| Revision as of 01:20, 25 March 2019 editLightandDark2000 (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers62,349 edits Fix.← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 02:20, 21 December 2024 edit undoABC paulista (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,151 edits →Climatological statistics: Update with Biguá | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Tropical cyclones in the South Atlantic Ocean}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2021}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| '''South Atlantic tropical cyclones''' are unusual weather events that occur in the ]. Strong ], which disrupts the formation of cyclones, as well as a lack of weather disturbances favorable for development in the South ] make any strong tropical system extremely rare, and ] in 2004 is the only recorded South ] in history. |
'''South Atlantic tropical cyclones''' are unusual weather events that occur in the ]. Strong ], which disrupts the formation of ], as well as a lack of weather disturbances favorable for development in the South ], make any strong tropical system extremely rare, and ] in 2004 is the only recorded South ] in history. Storms can develop year-round in the South Atlantic, with activity peaking during the months from November through May. Since 2011, the ] Hydrographic Center has assigned ] to tropical and subtropical systems in the western side of the ], near the eastern coast of Brazil, when they have sustained wind speeds of at least {{cvt|65|km/h|mph}}, the generally accepted minimum sustained wind speed for a disturbance to be designated as a ] in the North Atlantic basin. Below is a list of notable South Atlantic tropical and ]s. | ||
| ==Theories concerning infrequency of occurrence== | ==Theories concerning infrequency of occurrence== | ||
| It was initially thought that tropical cyclones did not develop within the South Atlantic.<ref name="GP March 2004">{{cite web|title=Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary March 2004 |access-date=7 February 2015 |url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0403.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151217034249/http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0403.htm |author=Padgett, Gary |archive-date=17 December 2015 |url-status=live }}</ref> Very strong vertical ] in the ] is considered a deterrent.<ref name="TC FAQ G6">{{cite book|author=Landsea, Christopher W |date=13 July 2005 |title=Tropical Cyclone Frequently Asked Question |chapter=Subject: Tropical Cyclone Names: G6) Why doesn't the South Atlantic Ocean experience tropical cyclones? |publisher=United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Hurricane Research Division |access-date=7 February 2015 |chapter-url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/tcfaq/G6.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150327070050/http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/tcfaq/G6.html |archive-date=27 March 2015 |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] drops one to two degrees south of the equator,<ref>{{cite book|title=Atlantic Hurricanes|url=https://archive.org/details/atlantichurrican0000dunn|url-access=registration|author1=Gordon E. Dunn |author2=Banner I. Miller |name-list-style=amp |publisher=Louisiana State University Press|date=1960|asin=B0006BM85S|page=}}</ref> not far enough from the equator for the ] to significantly aid development. Water temperatures in the tropics of the southern Atlantic are cooler than those in the tropical north Atlantic.<ref name="AOML FAQ A15">{{cite web|author=Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Hurricane Research Division|title=Frequently Asked Questions: How do tropical cyclones form?|publisher=]|access-date=26 July 2006|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/tcfaq/A15.html}}</ref> | |||
| Although they are rare, during April 1991 the United States' ] (NHC) reported that a tropical cyclone had developed over the Eastern South Atlantic.<ref name="GP March 2004"/><ref name="NHC">{{cite report|type=Diagnostic Report of the National Hurricane Center: June and July 1991|title=II. Tropical cyclone activity in the Atlantic Basin: A. Overview|author=National Hurricane Center|editor1=McAdie, Colin J|url=http://hdl.handle.net/2027/uiug.30112005414658|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|access-date=12 May 2013|pages=10–14|year=1991|hdl=2027/uiug.30112005414658|editor2=Rappaport, Edward N}}</ref> In subsequent years, a few systems were suspected to have the characteristics needed to be classified as a tropical cyclone, including in March 1994 and January 2004.<ref name="GP January 2004">{{cite web|title=Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary January 2004 |access-date=7 February 2015 |author=Padgett, Gary |url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0401.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151217034249/http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0403.htm |archive-date=17 December 2015 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="IWTCVI">{{cite conference|publisher=World Meteorological Organization |title=Topic 2a: The Catarina Phenomenon |url=http://severe.worldweather.org/iwtc/document/Topic_2a_Pedro_Silva_Dias.pdf |year=2006 |conference-url=http://severe.worldweather.org/iwtc/ |conference=The Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI) |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304035419/http://severe.worldweather.org/iwtc/document/Topic_2a_Pedro_Silva_Dias.pdf |archive-date=4 March 2016 |location=San José, Costa Rica |pages=329–360 |access-date=7 February 2015 }}</ref> During March 2004, an ] formally transitioned into a tropical cyclone and made landfall on Brazil, after becoming a Category 2 hurricane on the ]. While the system was threatening the Brazilian state of ], a newspaper used the headline "Furacão Catarina", which was originally presumed to mean "furacão (hurricane) threatening (Santa) Catarina (the state)".<ref name="GP March 2004"/> After international presses started monitoring the system, "Hurricane Catarina" has formally been adopted. | |||
| At the Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI) in 2006, it was questioned if any subtropical or tropical cyclones had developed within the South Atlantic before Catarina.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> It was noted that suspect systems had developed in January 1970, March 1994, January 2004, March 2004, May 2004, February 2006, and March 2006.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> It was also suggested that an effort should be made to locate any possible systems using satellite imagery and synoptic data; however, it was noted that this effort may be hindered by the lack of any geostationary imagery over the basin before 1966.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> A study was subsequently performed and published during 2012, which concluded that there had been 63 subtropical cyclones in the Southern Atlantic between 1957 and 2007.<ref>{{cite journal |
At the Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI) in 2006, it was questioned if any subtropical or tropical cyclones had developed within the South Atlantic before Catarina.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> It was noted that suspect systems had developed in January 1970, March 1994, January 2004, March 2004, May 2004, February 2006, and March 2006.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> It was also suggested that an effort should be made to locate any possible systems using satellite imagery and synoptic data; however, it was noted that this effort may be hindered by the lack of any geostationary imagery over the basin before 1966.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> A study was subsequently performed and published during 2012, which concluded that there had been 63 subtropical cyclones in the Southern Atlantic between 1957 and 2007.<ref>{{cite journal|author2=Braun, Aviva J|publisher=American Meteorological Society|year=2012|pages=7328–7340|title=A Climatology of Subtropical Cyclones in the South Atlantic|doi=10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00212.1|journal=Journal of Climate|issue=21|author1=Evans, Jenny L|volume = 25|bibcode=2012JCli...25.7328E|doi-access=free}}</ref> During January 2009, a subtropical storm developed in the basin, and in March 2010, a tropical storm developed, which was named Anita by the Brazilian public and private weather services.<ref name="GPJan2009">{{cite web|author=Padgett, Gary|date=7 April 2009|title=January 2009 Tropical Weather Summary|url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2009/summ0901.htm|access-date=15 April 2010}}</ref><ref name="GP March 2010">{{cite web|title=Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Tracks March 2010 |access-date=7 February 2015 |url=http://www.australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2010/trak1003.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151217034249/http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0403.htm |author=Padgett, Gary |archive-date=17 December 2015 |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2011, the ] started to assign ] to tropical and subtropical cyclones that develop within its area of responsibility, to the west of ], when they have sustained wind speeds of at least {{cvt|65|km/h|mph}}.<ref name="names_2011">{{cite web|title=Normas Da Autoridade Marítima Para As Atividades De Meteorologia Marítima |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/dhn/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.dhn/files/normam/normam_19.pdf |publisher=Brazilian Navy |access-date=5 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150206213534/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/dhn/downloads/normam/normam_19.pdf |archive-date=6 February 2015 |language=pt |date=2011 }}</ref> | ||
| == |
==Notable storms and impacts== | ||
| === Pre-2010s === | |||
| ===1991 Angola tropical storm=== | ====1991 Angola tropical storm==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| |Image= |
|Image=01Q 1991-04-12 1100Z.jpg | ||
| |Track= | |||
| |Track=1991 Angola Tropical Cyclone track.png | |||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=10 April 1991 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=14 April 1991 | ||
| |1-min winds=35 | |1-min winds=35 | ||
| |Pressure= | |Pressure= | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| A low |
A low-pressure area formed over the ] on 9 April. The next day it moved offshore northern ] with a curved cloud pattern. It moved westward over an area of warm waters while the circulation became better defined. According to the United States ], the system was probably either a tropical depression or a tropical storm at its peak intensity. On 14 April, the system rapidly dissipated, as it was absorbed into a large ].<ref name="NHC"/><ref>{{cite book|author=Marcel Leroux|title=The Meteorology and Climate of Tropical Africa|page=314|chapter=Tropical Cyclones|year=2001|publisher=Praxis Publishing Ltd.|isbn=978-3-540-42636-3|access-date=28 March 2013|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=v32qnYWh5gQC&q=1991+south+atlantic+storm+congo+april&pg=PA314}}</ref> This is the only recorded tropical cyclone in the eastern South Atlantic. | ||
| {{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| ===Hurricane Catarina=== | ====Hurricane Catarina==== | ||
| {{Verification|section|date=January 2023}} | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| |Image=Catarina |
|Image=Catarina 2004-03-27 1630Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Catarina 2004 track.png | |Track=Catarina 2004 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=24 March 2004 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=28 March 2004 | ||
| |1-min winds=85 | |1-min winds=85 | ||
| |Pressure=972 | |Pressure=972 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Main |
{{Main|Hurricane Catarina}} | ||
| Hurricane Catarina was an extraordinarily rare hurricane-strength tropical cyclone, forming in the southern |
Hurricane Catarina was an extraordinarily rare hurricane-strength tropical cyclone, forming in the southern Atlantic Ocean in March 2004.<ref name="College of Earth and Mineral Sciences">{{cite web|author1=College of Earth|author2=Mineral Sciences|name-list-style=amp|publisher=Pennsylvania State University|year=2004|access-date=14 May 2009|title=Upper-level lows|url=https://courseware.e-education.psu.edu/public/meteo/upperlevel_lows.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303214919/https://courseware.e-education.psu.edu/public/meteo/upperlevel_lows.html|archive-date=3 March 2016}}</ref> Just after becoming a hurricane, it hit the southern coast of Brazil in the state of ] on the evening of 28 March, with winds up to {{Convert|195|km/h|mph}} making it a Category 2-equivalent cyclone on the ].<ref name="GPTCS">{{cite web |author=Gary Padgett |year=2004 |title=March 2004 Tropical Cyclone Summary |url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0403.htm |access-date=23 October 2008 |publisher=Thomas R. Metcalf (Australian Severe Weather)}}</ref> Catarina killed 3 to 11 people and caused millions of dollars in damage in Brazil.<ref>{{cite news |author=Jefferson Bernardes |date=30 March 2004 |title=First South Atlantic hurricane hits Brazil |newspaper=USA Today |url=https://www.usatoday.com/weather/news/2004-03-28-brazil-storm_x.htm |access-date=23 February 2009}}</ref> | ||
| At the time, |
At the time, Brazilians were taken completely by surprise, and were initially skeptical that an actual tropical cyclone could have formed in the South Atlantic. Eventually, however, they were convinced, and adopted the previously unofficial name "Catarina" for the storm, after Santa Catarina state. This event is considered by some ]s to be a nearly once-in-a-lifetime occurrence. | ||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ===Tropical Storm Anita=== | ===2010s=== | ||
| ====Tropical Storm Anita==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| |Image=March 2010 TC South Atlantic.jpg | |Image=March 2010 TC South Atlantic.jpg | ||
| |Track=Anita 2010 track.png | |Track=Anita 2010 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=8 March 2010 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=12 March 2010 | ||
| |1-min winds=45 | |1-min winds=45 | ||
| |Pressure=995 | |Pressure=995 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| On |
On 8 March 2010, a previously extratropical cyclone developed tropical characteristics and was classified as a subtropical cyclone off the coast of southern Brazil. The following day, the ] began monitoring the system as a system of interest under the designation of ''90Q''. The ] also began monitoring the system as Low SL90. During the afternoon of 9 March, the system had attained an intensity of {{cvt|55|km/h|mph}} and a ] of 1000 hPa (mbar). It was declared a tropical storm on 10 March and became extratropical late on 12 March.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa20.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070523110742/http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa20.html|archive-date=2007-05-23|title=South American Synopsis |date=May 22, 2007 |website=The Hydrometeorological Prediction Center }}</ref> Anita's ] was estimated at 2.0525 by the Florida State University. There was no damage associated to the storm, except high sea in the coasts of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina. Post mortem, the cyclone was given the name "Anita" by private and public weather centers in Southern Brazil.<ref name="BZMet">{{cite web|publisher=Brazilian Meteorological Service |date=March 2010 |title=Monitoramento – Ciclone tropical na costa gaúcha |url=http://www.metsul.com/blog/ |language=pt |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100228054140/http://www.metsul.com/blog/ |archive-date=28 February 2010 }}</ref> | ||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ===Subtropical Storm Arani=== | ====Subtropical Storm Arani==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| |Type=subtropical | |Type=subtropical | ||
| |Image=Arani |
|Image=Arani 2011-03-16 1540Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Arani 2011 track.png | |Track=Arani 2011 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=14 March 2011 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=16 March 2011 | ||
| |1-min winds=45 | |1-min winds=45 | ||
| |Pressure= |
|Pressure=998 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Early on March |
Early on 14 March 2011, the Navy Hydrographic Center-] (SMM), in coordination with the National Institute of Meteorology, were monitoring an organizing area of ] near the southeast coast of Brazil.<ref>{{cite web |author=Chura |author2=Ledesma |author3=Davison |title=South American Synopsis |publisher=Hydrometeorological Prediction Center |date=14 March 2011 |access-date=14 March 2011 |url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa20.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101224082612/http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa20.html |archive-date=24 December 2010 }}</ref> Later that day a ] developed just east of ],<ref>{{cite web|author=Chura |author2=Ledesma |author3=Davison |title=South American Synopsis (2) |publisher=Hydrometeorological Prediction Center |date=14 March 2011 |access-date=14 March 2011 |url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa21.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110101134630/http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa21.html |archive-date=1 January 2011 }}</ref> and by 12:00 ], the system organized into a ], located about {{cvt|140|km|mi}} east of ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Marine Meteorological Service |publisher=Brazil Navy Hydrographic Center |date=14 March 2011 |title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 GMT – 14/MAR/2011 |access-date=14 March 2011 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 }}</ref> Guided by a ] and a weak ] to its north, the system moved slowly southeastward over an area of warm waters,<ref>{{cite web|author=Chura |author2=Ledesma |author3=Davison |title=South American Synopsis (3) |publisher=Hydrometeorological Prediction Center |date=15 March 2011 |access-date=15 March 2011 |url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa21.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110101134630/http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa21.html |archive-date=1 January 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author=Chura |author2=Ledesma |author3=Davison |title=South American Synopsis (4) |publisher=Hydrometeorological Prediction Center |date=15 March 2011 |access-date=15 March 2011 |url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa20.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101224082612/http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/fxsa20.html |archive-date=24 December 2010 }}</ref> intensifying into Subtropical Cyclone Arani on 15 March,<ref>{{cite web|author=Marine Meteorological Service |publisher=Brazil Navy Hydrographic Center |date=15 March 2011 |title=Severe Weather Warnings |access-date=15 March 2011 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/avisos/avisosing.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110709024728/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/avisos/avisosing.htm |archive-date=9 July 2011 }}</ref> as named by the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center,<ref name="March11BrazilianNavy">{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/avisos/avisosing.htm |title=Severe Weather Warnings – 11 March 2011 |date=11 March 2011 |publisher=] |access-date=15 March 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110709024728/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/avisos/avisosing.htm |archive-date=9 July 2011 }}</ref> and achieving its lowest pressure.<ref name=AraniTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL ARANI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_arani.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> The storm was classified as subtropical, as the convection was east of the center. On 16 March, Arani began experiencing {{cvt|25|kn|m/s km/h mph}} of wind shear because another ] bumped it from behind.<ref>{{cite web|author=Rob Gutro|publisher=National Aeronautics and Space Administration|date=15 March 2011|title=NASA's Aqua Satellite Spots Rare Southern Atlantic Sub-tropical Storm|access-date=15 March 2011|url=http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2011/h2011_90L.html}}</ref> As it moved east-southeastwards, it achieved its highest winds as it transitioned back to an extratropical cyclone, process that was concluded on early 17 March.<ref name=AraniTCR/> | ||
| Before it developed into a subtropical cyclone, Arani produced torrential rains over portions of southeastern ], resulting in flash flooding and landslides. Significant damage was reported in portions of ], though specifics are unknown.<ref>{{cite web|author=Unattributed|publisher=Climatempo|date= |
Before it developed into a subtropical cyclone, Arani produced torrential rains over portions of southeastern ], resulting in flash flooding and landslides. Significant damage was reported in portions of ], though specifics are unknown.<ref>{{cite web|author=Unattributed|publisher=Climatempo|date=16 March 2011|access-date=19 March 2011|title=Arani – tempestade subtropical afasta-se da costa do ES|url=http://www.climatempo.com.br/destaques/2011/03/16/arani-tempestade-subtropical-afasta-se-da-costa-do-es/|language=pt}}</ref> Increased swells along the coast prompted ocean travel warnings.<ref>{{cite web|author=Unattributed|publisher=Jornal De Tempo|date=16 March 2011|access-date=19 March 2011|title=Após formar um olho, ciclone subtropical Arani perde força nesta quarta|url=http://jornaldotempo.uol.com.br/noticias.html/52249/|language=pt}}</ref> | ||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ===Subtropical Storm Bapo=== | ====Subtropical Storm Bapo==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| Line 75: | Line 79: | ||
| |Image=Bapo 2015-02-06 1630Z.jpg | |Image=Bapo 2015-02-06 1630Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Bapo 2015 track.png | |Track=Bapo 2015 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=5 February 2015 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=7 February 2015 | ||
| |1-min winds=35 | |1-min winds=35 | ||
| |Pressure=992 | |Pressure=992 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| On 5 February 2015, a subtropical depression developed about {{convert|105|nmi|km mi|round=5}} to the southeast of ], ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre |access-date=5 February 2015 |date=5 February 2015 |title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 UTC for 5 February 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 }}</ref> During the next day, low-level ] decreased around the system, as it moved southeastwards away from the Brazilian coast and into anomalously warm waters, where it intensified further.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/hpcdiscussions.php?disc=fxsa21|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110923004305/http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/hpcdiscussions.php?disc=fxsa21|archive-date=2011-09-23|title=South American Forecast Discussion |website=Hydrometeorological Prediction Center}}</ref><ref name=BapoTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL BAPO - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_bapo.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> The system was named Bapo by the Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center during 6 February as it had intensified into a subtropical storm.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://thevane.gawker.com/rare-subtropical-storm-forms-off-the-coast-of-brazil-1684420069 |title=Rare Subtropical Storm Forms off the Coast of Brazil |newspaper=Gawker |access-date=8 February 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208225137/http://thevane.gawker.com/rare-subtropical-storm-forms-off-the-coast-of-brazil-1684420069 |archive-date=8 February 2015 |last1=Mersereau |first1=Dennis }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_06022015.pdf|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|access-date=6 February 2015|date=6 February 2015|title=Análise Sinótica – 06/02/2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923210940/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_06022015.pdf|archive-date=23 September 2015}}</ref> Over the next couple of days the system continued to move south-eastwards, achieving its peak intensity just before it transitioned into an ] during 8 February.<ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 0000 UTC – 08/FEB/2015 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=8 February 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 }}</ref><ref name=BapoTCR/> | |||
| On February 5, 2015, a subtropical depression developed about {{convert|105|mi|km|round=5|abbr=on}} to the southeast of ], ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Marinha do Brasil - Navy Hydrographic Centre |accessdate=February 5, 2015 |date=February 5, 2015 |title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 UTC for February 5, 2015 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/6W7f4mJbp?url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archivedate=February 5, 2015 |df= }}</ref> During the next day, low-level ] decreased around the system, as it moved southeastwards away from the Brazilian coast and intensified further.<ref>https://www.webcitation.org/6WC1P8mZO?url=http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/discussions/hpcdiscussions.php?disc=fxsa21</ref> The system was named Bapo by the Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center during February 6, after it had intensified into a subtropical storm.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://thevane.gawker.com/rare-subtropical-storm-forms-off-the-coast-of-brazil-1684420069 |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2015-02-08 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208225137/http://thevane.gawker.com/rare-subtropical-storm-forms-off-the-coast-of-brazil-1684420069 |archivedate=2015-02-08 |df= }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_06022015.pdf|publisher=CPTEC - INPE|accessdate=February 6, 2015|date=February 6, 2015|title=Análise Sinótica – 06/02/2015}}</ref> Over the next couple of days the system continued to move south-eastwards before it transitioned into an ] during February 8.<ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 0000 UTC - 08/FEB/2015 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center - Marine Meteorological Service |accessdate=February 8, 2015 |archiveurl=https://www.webcitation.org/6WBHXQFmA?url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archivedate=February 8, 2015 |deadurl=yes |df= }}</ref> | |||
| {{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| ===Subtropical Storm Cari=== | ====Subtropical Storm Cari==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| Line 90: | Line 93: | ||
| |Image=Cari Mar 11 2015 1255Z.jpg | |Image=Cari Mar 11 2015 1255Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Cari 2015 track.png | |Track=Cari 2015 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=10 March 2015 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=13 March 2015 | ||
| |1-min winds=35 | |1-min winds=35 | ||
| |Pressure=998 | |Pressure=998 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| On March |
On 10 March 2015, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy began issuing warnings on Subtropical Depression 3 during early afternoon,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15031012.jpg|publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre|access-date=11 March 2015|date=10 March 2015|title=Análise Sinótica de 1200 UTC|archive-date=3 April 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150403005708/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15031012.jpg}}</ref> while the ] (CPTEC in ]) already assigned the name ''Cari'' for the storm.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_10032015.pdf|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|access-date=11 March 2015|date=10 March 2015|title=Análise Sinótica – 10/03/2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402111751/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_10032015.pdf|archive-date=2 April 2015}}</ref> At 00:00 UTC on 11 March, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy upgraded Cari to a subtropical storm, also assigning this name to it.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre |access-date=11 March 2015 |date=11 March 2015 |title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 0000 UTC – 11/03/2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 }}</ref><ref name=CariTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL CARI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_cari.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> On 12 March, the Brazilian Hydrographic Center downgraded Cari to a subtropical depression as it achieved its lowest pressure,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15031200.jpg|publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre|access-date=12 March 2015|date=12 March 2015|title=Análise Sinótica de 0000 UTC|archive-date=3 April 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150403054158/https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15031200.jpg}}</ref><ref name=CariTCR/> while the CPTEC stated that the storm had become a "Hybrid cyclone"<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/noticias/noticia/127378|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|access-date=12 March 2015|date=12 March 2015|title=Análise Sinótica – 12/03/2015|archive-date=25 May 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150525131230/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/noticias/noticia/127378|url-status=dead}}</ref> as it moved away from the continental coastline.<ref name=CariTCR/> During early afternoon of 13 March, the Brazilian Navy declared that Cari became a remnant low.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15031312.jpg|publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre|access-date=14 March 2015|date=13 March 2015|title=Análise Sinótica de 1200 UTC|archive-date=8 April 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150408122623/https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15031312.jpg}}</ref> | ||
| Cari brought heavy rainfall, flooding and landslides to eastern cities of ] and ] states.<ref name="Metsul">{{cite web|url=http://www.metsul.com/blog2012/Home/home/843/Cari_%C3%A9_rebaixado_ao_enfraquecer_e_ciclone_se_afasta_do_continente|publisher=Metsul| |
Cari brought heavy rainfall, flooding and landslides to eastern cities of ] and ] states as it interacted with a ].<ref name="Metsul">{{cite web|url=http://www.metsul.com/blog2012/Home/home/843/Cari_%C3%A9_rebaixado_ao_enfraquecer_e_ciclone_se_afasta_do_continente|publisher=Metsul|access-date=14 March 2015|date=12 March 2015|title=Cari é rebaixado ao enfraquecer e ciclone se afasta do continente|language=pt|archive-date=22 March 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150322070735/http://www.metsul.com/blog2012/Home/home/843/Cari_%C3%A9_rebaixado_ao_enfraquecer_e_ciclone_se_afasta_do_continente}}</ref><ref name=CariTCR/> Rain totals from {{cvt|100|to|180|mm|in}} were observed associated with the storms and wind topped {{cvt|75|km/h|mph}} in ].<ref name="Metsul" /> A Navy buoy registered a {{convert|20|ft|m|0|adj=on|order=flip}} wave off the coast of Santa Catarina.<ref name="Metsul" /> | ||
| {{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| ===Subtropical Storm Deni=== | ====Subtropical Storm Deni==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| Line 106: | Line 109: | ||
| |Image=Deni 2016-11-16 1645Z.jpg | |Image=Deni 2016-11-16 1645Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Deni 2016 track.png | |Track=Deni 2016 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=15 November 2016 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=16 November 2016 | ||
| |1-min winds=40 | |1-min winds=40 | ||
| |Pressure=998 | |Pressure=998 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| On 15 November 2016, instability areas associated with a ] axis over ]'s coastline led to the formation of a subtropical depression southwest of it.<ref name=DeniTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL DENI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_deni.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 1200 UTC – 15/NOV/2016 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center |access-date=15 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 |date=15 November 2016 }}</ref> It intensified into a subtropical storm and received the name ''Deni'' on 16 November.<ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 16/NOV/2016|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=16 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161116034310/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm|archive-date=16 November 2016|date=16 November 2016}}</ref> Moving south-southeastwards, Deni soon became extratropical shortly before 00:00 UTC on 17 November,<ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 17/NOV/2016 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center |access-date=17 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 |date=17 November 2016 }}</ref> where it was absorbed by a mid-latitude frontal system.<ref name=DeniTCR/> | |||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ===Subtropical Storm Eçaí=== | ====Subtropical Storm Eçaí==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| Line 120: | Line 123: | ||
| |Image=Eçaí 2016-12-05 1655Z.jpg | |Image=Eçaí 2016-12-05 1655Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Eçaí 2016 track.png | |Track=Eçaí 2016 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=4 December 2016 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=6 December 2016 | ||
| |1-min winds=55 | |1-min winds=55 | ||
| |Pressure=992 | |Pressure=992 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| An extratropical cyclone entered the South Atlantic Ocean from ] early on December |
An extratropical cyclone entered the South Atlantic Ocean from ] early on 4 December 2016.<ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 4 Dec 2016|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C16120400.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=5 December 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161205084452/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C16120400.jpg|archive-date=5 December 2016|language=pt|format=JPEG|date=4 December 2016}}</ref> Later, it intensified quickly and then transitioned into a subtropical storm shortly before 22:00 ] (00:00 UTC on 5 December), with the name ''Eçaí'' assigned by the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy.<ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 05/DEC/2016 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center |access-date=5 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 |date=5 December 2016 }}</ref> Eçaí started to decay on 5 December as it moved Into cooler waters, and weakened into a subtropical depression at around 00:00 UTC on 6 December.<ref name=EçaíTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL EÇAÍ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_ecai.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 06/DEC/2016 |url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center |access-date=6 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 |date=6 December 2016 }}</ref> As it decayed and lost its subtropical characteristics, its center divided in two, with the new center moving away southeastwards and the old one degrading into a remnant frontal low.<ref name=EçaíTCR/> | ||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ===Subtropical Storm Guará=== | ====Subtropical Storm Guará==== | ||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| Line 134: | Line 137: | ||
| |Image=Guará 2017-12-10 1225Z.jpg | |Image=Guará 2017-12-10 1225Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Guará 2017 track.png | |Track=Guará 2017 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=9 December 2017 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=10 December 2017 | ||
| |1-min winds=40 | |1-min winds=40 | ||
| |Pressure=996 | |Pressure=996 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| According to the Hydrographic Center |
According to the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, on 8 December 2017 a ] aligned with a through axis led to the formation of several instability areas.<ref name=GuaráTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL GUARÁ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_guara.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> On 9 December a subtropical storm formed from this setup, on border between ] and ], moving southeastwards away from land.<ref name=GuaráTCR/><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletim.htm|title=METEOROMARINHA REFERENTE ANALISE DE 1200 HMG – 09/DEZ/2017|date=9 December 2017|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|language=pt|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060131224347/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletim.htm|archive-date=31 January 2006|access-date=9 December 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 9 Dec 2017|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C17120912.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=9 December 2017|format=JPEG|date=9 December 2017|archive-date=10 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171210015829/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C17120912.jpg}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_09122017.pdf|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|access-date=9 December 2017|date=9 December 2017|title=Análise Sinótica – 09/12/2017|archive-date=10 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171210021941/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_09122017.pdf}}</ref> On late 10 December, a ] pushed Guará southwards towards cooler waters, where it started transitioning into an ].<ref name=GuaráTCR/> On early 11 December Guará attained its peak intensity,<ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 11 Dec 2017|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C17121100.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=11 December 2017|format=JPEG|date=11 December 2017|archive-date=12 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171212193157/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C17121100.jpg}}</ref> shortly thereafter degenerating into a low-pressure area associated with a through axis.<ref name=GuaráTCR/><ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 11 Dec 2017|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C17121112.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=11 December 2017|format=JPEG|date=11 December 2017|archive-date=12 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171212193138/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C17121112.jpg}}</ref> | ||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ===Tropical Storm Iba=== | ====Tropical Storm Iba==== | ||
| {{Infobox |
{{Infobox tropical cyclone small | ||
| |name=Tropical Storm Iba | |||
| |category=storm | |||
| |type=tropical storm | |||
| |time=12:00 ] March 24 | |||
| |image=South Atlantic tropical depression 2019-03-24 1246Z.jpg | |||
| |track=Iba 2019 track.png | |||
| |lat=18.5|S|lon=36|W | |||
| |within_units=5 ] | |||
| |distance_from= | |||
| |1sustained={{convert|35|kn|round=5}} | |||
| |gusts={{convert|40|kn|round=5}} | |||
| |pressure={{convert|1008|hPa|inHg|abbr=on|2}} | |||
| |movement=] at {{convert|5|kn|0}} | |||
| }} | |||
| <!--{{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |Basin=SAtl | ||
| |Image= |
|Image=Iba 2019-03-25 1615Z.jpg | ||
| |Track=Iba 2019 track.png | |Track=Iba 2019 track.png | ||
| |Formed= |
|Formed=23 March 2019 | ||
| |Dissipated= |
|Dissipated=27 March 2019 | ||
| |1-min winds=45 | |||
| |Pressure=1006 | |||
| }} | |||
| According to the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, on 22 March 2019, a low-pressure area formed off the coast of ] after the passage of a frontal system.<ref name=IbaTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE TROPICAL IBA - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_iba.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> On the next day, the cyclone developed a deep warm-core, thus being designated as a tropical depression.<ref name=IbaTCR/><ref>{{cite web |title=Análise Sinótica |url=http://img0.cptec.inpe.br/~rgptimg/Produtos-Pagina/Carta-Sinotica/Analise/Superficie/superficie_atual.gif |publisher=CPTEC |access-date=23 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190323170653/http://img0.cptec.inpe.br/~rgptimg/Produtos-Pagina/Carta-Sinotica/Analise/Superficie/superficie_atual.gif |archive-date=23 March 2019 |language=pt |format=GIF |date=23 March 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=WARNING NR 205/2019 |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings |publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=23 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190323171340/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings |archive-date=23 March 2019 |date=23 March 2019}}</ref> On 24 March, the system intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name ''Iba'' from the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center.<ref name=IbaTCR/> After moving southwestward for a couple of days, on 26 March, Iba reached its peak intensity.<ref name=IbaTCR/> Afterward, a cold front would approach the storm, which helped intensify the wind shear impacting Iba, leading to its weakening and extratropical transition.<ref name=IbaTCR/> On early 28 March, Iba would degenerate into a remnant low, becoming fully extratropical a day later.<ref name=IbaTCR/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=28&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=3&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2019&field_horario_value=12HMG|title=Cartas sinóticas 28 de março|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=10 May 2021|format=JPEG|date=28 March 2019|language=pt}}</ref> | |||
| Iba was the first tropical storm to develop in the basin since Anita in 2010, as well as the first fully tropical system to be named from the Brazilian naming list.<ref>{{cite web |title=WARNING NR 208/2019 |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings |publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=24 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190324170626/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings |archive-date=24 March 2019 |date=24 March 2019}}</ref> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ====Subtropical Storm Jaguar==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image=Jaguar 2019-05-21 1605Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Jaguar 2019 track.png | |||
| |Formed=19 May 2019 | |||
| |Dissipated=21 May 2019 | |||
| |1-min winds=35 | |1-min winds=35 | ||
| |Pressure= |
|Pressure=1010 | ||
| }} |
}} | ||
| According to the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, on 19 May 2019 several instability areas formed from a through axis off the coast of ], which later coalesced into a subtropical depression.<ref name=JaguarTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL JAGUAR - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=22 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_jaguar.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> On 20 May, the system strengthened into a subtropical storm, receiving the name ''Jaguar'' from the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center.<ref>{{cite web |title=WARNING NR 422/2019 |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings |publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=20 May 2019 |date=20 May 2019 |archive-date=24 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190324170626/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings |url-status=dead }}</ref> However, the system did not intensify any further, as it soon encountered unfavorable conditions while moving southeastwards, weakening into a subtropical depression on early 21 May.<ref name=JaguarTCR/> Later that day, Jaguar degenerated into several sparse instability areas associated with a low-pressure area, which was absorbed by a frontal system on 22 May.<ref name=JaguarTCR/> | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ===2020s=== | |||
| ==== Subtropical Storm Kurumí ==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image=Kurumí 2020-01-24.jpg | |||
| |Track=Kurumí 2020 track.png | |||
| |Formed=23 January 2020 | |||
| |Dissipated=24 January 2020 | |||
| |1-min winds=35 | |||
| |Pressure=998 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{See also|2020 Brazilian floods and mudslides}} | |||
| On 21 January 2020, the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center began monitoring an area of persisting thunderstorms near ] for potential subtropical cyclone development. Generally tracking southeastward, the system began to organize within the afternoon hours of 22 January, aided by the establishment of a ], and was designated a subtropical depression in the early hours of 23 January.<ref name=KurumíTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL KURUMÍ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_kurumi.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> Several hours later, due to a lack of wind shear, the system intensified into a subtropical storm and was given the name ''Kurumí''.<ref>{{cite web|title=WARNINGS AND FORECASTS- SUBTROPICAL STORM KURUMI|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings|publisher=Marine Meteorological Service|access-date=24 January 2020|date=24 January 2020|archive-date=24 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190324170626/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings|url-status=dead}}</ref> After this bout of intensification, Kurumí moved southward and began to succumb to much more unfavorable conditions. It weakened back to a subtropical depression on late 24 January, due to an intensification of wind shear over its circulation due to the formation of an ] to its southeast.<ref name=KurumíTCR/><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings|title=SPECIAL WARNING – SUBTROPICAL DEPRESSION "KURUMI"|date=25 January 2020|website=Centro de Hidrografia da Marinha: MARINHA DO BRASIL|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200125202928/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm/warnings-and-forecasts/warnings|archive-date=25 January 2020}}</ref> The last advisory was issued on Kurumí later that same day, as it degenerated into a ] while also beginning to merge with the nearby frontal system.<ref name=KurumíTCR/> | |||
| The ] associated with Kurumí would later play a role in the ], producing heavy rainfall. Over 171.8 mm (6.76 in) of rain fell in the ] on 24 January, triggering a landslide and killing 3 people and leaving 1 missing.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2020-01/25/c_138732892.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200125162136/http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2020-01/25/c_138732892.htm|archive-date=25 January 2020|title=Heavy rains cause casualties, damage in southeast Brazilian region|date=24 January 2020|work=Xinhua News|access-date=1 February 2020}}</ref> | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ====Subtropical Storm Mani==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image=Mani 2020-10-26 1555Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Mani 2020 track.png | |||
| |Formed=25 October 2020 | |||
| |Dissipated=27 October 2020 | |||
| |1-min winds=35 | |||
| |Pressure=1004 | |||
| }} | |||
| According to the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy, on 24 October 2020, a ] persisted off the coast of the border between ] and ], which led to the formation of a subtropical depression on the next day.<ref name=ManiTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL MANI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_mani.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 25 October 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c20102512.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=25 October 2020|format=JPEG|date=25 October 2020|language=pt}}</ref> Later that day it intensified into a subtropical storm, which led it to be named ''Mani'' at 00:00 UTC on 26 October.<ref name=ManiTCR/><ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 26 October 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c20102600.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=26 October 2020|format=JPEG|date=26 October 2020|language=pt}}</ref> As it moved away from a ] on 27 October, Mani gradually lost its subtropical characteristics, until it weakened to a low pressure area.<ref name=ManiTCR/><ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 28 October 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c20102800.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=26 October 2020|format=JPEG|date=26 October 2020|language=pt}}</ref> | |||
| The storm caused significant damage in ], with landslides of stones and earth leaving more than 400 people homeless.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://portal.inmet.gov.br/noticias/tempestade-subtropical-mani-causou-chuva-no-estado-do-esp%C3%ADrito-santo-neste-fim-de-semana|title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL MANI FAVORECEU A OCORRÊNCIA DE CHUVA NO ESTADO DO ESPÍRITO SANTO NESTE FIM DE SEMANA.|language=Portuguese|website=portal.inmet.gov.br|author=Maisa Pereira de Souza|publisher=Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia|date=27 October 2020|access-date=16 February 2021}}</ref> The storm also impacted almost the entire state of ] and the northern region of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://metsul.com/ciclone-no-sudeste-tempestade-subtropical-mani-se-forma/|title=CICLONE NO SUDESTE – TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL MANÍ SE FORMA|language=Portuguese|author=|publisher=Metsul|date=26 October 2020|access-date=16 February 2021}}</ref> | |||
| {{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| ====Subtropical Storm Oquira==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image=Oquira 2020-12-29 1710Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Oquira 2020 track.png | |||
| |Formed=27 December 2020 | |||
| |Dissipated=30 December 2020 | |||
| |1-min winds=35 | |||
| |Pressure=998 | |||
| }} | |||
| According to the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy, on 26 December 2020, the prior presence of a ] and the subsequent passage of a frontal system led to the presence of several instability areas off the coast east of ],<ref name=OquiraTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL OQUIRA - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_oquira.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> which coalesced into a subtropical depression a day later.<ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 27 December 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c20122712.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=28 December 2020|format=JPEG|date=27 December 2020|language=pt}}</ref> Moving southwestward, the system's central pressure dropped to {{convert|1010|mbar|inHg}} by 00:00 UTC on 28 December.<ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 28 December 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c20122800.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=28 December 2020|format=JPEG|date=28 December 2020|language=pt}}</ref> Later that day, the system's winds intensified, and it was named ''Oquira'' by the Brazilian Hydrographic Center.<ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 28 December 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c20122812.jpg|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|access-date=28 December 2020|format=JPEG|date=28 December 2020|language=pt}}</ref> On 29 December, Oquira continued to strengthen, deepening while heading further southwestward away from the Brazilian mainland, and reaching a pressure of {{convert|1002|mbar|inHg}}.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Weather And Sea Bulletin Issued 1200 UTC – 29 / DEC / 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-meteoromarinha/weather-and-sea-bulletin|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201229171605/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-meteoromarinha/weather-and-sea-bulletin|archive-date=29 December 2020|website=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|language=pt}}</ref> Afterwards, Oquira's movements shifted southeastwards, and its winds decreased as it started to lose its subtropical characteristics, weakening to a subtropical depression on 30 December, but its pressure continued to drop, bottoming out at a minimum central pressure of {{convert|998|mbar|inHg}}.<ref name=OquiraTCR/><ref>{{Cite web|title=Weathed And Sea Bulletin Issued 1200 UTC – 30 / DEC / 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-meteoromarinha/weather-and-sea-bulletin|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201230165342/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-meteoromarinha/weather-and-sea-bulletin|archive-date=30 December 2020|website=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|language=pt}}</ref> Later that day, Oquira transitioned into an extratropical low, and the Hydrographic Center issued their final advisory on the storm as it was absorbed by a frontal system.<ref name=OquiraTCR/><ref>{{Cite web|title=Bad Weather Warnings / Thu 31 December 2020|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201230214648/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|archive-date=30 December 2020|website=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|language=pt}}</ref> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ====Tropical Storm 01Q==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Image=01Q 2021-02-06 Suomi NPP.jpg | |||
| |Track=01Q 2021 track.png | |||
| |Formed=4 February 2021 | |||
| |Dissipated=6 February 2021 | |||
| |1-min winds=35 | |||
| |Pressure=990 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{See also|List of unnamed tropical cyclones}} | |||
| On 4 February 2021, an extratropical storm off the coast of ] developed into a ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cnnbrasil.com.br/nacional/2021/02/04/raro-no-verao-ciclone-bomba-se-forma-na-fronteira-entre-brasil-e-uruguai|title=Raro no verão, ciclone bomba se forma na fronteira entre Brasil e Uruguai|author=Bruna Ostermann|language=Portuguese|publisher=Cable News Network|date=4 February 2021|access-date=16 February 2021}}</ref> On 6 February, the storm began separating from its weather fronts and developed subtropical characteristics, before fully separating from the frontal zone and transitioning into a fully-tropical storm later that day. As a result, the NOAA classified the system as a tropical storm at 17:30 UTC, with the system being designated as ''Tropical Storm 01Q''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ssd.noaa.gov/PS/TROP/DATA/2021/bulletins/satl/20210206173001Q.html|title=01Q (Noname) – 1730 UTC|author=Boris A. Konon|publisher=NOAA|date=6 February 2021|access-date=7 February 2021}}</ref> However, the storm was short-lived, as it lost its tropical characteristics several hours later, with the NOAA issuing their final bulletin on the storm at 23:30 UTC that day. The storm dissipated soon afterward.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ssd.noaa.gov/PS/TROP/storms/01Q.html|title=01Q|publisher=NOAA|date=6 February 2021|access-date=6 February 2021|archive-url=https://archive.today/20210207003705/https://www.ssd.noaa.gov/PS/TROP/storms/01Q.html|archive-date=7 February 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ssd.noaa.gov/PS/TROP/DATA/2021/bulletins/satl/20210206233001Q.html|title=01Q (Noname) – 2330 UTC|author=Adam Clark|publisher=NOAA|date=6 February 2021|access-date=7 February 2021}}</ref> Although the NOAA issued bulletins on the storm, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy did not monitor it. | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ==== Subtropical Depression #01-2021==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image=02Q 2021-02-16 1947Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=02Q 2021 track.png | |||
| |Formed=14 February 2021 | |||
| |Dissipated=16 February 2021 | |||
| |1-min winds=30 | |||
| |Pressure=1002 | |||
| }} | |||
| On 13 February 2021, according to the Brazilian Navy, instability areas associated with a ] off the coast of the state of ] acquired subtropical characteristics on the next day, becoming a subtropical depression about {{convert|700|km|mi}} from the state.<ref name=01-2021TCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=DEPRESSÃO SUBTROPICAL #01-2021 - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=25 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_2021_fev_ds-01.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-meteoromarinha/weather-and-sea-bulletin|title=Weather and Sea Bulletin|author=|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|date=14 February 2021|access-date=16 February 2021}}</ref> For the next few days, the storm slowly meandered southeastward and then southwestward alongside a trough axis to its east,<ref name=01-2021TCR/> until it lost its subtropical characteristics over high seas on 17 February, becoming a remnant low.<ref name=01-2021TCR/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=17&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=2&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2021&field_horario_value=12HMG|title=Cartas Sinóticas|author=|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|date=17 February 2021|access-date=18 February 2021}}</ref> | |||
| The Brazilian Navy noted in its post-season analysis that on late 14 February the system could have intensified into a subtropical storm, since the radiometer built into the AMSR-2 satellite found winds of 35 knots, but it wasn't upgraded because no other measurement confirmed such findings.<ref name=01-2021TCR/> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ==== Subtropical Storm Potira==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image=Potira 2021-04-23 1235Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Potira 2021 track.png | |||
| |Formed=19 April 2021 | |||
| |Dissipated=24 April 2021 | |||
| |1-min winds=40 | |||
| |Pressure=1006 | |||
| }} | |||
| A low south of Rio de Janeiro transitioned into a subtropical depression on 19 April 2021.<ref>{{cite web |title=WEATHER AND SEA BULLETIN ISSUED 1200 UTC 19/APR/2021 |url=https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/raw/fq/fqst02.sbbr..txt |publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=20 April 2021 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20210420034042/https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/raw/fq/fqst02.sbbr..txt |archive-date=20 April 2021 |date=19 April 2021}}</ref> | |||
| On 20 April 2021, the system intensified into a subtropical storm, which Brazilian Navy then decided to name it ''Potira''.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo |title=Avisos de Mau Tempo | Centro de Hidrografia da Marinha |access-date=31 December 2020 |archive-date=30 December 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201230214648/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo }}</ref> Potira moved slowly northeastwards for a couple of days over unusually warmer waters, favorable upper-level tropospheric winds and strong low-level convergence, which led to its intensification and persistence of its peak intensity until 23 April.<ref name=PotiraTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL POTIRA - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_potira.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> As it completed a clockwise loop, Potira weakened into a subtropical depression, with the Brazilian Navy downgrading it to a low-pressure area on late 24 January.<ref name=PotiraTCR/><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=25&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=4&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2021&field_horario_value=12HMG | title=Cartas Sinóticas | Centro de Hidrografia da Marinha }}</ref> | |||
| The storm caused a gale in the ] fort and the gusts of wind went over {{cvt|60|km/h}}.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://metsul.com/ciclone-potira-traz-vento-forte-no-rio-de-janeiro/|title=Ciclone Potira traz vento forte no Rio de Janeiro|date=20 April 2021}}</ref> In the municipalities of ] and ] (SC), the hangover caused by Potira caused flooding in the streets and damage to the sidewalks.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/sc/santa-catarina/noticia/2021/04/26/apos-semana-com-tempestade-subtropical-litoral-de-sc-registra-alagamentos-com-mare-alta.ghtml|title=Após semana com tempestade subtropical, litoral de SC registra alagamentos com maré alta|website=G1|date=26 April 2021 }}</ref> The ports of Itajaí and Navegantes were closed for 3 days. No economic or material damage caused by the cyclone has been reported.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://g1.globo.com/sc/santa-catarina/noticia/2021/04/24/portos-de-itajai-e-navegantes-sao-reabertos-apos-alivio-da-tempestade-potira.ghtml|title=Portos de Itajaí e Navegantes são reabertos após tempestade subtropical perder força|website=G1|date=24 April 2021 }}</ref> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ==== Subtropical Storm Raoni ==== | |||
| {{Infobox hurricane small | |||
| |Basin=SATL | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Image= Raoni 2021-06-29 1728Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Raoni 2021 track.png | |||
| |Formed=29 June 2021 | |||
| |Dissipated=1 July 2021 | |||
| |1-min winds=45 | |||
| |Pressure=986 | |||
| }} | |||
| An ] formed on 26 June 2021, about {{convert|520|km|abbr=on}} east-southeast of ], ], associated with a cold airmass that acted over the region.<ref name=RaoniTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL RAONI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_raoni.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> On the next day, the cyclone acquired a ] while intensifying, while it moved westwards and separated from the frontal system it was previously attached to.<ref name=RaoniTCR/> As the system ], the seclusion deepened and started to acquire subtropical characteristics, which led it to be designated as a subtropical storm on 29 June.<ref name=RaoniTCR/><ref>{{cite web |title=WEATHER AND SEA BULLETIN ISSUED 28/JUN/2021 1200Z |url=https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/raw/fq/fqst02.sbbr..txt |publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=29 June 2021 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20210629032003/https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/raw/fq/fqst02.sbbr..txt |archive-date=29 June 2021 |date=28 June 2021}}</ref> It remained unnamed due to it being outside of the ] area of responsibility.<ref>{{cite web |title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 29/JUN/2021 – 00Z |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c21062900.jpg |publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |access-date=29 June 2021}}</ref> By 23:30 UTC on 28 June, the Satellite Products and Services Division of the ] declared the system to have become a ], based on a ] of 3.5,<ref>{{cite report|url=https://www.ssd.noaa.gov/PS/TROP/DATA/2021/bulletins/satl/202106282330IN1.html|title=TXST21 KNES 290105|author=Kyle Matthew Hosley|date=28 June 2021|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|access-date=29 June 2021}}</ref> assigning an ''invest'' tag to it.<ref name=RaoniTCR/> Although being affected by strong wind shear to its north due to a ] caused by the presence of a frontal system nearby, it further intensified and achieved a minimum pressure {{convert|986|mbar|inHg}}, while tracking northeastwards towards the Brazilian area of authority.<ref name=RaoniTCR/><ref>{{cite web |title=Bad Weather Notices 29/JUN/2021 12Z|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210629131030/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |archive-date=29 June 2021|access-date=29 June 2021}}</ref> At around 12:00 UTC on the next day, as the storm entered the boundary of ] V, ]'s area of responsibility, thus it was assigned the name ''Raoni''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=29&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=6&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2021&field_horario_value=12HMG|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart, 12Z|work=Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center|date=29 June 2021|access-date=30 June 2021}}</ref> Continuing moving northeastwards, Raoni further developed an ] feature as well as a robust band to the east of the system.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://metsul.com/ciclone-raoni-na-costa-tem-algumas-caracteristicas-de-furacao-e-nao-oferece-perigo/|title=Ciclone Raoni na Costa Tem Algumas Características de Furacao e Năo Oferece Perigo|work=Metsul Meteorologia|date=29 June 2021|access-date=30 June 2021|archive-url=https://archive.today/20210630063459/https://metsul.com/ciclone-raoni-na-costa-tem-algumas-caracteristicas-de-furacao-e-nao-oferece-perigo/|archive-date=30 June 2021|url-status=live}}</ref> Raoni began to weaken by 30 June, as the subtropical jet broke the ] flow over it, and NESDIS dropped the tag as it lost its convective bands.<ref name=RaoniTCR/><ref>{{cite web |title=Bad Weather Notices 30/JUN/2021 12Z|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210630182208/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|publisher=Marine Meteorological Service |archive-date=30 June 2021|access-date=30 June 2021}}</ref> On 1 July, Raoni lost its subtropical characteristics and degenerated into a low-pressure area.<ref name=RaoniTCR/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=2&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=7&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2021&field_horario_value=00HMG|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210630182208/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo |archive-date=30 June 2021 |title=2021/07/02 Sea Level Pressure Chart, 00Z|work=Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center|date=2 July 2021|access-date=2 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| The predecessor ] of Raoni caused heavy rains and strong winds gust up to {{cvt|104|km/h|mph}}, downing trees and causing damages to different public and private establishments across ].<ref name="Uruguay">{{cite news|title=Ciclone Causa Estragos no Uruguai e se Aproxima Do Rio Grande do Sul|url=https://metsul.com/ciclone-causa-estragos-no-uruguai-e-se-aproxima-do-rio-grande-do-sul/|date=28 June 2021|access-date=30 June 2021|archive-url=https://archive.today/20210630064714/https://metsul.com/ciclone-causa-estragos-no-uruguai-e-se-aproxima-do-rio-grande-do-sul/|archive-date=30 June 2021|work=Metsul Meteorologia|url-status=live}}</ref> The area's waters were also rough due to the storm. Downpours with continuous gales were also experienced in ]'s capital ].<ref name="Uruguay"/> From 24 June to 2 July, Raoni channeled cold air from ] into portions of ], leading to an unusually potent ] across ], ], ], ], and Brazil, with the temperature dropping as much as 15 °C (27 °F) below average in some areas. The combination of the cyclone and the cold wave also produced snowfall across the southern portion of South America, with snowfall observed as far north as southern Brazil.<ref name="cold weather outbreak">{{cite news|url=https://www.severe-weather.eu/global-weather/south-hemisphere-america-cold-winter-outbreak-fa/|title=Unusually strong cold weather outbreak spreads from Antarctica into central South America, bringing early winter temperature records and first snowfall after decades|author=Andrej Flis|work=Severe Weather Europe|date=4 July 2021|access-date=23 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ====Subtropical Storm Ubá==== | |||
| {{Infobox hurricane small | |||
| |Basin=SATL | |||
| |Image=Ubá 2021-12-10 1210Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Ubá 2021 track.png | |||
| |Formed=9 December 2021 | |||
| |Dissipated=12 December 2021 | |||
| |1-min winds=35 | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Pressure=997 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Main|Subtropical Storm Ubá}} | |||
| On 9 December 2021, instability areas remained off the coast of ] and ] after the passage of a frontal system and a ].<ref name=UbáTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL UBÁ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_uba.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Baixa pressão no mar provoca temporais em SP e RJ |url=https://www.terra.com.br/noticias/climatempo/baixa-pressao-no-mar-provoca-temporais-em-sp-e-rj,f08ba4321980716ecb7ff022fd8b82091hvqq5at.html |access-date=12 December 2021 |agency=] |date=6 December 2021 |language=Portuguese |archive-date=12 December 2021 |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20211212021208/https://www.terra.com.br/noticias/climatempo/baixa-pressao-no-mar-provoca-temporais-em-sp-e-rj,f08ba4321980716ecb7ff022fd8b82091hvqq5at.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Overnight the system coalesced into an ], which transitioned into a subtropical depression.<ref name=UbáTCR/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=10&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=12&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2021&field_horario_value=12HMG|title=2021/12/10 Sea Level Pressure Chart, 00Z|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service|date=10 December 2021|access-date=10 December 2021}}</ref> On the morning of the next day, the system was upgraded to subtropical storm status, receiving the name ''Ubá''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|title=Bad Weather Notices 10/Dec/2021 13Z|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service|date=10 December 2021|access-date=10 December 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211210132155/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-avisos-de-mau-tempo/avisos-de-mau-tempo|archive-date=10 December 2021}}</ref> On 11 December Ubá gradually weakened while moving southeastwards, being downgraded to depression status.<ref name=UbáTCR/> It degenerated into a remnant low-pressure area on the next day.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=&field_horario_value=12HMG|title=2021/12/13 Sea Level Pressure Chart, 12Z|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service|date=13 December 2021|access-date=13 December 2021}}</ref> | |||
| The precursor extratropical cyclone and ] caused heavy rains in ], ] and southern ], where heavy precipitation accumulated {{cvt|450|mm}} in ] and {{cvt|331|mm|0}} in ], killing fifteen people.<ref>{{cite news |title=Sobe para 32 número de cidades em situação de emergência por causa das fortes chuvas na Bahia|url=https://g1.globo.com/ba/bahia/noticia/2021/12/13/sobe-para-32-numero-de-cidades-em-situacao-de-emergencia-por-causa-das-fortes-chuvas-na-bahia.ghtml|access-date=2021-12-13 |agency=] | |||
| |date=2021-12-13 |language=Portuguese }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Em 24 horas número de desabrigados pela chuva aumenta quase cinco vezes em MG|url=https://g1.globo.com/mg/minas-gerais/noticia/2021/12/11/em-24-horas-numero-de-desabrigados-pela-chuva-aumenta-quase-cinco-vezes-em-mg.ghtml|access-date=12 December 2021 |website=g1|date=11 December 2021|language=pt-br}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=CICLONE SE FORMA NA COSTA DO SUL DO BRASIL E PROVOCA CALAMIDADE NA BAHIA|url=https://metsul.com/ciclone-se-forma-na-costa-do-sul-do-brasil-e-provoca-calamidade-na-bahia/|access-date=12 December 2021 |agency=MetSul Meteorologia|date=10 December 2021 |language=Portuguese }}</ref> | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ====Subtropical Storm Yakecan==== | |||
| {{Infobox hurricane small | |||
| |Basin=SATL | |||
| |Image=Yakecan 2022-05-18 1720Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Yakecan 2022 path.png | |||
| |Formed=16 May 2022 | |||
| |Dissipated=19 May 2022 | |||
| |1-min winds=50 | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| |Pressure=990 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Main|Subtropical Storm Yakecan}} | |||
| On 15 May 2022, an extratropical cyclone moved through the southern region of Brazil and stopped offshore.<ref name=YakecanTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL YAKECAN - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO |access-date=24 January 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/arquivos/relatorio_pos_evento_yakecan.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> The low occluded and separated form its precursor extratropical cyclone, obtaining subtropical characteristics in the process.<ref name=YakecanTCR/> On the morning of 17 May, the cyclone fully transitioned into a subtropical storm, and was given the name ''Yakecan''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=17&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=5&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2022&field_horario_value=00HMG|date=17 May 2022|title=Cartas sinóticas 17 de maio de 2022|language=pt|access-date=27 September 2023|website=Brazilian Navy}}</ref> Taking a more northwestwardly movement, Yakecan moved away from the coastline, gradually losing its subtropical characteristics.<ref name=YakecanTCR/> On late 19 May, it acquired frontal characteristics and transitioned to an extratropical cyclone.<ref name=YakecanTCR/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=20&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=5&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2022&field_horario_value=00HMG|date=20 May 2022|title=Cartas sinóticas 20 de maio de 2022|language=pt|archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220523190537/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=20&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=5&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2022&field_horario_value=00HMG|access-date=23 May 2022|archive-date=23 May 2022|website=Brazilian Navy|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| During its trajectory, the storm caused snow in the Gaúcha and Catarinense Mountains, setting record lows for this time of year.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://metsul.com/umidade-do-ciclone-yakecan-e-ar-frio-trazem-neve-e-chuva-congelada/ | title=Umidade do ciclone Yakecan e ar frio trazem neve e chuva congelada | date=17 May 2022 }}</ref> Two people died in Uruguay and Brazil due to the passage of the cyclone.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://gauchazh.clicrbs.com.br/ambiente/noticia/2022/05/no-uruguai-yakecan-provoca-transtornos-e-causa-pelo-menos-uma-morte-cl3al945h003i019in0iqc5as.html | title=No Uruguai, Yakecan provoca transtornos e causa pelo menos uma morte | date=17 May 2022 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://g1.globo.com/rs/rio-grande-do-sul/noticia/2022/05/17/bombeiros-buscam-homem-que-desapareceu-apos-barco-afundar-em-porto-alegre.ghtml | title=Corpo é encontrado no Guaíba após barco afundar durante passagem de tempestade Yakecan no RS; suspeita é que seja de pescador desaparecido | date=17 May 2022 }}</ref> Yakecan is the last name from the regular naming list, which has been in use since 2011. | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ====Tropical Storm Akará==== | |||
| {{Infobox hurricane small | |||
| |Basin=SATL | |||
| |Image=Akará 2024-02-18 0000Z.jpg | |||
| |Track=Akará 2024 path.png | |||
| |Formed=16 February 2024 | |||
| |Dissipated=22 February 2024 | |||
| |1-min winds=45 | |||
| |Pressure=994 | |||
| }} | |||
| In February 2024, a low-pressure area began developing along a stalled cold front. Moisture from the tropics began feeding into the circulation of the developing disturbance, helping it to intensify.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-02-27 |title=Rare Tropical Storm Akará Forms off Brazilian Coast |url=https://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/news/rare-tropical-storm-akara-forms-brazilian-coast |access-date=2024-02-29 |website=National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service |language=en}}</ref> On 16 February 2024, the Brazilian Navy designated the system, which at the time was east southeast of ], as a subtropical depression.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-warnings_and_forecasts/warnings | archive-url=https://archive.today/20240216024426/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-warnings_and_forecasts/warnings | url-status=dead | archive-date=2024-02-16 | title= Hidrografia da Marinha - Special Warning| date=16 February 2024 }}</ref> Two days later, the system transitioned into a tropical cyclone.<ref></ref> In the early hours of 19 February, the system intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name ''Akará'' from the Brazilian Navy.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-02-19 |title=Carta Sinótica 19 fevereiro de 2024 - 0000H|url=https://archive.ph/jqAdg/449bf2e383c8ec965fadb2f02172496d2926c138.png |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240219035539/https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/dados-do-smm-cartas-sinoticas/cartas-sinoticas?field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bday%5D=19&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Bmonth%5D=2&field_data_value%5Bvalue%5D%5Byear%5D=2024&field_horario_value=00HMG |archive-date=2024-02-19 |access-date=2024-02-19 |website=] |lang=pt}}</ref> However, two days later, the system lost its tropical characteristics and weakened into a subtropical depression.<ref name=AkaráTCR>{{cite web|publisher=] |title=TEMPESTADE TROPICAL AKARÁ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO|access-date=15 December 2024|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/u1894/relatorio_pos_evento_akara.pdf|lang=pt}}</ref> The next day, the system lost its subtropical characteristics, thus the Brazilian Navy ceased all bulletins.<ref name=AkaráTCR/> | |||
| The precursor extratropical cyclone to Akará brought heavy rainfall to South America.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Wulfeck |first=Andrew |date=2024-02-17 |title=Tropical cyclone forms in Atlantic but not where you'd think |url=https://www.foxweather.com/weather-news/tracking-subtropical-storm-south-atlantic-2024 |access-date=2024-02-19 |website=FOX Weather |language=en-US}}</ref> ] was affected with intense rainfall and winds.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Newton |first=Lou |date=2024-02-22 |title=Watch: Baby rescued from car moments before being washed away in Brazilian storm |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2024/02/22/baby-rescued-car-tropical-storm-akara-flooding-brazil/ |access-date=2024-02-22 |work=The Telegraph |language=en-GB |issn=0307-1235}}</ref> Akará was the first named tropical storm to develop in the basin since Iba in 2019. | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| ====Subtropical Storm Biguá==== | |||
| {{Infobox tropical cyclone small | |||
| |Basin=SAtl | |||
| |Image=Biguá 2024-12-15 0000Z.jpg | |||
| |Track= | |||
| |Formed=14 December 2024 | |||
| |Dissipated=16 December 2024 | |||
| |1-min winds=50 | |||
| |Pressure=998 | |||
| |Type=subtropical | |||
| }} | |||
| Early on 15 December 2024, a subtropical storm formed off the coast of the ], receiving the name ''Biguá'' from the Brazilian Navy.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c24121500.png|date=15 December 2024|title=Carta sinótica de 15 de dezembro de 2024 - 0000Z|language=pt|access-date=15 December 2024|website=]}}</ref> As it moved southeastwards, away from the coastline, the system was downgraded to subtropical depression.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c24121612.png|date=16 December 2024|title=Carta sinótica de 16 de dezembro de 2024 - 1200Z|language=pt|access-date=17 December 2024|website=]}}</ref> On early 17 December 2024 December 17, the cyclone was downgraded to a low-pressure area as it transitioned to a ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c24121700.png|date=17 December 2024|title=Carta sinótica de 17 de dezembro de 2024 - 0000Z|language=pt|access-date=17 December 2024|website=]}}</ref> | |||
| The closeness to the Brazilian shore caused wind gusts over the southeastern ], leading to power losses and structural damages on nearby cities.<ref>{{cite web|first=Lisielle |last=Zanchettin |url=https://gauchazh.clicrbs.com.br/geral/noticia/2024/12/ciclone-bigua-provoca-transtornos-e-falta-de-luz-em-varios-pontos-do-rs-cm4q0u9ya01k5013n92almm6c.html |date=15 December 2024 |title=Ciclone Biguá provoca transtornos e falta de luz em vários pontos do RS |language=pt |access-date=15 December 2024 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==Other systems== | ==Other systems== | ||
| ===Pre-2004=== | ===Pre-2004=== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| According to a presentation at the Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI), satellite imagery from January 1970 showed that a system with an eyewall had developed behind a cold front and that the system needed further analysis to determine if it was tropical or subtropical.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> On March |
According to a presentation at the Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI), satellite imagery from January 1970 showed that a system with an eyewall had developed behind a cold front and that the system needed further analysis to determine if it was tropical or subtropical.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> On 27 March 1974, a weak area of low pressure that had originated over the Amazon River started to intensify further.<ref name="Catarina Analysis">{{cite journal|doi=10.1175/MWR3330.1|journal=Monthly Weather Review|publisher=American Meteorological Society|pages=3048–3049|volume=134|issue=11|title=Analysis of Hurricane Catarina (2004)|author4=Eyad, Atallah|author1=McTaggart-Cowan, Ron|bibcode=2006MWRv..134.3029M|author2=Bosart, Lance|author3=Davis, Christopher|year=2006|author5=Gyakum, John|author6=Emaunel, Kerry|doi-access=free}}</ref> Over the next 48 hours the system quickly developed further and was classified as subtropical, as it developed a banding structure and deep convection near its warm core.<ref name="Catarina Analysis"/> On 29 March, a north-westerly flow encroached on the systems environment, which caused the system to rapidly move towards 40S and the cold waters that were present to the south of 40°S.<ref name="Catarina Analysis"/> | ||
| In March 1994, a system that was thought to be weaker than Catarina was spawned but was located over cool and open waters.<ref name="WWCBH">{{cite web|author=Henson, Bob|publisher=University Corporation for Atmospheric Research|title=What was Catarina?|year=2005|access-date=8 February 2015|url=http://www.ucar.edu/communications/quarterly/summer05/catarina.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160603153603/http://www.ucar.edu/communications/quarterly/summer05/catarina.html|archive-date=3 June 2016}}</ref> According to the Zambia Meteorological Department, ] moved off the coast of ] and entered the South Atlantic Ocean on 19 January 1996. By the next day, the system had succumbed to cold waters and days of land interaction, dissipating completely. It was the first tropical cyclone known to have traversed southern Africa from the South-West Indian Ocean to the South Atlantic.<ref name="zmd">{{cite CiteSeerX |author1=Mudenda, O. S. |author2=Mumba, Z. L. S.|title=The Unusual Tropical Storm of January 1996 |citeseerx=10.1.1.601.2986}}</ref> | |||
| ===2004–2009=== | ===2004–2009=== | ||
| During 2004, the large-scale conditions over the South Atlantic were more conducive than usual for subtropical or tropical systems, with 4 systems noted.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> The first possible tropical cyclone developed within a trough of low pressure, to the southeast of Salvador, Brazil on |
During 2004, the large-scale conditions over the South Atlantic were more conducive than usual for subtropical or tropical systems, with 4 systems noted.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> The first possible tropical cyclone developed within a trough of low pressure, to the southeast of Salvador, Brazil on 18 January.<ref name="GP January 2004"/><ref name="IWTCVI"/> The system subsequently displayed a small ] (CDO) and was suspected to be at the peak of its development as either a tropical depression or a tropical storm during the next day.<ref name="GP January 2004"/> The system was subsequently affected by some strong shear, before it moved inland and weakened along the coast of Brazil before it was last noted during 21 January.<ref name="GP January 2004"/> Within Brazil the system caused heavy rain and flooding with a state of emergency declared in ], after the river overflowed and burst its banks which flooded homes, destroyed crops and caused parts of the highway to collapse.<ref name="GP January 2004"/> However, it was noted that not all of the heavy rain and impacts were attributable to the system, as a large monsoon low covered much of Brazil at the time.<ref name="GP January 2004"/> The second system was a possible hybrid cyclone that developed near south-eastern Brazil between 15 and 16 March.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> Hurricane Catarina was the third system, while the fourth system formed off the coast of Brazil on 15 May 2004.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| On February |
On 22 February 2006, a baroclinic cyclone intensified quickly and was estimated to have peaked with 1-minute sustained wind speeds of {{cvt|65|mph|km/h|order=flip}}, after radar data showed that the system had developed an eye and banding.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> However, there were questions about how tropical the system was, as it did not separate from the westerlies or the baroclinic zone it was in.<ref name="IWTCVI"/><ref name="GP February 2006">{{cite web|title=Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary February 2006|access-date=7 February 2015|author=Padgett, Gary|url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2006/summ0602.htm |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240531214349/https://www.webcitation.org/6W9TGRpqN?url=http://www.australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0403.htm|archive-date=31 May 2024|url-status=live }}</ref> Between 11 and 17 March 2006, another system with a warm core developed and moved southward along the South Atlantic Zone, before dissipating.<ref name="IWTCVI"/> | ||
| Two subtropical cyclones affected both ] and ] state in |
Two subtropical cyclones affected both ] and ] state in Brazil between 2009 and 2010. On 28 January 2009, a cold-core mid to upper-level ] in phase with a low-level warm-core ] formed a ] and moved eastward into the South Atlantic.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|date=30 January 2009|title=Boletim Técnico – 30/01/2009|url=http://tempo1.cptec.inpe.br/boletimTecnico/faces/boletim.jsp?idBoletim=508|language=pt|access-date=8 February 2009}}</ref> The storm produced rainfall in 24 hours of {{cvt|300|mm|in}} or more in some locations of ] (Uruguay) and southern Rio Grande do Sul. The weather station owned by MetSul Weather Center in ], Southern Brazil, recorded {{cvt|278.2|mm|in}} in a 24-hour period. The storm caused fourteen deaths and the evacuation of thousands, with an emergency declared in four cities.<ref name="GPJan2009" /> It lasted until 1 February, when the cyclone became extratropical.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|date=1 February 2009|title=Boletim Técnico – 01/02/2009|url=http://tempo1.cptec.inpe.br/boletimTecnico/faces/boletim.jsp?idBoletim=510|language=pt|access-date=8 February 2009}}</ref> | ||
| ===2010–2016=== | ===2010–2016=== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| On November |
On 16 November 2010, a cold-core mid to upper-level ] in phase with a low-level warm-core ] developed a low-pressure ] over ], and moved southeastward into the ], where it slightly deepened.<ref name="BMet">{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE |date=November 2010 |title=Análise Sinótica: 17/11/2010-00Z |url=http://tempo.cptec.inpe.br/bol_tecnico.shtml |language=pt |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100918230622/http://tempo.cptec.inpe.br/bol_tecnico.shtml |archive-date=18 September 2010 }}</ref> The system brought locally heavy rains in southern Brazil and northeast of Uruguay that exceeded 200 millimeters within a few hours, in some locations of Southern Rio Grande do Sul, northwest of Pelotas.<ref name="MetS">{{cite web|publisher=METSUL |date=November 2010 |title=Baixas começam a semana "em alta" |url=http://www.metsul.com/blog/ |language=pt |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100918230622/http://tempo.cptec.inpe.br/bol_tecnico.shtml |archive-date=18 September 2010 }}</ref> Damages and flooding were observed in Cerrito, São Lourenço do Sul and Pedro Osório.<ref name="MetS" /> Bañado de Pajas, department of Cerro Largo in Uruguay, recorded {{cvt|240|mm|in}} of rain.<ref name="MetS" /> The subtropical cyclone then became a weak trough on 19 November, according to the CPTEC.<ref>{{cite web|title=Boletim Technico 19/11/10 – 00z |url=http://tempo.cptec.inpe.br/bol_tecnico.shtml |publisher=CPTEC |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100918230622/http://tempo.cptec.inpe.br/bol_tecnico.shtml |archive-date=18 September 2010 }}</ref> | ||
| Between December |
Between 23 December 2013 and 24 January 2015, the CPTEC and Navy Hydrography Center monitored four subtropical depressions to the south of ]. The first one lasted until ], 2013.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|date=23 December 2013|title=Análise Sinótica – 23/12/2013|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_23122013.pdf|language=pt|access-date=24 February 2014|archive-date=28 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140228152754/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_23122013.pdf}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|date=24 December 2013|title=Análise Sinótica – 24/12/2013|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_24122013.pdf|language=pt|access-date=24 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140228151941/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_24122013.pdf|archive-date=28 February 2014}}</ref><ref name="CPTECDEC">{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|title=SÍNTESE SINÓTICA DEZEMBRO DE 2013|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/sintese_dezembro2013.pdf|language=pt|access-date=24 February 2014|archive-date=28 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140228153134/http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/sintese_dezembro2013.pdf}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|date=25 December 2013|title=Análise Sinótica – 25/12/2013|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_25122013.pdf|language=pt|access-date=24 February 2014}}</ref> Two subtropical depressions formed in 2014: one in late-February 2014 and the other in late-March 2014.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Navy Hydrography Center/Brazilian Navy |access-date=21 February 2014 |date=20 February 2014 |title=Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 UTC for 20 Feb 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150208083833/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |archive-date=8 February 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|publisher=CPTEC – INPE|date=28 March 2014|title=Análise Sinótica – 28/03/2014|url=http://www.cptec.inpe.br/~rupload/arquivo/analise_28032014.pdf|language=pt|access-date=7 January 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|publisher=Navy Hydrography Center|date=28 March 2014|title=Meteoromarinha referente à análise de 1200 HMG – 28/mar/2014|url=https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/iac/P14032812.iac|language=pt|access-date=7 January 2015|archive-date=11 January 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150111000442/https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/iac/P14032812.iac}}</ref> A fourth one formed in late January 2015.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15012312.jpg |publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre |access-date=25 January 2015 |date=23 January 2015 |title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 23 Jan 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150123225607/https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15012312.jpg |archive-date=23 January 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15012400.jpg |publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre |access-date=25 January 2015 |date=24 January 2015 |title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 24 Jan 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161220092447/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C15012400.jpg |archive-date=20 December 2016 }}</ref> | ||
| On January |
On 5 January 2016, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy issued warnings on a subtropical depression that formed east of ].<ref>{{cite web|title=Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC – 5 Jan 2016 |url=https://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/meteoro/boletiming.htm |publisher=Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Center |access-date=6 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160106083055/http://www.mar.mil.br/dhn/chm/meteo/prev/cartas/C16010512.jpg |archive-date=6 January 2016 |format=JPEG }}</ref> On the next day, the system strengthened into a tropical depression, and other agencies considered the system an invest, designating it as ''90Q'';<ref name="Jan 2016 South Atlantic storm">{{cite web|url=http://www.weather.com/storms/hurricane/news/subtropical-tropical-depression-storm-deni-south-atlantic|title=Could a Rare Tropical Storm Form in the South Atlantic Ocean?|website=weather.com|author=Jon Erdman|publisher=The Weather Company|date=6 January 2016|access-date=8 February 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |website=]–] |title=Invest-90Q Location File |url=http://www.nrlmry.navy.mil/archdat/test/kml/TC/2016/ATL/90Q/locationfile.txt}}{{dead link|date=July 2021}}</ref> however, on 7 January, the tropical depression dissipated.<ref name="Jan 2016 South Atlantic storm" /><ref name="Atlantic subtropical system">{{Cite web|url=http://www.wunderground.com/blog/JeffMasters/rare-january-depression-in-central-pacific-atlantic-subtropical-storm|title=Rare January Depression in Central Pacific; Atlantic Subtropical Storm Next Week?}}</ref> | ||
| ===2021–present=== | |||
| On 3 January 2021, according to the ], the remnants of ] from the South-West Indian Ocean crossed southern Africa and briefly emerged into the eastern South Atlantic before dissipating.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.meteo.fr/temps/domtom/La_Reunion/webcmrs9.0/anglais/activiteope/data/20202021/2020RE04.html|title=01-20072008 Du 12/10/2007 Au 13/10/2007|website=www.meteo.fr}}</ref> | |||
| On 7 January 2023, a subtropical depression formed about {{convert|500|km|abbr=on}} southeast of Rio de Janeiro.<ref>{{cite web |title=FQST02 SBBR 070000 |url=https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/raw/fq/fqst02.sbbr..txt |publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center |access-date=7 January 2023 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20230107052343/https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/raw/fq/fqst02.sbbr..txt |archive-date=7 January 2023 |date=7 January 2023}}</ref> Without affecting any area and moving away from the Brazilian coast, it lost its subtropical characteristics in the afternoon of 10 January, according to the Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/cartas-sinoticas/c23011012.png|title=Cartas Sinóticas|author=|publisher=Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center|date=10 January 2023|access-date=11 January 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ==Storm names== | ==Storm names== | ||
| The following names are published by the ] Hydrographic |
The following names are published by the ] Hydrographic Center's Marine Meteorological Service and used for tropical and subtropical storms that form in the area west of ] and south of equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. Originally announced in 2011,<ref name="names_2011"/> the list was extended from 10 to 15 names in 2018.<ref name="names_2018">{{cite web |title=NORMAS DA AUTORIDADE MARÍTIMA PARA AS ATIVIDADES DE METEOROLOGIA MARÍTIMA NORMAM-19 1a REVISÃO |url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/dhn/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.dhn/files/normam/NORMAN-19-REV-1--Ed2018-CHM.pdf |publisher=Brazilian Navy |access-date=6 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181106155111/https://www.marinha.mil.br/dhn/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.dhn/files/normam/NORMAN-19-REV-1--Ed2018-CHM.pdf |archive-date=6 November 2018 |page=C-1-1 |language=pt |date=2018}}</ref> In 2022, 32 new names were added after the previous ones were exhausted.<ref name="names_2022">{{cite web|title=NORMAS DA AUTORIDADE MARÍTIMA PARA AS ATIVIDADES DE METEOROLOGIA MARÍTIMA NORMAM-19 2ª REVISÃO 2022|url=https://www.marinha.mil.br/chm/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.chm/files/normam-19-dhn-2a-rev-2022.pdf|publisher=Brazilian Navy|access-date=15 December 2024|page=D-5|language=pt|date=2022|archive-date=31 March 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230331140443/http://www.marinha.mil.br/dhn/sites/www.marinha.mil.br.dhn/files/normam/NORMAM-19-DHN-2a-Rev-2022.pdf}}</ref> The names are assigned in alphabetical order and used sequentially without regard to year. | ||
| {| style="width:90%;" | {| style="width:90%;" | ||
| Line 202: | Line 391: | ||
| * Deni | * Deni | ||
| * Eçaí | * Eçaí | ||
| | | |||
| * Guará | * Guará | ||
| * |
* Iba | ||
| * |
* Jaguar | ||
| * |
* Kurumí | ||
| * |
* Mani | ||
| * Oquira | |||
| * Potira | |||
| * Raoni | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| | | | | ||
| * Akará | |||
| * {{tcname unused|Oquira}} | |||
| * Biguá | |||
| * {{tcname unused|Potira}} | |||
| * {{ |
* {{Tcname unused|Caiobá}} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Tcname unused|Endy}} | ||
| * {{ |
* {{Tcname unused|Guarani}} | ||
| * {{Tcname unused|Iguaçú}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Jaci}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Kaeté}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Maracá}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Okanga}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Poti}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Reri}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Sumé}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Tupã}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Upaba}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Ybatinga}} | |||
| | | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Aratu}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Buri}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Caiçara}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Esapé}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Guaí}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Itã}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Juru}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Katu}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Murici}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Oryba}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Peri}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Reia}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Samburá}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Taubaté}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Uruana}} | |||
| * {{Tcname unused|Ytu}} | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| === Retirements === | |||
| ''Kamby'' was replaced by ''Kurumí'' in 2018 without being used. | |||
| ''Kamby'' was replaced by ''Kurumí'' in 2018 without being used.<ref name="names_2011"/> | |||
| == Climatological statistics == | == Climatological statistics == | ||
| There have been |
There have been 88 recorded tropical and subtropical cyclones in the South Atlantic Ocean since 1957. Like most southern hemisphere cyclone seasons, most of the storms have formed between November and May. | ||
| {{center|'''List of storms, by month'''}} | |||
| <center> | |||
| '''List of storms, by month''' | |||
| </center> | |||
| {{col-begin}} | {{col-begin}} | ||
| {{col-2}} | {{col-2}} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" align="center" style="margin:auto;" | |||
| <center> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" align="center" | |||
| |- bgcolor="#CCCCCC" | |- bgcolor="#CCCCCC" | ||
| ! Month | ! Month | ||
| ! Number of recorded storms<br>in the South Atlantic Ocean | ! Number of recorded storms<br />in the South Atlantic Ocean | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | January || |
| January || 11 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | February || |
| February || 9 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | March || 11 | | March || 11 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | April || |
| April || 7 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | May || |
| May || 11 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | June || |
| June || 7 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | July || 5 | | July || 5 | ||
| Line 249: | Line 468: | ||
| | September || 5 | | September || 5 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | October || |
| October || 2 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | November || 9 | | November || 9 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | December || |
| December || 8 | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| </center> | |||
| {{col-2}} | {{col-2}} | ||
| Line 273: | Line 491: | ||
| width:15 textcolor:black shift:(5,-5) anchor:from fontsize:M | width:15 textcolor:black shift:(5,-5) anchor:from fontsize:M | ||
| bar:Jan from:0 till: |
bar:Jan from:0 till:11 color:cat5red text:"January" | ||
| bar:Feb from:0 till: |
bar:Feb from:0 till:9 color:cat5red text:"February" | ||
| bar:Mar from:0 till:11 color:cat5red text:"March" | bar:Mar from:0 till:11 color:cat5red text:"March" | ||
| bar:Apr from:0 till: |
bar:Apr from:0 till:7 color:cat5red text:"April" | ||
| bar:May from:0 till: |
bar:May from:0 till:11 color:cat5red text:"May" | ||
| bar:Jun from:0 till: |
bar:Jun from:0 till:7 color:cat5red text:"June" | ||
| bar:Jul from:0 till:5 color:cat5red text:"July" | bar:Jul from:0 till:5 color:cat5red text:"July" | ||
| bar:Aug from:0 till:5 color:cat5red text:"August" | bar:Aug from:0 till:5 color:cat5red text:"August" | ||
| bar:Sep from:0 till:5 color:cat5red text:"September" | bar:Sep from:0 till:5 color:cat5red text:"September" | ||
| bar:Oct from:0 till: |
bar:Oct from:0 till:2 color:cat5red text:"October" | ||
| bar:Nov from:0 till:9 color:cat5red text:"November" | bar:Nov from:0 till:9 color:cat5red text:"November" | ||
| bar:Dec from:0 till: |
bar:Dec from:0 till:8 color:cat5red text:"December" | ||
| ScaleMajor = gridcolor:line unit:year increment:3 start:0 | ScaleMajor = gridcolor:line unit:year increment:3 start:0 | ||
| Line 296: | Line 514: | ||
| </timeline> | </timeline> | ||
| </center> | |||
| {{col-end}} | {{col-end}} | ||
| {{center|'''List of storms, by decade'''}} | |||
| <center> | |||
| '''List of storms, by decade''' | |||
| </center> | |||
| {{col-begin}} | {{col-begin}} | ||
| {{col-2}} | {{col-2}} | ||
| {| class="wikitable" align="center" style="margin:auto;" | |||
| <center> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" align="center" | |||
| |- bgcolor="#CCCCCC" | |- bgcolor="#CCCCCC" | ||
| ! Decade | ! Decade | ||
| ! Number of recorded storms<br>in the South Atlantic Ocean | ! Number of recorded storms<br />in the South Atlantic Ocean | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1950s || 7 | | 1950s || 7 | ||
| Line 322: | Line 536: | ||
| | 2000s || 19 | | 2000s || 19 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 2010s || |
| 2010s || 15 | ||
| |- | |||
| | 2020s || 13 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| </center> | |||
| {{col-2}} | {{col-2}} | ||
| Line 348: | Line 563: | ||
| bar:1990s from:0 till:9 color:cat5red text:"1990s" | bar:1990s from:0 till:9 color:cat5red text:"1990s" | ||
| bar:2000s from:0 till:19 color:cat5red text:"2000s" | bar:2000s from:0 till:19 color:cat5red text:"2000s" | ||
| bar:2010s from:0 till: |
bar:2010s from:0 till:15 color:cat5red text:"2010s" | ||
| bar:2020s from:0 till:13 color:cat5red text:"2020s" | |||
| ScaleMajor = gridcolor:line unit:year increment:3 start:0 | ScaleMajor = gridcolor:line unit:year increment:3 start:0 | ||
| Line 360: | Line 576: | ||
| </timeline> | </timeline> | ||
| </center> | |||
| {{col-end}} | {{col-end}} | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Portal|Tropical cyclones}} | {{Portal|Tropical cyclones|South America}} | ||
| {{Commons category|South Atlantic tropical cyclones}} | {{Commons category|South Atlantic tropical cyclones}} | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] (North Atlantic tropical cyclone) | ||
| *] |
* ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category|South Atlantic tropical cyclones}} | {{Commons category|South Atlantic tropical cyclones}} | ||
| * {{pt}} | * {{in lang|pt}} | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * {{cite journal |last = Rosa |first = Marcelo Barbio |author2 = P. Satyamurty |author3 = N. J. Ferreira |author4 = L. T. Silva |title = A comparative study of intense surface cyclones off the coasts of southeastern Brazil and Mozambique |journal = Int. J. Climatol. |volume = 39 |issue = 8 |pages = 3523–3542 |date = 2019 |doi = 10.1002/joc.6036 |bibcode = 2019IJCli..39.3523R |s2cid = 134006347 }} | |||
| * | |||
| {{South Atlantic tropical cyclone}} | {{South Atlantic tropical cyclone}} | ||
| {{Cyclones}} | {{Cyclones}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:South Atlantic Tropical Cyclone}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:South Atlantic Tropical Cyclone}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:20, 21 December 2024
Tropical cyclones in the South Atlantic Ocean
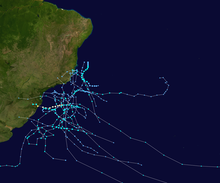
South Atlantic tropical cyclones are unusual weather events that occur in the Southern Hemisphere. Strong wind shear, which disrupts the formation of cyclones, as well as a lack of weather disturbances favorable for development in the South Atlantic Ocean, make any strong tropical system extremely rare, and Hurricane Catarina in 2004 is the only recorded South Atlantic hurricane in history. Storms can develop year-round in the South Atlantic, with activity peaking during the months from November through May. Since 2011, the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center has assigned names to tropical and subtropical systems in the western side of the basin, near the eastern coast of Brazil, when they have sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph), the generally accepted minimum sustained wind speed for a disturbance to be designated as a tropical storm in the North Atlantic basin. Below is a list of notable South Atlantic tropical and subtropical cyclones.
Theories concerning infrequency of occurrence
It was initially thought that tropical cyclones did not develop within the South Atlantic. Very strong vertical wind shear in the troposphere is considered a deterrent. The Intertropical Convergence Zone drops one to two degrees south of the equator, not far enough from the equator for the Coriolis force to significantly aid development. Water temperatures in the tropics of the southern Atlantic are cooler than those in the tropical north Atlantic.
Although they are rare, during April 1991 the United States' National Hurricane Center (NHC) reported that a tropical cyclone had developed over the Eastern South Atlantic. In subsequent years, a few systems were suspected to have the characteristics needed to be classified as a tropical cyclone, including in March 1994 and January 2004. During March 2004, an extratropical cyclone formally transitioned into a tropical cyclone and made landfall on Brazil, after becoming a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. While the system was threatening the Brazilian state of Santa Catarina, a newspaper used the headline "Furacão Catarina", which was originally presumed to mean "furacão (hurricane) threatening (Santa) Catarina (the state)". After international presses started monitoring the system, "Hurricane Catarina" has formally been adopted.
At the Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI) in 2006, it was questioned if any subtropical or tropical cyclones had developed within the South Atlantic before Catarina. It was noted that suspect systems had developed in January 1970, March 1994, January 2004, March 2004, May 2004, February 2006, and March 2006. It was also suggested that an effort should be made to locate any possible systems using satellite imagery and synoptic data; however, it was noted that this effort may be hindered by the lack of any geostationary imagery over the basin before 1966. A study was subsequently performed and published during 2012, which concluded that there had been 63 subtropical cyclones in the Southern Atlantic between 1957 and 2007. During January 2009, a subtropical storm developed in the basin, and in March 2010, a tropical storm developed, which was named Anita by the Brazilian public and private weather services. In 2011, the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center started to assign names to tropical and subtropical cyclones that develop within its area of responsibility, to the west of 20°W, when they have sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph).
Notable storms and impacts
Pre-2010s
1991 Angola tropical storm
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | 10 April 1991 – 14 April 1991 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); |
A low-pressure area formed over the Congo Basin on 9 April. The next day it moved offshore northern Angola with a curved cloud pattern. It moved westward over an area of warm waters while the circulation became better defined. According to the United States National Hurricane Center, the system was probably either a tropical depression or a tropical storm at its peak intensity. On 14 April, the system rapidly dissipated, as it was absorbed into a large squall line. This is the only recorded tropical cyclone in the eastern South Atlantic.
Hurricane Catarina
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "South Atlantic tropical cyclone" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
 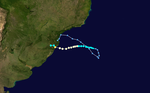 | |
| Duration | 24 March 2004 – 28 March 2004 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min); 972 hPa (mbar) |
Hurricane Catarina was an extraordinarily rare hurricane-strength tropical cyclone, forming in the southern Atlantic Ocean in March 2004. Just after becoming a hurricane, it hit the southern coast of Brazil in the state of Santa Catarina on the evening of 28 March, with winds up to 195 kilometres per hour (121 mph) making it a Category 2-equivalent cyclone on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. Catarina killed 3 to 11 people and caused millions of dollars in damage in Brazil.
At the time, Brazilians were taken completely by surprise, and were initially skeptical that an actual tropical cyclone could have formed in the South Atlantic. Eventually, however, they were convinced, and adopted the previously unofficial name "Catarina" for the storm, after Santa Catarina state. This event is considered by some meteorologists to be a nearly once-in-a-lifetime occurrence.
2010s
Tropical Storm Anita
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 8 March 2010 – 12 March 2010 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 995 hPa (mbar) |
On 8 March 2010, a previously extratropical cyclone developed tropical characteristics and was classified as a subtropical cyclone off the coast of southern Brazil. The following day, the United States Naval Research Laboratory began monitoring the system as a system of interest under the designation of 90Q. The National Hurricane Center also began monitoring the system as Low SL90. During the afternoon of 9 March, the system had attained an intensity of 55 km/h (34 mph) and a barometric pressure of 1000 hPa (mbar). It was declared a tropical storm on 10 March and became extratropical late on 12 March. Anita's accumulated cyclone energy was estimated at 2.0525 by the Florida State University. There was no damage associated to the storm, except high sea in the coasts of Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina. Post mortem, the cyclone was given the name "Anita" by private and public weather centers in Southern Brazil.
Subtropical Storm Arani
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 14 March 2011 – 16 March 2011 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
Early on 14 March 2011, the Navy Hydrographic Center-Brazilian Navy (SMM), in coordination with the National Institute of Meteorology, were monitoring an organizing area of convection near the southeast coast of Brazil. Later that day a low-pressure area developed just east of Vitória, Espírito Santo, and by 12:00 UTC, the system organized into a subtropical depression, located about 140 km (87 mi) east of Campos dos Goytacazes. Guided by a trough and a weak ridge to its north, the system moved slowly southeastward over an area of warm waters, intensifying into Subtropical Cyclone Arani on 15 March, as named by the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, and achieving its lowest pressure. The storm was classified as subtropical, as the convection was east of the center. On 16 March, Arani began experiencing 25 kn (13 m/s; 46 km/h; 29 mph) of wind shear because another frontal system bumped it from behind. As it moved east-southeastwards, it achieved its highest winds as it transitioned back to an extratropical cyclone, process that was concluded on early 17 March.
Before it developed into a subtropical cyclone, Arani produced torrential rains over portions of southeastern Brazil, resulting in flash flooding and landslides. Significant damage was reported in portions of Espírito Santo, though specifics are unknown. Increased swells along the coast prompted ocean travel warnings.
Subtropical Storm Bapo
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 5 February 2015 – 7 February 2015 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
On 5 February 2015, a subtropical depression developed about 105 nautical miles (195 km; 120 mi) to the southeast of São Paulo, Brazil. During the next day, low-level baroclinity decreased around the system, as it moved southeastwards away from the Brazilian coast and into anomalously warm waters, where it intensified further. The system was named Bapo by the Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center during 6 February as it had intensified into a subtropical storm. Over the next couple of days the system continued to move south-eastwards, achieving its peak intensity just before it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone during 8 February.
Subtropical Storm Cari
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 10 March 2015 – 13 March 2015 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
On 10 March 2015, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy began issuing warnings on Subtropical Depression 3 during early afternoon, while the Center for Weather Forecast and Climatic Studies (CPTEC in Portuguese) already assigned the name Cari for the storm. At 00:00 UTC on 11 March, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy upgraded Cari to a subtropical storm, also assigning this name to it. On 12 March, the Brazilian Hydrographic Center downgraded Cari to a subtropical depression as it achieved its lowest pressure, while the CPTEC stated that the storm had become a "Hybrid cyclone" as it moved away from the continental coastline. During early afternoon of 13 March, the Brazilian Navy declared that Cari became a remnant low.
Cari brought heavy rainfall, flooding and landslides to eastern cities of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul states as it interacted with a South Atlantic Convergence Zone. Rain totals from 100 to 180 mm (3.9 to 7.1 in) were observed associated with the storms and wind topped 75 km/h (47 mph) in Cabo de Santa Marta. A Navy buoy registered a 6-metre (20 ft) wave off the coast of Santa Catarina.
Subtropical Storm Deni
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 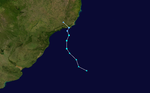 | |
| Duration | 15 November 2016 – 16 November 2016 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
On 15 November 2016, instability areas associated with a trough axis over Rio de Janeiro's coastline led to the formation of a subtropical depression southwest of it. It intensified into a subtropical storm and received the name Deni on 16 November. Moving south-southeastwards, Deni soon became extratropical shortly before 00:00 UTC on 17 November, where it was absorbed by a mid-latitude frontal system.
Subtropical Storm Eçaí
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 4 December 2016 – 6 December 2016 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
An extratropical cyclone entered the South Atlantic Ocean from Santa Catarina early on 4 December 2016. Later, it intensified quickly and then transitioned into a subtropical storm shortly before 22:00 BRST (00:00 UTC on 5 December), with the name Eçaí assigned by the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy. Eçaí started to decay on 5 December as it moved Into cooler waters, and weakened into a subtropical depression at around 00:00 UTC on 6 December. As it decayed and lost its subtropical characteristics, its center divided in two, with the new center moving away southeastwards and the old one degrading into a remnant frontal low.
Subtropical Storm Guará
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 9 December 2017 – 10 December 2017 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 996 hPa (mbar) |
According to the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, on 8 December 2017 a South Atlantic Convergence Zone aligned with a through axis led to the formation of several instability areas. On 9 December a subtropical storm formed from this setup, on border between Espírito Santo and Bahia, moving southeastwards away from land. On late 10 December, a Cold front pushed Guará southwards towards cooler waters, where it started transitioning into an extratropical cyclone. On early 11 December Guará attained its peak intensity, shortly thereafter degenerating into a low-pressure area associated with a through axis.
Tropical Storm Iba
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 23 March 2019 – 27 March 2019 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 1006 hPa (mbar) |
According to the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, on 22 March 2019, a low-pressure area formed off the coast of Bahia after the passage of a frontal system. On the next day, the cyclone developed a deep warm-core, thus being designated as a tropical depression. On 24 March, the system intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name Iba from the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center. After moving southwestward for a couple of days, on 26 March, Iba reached its peak intensity. Afterward, a cold front would approach the storm, which helped intensify the wind shear impacting Iba, leading to its weakening and extratropical transition. On early 28 March, Iba would degenerate into a remnant low, becoming fully extratropical a day later.
Iba was the first tropical storm to develop in the basin since Anita in 2010, as well as the first fully tropical system to be named from the Brazilian naming list.
Subtropical Storm Jaguar
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 19 May 2019 – 21 May 2019 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 1010 hPa (mbar) |
According to the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center, on 19 May 2019 several instability areas formed from a through axis off the coast of Espírito Santo, which later coalesced into a subtropical depression. On 20 May, the system strengthened into a subtropical storm, receiving the name Jaguar from the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center. However, the system did not intensify any further, as it soon encountered unfavorable conditions while moving southeastwards, weakening into a subtropical depression on early 21 May. Later that day, Jaguar degenerated into several sparse instability areas associated with a low-pressure area, which was absorbed by a frontal system on 22 May.
2020s
Subtropical Storm Kurumí
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 23 January 2020 – 24 January 2020 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
On 21 January 2020, the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center began monitoring an area of persisting thunderstorms near São Paulo for potential subtropical cyclone development. Generally tracking southeastward, the system began to organize within the afternoon hours of 22 January, aided by the establishment of a South Atlantic Convergence Zone, and was designated a subtropical depression in the early hours of 23 January. Several hours later, due to a lack of wind shear, the system intensified into a subtropical storm and was given the name Kurumí. After this bout of intensification, Kurumí moved southward and began to succumb to much more unfavorable conditions. It weakened back to a subtropical depression on late 24 January, due to an intensification of wind shear over its circulation due to the formation of an extratropical cyclone to its southeast. The last advisory was issued on Kurumí later that same day, as it degenerated into a trough while also beginning to merge with the nearby frontal system.
The front associated with Kurumí would later play a role in the 2020 Brazilian floods and mudslides, producing heavy rainfall. Over 171.8 mm (6.76 in) of rain fell in the Belo Horizonte metro area on 24 January, triggering a landslide and killing 3 people and leaving 1 missing.
Subtropical Storm Mani
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 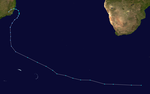 | |
| Duration | 25 October 2020 – 27 October 2020 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
According to the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy, on 24 October 2020, a trough axis persisted off the coast of the border between Espírito Santo and Bahia, which led to the formation of a subtropical depression on the next day. Later that day it intensified into a subtropical storm, which led it to be named Mani at 00:00 UTC on 26 October. As it moved away from a South Atlantic Convergence Zone on 27 October, Mani gradually lost its subtropical characteristics, until it weakened to a low pressure area.
The storm caused significant damage in Espírito Santo, with landslides of stones and earth leaving more than 400 people homeless. The storm also impacted almost the entire state of Minas Gerais and the northern region of Rio de Janeiro.
Subtropical Storm Oquira
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 27 December 2020 – 30 December 2020 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
According to the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy, on 26 December 2020, the prior presence of a South Atlantic Convergence Zone and the subsequent passage of a frontal system led to the presence of several instability areas off the coast east of Rio Grande do Sul, which coalesced into a subtropical depression a day later. Moving southwestward, the system's central pressure dropped to 1,010 millibars (30 inHg) by 00:00 UTC on 28 December. Later that day, the system's winds intensified, and it was named Oquira by the Brazilian Hydrographic Center. On 29 December, Oquira continued to strengthen, deepening while heading further southwestward away from the Brazilian mainland, and reaching a pressure of 1,002 millibars (29.6 inHg). Afterwards, Oquira's movements shifted southeastwards, and its winds decreased as it started to lose its subtropical characteristics, weakening to a subtropical depression on 30 December, but its pressure continued to drop, bottoming out at a minimum central pressure of 998 millibars (29.5 inHg). Later that day, Oquira transitioned into an extratropical low, and the Hydrographic Center issued their final advisory on the storm as it was absorbed by a frontal system.
Tropical Storm 01Q
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 4 February 2021 – 6 February 2021 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
On 4 February 2021, an extratropical storm off the coast of Rio Grande do Sul developed into a bomb cyclone. On 6 February, the storm began separating from its weather fronts and developed subtropical characteristics, before fully separating from the frontal zone and transitioning into a fully-tropical storm later that day. As a result, the NOAA classified the system as a tropical storm at 17:30 UTC, with the system being designated as Tropical Storm 01Q. However, the storm was short-lived, as it lost its tropical characteristics several hours later, with the NOAA issuing their final bulletin on the storm at 23:30 UTC that day. The storm dissipated soon afterward. Although the NOAA issued bulletins on the storm, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy did not monitor it.
Subtropical Depression #01-2021
| Subtropical depression (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 14 February 2021 – 16 February 2021 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
On 13 February 2021, according to the Brazilian Navy, instability areas associated with a low-pressure area off the coast of the state of Rio Grande do Sul acquired subtropical characteristics on the next day, becoming a subtropical depression about 700 kilometres (430 mi) from the state. For the next few days, the storm slowly meandered southeastward and then southwestward alongside a trough axis to its east, until it lost its subtropical characteristics over high seas on 17 February, becoming a remnant low.
The Brazilian Navy noted in its post-season analysis that on late 14 February the system could have intensified into a subtropical storm, since the radiometer built into the AMSR-2 satellite found winds of 35 knots, but it wasn't upgraded because no other measurement confirmed such findings.
Subtropical Storm Potira
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 19 April 2021 – 24 April 2021 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min); 1006 hPa (mbar) |
A low south of Rio de Janeiro transitioned into a subtropical depression on 19 April 2021. On 20 April 2021, the system intensified into a subtropical storm, which Brazilian Navy then decided to name it Potira. Potira moved slowly northeastwards for a couple of days over unusually warmer waters, favorable upper-level tropospheric winds and strong low-level convergence, which led to its intensification and persistence of its peak intensity until 23 April. As it completed a clockwise loop, Potira weakened into a subtropical depression, with the Brazilian Navy downgrading it to a low-pressure area on late 24 January.
The storm caused a gale in the Copacabana fort and the gusts of wind went over 60 km/h (37 mph). In the municipalities of Balneário Camboriú and Florianópolis (SC), the hangover caused by Potira caused flooding in the streets and damage to the sidewalks. The ports of Itajaí and Navegantes were closed for 3 days. No economic or material damage caused by the cyclone has been reported.
Subtropical Storm Raoni
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 29 June 2021 – 1 July 2021 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 986 hPa (mbar) |
An extratropical cyclone formed on 26 June 2021, about 520 km (320 mi) east-southeast of Montevideo, Uruguay, associated with a cold airmass that acted over the region. On the next day, the cyclone acquired a warm seclusion while intensifying, while it moved westwards and separated from the frontal system it was previously attached to. As the system occluded, the seclusion deepened and started to acquire subtropical characteristics, which led it to be designated as a subtropical storm on 29 June. It remained unnamed due to it being outside of the Brazilian Navy's area of responsibility. By 23:30 UTC on 28 June, the Satellite Products and Services Division of the NESDIS declared the system to have become a tropical storm, based on a Dvorak rating of 3.5, assigning an invest tag to it. Although being affected by strong wind shear to its north due to a subtropical jet caused by the presence of a frontal system nearby, it further intensified and achieved a minimum pressure 986 millibars (29.1 inHg), while tracking northeastwards towards the Brazilian area of authority. At around 12:00 UTC on the next day, as the storm entered the boundary of METAREA V, Brazilian Navy's area of responsibility, thus it was assigned the name Raoni. Continuing moving northeastwards, Raoni further developed an eye feature as well as a robust band to the east of the system. Raoni began to weaken by 30 June, as the subtropical jet broke the barotropic flow over it, and NESDIS dropped the tag as it lost its convective bands. On 1 July, Raoni lost its subtropical characteristics and degenerated into a low-pressure area.
The predecessor extratropical cyclone of Raoni caused heavy rains and strong winds gust up to 104 km/h (65 mph), downing trees and causing damages to different public and private establishments across Punta del Este. The area's waters were also rough due to the storm. Downpours with continuous gales were also experienced in Uruguay's capital Montevideo. From 24 June to 2 July, Raoni channeled cold air from Antarctica into portions of South America, leading to an unusually potent cold wave across Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, and Brazil, with the temperature dropping as much as 15 °C (27 °F) below average in some areas. The combination of the cyclone and the cold wave also produced snowfall across the southern portion of South America, with snowfall observed as far north as southern Brazil.
Subtropical Storm Ubá
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 9 December 2021 – 12 December 2021 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (1-min); 997 hPa (mbar) |
On 9 December 2021, instability areas remained off the coast of Espírito Santo and Rio de Janeiro after the passage of a frontal system and a South Atlantic Convergence Zone. Overnight the system coalesced into an occluded front, which transitioned into a subtropical depression. On the morning of the next day, the system was upgraded to subtropical storm status, receiving the name Ubá. On 11 December Ubá gradually weakened while moving southeastwards, being downgraded to depression status. It degenerated into a remnant low-pressure area on the next day.
The precursor extratropical cyclone and South Atlantic Convergence Zone caused heavy rains in Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo and southern Bahia, where heavy precipitation accumulated 450 mm (18 in) in Itamaraju and 331 mm (13 in) in Monte Formoso, killing fifteen people.
Subtropical Storm Yakecan
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 16 May 2022 – 19 May 2022 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
On 15 May 2022, an extratropical cyclone moved through the southern region of Brazil and stopped offshore. The low occluded and separated form its precursor extratropical cyclone, obtaining subtropical characteristics in the process. On the morning of 17 May, the cyclone fully transitioned into a subtropical storm, and was given the name Yakecan. Taking a more northwestwardly movement, Yakecan moved away from the coastline, gradually losing its subtropical characteristics. On late 19 May, it acquired frontal characteristics and transitioned to an extratropical cyclone.
During its trajectory, the storm caused snow in the Gaúcha and Catarinense Mountains, setting record lows for this time of year. Two people died in Uruguay and Brazil due to the passage of the cyclone. Yakecan is the last name from the regular naming list, which has been in use since 2011.
Tropical Storm Akará
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 16 February 2024 – 22 February 2024 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
In February 2024, a low-pressure area began developing along a stalled cold front. Moisture from the tropics began feeding into the circulation of the developing disturbance, helping it to intensify. On 16 February 2024, the Brazilian Navy designated the system, which at the time was east southeast of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, as a subtropical depression. Two days later, the system transitioned into a tropical cyclone. In the early hours of 19 February, the system intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name Akará from the Brazilian Navy. However, two days later, the system lost its tropical characteristics and weakened into a subtropical depression. The next day, the system lost its subtropical characteristics, thus the Brazilian Navy ceased all bulletins.
The precursor extratropical cyclone to Akará brought heavy rainfall to South America. Nova Iguaçu was affected with intense rainfall and winds. Akará was the first named tropical storm to develop in the basin since Iba in 2019.
Subtropical Storm Biguá
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
 | |
| Duration | 14 December 2024 – 16 December 2024 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
Early on 15 December 2024, a subtropical storm formed off the coast of the Brazil–Uruguay border, receiving the name Biguá from the Brazilian Navy. As it moved southeastwards, away from the coastline, the system was downgraded to subtropical depression. On early 17 December 2024 December 17, the cyclone was downgraded to a low-pressure area as it transitioned to a extratropical cyclone.
The closeness to the Brazilian shore caused wind gusts over the southeastern Rio Grande do Sul, leading to power losses and structural damages on nearby cities.
Other systems
Pre-2004

According to a presentation at the Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI), satellite imagery from January 1970 showed that a system with an eyewall had developed behind a cold front and that the system needed further analysis to determine if it was tropical or subtropical. On 27 March 1974, a weak area of low pressure that had originated over the Amazon River started to intensify further. Over the next 48 hours the system quickly developed further and was classified as subtropical, as it developed a banding structure and deep convection near its warm core. On 29 March, a north-westerly flow encroached on the systems environment, which caused the system to rapidly move towards 40S and the cold waters that were present to the south of 40°S.
In March 1994, a system that was thought to be weaker than Catarina was spawned but was located over cool and open waters. According to the Zambia Meteorological Department, Cyclone Bonita moved off the coast of Angola and entered the South Atlantic Ocean on 19 January 1996. By the next day, the system had succumbed to cold waters and days of land interaction, dissipating completely. It was the first tropical cyclone known to have traversed southern Africa from the South-West Indian Ocean to the South Atlantic.
2004–2009
During 2004, the large-scale conditions over the South Atlantic were more conducive than usual for subtropical or tropical systems, with 4 systems noted. The first possible tropical cyclone developed within a trough of low pressure, to the southeast of Salvador, Brazil on 18 January. The system subsequently displayed a small central dense overcast (CDO) and was suspected to be at the peak of its development as either a tropical depression or a tropical storm during the next day. The system was subsequently affected by some strong shear, before it moved inland and weakened along the coast of Brazil before it was last noted during 21 January. Within Brazil the system caused heavy rain and flooding with a state of emergency declared in Aracaju, after the river overflowed and burst its banks which flooded homes, destroyed crops and caused parts of the highway to collapse. However, it was noted that not all of the heavy rain and impacts were attributable to the system, as a large monsoon low covered much of Brazil at the time. The second system was a possible hybrid cyclone that developed near south-eastern Brazil between 15 and 16 March. Hurricane Catarina was the third system, while the fourth system formed off the coast of Brazil on 15 May 2004.

On 22 February 2006, a baroclinic cyclone intensified quickly and was estimated to have peaked with 1-minute sustained wind speeds of 105 km/h (65 mph), after radar data showed that the system had developed an eye and banding. However, there were questions about how tropical the system was, as it did not separate from the westerlies or the baroclinic zone it was in. Between 11 and 17 March 2006, another system with a warm core developed and moved southward along the South Atlantic Zone, before dissipating.
Two subtropical cyclones affected both Uruguay and Rio Grande do Sul state in Brazil between 2009 and 2010. On 28 January 2009, a cold-core mid to upper-level trough in phase with a low-level warm-core low formed a system and moved eastward into the South Atlantic. The storm produced rainfall in 24 hours of 300 mm (12 in) or more in some locations of Rocha (Uruguay) and southern Rio Grande do Sul. The weather station owned by MetSul Weather Center in Morro Redondo, Southern Brazil, recorded 278.2 mm (10.95 in) in a 24-hour period. The storm caused fourteen deaths and the evacuation of thousands, with an emergency declared in four cities. It lasted until 1 February, when the cyclone became extratropical.
2010–2016

On 16 November 2010, a cold-core mid to upper-level trough in phase with a low-level warm-core low developed a low-pressure system over Brazil, and moved southeastward into the South Atlantic, where it slightly deepened. The system brought locally heavy rains in southern Brazil and northeast of Uruguay that exceeded 200 millimeters within a few hours, in some locations of Southern Rio Grande do Sul, northwest of Pelotas. Damages and flooding were observed in Cerrito, São Lourenço do Sul and Pedro Osório. Bañado de Pajas, department of Cerro Largo in Uruguay, recorded 240 mm (9.4 in) of rain. The subtropical cyclone then became a weak trough on 19 November, according to the CPTEC.
Between 23 December 2013 and 24 January 2015, the CPTEC and Navy Hydrography Center monitored four subtropical depressions to the south of Rio de Janeiro. The first one lasted until Christmas Day, 2013. Two subtropical depressions formed in 2014: one in late-February 2014 and the other in late-March 2014. A fourth one formed in late January 2015.
On 5 January 2016, the Hydrographic Center of the Brazilian Navy issued warnings on a subtropical depression that formed east of Vitória, Espírito Santo. On the next day, the system strengthened into a tropical depression, and other agencies considered the system an invest, designating it as 90Q; however, on 7 January, the tropical depression dissipated.
2021–present
On 3 January 2021, according to the Météo-France, the remnants of Tropical Storm Chalane from the South-West Indian Ocean crossed southern Africa and briefly emerged into the eastern South Atlantic before dissipating.
On 7 January 2023, a subtropical depression formed about 500 km (310 mi) southeast of Rio de Janeiro. Without affecting any area and moving away from the Brazilian coast, it lost its subtropical characteristics in the afternoon of 10 January, according to the Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center.
Storm names
The following names are published by the Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center's Marine Meteorological Service and used for tropical and subtropical storms that form in the area west of 20ºW and south of equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. Originally announced in 2011, the list was extended from 10 to 15 names in 2018. In 2022, 32 new names were added after the previous ones were exhausted. The names are assigned in alphabetical order and used sequentially without regard to year.
|
|
Retirements
Kamby was replaced by Kurumí in 2018 without being used.
Climatological statistics
There have been 88 recorded tropical and subtropical cyclones in the South Atlantic Ocean since 1957. Like most southern hemisphere cyclone seasons, most of the storms have formed between November and May.
List of storms, by month
|

|
|

|
See also
- Unusual areas of tropical cyclone formation
- List of South America hurricanes
- Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone
- Atlantic hurricane (North Atlantic tropical cyclone)
- Atlantic Equatorial mode
- Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone
- Tropical cyclone basins
- 2006 Central Pacific cyclone
- 1996 Lake Huron cyclone
- Subtropical Cyclone Katie
- Subtropical Cyclone Lexi
- Cyclone Yaku
References
- ^ Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary March 2004". Archived from the original on 17 December 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- Landsea, Christopher W (13 July 2005). "Subject: Tropical Cyclone Names: G6) Why doesn't the South Atlantic Ocean experience tropical cyclones?". Tropical Cyclone Frequently Asked Question. United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Hurricane Research Division. Archived from the original on 27 March 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- Gordon E. Dunn & Banner I. Miller (1960). Atlantic Hurricanes. Louisiana State University Press. p. 33. ASIN B0006BM85S.
- Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, Hurricane Research Division. "Frequently Asked Questions: How do tropical cyclones form?". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 26 July 2006.
- ^ National Hurricane Center (1991). McAdie, Colin J; Rappaport, Edward N (eds.). II. Tropical cyclone activity in the Atlantic Basin: A. Overview (Diagnostic Report of the National Hurricane Center: June and July 1991). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. pp. 10–14. hdl:2027/uiug.30112005414658. Retrieved 12 May 2013.
- ^ Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary January 2004". Archived from the original on 17 December 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ Topic 2a: The Catarina Phenomenon (PDF). The Sixth WMO International Workshop on Tropical Cyclones (IWTC-VI). San José, Costa Rica: World Meteorological Organization. 2006. pp. 329–360. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- Evans, Jenny L; Braun, Aviva J (2012). "A Climatology of Subtropical Cyclones in the South Atlantic". Journal of Climate. 25 (21). American Meteorological Society: 7328–7340. Bibcode:2012JCli...25.7328E. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00212.1.
- ^ Padgett, Gary (7 April 2009). "January 2009 Tropical Weather Summary". Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Tracks March 2010". Archived from the original on 17 December 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Normas Da Autoridade Marítima Para As Atividades De Meteorologia Marítima" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 February 2015. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- Marcel Leroux (2001). "Tropical Cyclones". The Meteorology and Climate of Tropical Africa. Praxis Publishing Ltd. p. 314. ISBN 978-3-540-42636-3. Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- College of Earth & Mineral Sciences (2004). "Upper-level lows". Pennsylvania State University. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- Gary Padgett (2004). "March 2004 Tropical Cyclone Summary". Thomas R. Metcalf (Australian Severe Weather). Retrieved 23 October 2008.
- Jefferson Bernardes (30 March 2004). "First South Atlantic hurricane hits Brazil". USA Today. Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- "South American Synopsis". The Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. 22 May 2007. Archived from the original on 23 May 2007.
- "Monitoramento – Ciclone tropical na costa gaúcha" (in Portuguese). Brazilian Meteorological Service. March 2010. Archived from the original on 28 February 2010.
- Chura; Ledesma; Davison (14 March 2011). "South American Synopsis". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- Chura; Ledesma; Davison (14 March 2011). "South American Synopsis (2)". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 1 January 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- Marine Meteorological Service (14 March 2011). "Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 GMT – 14/MAR/2011". Brazil Navy Hydrographic Center. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- Chura; Ledesma; Davison (15 March 2011). "South American Synopsis (3)". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 1 January 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- Chura; Ledesma; Davison (15 March 2011). "South American Synopsis (4)". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- Marine Meteorological Service (15 March 2011). "Severe Weather Warnings". Brazil Navy Hydrographic Center. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- "Severe Weather Warnings – 11 March 2011". Brazilian Navy. 11 March 2011. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL ARANI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- Rob Gutro (15 March 2011). "NASA's Aqua Satellite Spots Rare Southern Atlantic Sub-tropical Storm". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- Unattributed (16 March 2011). "Arani – tempestade subtropical afasta-se da costa do ES" (in Portuguese). Climatempo. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- Unattributed (16 March 2011). "Após formar um olho, ciclone subtropical Arani perde força nesta quarta" (in Portuguese). Jornal De Tempo. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 UTC for 5 February 2015". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 5 February 2015. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- "South American Forecast Discussion". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on 23 September 2011.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL BAPO - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- Mersereau, Dennis. "Rare Subtropical Storm Forms off the Coast of Brazil". Gawker. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- "Análise Sinótica – 06/02/2015" (PDF). CPTEC – INPE. 6 February 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 0000 UTC – 08/FEB/2015". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- "Análise Sinótica de 1200 UTC". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 10 March 2015. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- "Análise Sinótica – 10/03/2015" (PDF). CPTEC – INPE. 10 March 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 0000 UTC – 11/03/2015". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 11 March 2015. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL CARI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- "Análise Sinótica de 0000 UTC". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 12 March 2015. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- "Análise Sinótica – 12/03/2015". CPTEC – INPE. 12 March 2015. Archived from the original on 25 May 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- "Análise Sinótica de 1200 UTC". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 13 March 2015. Archived from the original on 8 April 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "Cari é rebaixado ao enfraquecer e ciclone se afasta do continente" (in Portuguese). Metsul. 12 March 2015. Archived from the original on 22 March 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL DENI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 1200 UTC – 15/NOV/2016". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 15 November 2016. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 16/NOV/2016". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 16 November 2016. Archived from the original on 16 November 2016. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 17/NOV/2016". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 17 November 2016. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 4 Dec 2016" (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 4 December 2016. Archived from the original (JPEG) on 5 December 2016. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 05/DEC/2016". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 5 December 2016. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL EÇAÍ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Issued at 0000 UTC – 06/DEC/2016". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 6 December 2016. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL GUARÁ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- "METEOROMARINHA REFERENTE ANALISE DE 1200 HMG – 09/DEZ/2017" (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 9 December 2017. Archived from the original on 31 January 2006. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 9 Dec 2017". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 9 December 2017. Archived from the original (JPEG) on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- "Análise Sinótica – 09/12/2017" (PDF). CPTEC – INPE. 9 December 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 11 Dec 2017". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 11 December 2017. Archived from the original (JPEG) on 12 December 2017. Retrieved 11 December 2017.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 11 Dec 2017". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 11 December 2017. Archived from the original (JPEG) on 12 December 2017. Retrieved 11 December 2017.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE TROPICAL IBA - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- "Análise Sinótica" (in Portuguese). CPTEC. 23 March 2019. Archived from the original (GIF) on 23 March 2019. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- "WARNING NR 205/2019". Marine Meteorological Service. 23 March 2019. Archived from the original on 23 March 2019. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- "Cartas sinóticas 28 de março" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 28 March 2019. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- "WARNING NR 208/2019". Marine Meteorological Service. 24 March 2019. Archived from the original on 24 March 2019. Retrieved 24 March 2019.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL JAGUAR - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- "WARNING NR 422/2019". Marine Meteorological Service. 20 May 2019. Archived from the original on 24 March 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL KURUMÍ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "WARNINGS AND FORECASTS- SUBTROPICAL STORM KURUMI". Marine Meteorological Service. 24 January 2020. Archived from the original on 24 March 2019. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- "SPECIAL WARNING – SUBTROPICAL DEPRESSION "KURUMI"". Centro de Hidrografia da Marinha: MARINHA DO BRASIL. 25 January 2020. Archived from the original on 25 January 2020.
- "Heavy rains cause casualties, damage in southeast Brazilian region". Xinhua News. 24 January 2020. Archived from the original on 25 January 2020. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL MANI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 25 October 2020" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 25 October 2020. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 26 October 2020" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 26 October 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 28 October 2020" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 26 October 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- Maisa Pereira de Souza (27 October 2020). "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL MANI FAVORECEU A OCORRÊNCIA DE CHUVA NO ESTADO DO ESPÍRITO SANTO NESTE FIM DE SEMANA". portal.inmet.gov.br (in Portuguese). Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- "CICLONE NO SUDESTE – TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL MANÍ SE FORMA" (in Portuguese). Metsul. 26 October 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL OQUIRA - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 27 December 2020" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 27 December 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 28 December 2020" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 28 December 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 28 December 2020" (JPEG) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 28 December 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- "Weather And Sea Bulletin Issued 1200 UTC – 29 / DEC / 2020". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 29 December 2020.
- "Weathed And Sea Bulletin Issued 1200 UTC – 30 / DEC / 2020". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 30 December 2020.
- "Bad Weather Warnings / Thu 31 December 2020". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 30 December 2020.
- Bruna Ostermann (4 February 2021). "Raro no verão, ciclone bomba se forma na fronteira entre Brasil e Uruguai" (in Portuguese). Cable News Network. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- Boris A. Konon (6 February 2021). "01Q (Noname) – 1730 UTC". NOAA. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- "01Q". NOAA. 6 February 2021. Archived from the original on 7 February 2021. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- Adam Clark (6 February 2021). "01Q (Noname) – 2330 UTC". NOAA. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- ^ "DEPRESSÃO SUBTROPICAL #01-2021 - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 14 February 2021. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- "Cartas Sinóticas". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 17 February 2021. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- "WEATHER AND SEA BULLETIN ISSUED 1200 UTC 19/APR/2021". Marine Meteorological Service. 19 April 2021. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- "Avisos de Mau Tempo | Centro de Hidrografia da Marinha". Archived from the original on 30 December 2020. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL POTIRA - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "Cartas Sinóticas | Centro de Hidrografia da Marinha".
- "Ciclone Potira traz vento forte no Rio de Janeiro". 20 April 2021.
- "Após semana com tempestade subtropical, litoral de SC registra alagamentos com maré alta". G1. 26 April 2021.
- "Portos de Itajaí e Navegantes são reabertos após tempestade subtropical perder força". G1. 24 April 2021.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL RAONI - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "WEATHER AND SEA BULLETIN ISSUED 28/JUN/2021 1200Z". Marine Meteorological Service. 28 June 2021. Archived from the original on 29 June 2021. Retrieved 29 June 2021.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 29/JUN/2021 – 00Z". Marine Meteorological Service. Retrieved 29 June 2021.
- Kyle Matthew Hosley (28 June 2021). TXST21 KNES 290105 (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 29 June 2021.
- "Bad Weather Notices 29/JUN/2021 12Z". Marine Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on 29 June 2021. Retrieved 29 June 2021.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart, 12Z". Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center. 29 June 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2021.
- "Ciclone Raoni na Costa Tem Algumas Características de Furacao e Năo Oferece Perigo". Metsul Meteorologia. 29 June 2021. Archived from the original on 30 June 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2021.
- "Bad Weather Notices 30/JUN/2021 12Z". Marine Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on 30 June 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2021.
- "2021/07/02 Sea Level Pressure Chart, 00Z". Brazilian Navy Hydrographic Center. 2 July 2021. Archived from the original on 30 June 2021. Retrieved 2 July 2021.
- ^ "Ciclone Causa Estragos no Uruguai e se Aproxima Do Rio Grande do Sul". Metsul Meteorologia. 28 June 2021. Archived from the original on 30 June 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2021.
- Andrej Flis (4 July 2021). "Unusually strong cold weather outbreak spreads from Antarctica into central South America, bringing early winter temperature records and first snowfall after decades". Severe Weather Europe. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL UBÁ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "Baixa pressão no mar provoca temporais em SP e RJ" (in Portuguese). Terra (company). 6 December 2021. Archived from the original on 12 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- "2021/12/10 Sea Level Pressure Chart, 00Z". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service. 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- "Bad Weather Notices 10/Dec/2021 13Z". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service. 10 December 2021. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- "2021/12/13 Sea Level Pressure Chart, 12Z". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service. 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- "Sobe para 32 número de cidades em situação de emergência por causa das fortes chuvas na Bahia" (in Portuguese). g1. 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- "Em 24 horas número de desabrigados pela chuva aumenta quase cinco vezes em MG". g1 (in Brazilian Portuguese). 11 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- "CICLONE SE FORMA NA COSTA DO SUL DO BRASIL E PROVOCA CALAMIDADE NA BAHIA" (in Portuguese). MetSul Meteorologia. 10 December 2021. Retrieved 12 December 2021.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE SUBTROPICAL YAKECAN - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- "Cartas sinóticas 17 de maio de 2022". Brazilian Navy (in Portuguese). 17 May 2022. Retrieved 27 September 2023.
- "Cartas sinóticas 20 de maio de 2022". Brazilian Navy (in Portuguese). 20 May 2022. Archived from the original on 23 May 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2022.
- "Umidade do ciclone Yakecan e ar frio trazem neve e chuva congelada". 17 May 2022.
- "No Uruguai, Yakecan provoca transtornos e causa pelo menos uma morte". 17 May 2022.
- "Corpo é encontrado no Guaíba após barco afundar durante passagem de tempestade Yakecan no RS; suspeita é que seja de pescador desaparecido". 17 May 2022.
- "Rare Tropical Storm Akará Forms off Brazilian Coast". National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service. 27 February 2024. Retrieved 29 February 2024.
- "Hidrografia da Marinha - Special Warning". 16 February 2024. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024.
- Marinha - Special Warning (Feb. 18, 2024)
- "Carta Sinótica 19 fevereiro de 2024 - 0000H". Brazilian Navy (in Portuguese). 19 February 2024. Archived from the original on 19 February 2024. Retrieved 19 February 2024.
- ^ "TEMPESTADE TROPICAL AKARÁ - RELATÓRIO PÓS-EVENTO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. Retrieved 15 December 2024.
- Wulfeck, Andrew (17 February 2024). "Tropical cyclone forms in Atlantic but not where you'd think". FOX Weather. Retrieved 19 February 2024.
- Newton, Lou (22 February 2024). "Watch: Baby rescued from car moments before being washed away in Brazilian storm". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 22 February 2024.
- "Carta sinótica de 15 de dezembro de 2024 - 0000Z". Brazilian Navy (in Portuguese). 15 December 2024. Retrieved 15 December 2024.
- "Carta sinótica de 16 de dezembro de 2024 - 1200Z". Brazilian Navy (in Portuguese). 16 December 2024. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- "Carta sinótica de 17 de dezembro de 2024 - 0000Z". Brazilian Navy (in Portuguese). 17 December 2024. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- Zanchettin, Lisielle (15 December 2024). "Ciclone Biguá provoca transtornos e falta de luz em vários pontos do RS". GZH (in Portuguese). Retrieved 15 December 2024.
- ^ McTaggart-Cowan, Ron; Bosart, Lance; Davis, Christopher; Eyad, Atallah; Gyakum, John; Emaunel, Kerry (2006). "Analysis of Hurricane Catarina (2004)". Monthly Weather Review. 134 (11). American Meteorological Society: 3048–3049. Bibcode:2006MWRv..134.3029M. doi:10.1175/MWR3330.1.
- Henson, Bob (2005). "What was Catarina?". University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- Mudenda, O. S.; Mumba, Z. L. S. "The Unusual Tropical Storm of January 1996". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.601.2986.
- Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary February 2006". Archived from the original on 31 May 2024. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- "Boletim Técnico – 30/01/2009" (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. 30 January 2009. Retrieved 8 February 2009.
- "Boletim Técnico – 01/02/2009" (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. 1 February 2009. Retrieved 8 February 2009.
- "Análise Sinótica: 17/11/2010-00Z" (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. November 2010. Archived from the original on 18 September 2010.
- ^ "Baixas começam a semana "em alta"" (in Portuguese). METSUL. November 2010. Archived from the original on 18 September 2010.
- "Boletim Technico 19/11/10 – 00z". CPTEC. Archived from the original on 18 September 2010.
- "Análise Sinótica – 23/12/2013" (PDF) (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. 23 December 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- "Análise Sinótica – 24/12/2013" (PDF) (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. 24 December 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- "SÍNTESE SINÓTICA DEZEMBRO DE 2013" (PDF) (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- "Análise Sinótica – 25/12/2013" (PDF) (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. 25 December 2013. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- "Weather and Sea Bulletin Referent Analysis 1200 UTC for 20 Feb 2014". Navy Hydrography Center/Brazilian Navy. 20 February 2014. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- "Análise Sinótica – 28/03/2014" (PDF) (in Portuguese). CPTEC – INPE. 28 March 2014. Retrieved 7 January 2015.
- "Meteoromarinha referente à análise de 1200 HMG – 28/mar/2014" (in Portuguese). Navy Hydrography Center. 28 March 2014. Archived from the original on 11 January 2015. Retrieved 7 January 2015.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC for 23 Jan 2015". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 23 January 2015. Archived from the original on 23 January 2015. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 0000 UTC for 24 Jan 2015". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Centre. 24 January 2015. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- "Sea Level Pressure Chart 1200 UTC – 5 Jan 2016". Marinha do Brasil – Navy Hydrographic Center. Archived from the original (JPEG) on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 6 January 2016.
- ^ Jon Erdman (6 January 2016). "Could a Rare Tropical Storm Form in the South Atlantic Ocean?". weather.com. The Weather Company. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- "Invest-90Q Location File". United States Naval Research Laboratory–Monterey.
- "Rare January Depression in Central Pacific; Atlantic Subtropical Storm Next Week?".
- "01-20072008 Du 12/10/2007 Au 13/10/2007". www.meteo.fr.
- "FQST02 SBBR 070000". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 7 January 2023. Archived from the original on 7 January 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- "Cartas Sinóticas". Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center. 10 January 2023. Retrieved 11 January 2023.
- "NORMAS DA AUTORIDADE MARÍTIMA PARA AS ATIVIDADES DE METEOROLOGIA MARÍTIMA NORMAM-19 1a REVISÃO" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. 2018. p. C-1-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- "NORMAS DA AUTORIDADE MARÍTIMA PARA AS ATIVIDADES DE METEOROLOGIA MARÍTIMA NORMAM-19 2ª REVISÃO 2022" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Brazilian Navy. 2022. p. D-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 15 December 2024.
External links
- Brazilian Navy Hydrography Center – Marine Meteorological Service (in Portuguese)
- NOAA info on South Atlantic Tropical Cyclones
- CIMSS Satellite Blog: "Another tropical cyclone in the South Atlantic Ocean?"
- Meteogroup Weathercast: Do hurricanes form in the South Atlantic?
- Satellite animation of the 1991 Angola tropical storm
- Rosa, Marcelo Barbio; P. Satyamurty; N. J. Ferreira; L. T. Silva (2019). "A comparative study of intense surface cyclones off the coasts of southeastern Brazil and Mozambique". Int. J. Climatol. 39 (8): 3523–3542. Bibcode:2019IJCli..39.3523R. doi:10.1002/joc.6036. S2CID 134006347.
- NOAA bulletins for the South Atlantic
| South Atlantic tropical and subtropical cyclones | ||
|---|---|---|
 | TS"Angola" 2Catarina TSAnita SSArani SSBapo SSCari SSDeni SSEçaí SSGuará TSIba SSJaguar SSKurumí SSMani SSOquira TS01Q SD#01-2021 SSPotira SSRaoni SSUbá SSYakecan TSAkará SSBiguá | |
