| Revision as of 15:04, 18 May 2005 view sourceBobblewik (talk | contribs)66,026 editsm units← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 00:59, 17 December 2024 view source Thenightaway (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users51,758 edits →Great DepressionTag: Visual edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Monetary system based on the value of gold}} | |||
| :''This article is on the monetary principle. For '''gold standard''' in diagnostic testing, see ].'' | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{pp-sock|small=yes}} | |||
| The '''gold standard''' is a ] in which the standard ] ] is a fixed weight of ]. When several nations are using such a fixed unit of account, the ] among national currencies effectively become fixed. | |||
| ], which was based on a gold standard. The coin to the left is ] and the one on the right is ].]] | |||
| The gold standard can also be viewed as a monetary system in which changes in the ] of gold determine the ] of goods and services in relation to their supply and demand. | |||
| ]s were used as ] in the ] from 1882 to 1933. These certificates were freely convertible into ]s.]] | |||
| A '''gold standard''' is a ] in which the standard ] ] is based on a fixed quantity of ]. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932<ref>{{Cite book|last=Eichengreen|first=Barry|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System|date=2019|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|edition=3rd|pages=7, 79|doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg|jstor=j.ctvd58rxg|s2cid=240840930}}</ref><ref name=":9">{{Citation|last1=Eichengreen|first1=Barry|title=International Finance|date=2021|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/cambridge-economic-history-of-the-modern-world/international-finance/69BA1D520B1CACCB1A4B69AAE8ED4367|work=The Cambridge Economic History of the Modern World: Volume 2: 1870 to the Present|volume=2|pages=501–525|editor-last=Fukao|editor-first=Kyoji|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-107-15948-8|last2=Esteves|first2=Rui Pedro|editor2-last=Broadberry|editor2-first=Stephen}}</ref> as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated ] of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Eichengreen|first=Barry|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System|date=2019|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|edition=3rd|pages=86–127|doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg|jstor=j.ctvd58rxg|s2cid=240840930}}</ref> Many states nonetheless hold substantial ]s.<ref>{{cite web|title=Gold standard Facts, information, pictures Encyclopedia.com articles about Gold standard|url=http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Gold_standard.aspx|access-date=2015-12-05|website=Encyclopedia.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite magazine|author=William O. Scroggs|title=What Is Left of the Gold Standard?|url=http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/69483/william-o-scroggs/what-is-left-of-the-gold-standard|access-date=28 January 2015|website=Foreignaffairs.com|date=11 October 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Historically, the ] and ] have been more common than the gold standard.<ref name=":02">{{Cite book|last=Eichengreen|first=Barry|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System|date=2019|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|edition=3rd|pages=5–40|doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg|jstor=j.ctvd58rxg|s2cid=240840930}}</ref><ref>{{Citation|last1=Esteves|first1=Rui Pedro|title=Monetary Systems and the Global Balance of Payments Adjustment in the Pre-Gold Standard Period, 1700–1870|date=2021|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/cambridge-economic-history-of-the-modern-world/monetary-systems-and-the-global-balance-of-payments-adjustment-in-the-pregold-standard-period-17001870/0FC7DA2F9137FE2A274D8F4063BD9074|work=The Cambridge Economic History of the Modern World: Volume 1: 1700 to 1870|volume=1|pages=438–467|editor-last=Fukao|editor-first=Kyoji|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-107-15945-7|last2=Nogues-Marco|first2=Pilar|editor2-last=Broadberry|editor2-first=Stephen}}</ref> The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, ], and ].<ref name=":02" /> Great Britain accidentally adopted a ''de facto'' gold standard in 1717 when ], then-master of the ], set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation.<ref name=":4">{{Cite book|last=Eichengreen|first=Barry|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System|date=2019|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|edition=3rd|page=5|doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg|jstor=j.ctvd58rxg|s2cid=240840930}}</ref> As Great Britain became the world's leading financial and ] in the 19th century, other states increasingly adopted Britain's monetary system.<ref name=":4" /> | |||
| == Why gold? == | |||
| Due to its rarity and durability, gold has long been used as a ]. The exact nature of the evolution of money varies significantly across time and place, though it is believed by historians that gold's high value for its utility, ], resistance to ], uniformity, and easy divisibility made it useful both as a ] and as a unit of account for stored value of other kinds — in ] a bushel of ] was the unit of account, with a weight in gold used as the token to transport value. Early monetary systems based on grain used gold to represent the stored value. Banking began when gold deposited in a ] could be transferred from one bank account to another by a ] system, or lent at ]. | |||
| The gold standard was largely abandoned during the ] before being re-instated in a limited form as part of the post-] ]. The gold standard was abandoned due to its propensity for volatility, as well as the constraints it imposed on governments: by retaining a ], governments were hamstrung in engaging in ] to, for example, reduce unemployment during economic ]s.<ref name=":04">{{Cite book|last=Eichengreen|first=Barry|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System|date=2019|publisher=Princeton University Press|doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg|jstor=j.ctvd58rxg|isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|s2cid=240840930|edition=3rd}}</ref><ref name=":22">{{Cite book|last=Polanyi|first=Karl|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=848GAQAAIAAJ|title=The Great Transformation|date=1957|publisher=Beacon Press|isbn=978-0-8070-5679-0|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| When used as part of a hard-money system, the function of ] is to reduce the danger of transporting gold, reduce the possibility of ] of coins, and avoid the reduction in circulating medium to hoarding and losses. The early development of paper money was spurred originally by the unreliability of transportation and the dangers of long voyages, as well as by the desire of governments to control or regulate the flow of commerce within their dominion. Money backed by a ] is sometimes called ], and the notes issued are often called ]s, to differentiate them from other forms of paper money. | |||
| According to a 2012 survey of 39 economists, the vast majority (92 percent) agreed that a return to the gold standard would not improve price-stability and employment outcomes,<ref name=":03">{{cite web|date=12 January 2012|title=Gold Standard|url=http://www.igmchicago.org/igm-economic-experts-panel/poll-results?SurveyID=SV_cw1nNUYOXSAKwrq|access-date=27 December 2015|publisher=]}}</ref> and two-thirds of economic historians surveyed in the mid-1990s rejected the idea that the gold standard "was effective in stabilizing prices and moderating business-cycle fluctuations during the nineteenth century."<ref name=":8" /> The consensus view among economists is that the gold standard helped prolong and deepen the ].<ref name=":11" /><ref name=":13" /> Historically, ] were more common during periods under the gold standard while ] were less common.<ref name=":9" /> According to economist ], the gold standard has three benefits that made its use popular during certain historical periods: "its record as a stable nominal anchor; its automaticity; and its role as a credible commitment mechanism."<ref name=":10" /> The gold standard is supported by many followers of the ], ], and some ].<ref name=":12" /> | |||
| Through most of human history, however, ] was the primary circulating medium and major monetary metal. Gold was the metal that was used as an ultimate store of value, and as means of payment when portability was at a premium, particularly for payment of armies. Gold would supplant silver as the basic unit of international trade at various times, including the Islamic golden age, the peak of the Italian trading states during the ], and most prominently during the 19th century. Gold would remain the metal of monetary reserve accounting until the collapse of the ] agreement in ], and remains an important hedge against the actions of central banks and governments, a means of maintaining general liquidity, and as a store of value. | |||
| {{toclimit|3}} | |||
| ==Implementation== | |||
| == Early coinage == | |||
| The United Kingdom slipped into a '''gold specie standard''' in 1717 by over-valuing gold at {{frac|15|1|5}} times its weight in silver. It was unique among nations to use gold in conjunction with clipped, underweight silver shillings, addressed only before the end of the 18th century by the acceptance of gold proxies like token silver coins and banknotes. | |||
| From the more widespread acceptance of paper money in the 19th century emerged the '''gold bullion standard''', a system where gold coins do not circulate, but authorities like ]s agree to exchange circulating currency for gold bullion at a fixed price. First emerging in the late 18th century to regulate exchange between London and Edinburgh, Keynes (1913) noted how such a standard became the predominant means of implementing the gold standard internationally in the 1870s.<ref name="Keynes gold">{{cite wikisource |title=Indian Currency and Finance |author=John Maynard Keynes |chapter=Chapter II: The Gold Exchange Standard |chapter-url=https://en.wikisource.org/Indian_Currency_and_Finance/Chapter_2 |page=21}}</ref> | |||
| The first ] used as a ] was ], before ], when silver ]s were used in ], and it was not until 1500 years later that the first ]age of pure gold was introduced. However, long before this time gold had been the basis of trade contracts in ], and later in ]. Silver remained the most common monetary metal used in ordinary transactions through the 19th century. | |||
| Restricting the free circulation of gold under the Classical Gold Standard period from the 1870s to 1914 was also needed in countries which decided to implement the gold standard while guaranteeing the exchangeability of huge amounts of legacy silver coins into gold at the fixed rate (rather than valuing publicly held silver at its depreciated value). The term '''limping standard''' is often used in countries maintaining significant amounts of silver coin at par with gold, thus an additional element of uncertainty with the currency's value versus gold. The most common silver coins kept at limping standard parity included ], ], ]s, ]s, and U.S. ]s. | |||
| The ] collected ]es in gold and, when conquered by ], this gold became the basis for the gold coinage of his ]. The paying of ] and ] in gold solidified its importance: gold became synonymous with paying for military operations, as mentioned by ] in '']'' two thousand years later. The ] ] two important gold coins: ], which was approximately 7 ]s of gold ]ed with silver, and the smaller ], which weighed 4.4 grams, of which 4.2 was gold. The Roman mints were fantastically active — the Romans minted, and circulated, millions of coins during the course of the ] and the Empire. | |||
| Lastly, countries may implement a '''gold exchange standard''', where the government guarantees a fixed exchange rate, not to a specified amount of gold, but rather to the currency of another country that is under a gold standard. This became the predominant international standard under the ] from 1945 to 1971 by the fixing of world currencies to the ], the only currency after World War II to be on the gold bullion standard. | |||
| After the collapse of the ] and the exhaustion of the ]s in ], the ] continued to mint successor coins to the solidus called the ] or ]. They were forced to mix more and more base metal with the gold until, by the turn of the millennium, the coinage in circulation was only 25% gold by weight. This represented a tremendous drop in real value from the old 95% pure Roman coins. Thus, trade was increasingly conducted via the coinage in use in the ], produced from African gold: the ]. | |||
| ==History before 1873== | |||
| The dinar and ] were gold and silver coins, respectively, originally minted by the Persians. The ]s in the ]ic world adopted these coins, but it is with Caliph ] (]–]) who reformed the currency that the history of the dinar is usually thought to begin. He removed depictions from coins, established standard references to ] on the coins, and fixed ratios of silver to gold. The growth of Islamic power and trade made the dinar the dominant coin from the Western coast of Africa to northern ] until the late ], and it continued to be one of the predominant coins for hundreds of years afterwards. | |||
| {{Hatnote|All references to "dollars" in this section refer to the ], unless otherwise stated.}} | |||
| ===Silver and bimetallic standards until the 19th century=== | |||
| In ], the ] coined their first solid gold coin, the ], which was to become the standard of European coinage for the next 600 years. Other coins, the ], ], ], ], and ], were also introduced at this time by other European states to facilitate growing trade. The ducat, because of Venice's pre-eminent role in trade with the Islamic world and its ability to secure fresh stocks of gold, would remain the standard against which other coins were measured. | |||
| The use of gold as money began around 600 ] in Asia Minor<ref>{{cite web|title = World's Oldest Coin - First Coins|url = http://rg.ancients.info/lion/article.html|website = rg.ancients.info|access-date = 2015-12-05}}</ref> and has been widely accepted ever since,{{sfn|Lipsey|1975|pp=683-702}} together with various other commodities used as ], with those that lose the least value over time becoming the accepted form.<ref>{{harvnb|Bordo|Dittmar|Gavin|2003}} "in a world with two capital goods, the one with the lower depreciation rate emerges as commodity money"</ref> In the early and high ], the ] gold ] or '']'' was used widely throughout Europe and the Mediterranean, but its use waned with the decline of the Byzantine Empire's economic influence.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Lopez|first=Robert Sabatino|title=The Dollar of the Middle Ages|journal=The Journal of Economic History|date=Summer 1951|volume=11|issue=3|pages=209–234|jstor=2113933|doi=10.1017/s0022050700084746|s2cid=153550781 }}</ref> | |||
| Beginning with the conquest of the ] and ], ] had access to stocks of new gold for coinage in addition to silver. The primary Spanish gold unit of account was the ], and the basic coin the 8 escudos piece, or "doubloon", which was originally set at 27.4680 grams of 22 carat (92%) gold, using current measures, and was valued at 16 times the equivalent weight of silver. The wide availability of milled and cob gold coins made it possible for the ] to make gold the only legal tender in 1704. The circulation of Spanish coins would create the unit of account for the United States, the "dollar" based on the Spanish silver real, and Philadelphia's currency market would trade in Spanish colonial coins. | |||
| However, economic systems using gold as the sole currency and unit of account never emerged before the 18th century. For millennia it was silver, not gold, which was the real basis of the domestic economies: the foundation for most money-of-account systems, for payment of wages and salaries, and for most local retail trade.<ref name="moneylec">{{cite web|pages=13–14 sec 5(f)(g)(h)|url=https://www.economics.utoronto.ca/munro5/MONEYLEC.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.economics.utoronto.ca/munro5/MONEYLEC.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=MONEY AND COINAGE IN LATE MEDIEVAL AND EARLY MODERN EUROPE|website=Economics.utoronto.ca|access-date=3 March 2022}}</ref> Gold functioning as currency and unit of account for daily transactions was not possible due to various hindrances which were only solved by tools that emerged in the 19th century, among them: | |||
| == History of the modern gold standard == | |||
| * '''Divisibility:''' Gold as currency was hindered by its small size and rarity, with the dime-sized ] of 3.4 grams representing 7 days' salary for the highest-paid workers. In contrast, coins of silver and ] easily corresponded to daily labor costs and food purchases, making silver more effective as currency and unit of account. In mid-15th century England, most highly paid skilled artisans earned 6d a day (six pence, or 5.4 g silver), and a whole sheep cost 12d. This made the ducat of 40d and the half-ducat of 20d of little use for domestic trade.<ref name="moneylec" /> | |||
| * '''Non-existence of token coinage for gold:''' Sargent and Velde (1997) explained how token coins of copper or billon exchangeable for silver or gold were almost non-existent before the 19th century. Small change was issued at almost full intrinsic value and without conversion provisions into specie. Tokens of little intrinsic value were widely mistrusted, were viewed as a precursor to currency devaluation, and were easily counterfeited in the pre-industrial era. This made the gold standard impossible anywhere with token silver coins; Britain itself only accepted the latter in the 19th century.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.chicagofed.org/publications/working-papers/1997/wp-13|title = The Evolution of Small Change - Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago}}</ref> | |||
| * '''Non-existence of banknotes:''' Banknotes were mistrusted as currency in the first half of the 18th century following France's failed banknote issuance in 1716 under ]. Banknotes only became accepted across Europe with the further maturing of banking institutions, and also as a result of the Napoleonic Wars of the early 19th century. Counterfeiting concerns also applied to banknotes. | |||
| The earliest European currency standards were therefore based on the ], from the denarius of the Roman Empire to the penny (denier) introduced by ] throughout Western Europe, to the ] and the German ] and ] which survived well into the 19th century. Gold functioned as a medium for international trade and high-value transactions, but it generally fluctuated in price versus everyday silver money.<ref name="moneylec" /> | |||
| The adoption of gold standards proceeded gradually. This has led to conflicts between different economic historians as to when the "real" gold standard began. Sir ] included a ratio of gold to silver in his ] of coinage in ] which created a relationship between gold coins and the silver ] which was to be the standard unit of account in the ]; for some historians this marks the beginning of the "gold standard" in ]. However, more generally accepted is that a full gold standard requires that there be one source of notes and ], and that this source is backed by convertibility to gold. Since this was not the case throughout the ], the generally accepted view is that England was not on a gold standard at this time. | |||
| A ] emerged under a silver standard in the process of giving popular gold coins like ]s a fixed value in terms of silver. In light of fluctuating gold–silver ratios in other countries, bimetallic standards were rather unstable and ''de facto'' transformed into a ''parallel bimetallic standard'' (where gold circulates at a floating exchange rate to silver) or reverted to a mono-metallic standard.<ref> | |||
| (See also ]) | |||
| {{cite web|title=Swedish monetary standards in a historical perspective |author=Rodney Edvinsson |pages=33–34 |url=https://www.riksbank.se/globalassets/media/forskning/monetar-statistik/volym1/2.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.riksbank.se/globalassets/media/forskning/monetar-statistik/volym1/2.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live}}</ref> France was the most important country which maintained a bimetallic standard during most of the 19th century. | |||
| ===Gold standard origin in Britain=== | |||
| === The crisis of silver currency and bank notes (]–]) === | |||
| The English ] introduced {{Circa|800 CE}} was initially a silver standard unit worth 20 shillings or 240 silver pennies. The latter initially contained 1.35 g fine silver, reduced by 1601 to 0.464 g (hence giving way to the shilling of 5.57 g fine silver). Hence the pound sterling was originally 324 g fine silver reduced to 111.36 g by 1601. | |||
| The problem of clipped, underweight silver pennies and shillings was a persistent, unresolved issue from the late 17th century to the early 19th century. In 1717 the value of the ] was fixed at 21 shillings, resulting in a gold–silver ratio of 15.2, higher than prevailing ratios in Continental Europe. Great Britain was therefore ''de jure'' under a bimetallic standard with gold serving as the cheaper and more reliable currency compared to clipped silver<ref name=":4" /> (full-weight silver coins did not circulate and went to Europe where 21 shillings fetched over a guinea in gold). Several factors helped extend the British gold standard into the 19th century, namely: | |||
| To understand the adoption of the international gold standard in the late ], it is important to follow the events of the late ] and early 19th. In the late 18th century, wars and trade with ], which sold to Europe, but had little use for European goods, drained silver from the economies of ] and the ]. Coins were struck in smaller and smaller amounts, and there was a proliferation of bank and ]s used as money. | |||
| * The ] of the 18th century supplying significant quantities of gold to Portugal and Britain, with ] also legal tender in Britain. | |||
| * Ongoing trade deficits with China (which sold to Europe but had little use for European goods) drained silver from the economies of most of Europe. Combined with greater confidence in banknotes issued by the ], it opened the way for gold as well as banknotes becoming acceptable currency in lieu of silver. | |||
| * The acceptability of token / subsidiary silver coins as substitutes for gold before the end of the 18th century. Initially issued by the Bank of England and other private companies, permanent issuance of subsidiary coinage from the ] commenced after the ]. | |||
| A proclamation from ] in 1704 introduced the ] to the gold standard; however, it did not result in the wide use of gold currency and the gold standard, given Britain's ] of hoarding gold and silver from its colonies for use at home. Prices were quoted ''de jure'' in gold pounds sterling but were rarely paid in gold; the colonists' ''de facto'' daily medium of exchange and unit of account was predominantly the ].<ref>{{Cite magazine|url=https://time.com/4675303/money-colonial-america-currency-history/|title=Early American Colonists Had a Cash Problem. Here's How They Solved It|magazine=Time}}</ref> {{Crossreference|(Also explained in the ].)}} | |||
| In the ] England suffered a massive shortage of silver coinage, and ceased to mint larger silver coins, issued "token" silver coins and overstruck foreign coins. With the end of the ], England began a massive recoinage program, that created standard gold sovereigns and circulating crowns and half-crowns, and eventually copper farthings in ]. The recoinage of silver in England after a long drought produced a burst of coins: England struck nearly 40 million shillings between ] and ], 17 million half crowns and 1.3 million silver crowns. The ] ] set ] as the date for resumption of convertibility, reached instead by 1821. Throughout the ] small notes were issued by regional banks, which were finally restricted in ], while the ] was allowed to set up regional branches. In ], however, the Bank of England notes were made legal tender, and redemption by other banks was discouraged. In ] the ] established that Bank of England Notes, fully backed by gold, were the legal standard. According to the strict interpretation of the gold standard, this 1844 act marks the establishment of a full gold standard for British money. | |||
| ] or £1 coin was the preeminent circulating gold coin during the classical gold standard period.]] | |||
| The US adopted a silver standard based on the "]" in ]. This was codified in the ] ], and by the ]'s use of the "]" to hold its reserves, as well as establishing a fixed ratio of gold to the ]. This was, in effect, a derivative silver standard, since the bank was not required to keep silver to back all of its currency. This began a long series of attempts for America to create a ] standard for the ], which would continue until the ]. Gold and silver coins were legal tender, including the Spanish ], a silver coin struck in the ]. Because of the huge ] taken on by the US Federal Government to finance the ], silver coins struck by the government left circulation, and in 1806 ] suspended the minting of silver coins. | |||
| Following the Napoleonic Wars, Britain legally moved from the bimetallic to the gold standard in the 19th century in several steps, namely: | |||
| * The 21-shilling guinea was discontinued in favor of the ], or £1 coin, which contained 7.32238 g fine gold | |||
| * The permanent issuance of subsidiary, limited legal tender silver coinage, commencing with the ] | |||
| * The 1819 Act for the Resumption of Cash Payments, which set 1823 as the date for resumption of convertibility of Bank of England banknotes into gold sovereigns, and | |||
| * The ], which institutionalized the gold standard in Britain by establishing a ratio between gold reserves held by the ] versus the banknotes which it could issue, and by significantly curbing the privilege of other British banks to issue banknotes. | |||
| From the second half of the 19th century Britain then introduced its gold standard to Australia, New Zealand, and the ] in the form of circulating gold sovereigns as well as banknotes that were convertible at par into sovereigns or Bank of England banknotes.<ref name=":4" /> Canada introduced its own gold dollar in 1867 at par with the ] and with a fixed exchange rate to the gold sovereign.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bankofcanada.ca/wp-content/uploads/2010/07/dollar_book.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.bankofcanada.ca/wp-content/uploads/2010/07/dollar_book.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|author=James Powell|title=A History of the Canadian Dollar|publisher=Ottawa: Bank of Canada|date=2005|pages= 22–23, 33}}</ref> | |||
| The ] was put on a strict hard money standard, doing business only in gold or silver coin as part of the ] of 1848, which legally separated the accounts of the Federal Government from the ]. However the fixed rate of gold to silver overvalued silver in relation to the demand for gold to trade or borrow from England. The drain of gold in favor of silver led to the search for gold, including the "]" of ]. Following ], silver poured into the US, which traded with other silver nations, and gold moved out. In ] the US reduced the silver weight of coins, to keep them in circulation, and in ] removed legal tender status from foreign coinage. | |||
| ===Effects of the 19th century gold rush=== | |||
| In 1857 the final crisis of the free banking era of international finance began, as American banks suspended payment in silver, rippling through the very young international financial system of ]s. In the United States this collapse was a contributory factor in the ], and in ] the US government suspended payment in gold and silver, effectively ending the attempts to form a silver standard basis for the dollar. Through the ]–] period various attempts to resurrect bi-metallic standards were made, including one based on the gold and silver ], however, with the rapid influx of silver from new deposits, the expectation of scarcity of silver ended. | |||
| ]s were minted as a result of the ].]] | |||
| Up until 1850 only Britain and a few of its colonies were on the gold standard, with the majority of other countries being on the silver standard. France and the United States were two of the more notable countries on the ]. France's actions in maintaining the ] at either 4.5 g fine silver or 0.29032 g fine gold stabilized world gold–silver price ratios close to the French ratio of 15.5 in the first three quarters of the 19th century by offering to mint the cheaper metal in unlimited quantities – gold 20-franc coins whenever the ratio is below 15.5, and silver 5-franc coins whenever the ratio is above 15.5. The ] was also bimetallic ''de jure'' until 1900, worth either 24.0566 g fine silver, or 1.60377 g fine gold (ratio 15.0); the latter revised to 1.50463 g fine gold (ratio 15.99) from 1837 to 1934. The silver dollar was generally the cheaper currency before 1837, while the gold dollar was cheaper between 1837 and 1873. | |||
| The nearly coincidental ] of 1849 and the ] of 1851 significantly increased world gold supplies and the minting of gold francs and dollars as the gold–silver ratio went below 15.5, pushing France and the United States into the gold standard with Great Britain during the 1850s. The benefits of the gold standard were first felt by this larger bloc of countries, with Britain and France being the world's leading financial and industrial powers of the 19th century while the United States was an emerging power. | |||
| The interaction between central banking and currency basis formed the primary source of monetary instability during this period. The combination that produced economic stability was restriction of supply of new notes, a government monopoly on the issuance of notes directly and indirectly, a central bank and a single unit of value. Attempts to evade these conditions produced periodic monetary crisis — as notes devalued, or silver ceased to circulate as a store of value, or there was a depression as governments, demanding ] as payment, drained the circulating medium out of the economy. At the same time there was a dramatically expanded need for ], and large banks were being ]ed in various states, including, by ], ]. The need for a solid basis in monetary affairs would produce a rapid acceptance of the gold standard in the period that followed. | |||
| By the time the gold–silver ratio reverted to 15.5 in the 1860s, this bloc of gold-utilizing countries grew further and provided momentum to an international gold standard before the end of the 19th century: | |||
| === Establishment of the International Gold Standard (]–]) === | |||
| * Portugal and several British colonies commenced with the gold standard in the 1850s and 1860s | |||
| * France was joined by Belgium, Switzerland and Italy in a larger ] based on both the gold and silver ]s. | |||
| * Several ] in the last third of the 19th century began to consider the merits of an international gold standard, albeit with concerns on its impact on the price of silver should several countries make the switch.<ref>{{cite book |title=The History of Currency, 1252–1894 |author=William Arthur Shaw |edition=3rd |publisher=Putnam |year=1896 |pages=275–294 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GrJCAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA275}}</ref> | |||
| ==The international classical gold standard, 1873–1914== | |||
| ] was created as a unified country following the ]; it established the ], went on to a strict gold standard, and used gold mined in ] to expand the ]. Rapidly most other nations followed suit, since gold became a transportable, universal and stable unit of valuation. See ]. | |||
| {{See also|Latin Monetary Union|German gold mark|Central Bank|price–specie flow mechanism}} | |||
| ===Rollout in Europe and the United States=== | |||
| '''Dates of Adoption of a Gold Standard:''' | |||
| The international classical gold standard commenced in 1873 after the ] decided to transition from the silver ] and ] to the ], reflecting the sentiment of the ] in 1867, and utilizing the 5 billion gold francs (worth 4.05 billion marks or 1,451 ]s) in indemnity demanded from France at the end of the ]. This transition done by a large, centrally located European economy also triggered a switch to gold by several European countries in the 1870s and led as well to the suspension of the unlimited minting of silver 5-franc coins in the Latin Monetary Union in 1873.<ref name=":5">{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8 |edition=3rd |pages=14–16 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref> | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] ] (], ], ], ]) | |||
| * ] ] de facto | |||
| * ] ] by monetary Union: ], ] and ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] internally ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * ] ] ]. | |||
| The following countries switched from silver or bimetallic currencies to gold in the following years (Britain is included for completeness): | |||
| Throughout the decade of the ] ]ary and ]ary economics created periodic demands for silver currency. However, such attempts generally failed, and continued the general pressure towards a gold standard. By 1879, only gold coins were accepted through the ], composed of France, Italy, Belgium, Switzerland and later ], even though silver was, in theory, a circulating medium. | |||
| * 1816, ]: one ]: from 111.37 g silver to 7.32238 g gold; ratio 15.21 | |||
| * 1873, ]: one ] or 1{{frac|3|4}} ] of 16.67 g silver, converted to 3 ]s of 3/2.79 = 1.0753 g gold; ratio 15.5 | |||
| * 1873, ] franc: from 4.5 g silver to 9/31 = 0.29032 g gold; ratio 15.5 | |||
| * 1873, ], by the ]: from 24.0566 g silver to 1.50463 g gold; ratio 15.99 | |||
| * 1875, ]: ] of 25.28 g silver, converted to 4 ] (or ]) of 4/2.48 = 1.6129 g gold; ratio 15.67 | |||
| * 1875, Netherlands: the ] from 9.45 g silver to 0.6048 g gold; ratio 15.625. | |||
| * 1881, ]: the ] | |||
| * 1892, ]: the ] of 11.11 g silver, converted to two ] of 2/3.28 = 0.60976 g gold; ratio 18.22 | |||
| * 1897, ]: the ] from 18 g silver to 0.7742 g gold; ratio 23.25. | |||
| The gold standard became the basis for the international monetary system after 1873.<ref name=":3">{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8 |edition=3rd |page=7 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref><ref name=":2">{{Cite book |last=Oatley |first=Thomas |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4GJoDwAAQBAJ|title=International Political Economy: Sixth Edition |date=2019 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-351-03464-7 |page=43 |language=en}}</ref> According to economic historian ], "only then did countries settle on gold as the basis for their money supplies. Only then were pegged exchange rates based on the gold standard firmly established."<ref name=":3" /> Adopting and maintaining a singular monetary arrangement encouraged international trade and investment by stabilizing international price relationships and facilitating foreign borrowing.<ref name=":2" /><ref name="Eichengreen 2019 13">{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|edition=3rd|page=13 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref> The gold standard was not firmly established in non-industrial countries.<ref name=":6">{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8 |edition=3rd |pages=44–46, 71–79 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref> | |||
| By creating a standard unit of account which was easily redeemable, relatively stable in quantity, and verifiable in its purity, the gold standard ushered in a period of dramatically expanded trade between industrializing nations, and "periphery" nations which produced agricultural goods — the so called "bread baskets". This "First Era of ]" was not, however, without its costs. One of the most dramatic was the ], where even as people began to starve it was more profitable to ] food to Britain. The result turned a blight into a humanitarian disaster. ] in his work on ]s theorized that famines are caused by an increase in the price of food, not by food shortage itself, and hence the root cause of trade based famines is an imbalance in wealth between the food exporter and the food importer. | |||
| ===Central banks and the gold exchange standard=== | |||
| At the same time it caused a dramatic fall in ], and a series of long Depressions in the United States and the United Kingdom. This should not be confused with the failure to ] or a slowing of total output of goods. Thus the attempts to produce alternate currencies include the introduction of ]s in Britain in ], later made legal tender during ], and the "]" party in the US, which advocated the slowing of the retirement of paper currency not backed by gold. | |||
| ]s continuing to circulate at par with ]s despite their silver value being less.]] | |||
| As feared by the various international monetary conferences, the switch to gold, combined with record U.S. silver output from the ], plunged the price of silver after 1873 with the gold–silver ratio climbing to historic highs of 18 by 1880. Most of continental Europe made the conscious decision to move to the gold standard while leaving the mass of legacy (and erstwhile depreciated) silver coins remaining unlimited legal tender and convertible at face value for new gold currency. The term '''limping standard''' was used to describe currencies whose nations' commitment to the gold standard was put into doubt by the huge mass of silver coins still tendered for payment, the most numerous of which were ], ], ]s and American ]s.<ref name="limping">{{Cite journal |last=Conant |first=Charles A. |date=1903 |title=The Future of the Limping Standard |journal=Political Science Quarterly |volume=18 |issue=2 |pages=216–237 |doi=10.2307/2140681 |jstor=2140681 |issn=0032-3195}}</ref> | |||
| Britain's original gold specie standard with gold in circulation was not feasible anymore with the rest of Continental Europe also switching to gold. The problem of scarce gold and legacy silver coins was only resolved by national ]s taking over the replacement of silver with national bank notes and token coins, centralizing the nation's supply of scarce gold, providing for reserve assets to guarantee convertibility of legacy silver coins, and allowing the conversion of banknotes into gold bullion or other gold-standard currencies solely for external purchases. This system is known as either a '''gold bullion standard''' whenever gold bars are offered, or a '''gold exchange standard''' whenever other gold-convertible currencies are offered. | |||
| By encouraging industrial specialization, industrializing countries grew rapidly in population, and therefore needed sources of agricultural goods. The need for cheap agricultural imports, in turn, further pressured states to reduce ]s and other ]s, so as to be able to exchange with the industrial nations for capital goods, such as factory machinery, which were needed to industrialize in turn. Eventually this pressured taxation systems, and pushed nations towards income and sales taxes, and away from tariffs. It also produced a constant downward pressure on ]s, which contributed to the "agony of industrialization". The role of the gold standard in this process remains hotly debated, with new articles being published attempting to trace the interconnections between monetary basis, wages and ]s. | |||
| ] referred to both standards above as simply the gold exchange standard in his 1913 book ''Indian Currency and Finance''. He described this as the predominant form of the international gold standard before the First World War, that a gold standard was generally impossible to implement before the 19th century due to the absence of recently developed tools (like central banking institutions, banknotes, and token currencies), and that a gold exchange standard was even superior to Britain's gold specie standard with gold in circulation. As discussed by Keynes:<ref name="Keynes gold" /> | |||
| By the ] in the United States, a reaction against the gold standard had emerged centered in the ] and ]. Many farmers began to view the scarcity of gold, especially outside the banking centers of the East, as an instrument to allow Eastern bankers to instigate credit squeezes that would force western farmers into widespread debt, leading to a consolidation of western property into the hands of the centralized banks. The formation of the ] in ] specifically centered around the use of "easy money" that was not backed by gold and which could flow more easily through regional and rural banks, providing farmers access to needed credit. Opposition to the gold standard during this era reached its climax with the ] of ] ] of ]. Bryan argued against the gold standard in his ] in ], comparing the gold standard (and specifically its effects on western farmers) to the ] worn by ] at his ]. After being defeated in 1896, Bryan ran and lost again in ] and ], each time carrying mostly Southern and Great Plains states. | |||
| {{blockquote|The Gold-Exchange Standard arises out of the discovery that, so long as gold is available for payments of international indebtedness at an approximately constant rate in terms of the national currency, it is a matter of comparative indifference whether it actually forms the national currency ... The Gold-Exchange Standard may be said to exist when gold does not circulate in a country to an appreciable extent, when the local currency is not necessarily redeemable in gold, but when the Government or Central Bank makes arrangements for the provision of foreign remittances in gold at a fixed maximum rate in terms of the local currency, the reserves necessary to provide these remittances being kept to a considerable extent abroad. | |||
| The key change in this period was the adoption of a monetary policy to raise interest rates in response to gold outflows, or to maintain large stocks of gold in the reserves of the central bank. This policy created a credibility of commitment to the gold standard. According to ] and ], this can be seen from the relationship between the Bank of England rate, and the flow between the pound and the dollar, mark and franc. From 1889 through 1908, the pound maintained a direct bank rate rule relationship with the dollar 99% of the time, and 92% of the time with the mark. Thus, according to the theory of gold standard monetary dynamics, the key to this credibility was the willingness of the Bank of England to make adjustments to the discount rate to stabilize sterling to other currencies in the gold, or de facto gold, standard world, during the peak period of the gold standard composed of 360 months, the Bank of England bank rate was adjusted over 200 times in response to gold flows, a rate of change higher than current central banks. | |||
| Its theoretical advantages were first set forth by Ricardo (i.e. ], 1824) at the time of the Bullionist Controversy. He laid it down that a currency is in its most perfect state when it consists of a cheap material, but having an equal value with the gold it professes to represent; and he suggested that convertibility for the purposes of the foreign exchanges should be ensured by the tendering on demand of gold bars (not coin) in exchange for notes, so that gold might be available for purposes of export only, and would be prevented from entering into the internal circulation of the country. | |||
| === Gold Standard from peak to crisis (]–]) === | |||
| The first crude attempt in recent times at establishing a standard of this type was made by Holland. The free coinage of silver was suspended in 1877. But the currency continued to consist mainly of silver and paper. It has been maintained since that date at a constant value in terms of gold by the Bank's regularly providing gold when it is required for export and by its using its authority at the same time for restricting so far as possible the use of gold at home. To make this policy possible, the Bank of Holland has kept a reserve, of a moderate and economical amount, partly in gold, partly in foreign bills. | |||
| By ] the need for a ] had become clear to most major ]s. The importance of central banking to the financial system was proven largely by examples such as the ] ] of ] by the Bank of England. Barings had been threatened by imminent ]. Only the United States still lacked a central banking system. | |||
| Since the Indian system (gold exchange standard implemented in 1893) has been perfected and its provisions generally known, it has been widely imitated both in Asia and elsewhere ... Something similar has existed in Java under Dutch influences for many years ... The Gold-Exchange Standard is the only possible means of bringing China onto a gold basis ...}} | |||
| There had been occasional panics since the end of the depressions of the ] and ] which some attributed to the centralization of production and banking. The increased rate of industrialization and imperial colonization, however, had also served to push living standards higher. Peace and prosperity reigned through most of Europe, albeit with growing agitation in favor of ] and ] because of the extremely harsh conditions of early industrialization. | |||
| The classical gold standard of the late 19th century was therefore not merely a superficial switch from circulating silver to circulating gold. The bulk of silver currency was actually replaced by banknotes and token currency whose gold value was guaranteed by gold bullion and other reserve assets held inside central banks. In turn, the gold exchange standard was just one step away from modern ] with banknotes issued by central banks, and whose value is secured by the bank's reserve assets, but whose exchange value is determined by the central bank's ] objectives on its purchasing power in lieu of a fixed equivalence to gold. | |||
| This came to an abrupt halt with the outbreak of ]. ] was almost immediately forced to take steps that would lead to its gradually leaving its gold standard, ending convertibility to Bank of England notes starting in ]. By the end of the war England was on a series of ] regulations, which monetized Postal Money Orders and ]s. The need for larger and larger engines of war, including ]s and ]s, created ]. Nations responded by printing more money than could be redeemed in gold, effectively betting on winning the war and redeeming out of reparations, as Germany had in the ]. The US and the UK both instituted a variety of measures to control the movement of gold, and to reform the banking system, but both were forced to suspend use of the gold standard by the costs of the war. The ] instituted punitive reparations on Germany and the defeated ], and France hoped to use these to rebuild her shattered economy, as much of the war had been fought on French soil. Germany, facing the prospect of yielding much of her gold in reparations, could no longer coin gold "Reichsmarks", and moved to paper currency. The series of arrangements to prop up the gold standard in the 1920s would constitute a book length study unto themselves, with the ] superseded by the ]. In effect the US, as the most persistent positive ] nation, loaned the money to Germany to pay off France, so that France could pay off the United States. After the war, the ] suffered from ] and introduced "]s", an ], to halt it. These were withdrawn from circulation in favor of a restored gold Reichsmark in ]. | |||
| ===Rollout outside Europe=== | |||
| In the UK the ] was returned to the gold standard in ], by the somewhat reluctant ] ], on the advice of conservative economists at the time. Although a higher gold price and significant inflation had followed the WWI ending of the gold standard, Churchill returned to the standard at the pre-war gold price. For five years prior to 1925 the gold price was managed downward to the pre-war level, meaning a significant ] was forced onto the economy. | |||
| The final chapter of the classical gold standard ending in 1914 saw the gold exchange standard extended to many Asian countries by fixing the value of local currencies to gold or to the gold standard currency of a Western colonial power. The ] guilder was the first Asian currency pegged to gold in 1875 via a gold exchange standard which maintained its parity with the gold ]. | |||
| Various ] were called up until 1892, with various countries actually pledging to maintain the limping standard of freely circulating legacy silver coins in order to prevent the further deterioration of the gold–silver ratio which reached 20 in the 1880s.<ref name="limping" /> After 1890 however, silver's price decline could not be prevented further and the gold–silver ratio rose sharply above 30. | |||
| ] was one economist who argued against the adoption of the pre-war gold price believing that the rate of conversion was far too high and that the monetary basis would collapse. He called the gold standard "that barbarous relic". This deflation reached across the remnants of the ] everywhere the ] was still used as the primary unit of account. In the UK the standard was again abandoned in ]. ] abandoned the gold standard in ], the US in ], and other nations were, to one degree or another, forced off the gold standard. | |||
| In 1893 the ] of 10.69 g fine silver was fixed at 16 British pence (or £1 = 15 rupees; gold–silver ratio 21.9), with legacy silver rupees remaining legal tender. In 1906 the ] of 24.26 g silver was fixed at 28 pence (or £1 = 8{{frac|4|7}} dollars; ratio 28.4). | |||
| As part of this process, many nations, including the US, banned ] of large gold stocks. Instead, citizens were required to hold only legal tender in the form of central bank notes. While this move was argued for under national emergency, it was controversial at the time, and there are still those who regard it as an illegal and unconstitutional usurpation of ]. | |||
| Nearly similar gold standards were implemented in Japan in 1897, in the Philippines in 1903, and in Mexico in 1905 when the previous ] or ] of 24.26 g silver was redefined to approximately 0.75 g gold or half a ] (ratio 32.3). Japan gained the needed gold reserves after the Sino-Japanese War of 1894–1895. For Japan, moving to gold was considered vital for gaining access to Western capital markets.<ref name="ease">{{Cite book |first=Mark |last=Metzler |title=Lever of Empire: The International Gold Standard and the Crisis of Liberalism in Prewar Japan |publisher=University of California Press |location=Berkeley |year=2006 |url=http://eh.net/bookreviews/library/1166 |isbn=978-0-520-24420-7 |access-date=2009-11-26 |archive-date=2009-11-03 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091103141127/http://eh.net/bookreviews/library/1166 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| === The Depression and Second World War (]–]) === | |||
| ==="Rules of the Game"=== | |||
| In 1933 the ] marked the death of the international gold standard as it had developed to that point in time. While the United Kingdom and the United States desired an eventual return to the Gold Standard, with President ] saying that a return to international stability "must be based on gold" — neither was willing to do so immediately. France and Italy both sent delegations insisting on an immediate return to a fully convertible international gold standard. A proposal was floated to stabilize exchange rates between France, Britain and the United States based on a system of drawing rights, but this too collapsed. | |||
| In the 1920s ] retrospectively developed the phrase "rules of the game" to describe how central banks would ideally implement a gold standard during the prewar classical era, assuming international trade flows followed the ideal ]. Violations of the "rules" actually observed during the classical gold standard era from 1873 to 1914, however, reveal how much more powerful national central banks actually are in influencing price levels and specie flows, compared to the "self-correcting" flows predicted by the price-specie flow mechanism.<ref name="GSW">{{Cite web|quote=How the Gold Standard Worked:<br/><br/>In theory, international settlement in gold meant that the international monetary system based on the Gold Standard was self-correcting.<br/><br/> ... although in practice it was more complex. ... The main tool was the discount rate (...) which would in turn influence market interest rates. A rise in interest rates would speed up the adjustment process through two channels. First, it would make borrowing more expensive, reducing investment spending and domestic demand, which in turn would put downward pressure on domestic prices, ... Second, higher interest rates would attract money from abroad, ... The central bank could also directly affect the amount of money in circulation by buying or selling domestic assets ... <br/><br/>The use of such methods meant that any correction of an economic imbalance would be accelerated and normally it would not be necessary to wait for the point at which substantial quantities of gold needed to be transported from one country to another. |url=https://www.gold.org/about-gold/history-of-gold/the-gold-standard |access-date=2022-04-16 |title=The Classical Gold Standard |work=World Gold Council |via=www.gold.org}}</ref> | |||
| Keynes premised the "rules of the game" on best practices of central banks to implement the pre-1914 international gold standard, namely: | |||
| The central point at issue was what value the gold standard should take. ], the ], was instructed to require that reflation of prices occur before returning to the Gold Standard. There was also deep suspicion that Britain would use favorable trading arrangements in the ] to avoid fiscal discipline. Since the collapse of the Gold Standard was attributed, at the time, to the US and the UK trying to maintain an artificially low peg to gold, agreement became impossible. Another fundamental disagreement was the role of ]s in the collapse of the gold standard, with the liberal government of the United States taking the position that the actions of the previous American Administration had exacerbated the crisis by raising tariff barriers. | |||
| * To substitute gold with fiat currency in circulation, so that gold reserves may be centralized | |||
| * To actually allow a prudently determined ratio of gold reserves to fiat currency of less than 100%, with the difference made up by other loans and invested assets, such reserve ratio amounts consistent with ] practices | |||
| * To exchange circulating currency for gold or other foreign currencies at a fixed gold price, and to freely permit gold imports and exports | |||
| * Central banks were actually allowed modest margins in exchange rates to reflect gold delivery costs while still adhering to the gold standard. To illustrate this point, France may ideally allow the ] (worth 25.22 francs based on ratios of their gold content) to trade between so-called ''gold points'' of 25.02F to 25.42F (plus or minus an assumed 0.20F/£ in gold delivery costs). France prevents sterling from climbing above 25.42F by delivering gold worth 25.22F or £1 (spending 0.20F for delivery), and from falling below 25.02F by the reverse process of ordering £1 in gold worth 25.22F in France (and again, minus 0.20F in costs). | |||
| * Finally, central banks were authorized to suspend the gold standard in times of war until it could be restored again as the contingency subsides. | |||
| Central banks were also expected to maintain the gold standard on the ideal assumption of international trade operating under the ] proposed by economist ] wherein: | |||
| In the years that followed nations pursued ] trading agreements, and by ], the economic policies of most Western nations were increasingly dominated by the growing realization that a global conflict was highly likely, or even inevitable. During the ] the austerity measures taken to restabilize the ] had cut military expenditures drastically, but with the arming of the ], war in ], and fears of the ] exporting ], the priority shifted toward armament, and away from re-establishing a gold standard. The last gasp of the 19th century gold standard came when the attempt to balance the ] in ] led to the "]". Even such gold advocates as Roosevelt's budget director conceded that until it was possible to balance the budget, a gold standard would be impossible. | |||
| * Countries which exported more goods would receive specie (gold or silver) inflows, at the expense of countries which imported those goods. | |||
| * More specie in exporting countries will result in higher price levels there, and conversely in lower price levels amongst countries spending their specie. | |||
| * Price disparities will self-correct as lower prices in specie-deficient will attract spending from specie-rich countries, until price levels in both places equalize again. | |||
| In practice, however, specie flows during the classical gold standard era failed to exhibit the self-corrective behavior described above. Gold finding its way back from surplus to deficit countries to exploit price differences was a painfully slow process, and central banks found it far more effective to raise or lower domestic price levels by lowering or raising domestic interest rates. High price level countries may raise interest rates to lower domestic demand and prices, but it may also trigger gold inflows from investors – contradicting the premise that gold will flow out of countries with high price levels. Developed economies deciding to buy or sell domestic assets to international investors also turned out to be more effective in influencing gold flows than the self-correcting mechanism predicted by Hume.<ref name="GSW" /> | |||
| ], as part of its ] against various minorities including ], the physically or mentally handicapped, ] citizens, ], and ]s, used the gold looted from them to finance its war effort. Some ]s were among the international banks who ended up handling gold deposits from this source. The gold was then deposited with the ] and used as the basis for notes to be issued which were to be accepted as currency. The Reich then instituted wage and price controls, backed by internment in prison camps, to prevent this "Mefo financing" from producing hyper-inflation. | |||
| Another set of violations to the "rules of the game" involved central banks not intervening in a timely manner even as exchange rates went outside the "gold points" (in the example above, cases existed of the pound climbing above 25.42 francs or falling below 25.02 francs). Central banks were found to pursue other objectives other than fixed exchange rates to gold (like e.g., lower domestic prices, or stopping huge gold outflows), though such behavior is limited by public credibility on their adherence to the gold standard. Keynes described such violations occurring before 1913 by French banks limiting gold payouts to 200 francs per head and charging a 1% premium, and by the German Reichsbank partially suspending free payment in gold, though "covertly and with shame".<ref name="Keynes gold" /> | |||
| During the ]–] period, Britain depleted much of its gold stock in purchases of munitions and weaponry on a "cash and carry" basis from the US and other nations. This depletion of Britain's reserve signalled to Winston Churchill that returning to a pre-war style gold standard was impractical; instead, John Maynard Keynes, who had argued against such a gold standard, became increasingly influential: his proposals, a more wide ranging version of the "stability pact" style gold standard, would find expression in the ]. | |||
| Some countries had limited success in implementing the gold standard even while disregarding such "rules of the game" in its pursuit of other monetary policy objectives. Inside the ], the ] and the ] traded outside typical gold-standard levels of 25.02–25.42F/£ for extended periods of time:<ref>{{cite book |title=European Currency and Finance |publisher=United States Congress Commission of Gold and Silver Inquiry |first=John |last=Parke Young |year=1925 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ytFEAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA253}} Vol. I: Italy, p. 347; Vol. II: Spain p. 223.</ref> | |||
| === Post-war International Gold Standard (]–]) === | |||
| * Italy tolerated in 1866 the issuance of {{lang|it|corso forzoso}} (forced legal tender paper currency) worth less than the Latin Monetary Union franc. It also flooded the Union with low-valued subsidiary silver coins worth less than the franc. For the rest of the 19th century the ] traded at a fluctuating discount versus the standard gold franc. | |||
| * In 1883 the ] went off the gold standard and traded below parity with the gold ]. However, as the free minting of silver was suspended to the general public, the peseta had a floating exchange rate between the value of the gold franc and the silver franc. The Spanish government captured all profits from minting {{lang|es|duros}} (5-peseta coins) out of silver bought for less than 5 ptas. While total issuance was limited to prevent the peseta from falling below the silver franc, the abundance of {{lang|es|duros}} in circulation prevented the peseta from returning at par with the gold franc. Spain's system where the silver {{lang|es|duro}} traded at a premium above its metallic value due to relative scarcity is called the ''fiduciary standard'' and was similarly implemented in the Philippines and other Spanish colonies in the end of the 19th century.<ref>{{cite journal |page=31 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231884087 |title=The Philippine currency system during the American colonial period: Transformation from the gold exchange standard to the dollar exchange standard |date=January 2010 |journal=International Journal of Asian Studies |volume=7 |issue=1 |doi=10.1017/S1479591409990428 |first=Yoshiko |last=Nagano |s2cid=154276782 }}</ref> | |||
| ==In the United States== | |||
| ''This is discussed in the article on ]'' | |||
| {{See also|United States dollar}} | |||
| <div style="width:auto;margin:0 auto;">], was steady until the collapse of the ] in the mid-1970s.|left]]</div> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| == |
===Inception=== | ||
| In the 1780s, ], ] and ] recommended to Congress that a decimal currency system be adopted by the United States. The initial recommendation in 1785 was a ] based on the ] (finalized at 371.25 grains or 24.0566 g fine silver), but in the final version of the ] Hamilton's recommendation to include a ] was also approved, containing 247.5 grains (16.0377 g) fine gold. Hamilton therefore put the ] on a ] with a gold–silver ratio of 15.0.{{sfn|Walton|Rockoff|2010}} | |||
| American-issued dollars and cents remained less common in circulation than Spanish dollars and ] for the next six decades until foreign currency was demonetized in 1857. $10 gold eagles were exported to Europe where it could fetch over ten Spanish dollars due to their higher gold ratio of 15.5. American silver dollars also compared favorably with Spanish dollars and were easily used for overseas purchases. In 1806 President Jefferson suspended the minting of exportable gold coins and silver dollars in order to divert the ]'s limited resources into fractional coins which stayed in circulation. | |||
| The essential features of the gold standard in theory rest on the idea that ] is caused by an increase in the ], an idea advocated by ], and that uncertainty over the future purchasing power of money depresses ] and leads to reduced trade and capital investment. The central thesis of the gold standard is that removing uncertainty, friction between kinds of currency, and possible limitations in future trading partners will dramatically benefit an economy, by expanding both the market for its own goods, the solidity of its credit, and the markets from which its consumers may purchase goods. In much of gold standard theory, the benefits of enforcing ] and ] discipline on the government are central to the benefits obtained, advocates of the gold standard often believe that governments are almost entirely destructive of economic activity, and that a gold standard, by reducing their ability to intervene in markets, will increase personal liberty and economic vitality. | |||
| ===Pre-Civil War=== | |||
| === Differing definitions of "gold standard" === | |||
| The United States also embarked on establishing a national bank with the ] in 1791 and the ] in 1816. In 1836, President ] failed to extend the Second Bank's charter, reflecting his sentiments against banking institutions as well as his preference for the use of gold coins for large payments rather than privately issued banknotes. The return of gold could only be possible by reducing the dollar's gold equivalence, and in the ] the gold–silver ratio was increased to 16.0 (ratio finalized in 1837 to 15.99 when the fine gold content of the $10 eagle was set at 232.2 grains or 15.0463 g). | |||
| ] in 1848 and later in Australia lowered the gold price relative to silver; this drove silver money from circulation because it was worth more in the market than as money.{{sfn|Elwell|2011}} Passage of the Independent Treasury Act of 1848 placed the U.S. on a strict hard-money standard. Doing business with the American government required gold or silver coins. | |||
| If the monetary authority holds sufficient gold to convert all circulating money, then this is known as a 100% reserve gold standard, or a full gold standard. Some believe there is no other form of gold standard, since on any "partial" gold standard the value of circulating representative paper in a free economy will always reflect the faith that the market has in that note being redeemable for gold. Others, such as some modern advocates of ] contest that so long as gold is the accepted unit of account then it is a true gold standard. | |||
| Government accounts were legally separated from the banking system. However, the mint ratio (the fixed exchange rate between gold and silver at the mint) continued to overvalue gold. In 1853, silver coins 50 cents and below were reduced in silver content and cannot be requested for minting by the general public (only the U.S. government can request for it). In 1857 the legal tender status of Spanish dollars and other foreign coinage was repealed. In 1857 the final crisis of the free banking era began as American banks suspended payment in silver, with ripples through the developing international financial system. | |||
| In an internal gold-standard system, gold coins circulate as legal tender or paper money is freely convertible into gold at a fixed price. | |||
| ===Post-Civil War=== | |||
| In an international gold-standard system, which may exist in the absence of any internal gold standard, gold or a currency that is convertible into gold at a fixed price is used as a means of making international payments. Under such a system, when exchange rates rise above or fall below the fixed mint rate by more than the cost of shipping gold from one country to another, large inflows or outflows occur until the rates return to the official level. International gold standards often limit which entities have the right to redeem currency for gold. Under the Bretton Woods system, these were called "SDRs" for ]. | |||
| ] ran for president on the basis of the gold standard.]] | |||
| Due to the inflationary finance measures undertaken to help pay for the U.S. ], the government found it difficult to pay its obligations in gold or silver and suspended payments of obligations not legally specified in specie (gold bonds); this led banks to suspend the conversion of bank liabilities (bank notes and deposits) into specie. In 1862 paper money was made legal tender. It was a ] (not convertible on demand at a fixed rate into specie). These notes came to be called "]".{{sfn|Elwell|2011}} | |||
| After the Civil War, Congress wanted to reestablish the metallic standard at pre-war rates. The market price of gold in greenbacks was above the pre-war fixed price ($20.67 per ounce of gold) requiring ] to achieve the pre-war price. This was accomplished by growing the stock of money less rapidly than real output. By 1879 the market price of the greenback matched the mint price of gold, and according to Barry Eichengreen, the United States was effectively on the gold standard that year.<ref name=":5"/> | |||
| === Effects of gold-backed currency === | |||
| The ] (also known as the Crime of ‘73) suspended the minting of the standard silver dollar (of 412.5 grains, 90% fine), the only fully legal tender coin that individuals could convert silver bullion into in unlimited (or ]) quantities, and right at the onset of the silver rush from the Comstock Lode in the 1870s. Political agitation over the inability of silver miners to monetize their produce resulted in the ] of 1878 and ] of 1890 which made compulsory the minting of significant quantities of the silver ]. | |||
| The commitment to maintain gold convertibility tightly restrains credit creation. Credit creation by banking entities under a gold standard threatens the convertibility of the notes they have issued, and consequently leads to undesirable gold outflows from that bank. The result of a failure of confidence produces a run on the specie basis, which is generally responded to by the bankers suspending specie payments. Hence, notes circulating in any "partial" gold standard will either be redeemed for their ] of gold (which would be higher than its ]) — this constitutes a bank "run"; or the ] of such notes will be viewed as less than a gold coin representing the same amount. | |||
| With the resumption of convertibility on June 30, 1879, the government again paid its debts in gold, accepted greenbacks for customs and redeemed greenbacks on demand in gold. While greenbacks made suitable substitutes for gold coins, American implementation of the gold standard was hobbled by the continued over-issuance of silver dollars and ] emanating from political pressures. Lack of public confidence in the ubiquitous silver currency resulted in a run on U.S. gold reserves during the ]. | |||
| In the international gold standard imbalances in ] were rectified by requiring nations to pay accounts in gold. A country in deficit would have to pay its debts in gold thus depleting gold reserves and would therefore have to reduce its money supply. This would cause prices to deflate, reducing economic activity and, consequently, demand would fall. The resulting fall in demand would reduce imports; thus theoretically the deficit would be rectified when the nation was again importing less than it exported. This led to a constant pressure to close economies in the face of currency drains in what critics called "beggar thy neighbor" policies. Such ] gold standard systems showed periodic imbalances which had to be corrected by rapid falls in output. | |||
| During the latter part of the nineteenth century the use of silver and a return to the bimetallic standard were recurrent political issues, raised especially by ], the ] and the ] movement. In 1900 the gold dollar was declared the standard unit of account and a gold reserve for government issued paper notes was established. Greenbacks, silver certificates, and silver dollars continued to be legal tender, all redeemable in gold.{{sfn|Elwell|2011}} | |||
| In practice however this could seriously destabilize the economy of countries which ran a ], because people tended to make a run on the bank to retrieve their money before gold reserves were exported, thus causing banks to collapse and wiping out savings. ]s and failures were a common feature of life during the period when the gold standard was the established economic system. It also created a counter-cyclical effect, as governments taxed trade, they accumulated gold and silver coin, which reduced the monetary base for the private economy. This paradox lead to "money droughts" and inflation, as governments taxed, often to pay for wars, and paid in coin, while the velocity of money decreased in the private economy as individuals hedged against the uncertain political situation by hoarding gold. Each attempt to introduce paper money was met, sooner or later, with either over-printing of money and the resulting collapse of the "fiat" money, including paper francs, continentals printed by the pre-Constitutional US Congress and various "bubbles". Or it would create the demand by the government to be paid only in specie, which devalued the existing paper money. | |||
| ===Fluctuations in the U.S. gold stock, 1862–1877=== | |||
| The gold standard, in theory, limits the power of governments to cause price inflation by excessive issue of paper currency, although there is evidence that before World War I monetary authorities did not expand or contract the supply of money when the country incurred a gold outflow. It is also supposed to create certainty in international trade by providing a fixed pattern of exchange rates. The gold standard in fact is deflationary, as the rate of growth of economies generally outpaces the growth in gold reserves. This, after the inflationary silver standards of the 1700s was regarded as a welcome relief, and an inducement to trade. However by the late 19th century, agitation against the gold standard drove political movements in most industrialized nations for some form of silver, or even paper based, currency. | |||
| {| class="wikitable floatright" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan=2|US gold stock | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1862 || 59 tons | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1866 || 81 tons | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1875 || 50 tons | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1878 || 78 tons | |||
| |} | |||
| The U.S. had a gold stock of {{convert|1.9|e6ozt|t|abbr=unit}} in 1862. Stocks rose to {{convert|2.6|e6ozt|t|abbr=unit}} in 1866, declined in 1875 to {{convert|1.6|e6ozt|t|abbr=unit}} and rose to {{convert|2.5|e6ozt|t|abbr=unit}} in 1878. Net exports did not mirror that pattern. In the decade before the Civil War net exports were roughly constant; postwar they varied erratically around pre-war levels but fell significantly in 1877 and became negative in 1878 and 1879. The net import of gold meant that the foreign demand for American currency to purchase goods, services, and investments exceeded the corresponding American demands for foreign currencies. In the final years of the greenback period (1862–1879), gold production increased while gold exports decreased. The decrease in gold exports was considered by some to be a result of changing monetary conditions. The demands for gold during this period were as a speculative vehicle, and for its primary use in the foreign exchange markets financing international trade. The major effect of the increase in gold demand by the public and Treasury was to reduce exports of gold and increase the Greenback price of gold relative to purchasing power.{{sfn|Friedman|Schwartz|1963|p=79}} | |||
| ==Abandonment of the gold standard== | |||
| Under the classical international gold standard, disturbances in the price level in one country would be wholly or partly offset by an automatic balance-of-payment adjustment mechanism called the '''price-specie-flow mechanism'''. (''Specie'' refers to gold coins.) The steps in this mechanism are first: when the price of a good drops, because of oversupply, capital improvement, drop in input costs or competition, buyers will prefer that good over others. Because the stabilization of currencies to gold, buyers within the gold based economies will preferentially buy the lowest priced good, and gold will flow into the most efficient economies. This flow of gold into the more productive economy will then increase the money supply, and produce sufficient inflationary pressure to offset the original drop in prices in the more productive economy, and would reduce the circulating specie in the less productive economies, forcing prices down until equilibrium was restored. | |||
| === Impact of World War I === | |||
| Central banks, in order to limit gold outflows, would reinforce this by raising interest rates, so as to bring prices back into international equilibrium more quickly. In theory, as long as nations remained on the gold standard, there would be no sustained period of either high inflation, or uncontrolled deflation. Since, at the time, it was believed that markets internally always clear (See ]), and that deflation would alter the price of capital first, it meant that this would reduce the price of capital, and allow more growth as well as long term price stability. | |||
| Governments with insufficient tax revenue suspended ] repeatedly in the 19th century. The real test, however, came in the form of ], a test which "it failed utterly" according to economist ].{{sfn|Lipsey|1975|pp=683-702}} The gold specie standard came to an end in the United Kingdom and the rest of the British Empire with the outbreak of World War I.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.parliament.uk/business/publications/research/olympic-britain/the-economy/small-change/|title=Small change|website=Parliament.uk|language=en|access-date=2019-02-09}}</ref> | |||
| By the end of 1913, the classical gold standard was at its peak, but World War I caused many countries to suspend or abandon it.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Nicholson, J. S.|author-link=Joseph Shield Nicholson |title=The Abandonment of the Gold Standard|journal=The Quarterly Review|date=April 1915|volume=223 |pages=409–423|url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=umn.31951d001510207;view=1up;seq=431}}</ref> According to Lawrence Officer the main cause of the gold standard's failure to resume its previous position after World War I was "the Bank of England's precarious liquidity position and the gold-exchange standard". A ] caused Britain to impose ] that fatally weakened the standard; convertibility was not legally suspended, but gold prices no longer played the role that they did before.<ref>{{cite web |last=Officer |first=Lawrence |title=Gold Standard |website=EH.Net Encyclopedia |editor=Robert Whaples |date=March 26, 2008 |url=http://eh.net/encyclopedia/gold-standard/}}</ref> In financing the war and abandoning gold, many of the belligerents suffered drastic ]s. Price levels doubled in the U.S. and Britain, tripled in France and quadrupled in Italy. Exchange rates changed less, even though European inflation rates were more severe than America's. This meant that the costs of American goods decreased relative to those in Europe. Between August 1914 and spring of 1915, the dollar value of U.S. exports tripled, and its trade surplus exceeded $1 billion for the first time.{{sfn|Eichengreen|1995}} | |||
| ===Advocates of a renewed gold standard === | |||
| Thus, the internal gold standard is supported by anti-government economists, including extreme ], ], followers of the ] and even many proponents of ]. Much of the support for a gold standard is related to a distrust of ]s and governments, as a gold standard removes the ability of a government to manage the value of money, even though, historically, the establishment of a gold standard was part of establishing a national banking system, and generally a central bank. | |||
| Ultimately, the system could not deal quickly enough with the large ]; this was previously attributed to downward wage rigidity brought about by the advent of ] but is now considered as an inherent fault of the system that arose under the pressures of war and rapid technological change. In any case, prices had not reached equilibrium by the time of the ], which served to kill off the system completely.{{sfn|Lipsey|1975|pp=683–702}} | |||
| The international gold standard still has advocates who wish to return to a ]—style system, in order to reduce the volatility of currencies, but the unworkability of Bretton Woods, due to its government-ordained exchange ratio, has allowed the followers of Austrian economists ], ] and ] to foster the idea of a total emancipation of the gold price from a State-decreed rate of exchange and an end to government monopoly on the issuance of gold currency. | |||
| For example, ] had gone off the gold standard in 1914 and could not effectively return to it because ] had cost it much of its gold reserves. During the ] the German central bank (]) issued enormous sums of non-convertible marks to support workers who were on strike against the French occupation and to buy foreign currency for reparations; this led to the ] and the decimation of the German middle class. | |||
| Many nations back their currencies in part with gold reserves, using these not to redeem notes, but as a store of value to sell in case their currency is attacked or rapidly devalues. Gold advocates claim that this extra step would no longer be necessary since the currency itself would have its own intrinsic store of value. A Gold Standard then is generally promoted by those who regard a stable store of value as the most important element to business confidence. | |||
| The U.S. did not suspend the gold standard during the war. The newly created ] intervened in currency markets and sold bonds to "]" some of the gold imports that would have otherwise increased the stock of money.{{citation needed|date=September 2014}} By 1927 many countries had returned to the gold standard.{{sfn|Elwell|2011}} As a result of World War I the United States, which had been a net debtor country, had become a net creditor by 1919.<ref>Drummond, Ian M. (1987). ''The Gold Standard and the International Monetary System 1900–1939''. Macmillan Education.</ref> | |||
| It is generally opposed by the vast majority of governments and economists, because the gold standard has frequently been shown to provide insufficient flexibility in the ] and in fiscal policy, because the supply of newly mined gold is finite and must be carefully husbanded and accounted for. | |||
| === Interwar period === | |||
| A single country may also not be able to isolate its economy from depression or inflation in the rest of the world. In addition, the process of adjustment for a country with a payments deficit can be long and painful whenever an increase in unemployment or decline in the rate of economic expansion occurs. | |||
| The gold specie standard ended in the United Kingdom and the rest of the British Empire at the outbreak of World War I, when Treasury notes replaced the circulation of gold sovereigns and gold half sovereigns. Legally, the gold specie standard was not abolished. The end of the gold standard was successfully effected by the Bank of England through appeals to patriotism urging citizens not to redeem paper money for gold specie. It was only in 1925, when Britain returned to the gold standard in conjunction with Australia and South Africa, that the gold specie standard was officially ended. | |||
| {{Infobox UK legislation | |||
| One of the foremost opponents of the gold standard was John Maynard Keynes who scorned basing the money supply on "dead metal". ] argue that the gold standard creates ] which intensifies recessions as people are unwilling to spend money as prices fall, thus creating a downward spiral of economic activity. They also argue that the gold standard also removes the ability of governments to fight recessions by increasing the money supply to boost economic growth. | |||
| | short_title = Gold Standard Act 1925 | |||
| | type = Act | |||
| | parliament = Parliament of the United Kingdom | |||
| | long_title = An Act to facilitate the return to a gold standard and for purposes connected therewith. | |||
| | year = 1925 | |||
| | citation = ]. c. 29 | |||
| | introduced_commons = | |||
| | introduced_lords = | |||
| | territorial_extent = | |||
| | royal_assent = 13 May 1925 | |||
| | commencement = | |||
| | expiry_date = | |||
| | repeal_date = | |||
| | amends = | |||
| | replaces = | |||
| | amendments = | |||
| | repealing_legislation = | |||
| | related_legislation = | |||
| | status = | |||
| | legislation_history = | |||
| | theyworkforyou = | |||
| | millbankhansard = | |||
| | original_text = | |||
| | revised_text = | |||
| | use_new_UK-LEG = | |||
| | UK-LEG_title = | |||
| | collapsed = yes | |||
| }} | |||
| The British '''{{visible anchor|Gold Standard Act 1925}}'''<!-- no link, it redirects here --> both introduced the gold bullion standard and simultaneously repealed the gold specie standard.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Morrison |first=James Ashley |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mXkOEAAAQBAJ |title=England's Cross of Gold: Keynes, Churchill, and the Governance of Economic Beliefs |date=2021 |publisher=Cornell University Press |isbn=978-1-5017-5843-0 |language=en}}</ref> The new standard ended the circulation of gold specie coins. Instead, the law compelled the authorities to sell gold bullion on demand at a fixed price, but "only in the form of bars containing approximately four hundred ] of ]".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://archive.org/details/pdfy-eda-a8jaQS5E9hKh|title=Gold Standard Act 1925 (15 & 16 Geo. 5 c. 29)|date=1 January 2014 |orig-date=13 May 1925 |via=Internet Archive }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://freetheplanet.net/articles/101/gold-standard-act-1925 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120713131546/http://freetheplanet.net/articles/101/gold-standard-act-1925 |url-status=dead |archive-date=2012-07-13 |title=Articles: Free the Planet: Gold Standard Act 1925 |publisher=Free the Planet |date=2009-06-10 |access-date=2012-07-09 }}</ref> ], citing deflationary dangers, argued against resumption of the gold standard.<ref>{{cite book|first=John Maynard |last=Keynes |author-link=John Maynard Keynes |title=Economic Consequences of the Peace |url=https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.135642 |publisher=Harcourt, Brace and Rowe |location = New York |year=1920}}</ref> By fixing the price at a level which restored the pre-war exchange rate of US$4.86 per pound sterling, as ], ] is argued to have made an error that led to depression, unemployment and the ]. The decision was described by ] as a "historic mistake".<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2017/dec/29/thatcher-warned-major-about-exchange-rate-risks-before-erm-crisis |title=Thatcher warned Major about exchange rate risks before ERM crisis |newspaper=] |date=2017-12-29 |access-date=2017-12-29 }}</ref> | |||
| The pound left the gold standard in 1931 and a number of currencies of countries that historically had performed a large amount of their trade in sterling were pegged to sterling instead of to gold. The Bank of England took the decision to leave the gold standard abruptly and unilaterally.<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |last=Morrison |first=James Ashley |date=2016 |title=Shocking Intellectual Austerity: The Role of Ideas in the Demise of the Gold Standard in Britain |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/international-organization/article/shocking-intellectual-austerity-the-role-of-ideas-in-the-demise-of-the-gold-standard-in-britain/CD7287FFF28C7868C5925E68E3AA2E56 |journal=International Organization |language=en |volume=70 |issue=1 |pages=175–207 |doi=10.1017/S0020818315000314 |s2cid=155189356 |issn=0020-8183}}</ref> | |||
| Gold standard proponents point to the era of industrialization and globalization of the 19th century as the proof of the viability and supremacy of the gold standard, and point to Britain's rise to being an imperial power, conquering nearly one quarter of the world's population and forming a trading empire which would eventually become the ] as imperial provinces gained independence. | |||
| === Great Depression=== | |||
| Gold standard advocates have a strong following among commodity traders and hedge funds with a ] orientation. The expectation of a global fiscal meltdown, and the return to a hard gold standard has been central to many hedge financial theories. More moderate ]s point to gold as a hedge against commodity inflation, and a representation of resource extraction, in their view gold is a play against monetary policy follies of central banks, and a means of hedging against currency fluctuations, since gold can be sold in any currency, on a highly liquid world market, in nearly any country in the world. For this reason they believe that eventually there will be a return to a gold standard, since this is the only "stable" unit of value. That monetary gold would soar to $5,000 an ounce, over 10 times its current value, may well have something to do with some of the advocacy of a renewed gold standard, holders of gold would stand to make an enormous profit. | |||
| {{main|Great Depression}} | |||
| ]<ref>International data from {{cite web|first=Angus|last=Maddison|author-link=Angus Maddison|title=Historical Statistics for the World Economy: 1–2003 AD|date=27 July 2016 |url=http://www.ggdc.net/Maddison/Historical_Statistics/}}{{dead link|date=October 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}. Gold dates culled from historical sources, principally {{Cite book|title=Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939|author-link=Barry Eichengreen|first=Barry|last=Eichengreen|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=New York|year=1992|isbn=978-0-19-506431-5|url=https://archive.org/details/goldenfettersgol00eich}}</ref>]] | |||
| Many other countries followed Britain in returning to the gold standard, leading to a period of relative stability but also deflation.<ref>Cassel, Gustav (1936). ''The Downfall of the Gold Standard''. Oxford University Press.</ref> This state of affairs lasted until the ] (1929–1939) forced countries off the gold standard.<ref name=":6"/> Primary-producing countries were first to abandon the gold standard.<ref name=":6" /> In the summer of 1931, a Central European banking crisis led Germany and Austria to suspend gold convertibility and impose exchange controls.<ref name=":6" /> A May 1931 ] on ] had caused it to ]. The run spread to Germany, where the central bank also collapsed. International financial assistance was too late and in July 1931 Germany adopted exchange controls, followed by Austria in October. The Austrian and German experiences, as well as British budgetary and political difficulties, were among the factors that destroyed confidence in sterling, which occurred in mid-July 1931. Runs ensued and the Bank of England lost much of its reserves. | |||
| Few economists today advocate a return to the gold standard. Notable exceptions are some proponents of ] and some proponents of ]. However, many prominent economists, while they do not advocate a return to gold, are sympathetic with hard currency basis, and argue against ]. This school of thought includes US central banker ] and macro-economist ]. The current monetary system relies on the US Dollar as an "anchor currency" which major transactions, such as the price of gold itself, are measured in. Currency instabilities, inconvertibility and credit access restriction are a few reasons why the current system has been criticized, with a host of alternatives suggested, including energy based currencies, market baskets of currencies or commodities. Gold is merely one of these alternatives. | |||
| On September 19, 1931, speculative attacks on the pound led the Bank of England to abandon the gold standard, ostensibly "temporarily".<ref name=":1"/> However, the ostensibly temporary departure from the gold standard had unexpectedly positive effects on the economy, leading to greater acceptance of departing from the gold standard.<ref name=":1" /> Loans from American and French central banks of £50 million were insufficient and exhausted in a matter of weeks, due to large gold outflows across the Atlantic.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://freetheplanet.net/articles/119/chancellor-s-commons-speech-21-september-1931 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120709081110/http://freetheplanet.net/articles/119/chancellor-s-commons-speech-21-september-1931 |url-status=dead |archive-date=2012-07-09 |title=Chancellor's Commons Speech |work=Free the Planet |access-date=2012-07-09 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Barry J. |last=Eichengreen|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System|url={{google books |id=_iNqESd-9R0C|p=61-|plainurl=yes}}|access-date=November 23, 2010|date=September 15, 2008 |publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-13937-1|pages=61ff}}</ref>{{sfn|Officer|2010 |loc=Breakdown of the Interwar Gold Standard}} The British benefited from this departure. They could now use monetary policy to stimulate the economy. Australia and New Zealand had already left the standard and Canada quickly followed suit. | |||
| The reason these visions are not practically pursued is based on the same reasons that the gold standard fell apart in the first place: a fixed rate of exchange decreed by governments has no organic relationship between the supply and demand of gold and the supply and demand of goods. | |||
| The interwar partially backed gold standard was inherently unstable because of the conflict between the expansion of liabilities to foreign central banks and the resulting deterioration in the Bank of England's reserve ratio. France was then attempting to make Paris a world class financial center, and it received large gold flows as well.<ref>{{harvnb|Officer|2010 |loc=Instability of the Interwar Gold Standard}}: "there was ongoing tension with France, that resented the sterling-dominated gold- exchange standard and desired to cash in its sterling holding for gold to aid its objective of achieving first-class financial status for Paris."</ref> | |||
| Thus gold standards have a tendency to fall apart as soon as it becomes advantageous for governments to overlook them. By itself, the gold standard does not prevent nations from switching to a fiat currency when there is a war or other exigency, even though gold gains in value through such circumstances as people use it to preserve value since fiat currency is typically introduced to allow deficit spending, which often leads to either inflation or to rationing. | |||
| Upon taking office in March 1933, U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt departed from the gold standard.<ref name=":7">{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8 |edition=3rd |pages=79–81 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref> | |||
| The practical difficulty that gold is not currently distributed according to economic strength is also a factor: Japan, while one of the world's largest economies, has gold reserves far less than would be required to support that economy. Finally the quantity of gold available for reserves, even if all of it were confiscated and used as the unit of account, would put the value of gold upwards of 5000 dollars an ounce on a purchasing parity basis. If the current holders of gold imagine that this is the price that they will be paid for giving up their gold, they are quite likely to be disappointed. For these practical reasons — inefficiency, misallocation, instability, and insufficiency of supply — the gold standard is likely to be more honoured in literature than practiced in fact. | |||
| By the end of 1932, the gold standard had been abandoned as a global monetary system.<ref name=":7" /> Czechoslovakia, Belgium, France, the Netherlands and Switzerland abandoned the gold standard in the mid-1930s.<ref name=":7" /> According to Barry Eichengreen, there were three primary reasons for the collapse of the gold standard:<ref>{{Cite book|last=Eichengreen|first=Barry|title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-19390-8|edition=3rd|pages=84–85|doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg|jstor=j.ctvd58rxg|s2cid=240840930}}</ref> | |||
| == Gold as a reserve today == | |||
| ], still form an important currency reserve and store of private wealth.]] | |||
| # '''Tradeoffs between currency stability and other domestic economic objectives:''' Governments in the 1920s and 1930s faced conflictual pressures between maintaining currency stability and reducing unemployment. ], ]s, and labor parties pressured governments to focus on reducing unemployment rather than maintaining currency stability. | |||
| During the 1990s ] liquidated much of the former USSR's gold reserves, while several other nations accumulated gold in preparation for the Economic and Monetary Union. The Swiss Franc left a full gold-convertible backing. However, ] are held in significant quantity by many nations as a means of defending their currency, and hedging against the US Dollar, which forms the bulk of liquid currency reserves. Weakness in the US Dollar tends to be offset by strengthening of gold prices. Gold remains a principal financial asset of almost all central banks alongside foreign currencies and government bonds. It is also held by central banks as a way of hedging against loans to their own governments as an "internal reserve". | |||
| # '''Increased risk of destabilizing capital flight''': International finance doubted the credibility of national governments to maintain currency stability, which led to ] during crises, which aggravated the crises. | |||
| # '''The U.S., not Britain, was the main financial center''': Whereas Britain had during past periods been capable of managing a harmonious international monetary system, the U.S. was not. | |||
| According to ], the gold standard contributed to policymakers' turning to extreme protectionism in the 1930s. Policymakers were reluctant to abandon the gold standard, which would have allowed their currencies to depreciate. This instead led policymakers to impose higher tariffs and other protectionist measures.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Irwin |first=Douglas A. |url=https://books.google.com/books/about/Trade_Policy_Disaster.html?id=hsuMEAAAQBAJ&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |title=Trade Policy Disaster: Lessons from the 1930s |date=2011 |publisher=MIT Press |isbn=978-0-262-01671-1 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Causes of the Great Depression === | |||
| In addition to other ]s, it has several competitors as ]: the US dollar itself and ]. As with all stores of value, the basic confidence in property rights determines the selection of which one is chosen, as all of these have been confiscated or heavily taxed by governments. In the view of gold investors, none of these has the stability that gold had, thus there are occasionally calls to restore the gold standard. Occasionally politicians emerge who call for a restoration of the gold standard, particularly from the ] right and the anti-government left. Mainstream conservative economists such as Barro and Greenspan have admitted a preference for some tangibly backed monetary standard, and have stated that a gold standard is among the possible range of choices. | |||
| {{main|Causes of the Great Depression}} | |||
| Economists, such as ], ] and ], allocate at least part of the blame for prolonging the ] on the gold standard of the 1920s. The ] started in 1929 and lasted for about a decade.{{sfn|Eichengreen|1995|loc=Preface}}<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Eichengreen |first1=Barry|last2=Temin|first2=Peter|date=2000|title=The Gold Standard and the Great Depression |journal=Contemporary European History|volume=9 |issue=2|pages=183–207|doi=10.1017/S0960777300002010 |jstor=20081742|s2cid=158383956|issn=0960-7773|url=http://www.nber.org/papers/w6060.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.nber.org/papers/w6060.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last1=Bernanke|first1=Ben |last2=James|first2=Harold|author-link=Ben Bernanke|year=1991|chapter=The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison|pages=33–68|publisher=University of Chicago Press|location=Chicago|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MEfUi2H4cqwC|editor=R. Glenn Hubbard|title=Financial markets and financial crises |isbn=978-0-226-35588-7 |oclc=231281602 |editor-link=Glenn Hubbard (economics) }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Eichengreen |first1=Barry |last2=Temin |first2=Peter |title=The Gold Standard and the Great Depression |journal=Contemporary European History |date=July 2000 |volume=9 |issue=2 |pages=183–207 |doi=10.1017/S0960777300002010 |s2cid=150932332 |url=https://www.nber.org/papers/w6060}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Crafts|first1=Nicholas|last2=Fearon |first2=Peter|date=2010|title=Lessons from the 1930s Great Depression|url=https://academic.oup.com/oxrep/article/26/3/285/374047|journal=Oxford Review of Economic Policy|language=en|volume=26|issue=3|pages=285–317 |doi=10.1093/oxrep/grq030|issn=0266-903X|quote=The key element in the transmission of the Great Depression, the mechanism that linked the economies of the world together in this downward spiral, was the gold standard. It is generally accepted that adherence to fixed exchange rates was the key element in explaining the timing and the differential severity of the crisis. Monetary and fiscal policies were used to defend the gold standard and not to arrest declining output and rising unemployment.|doi-access=free|s2cid=154672656}}</ref> The gold standard theory of the Depression has been described as the "consensus view" among economists.<ref name=":11">{{Cite journal|last1=Bordo|first1=Michael D.|last2=Choudhri|first2=Ehsan U. |last3=Schwartz|first3=Anna J.|date=2002|title=Was Expansionary Monetary Policy Feasible during the Great Contraction? An Examination of the Gold Standard Constraint |url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014498301907788|journal=Explorations in Economic History|language=en|volume=39|issue=1|pages=1–28 |doi=10.1006/exeh.2001.0778|issn=0014-4983}}</ref><ref name=":13">{{Cite SSRN |last=Irwin|first=Douglas A.|date=2011-11-21|title=Anticipating the Great Depression? Gustav Cassel's Analysis of the Interwar Gold Standard |ssrn=1962488}}{{doi|10.3386/w17597}}{{s2cid|153294427}}</ref> This view is based on two arguments: "(1) Under the gold standard, deflationary shocks were transmitted between countries and, (2) for most countries, continued adherence to gold prevented monetary authorities from offsetting banking panics and blocked their recoveries."<ref name=":11" /> However, a 2002 paper argues that the second argument would only apply "to small open economies with limited gold reserves. This was not the case for the United States, the largest country in the world, holding massive gold reserves. The United States was not constrained from using expansionary policy to offset banking panics, deflation, and declining economic activity."<ref name=":11" /> According to Edward C. Simmons, in the United States, adherence to the gold standard prevented the Federal Reserve from expanding the money supply to stimulate the economy, fund insolvent banks and fund government deficits that could "prime the pump" for an expansion. Once off the gold standard, it became free to engage in such ]. The gold standard limited the flexibility of the central banks' monetary policy by limiting their ability to expand the money supply. In the US, the central bank was required by the ] (1913) to have gold backing 40% of its demand notes.<ref>{{cite journal|title=The Elasticity of The Federal Reserve Note |first=Edward C. |last=Simmons |journal=The American Economic Review |publisher=American Economic Association |jstor=1807996 |volume=26 |issue=4 |date=December 1936 |pages=683–690}}</ref> A 2024 study in the '']'' found that for a sample of 27 countries, leaving the gold standard helped states to recover from the Great Depression.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Ellison |first1=Martin |last2=Lee |first2=Sang Seok |last3=O'Rourke |first3=Kevin Hjortshøj |date=2024 |title=The Ends of 27 Big Depressions |url=https://www.aeaweb.org/articles?id=10.1257/aer.20221479 |journal=American Economic Review |language=en |volume=114 |issue=1 |pages=134–168 |doi=10.1257/aer.20221479 |s2cid=266612576 |issn=0002-8282}}</ref> | |||
| Some privately issued modern notes (such as ]) are backed by gold bullion, and gold. Both coins and bullion are widely traded in deeply liquid markets, and therefore still serve as a private store of wealth. In effect, the holder of such currencies is long gold, short their own currency and writing checks on their account. | |||
| Higher interest rates intensified the deflationary pressure on the dollar and reduced investment in U.S. banks. Commercial banks converted ] to gold in 1931, reducing its gold reserves and forcing a corresponding reduction in the amount of currency in circulation. This ] attack created a panic in the U.S. banking system. Fearing imminent devaluation many depositors withdrew funds from U.S. banks.<ref name="federalreserve2004">{{cite web|url=http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2004/200403022/default.htm |title=FRB: Speech, Bernanke-Money, Gold, and the Great Depression |publisher=Federal Reserve |date=2004-03-02 |access-date=2010-07-24}}</ref> As bank runs grew, a reverse multiplier effect caused a contraction in the money supply.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://mises.org/rothbard/AGD/chapter10.asp |title=1931—'The Tragic Year' |date=January 1963 |publisher=Ludwig von Mises Institute |access-date=December 24, 2011|quote=The inflationary attempts of the government from January to October were thus offset by the people's attempts to convert their bank deposits into legal tender ... Hence, the will of the public caused bank reserves to decline by $400 million in the latter half of 1931, and the money supply, as a consequence, fell by over four billion dollars in the same period.}}</ref> Additionally the New York Fed had loaned over {{US$|150 million|long=no}} in gold (over 240 tons) to European Central Banks. This transfer contracted the U.S. money supply. The foreign loans became questionable once ], Germany, Austria and other European countries went off the gold standard in 1931 and weakened confidence in the dollar.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://mises.org/rothbard/AGD/chapter10.asp |title=1931—'The Tragic Year' |date=January 1963 |quote=Throughout the European crisis, the Federal Reserve, particularly the New York Bank, tried its best to aid the European governments and to prop up unsound credit positions. ... The New York Federal Reserve loaned, in 1931, $125 million to the Bank of England, $25 million to the German Reichsbank, and smaller amounts to Hungary and Austria. As a result, much frozen assets were shifted, to become burdens to the United States. |publisher=Ludwig von Mises Institute |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> | |||
| In 1999, to protect the value of gold as a reserve, ]ers signed the "Washington Agreement", which stated they would not allow gold leasing for speculative purposes, nor would they "enter the market as sellers" except for sales that had already been agreed upon. A selling band was set. This was intended to prevent further deterioration in the price of gold. (See ]) | |||
| The forced contraction of the money supply resulted in deflation. Even as nominal interest rates dropped, deflation-adjusted real interest rates remained high, rewarding those who held onto money instead of spending it, further slowing the economy.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eh.net/Clio/ASSAPapers/Hanes.pdf |title=The Liquidity Trap and U.S. Interest Rates in the 1930s |first=Christopher |last=Hanes |quote=In the 1930s, the United States was in a situation that satisfied the conditions for a liquidity trap. Over 1929–1933 overnight rates fell to zero, and they remained on the floor through the 1930s.|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040722174808/http://www.eh.net/Clio/ASSAPapers/Hanes.pdf |archive-date=2004-07-22}}</ref> Recovery in the United States was slower than in Britain, in part due to Congressional reluctance to abandon the gold standard and float the U.S. currency as Britain had done.<ref>Feinstein, Temin, and Toniolo. ''The European Economy between Wars''.{{full citation needed|date=April 2022}}</ref> | |||
| In ] ]n Prime Minister ] proposed a new currency that would be used initially for international trade between Muslim nations. The currency he proposed was called the ] and it was defined as 4.25 grams of 24 ] (100%) gold. Mahathir Mohamad promoted the concept on the basis of its economic merits as a stable unit of account and also as a political symbol to create greater unity between Islamic nations. | |||
| In the early 1930s, the Federal Reserve defended the dollar by raising interest rates, trying to increase the demand for dollars. This helped attract international investors who bought foreign assets with gold.<ref name="federalreserve2004"/> | |||
| Congress passed the ] on 30 January 1934; the measure nationalized all gold by ordering Federal Reserve banks to turn over their supply to the U.S. Treasury. In return, the banks received gold certificates to be used as reserves against deposits and Federal Reserve notes. The act also authorized the president to devalue the gold dollar. Under this authority, the president, on 31 January 1934, changed the value of the dollar from {{US$|20.67|long=no}} to the ] to {{US$|35|long=no}} to the troy ounce, a devaluation of over 40%. | |||
| Other causal factors, or factors in the prolongation of the Great Depression include ] and the reduction in ] caused by barriers such as ] in the U.S.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Stein |first=Ben |date=2009-05-09 |title=The Smoot-Hawley Act Is More Than a Laugh Line |language=en-US |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/05/10/business/10every.html |access-date=2023-10-06 |issn=0362-4331}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2018-09-20 |title=The Great Depression Lesson About 'Trade Wars' |url=https://www.history.com/news/trade-war-great-depression-trump-smoot-hawley |access-date=2023-10-06 |website=HISTORY |language=en}}</ref> and the ] policies of Great Britain, the failure of central banks to act responsibly,<ref>M. Friedman: "the severity of each of the major contractions – 1920–21, 1929–33 and 1937–38 is directly attributable to acts of commission and omission by the Reserve authorities".{{quote without source|date=April 2022}}</ref> government policies designed to prevent wages from falling, such as the ] of 1931, during the deflationary period resulting in production costs dropping slower than sales prices, thereby injuring business profits<ref>{{cite web |first=Robert P. |last=Murphy |url=https://mises.org/daily/3778 |title=The Gold Standard and the Great Depression |date=30 October 2009 |quote=Another major factor is that governments in the 1930s were interfering with wages and prices more so than at any prior point in (peacetime) history |publisher=Mises.org |access-date=2012-07-09 |archive-date=2012-07-09 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120709100220/http://mises.org/daily/3778 |url-status=dead }}</ref> and increases in taxes to reduce budget deficits and to support new programs such as ]. The U.S. top marginal income tax rate went from 25% to 63% in 1932 and to 79% in 1936,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.cato.org/pubs/tbb/tbb-0303-14.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.cato.org/pubs/tbb/tbb-0303-14.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=High Taxes and High Budget Deficits – The Hoover–Roosevelt Tax Increases of the 1930s|publisher=Cato Institute|access-date=3 March 2022}}</ref> while the bottom rate increased over tenfold, from .375% in 1929 to 4% in 1932.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://mjperry.blogspot.com/2008/11/10x-increase-in-taxes-during-great.html |work=Mark J. Perry's Blog for Economics and Finance |title=10X Increase in Lowest Tax Rate in Early 1930s |first=Mark J. |last=Perry |publisher=Mjperry.blogspot.com |date=2008-11-09 |access-date=2012-07-09}}</ref> The concurrent massive drought resulted in the U.S. ]. | |||
| The ] argued that the Great Depression was the result of a credit bust.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Eichengreen |first1=Barry |last2=Mitchener |first2=Kris |title=The Great Depression as a Credit Boom Gone Wrong |url=http://elsa.berkeley.edu/~eichengr/research/bisconferencerevision5jul30-03.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://elsa.berkeley.edu/~eichengr/research/bisconferencerevision5jul30-03.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |date=August 2003 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> ] wrote that the bank failures of the 1930s were sparked by Great Britain dropping the gold standard in 1931. This act "tore asunder" any remaining confidence in the banking system.<ref>Alan Greenspan (1966). ''Gold and Economic Freedom''. "Great Britain fared even worse, and rather than absorb the full consequences of her previous folly, she abandoned the gold standard completely in 1931, tearing asunder what remained of the fabric of confidence and inducing a world-wide series of bank failures."{{full citation needed|date=April 2022}}</ref> Financial historian ] wrote that what made the Great Depression truly 'great' was the ].<ref>{{cite web|last=Farrell |first=Paul B. |url=http://www.marketwatch.com/story/our-decade-from-hell-will-get-worse-in-2012-2011-12-13?link=MW_story_popular |title=Our decade from hell will get worse in 2012 |quote=As financial historian Niall Ferguson writes in Newsweek: 'Double-Dip Depression ... We forget that the Great Depression was like a soccer match, there were two halves.' The 1929 crash kicked off the first half. But what 'made the depression truly "great" ... began with the European banking crisis of 1931.' Sound familiar? |publisher=MarketWatch |date=December 13, 2011 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> According to Federal Reserve Chairman ], the root cause was the concentration of wealth resulting in a stagnating or decreasing standard of living for the poor and middle class. These classes went into debt, producing the credit explosion of the 1920s. Eventually, the debt load grew too heavy, resulting in the massive defaults and financial panics of the 1930s.<ref>Robert B. Reich (2010). ''Aftershock''. Chapter 1: Eccles's Insight.</ref> | |||
| ====Trying to return to the Gold Standard==== | |||
| :See also: ], ], ] | |||
| During ] many countries suspended their Gold standard in varying ways. There was high inflation from WWI, and in the 1920s in the ], ], and throughout Europe. In the late 1920s there was a scramble to deflate prices to get the gold standard's conversion rates back on track to pre-WWI levels, by causing ] and high unemployment through ]. In 1933 ] signed ] and in 1934 signed the ].<ref>https://www.cato.org/blog/world-war-i-gold-great-depression#:~:text=The%20result%20was%20a%20second,4%20years%20in%20a%20row.{{Bare URL inline|date=August 2024}}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |+ Gold Standard Policies by Country<ref>https://www.nber.org/system/files/chapters/c11482/c11482.pdf</ref> | |||
| ! Country !! Return to Gold !! Suspension of Gold Standard !! Foreign Exchange Control !! Devaluation | |||
| |- | |||
| | Australia || April 1925 || December 1929 || — || March 1930 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Austria || April 1925 || April 1933 || October 1931 || September 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Belgium || October 1926 || — || — || March 1935 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Canada || July 1926 || October 1931 || — || September 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Czechoslovakia || April 1926 || — || September 1931 || February 1934 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Denmark || January 1927 || September 1931 || November 1931 || September 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Estonia || January 1928 || June 1933 || November 1931 || June 1933 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Finland || January 1926 || October 1931 || — || October 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | France || August 1926-June 1928 || — || — || October 1936 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Germany || September 1924 || — || July 1931 || — | |||
| |- | |||
| | Greece || May 1928 || April 1932 || September 1931 || April 1932 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Hungary || April 1925 || — || July 1931 || — | |||
| |- | |||
| | Italy || December 1927 || — || May 1934 || October 1936 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Japan || December 1930 || December 1931 || July 1932 || December 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Latvia || August 1922 || — || October 1931 || — | |||
| |- | |||
| | Netherlands || April 1925 || — || — || October 1936 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Norway || May 1928 || September 1931 || — || September 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | New Zealand || April 1925 || September 1931 || — || April 1930 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Poland || October 1927 || — || April 1936 || October 1936 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Romania || March 1927-February 1929 || — || May 1932 || — | |||
| |- | |||
| | Sweden || April 1924 || September 1931 || — || September 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Spain || — || — || May 1931 || — | |||
| |- | |||
| | United Kingdom || May 1925 || September 1931 || — || September 1931 | |||
| |- | |||
| | United States || June 1919 || March 1933 || March 1933 || April 1933 | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Bretton Woods=== | |||
| {{Main|Bretton Woods system}} | |||
| Under the ], the gold standard was kept without domestic convertibility. The role of gold was severely constrained, as other countries' currencies were fixed in terms of the dollar. Many countries kept reserves in gold and settled accounts in gold. Still, they preferred to settle balances with other currencies, with the US dollar becoming the favorite. The ] was established to help with the exchange process and assist nations in maintaining fixed rates. Within Bretton Woods adjustment was cushioned through credits that helped countries avoid deflation. Under the old standard, a country with an overvalued currency would lose gold and experience deflation until the currency was again valued correctly. Most countries defined their currencies in terms of dollars, but some countries imposed trading restrictions to protect reserves and exchange rates. Therefore, most countries' currencies were still basically inconvertible. In the late 1950s, the exchange restrictions were dropped and gold became an important element in international financial settlements.{{sfn|Elwell|2011}} | |||
| After the ], a system similar to a gold standard and sometimes described as a "gold exchange standard" was established by the Bretton Woods Agreements. Under this system, many countries fixed their exchange rates relative to the U.S. dollar and central banks could exchange dollar holdings into gold at the official exchange rate of {{US$|35|long=no}} per ounce; this option was not available to firms or individuals. All currencies pegged to the dollar thereby had a fixed value in terms of gold.{{sfn|Lipsey|1975|pp=683–702}} Since private parties could not exchange gold at the official rate, market prices fluctuated. Large jumps in the market price 1960 lead to the creation of the ]. | |||
| Starting in the 1959–1969 administration of President ] and continuing until 1970, France reduced its dollar reserves, exchanging them for gold at the official exchange rate, reducing U.S. economic influence. This, along with the fiscal strain of federal expenditures for the ] and persistent balance of payments deficits, led U.S. President ] to end international convertibility of the U.S. dollar to gold on August 15, 1971 (the "]"). | |||
| This was meant to be a temporary measure, with the gold price of the dollar and the official rate of exchanges remaining constant. Revaluing currencies was the main purpose of this plan. No official revaluation or redemption occurred. The dollar subsequently floated. In December 1971, the "]" was reached. In this agreement, the dollar was devalued from {{US$|35|long=no}} per troy ounce of gold to {{US$|38|long=no}}. Other countries' currencies appreciated. However, gold convertibility did not resume. In October 1973, the price was raised to {{US$|42.22|long=no}}. Once again, the devaluation was insufficient. Within two weeks of the second devaluation the dollar was left to float. The {{US$|42.22|long=no}} par value was made official in September 1973, long after it had been abandoned in practice. In October 1976, the government officially changed the definition of the dollar; references to gold were removed from statutes. From this point, the ] was made of pure ]. However, gold has persisted as a significant reserve asset since the collapse of the classical gold standard.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Jabko |first1=Nicolas |last2=Schmidt |first2=Sebastian |date=2022 |title=The Long Twilight of Gold: How a Pivotal Practice Persisted in the Assemblage of Money |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/international-organization/article/abs/long-twilight-of-gold-how-a-pivotal-practice-persisted-in-the-assemblage-of-money/4D6FD92E9BAB8192D207E2A5CBFD87E6 |journal=International Organization |volume=76 |issue=3 |pages=625–655 |language=en |doi=10.1017/S0020818321000461 |s2cid=245413975 |issn=0020-8183}}</ref> | |||
| === Modern gold production === | |||
| An estimated total of 174,100 ]s of gold have been mined in human history, according to ] as of 2012. This is roughly equivalent to 5.6 billion ]s or, in terms of volume, about {{convert|9261|m3}}, or a ] {{convert|21|m}} on a side. There are varying estimates of the total volume of gold mined. One reason for the variance is that gold has been mined for thousands of years. Another reason is that some nations are not particularly open about how much gold is being mined. In addition, it is difficult to account for the gold output in illegal mining activities.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-21969100|title=How much gold is there in the world?|last=Prior|first=Ed|work=BBC News|date=1 April 2013}}</ref> | |||
| World production for 2011 was circa 2,700 ]s. Since the 1950s, annual gold output growth has approximately kept pace with ] growth (i.e. a doubling in this period)<ref name="World Gold Council FAQ">{{cite web|url=http://www.gold.org/investment/why_how_and_where/faqs/#q022|title=FAQs | Investment |publisher=World Gold Council|access-date=2013-09-12}}</ref> although it has lagged behind world economic growth (an approximately eightfold increase since the 1950s,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.measuringworth.com/datasets/usgdp/result.php?year_source=1990&year_result=2012&use%5B%5D=GDPDEFLATION|title=Measuring Worth - GDP result|website=Measuringworth.com}}</ref> and fourfold since 1980.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/weodata/download.aspx|title=Download entire World Economic Outlook database, April 2013|website=International Monetary Fund}}</ref> | |||
| ==Reintroduction== | |||
| In 2024, ] became the first country in the 21st century to use a gold standard for its currency, in order to tackle inflation and create confidence within the economy. The ] (ZiG) is backed by US$400 million and 2,522 kg of gold, thus giving a total of US$575 million worth of hard assets. This development came after the ] crashed based on official rate from US$1:ZWL2.50 at introduction to US$1:ZWL30,672.42 on 5 April 2024, whilst parallel market was trading at US$1:ZWL42,500 at the time of removal.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Zimbabwe Gold |url=https://www.chronicle.co.zw/zim-gets-new-currency-zig-to-restore-stability/ |access-date=2024-04-06 |website=Chronicles Zimbabwe}}</ref> | |||
| ==Theory== | |||
| ] is inconvenient to store and transport in large amounts. Furthermore, it does not allow a government to manipulate the flow of commerce with the same ease that a fiat currency does. As such, commodity money gave way to ] and gold and other ] were retained as its backing. | |||
| Gold was a preferred form of money due to its rarity, durability, divisibility, ] and ease of identification,<ref name=autogenerated1>{{Cite book|first=Shepard |last=Krech III |author2-first=John Robert |author2-last=McNeill |author3-first=Carolyn |author3-last=Merchant |author3-link=Carolyn Merchant |title=Encyclopedia of World Environmental History |publisher=] |location=] |year=2004 |volume=2 |isbn=978-0-415-93734-4 |oclc=174950341 |page=}}</ref> often in conjunction with silver. Silver was typically the main circulating medium, with gold as the monetary reserve. Commodity money was anonymous, as identifying marks can be removed. Commodity money retains its value despite what may happen to the monetary authority. After the fall of ], many refugees carried their wealth to the West in gold after the national currency became worthless.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-08-29 |title=How the End of the Vietnam War Led to a Refugee Crisis |url=https://www.history.com/news/vietnam-war-refugees |access-date=2023-10-06 |website=HISTORY |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Under commodity standards currency itself has no intrinsic value but is accepted by traders because it can be redeemed any time for the equivalent specie. A U.S. ], for example, could be redeemed for an actual piece of silver. | |||
| Representative money and the gold standard protect citizens from ] and other abuses of monetary policy, as were seen in some countries during the Great Depression. Commodity money conversely led to deflation.<ref>{{cite book |first=Nick |last=Mayhew |url=https://brill.com/view/book/edcoll/9789004383098/BP000012.xml |title=Money and the Economy in: Money and Coinage in the Middle Ages |doi=10.1163/9789004383098_010 |publisher=Brill.com |date=2019-03-21 |isbn=9789004383098 |s2cid=159368019 |access-date=2022-03-03}}</ref> | |||
| Countries that left the gold standard earlier than other countries recovered from the Great Depression sooner. For example, Great Britain and the Scandinavian countries, which left the gold standard in 1931, recovered much earlier than France and Belgium, which remained on gold much longer. Countries such as China, which had a silver standard, almost entirely avoided the depression (due to the fact it was then barely integrated into the global economy). The connection between leaving the gold standard and the severity and duration of the depression was consistent for dozens of countries, including developing countries. This may explain why the experience and length of the depression differed between national economies.<ref>Bernanke, Ben (March 2, 2004), "Remarks by Governor Ben S. Bernanke: Money, Gold and the Great Depression", At the H. Parker Willis Lecture in Economic Policy, Washington and Lee University, Lexington, Virginia.</ref> | |||
| ===Variations=== | |||
| A ''full or 100%-reserve'' gold standard exists when the monetary authority holds sufficient gold to convert all the circulating representative money into gold at the promised exchange rate. It is sometimes referred to as the gold specie standard to more easily distinguish it. Opponents of a full standard consider it difficult to implement, saying that the quantity of gold in the world is too small to sustain worldwide economic activity at or near current gold prices; implementation would entail a many-fold increase in the price of gold.<ref>{{Cite web |title=International payment and exchange - Gold Standard, Currency Exchange, Global Economy {{!}} Britannica Money |url=https://www.britannica.com/money/topic/international-payment/Problems-with-the-gold-standard |access-date=2023-10-06 |website=www.britannica.com |language=en}}</ref> Gold standard proponents have said, "Once a money is established, any stock of money becomes compatible with any amount of employment and real income."<ref>{{cite book|last=Hoppe|first=Hans-Herman|editor=Mark Skousen|title=Dissent on Keynes, A Critical Appraisal of Economics|url=https://mises.org/daily/2492#i2|year=1992|pages=199–223|access-date=2014-09-15|archive-date=2014-09-15|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140915120724/https://mises.org/daily/2492#i2|url-status=dead}}</ref> While prices would necessarily adjust to the supply of gold, the process may involve considerable economic disruption, as was experienced during earlier attempts to maintain gold standards.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://mises.org/Community/wikis/economics/gold-as-money-faq.aspx |title=Gold as Money: FAQ |website=Mises.org |publisher=Ludwig von Mises Institute |access-date=12 August 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110714174608/http://mises.org/Community/wikis/economics/gold-as-money-faq.aspx |archive-date=July 14, 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| In an ''international gold-standard system'' (which is necessarily based on an internal gold standard in the countries concerned),<ref>The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd edition (2008), Vol.3, S.695</ref> gold or a currency that is convertible into gold at a fixed price is used to make international payments. Under such a system, when exchange rates rise above or fall below the fixed mint rate by more than the cost of shipping gold, inflows or outflows occur until rates return to the official level. International gold standards often limit which entities have the right to redeem currency for gold. | |||
| == Impact == | |||
| A poll of 39 prominent U.S. economists conducted by the IGM Economic Experts Panel in 2012 found that none of them believed that returning to the gold standard would improve price-stability and employment outcomes. The specific statement with which the economists were asked to agree or disagree was: "If the U.S. replaced its discretionary monetary policy regime with a gold standard, defining a 'dollar' as a specific number of ounces of gold, the price-stability and employment outcomes would be better for the average American." 40% of the economists disagreed, and 53% strongly disagreed with the statement; the rest did not respond to the question. The panel of polled economists included past Nobel Prize winners, former economic advisers to both Republican and Democratic presidents, and senior faculty from Harvard, Chicago, Stanford, MIT, and other well-known research universities.<ref name=":0">{{cite web |url=http://www.igmchicago.org/igm-economic-experts-panel/poll-results?SurveyID=SV_cw1nNUYOXSAKwrq|title=Gold Standard|date=12 January 2012|publisher=]|access-date=27 December 2015}}</ref> A 1995 study reported on survey results among economic historians showing that two-thirds of economic historians disagreed that the gold standard "was effective in stabilizing prices and moderating business-cycle fluctuations during the nineteenth century."<ref name=":8">{{Cite journal|last=Whaples|first=Robert|date=1995|title=Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions|journal=The Journal of Economic History |volume=55|issue=1|pages=139–154|doi=10.1017/S0022050700040602|jstor=2123771|s2cid=145691938 |issn=0022-0507}}</ref> | |||
| ===Advantages=== | |||
| According to economist ], the gold standard has three benefits: "its record as a stable nominal anchor; its automaticity; and its role as a credible commitment mechanism":<ref name=":10">{{Cite book|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/gold-standard-and-related-regimes/3AD22F72A4C16DA08DDF52B58AEC56DF|title=The Gold Standard and Related Regimes: Collected Essays|last=Bordo|first=Michael D.|date=May 1999|publisher=Cambridge University Press|language=en|doi=10.1017/cbo9780511559624|isbn=9780521550062|access-date=2020-03-28}}</ref> | |||
| * A gold standard does not allow some types of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2011/06/reinhart.htm |title=Financial Repression Redux |quote=Financial repression occurs when governments implement policies to channel to themselves funds that in a deregulated market environment would go elsewhere |publisher=International Monetary Fund |date=June 2011 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> Financial repression acts as a mechanism to transfer wealth from creditors to debtors, particularly the governments that practice it. Financial repression is most successful in reducing debt when accompanied by inflation and can be considered a form of ].<ref>{{Cite book |title=This Time is Different |last1=Reinhart |first1=Carmen M. |last2=Rogoff |first2=Kenneth S. |publisher=Princeton University Press |year=2008 |page=143}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |jstor = 2117587|title = Government Revenue from Financial Repression|journal = The American Economic Review|volume = 83|issue = 4|pages = 953–963|last1 = Giovannini|first1 = Alberto|last2 = De Melo|first2 = Martha|year = 1993}}</ref> In 1966 ] wrote "] is simply a scheme for the confiscation of wealth. Gold stands in the way of this insidious process. It stands as a protector of property rights. If one grasps this, one has no difficulty in understanding the statists' antagonism toward the gold standard."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.constitution.org/mon/greenspan_gold.htm |title=Gold and Economic Freedom |first=Alan |last=Greenspan |publisher=Constitution.org |year=1966 |access-date=December 24, 2011 |archive-date=September 25, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100925231456/http://constitution.org/mon/greenspan_gold.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| * Long-term ] has been described as one of the virtues of the gold standard,{{sfn|Bordo|2008}} but historical data shows that the magnitude of short run swings in prices were far higher under the gold standard.<ref>{{cite magazine|url=https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2012/08/why-the-gold-standard-is-the-worlds-worst-economic-idea-in-2-charts/261552/ |title=Why the Gold Standard Is the World's Worst Economic Idea, in 2 Charts |first=Matthew |last=O'Brien |magazine=The Atlantic |date=2012-08-26 |access-date=2013-04-19}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|chapter-url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/gold-standard-and-related-regimes/gold-standard-as-a-commitment-mechanism/2E8AFBB653A1320325BA6A15741F3E7D|chapter=The Gold Standard as a Commitment Mechanism|last=Kydland|first=Finn E.|title=The Gold Standard and Related Regimes|date=1999|pages=195–237|publisher=Cambridge University Press|doi=10.1017/CBO9780511559624.008|isbn=9780521550062|language=en|access-date=2020-03-28}}</ref>{{sfn|Bordo|2008}} | |||
| *] were less frequent under the gold standard than in periods without the gold standard.<ref name=":9" /> However, banking crises were more frequent.<ref name=":9" /> | |||
| * The gold standard provides fixed international exchange rates between participating countries and thus reduces uncertainty in international trade. Historically, imbalances between price levels were offset by a balance-of-payment adjustment mechanism called the "]".<ref name="mises">{{cite web|url=https://mises.org/books/goldstandard.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://mises.org/books/goldstandard.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=Advantages of the Gold Standard|work=The Gold Standard: Perspectives in the Austrian School|date=27 January 1935 |publisher=The Ludwig von Mises Institute|access-date=9 January 2011}}</ref> Gold used to pay for imports reduces the money supply of importing nations, causing deflation, which makes them more competitive, while the importation of gold by net exporters serves to increase their money supply, causing inflation, making them less competitive.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/publications/fsr/fs_paper13.pdf |title=Reform of the International Monetary and Financial System |publisher=Bank of England |quote=Countries with current account surpluses accumulated gold, while deficit countries saw their gold stocks diminish. This, in turn, contributed to upward pressure on domestic spending and prices in surplus countries and downward pressure on them in deficit countries, thereby leading to a change ... that should, eventually, have reduced imbalances. |date=December 2011 |access-date=December 24, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111218105433/http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/publications/fsr/fs_paper13.pdf |archive-date=December 18, 2011 |url-status=dead |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| * Hyper-inflation, a common correlator with government overthrows and economic failures, is more difficult when a gold standard exists. This is because hyper-inflation, by definition, is a loss in trust of failing fiat and those governments that create the fiat. | |||
| ===Disadvantages=== | |||
| ] | |||
| * The unequal distribution of gold deposits makes the gold standard more advantageous for those countries that produce gold.<ref>Goodman, George J. W. (1981). ''Paper Money''. pp. 165–66</ref> In 2010 the largest producers of gold, in order, were China, Australia, the U.S., South Africa, and Russia.<ref>{{cite web |first=Liezel |last=Hill |url=http://www.miningweekly.com/article/gold-mine-output-hit-record-in-2010-more-gains-likely-this-year-gfms-2011-01-13 |title=Gold mine output hit record in 2010, more gains likely this year – GFMS |publisher=Mining Weekly |date=January 13, 2011 |access-date=December 24, 2011 |archive-date=November 29, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111129041110/http://www.miningweekly.com/article/gold-mine-output-hit-record-in-2010-more-gains-likely-this-year-gfms-2011-01-13 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The country with the largest unmined gold deposits is Australia.<ref>{{cite web|title=GOLD|url=http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/gold/mcs-2011-gold.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/gold/mcs-2011-gold.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|work=U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|access-date=10 July 2012|date=January 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| * Some economists believe that the gold standard acts as a limit on economic growth. According to David Mayer, "As an economy's productive capacity grows, then so should its money supply. Because a gold standard requires that money be backed in the metal, then the scarcity of the metal constrains the ability of the economy to produce more capital and grow."<ref name=EverythingEc>Mayer, David A. (2010). {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230326164811/https://books.google.com/books?id=HObsDQAAQBAJ |date=2023-03-26 }}. {{ISBN|978-1-4405-0602-4}}. pp. 33–34.</ref> | |||
| * ] believe that economic recessions can be largely mitigated by increasing the money supply during economic downturns.<ref name="Mankiw">{{Cite book |last=Mankiw |first=N. Gregory |title=Macroeconomics |publisher=Worth |year=2002 |edition=5th |pages= |isbn=978-0-324-17190-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/briefprincipleso00mank/page/238 }}</ref> A gold standard means that the money supply would be determined by the gold supply and hence monetary policy could no longer be used to stabilize the economy.<ref name="Slate: Krugman">{{cite web |url=http://www.slate.com/id/1912/ |title=The Gold Bug Variations |last=Krugman |first=Paul |date=23 November 1996 |work=Slate |access-date=2009-02-13}}</ref> | |||
| * Although the gold standard brings long-run price stability, it is historically associated with high short-run price ].{{sfn|Bordo|2008}}{{sfn|Bordo|Dittmar|Gavin|2003}} It has been argued by Schwartz, among others, that instability in short-term price levels can lead to financial instability as lenders and borrowers become uncertain about the value of debt.{{sfn|Bordo|Dittmar|Gavin|2003}} Historically, discoveries of gold and rapid increases in gold production have caused volatility.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8 |edition=3rd |page=11 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref> | |||
| * Deflation punishes debtors.<ref>{{cite news |last=Keogh |first=Bryan |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=newsarchive&sid=am.gkYZFlB0A |title=Real Rate Shock Hits CEOs as Borrowing Costs Impede Recovery |quote='Deflation hurts borrowers and rewards savers,' said Drew Matus, senior economist at Banc of America Securities-Merrill Lynch in New York, in a telephone interview. 'If you do borrow right now, and we go through a period of deflation, your cost of borrowing just went through the roof.' |work=Bloomberg |date=May 13, 2009 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last1=Mauldin |first1=John |title=Endgame: The End of the Debt SuperCycle and How It Changes Everything |publisher=John Wiley |location=Hoboken, New Jersey |isbn=978-1-118-00457-9 |url={{google books|id=amaQ6ZNBpYoC|p=135|plainurl=yes}} |last2=Tepper |first2=Jonathan |date=2011-02-09}}</ref> Real debt burdens therefore rise, causing borrowers to cut spending to service their debts or to default. Lenders become wealthier, but may choose to save some of the additional wealth, reducing ].<ref name="economist.com">{{cite magazine |title=The greater of two evils |url=http://www.economist.com/node/13610845 |magazine=The Economist |access-date=December 24, 2011 |date=May 7, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| * The money supply would essentially be determined by the rate of gold production. When gold stocks increase more rapidly than the economy, there is inflation and the reverse is also true.{{sfn|Bordo|2008}}<ref name="BradDeLong">{{cite web |url=http://www.j-bradford-delong.net/Politics/whynotthegoldstandard.html |title=Why Not the Gold Standard? |date=1996-08-10 |last=DeLong |first=Brad |author-link=J. Bradford DeLong |publisher=] |location=] |access-date=2008-09-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101018035441/http://www.j-bradford-delong.net/politics/whynotthegoldstandard.html |archive-date=2010-10-18 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The consensus view is that the gold standard contributed to the severity and length of the Great Depression, as under the gold standard central banks could not expand credit at a fast enough rate to offset deflationary forces.<ref name="econjwatch.org">{{cite journal |last=Timberlake |first=Richard H. |year=2005 |title=Gold Standards and the Real Bills Doctrine in US Monetary Policy |journal=] |volume=2 |issue=2 |pages=196–233 |url=http://econjwatch.org/issues/volume-2-issue-2-august-2005}}</ref><ref name=Warburton>{{Cite book|last=Warburton |first=Clark |title=Depression, Inflation, and Monetary Policy: Selected Papers, 1945–1953 |year=1966 |publisher=] |location=] |oclc=736401 |pages=25–35 |chapter=The Monetary Disequilibrium Hypothesis}}</ref>{{sfn|Hamilton|2005}} | |||
| * Hamilton contended that the gold standard is susceptible to ]s when a government's financial position appears weak. Conversely, this threat discourages governments from engaging in risky policy {{Crossreference|(see ])}}. For example, the U.S. was forced to contract the money supply and raise interest rates in September 1931 to defend the dollar after speculators forced the UK off the gold standard.{{sfn|Hamilton|2005}}{{sfn|Hamilton|1988}}<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2004/200403022/default.htm |title=Remarks by Governor Ben S. Bernanke |quote=In September 1931, following a period of financial upheaval in Europe that created concerns about British investments on the Continent, speculators attacked the British pound, presenting pounds to the Bank of England and demanding gold in return. ... Unable to continue supporting the pound at its official value, Great Britain was forced to leave the gold standard, ... With the collapse of the pound, speculators turned their attention to the U.S. dollar |publisher=The Federal Reserve Board |date=March 2, 2004 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> | |||
| * Devaluing a currency under a gold standard would generally produce sharper changes than the smooth declines seen in fiat currencies, depending on the method of devaluation.<ref>{{Cite news |first=Megan |last=McArdle |author-link=Megan McArdle |title=There's gold in them thar standards! |url=http://meganmcardle.theatlantic.com/archives/2007/09/theres_gold_in_them_thar_stand.php |work=] |date=2007-09-04 |access-date=2008-11-12 |archive-date=2010-01-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100113083500/http://meganmcardle.theatlantic.com/archives/2007/09/theres_gold_in_them_thar_stand.php |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| * Most economists favor a low, positive rate of inflation of around 2%. This reflects fear of deflationary shocks and the belief that active monetary policy can dampen fluctuations in output and unemployment. Inflation gives them room to tighten policy without inducing deflation.<ref name="econjournalwatch.org">Hummel, Jeffrey Rogers (January 2007). . p. 56</ref> | |||
| * A gold standard provides practical constraints against the measures that central banks might otherwise use to respond to economic crises.<ref>{{Cite journal |first=Asli |last=Demirgüç-Kunt |author2=Enrica Detragiache |author-link2=Enrica Detragiache |date=April 2005 |title=Cross-Country Empirical Studies of Systemic Bank Distress: A Survey |journal=] |volume=192 |issue=1 |pages=68–83 |doi=10.1177/002795010519200108 |s2cid=153360324 |url=http://ner.sagepub.com/cgi/reprint/192/1/68 |access-date=2008-11-12 |oclc=90233776 |issn=0027-9501 |hdl=10986/8266 |hdl-access=free |archive-date=2009-05-31 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090531220818/http://ner.sagepub.com/cgi/reprint/192/1/68 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Creation of new money reduces interest rates and thereby increases demand for new lower cost debt, raising the demand for money.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.econ.washington.edu/user/cnelson/Chap07.pdf |title=the quantity of money supplied by the Fed must be equal to the quantity demanded by money holders |access-date=2012-07-09 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120616230152/http://www.econ.washington.edu/user/cnelson/Chap07.pdf |archive-date=June 16, 2012 }}</ref> | |||
| *The late emergence of the gold standard may in part have been a consequence of its higher value than other metals, which made it unpractical for most laborers to use in everyday transactions (relative to less valuable silver coins).<ref>{{Cite book |last=Eichengreen |first=Barry |title=Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System |date=2019 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-19390-8 |edition=3rd |pages=11–12 |doi=10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg |jstor=j.ctvd58rxg |s2cid=240840930}}</ref> | |||
| ==Advocates== | |||
| A return to the gold standard was considered by the U.S. Gold Commission in 1982 but found only minority support.<ref name="Paul">{{Cite book|first=Ron |last=Paul |author-link=Ron Paul |author2=] |title=The case for gold: a minority report of the U.S. Gold Commission |url=https://www.mises.org/books/caseforgold.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://www.mises.org/books/caseforgold.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |access-date=2008-11-12 |publisher=] |location=] |year=1982 |page=160 |isbn=978-0-932790-31-6 |oclc=8763972}}</ref> In 2001 ] ] proposed a new currency that would be used initially for international trade among Muslim nations, using a ], defined as 4.25 grams of pure (24-]) gold. Mahathir claimed it would be a stable unit of account and a political symbol of unity between Islamic nations. This would purportedly reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar and establish a non-debt-backed currency in accord with ] that prohibited the charging of interest.<ref>{{cite web |first=Muhammad |last=al-'Amraawi |author2=Al-Khammar al-Baqqaali |author3=Ahmad Saabir |author4=Al-Hussayn ibn Haashim |author5=Abu Sayf Kharkhaash |author6=Mubarak Sa'doun al-Mutawwa' |author7=Malik Abu Hamza Sezgin |author8=Abdassamad Clarke |author9=Asadullah Yate |url=http://www.islamidag.dk/ulamaongold.html |title=Declaration of 'Ulama on the Gold Dinar |access-date=2008-11-14 |publisher=Islam i Dag |date=2001-07-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080624073052/http://www.islamidag.dk/ulamaongold.html |archive-date=2008-06-24 |url-status=dead }}</ref> However, this proposal has not been taken up, and the global monetary system continues to rely on the U.S. dollar as the main trading and ].<ref>{{cite news|last=McGregor |first=Richard |url=http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/ae01a8f6-21b7-11e0-9e3b-00144feab49a.html#ixzz1CttyOPaR |title=Hu questions future role of US dollar |newspaper=Financial Times |date=2011-01-16 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Former ] Chairman Alan Greenspan acknowledged he was one of "a small minority" within the central bank that had some positive view on the gold standard.<ref>{{Cite journal |url=https://fraser.stlouisfed.org/title/monetary-policy-oversight-672/conduct-monetary-policy-report-federal-reserve-board-pursuant-full-employment-balanced-growth-act-1978-pl-95-523-state-economy-22429?start_page=27 |title=Conduct of Monetary Policy: Report of the Federal Reserve Board Pursuant to the Full Employment and Balanced Growth Act of 1978, P.L. 95-523 and The State of the Economy: Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Domestic and International Monetary Policy of the Committee on Banking and Financial Services, House of Representatives |date=July 22, 1998 |journal=Monetary Policy Oversight: House of Representatives Hearings|series=Monetary Policy Oversight : House of Representatives Hearings }}</ref> In a 1966 essay he contributed to a book by ], titled ''Gold and Economic Freedom'', Greenspan argued the case for returning to a 'pure' gold standard; in that essay he described supporters of fiat currencies as "welfare statists" intending to use monetary policy to finance deficit spending.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Greenspan |first=Alan |author-link=Alan Greenspan |date=July 1966 |title=Gold and Economic Freedom |journal=] |volume=5 |issue=7 |url=http://www.constitution.org/mon/greenspan_gold.htm |access-date=2008-10-16 |archive-date=2010-09-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100925231456/http://constitution.org/mon/greenspan_gold.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> More recently he claimed that by focusing on targeting inflation "central bankers have behaved as though we were on the gold standard", rendering a return to the standard unnecessary.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Paul |first=Ron |title=End the Fed |page=xxiii }}</ref> Similarly, economists like ] argued that whilst some form of "monetary constitution" is essential for stable, depoliticized monetary policy, the form this constitution takes – for example, a gold standard, some other commodity-based standard, or a fiat currency with fixed rules for determining the quantity of money – is considerably less important.{{sfn|Salerno|1982}} | |||
| The gold standard is supported by many followers of the ], ], and some ].<ref name=":12">{{cite web |url=https://www.cato.org/blog/time-think-about-gold-standard |title=Time to Think about the Gold Standard? |last=Boaz |first=David |date=2009-03-12 |website=Cato Institute |access-date=2018-05-05}}</ref> | |||
| ===U.S. politics=== | |||
| Former congressman ] is a long-term, high-profile advocate of a gold standard, but has also expressed support for using a standard based on a basket of commodities that better reflects the state of the economy.<ref>Interview with Ron Paul. ''Squawkbox''. CNBC. 13 November 2009.</ref> | |||
| In 2011 the ] legislature passed a ] to accept federally issued gold and silver coins as legal tender to pay taxes.<ref>{{cite news|last=Clark |first=Stephen |url=https://www.foxnews.com/politics/utah-considers-return-to-gold-silver-coins/ |title=Utah Considers Return to Gold, Silver Coins |publisher=Fox News |date=March 3, 2011 |access-date=December 24, 2011}}</ref> As federally issued currency, the coins were already legal tender for taxes, although the market price of their metal content currently exceeds their monetary value. As of 2011 similar legislation was under consideration in other U.S. states.<ref>{{cite news |publisher=CNN |title=Utah: Forget dollars. How about gold? |url=https://money.cnn.com/2011/03/29/news/economy/utah_gold_currency/index.htm | date=2011-03-29}}</ref> The bill was initiated by newly elected ] ]s associated with the ] and was driven by anxiety over the policies of President ].<ref>{{cite news| url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/us-politics/8391504/Tea-Party-legislation-reveals-anxiety-at-US-direction-under-Barack-Obama.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220111/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/us-politics/8391504/Tea-Party-legislation-reveals-anxiety-at-US-direction-under-Barack-Obama.html |archive-date=2022-01-11 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live | location=London | newspaper=] | first=Alex | last=Spillius | title=Tea Party legislation reveals anxiety at US direction under Barack Obama | date=2011-03-18}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| In 2013, the ] passed SB 1439, which would have made gold and silver coin a legal tender in payment of debt, but the bill was vetoed by the Governor.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.azleg.gov/govlettr/51leg/1R/SB1439.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://www.azleg.gov/govlettr/51leg/1R/SB1439.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live |title=Letter regarding Senate Bill 1439 (legal tender) |website=Azleg.gov |access-date=3 March 2022}}</ref> | |||
| In 2015, some Republican candidates for the ] advocated for a gold standard, based on concern that the ]'s attempts to increase economic growth may create inflation. Economic historians did not agree with the candidates' assertions that the gold standard would benefit the U.S. economy.<ref name="NYT2015">{{Cite news |last=Appelbaum |first=Binyamin |date=2015-12-01 |title=The Good Old Days of the Gold Standard? Not Really, Historians Say |newspaper=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/12/02/business/economy/the-good-old-days-of-the-gold-standard-not-really-historians-say.html |access-date=2015-12-02 |issn=0362-4331}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Portal|Money|Numismatics}} | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=15em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]—Also referred to as the ''Gold Panic of 1869'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ===International institutions=== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| == |
==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| * The Gold Standard in Theory and History, ] (Editor), ], 1997, ISBN 0415150612 | |||
| * The Gold Standard and Related Regimes : Collected Essays (Studies in Macroeconomic History), ] (Editor), ] (Editor), ] (Editor), 1999, ISBN 0521550068 | |||
| * A Retrospective on the Classical Gold Standard, 1821–1931 (National Bureau of Economic Research Conference Report), Michael D. Bordo (Editor), ] (Editor), 1984, ISBN 0226065901 | |||
| * Between the Dollar-Sterling Gold Points: Exchange Rates, Parity, and Market Behavior. ], Cambridge University Press, 1996 | |||
| * Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939 (NBER Series on Long-Term Factors in Economic Development), Barry Eichengreen, 1996, ISBN 0195101138 | |||
| * Money and Politics: European Monetary Unification and the International Gold Standard (1865–1873) Luca Einaudi 2001 | |||
| * Keynes, the Liquidity Trap and the Gold Standard: A Possible Application of the Rational Expectations Hypothesis, Robert Marks 1995 | |||
| * Ideology and the Evolution of Vital Economic Institutions: Guilds, The Gold Standard, and Modern International Cooperation Earl A. Thompson, Charles R. Hickson, 2000 | |||
| * Gold Standard and Employment Policies between the Wars, Sidney Pollard Ed. 1970 | |||
| * Stability of International Exchange: Report on the Introduction of the Gold-Exchange Standard into China and Other Silver-Using Countries, Commission on International Exchange, 2001 | |||
| * Ken Elks' series on British Coinage | |||
| * Banking in Modern Japan Research Division of the Fuji Bank, 1967 | |||
| * Bordo, Michael D. "Bimetallism". In The New Palgrave Encyclopedia of Money and Finance edited by Peter K. Newman, Murray Milgate and John Eatwell. New York: Stockton Press, 1992. | |||
| * Gold Standard and the International Monetary System, 1900–1939, Ian M. Drummond 1983 | |||
| * The Gold Standard in Theory and Practice, RG Hawtrey, Longmans and Green | |||
| * Glitter of Gold: France, Bimetallism, and the Emergence of the International Gold Standard, 1848–1873 Marc Flandreau 2003 | |||
| * Cyclopædia of Political Science, Political Economy, and the Political History of the United States by the Best American and European Writers, John Lalor, 1881 | |||
| * The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison Ben Bernanke, Harold James 1990 | |||
| * The World Currency Crisis Murray Rothbard | |||
| * The Downfall of the Gold Standard Gustav Cassel 1966 | |||
| * Currency Convertibility: The Gold Standard and Beyond Jorge Braga de Macedo (Editor) 1996 | |||
| * Deceit of the Gold Standard and of Gold Monetization, William H. Russell 1982 | |||
| * Gold, Prices and Wages under the Greenback Standard Wesley Clair Mitchell | |||
| * Gold Standard Illusion: France, the Bank of France, and the International Gold Standard, 1914–1939 Kenneth Moure | |||
| * Modern Perspectives on the Gold Standard Tamim Bayoumi (Editor), Mark P. Taylor (Editor), 1997 | |||
| * Keynes, John M. ]; ''The Economic Consequences of Mr. Churchill'' (Criticism of returning to the gold standard at the pre-war level – ) | |||
| * A Treatise on Money, John Maynard Keynes 1930 | |||
| * Credibility of the Interwar Gold Standard, Uncertainty, and the Great Depression J. Peter Ferderer 1999 | |||
| * Monetary Standards in the Periphery: Paper,Silver and Gold,1854–1933, Pablo Martin Acena (Editor), Jaime Reis (Editor), 2000 | |||
| * The Bank of England updated 2004 | |||
| * Anatomy of an International Monetary Regime: The Classical Gold Standard, 1880–1914 Guilio M Gallarotti | |||
| * Canada and the Gold Standard: Balance of Payments Adjustments under Fixed Exchange Rates 1871–1913 Trevor Dick, John E. Floyd 1992 | |||
| ===Sources=== | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{refbegin|40em}} | |||
| * {{cite web| last1 = Bordo| first1 = Michael D.|first2=Robert D. |last2=Dittmar |first3=William T. |last3=Gavin | title = Gold, Fiat Money and Price Stability| work = Working Paper Series| publisher = Research Division – ]| url = http://research.stlouisfed.org/wp/2003/2003-014.pdf|date=June 2003 |access-date=December 24, 2011}} | |||
| * {{cite web |last1=Bordo |first1=Michael |title=Gold Standard |date=2008 |url=http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/GoldStandard.html |website=Econlib}} | |||
| * Cassel, Gustav. The Downfall of the Gold Standard. Oxford University Press, 1936. | |||
| * Drummond, Ian M. The Gold Standard and the International Monetary System 1900–1939. Macmillan Education, LTD, 1987. | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Barry J. |last=Eichengreen |author-link=Barry Eichengreen |title=Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939 |publisher=] |location=] |year=1995 |isbn=978-0-19-510113-3|oclc=34383450 }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Elwell |first=Craig K. |title=Brief History of the Gold Standard in the United States | year=2011 |url={{google books|id=ztHyT2ew3QUC|plainurl=yes}} |publisher=Congressional Research Service }} | |||
| * {{cite web |last1=Hamilton |first1=James D. |title=The gold standard and the Great Depression |website=Econbrowser |date=2005 |url=http://www.econbrowser.com/archives/2005/12/the_gold_standa.html |access-date=12 November 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081013081425/http://www.econbrowser.com/archives/2005/12/the_gold_standa.html |archive-date=13 October 2008}} | |||
| * {{cite book|url={{Google books|id=Q7J_EUM3RfoC|plainurl=yes}}|title=A Monetary History of the US 1867–1960 |last1=Friedman |first1=Milton |last2=Schwartz |first2= Anna Jacobson |page= 543 |publisher= Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-04147-6 |year=1963 |access-date=2012-07-09 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|first=James D. |last=Hamilton |author-link=James D. Hamilton |date=April 1988 |title=Role of the International Gold Standard in Propagating the Great Depression|journal=] |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=67–89 |doi=10.1111/j.1465-7287.1988.tb00286.x |url=http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/120017201/abstract |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130105094836/http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/120017201/abstract |url-status=dead |archive-date=2013-01-05 |access-date=2008-11-12}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|title=An introduction to positive economics|edition=4th|pages=683–702|first=Richard G. |last=Lipsey|year=1975|publisher=Weidenfeld & Nicolson|isbn=978-0-297-76899-9}} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |last=Officer |first=Lawrence |title=Gold Standard |date=1 February 2010 |encyclopedia=Eh.net Encyclopedia |url=http://eh.net/encyclopedia/article/officer.gold.standard |access-date=2012-07-09 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120627100816/http://eh.net/encyclopedia/article/officer.gold.standard |archive-date=2012-06-27 |url-status=dead}} | |||
| * {{cite web |last=Salerno |first=Joseph T. |url=http://www.cato.org/pubs/pas/pa016.html |title=The Gold Standard: An Analysis of Some Recent Proposals |date=1982-09-09 |work=Cato Policy Analysis |publisher=Cato Institute |access-date=2009-03-23 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Walton |first1=Gary M. |last2=Rockoff |first2=Hugh |title=History of the American Economy |date=2010 |publisher=South-Western |isbn=978-1-4390-3752-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9zaRPwAACAAJ |language=en}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Cite book|title=Banking in modern Japan |publisher=] |location=] |year=1967 |oclc=254964565 |isbn=978-0-333-71139-2}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Richard Franklin |last=Bensel |author-link=Richard Bensel |title=The political economy of American industrialization, 1877–1900 |publisher=] |location=] |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-521-77604-2 |oclc=43552761}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Cite journal |first1=Ben |last1=Bernanke |author-link=Ben Bernanke |first2=Harold |last2=James |date=October 1990 |title=The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison |journal=NBER Working Paper No. 3488 |doi=10.3386/w3488 |doi-access=free }} Also published as: {{Cite book|first1=Ben |last1=Bernanke |author-link=Ben Bernanke |first2=Harold |last2=James |chapter=The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MEfUi2H4cqwC |editor=R. Glenn Hubbard |editor-link=Glenn Hubbard (economics) |title=Financial markets and financial crises |publisher=] |location=] |year=1991 |pages=33–68 |isbn=978-0-226-35588-7 |oclc=231281602}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Michael D. |last=Bordo |author-link=Michael D. Bordo|title=Gold standard and related regimes: collected essays |publisher=] |location=] |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-521-55006-2 |oclc=59422152}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Michael D |last=Bordo |author2=] |author3=] |title=A Retrospective on the classical gold standard, 1821–1931 |publisher=] |location=] |year=1984 |isbn=978-0-226-06590-8 |oclc=10559587}} | |||
| * Coletta, Paolo E. in H. Wayne Morgan (ed.), The Gilded Age: A Reappraisal. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 1963; pp. 111–139. | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Barry J. |last=Eichengreen |author-link=Barry Eichengreen |author2=Marc Flandreau |title=The gold standard in theory and history |publisher=] |location=] |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-415-15061-3 |oclc=37743323}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Luca |last=Einaudi |title=Money and politics: European monetary unification and the international gold standard (1865–1873) |publisher=] |location=] |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-19-924366-2 |oclc=45556225}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|first=Mark A |last=Roberts |date=March 1995 |title=Keynes, the Liquidity Trap and the Gold Standard: A Possible Application of the Rational Expectations Hypothesis |journal=The Manchester School of Economic & Social Studies |volume=61 |issue=1 |pages=82–92 |doi=10.1111/j.1467-9957.1995.tb00270.x }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Earl A. |last=Thompson |author2=Charles Robert Hickson |title=Ideology and the evolution of vital institutions: guilds, the gold standard, and modern international cooperation |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-7923-7390-2 |oclc=46836861 |publisher=Kluwer Acad. Publ. |location=Boston}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |first=Sidney |last=Pollard |title=The gold standard and employment policies between the Wars |publisher=Methuen |location=] |year=1970 |isbn=978-0-416-14250-1 |oclc=137456 |url=https://archive.org/details/goldstandardempl0000poll }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Hugh Henry |last=Hanna |author2=] |author3=] |title=Stability of international exchange: Report on the introduction of the gold-exchange standard into China and other silver-using countries |year=1903 |oclc=6671835}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Ian M. |last=Drummond |author2=] |title=The gold standard and the international monetary system 1900–1939 |publisher=Macmillan Education |location=Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire |year=1987 |isbn=978-0-333-37208-1 |oclc=18324084}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Ralph George |last=Hawtrey |author-link=Ralph George Hawtrey |title=The Gold Standard in theory and practice |year=1927 |publisher=] |location=] |oclc=250855462 |isbn=978-0-313-22104-0}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Marc |last=Flandreau |title=The glitter of gold: France, bimetallism, and the emergence of the international gold standard, 1848–1873 |publisher=] |location=] |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-19-925786-7 |oclc=54826941}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=John |last=Lalor |title=Cyclopedia of Political Science, Political Economy and the Political History of the United States |publisher=Thoemmes Continuum |location=London |orig-year=1881 |year=2003 |isbn=978-1-84371-093-6 |oclc=52565505}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Murray Newton |last=Rothbard |author-link=Murray Rothbard |chapter=The World Currency Crisis |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=elPzEDHG9ysC |title=Making Economic Sense |publisher=] |location=] |year=2006 |pages=295–299 |isbn=978-0-945466-46-8 |oclc=78624652}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Gustav |last=Cassel |author-link=Gustav Cassel |title=The downfall of the gold standard |year=1936 |publisher=Clarendon Press |location=] |oclc=237252}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Jorge |last=Braga de Macedo |author2=Barry J. Eichengreen |author3=Jaime Reis |title=Currency convertibility: the gold standard and beyond |publisher=] |location=] |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-415-14057-7 |oclc=33132906}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=William H. |last=Russell |author-link=William Huntington Russell |title=The Deceit of the Gold Standard and of Gold Monetization |year=1982 |publisher=American Classical College Press |isbn=978-0-89266-324-8}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Wesley C. |last=Mitchell |author-link=Wesley Clair Mitchell |title=Gold, prices, and wages under the greenback standard |year=1908 |publisher=The University Press |location=] |oclc=1088693}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Kenneth |last=Mouré |title=The gold standard illusion: France, the Bank of France, and the International Gold Standard, 1914–1939 |publisher=] |location=] |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-19-924904-6 |oclc=48544538}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Tamim A. |last=Bayoumi |author2=] and Mark P. Taylor |title=Modern perspectives on the gold standard |publisher=] |location=] |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-521-57169-2 |oclc=34245103}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=John Maynard |last=Keynes |author-link=John Maynard Keynes |title=The economic consequences of Mr. Churchill |year=1925 |publisher=] |location=] |oclc=243857880}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=John Maynard |last=Keynes |author-link=John Maynard Keynes |title=A treatise on money in two volumes |year=1930 |publisher=MacMillan |location=] |oclc=152413612}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=J. Peter |last=Ferderer |title=Credibility of the interwar gold standard, uncertainty, and the Great Depression |year=1994 |publisher=Jerome Levy Economics Institute |location=] |oclc=31141890}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Pablo Martín |last=Aceña |author2=Jaime Reis |title=Monetary standards in the periphery: paper, silver and gold, 1854–1933 |publisher=Macmillan Press |location=] |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-333-67020-0 |oclc=247963508}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |first=Giulio M. |last=Gallarotti |title=The anatomy of an international monetary regime: the classical gold standard, 1880–1914 |publisher=] |location=] |year=1995 |isbn=978-0-19-508990-5 |oclc=30511110 |url=https://archive.org/details/anatomyofinterna0000gall }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Trevor J. O. |last=Dick |author2=] |title=Canada and the Gold Standard: Balance of Payments Adjustment Under Fixed Exchange Rates, 1871–1913 |publisher=] |location=] |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-521-61706-2 |oclc=59135525}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Richard |last=Hofstadter |author-link=Richard Hofstadter |title=The Paranoid Style in American Politics and Other Essays |chapter=Free Silver and the Mind of "Coin" Harvey |publisher=] |location=] |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-674-65461-7 |oclc=34772674}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=A.G. |last=Kenwood |author2=A. L. Lougheed |title=The growth of the international economy 1820–1990 |publisher=] |location=] |year=1992 |isbn=978-91-44-00079-4}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Nathan K. |last=Lewis |title=Gold: The Once and Future Money |publisher=Wiley |location=New York |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-470-04766-8 |oclc=87151964}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Mark |last=Metzler |title=Lever of Empire: The International Gold Standard and the Crisis of Liberalism in Prewar Japan. |publisher=] |location=] |year=2006 |page= |isbn=978-0-520-24420-7}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Lawrence H. |last=Officer |title=Between the Dollar-Sterling Gold Points: Exchange Rates, Parity and Market Behavior |publisher=] |location=] |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-521-03821-8 |oclc=124025586}} | |||
| * {{Cite encyclopedia |first=Lawrence H. |last=Officer |editor=] and ] |title=The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics |encyclopedia=] |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |location=] |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-333-78676-5 |oclc=181424188 |chapter-url=http://www.dictionaryofeconomics.com/article?id=pde2008_B000137&goto=bimetalism&result_number=140 |access-date=2008-11-13 |doi=10.1057/9780230226203.0136 |chapter=bimetallism |pages=1–6 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=David |last=Pietrusza |title='It Shines for All': The Gold Standard Editorials of The New York Sun |publisher=New York Sun Books |location=] |year=2011 |isbn= 978-1-4611-5612-3}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|first=Hartley |last=Withers |authorlink=Hartley Withers|title=War-Time Financial Problems |year=1919 |url=https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/13045 |access-date=2008-11-14 |publisher=] |location=] |oclc=2458983}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == |
==External links== | ||
| {{Spoken Misplaced Pages|EN_Gold_Standard.ogg|date=2007-12-04}} | |||
| * by ] | |||
| * | |||
| * by ] describes the gold standard as an "economic myth". | |||
| * University of Iowa Center for International Finance and Development | |||
| * by ] (Advocates for a return to a gold standard) | |||
| * Bank of England | |||
| * — A ] view of the gold standard. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Gold Standard}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:59, 17 December 2024
Monetary system based on the value of gold For other uses, see Gold standard (disambiguation).


A gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932 as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. Many states nonetheless hold substantial gold reserves.
Historically, the silver standard and bimetallism have been more common than the gold standard. The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, network externalities, and path dependence. Great Britain accidentally adopted a de facto gold standard in 1717 when Isaac Newton, then-master of the Royal Mint, set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation. As Great Britain became the world's leading financial and commercial power in the 19th century, other states increasingly adopted Britain's monetary system.
The gold standard was largely abandoned during the Great Depression before being re-instated in a limited form as part of the post-World War II Bretton Woods system. The gold standard was abandoned due to its propensity for volatility, as well as the constraints it imposed on governments: by retaining a fixed exchange rate, governments were hamstrung in engaging in expansionary policies to, for example, reduce unemployment during economic recessions.
According to a 2012 survey of 39 economists, the vast majority (92 percent) agreed that a return to the gold standard would not improve price-stability and employment outcomes, and two-thirds of economic historians surveyed in the mid-1990s rejected the idea that the gold standard "was effective in stabilizing prices and moderating business-cycle fluctuations during the nineteenth century." The consensus view among economists is that the gold standard helped prolong and deepen the Great Depression. Historically, banking crises were more common during periods under the gold standard while currency crises were less common. According to economist Michael D. Bordo, the gold standard has three benefits that made its use popular during certain historical periods: "its record as a stable nominal anchor; its automaticity; and its role as a credible commitment mechanism." The gold standard is supported by many followers of the Austrian School, free-market libertarians, and some supply-siders.
Implementation
The United Kingdom slipped into a gold specie standard in 1717 by over-valuing gold at 15+1⁄5 times its weight in silver. It was unique among nations to use gold in conjunction with clipped, underweight silver shillings, addressed only before the end of the 18th century by the acceptance of gold proxies like token silver coins and banknotes.
From the more widespread acceptance of paper money in the 19th century emerged the gold bullion standard, a system where gold coins do not circulate, but authorities like central banks agree to exchange circulating currency for gold bullion at a fixed price. First emerging in the late 18th century to regulate exchange between London and Edinburgh, Keynes (1913) noted how such a standard became the predominant means of implementing the gold standard internationally in the 1870s.
Restricting the free circulation of gold under the Classical Gold Standard period from the 1870s to 1914 was also needed in countries which decided to implement the gold standard while guaranteeing the exchangeability of huge amounts of legacy silver coins into gold at the fixed rate (rather than valuing publicly held silver at its depreciated value). The term limping standard is often used in countries maintaining significant amounts of silver coin at par with gold, thus an additional element of uncertainty with the currency's value versus gold. The most common silver coins kept at limping standard parity included French 5-franc coins, German 3-mark thalers, Dutch guilders, Indian rupees, and U.S. Morgan dollars.
Lastly, countries may implement a gold exchange standard, where the government guarantees a fixed exchange rate, not to a specified amount of gold, but rather to the currency of another country that is under a gold standard. This became the predominant international standard under the Bretton Woods Agreement from 1945 to 1971 by the fixing of world currencies to the U.S. dollar, the only currency after World War II to be on the gold bullion standard.
History before 1873
All references to "dollars" in this section refer to the United States dollar, unless otherwise stated.Silver and bimetallic standards until the 19th century
The use of gold as money began around 600 BCE in Asia Minor and has been widely accepted ever since, together with various other commodities used as money, with those that lose the least value over time becoming the accepted form. In the early and high Middle Ages, the Byzantine gold solidus or bezant was used widely throughout Europe and the Mediterranean, but its use waned with the decline of the Byzantine Empire's economic influence.
However, economic systems using gold as the sole currency and unit of account never emerged before the 18th century. For millennia it was silver, not gold, which was the real basis of the domestic economies: the foundation for most money-of-account systems, for payment of wages and salaries, and for most local retail trade. Gold functioning as currency and unit of account for daily transactions was not possible due to various hindrances which were only solved by tools that emerged in the 19th century, among them:
- Divisibility: Gold as currency was hindered by its small size and rarity, with the dime-sized ducat of 3.4 grams representing 7 days' salary for the highest-paid workers. In contrast, coins of silver and billon (low-grade silver) easily corresponded to daily labor costs and food purchases, making silver more effective as currency and unit of account. In mid-15th century England, most highly paid skilled artisans earned 6d a day (six pence, or 5.4 g silver), and a whole sheep cost 12d. This made the ducat of 40d and the half-ducat of 20d of little use for domestic trade.
- Non-existence of token coinage for gold: Sargent and Velde (1997) explained how token coins of copper or billon exchangeable for silver or gold were almost non-existent before the 19th century. Small change was issued at almost full intrinsic value and without conversion provisions into specie. Tokens of little intrinsic value were widely mistrusted, were viewed as a precursor to currency devaluation, and were easily counterfeited in the pre-industrial era. This made the gold standard impossible anywhere with token silver coins; Britain itself only accepted the latter in the 19th century.
- Non-existence of banknotes: Banknotes were mistrusted as currency in the first half of the 18th century following France's failed banknote issuance in 1716 under economist John Law. Banknotes only became accepted across Europe with the further maturing of banking institutions, and also as a result of the Napoleonic Wars of the early 19th century. Counterfeiting concerns also applied to banknotes.
The earliest European currency standards were therefore based on the silver standard, from the denarius of the Roman Empire to the penny (denier) introduced by Charlemagne throughout Western Europe, to the Spanish dollar and the German Reichsthaler and Conventionsthaler which survived well into the 19th century. Gold functioned as a medium for international trade and high-value transactions, but it generally fluctuated in price versus everyday silver money.
A bimetallic standard emerged under a silver standard in the process of giving popular gold coins like ducats a fixed value in terms of silver. In light of fluctuating gold–silver ratios in other countries, bimetallic standards were rather unstable and de facto transformed into a parallel bimetallic standard (where gold circulates at a floating exchange rate to silver) or reverted to a mono-metallic standard. France was the most important country which maintained a bimetallic standard during most of the 19th century.
Gold standard origin in Britain
The English pound sterling introduced c. 800 CE was initially a silver standard unit worth 20 shillings or 240 silver pennies. The latter initially contained 1.35 g fine silver, reduced by 1601 to 0.464 g (hence giving way to the shilling of 5.57 g fine silver). Hence the pound sterling was originally 324 g fine silver reduced to 111.36 g by 1601.
The problem of clipped, underweight silver pennies and shillings was a persistent, unresolved issue from the late 17th century to the early 19th century. In 1717 the value of the gold guinea (of 7.6885 g fine gold) was fixed at 21 shillings, resulting in a gold–silver ratio of 15.2, higher than prevailing ratios in Continental Europe. Great Britain was therefore de jure under a bimetallic standard with gold serving as the cheaper and more reliable currency compared to clipped silver (full-weight silver coins did not circulate and went to Europe where 21 shillings fetched over a guinea in gold). Several factors helped extend the British gold standard into the 19th century, namely:
- The Brazilian Gold Rush of the 18th century supplying significant quantities of gold to Portugal and Britain, with Portuguese gold coins also legal tender in Britain.
- Ongoing trade deficits with China (which sold to Europe but had little use for European goods) drained silver from the economies of most of Europe. Combined with greater confidence in banknotes issued by the Bank of England, it opened the way for gold as well as banknotes becoming acceptable currency in lieu of silver.
- The acceptability of token / subsidiary silver coins as substitutes for gold before the end of the 18th century. Initially issued by the Bank of England and other private companies, permanent issuance of subsidiary coinage from the Royal Mint commenced after the Great Recoinage of 1816.
A proclamation from Queen Anne in 1704 introduced the British West Indies to the gold standard; however, it did not result in the wide use of gold currency and the gold standard, given Britain's mercantilist policy of hoarding gold and silver from its colonies for use at home. Prices were quoted de jure in gold pounds sterling but were rarely paid in gold; the colonists' de facto daily medium of exchange and unit of account was predominantly the Spanish silver dollar. (Also explained in the history of the Trinidad and Tobago dollar.)

Following the Napoleonic Wars, Britain legally moved from the bimetallic to the gold standard in the 19th century in several steps, namely:
- The 21-shilling guinea was discontinued in favor of the 20-shilling gold sovereign, or £1 coin, which contained 7.32238 g fine gold
- The permanent issuance of subsidiary, limited legal tender silver coinage, commencing with the Great Recoinage of 1816
- The 1819 Act for the Resumption of Cash Payments, which set 1823 as the date for resumption of convertibility of Bank of England banknotes into gold sovereigns, and
- The Bank Charter Act 1844, which institutionalized the gold standard in Britain by establishing a ratio between gold reserves held by the Bank of England versus the banknotes which it could issue, and by significantly curbing the privilege of other British banks to issue banknotes.
From the second half of the 19th century Britain then introduced its gold standard to Australia, New Zealand, and the British West Indies in the form of circulating gold sovereigns as well as banknotes that were convertible at par into sovereigns or Bank of England banknotes. Canada introduced its own gold dollar in 1867 at par with the U.S. gold dollar and with a fixed exchange rate to the gold sovereign.
Effects of the 19th century gold rush

Up until 1850 only Britain and a few of its colonies were on the gold standard, with the majority of other countries being on the silver standard. France and the United States were two of the more notable countries on the bimetallic standard. France's actions in maintaining the French franc at either 4.5 g fine silver or 0.29032 g fine gold stabilized world gold–silver price ratios close to the French ratio of 15.5 in the first three quarters of the 19th century by offering to mint the cheaper metal in unlimited quantities – gold 20-franc coins whenever the ratio is below 15.5, and silver 5-franc coins whenever the ratio is above 15.5. The United States dollar was also bimetallic de jure until 1900, worth either 24.0566 g fine silver, or 1.60377 g fine gold (ratio 15.0); the latter revised to 1.50463 g fine gold (ratio 15.99) from 1837 to 1934. The silver dollar was generally the cheaper currency before 1837, while the gold dollar was cheaper between 1837 and 1873.
The nearly coincidental California gold rush of 1849 and the Australian gold rushes of 1851 significantly increased world gold supplies and the minting of gold francs and dollars as the gold–silver ratio went below 15.5, pushing France and the United States into the gold standard with Great Britain during the 1850s. The benefits of the gold standard were first felt by this larger bloc of countries, with Britain and France being the world's leading financial and industrial powers of the 19th century while the United States was an emerging power.
By the time the gold–silver ratio reverted to 15.5 in the 1860s, this bloc of gold-utilizing countries grew further and provided momentum to an international gold standard before the end of the 19th century:
- Portugal and several British colonies commenced with the gold standard in the 1850s and 1860s
- France was joined by Belgium, Switzerland and Italy in a larger Latin Monetary Union based on both the gold and silver French francs.
- Several international monetary conferences in the last third of the 19th century began to consider the merits of an international gold standard, albeit with concerns on its impact on the price of silver should several countries make the switch.
The international classical gold standard, 1873–1914
See also: Latin Monetary Union, German gold mark, Central Bank, and price–specie flow mechanismRollout in Europe and the United States
The international classical gold standard commenced in 1873 after the German Empire decided to transition from the silver North German thaler and South German gulden to the German gold mark, reflecting the sentiment of the first international monetary conference in 1867, and utilizing the 5 billion gold francs (worth 4.05 billion marks or 1,451 metric tons) in indemnity demanded from France at the end of the Franco-Prussian War. This transition done by a large, centrally located European economy also triggered a switch to gold by several European countries in the 1870s and led as well to the suspension of the unlimited minting of silver 5-franc coins in the Latin Monetary Union in 1873.
The following countries switched from silver or bimetallic currencies to gold in the following years (Britain is included for completeness):
- 1816, British Empire: one pound: from 111.37 g silver to 7.32238 g gold; ratio 15.21
- 1873, German Empire: one North German thaler or 13⁄4 South German gulden of 16.67 g silver, converted to 3 German gold marks of 3/2.79 = 1.0753 g gold; ratio 15.5
- 1873, Latin Monetary Union franc: from 4.5 g silver to 9/31 = 0.29032 g gold; ratio 15.5
- 1873, United States dollar, by the Coinage Act of 1873: from 24.0566 g silver to 1.50463 g gold; ratio 15.99
- 1875, Scandinavian Monetary Union: Rigsdaler specie of 25.28 g silver, converted to 4 krone (or krona) of 4/2.48 = 1.6129 g gold; ratio 15.67
- 1875, Netherlands: the Dutch Guilder from 9.45 g silver to 0.6048 g gold; ratio 15.625.
- 1881, Ottoman Empire: the Ottoman lira
- 1892, Austria-Hungary: the Austro-Hungarian florin of 11.11 g silver, converted to two Austro-Hungarian krone of 2/3.28 = 0.60976 g gold; ratio 18.22
- 1897, Russian Empire: the ruble from 18 g silver to 0.7742 g gold; ratio 23.25.
The gold standard became the basis for the international monetary system after 1873. According to economic historian Barry Eichengreen, "only then did countries settle on gold as the basis for their money supplies. Only then were pegged exchange rates based on the gold standard firmly established." Adopting and maintaining a singular monetary arrangement encouraged international trade and investment by stabilizing international price relationships and facilitating foreign borrowing. The gold standard was not firmly established in non-industrial countries.
Central banks and the gold exchange standard

As feared by the various international monetary conferences, the switch to gold, combined with record U.S. silver output from the Comstock Lode, plunged the price of silver after 1873 with the gold–silver ratio climbing to historic highs of 18 by 1880. Most of continental Europe made the conscious decision to move to the gold standard while leaving the mass of legacy (and erstwhile depreciated) silver coins remaining unlimited legal tender and convertible at face value for new gold currency. The term limping standard was used to describe currencies whose nations' commitment to the gold standard was put into doubt by the huge mass of silver coins still tendered for payment, the most numerous of which were French 5-franc coins, German 3-mark Vereinsthalers, Dutch guilders and American Morgan dollars.
Britain's original gold specie standard with gold in circulation was not feasible anymore with the rest of Continental Europe also switching to gold. The problem of scarce gold and legacy silver coins was only resolved by national central banks taking over the replacement of silver with national bank notes and token coins, centralizing the nation's supply of scarce gold, providing for reserve assets to guarantee convertibility of legacy silver coins, and allowing the conversion of banknotes into gold bullion or other gold-standard currencies solely for external purchases. This system is known as either a gold bullion standard whenever gold bars are offered, or a gold exchange standard whenever other gold-convertible currencies are offered.
John Maynard Keynes referred to both standards above as simply the gold exchange standard in his 1913 book Indian Currency and Finance. He described this as the predominant form of the international gold standard before the First World War, that a gold standard was generally impossible to implement before the 19th century due to the absence of recently developed tools (like central banking institutions, banknotes, and token currencies), and that a gold exchange standard was even superior to Britain's gold specie standard with gold in circulation. As discussed by Keynes:
The Gold-Exchange Standard arises out of the discovery that, so long as gold is available for payments of international indebtedness at an approximately constant rate in terms of the national currency, it is a matter of comparative indifference whether it actually forms the national currency ... The Gold-Exchange Standard may be said to exist when gold does not circulate in a country to an appreciable extent, when the local currency is not necessarily redeemable in gold, but when the Government or Central Bank makes arrangements for the provision of foreign remittances in gold at a fixed maximum rate in terms of the local currency, the reserves necessary to provide these remittances being kept to a considerable extent abroad.
Its theoretical advantages were first set forth by Ricardo (i.e. David Ricardo, 1824) at the time of the Bullionist Controversy. He laid it down that a currency is in its most perfect state when it consists of a cheap material, but having an equal value with the gold it professes to represent; and he suggested that convertibility for the purposes of the foreign exchanges should be ensured by the tendering on demand of gold bars (not coin) in exchange for notes, so that gold might be available for purposes of export only, and would be prevented from entering into the internal circulation of the country.
The first crude attempt in recent times at establishing a standard of this type was made by Holland. The free coinage of silver was suspended in 1877. But the currency continued to consist mainly of silver and paper. It has been maintained since that date at a constant value in terms of gold by the Bank's regularly providing gold when it is required for export and by its using its authority at the same time for restricting so far as possible the use of gold at home. To make this policy possible, the Bank of Holland has kept a reserve, of a moderate and economical amount, partly in gold, partly in foreign bills.
Since the Indian system (gold exchange standard implemented in 1893) has been perfected and its provisions generally known, it has been widely imitated both in Asia and elsewhere ... Something similar has existed in Java under Dutch influences for many years ... The Gold-Exchange Standard is the only possible means of bringing China onto a gold basis ...
The classical gold standard of the late 19th century was therefore not merely a superficial switch from circulating silver to circulating gold. The bulk of silver currency was actually replaced by banknotes and token currency whose gold value was guaranteed by gold bullion and other reserve assets held inside central banks. In turn, the gold exchange standard was just one step away from modern fiat currency with banknotes issued by central banks, and whose value is secured by the bank's reserve assets, but whose exchange value is determined by the central bank's monetary policy objectives on its purchasing power in lieu of a fixed equivalence to gold.
Rollout outside Europe
The final chapter of the classical gold standard ending in 1914 saw the gold exchange standard extended to many Asian countries by fixing the value of local currencies to gold or to the gold standard currency of a Western colonial power. The Netherlands East Indies guilder was the first Asian currency pegged to gold in 1875 via a gold exchange standard which maintained its parity with the gold Dutch guilder.
Various international monetary conferences were called up until 1892, with various countries actually pledging to maintain the limping standard of freely circulating legacy silver coins in order to prevent the further deterioration of the gold–silver ratio which reached 20 in the 1880s. After 1890 however, silver's price decline could not be prevented further and the gold–silver ratio rose sharply above 30.
In 1893 the Indian rupee of 10.69 g fine silver was fixed at 16 British pence (or £1 = 15 rupees; gold–silver ratio 21.9), with legacy silver rupees remaining legal tender. In 1906 the Straits dollar of 24.26 g silver was fixed at 28 pence (or £1 = 84⁄7 dollars; ratio 28.4).
Nearly similar gold standards were implemented in Japan in 1897, in the Philippines in 1903, and in Mexico in 1905 when the previous yen or peso of 24.26 g silver was redefined to approximately 0.75 g gold or half a U.S. dollar (ratio 32.3). Japan gained the needed gold reserves after the Sino-Japanese War of 1894–1895. For Japan, moving to gold was considered vital for gaining access to Western capital markets.
"Rules of the Game"
In the 1920s John Maynard Keynes retrospectively developed the phrase "rules of the game" to describe how central banks would ideally implement a gold standard during the prewar classical era, assuming international trade flows followed the ideal price–specie flow mechanism. Violations of the "rules" actually observed during the classical gold standard era from 1873 to 1914, however, reveal how much more powerful national central banks actually are in influencing price levels and specie flows, compared to the "self-correcting" flows predicted by the price-specie flow mechanism.
Keynes premised the "rules of the game" on best practices of central banks to implement the pre-1914 international gold standard, namely:
- To substitute gold with fiat currency in circulation, so that gold reserves may be centralized
- To actually allow a prudently determined ratio of gold reserves to fiat currency of less than 100%, with the difference made up by other loans and invested assets, such reserve ratio amounts consistent with fractional reserve banking practices
- To exchange circulating currency for gold or other foreign currencies at a fixed gold price, and to freely permit gold imports and exports
- Central banks were actually allowed modest margins in exchange rates to reflect gold delivery costs while still adhering to the gold standard. To illustrate this point, France may ideally allow the pound sterling (worth 25.22 francs based on ratios of their gold content) to trade between so-called gold points of 25.02F to 25.42F (plus or minus an assumed 0.20F/£ in gold delivery costs). France prevents sterling from climbing above 25.42F by delivering gold worth 25.22F or £1 (spending 0.20F for delivery), and from falling below 25.02F by the reverse process of ordering £1 in gold worth 25.22F in France (and again, minus 0.20F in costs).
- Finally, central banks were authorized to suspend the gold standard in times of war until it could be restored again as the contingency subsides.
Central banks were also expected to maintain the gold standard on the ideal assumption of international trade operating under the price–specie flow mechanism proposed by economist David Hume wherein:
- Countries which exported more goods would receive specie (gold or silver) inflows, at the expense of countries which imported those goods.
- More specie in exporting countries will result in higher price levels there, and conversely in lower price levels amongst countries spending their specie.
- Price disparities will self-correct as lower prices in specie-deficient will attract spending from specie-rich countries, until price levels in both places equalize again.
In practice, however, specie flows during the classical gold standard era failed to exhibit the self-corrective behavior described above. Gold finding its way back from surplus to deficit countries to exploit price differences was a painfully slow process, and central banks found it far more effective to raise or lower domestic price levels by lowering or raising domestic interest rates. High price level countries may raise interest rates to lower domestic demand and prices, but it may also trigger gold inflows from investors – contradicting the premise that gold will flow out of countries with high price levels. Developed economies deciding to buy or sell domestic assets to international investors also turned out to be more effective in influencing gold flows than the self-correcting mechanism predicted by Hume.
Another set of violations to the "rules of the game" involved central banks not intervening in a timely manner even as exchange rates went outside the "gold points" (in the example above, cases existed of the pound climbing above 25.42 francs or falling below 25.02 francs). Central banks were found to pursue other objectives other than fixed exchange rates to gold (like e.g., lower domestic prices, or stopping huge gold outflows), though such behavior is limited by public credibility on their adherence to the gold standard. Keynes described such violations occurring before 1913 by French banks limiting gold payouts to 200 francs per head and charging a 1% premium, and by the German Reichsbank partially suspending free payment in gold, though "covertly and with shame".
Some countries had limited success in implementing the gold standard even while disregarding such "rules of the game" in its pursuit of other monetary policy objectives. Inside the Latin Monetary Union, the Italian lira and the Spanish peseta traded outside typical gold-standard levels of 25.02–25.42F/£ for extended periods of time:
- Italy tolerated in 1866 the issuance of corso forzoso (forced legal tender paper currency) worth less than the Latin Monetary Union franc. It also flooded the Union with low-valued subsidiary silver coins worth less than the franc. For the rest of the 19th century the Italian lira traded at a fluctuating discount versus the standard gold franc.
- In 1883 the Spanish peseta went off the gold standard and traded below parity with the gold French franc. However, as the free minting of silver was suspended to the general public, the peseta had a floating exchange rate between the value of the gold franc and the silver franc. The Spanish government captured all profits from minting duros (5-peseta coins) out of silver bought for less than 5 ptas. While total issuance was limited to prevent the peseta from falling below the silver franc, the abundance of duros in circulation prevented the peseta from returning at par with the gold franc. Spain's system where the silver duro traded at a premium above its metallic value due to relative scarcity is called the fiduciary standard and was similarly implemented in the Philippines and other Spanish colonies in the end of the 19th century.
In the United States
See also: United States dollar
Inception
In the 1780s, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Morris and Alexander Hamilton recommended to Congress that a decimal currency system be adopted by the United States. The initial recommendation in 1785 was a silver standard based on the Spanish milled dollar (finalized at 371.25 grains or 24.0566 g fine silver), but in the final version of the Coinage Act of 1792 Hamilton's recommendation to include a $10 gold eagle was also approved, containing 247.5 grains (16.0377 g) fine gold. Hamilton therefore put the U.S. dollar on a bimetallic standard with a gold–silver ratio of 15.0.
American-issued dollars and cents remained less common in circulation than Spanish dollars and reales (1/8th dollar) for the next six decades until foreign currency was demonetized in 1857. $10 gold eagles were exported to Europe where it could fetch over ten Spanish dollars due to their higher gold ratio of 15.5. American silver dollars also compared favorably with Spanish dollars and were easily used for overseas purchases. In 1806 President Jefferson suspended the minting of exportable gold coins and silver dollars in order to divert the United States Mint's limited resources into fractional coins which stayed in circulation.
Pre-Civil War
The United States also embarked on establishing a national bank with the First Bank of the United States in 1791 and the Second Bank of the United States in 1816. In 1836, President Andrew Jackson failed to extend the Second Bank's charter, reflecting his sentiments against banking institutions as well as his preference for the use of gold coins for large payments rather than privately issued banknotes. The return of gold could only be possible by reducing the dollar's gold equivalence, and in the Coinage Act of 1834 the gold–silver ratio was increased to 16.0 (ratio finalized in 1837 to 15.99 when the fine gold content of the $10 eagle was set at 232.2 grains or 15.0463 g).
Gold discoveries in California in 1848 and later in Australia lowered the gold price relative to silver; this drove silver money from circulation because it was worth more in the market than as money. Passage of the Independent Treasury Act of 1848 placed the U.S. on a strict hard-money standard. Doing business with the American government required gold or silver coins.
Government accounts were legally separated from the banking system. However, the mint ratio (the fixed exchange rate between gold and silver at the mint) continued to overvalue gold. In 1853, silver coins 50 cents and below were reduced in silver content and cannot be requested for minting by the general public (only the U.S. government can request for it). In 1857 the legal tender status of Spanish dollars and other foreign coinage was repealed. In 1857 the final crisis of the free banking era began as American banks suspended payment in silver, with ripples through the developing international financial system.
Post-Civil War

Due to the inflationary finance measures undertaken to help pay for the U.S. Civil War, the government found it difficult to pay its obligations in gold or silver and suspended payments of obligations not legally specified in specie (gold bonds); this led banks to suspend the conversion of bank liabilities (bank notes and deposits) into specie. In 1862 paper money was made legal tender. It was a fiat money (not convertible on demand at a fixed rate into specie). These notes came to be called "greenbacks".
After the Civil War, Congress wanted to reestablish the metallic standard at pre-war rates. The market price of gold in greenbacks was above the pre-war fixed price ($20.67 per ounce of gold) requiring deflation to achieve the pre-war price. This was accomplished by growing the stock of money less rapidly than real output. By 1879 the market price of the greenback matched the mint price of gold, and according to Barry Eichengreen, the United States was effectively on the gold standard that year.
The Coinage Act of 1873 (also known as the Crime of ‘73) suspended the minting of the standard silver dollar (of 412.5 grains, 90% fine), the only fully legal tender coin that individuals could convert silver bullion into in unlimited (or Free silver) quantities, and right at the onset of the silver rush from the Comstock Lode in the 1870s. Political agitation over the inability of silver miners to monetize their produce resulted in the Bland–Allison Act of 1878 and Sherman Silver Purchase Act of 1890 which made compulsory the minting of significant quantities of the silver Morgan dollar.
With the resumption of convertibility on June 30, 1879, the government again paid its debts in gold, accepted greenbacks for customs and redeemed greenbacks on demand in gold. While greenbacks made suitable substitutes for gold coins, American implementation of the gold standard was hobbled by the continued over-issuance of silver dollars and silver certificates emanating from political pressures. Lack of public confidence in the ubiquitous silver currency resulted in a run on U.S. gold reserves during the Panic of 1893.
During the latter part of the nineteenth century the use of silver and a return to the bimetallic standard were recurrent political issues, raised especially by William Jennings Bryan, the People's Party and the Free Silver movement. In 1900 the gold dollar was declared the standard unit of account and a gold reserve for government issued paper notes was established. Greenbacks, silver certificates, and silver dollars continued to be legal tender, all redeemable in gold.
Fluctuations in the U.S. gold stock, 1862–1877
| US gold stock | |
|---|---|
| 1862 | 59 tons |
| 1866 | 81 tons |
| 1875 | 50 tons |
| 1878 | 78 tons |
The U.S. had a gold stock of 1.9 million ozt (59 t) in 1862. Stocks rose to 2.6 million ozt (81 t) in 1866, declined in 1875 to 1.6 million ozt (50 t) and rose to 2.5 million ozt (78 t) in 1878. Net exports did not mirror that pattern. In the decade before the Civil War net exports were roughly constant; postwar they varied erratically around pre-war levels but fell significantly in 1877 and became negative in 1878 and 1879. The net import of gold meant that the foreign demand for American currency to purchase goods, services, and investments exceeded the corresponding American demands for foreign currencies. In the final years of the greenback period (1862–1879), gold production increased while gold exports decreased. The decrease in gold exports was considered by some to be a result of changing monetary conditions. The demands for gold during this period were as a speculative vehicle, and for its primary use in the foreign exchange markets financing international trade. The major effect of the increase in gold demand by the public and Treasury was to reduce exports of gold and increase the Greenback price of gold relative to purchasing power.
Abandonment of the gold standard
Impact of World War I
Governments with insufficient tax revenue suspended convertibility repeatedly in the 19th century. The real test, however, came in the form of World War I, a test which "it failed utterly" according to economist Richard Lipsey. The gold specie standard came to an end in the United Kingdom and the rest of the British Empire with the outbreak of World War I.
By the end of 1913, the classical gold standard was at its peak, but World War I caused many countries to suspend or abandon it. According to Lawrence Officer the main cause of the gold standard's failure to resume its previous position after World War I was "the Bank of England's precarious liquidity position and the gold-exchange standard". A run on sterling caused Britain to impose exchange controls that fatally weakened the standard; convertibility was not legally suspended, but gold prices no longer played the role that they did before. In financing the war and abandoning gold, many of the belligerents suffered drastic inflations. Price levels doubled in the U.S. and Britain, tripled in France and quadrupled in Italy. Exchange rates changed less, even though European inflation rates were more severe than America's. This meant that the costs of American goods decreased relative to those in Europe. Between August 1914 and spring of 1915, the dollar value of U.S. exports tripled, and its trade surplus exceeded $1 billion for the first time.
Ultimately, the system could not deal quickly enough with the large deficits and surpluses; this was previously attributed to downward wage rigidity brought about by the advent of unionized labor but is now considered as an inherent fault of the system that arose under the pressures of war and rapid technological change. In any case, prices had not reached equilibrium by the time of the Great Depression, which served to kill off the system completely.
For example, Germany had gone off the gold standard in 1914 and could not effectively return to it because war reparations had cost it much of its gold reserves. During the occupation of the Ruhr the German central bank (Reichsbank) issued enormous sums of non-convertible marks to support workers who were on strike against the French occupation and to buy foreign currency for reparations; this led to the German hyperinflation of the early 1920s and the decimation of the German middle class.
The U.S. did not suspend the gold standard during the war. The newly created Federal Reserve intervened in currency markets and sold bonds to "sterilize" some of the gold imports that would have otherwise increased the stock of money. By 1927 many countries had returned to the gold standard. As a result of World War I the United States, which had been a net debtor country, had become a net creditor by 1919.
Interwar period
The gold specie standard ended in the United Kingdom and the rest of the British Empire at the outbreak of World War I, when Treasury notes replaced the circulation of gold sovereigns and gold half sovereigns. Legally, the gold specie standard was not abolished. The end of the gold standard was successfully effected by the Bank of England through appeals to patriotism urging citizens not to redeem paper money for gold specie. It was only in 1925, when Britain returned to the gold standard in conjunction with Australia and South Africa, that the gold specie standard was officially ended.
United Kingdom legislation| Gold Standard Act 1925 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 Parliament of the United Kingdom Parliament of the United Kingdom | |
| Long title | An Act to facilitate the return to a gold standard and for purposes connected therewith. |
| Citation | 15 & 16 Geo. 5. c. 29 |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 13 May 1925 |
The British Gold Standard Act 1925 both introduced the gold bullion standard and simultaneously repealed the gold specie standard. The new standard ended the circulation of gold specie coins. Instead, the law compelled the authorities to sell gold bullion on demand at a fixed price, but "only in the form of bars containing approximately four hundred ounces troy of fine gold". John Maynard Keynes, citing deflationary dangers, argued against resumption of the gold standard. By fixing the price at a level which restored the pre-war exchange rate of US$4.86 per pound sterling, as Chancellor of the Exchequer, Churchill is argued to have made an error that led to depression, unemployment and the 1926 general strike. The decision was described by Andrew Turnbull as a "historic mistake".
The pound left the gold standard in 1931 and a number of currencies of countries that historically had performed a large amount of their trade in sterling were pegged to sterling instead of to gold. The Bank of England took the decision to leave the gold standard abruptly and unilaterally.
Great Depression
Main article: Great Depression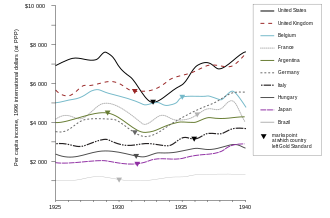
Many other countries followed Britain in returning to the gold standard, leading to a period of relative stability but also deflation. This state of affairs lasted until the Great Depression (1929–1939) forced countries off the gold standard. Primary-producing countries were first to abandon the gold standard. In the summer of 1931, a Central European banking crisis led Germany and Austria to suspend gold convertibility and impose exchange controls. A May 1931 run on Austria's largest commercial bank had caused it to fail. The run spread to Germany, where the central bank also collapsed. International financial assistance was too late and in July 1931 Germany adopted exchange controls, followed by Austria in October. The Austrian and German experiences, as well as British budgetary and political difficulties, were among the factors that destroyed confidence in sterling, which occurred in mid-July 1931. Runs ensued and the Bank of England lost much of its reserves.
On September 19, 1931, speculative attacks on the pound led the Bank of England to abandon the gold standard, ostensibly "temporarily". However, the ostensibly temporary departure from the gold standard had unexpectedly positive effects on the economy, leading to greater acceptance of departing from the gold standard. Loans from American and French central banks of £50 million were insufficient and exhausted in a matter of weeks, due to large gold outflows across the Atlantic. The British benefited from this departure. They could now use monetary policy to stimulate the economy. Australia and New Zealand had already left the standard and Canada quickly followed suit.
The interwar partially backed gold standard was inherently unstable because of the conflict between the expansion of liabilities to foreign central banks and the resulting deterioration in the Bank of England's reserve ratio. France was then attempting to make Paris a world class financial center, and it received large gold flows as well.
Upon taking office in March 1933, U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt departed from the gold standard.
By the end of 1932, the gold standard had been abandoned as a global monetary system. Czechoslovakia, Belgium, France, the Netherlands and Switzerland abandoned the gold standard in the mid-1930s. According to Barry Eichengreen, there were three primary reasons for the collapse of the gold standard:
- Tradeoffs between currency stability and other domestic economic objectives: Governments in the 1920s and 1930s faced conflictual pressures between maintaining currency stability and reducing unemployment. Suffrage, trade unions, and labor parties pressured governments to focus on reducing unemployment rather than maintaining currency stability.
- Increased risk of destabilizing capital flight: International finance doubted the credibility of national governments to maintain currency stability, which led to capital flight during crises, which aggravated the crises.
- The U.S., not Britain, was the main financial center: Whereas Britain had during past periods been capable of managing a harmonious international monetary system, the U.S. was not.
According to Douglas Irwin, the gold standard contributed to policymakers' turning to extreme protectionism in the 1930s. Policymakers were reluctant to abandon the gold standard, which would have allowed their currencies to depreciate. This instead led policymakers to impose higher tariffs and other protectionist measures.
Causes of the Great Depression
Main article: Causes of the Great DepressionEconomists, such as Barry Eichengreen, Peter Temin and Ben Bernanke, allocate at least part of the blame for prolonging the economic depression on the gold standard of the 1920s. The Great Depression started in 1929 and lasted for about a decade. The gold standard theory of the Depression has been described as the "consensus view" among economists. This view is based on two arguments: "(1) Under the gold standard, deflationary shocks were transmitted between countries and, (2) for most countries, continued adherence to gold prevented monetary authorities from offsetting banking panics and blocked their recoveries." However, a 2002 paper argues that the second argument would only apply "to small open economies with limited gold reserves. This was not the case for the United States, the largest country in the world, holding massive gold reserves. The United States was not constrained from using expansionary policy to offset banking panics, deflation, and declining economic activity." According to Edward C. Simmons, in the United States, adherence to the gold standard prevented the Federal Reserve from expanding the money supply to stimulate the economy, fund insolvent banks and fund government deficits that could "prime the pump" for an expansion. Once off the gold standard, it became free to engage in such money creation. The gold standard limited the flexibility of the central banks' monetary policy by limiting their ability to expand the money supply. In the US, the central bank was required by the Federal Reserve Act (1913) to have gold backing 40% of its demand notes. A 2024 study in the American Economic Review found that for a sample of 27 countries, leaving the gold standard helped states to recover from the Great Depression.
Higher interest rates intensified the deflationary pressure on the dollar and reduced investment in U.S. banks. Commercial banks converted Federal Reserve Notes to gold in 1931, reducing its gold reserves and forcing a corresponding reduction in the amount of currency in circulation. This speculative attack created a panic in the U.S. banking system. Fearing imminent devaluation many depositors withdrew funds from U.S. banks. As bank runs grew, a reverse multiplier effect caused a contraction in the money supply. Additionally the New York Fed had loaned over $150 million in gold (over 240 tons) to European Central Banks. This transfer contracted the U.S. money supply. The foreign loans became questionable once Britain, Germany, Austria and other European countries went off the gold standard in 1931 and weakened confidence in the dollar.
The forced contraction of the money supply resulted in deflation. Even as nominal interest rates dropped, deflation-adjusted real interest rates remained high, rewarding those who held onto money instead of spending it, further slowing the economy. Recovery in the United States was slower than in Britain, in part due to Congressional reluctance to abandon the gold standard and float the U.S. currency as Britain had done.
In the early 1930s, the Federal Reserve defended the dollar by raising interest rates, trying to increase the demand for dollars. This helped attract international investors who bought foreign assets with gold.
Congress passed the Gold Reserve Act on 30 January 1934; the measure nationalized all gold by ordering Federal Reserve banks to turn over their supply to the U.S. Treasury. In return, the banks received gold certificates to be used as reserves against deposits and Federal Reserve notes. The act also authorized the president to devalue the gold dollar. Under this authority, the president, on 31 January 1934, changed the value of the dollar from $20.67 to the troy ounce to $35 to the troy ounce, a devaluation of over 40%.
Other causal factors, or factors in the prolongation of the Great Depression include trade wars and the reduction in international trade caused by barriers such as Smoot–Hawley Tariff in the U.S. and the Imperial Preference policies of Great Britain, the failure of central banks to act responsibly, government policies designed to prevent wages from falling, such as the Davis–Bacon Act of 1931, during the deflationary period resulting in production costs dropping slower than sales prices, thereby injuring business profits and increases in taxes to reduce budget deficits and to support new programs such as Social Security. The U.S. top marginal income tax rate went from 25% to 63% in 1932 and to 79% in 1936, while the bottom rate increased over tenfold, from .375% in 1929 to 4% in 1932. The concurrent massive drought resulted in the U.S. Dust Bowl.
The Austrian School argued that the Great Depression was the result of a credit bust. Alan Greenspan wrote that the bank failures of the 1930s were sparked by Great Britain dropping the gold standard in 1931. This act "tore asunder" any remaining confidence in the banking system. Financial historian Niall Ferguson wrote that what made the Great Depression truly 'great' was the European banking crisis of 1931. According to Federal Reserve Chairman Marriner Eccles, the root cause was the concentration of wealth resulting in a stagnating or decreasing standard of living for the poor and middle class. These classes went into debt, producing the credit explosion of the 1920s. Eventually, the debt load grew too heavy, resulting in the massive defaults and financial panics of the 1930s.
Trying to return to the Gold Standard
During World War I many countries suspended their Gold standard in varying ways. There was high inflation from WWI, and in the 1920s in the Weimar Republic, Austria, and throughout Europe. In the late 1920s there was a scramble to deflate prices to get the gold standard's conversion rates back on track to pre-WWI levels, by causing deflation and high unemployment through tight monetary policy. In 1933 FDR signed Executive Order 6102 and in 1934 signed the Gold Reserve Act.
| Country | Return to Gold | Suspension of Gold Standard | Foreign Exchange Control | Devaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | April 1925 | December 1929 | — | March 1930 |
| Austria | April 1925 | April 1933 | October 1931 | September 1931 |
| Belgium | October 1926 | — | — | March 1935 |
| Canada | July 1926 | October 1931 | — | September 1931 |
| Czechoslovakia | April 1926 | — | September 1931 | February 1934 |
| Denmark | January 1927 | September 1931 | November 1931 | September 1931 |
| Estonia | January 1928 | June 1933 | November 1931 | June 1933 |
| Finland | January 1926 | October 1931 | — | October 1931 |
| France | August 1926-June 1928 | — | — | October 1936 |
| Germany | September 1924 | — | July 1931 | — |
| Greece | May 1928 | April 1932 | September 1931 | April 1932 |
| Hungary | April 1925 | — | July 1931 | — |
| Italy | December 1927 | — | May 1934 | October 1936 |
| Japan | December 1930 | December 1931 | July 1932 | December 1931 |
| Latvia | August 1922 | — | October 1931 | — |
| Netherlands | April 1925 | — | — | October 1936 |
| Norway | May 1928 | September 1931 | — | September 1931 |
| New Zealand | April 1925 | September 1931 | — | April 1930 |
| Poland | October 1927 | — | April 1936 | October 1936 |
| Romania | March 1927-February 1929 | — | May 1932 | — |
| Sweden | April 1924 | September 1931 | — | September 1931 |
| Spain | — | — | May 1931 | — |
| United Kingdom | May 1925 | September 1931 | — | September 1931 |
| United States | June 1919 | March 1933 | March 1933 | April 1933 |
Bretton Woods
Main article: Bretton Woods systemUnder the Bretton Woods international monetary agreement of 1944, the gold standard was kept without domestic convertibility. The role of gold was severely constrained, as other countries' currencies were fixed in terms of the dollar. Many countries kept reserves in gold and settled accounts in gold. Still, they preferred to settle balances with other currencies, with the US dollar becoming the favorite. The International Monetary Fund was established to help with the exchange process and assist nations in maintaining fixed rates. Within Bretton Woods adjustment was cushioned through credits that helped countries avoid deflation. Under the old standard, a country with an overvalued currency would lose gold and experience deflation until the currency was again valued correctly. Most countries defined their currencies in terms of dollars, but some countries imposed trading restrictions to protect reserves and exchange rates. Therefore, most countries' currencies were still basically inconvertible. In the late 1950s, the exchange restrictions were dropped and gold became an important element in international financial settlements.
After the Second World War, a system similar to a gold standard and sometimes described as a "gold exchange standard" was established by the Bretton Woods Agreements. Under this system, many countries fixed their exchange rates relative to the U.S. dollar and central banks could exchange dollar holdings into gold at the official exchange rate of $35 per ounce; this option was not available to firms or individuals. All currencies pegged to the dollar thereby had a fixed value in terms of gold. Since private parties could not exchange gold at the official rate, market prices fluctuated. Large jumps in the market price 1960 lead to the creation of the London Gold Pool.
Starting in the 1959–1969 administration of President Charles de Gaulle and continuing until 1970, France reduced its dollar reserves, exchanging them for gold at the official exchange rate, reducing U.S. economic influence. This, along with the fiscal strain of federal expenditures for the Vietnam War and persistent balance of payments deficits, led U.S. President Richard Nixon to end international convertibility of the U.S. dollar to gold on August 15, 1971 (the "Nixon Shock").
This was meant to be a temporary measure, with the gold price of the dollar and the official rate of exchanges remaining constant. Revaluing currencies was the main purpose of this plan. No official revaluation or redemption occurred. The dollar subsequently floated. In December 1971, the "Smithsonian Agreement" was reached. In this agreement, the dollar was devalued from $35 per troy ounce of gold to $38. Other countries' currencies appreciated. However, gold convertibility did not resume. In October 1973, the price was raised to $42.22. Once again, the devaluation was insufficient. Within two weeks of the second devaluation the dollar was left to float. The $42.22 par value was made official in September 1973, long after it had been abandoned in practice. In October 1976, the government officially changed the definition of the dollar; references to gold were removed from statutes. From this point, the international monetary system was made of pure fiat money. However, gold has persisted as a significant reserve asset since the collapse of the classical gold standard.
Modern gold production
An estimated total of 174,100 tonnes of gold have been mined in human history, according to GFMS as of 2012. This is roughly equivalent to 5.6 billion troy ounces or, in terms of volume, about 9,261 cubic metres (327,000 cu ft), or a cube 21 metres (69 ft) on a side. There are varying estimates of the total volume of gold mined. One reason for the variance is that gold has been mined for thousands of years. Another reason is that some nations are not particularly open about how much gold is being mined. In addition, it is difficult to account for the gold output in illegal mining activities.
World production for 2011 was circa 2,700 tonnes. Since the 1950s, annual gold output growth has approximately kept pace with world population growth (i.e. a doubling in this period) although it has lagged behind world economic growth (an approximately eightfold increase since the 1950s, and fourfold since 1980.
Reintroduction
In 2024, Zimbabwe became the first country in the 21st century to use a gold standard for its currency, in order to tackle inflation and create confidence within the economy. The Zimbabwe Gold (ZiG) is backed by US$400 million and 2,522 kg of gold, thus giving a total of US$575 million worth of hard assets. This development came after the Zimdollar crashed based on official rate from US$1:ZWL2.50 at introduction to US$1:ZWL30,672.42 on 5 April 2024, whilst parallel market was trading at US$1:ZWL42,500 at the time of removal.
Theory
Commodity money is inconvenient to store and transport in large amounts. Furthermore, it does not allow a government to manipulate the flow of commerce with the same ease that a fiat currency does. As such, commodity money gave way to representative money and gold and other specie were retained as its backing.
Gold was a preferred form of money due to its rarity, durability, divisibility, fungibility and ease of identification, often in conjunction with silver. Silver was typically the main circulating medium, with gold as the monetary reserve. Commodity money was anonymous, as identifying marks can be removed. Commodity money retains its value despite what may happen to the monetary authority. After the fall of South Vietnam, many refugees carried their wealth to the West in gold after the national currency became worthless.
Under commodity standards currency itself has no intrinsic value but is accepted by traders because it can be redeemed any time for the equivalent specie. A U.S. silver certificate, for example, could be redeemed for an actual piece of silver.
Representative money and the gold standard protect citizens from hyperinflation and other abuses of monetary policy, as were seen in some countries during the Great Depression. Commodity money conversely led to deflation.
Countries that left the gold standard earlier than other countries recovered from the Great Depression sooner. For example, Great Britain and the Scandinavian countries, which left the gold standard in 1931, recovered much earlier than France and Belgium, which remained on gold much longer. Countries such as China, which had a silver standard, almost entirely avoided the depression (due to the fact it was then barely integrated into the global economy). The connection between leaving the gold standard and the severity and duration of the depression was consistent for dozens of countries, including developing countries. This may explain why the experience and length of the depression differed between national economies.
Variations
A full or 100%-reserve gold standard exists when the monetary authority holds sufficient gold to convert all the circulating representative money into gold at the promised exchange rate. It is sometimes referred to as the gold specie standard to more easily distinguish it. Opponents of a full standard consider it difficult to implement, saying that the quantity of gold in the world is too small to sustain worldwide economic activity at or near current gold prices; implementation would entail a many-fold increase in the price of gold. Gold standard proponents have said, "Once a money is established, any stock of money becomes compatible with any amount of employment and real income." While prices would necessarily adjust to the supply of gold, the process may involve considerable economic disruption, as was experienced during earlier attempts to maintain gold standards.
In an international gold-standard system (which is necessarily based on an internal gold standard in the countries concerned), gold or a currency that is convertible into gold at a fixed price is used to make international payments. Under such a system, when exchange rates rise above or fall below the fixed mint rate by more than the cost of shipping gold, inflows or outflows occur until rates return to the official level. International gold standards often limit which entities have the right to redeem currency for gold.
Impact
A poll of 39 prominent U.S. economists conducted by the IGM Economic Experts Panel in 2012 found that none of them believed that returning to the gold standard would improve price-stability and employment outcomes. The specific statement with which the economists were asked to agree or disagree was: "If the U.S. replaced its discretionary monetary policy regime with a gold standard, defining a 'dollar' as a specific number of ounces of gold, the price-stability and employment outcomes would be better for the average American." 40% of the economists disagreed, and 53% strongly disagreed with the statement; the rest did not respond to the question. The panel of polled economists included past Nobel Prize winners, former economic advisers to both Republican and Democratic presidents, and senior faculty from Harvard, Chicago, Stanford, MIT, and other well-known research universities. A 1995 study reported on survey results among economic historians showing that two-thirds of economic historians disagreed that the gold standard "was effective in stabilizing prices and moderating business-cycle fluctuations during the nineteenth century."
Advantages
According to economist Michael D. Bordo, the gold standard has three benefits: "its record as a stable nominal anchor; its automaticity; and its role as a credible commitment mechanism":
- A gold standard does not allow some types of financial repression. Financial repression acts as a mechanism to transfer wealth from creditors to debtors, particularly the governments that practice it. Financial repression is most successful in reducing debt when accompanied by inflation and can be considered a form of taxation. In 1966 Alan Greenspan wrote "Deficit spending is simply a scheme for the confiscation of wealth. Gold stands in the way of this insidious process. It stands as a protector of property rights. If one grasps this, one has no difficulty in understanding the statists' antagonism toward the gold standard."
- Long-term price stability has been described as one of the virtues of the gold standard, but historical data shows that the magnitude of short run swings in prices were far higher under the gold standard.
- Currency crises were less frequent under the gold standard than in periods without the gold standard. However, banking crises were more frequent.
- The gold standard provides fixed international exchange rates between participating countries and thus reduces uncertainty in international trade. Historically, imbalances between price levels were offset by a balance-of-payment adjustment mechanism called the "price–specie flow mechanism". Gold used to pay for imports reduces the money supply of importing nations, causing deflation, which makes them more competitive, while the importation of gold by net exporters serves to increase their money supply, causing inflation, making them less competitive.
- Hyper-inflation, a common correlator with government overthrows and economic failures, is more difficult when a gold standard exists. This is because hyper-inflation, by definition, is a loss in trust of failing fiat and those governments that create the fiat.
Disadvantages

- The unequal distribution of gold deposits makes the gold standard more advantageous for those countries that produce gold. In 2010 the largest producers of gold, in order, were China, Australia, the U.S., South Africa, and Russia. The country with the largest unmined gold deposits is Australia.
- Some economists believe that the gold standard acts as a limit on economic growth. According to David Mayer, "As an economy's productive capacity grows, then so should its money supply. Because a gold standard requires that money be backed in the metal, then the scarcity of the metal constrains the ability of the economy to produce more capital and grow."
- Mainstream economists believe that economic recessions can be largely mitigated by increasing the money supply during economic downturns. A gold standard means that the money supply would be determined by the gold supply and hence monetary policy could no longer be used to stabilize the economy.
- Although the gold standard brings long-run price stability, it is historically associated with high short-run price volatility. It has been argued by Schwartz, among others, that instability in short-term price levels can lead to financial instability as lenders and borrowers become uncertain about the value of debt. Historically, discoveries of gold and rapid increases in gold production have caused volatility.
- Deflation punishes debtors. Real debt burdens therefore rise, causing borrowers to cut spending to service their debts or to default. Lenders become wealthier, but may choose to save some of the additional wealth, reducing GDP.
- The money supply would essentially be determined by the rate of gold production. When gold stocks increase more rapidly than the economy, there is inflation and the reverse is also true. The consensus view is that the gold standard contributed to the severity and length of the Great Depression, as under the gold standard central banks could not expand credit at a fast enough rate to offset deflationary forces.
- Hamilton contended that the gold standard is susceptible to speculative attacks when a government's financial position appears weak. Conversely, this threat discourages governments from engaging in risky policy (see moral hazard). For example, the U.S. was forced to contract the money supply and raise interest rates in September 1931 to defend the dollar after speculators forced the UK off the gold standard.
- Devaluing a currency under a gold standard would generally produce sharper changes than the smooth declines seen in fiat currencies, depending on the method of devaluation.
- Most economists favor a low, positive rate of inflation of around 2%. This reflects fear of deflationary shocks and the belief that active monetary policy can dampen fluctuations in output and unemployment. Inflation gives them room to tighten policy without inducing deflation.
- A gold standard provides practical constraints against the measures that central banks might otherwise use to respond to economic crises. Creation of new money reduces interest rates and thereby increases demand for new lower cost debt, raising the demand for money.
- The late emergence of the gold standard may in part have been a consequence of its higher value than other metals, which made it unpractical for most laborers to use in everyday transactions (relative to less valuable silver coins).
Advocates
A return to the gold standard was considered by the U.S. Gold Commission in 1982 but found only minority support. In 2001 Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad proposed a new currency that would be used initially for international trade among Muslim nations, using a modern Islamic gold dinar, defined as 4.25 grams of pure (24-carat) gold. Mahathir claimed it would be a stable unit of account and a political symbol of unity between Islamic nations. This would purportedly reduce dependence on the U.S. dollar and establish a non-debt-backed currency in accord with Sharia law that prohibited the charging of interest. However, this proposal has not been taken up, and the global monetary system continues to rely on the U.S. dollar as the main trading and reserve currency.
Former U.S. Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan acknowledged he was one of "a small minority" within the central bank that had some positive view on the gold standard. In a 1966 essay he contributed to a book by Ayn Rand, titled Gold and Economic Freedom, Greenspan argued the case for returning to a 'pure' gold standard; in that essay he described supporters of fiat currencies as "welfare statists" intending to use monetary policy to finance deficit spending. More recently he claimed that by focusing on targeting inflation "central bankers have behaved as though we were on the gold standard", rendering a return to the standard unnecessary. Similarly, economists like Robert Barro argued that whilst some form of "monetary constitution" is essential for stable, depoliticized monetary policy, the form this constitution takes – for example, a gold standard, some other commodity-based standard, or a fiat currency with fixed rules for determining the quantity of money – is considerably less important.
The gold standard is supported by many followers of the Austrian School of economics, free-market libertarians, and some supply-siders.
U.S. politics
Former congressman Ron Paul is a long-term, high-profile advocate of a gold standard, but has also expressed support for using a standard based on a basket of commodities that better reflects the state of the economy.
In 2011 the Utah legislature passed a bill to accept federally issued gold and silver coins as legal tender to pay taxes. As federally issued currency, the coins were already legal tender for taxes, although the market price of their metal content currently exceeds their monetary value. As of 2011 similar legislation was under consideration in other U.S. states. The bill was initiated by newly elected Republican Party legislators associated with the Tea Party movement and was driven by anxiety over the policies of President Barack Obama.
In 2013, the Arizona Legislature passed SB 1439, which would have made gold and silver coin a legal tender in payment of debt, but the bill was vetoed by the Governor.
In 2015, some Republican candidates for the 2016 presidential election advocated for a gold standard, based on concern that the Federal Reserve's attempts to increase economic growth may create inflation. Economic historians did not agree with the candidates' assertions that the gold standard would benefit the U.S. economy.
See also
- A Program for Monetary Reform (1939) – The Gold Standard
- Black Friday (1869)—Also referred to as the Gold Panic of 1869
- Executive Order 6102
- Full-reserve banking
- Gold as an investment
- Gold dinar
- Gold points
- Hard money (policy)
- Metal as money
- Metallism
International institutions
- Bank for International Settlements
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference
- World Bank
References
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 7, 79. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry; Esteves, Rui Pedro (2021), Fukao, Kyoji; Broadberry, Stephen (eds.), "International Finance", The Cambridge Economic History of the Modern World: Volume 2: 1870 to the Present, vol. 2, Cambridge University Press, pp. 501–525, ISBN 978-1-107-15948-8
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 86–127. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- "Gold standard Facts, information, pictures Encyclopedia.com articles about Gold standard". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2015-12-05.
- William O. Scroggs (11 October 2011). "What Is Left of the Gold Standard?". Foreignaffairs.com. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 5–40. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Esteves, Rui Pedro; Nogues-Marco, Pilar (2021), Fukao, Kyoji; Broadberry, Stephen (eds.), "Monetary Systems and the Global Balance of Payments Adjustment in the Pre-Gold Standard Period, 1700–1870", The Cambridge Economic History of the Modern World: Volume 1: 1700 to 1870, vol. 1, Cambridge University Press, pp. 438–467, ISBN 978-1-107-15945-7
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 5. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Polanyi, Karl (1957). The Great Transformation. Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-5679-0.
- "Gold Standard". IGM Forum. 12 January 2012. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- ^ Whaples, Robert (1995). "Where Is There Consensus Among American Economic Historians? The Results of a Survey on Forty Propositions". The Journal of Economic History. 55 (1): 139–154. doi:10.1017/S0022050700040602. ISSN 0022-0507. JSTOR 2123771. S2CID 145691938.
- ^ Bordo, Michael D.; Choudhri, Ehsan U.; Schwartz, Anna J. (2002). "Was Expansionary Monetary Policy Feasible during the Great Contraction? An Examination of the Gold Standard Constraint". Explorations in Economic History. 39 (1): 1–28. doi:10.1006/exeh.2001.0778. ISSN 0014-4983.
- ^ Irwin, Douglas A. (2011-11-21). "Anticipating the Great Depression? Gustav Cassel's Analysis of the Interwar Gold Standard". SSRN 1962488.doi:10.3386/w17597S2CID 153294427
- ^ Bordo, Michael D. (May 1999). The Gold Standard and Related Regimes: Collected Essays. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511559624. ISBN 9780521550062. Retrieved 2020-03-28.
- ^ Boaz, David (2009-03-12). "Time to Think about the Gold Standard?". Cato Institute. Retrieved 2018-05-05.
- ^ John Maynard Keynes. "Chapter II: The Gold Exchange Standard". Indian Currency and Finance . p. 21 – via Wikisource.
- "World's Oldest Coin - First Coins". rg.ancients.info. Retrieved 2015-12-05.
- ^ Lipsey 1975, pp. 683–702.
- Bordo, Dittmar & Gavin 2003 "in a world with two capital goods, the one with the lower depreciation rate emerges as commodity money"
- Lopez, Robert Sabatino (Summer 1951). "The Dollar of the Middle Ages". The Journal of Economic History. 11 (3): 209–234. doi:10.1017/s0022050700084746. JSTOR 2113933. S2CID 153550781.
- ^ "MONEY AND COINAGE IN LATE MEDIEVAL AND EARLY MODERN EUROPE" (PDF). Economics.utoronto.ca. pp. 13–14 sec 5(f)(g)(h). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- "The Evolution of Small Change - Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago".
- Rodney Edvinsson. "Swedish monetary standards in a historical perspective" (PDF). pp. 33–34. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- "Early American Colonists Had a Cash Problem. Here's How They Solved It". Time.
- James Powell (2005). "A History of the Canadian Dollar" (PDF). Ottawa: Bank of Canada. pp. 22–23, 33. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- William Arthur Shaw (1896). The History of Currency, 1252–1894 (3rd ed.). Putnam. pp. 275–294.
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 14–16. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 7. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- ^ Oatley, Thomas (2019). International Political Economy: Sixth Edition. Routledge. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-351-03464-7.
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 13. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 44–46, 71–79. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- ^ Conant, Charles A. (1903). "The Future of the Limping Standard". Political Science Quarterly. 18 (2): 216–237. doi:10.2307/2140681. ISSN 0032-3195. JSTOR 2140681.
- Metzler, Mark (2006). Lever of Empire: The International Gold Standard and the Crisis of Liberalism in Prewar Japan. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24420-7. Archived from the original on 2009-11-03. Retrieved 2009-11-26.
- ^ "The Classical Gold Standard". World Gold Council. Retrieved 2022-04-16 – via www.gold.org.
How the Gold Standard Worked:
In theory, international settlement in gold meant that the international monetary system based on the Gold Standard was self-correcting.
... although in practice it was more complex. ... The main tool was the discount rate (...) which would in turn influence market interest rates. A rise in interest rates would speed up the adjustment process through two channels. First, it would make borrowing more expensive, reducing investment spending and domestic demand, which in turn would put downward pressure on domestic prices, ... Second, higher interest rates would attract money from abroad, ... The central bank could also directly affect the amount of money in circulation by buying or selling domestic assets ...
The use of such methods meant that any correction of an economic imbalance would be accelerated and normally it would not be necessary to wait for the point at which substantial quantities of gold needed to be transported from one country to another. - Parke Young, John (1925). European Currency and Finance. United States Congress Commission of Gold and Silver Inquiry. Vol. I: Italy, p. 347; Vol. II: Spain p. 223.
- Nagano, Yoshiko (January 2010). "The Philippine currency system during the American colonial period: Transformation from the gold exchange standard to the dollar exchange standard". International Journal of Asian Studies. 7 (1): 31. doi:10.1017/S1479591409990428. S2CID 154276782.
- Walton & Rockoff 2010.
- ^ Elwell 2011.
- Friedman & Schwartz 1963, p. 79.
- "Small change". Parliament.uk. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- Nicholson, J. S. (April 1915). "The Abandonment of the Gold Standard". The Quarterly Review. 223: 409–423.
- Officer, Lawrence (March 26, 2008). Robert Whaples (ed.). "Gold Standard". EH.Net Encyclopedia.
- Eichengreen 1995.
- Drummond, Ian M. (1987). The Gold Standard and the International Monetary System 1900–1939. Macmillan Education.
- Morrison, James Ashley (2021). England's Cross of Gold: Keynes, Churchill, and the Governance of Economic Beliefs. Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-1-5017-5843-0.
- "Gold Standard Act 1925 (15 & 16 Geo. 5 c. 29)". 1 January 2014 – via Internet Archive.
- "Articles: Free the Planet: Gold Standard Act 1925". Free the Planet. 2009-06-10. Archived from the original on 2012-07-13. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- Keynes, John Maynard (1920). Economic Consequences of the Peace. New York: Harcourt, Brace and Rowe.
- "Thatcher warned Major about exchange rate risks before ERM crisis". The Guardian. 2017-12-29. Retrieved 2017-12-29.
- ^ Morrison, James Ashley (2016). "Shocking Intellectual Austerity: The Role of Ideas in the Demise of the Gold Standard in Britain". International Organization. 70 (1): 175–207. doi:10.1017/S0020818315000314. ISSN 0020-8183. S2CID 155189356.
- International data from Maddison, Angus (27 July 2016). "Historical Statistics for the World Economy: 1–2003 AD".. Gold dates culled from historical sources, principally Eichengreen, Barry (1992). Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-506431-5.
- Cassel, Gustav (1936). The Downfall of the Gold Standard. Oxford University Press.
- "Chancellor's Commons Speech". Free the Planet. Archived from the original on 2012-07-09. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- Eichengreen, Barry J. (September 15, 2008). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System. Princeton University Press. pp. 61ff. ISBN 978-0-691-13937-1. Retrieved November 23, 2010.
- Officer 2010, Breakdown of the Interwar Gold Standard.
- Officer 2010, Instability of the Interwar Gold Standard: "there was ongoing tension with France, that resented the sterling-dominated gold- exchange standard and desired to cash in its sterling holding for gold to aid its objective of achieving first-class financial status for Paris."
- ^ Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 79–81. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 84–85. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Irwin, Douglas A. (2011). Trade Policy Disaster: Lessons from the 1930s. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-01671-1.
- Eichengreen 1995, Preface.
- Eichengreen, Barry; Temin, Peter (2000). "The Gold Standard and the Great Depression" (PDF). Contemporary European History. 9 (2): 183–207. doi:10.1017/S0960777300002010. ISSN 0960-7773. JSTOR 20081742. S2CID 158383956. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- Bernanke, Ben; James, Harold (1991). "The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison". In R. Glenn Hubbard (ed.). Financial markets and financial crises. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 33–68. ISBN 978-0-226-35588-7. OCLC 231281602.
- Eichengreen, Barry; Temin, Peter (July 2000). "The Gold Standard and the Great Depression". Contemporary European History. 9 (2): 183–207. doi:10.1017/S0960777300002010. S2CID 150932332.
- Crafts, Nicholas; Fearon, Peter (2010). "Lessons from the 1930s Great Depression". Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 26 (3): 285–317. doi:10.1093/oxrep/grq030. ISSN 0266-903X. S2CID 154672656.
The key element in the transmission of the Great Depression, the mechanism that linked the economies of the world together in this downward spiral, was the gold standard. It is generally accepted that adherence to fixed exchange rates was the key element in explaining the timing and the differential severity of the crisis. Monetary and fiscal policies were used to defend the gold standard and not to arrest declining output and rising unemployment.
- Simmons, Edward C. (December 1936). "The Elasticity of The Federal Reserve Note". The American Economic Review. 26 (4). American Economic Association: 683–690. JSTOR 1807996.
- Ellison, Martin; Lee, Sang Seok; O'Rourke, Kevin Hjortshøj (2024). "The Ends of 27 Big Depressions". American Economic Review. 114 (1): 134–168. doi:10.1257/aer.20221479. ISSN 0002-8282. S2CID 266612576.
- ^ "FRB: Speech, Bernanke-Money, Gold, and the Great Depression". Federal Reserve. 2004-03-02. Retrieved 2010-07-24.
- "1931—'The Tragic Year'". Ludwig von Mises Institute. January 1963. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
The inflationary attempts of the government from January to October were thus offset by the people's attempts to convert their bank deposits into legal tender ... Hence, the will of the public caused bank reserves to decline by $400 million in the latter half of 1931, and the money supply, as a consequence, fell by over four billion dollars in the same period.
- "1931—'The Tragic Year'". Ludwig von Mises Institute. January 1963. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
Throughout the European crisis, the Federal Reserve, particularly the New York Bank, tried its best to aid the European governments and to prop up unsound credit positions. ... The New York Federal Reserve loaned, in 1931, $125 million to the Bank of England, $25 million to the German Reichsbank, and smaller amounts to Hungary and Austria. As a result, much frozen assets were shifted, to become burdens to the United States.
- Hanes, Christopher. "The Liquidity Trap and U.S. Interest Rates in the 1930s" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2004-07-22.
In the 1930s, the United States was in a situation that satisfied the conditions for a liquidity trap. Over 1929–1933 overnight rates fell to zero, and they remained on the floor through the 1930s.
- Feinstein, Temin, and Toniolo. The European Economy between Wars.
- Stein, Ben (2009-05-09). "The Smoot-Hawley Act Is More Than a Laugh Line". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2023-10-06.
- "The Great Depression Lesson About 'Trade Wars'". HISTORY. 2018-09-20. Retrieved 2023-10-06.
- M. Friedman: "the severity of each of the major contractions – 1920–21, 1929–33 and 1937–38 is directly attributable to acts of commission and omission by the Reserve authorities".
- Murphy, Robert P. (30 October 2009). "The Gold Standard and the Great Depression". Mises.org. Archived from the original on 2012-07-09. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
Another major factor is that governments in the 1930s were interfering with wages and prices more so than at any prior point in (peacetime) history
- "High Taxes and High Budget Deficits – The Hoover–Roosevelt Tax Increases of the 1930s" (PDF). Cato Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- Perry, Mark J. (2008-11-09). "10X Increase in Lowest Tax Rate in Early 1930s". Mark J. Perry's Blog for Economics and Finance. Mjperry.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- Eichengreen, Barry; Mitchener, Kris (August 2003). "The Great Depression as a Credit Boom Gone Wrong" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- Alan Greenspan (1966). Gold and Economic Freedom. "Great Britain fared even worse, and rather than absorb the full consequences of her previous folly, she abandoned the gold standard completely in 1931, tearing asunder what remained of the fabric of confidence and inducing a world-wide series of bank failures."
- Farrell, Paul B. (December 13, 2011). "Our decade from hell will get worse in 2012". MarketWatch. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
As financial historian Niall Ferguson writes in Newsweek: 'Double-Dip Depression ... We forget that the Great Depression was like a soccer match, there were two halves.' The 1929 crash kicked off the first half. But what 'made the depression truly "great" ... began with the European banking crisis of 1931.' Sound familiar?
- Robert B. Reich (2010). Aftershock. Chapter 1: Eccles's Insight.
- https://www.cato.org/blog/world-war-i-gold-great-depression#:~:text=The%20result%20was%20a%20second,4%20years%20in%20a%20row.
- https://www.nber.org/system/files/chapters/c11482/c11482.pdf
- Jabko, Nicolas; Schmidt, Sebastian (2022). "The Long Twilight of Gold: How a Pivotal Practice Persisted in the Assemblage of Money". International Organization. 76 (3): 625–655. doi:10.1017/S0020818321000461. ISSN 0020-8183. S2CID 245413975.
- Prior, Ed (1 April 2013). "How much gold is there in the world?". BBC News.
- "FAQs | Investment". World Gold Council. Retrieved 2013-09-12.
- "Measuring Worth - GDP result". Measuringworth.com.
- "Download entire World Economic Outlook database, April 2013". International Monetary Fund.
- "Zimbabwe Gold". Chronicles Zimbabwe. Retrieved 2024-04-06.
- Krech III, Shepard; McNeill, John Robert; Merchant, Carolyn (2004). Encyclopedia of World Environmental History. Vol. 2. New York City: Routledge. p. 597. ISBN 978-0-415-93734-4. OCLC 174950341.
- "How the End of the Vietnam War Led to a Refugee Crisis". HISTORY. 2023-08-29. Retrieved 2023-10-06.
- Mayhew, Nick (2019-03-21). Money and the Economy in: Money and Coinage in the Middle Ages. Brill.com. doi:10.1163/9789004383098_010. ISBN 9789004383098. S2CID 159368019. Retrieved 2022-03-03.
- Bernanke, Ben (March 2, 2004), "Remarks by Governor Ben S. Bernanke: Money, Gold and the Great Depression", At the H. Parker Willis Lecture in Economic Policy, Washington and Lee University, Lexington, Virginia.
- "International payment and exchange - Gold Standard, Currency Exchange, Global Economy | Britannica Money". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2023-10-06.
- Hoppe, Hans-Herman (1992). Mark Skousen (ed.). Dissent on Keynes, A Critical Appraisal of Economics. pp. 199–223. Archived from the original on 2014-09-15. Retrieved 2014-09-15.
- "Gold as Money: FAQ". Mises.org. Ludwig von Mises Institute. Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2011.
- The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd edition (2008), Vol.3, S.695
- "Gold Standard". IGM Forum. 12 January 2012. Retrieved 27 December 2015.
- "Financial Repression Redux". International Monetary Fund. June 2011. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
Financial repression occurs when governments implement policies to channel to themselves funds that in a deregulated market environment would go elsewhere
- Reinhart, Carmen M.; Rogoff, Kenneth S. (2008). This Time is Different. Princeton University Press. p. 143.
- Giovannini, Alberto; De Melo, Martha (1993). "Government Revenue from Financial Repression". The American Economic Review. 83 (4): 953–963. JSTOR 2117587.
- Greenspan, Alan (1966). "Gold and Economic Freedom". Constitution.org. Archived from the original on September 25, 2010. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- ^ Bordo 2008.
- O'Brien, Matthew (2012-08-26). "Why the Gold Standard Is the World's Worst Economic Idea, in 2 Charts". The Atlantic. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
- Kydland, Finn E. (1999). "The Gold Standard as a Commitment Mechanism". The Gold Standard and Related Regimes. Cambridge University Press. pp. 195–237. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511559624.008. ISBN 9780521550062. Retrieved 2020-03-28.
- "Advantages of the Gold Standard" (PDF). The Gold Standard: Perspectives in the Austrian School. The Ludwig von Mises Institute. 27 January 1935. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- "Reform of the International Monetary and Financial System" (PDF). Bank of England. December 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 18, 2011. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
Countries with current account surpluses accumulated gold, while deficit countries saw their gold stocks diminish. This, in turn, contributed to upward pressure on domestic spending and prices in surplus countries and downward pressure on them in deficit countries, thereby leading to a change ... that should, eventually, have reduced imbalances.
- Goodman, George J. W. (1981). Paper Money. pp. 165–66
- Hill, Liezel (January 13, 2011). "Gold mine output hit record in 2010, more gains likely this year – GFMS". Mining Weekly. Archived from the original on November 29, 2011. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- "GOLD" (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries. U.S. Geological Survey. January 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 10 July 2012.
- Mayer, David A. (2010). The Everything Economics Book Archived 2023-03-26 at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 978-1-4405-0602-4. pp. 33–34.
- Mankiw, N. Gregory (2002). Macroeconomics (5th ed.). Worth. pp. 238–255. ISBN 978-0-324-17190-7.
- Krugman, Paul (23 November 1996). "The Gold Bug Variations". Slate. Retrieved 2009-02-13.
- ^ Bordo, Dittmar & Gavin 2003.
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. p. 11. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Keogh, Bryan (May 13, 2009). "Real Rate Shock Hits CEOs as Borrowing Costs Impede Recovery". Bloomberg. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
'Deflation hurts borrowers and rewards savers,' said Drew Matus, senior economist at Banc of America Securities-Merrill Lynch in New York, in a telephone interview. 'If you do borrow right now, and we go through a period of deflation, your cost of borrowing just went through the roof.'
- Mauldin, John; Tepper, Jonathan (2011-02-09). Endgame: The End of the Debt SuperCycle and How It Changes Everything. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley. ISBN 978-1-118-00457-9.
- "The greater of two evils". The Economist. May 7, 2009. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- DeLong, Brad (1996-08-10). "Why Not the Gold Standard?". Berkeley, California: University of California, Berkeley. Archived from the original on 2010-10-18. Retrieved 2008-09-25.
- Timberlake, Richard H. (2005). "Gold Standards and the Real Bills Doctrine in US Monetary Policy". Econ Journal Watch. 2 (2): 196–233.
- Warburton, Clark (1966). "The Monetary Disequilibrium Hypothesis". Depression, Inflation, and Monetary Policy: Selected Papers, 1945–1953. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 25–35. OCLC 736401.
- ^ Hamilton 2005.
- Hamilton 1988.
- "Remarks by Governor Ben S. Bernanke". The Federal Reserve Board. March 2, 2004. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
In September 1931, following a period of financial upheaval in Europe that created concerns about British investments on the Continent, speculators attacked the British pound, presenting pounds to the Bank of England and demanding gold in return. ... Unable to continue supporting the pound at its official value, Great Britain was forced to leave the gold standard, ... With the collapse of the pound, speculators turned their attention to the U.S. dollar
- McArdle, Megan (2007-09-04). "There's gold in them thar standards!". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 2010-01-13. Retrieved 2008-11-12.
- Hummel, Jeffrey Rogers (January 2007). "Death and Taxes, Including Inflation: The Public versus Economists". p. 56
- Demirgüç-Kunt, Asli; Enrica Detragiache (April 2005). "Cross-Country Empirical Studies of Systemic Bank Distress: A Survey". National Institute Economic Review. 192 (1): 68–83. doi:10.1177/002795010519200108. hdl:10986/8266. ISSN 0027-9501. OCLC 90233776. S2CID 153360324. Archived from the original on 2009-05-31. Retrieved 2008-11-12.
- "the quantity of money supplied by the Fed must be equal to the quantity demanded by money holders" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 16, 2012. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- Eichengreen, Barry (2019). Globalizing Capital: A History of the International Monetary System (3rd ed.). Princeton University Press. pp. 11–12. doi:10.2307/j.ctvd58rxg. ISBN 978-0-691-19390-8. JSTOR j.ctvd58rxg. S2CID 240840930.
- Paul, Ron; Lewis Lehrman (1982). The case for gold: a minority report of the U.S. Gold Commission (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Cato Institute. p. 160. ISBN 978-0-932790-31-6. OCLC 8763972. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2008-11-12.
- al-'Amraawi, Muhammad; Al-Khammar al-Baqqaali; Ahmad Saabir; Al-Hussayn ibn Haashim; Abu Sayf Kharkhaash; Mubarak Sa'doun al-Mutawwa'; Malik Abu Hamza Sezgin; Abdassamad Clarke; Asadullah Yate (2001-07-01). "Declaration of 'Ulama on the Gold Dinar". Islam i Dag. Archived from the original on 2008-06-24. Retrieved 2008-11-14.
- McGregor, Richard (2011-01-16). "Hu questions future role of US dollar". Financial Times. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- "Conduct of Monetary Policy: Report of the Federal Reserve Board Pursuant to the Full Employment and Balanced Growth Act of 1978, P.L. 95-523 and The State of the Economy: Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Domestic and International Monetary Policy of the Committee on Banking and Financial Services, House of Representatives". Monetary Policy Oversight: House of Representatives Hearings. Monetary Policy Oversight : House of Representatives Hearings. July 22, 1998.
- Greenspan, Alan (July 1966). "Gold and Economic Freedom". The Objectivist. 5 (7). Archived from the original on 2010-09-25. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- Paul, Ron. End the Fed. p. xxiii.
- Salerno 1982.
- Interview with Ron Paul. Squawkbox. CNBC. 13 November 2009.
- Clark, Stephen (March 3, 2011). "Utah Considers Return to Gold, Silver Coins". Fox News. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- "Utah: Forget dollars. How about gold?". CNN. 2011-03-29.
- Spillius, Alex (2011-03-18). "Tea Party legislation reveals anxiety at US direction under Barack Obama". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 2022-01-11.
- "Letter regarding Senate Bill 1439 (legal tender)" (PDF). Azleg.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- Appelbaum, Binyamin (2015-12-01). "The Good Old Days of the Gold Standard? Not Really, Historians Say". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2015-12-02.
Sources
- Bordo, Michael D.; Dittmar, Robert D.; Gavin, William T. (June 2003). "Gold, Fiat Money and Price Stability" (PDF). Working Paper Series. Research Division – Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Retrieved December 24, 2011.
- Bordo, Michael (2008). "Gold Standard". Econlib.
- Cassel, Gustav. The Downfall of the Gold Standard. Oxford University Press, 1936.
- Drummond, Ian M. The Gold Standard and the International Monetary System 1900–1939. Macmillan Education, LTD, 1987.
- Eichengreen, Barry J. (1995). Golden Fetters: The Gold Standard and the Great Depression, 1919–1939. New York City: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-510113-3. OCLC 34383450.
- Elwell, Craig K. (2011). Brief History of the Gold Standard in the United States. Congressional Research Service.
- Hamilton, James D. (2005). "The gold standard and the Great Depression". Econbrowser. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008. Retrieved 12 November 2008.
- Friedman, Milton; Schwartz, Anna Jacobson (1963). A Monetary History of the US 1867–1960. Princeton University Press. p. 543. ISBN 978-0-691-04147-6. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- Hamilton, James D. (April 1988). "Role of the International Gold Standard in Propagating the Great Depression". Contemporary Economic Policy. 6 (2): 67–89. doi:10.1111/j.1465-7287.1988.tb00286.x. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05. Retrieved 2008-11-12.
- Lipsey, Richard G. (1975). An introduction to positive economics (4th ed.). Weidenfeld & Nicolson. pp. 683–702. ISBN 978-0-297-76899-9.
- Officer, Lawrence (1 February 2010). "Gold Standard". Eh.net Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 2012-06-27. Retrieved 2012-07-09.
- Salerno, Joseph T. (1982-09-09). "The Gold Standard: An Analysis of Some Recent Proposals". Cato Policy Analysis. Cato Institute. Retrieved 2009-03-23.
- Walton, Gary M.; Rockoff, Hugh (2010). History of the American Economy. South-Western. ISBN 978-1-4390-3752-2.
Further reading
- Banking in modern Japan. Tokyo: Fuji Bank. 1967. ISBN 978-0-333-71139-2. OCLC 254964565.
- Bensel, Richard Franklin (2000). The political economy of American industrialization, 1877–1900. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77604-2. OCLC 43552761.
- Bernanke, Ben; James, Harold (October 1990). "The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison". NBER Working Paper No. 3488. doi:10.3386/w3488. Also published as: Bernanke, Ben; James, Harold (1991). "The Gold Standard, Deflation, and Financial Crisis in the Great Depression: An International Comparison". In R. Glenn Hubbard (ed.). Financial markets and financial crises. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 33–68. ISBN 978-0-226-35588-7. OCLC 231281602.
- Bordo, Michael D. (1999). Gold standard and related regimes: collected essays. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-55006-2. OCLC 59422152.
- Bordo, Michael D; Anna Jacobson Schwartz; National Bureau of Economic Research (1984). A Retrospective on the classical gold standard, 1821–1931. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-06590-8. OCLC 10559587.
- Coletta, Paolo E. "Greenbackers, Goldbugs, and Silverites: Currency Reform and Politics, 1860-1897,” in H. Wayne Morgan (ed.), The Gilded Age: A Reappraisal. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 1963; pp. 111–139.
- Eichengreen, Barry J.; Marc Flandreau (1997). The gold standard in theory and history. New York City: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-15061-3. OCLC 37743323.
- Einaudi, Luca (2001). Money and politics: European monetary unification and the international gold standard (1865–1873). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924366-2. OCLC 45556225.
- Roberts, Mark A (March 1995). "Keynes, the Liquidity Trap and the Gold Standard: A Possible Application of the Rational Expectations Hypothesis". The Manchester School of Economic & Social Studies. 61 (1): 82–92. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9957.1995.tb00270.x.
- Thompson, Earl A.; Charles Robert Hickson (2001). Ideology and the evolution of vital institutions: guilds, the gold standard, and modern international cooperation. Boston: Kluwer Acad. Publ. ISBN 978-0-7923-7390-2. OCLC 46836861.
- Pollard, Sidney (1970). The gold standard and employment policies between the Wars. London: Methuen. ISBN 978-0-416-14250-1. OCLC 137456.
- Hanna, Hugh Henry; Charles Arthur Conant; Jeremiah Jenks (1903). Stability of international exchange: Report on the introduction of the gold-exchange standard into China and other silver-using countries. OCLC 6671835.
- Drummond, Ian M.; The Economic History Society (1987). The gold standard and the international monetary system 1900–1939. Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: Macmillan Education. ISBN 978-0-333-37208-1. OCLC 18324084.
- Hawtrey, Ralph George (1927). The Gold Standard in theory and practice. London: Longman. ISBN 978-0-313-22104-0. OCLC 250855462.
- Flandreau, Marc (2004). The glitter of gold: France, bimetallism, and the emergence of the international gold standard, 1848–1873. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-925786-7. OCLC 54826941.
- Lalor, John (2003) . Cyclopedia of Political Science, Political Economy and the Political History of the United States. London: Thoemmes Continuum. ISBN 978-1-84371-093-6. OCLC 52565505.
- Rothbard, Murray Newton (2006). "The World Currency Crisis". Making Economic Sense. Burlingame, California: Ludwig von Mises Institute. pp. 295–299. ISBN 978-0-945466-46-8. OCLC 78624652.
- Cassel, Gustav (1936). The downfall of the gold standard. Oxford: Clarendon Press. OCLC 237252.
- Braga de Macedo, Jorge; Barry J. Eichengreen; Jaime Reis (1996). Currency convertibility: the gold standard and beyond. New York City: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-14057-7. OCLC 33132906.
- Russell, William H. (1982). The Deceit of the Gold Standard and of Gold Monetization. American Classical College Press. ISBN 978-0-89266-324-8.
- Mitchell, Wesley C. (1908). Gold, prices, and wages under the greenback standard. Berkeley, California: The University Press. OCLC 1088693.
- Mouré, Kenneth (2002). The gold standard illusion: France, the Bank of France, and the International Gold Standard, 1914–1939. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924904-6. OCLC 48544538.
- Bayoumi, Tamim A.; Barry J. Eichengreen and Mark P. Taylor (1996). Modern perspectives on the gold standard. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-57169-2. OCLC 34245103.
- Keynes, John Maynard (1925). The economic consequences of Mr. Churchill. London: Hogarth Press. OCLC 243857880.
- Keynes, John Maynard (1930). A treatise on money in two volumes. London: MacMillan. OCLC 152413612.
- Ferderer, J. Peter (1994). Credibility of the interwar gold standard, uncertainty, and the Great Depression. Annandale-on-Hudson, New York: Jerome Levy Economics Institute. OCLC 31141890.
- Aceña, Pablo Martín; Jaime Reis (2000). Monetary standards in the periphery: paper, silver and gold, 1854–1933. London: Macmillan Press. ISBN 978-0-333-67020-0. OCLC 247963508.
- Gallarotti, Giulio M. (1995). The anatomy of an international monetary regime: the classical gold standard, 1880–1914. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-508990-5. OCLC 30511110.
- Dick, Trevor J. O.; John E. Floyd (2004). Canada and the Gold Standard: Balance of Payments Adjustment Under Fixed Exchange Rates, 1871–1913. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-61706-2. OCLC 59135525.
- Hofstadter, Richard (1996). "Free Silver and the Mind of "Coin" Harvey". The Paranoid Style in American Politics and Other Essays. Harvard: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-65461-7. OCLC 34772674.
- Kenwood, A.G.; A. L. Lougheed (1992). The growth of the international economy 1820–1990. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-91-44-00079-4.
- Lewis, Nathan K. (2006). Gold: The Once and Future Money. New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-04766-8. OCLC 87151964.
- Metzler, Mark (2006). Lever of Empire: The International Gold Standard and the Crisis of Liberalism in Prewar Japan. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. p. . ISBN 978-0-520-24420-7.
- Officer, Lawrence H. (2007). Between the Dollar-Sterling Gold Points: Exchange Rates, Parity and Market Behavior. Chicago: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-03821-8. OCLC 124025586.
- Officer, Lawrence H. (2008). "bimetallism". In Steven N. Durlauf and Lawrence E. Blume (ed.). The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd Edition. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 1–6. doi:10.1057/9780230226203.0136. ISBN 978-0-333-78676-5. OCLC 181424188. Retrieved 2008-11-13.
- Pietrusza, David (2011). 'It Shines for All': The Gold Standard Editorials of The New York Sun. New York City, New York: New York Sun Books. ISBN 978-1-4611-5612-3.
- Withers, Hartley (1919). War-Time Financial Problems. London: J. Murray. OCLC 2458983. Retrieved 2008-11-14.
External links
Listen to this article (25 minutes)- 1925: Churchill & The Gold Standard - UK Parliament Living Heritage
- What is The Gold Standard? University of Iowa Center for International Finance and Development
- History of the Bank of England Bank of England
- Timeline: Gold's history as a currency standard