| Revision as of 05:13, 5 July 2022 editSmasongarrison (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers723,823 edits General fixes + punctuation fixed per MOS:CONFORM etc, typo(s) fixed: 3-010 → 3–010 (2)Tag: AWB← Previous edit |
Latest revision as of 15:01, 12 December 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,408,899 edits Added doi-access. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Dominic3203 | Category:CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI | #UCB_Category 3/10 |
| (5 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) |
| Line 21: |
Line 21: |
|
| MeshID = D018759 |
|
| MeshID = D018759 |
|
}} |
|
}} |
|
]]] |
|
]]] |
|
]]] |
|
]]] |
|
|
|
|
|
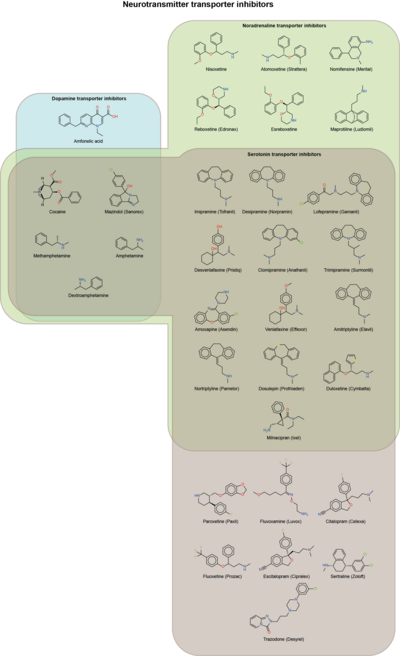
A '''norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor''' ('''NRI''', '''NERI''') or '''noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor''' or '''adrenergic reuptake inhibitor''' ('''ARI'''), is a type of ] that acts as a ] for the ]s ] (noradrenaline) and ] (adrenaline) by blocking the ] of the ] (NET). This in turn leads to increased ] ]s of norepinephrine and epinephrine and therefore can increase ] ]. |
|
A '''norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor''' ('''NRI''', '''NERI''') or '''noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor''' or '''adrenergic reuptake inhibitor''' ('''ARI'''), is a type of ] that acts as a ] for the ]s ] (noradrenaline) and ] (adrenaline) by blocking the ] of the ] (NET). This in turn leads to increased ] ]s of norepinephrine and epinephrine and therefore can increase ] ]. |
|
|
|
|
|
== Medical use == |
|
== Medical use == |
|
NRIs are commonly used in the treatment of conditions like ] and ] due to their ] effects and in ] due to their ] effects. They are also frequently used as ]s for the treatment of ], ] and ]. Additionally, many ] such as ] and ] possess NRI activity, though NRIs without combined ] (DRI) properties are not significantly rewarding and hence are considered to have negligible potential for addiction.<ref name="pmid15283948">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wee S, Woolverton WL | title = Evaluation of the reinforcing effects of atomoxetine in monkeys: comparison to methylphenidate and desipramine | journal = Drug and Alcohol Dependence | volume = 75 | issue = 3 | pages = 271–6 |date=September 2004 | pmid = 15283948 | doi = 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2004.03.010 }}</ref><ref name="pmid15526000">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gasior M, Bergman J, Kallman MJ, Paronis CA | title = Evaluation of the reinforcing effects of monoamine reuptake inhibitors under a concurrent schedule of food and i.v. drug delivery in rhesus monkeys | journal = Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 30 | issue = 4 | pages = 758–64 |date=April 2005 | pmid = 15526000 | doi = 10.1038/sj.npp.1300593 | doi-access = free }}</ref> However, norepinephrine has been implicated as acting synergistically with dopamine when actions on the two neurotransmitters are combined (e.g., in the case of ]s) to produce rewarding effects in psychostimulant addictive substances.<ref name="pmid11071707">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Dersch CM, etal | title = Amphetamine-type central nervous system stimulants release norepinephrine more potently than they release dopamine and serotonin | journal = Synapse | volume = 39 | issue = 1 | pages = 32–41 |date=January 2001 | pmid = 11071707 | doi = 10.1002/1098-2396(20010101)39:1<32::AID-SYN5>3.0.CO;2-3 }}</ref> |
|
NRIs are commonly used in the treatment of conditions like ] and ] due to their ] effects and in ] due to their ] effects. They are also frequently used as ]s for the treatment of ], ] and ]. Additionally, many ] such as ] and ] possess NRI activity, though NRIs without combined ] (DRI) properties are not significantly rewarding and hence are considered to have negligible potential for addiction.<ref name="pmid15283948">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wee S, Woolverton WL | title = Evaluation of the reinforcing effects of atomoxetine in monkeys: comparison to methylphenidate and desipramine | journal = Drug and Alcohol Dependence | volume = 75 | issue = 3 | pages = 271–6 |date=September 2004 | pmid = 15283948 | doi = 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2004.03.010 }}</ref><ref name="pmid15526000">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gasior M, Bergman J, Kallman MJ, Paronis CA | title = Evaluation of the reinforcing effects of monoamine reuptake inhibitors under a concurrent schedule of food and i.v. drug delivery in rhesus monkeys | journal = Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 30 | issue = 4 | pages = 758–64 |date=April 2005 | pmid = 15526000 | doi = 10.1038/sj.npp.1300593 | doi-access = free }}</ref> However, norepinephrine has been implicated as acting synergistically with dopamine when actions on the two neurotransmitters are combined (e.g., in the case of ]s) to produce rewarding effects in psychostimulant addictive substances.<ref name="pmid11071707">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Dersch CM, etal | title = Amphetamine-type central nervous system stimulants release norepinephrine more potently than they release dopamine and serotonin | journal = Synapse | volume = 39 | issue = 1 | pages = 32–41 |date=January 2001 | pmid = 11071707 | doi = 10.1002/1098-2396(20010101)39:1<32::AID-SYN5>3.0.CO;2-3 | s2cid = 15573624 }}</ref> |
|
|
|
|
|
=== Depression === |
|
=== Depression === |
| Line 44: |
Line 44: |
|
*** ] (Strattera) |
|
*** ] (Strattera) |
|
*** ] (Edronax, Vestra) |
|
*** ] (Edronax, Vestra) |
|
|
*** ] (Qelbree, Vivalan) – but also has some other weaker activities<ref name="YuGarcia-OlivaresCandler2020">{{cite journal | vauthors = Yu C, Garcia-Olivares J, Candler S, Schwabe S, Maletic V | title = New Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Viloxazine: Serotonin and Norepinephrine Modulating Properties | journal = J Exp Pharmacol | volume = 12 | issue = | pages = 285–300 | date = 2020 | pmid = 32943948 | pmc = 7473988 | doi = 10.2147/JEP.S256586 | doi-access = free | url = }}</ref> |
|
*** ] (Qelbree, Vivalan) |
|
|
** Never marketed |
|
** Never marketed |
|
*** ] (UK-3540-1) |
|
*** ] (UK-3540-1) |
| Line 65: |
Line 65: |
|
*** ] (Lucelan, Metatone) |
|
*** ] (Lucelan, Metatone) |
|
** Never marketed |
|
** Never marketed |
|
|
*** ] (TD-9855) |
|
*** ] (Wy-23,409) |
|
*** ] (Wy-23,409) |
|
*** ] |
|
*** ] |
| Line 73: |
Line 74: |
|
|
|
|
|
==See also== |
|
==See also== |
|
⚫ |
* ] |
|
*] |
|
* ] |
|
*], similar type of drugs used to block ] and norepinephrine ]s |
|
* ], similar type of drugs used to block ] and norepinephrine ]s |
| ⚫ |
*] |
|
|
|
* ] |
|
|
|
|
|
== References == |
|
== References == |