| Revision as of 11:34, 12 February 2009 edit199.43.13.100 (talk) →Short butterfly← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:10, 22 December 2024 edit undoJohsmithson (talk | contribs)2 edits Added contextTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| (97 intermediate revisions by 58 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Options trading strategy}} | |||
| {{mergefrom|Iron Butterfly Spread|Talk:DESTINATIONPAGE#Merger proposal|date=October 2007}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| In ], a '''butterfly''' (or simply '''fly''') is a limited risk, non-directional ] that is designed to have a high ] of earning a limited profit when the future ] of the underlying asset is expected to be lower (when long the butterfly) or less lower (when short the butterfly) than that asset's current ]. | |||
| In ] trading, a '''long butterfly''' (sometimes simply butterfly) is a combination trade resulting in the following net ]: | |||
| ] | |||
| * ] 1 ] at (X − a) strike | |||
| ⚫ | * ] 2 |
||
| * Long 1 ] at (X + a) strike | |||
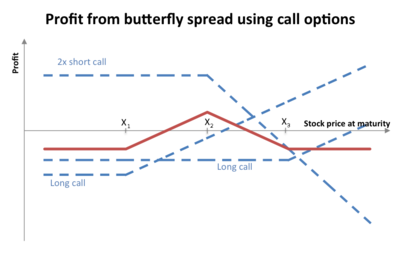
| all with the same ] date. At expiration the position will be worth zero if the underlying is below X−a or above X+a, and will be worth a positive amount between these two values. The payoff function is shaped like an upside-down V, and the maximum payoff occurs at X (see diagram). | |||
| ⚫ | == Long butterfly == | ||
| Since the payoff is sometimes zero, sometimes positive, the price of a butterfly is always non-negative (to avoid an arbitrage opportunity). | |||
| A ] butterfly position will make profit if the future volatility is lower than the implied volatility. | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| * Long 1 ] at (X − a) strike | |||
| A long butterfly options strategy consists of the following ]: | |||
| ⚫ | * Short 2 |
||
| * Long 1 ] |
* ] 1 ] with a ] of (X − a) | ||
| ⚫ | * ] 2 calls with a strike price of X | ||
| and this is equivalent to the call version (as can be verified via ]). | |||
| * Long 1 call with a strike price of (X + a) | |||
| where X = the spot price (i.e. current market price of underlying) and a > 0. | |||
| ⚫ | Using ] a long butterfly can also be created as follows: | ||
| ⚫ | The double position in the middle is called the body, while the two other positions are called the wings. |
||
| * Long 1 put with a strike price of (X + a) | |||
| ⚫ | * Short 2 puts with a strike price of X | ||
| * Long 1 put with a strike price of (X − a) | |||
| where X = the spot price and a > 0. | |||
| All the options have the same ] date. | |||
| In an ''unbalanced butterfly'' the variable a can have 2 different values. | |||
| At expiration the value (but not the profit) of the butterfly will be: | |||
| ⚫ | ==Long butterfly== | ||
| * zero if the price of the underlying is below (X − a) or above (X + a) | |||
| The butterfly spread is a neutral ] that is a combination of a ] and a ]. It is a limited profit, limited risk options strategy. There are 3 striking prices involved in a butterfly spread and it can be constructed using calls or puts. | |||
| * positive if the price of the underlying is between (X - a) and (X + a) | |||
| The maximum value occurs at X (see diagram). | |||
| '''Long butterflies''' are entered when the investor thinks that the underlying stock will not rise or fall much by expiration (i.e. when the investor is bearish on volatility). Using calls, the long butterfly can be constructed by buying one lower striking in-the-money call, writing two at-the-money calls and buying another higher striking out-of-the-money call. A resulting net debit is taken to enter the trade, hence it is also a debit spread. | |||
| ⚫ | == Short butterfly == | ||
| A long butterfly spread can also be constructed using puts and is known as a long put butterfly. The long put butterfly spread is a neutral ] that is a combination of a bull put spread and a bear put spread. It is a limited profit, limited risk options trading strategy that is taken when the options trader thinks that the underlying stock will not rise or fall much by expiration. There are 3 striking prices involved in a long put butterfly spread and it is constructed by buying one lower striking put, writing two at-the-money puts and buying another higher striking put for a net debit. | |||
| A ] butterfly position will make profit if the future volatility is higher than the implied volatility. | |||
| ⚫ | ==Short butterfly== | ||
| '''Short butterfly''' is the name of a neutral-outlook, ] that involves trading options at three different ]s. The short butterfly is a neutral strategy like the long butterfly spread but bullish on volatility. It is a limited profit, limited risk options trading strategy and it can be constructed using calls or puts. | |||
| A short butterfly options strategy consists of the same options as a long butterfly. However now the middle strike option position is a long position and the upper and lower strike option positions are short. | |||
| Using calls, the short butterfly can be constructed by writing one lower striking call, buying two at-the-money calls and writing another higher striking call. A net credit is received upon entering this spread. Hence, the short butterfly is also a credit spread. | |||
| == Margin requirements == | |||
| "Probably the most expensive of all option strategies is the 'butterfly spread'. This is a strategy that is often touted by stockbrokers because they want to improve their own income. It sounds fancy, and the profits look pretty good, but CAUTION: the butterfly spread has not four commissions, but six commissions. This spread requires three different option positions to establish and maintain the strategy, and that adds up to six different commissions incurred during the life of that strategy." Kenneth R. Trester, Complete Option Player | |||
| In the United States, margin requirements for all options positions, including a butterfly, are governed by what is known as ]. However brokers are permitted to apply more stringent margin requirements than the regulations. | |||
| == Use in calculating implied distributions == | |||
| The price of a butterfly centered around some strike price can be used to estimate the implied probability of the underlying being at that strike price at expiry. This means the set of market prices for butterflies centered around different strike prices can be used to infer the market's belief about the probability distribution for the underlying price at expiry. This implied distribution may be different from the ] assumed in the popular ], and studying it can reveal ways in which real-world assets differ from the idealized assets described by Black-Scholes.<ref name="Natenberg chapter 24">{{cite book |last1=Natenberg |first1=Sheldon |title=Option volatility and pricing: advanced trading strategies and techniques |date=2015 |location=New York |isbn=9780071818780 |edition=Second |chapter=Chapter 24}}</ref> | |||
| == Butterfly variations == | |||
| ⚫ | #The double option position in the middle is called the body, while the two other positions are called the wings. | ||
| #In case the distance between middle strike price and strikes above and below is unequal, such position is referred to as "broken wings" butterfly (or "broken fly" for short). | |||
| # An ] recreates the payoff diagram of a butterfly, but with a combination of two calls and two puts. | |||
| # The option strategy where the middle options (the body) have different strike prices is known as a ]. | |||
| # A Christmas tree butterfly (not to be confused with the ]) consists of six options used to create a payoff diagram similar to a butterfly but slightly ] or ] instead of directionally neutral.<ref>{{cite web |title=Christmas Tree Butterfly Call |url=https://www.optionsplaybook.com/option-strategies/christmas-tree-butterfly-call/ |website=www.optionsplaybook.com |access-date=19 March 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Christmas Tree Butterfly Put |url=https://www.optionsplaybook.com/option-strategies/christmas-tree-butterfly-put/ |website=www.optionsplaybook.com |access-date=19 March 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | last = McMillan| first = Lawrence G. | | last = McMillan| first = Lawrence G. | ||
| | title = Options as a Strategic Investment | | title = Options as a Strategic Investment | ||
| | edition = 4th |
| edition = 4th | ||
| | publisher = New York : New York Institute of Finance | | publisher = New York : New York Institute of Finance | ||
| | year = 2002 | | year = 2002 | ||
| | isbn = 0-7352-0197-8 | | isbn = 0-7352-0197-8 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{Citation | |||
| |year=1986 | |||
| |title=Credit By Brokers And Dealers (Regulation T) | |||
| |publisher=FINRA | |||
| |url=http://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?tpl\=/ecfrbrowse/Title12/12cfr220_main_02.tpl | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Derivatives market}} | {{Derivatives market}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:10, 22 December 2024
Options trading strategy
In finance, a butterfly (or simply fly) is a limited risk, non-directional options strategy that is designed to have a high probability of earning a limited profit when the future volatility of the underlying asset is expected to be lower (when long the butterfly) or less lower (when short the butterfly) than that asset's current implied volatility.
Long butterfly
A long butterfly position will make profit if the future volatility is lower than the implied volatility.
A long butterfly options strategy consists of the following options:
- Long 1 call with a strike price of (X − a)
- Short 2 calls with a strike price of X
- Long 1 call with a strike price of (X + a)
where X = the spot price (i.e. current market price of underlying) and a > 0.
Using put–call parity a long butterfly can also be created as follows:
- Long 1 put with a strike price of (X + a)
- Short 2 puts with a strike price of X
- Long 1 put with a strike price of (X − a)
where X = the spot price and a > 0.
All the options have the same expiration date.
At expiration the value (but not the profit) of the butterfly will be:
- zero if the price of the underlying is below (X − a) or above (X + a)
- positive if the price of the underlying is between (X - a) and (X + a)
The maximum value occurs at X (see diagram).
Short butterfly
A short butterfly position will make profit if the future volatility is higher than the implied volatility.
A short butterfly options strategy consists of the same options as a long butterfly. However now the middle strike option position is a long position and the upper and lower strike option positions are short.
Margin requirements
In the United States, margin requirements for all options positions, including a butterfly, are governed by what is known as Regulation T. However brokers are permitted to apply more stringent margin requirements than the regulations.
Use in calculating implied distributions
The price of a butterfly centered around some strike price can be used to estimate the implied probability of the underlying being at that strike price at expiry. This means the set of market prices for butterflies centered around different strike prices can be used to infer the market's belief about the probability distribution for the underlying price at expiry. This implied distribution may be different from the lognormal distribution assumed in the popular Black-Scholes model, and studying it can reveal ways in which real-world assets differ from the idealized assets described by Black-Scholes.
Butterfly variations
- The double option position in the middle is called the body, while the two other positions are called the wings.
- In case the distance between middle strike price and strikes above and below is unequal, such position is referred to as "broken wings" butterfly (or "broken fly" for short).
- An iron butterfly recreates the payoff diagram of a butterfly, but with a combination of two calls and two puts.
- The option strategy where the middle options (the body) have different strike prices is known as a Condor.
- A Christmas tree butterfly (not to be confused with the unrelated option combination also called a Christmas tree) consists of six options used to create a payoff diagram similar to a butterfly but slightly bearish or bullish instead of directionally neutral.
References
- Natenberg, Sheldon (2015). "Chapter 24". Option volatility and pricing: advanced trading strategies and techniques (Second ed.). New York. ISBN 9780071818780.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Christmas Tree Butterfly Call". www.optionsplaybook.com. Retrieved 19 March 2022.
- "Christmas Tree Butterfly Put". www.optionsplaybook.com. Retrieved 19 March 2022.
- McMillan, Lawrence G. (2002). Options as a Strategic Investment (4th ed.). New York : New York Institute of Finance. ISBN 0-7352-0197-8.
- Credit By Brokers And Dealers (Regulation T), FINRA, 1986