound-588674|access-date=2021-07-06|website=Guinness World Records|language=en-GB|archive-date=2021-08-04|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210804002359/https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/news/2019/9/meet-the-smallest-horse-in-the-world-thats-shorter-than-a-greyhound-588674|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Domestication of the horse and surviving wild species== | |||
| {{main|Domestication of the horse}} | |||
| ====Ponies==== | |||
| Competing theories exist as to the time and place of initial domestication. The earliest evidence for the ] comes from ] and dates to approximately ]. ] finds such as the ] ]s provided unequivocal evidence that the horse was definitely domesticated by 2000 BCE. | |||
| {{Main|Pony}} | |||
| ] are ] the same animals as horses. The distinction between a horse and pony is commonly drawn on the basis of height, especially for competition purposes. However, height alone is not dispositive; the difference between horses and ponies may also include aspects of ], including conformation and temperament. | |||
| The traditional standard for height of a horse or a pony at maturity is {{hands|14.2|lk=off}}. An animal {{hands|14.2|lk=off}} or over is usually considered to be a horse and one less than {{hands|14.2|lk=off}} a pony,{{r|EnsmingerHT|page=12}} but there are many exceptions to the traditional standard. In Australia, ponies are considered to be those under {{hands|14|lk=off}}.<ref>{{cite book|author1=Howlett, Lorna |author2=Philip Mathews |title=Ponies in Australia |publisher=Philip Mathews Publishers |location=Milson's Point, NSW |isbn=0-908001-13-4 |year=1979 |page=14}}</ref> For competition in the ] division of the ], the cutoff is {{hands|14.1|lk=off}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.usef.org/_IFrames/RuleBook/rulebooks.aspx |title=2012 United States Equestrian Federation, Inc. Rule Book |publisher=United States Equestrian Federation |page=Rule WS 101 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120415003731/http://www.usef.org/_IFrames/RuleBook/rulebooks.aspx |archive-date=2012-04-15 }}</ref> The ], the world governing body for horse sport, uses ] measurements and defines a pony as being any horse measuring less than {{convert|148|cm|in|2}} at the withers without shoes, which is just over {{hands|14.2|lk=off}}, and {{convert|149|cm|in hands|2|lk=off}}, with shoes.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.fei.org/sites/default/files/Annex%20XVII%20-%20Extracts%20Ponies.pdf | title=Annex XVII: Extracts from Rules for Pony Riders and Children, 9th edition | publisher=Fédération Equestre Internationale | year=2009 | access-date=2010-03-07 | url-status=dead | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120911122158/http://www.fei.org/sites/default/files/Annex%20XVII%20-%20Extracts%20Ponies.pdf | archive-date=2012-09-11 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Wild species=== | |||
| :''see also'' ] | |||
| Most "wild" horses today are actually '']'' horses, animals who had domesticated ancestors but were themselves born and live in the wild, often for generations. However, there are also some truly wild horses whose ancestors were never successfully domesticated. | |||
| Height is not the sole criterion for distinguishing horses from ponies. ] for horses that typically produce individuals both under and over {{hands|14.2|lk=off}} consider all animals of that breed to be horses regardless of their height.<ref>For example, the ], or the ]. See ], pp. 192, 218</ref> Conversely, some pony breeds may have features in common with horses, and individual animals may occasionally mature at over {{hands|14.2|lk=off}}, but are still considered to be ponies.<ref>For example, the ]. See ], pp. 52–63</ref> | |||
| Historical wild species include the Forest Horse (''Equus ferus silvaticus'', also called the Diluvial Horse), thought to have evolved into ''Equus ferus germanicus'', and may have contributed to the development of the heavy horses of northern ], such as ]. | |||
| Ponies often exhibit thicker manes, tails, and overall coat. They also have proportionally shorter legs, wider barrels, heavier bone, shorter and thicker necks, and short heads with broad foreheads. They may have calmer temperaments than horses and also a high level of intelligence that may or may not be used to cooperate with human handlers.{{r|EnsmingerHT|pages=11-12}}{{Failed verification|date=April 2024|reason=Is not found on pages 11-12, and doesn't appear to be in this book.}} Small size, by itself, is not an exclusive determinant. For example, the ] which averages {{hands|10|lk=off}}, is considered a pony.{{r|EnsmingerHT|page=12}}Conversely, breeds such as the ] and other ]s, which can be no taller than {{convert|30|in|cm hand|lk=off|order=flip}}, are classified by their ] as very small horses, not ponies.<ref>], p. 200</ref> | |||
| There is a theory that there were additional "proto" horses that developed with adaptations to their environment prior to domestication. There are competing theories, but in addition to the Forest Horse, three other types are thought to have developed:<ref name="Bennett"> Bennett, Deb. Conquerors: The Roots of New World Horsemanship. Amigo Publications Inc; 1st edition 1998. ISBN 0965853306</ref> | |||
| ===Genetics=== | |||
| * A small, sturdy, heavyset pony-sized animal with a heavy hair coat, arising in northern Europe, adapted to cold, damp climates, somewhat resembling today's ] | |||
| Horses have 64 ]s.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/medgen/chromo/species.html |title=Chromosome Numbers in Different Species |publisher=Vivo.colostate.edu |date=1998-01-30 |access-date=2013-04-17 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130511210119/http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/medgen/chromo/species.html |archive-date=2013-05-11 }}</ref> The ] was ] in 2007. It contains 2.7 billion DNA ]s,<ref name=Cornell>{{cite web |url=http://www.vet.cornell.edu/news/articles/09antczakscience.cfm |title=Sequenced horse genome expands understanding of equine, human diseases |publisher=Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine |date=2012-08-21 |access-date=2013-04-01 |archive-date=2017-10-10 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.vet.cornell.edu/news/articles/09antczakscience.cfm |url-status=live }}</ref> which is larger than the ], but smaller than the ] or the ].<ref name=ScienceDaily>{{Cite journal |url=https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/11/091105143708.htm |title=Domestic Horse Genome Sequenced |journal=Science |volume=326 |issue=5954 |pages=865–867 |doi=10.1126/science.1178158 |pmid=19892987 |pmc=3785132 |date=2009-11-05 |access-date=2013-04-01 |last1=Wade |first1=C. M |last2=Giulotto |first2=E |last3=Sigurdsson |first3=S |last4=Zoli |first4=M |last5=Gnerre |first5=S |last6=Imsland |first6=F |last7=Lear |first7=T. L |last8=Adelson |first8=D. L |last9=Bailey |first9=E |last10=Bellone |first10=R. R |last11=Blocker |first11=H |last12=Distl |first12=O |last13=Edgar |first13=R. C |last14=Garber |first14=M |last15=Leeb |first15=T |last16=Mauceli |first16=E |last17=MacLeod |first17=J. N |last18=Penedo |first18=M. C. T |last19=Raison |first19=J. M |last20=Sharpe |first20=T |last21=Vogel |first21=J |last22=Andersson |first22=L |last23=Antczak |first23=D. F |last24=Biagi |first24=T |last25=Binns |first25=M. M |last26=Chowdhary |first26=B. P |last27=Coleman |first27=S. J |last28=Della Valle |first28=G |last29=Fryc |first29=S |last30=Guerin |first30=G |display-authors=29 |bibcode=2009Sci...326..865W |archive-date=2018-11-18 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181118204110/https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/11/091105143708.htm |url-status=live |issn = 0036-8075}}</ref> The map is available to researchers.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://uswest.ensembl.org/Equus_caballus/Info/Index |title=Ensembl genome browser 71: Equus caballus – Description |publisher=Uswest.ensembl.org |access-date=2013-04-17 |archive-date=2017-10-10 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://uswest.ensembl.org/Equus_caballus/Info/Index |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| * A taller, slim, refined and agile animal arising in western ], adapted to hot, dry climates, thought to be the progenitor of the modern ] and ] | |||
| * A dun-colored, sturdy animal, the size of a large pony, adapted to the cold, dry climates of northern Asia, the predecessor to the Tarpan and Przewalski's Horse. | |||
| ===Colors and markings=== | |||
| The ], ''Equus ferus ferus'', became extinct in 1880. Its genetic line is lost, but its ] has been recreated by a "]" process, in which living domesticated horses with primitive features were repeatedly interbred. Thanks to the efforts of the brothers Lutz Heck (director of the ] ]) and Heinz Heck (director of Munich ]), the resulting ''Wild Polish Horse'' or '']'' more closely resembles the tarpan than any other living horse. | |||
| ] (left) and ] (sometimes called "sorrel") are two of the most common coat colors, seen in almost all breeds.|alt=Two horses in a field. The one on the left is a dark brown with a black mane and tail. The one on the right is a light red all over.]] | |||
| {{Main|Equine coat color|Equine coat color genetics|Horse markings}} | |||
| Horses exhibit a diverse array of ] and distinctive ], described by a specialized vocabulary. Often, a horse is classified first by its coat color, before breed or sex.<ref>{{cite book|author=Vogel, Colin B.V.M. |title=The Complete Horse Care Manual |publisher=Dorling Kindersley Publishing, Inc. |location=New York |year=1995 |isbn=0-7894-0170-3 |oclc=32168476 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/completehorsecar0000voge/page/14}}</ref> Horses of the same color may be distinguished from one another by white ],<ref>{{cite book |title=A Basic Guide to Horse Care and Management|author1=Mills, Bruce |author2=Barbara Carne |year=1988 |publisher=Howell Book House |location=New York |isbn=0-87605-871-3 |oclc=17507227|pages= 72–73}}</ref> which, along with various spotting patterns, are inherited separately from coat color.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=4354 |title=A Horse of a Different Color |journal=The Horse |url-access=registration |access-date=2010-02-11 |author=Corum, Stephanie J. |date=May 1, 2003 |archive-date=2015-09-18 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150918013937/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/13855/a-horse-of-a-different-color |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] (''Equus ferus przewalskii''), a rare Asian species, is the only true wild horse alive today. ]ns know it as the ''taki'', while the ] people call it a ''kirtag''. Small wild breeding populations of this animal, named after the ]n explorer ], exist in Mongolia. <ref>http://www.treemail.nl/takh/</ref> There are also small populations maintained at zoos throughout the world. | |||
| Many ] that create horse coat colors and patterns have been identified. Current genetic tests can identify at least 13 different ]s influencing coat color,<ref name=UCVGL/> and research continues to discover new genes linked to specific traits. The basic coat colors of ] and ] are determined by the ] controlled by the ],<ref name=Marklund1996>{{cite journal |last=Marklund |first=L. |author2=M. Johansson Moller |author3=K. Sandberg |author4=L. Andersson |title=A missense mutation in the gene for melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MC1R) is associated with the chestnut coat color in horses |journal=Mammalian Genome |volume=7 |pages=895–899 |year=1996 |doi=10.1007/s003359900264 |pmid=8995760 |issue=12 |s2cid=29095360}}</ref> also known as the "extension gene" or "red factor".<ref name=UCVGL/> Its recessive form is "red" (chestnut) and its dominant form is black.<ref name=UCDIntro/> Additional ]s control suppression of black color to ] that results in a ], spotting patterns such as ] or ], ]s such as ] or ], as well as ], and all the other factors that create the many possible coat colors found in horses.<ref name=UCVGL>{{cite web|url= http://www.vgl.ucdavis.edu/services/coatcolorhorse.php|title= Horse Coat Color Tests|access-date= 2008-05-01|website= Veterinary Genetics Laboratory|publisher= University of California|archive-date= 2008-02-19|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080219095454/http://www.vgl.ucdavis.edu/services/coatcolorhorse.php|url-status= live}}</ref> | |||
| Other truly wild equids alive today include the ] and the ]. | |||
| Horses that have a white coat color are often mislabeled; a horse that looks "white" is usually a middle-aged or older ]. Grays are born a darker shade, get lighter as they age, but usually keep black skin underneath their white hair coat (with the exception of pink skin under white ]). The only horses properly called ] are born with a predominantly white hair coat and pink skin, a fairly rare occurrence.<ref name=UCDIntro>{{cite web|url= http://www.vgl.ucdavis.edu/services/coatcolor.php|title= Introduction to Coat Color Genetics|access-date= 2008-05-01|website= Veterinary Genetics Laboratory|publisher= University of California|archive-date= 2017-10-10|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.vgl.ucdavis.edu/services/coatcolor.php|url-status= live}}</ref> Different and unrelated ] factors can produce white coat colors in horses, including several different alleles of ] and the ].<ref name=haase2009-similar>{{cite journal |author=Haase B |title=Allelic Heterogeneity at the Equine KIT Locus in Dominant White (W) Horses |journal=PLOS Genetics |volume=3 |issue=11 |pages=e195 |year=2007 |pmid=17997609 |pmc=2065884 |doi=10.1371/journal.pgen.0030195 |author2=Brooks SA |author3=Schlumbaum A |display-authors=3 |last4=Azor |first4=Pedro J. |last5=Bailey |first5=Ernest |last6=Alaeddine |first6=Ferial |last7=Mevissen |first7=Meike |last8=Burger |first8=Dominik |last9=Poncet |first9=Pierre-André |doi-access=free }}</ref> However, there are no "]" horses, defined as having both pink skin and red eyes.<ref name=Duplicatetest>{{cite journal |title= Genetic mapping of dominant white (W), a homozygous lethal condition in the horse (''Equus caballus'') |author1= Mau, C. |author2= Poncet, P. A. |author3= Bucher, B. |author4= Stranzinger, G. |author5= Rieder, S. |journal= Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics|volume= 121|doi= 10.1111/j.1439-0388.2004.00481.x |year= 2004 |pages= 374–383 |issue= 6}}</ref> | |||
| ===Feral horses=== | |||
| ]s (Utah, 2005)]] | |||
| ''Wild'' animals, whose ancestors have never undergone domestication, are distinct from '']'' ones, who had domesticated ancestors but were born and live in the wild. Several populations of feral horses exist, including those in the western ] and ] (often called "]"), and in parts of ] ("]") and ] ("]s"). Isolated feral populations are often named for their geographic location: ] has its Namib Desert Horses; the ] lives in Spain; ] Horses reside in ], ]; and ] have been part of ], ] for a thousand years. | |||
| ===Reproduction and development=== | |||
| Studies of feral horses have provided useful insights into the behavior of ancestral wild horses, as well as greater understanding of the instincts and behaviors that drive "tame" horses. | |||
| {{Main|Horse breeding}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Other modern equids== | |||
| ] lasts approximately 340 days, with an average range 320–370 days,<ref name=Ensminger156>], p. 156</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=How Long is a Horse Pregnant? |url=https://talkoftheturf.com/article/how-long-is-a-horse-pregnant |access-date=2023-03-25 |website=Talk of the Turf |language=en}}</ref> and usually results in one ]; twins are rare.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www2.okstate.edu/pio/twinfoals.html|access-date= 2008-09-23|title= Rare Twin Foals Born at Vet Hospital: Twin Birth Occurrences Number One in Ten Thousand|author= Johnson, Tom|website= Communications Services, Oklahoma State University|publisher= Oklahoma State University|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121012052136/http://www2.okstate.edu/pio/twinfoals.html|archive-date= 2012-10-12|url-status= dead}}</ref> Horses are a precocial species, and foals are capable of standing and running within a short time following birth.<ref>{{cite book |author1=Miller, Robert M. |author2=Rick Lamb|title=Revolution in Horsemanship and What it Means to Mankind |publisher= Lyons Press|location=Guilford, CT|year=2005|isbn=1-59228-387-X |oclc=57005594|pages=102–103}}</ref> Foals are usually born in the spring. The ] of a mare occurs roughly every 19–22 days and occurs from early spring into autumn. Most mares enter an ''anestrus'' period during the winter and thus do not cycle in this period.<ref name=Ensminger150>], p. 150</ref> Foals are generally ] from their mothers between four and six months of age.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.extension.org/pages/29352/reducing-weaning-stress-in-foals|author=Kline, Kevin H.|title=Reducing weaning stress in foals |publisher=Montana State University eXtension|date=2010-10-07|access-date=2012-04-03|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120322182958/http://www.extension.org/pages/29352/reducing-weaning-stress-in-foals|archive-date=2012-03-22}}</ref> | |||
| :''Main article'': see ] for full species list. | |||
| Horses, particularly colts, are sometimes physically capable of reproduction at about 18 months, but domesticated horses are rarely allowed to breed before the age of three, especially females.{{r|EnsmingerHT|page=129}} Horses four years old are considered mature, although the skeleton normally continues to develop until the age of six; maturation also depends on the horse's size, breed, sex, and quality of care. Larger horses have larger bones; therefore, not only do the bones take longer to form ], but the ]s are larger and take longer to convert from ] to bone. These plates convert after the other parts of the bones, and are crucial to development.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.equineortho.colostate.edu/questions/dod.htm|title=Developmental Orthopaedic Disease: Problems of Limbs in young Horses|access-date=2008-04-20|author=McIlwraith, C.W.|publisher=Colorado State University|website=Orthopaedic Research Center|archive-date=2013-01-14|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130114221212/http://csu-cvmbs.colostate.edu/academics/clinsci/equine-orthopaedic-research-center/Pages/default.aspx|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Other members of the horse family include ]s, ]s, and ]s. The Donkey, Burro or Domestic Ass, ''Equus asinus'', like the horse, has many breeds. A ] is a hybrid of a male ass (jack) and a mare, and is usually infertile. A ] is the less common hybrid of a female ass (jenny) and a ]. Breeders have also tried crossing various species of zebra with mares or female asses to produce "zebra mules" (]s, and ]s (also called ]s)). This will probably remain a novelty hybrid as these individuals tend to inherit some of the undomesticated nature of their zebra parent, but they may inherit the zebra's resistance to ]: zorses, also called ]s, have been used in Central African game parks for light haulage.{{citation needed}} | |||
| Depending on maturity, breed, and work expected, horses are usually put under saddle and ] to be ridden between the ages of two and four.<ref name=Train163>{{cite book|author=Thomas, Heather Smith |title=Storey's Guide to Training Horses: Ground Work, Driving, Riding |publisher=Storey Publishing |location=North Adams, MA |year=2003 |isbn=1-58017-467-1 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/storeysguidetotr0000thom/page/163}}</ref> Although ] ] are put on the track as young as the age of two in some countries,<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.jockeyclub.com/factbook.asp?section=11|title= 2-Year-Old Racing (US and Canada)|access-date= 2008-04-28|website= Online Fact Book|publisher= Jockey Club|archive-date= 2013-02-16|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130216002618/http://www.jockeyclub.com/factbook.asp?section=11|url-status= live}}</ref> horses specifically bred for sports such as ] are generally not put under saddle until they are three or four years old, because their bones and muscles are not solidly developed.<ref>{{cite book |title=The USDF Guide to Dressage |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9NNobNYAiroC&pg=PA272 |author1=Bryant, Jennifer Olson |author2=George Williams |publisher=Storey Publishing |year=2006 |isbn=978-1-58017-529-6 |pages=271–272 |access-date=2020-09-28 |archive-date=2023-03-20 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223812/https://books.google.com/books?id=9NNobNYAiroC&pg=PA272 |url-status=live }}</ref> For ] competition, horses are not deemed mature enough to compete until they are a full 60 calendar months (five years) old.<ref name=Endurance/> | |||
| ==Horse behavior== | |||
| {{main|Horse behavior}} | |||
| Horses are prey animals with a well-developed ] instinct. Their first response to threat is to flee, although they are known to stand their ground and defend themselves or their offspring in cases where flight is not possible, such as when a foal would be threatened. Through selective breeding, some breeds of horses have been bred to be quite docile, particularly certain large draft horses. However, most light horse riding breeds were developed for speed, agility, alertness and endurance; natural qualities that extend from their wild ancestors. | |||
| ===Anatomy=== | |||
| Horses are herd animals, and become very attatched to their species and to humans. They communicate in various ways, such as nickering, grooming, and body language. Some horses will become flighty, and hard to manage if they are away from their herd. This is called being "herd-bound." | |||
| {{Main|Equine anatomy|Muscular system of the horse|Respiratory system of the horse|Circulatory system of the horse}} | |||
| ====Skeletal system==== | |||
| ==Horses within the human economy== | |||
| {{Main|Skeletal system of the horse}} | |||
| Horses in rich countries are primarily kept for leisure or sport purposes. Around the world, they play a role within human economies. | |||
| ] | |||
| The horse skeleton averages 205 bones.<ref name=Evans90>{{cite book|author=Evans, J. |title=The Horse |edition=Second |publisher=Freeman |location=New York |year=1990 |isbn=0-7167-1811-1 |oclc=20132967 |page= |url= https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780716718116/page/90}}</ref> A significant difference between the horse skeleton and that of a human is the lack of a ]—the horse's ] are attached to the ] by a powerful set of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that attach the ] to the torso. The horse's four legs and hooves are also unique structures. Their leg bones are proportioned differently from those of a human. For example, the body part that is called a horse's "knee" is actually made up of the ] that correspond to the human ]. Similarly, the ] contains bones equivalent to those in the human ] and ]. The lower leg bones of a horse correspond to the bones of the human hand or foot, and the ] (incorrectly called the "ankle") is actually the proximal ]s between the ] bones (a single equivalent to the human ] or ]) and the ], located where one finds the "knuckles" of a human. A horse also has no muscles in its legs below the knees and hocks, only skin, hair, bone, ]s, ]s, ], and the assorted specialized tissues that make up the ].<ref name=Ensminger21>], pp. 21–25</ref> | |||
| === |
====Hooves==== | ||
| {{Main|Horse hoof|Horseshoe|Farrier}} | |||
| ]Many countries use horses for leisure. Some countries are more adept than others at producing quality horses and using them for leisure and sport. Such as: ], ], ], ] and ]. When the British parliament banned ], countryside stables prophesied a disastrous effect on their industry. Australia is known for their well mannered, elegant and hardy Australian stock horses and fast racing Thoroughbreds. Germany produces fine quality ] horses for dressage, stunning ]s for harness and dressage, ]s mainly for harness and Warmbloods for eventing. Spain breeds the beautiful and magnificent ]s (Pura Raza Espanola) and ] horses, because of their beauty and agility, are used mainly for dressage and High School work in Vienna and other places. Denmark produces similar horse to Germany, while Britain breeds fast Thoroughbreds, heavy horses and an array of tough ponies, such as the Dartmoor, Exmoor and Welsh mountain. Many people find being around horses soothing and therapeutic. Therefore many people may not have horses for work or play, they sometimes simply have companion horses or breed them. | |||
| The critical importance of the feet and legs is summed up by the traditional adage, "no foot, no horse".<ref name=Ensminger367>], p. 367</ref> The ] begins with the ], the equivalent of the human fingertip or tip of the toe, surrounded by ] and other specialized, blood-rich soft tissues such as the ]. The exterior hoof wall and horn of the sole is made of ], the same material as a human ].<ref>], p. 304</ref> The result is that a horse, weighing on average {{convert|500|kg}},<ref>], p. 457</ref> travels on the same bones as would a human on tiptoe.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.cvm.uiuc.edu/petcolumns/showarticle_pf.cfm?id=118|title= Yes, The Shin Bone Is Connected to the Ankle Bone |access-date=2008-04-05 |author= Fuess, Theresa A.|website= Pet Column |publisher= University of Illinois |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20060909161307/http://www.cvm.uiuc.edu/petcolumns/showarticle_pf.cfm?id=118 |archive-date = September 9, 2006}}</ref> For the protection of the hoof under certain conditions, some horses have ]s placed on their feet by a professional ]. The hoof continually grows, and in most domesticated horses needs to be trimmed (and ]s reset, if used) every five to eight weeks,<ref>], pp. 310–312</ref> though the hooves of horses in the wild wear down and regrow at a rate suitable for their terrain. | |||
| ===Horses for sport=== | |||
| <!-- There is a whole article about Equestrianism for all details about every possible sport. This article should only give the bare sumamry. So, please do not add elaborate sections of your own favorite horse sport here. --> | |||
| ====Teeth==== | |||
| {{Main article|Equestrianism}} | |||
| {{Main|Horse teeth}} | |||
| Horses are adapted to ]. In an adult horse, there are 12 ]s at the front of the mouth, adapted to biting off the grass or other vegetation. There are 24 teeth adapted for chewing, the ]s and ], at the back of the mouth. Stallions and geldings have four additional teeth just behind the incisors, a type of ] called "tushes". Some horses, both male and female, will also develop one to four very small ] teeth in front of the molars, known as "wolf" teeth, which are generally removed because they can interfere with the ]. There is an empty interdental space between the incisors and the molars where the bit rests directly on the gums, or "bars" of the horse's mouth when the horse is ]d.<ref>{{cite book |last=Kreling |first=Kai |title=Horses' Teeth and Their Problems: Prevention, Recognition, and Treatment |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3q1LINmOkOIC&pg=PA117-IA1 |year=2005 |publisher=Globe Pequot |location=Guilford, CT |isbn=1-59228-696-8 |chapter=The Horse's Teeth |oclc=59163221 |pages=12–13 }}{{Dead link|date=April 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | |||
| Horses are used in two ways for sports: as mounts for competitors and as competitors themselves. Sports such as ] and ] use horses as mounts on which the main competitors ride. Although their riders perform the main actions, horses serve as a necessary part of the game. In medeival ], for example, the main goal is for one rider to dismount the other. Although the horse is important to this, its overall performance has a negligible impact on the outcome of the event. Horses used as competitors, however, are trained to be ridden through a particular event. Examples include ], ], ], ], and ]. Although the scoring depends on the event, most emphasize the horse's speed, maneuverability, and precision, along with the ] of the rider. | |||
| An estimate of a horse's age can be made from looking at its teeth. The teeth continue to erupt throughout life and are worn down by grazing. Therefore, the incisors show changes as the horse ages; they develop a distinct wear pattern, changes in tooth shape, and changes in the angle at which the chewing surfaces meet. This allows a very rough estimate of a horse's age, although diet and veterinary care can also affect the rate of tooth wear.<ref name=Ensminger46>], pp. 46–50</ref> | |||
| ===Horses for work=== | |||
| There are certain jobs that horses do very well, and no amount of technology appears able to supercede. ] are used for crowd control. Some land management practices such as ] are most efficiently done with horses, to avoid vehicular disruption to delicate soil such as a nature reserve. Forestry rangers may choose to use horses for their patrols. | |||
| ====Digestion==== | |||
| In poor countries such as ], horses are widely used for agriculture, mainly pulling plows. | |||
| {{Main|Equine anatomy#Digestive system|Equine nutrition|l1=Equine digestive system}} | |||
| Horses are ]s with a digestive system adapted to a ] diet of grasses and other plant material, consumed steadily throughout the day. Therefore, compared to humans, they have a relatively small stomach but very long intestines to facilitate a steady flow of nutrients. A {{convert|450|kg|adj=on}} horse will eat {{convert|7|to|11|kg}} of food per day and, under normal use, drink {{convert|38|to|45|L}} of ]. Horses are not ]s, having only one stomach, like humans. But unlike humans, they can digest ], a major component of grass, through the process of ]. Cellulose fermentation by symbiotic bacteria and other microbes occurs in the ] and the ]. Horses cannot ], so digestion problems can quickly cause ], a leading cause of death.<ref>], p. 175</ref> Although horses do not have a ], they tolerate high amounts of fat in their diet.<ref>{{Cite journal |date=2001 |title=Role of dietary carbohydrate and fat in horses with equine polysaccharide storage myopathy |journal=Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association |doi=10.2460/javma.2001.219.1537 |last1=Valentine |first1=Beth A. |last2=Van Saun |first2=Robert J. |last3=Thompson |first3=Kent N. |last4=Hintz |first4=Harold F. |volume=219 |issue=11 |pages=1537–1544 |pmid=11759989 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |date=2010 |title=The gall bladder and bile ducts |url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0263931910000542 |journal=Surgery (Oxford) |doi=10.1016/j.mpsur.2010.02.007 |last1=Ellis |first1=Harold |volume=28 |issue=5 |pages=218–221 |access-date=2021-05-11 |archive-date=2021-05-12 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210512150222/https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0263931910000542 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ====Senses==== | |||
| In countries such as ], horse-riding is still the most common means of transport, at least in the countryside. | |||
| ] | |||
| {{See also|Equine vision}} | |||
| The horses' senses are based on their status as ], where they must be aware of their surroundings at all times.<ref name=Ensminger309>], pp. 309–310</ref> The equine eye is one of the largest of any land mammal.<ref name="Hartley 2016">{{cite book|last1=Hartley|first1=C|last2=Grundon|first2=RA|editor1-last=Gilger|editor1-first=BC|title=Equine Ophthalmology|date=2016|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=9781119047742|page=151|edition=3rd|chapter=Chapter 5: Diseases and surgery of the globe and orbit}}</ref> Horses are lateral-eyed, meaning that their eyes are positioned on the sides of their heads.<ref>{{cite journal |url = http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=15938 |title = Eye Position and Animal Agility Study Published |journal = The Horse |date = March 7, 2010 |access-date = 2010-03-11 |archive-date = 2015-07-23 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20150723214909/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/25141/eye-position-and-animal-agility-study-published |url-status = live }} Press Release, citing February 2010 Journal of Anatomy, Dr. Nathan Jeffery, co-author, University of Liverpool.</ref> This means that horses have a range of vision of more than 350°, with approximately 65° of this being ] and the remaining 285° ].<ref name="Sellnow">{{cite book |author=Sellnow, Les |url=https://archive.org/details/happytrailsyourc00sell/page/46 |title=Happy Trails: Your Complete Guide to Fun and Safe Trail Riding |publisher=Eclipse Press |year=2004 |isbn=1-58150-114-5 |page= |oclc=56493380}}</ref> Horses have excellent day and ], but they have two-color, or ]; their ] is somewhat like red-green ] in humans, where certain colors, especially red and related colors, appear as a shade of green.<ref>{{cite journal |url= http://www.thehorse.com/viewarticle.aspx?ID=9670 |title= In Living Color |url-access= registration |access-date= 2007-07-27 |author= McDonnell, Sue |journal= The Horse |date= June 1, 2007 |archive-date= 2007-09-27 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070927223341/http://www.thehorse.com/viewarticle.aspx?ID=9670 |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| Their ], while much better than that of humans, is not quite as good as that of a dog. It is believed to play a key role in the social interactions of horses as well as detecting other key scents in the environment. Horses have two olfactory centers. The first system is in the nostrils and nasal cavity, which analyze a wide range of odors. The second, located under the nasal cavity, are the ]s, also called Jacobson's organs. These have a separate nerve pathway to the brain and appear to primarily analyze ]s.<ref name="Briggs smell">{{cite web |last=Briggs |first=Karen |title=Equine Sense of Smell |url=http://www.thehorse.com/articles/10055/equine-sense-of-smell |publisher=The Horse |access-date=2013-12-15 |date=2013-12-11 |archive-date=2018-02-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180201013608/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/10055/equine-sense-of-smell |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Horses in warfare=== | |||
| ]{{main|War horse}} | |||
| Horses have played a role in warfare since at least the ], when they were used in ] warfare, and have been used ever since until today in wars. Today, horses are still used in the armies of some third world countries although in western societies, they are now largely used for peaceful applications. | |||
| A horse's hearing is good,<ref name=Ensminger309/> and the ] of each ear can rotate up to 180°, giving the potential for 360° hearing without having to move the head.<ref>{{cite book |author=Myers, Jane |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-gAgchKMXdkC |title=Horse Safe: A Complete Guide to Equine Safety |publisher=CSIRO Publishing |location=Collingwood, UK |year=2005 |isbn=0-643-09245-5 |oclc=65466652 |page=7 |access-date=2020-09-28 |archive-date=2023-03-20 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223812/https://books.google.com/books?id=-gAgchKMXdkC |url-status=live }}</ref> Noise affects the behavior of horses and certain kinds of noise may contribute to stress—a 2013 study in the UK indicated that stabled horses were calmest in a quiet setting, or if listening to country or classical music, but displayed signs of nervousness when listening to jazz or rock music. This study also recommended keeping music under a volume of 21 ]s.<ref name="Music">{{cite web |url=http://www.thehorse.com/articles/31229/music-genres-effect-on-horse-behavior-evaluated |title=Music Genre's Effect on Horse Behavior Evaluated |last=Lesté-Lasserre |first=Christa |date=January 18, 2013 |website=The Horse |publisher=Blood Horse Publications |access-date=23 January 2013 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/31229/music-genres-effect-on-horse-behavior-evaluated |url-status=live }}</ref> An Australian study found that stabled racehorses listening to talk radio had a higher rate of gastric ulcers than horses listening to music, and racehorses stabled where a radio was played had a higher overall rate of ulceration than horses stabled where there was no radio playing.<ref name="EquiNews">{{cite web |url=http://www.equinews.com/article/radios-causing-gastric-ulcers |title=Radios Causing Gastric Ulcers |author=Kentucky Equine Research Staff |date=February 15, 2010 |website=EquiNews |publisher=Kentucky Equine Research |access-date=23 January 2013 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.equinews.com/article/radios-causing-gastric-ulcers |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Horse products=== | |||
| *] has been used as food for animals and humans throughout the ages. It is eaten in many parts of the world and is an export industry in the USA and other countries. Bills have been introduced in both the House and the Senate which would put an end to this practice in the US. {{fact}} | |||
| Horses have a great sense of balance, due partly to their ability to feel their footing and partly to highly developed ]—the unconscious sense of where the body and limbs are at all times.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.thoroughbredtimes.com/horse-health/1998/October/17/True-horse-sense.aspx|title= True Horse Sense |access-date= 2008-07-08 |author= Thomas, Heather Smith |website= Thoroughbred Times |publisher= Thoroughbred Times Company |archive-date= 2012-11-02 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121102020057/http://www.thoroughbredtimes.com/horse-health/1998/october/17/true-horse-sense.aspx |url-status= dead}}</ref> A horse's ] is well-developed. The most sensitive areas are around the eyes, ears, and nose.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unce.unr.edu/publications/files/ag/other/fs9829.pdf |title=Horse Handling and Riding Guidelines Part 1: Equine Senses |access-date=2008-07-09 |author1=Cirelli, Al Jr. |author2=Brenda Cloud |website=Cooperative Extension |page=4 |publisher=University of Nevada |archive-date=2015-09-08 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150908031752/http://www.unce.unr.edu/publications/files/ag/other/fs9829.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Horses are able to sense contact as subtle as an insect landing anywhere on the body.<ref>{{cite book|author1= Hairston, Rachel|author2= Madelyn Larsen |title= The Essentials of Horsekeeping |publisher= Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. |year= 2004 |isbn= 0-8069-8817-7 |location= New York |url= https://archive.org/details/essentialsofhors00rach/page/77 |oclc= 53186526 |page= }}</ref> | |||
| *Mare's milk is used by people with large horse-herds, such as the ]. They may let it ferment to produce ]. However, mares produce a much lower yield of milk than do ]s. | |||
| Horses have an advanced sense of taste, which allows them to sort through ] and choose what they would most like to eat,<ref>], p. 28</ref> and their ] lips can easily sort even small grains. Horses generally will not eat poisonous plants, however, there are exceptions; horses will occasionally eat toxic amounts of poisonous plants even when there is adequate healthy food.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.cvm.uiuc.edu/petcolumns/showarticle.cfm?id=16|title= Horse Pasture is No Place for Poisonous Plants |access-date=2008-07-09 |author= Gustavson, Carrie |website= Pet Column July 24, 2000 |publisher= University of Illinois |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070809051147/http://www.cvm.uiuc.edu/petcolumns/showarticle.cfm?id=16 |archive-date = August 9, 2007}}</ref> | |||
| *Horse ] was also used as food by the Mongols and other nomadic tribes. | |||
| ===Movement=== | |||
| *] is a mixture of female hormones (]s) extracted from horse urine of pregnant mares ('''pre'''gnant '''mar'''es' ur'''in'''e), and is a widely used drug for ], despite that the natural ] for humans is can be easily produced synthetically. Premarin has created much controversy amongst horse lovers, since its productions necessitates that the mare is kept pregnant, and as a by product many foals are produced. Unfortunately, the foal is often of no economic use and may be sent to slaughter. | |||
| {{Main|Horse gait|Trot|Canter|Ambling}} | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Muybridge horse walking animated.gif|''Walk'' {{convert|5|–|8|km/h|mph|abbr=on}} | |||
| File:Trot animated.gif|''Trot'' {{convert|8|–|13|km/h|mph|abbr=on}} | |||
| File:Muybridge_horse_pacing_animated.gif|''Pace'' {{convert|8|–|13|km/h|mph|abbr=on}} | |||
| File:Canter animated.gif|''Canter'' {{convert|16|–|27|km/h|mph|abbr=on}} | |||
| File:Muybridge race horse animated.gif|''Gallop'' {{convert|40|–|48|km/h|mph|abbr=on}}, record: {{convert|70.76|km/h|abbr=on|sortable=on}} | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| All horses move naturally with four basic ]:<ref name=HorseGaits32>], p. 32</ref> | |||
| *the four-beat ], which averages {{convert|6.4|km/h}}; | |||
| *the two-beat ] at {{convert|13|to|19|km/h}} (faster for ] horses); | |||
| *the ], a three-beat gait that is {{convert|19|to|24|km/h}}; | |||
| *the ], which averages {{convert|40|to|48|km/h}},<ref name=Harris47>], pp. 47–49</ref> but the world record for a horse galloping over a short, sprint distance is {{convert|70.76|km/h}}.<ref name=guinness>{{cite web|title = Fastest speed for a race horse|website = Guinness World Records| date=14 May 2008 |access-date = 8 January 2013|url = http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/fastest-speed-for-a-race-horse/|archive-date = 28 August 2017|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170828102736/http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/fastest-speed-for-a-race-horse|url-status = live}}</ref> | |||
| Besides these basic gaits, some horses perform a two-beat ], instead of the trot.<ref name=HorseGaits50>], p. 50</ref> There also are several four-beat ']' gaits that are approximately the speed of a trot or pace, though smoother to ride. These include the lateral ], ], and ] as well as the diagonal ].<ref name="Lieberman">{{cite journal |author=Lieberman, Bobbie | year=2007 |title=Easy Gaited Horses|journal=Equus|issue= 359|pages=47–51}}</ref> Ambling gaits are often genetic in some breeds, known collectively as ]s.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Equus Staff | year=2007 |title=Breeds that Gait|journal=Equus |issue= 359|pages=52–54}}</ref> These horses replace the trot with one of the ambling gaits<!--but some horses both trot and amble, can the Harris book support adding this?-->.<ref name=HorseGaits51>], pp. 50–55</ref> | |||
| ===Behavior=== | |||
| *The tail hair of the horse is used for making ]s for ]s such as the ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| {{Main|Horse behavior|Stable vices}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Horses are prey animals with a strong ]. Their first reaction to a threat is to startle and usually flee, although they will stand their ground and defend themselves when flight is impossible or if their young are threatened.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.extension.org/pages/23342/horse-fight-vs-flight-instinct |title=Horse Fight vs Flight Instinct |publisher=eXtension |date=2009-09-24 |access-date=2013-04-17 |archive-date=2013-05-15 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130515125847/http://www.extension.org/pages/23342/horse-fight-vs-flight-instinct |url-status=dead }}</ref> They also tend to be curious; when startled, they will often hesitate an instant to ascertain the cause of their fright, and may not always flee from something that they perceive as non-threatening. Most light horse riding breeds were developed for speed, agility, alertness and endurance; natural qualities that extend from their wild ancestors. However, through selective breeding, some breeds of horses are quite docile, particularly certain draft horses.<ref name=Natural226>{{cite book|ref=McBane |author= McBane, Susan |title= A Natural Approach to Horse Management |publisher= Methuen |location= London |year= 1992|isbn= 0-413-62370-X |oclc= 26359746|pages= 226–228}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Specialized vocabulary== | |||
| Horses are ]s, with a clear hierarchy of rank, led by a dominant individual, usually a mare. They are also social creatures that are able to form companionship attachments to their own species and to other animals, including humans. They communicate in various ways, including vocalizations such as nickering or whinnying, mutual ], and ]. Many horses will become difficult to manage if they are isolated, but with training, horses can learn to accept a human as a companion, and thus be comfortable away from other horses.<ref name=Ensminger305>], pp. 305–309</ref> However, when confined with insufficient companionship, exercise, or stimulation, individuals may develop ], an assortment of bad habits, mostly ] of psychological origin, that include wood chewing, wall kicking, "weaving" (rocking back and forth), and other problems.<ref name=Prince214>{{cite book|author1= Prince, Eleanor F. |author2= Gaydell M. Collier |title= Basic Horsemanship: English and Western |publisher= Doubleday |location= New York |year= 1974|isbn= 0-385-06587-6|oclc= 873660|pages= |url= https://archive.org/details/basichorsemanshi00prin/page/214}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Horse anatomy|Horse coat color|Equine coat color genetics}} | |||
| Because horses and humans have lived and worked together for thousands of years, an extensive specialized vocabulary has arisen to describe virtually every horse behavioral and anatomical characteristic with a high degree of precision. | |||
| ====Intelligence and learning==== | |||
| In ] the definitions of colt, filly, mare, and horse may differ from those given above. In the United Kingdom, ] racing defines a '''colt''' as a male horse less than five years old and a filly as a female horse less than five years old; ] defines colts and fillies as less than four years old. Horses older than colts and fillies become known as horses and mares respectively. | |||
| Studies have indicated that horses perform a number of ] tasks on a daily basis, meeting mental challenges that include ] and identification of individuals within a ]. They also have good ] abilities.<ref name=Hanggi>{{cite web |url=http://www.horsetalk.co.nz/features/horseintelligence-119.shtml |title=Understanding horse intelligence |author=Clarkson, Neil |date=2007-04-16 |access-date=2008-09-16 |website=Horsetalk 2007 |publisher=Horsetalk |archive-date=2013-01-24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130124164951/http://horsetalk.co.nz/2012/10/11/understanding-horse-intelligence/ |url-status=live }}</ref> They are naturally curious and apt to investigate things they have not seen before.<ref>{{Cite book |title=True horsemanship through feel |last=Dorrance |first=Bill |publisher=The Lion Press|year=1999|isbn=1-58574-321-6|location=Guilford, CT |pages=1}}</ref> Studies have assessed equine intelligence in areas such as ], speed of learning, and ]. Horses excel at simple learning, but also are able to use more advanced cognitive abilities that involve ] and ]. They can learn using ], ], ], and ], and positive and negative ].<ref name=Hanggi/> One study has indicated that horses can differentiate between "more or less" if the quantity involved is less than four.<ref name="count">{{cite web |url=http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=15396 |title=Horses Demonstrate Ability to Count in New Study |author=Lesté-Lasserre, Christa |access-date=2009-12-06 |website=The Horse |archive-date=2016-01-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160101025607/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/24628/horses-demonstrate-ability-to-count-in-new-study |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Domesticated horses may face greater mental challenges than wild horses, because they live in artificial environments that prevent ]ive behavior whilst also learning tasks that are not natural.<ref name=Hanggi/> Horses are animals of ] that respond well to regimentation, and respond best when the same routines and techniques are used consistently. One trainer believes that "intelligent" horses are reflections of intelligent trainers who effectively use response conditioning techniques and positive reinforcement to train in the style that best fits with an individual animal's natural inclinations.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://cs.bloodhorse.com/blogs/nicanor/archive/2008/06/17/equine-iq-what-big-brown-couldn-t-tell-you-and-mr-ed-kept-to-himself.aspx |title=What Big Brown Couldn't Tell You and Mr. Ed Kept to Himself (part 1) |author=Coarse, Jim |date=2008-06-17 |access-date=2008-09-16 |website=The Blood Horse |archive-date=2012-05-21 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120521084441/http://cs.bloodhorse.com/blogs/nicanor/archive/2008/06/17/equine-iq-what-big-brown-couldn-t-tell-you-and-mr-ed-kept-to-himself.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The ] comes with a large number of horse specific terms. | |||
| ====Temperament====<!--] and ] redirect to this section so if the section name is changed change the redirects--> | |||
| Horses exhibit a diverse array of ] and distinctive markings, and a specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe them. Often, one will refer to a horse in the field by its coat color rather than by breed or by sex. The ] has largely been resolved, although discussion continues about some of the details. | |||
| {{Main|Draft horse|Warmblood|Oriental horse|Hot-blooded horse}} | |||
| Horses are ]s. As such, they are ], or ]ic creatures, as opposed to cold-blooded, or ]ic animals. However, these words have developed a separate meaning in the context of equine terminology, used to describe temperament, not ]. For example, the "]", such as many ], exhibit more sensitivity and energy,<ref name="Belknap255">], p. 255</ref> while the "cold-bloods", such as most ], are quieter and calmer.<ref name="Belknap112">], p. 112</ref> Sometimes "hot-bloods" are classified as "light horses" or "riding horses",<ref name="Ensminger71">], pp. 71–73</ref> with the "cold-bloods" classified as "draft horses" or "work horses".<ref name="Ensminger84">], p. 84</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The English-speaking world measures the height of horses in ''hands''. One hand is defined in British law as 101.6 mm, a figure derived from the previous measure of 4 ] ]es. Horse height is measured at the highest point of an animal's '']''. Perhaps because of extensive selective breeding, modern adult horses vary widely in size, ranging from ]s measuring 5 hands (0.5 m) to draft animals measuring 19 hands (1.8 m) or more. By convention, 15.2 hh ''means'' 15 hands, 2 inches (1.57 m) in height. | |||
| "Hot blooded" breeds include "]s" such as the ], ], ], and now-extinct ], as well as the ], a breed developed in England from the older oriental breeds.<ref name=Belknap255/> Hot bloods tend to be spirited, bold, and learn quickly. They are bred for agility and speed.<ref name=Catalog18/> They tend to be physically refined—thin-skinned, slim, and long-legged.<ref>{{cite book |author=DeFilippis, Chris |title=The Everything Horse Care Book |publisher=Adams Media |location= Avon, MA |year=2006 |isbn=978-1-59337-530-0 |oclc=223814651|page=4}}</ref> The original oriental breeds were brought to Europe from the Middle East and North Africa when European breeders wished to infuse these traits into racing and light ] horses.<ref name=Whitaker43>], p. 43</ref><ref name=Whitaker194>], pp. 194–197</ref> | |||
| Muscular, heavy ]s are known as "cold bloods." They are bred not only for strength, but also to have the calm, patient temperament needed to pull a plow or a heavy carriage full of people.<ref name=Belknap112/> They are sometimes nicknamed "gentle giants".<ref name=Catalog15>], p. 15</ref> Well-known draft breeds include the ] and the ].<ref name=Catalog15/> Some, like the ], are lighter and livelier, developed to pull carriages or to plow large fields in drier climates.<ref name=Guide87>], entry 87</ref> Others, such as the ], are slower and more powerful, bred to plow fields with heavy, clay-based soils.<ref name=Ens124>], pp. 124–125</ref> The cold-blooded group also includes some pony breeds.<ref name="Bennett7" /> | |||
| An entire equine dictionary can be found at: | |||
| "]" breeds, such as the ] or ], developed when European carriage and ] were crossed with Arabians or Thoroughbreds, producing a riding horse with more refinement than a draft horse, but greater size and milder temperament than a lighter breed.<ref>], pp. 122–123</ref> Certain ] breeds with warmblood characteristics have been developed for smaller riders.<ref>Examples are the ] and the ], see ], pp. 178–179, 208–209</ref> Warmbloods are considered a "light horse" or "riding horse".<ref name=Ensminger71/> | |||
| ===Horses versus ponies=== | |||
| Ponies are smaller than horses and stay that way through their lives. To be a pony the equus in question must stand 14.2hh or lower at the withers. Many breeds do not grow bigger than this measurement of size, and part of the breed charicteristics is pony. Therefore, any equus in that breed must be pony sized to be registered. | |||
| However, some breeds are both pony and horse sized. Take the Arabian for example. It only grows to be around 15.0hh. Some horses of this breed stand under 14.2hh. Even so, this does not happen very often. The Rocky Mountain Pony is another case. Even though it stands around 14.2hh, it is often called a horse. This is because it has many horse conformation features such as a rifined head, and clean legs. Being fine-boned, it has a very delacate appearance. The strides of this equus are long and flowing, unlike the short, choppy strides of a pony. | |||
| ==Gaits== | |||
| Today, the term "Warmblood" refers to a specific subset of ] breeds that are used for competition in ] and ].<ref name=Lyons231>{{cite book |author=Price, Steven D. |author2=Shiers, Jessie |title=The Lyons Press Horseman's Dictionary |publisher=Lyons Press |location=Guilford, CT |year=2007 |edition=Revised |isbn=978-1-59921-036-0|page=231}}</ref> Strictly speaking, the term "]" refers to any ] between cold-blooded and hot-blooded breeds.<ref name=Belknap523>], p. 523</ref> Examples include breeds such as the ] or the ]. The term was once used to refer to breeds of light riding horse other than Thoroughbreds or Arabians, such as the ].<ref name=Catalog18>], p. 18</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Horse gait}} | |||
| All horses move naturally with four basic ]s; these are referred to as ], ] ("English") or ] ("Western"), ] ("English") or ] ("Western"), and ]. | |||
| ====Sleep patterns==== | |||
| Besides these basic gaits, additional gaits such as ], ], ], ] and ] can be distinguished. These special gaits are often found in specific breeds, and are referred to as "gaited" because they naturally possess additional "single-footed" gaits that are approximately the same speed as the trot but smoother to ride. | |||
| {{See also|Horse behavior#Sleep patterns|l1=Horse sleep patterns|Sleep in non-human animals|l2=Sleep in non-humans}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Horses are able to sleep both standing up and lying down. In an adaptation from life in the wild, horses are able to enter light sleep by using a "]" in their legs, allowing them to doze without collapsing.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://equisearch.com/horses_care/health/behavior/eqzzz629/ |title= How Horses Sleep |access-date= 2007-03-23 |author= Pascoe, Elaine |website= Equisearch.com |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070927193341/http://equisearch.com/horses_care/health/behavior/eqzzz629/ |archive-date= 2007-09-27}}</ref> Horses sleep better when in groups because some animals will sleep while others stand guard to watch for predators. A horse kept alone will not sleep well because its ]s are to keep a constant eye out for danger.<ref name="Horse sleep pt. 2"/> | |||
| Unlike humans, horses do not sleep in a solid, unbroken period of time, but take many short periods of rest. Horses spend four to fifteen hours a day in standing rest, and from a few minutes to several hours lying down. Total sleep time in a 24-hour period may range from several minutes to a couple of hours,<ref name="Horse sleep pt. 2">{{cite web |url= http://equisearch.com/horses_care/health/behavior/eqpowernap1771/ |title= How Horses Sleep, Pt. 2 – Power Naps |access-date= 2007-03-23|author= Pascoe, Elaine |website= Equisearch.com |date= 2002-03-12 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070927193158/http://equisearch.com/horses_care/health/behavior/eqpowernap1771/ |archive-date= 2007-09-27}}</ref> mostly in short intervals of about 15 minutes each.<ref name=Ensminger310>], p. 310.</ref> The average sleep time of a domestic horse is said to be 2.9 hours per day.<ref>{{cite journal|title=40 Winks? |author=Holland, Jennifer S. |journal=National Geographic |volume=220 |date=July 2011 |issue=1}}</ref> | |||
| Horse breeds with additional gaits include the ] with its running walk, the ] with its "slow gait" and rack, the ] horse with the paso corto and paso largo and ] which are known for the tölt. The Fox Trot is found in several gaited breeds, while some ]s, ] instead of trot. | |||
| Horses must lie down to reach ]. They only have to lie down for an hour or two every few days to meet their minimum REM sleep requirements.<ref name="Horse sleep pt. 2"/> However, if a horse is never allowed to lie down, after several days it will become sleep-deprived, and in rare cases may suddenly collapse because it slips, involuntarily, into REM sleep while still standing.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://equisearch.com/horses_care/health/behavior/sleepdisorder_121506/ |title= Equine Sleep Disorder Videos |access-date= 2007-03-23 |author= EQUUS Magazine Staff |website= Equisearch.com |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20070510051620/http://equisearch.com/horses_care/health/behavior/sleepdisorder_121506/ |archive-date= 2007-05-10}}</ref> This condition differs from ], although horses may also suffer from that disorder.<ref name="Smith">{{cite book |author=Smith, BP |title=Large Animal Internal Medicine |publisher=Mosby |location=St. Louis, MO |year=1996 |edition=Second |isbn=0-8151-7724-0 |oclc=33439780|pages= 1086–1087}}</ref> | |||
| ==The origin of modern horse breeds== | |||
| Horses come in various sizes and shapes. The ]s can top 20 hands (80 inches, 2 metres) while the smallest miniature horses can stand as low as 5.2 hands (22 inches, 0.56 metres). The ], usually considered the smallest horse in the world, compares in size to a ]. | |||
| ==Taxonomy and evolution== | |||
| Several schools of thought exist to explain how this range of size and shape came about. These schools grew up reasoning from the type of dentition and from the horses' outward appearance. One school, which we can call the "Four Foundations", suggests that the modern horse evolved from two types of early domesticated pony and two types of early domesticated horse; the differences between these types account for the differences in type of the modern breeds. A second school -- the "Single Foundation" -- holds only one breed of horse underwent domestication, and it diverged in form after domestication through human selective breeding (or in the case of feral horses, through ecological pressures). Finally, certain geneticists have started evaluating the ] and ] to construct family trees. See: ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Evolution of the horse|Equus (genus)|Equidae}} | |||
| The horse ] to survive in areas of wide-open terrain with sparse vegetation, surviving in an ] where other large grazing animals, especially ]s, could not.<ref name="Budiansky">{{cite book|author= Budiansky, Stephen |title= The Nature of Horses |publisher= Free Press |location= New York |year= 1997 |isbn= 0-684-82768-9 |oclc= 35723713 |page= |url=https://archive.org/details/natureofhorsesex00budi/page/31}}</ref> Horses and other equids are ]s of the ] ], a group of mammals dominant during the ] period. In the past, this order contained 14 ], but only three—] (the horse and related species), ] (the ]), and ] (the ]es)—have survived to the present day.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Perissodactyla.html |title= Order Perissodactyla |access-date= 2008-07-09 |author= Myers, Phil |website= Animal Diversity Web |publisher= University of Michigan |archive-date= 2013-01-22 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130122033502/http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/accounts/information/Perissodactyla.html |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| The earliest known member of the family Equidae was the '']'', which lived between 45 and 55 million years ago, during the ] period. It had 4 toes on each front foot, and 3 toes on each back foot.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fhc/hyraco1.htm|title= Hyracotherium|access-date= 2008-07-09|website= Fossil Horses in Cyberspace|publisher= ]|archive-date= 2013-01-31|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130131105733/http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fhc/hyraco1.htm|url-status= live}}</ref> The extra toe on the front feet soon disappeared with the '']'', which lived 32 to 37 million years ago.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fhc/mesoh1.htm|title= Mesohippus|access-date= 2008-07-09|website= Fossil Horses in Cyberspace|publisher= Florida Museum of Natural History|archive-date= 2013-01-22|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130122033356/http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fhc/mesoh1.htm|url-status= live}}</ref> Over time, the extra side toes shrank in size until they vanished. All that remains of them in modern horses is a set of small ] bones on the leg below the knee,<ref name=Natural>{{cite web |url= http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/horse/?section=evolution&page=evolution_b |title= The Evolution of Horses |access-date= 2008-07-09 |website= The Horse |publisher= American Museum of Natural History |archive-date= 2013-01-28 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130128123829/http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/past-exhibitions/horse |url-status= live }}</ref> known informally as splint bones.<ref>], p. 20</ref> Their legs also lengthened as their toes disappeared until they were a hooved animal capable of running at great speed.<ref name=Natural/> By about 5 million years ago, the modern ''Equus'' had evolved.<ref name=Florida>{{cite web |url= http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fhc/equus1.htm |title= Equus |access-date= 2008-07-09 |website= Fossil Horses in Cyberspace |publisher= Florida Museum of Natural History |archive-date= 2013-01-22 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130122033350/http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fhc/equus1.htm |url-status= live }}</ref> Equid teeth also evolved from browsing on soft, tropical plants to adapt to browsing of drier plant material, then to grazing of tougher plains grasses. Thus proto-horses changed from leaf-eating forest-dwellers to grass-eating inhabitants of semi-arid regions worldwide, including the ]s of Eurasia and the ] of North America. | |||
| The ] (]-sized but called a horse) provides an opportunity to compare contemporary and historical breed appearances and behaviour. Introduced by the ] into ], these horses did not subsequently undergo the intensive ] that took place in the rest of Europe from the ] onwards, and consequently bear a closer resemblance to pre-Medieval breeds. The Icelandic horse has a four-beat ] called the "]", similar to the "rack" of certain American gaited breeds. | |||
| By about 15,000 years ago, ''Equus ferus'' was a widespread ] species. Horse bones from this time period, the late ], are found in Europe, Eurasia, ], and North America.<ref name = Weinstock>{{cite journal|last1=Weinstock|first1=J.|year=2005|title=Evolution, Systematics, and Phylogeography of Pleistocene Horses in the New World: A Molecular Perspective |journal=] |pmid=15974804 |volume=3 |issue=8 |pmc=1159165 |pages=e241 | doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.0030241 |display-authors=1 |last2=Willerslev |first2=Eske |last3=Sher |first3=Andrei |last4=Tong |first4=Wenfei |last5=Ho |first5=Simon Y.W. |last6=Rubenstein |first6=Dan |last7=Storer |first7=John |last8=Burns |first8=James |last9=Martin |first9=Larry |doi-access=free }}</ref> Yet between 10,000 and 7,600 years ago, the horse became extinct in North America.<ref name = VilaWidespreadOrigins>{{cite journal|last=Vila |first=C.|year=2001|title=Widespread Origins of Domestic Horse Lineages |journal=] |volume=291 |doi=10.1126/science.291.5503.474 |url=http://www.uky.edu/Ag/Horsemap/Maps/VILA.PDF |pages=474–477 |pmid=11161199 |issue=5503 |display-authors=etal |bibcode=2001Sci...291..474V |access-date=2009-03-17 |archive-date=2012-10-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121013082210/http://www.uky.edu/Ag/Horsemap/Maps/VILA.PDF |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name = IberianOrigins>{{cite journal|last=Luís |first= Cristina |year=2006 |title=Iberian Origins of New World Horse Breeds |journal=Quaternary Science Reviews |volume=97 |issue=2 | pages=107–113 |doi=10.1093/jhered/esj020 |pmid=16489143 |display-authors=etal |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name=Haile>{{cite journal|title=Ancient DNA reveals late survival of mammoth and horse in interior Alaska |doi=10.1073/pnas.0912510106 |author=Haile, James |journal=PNAS |year=2009 |volume=106|issue= 52 |pages=22352–22357 |display-authors=1 |last2=Froese |first2=D. G. |last3=MacPhee |first3=R. D. E. |last4=Roberts |first4=R. G. |last5=Arnold |first5=L. J. |last6=Reyes |first6=A. V. |last7=Rasmussen |first7=M. |last8=Nielsen |first8=R. |last9=Brook |first9=B. W. |pmid=20018740 |pmc=2795395 |bibcode=2009PNAS..10622352H |doi-access=free}}</ref> The reasons for this extinction are not fully known, but one theory notes that extinction in North America paralleled human arrival.<ref name = Buck>{{cite journal |last=Buck |first=Caitlin E. |author2=Bard, Edouard |year=2007 |title=A calendar chronology for Pleistocene mammoth and horse extinction in North America based on Bayesian radiocarbon calibration |journal=Quaternary Science Reviews |volume=26 |issue=17–18 |doi=10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.06.013 |pages=2031–2035 |bibcode=2007QSRv...26.2031B |url=https://zenodo.org/record/886512 |access-date=2017-09-06 |archive-date=2018-11-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181106193405/https://zenodo.org/record/886512 |url-status=live }}</ref> Another theory points to ], noting that approximately 12,500 years ago, the grasses characteristic of a ] ecosystem gave way to shrub ], which was covered with unpalatable plants.<ref name="LeQuire">{{cite web | url=http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=4849 | author=LeQuire, Elise | title=No Grass, No Horse | publisher=The Horse | url-access=registration | date=2004-01-04 | access-date=2009-06-08 | archive-date=2013-01-09 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130109101503/http://www.thehorse.com/articles/14327/no-grass-no-horse | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Breeds, studbooks, purebreds, and landraces=== | |||
| ], one of the most well-known race horses]]Selective breeding of horses has occurred as long as man has domesticated them. However, the concept of controlled breed registries has gained much wider importance during the 20th century. One of the earliest formal registries was General Stud Book for thoroughbreds<ref>http://www.imh.org/imh/bw/tbred.html#hist</ref>, a process that started in 1791 tracing back to the foundation sires for that breed. These sires were Arabians, brought to England from the Middle East. | |||
| ===Wild species surviving into modern times=== | |||
| The ]s had a reputation for breeding their prize ] mares to only the most worthy stallions, and kept extensive pedigrees of their "]" (purebred) horses. During the late Middle Ages the ] monks of southern Spain, themselves forbidden to ride, bred horses which nobles throughout Europe prized; the lineage survives to this day in the ] or ''caballo de pura raza español''. | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Wild horse}} | |||
| A truly ] is a species or subspecies with no ancestors that were ever successfully domesticated. Therefore, most "wild" horses today are actually ]s, animals that escaped or were turned loose from domestic herds and the descendants of those animals.<ref name=Olsen46>{{cite book|author= Olsen, Sandra L.|chapter= Horse Hunters of the Ice Age |title= Horses Through Time |edition= First |publisher= Roberts Rinehart Publishers |location= Boulder, CO |year= 1996 |isbn= 1-57098-060-8 |oclc=36179575 |page= |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/horsesthroughtim00olse/page/46}}</ref> Only two wild subspecies, the ] and the ], survived into recorded history and only the latter survives today. | |||
| The ] (''Equus ferus przewalskii''), named after the Russian explorer ], is a rare Asian animal. It is also known as the Mongolian wild horse; ]n people know it as the ''taki'', and the ] call it a ''kirtag''. The subspecies was presumed extinct in the wild between 1969 and 1992, while a small breeding population survived in zoos around the world. In 1992, it was reestablished in the wild by the conservation efforts of numerous zoos.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.zsl.org/about-us/media/press-releases/null,1790,PR.html |title= An extraordinary return from the brink of extinction for world's last wild horse |date= 2005-12-19 |access-date= 2012-06-06 |website= ZSL Press Releases |publisher= Zoological Society of London |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130516230420/http://www.zsl.org/about-us/media/press-releases/null,1790,PR.html |archive-date= 2013-05-16}}</ref> Today, a small wild breeding population exists in Mongolia.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.treemail.nl/takh/ |title= Home |access-date= 2008-04-03 |publisher= The Foundation for the Preservation and Protection of the Przewalski Horse |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.treemail.nl/takh/ |archive-date=2017-10-10 |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name=Dohner298>], pp. 298–299</ref> There are additional animals still maintained at zoos throughout the world. | |||
| Standardbreds are another racing breed. They have an additional gait, ], and are usually driven, pulling a light carriage known as a ], rather than ridden. | |||
| Their status as a truly wild horse was called into question when domestic horses of the 5,000-year-old ] of Central Asia were found to be more closely related to Przewalski's horses than to ''E. f. caballus''. The study raised the possibility that modern Przewalski's horses could be the feral descendants of the domestic Botai horses. The study concluded that the Botai animals appear to have been an independent domestication attempt and apparently unsuccessful in terms of genetic markers carrying through to modern domesticated equines. However, the question of whether all Przewalski's horses descend from this population is also unresolved, as only one of seven modern Przewalski’s horses in the study shared this ancestry. It may also be that both the Botai horses and the modern Przewalski's horses descend separately from the same ancient wild Przewalski's horse population.<ref name="Pennisi">{{cite web |author=Pennisi, Elizabeth |author-link=Elizabeth Pennisi |title=Ancient DNA upends the horse family tree |website=sciencemag.org |date=22 February 2018 |url=https://www.science.org/content/article/ancient-dna-upends-horse-family-tree |access-date=30 June 2022 |archive-date=21 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220921222121/https://www.science.org/content/article/ancient-dna-upends-horse-family-tree |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=Orlando>{{Cite journal |last1=Orlando |first1=Ludovic |last2=Outram |first2=Alan K. |last3=Librado| first3=Pablo |last4=Willerslev |first4=Eske |last5=Zaibert |first5=Viktor |last6=Merz |first6=Ilja |last7=Merz |first7=Victor |last8=Wallner |first8=Barbara |last9=Ludwig |first9=Arne |date=2018-04-06 |df=dmy-all |title=Ancient genomes revisit the ancestry of domestic and Przewalski's horses |journal=Science |language=en |volume=360 |issue=6384 |pages=111–114 |doi=10.1126/science.aao3297 |issn=0036-8075 |pmid=29472442|bibcode=2018Sci...360..111G |doi-access=free|hdl=10871/31710 |hdl-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://arstechnica.com/science/2018/02/ancient-dna-rules-out-archeologists-best-bet-for-horse-domestication/|date=February 25, 2018|title=Ancient DNA rules out archeologists' best bet for horse domestication|publisher=]|access-date=24 June 2020|archive-date=25 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200625064751/https://arstechnica.com/science/2018/02/ancient-dna-rules-out-archeologists-best-bet-for-horse-domestication/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The modern landscape of breed designation presents a complicated picture. Some breeds have closed ]s; a registered ], ], or ] must have two registered parents of the same breed, and no other criteria for registration apply. Other breeds tolerate limited infusions from other breeds—the modern ] for instance must have at least one Appaloosa parent but may also have a ], Thoroughbred, or Arabian parent and must also exhibit spotted coloration to gain full registration. Still other breeds, such as most of the warmblood sporthorses, require individual judging of an individual animal's quality before registration or breeding approval. | |||
| The ] or European wild horse (''Equus ferus ferus'') was found in Europe and much of Asia. It survived into the historical era, but became ] in 1909, when the last captive died in a Russian zoo.<ref name=Dohner300>], p. 300</ref> Thus, the genetic line was lost. Attempts have been made to recreate the tarpan,<ref name=Dohner300/><ref name=OSU>{{cite web|url=http://www.ansi.okstate.edu/breeds/horses/tarpan/ |title=Tarpan |publisher=Oklahoma State University |website=Breeds of Livestock |access-date=2009-01-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090116022102/http://www.ansi.okstate.edu/breeds/horses/TARPAN/ |archive-date=2009-01-16}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |url=https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=894&dat=20020621&id=YiALAAAAIBAJ&pg=6481,3069519 |journal=The Daily Courier |date=June 21, 2002 |access-date=2009-10-21 |title=Ponies from the past?: Oregon couple revives prehistoric Tarpan horses |archive-date=2021-04-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210417182639/https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=894&dat=20020621&id=YiALAAAAIBAJ&pg=6481,3069519 |url-status=live }}</ref> which resulted in horses with outward physical similarities, but nonetheless descended from domesticated ancestors and not true wild horses. | |||
| Breed registries also differ as to their acceptance or rejection of breeding technology. For example, all ] Thoroughbred registries require that a registered Thoroughbred be a product of a natural mating ('live cover' in horse parlance). A foal born of two Thoroughbred parents, but by means of ], is barred from the Thoroughbred studbook. Any Thoroughbred bred outside of these constraints can, however, become part of the Performance Horse Registry. | |||
| Periodically, populations of horses in isolated areas are speculated to be ] populations of wild horses, but generally have been proven to be feral or domestic. For example, the ] of Tibet was proposed as such,<ref name=Dohner298/> but testing did not reveal genetic differences from domesticated horses.<ref name=Tibet>{{cite book |title=Tibet: The Secret Continent |author=Peissel, Michel |year=2002 |publisher=Macmillan |isbn=0-312-30953-8 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6sFWvuBug8IC&pg=PA36 |page=36 |access-date=2020-09-28 |archive-date=2023-03-20 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223812/https://books.google.com/books?id=6sFWvuBug8IC&pg=PA36 |url-status=live }}</ref> Similarly, the ] of Portugal was proposed as a direct descendant of the ] on the basis of shared characteristics,<ref name="Royo">{{cite journal|author1=Royo, L.J. |author2=Álvarez, I. |author3=Beja-Pereira, A. |author4=Molina, A. |author5=Fernández, I. |author6=Jordana, J. |author7=Gómez, E. |author8=Gutiérrez, J. P. |author9=Goyache, F. |year=2005 |title=The Origins of Iberian Horses Assessed via Mitochondrial DNA |journal=Journal of Heredity |volume=96 |issue=6 |pages=663–669 |doi=10.1093/jhered/esi116|pmid=16251517|doi-access=free}}<!--|access-date=2008-12-15--></ref><ref name=Edwards>], pp. 104–105</ref> but genetic studies have shown that the Sorraia is more closely related to other horse breeds, and that the outward similarity is an unreliable measure of relatedness.<ref name=Royo/><ref name=Lira/> | |||
| Many breed registries allow ] (AI), ], or both. The high value of stallions has helped with the acceptance of these techniques because they 1) allow for more doses with each stallion 'collection' and 2) take away the risk of injury during mating. | |||
| ===Other modern equids=== | |||
| ===Hotbloods, warmbloods, and coldbloods=== | |||
| {{Main|Equus (genus)}} | |||
| {{main|List of horse breeds}} | |||
| Besides the horse, there are six other species of ] ''Equus'' in the Equidae ]. These are the ass or ], ''Equus asinus''; the ], ''Equus zebra''; ], ''Equus quagga''; ], ''Equus grevyi''; the ], ''Equus kiang''; and the ], ''Equus hemionus''.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=14100020 |title=Equus hemionus |author=Pallas |year=1775 |website=Wilson & Reeder's mammal species of the world |publisher=] |access-date=September 1, 2010 |archive-date=September 26, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130926213002/http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=14100020 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Horses can ] with other members of their genus. The most common ] is the ], a cross between a "jack" (male donkey) and a ]. A related hybrid, a ], is a cross between a stallion and a "jenny" (female donkey).<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.britishmulesociety.org.uk/|title= Mule Information |access-date= 2008-07-10 |website= BMS Website |publisher= British Mule Society |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.britishmulesociety.org.uk/ |archive-date= 2017-10-10 |url-status= dead}}</ref> Other hybrids include the ], a cross between a zebra and a horse.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/1408717.stm|title=Zebra hybrid is cute surprise|date=June 26, 2001|access-date=2010-02-06|work=BBC News|archive-date=2017-06-14|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170614032715/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/1408717.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> With rare exceptions, most hybrids are ] and cannot reproduce.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=12260255 |title=Befuddling Birth: The Case of the Mule's Foal |access-date=2008-08-16 |newspaper=NPR.org |publisher=National Public Radio |archive-date=2008-12-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081206052236/http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=12260255 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Horses are ] and as such are all warm-blooded creatures, as opposed to ], which are cold-blooded. However, these words have developed a separate meaning in the context of equine description, with the "hot-bloods" generally originating from hotter countries and exhibiting more sensitivity and energy, while the "cold-bloods" are heavier, calmer creatures such as the draft giants. | |||
| ==Domestication and history== | |||
| '''Hotbloods''' | |||
| {{Main|History of horse domestication theories|Domestication of the horse}}{{Anchor|Domestication}}] rock painting showing a man riding on a horse, India]] | |||
| Domestication of the horse most likely took place in central Asia prior to 3500 BCE. Two major sources of information are used to determine where and when the horse was first domesticated and how the domesticated horse spread around the world. The first source is based on ] and archaeological discoveries; the second source is a comparison of DNA obtained from modern horses to that from bones and teeth of ancient horse remains. | |||
| The earliest archaeological evidence for attempted ] comes from sites in ] and ], dating to approximately 4000–3500 BCE.<ref>{{Cite journal | pmid = 19265018| year = 2009| last1 = Outram| first1 = A. K.| title = The earliest horse harnessing and milking| journal = Science| volume = 323| issue = 5919| pages = 1332–1335| last2 = Stear| first2 = N. A.| last3 = Bendrey| first3 = R| last4 = Olsen| first4 = S| last5 = Kasparov| first5 = A| last6 = Zaibert| first6 = V| last7 = Thorpe| first7 = N| last8 = Evershed| first8 = R. P.| doi = 10.1126/science.1168594| bibcode = 2009Sci...323.1332O| s2cid = 5126719}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author= Matossian, Mary Kilbourne |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=LkRATLisN0sC&pg=PA43 |title= Shaping World History: Breakthroughs in Ecology, Technology, Science, and Politics |publisher= M.E. Sharpe |location= Armonk, NY |year= 1997 |isbn= 0-585-02397-2 |oclc= 156944228 |page= 43 |access-date= 2020-09-28 |archive-date= 2023-03-20 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223830/https://books.google.com/books?id=LkRATLisN0sC&pg=PA43 |url-status= live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Horsey-aeology, Binary Black Holes, Tracking Red Tides, Fish Re-evolution, Walk Like a Man, Fact or Fiction|url=http://www.cbc.ca/quirks/episode/2009/03/07/horsey-aeology-binary-black-holes-tracking-red-tides-fish-re-evolution-walk-like-a-man-fact-or-ficti/|work=Quirks and Quarks Podcast with Bob Macdonald|publisher=]|date=2009-03-07|access-date=2010-09-18|archive-date=2014-10-07|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141007100308/http://www.cbc.ca/quirks/episode/2009/03/07/horsey-aeology-binary-black-holes-tracking-red-tides-fish-re-evolution-walk-like-a-man-fact-or-ficti/|url-status=live}}</ref> However the horses domesticated at the Botai culture in Kazakhstan were Przewalski's horses and not the ancestors of modern horses.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Taylor |first1=William Timothy Treal |last2=Barrón-Ortiz |first2=Christina Isabelle |date=2021-04-02 |title=Rethinking the evidence for early horse domestication at Botai |journal=Scientific Reports |language=en |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=7440 |doi=10.1038/s41598-021-86832-9 |pmid=33811228 |pmc=8018961 |bibcode=2021NatSR..11.7440T |issn=2045-2322}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Librado |first1=Pablo |last2=Khan |first2=Naveed |last3=Fages |first3=Antoine |last4=Kusliy |first4=Mariya A. |last5=Suchan |first5=Tomasz |last6=Tonasso-Calvière |first6=Laure |last7=Schiavinato |first7=Stéphanie |last8=Alioglu |first8=Duha |last9=Fromentier |first9=Aurore |last10=Perdereau |first10=Aude |last11=Aury |first11=Jean-Marc |last12=Gaunitz |first12=Charleen |last13=Chauvey |first13=Lorelei |last14=Seguin-Orlando |first14=Andaine |last15=Der Sarkissian |first15=Clio |date=2021 |title=The origins and spread of domestic horses from the Western Eurasian steppes |journal=Nature |language=en |volume=598 |issue=7882 |pages=634–640 |doi=10.1038/s41586-021-04018-9 |issn=1476-4687 |pmc=8550961 |pmid=34671162|bibcode=2021Natur.598..634L }}</ref> | |||
| ]s, whether originating on the ]n peninsula or from the European studs (breeding establishments) of the 18th and 19th centuries, gained the title of "hotbloods" for their temperament, characterised by sensitivity, keen awareness, athleticism, and energy. It was these traits, combined with the lighter, aesthetically refined bone structure, which was used as the foundation of the thoroughbreds. The European breeders wished to infuse some of this energy and athleticism into their own best cavalry horses. | |||
| By 3000 BCE, the horse was completely domesticated and by 2000 BCE there was a sharp increase in the number of horse bones found in human settlements in northwestern Europe, indicating the spread of domesticated horses throughout the continent.<ref>{{cite book |author=Evans, James Warren |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QofYEVPeIBUC&pg=PA56 |title=Horse Breeding and Management |publisher=Elsevier Health Sciences |location=Amsterdam |year=1992 |isbn=0-444-88282-0 |oclc=243738023 |page=56 }}{{Dead link|date=April 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> The most recent, but most irrefutable evidence of domestication comes from sites where horse remains were interred with chariots in graves of the Indo-European ] and ] cultures {{circa}} 2100 BCE.<ref name="Kuznetsov2006">{{cite journal | last = Kuznetsov | first = P. F. | year = 2006 | title = The emergence of Bronze Age chariots in eastern Europe | journal = ] | volume = 80 | issue = 309 | pages = 638–645 | doi=10.1017/S0003598X00094096| s2cid = 162580424 }}</ref> | |||
| The ] is unique to all breeds in that its muscles can be trained for either fast-twitch (for sprinting) or slow-twitch (for endurance), making them an extremely versatile breed. Arabians are used in the sport horse world almost exclusively for endurance competitions. Breeders continue to use Arabian sires with Thoroughbred dams to enhance the sensitivity of the offspring for use in equestrian sports. This Arabian/Thoroughbred cross is known as an ]. | |||
| A 2021 genetic study suggested that most modern domestic horses descend from the lower ]. ] indicate that these populations influenced <!--mostly stallions crossed on local mares-->almost all local populations as they expanded rapidly throughout ], beginning about 4,200 years ago. It also shows that certain adaptations were strongly selected due to ], and that ], including ] spoke-wheeled ]s spread with the horse itself.<ref>{{cite news |author-first1=Jonathan |author-last1=Lambert |title=Scientists found modern domestic horses' homeland in southwestern Russia |url=https://www.sciencenews.org/article/dna-genes-modern-domestic-horses-origin-russia |access-date=14 November 2021 |work=Science News |date=20 October 2021 |archive-date=14 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211114232955/https://www.sciencenews.org/article/dna-genes-modern-domestic-horses-origin-russia |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Pablo Librado |display-authors=et al. |title=The origins and spread of domestic horses from the Western Eurasian steppes |journal=Nature |date=October 2021 |volume=598 |issue=7882 |pages=634–640 |doi=10.1038/s41586-021-04018-9 |pmid=34671162 |pmc=8550961 |bibcode=2021Natur.598..634L |language=en |issn=1476-4687}}</ref> | |||
| True hotbloods usually offer greater riding challenges and rewards than other horses. Their sensitivity and intelligence enable quick learning, and greater communication and cooperation with their riders. However, they sometimes decide that a new flowerpot is really a dragon, and the rider must spend the next five minutes calming them down. | |||
| Domestication is also studied by using the genetic material of present-day horses and comparing it with the genetic material present in the bones and teeth of horse remains found in archaeological and palaeological excavations. The variation in the genetic material shows that very few wild stallions contributed to the domestic horse,<ref name=Lau>{{cite journal|doi=10.1093/molbev/msn239|author1=Lau, A. N. |author2= Peng, L.|author3= Goto, H.|author4= Chemnick, L.|author5= Ryder, O. A. |author6= Makova, K. D. |year= 2009 |title= Horse Domestication and Conservation Genetics of Przewalski's Horse Inferred from Sex Chromosomal and Autosomal Sequences| journal= Molecular Biology and Evolution |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages= 199–208 |pmid=18931383 |doi-access= free}}</ref><ref name="Lindgren2004">{{cite journal | last = Lindgren | first = Gabriella |author2=Niclas Backström |author3=June Swinburne |author4=Linda Hellborg |author5=Annika Einarsson |author6=Kaj Sandberg |author7=Gus Cothran |author8=Carles Vilà |author9=Matthew Binns |author10=Hans Ellegren | year =2004 | title = Limited number of patrilines in horse domestication | journal = ] | pmid = 15034578 | volume = 36 | issue = 4 | pages = 335–336 | doi = 10.1038/ng1326| doi-access =free}}</ref> while many mares were part of early domesticated herds.<ref name=Lira>{{cite journal | title=Ancient DNA reveals traces of Iberian Neolithic and Bronze Age lineages in modern Iberian horses | author=Lira, Jaime | journal=Molecular Ecology | volume=19 | issue=1 | pages=64–78 | year=2010 | pmid=19943892 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04430.x | bibcode=2010MolEc..19...64L | s2cid=1376591 | display-authors=etal | url=http://eprints.ucm.es/10548/2/Mol_Ecol_2009_Lira_et_al_Ancient_Iberian_horses.pdf | access-date=2018-04-20 | archive-date=2017-08-10 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170810142737/http://eprints.ucm.es/10548/2/Mol_Ecol_2009_Lira_et_al_Ancient_Iberian_horses.pdf | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Vila2001">{{cite journal | last1 = Vilà | first1 = C. | year = 2001 | title = Widespread origins of domestic horse lineages | journal = ] | volume = 291 | issue = 5503 | pages = 474–477 | doi = 10.1126/science.291.5503.474 | pmid = 11161199 | display-authors = 1 | last2 = Leonard | first2 = JA | last3 = Gotherstrom | first3 = A | last4 = Marklund | first4 = S | last5 = Sandberg | first5 = K | last6 = Liden | first6 = K | last7 = Wayne | first7 = RK | last8 = Ellegren | first8 = H| bibcode = 2001Sci...291..474V}}</ref><ref name=Cai>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1016/j.jas.2008.11.006 | last1 = Cai | first1 = D. W. | last2 = Tang | first2 = Z. W. | last3 = Han | first3 = L. | last4 = Speller | first4 = C. F. | last5 = Yang | first5 = D. Y. Y. | last6 = Ma | first6 = X. L. | last7 = Cao | first7 = J. E. | last8 = Zhu | first8 = H. | last9 = Zhou | first9 = H. | year = 2009 | title = Ancient DNA provides new insights into the origin of the Chinese domestic horse | url = https://www.sfu.ca/~donyang/adnaweb/Cai%20DW%20JAS2009.pdf | access-date = 17 January 2011 | journal = Journal of Archaeological Science | volume = 36 | issue = 3 | pages = 835–842 | bibcode = 2009JArSc..36..835C | display-authors = etal | archive-date = 29 June 2011 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110629014405/http://www.sfu.ca/~donyang/adnaweb/Cai%20DW%20JAS2009.pdf | url-status = live }}</ref> This is reflected in the difference in genetic variation between the DNA that is passed on along the paternal, or sire line (]) versus that passed on along the maternal, or dam line (]). There are very low levels of Y-chromosome variability,<ref name=Lau/><ref name="Lindgren2004" /> but a great deal of genetic variation in mitochondrial DNA.<ref name=Lira/><ref name="Vila2001"/><ref name=Cai/> There is also regional variation in mitochondrial DNA due to the inclusion of wild mares in domestic herds.<ref name=Lira/><ref name="Vila2001"/><ref name=Cai/><ref>{{cite encyclopedia |author=Olsen, Sandra L.|title=Early Horse Domestication: Weighing the Evidence| encyclopedia=Horses & Humans: The Evolution of Human-Equine Relationships |editor1=Olsen, Sandra L |editor2=Grant, Susan |editor3=Choyke, Alice M. |editor4=Bartosiewicz, Laszlo |publisher=Archaeopress |location=Oxford, UK |year=2006 |pages=81–113 |isbn=978-1-84171-990-0}}</ref> Another characteristic of domestication is an increase in coat color variation.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Epstein, H. |year=1955 |title=Domestication Features in Animals as Functions of Human Society |journal=Agricultural History Society |volume= 29|issue=4|pages= 137–146 |jstor=3740046}}</ref> In horses, this increased dramatically between 5000 and 3000 BCE.<ref name=coatColor>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1126/science.1172750 | last1 = Ludwig | first1 = A. | last2 = Pruvost | first2 = M. | last3 = Reissmann | first3 = M. | last4 = Benecke | first4 = N. | last5 = Brockmann | first5 = G.A. | last6 = Castanos | first6 = P. | last7 = Cieslak | first7 = M. | last8 = Lippold | first8 = S. | last9 = Llorente | first9 = L.| year = 2009 | title = Coat Color Variation at the Beginning of Horse Domestication |journal = Science | volume = 324 | issue = 5926| pages = 485 | pmid=19390039|display-authors=etal | pmc=5102060| bibcode = 2009Sci...324..485L}}</ref> | |||
| '''Coldbloods''' | |||
| Before the availability of DNA techniques to resolve the questions related to the domestication of the horse, various hypotheses were proposed. One classification was based on body types and conformation, suggesting the presence of four basic prototypes that had adapted to their environment prior to domestication.<ref name="Bennett7">{{cite book |author= Bennett, Deb |title= Conquerors: The Roots of New World Horsemanship |edition= First |publisher= Amigo Publications, Inc. |location= Solvang, CA |year= 1998 |isbn=0-9658533-0-6 |oclc= 39709067|page=7}}</ref> Another hypothesis held that the four prototypes originated from a single wild species and that all different body types were entirely a result of ] after domestication.<ref>{{cite book |author=Edwards, Gladys Brown |title=The Arabian: War Horse to Show Horse |publisher=Rich Publishing |year=1973 |edition=Revised Collectors |pages= 1, 3}}</ref> However, the lack of a detectable substructure <!--huh? what's that? Can we explain in everyday language?--> in the horse has resulted in a rejection of both hypotheses.<!--I will add the ref for it once I find the book back--><!--OK--> | |||
| Muscular and heavy draft horses are known as "coldbloods", as they have been bred to be workhorses and carriage horses with calm temperaments. Harnessing a horse to a carriage requires some level of trust in the horse to remain calm when restrained. One of the most common draft breeds in the United States is the Belgian. The best known coldbloods would probably be the Budweiser ]. | |||
| <ref>http://images.google.com/images?&q=budweiser+clydesdale&btnG=Search</ref> | |||
| ===Feral populations=== | |||
| '''Warmbloods''' | |||
| {{Main|Feral horse}} | |||
| ] horses are born and live in the wild, but are descended from domesticated animals.<ref name=Olsen46/> Many populations of ]s exist throughout the world.<ref>], p. 291</ref><ref>{{cite book|author= Anthony, David W. |chapter= Bridling Horse Power: The Domestication of the Horse |title= Horses Through Time |edition= First |publisher= Roberts Rinehart Publishers| location= Boulder, CO |year= 1996 |isbn= 1-57098-060-8 |oclc= 36179575 |pages= |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/horsesthroughtim00olse/page/66}}</ref> Studies of feral herds have provided useful insights into the behavior of prehistoric horses,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.carnegiemnh.org/anthro/olsen_horse.html | author=Olsen, Sandra L. |title= Horses in Prehistory |website=Anthropology Research | publisher=Carnegie Museum of Natural History |access-date=2008-08-16 |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080525183100/http://www.carnegiemnh.org/anthro/olsen_horse.html |archive-date = May 25, 2008}}</ref> as well as greater understanding of the instincts and behaviors that drive horses that live in domesticated conditions.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=15037 |title=Mares' Social Bonds Might Enhance Reproductive Success |date=October 7, 2009 |access-date=2009-10-21 |website=The Horse |url-access=registration | author=Lesté-Lasserre, Christa |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120415005227/http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=15037 |archive-date=April 15, 2012 |url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| There are also ] horses in many parts of the world, such as ] and the ] in the UK, where the animals are all privately owned but live for significant amounts of time in "wild" conditions on undeveloped, often public, lands. Owners of such animals often pay a fee for grazing rights.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.dartmoorcommonerscouncil.org.uk/menu_page.php?id=53 |publisher=Dartmoor Commoners' Council |title=Animals on the Moor |access-date=2012-03-29 |archive-date=2017-10-10 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.dartmoorcommonerscouncil.org.uk/menu_page.php?id=53 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=Fear75>{{cite book |author=Fear, Sally |title=New Forest Drift: A Photographic Portrait of Life in the National Park |publisher= Perspective Photo Press |year= 2006 |isbn=978-0-9553253-0-4 |page= 75}}</ref><!-- could also include Carmarque horse of France and a lot of the big QH ranches in Texas--> | |||
| ] breeds began in much the same way as the Thoroughbred. The best of the European carriage or cavalry horses were bred to Arabian, Anglo-Arabian and Thoroughbred sires. The term "]s" is sometimes used to mean any draft/Thoroughbred cross although this is becoming less common. The warmblood name has become the term to specifically refer to the sporthorse breed registries than began in Europe, although now worldwide. These registries, or societies, such as the ], ], ], and ] have dominated the ] and ] in ] and ] since the ]. | |||
| ===Breeds=== | |||
| The ] provides a partial alphabetical list of breeds of horse extant today, plus a discussion of rare breeds' conservation. | |||
| {{Main|Horse breed||List of horse breeds|Horse breeding}} | |||
| The concept of ] bloodstock and a controlled, written ] has come to be particularly significant and important in modern times. Sometimes purebred horses are incorrectly or inaccurately called "thoroughbreds". ] is a specific breed of horse, while a "purebred" is a horse (or any other animal) with a defined ] recognized by a breed registry.<ref name=Ensminger424>], p. 424</ref> Horse breeds are groups of horses with distinctive characteristics that are transmitted consistently to their offspring, such as ], color, performance ability, or disposition. These inherited traits result from a combination of natural crosses and ] methods. Horses have been ] since their ]. An early example of people who practiced selective ] were the ], who had a reputation for careful practices, keeping extensive pedigrees of their ]s and placing great value upon pure bloodlines.<ref>{{cite book |author=Edwards, Gladys Brown |title=The Arabian: War Horse to Show Horse |publisher=Rich Publishing |year=1973 |edition=Revised Collectors |pages=22–23}}</ref> These pedigrees were originally transmitted via an ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.waho.org/History.html |title=Is Purity the Issue? |access-date=2008-04-29 |website=WAHO Publication Number 21 January 1998 |publisher=World Arabian Horse Organization |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080705105054/http://www.waho.org/Purityissue.html |archive-date=5 July 2008 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Tack and equipment== | |||
| Breeds developed due to a need for "form to function", the necessity to develop certain characteristics in order to perform a particular type of work.<ref name=Sponenberg155>], p. 155</ref> Thus, a powerful but refined breed such as the Andalusian developed as riding horses with an aptitude for ].<ref name=Sponenberg155/> Heavy draft horses were developed out of a need to perform demanding ] work and pull heavy wagons.<ref>], pp. 156–157</ref> Other horse breeds had been developed specifically for light agricultural work, carriage and road work, various sport disciplines, or simply as pets.<ref name=Spon162>], p. 162</ref> Some breeds developed through centuries of crossing other breeds, while others descended from a single ], or other limited or restricted foundation bloodstock. One of the earliest formal registries was ] for Thoroughbreds, which began in 1791 and traced back to the ] for the breed.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.britishhorseracing.com/goracing/racing/racehorses/history.asp |title=History of Thoroughbreds |access-date=2008-04-03 |website=Britishhorseracing.com |publisher=British Horseracing Authority |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140201154621/http://www.britishhorseracing.com/goracing/racing/racehorses/history.asp |archive-date=2014-02-01 }}</ref> There are more than 300 horse breeds in the world today.<ref>{{cite book |author1=Hedge, Juliet |author2=Don M. Wagoner |title= Horse Conformation: Structure, Soundness and Performance |publisher= Globe Pequot |location=Guilford, CT |year= 2004|isbn= 1-59228-487-6 |oclc= 56012597|pages=307–308}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|Horse tack}} | |||
| ==Interaction with humans== | |||
| "Tack" (also known as saddlery) refers to equipment worn by the horse, normally when being ridden or longed for exercise. The tack may be made from ] or from a synthetic material, which tends to be lighter to carry and cheaper to buy. | |||
| ] pulling a heavy wagon.]] | |||
| Worldwide, horses play a role within human cultures and have done so for millennia. Horses are used for leisure activities, sports, and working purposes. The ] (FAO) estimates that in 2008, there were almost 59,000,000 horses in the world, with around 33,500,000 in the Americas, 13,800,000 in Asia and 6,300,000 in Europe and smaller portions in Africa and Oceania. There are estimated to be 9,500,000 horses in the United States alone.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://faostat.fao.org/site/573/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=573#ancor |publisher=Food and Agriculture Organization |date=December 16, 2009 |access-date=2010-02-05 |title=FAO Stat – Live Animals |archive-date=2013-01-19 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130119095737/http://faostat.fao.org/site/573/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=573#ancor |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] estimates that horse-related activities have a direct impact on the economy of the United States of over $39 billion, and when indirect spending is considered, the impact is over $102 billion.<ref>{{cite press release |url= http://www.cthorsecouncil.org/AHC2005JuneEconStudy.pdf|title= Most Comprehensive Horse Study Ever Reveals A Nearly $40 Billion Impact On The U.S. Economy |access-date=2005-06-20 |publisher= American Horse Council |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20060625083812/http://www.cthorsecouncil.org/AHC2005JuneEconStudy.pdf |archive-date = June 25, 2006}}</ref> In a 2004 "poll" conducted by ], more than 50,000 viewers from 73 countries voted for the horse as the world's 4th favorite animal.<ref name=IOL>{{cite web|url= http://www.iol.co.za/news/back-page/tiger-tops-dog-as-world-s-favourite-animal-1.228797|title= Tiger tops dog as world's favourite animal|access-date= 2011-06-01|website= Independent Online|publisher= Independent|archive-date= 2012-10-28|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121028071911/http://www.iol.co.za/news/back-page/tiger-tops-dog-as-world-s-favourite-animal-1.228797|url-status= live}}</ref> | |||
| Communication between human and horse is paramount in any equestrian activity;<ref name="Olsen"/> to aid this process horses are usually ridden with a ] on their backs to assist the rider with balance and positioning, and a ] or related headgear to assist the rider in maintaining control.<ref>{{cite book |author=Edwards, Elwyn Hartley |title=Horses |edition=Second American |publisher=Dorling Kindersley |location= New York |year=2002 |isbn=0-7894-8982-1 |oclc=50798049|pages= 32–34}}</ref> Sometimes horses are ridden without a saddle,<ref>{{cite book|author=Self, Margaret Cabell|title=Riding Simplified|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iUTm7aD1Mf8C&pg=PA55|publisher=Kessinger Publishing|year=2005|isbn=1-4191-0087-4|page=55}}{{Dead link|date=March 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> and occasionally, horses are trained to perform without a bridle or other headgear.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |author=Thorson, Juli S. |title=Rugged Lark |editor= Martindale, Cathy and Kathy Swan |encyclopedia= Legends 7: Outstanding Quarter Horse Stallions and Mares |publisher=Western Horseman |location= Colorado Springs, CO |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-911647-79-2 |page=218}}</ref> Many horses are also ], which requires a ], bridle, and some type of ].<ref>{{cite book |author= Mettler, John J Jr.|title= Horse Sense: A Complete Guide to Horse Selection and Care |url= https://archive.org/details/horsesensecomple00mett|url-access= registration |publisher= Storey Communications, Inc. |location= Pownal, VT |year= 1989 |isbn=0-88266-549-9 |oclc= 19324181 |pages=}}</ref> | |||
| The basic equipment a horse requires includes: | |||
| * A ], including a bit and ] | |||
| * A ], which includes ] leathers, stirrups, and a girth or cinch. | |||
| * A saddle pad or blanket | |||
| * A ] and lead rope | |||
| * Grooming supplies, including brushes, a currycomb (a rubber brush-like device used to remove mud and deep dirt), and hoof pick for cleaning out the horse's feet. | |||
| ===Sport=== | |||
| Other instruments which are used in the riding and training horses include lunge whips, crops, and spurs. To an observer who has had no experience dealing with horses, these devices can seem cruel. These devices are not designed to inflict pain when used properly (however almost any 'tool' can be abusive in the wrong hands), but are merely tools to allow better communication to a horse when used by an experienced rider/handler/trainer. | |||
| <!-- There is a whole article about Equestrianism for all details about every possible sport. This article should only give the bare summary. So, please do not add elaborate sections of your own favorite horse sport here. --> | |||
| ] competition at the ]|alt=A chestnut (reddish-brown) horse being ridden by a rider in a black coat and top hat. They are stopped in a riding arena with the rider tipping his hat.]] | |||
| {{Main|Equestrianism|Horse racing|Horse training|Horse tack}} | |||
| Historically, equestrians honed their skills through games and races. Equestrian sports provided entertainment for crowds and honed the excellent horsemanship that was needed in battle. Many sports, such as ], ], and ], have origins in ], which were focused on control and balance of both horse and rider. Other sports, such as ], developed from practical skills such as those needed on working ]es and ]. Sport hunting from horseback evolved from earlier practical hunting techniques.<ref name="Olsen">{{cite book|author= Olsen, Sandra L. |chapter= In the Winner's Circle: The History of Equestrian Sports |title= Horses Through Time |edition= First |publisher= Roberts Rinehart Publishers |location= Boulder, CO |year= 1996 |isbn= 1-57098-060-8 |oclc= 36179575 |pages= |chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/horsesthroughtim00olse/page/105}}</ref> ] of all types evolved from impromptu competitions between riders or drivers. All forms of competition, requiring demanding and specialized skills from both horse and rider, resulted in the systematic development of specialized breeds and equipment for each sport. The popularity of equestrian sports through the centuries has resulted in the preservation of skills that would otherwise have disappeared after horses stopped being used in combat.<ref name="Olsen"/> | |||
| Horses are trained to be ridden or driven in a variety of sporting competitions. Examples include ], ], three-day ], ], ], ], ]s, and ].<ref>], pp. 346–356, 366–371</ref> ]s, which have their origins in medieval European fairs, are held around the world. They host a huge range of classes, covering all of the mounted and harness disciplines, as well as ] classes where the horses are led, rather than ridden, to be evaluated on their conformation. The method of judging varies with the discipline, but winning usually depends on style and ability of both horse and rider.<ref>], pp. 376–377</ref> | |||
| ==Miscellaneous== | |||
| Sports such as ] do not judge the horse itself, but rather use the horse as a partner for human competitors as a necessary part of the game. Although the horse requires specialized training to participate, the details of its performance are not judged, only the result of the rider's actions—be it getting a ball through a goal or some other task.<ref name=Edwards360>], p. 360</ref> Examples of these sports of partnership between human and horse include ], in which the main goal is for one rider to unseat the other,<ref>{{cite book|author1=Collins, Tony|author2=Martin, John|author3=Vamplew, Wray|title=Encyclopedia of Traditional British Rural Sports|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NWu6sLJn7-kC&pg=PA174|publisher=Routledge|year=2005|location=London|isbn=0-415-35224-X|oclc=57005595|pages=173–174|access-date=2020-09-28|archive-date=2023-03-20|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223813/https://books.google.com/books?id=NWu6sLJn7-kC&pg=PA174|url-status=live}}</ref> and ], a team game played throughout ], the aim being to capture a goat carcass while on horseback.<ref name=Edwards360/> | |||
| ===Saddling and mounting=== | |||
| The common European practice and tradition of ] and mounting the horse from the left hand side is sometimes said to originate from the practice of right-handed fighters carrying their sheathed ] on their left hip, making it easier to throw their right leg over the horse when mounting. However, several other explanations are equally plausible. | |||
| ] is an equestrian sport and major international industry, watched in almost every nation of the world. There are three types: "flat" racing; ], i.e. racing over jumps; and ], where horses trot or pace while pulling a driver in a small, light cart known as a ].<ref>], pp. 332–337</ref> A major part of horse racing's economic importance lies in the ] associated with it.<ref>{{cite book |author=Campbell, B.N. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-p7ZF9KW8-MC |title=National Gambling Impact Study Commission Final Report (1999) |publisher=DIANE Publishing |location=Darby, PA |year=2001 |isbn=0-7567-0701-3 |page=111 |access-date=2015-11-15 |archive-date=2023-03-20 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223813/https://books.google.com/books?id=-p7ZF9KW8-MC |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Horses can be mounted bareback with a ] from the ground or by grabbing the mane to provide leverage as a rider makes a small jump and scrambles up onto the horse's back (an awkward but popular method used by children). In actual practice, however, most bareback riders use a fence or mounting block. | |||
| === |
===Work=== | ||
| {{multiple image | |||
| The '''horse''' features in the 12-year cycle of animals which appear in the ] related to the ]. According to Chinese folklore, each animal is associated with certain personality traits, and those born in the year of the horse are: intelligent, independent and free-spirited. See: ]. | |||
| | footer = | |||
| | total_width=400 | |||
| | image1 = Tanga (carriage) at Darbhanga Bihar.jpg | |||
| | height1=240 | |||
| | width1= | |||
| | alt1 = Tired-looking bay horse hitched to a rustic cart | |||
| | caption1 = Horse pulling a cart | |||
| | image2 = Policja konna Poznań.jpg | |||
| | height2=240 | |||
| | width2= | |||
| | alt2 = A mounted man in a blue uniform on a dark brown horse | |||
| | caption2 = A mounted police officer in Poland | |||
| }} | |||
| There are certain jobs that horses do very well, and no technology has yet developed to fully replace them. For example, ] horses are still effective for certain types of patrol duties and crowd control.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nps.gov/uspp/fhorsepage.htm |title=Horse Mounted Unit |access-date=2008-04-07 |website=United States Park Police |publisher=National Park Service |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080218130631/http://www.nps.gov/uspp/fhorsepage.htm |archive-date=February 18, 2008}}</ref> Cattle ]es still require riders on horseback to round up cattle that are scattered across remote, rugged terrain.<ref>], pp. 226–227</ref> ] organizations in some countries depend upon ] teams to locate people, particularly hikers and children, and to provide disaster relief assistance.<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.sbcsheriff.org/msru_job.html|title= Volunteer Mounted Search and Rescue Unit |access-date= 2008-07-08 |website= Employment |publisher= San Benito County Sheriff's Office |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080509194223/http://www.sbcsheriff.org/msru_job.html |archive-date= 2008-05-09|url-status= dead}}</ref> Horses can also be used in areas where it is necessary to avoid vehicular disruption to delicate soil, such as nature reserves. They may also be the only form of transport allowed in ]s. Horses are quieter than motorized vehicles. ]s such as ]s or ]s may use horses for patrols, and horses or mules may also be used for clearing trails or other work in areas of rough terrain where vehicles are less effective.<ref>{{cite book |chapter-url=http://www.fs.fed.us/r9/publications/success_story_updates/2003-05.pdf |title=Success Stories |access-date=2008-04-20 |author=US Forest Service |date=May 2003 |chapter=Mules Key in Accomplishing Trail Work |publisher=US Department of Agriculture |page=4 |archive-date=2008-05-27 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080527220145/http://www.fs.fed.us/r9/publications/success_story_updates/2003-05.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Although machinery has replaced horses in many parts of the world, an estimated 100 million horses, donkeys and mules are still used for agriculture and transportation in less developed areas. This number includes around 27 million ]s in Africa alone.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=7001 |title=At Work in Morocco |url-access=registration |author=Brown, Kimberly S. |journal=The Horse |date=June 1, 2006 |access-date=2009-10-21 |archive-date=2007-12-22 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071222073228/http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=7001 |url-status=live }}</ref> Some land management practices such as cultivating and logging can be efficiently performed with horses. In agriculture, less fossil fuel is used and increased environmental conservation occurs over time with the use of ] such as horses.<ref>{{cite book|author=Gifford, Angela |chapter=Working Draught Horses as Singles and Pairs |title=The Working Horse Manual |publisher=Farming Press |location=Tonbridge, UK |isbn=0-85236-401-6|orig-year=1998|year=2000|oclc=40464050|page=85}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Miller, Lynn R. |title=Work Horse Handbook |publisher=Small Farmer's Journal Inc. |location=Sisters, OR |orig-year=1981 |year=2000 |edition=First Edition, Fifteenth Impression |isbn=0-9607268-0-2 |oclc=234277549 |page=13}}</ref> Logging with horses can result in reduced damage to soil structure and less damage to trees due to more selective logging.<ref>{{cite book|author=Gifford, Angela |chapter=Working Horses in Forestry |title=The Working Horse Manual |publisher=Farming Press |location= Tonbridge, UK |isbn=0-85236-401-6|orig-year=1998|year=2000|oclc=40464050|page=145}}</ref> | |||
| == References== | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <references /> | |||
| </div> | |||
| == |
===Warfare=== | ||
| {{Main|Horses in warfare}} | |||
| *''Book of Horses: A Complete Medical Reference Guide for Horses and Foals'', edited by Mordecai Siegal. (By members of the faculty and staff, University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine.) Harper Collins, 1996. | |||
| ] cavalry, 1917|alt=Black-and-white photo of mounted soldiers with middle eastern headwraps, carrying rifles, walking down a road away from the camera]] | |||
| *''Illustrated Atlas of Clinical Equine Anatomy and Common Disorders of the Horse'', by Ronald J. Riegal, D.V.M. and Susan E. Hakola, B.S., R.N., C.M.I. Equistar Publications, Ltd., 1996. | |||
| Horses have been used in warfare for most of recorded history. The first archaeological evidence of horses used in warfare dates to between 4000 and 3000 BCE,<ref name="Science Show">{{cite web |url=http://www.abc.net.au/radionational/programs/scienceshow/the-horse-in-history/3556066 |title=The Horse in History |access-date=2012-01-04 |author1=Newby, Jonica |author2=Diamond, Jared |author3=Anthony, David |website=The Science Show |date=1999-11-13 |publisher=Radio National |archive-date=2013-01-19 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130119105447/http://www.abc.net.au/radionational/programs/scienceshow/the-horse-in-history/3556066 |url-status=live }}</ref> and the use of horses in warfare was widespread by the end of the ].<ref name="Hartwick">{{cite web|url=http://users.hartwick.edu/anthonyd/harnessing%20horsepower.html |title=The Earliest Horseback Riding and its Relation to Chariotry and Warfare|author1=Anthony, David W.|author2=Dorcas R. Brown |website=Harnessing Horsepower |publisher=Institute for Ancient Equestrian Studies|access-date=2007-10-09|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://users.hartwick.edu/anthonyd/harnessing%20horsepower.html |archive-date=2017-10-10|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name=Whitaker30>], pp. 30–31</ref> Although mechanization has largely replaced the horse as a weapon of war, horses are still seen today in limited military uses, mostly for ceremonial purposes, or for reconnaissance and transport activities in areas of rough terrain where motorized vehicles are ineffective. Horses have been used in the 21st century by the ] militias in the ].<ref>{{cite news |url= https://www.nytimes.com/2004/05/04/international/africa/04DARF.html |title= In Sudan, Militiamen on Horses Uproot a Million |access-date= 2011-01-04 |author= Lacey, Marc |work= The New York Times |date= 2004-05-04 |archive-date= 2009-04-23 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090423111741/http://www.nytimes.com/2004/05/04/international/africa/04DARF.html |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| *International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature. 2003. Opinion 2027 (Case 3010). ''Usage of 17 specific names based on wild species which are pre-dated by or contemporary with those based on domestic animals (Lepidoptera, Osteichthyes, Mammalia): conserved''. Bull.Zool.Nomencl., 60:81-84. | |||
| *Bennett, Deb. Conquerors: The Roots of New World Horsemanship. Amigo Publications Inc; 1st edition 1998. ISBN 0965853306 | |||
| ===Entertainment and culture=== | |||
| *Budiansky, Stephen. ''The Nature of Horses.'' Free Press, 1997. ISBN 0684827689 | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| {{See also|Horse symbolism|Horses in art|Horse worship}} | |||
| Modern horses are often used to reenact many of their historical work purposes. Horses are used, complete with equipment that is authentic or a meticulously recreated replica, in various live action ]s of specific periods of history, especially recreations of famous battles.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.blackhorsetroop.org/activities/ |title= Unit Activities |access-date= 2008-04-29 |author= Stoddard, Samuel |website= Co H, 4th Virginia Cavalry |publisher= Washington Webworks, LLC |archive-date= 2008-01-18 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080118205712/http://blackhorsetroop.org/activities/ |url-status= live }}</ref> Horses are also used to preserve cultural traditions and for ceremonial purposes. Countries such as the United Kingdom still use horse-drawn carriages to convey royalty and other VIPs to and from certain culturally significant events.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.royal.gov.uk/TheRoyalHousehold/Transport/Transport.aspx |title= Transport |access-date= 2009-08-30 |publisher= British Monarchy |archive-date= 2009-02-16 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20090216150048/http://www.royal.gov.uk/TheRoyalHousehold/Transport/Transport.aspx |url-status= live }}</ref> Public exhibitions are another example, such as the ], seen in parades and other public settings, a team of ]s that pull a beer wagon similar to that used before the invention of the modern motorized truck.<ref>{{cite news |title=Anheuser-Busch gives face time to Budweiser Clydesdales |work=St. Louis Post-Dispatch |author=McWilliams, Jeremiah |access-date=2010-09-18 |date=December 3, 2008 |url=http://www.stltoday.com/business/columns/lager-heads/article_98704685-a144-52b1-aba7-7b580e8f8c08.html |archive-date=2012-05-14 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120514075122/http://www.stltoday.com/business/columns/lager-heads/article_98704685-a144-52b1-aba7-7b580e8f8c08.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Horses are frequently used in television, films and literature. They are sometimes featured as a major character in films about particular animals, but also used as visual elements that assure the accuracy of historical stories.<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=6630|title=Hollywood Horses|author=Sellnow, Les|date=March 1, 2006|access-date=2009-10-21|url-access=registration|journal=The Horse|archive-date=2011-09-05|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110905044227/http://www.thehorse.com/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=6630|url-status=live}}</ref> Both live horses and ] images of horses are used in ] to promote a variety of products.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hippomaxx-muenster.de/english/sonderausstellung.php?navid=7|title=Trademark Horse – Horses as advertising mediums |publisher=Westfälische Pferdemuseum (Westphalian Horse Museum) |access-date=2008-08-16 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20081011201036/http://www.hippomaxx-muenster.de/english/sonderausstellung.php?navid=7|archive-date=2008-10-11 |url-status=dead}}</ref> The horse frequently appears in coats of arms in ], in a variety of poses and equipment.<ref>{{cite book|author=Fox-Davies, Arthur Charles|title=A Complete Guide to Heraldry|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xSeEWjQCTIAC&pg=PA202|publisher=Skyhorse Publishing Inc|year=2007|isbn=978-1-60239-001-0|page=201|access-date=2020-09-28|archive-date=2023-03-20|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320223813/https://books.google.com/books?id=xSeEWjQCTIAC&pg=PA202|url-status=live}}</ref> The ] of many cultures, including ], ], ], and ], include references to both normal horses and those with wings or additional limbs, and multiple myths also call upon the horse to draw the chariots of the Moon and Sun.<ref>{{cite book|author=Tozer, Basil |title=The Horse in History |url=https://archive.org/details/TheHorseInHistory |publisher=Methuen |year=1908 |location=London |oclc=2484673 |pages=, 98–100}}</ref> The horse also appears in the 12-year cycle of animals in the ] related to the ].<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.c-c-c.org/chineseculture/zodiac/Horse.html|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20110716104433/http://www.c-c-c.org/chineseculture/zodiac/Horse.html|archive-date= 2011-07-16|title= Year of the Horse |access-date=2007-07-22|publisher= Chinese Culture Center of San Francisco}}</ref> | |||
| Horses serve as the inspiration for many modern automobile names and logos, including the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]/], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.autoguide.com/auto-news/2016/02/top-10-horse-themed-cars.html |title=Giddy Up: Top 10 Horse-Themed Cars |work=Autoguide.com |last=Cole |first=Craig |date=8 November 2021 |access-date=7 July 2022 |archive-date=25 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220525011426/https://www.autoguide.com/auto-news/2016/02/top-10-horse-themed-cars.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.globalcarsbrands.com/cars-with-horse-logos/ | title=Cars with Horse Logos: How Many of Them do You Know? | date=9 January 2022 | access-date=18 June 2022 | archive-date=28 May 2022 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220528160402/https://www.globalcarsbrands.com/cars-with-horse-logos/ | url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://journal.classiccars.com/2021/05/08/top-11-cars-named-after-horses-which-is-your-favorite/ | title=Top 11 cars named after horses, which is your favorite? | date=8 May 2021 | access-date=18 June 2022 | archive-date=16 August 2022 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220816110754/https://journal.classiccars.com/2021/05/08/top-11-cars-named-after-horses-which-is-your-favorite/ | url-status=live }}</ref> Indian ] also uses a horse on their motorcycles & scooters. | |||
| ===Therapeutic use=== | |||
| {{See also|Equine-assisted therapy|Therapeutic horseback riding}} | |||
| People of all ages with physical and mental disabilities obtain beneficial results from an association with horses. Therapeutic riding is used to mentally and physically stimulate disabled persons and help them improve their lives through improved balance and coordination, increased self-confidence, and a greater feeling of freedom and independence.<ref>{{cite book |author1=Bush, Karen |author2=Julian Marczak |title=The Principles of Teaching Riding: The Official Manual of the Association of British Riding Schools |publisher=David & Charles |year=2005 |isbn=0-7153-1902-7 |ol=7832270M |oclc=224946044 |page=58 }}</ref> The benefits of equestrian activity for people with disabilities has also been recognized with the addition of equestrian events to the ] and recognition of ] events by the ] (FEI).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fei.org/disciplines/dressage/about-para-equestrian-dressage |title=About Para Equestrian Dressage |access-date=2010-03-07 |publisher=Federation Equestre Internationale |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130508135709/http://www.fei.org/disciplines/dressage/about-para-equestrian-dressage |archive-date=2013-05-08 }}</ref> Hippotherapy and therapeutic horseback riding are names for different physical, occupational, and speech therapy treatment strategies that use equine movement. In hippotherapy, a therapist uses the horse's movement to improve their patient's cognitive, coordination, balance, and fine motor skills, whereas therapeutic horseback riding uses specific riding skills.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.narha.org/PDFFiles/FAQ_Hippotherapy.pdf|title= Frequently Asked Questions About Hippotherapy |access-date=2008-07-08 |website= FAQ – AHA, April 2005|publisher= American Hippotherapy Association |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20070919090815/http://www.narha.org/PDFFiles/FAQ_Hippotherapy.pdf |archive-date = September 19, 2007}}</ref> | |||
| Horses also provide psychological benefits to people whether they actually ride or not. "Equine-assisted" or "equine-facilitated" therapy is a form of experiential ] that uses horses as companion animals to assist people with mental illness, including anxiety disorders, psychotic disorders, mood disorders, behavioral difficulties, and those who are going through major life changes.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.narha.org/SecEFMHA/FactSheet.asp|title=Equine Facilitated Psychotherapy (EFP) Fact Sheet |access-date=2008-07-08 |publisher= Equine Facilitated Mental Health Association |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080430025532/http://www.narha.org/SecEFMHA/FactSheet.asp |archive-date = April 30, 2008}}</ref> There are also experimental programs using horses in ] settings. Exposure to horses appears to improve the behavior of inmates and help reduce ] when they leave.<ref>{{cite news |author= Wise, Mike |date=2003-08-10|title= Partners, Horse and Man, in Prison Pasture |work= New York Times |url= https://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9404E6D91331F933A2575BC0A9659C8B63 |access-date=2008-07-08}}</ref> | |||
| ===Products=== | |||
| Horses are raw material for many products made by humans throughout history, including byproducts from the ] of horses as well as materials collected from living horses. | |||
| Products collected from living horses include mare's milk, used by people with large horse herds, such as the ], who let it ferment to produce ].<ref name=NewYorker>{{cite magazine |url= http://www.newyorker.com/archive/2005/04/25/050425fa_fact4 |title= Invaders: Destroying Baghdad |access-date= 2008-04-03 |author= Frazier, Ian |magazine= The New Yorker |date= 2005-04-18 |archive-date= 2017-10-10 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.newyorker.com/archive/2005/04/25/050425fa_fact4 |url-status= live }}</ref> Horse blood was once used as food by the Mongols and other ]ic tribes, who found it a convenient source of nutrition when traveling. Drinking their own horses' blood allowed the Mongols to ride for extended periods of time without stopping to eat.<ref name=NewYorker/> The drug ] is a mixture of ]s extracted from the urine of pregnant mares ('''pre'''gnant '''mar'''es' ur'''in'''e), and was previously a widely used drug for ].<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.humanesociety.org/news/news/2009/08/a_good_life_for_horses_at_duchess_sanctuary.html|title= A Good Life for Horses at the Duchess Sanctuary|access-date= 2011-06-01|date= August 19, 2001|author= Ballard, Pepper|publisher= The Humane Society of the United States|archive-date= 2013-01-28|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130128074914/http://www.humanesociety.org/news/news/2009/08/a_good_life_for_horses_at_duchess_sanctuary.html|url-status= dead}}</ref> The tail hair of horses can be used for making ] for ]s such as the ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite book |title=Descriptionary: A Thematic Dictionary |author=McCutcheon, Marc |publisher=Checkmark Books (Facts On File imprint) |location=New York |edition=Second |isbn=0-8160-4105-9 |page= |year=2000 |url=https://archive.org/details/descriptionary00mccu_0/page/285}}</ref> | |||
| ] has been used as food for humans and ] throughout the ages. Approximately 5 million horses are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QL|title=FAOSTAT|website=Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations|access-date=2019-10-25|archive-date=2019-05-24|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190524180621/http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QL|url-status=live}}</ref> It is eaten in many parts of the world, though consumption is ] in some cultures,<ref name=USDA>{{cite web|url= http://www.igha.org/USDA.html|title= U.S.D.A. Promotes Horse & Goat Meat |access-date= 2008-04-03 |website= I.G.H.A./HorseAid's U.S.D.A. Report |publisher= U.S. Department of Agriculture |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20171010200000/http://www.igha.org/USDA.html |archive-date= 2017-10-10|url-status= dead}}</ref> and a subject of political controversy in others.<ref>{{cite news |url= http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?file=%2Fc%2Fa%2F2006%2F09%2F08%2FMNGI9L1RMK1.DTL |title= House votes to outlaw slaughter of horses for human consumption |access-date= 2008-04-03 |author= Coile, Zachary |work= SF Gate |publisher= San Francisco Chronicle |date= 2006-09-08 |archive-date= 2012-11-23 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20121123023618/http://www.sfgate.com/politics/article/House-votes-to-outlaw-slaughter-of-horses-for-2469915.php |url-status= live }}</ref> Horsehide leather has been used for boots, gloves, ],<ref name="by-product">{{cite book |last=Ockerman |first=Herbert W. |author2=Hansen, Conly L. |title=Animal By-product Processing & Utilization |year=2000|publisher=CRC Press |location= Lancaster, PA |isbn=1-56676-777-6 |oclc=43685745|page=129}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url= http://www.baseball-fever.com/showthread.php?p=309566|title= Inside a Modern Baseball|access-date= 2008-04-03|website= Baseball Fever|date= August 30, 2002|publisher= Baseball Almanac|archive-date= 2013-08-12|archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130812083051/http://www.baseball-fever.com/showthread.php?3886-Inside-A-Modern-Baseball|url-status= live}}</ref> and baseball gloves. Horse hooves can also be used to produce ].<ref>{{cite book|author=Bartlett, Virginia K.|title=Keeping House: Women's Lives in Western Pennsylvania, 1790–1850 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oZIlEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA35 |ol=1098280M |year=1994|publisher=]|isbn=0-8229-5538-5|oclc=30978921|pages=34–35|access-date=2020-09-28}}</ref> Horse bones can be used to make implements.<ref>{{cite book |author= MacGregor, Arthur |title= Bone, Antler, Ivory and Horn: Technology of Skeletal Materials Since the Roman Period |publisher= Barnes & Noble |location= Totowa, NJ |year= 1985 |isbn=0-389-20531-1 |oclc= 11090630|page= 31}}</ref> Specifically, in Italian cuisine, the horse ] is sharpened into a probe called a ''spinto'', which is used to test the readiness of a (pig) ham as it cures.<ref>{{cite book|author= Fort, Matthew |title= Eating Up Italy: Voyages on a Vespa |publisher= Centro Books |location= London |year= 2005|isbn= 0-00-721481-2|oclc= 60419304|page= |url= https://archive.org/details/eatingupitalyvoy0000fort/page/171}}</ref> In Asia, the ''saba'' is a horsehide vessel used in the production of ].<ref>{{cite book |translator=Hurd, Edward Payson |title=Diseases of the Stomach and Intestines |year=1886|location=New York |publisher=W. Wood & Company|url=https://archive.org/details/diseasesstomach00dujagoog|page=}}</ref> | |||
| ===Care=== | |||
| {{Main|Horse care}} | |||
| {{See also|Equine nutrition|Horse grooming|Veterinary medicine|Farrier}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Horses are ] animals, and their major source of nutrients is good-quality ] from ] or ].<ref>{{cite journal|author=Kellon, Eleanor |title=Focus on Feed Costs |journal=Horse Journal |volume= 16| issue = 6|year=2008|pages=11–12}}</ref> They can consume approximately 2% to 2.5% of their body weight in dry feed each day. Therefore, a {{convert|450|kg|adj=on}} adult horse could eat up to {{convert|11|kg}} of food.<ref name="Penn">{{cite web|author1=Hall, Marvin H.|author2=Patricia M. Comerford|url=http://pubs.cas.psu.edu/FreePubs/pdfs/uc099.pdf|title=Pasture and Hay for Horses – Agronomy Facts 32|year=1992|publisher=University of Pennsylvania |website=Cooperative Extension Service|access-date=2007-02-14|archive-date=2012-12-24|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121224173129/http://pubs.cas.psu.edu/freepubs/pdfs/uc099.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> Sometimes, concentrated feed such as ] is fed in addition to pasture or hay, especially when the animal is very active.<ref>], pp. 476–477</ref> When grain is fed, equine nutritionists recommend that 50% or more of the animal's diet by weight should still be forage.<ref name="Feeding factors">{{cite web|url=http://ohioline.osu.edu/b762/b762_12.html |archive-url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20090708015738/http://ohioline.osu.edu/b762/b762_12.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=2009-07-08 |title=Feeding Factors |publisher=Ohio State University |website=Horse Nutrition |access-date=2007-02-09}}</ref> | |||
| Horses require a plentiful supply of clean water, a minimum of {{convert|10|to|12|USgal|L|order=flip}} per day.<ref>], p. 455</ref> Although horses are adapted to live outside, they require shelter from the wind and ], which can range from a simple shed or shelter to an elaborate ].<ref>], p. 482</ref> | |||
| Horses require routine ] care from a ], as well as ]s to protect against various diseases, and ] examinations from a ] or a specialized equine dentist.<ref>], pp. 62, 168, 310</ref> If horses are kept inside in a barn, they require regular daily exercise for their physical health and mental well-being.<ref>{{cite book|author=Harris, Susan E.|title=The United States Pony Club Manual of Horsemanship: Basics for Beginners – D Level|publisher=Howell Book House|location=New York|year=1994|isbn=0-87605-952-3|pages= 160–161}}</ref> When turned outside, they require well-maintained, sturdy ] to be safely contained.<ref>{{cite book |last=Wheeler |first=Eileen |title=Horse Stable And Riding Arena Design |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=c3dGxSY6E54C&pg=PA215 |year=2006 |publisher=Blackwell Publishing |location=Armes, IA |isbn=978-0-8138-2859-6 |chapter=Fence Planning |oclc=224324847 |page=215 |access-date=2020-09-28 |archive-date=2023-03-20 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320224329/https://books.google.com/books?id=c3dGxSY6E54C&pg=PA215 |url-status=live }}</ref> Regular ] is also helpful to help the horse maintain good health of the hair coat and underlying skin.<ref>], p. 90</ref> | |||
| ===Climate change=== | |||
| {{excerpt|Effects of climate change on livestock#Equines}} | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| *] | |||
| {{Reflist|refs= | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| <ref name=EnsmingerHT>{{cite book |last=Ensminger |first=M. Eugene |title=Horses and Tack |edition=Revised |publisher=Houghton Mifflin Company |location=Boston, MA |year=1991 |isbn=0395544130 |oclc=21561287 |ol=1877441M}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| }} | |||
| *] | |||
| *], a ] ] meaning ''horse'' | |||
| ==Sources== | |||
| *], a ritual in ] mythology | |||
| {{Refbegin|60em}} | |||
| *] | |||
| * {{cite book |ref=Belknap |author=Belknap, Maria |title=Horsewords: The Equine Dictionary |edition=Second |publisher=Trafalgar Square Publishing |location=North Pomfret, VT |year=2004 |isbn=1-57076-274-0}} | |||
| *] | |||
| * {{cite book |ref=Bongianni |author=Bongianni, Maurizio |title=Simon & Schuster's Guide to Horses and Ponies |publisher=Fireside |location=New York |year=1987 |isbn=0-671-66068-3 |url=https://archive.org/details/lish00maur }} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia|ref=Dohner |author=Dohner, Janet Vorwald |editor= Dohner, Janet Vorwald |title=Equines: Natural History |encyclopedia=Historic and Endangered Livestock and Poultry Breeds |year=2001 |publisher=Yale University Press |location=Topeka, KS |pages=400–401 | isbn = 0-300-08880-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book|ref=Edwards |author=Edwards, Elwyn Hartley |title=The Encyclopedia of the Horse |publisher=Dorling Kindersley |location= London |year=1994 |isbn=1-56458-614-6 |oclc=29670649}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref=Ensminger |author= Ensminger, M. E.|title= Horses and Horsemanship: Animal Agricultural Series |edition= Sixth |publisher= Interstate Publishers |location= Danville, IN |year= 1990|isbn=0-8134-2883-1 |oclc= 21977751}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref=Giffin |author1=Giffin, James M. |author2=Tom Gore |title=Horse Owner's Veterinary Handbook |edition=Second |publisher=Howell Book House |location=New York |year=1998 |isbn=0-87605-606-0 |oclc=37245445 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/horseownersveter0002giff }} | |||
| * {{cite book|ref=Harris |author= Harris, Susan E. |title= Horse Gaits, Balance and Movement |publisher= Howell Book House| location= New York |year=1993 |isbn=0-87605-955-8 |oclc= 25873158}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref=McBane |title=The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Horse Breeds |last=McBane |first=Susan |year=1997 |publisher=Wellfleet Press |location=Edison, NJ |isbn=0-7858-0604-0 |oclc=244110821 |url=https://archive.org/details/illustratedencyc00susa }} | |||
| * {{cite book|ref=Miller|author=Miller, Robert M.|title=Understanding the Ancient Secrets of the Horse's Mind|publisher=Russell Meerdink Company Ltd|location=Neenah, WI|year=1999|isbn=0-929346-65-3|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5Qat2gs43owC&pg=PA28|oclc=42389612|access-date=2020-09-28|archive-date=2023-03-20|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320224329/https://books.google.com/books?id=5Qat2gs43owC&pg=PA28|url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite book|ref=Price |editor1= Price, Steven D.|editor2= Spector, David L. |editor3= Rentsch, Gail|editor4= Burn, Barbara B. |title= The Whole Horse Catalog: Revised and Updated |edition=Revised |publisher=Fireside |location=New York |year=1998 |isbn=0-684-83995-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book|ref= Sponenberg|author= Sponenberg, D. Phillip|chapter= The Proliferation of Horse Breeds|title= Horses Through Time|edition= First|publisher= Roberts Rinehart Publishers|location= Boulder, CO|year= 1996|isbn= 1-57098-060-8|oclc= 36179575|chapter-url= https://archive.org/details/horsesthroughtim00olse|url-access= registration|url= https://archive.org/details/horsesthroughtim00olse}} | |||
| * {{cite book|ref=Whitaker | author=Whitaker, Julie |author2=Whitelaw, Ian |title=The Horse: A Miscellany of Equine Knowledge |publisher=St. Martin's Press |location=New York |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-312-37108-1}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| {{Refbegin}} | |||
| * {{cite book |author= Chamberlin, J. Edward |title= Horse: How the Horse Has Shaped Civilizations |publisher= Bluebridge |location= New York |year= 2006|isbn=978-0-9742405-9-6 |oclc= 61704732}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{ |
{{Wikispecies|Equus caballus}} | ||
| <!-- ****************************************************************** | |||
| {{wikispecies|Equus caballus}} | |||
| Please read WP:EL#Links_to_normally_avoid and don't even bother inserting forum links here, we will revert them! | |||
| * | |||
| ******************************************************************* --> | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * Animals Pictures - | |||
| * {{Cite NIE|wstitle=Horse|short=x}} | |||
| * - Encyclopaedic dictionary from Oklahoma State University | |||
| * {{Cite EB1911|wstitle=Horse|short=x}} | |||
| * Essay: The Przewalski Horse | |||
| * , via ] | |||
| * | |||
| * , via ] | |||
| * | |||
| * , via ] | |||
| * | |||
| * , via ] | |||
| * - Information about common horse diseases | |||
| * - Equestrian community dedicated to all aspects of riding and horsemanship | |||
| {{Perissodactyla}} | |||
| * for a brief overview of horse history from 55 million B.C. to present | |||
| {{Horse topics}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Working animals}} | |||
| * published on ] stored with a search function | |||
| {{Subject bar |portal1=Horses |commons=y |commons-search=Horses |q=y |q-search=Horses}} | |||
| * - Research on and education about the horse-human relationship | |||
| {{Taxonbar|from=Q726}} | |||
| * - Wild Horse and Burro Adoption | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| * | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| <!-- The below are interlanguage links. --> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 06:14, 8 December 2024
Domesticated equineFor other uses, see Horse (disambiguation).
| Horse | |
|---|---|

| |
| Conservation status | |
| Domesticated | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Perissodactyla |
| Family: | Equidae |
| Genus: | Equus |
| Species: | E. ferus |
| Subspecies: | E. f. caballus |
| Trinomial name | |
| Equus ferus caballus Linnaeus, 1758 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
at least 48 published | |
The horse (Equus ferus caballus) is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature, Eohippus, into the large, single-toed animal of today. Humans began domesticating horses around 4000 BCE, and their domestication is believed to have been widespread by 3000 BCE. Horses in the subspecies caballus are domesticated, although some domesticated populations live in the wild as feral horses. These feral populations are not true wild horses, which are horses that never have been domesticated. There is an extensive, specialized vocabulary used to describe equine-related concepts, covering everything from anatomy to life stages, size, colors, markings, breeds, locomotion, and behavior.
Horses are adapted to run, allowing them to quickly escape predators, and possess a good sense of balance and a strong fight-or-flight response. Related to this need to flee from predators in the wild is an unusual trait: horses are able to sleep both standing up and lying down, with younger horses tending to sleep significantly more than adults. Female horses, called mares, carry their young for approximately 11 months and a young horse, called a foal, can stand and run shortly following birth. Most domesticated horses begin training under a saddle or in a harness between the ages of two and four. They reach full adult development by age five, and have an average lifespan of between 25 and 30 years.
Horse breeds are loosely divided into three categories based on general temperament: spirited "hot bloods" with speed and endurance; "cold bloods", such as draft horses and some ponies, suitable for slow, heavy work; and "warmbloods", developed from crosses between hot bloods and cold bloods, often focusing on creating breeds for specific riding purposes, particularly in Europe. There are more than 300 breeds of horse in the world today, developed for many different uses.
Horses and humans interact in a wide variety of sport competitions and non-competitive recreational pursuits as well as in working activities such as police work, agriculture, entertainment, and therapy. Horses were historically used in warfare, from which a wide variety of riding and driving techniques developed, using many different styles of equipment and methods of control. Many products are derived from horses, including meat, milk, hide, hair, bone, and pharmaceuticals extracted from the urine of pregnant mares. Humans provide domesticated horses with food, water, and shelter, as well as attention from specialists such as veterinarians and farriers.
Biology
Main article: Equine anatomy
Lifespan and life stages
Depending on breed, management and environment, the modern domestic horse has a life expectancy of 25 to 30 years. Uncommonly, a few animals live into their 40s and, occasionally, beyond. The oldest verifiable record was "Old Billy", a 19th-century horse that lived to the age of 62. In modern times, Sugar Puff, who had been listed in Guinness World Records as the world's oldest living pony, died in 2007 at age 56.
Regardless of a horse or pony's actual birth date, for most competition purposes a year is added to its age each January 1 of each year in the Northern Hemisphere and each August 1 in the Southern Hemisphere. The exception is in endurance riding, where the minimum age to compete is based on the animal's actual calendar age.
The following terminology is used to describe horses of various ages:
- Foal
- A horse of either sex less than one year old. A nursing foal is sometimes called a suckling, and a foal that has been weaned is called a weanling. Most domesticated foals are weaned at five to seven months of age, although foals can be weaned at four months with no adverse physical effects.
- Yearling
- A horse of either sex that is between one and two years old.
- Colt
- A male horse under the age of four. A common terminology error is to call any young horse a "colt", when the term actually only refers to young male horses.
- Filly
- A female horse under the age of four.
- Mare
- A female horse four years old and older.
- Stallion
- A non-castrated male horse four years old and older. The term "horse" is sometimes used colloquially to refer specifically to a stallion.
- Gelding
- A castrated male horse of any age.
In horse racing, these definitions may differ: For example, in the British Isles, Thoroughbred horse racing defines colts and fillies as less than five years old. However, Australian Thoroughbred racing defines colts and fillies as less than four years old.
Size and measurement
The height of horses is measured at the highest point of the withers, where the neck meets the back. This point is used because it is a stable point of the anatomy, unlike the head or neck, which move up and down in relation to the body of the horse.

In English-speaking countries, the height of horses is often stated in units of hands and inches: one hand is equal to 4 inches (101.6 mm). The height is expressed as the number of full hands, followed by a point, then the number of additional inches, and ending with the abbreviation "h" or "hh" (for "hands high"). Thus, a horse described as "15.2 h" is 15 hands plus 2 inches, for a total of 62 inches (157.5 cm) in height.
The size of horses varies by breed, but also is influenced by nutrition. Light-riding horses usually range in height from 14 to 16 hands (56 to 64 inches, 142 to 163 cm) and can weigh from 380 to 550 kilograms (840 to 1,210 lb). Larger-riding horses usually start at about 15.2 hands (62 inches, 157 cm) and often are as tall as 17 hands (68 inches, 173 cm), weighing from 500 to 600 kilograms (1,100 to 1,320 lb). Heavy or draft horses are usually at least 16 hands (64 inches, 163 cm) high and can be as tall as 18 hands (72 inches, 183 cm) high. They can weigh from about 700 to 1,000 kilograms (1,540 to 2,200 lb).
The largest horse in recorded history was probably a Shire horse named Mammoth, who was born in 1848. He stood 21.2⁄4 hands (86.25 inches, 219 cm) high and his peak weight was estimated at 1,524 kilograms (3,360 lb). The record holder for the smallest horse ever is Thumbelina, a fully mature miniature horse affected by dwarfism. She was 43 centimetres; 4.1 hands (17 in) tall and weighed 26 kg (57 lb).
Ponies
Main article: PonyPonies are taxonomically the same animals as horses. The distinction between a horse and pony is commonly drawn on the basis of height, especially for competition purposes. However, height alone is not dispositive; the difference between horses and ponies may also include aspects of phenotype, including conformation and temperament.
The traditional standard for height of a horse or a pony at maturity is 14.2 hands (58 inches, 147 cm). An animal 14.2 hands (58 inches, 147 cm) or over is usually considered to be a horse and one less than 14.2 hands (58 inches, 147 cm) a pony, but there are many exceptions to the traditional standard. In Australia, ponies are considered to be those under 14 hands (56 inches, 142 cm). For competition in the Western division of the United States Equestrian Federation, the cutoff is 14.1 hands (57 inches, 145 cm). The International Federation for Equestrian Sports, the world governing body for horse sport, uses metric measurements and defines a pony as being any horse measuring less than 148 centimetres (58.27 in) at the withers without shoes, which is just over 14.2 hands (58 inches, 147 cm), and 149 centimetres (58.66 in; 14.2+1⁄2 hands), with shoes.
Height is not the sole criterion for distinguishing horses from ponies. Breed registries for horses that typically produce individuals both under and over 14.2 hands (58 inches, 147 cm) consider all animals of that breed to be horses regardless of their height. Conversely, some pony breeds may have features in common with horses, and individual animals may occasionally mature at over 14.2 hands (58 inches, 147 cm), but are still considered to be ponies.
Ponies often exhibit thicker manes, tails, and overall coat. They also have proportionally shorter legs, wider barrels, heavier bone, shorter and thicker necks, and short heads with broad foreheads. They may have calmer temperaments than horses and also a high level of intelligence that may or may not be used to cooperate with human handlers. Small size, by itself, is not an exclusive determinant. For example, the Shetland pony which averages 10 hands (40 inches, 102 cm), is considered a pony.Conversely, breeds such as the Falabella and other miniature horses, which can be no taller than 76 centimetres; 7.2 hands (30 in), are classified by their registries as very small horses, not ponies.
Genetics
Horses have 64 chromosomes. The horse genome was sequenced in 2007. It contains 2.7 billion DNA base pairs, which is larger than the dog genome, but smaller than the human genome or the bovine genome. The map is available to researchers.
Colors and markings

Horses exhibit a diverse array of coat colors and distinctive markings, described by a specialized vocabulary. Often, a horse is classified first by its coat color, before breed or sex. Horses of the same color may be distinguished from one another by white markings, which, along with various spotting patterns, are inherited separately from coat color.
Many genes that create horse coat colors and patterns have been identified. Current genetic tests can identify at least 13 different alleles influencing coat color, and research continues to discover new genes linked to specific traits. The basic coat colors of chestnut and black are determined by the gene controlled by the Melanocortin 1 receptor, also known as the "extension gene" or "red factor". Its recessive form is "red" (chestnut) and its dominant form is black. Additional genes control suppression of black color to point coloration that results in a bay, spotting patterns such as pinto or leopard, dilution genes such as palomino or dun, as well as greying, and all the other factors that create the many possible coat colors found in horses.
Horses that have a white coat color are often mislabeled; a horse that looks "white" is usually a middle-aged or older gray. Grays are born a darker shade, get lighter as they age, but usually keep black skin underneath their white hair coat (with the exception of pink skin under white markings). The only horses properly called white are born with a predominantly white hair coat and pink skin, a fairly rare occurrence. Different and unrelated genetic factors can produce white coat colors in horses, including several different alleles of dominant white and the sabino-1 gene. However, there are no "albino" horses, defined as having both pink skin and red eyes.
Reproduction and development
Main article: Horse breeding
Gestation lasts approximately 340 days, with an average range 320–370 days, and usually results in one foal; twins are rare. Horses are a precocial species, and foals are capable of standing and running within a short time following birth. Foals are usually born in the spring. The estrous cycle of a mare occurs roughly every 19–22 days and occurs from early spring into autumn. Most mares enter an anestrus period during the winter and thus do not cycle in this period. Foals are generally weaned from their mothers between four and six months of age.
Horses, particularly colts, are sometimes physically capable of reproduction at about 18 months, but domesticated horses are rarely allowed to breed before the age of three, especially females. Horses four years old are considered mature, although the skeleton normally continues to develop until the age of six; maturation also depends on the horse's size, breed, sex, and quality of care. Larger horses have larger bones; therefore, not only do the bones take longer to form bone tissue, but the epiphyseal plates are larger and take longer to convert from cartilage to bone. These plates convert after the other parts of the bones, and are crucial to development.
Depending on maturity, breed, and work expected, horses are usually put under saddle and trained to be ridden between the ages of two and four. Although Thoroughbred race horses are put on the track as young as the age of two in some countries, horses specifically bred for sports such as dressage are generally not put under saddle until they are three or four years old, because their bones and muscles are not solidly developed. For endurance riding competition, horses are not deemed mature enough to compete until they are a full 60 calendar months (five years) old.
Anatomy
Main articles: Equine anatomy, Muscular system of the horse, Respiratory system of the horse, and Circulatory system of the horseSkeletal system
Main article: Skeletal system of the horse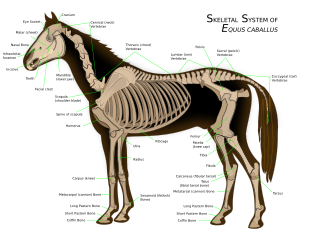
The horse skeleton averages 205 bones. A significant difference between the horse skeleton and that of a human is the lack of a collarbone—the horse's forelimbs are attached to the spinal column by a powerful set of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that attach the shoulder blade to the torso. The horse's four legs and hooves are also unique structures. Their leg bones are proportioned differently from those of a human. For example, the body part that is called a horse's "knee" is actually made up of the carpal bones that correspond to the human wrist. Similarly, the hock contains bones equivalent to those in the human ankle and heel. The lower leg bones of a horse correspond to the bones of the human hand or foot, and the fetlock (incorrectly called the "ankle") is actually the proximal sesamoid bones between the cannon bones (a single equivalent to the human metacarpal or metatarsal bones) and the proximal phalanges, located where one finds the "knuckles" of a human. A horse also has no muscles in its legs below the knees and hocks, only skin, hair, bone, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and the assorted specialized tissues that make up the hoof.
Hooves
Main articles: Horse hoof, Horseshoe, and FarrierThe critical importance of the feet and legs is summed up by the traditional adage, "no foot, no horse". The horse hoof begins with the distal phalanges, the equivalent of the human fingertip or tip of the toe, surrounded by cartilage and other specialized, blood-rich soft tissues such as the laminae. The exterior hoof wall and horn of the sole is made of keratin, the same material as a human fingernail. The result is that a horse, weighing on average 500 kilograms (1,100 lb), travels on the same bones as would a human on tiptoe. For the protection of the hoof under certain conditions, some horses have horseshoes placed on their feet by a professional farrier. The hoof continually grows, and in most domesticated horses needs to be trimmed (and horseshoes reset, if used) every five to eight weeks, though the hooves of horses in the wild wear down and regrow at a rate suitable for their terrain.
Teeth
Main article: Horse teethHorses are adapted to grazing. In an adult horse, there are 12 incisors at the front of the mouth, adapted to biting off the grass or other vegetation. There are 24 teeth adapted for chewing, the premolars and molars, at the back of the mouth. Stallions and geldings have four additional teeth just behind the incisors, a type of canine teeth called "tushes". Some horses, both male and female, will also develop one to four very small vestigial teeth in front of the molars, known as "wolf" teeth, which are generally removed because they can interfere with the bit. There is an empty interdental space between the incisors and the molars where the bit rests directly on the gums, or "bars" of the horse's mouth when the horse is bridled.
An estimate of a horse's age can be made from looking at its teeth. The teeth continue to erupt throughout life and are worn down by grazing. Therefore, the incisors show changes as the horse ages; they develop a distinct wear pattern, changes in tooth shape, and changes in the angle at which the chewing surfaces meet. This allows a very rough estimate of a horse's age, although diet and veterinary care can also affect the rate of tooth wear.
Digestion
Main articles: Equine digestive system and Equine nutritionHorses are herbivores with a digestive system adapted to a forage diet of grasses and other plant material, consumed steadily throughout the day. Therefore, compared to humans, they have a relatively small stomach but very long intestines to facilitate a steady flow of nutrients. A 450-kilogram (990 lb) horse will eat 7 to 11 kilograms (15 to 24 lb) of food per day and, under normal use, drink 38 to 45 litres (8.4 to 9.9 imp gal; 10 to 12 US gal) of water. Horses are not ruminants, having only one stomach, like humans. But unlike humans, they can digest cellulose, a major component of grass, through the process of hindgut fermentation. Cellulose fermentation by symbiotic bacteria and other microbes occurs in the cecum and the large intestine. Horses cannot vomit, so digestion problems can quickly cause colic, a leading cause of death. Although horses do not have a gallbladder, they tolerate high amounts of fat in their diet.
Senses

The horses' senses are based on their status as prey animals, where they must be aware of their surroundings at all times. The equine eye is one of the largest of any land mammal. Horses are lateral-eyed, meaning that their eyes are positioned on the sides of their heads. This means that horses have a range of vision of more than 350°, with approximately 65° of this being binocular vision and the remaining 285° monocular vision. Horses have excellent day and night vision, but they have two-color, or dichromatic vision; their color vision is somewhat like red-green color blindness in humans, where certain colors, especially red and related colors, appear as a shade of green.
Their sense of smell, while much better than that of humans, is not quite as good as that of a dog. It is believed to play a key role in the social interactions of horses as well as detecting other key scents in the environment. Horses have two olfactory centers. The first system is in the nostrils and nasal cavity, which analyze a wide range of odors. The second, located under the nasal cavity, are the vomeronasal organs, also called Jacobson's organs. These have a separate nerve pathway to the brain and appear to primarily analyze pheromones.
A horse's hearing is good, and the pinna of each ear can rotate up to 180°, giving the potential for 360° hearing without having to move the head. Noise affects the behavior of horses and certain kinds of noise may contribute to stress—a 2013 study in the UK indicated that stabled horses were calmest in a quiet setting, or if listening to country or classical music, but displayed signs of nervousness when listening to jazz or rock music. This study also recommended keeping music under a volume of 21 decibels. An Australian study found that stabled racehorses listening to talk radio had a higher rate of gastric ulcers than horses listening to music, and racehorses stabled where a radio was played had a higher overall rate of ulceration than horses stabled where there was no radio playing.
Horses have a great sense of balance, due partly to their ability to feel their footing and partly to highly developed proprioception—the unconscious sense of where the body and limbs are at all times. A horse's sense of touch is well-developed. The most sensitive areas are around the eyes, ears, and nose. Horses are able to sense contact as subtle as an insect landing anywhere on the body.
Horses have an advanced sense of taste, which allows them to sort through fodder and choose what they would most like to eat, and their prehensile lips can easily sort even small grains. Horses generally will not eat poisonous plants, however, there are exceptions; horses will occasionally eat toxic amounts of poisonous plants even when there is adequate healthy food.
Movement
Main articles: Horse gait, Trot, Canter, and Ambling-
 Walk 5–8 km/h (3.1–5.0 mph)
Walk 5–8 km/h (3.1–5.0 mph)
-
 Trot 8–13 km/h (5.0–8.1 mph)
Trot 8–13 km/h (5.0–8.1 mph)
-
 Pace 8–13 km/h (5.0–8.1 mph)
Pace 8–13 km/h (5.0–8.1 mph)
-
 Canter 16–27 km/h (9.9–16.8 mph)
Canter 16–27 km/h (9.9–16.8 mph)
-
 Gallop 40–48 km/h (25–30 mph), record: 70.76 km/h (43.97 mph)
Gallop 40–48 km/h (25–30 mph), record: 70.76 km/h (43.97 mph)
All horses move naturally with four basic gaits:
- the four-beat walk, which averages 6.4 kilometres per hour (4.0 mph);
- the two-beat trot or jog at 13 to 19 kilometres per hour (8.1 to 11.8 mph) (faster for harness racing horses);
- the canter or lope, a three-beat gait that is 19 to 24 kilometres per hour (12 to 15 mph);
- the gallop, which averages 40 to 48 kilometres per hour (25 to 30 mph), but the world record for a horse galloping over a short, sprint distance is 70.76 kilometres per hour (43.97 mph).
Besides these basic gaits, some horses perform a two-beat pace, instead of the trot. There also are several four-beat 'ambling' gaits that are approximately the speed of a trot or pace, though smoother to ride. These include the lateral rack, running walk, and tölt as well as the diagonal fox trot. Ambling gaits are often genetic in some breeds, known collectively as gaited horses. These horses replace the trot with one of the ambling gaits.
Behavior
Main articles: Horse behavior and Stable vicesHorses are prey animals with a strong fight-or-flight response. Their first reaction to a threat is to startle and usually flee, although they will stand their ground and defend themselves when flight is impossible or if their young are threatened. They also tend to be curious; when startled, they will often hesitate an instant to ascertain the cause of their fright, and may not always flee from something that they perceive as non-threatening. Most light horse riding breeds were developed for speed, agility, alertness and endurance; natural qualities that extend from their wild ancestors. However, through selective breeding, some breeds of horses are quite docile, particularly certain draft horses.

Horses are herd animals, with a clear hierarchy of rank, led by a dominant individual, usually a mare. They are also social creatures that are able to form companionship attachments to their own species and to other animals, including humans. They communicate in various ways, including vocalizations such as nickering or whinnying, mutual grooming, and body language. Many horses will become difficult to manage if they are isolated, but with training, horses can learn to accept a human as a companion, and thus be comfortable away from other horses. However, when confined with insufficient companionship, exercise, or stimulation, individuals may develop stable vices, an assortment of bad habits, mostly stereotypies of psychological origin, that include wood chewing, wall kicking, "weaving" (rocking back and forth), and other problems.
Intelligence and learning
Studies have indicated that horses perform a number of cognitive tasks on a daily basis, meeting mental challenges that include food procurement and identification of individuals within a social system. They also have good spatial discrimination abilities. They are naturally curious and apt to investigate things they have not seen before. Studies have assessed equine intelligence in areas such as problem solving, speed of learning, and memory. Horses excel at simple learning, but also are able to use more advanced cognitive abilities that involve categorization and concept learning. They can learn using habituation, desensitization, classical conditioning, and operant conditioning, and positive and negative reinforcement. One study has indicated that horses can differentiate between "more or less" if the quantity involved is less than four.
Domesticated horses may face greater mental challenges than wild horses, because they live in artificial environments that prevent instinctive behavior whilst also learning tasks that are not natural. Horses are animals of habit that respond well to regimentation, and respond best when the same routines and techniques are used consistently. One trainer believes that "intelligent" horses are reflections of intelligent trainers who effectively use response conditioning techniques and positive reinforcement to train in the style that best fits with an individual animal's natural inclinations.
Temperament
Main articles: Draft horse, Warmblood, Oriental horse, and Hot-blooded horseHorses are mammals. As such, they are warm-blooded, or endothermic creatures, as opposed to cold-blooded, or poikilothermic animals. However, these words have developed a separate meaning in the context of equine terminology, used to describe temperament, not body temperature. For example, the "hot-bloods", such as many race horses, exhibit more sensitivity and energy, while the "cold-bloods", such as most draft breeds, are quieter and calmer. Sometimes "hot-bloods" are classified as "light horses" or "riding horses", with the "cold-bloods" classified as "draft horses" or "work horses".

"Hot blooded" breeds include "oriental horses" such as the Akhal-Teke, Arabian horse, Barb, and now-extinct Turkoman horse, as well as the Thoroughbred, a breed developed in England from the older oriental breeds. Hot bloods tend to be spirited, bold, and learn quickly. They are bred for agility and speed. They tend to be physically refined—thin-skinned, slim, and long-legged. The original oriental breeds were brought to Europe from the Middle East and North Africa when European breeders wished to infuse these traits into racing and light cavalry horses.
Muscular, heavy draft horses are known as "cold bloods." They are bred not only for strength, but also to have the calm, patient temperament needed to pull a plow or a heavy carriage full of people. They are sometimes nicknamed "gentle giants". Well-known draft breeds include the Belgian and the Clydesdale. Some, like the Percheron, are lighter and livelier, developed to pull carriages or to plow large fields in drier climates. Others, such as the Shire, are slower and more powerful, bred to plow fields with heavy, clay-based soils. The cold-blooded group also includes some pony breeds.
"Warmblood" breeds, such as the Trakehner or Hanoverian, developed when European carriage and war horses were crossed with Arabians or Thoroughbreds, producing a riding horse with more refinement than a draft horse, but greater size and milder temperament than a lighter breed. Certain pony breeds with warmblood characteristics have been developed for smaller riders. Warmbloods are considered a "light horse" or "riding horse".
Today, the term "Warmblood" refers to a specific subset of sport horse breeds that are used for competition in dressage and show jumping. Strictly speaking, the term "warm blood" refers to any cross between cold-blooded and hot-blooded breeds. Examples include breeds such as the Irish Draught or the Cleveland Bay. The term was once used to refer to breeds of light riding horse other than Thoroughbreds or Arabians, such as the Morgan horse.
Sleep patterns
See also: Horse sleep patterns and Sleep in non-humans
Horses are able to sleep both standing up and lying down. In an adaptation from life in the wild, horses are able to enter light sleep by using a "stay apparatus" in their legs, allowing them to doze without collapsing. Horses sleep better when in groups because some animals will sleep while others stand guard to watch for predators. A horse kept alone will not sleep well because its instincts are to keep a constant eye out for danger.
Unlike humans, horses do not sleep in a solid, unbroken period of time, but take many short periods of rest. Horses spend four to fifteen hours a day in standing rest, and from a few minutes to several hours lying down. Total sleep time in a 24-hour period may range from several minutes to a couple of hours, mostly in short intervals of about 15 minutes each. The average sleep time of a domestic horse is said to be 2.9 hours per day.
Horses must lie down to reach REM sleep. They only have to lie down for an hour or two every few days to meet their minimum REM sleep requirements. However, if a horse is never allowed to lie down, after several days it will become sleep-deprived, and in rare cases may suddenly collapse because it slips, involuntarily, into REM sleep while still standing. This condition differs from narcolepsy, although horses may also suffer from that disorder.
Taxonomy and evolution

The horse adapted to survive in areas of wide-open terrain with sparse vegetation, surviving in an ecosystem where other large grazing animals, especially ruminants, could not. Horses and other equids are odd-toed ungulates of the order Perissodactyla, a group of mammals dominant during the Tertiary period. In the past, this order contained 14 families, but only three—Equidae (the horse and related species), Tapiridae (the tapir), and Rhinocerotidae (the rhinoceroses)—have survived to the present day.
The earliest known member of the family Equidae was the Hyracotherium, which lived between 45 and 55 million years ago, during the Eocene period. It had 4 toes on each front foot, and 3 toes on each back foot. The extra toe on the front feet soon disappeared with the Mesohippus, which lived 32 to 37 million years ago. Over time, the extra side toes shrank in size until they vanished. All that remains of them in modern horses is a set of small vestigial bones on the leg below the knee, known informally as splint bones. Their legs also lengthened as their toes disappeared until they were a hooved animal capable of running at great speed. By about 5 million years ago, the modern Equus had evolved. Equid teeth also evolved from browsing on soft, tropical plants to adapt to browsing of drier plant material, then to grazing of tougher plains grasses. Thus proto-horses changed from leaf-eating forest-dwellers to grass-eating inhabitants of semi-arid regions worldwide, including the steppes of Eurasia and the Great Plains of North America.
By about 15,000 years ago, Equus ferus was a widespread holarctic species. Horse bones from this time period, the late Pleistocene, are found in Europe, Eurasia, Beringia, and North America. Yet between 10,000 and 7,600 years ago, the horse became extinct in North America. The reasons for this extinction are not fully known, but one theory notes that extinction in North America paralleled human arrival. Another theory points to climate change, noting that approximately 12,500 years ago, the grasses characteristic of a steppe ecosystem gave way to shrub tundra, which was covered with unpalatable plants.
Wild species surviving into modern times

A truly wild horse is a species or subspecies with no ancestors that were ever successfully domesticated. Therefore, most "wild" horses today are actually feral horses, animals that escaped or were turned loose from domestic herds and the descendants of those animals. Only two wild subspecies, the tarpan and the Przewalski's horse, survived into recorded history and only the latter survives today.
The Przewalski's horse (Equus ferus przewalskii), named after the Russian explorer Nikolai Przhevalsky, is a rare Asian animal. It is also known as the Mongolian wild horse; Mongolian people know it as the taki, and the Kyrgyz people call it a kirtag. The subspecies was presumed extinct in the wild between 1969 and 1992, while a small breeding population survived in zoos around the world. In 1992, it was reestablished in the wild by the conservation efforts of numerous zoos. Today, a small wild breeding population exists in Mongolia. There are additional animals still maintained at zoos throughout the world.
Their status as a truly wild horse was called into question when domestic horses of the 5,000-year-old Botai culture of Central Asia were found to be more closely related to Przewalski's horses than to E. f. caballus. The study raised the possibility that modern Przewalski's horses could be the feral descendants of the domestic Botai horses. The study concluded that the Botai animals appear to have been an independent domestication attempt and apparently unsuccessful in terms of genetic markers carrying through to modern domesticated equines. However, the question of whether all Przewalski's horses descend from this population is also unresolved, as only one of seven modern Przewalski’s horses in the study shared this ancestry. It may also be that both the Botai horses and the modern Przewalski's horses descend separately from the same ancient wild Przewalski's horse population.
The tarpan or European wild horse (Equus ferus ferus) was found in Europe and much of Asia. It survived into the historical era, but became extinct in 1909, when the last captive died in a Russian zoo. Thus, the genetic line was lost. Attempts have been made to recreate the tarpan, which resulted in horses with outward physical similarities, but nonetheless descended from domesticated ancestors and not true wild horses.
Periodically, populations of horses in isolated areas are speculated to be relict populations of wild horses, but generally have been proven to be feral or domestic. For example, the Riwoche horse of Tibet was proposed as such, but testing did not reveal genetic differences from domesticated horses. Similarly, the Sorraia of Portugal was proposed as a direct descendant of the Tarpan on the basis of shared characteristics, but genetic studies have shown that the Sorraia is more closely related to other horse breeds, and that the outward similarity is an unreliable measure of relatedness.
Other modern equids
Main article: Equus (genus)Besides the horse, there are six other species of genus Equus in the Equidae family. These are the ass or donkey, Equus asinus; the mountain zebra, Equus zebra; plains zebra, Equus quagga; Grévy's zebra, Equus grevyi; the kiang, Equus kiang; and the onager, Equus hemionus.
Horses can crossbreed with other members of their genus. The most common hybrid is the mule, a cross between a "jack" (male donkey) and a mare. A related hybrid, a hinny, is a cross between a stallion and a "jenny" (female donkey). Other hybrids include the zorse, a cross between a zebra and a horse. With rare exceptions, most hybrids are sterile and cannot reproduce.
Domestication and history
Main articles: History of horse domestication theories and Domestication of the horse
Domestication of the horse most likely took place in central Asia prior to 3500 BCE. Two major sources of information are used to determine where and when the horse was first domesticated and how the domesticated horse spread around the world. The first source is based on palaeological and archaeological discoveries; the second source is a comparison of DNA obtained from modern horses to that from bones and teeth of ancient horse remains.
The earliest archaeological evidence for attempted domestication of the horse comes from sites in Ukraine and Kazakhstan, dating to approximately 4000–3500 BCE. However the horses domesticated at the Botai culture in Kazakhstan were Przewalski's horses and not the ancestors of modern horses.
By 3000 BCE, the horse was completely domesticated and by 2000 BCE there was a sharp increase in the number of horse bones found in human settlements in northwestern Europe, indicating the spread of domesticated horses throughout the continent. The most recent, but most irrefutable evidence of domestication comes from sites where horse remains were interred with chariots in graves of the Indo-European Sintashta and Petrovka cultures c. 2100 BCE.
A 2021 genetic study suggested that most modern domestic horses descend from the lower Volga-Don region. Ancient horse genomes indicate that these populations influenced almost all local populations as they expanded rapidly throughout Eurasia, beginning about 4,200 years ago. It also shows that certain adaptations were strongly selected due to riding, and that equestrian material culture, including Sintashta spoke-wheeled chariots spread with the horse itself.
Domestication is also studied by using the genetic material of present-day horses and comparing it with the genetic material present in the bones and teeth of horse remains found in archaeological and palaeological excavations. The variation in the genetic material shows that very few wild stallions contributed to the domestic horse, while many mares were part of early domesticated herds. This is reflected in the difference in genetic variation between the DNA that is passed on along the paternal, or sire line (Y-chromosome) versus that passed on along the maternal, or dam line (mitochondrial DNA). There are very low levels of Y-chromosome variability, but a great deal of genetic variation in mitochondrial DNA. There is also regional variation in mitochondrial DNA due to the inclusion of wild mares in domestic herds. Another characteristic of domestication is an increase in coat color variation. In horses, this increased dramatically between 5000 and 3000 BCE.
Before the availability of DNA techniques to resolve the questions related to the domestication of the horse, various hypotheses were proposed. One classification was based on body types and conformation, suggesting the presence of four basic prototypes that had adapted to their environment prior to domestication. Another hypothesis held that the four prototypes originated from a single wild species and that all different body types were entirely a result of selective breeding after domestication. However, the lack of a detectable substructure in the horse has resulted in a rejection of both hypotheses.
Feral populations
Main article: Feral horseFeral horses are born and live in the wild, but are descended from domesticated animals. Many populations of feral horses exist throughout the world. Studies of feral herds have provided useful insights into the behavior of prehistoric horses, as well as greater understanding of the instincts and behaviors that drive horses that live in domesticated conditions.
There are also semi-feral horses in many parts of the world, such as Dartmoor and the New Forest in the UK, where the animals are all privately owned but live for significant amounts of time in "wild" conditions on undeveloped, often public, lands. Owners of such animals often pay a fee for grazing rights.
Breeds
Main articles: Horse breed, List of horse breeds, and Horse breedingThe concept of purebred bloodstock and a controlled, written breed registry has come to be particularly significant and important in modern times. Sometimes purebred horses are incorrectly or inaccurately called "thoroughbreds". Thoroughbred is a specific breed of horse, while a "purebred" is a horse (or any other animal) with a defined pedigree recognized by a breed registry. Horse breeds are groups of horses with distinctive characteristics that are transmitted consistently to their offspring, such as conformation, color, performance ability, or disposition. These inherited traits result from a combination of natural crosses and artificial selection methods. Horses have been selectively bred since their domestication. An early example of people who practiced selective horse breeding were the Bedouin, who had a reputation for careful practices, keeping extensive pedigrees of their Arabian horses and placing great value upon pure bloodlines. These pedigrees were originally transmitted via an oral tradition.
Breeds developed due to a need for "form to function", the necessity to develop certain characteristics in order to perform a particular type of work. Thus, a powerful but refined breed such as the Andalusian developed as riding horses with an aptitude for dressage. Heavy draft horses were developed out of a need to perform demanding farm work and pull heavy wagons. Other horse breeds had been developed specifically for light agricultural work, carriage and road work, various sport disciplines, or simply as pets. Some breeds developed through centuries of crossing other breeds, while others descended from a single foundation sire, or other limited or restricted foundation bloodstock. One of the earliest formal registries was General Stud Book for Thoroughbreds, which began in 1791 and traced back to the foundation bloodstock for the breed. There are more than 300 horse breeds in the world today.
Interaction with humans

Worldwide, horses play a role within human cultures and have done so for millennia. Horses are used for leisure activities, sports, and working purposes. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that in 2008, there were almost 59,000,000 horses in the world, with around 33,500,000 in the Americas, 13,800,000 in Asia and 6,300,000 in Europe and smaller portions in Africa and Oceania. There are estimated to be 9,500,000 horses in the United States alone. The American Horse Council estimates that horse-related activities have a direct impact on the economy of the United States of over $39 billion, and when indirect spending is considered, the impact is over $102 billion. In a 2004 "poll" conducted by Animal Planet, more than 50,000 viewers from 73 countries voted for the horse as the world's 4th favorite animal.
Communication between human and horse is paramount in any equestrian activity; to aid this process horses are usually ridden with a saddle on their backs to assist the rider with balance and positioning, and a bridle or related headgear to assist the rider in maintaining control. Sometimes horses are ridden without a saddle, and occasionally, horses are trained to perform without a bridle or other headgear. Many horses are also driven, which requires a harness, bridle, and some type of vehicle.
Sport

Historically, equestrians honed their skills through games and races. Equestrian sports provided entertainment for crowds and honed the excellent horsemanship that was needed in battle. Many sports, such as dressage, eventing, and show jumping, have origins in military training, which were focused on control and balance of both horse and rider. Other sports, such as rodeo, developed from practical skills such as those needed on working ranches and stations. Sport hunting from horseback evolved from earlier practical hunting techniques. Horse racing of all types evolved from impromptu competitions between riders or drivers. All forms of competition, requiring demanding and specialized skills from both horse and rider, resulted in the systematic development of specialized breeds and equipment for each sport. The popularity of equestrian sports through the centuries has resulted in the preservation of skills that would otherwise have disappeared after horses stopped being used in combat.
Horses are trained to be ridden or driven in a variety of sporting competitions. Examples include show jumping, dressage, three-day eventing, competitive driving, endurance riding, gymkhana, rodeos, and fox hunting. Horse shows, which have their origins in medieval European fairs, are held around the world. They host a huge range of classes, covering all of the mounted and harness disciplines, as well as "In-hand" classes where the horses are led, rather than ridden, to be evaluated on their conformation. The method of judging varies with the discipline, but winning usually depends on style and ability of both horse and rider. Sports such as polo do not judge the horse itself, but rather use the horse as a partner for human competitors as a necessary part of the game. Although the horse requires specialized training to participate, the details of its performance are not judged, only the result of the rider's actions—be it getting a ball through a goal or some other task. Examples of these sports of partnership between human and horse include jousting, in which the main goal is for one rider to unseat the other, and buzkashi, a team game played throughout Central Asia, the aim being to capture a goat carcass while on horseback.
Horse racing is an equestrian sport and major international industry, watched in almost every nation of the world. There are three types: "flat" racing; steeplechasing, i.e. racing over jumps; and harness racing, where horses trot or pace while pulling a driver in a small, light cart known as a sulky. A major part of horse racing's economic importance lies in the gambling associated with it.
Work
 Horse pulling a cart
Horse pulling a cart A mounted police officer in Poland
A mounted police officer in Poland
There are certain jobs that horses do very well, and no technology has yet developed to fully replace them. For example, mounted police horses are still effective for certain types of patrol duties and crowd control. Cattle ranches still require riders on horseback to round up cattle that are scattered across remote, rugged terrain. Search and rescue organizations in some countries depend upon mounted teams to locate people, particularly hikers and children, and to provide disaster relief assistance. Horses can also be used in areas where it is necessary to avoid vehicular disruption to delicate soil, such as nature reserves. They may also be the only form of transport allowed in wilderness areas. Horses are quieter than motorized vehicles. Law enforcement officers such as park rangers or game wardens may use horses for patrols, and horses or mules may also be used for clearing trails or other work in areas of rough terrain where vehicles are less effective.
Although machinery has replaced horses in many parts of the world, an estimated 100 million horses, donkeys and mules are still used for agriculture and transportation in less developed areas. This number includes around 27 million working animals in Africa alone. Some land management practices such as cultivating and logging can be efficiently performed with horses. In agriculture, less fossil fuel is used and increased environmental conservation occurs over time with the use of draft animals such as horses. Logging with horses can result in reduced damage to soil structure and less damage to trees due to more selective logging.
Warfare
Main article: Horses in warfare
Horses have been used in warfare for most of recorded history. The first archaeological evidence of horses used in warfare dates to between 4000 and 3000 BCE, and the use of horses in warfare was widespread by the end of the Bronze Age. Although mechanization has largely replaced the horse as a weapon of war, horses are still seen today in limited military uses, mostly for ceremonial purposes, or for reconnaissance and transport activities in areas of rough terrain where motorized vehicles are ineffective. Horses have been used in the 21st century by the Janjaweed militias in the War in Darfur.
Entertainment and culture

Modern horses are often used to reenact many of their historical work purposes. Horses are used, complete with equipment that is authentic or a meticulously recreated replica, in various live action historical reenactments of specific periods of history, especially recreations of famous battles. Horses are also used to preserve cultural traditions and for ceremonial purposes. Countries such as the United Kingdom still use horse-drawn carriages to convey royalty and other VIPs to and from certain culturally significant events. Public exhibitions are another example, such as the Budweiser Clydesdales, seen in parades and other public settings, a team of draft horses that pull a beer wagon similar to that used before the invention of the modern motorized truck.
Horses are frequently used in television, films and literature. They are sometimes featured as a major character in films about particular animals, but also used as visual elements that assure the accuracy of historical stories. Both live horses and iconic images of horses are used in advertising to promote a variety of products. The horse frequently appears in coats of arms in heraldry, in a variety of poses and equipment. The mythologies of many cultures, including Greco-Roman, Hindu, Islamic, and Germanic, include references to both normal horses and those with wings or additional limbs, and multiple myths also call upon the horse to draw the chariots of the Moon and Sun. The horse also appears in the 12-year cycle of animals in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar.
Horses serve as the inspiration for many modern automobile names and logos, including the Ford Pinto, Ford Bronco, Ford Mustang, Hyundai Equus, Hyundai Pony, Mitsubishi Starion, Subaru Brumby, Mitsubishi Colt/Dodge Colt, Pinzgauer, Steyr-Puch Haflinger, Pegaso, Porsche, Rolls-Royce Camargue, Ferrari, Carlsson, Kamaz, Corre La Licorne, Iran Khodro, Eicher, and Baojun. Indian TVS Motor Company also uses a horse on their motorcycles & scooters.
Therapeutic use
See also: Equine-assisted therapy and Therapeutic horseback ridingPeople of all ages with physical and mental disabilities obtain beneficial results from an association with horses. Therapeutic riding is used to mentally and physically stimulate disabled persons and help them improve their lives through improved balance and coordination, increased self-confidence, and a greater feeling of freedom and independence. The benefits of equestrian activity for people with disabilities has also been recognized with the addition of equestrian events to the Paralympic Games and recognition of para-equestrian events by the International Federation for Equestrian Sports (FEI). Hippotherapy and therapeutic horseback riding are names for different physical, occupational, and speech therapy treatment strategies that use equine movement. In hippotherapy, a therapist uses the horse's movement to improve their patient's cognitive, coordination, balance, and fine motor skills, whereas therapeutic horseback riding uses specific riding skills.
Horses also provide psychological benefits to people whether they actually ride or not. "Equine-assisted" or "equine-facilitated" therapy is a form of experiential psychotherapy that uses horses as companion animals to assist people with mental illness, including anxiety disorders, psychotic disorders, mood disorders, behavioral difficulties, and those who are going through major life changes. There are also experimental programs using horses in prison settings. Exposure to horses appears to improve the behavior of inmates and help reduce recidivism when they leave.
Products
Horses are raw material for many products made by humans throughout history, including byproducts from the slaughter of horses as well as materials collected from living horses.
Products collected from living horses include mare's milk, used by people with large horse herds, such as the Mongols, who let it ferment to produce kumis. Horse blood was once used as food by the Mongols and other nomadic tribes, who found it a convenient source of nutrition when traveling. Drinking their own horses' blood allowed the Mongols to ride for extended periods of time without stopping to eat. The drug Premarin is a mixture of estrogens extracted from the urine of pregnant mares (pregnant mares' urine), and was previously a widely used drug for hormone replacement therapy. The tail hair of horses can be used for making bows for string instruments such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass.
Horse meat has been used as food for humans and carnivorous animals throughout the ages. Approximately 5 million horses are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. It is eaten in many parts of the world, though consumption is taboo in some cultures, and a subject of political controversy in others. Horsehide leather has been used for boots, gloves, jackets, baseballs, and baseball gloves. Horse hooves can also be used to produce animal glue. Horse bones can be used to make implements. Specifically, in Italian cuisine, the horse tibia is sharpened into a probe called a spinto, which is used to test the readiness of a (pig) ham as it cures. In Asia, the saba is a horsehide vessel used in the production of kumis.
Care
Main article: Horse care See also: Equine nutrition, Horse grooming, Veterinary medicine, and Farrier
Horses are grazing animals, and their major source of nutrients is good-quality forage from hay or pasture. They can consume approximately 2% to 2.5% of their body weight in dry feed each day. Therefore, a 450-kilogram (990 lb) adult horse could eat up to 11 kilograms (24 lb) of food. Sometimes, concentrated feed such as grain is fed in addition to pasture or hay, especially when the animal is very active. When grain is fed, equine nutritionists recommend that 50% or more of the animal's diet by weight should still be forage.
Horses require a plentiful supply of clean water, a minimum of 38 to 45 litres (10 to 12 US gal) per day. Although horses are adapted to live outside, they require shelter from the wind and precipitation, which can range from a simple shed or shelter to an elaborate stable.
Horses require routine hoof care from a farrier, as well as vaccinations to protect against various diseases, and dental examinations from a veterinarian or a specialized equine dentist. If horses are kept inside in a barn, they require regular daily exercise for their physical health and mental well-being. When turned outside, they require well-maintained, sturdy fences to be safely contained. Regular grooming is also helpful to help the horse maintain good health of the hair coat and underlying skin.
Climate change
This section is an excerpt from Effects of climate change on livestock § Equines.
As of 2019, there are around 17 million horses in the world. Healthy body temperature for adult horses is in the range between 37.5 and 38.5 °C (99.5 and 101.3 °F), which they can maintain while ambient temperatures are between 5 and 25 °C (41 and 77 °F). However, strenuous exercise increases core body temperature by 1 °C (1.8 °F)/minute, as 80% of the energy used by equine muscles is released as heat. Along with bovines and primates, equines are the only animal group which use sweating as their primary method of thermoregulation: in fact, it can account for up to 70% of their heat loss, and horses sweat three times more than humans while undergoing comparably strenuous physical activity. Unlike humans, this sweat is created not by eccrine glands but by apocrine glands. In hot conditions, horses during three hours of moderate-intersity exercise can lose 30 to 35 L of water and 100g of sodium, 198 g of choloride and 45 g of potassium. In another difference from humans, their sweat is hypertonic, and contains a protein called latherin, which enables it to spread across their body easier, and to foam, rather than to drip off. These adaptations are partly to compensate for their lower body surface-to-mass ratio, which makes it more difficult for horses to passively radiate heat. Yet, prolonged exposure to very hot and/or humid conditions will lead to consequences such as anhidrosis, heat stroke, or brain damage, potentially culminating in death if not addressed with measures like cold water applications. Additionally, around 10% of incidents associated with horse transport have been attributed to heat stress. These issues are expected to worsen in the future.
African horse sickness (AHS) is a viral illness with a mortality close to 90% in horses, and 50% in mules. A midge, Culicoides imicola, is the primary vector of AHS, and its spread is expected to benefit from climate change. The spillover of Hendra virus from its flying fox hosts to horses is also likely to increase, as future warming would expand the hosts' geographic range. It has been estimated that under the "moderate" and high climate change scenarios, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5, the number of threatened horses would increase by 110,000 and 165,000, respectively, or by 175 and 260%.See also
References
- Linnaeus, Carolus (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae :secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Vol. 1 (10th ed.). Holmiae (Laurentii Salvii). p. 73. Archived from the original on October 12, 2018. Retrieved September 8, 2008.
- ^ Grubb, P. (2005). "Order Perissodactyla". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 630–631. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (2003). "Usage of 17 specific names based on wild species which are pre-dated by or contemporary with those based on domestic animals (Lepidoptera, Osteichthyes, Mammalia): conserved. Opinion 2027 (Case 3010)". Bull. Zool. Nomencl. 60 (1): 81–84. Archived from the original on August 21, 2007.
- "Do You Know How Horses Sleep?". Archived from the original on January 22, 2018. Retrieved September 12, 2018.
- Goody, John (2000). Horse Anatomy (2nd ed.). J A Allen. ISBN 0-85131-769-3.
- Pavord, Tony; Pavord, Marcy (2007). Complete Equine Veterinary Manual. David & Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-1883-6.
- ^ Ensminger, pp. 46–50
- Wright, B. (March 29, 1999). "The Age of a Horse". Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs. Government of Ontario. Archived from the original on January 20, 2010. Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- Ryder, Erin. "World's Oldest Living Pony Dies at 56". The Horse. Archived from the original on January 24, 2014. Retrieved May 31, 2007.
- British Horse Society (1966). The Manual of Horsemanship of the British Horse Society and the Pony Club (6th edition, reprinted 1970 ed.). Kenilworth, UK: British Horse Society. p. 255. ISBN 0-9548863-1-3.
- "Rules of the Australian Stud Book" (PDF). Australian Jockey Club. 2007. p. 7. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- ^ "Equine Age Requirements for AERC Rides". American Endurance Riding Conference. Archived from the original on August 11, 2011. Retrieved July 25, 2011.
- ^ Ensminger, p. 418
- Giffin, p. 431
- Ensminger, p. 430
- Ensminger, p. 415
- Becker, Marty; Pavia, Audrey; Spadafori, Gina; Becker, Teresa (2007). Why Do Horses Sleep Standing Up?: 101 of the Most Perplexing Questions Answered About Equine Enigmas, Medical Mysteries, and Befuddling Behaviors. HCI. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-7573-0608-2.
- Ensminger, p. 422
- Ensminger, p. 427
- Ensminger, p. 420
- "Glossary of Horse Racing Terms". Equibase.com. Equibase Company, LLC. Archived from the original on May 12, 2008. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- "Rules of the Australian Stud Book". Australian Jockey Club Ltd and Victoria Racing Club Ltd. July 2008. p. 9. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2010.
- Whitaker, p. 77
- Ensminger, p. 51
- Bongianni, entries 1, 68, 69
- Bongianni, entries 12, 30, 31, 32, 75
- Bongianni, entries 86, 96, 97
- Whitaker, p. 60
- Douglas, Jeff (March 19, 2007). "World's smallest horse has tall order". The Washington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on March 15, 2017. Retrieved March 14, 2017.
- "Meet the smallest horse in the world that's shorter than a greyhound". Guinness World Records. September 5, 2019. Archived from the original on August 4, 2021. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ Ensminger, M. Eugene (1991). Horses and Tack (Revised ed.). Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Company. ISBN 0395544130. OCLC 21561287. OL 1877441M.
- Howlett, Lorna; Philip Mathews (1979). Ponies in Australia. Milson's Point, NSW: Philip Mathews Publishers. p. 14. ISBN 0-908001-13-4.
- "2012 United States Equestrian Federation, Inc. Rule Book". United States Equestrian Federation. p. Rule WS 101. Archived from the original on April 15, 2012.
- "Annex XVII: Extracts from Rules for Pony Riders and Children, 9th edition" (PDF). Fédération Equestre Internationale. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 11, 2012. Retrieved March 7, 2010.
- For example, the Missouri Fox Trotter, or the Arabian horse. See McBane, pp. 192, 218
- For example, the Welsh Pony. See McBane, pp. 52–63
- McBane, p. 200
- "Chromosome Numbers in Different Species". Vivo.colostate.edu. January 30, 1998. Archived from the original on May 11, 2013. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- "Sequenced horse genome expands understanding of equine, human diseases". Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine. August 21, 2012. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved April 1, 2013.
- Wade, C. M; Giulotto, E; Sigurdsson, S; Zoli, M; Gnerre, S; Imsland, F; Lear, T. L; Adelson, D. L; Bailey, E; Bellone, R. R; Blocker, H; Distl, O; Edgar, R. C; Garber, M; Leeb, T; Mauceli, E; MacLeod, J. N; Penedo, M. C. T; Raison, J. M; Sharpe, T; Vogel, J; Andersson, L; Antczak, D. F; Biagi, T; Binns, M. M; Chowdhary, B. P; Coleman, S. J; Della Valle, G; Fryc, S; et al. (November 5, 2009). "Domestic Horse Genome Sequenced". Science. 326 (5954): 865–867. Bibcode:2009Sci...326..865W. doi:10.1126/science.1178158. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 3785132. PMID 19892987. Archived from the original on November 18, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2013.
- "Ensembl genome browser 71: Equus caballus – Description". Uswest.ensembl.org. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- Vogel, Colin B.V.M. (1995). The Complete Horse Care Manual. New York: Dorling Kindersley Publishing, Inc. p. 14. ISBN 0-7894-0170-3. OCLC 32168476.
- Mills, Bruce; Barbara Carne (1988). A Basic Guide to Horse Care and Management. New York: Howell Book House. pp. 72–73. ISBN 0-87605-871-3. OCLC 17507227.
- Corum, Stephanie J. (May 1, 2003). "A Horse of a Different Color". The Horse. Archived from the original on September 18, 2015. Retrieved February 11, 2010.
- ^ "Horse Coat Color Tests". Veterinary Genetics Laboratory. University of California. Archived from the original on February 19, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2008.
- Marklund, L.; M. Johansson Moller; K. Sandberg; L. Andersson (1996). "A missense mutation in the gene for melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MC1R) is associated with the chestnut coat color in horses". Mammalian Genome. 7 (12): 895–899. doi:10.1007/s003359900264. PMID 8995760. S2CID 29095360.
- ^ "Introduction to Coat Color Genetics". Veterinary Genetics Laboratory. University of California. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved May 1, 2008.
- Haase B; Brooks SA; Schlumbaum A; et al. (2007). "Allelic Heterogeneity at the Equine KIT Locus in Dominant White (W) Horses". PLOS Genetics. 3 (11): e195. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030195. PMC 2065884. PMID 17997609.
- Mau, C.; Poncet, P. A.; Bucher, B.; Stranzinger, G.; Rieder, S. (2004). "Genetic mapping of dominant white (W), a homozygous lethal condition in the horse (Equus caballus)". Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. 121 (6): 374–383. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0388.2004.00481.x.
- Ensminger, p. 156
- "How Long is a Horse Pregnant?". Talk of the Turf. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- Johnson, Tom. "Rare Twin Foals Born at Vet Hospital: Twin Birth Occurrences Number One in Ten Thousand". Communications Services, Oklahoma State University. Oklahoma State University. Archived from the original on October 12, 2012. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- Miller, Robert M.; Rick Lamb (2005). Revolution in Horsemanship and What it Means to Mankind. Guilford, CT: Lyons Press. pp. 102–103. ISBN 1-59228-387-X. OCLC 57005594.
- Ensminger, p. 150
- Kline, Kevin H. (October 7, 2010). "Reducing weaning stress in foals". Montana State University eXtension. Archived from the original on March 22, 2012. Retrieved April 3, 2012.
- McIlwraith, C.W. "Developmental Orthopaedic Disease: Problems of Limbs in young Horses". Orthopaedic Research Center. Colorado State University. Archived from the original on January 14, 2013. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- Thomas, Heather Smith (2003). Storey's Guide to Training Horses: Ground Work, Driving, Riding. North Adams, MA: Storey Publishing. p. 163. ISBN 1-58017-467-1.
- "2-Year-Old Racing (US and Canada)". Online Fact Book. Jockey Club. Archived from the original on February 16, 2013. Retrieved April 28, 2008.
- Bryant, Jennifer Olson; George Williams (2006). The USDF Guide to Dressage. Storey Publishing. pp. 271–272. ISBN 978-1-58017-529-6. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- Evans, J. (1990). The Horse (Second ed.). New York: Freeman. p. 90. ISBN 0-7167-1811-1. OCLC 20132967.
- Ensminger, pp. 21–25
- Ensminger, p. 367
- Giffin, p. 304
- Giffin, p. 457
- Fuess, Theresa A. "Yes, The Shin Bone Is Connected to the Ankle Bone". Pet Column. University of Illinois. Archived from the original on September 9, 2006. Retrieved April 5, 2008.
- Giffin, pp. 310–312
- Kreling, Kai (2005). "The Horse's Teeth". Horses' Teeth and Their Problems: Prevention, Recognition, and Treatment. Guilford, CT: Globe Pequot. pp. 12–13. ISBN 1-59228-696-8. OCLC 59163221.
- Giffin, p. 175
- Valentine, Beth A.; Van Saun, Robert J.; Thompson, Kent N.; Hintz, Harold F. (2001). "Role of dietary carbohydrate and fat in horses with equine polysaccharide storage myopathy". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 219 (11): 1537–1544. doi:10.2460/javma.2001.219.1537. PMID 11759989.
- Ellis, Harold (2010). "The gall bladder and bile ducts". Surgery (Oxford). 28 (5): 218–221. doi:10.1016/j.mpsur.2010.02.007. Archived from the original on May 12, 2021. Retrieved May 11, 2021.
- ^ Ensminger, pp. 309–310
- Hartley, C; Grundon, RA (2016). "Chapter 5: Diseases and surgery of the globe and orbit". In Gilger, BC (ed.). Equine Ophthalmology (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 151. ISBN 9781119047742.
- "Eye Position and Animal Agility Study Published". The Horse. March 7, 2010. Archived from the original on July 23, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2010. Press Release, citing February 2010 Journal of Anatomy, Dr. Nathan Jeffery, co-author, University of Liverpool.
- Sellnow, Les (2004). Happy Trails: Your Complete Guide to Fun and Safe Trail Riding. Eclipse Press. p. 46. ISBN 1-58150-114-5. OCLC 56493380.
- McDonnell, Sue (June 1, 2007). "In Living Color". The Horse. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved July 27, 2007.
- Briggs, Karen (December 11, 2013). "Equine Sense of Smell". The Horse. Archived from the original on February 1, 2018. Retrieved December 15, 2013.
- Myers, Jane (2005). Horse Safe: A Complete Guide to Equine Safety. Collingwood, UK: CSIRO Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 0-643-09245-5. OCLC 65466652. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- Lesté-Lasserre, Christa (January 18, 2013). "Music Genre's Effect on Horse Behavior Evaluated". The Horse. Blood Horse Publications. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- Kentucky Equine Research Staff (February 15, 2010). "Radios Causing Gastric Ulcers". EquiNews. Kentucky Equine Research. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- Thomas, Heather Smith. "True Horse Sense". Thoroughbred Times. Thoroughbred Times Company. Archived from the original on November 2, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- Cirelli, Al Jr.; Brenda Cloud. "Horse Handling and Riding Guidelines Part 1: Equine Senses" (PDF). Cooperative Extension. University of Nevada. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 8, 2015. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- Hairston, Rachel; Madelyn Larsen (2004). The Essentials of Horsekeeping. New York: Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. p. 77. ISBN 0-8069-8817-7. OCLC 53186526.
- Miller, p. 28
- Gustavson, Carrie. "Horse Pasture is No Place for Poisonous Plants". Pet Column July 24, 2000. University of Illinois. Archived from the original on August 9, 2007. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- Harris, p. 32
- Harris, pp. 47–49
- "Fastest speed for a race horse". Guinness World Records. May 14, 2008. Archived from the original on August 28, 2017. Retrieved January 8, 2013.
- Harris, p. 50
- Lieberman, Bobbie (2007). "Easy Gaited Horses". Equus (359): 47–51.
- Equus Staff (2007). "Breeds that Gait". Equus (359): 52–54.
- Harris, pp. 50–55
- "Horse Fight vs Flight Instinct". eXtension. September 24, 2009. Archived from the original on May 15, 2013. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- McBane, Susan (1992). A Natural Approach to Horse Management. London: Methuen. pp. 226–228. ISBN 0-413-62370-X. OCLC 26359746.
- Ensminger, pp. 305–309
- Prince, Eleanor F.; Gaydell M. Collier (1974). Basic Horsemanship: English and Western. New York: Doubleday. pp. 214–223. ISBN 0-385-06587-6. OCLC 873660.
- ^ Clarkson, Neil (April 16, 2007). "Understanding horse intelligence". Horsetalk 2007. Horsetalk. Archived from the original on January 24, 2013. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- Dorrance, Bill (1999). True horsemanship through feel. Guilford, CT: The Lion Press. p. 1. ISBN 1-58574-321-6.
- Lesté-Lasserre, Christa. "Horses Demonstrate Ability to Count in New Study". The Horse. Archived from the original on January 1, 2016. Retrieved December 6, 2009.
- Coarse, Jim (June 17, 2008). "What Big Brown Couldn't Tell You and Mr. Ed Kept to Himself (part 1)". The Blood Horse. Archived from the original on May 21, 2012. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ^ Belknap, p. 255
- ^ Belknap, p. 112
- ^ Ensminger, pp. 71–73
- Ensminger, p. 84
- ^ Price, p. 18
- DeFilippis, Chris (2006). The Everything Horse Care Book. Avon, MA: Adams Media. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-59337-530-0. OCLC 223814651.
- Whitaker, p. 43
- Whitaker, pp. 194–197
- ^ Price, p. 15
- Bongianni, entry 87
- Ensminger, pp. 124–125
- ^ Bennett, Deb (1998). Conquerors: The Roots of New World Horsemanship (First ed.). Solvang, CA: Amigo Publications, Inc. p. 7. ISBN 0-9658533-0-6. OCLC 39709067.
- Edwards, pp. 122–123
- Examples are the Australian Riding Pony and the Connemara, see Edwards, pp. 178–179, 208–209
- Price, Steven D.; Shiers, Jessie (2007). The Lyons Press Horseman's Dictionary (Revised ed.). Guilford, CT: Lyons Press. p. 231. ISBN 978-1-59921-036-0.
- Belknap, p. 523
- Pascoe, Elaine. "How Horses Sleep". Equisearch.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved March 23, 2007.
- ^ Pascoe, Elaine (March 12, 2002). "How Horses Sleep, Pt. 2 – Power Naps". Equisearch.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved March 23, 2007.
- Ensminger, p. 310.
- Holland, Jennifer S. (July 2011). "40 Winks?". National Geographic. 220 (1).
- EQUUS Magazine Staff. "Equine Sleep Disorder Videos". Equisearch.com. Archived from the original on May 10, 2007. Retrieved March 23, 2007.
- Smith, BP (1996). Large Animal Internal Medicine (Second ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby. pp. 1086–1087. ISBN 0-8151-7724-0. OCLC 33439780.
- Budiansky, Stephen (1997). The Nature of Horses. New York: Free Press. p. 31. ISBN 0-684-82768-9. OCLC 35723713.
- Myers, Phil. "Order Perissodactyla". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- "Hyracotherium". Fossil Horses in Cyberspace. Florida Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on January 31, 2013. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- "Mesohippus". Fossil Horses in Cyberspace. Florida Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- ^ "The Evolution of Horses". The Horse. American Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- Miller, p. 20
- "Equus". Fossil Horses in Cyberspace. Florida Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- Weinstock, J.; et al. (2005). "Evolution, Systematics, and Phylogeography of Pleistocene Horses in the New World: A Molecular Perspective". PLOS Biology. 3 (8): e241. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030241. PMC 1159165. PMID 15974804.
- Vila, C.; et al. (2001). "Widespread Origins of Domestic Horse Lineages" (PDF). Science. 291 (5503): 474–477. Bibcode:2001Sci...291..474V. doi:10.1126/science.291.5503.474. PMID 11161199. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 13, 2012. Retrieved March 17, 2009.
- Luís, Cristina; et al. (2006). "Iberian Origins of New World Horse Breeds". Quaternary Science Reviews. 97 (2): 107–113. doi:10.1093/jhered/esj020. PMID 16489143.
- Haile, James; et al. (2009). "Ancient DNA reveals late survival of mammoth and horse in interior Alaska". PNAS. 106 (52): 22352–22357. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10622352H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912510106. PMC 2795395. PMID 20018740.
- Buck, Caitlin E.; Bard, Edouard (2007). "A calendar chronology for Pleistocene mammoth and horse extinction in North America based on Bayesian radiocarbon calibration". Quaternary Science Reviews. 26 (17–18): 2031–2035. Bibcode:2007QSRv...26.2031B. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.06.013. Archived from the original on November 6, 2018. Retrieved September 6, 2017.
- LeQuire, Elise (January 4, 2004). "No Grass, No Horse". The Horse. Archived from the original on January 9, 2013. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ Olsen, Sandra L. (1996). "Horse Hunters of the Ice Age". Horses Through Time (First ed.). Boulder, CO: Roberts Rinehart Publishers. p. 46. ISBN 1-57098-060-8. OCLC 36179575.
- "An extraordinary return from the brink of extinction for world's last wild horse". ZSL Press Releases. Zoological Society of London. December 19, 2005. Archived from the original on May 16, 2013. Retrieved June 6, 2012.
- "Home". The Foundation for the Preservation and Protection of the Przewalski Horse. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- ^ Dohner, pp. 298–299
- Pennisi, Elizabeth (February 22, 2018). "Ancient DNA upends the horse family tree". sciencemag.org. Archived from the original on September 21, 2022. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- Orlando, Ludovic; Outram, Alan K.; Librado, Pablo; Willerslev, Eske; Zaibert, Viktor; Merz, Ilja; Merz, Victor; Wallner, Barbara; Ludwig, Arne (6 April 2018). "Ancient genomes revisit the ancestry of domestic and Przewalski's horses". Science. 360 (6384): 111–114. Bibcode:2018Sci...360..111G. doi:10.1126/science.aao3297. hdl:10871/31710. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 29472442.
- "Ancient DNA rules out archeologists' best bet for horse domestication". ArsTechnica. February 25, 2018. Archived from the original on June 25, 2020. Retrieved June 24, 2020.
- ^ Dohner, p. 300
- "Tarpan". Breeds of Livestock. Oklahoma State University. Archived from the original on January 16, 2009. Retrieved January 13, 2009.
- "Ponies from the past?: Oregon couple revives prehistoric Tarpan horses". The Daily Courier. June 21, 2002. Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- Peissel, Michel (2002). Tibet: The Secret Continent. Macmillan. p. 36. ISBN 0-312-30953-8. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Royo, L.J.; Álvarez, I.; Beja-Pereira, A.; Molina, A.; Fernández, I.; Jordana, J.; Gómez, E.; Gutiérrez, J. P.; Goyache, F. (2005). "The Origins of Iberian Horses Assessed via Mitochondrial DNA". Journal of Heredity. 96 (6): 663–669. doi:10.1093/jhered/esi116. PMID 16251517.
- Edwards, pp. 104–105
- ^ Lira, Jaime; et al. (2010). "Ancient DNA reveals traces of Iberian Neolithic and Bronze Age lineages in modern Iberian horses" (PDF). Molecular Ecology. 19 (1): 64–78. Bibcode:2010MolEc..19...64L. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04430.x. PMID 19943892. S2CID 1376591. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 10, 2017. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- Pallas (1775). "Equus hemionus". Wilson & Reeder's mammal species of the world. Bucknell University. Archived from the original on September 26, 2013. Retrieved September 1, 2010.
- "Mule Information". BMS Website. British Mule Society. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved July 10, 2008.
- "Zebra hybrid is cute surprise". BBC News. June 26, 2001. Archived from the original on June 14, 2017. Retrieved February 6, 2010.
- "Befuddling Birth: The Case of the Mule's Foal". NPR.org. National Public Radio. Archived from the original on December 6, 2008. Retrieved August 16, 2008.
- Outram, A. K.; Stear, N. A.; Bendrey, R; Olsen, S; Kasparov, A; Zaibert, V; Thorpe, N; Evershed, R. P. (2009). "The earliest horse harnessing and milking". Science. 323 (5919): 1332–1335. Bibcode:2009Sci...323.1332O. doi:10.1126/science.1168594. PMID 19265018. S2CID 5126719.
- Matossian, Mary Kilbourne (1997). Shaping World History: Breakthroughs in Ecology, Technology, Science, and Politics. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe. p. 43. ISBN 0-585-02397-2. OCLC 156944228. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- "Horsey-aeology, Binary Black Holes, Tracking Red Tides, Fish Re-evolution, Walk Like a Man, Fact or Fiction". Quirks and Quarks Podcast with Bob Macdonald. CBC Radio. March 7, 2009. Archived from the original on October 7, 2014. Retrieved September 18, 2010.
- Taylor, William Timothy Treal; Barrón-Ortiz, Christina Isabelle (April 2, 2021). "Rethinking the evidence for early horse domestication at Botai". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 7440. Bibcode:2021NatSR..11.7440T. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86832-9. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 8018961. PMID 33811228.
- Librado, Pablo; Khan, Naveed; Fages, Antoine; Kusliy, Mariya A.; Suchan, Tomasz; Tonasso-Calvière, Laure; Schiavinato, Stéphanie; Alioglu, Duha; Fromentier, Aurore; Perdereau, Aude; Aury, Jean-Marc; Gaunitz, Charleen; Chauvey, Lorelei; Seguin-Orlando, Andaine; Der Sarkissian, Clio (2021). "The origins and spread of domestic horses from the Western Eurasian steppes". Nature. 598 (7882): 634–640. Bibcode:2021Natur.598..634L. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04018-9. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 8550961. PMID 34671162.
- Evans, James Warren (1992). Horse Breeding and Management. Amsterdam: Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 56. ISBN 0-444-88282-0. OCLC 243738023.
- Kuznetsov, P. F. (2006). "The emergence of Bronze Age chariots in eastern Europe". Antiquity. 80 (309): 638–645. doi:10.1017/S0003598X00094096. S2CID 162580424.
- Lambert, Jonathan (October 20, 2021). "Scientists found modern domestic horses' homeland in southwestern Russia". Science News. Archived from the original on November 14, 2021. Retrieved November 14, 2021.
- Pablo Librado; et al. (October 2021). "The origins and spread of domestic horses from the Western Eurasian steppes". Nature. 598 (7882): 634–640. Bibcode:2021Natur.598..634L. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04018-9. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 8550961. PMID 34671162.
- ^ Lau, A. N.; Peng, L.; Goto, H.; Chemnick, L.; Ryder, O. A.; Makova, K. D. (2009). "Horse Domestication and Conservation Genetics of Przewalski's Horse Inferred from Sex Chromosomal and Autosomal Sequences". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 26 (1): 199–208. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn239. PMID 18931383.
- ^ Lindgren, Gabriella; Niclas Backström; June Swinburne; Linda Hellborg; Annika Einarsson; Kaj Sandberg; Gus Cothran; Carles Vilà; Matthew Binns; Hans Ellegren (2004). "Limited number of patrilines in horse domestication". Nature Genetics. 36 (4): 335–336. doi:10.1038/ng1326. PMID 15034578.
- ^ Vilà, C.; et al. (2001). "Widespread origins of domestic horse lineages". Science. 291 (5503): 474–477. Bibcode:2001Sci...291..474V. doi:10.1126/science.291.5503.474. PMID 11161199.
- ^ Cai, D. W.; Tang, Z. W.; Han, L.; Speller, C. F.; Yang, D. Y. Y.; Ma, X. L.; Cao, J. E.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, H.; et al. (2009). "Ancient DNA provides new insights into the origin of the Chinese domestic horse" (PDF). Journal of Archaeological Science. 36 (3): 835–842. Bibcode:2009JArSc..36..835C. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2008.11.006. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 29, 2011. Retrieved January 17, 2011.
- Olsen, Sandra L. (2006). "Early Horse Domestication: Weighing the Evidence". In Olsen, Sandra L; Grant, Susan; Choyke, Alice M.; Bartosiewicz, Laszlo (eds.). Horses & Humans: The Evolution of Human-Equine Relationships. Oxford, UK: Archaeopress. pp. 81–113. ISBN 978-1-84171-990-0.
- Epstein, H. (1955). "Domestication Features in Animals as Functions of Human Society". Agricultural History Society. 29 (4): 137–146. JSTOR 3740046.
- Ludwig, A.; Pruvost, M.; Reissmann, M.; Benecke, N.; Brockmann, G.A.; Castanos, P.; Cieslak, M.; Lippold, S.; Llorente, L.; et al. (2009). "Coat Color Variation at the Beginning of Horse Domestication". Science. 324 (5926): 485. Bibcode:2009Sci...324..485L. doi:10.1126/science.1172750. PMC 5102060. PMID 19390039.
- Edwards, Gladys Brown (1973). The Arabian: War Horse to Show Horse (Revised Collectors ed.). Rich Publishing. pp. 1, 3.
- Edwards, p. 291
- Anthony, David W. (1996). "Bridling Horse Power: The Domestication of the Horse". Horses Through Time (First ed.). Boulder, CO: Roberts Rinehart Publishers. pp. 66–67. ISBN 1-57098-060-8. OCLC 36179575.
- Olsen, Sandra L. "Horses in Prehistory". Anthropology Research. Carnegie Museum of Natural History. Archived from the original on May 25, 2008. Retrieved August 16, 2008.
- Lesté-Lasserre, Christa (October 7, 2009). "Mares' Social Bonds Might Enhance Reproductive Success". The Horse. Archived from the original on April 15, 2012. Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- "Animals on the Moor". Dartmoor Commoners' Council. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved March 29, 2012.
- Fear, Sally (2006). New Forest Drift: A Photographic Portrait of Life in the National Park. Perspective Photo Press. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-9553253-0-4.
- Ensminger, p. 424
- Edwards, Gladys Brown (1973). The Arabian: War Horse to Show Horse (Revised Collectors ed.). Rich Publishing. pp. 22–23.
- "Is Purity the Issue?". WAHO Publication Number 21 January 1998. World Arabian Horse Organization. Archived from the original on July 5, 2008. Retrieved April 29, 2008.
- ^ Sponenberg, p. 155
- Sponenberg, pp. 156–157
- Sponenberg, p. 162
- "History of Thoroughbreds". Britishhorseracing.com. British Horseracing Authority. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- Hedge, Juliet; Don M. Wagoner (2004). Horse Conformation: Structure, Soundness and Performance. Guilford, CT: Globe Pequot. pp. 307–308. ISBN 1-59228-487-6. OCLC 56012597.
- "FAO Stat – Live Animals". Food and Agriculture Organization. December 16, 2009. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2010.
- "Most Comprehensive Horse Study Ever Reveals A Nearly $40 Billion Impact On The U.S. Economy" (PDF) (Press release). American Horse Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 25, 2006. Retrieved June 20, 2005.
- "Tiger tops dog as world's favourite animal". Independent Online. Independent. Archived from the original on October 28, 2012. Retrieved June 1, 2011.
- ^ Olsen, Sandra L. (1996). "In the Winner's Circle: The History of Equestrian Sports". Horses Through Time (First ed.). Boulder, CO: Roberts Rinehart Publishers. pp. 105, 111–113, 121. ISBN 1-57098-060-8. OCLC 36179575.
- Edwards, Elwyn Hartley (2002). Horses (Second American ed.). New York: Dorling Kindersley. pp. 32–34. ISBN 0-7894-8982-1. OCLC 50798049.
- Self, Margaret Cabell (2005). Riding Simplified. Kessinger Publishing. p. 55. ISBN 1-4191-0087-4.
- Thorson, Juli S. (2006). "Rugged Lark". In Martindale, Cathy and Kathy Swan (ed.). Legends 7: Outstanding Quarter Horse Stallions and Mares. Colorado Springs, CO: Western Horseman. p. 218. ISBN 978-0-911647-79-2.
- Mettler, John J Jr. (1989). Horse Sense: A Complete Guide to Horse Selection and Care. Pownal, VT: Storey Communications, Inc. pp. 47–54. ISBN 0-88266-549-9. OCLC 19324181.
- Edwards, pp. 346–356, 366–371
- Edwards, pp. 376–377
- ^ Edwards, p. 360
- Collins, Tony; Martin, John; Vamplew, Wray (2005). Encyclopedia of Traditional British Rural Sports. London: Routledge. pp. 173–174. ISBN 0-415-35224-X. OCLC 57005595. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- Edwards, pp. 332–337
- Campbell, B.N. (2001). National Gambling Impact Study Commission Final Report (1999). Darby, PA: DIANE Publishing. p. 111. ISBN 0-7567-0701-3. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved November 15, 2015.
- "Horse Mounted Unit". United States Park Police. National Park Service. Archived from the original on February 18, 2008. Retrieved April 7, 2008.
- Edwards, pp. 226–227
- "Volunteer Mounted Search and Rescue Unit". Employment. San Benito County Sheriff's Office. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- US Forest Service (May 2003). "Mules Key in Accomplishing Trail Work" (PDF). Success Stories. US Department of Agriculture. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 27, 2008. Retrieved April 20, 2008.
- Brown, Kimberly S. (June 1, 2006). "At Work in Morocco". The Horse. Archived from the original on December 22, 2007. Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- Gifford, Angela (2000) . "Working Draught Horses as Singles and Pairs". The Working Horse Manual. Tonbridge, UK: Farming Press. p. 85. ISBN 0-85236-401-6. OCLC 40464050.
- Miller, Lynn R. (2000) . Work Horse Handbook (First Edition, Fifteenth Impression ed.). Sisters, OR: Small Farmer's Journal Inc. p. 13. ISBN 0-9607268-0-2. OCLC 234277549.
- Gifford, Angela (2000) . "Working Horses in Forestry". The Working Horse Manual. Tonbridge, UK: Farming Press. p. 145. ISBN 0-85236-401-6. OCLC 40464050.
- Newby, Jonica; Diamond, Jared; Anthony, David (November 13, 1999). "The Horse in History". The Science Show. Radio National. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- Anthony, David W.; Dorcas R. Brown. "The Earliest Horseback Riding and its Relation to Chariotry and Warfare". Harnessing Horsepower. Institute for Ancient Equestrian Studies. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved October 9, 2007.
- Whitaker, pp. 30–31
- Lacey, Marc (May 4, 2004). "In Sudan, Militiamen on Horses Uproot a Million". The New York Times. Archived from the original on April 23, 2009. Retrieved January 4, 2011.
- Stoddard, Samuel. "Unit Activities". Co H, 4th Virginia Cavalry. Washington Webworks, LLC. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved April 29, 2008.
- "Transport". British Monarchy. Archived from the original on February 16, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2009.
- McWilliams, Jeremiah (December 3, 2008). "Anheuser-Busch gives face time to Budweiser Clydesdales". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Archived from the original on May 14, 2012. Retrieved September 18, 2010.
- Sellnow, Les (March 1, 2006). "Hollywood Horses". The Horse. Archived from the original on September 5, 2011. Retrieved October 21, 2009.
- "Trademark Horse – Horses as advertising mediums". Westfälische Pferdemuseum (Westphalian Horse Museum). Archived from the original on October 11, 2008. Retrieved August 16, 2008.
- Fox-Davies, Arthur Charles (2007). A Complete Guide to Heraldry. Skyhorse Publishing Inc. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-60239-001-0. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- Tozer, Basil (1908). The Horse in History. London: Methuen. pp. 94, 98–100. OCLC 2484673.
- "Year of the Horse". Chinese Culture Center of San Francisco. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved July 22, 2007.
- Cole, Craig (November 8, 2021). "Giddy Up: Top 10 Horse-Themed Cars". Autoguide.com. Archived from the original on May 25, 2022. Retrieved July 7, 2022.
- "Cars with Horse Logos: How Many of Them do You Know?". January 9, 2022. Archived from the original on May 28, 2022. Retrieved June 18, 2022.
- "Top 11 cars named after horses, which is your favorite?". May 8, 2021. Archived from the original on August 16, 2022. Retrieved June 18, 2022.
- Bush, Karen; Julian Marczak (2005). The Principles of Teaching Riding: The Official Manual of the Association of British Riding Schools. David & Charles. p. 58. ISBN 0-7153-1902-7. OCLC 224946044. OL 7832270M.
- "About Para Equestrian Dressage". Federation Equestre Internationale. Archived from the original on May 8, 2013. Retrieved March 7, 2010.
- "Frequently Asked Questions About Hippotherapy" (PDF). FAQ – AHA, April 2005. American Hippotherapy Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 19, 2007. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- "Equine Facilitated Psychotherapy (EFP) Fact Sheet". Equine Facilitated Mental Health Association. Archived from the original on April 30, 2008. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- Wise, Mike (August 10, 2003). "Partners, Horse and Man, in Prison Pasture". New York Times. Retrieved July 8, 2008.
- ^ Frazier, Ian (April 18, 2005). "Invaders: Destroying Baghdad". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- Ballard, Pepper (August 19, 2001). "A Good Life for Horses at the Duchess Sanctuary". The Humane Society of the United States. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved June 1, 2011.
- McCutcheon, Marc (2000). Descriptionary: A Thematic Dictionary (Second ed.). New York: Checkmark Books (Facts On File imprint). p. 285. ISBN 0-8160-4105-9.
- "FAOSTAT". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Archived from the original on May 24, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2019.
- "U.S.D.A. Promotes Horse & Goat Meat". I.G.H.A./HorseAid's U.S.D.A. Report. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- Coile, Zachary (September 8, 2006). "House votes to outlaw slaughter of horses for human consumption". SF Gate. San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on November 23, 2012. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- Ockerman, Herbert W.; Hansen, Conly L. (2000). Animal By-product Processing & Utilization. Lancaster, PA: CRC Press. p. 129. ISBN 1-56676-777-6. OCLC 43685745.
- "Inside a Modern Baseball". Baseball Fever. Baseball Almanac. August 30, 2002. Archived from the original on August 12, 2013. Retrieved April 3, 2008.
- Bartlett, Virginia K. (1994). Keeping House: Women's Lives in Western Pennsylvania, 1790–1850. University of Pittsburgh Press. pp. 34–35. ISBN 0-8229-5538-5. OCLC 30978921. OL 1098280M. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- MacGregor, Arthur (1985). Bone, Antler, Ivory and Horn: Technology of Skeletal Materials Since the Roman Period. Totowa, NJ: Barnes & Noble. p. 31. ISBN 0-389-20531-1. OCLC 11090630.
- Fort, Matthew (2005). Eating Up Italy: Voyages on a Vespa. London: Centro Books. p. 171. ISBN 0-00-721481-2. OCLC 60419304.
- Diseases of the Stomach and Intestines. Translated by Hurd, Edward Payson. New York: W. Wood & Company. 1886. p. 29.
- Kellon, Eleanor (2008). "Focus on Feed Costs". Horse Journal. 16 (6): 11–12.
- Hall, Marvin H.; Patricia M. Comerford (1992). "Pasture and Hay for Horses – Agronomy Facts 32" (PDF). Cooperative Extension Service. University of Pennsylvania. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 24, 2012. Retrieved February 14, 2007.
- Giffin, pp. 476–477
- "Feeding Factors". Horse Nutrition. Ohio State University. Archived from the original on July 8, 2009. Retrieved February 9, 2007.
- Giffin, p. 455
- Giffin, p. 482
- Giffin, pp. 62, 168, 310
- Harris, Susan E. (1994). The United States Pony Club Manual of Horsemanship: Basics for Beginners – D Level. New York: Howell Book House. pp. 160–161. ISBN 0-87605-952-3.
- Wheeler, Eileen (2006). "Fence Planning". Horse Stable And Riding Arena Design. Armes, IA: Blackwell Publishing. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-8138-2859-6. OCLC 224324847. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- Giffin, p. 90
- ^ Kang, Hyungsuk; Zsoldos, Rebeka R.; Sole-Guitart, Albert; Narayan, Edward; Cawdell-Smith, A. Judith; Gaughan, John B. (April 15, 2023). "Heat stress in horses: a literature review". International Journal of Biometeorology. 67 (6): 957–973. Bibcode:2023IJBm...67..957K. doi:10.1007/s00484-023-02467-7. PMC 10267279. PMID 37060454.
- ^ McCutcheon, L. Jill; Geor, Raymond J. (1998). "Sweating: Fluid and Ion Losses and Replacement". Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice. 14 (1): 75–95. doi:10.1016/s0749-0739(17)30213-4. ISSN 0749-0739. PMID 9561689.
- McDonald, Rhona E.; Fleming, Rachel I.; Beeley, John G.; Bovell, Douglas L.; Lu, Jian R.; Zhao, Xiubo; Cooper, Alan; Kennedy, Malcolm W. (2009). "Latherin: A Surfactant Protein of Horse Sweat and Saliva". PLOS ONE. 4 (5): e5726. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.5726M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005726. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 2684629. PMID 19478940.
- Gao, Hongyan; Wang, Long; Ma, Jun; Gao, Xiang; Xiao, Jianhua; Wang, Hongbing (October 29, 2021). "Modeling the current distribution suitability and future dynamics of Culicoides imicola under climate change scenarios". PeerJ Life & Environment. 9: e12308. doi:10.7717/peerj.12308. PMC 8559603. PMID 34760364.
- Martin, Gerardo; Yanez-Arenas, Carlos; Chen, Carla; Plowright, Raina K.; Webb, Rebecca J.; Skerratt, Lee F. (March 19, 2018). "Climate Change Could Increase the Geographic Extent of Hendra Virus Spillover Risk". EcoHealth. 15 (3): 509–525. doi:10.1007/s10393-018-1322-9. PMC 6245089. PMID 29556762.
Sources
- Belknap, Maria (2004). Horsewords: The Equine Dictionary (Second ed.). North Pomfret, VT: Trafalgar Square Publishing. ISBN 1-57076-274-0.
- Bongianni, Maurizio (1987). Simon & Schuster's Guide to Horses and Ponies. New York: Fireside. ISBN 0-671-66068-3.
- Dohner, Janet Vorwald (2001). "Equines: Natural History". In Dohner, Janet Vorwald (ed.). Historic and Endangered Livestock and Poultry Breeds. Topeka, KS: Yale University Press. pp. 400–401. ISBN 0-300-08880-9.
- Edwards, Elwyn Hartley (1994). The Encyclopedia of the Horse. London: Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 1-56458-614-6. OCLC 29670649.
- Ensminger, M. E. (1990). Horses and Horsemanship: Animal Agricultural Series (Sixth ed.). Danville, IN: Interstate Publishers. ISBN 0-8134-2883-1. OCLC 21977751.
- Giffin, James M.; Tom Gore (1998). Horse Owner's Veterinary Handbook (Second ed.). New York: Howell Book House. ISBN 0-87605-606-0. OCLC 37245445.
- Harris, Susan E. (1993). Horse Gaits, Balance and Movement. New York: Howell Book House. ISBN 0-87605-955-8. OCLC 25873158.
- McBane, Susan (1997). The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Horse Breeds. Edison, NJ: Wellfleet Press. ISBN 0-7858-0604-0. OCLC 244110821.
- Miller, Robert M. (1999). Understanding the Ancient Secrets of the Horse's Mind. Neenah, WI: Russell Meerdink Company Ltd. ISBN 0-929346-65-3. OCLC 42389612. Archived from the original on March 20, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- Price, Steven D.; Spector, David L.; Rentsch, Gail; Burn, Barbara B., eds. (1998). The Whole Horse Catalog: Revised and Updated (Revised ed.). New York: Fireside. ISBN 0-684-83995-4.
- Sponenberg, D. Phillip (1996). "The Proliferation of Horse Breeds". Horses Through Time (First ed.). Boulder, CO: Roberts Rinehart Publishers. ISBN 1-57098-060-8. OCLC 36179575.
- Whitaker, Julie; Whitelaw, Ian (2007). The Horse: A Miscellany of Equine Knowledge. New York: St. Martin's Press. ISBN 978-0-312-37108-1.
Further reading
- Chamberlin, J. Edward (2006). Horse: How the Horse Has Shaped Civilizations. New York: Bluebridge. ISBN 978-0-9742405-9-6. OCLC 61704732.
External links
- "Ancient horse bone yields oldest DNA sequence"
- "Horse" . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
- "Horse" . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
- Genome of Equus caballus, via Ensembl
- Genome of Equus caballus (version EquCab3.0/equCab3), via UCSC Genome Browser
- Data of the genome of Equus caballus, via NCBI
- Data of the genome assembly of Equus caballus (versión EquCab3.0/equCab3), via NCBI
| Extant Perissodactyla (Odd-toed ungulates) species by suborder | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Horses | |
|---|---|
| Equine science and management | |
| Equestrianism and sport | |
| History | |
| Warfare | |
| Horse breeds and types | |
| Culture | |
| Working animals | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dog |  | |
| Horse | ||
| Other species | ||
| Related topics | ||
 Media from Commons
Media from Commons Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Taxa from Wikispecies
Taxa from Wikispecies
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Equus ferus caballus | |
- Domesticated animals
- Horses
- Animal-powered transport
- Mammals described in 1758
- Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
- Equus (genus)
- Herbivorous mammals
- Horse subspecies
- Livestock
- National symbols of Burkina Faso
- National symbols of Lesotho
- National symbols of Mongolia
- National symbols of Nigeria
- National symbols of Turkmenistan
- Pack animals
- Symbols of New Jersey