| Revision as of 15:16, 19 May 2009 edit98.230.177.79 (talk) →Silent ethnic cleansing← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:07, 23 December 2024 edit undoDuncanHill (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers162,240 edits Fixing harv/sfn error. Please watchlist Category:Harv and Sfn no-target errors and install User:Trappist the monk/HarvErrors.js to help you spot such errors when reading and editing.Tag: RevertedNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Systematic removal of a certain ethnic or religious group}} | |||
| {{For|the video game|Ethnic Cleansing (video game)}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| {{Discrimination sidebar}} | |||
| {{use mdy dates|date=September 2017}} | |||
| '''Ethnic cleansing''' is a ] referring to the persecution through imprisonment, expulsion, or killing of members of an ethnic minority by a majority to achieve ethnic homogeneity in majority-controlled territory.<ref></ref> It is sometimes used interchangeably with the more connotatively severe term ]. The term entered English and international media usage in the early 1990s to describe ] in the former ]. Examples range from ancient history to modern day situations. | |||
| {{discrimination sidebar}} | |||
| ] in Europe from 1100 to 1600]] | |||
| '''Ethnic cleansing''' is the systematic forced removal of ], ], or ] groups from a given area, with the intent of making the society ethnically ]. Along with direct removal such as ] or ], it also includes indirect methods aimed at ] by coercing the victim group to flee and preventing its return, such as murder, rape, and property destruction.<ref name=UN/><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Walling |first1=Carrie Booth |title=The history and politics of ethnic cleansing |journal=The International Journal of Human Rights |date=2000 |volume=4 |issue=3–4 |pages=47–66 |doi=10.1080/13642980008406892 |s2cid=144001685 |quote=Most frequently, however, the aim of ethnic cleansing is to expel the despised ethnic group through either indirect coercion or direct force, and to ensure that return is impossible. Terror is the fundamental method used to achieve this end.<br />Methods of indirect coercion can include: introducing repressive laws and discriminatory measures designed to make minority life difficult; the deliberate failure to prevent mob violence against ethnic minorities; using surrogates to inflict violence; the destruction of the physical infrastructure upon which minority life depends; the imprisonment of male members of the ethnic group; threats to rape female members, and threats to kill. If ineffective, these indirect methods are often escalated to coerced emigration, where the removal of the ethnic group from the territory is pressured by physical force. This typically includes physical harassment and the expropriation of property. Deportation is an escalated form of direct coercion in that the forcible removal of 'undesirables' from the state's territory is organised, directed and carried out by state agents. The most serious of the direct methods, excluding genocide, is murderous cleansing, which entails the brutal and often public murder of some few in order to compel flight of the remaining group members.13 Unlike during genocide, when murder is intended to be total and an end in itself, murderous cleansing is used as a tool towards the larger aim of expelling survivors from the territory. The process can be made complete by revoking the citizenship of those who emigrate or flee.}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Schabas |first1=William A. |title='Ethnic Cleansing' and Genocide: Similarities and Distinctions |journal=European Yearbook of Minority Issues Online |date=2003 |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=109–128 |doi=10.1163/221161104X00075 |quote=The Commission considered techniques of ethnic cleansing to include murder, torture, arbitrary arrest and detention, extrajudicial executions, sexual assault, confinement of civilian populations in ghetto areas, forcible removal, displacement and deportation of civilian populations, deliberate military attacks or threats of attacks on civilians and civilian areas, and wanton destruction of property.|doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>The danger of overstretching the term can be avoided...The goal of ethnic cleansing is to permanently remove a group from the area it inhabits...There is a popular dimension to ethnic cleansing because there are people needed to threaten with violence, to evict homes, organize mass transports, and to prevent the return of the unwanted...The main goal of ethnic cleansing was the removal of a group from a certain territory ''The Oxford Handbook of Postwar European History''. (2012). United Kingdom: OUP Oxford.</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Joireman |first1=Sandra Fullerton |title=Peace, preference, and property : return migration after violent conflict |publisher=University of Michigan |page=49 |quote=Violent conflict changes communities. "Returnees painfully discover that in their period of absence the homeland communities and their identities have undergone transformation, and these ruptures and changes have serious implications for their ability to reclaim a sense of home upon homecoming." The first issue in terms of returning home is usually the restoration of property, specifically the return or rebuilding of homes. People want their property restored, often before they return. But home means more than property, it also refers to the nature of the community. Anthropological literature emphasizes that time and the experience of violence changes people's sense of home and desire to return, and the nature of their communities of origin. To sum up, previous research has identified factors that influence decisions to return: time, trauma, family characteristics and economic opportunities. |author-link=Sandra Joireman}}</ref> Both the definition and charge of ethnic cleansing is often disputed, with some researchers including and others excluding ] or mass killings as a means of depopulating an area of a particular group.{{sfn|Bulutgil|2018|p=1136}}<ref name=Garrity/><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Kirby-McLemore |first1=Jennifer |title=Settling the Genocide v. Ethnic Cleansing Debate: Ending Misuse of the Euphemism Ethnic Cleansing |journal=Denver Journal of International Law and Policy |date=2021–2022 |volume=50 |page=115 |url=https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/denilp50&div=11&id=&page=}}</ref> | |||
| Synonyms include ''ethnic purification'' .<ref>Drazen Petrovic, , ''European Journal of International Law'', Vol. No. 3. Retrieved 20 May 2006.</ref> | |||
| Although scholars do not agree on which events constitute ethnic cleansing,<ref name=Garrity>{{cite journal |last1=Garrity |first1=Meghan M |title='Ethnic Cleansing': An Analysis of Conceptual and Empirical Ambiguity |journal=Political Science Quarterly |date=27 September 2023 |volume=138 |issue=4 |pages=469–489 |doi=10.1093/psquar/qqad082}}</ref> ] throughout history. The term was first used to describe ] treatment of the ] in the 1980s,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Who first coined the euphemism "ethnic cleansing" for racial murder and persecution? Surely it must have been a dictator? {{!}} Notes and Queries {{!}} guardian.co.uk |url=https://www.theguardian.com/notesandqueries/query/0,,-2894,00.html |access-date=2024-09-13 |website=www.theguardian.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Howe |first=Marvine |date=12 July 1982 |title=Exodus of Serbians stirs province in Yugoslavia |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1982/07/12/world/exodus-of-serbians-stirs-province-in-yugoslavia.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://archive.today/20180317141650/https://www.nytimes.com/1982/07/12/world/exodus-of-serbians-stirs-province-in-yugoslavia.html |archive-date=17 March 2018 |access-date= |work=The New York Times |pages=8}}</ref> and entered widespread use during the ] in the 1990s. Since then, the term has gained widespread acceptance due to journalism.{{sfn|Thum|2010|p=75|ps=: way. Despite its euphemistic character and its origin in the language of the perpetrators, 'ethnic cleansing' is now the widely accepted scholarly term used to describe the systematic and violent removal of undesired ethnic groups from a given territory.}} Although research originally focused on deep-rooted animosities as an explanation for ethnic cleansing events, more recent studies depict ethnic cleansing as "a natural extension of the homogenizing tendencies of ]" or emphasize security concerns and the effects of ], portraying ethnic tensions as a contributing factor. Research has also focused on the role of war as a causative or potentiating factor in ethnic cleansing. However, states in a similar strategic situation can have widely varying policies towards minority ethnic groups perceived as a security threat.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Bulutgil |first1=H. Zeynep |title=The state of the field and debates on ethnic cleansing |journal=Nationalities Papers |date=2018 |volume=46 |issue=6 |pages=1136–1145 |doi=10.1080/00905992.2018.1457018|s2cid=158519257 }}</ref> | |||
| ==Definitions== | |||
| The term ethnic cleansing has been variously defined. In the words of ]: | |||
| Ethnic cleansing has no legal definition under ], but the methods by which it is carried out are considered ] and may also fall under the ].<ref name=UN>{{cite web |publisher=United Nations Office on Genocide Prevention and the Responsibility to Protect |title=Ethnic cleansing|url=https://www.un.org/en/genocideprevention/ethnic-cleansing.shtml |website=United Nations |access-date=20 December 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Jones |first1=Adam |title=Crimes Against Humanity: A Beginner's Guide |date=2012 |publisher=Simon and Schuster |isbn=978-1-78074-146-8 |language=en |chapter='Ethnic cleansing' and genocide}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Schabas |first1=William A. |title='Ethnic Cleansing' and Genocide: Similarities and Distinctions |journal=European Yearbook of Minority Issues Online |date=2003 |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=109–128 |doi=10.1163/221161104X00075 |quote='Ethnic cleansing' is probably better described as a popular or journalistic expression, with no recognized legal meaning in a technical sense... 'ethnic cleansing' is equivalent to deportation,' a grave breach of the Geneva Conventions as well as a crime against humanity, and therefore a crime within the jurisdiction of the Tribunal. |doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| :''thnic cleansing defies easy definition. At one end it is virtually indistinguishable from forced emigration and population exchange while at the other it merges with ] and genocide. At the most general level, however, ethnic cleansing can be understood as the expulsion of a population from a given territory''.<ref>Andrew Bell-Fialkoff, "", Foreign Affairs 72 (3): 110, Summer 1993. Retrieved 20 May 2006.</ref> | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| The official ] definition of ethnic cleansing is "rendering an area ethnically homogeneous by using force or ] to remove from a given area persons of another ethnic or religious group"<ref>Hayden, Robert M. (1996) . '']'' 55 (4), 727-48.</ref> | |||
| ]. The ] aimed to reduce the number of Armenians to below 5–10% of the population in any part of the ], which resulted in the elimination of a million Armenians.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Akçam |first1=Taner |author1-link=Taner Akcam |title=] |date=2011 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-15333-9 |language=en |chapter=Demographic Policy and the Annihilation of the Armenians|quote=The thesis being proposed here is that the Armenian Genocide was not implemented solely as demographic engineering, but also as destruction and annihilation, and that the 5 to 10 percent principle was decisive in achieving this goal. Care was taken so that the number of Armenians deported to Syria, and those who remained behind, would not exceed 5 to 10 percent of the population of the places in which they were found. Such a result could be achieved only through annihilation... According to official Ottoman statistics, it was necessary to reduce the prewar population of 1.3 million Armenians to approximately 200,000.}}</ref>]] | |||
| ] leave ] in 1947 during the ], which followed the ]]] | |||
| An antecedent to the term is the Greek word {{lang|grc-Latn|andrapodismos}} ({{lang|grc|ἀνδραποδισμός}}; lit. "enslavement"), which was used in ancient texts. e.g., to describe atrocities that accompanied ]'s ] in 335 ].<ref name="Booth">{{cite book|year=2012|title=The Kosovo Tragedy: The Human Rights Dimensions|editor-last=Booth|editor-first=Ken |first=Carrie |last=Booth Walling |contribution=The History and Politics of Ethnic Cleansing|publisher=Routledge|location=London|isbn=978-1-13633-476-4|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=e4MsBgAAQBAJ|page=48}}</ref> The ] from Spain between 1609 and 1614 is considered by some authors to be one of the first episodes of state-sponsored ethnic cleansing in the modern western world.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Saldanha |first1=Arun |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4bRvAAAAQBAJ&q=ethnic+cleansing&pg=PA51 |title=Deleuze and Race |date=2012 |publisher=Edinburgh University Press |isbn=978-0-7486-6961-5 |pages=51, 70 |language=en}}</ref> ], who coined the term "genocide", considered the ] by American settlers as a historical example of genocide.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=McDonnell |first1=M. A. |last2=Moses |first2=A. D. |author2-link=A. Dirk Moses |date=2005 |title=Raphael Lemkin as historian of genocide in the Americas |journal=] |volume=7 |pages=501–529 |doi=10.1080/14623520500349951 |s2cid=72663247 |number=4}}</ref> Others, like historian Gary Anderson, contend that genocide does not accurately characterize any aspect of American history, suggesting instead that ethnic cleansing is a more appropriate term.<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal |last=Sousa |first=Ashley |date=2016 |title=Ethnic Cleansing and the Indian: The Crime That Should Haunt America by Gary Clayton Anderson |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1353/soh.2016.0023 |journal=Journal of Southern History |volume=82 |issue=1 |pages=135–136 |doi=10.1353/soh.2016.0023 |s2cid=159731284 |issn=2325-6893}}</ref> Circassian genocide, also known as "]", is often regarded by various historians as the first large-scale ethnic cleansing campaign launched by a state during the 19th century ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Richmond |first=Walter |title=The Circassian Genocide |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-8135-6068-7 |location=New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA |pages=66|chapter=3: From War to Genocide}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Levene |first=Mark |author-link=Mark Levene |isbn= 1-84511-057-9 | title=Genocide in the Age of the Nation-State Volume II: The Rise of the West and the Coming of Genocide |year=2005|pages=298–302|chapter=6: Declining Powers |publisher=175 Fifth Avenue, New York NY 10010}}</ref> ] general ], who supervised the operations of ] during 1860s, dehumanised Muslim Circassians as "a pestilence" to be expelled from their native lands. Russian objective was the annexation of land; and the Russian military operations that forcibly deported Circassians were designated by Yevdakimov as “''ochishchenie''” (cleansing).<ref name="Richmond 2013 96, 97"/> | |||
| However, ethnic cleansing rarely aims at complete ethnic homogeneity. The common practice is the removal of stigmatized ethnic groups, and thus can be defined as "the forcible removal of an ethnically defined population from a given territory", occupying the middle part of a somewhat fuzzy continuum between nonviolent pressured ethnic emigration and ].<ref name="martin">Martin, Terry (1998). . '']'' 70 (4), 813-861.</ref> | |||
| In the early 1900s, regional variants of the term could be found among the Czechs ({{lang|cs|očista}}), the Poles ({{lang|pl|czystki etniczne}}), the French ({{lang|fr|épuration}}) and the Germans ({{lang|de|Säuberung}}).<ref>{{cite book |first=Philipp |last=Ther |editor1-first=Rainer |editor1-last=Munz |editor2-first=Rainer |editor2-last=Ohliger |year=2004 |title=Diasporas and Ethnic Migrants: Germany, Israel and Russia in Comparative Perspective |chapter=The Spell of the Homogeneous Nation State: Structural Factors and Agents of Ethnic Cleansing |publisher=Routledge |location=London |isbn=978-1-13575-938-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kEOQAgAAQBAJ |access-date=August 31, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200126110924/https://books.google.com/books?id=kEOQAgAAQBAJ |archive-date=January 26, 2020 |url-status=live }}</ref>{{page needed|date=September 2016}} A 1913 ] report condemning the actions of all participants in the ] contained various new terms to describe brutalities committed toward ethnic groups.<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://balkanologie.revues.org/2365|title=The Two Carnegie Reports: From the Balkan Expedition of 1913 to the Albanian Trip of 1921|first=Nadine|last=Akhund|date=December 31, 2012|journal=Balkanologie. Revue d'études pluridisciplinaires|volume=XIVb|issue=1–2|doi=10.4000/balkanologie.2365|via=balkanologie.revues.org|access-date=April 3, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170404043111/https://balkanologie.revues.org/2365|archive-date=April 4, 2017|url-status=live|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| In reviewing the ] (ICJ) ] in the judgement of ] on ] 2007 the ] selectively quoted from the ICJ ruling on the ''Bosnian Genocide Case'' to explain that ''ethnic cleansing'' was not enough on its own to establish that a genocide had occurred: | |||
| ] following the end of World War II]] | |||
| {{quotation|The term 'ethnic cleansing' has frequently been employed to refer to the events in ] which are the subject of this case ... ] resolution 47/121 referred in its Preamble to 'the abhorrent policy of 'ethnic cleansing', which is a form of genocide', as being carried on in Bosnia and Herzegovina. ... It can only be a form of genocide within the meaning of the Convention]], if it corresponds to or falls within one of the categories of acts prohibited by Article II of the Convention. Neither the intent, as a matter of policy, to render an area “ethnically homogeneous”, nor the operations that may be carried out to implement such policy, can as such be designated as genocide: the intent that characterizes genocide is “to destroy, in whole or in part” a particular group, and deportation or displacement of the members of a group, even if effected by force, is not necessarily equivalent to destruction of that group, nor is such destruction an automatic consequence of the displacement. This is not to say that acts described as 'ethnic cleansing' may never constitute genocide, if they are such as to be characterized as, for example, 'deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part', contrary to Article II, paragraph (c), of the Convention, provided such action is carried out with the necessary specific intent ('']''), that is to say with a view to the destruction of the group, as distinct from its removal from the region. As the ] has observed, while 'there are obvious similarities between a genocidal policy and the policy commonly known as 'ethnic cleansing' ' (''Krstić,'' IT-98-33-T, Trial Chamber Judgment, 2 August 2001, para. 562), yet ' clear distinction must be drawn between physical destruction and mere dissolution of a group. The expulsion of a group or part of a group does not in itself suffice for genocide. |ECHR quoting the ICJ<ref>] §45 citing Bosnia and Herzegovina v. Serbia and Montenegro (“Case concerning the application of the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide”) the International Court of Justice (ICJ) found under the heading of “intent and 'ethnic cleansing'” § 190</ref>}} | |||
| During the ] in ], ] pursued a policy of ensuring that Europe was "cleaned of Jews" ({{lang|de|]}}<!-- lower case because it's an adjective -->).<ref>{{cite book|first=Mary|last=Fulbrooke|year=2004|title=A Concise History of Germany|publisher=Cambridge University Press|location=Cambridge|isbn=978-0-52154-071-1|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zFBu8ujJWzkC|page=197|access-date=August 31, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200126110933/https://books.google.com/books?id=zFBu8ujJWzkC|archive-date=January 26, 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> The Nazi {{lang|de|]}} called for the genocide and ethnic cleansing of most ] in central and eastern Europe for the purpose of providing more ] for the Germans.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Eichholtz |first=Dietrich |title='Generalplan Ost' zur Versklavung osteuropäischer Völker |trans-title='General Plan East' for the enslavement of Eastern European peoples |journal=Utopie Kreativ |volume=167 |date=September 2004 |via=] |pages=800–808 |language=de |url=https://www.rosalux.de/publikation/id/3303/utopie-kreativ-167/}}</ref> During the ], the euphemism {{lang|hr|čišćenje terena}} ("cleansing the terrain") was used by the Croatian ] to describe military actions in which non-Croats were purposely systematically killed or otherwise uprooted from their homes.<ref name="Toal">{{cite book|last1=Toal|first1=Gerard|last2=Dahlman|first2=Carl T.|title=Bosnia Remade: Ethnic Cleansing and Its Reversal|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=New York|year=2011|isbn=978-0-19-973036-0|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Q1TrvGxJeasC|page=3|access-date=March 1, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140706230527/http://books.google.com/books?id=Q1TrvGxJeasC|archive-date=July 6, 2014|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Richard |last=West|year=1994|title=Tito and the Rise and Fall of Yugoslavia|publisher=Carroll & Graf|location=New York|isbn=978-0-7867-0332-6|page=93}}</ref> The term was also used in the December 20, 1941 directive of Serbian ] in reference to the ] against ] and ] between 1941 and 1945.<ref>{{cite book|first=Edina|last=Becirevic|year=2014|title=Genocide on the River Drina|publisher=Yale University Press|location=New Haven, Connecticut|isbn=978-0-3001-9258-2|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=N0X4AwAAQBAJ|pages=22–23|access-date=August 31, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200126110928/https://books.google.com/books?id=N0X4AwAAQBAJ|archive-date=January 26, 2020|url-status=live}}</ref> The Russian phrase {{lang|ru|очистка границ}} ({{lang|ru-Latn|ochistka granits}}; lit. "cleansing of borders") was used in ] documents of the early 1930s to refer to the ] from the {{convert|22|km|adj=on}} ] in the ] and ].{{Citation needed|reason=Not in the source provided for the next sentence|date=August 2021}} This process of the ] was repeated on an even larger scale in 1939–1941, involving many other groups suspected of disloyalty.<ref name="martin"/> | |||
| ], at least 750,000 Palestinians were ] from what is now Israel.<ref>{{cite news |title=The Nakba did not start or end in 1948 |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2017/5/23/the-nakba-did-not-start-or-end-in-1948 |work=Al Jazeera |date=23 May 2017}}</ref>]] | |||
| In its complete form, the term appeared for the first time in the Romanian language ({{lang|ro|purificare etnică}}) in an address by Vice Prime Minister ] to cabinet members in July 1941. After the beginning of the ],{{clarify|date=October 2017}} he concluded: "I do not know when the Romanians will have such chance for ethnic cleansing."<ref>{{Cite book|title=Ethnopolitical Temptations Reach Southeastern Europe: Wartime Policy Papers of Vasa Čubrilović and Sabin Manuilă|last=Petrovic|first=Vladimir|publisher=CEU Press|year=2017}}</ref> In the 1980s, the Soviets used the term "etnicheskoye chishcheniye" which literally translates to "ethnic cleansing" to describe Azerbaijani efforts to drive Armenians away from ].<ref>Allen, Tim, and Jean Seaton, eds. ''The media of conflict: War reporting and representations of ethnic violence''. Zed Books, 1999. p. 152</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Feierstein |first=Daniel |date=2023-04-04 |title=The Meaning of Concepts: Some Reflections on the Difficulties in Analysing State Crimes |url=https://ojs.ub.rub.de/index.php/HARM/article/view/10453 |journal=HARM – Journal of Hostility, Aggression, Repression and Malice |volume=1 |doi=10.46586/harm.2023.10453 |issn=2940-3073 |quote=The concept seems to have been borrowed from the Slavic expression etnicheskoye chishcheniye, first used by Soviet authorities in the 1980s to describe Azeri attempts to expel Armenians from the Nagorno-Karabakh area, and then immediately reappropriated by Serb nationalists to describe their policies in the central region of Yugoslavia.}}</ref><ref>Cox, Caroline. {{Dead link|date=August 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} ''Contemporary Review'' 270 (1997): 8–13: "These operations were part of a policy designated `Operation Ring, comprising the proposed ethnic cleansing (a word used in relation to Azerbaijan's policy before it became familiar to the world in the context of the former Yugoslavia) of all Armenians from their ancient homeland of Karabakh."</ref> It was widely popularized by the Western media during the ] (1992–1995). | |||
| In 1992, the German equivalent of ''ethnic cleansing'' ({{langx|de|ethnische Säuberung}}, {{IPA|de|ˈʔɛtnɪʃə ˈzɔɪ̯bəʁʊŋ|pron|De-ethnische Säuberung.ogg}}) was named ] by the '']'' due to its euphemistic, inappropriate nature.<ref>{{cite news |first=Christoph |last=Gunkel |date=October 31, 2010 |url=http://einestages.spiegel.de/external/ShowTopicAlbumBackground/a23795/l18/l0/F.html#featuredEntry |work=] |title=Ein Jahr, ein (Un-)Wort! |language=de |trans-title=One year, one (un)word! |access-date=February 17, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130512233554/http://einestages.spiegel.de/external/ShowTopicAlbumBackground/a23795/l18/l0/F.html#featuredEntry |archive-date=May 12, 2013 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==Origins of the term== | |||
| The term "ethnic cleansing" entered the English lexicon as a ] of the ] phrase ''etničko čišćenje'' ({{IPA-all|ětnitʃkoː tʃîʃtɕeːɲe}}) and has become synonymous with the term ].<ref>http://books.google.com/books?id=tVeh3C8XGP4C&pg=PA67</ref> | |||
| During the 1990s it was used extensively by the media in the former ] in relation to the ], and appears to have been popularised by the international media some time around 1992. The term may have originated some time before the 1990s in the military doctrine of the former ], which spoke of "cleansing the field" (''čišćenje terena'', {{IPA-all|tʃîʃtɕeːɲe terěːna}}) of enemies to take total control of a conquered area. The origins of this doctrine are unclear, but may have been a legacy of the ] era. | |||
| == Definitions == | |||
| A ] report on the ] in 1914 points out that village-burning and ethnic cleansing have traditionally accompanied ] wars, regardless of ethnicities involved. In probably the earliest attestation of the term, ] makes use of the word ''cleanse'' to describe what happened to the ] in ] when the city was captured by the ]'s forces in 1806<ref>{{cite book |author=Judah, Tim |title=The Serbs: History, Myth and the Destruction of Yugoslavia |year=1997 |location=New Haven and London |publisher=Yale University Press|pages=75}}</ref>. ] wrote in his biography of famous Serbian leader published in 1883 that after the fighting ''"the ], in their bitterness (after 500 of Turkish occupation), slit the throats of the Turks everywhere they found them, sparing neither the wounded, nor the woman, nor the Turkish children"''.<ref>{{cite book |author=Mirko Grmek, Marc Gjidara, Neven Simac|title=Le Nettoyage ethnique: Documents historiques sur une idéologie serbe |year=1993 |location=Paris |language=French|pages=24}}</ref> | |||
| The Final Report of the Commission of Experts established pursuant to ] defined ethnic cleansing as: | |||
| {{blockquote|a purposeful policy designed by one ethnic or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas", ]] " 'ethnic cleansing' has been carried out by means of murder, torture, ], extra-judicial executions, ] and sexual assaults, confinement of civilian population in ghetto areas, forcible removal, displacement and deportation of civilian population, deliberate military attacks or threats of attacks on civilians and civilian areas, and wanton destruction of property. Those practices constitute ] and can be assimilated to specific ]s. Furthermore, such acts could also fall within the meaning of the ].<ref>{{cite web |date=May 27, 1994 |title=Final Report of the Commission of Experts Established Pursuant to United Nations Security Council Resolution 780 (1992) |url=https://www.refworld.org/legal/resolution/unsc/1994/en/113325 |archive-url= |archive-date= |access-date= |publisher=United Nations Security Council |page=33 |format=PDF}} Paragraph 129</ref><ref name="SCRes780-Report-130">{{cite web |title=Final Report of the Commission of Experts Established Pursuant to United Nations Security Council Resolution 780 (1992) |date=May 27, 1994 |url=https://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=S/1994/674 |publisher=United Nations Security Council |format=PDF |page=33 <!--paragraph 130--> |quote=Upon examination of reported information, specific studies and investigations, the Commission confirms its earlier view that 'ethnic cleansing' is a purposeful policy designed by one ethnic or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas. To a large extent, it is carried out in the name of misguided nationalism, historic grievances and a powerful driving sense of revenge. This purpose appears to be the occupation of territory to the exclusion of the purged group or groups. This policy and the practices of warring factions are described separately in the following paragraphs. |access-date=May 25, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514200247/http://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=S%2F1994%2F674 |archive-date=May 14, 2011 |url-status=live }} Paragraph 130.</ref>}} | |||
| Later attestation of the term ''cleansing'' can be found on ], ], during the ], by one ], a commander in the Croatian ] faction, the ]: ''Every Croat who today solicits for our enemies not only is not a good Croat, but also an opponent and disrupter of the prearranged, well-calculated plan for cleansing '''' our ] of unwanted elements .''<ref></ref>{{Verify credibility|date=June 2008}} The Ustaše carried out large-scale ethnic cleansing and genocide of ] during the ] and sometimes used the term "cleansing" to describe it.<ref></ref>. | |||
| The official United Nations definition of ethnic cleansing is "rendering an area ethnically homogeneous by using force or ] to remove from a given area persons of another ethnic or religious group."<ref>Hayden, Robert M. (1996) {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160411202522/http://www.jstor.org/stable/2501233 |date=April 11, 2016 }}. '']'' 55 (4), 727–48.</ref> As a category, ethnic cleansing encompasses a continuum or spectrum of policies. In the words of ], "ethnic cleansing ... defies easy definition. At one end it is virtually indistinguishable from forced emigration and population exchange while at the other it merges with deportation and genocide. At the most general level, however, ethnic cleansing can be understood as the expulsion of a population from a given territory."<ref>Andrew Bell-Fialkoff, {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040203190219/http://www.foreignaffairs.org/19930601faessay5199/andrew-bell-fialkoff/a-brief-history-of-ethnic-cleansing.html |date=February 3, 2004 }}, ''Foreign Affairs'' 72 (3): 110, Summer 1993. Retrieved May 20, 2006.</ref> | |||
| Some time later, on 30 June, 1941, ], a lawyer from ] who was an ideologue of the ]s, published a booklet with the title ''On Our State and Its Borders''. Moljević assessed the circumstances in the following manner: ''"One must take the opportunity of the war conditions and at a suitable moment take hold of the territory marked on the map, cleanse '''' it before anybody notices and with strong battalions occupy the key places (...) and the territory surrounding these cities, freed of non-] elements. The guilty must be promptly punished and the others deported - the ] to Croatia, the ] to ] or perhaps ] - while the vacated territory is settled with Serb refugees now located in Serbia.''<ref></ref> | |||
| Terry Martin has defined ethnic cleansing as "the forcible removal of an ethnically defined population from a given territory" and as "occupying the central part of a continuum between genocide on one end and nonviolent pressured ethnic emigration on the other end."<ref name="martin">Martin, Terry (1998). {{Webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190724042805/https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/235168 |date=July 24, 2019}}. '']'' 70 (4), 813–861. pg. 822</ref> | |||
| The term "cleansing", more specifically the ] term "cleansing of borders", ''ochistka granits'' (очистка границ), was used in ] documents of the early 1930s in reference to the resettlement of ] from the 22-km ] in ] and ]. The process was repeated on a larger and wider scale in 1939–1941, involving many other ethnicities with cross-border ties to foreign ], see ] and ].<ref name="martin"/> | |||
| ], the founder of ], has criticised the rise of the term and its use for events that he feels should be called "genocide": because "ethnic cleansing" has no legal definition, its media use can detract attention from events that should be prosecuted as genocide.<ref name=":1"/><ref name=":2">Douglas Singleterry (April 2010), "Ethnic Cleansing and Genocidal Intent: A Failure of Judicial Interpretation?", ''Genocide Studies and Prevention'' 5, 1</ref> | |||
| A similar term with the same intent was used by the ] administration in ] under ]. When an area under Nazi control had its entire ]ish population removed, whether by driving the population out, by deportation to ]s, and/or ], the area was declared '']'', (lit. "Jew Clean"): "cleansed of Jews".(cf. ]). | |||
| === As a crime under international law === | |||
| ==Ethnic cleansing as a military and political tactic== | |||
| There is no international treaty that specifies a specific crime of ethnic cleansing;<ref>{{cite journal |first=Ward |last=Ferdinandusse |url=http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol15/No5/9.pdf |title=The Interaction of National and International Approaches in the Repression of International Crimes |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080705180121/http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol15/No5/9.pdf |archive-date=July 5, 2008 |journal=The European Journal of International Law |volume=15 |number=5 |year=2004 |page=1042, note 7|doi=10.1093/ejil/15.5.1041 |doi-access=free }}</ref> however, ethnic cleansing in the broad sense—the forcible deportation of a population—is defined as a ] under the statutes of both the ] (ICC) and the ] (ICTY).<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080113100723/http://www.un.org/law/icc/statute/99_corr/2.htm |date=January 13, 2008 }}, Article 7; {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090806141633/http://www.un.org/icty/legaldoc-e/index.htm |date=August 6, 2009 }}, Article 5.</ref> The gross human rights violations integral to stricter definitions of ethnic cleansing are treated as separate crimes falling under public international law of ] and in certain circumstances ].<ref>{{cite journal |first1=Daphna |last1=Shraga |first2=Ralph |last2=Zacklin |url=http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol5/No3/art4-01.html |title=The International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927233818/http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol5/No3/art4-01.html |archive-date=September 27, 2007 |journal=The European Journal of International Law |volume=15 |number=3 |year=2004}}</ref> There are also situations, such as the ], where ethnic cleansing has taken place without legal redress (see '']''). '']''<!-- a person, not a court case --> argues that similar ethnic cleansing could go unpunished in the future.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181106100246/http://law.bepress.com/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4600&context=expresso |date=November 6, 2018 }}, Paper 951, 2006, ] School of Law. Retrieved on 2006, 12–13</ref> | |||
| ] which was held in ] in 2005. One of the visitors of the gallery recognized her dead son on the photograph]] | |||
| <!-- The emergence of ethnic cleansing as a distinct category of war crime has been a somewhat complex process. Each individual element of a programme of ethnic cleansing could be considered as an individual violation of humanitarian law—a killing here, a house-burning there—thus missing the systematic way in which such violations were perpetrated with a single aim in mind. International courts consider individual incidents in the light of a possible pattern of ethnic cleansing. In the Yugoslav case, the ICTY considers the widespread massacres and abuses of human rights in Bosnia and Kosovo as part of an overall "]" to carve out ethnically pure states in the region; however, many alleged "ethnic cleansings" in the past do not fit the modern definition of "crimes against humanity"; the post-World War II ] were sanctioned by the international agreement at ], requiring that the actions proceed humanely. --> | |||
| The purpose of ethnic cleansing is to remove the conditions for potential and actual opposition, whether political, guerrilla or military, by physically removing any potentially or actually hostile ethnic communities. Although it has sometimes been motivated by a doctrine that claim an ethnic group is literally "unclean" (as in the case of the ]), more usually it has been a rational (if brutal) way of ensuring that total control can be asserted over an area. | |||
| === Mutual ethnic cleansing === | |||
| Ethnic cleansing was a common phenomenon in the ]. This typically entailed intimidation, forced expulsion and/or killing of the undesired ethnic group as well as the destruction or removal of the physical vestiges of the ethnic group, such as places of worship, cemeteries and cultural and historical buildings. According to numerous ICTY verdicts, Serb<ref name="ICTY: Radoslav Brđanin judgement">{{cite web|url=http://www.un.org/icty/brdjanin/trialc/judgement/index.htm|title=ICTY: Radoslav Brđanin judgement}}</ref> and Croat<ref name="ICTY: Kordić and Čerkez verdict">{{cite web|url=http://www.un.org/icty/kordic/trialc/judgement/index.htm|title=ICTY: Kordić and Čerkez verdict}}</ref> forces performed ethnic cleansing of their territories planned by their political leadership in order to create ethnically pure states (] and ]). Furthermore, Serb forces committed ] at the end of the war.<ref>ICTY; "Address by ICTY President Theodor Meron, at Potočari Memorial Cemetery" The Hague, 23 June 2004 </ref> | |||
| '''Mutual ethnic cleansing''' occurs when two groups commit ethnic cleansing against minority members of the other group within their own territories. For instance in the 1920s, Turkey expelled its Greek minority and Greece expelled its Turkish minority following the ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Pinxten |first1=Rik |last2=Dikomitis |first2=Lisa |title=When God Comes to Town: Religious Traditions in Urban Contexts |date=1 May 2009 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-1-84545-920-8 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hMF-mjzt1fsC |access-date=31 December 2021 |language=en}}</ref> Other examples where mutual ethnic cleansing occurred include the ]<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Cornell |first1=Svante E. |title=Religion as a factor in Caucasian conflicts |journal=Civil Wars |date=September 1998 |volume=1 |issue=3 |pages=46–64 |doi=10.1080/13698249808402381 |language=en |issn=1369-8249}}</ref> and the population transfers by the Soviets of Germans, Poles, and Ukrainians after ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Snyder |first1=Timothy |title=The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999 |date=11 July 2004 |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-300-10586-5 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xSpEynLxJ1MC |access-date=31 December 2021 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| == Causes == | |||
| Based on the evidence of numerous Croat forces attacks against Bosnian Muslims (Bosniaks), the ICTY Trial Chamber concluded in the ''Kordić and Čerkez case'' that by April 1993 Croat leadership from Bosnia and Herzegovina had a common design or plan conceived and executed to ] in Central Bosnia. ], as the local political leader, was found to be the planner and ] of this plan. <ref name="ICTY: Kordić and Čerkez verdict - IV. Attacks on towns and villages: killings - C. The April 1993 Conflagration in Vitez and the Lašva Valley - 3. The Attack on Ahmići (Paragraph 642)">{{cite web|url=http://www.un.org/icty/kordic/trialc/judgement/kor-tj010226e-5.htm#IVC3|title=ICTY: Kordić and Čerkez verdict - IV. Attacks on towns and villages: killings - C. The April 1993 Conflagration in Vitez and the Lašva Valley - 3. The Attack on Ahmići (Paragraph 642)}}</ref> | |||
| ] in 1943. Most ] of Volhynia had either been murdered or had fled the area.]] | |||
| According to ], in '']'' (2004), murderous ethnic cleansing is strongly related to the creation of democracies. He argues that murderous ethnic cleansing is due to the rise of ], which associates citizenship with a specific ]. Democracy, therefore, is tied to ethnic and national forms of exclusion. Nevertheless, it is not democratic states that are more prone to commit ethnic cleansing, because minorities tend to have constitutional guarantees. Neither are stable authoritarian regimes (except the nazi and communist regimes) which are likely perpetrators of murderous ethnic cleansing, but those regimes that are in process of democratization. Ethnic hostility appears where ethnicity overshadows social classes as the primordial system of social stratification. Usually, in deeply divided societies, categories such as class and ethnicity are deeply intertwined, and when an ethnic group is seen as oppressor or exploitative of the other, serious ethnic conflict can develop. Michael Mann holds that when two ethnic groups claim sovereignty over the same territory and can feel threatened, their differences can lead to severe grievances and danger of ethnic cleansing. The perpetration of murderous ethnic cleansing tends to occur in unstable geopolitical environments and in contexts of war. As ethnic cleansing requires high levels of organisation and is usually directed by states or other authoritative powers, perpetrators are usually state powers or institutions with some coherence and capacity, not failed states as it is generally perceived. The perpetrator powers tend to get support by core constituencies that favour combinations of ], ], and violence.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200503062111/https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/dark-side-of-democracy/7E75A132A188A2804E91F4F209B6FE1F|date=May 3, 2020}}, Mann, Michael (2005), The Dark Side of Democracy: Explaining Ethnic Cleansing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, Ch. 1 "The Argument," pp. 1–33.</ref> | |||
| In 1993, during the ], armed ] ] insurgency, confronted with large population of ethnic ], implemented a campaign of ] against the ethnic Georgians (Georgians formed the single largest ethnic group in pre-war Abkhazia, with a 45.7% plurality as of 1989) of ]. <ref>US State Department, Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 1993, Abkhazia case </ref> As the results, more than 250,000 ethnic Georgians were forced to flee and approximately 30,000 people were killed during separate incidents involving massacres and expulsion. (see ]) <ref> Chervonnaia, Svetlana Mikhailovna. ''Conflict in the Caucasus: Georgia, Abkhazia, and the Russian Shadow.'' Gothic Image Publications, 1994. </ref><ref> ''S State Department, Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 1993, February 1994, Chapter 17. </ref> This was recognized as ethnic cleansing by ] conventions and was also mentioned in ] GA/10708. <ref></ref> | |||
| Ethnic cleansing was prevalent during the ] in Europe (19th and 20th centuries).<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last1=Müller-Crepon |first1=Carl |last2=Schvitz |first2=Guy |last3=Cederman |first3=Lars-Erik |date=2024 |title="Right-Peopling" the State: Nationalism, Historical Legacies, and Ethnic Cleansing in Europe, 1886–2020 |url=http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00220027241227897 |journal=Journal of Conflict Resolution |language=en |doi=10.1177/00220027241227897 |issn=0022-0027|hdl=20.500.11850/657611 |hdl-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Mylonas |first=Harris |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/politics-of-nationbuilding/C9E4A27E97D35705F0549C0FC1C03457 |title=The Politics of Nation-Building: Making Co-Nationals, Refugees, and Minorities |date=2013 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-107-02045-0 |doi=10.1017/cbo9781139104005}}</ref> Multi-ethnic European engaged in ethnic cleansing against minorities in order to pre-empt their secession and the loss of territory.<ref name=":0" /> Ethnic cleansing was particularly prevalent during periods of interstate war.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| As a tactic, ethnic cleansing has a number of significant impacts. It enables a force to eliminate civilian support for resistance by eliminating the civilians — recognizing ]'s dictum that guerrillas among a civilian population are fish in water, it removes the fish by draining the water. When enforced as part of a political settlement, as happened with the ] after 1945, it can contribute to long-term stability.<ref> Judt, Tony. ''Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945'' Penguin Press, 2005</ref> Some individuals of the large German population in ] and prewar ] had encouraged Nazi ] before the Second World War, but this was forcibly resolved<ref> Judt, Tony. ''Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945'' Penguin Press, 2005. </ref>. It thus establishes "]" - radical demographic changes which can be very hard to reverse. | |||
| == Genocide == | |||
| For the most part, ethnic cleansing is such a brutal tactic and so often accompanied by large-scale bloodshed that it is widely reviled. It is generally regarded as lying somewhere between ]s and ] on a scale of odiousness, and is treated by ] as a ]. | |||
| ]. From 1914 until 1923, ] in ] and ] were subject to a campaign including massacres and deportations. The ] (IAGS) recognizes it as genocide and refers to the campaign as the '']''.<ref>{{cite web|author=International Association of Genocide Scholars|title=Genocide Scholars Association Officially Recognizes Assyrian, Greek Genocides|date=December 16, 2007|url=http://genocidescholars.org/images/PRelease16Dec07IAGS_Officially_Recognizes_Assyrian_Greek_Genocides.pdf|access-date=15 August 2011|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110601144026/http://genocidescholars.org/images/PRelease16Dec07IAGS_Officially_Recognizes_Assyrian_Greek_Genocides.pdf|archive-date=1 June 2011}}</ref>]] | |||
| Ethnic cleansing has been described as part of a continuum of violence whose most extreme form is ]. Ethnic cleansing is similar to forced ] or ]. While ethnic cleansing and genocide may share the same goal and methods (e.g., ]), ethnic cleansing is intended to displace a persecuted population from a given territory, while genocide is intended to destroy a group.<ref name=Schabas>{{cite book |last=Schabas |first=William |year=2000 |title=Genocide in International Law |location=Cambridge |publisher=Cambridge University Press |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pYptuRHDQPgC |pages=199–201 |isbn=9780521787901 |access-date=October 29, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102083003/https://books.google.com/books?id=pYptuRHDQPgC&printsec=frontcover |archive-date=January 2, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>Ethnic cleansing versus genocide: | |||
| ]n civilians, being cleansed from their homeland during the ]]] | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Lieberman |first1=Benjamin |editor1-last=Bloxham |editor1-first=Donald |editor2-last=Moses |editor2-first=A. Dirk |title=The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies |publisher= Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-923211-6 |chapter='Ethnic cleansing' versus genocide?|date= 2010 |quote=Explaining the relationship between ethnic cleansing and genocide has caused controversy. Ethnic cleansing shares with genocide the goal of achieving purity but the two can differ in their ultimate aims: ethnic cleansing seeks the forced removal of an undesired group or groups where genocide pursues the group's 'destruction'. Ethnic cleansing and genocide therefore fall along a spectrum of violence against groups with genocide lying on the far end of the spectrum.}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Martin |first1=Terry |title=The Origins of Soviet Ethnic Cleansing |journal=The Journal of Modern History |date=1998 |volume=70 |issue=4 |pages=813–861 |doi=10.1086/235168 |jstor=10.1086/235168 |s2cid=32917643 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/235168 |issn=0022-2801 |quote=When murder itself becomes the primary goal, it is typically called genocide... Ethnic cleansing is probably best understood as occupying the central part of a continuum between genocide on one end and nonviolent pressured ethnic emigration on the other end. Given this continuum, there will always be ambiguity as to when ethnic cleansing shades into genocide}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Schabas |first1=William A. |title='Ethnic Cleansing' and Genocide: Similarities and Distinctions |journal=European Yearbook of Minority Issues Online |date=2003 |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=109–128 |doi=10.1163/221161104X00075 |quote=The crime of genocide is aimed at the intentional destruction of an ethnic group. 'Ethnic cleansing' would seem to be targeted at something different, the expulsion of a group with a view to encouraging or at least tolerating its survival elsewhere. Yet ethnic cleansing may well have the effect of rendering the continued existence of a group impossible, thereby effecting its destruction. In other words, forcible deportation may achieve the same result as extermination camps.|doi-access=free }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Walling |first1=Carrie Booth |title=The history and politics of ethnic cleansing |journal=The International Journal of Human Rights |date=2000 |volume=4 |issue=3–4 |pages=47–66 |doi=10.1080/13642980008406892 |s2cid=144001685 |quote=These methods are a part of a wider continuum ranging from genocide at one extreme to emigration under pressure at the other... It is important - politically and legally - to distinguish between genocide and ethnic cleansing. The goal of the former is extermination: the complete annihilation of an ethnic, national or racial group. It contains both a physical element (acts such as murder) and a mental element (those acts are undertaken to destroy, in whole or in part, the said group). Ethnic cleansing involves population expulsions, sometimes accompanied by murder, but its aim is consolidation of power over territory, not the destruction of a complete people.}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Naimark |first1=Norman M. |author1-link=Norman Naimark |title=Fires of Hatred |date=2002|url=https://www.hoover.org/research/fires-hatred |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=978-0-674-00994-3 |pages=2–5 |quote=A new term was needed because ethnic cleansing and genocide two different activities, and the differences between them are important. As in the case of determining first-degree murder, intentionality is a critical distinction. Genocide is the intentional killing off of part or all of an ethnic, religious, or national group; the murder of a people or peoples (in German, ''Völkermord'') is the objective. The intention of ethnic cleansing is to remove a people and often all traces of them from a concrete territory. The goal, in other words, is to get rid of the "alien" nationality, ethnic, or religious group and to seize control of the territory it had formerly inhabited. At one extreme of its spectrum, ethnic cleansing is closer to forced deportation or what has been called "population transfer"; the idea is to get people to move, and the means are meant to be legal and semi-legal. At the other extreme, however, ethnic cleansing and genocide are distinguishable only by the ultimate intent. Here, both literally and figuratively, ethnic cleansing bleeds into genocide, as mass murder is committed in order to rid the land of a people.}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Hayden |first1=Robert M. |title=Schindler's Fate: Genocide, Ethnic Cleansing, and Population Transfers |journal=Slavic Review |date=1996 |volume=55 |issue=4 |pages=727–748 |doi=10.2307/2501233 |jstor=2501233 |s2cid=232725375 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/2501233 |issn=0037-6779 |quote=Hitler wanted the Jews utterly exterminated, not simply driven from particular places. Ethnic cleansing, on the other hand, involves removals rather than extermination and is not exceptional but rather common in particular circumstances.}}</ref> | |||
| Some academics consider genocide to be a subset of "murderous ethnic cleansing".<ref name=Mann>{{cite book |last=Mann |first=Michael |year=2005 |title=The Dark Side of Democracy: Explaining Ethnic Cleansing |location=Cambridge |publisher=Cambridge University Press. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cGHGPgj1_tIC&q=The+Dark+Side+of+Democracy |page=17 |isbn=9780521538541 |access-date=October 29, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102083003/https://books.google.com/books?id=cGHGPgj1_tIC&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+Dark+Side+of+Democracy |archive-date=January 2, 2016 |url-status=live }}</ref> Norman Naimark writes that these concepts are different but related, for "literally and figuratively, ethnic cleansing bleeds into genocide, as mass murder is committed in order to rid the land of a people."<ref name=MassVio>{{cite encyclopedia |last=Naimark |first=Norman |date=4 November 2007 |url=http://www.massviolence.org/Ethnic-Cleansing |title=Theoretical Paper: Ethnic Cleansing |encyclopedia=Online Encyclopedia of Mass Violence |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160306173512/http://www.massviolence.org/Ethnic-Cleansing |archive-date=6 March 2016}}</ref> William Schabas states "ethnic cleansing is also a warning sign of genocide to come. Genocide is the last resort of the frustrated ethnic cleanser."<ref name="Schabas"/> Multiple genocide scholars have criticized distinguishing between ethnic cleansing and ], with ] arguing that forced deportation necessarily results in the destruction of a group and this must be foreseen by the perpetrators.{{efn| "How could ‘forced deportation’ ever be achieved without extreme coercion, indeed violence? How, indeed, could deportation not be forced? How could people not resist? How could it not involve the destruction of a community, of the way of life that a group has enjoyed over a period of time? How could those who deported a group not intend this destruction? In what significant way is the forcible removal of a population from their homeland different from the destruction’ of a group? If the boundary between ‘cleansing’ and genocide is unreal, why police it?"<ref name=shawcriti/>}}<ref name=shawcriti>Shaw, Martin (2015b), What is Genocide, Polity Press, ISBN 978-0-7456-8706-3 ‘Cleansing’ and genocide.</ref><ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /> | |||
| ==Ethnic cleansing as a crime under international law== | |||
| There is no formal legal definition of ethnic cleansing.<ref> Ward Ferdinandusse, [http://www.ejil.org/journal/Vol15/No5/9.pdf The Interaction of National and | |||
| International Approaches in the Repression of International Crimes], The European Journal of International Law Vol. 15 no.5 (2004), p. 1042, note 7.</ref> However, ethnic cleansing in the broad sense - the forcible deportation of a population - is defined as a crime against humanity under the statutes of both ] (ICC) and the ] (ICTY).<ref>, Article 7; , Article 5.</ref> The gross human-rights violations integral to stricter definitions of ethnic cleansing are treated as separate crimes falling under the definitions for genocide or crimes against humanity of the statutes.<ref>Daphna Shraga and Ralph Zacklin , The European Journal of International Law Vol. 15 no.3 (2004).</ref> | |||
| == As a military, political, and economic tactic == | |||
| The UN Commission of Experts (established pursuant to Security Council Resolution 780) held that the practices associated with ethnic cleansing "constitute crimes against humanity and can be assimilated to specific war crimes. Furthermore ... such acts could also fall within the meaning of the Genocide Convention." The UN General Assembly condemned "ethnic cleansing" and racial hatred in a 1992 resolution.<ref> ""Ethnic cleansing" and racial hatred" United Nations. 12/16/1992. Retrieved on 2006, 09-03</ref> | |||
| ] victims]] | |||
| ]. Poles are led to trains under German army escort, as part of the ethnic cleansing of western Poland annexed to the ] following ].]] | |||
| ] from the ] close by ], Bosnia and Herzegovina that were forced out of their homes and villages by ] forces in 1993]] | |||
| ] carried out by ] forces, part of the ]]] | |||
| ], who organized the extermination campaigns of "]", designated Russian military operations targeting Circassian natives by the term “''ochishchenie''” (cleansing).<ref name="Richmond 2013 96, 97">{{Cite book |last=Richmond |first=Walter |title=The Circassian Genocide |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-8135-6068-7 |location=New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA |pages=96, 97 |chapter=4: 1864}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Levene |first=Mark |author-link=Mark Levene |isbn= 1-84511-057-9 | title=Genocide in the Age of the Nation-State Volume II: The Rise of the West and the Coming of Genocide |year=2005|pages=299–300|chapter=6: Declining Powers |publisher=175 Fifth Avenue, New York NY 10010}}</ref>]] | |||
| ]. According to some authors, Russian military forces massacred and forcibly deported between 95 and 97% of all native Circassians during the ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Jones |first1=Adam |year=2016 |title=Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KC8lDwAAQBAJ&dq=Yevdokimov+circassian+deportations+deaths&pg=PA110 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-317-53386-3 |pages=108–110|via=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Richmond |first=Walter |title=The Circassian Genocide |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-8135-6068-7 |location=New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA |pages= 97, 132}}</ref>]] | |||
| The ] ({{Langx|it|massacri delle foibe}}; {{Langx|sl|poboji v fojbah}}; {{Langx|hr|masakri fojbe}}), or simply "the foibe", refers to ethnic cleansing, mass killings and deportations both during and immediately after ], mainly committed by ] and ] in the ]{{efn|Successively lost by Italy to Yugoslavia after the ].}} of ] (] and ]), ] and ], against local Italians (] and ]){{sfn|Bloxham|Dirk Moses|2011}}{{sfn|Konrád|Barth|Mrňka|2021}} and Slavs, primarily members of fascist and collaborationist forces, and civilians opposed to the new Yugoslav authorities,{{sfn|Baracetti|2009|loc=p. 664, "That fascists were specifically targeted by the repression is also confirmed by various Italian sources. A letter attached to the Hazarich report on the excavations carried out in the foibe in 1943 mentions corpses of fascists thrown there; another the extractions of the bodies of "our unfortunate squadristi (members of the fascist militia). An Italian report on "the grim fate of Pisino" (a city in istria) mentions only the killings of squadristi, which contrasts markedly with the subsequent report on the German offensive: random shootings of civilians, burning of houses and bombings"}}{{sfn|Baracetti|2009|loc="In 1947, British envoy W. J. Sullivan wrote of Italians arrested and deported by Yugoslav forces from around Trieste: "There is little doubt, while some of the persons deported may have been innocent, others were undoubtedly active fascists with more than mere party memberships on their conscience. Some of these have returned to Trieste but have kept well out of the Allied authorities, not participating in enquiries about the deportations for fear of arrest and trial 'for their former fascist activities'"}}<ref name=":3">{{Cite web|last=Troha|first=Nevenka|date=2014|title=Nasilje vojnih in povojnih dni|url=https://www.sistory.si/11686/www.sistory.si/11686/42309|access-date=4 June 2023|website=www.sistory.si|publisher=Inštitut za novejšo zgodovino|language=sl|quote=By this definition, among the 601 victims , 475 were members of armed formations and 126 were civilians.}}</ref> and ], ], ] and ] ] against the regime of ], presumed to be associated with ], ], collaboration with ]{{sfn|Konrád|Barth|Mrňka|2021}}{{sfn|Rumici|2002|p=350}} and reventive purge of real, potential or presumed opponents of ]{{sfn|Italian-Slovene commission}} The foibe massacres were followed by the ], which was the post-] exodus and departure of between 230,000 and 350,000 local ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) towards ], and in smaller numbers, towards the ], ] and ].<ref name="rainews">{{cite web|url=https://www.rainews.it/dl/rainews/articoli/giorno-ricordo-10-febbraio-2004-2014-dieci-anni-strage-foibe-eccidio-tito-comunisti-slavi-esodo-giuliano-dalmata-77ba65a1-a1e5-460e-bb57-946819b4b905.html|title=Il Giorno del Ricordo|date=February 10, 2014 |access-date=16 October 2021|language=it}}</ref><ref name="ilgiornale">{{cite web|url=https://www.ilgiornale.it/news/spettacoli/lesodo-giuliano-dalmata-e-quegli-italiani-fuga-che-nacquero-1639585.html|title=L'esodo giuliano-dalmata e quegli italiani in fuga che nacquero due volte|date=February 5, 2019 |access-date=24 January 2023|language=it}}</ref> From 1947, after the war, they were subject by Yugoslav authorities to less violent forms of intimidation, such as nationalization, expropriation, and discriminatory taxation,<ref name="books.google.fr">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JHnEI2m5tFIC&pg=PA309|title=Genocide: Truth, Memory, and Representation|page=295|author=Pamela Ballinger|date=7 April 2009|publisher=Duke University Press |isbn=978-0822392361|access-date=30 December 2015}}</ref> which gave them little option other than emigration.<ref name="ReferenceA">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ia-qdCeUaXIC&pg=PA136 |title=Ethnic Cleansing and the European Union – Page 136, Lynn Tesser|isbn=9781137308771|last1=Tesser|first1=L.|date=14 May 2013|publisher=Springer }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=da6acnbbEpAC&pg=PA103 |title=History in Exile: Memory and Identity at the Borders of the Balkans |page=103 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0691086974 |last1=Ballinger|first1=Pamela|year=2003}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ykMVAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA133|title=Refugees in the Age of Total War|pages=139, 143|author=Anna C. Bramwell, University of Oxford, UK|date=1988|publisher=Unwin Hyman |isbn=9780044451945}}</ref> In 1953, there were 36,000 declared Italians in Yugoslavia, just about 16% of the original Italian population before World War II.<ref>Matjaž Klemenčič, ''The Effects of the Dissolution of Yugoslavia on Minority Rights: the Italian Minority in Post-Yugoslav Slovenia and Croatia.'' See {{cite web |url=http://www.cliohres.net/books/7/26.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=23 April 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110724111950/http://www.cliohres.net/books/7/26.pdf |archive-date=24 July 2011 }}</ref> According to the census organized in ] in 2001 and that organized in ] in 2002, the Italians who remained in the former ] amounted to 21,894 people (2,258 ] and 19,636 ]).<ref name="dzs">{{Croatian Census 2001 | url=http://web.dzs.hr/Eng/censuses/Census2001/Popis/E01_02_02/E01_02_02.html | title=12. Population by ethnicity, by towns/municipalities, census 2001 |access-date=10 June 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.stat.si/Popis2002/en/rezultati/rezultati_red.asp?ter=SLO&st=7|title=Popis 2002|access-date=10 June 2017}}</ref> | |||
| There are however situations, such as the ], where ethnic cleansing has taken place without legal redress. ] argues that if similar circumstances arise in the future, this precedent would allow the ethnic cleansing of other populations under international law.<ref>, Paper 951, 2006, ] School of Law. Retrieved on 2006, 12-13</ref> | |||
| The ] in the 9th and 7th centuries BC is considered by some scholars to be one of the first cases of ethnic cleansing.<ref>{{cite news |title=Ethnic cleansing |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/ethnic-cleansing |work=Encyclopaedia Britannica}}</ref> | |||
| <!--The emergence of ethnic cleansing as a distinct category of war crime has been a somewhat complex process. Each individual element of a programme of ethnic cleansing could be considered as an individual violation of humanitarian law - a killing here, a house-burning there - thus missing the systematic way in which such violations were perpetrated with a single aim in mind. International courts therefore consider individual incidents in the light of a possible pattern of ethnic cleansing. In the Yugoslav case, for instance, the ICTY considers the widespread massacres and abuses of human rights in Bosnia and Kosovo as part of an overall "joint criminal enterprise" to carve out ethnically pure states in the region. | |||
| During the 1980s, in ], ethnic cleansing was common during all phases of the conflict, notable incidents were seen in the early phase of the war, such as the ], the ], the ], and during the ] such as the ] committed by Lebanese Maronite forces backed by ] against ] and ] civilians. After the Israeli withdrawal from the Chouf, the ] broke out, where ethnic cleansings (mostly in the form of tit-for-tat killings) occurred. During that time, the Syrian backed, mostly Druze dominated ] used a policy they called "territorial cleansing" to "drain" the ] of Maronite Christians in order to deny them of resisting the advance of the PSP. As a result, 163,670 Christian villagers were displaced due to these operations. In response to these massacres, the ] conducted a similar policy, which resulted in 20,000 Druze displaced. | |||
| However, many alleged "ethnic cleansings" in the past do not fit the modern definition of "crimes against humanity." For example, the post-WW2 ] were sanctioned by the international agreement at ], requiring that the actions proceed humanely.--> | |||
| Ethnic cleansing was a common phenomenon in the wars in Croatia, Kosovo, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. This entailed intimidation, ], or ] of the unwanted ethnic group as well as the destruction of the places of worship, cemeteries and cultural and historical buildings of that ethnic group in order to alter the population composition of an area in the favour of another ethnic group which would become the majority. | |||
| ==Silent ethnic cleansing== | |||
| According to numerous ICTY verdicts and indictments, Serb<ref name="Prosecutor v. Vujadin Popovic, Ljubisa Beara, Drago Nikolic, Ljubomir Borovcanin, Radivoje Miletic, Milan Gvero, and Vinko Pandurevic">{{cite web|url=http://www.icty.org/x/cases/popovic/tdec/en/060926.pdf|title=Prosecutor v. Vujadin Popovic, Ljubisa Beara, Drago Nikolic, Ljubomir Borovcanin, Radivoje Miletic, Milan Gvero, and Vinko Pandurevic|quote=In the Motion, the Prosecution submits that both the existence and implementation of the plan to create an ethnically pure Bosnian Serb state by Bosnian Serb political and military leaders are facts of common knowledge and have been held to be historical and accurate in a wide range of sources.|access-date=8 February 2023|archive-date=11 December 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211211023111/https://www.icty.org/x/cases/popovic/tdec/en/060926.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="ICTY: Radoslav Brđanin judgement">{{cite web|url=https://www.un.org/icty/brdjanin/trialc/judgement/index.htm |title=ICTY: Radoslav Brđanin judgement |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090414072922/http://www.un.org/icty/brdjanin/trialc/judgement/index.htm |archive-date=14 April 2009 }}</ref><ref name="Tadic Case: The Verdict">{{cite web|url=http://www.icty.org/sid/7537|title=Tadic Case: The Verdict|quote=Importantly, the objectives remained the same: to create an ethnically pure Serb State by uniting Serbs in Bosnia and Herzegovina and extending that State from the FRY to the Croatian Krajina along the important logistics and supply line that went through opstina Prijedor, thereby necessitating the expulsion of the non-Serb population of the opstina.|access-date=8 February 2023|archive-date=14 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211014175448/https://www.icty.org/sid/7537|url-status=live}}</ref> and Croat<ref name="Prosecuter v. Jadranko Prlic, Bruno Stojic, Slobodan Praljak, Milivoj Petkovic and Valentin Coric and Berislav Pusic">{{cite web|url=http://www.icty.org/x/cases/prlic/acdec/en/080311.pdf|title=Prosecutor v. Jadranko Prlic, Bruno Stojic, Slobodan Praljak, Milivoj Petkovic, Valentin Coric and Berislav Pusic|quote=Significantly, the Trial Chamber held that a reasonable Trial Chamber, could make a finding beyond any reasonable doubt that all of these acts were committed to carry out a plan aimed at changing the ethnic balance of the areas that formed Herceg-Bosna and mainly to deport the Muslim population and other non-Croat population out of Herceg-Bosna to create an ethnically pure Croatian territory within Herceg-Bosna.|access-date=8 February 2023|archive-date=5 September 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210905185823/https://www.icty.org/x/cases/prlic/acdec/en/080311.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> forces performed ethnic cleansing of their territories planned by their political leadership to create ethnically pure states (] and ] by the Serbs; and ] by the Croats). | |||
| '''Silent ethnic cleansing''' is a term coined in the mid-1990s by some observers of the ]. Apparently concerned with ] media representations of atrocities committed in the conflict — which generally focused on those perpetrated by the ] — atrocities committed against Serbs were dubbed "silent", on the grounds that they were not receiving adequate coverage. <ref>Krauthammer, Charles: "When Serbs Are 'Cleansed,' Moralists Stay Silent", ''International Herald Tribune'', 12 August 1995</ref> | |||
| Survivors of the ethnic cleansing were left severely traumatized as a consequence of this campaign.{{sfnp|Weine|Becker|Vojvoda|Hodzic|1998|p=147}} | |||
| Since that time, the term has been used by other ethnically oriented groups for situations that they perceive to be similar — examples include both sides in ]'s ], and those who object to the expulsion of ] from former German territories during and after ]. | |||
| ] have engaged in a systemic displacement of Palestinian herders in ] as a form of nationalist and economic warfare.<ref>{{cite journal| first=Saad |last=Amira |year=2021 |title=The slow violence of Israeli settler-colonialism and the political ecology of ethnic cleansing in the West Bank |journal=Settler Colonial Studies |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=512–532 |doi=10.1080/2201473X.2021.2007747|s2cid=244736676 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/oct/21/the-most-successful-land-grab-strategy-since-1967-as-settlers-push-bedouins-off-west-bank-territory |title='The most successful land-grab strategy since 1967' as settlers push Bedouins off West Bank territory |date= October 21, 2023|work=The Guardian |archive-url=https://archive.today/20231022174942/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/oct/21/the-most-successful-land-grab-strategy-since-1967-as-settlers-push-bedouins-off-west-bank-territory |archive-date=22 Oct 2023 |last1=Graham-Harrison |first1=Emma |last2=Kierszenbaum |first2=Quique |location=Ein Rashash}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=בעוד העיניים נשואות לדרום ולעזה, הטיהור האתני בגדה מואץ |language=he |url=https://www.mekomit.co.il/%D7%91%D7%A2%D7%95%D7%93-%D7%94%D7%A2%D7%99%D7%A0%D7%99%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%A0%D7%A9%D7%95%D7%90%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%9C%D7%93%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%9D-%D7%95%D7%9C%D7%A2%D7%96%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%98%D7%99%D7%94%D7%95/ |date=19 Oct 2023 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20231022180318/https://www.mekomit.co.il/%D7%91%D7%A2%D7%95%D7%93-%D7%94%D7%A2%D7%99%D7%A0%D7%99%D7%99%D7%9D-%D7%A0%D7%A9%D7%95%D7%90%D7%95%D7%AA-%D7%9C%D7%93%D7%A8%D7%95%D7%9D-%D7%95%D7%9C%D7%A2%D7%96%D7%94-%D7%94%D7%98%D7%99%D7%94%D7%95/ |archive-date=22 Oct 2023 |work=Mekomit |last=Ziv |first=Oren |trans-title=While the eyes are on the south and Gaza, the ethnic cleansing in the West Bank is accelerating}}</ref> | |||
| Some observers, however, assert that the term should only be used to denote population changes that do not occur as the result of overt violent action, or at least not from more or less organized aggression - the absence of such stressors being the very factor that makes it "silent", although some form of coercion is still used. | |||
| When enforced as part of a political settlement, as happened with the ] through the forced resettlement of ethnic Germans to Germany in its reduced borders after 1945, the forced population movements, constituting a type of ethnic cleansing, may contribute to long-term stability of a post-conflict nation.<ref name="Judt, Tony 2005">Judt, Tony (2005). ''Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945''. Penguin Press.</ref>{{page needed|date=September 2016}} Some justifications may be made as to why the targeted group will be moved in the conflict resolution stages, as in the case of the ethnic Germans, some individuals of the large German population in ] and prewar ] had encouraged Nazi ] before World War II, but this was forcibly resolved.<ref name="Judt, Tony 2005"/>{{page needed|date=September 2016}} | |||
| An example of what may be defined as silent ethnic cleansing could be{{Fact|date=May 2009}} Israel's administrative policies in the occupied territories since the ] in 1967, which include land confiscations, court-ordered house demolitions and building of Jewish settlements and bypass roads, which some claim{{Who|date=May 2009}} are designed to "herd" the Palestinian population into enclaves. Such claims were made by Nobel Peace Prize Laureate ] in an open letter to President ] in May 2009. <ref name="open letter"></ref> | |||
| According to historian ], during an ethnic cleansing process, there may be destruction of physical symbols of the victims including ]s, books, monuments, graveyards, and street names: "Ethnic cleansing involves not only the forced deportation of entire nations but the eradication of the memory of their presence."<ref>{{Cite book |last=Naimark |first=Norman M. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=L-QLXnX16kAC |title=Fires of Hatred: Ethnic Cleansing in Twentieth-Century Europe |date=2002-09-19 |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=978-0-674-00994-3 |pages=209–211 |language=en}}</ref> In many cases, the side perpetrating the alleged ethnic cleansing and its allies have fiercely disputed the charge.{{Clarify|reason=please expand this|date=February 2024}} | |||
| ==Instances of ethnic cleansing == | |||
| {{Section OR|date=May 2009}} | |||
| This section lists incidents that have been termed "ethnic cleansing" by some academic or legal experts. Not all experts agree on every case; nor do all the claims necessarily follow definitions given in this article. Where claims of ethnic cleansing originate from non-experts (e.g., journalists or politicians) this is noted. | |||
| == |
== Instances == | ||
| {{main list|List of ethnic cleansing campaigns}} | |||
| Ancient ] began to utilize ] as a punishment for rebellions starting in the 13th century BC. By the 9th century BC, the Assyrians were regularly deporting thousands of restless subjects to other lands.{{Fact|date=April 2009}} | |||
| == See also == | |||
| ] was completely destroyed by ] in the ] (149-146 BC). Fifty thousand Carthaginians, perhaps a tenth of the original pre-war population, were sold into ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> After conquering western ] in 88 BC, ] reportedly ordered the killing of all ] living there. The massacre of Roman men, women and children is known as the ].<ref>Staff. , ]., Accessed ] 2007</ref> | |||
| {{Portal|Genocide}} | |||
| {{Main|Outline of genocide studies}}{{col div|colwidth=30em}}<!-- Please only list general topics, not any examples. That's for ] --> | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{colend}} | |||
| ==Explanatory notes== | |||
| During ]'s campaign against the ], the ]ic inhabitants of modern ], approximately 60% of the tribe was killed, and another 20% was taken into slavery. The remainder of the Helvetii were driven back into their old lands. During the war against ] trying to resist the Romans, Rome, led by ] ], pursued an extermination policy{{Fact|date=June 2008}} which included cleansing of the entire adult male population of ] and ], and all of its culture were forcibly shattered and replaced by Roman or pro-Roman ]s. There was ethnic cleansing and massacres of the ] population of ] by ]ic Britons during ]'s revolt in 60-61 AD.<ref></ref> | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| == |
== Notes == | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| * The Germanic ] were enslaved and deported from ] after the Vandal kingdom in North Africa was defeated by a ] army during a ] in 533 and 534.<ref></ref> | |||
| * {{Cite journal|last=Baracetti|first=Gaia|date=2009|title=Foibe: Nationalism, Revenge and Ideology in Venezia Giulia and Istria, I943-5|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/40542981|journal=Journal of Contemporary History|volume=44|issue=4|pages=657–674|doi=10.1177/0022009409339344|jstor=40542981|s2cid=159919208|issn=0022-0094}} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| | doi=10.2307/20045626 | |||
| | last=Bell-Fialkoff | first=Andrew | |||
| | title=A Brief History of Ethnic Cleansing | |||
| | journal=Foreign Affairs |volume=72 |issue=3 |year=1993 | |||
| | url=http://www.foreignaffairs.org/19930601faessay5199/andrew-bell-fialkoff/a-brief-history-of-ethnic-cleansing.html | |||
| | jstor=20045626 |pages=110–121 |url-status=dead | |||
| | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040203190219/http://www.foreignaffairs.org/19930601faessay5199/andrew-bell-fialkoff/a-brief-history-of-ethnic-cleansing.html | |||
| | archive-date=February 3, 2004 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| | first1 = Donald | |||
| | last1 = Bloxham | |||
| | author-link1 = Donald Bloxham | |||
| | first2 = Anthony | |||
| | last2 = Dirk Moses | |||
| | author-link2 = A. Dirk Moses | |||
| | editor-first1 = Donald | |||
| | editor-last1 = Bloxham | |||
| | editor-first2 = Robert | |||
| | editor-last2 = Gerwarth | |||
| | title = Political Violence in Twentieth-Century Europe | |||
| | chapter = Genocide and ethnic cleansing | |||
| | page = 125 | |||
| | year = 2011 | |||
| | publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| | doi = 10.1017/CBO9780511793271.004 | |||
| | isbn = 9781107005037 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|language = en | |||
| | location = Koper-Capodistria|date = 25 July 2000 | |||
| | title = Slovene-Italian Relations 1880–1956 | |||
| | url = https://www.kozina.com/premik/indexeng_porocilo.htm | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200223115751/https://www.kozina.com/premik/indexeng_porocilo.htm | |||
| | archive-date = 23 February 2020 | |||
| | chapter = Period 1941–1945 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20201105021740/http://www.kozina.com/premik/poreng4.htm | |||
| | ref={{harvid|Italian-Slovene commission}} | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| | editor-first1 = Ota | |||
| | editor-last1 = Konrád | |||
| | editor-first2 = Boris | |||
| | editor-last2 = Barth | |||
| | editor-first3 = Jaromír | |||
| | editor-last3 = Mrňka | |||
| | title = Collective Identities and Post-War Violence in Europe, 1944–48 | |||
| | year = 2021 | |||
| | publisher = Springer International Publishing | |||
| | page = 20 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=xXRREAAAQBAJ&pg=PA20 | |||
| | isbn = 9783030783860 | |||
| | access-date = 5 November 2022 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| | last=Petrovic |first=Drazen | |||
| | title=Ethnic Cleansing – An Attempt at Methodology | |||
| | journal=European Journal of International Law |volume=5 |issue=4 |year=1998 | |||
| | page=817 |url=http://www.ejil.org/pdfs/5/1/1247.pdf }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| | last = Thum | first = Gregor | |||
| | year = 2010 | |||
| | title = Review: Ethnic Cleansing in Eastern Europe after 1945 | |||
| | journal= Contemporary European History | volume= 19 | issue=1 | pages= 75–81 | |||
| | doi=10.1017/S0960777309990257 | s2cid = 145605508 | |||
| }} | |||
| * Vladimir Petrović (2007), (Ethnicisation of Cleansing), Hereticus 1/2007, 11–36 | |||
| * {{cite book | |||
| | first = Guido | |||
| | last = Rumici | |||
| | language = it | |||
| | title = Infoibati (1943–1945). I Nomi, I Luoghi, I Testimoni, I Documenti | |||
| | year = 2002 | |||
| | publisher = Ugo Mursia | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=x0ZnAAAAMAAJ&q=massacri+foibe+sloveni+croati+anticomunisti | |||
| | isbn = 978-88-425-2999-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Weine |last2=Becker |last3=Vojvoda |last4=Hodzic |title=Individual change after genocide in Bosnian survivors of "ethnic cleansing": Assessing personality dysfunction |first1 = Stevan M. |first2= Daniel F. |first3=Dolores |first4=Emir |year=1998 |doi=10.1023/A:1024469418811 |volume=11 |issue=1 |pmid=9479683 |journal=] |pages=147–153 |s2cid=31419500 }} | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| * According to a new study. According to research led by ] In early ], the ] sought to limit the entry of native ] genes into their population by restricting intermarriage, a policy that successfully wiped out a majority of original British genes in favour of ] ones, Anglo-Saxon settlers enjoyed a substantial social and economic advantage over the native ]<ref></ref> who lived in what is now ], for more than 300 years from the middle of the 5th century.<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| {{Library resources box}} | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| *In the ] of 1002, the Anglo-Saxon king ] ordered the death of all the ] living in the ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Basso |first1=Andrew R. |title=Destroy Them Gradually: Displacement as Atrocity |date=2024 |publisher=Rutgers University Press |isbn=978-1-9788-3130-8 |language=en}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Bulutgil |first1=H. Zeynep |title=The Roots of Ethnic Cleansing in Europe |date=2016 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-1-316-56528-5 |language=en}} | |||
| * The ], nomadic ] from the ], were nearly annihilated at the ] by a combined ] and ] army in 1091. Attacked again in 1094 by the Cumans, many Pechenegs were slain or absorbed.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Dahbour |first1=Omar |title=Nationalism and Human Rights: In Theory and Practice in the Middle East, Central Europe, and the Asia-Pacific |date=2012 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan US |isbn=978-1-137-01202-9 |pages=97–122 |language=en |chapter=National Rights, Minority Rights, and Ethnic Cleansing}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Gordon |first1=Neve|author-link=Neve Gordon |last2=Ram |first2=Moriel |title=Ethnic cleansing and the formation of settler colonial geographies |journal=Political Geography |date=2016 |volume=53 |pages=20–29 |doi=10.1016/j.polgeo.2016.01.010|url=https://eprints.soas.ac.uk/31016/1/Gordon_Ethnic%20cleansing%20and%20the%20formation%20of%20settler%20colonial%20geographies.pdf }} | |||
| * ] were frequently ] and exiled from various European countries. The persecutions rose during the ]. During the ] (1096) flourishing communities on the Rhine and the Danube were utterly destroyed; see ]. In the ] (1147) the ] were subject to frequent massacres. The Crusades were followed by expulsions, including in, 1290, the banishing of all English Jews; in 1396, 100,000 Jews were expelled from France.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Jenne |first1=Erin K. |title=The Routledge Handbook of Ethnic Conflict |date=2016 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-315-72042-5 |chapter=The causes and consequences of ethnic cleansing}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Lieberman |first1=Benjamin |title=Terrible Fate: Ethnic Cleansing in the Making of Modern Europe |date=2013 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |isbn=978-1-4422-3038-5 |language=en}} | |||
| * ] and ] expelled from ] and ] during the reign of ] dynasty of ] in the 12th century. Almohads gave a choice of either death or conversion to ], or exile. Some, such the family of ], fled east to the more tolerant ], while others went northward to settle in the growing Christian kingdoms.<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Pegorier |first1=Clotilde |title=Ethnic Cleansing: A Legal Qualification |date=2013 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-134-06783-1 |language=en}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Rikhof |first1=Joseph |title=Serious International Crimes, Human Rights, and Forced Migration |date=2022 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-003-09438-8 |chapter=Ethnic cleansing and exclusion}} | |||
| * At the beginning of the 13th century the eastern part of the ] was devastated by the ], which turned northern and eastern ] into a desert. Over much of ] speakers of ] were replaced by speakers of ].<ref></ref> | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Ther |first1=Philipp|author-link=Philipp Ther |title=The Dark Side of Nation-States |date=2014 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-1-78238-303-1 |language=en |chapter=The Dark Side of Nation-States: Ethnic Cleansing in Modern Europe}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * The ] was accomplished with much bloodshed over more than 50 years, during which native ] who remained unbaptised were subjugated, killed, or exiled. To replace the partially exterminated native population, the ] encouraged the ] of German colonists.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * In the 12th to 15th centuries, the Kingdom of France organized the near-total massacre of inhabitants of the southern provinces (the modern-day French regions of ], ], ] and ]). The effects of what was perceived the first recorded genocide in European history is a decline in the ] spoken there, although other factors like ] under the ] of the 19th and 20th centuries also applied. One major cause of the genocides in Southern France was religious schisms within the Roman Catholic Church: Included victims were the separate Christian sects like the ] and ] that developed in southern France at the time. | |||
| * In 1270, the Jews of ] were required either to leave or to embrace Islam.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ethnic cleansing of the ] from ] during the ] in 1282.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ] in 1325 was part of the ethnic cleansing of the Initial Coalescent people by the Middle Missouri villagers.<ref></ref> | |||
| * Northern ] remained predominantly ] until the destructions of ], a ] conqueror, at the end of the 14th century.<ref></ref> | |||
| * Between the 11th and 18th centuries, the ] expanded southward in a process known as {{lang|vi|nam tiến}} (''southward expansion''). In 1471 the kingdom of ] suffered a massive defeat by the Vietnamese, in which 120,000 ] were either captured or killed, and the kingdom was reduced to a small enclave near ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| *]'s large ] and ] minorities, inherited from that country's former ], were expelled following a ] in 1492, while ], called ]s or ]s, were ] between 1609 and 1614.<ref> Rezun, Miron, "Europe's Nightmare: The Struggle for Kosovo", (p. 6), Praeger/Greenwood (2001) ISBN 0-275-97072-8; Parker, Geoffrey, "Europe in Crisis", (p. 18), Blackwell Publishing (1979, 2000) ISBN 0-631-22028-3; Gadalla, Moustafa, "Egyptian Romany: The Essence of Hispania" (pp. 28-9), Tehuti Research Foundation (2004) ISBN 1-931446-19-9 </ref> | |||
| ===In early modern history=== | |||
| * Deportations of ] by Persian ], which begun in the 1530s under ]. Between 1604 and 1605 ] relocated some 150,000 Armenians to an area of ] called ].{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * Hundreds of thousands of ] and ] had been wiped out or driven from the lands of present-day Ukraine by ] during the ] (1648-1654).<ref></ref> As a result of events during ], population of ] dropped by one-third. | |||
| * After the ] and ] in 1652, ] had most of their lands confiscated and were banned from living in towns. As many as 100,000 ] men, women and children were forcibly taken to the colonies in the ] and ] as ] or ].<ref></ref> The contemporary commentator Prendergast reported that four fifths of Ireland's population was removed or killed and that whole counties were empty. Many were forcibly removed to poorer agricultural land in ]. Several thousand Irish soldiers were sold to the King of Spain, the Dutch and a Polish privateer. The death toll could have been over 1 million. | |||
| *] was taken temporarily by the ] forces during the ] with help of ] soldiers who lived in the Krajina within the Monarchy. After the Austrians retreated in 1690, hundreds of thousands of Serbs from Kosovo had to flee to ] and ] to evade ] reprisals.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| ===18th and 19th centuries=== | |||
| * Conflict between ] groups and newly arrived ] settlers increased during the 18th century under repressive economic and cultural reforms imposed by the ]. This led to armed conflict and large-scale migrations continuing into the late 19th century, the period during which most ] emigrated to ].<ref>Culas & Michaud, 68–74.</ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * In the ] of 1755 after the ] (]), the British deported around 4000 to 5000 French ] were deported from ]; many later settled in ], where they became known as ]{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * In 18th century, the ] were annihilated by ] in several campaigns. About 80% of the Dzungar population, or around 500.000 to 800.000 people, were killed during or after the Chinese conquest in 1755-1757.<ref></ref> The ] filled in the depopulated area with immigrants from many parts of their empire, but a century later the ] ravaged the same region. | |||
| * Expulsion and ethnic cleansing of the ]’s 40,000 ] settlers during the ] from 1791 to 1804. ], first ruler of an independent ], declared Haiti an all-black nation, slaughtered remaining whites on the island and forbade ] from ever again owning property or land there. | |||
| * Expulsion by Russia of more than a million ], ] and ] of the ] and ] steppes to ] after the ] was annexed by Russia in 1783.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * When the ] started, the Spanish enlisted the ]s, playing on their dislike of the '']s'' of the independence movement. ] led an army of llaneros which routinely killed white Venezuelans. After several more years of war, which killed half of ]'s white population, the country achieved independence from Spain in 1821.<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * During the ] in 1822, ] troops killed about 42,000 ] islanders of ]; sold 45,000 into ]; and exiled 23,000. Fewer than 2,000 Greeks managed to survive on the island.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * In the immediate aftermath of ]’s abdication in 1831, the poor people of color, including slaves, staged anti-] riots in the streets of ]'s larger cities.<ref></ref> | |||
| * On ] ], mainland ] invaded the ]. They massacred some 300 ] men, women and children, and enslaved the remaining 1,300 survivors. By 1862, only 101 Morioris were alive. Modern inhabitants are descendants of those who invaded and conquered the archipelago in 1835.<ref></ref> | |||
| * In the United States in the 19th century, particularly during the 1830s, the US government forced relocation of various Native American peoples from their traditional areas to more western, often remote reservations elsewhere in the country, a process known as ]. The ], which led to the deaths of about 2,000 to 8,000 ] from disease, and the ], are well-known examples.<ref>Perdue, Theda, "Cherokee Women and the Trail of Tears", in ''American Encounters: Natives and Newcomers from European Contact to Indian Removal, 1500-1850'', p. 526, (Routledge (UK), 2000)</ref><ref>Committee on Indian Affairs, US Senate, ''Cherokee Settlement and Accommodation Agreements Concerning the Navajo and Hopi Land Dispute'', (US Government Printing Office, 1996)</ref> | |||
| *]: 16,000 Cherokee who had adopted colonial white cultural norms of housing, clothes, business and language were forcibly removed from their ancestral lands and placed into internment camps where 2000 to 3000 would die from disease. The Survivors were then ] 1200 miles to tribal reservation lands, 2000 to 3000 more died of disease, exposure, and starvation in these marches{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| *], On February 25, 1831, U.S. President ] began the forced marched of 15,000 Choctaw out of their ancestral lands, 2500 died of starvation and exposure along the way.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ], estimated at 8,000 people in 1803, were reduced to a population of around 300 by 1833, although much of this has been attributed to the effect of ]s to which they had no natural immunity (including ] and ]) and ].<ref></ref> Estimates of the total number of Tasmanian deaths at the hands of European settlers vary, with some controversial estimates ranging as low as 118 in the period from 1803 until 1847.<ref></ref> This conflict is a subject of the ]n ].{{Fact|date=May 2009|No citiation that this was ethnic cleansing}} | |||
| * during the ], the ] performed ethnic cleansing of the white ] and light-skinned ] people from the eastern ] and the territory of ]. The greatest success of the Maya revolt was reached in the spring of 1848, with the Europeans and Mestizos driven from most of the peninsula, other than the walled cities of ] and ] and the south-west coast.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] are an ethnic group indigenous to ], northern ], the ], much of ], and the southernmost third of the ]. As Japanese settlement expanded, the Ainu were pushed northward, until by the ], they were confined by the government to a small area in Hokkaidō, in a manner similar to the placing of Native Americans on reservations.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] tribes, in 1842-1847, expelled the ] Christian population from Eastern ].<ref></ref> | |||
| * After the ] countries (e.g., ], ], ]) achieved independence from the ] from early 1800s to early 1900, they expelled Turkish, Muslim, and Jewish populations from within their territories.<ref>Justin McCarthy, ''Death and Exile: The Ethnic Cleansing of Ottoman Muslims, 1821-1922'', (Princeton, N.J: Darwin Press, c1995</ref> | |||
| *Expulsion of Muslim populations in ] by imperial ] throughout 19th century. Particularly, expulsion of ] to ] in 1864.<ref>McCarthy, ''ibid.''</ref> (see ] for more details) | |||
| * During the mid-19th century, the ]s of ] revolted against the ], most notably in the ] (1862-1877) and the ] 1856-1873) in ]. The Manchu government committed genocide to suppress these little known revolts.<ref>Levene, Mark. Genocide in the Age of the Nation-State. I.B.Tauris, 2005. ISBN 1845110579, page 288</ref><ref>Giersch, Charles Patterson. Asian Borderlands: The Transformation of Qing China's Yunnan Frontier. Harvard University Press, 2006. ISBN 1845110579, page 219</ref><ref>Dillon, Michael. . Curzon, 1999. ISBN 0700710264, page xix</ref> killing a million people in the ],<ref>Damsan Harper, Steve Fallon, Katja Gaskell, Julie Grundvig, | |||
| Carolyn Heller, Thomas Huhti, Bradley Maynew, Christopher Pitts. Lonely | |||
| Planet China. 9. 2005. ISBN 1740596870</ref><ref name=chineseciv>Gernet, | |||
| Jacques. A History of Chinese Civilization. 2. New York: Cambridge | |||
| University Press, 1996.ISBN 0521497124 </ref> and several million in the ].<ref name=chineseciv/> A ''"washing off the Muslims"''(洗回 (xi Hui)) policy had been long advocated by officials in the ] government.<ref>Jonathan N. Lipman, "Familiar Strangers: A History of Muslims in Northwest China (Studies on Ethnic Groups in China)", University of Washington Press (February 1998), ISBN 0295976446.</ref> | |||
| ===20th century=== | |||
| * ] (1914-23); Violent campaigns instigated by the Ottoman Turks against the ] community of ] ] area. In this area an estimated 350,000 were killed.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] (1919); Greece and Bulgaria exchange minority populations, with some exceptions.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] and ] by Greek troops after their defeat in the Greco Turkish War. ] and sack of ] by Turkish troops.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ] of Greeks from Turkey and of Turks from Greece after the ] as a consequence of the ] in 1923.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ] regime killed or deported an estimated 300,000 to 500,000 ] during the ], in 1919-1920.<ref>Kort, Michael (2001). ''The Soviet Colossus: History and Aftermath'', p. 133. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 0-7656-0396-9.</ref> | |||
| *Thousands of armed whites burned down a black neighborhood, known as the ] of Tulsa, Oklahoma in the ], one of the USA's costliest racial riots and civil disorder.<ref name="Tulsa Race Riot" /> Sixteen hours of rioting on May 31 and June 1, 1921 resulted in over 800 people admitted to local hospitals with injuries, an estimated 10,000 left homeless, 35 city blocks composed of 1,256 residences destroyed by fire, and $1.8 million in property damage.<ref name="Tulsa Race Riot" /> Twenty-three black and 16 white citizens were reported killed, but estimates suggest as many as 300, mostly blacks, died.<ref name="Tulsa Race Riot" /> | |||
| *] In January 1923, mobs of "whites" attacked a small Black community of 350 people, murdered more six blacks and burned every house and church to the ground. ], a rural village several miles outside ], was never repopulated.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ] deported ] from ], ] and European Russia to ] in 1934-1938.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] by the ] from the ] to ] from September to October 1937. More than 172,000 Koreans were deported.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * During the ], the US government pushed out an estimated half million ] from the ] to ], in the ]. Approximately 60% of those hastily deported were naturalized citizens and descendants who lived in the US for over 10 years, including US-born children of Mexican parents. Mexican-Americans whose ancestry dated back to the 19th century pre-annexation period were harassed by INS officials out of ] and fears of a "]" of the American Southwest.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * Forced displacement of 150,000 ] after October 1, 1938, when the German army entered the border regions of ] surrendered in accordance with the ].<ref>, Radio Prague</ref> | |||
| * The German government's persecutions and expulsions of ] in ], ] and other ]-controlled areas prior to the initiation of ]. Estimated number of those who died in the process is being debated by historians and between 750,000 - 6 million Jews.<ref>Naimark, ''op. cit.''</ref> | |||
| * During the ] occupation of ] during ] the Russian-speaking population of the city of ] was held in an ].{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * Expulsion of ethnic ] and ] from ], ], and ] following the ] and ].{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ]. During World War II, Nazis planned to ethnically cleanse the whole Polish population. Eventually during ] up to 1.6 to 2 million ] were expelled, not counting millions of ] deported from Poland.<ref></ref> | |||
| * More than 250,000 ] were expelled from ] by the extreme nationalist ] regime during the ], in 1941-1945.<ref></ref> | |||
| *During WWII, ] and ] in camps due to fears that Japanese immigrants might be a ] supporting the ].{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * During WWII, in ], some 10,000 Serbs lost their lives<ref name=Krizman>Serge Krizman, Maps of Yugoslavia at War, Washington 1943.</ref><ref name=Istorija>ISBN 86-17-09287-4: Kosta Nikolić, Nikola Žutić, Momčilo Pavlović, Zorica Špadijer: Историја за трећи разред гимназије природно-математичког смера и четврти разред гимназије општег и друштвено-језичког смера, Belgrade, 2002, pg. 182</ref>, and about 80<ref name=Krizman/> to 100,000<ref name=Krizman/><ref name=Annexe>, by the Serbian Information Centre-London to a report of the Select Committee on Foreign Affairs of the ] of the ].</ref> or more<ref name=Istorija/> were ethnically cleansed. | |||
| * Deportation of ]s by ] to ], ], ], and other remote areas, in 1941-1942.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] of ], ], ], ], ], ]s, and ] by ] to ] and ], 1943-1944.<ref></ref> | |||
| * The ethnic cleansing of ], or the ] by ] partisans during the winter of 1944-45, about 40.000 massacred.<ref>''</ref> Afterwards, between 45-48, internation camps were set which led directly to the death of 70.000 more, of famine, frost, plagues, tortures and executions{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ethnic cleansing and ] by nationalist ] which took place in 1943 and 1944, with the bulk of victims reported for summer and autumn 1944.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The ethnic cleansing of ] from Southern ] by Greeks which took place in 1944 and 1945, circa 18,000-35000<ref> Victor Roudometof, Collective Memory, National Identity, and Ethnic Conflict Greece, Bulgaria, and the Macedonian Question, p.181-182 The figure of 30,000 is adopted from the Cham associations without checking the other sources used in the discussion in this chapter.</ref> ] to Albania, and from several hundred to 2,800 killed. | |||
| * ]. From 1944 until 1948, between 13.5 and 16.5 million ] were expelled, ] or fled from Central and Eastern Europe, making this the largest single instance of ethnic cleansing in recorded history. Estimated number of those who died in the process is being debated by historians and estimated between 500,000 and 3,000,000.<ref>'''', European University Institute, Florense. EUI Working Paper HEC No. 2004/1, Edited by Steffen Prauser and Arfon Rees pp. 4</ref> | |||
| * ] during and after World War II. The ] of 350,000 ] from ], ] and dalmatian ] lands, after the collapse of Italian ] regime and the annexation of the region to Yugoslavia.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ], under Soviet occupation following ] and soon to become a battlefield between the ] and the ] was home to hundreds of thousands of ] citizens. ] and ], now free from Japanese rule, and ], under Soviet military occupation, were Japanese territories before World War II and had millions of ] residents. All these were now to be expelled. {{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * The mass deportation of ] speaking ethnic minorities from the territory of ] after ], culminating in 1947 with the start of ]. Millions of ] were simultaneously deported from ] into the western territories, which Soviets transferred from Germany to Poland. By 1950, 5 million Poles had been settled in what the government called the ].{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * ] regime in ] begins evictions of the ] community, approx. 75,000 migrate.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * Mass expulsions of ]s and ]s from ] to ], and of ] from India to Pakistan. The controversy surrounding the ] in 1947<ref> Talbot, Ian: "India and Pakistan", (pp. 198-99), Oxford University Press (2000) ISBN 0-340-70632-5 </ref>, resulted in the killings of ]s, ]s and ]s in riots. Well over 10 million people were violently displaced, and up to 500,000 lost their lives. However, unlike most other instances, ''no government agencies'' actively took part in the bloodshed, although reportedly a limited number of Indian and Pakistani troops and police posted along the border were partisan in their sympathies and abetted the rioters. Those that did not (as well as the last remaining British officers) were simply overwhelmed by the magnitude of the violence and could do little to stop it.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * After India's annexation of the ] state of ] by India in 1948, they interned or deported about 7,000 Hadrami ]. <ref></ref> | |||
| * The ], in which the substantial majority of Arab ] (approximately 700,000) in the areas of ] that became part of ] fled or were forced to leave in the ].<ref> ], The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. Cambridge University Press. (2004) ISBN 0-521-00967-7 </ref><ref>Yoav Gelber, Palestine 1948: War, Escape and the Emergence of the Palestinian Refugee Problem. Sussex Academic Press. (2005) ISBN 1-84519-075-0 </ref><ref> ], Ethnic Cleansing of Palestine. Oxford: Oneworld. (2006) ISBN 1-85168-467-0 </ref> The circumstances of these events are still hotly debated among historians and commentators of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. | |||
| * Between the ] and the ] in 1967, there was a ], in which 99 percent of ] (approximately 800,000 people) left Arab countries of North Africa and the Mediterranean. Many migrated to Israel; others to the United States and Europe. The major populations affected were in ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ].<ref> Itamar Levin, ''Locked Doors: The Seizure of Jewish Property in Arab Countries''. Praeger/Greenwood. (2001) ISBN 0-275-97134-1 </ref><ref>Shohat, Ella: "Sephardim in Israel: Zionism from the Standpoint of Its Jewish Victims", ''Social Text'', No. 19/20, (Autumn, 1988), (pp. 1-35), Duke University Press</ref><ref> Maurice Roumani, The Case of the Jews from Arab Countries: A Neglected Issue, Tel Aviv: World Organization of Jews from Arab Countries. (1977) ASIN B0006EGL5I</ref><ref> Malka Hillel Schulewitz, The Forgotten Millions: The Modern Jewish Exodus from Arab Lands. London. (2001) ISBN 0-8264-4764-3</ref><ref>Ran HaCohen, </ref> | |||
| * After the ] achieved independence from ] in 1949, around 300.000 people, predominantly ]s or Dutch Indonesians (people of mixed Indonesian and European descent), fled or were expelled.<ref></ref> | |||
| * ]is who have fled the Indian military action in Kashmir, have migrated to Pakistan, as well as to Great Britain, Canada and the USA.<ref></ref> ] have also been displaced due to the ongoing and anti-] insurgency. Some 300,000 Hindus have been internally displaced from Kashmir due to the violence.<ref>, ''The World Factbook''. Retrieved 20 May 2006.</ref> | |||
| *In the aftermath of the 1949 Durban Riots (an inter-racial conflict between ]s and ]), hundreds of Indians fled Cato Manor.<ref>, TheIndianStar.com</ref> | |||
| * On 5 and 6 September 1955 the ] or "Septembrianá"/"Σεπτεμβριανά", secretly backed by the Turkish government, was launched against the Greek population of ]. The mob also attacked some Jews and Armenians of the city. The event contributed greatly to the gradual extinction of the Greek minority in the city and country, which numbered 100,000 in 1924 after the Turko-Greek population exchange treaty. By 2007 there were only 5000 Greeks. The Turkish government further forced expulsion of the Greek minority in the ] and ] islands in the period 1923-1993.{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * Between 1957-1962 President ] of Egypt carried out an Aati-European policy, which resulted in the expulsion of 100-200,000 ] from ] and the rest of ]. Many other ] were expelled, such as ] and ].{{Fact|date=May 2009}} | |||
| * On 5 July 1960, five days after the ] gained independence from Belgium, the ] garrison near ] mutinied against its white officers and attacked numerous European targets. This caused the fear amongst the approximately 100,000 ] still resident in the Congo and led to their mass exodus from the country.<ref></ref> | |||
| *] rise to power in 1962 and his relentless persecution of "resident aliens" (immigrant groups not recognised as citizens of the ]) led to an exodus of some 300,000 ]. They migrated to escape racial discrimination and wholesale nationalisation of private enterprise a few years later in 1964.<ref>{{cite book|author=Martin Smith|year=1991|title=Burma - Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity|publisher=Zed Books|location=London,New Jersey|pages=43–44,98,56–57,176}}</ref><ref>, TIME</ref> | |||
| *The creation of the ] system in South Africa, which began in 1948 but reached full flower in the 1960s and 1970s, involved some ethnic cleansing, including the separation of blacks, ], and whites into separate residential areas and private spheres. The government created ], which involved ] of non-white populations to reserved lands.<ref> Bell, Terry: ''Unfinished Business: South Africa, Apartheid and Truth'', (pp. 63-4), Verso, (2001, 2003) ISBN 1-85984-545-2 </ref><ref> Valentino, Benjamin A., ''Final Solutions: Mass Killing and Genocide in the Twentieth Century'', (p. 189), Cornell University Press, (2004) ISBN 0-8014-3965-5. </ref> The governing minority forced relocation of the majority to different areas, as well as restricting their movement, education and social activities.{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * As Algeria fought for independence, it expelled the '']'' population of European descent and ]; most fled to ], where they had citizenship. In just a few months in 1962, 900,000 of these European descendants and native Jewish people left the country.<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * ] forced ethnic cleansing of ] and ] from the nation in 1964.<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * Some 150,000 Italians settled in ], constituting about 18% of the total population.<ref></ref> In 1970, the government expelled all of Libya's ethnic ], a year after ] seized power (a "day of vengeance" on 7 October, 1970).<ref></ref> | |||
| * By 1969, more than 350,000 ]ans were living in ]. In 1969, Honduras enacted a new land reform law. This law took land away from Salvadoran immigrants and redistributed this land to native-born Honduran peoples. Thousands of Salvadorans were displaced by this law (see ]).{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * During the ] of 1971 around 10 million ], mainly ], fled the country to escape the killings and ] committed by the ] Army. Furthermore, many intellectuals and other religious minorities were targeted by death squads and '']''. {{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * ]'s regime forced the expulsion in 1972 of ]'s entire ethnic ] population, mostly of Indian descent.<ref></ref> | |||
| *Greek Cypriots and Greek military forced ] out of Greek territory in Cyprus from 1963-1974. <ref></ref> | |||
| * The ethnic cleansing in 1974-76 of the ] population of the areas under Turkish military occupation in ] during and after the ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9E0CE7D6143AF936A3575AC0A964958260|title='Ethnic cleansing', Cypriot style|date=1992-09-05|work=New York Times|accessdate=2008-12-29}}</ref> | |||
| * Following the U.S. withdrawal from ] in 1975, the Lao kingdom was overthrown by the communists and the ] became targets of retaliation and persecution. Thousands made the trek to and across the ] into ], often under attack. This marked the beginning of a ] from ].{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * The ] regime in ] disproportionately targeted ethnic minority groups. These included ethnic ], ] and ]. In the late 1960s, an estimated 425,000 ethnic Chinese lived in Cambodia, but by 1984, as a result of Khmer Rouge ] and emigration, only about 61,400 Chinese remained in the country. The ] Muslims suffered serious purges with as much as half of their population exterminated. A Khmer Rouge order stated that henceforth “The Cham nation no longer exists on Kampuchean soil belonging to the ]” (U.N. Doc. A.34/569 at 9).<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * Subsequent waves of hundreds of thousands of ] fled ] and many refugees inundated neighbouring Bangladesh including 250,000 in 1978 as a result of the ].{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * The ] resulted in the discrimination and consequent migration of ]'s ]. Many of these people fled as "]". In 1978-79, some 450,000 ethnic Chinese left Vietnam by boat as refugees (many officially encouraged and assisted) or were expelled across the land border with China.{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * Aftermath of ] assassination in 1984 Oct 31, the ruling party ] supporters formed large mobs and killed around 3000 ] around Delhi which is known as the ] during the next four days. The mobs using the support of ruling party leaders used the Election voting list to identify Sikhs and kill them. | |||
| ] ]] | |||
| * The forced assimilation campaign of the late 80s directed against ethnic ] resulted in the emigration of some 300,000 ] to Turkey.{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * The ] conflict has resulted in the displacement of population from both sides. 528,000 ] from Nagorno Karabakh Armenian controlled territories including Nagorno-Karabakh, and 185,000<ref name="autogenerated1">Building Security in Europe's New Borderlands, Renata Dwan, M.E. Sharpe (1999) p. 148</ref> to 220,000 Azeris, 18,000 ] and 3,500 Russians fled from ] to Azerbaijan from 1988 to 1989.<ref>De Waal, ''Black Garden'', p. 285</ref> 280,000 to 304,000<ref name="autogenerated1" /> persons—virtually all ethnic ]—fled ] during the 1988–1993 war over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh.<ref></ref> | |||
| * Since April 1989, some 70,000 black Mauritanians—members of the ], ], ] and ] ethnic groups—have been expelled from ] by the Mauritanian government.<ref></ref> | |||
| * In 1989, after bloody pogroms against the ] by ] in Central Asia's ], nearly 90,000 Meskhetian Turks left ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * In 1991, following a crackdown on ] Muslims in ], 250,000 refugees took shelter in the ] district of neighbouring Bangladesh.<ref>, BBC News</ref> | |||
| * As a result of ], about 100,000 ethnic ] fled ] and Georgia proper, most across the border into North Ossetia. A further 23,000 ethnic ] fled South Ossetia and settled in other parts of ].<ref> Human Rights Watch/Helsinki, , May 1996.</ref> According to ], the campaign of ethnic-cleansing was orchestrated by the Ossetian militants, during the events of ], which resulted in ] of approximately 60,000 ] inhabitants from Prigorodny District.<ref>Russia: The Ingush-Ossetian Conflict in the Prigorodnyi Region (Paperback) by Human Rights Watch Helsinki Human Rights Watch (April 1996) ISBN 1564321657</ref> | |||
| * The widespread ethnic cleansing accompanying the ] from 1991 to 1999, of which the most significant examples occurred in eastern ] and self-proclaimed ] (1991-1995) (see ]), in most of ] (1992-1995), and in the ]-dominated breakaway ] province (of ]) (1999). Large numbers of ], ], ] and ] were forced to flee their homes and expelled.<ref>Committee on Foreign Relations, US Senate, ''The Ethnic Cleansing of Bosnia-Hercegovina'', (US Government Printing Office, 1992)</ref> Beginning in 1991, political upheavals in the ] displaced about 2,700,000 people by mid-1992, of which over 700,000 of them sought asylum in ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * The forced displacement and ] of more than 250,000 people, mostly ] but some others too, from ] during the conflict and after in 1993 and 1998.<ref> Bookman, Milica Zarkovic, "The Demographic Struggle for Power", (p. 131), Frank Cass and Co. Ltd. (UK), (1997) ISBN 0-7146-4732-2 </ref> | |||
| * The 1994 massacres of nearly 1,000,000 ] by ], known as the ]<ref> Leeder, Elaine J., "The Family in Global Perspective: A Gendered Journey", (p. 164-65), Sage Publications, (2004) ISBN 0-7619-2837-5 </ref><sup></sup>{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * The mass expulsion of southern ]s (Bhutanese of Nepalese origin) by the northern ] majority of ] in 1990.<ref> </ref> The number of refugees is approximately 103,000.<ref></ref> | |||
| * An estimated 1,000 ] were killed, tens of thousands of houses were destroyed by the ]-dominated government of ] in what is commonly known as ].The murder, looting and general destruction of property was well organized. Mobs armed with petrol were seen stopping passing motorists at critical street junctions and, after ascertaining the ethnic identity of the driver and passengers, setting alight the vehicle with the driver and passengers trapped within it. Mobs were also seen stopping buses to identify Tamil passengers and subsequently these passengers were knifed, clubbed to death or burned alive.{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * In October 1990, the militant ] (LTTE), forcibly ] the entire ethnic ] population (approx 75,000) from the Northern Province of ]. The Muslims were given 48 hours to vacate the premises of their homes while their properties were subsequently looted by ]. Those who refused to leave were killed. This act of ethnic cleansing was carried out so the ] could facilitate their goal of creating a mono-ethnic Tamil state in Northern Sri Lanka.{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| * Displacement of more than 500,000 ] and ethnic ] civilians living in ] during the ] in 1994-1996.<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * The ] targeted many ]s. Suffering from lootings and arsons, many Chinese Indonesians fled from ].<ref>, August 29, 1998, CNN</ref><ref>, Business Week</ref> | |||
| * More than 800,000 Kosovar ] fled their homes in ] during the ] in 1998-9, after being expelled. Although on the contrary over 200,000 ] and other non-Albanian minorities were forced out of Kosovo during and after the war while most ] returned.<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * There have been serious outbreaks of inter-ethnic ] on the island of Kalimantan since 1997, involving the indigenous ]s and immigrants from the island of ]. In 2001 in the Central ] town of Sampit, at least 500 ] were killed and up to 100,000 Madurese were forced to flee. Some Madurese bodies were decapitated in a ritual reminiscent of the ] tradition of the Dayaks of old.<ref></ref> | |||
| ===21st century=== | |||
| * In 2003, Sinafasi Makelo, a representative of ] ], told the UN's Indigenous People's Forum that during the ], his people were hunted down and eaten as though they were game animals. Both sides of the war regarded them as "subhuman" and some say their flesh can confer magical powers. Makelo asked the ] to recognise ] as a crime against humanity and an act of ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * In the late-1990s and early 2000s, ] organized and armed by the ]n military and police forces murdered large numbers of civilians in ].<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref><ref>James M. Lutz, Brenda J. Lutz, ''''</ref><ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * Since the mid-1990s the central government of ] has been trying to move ] out of the ]. As of October 2005, the government has resumed its policy of forcing all Bushmen off their lands in the Game Reserve, using armed police and threats of violence or death.<ref name="Daily Telegraph">{{cite web |url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2005/10/29/wbot29.xml&sSheet=/news/2005/10/29/ixworld.html | |||
| |title=Bushmen forced out of desert after living off land for thousands of years |publisher=The Daily Telegraph |accessdate=2005-10-29}}</ref> Many of the involuntarily displaced Bushmen live in squalid resettlement camps and some have resorted to ] and ], while about 250 others remain or have surreptitiously returned to the ] to resume their independent lifestyle.<ref></ref> “How can we continue to have ] creatures in an age of computers?“ asked Botswana’s president ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| * Attacks by the ], militias of ] on the ] population of ], a region of western Sudan.<ref> Collins, Robert O., "Civil Wars and Revolution in the Sudan: Essays on the Sudan, Southern Sudan, and Darfur, 1962-2004 | |||
| ", (p. 156), Tsehai Publishers (US), (2005) ISBN 0-9748198-7-5 .</ref><ref>Power, Samantha "Dying in Darfur: | |||
| Can the ethnic cleansing in Sudan be stopped?", ''The New Yorker'', ] ]. | |||
| Human Rights Watch, (web site, retrieved ] ]). | |||
| Hilary Andersson, , ''BBC News'', 27 May 2004.</ref> A ] ] article notes that in the past two months up to 75,000 Arabs from ] and ] crossed the border into Darfur. Most have been relocated by the Sudanese government to former villages of displaced non-Arab people. Some 2.5 million have now been forced to flee their homes after attacks by Sudanese troops and Janjaweed militia.<ref></ref> | |||
| *Currently in the ] (2003 to present), entire neighborhoods in ] are being ethnically cleansed by ] and ] militias.<ref></ref><ref></ref> Some areas are being evacuated by every member of a particular group due to lack of security, moving into new areas because of fear of reprisal killings. As of ] ], the ] estimated that 2.2 million Iraqis had been displaced to neighboring countries, and 2 million were displaced internally, with nearly 100,000 Iraqis fleeing to Syria and Jordan each month.<ref></ref><ref>. Alexander G. Higgins, ''],'' ], ]</ref><ref></ref> | |||
| *Although ] represent less than 5% of the total Iraqi population, they make up 40% of the ] now living in nearby countries, according to ].<ref></ref><ref></ref> In the 16th century, Christians constituted half of Iraq's population.<ref></ref> In 1987, the last Iraqi census counted 1.4 million Christians.<ref></ref> But as the ] has allowed the growth of militant ], Christians' total numbers slumped to about 500,000, of whom 250,000 live in Baghdad.<ref></ref> Furthermore, the ] and ] communities are at the risk of elimination due to the ongoing atrocities by ] extremists.<ref></ref><ref></ref> A ] ] article notes that in the past 7 months only 69 people from Iraq have been granted ] in the ].<ref>Ann McFeatters: . '']'' May 25, 2007</ref> | |||
| * The ethnic cleansing of ] population of some racially mixed ] neighborhoods by ] ]. According to gang experts and law enforcement agents the ] leaders, or shot callers, have issued a "green light" on all blacks.<ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| *In October 2006, ] announced that it would deport the ] living in the Diffa region of eastern Niger to Chad.<ref></ref> This population numbered about 150,000.<ref></ref> While the government was rounding Arabs in preparation for the ], two girls died, reportedly after fleeing government forces, and three women suffered miscarriages. Niger's government had eventually suspended a controversial decision to deport Arabs.<ref></ref><ref></ref> | |||
| *In 1950, the ] had become the largest of 20 minority groups participating in an insurgency against the ] in ]. The conflict continues as of 2008. In 2004, the BBC, citing ], estimates that up to 200,000 Karen have been driven from their homes during decades of war, with 120,000 more refugees from Burma, mostly Karen, living in ]s on the Thai side of the border. Many accuse the military government of Burma of ethnic cleansing.<ref>, BBC News</ref> As a result of the ] in minority group areas more than two million people have fled Burma to ].<ref>, Refugees International</ref> | |||
| *] erupted in December 2007.<ref></ref> By ], ], the death toll from the violence was at around 800.<ref></ref> The United Nations estimated that as many as 600,000 people have been displaced.<ref></ref><ref></ref> A government spokesman claimed that Odinga's supporters were "engaging in ethnic cleansing".<ref></ref> | |||
| *The ] began on February 3, 2008. Incidences of violence against ]ns and their property were reported in ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. Nearly 25,000 North Indian workers fled Pune,<ref name="IE_Pune_flee">{{cite news|url=http://www.expressindia.com/latest-news/25-000-North-Indian-workers-leave-Pune/276576/3/|accessdate=2008-04-06|title=25000 North Indian workers leave Pune|publisher='']''}}</ref><ref name="TOI_Pune_flee">{{cite news|title=25000 North Indians leave, Pune realty projects hit|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/25000_North_Indians_leave_Pune_realty_projects_hit_/articleshow/2809937.cms|accessdate=2008-04-04|publisher='']''}}</ref> and another 15,000 fled Nashik in the wake of the attacks.<ref name="TOI_Nashik_flee">{{cite news|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/articleshow/2780795.cms|accessdate=2008-04-06|publisher='']''|date=2008-02-14|title=Maha exodus: 10,000 north Indians flee in fear}}</ref><ref name="Red_Nashik_flee">{{cite news|url=http://www.rediff.com/news/2008/feb/13nasik1.htm|accessdate=2008-04-06|title=MNS violence: North Indians flee Nashik, industries hit|date=2008-02-13|publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| *] erupted on 11 May 2008 within three weeks the death toll was with 670 injured by the violence when South Africans ejected non-nationals in a nationwide ethnic cleansing / Xenophobic outburst ejecting the "makwerekwere" . The most affected have been Zimbabweans (30 000), Mozambiqueans (20 000 have returned to Mozambique), Somalians, Ethiopians, Congolese, Angolans. Local South Africans have also been caught up in the violence and so have other non-African nationals. Arvin Gupta, a senior UNHCR protection officer, said the UNHCR did not agree with the City of Cape Town that those displaced by the violence should be held at camps across the city.{{Fact|date=May 2009|citation needed that caims that this was ethnic cleansing.}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Genocide|GenocidePortalLogo(ESR)2.JPG}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], civilian, non-combatant persons killed or injured by direct military action | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], a computer game. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ===Bibliography=== | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Bell-Fialkoff, Andrew |title=A Brief History of Ethnic Cleansing |journal=Foreign Affairs |volume=72 |issue=3 |year=1993 |pages=110}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Jackson Preece, Jennifer |title=Ethnic Cleansing As An Instrument of Nation-State Creation |journal=Human Rights Quarterly |volume=20 |issue=4 |year=1998 |pages=359 |doi=10.1353/hrq.1998.0039}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |author=Petrovic, Drazen |title=Ethnic Cleansing - An Attempt at Methodology |journal=European Journal of International Law |volume=5 |issue=4 |year=1998 |pages=817}} | |||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| {{Commons category|Ethnic cleansing|lcfirst=yes}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{wiktionary|ethnic cleansing}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{ethnicity}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{genocide topics}} | |||
| * - Images of ethnic cleansing in Sudan | |||
| {{nationalism}} | |||
| * , Paper 951, 2006, ] School of Law (PDF) | |||
| {{segregation by type}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{racism topics|state=collapsed}}{{Discrimination}}{{Authority control}} | |||
| * | |||
| * ] ], World Science | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Racism topics|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Ethnic Cleansing}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 21:07, 23 December 2024
Systematic removal of a certain ethnic or religious group For other uses, see Ethnic cleansing (disambiguation).
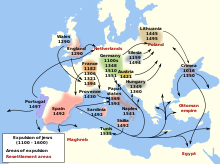
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, or religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making the society ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal such as deportation or population transfer, it also includes indirect methods aimed at forced migration by coercing the victim group to flee and preventing its return, such as murder, rape, and property destruction. Both the definition and charge of ethnic cleansing is often disputed, with some researchers including and others excluding coercive assimilation or mass killings as a means of depopulating an area of a particular group.
Although scholars do not agree on which events constitute ethnic cleansing, many instances have occurred throughout history. The term was first used to describe Albanian nationalist treatment of the Kosovo Serbs in the 1980s, and entered widespread use during the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s. Since then, the term has gained widespread acceptance due to journalism. Although research originally focused on deep-rooted animosities as an explanation for ethnic cleansing events, more recent studies depict ethnic cleansing as "a natural extension of the homogenizing tendencies of nation states" or emphasize security concerns and the effects of democratization, portraying ethnic tensions as a contributing factor. Research has also focused on the role of war as a causative or potentiating factor in ethnic cleansing. However, states in a similar strategic situation can have widely varying policies towards minority ethnic groups perceived as a security threat.
Ethnic cleansing has no legal definition under international criminal law, but the methods by which it is carried out are considered crimes against humanity and may also fall under the Genocide Convention.
Etymology


An antecedent to the term is the Greek word andrapodismos (ἀνδραποδισμός; lit. "enslavement"), which was used in ancient texts. e.g., to describe atrocities that accompanied Alexander the Great's conquest of Thebes in 335 BCE. The expulsion of the Moriscos from Spain between 1609 and 1614 is considered by some authors to be one of the first episodes of state-sponsored ethnic cleansing in the modern western world. Raphael Lemkin, who coined the term "genocide", considered the displacement of Native Americans by American settlers as a historical example of genocide. Others, like historian Gary Anderson, contend that genocide does not accurately characterize any aspect of American history, suggesting instead that ethnic cleansing is a more appropriate term. Circassian genocide, also known as "Tsitsekun", is often regarded by various historians as the first large-scale ethnic cleansing campaign launched by a state during the 19th century industrial era. Imperial Russian general Nikolay Yevdakimov, who supervised the operations of Circassian genocide during 1860s, dehumanised Muslim Circassians as "a pestilence" to be expelled from their native lands. Russian objective was the annexation of land; and the Russian military operations that forcibly deported Circassians were designated by Yevdakimov as “ochishchenie” (cleansing).
In the early 1900s, regional variants of the term could be found among the Czechs (očista), the Poles (czystki etniczne), the French (épuration) and the Germans (Säuberung). A 1913 Carnegie Endowment report condemning the actions of all participants in the Balkan Wars contained various new terms to describe brutalities committed toward ethnic groups.

During the Holocaust in World War II, Nazi Germany pursued a policy of ensuring that Europe was "cleaned of Jews" (judenrein). The Nazi Generalplan Ost called for the genocide and ethnic cleansing of most Slavic people in central and eastern Europe for the purpose of providing more living space for the Germans. During the Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, the euphemism čišćenje terena ("cleansing the terrain") was used by the Croatian Ustaše to describe military actions in which non-Croats were purposely systematically killed or otherwise uprooted from their homes. The term was also used in the December 20, 1941 directive of Serbian Chetniks in reference to the genocidal massacres they committed against Bosniaks and Croats between 1941 and 1945. The Russian phrase очистка границ (ochistka granits; lit. "cleansing of borders") was used in Soviet documents of the early 1930s to refer to the forced resettlement of Polish people from the 22-kilometre (14 mi) border zone in the Byelorussian and Ukrainian SSRs. This process of the population transfer in the Soviet Union was repeated on an even larger scale in 1939–1941, involving many other groups suspected of disloyalty.

In its complete form, the term appeared for the first time in the Romanian language (purificare etnică) in an address by Vice Prime Minister Mihai Antonescu to cabinet members in July 1941. After the beginning of the invasion by the Soviet Union, he concluded: "I do not know when the Romanians will have such chance for ethnic cleansing." In the 1980s, the Soviets used the term "etnicheskoye chishcheniye" which literally translates to "ethnic cleansing" to describe Azerbaijani efforts to drive Armenians away from Nagorno-Karabakh. It was widely popularized by the Western media during the Bosnian War (1992–1995).
In 1992, the German equivalent of ethnic cleansing (German: ethnische Säuberung, pronounced [ˈʔɛtnɪʃə ˈzɔɪ̯bəʁʊŋ] ) was named German Un-word of the Year by the Gesellschaft für deutsche Sprache due to its euphemistic, inappropriate nature.
Definitions
The Final Report of the Commission of Experts established pursuant to Security Council Resolution 780 defined ethnic cleansing as:
a purposeful policy designed by one ethnic or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas", " 'ethnic cleansing' has been carried out by means of murder, torture, arbitrary arrest and detention, extra-judicial executions, rape and sexual assaults, confinement of civilian population in ghetto areas, forcible removal, displacement and deportation of civilian population, deliberate military attacks or threats of attacks on civilians and civilian areas, and wanton destruction of property. Those practices constitute crimes against humanity and can be assimilated to specific war crimes. Furthermore, such acts could also fall within the meaning of the Genocide Convention.
The official United Nations definition of ethnic cleansing is "rendering an area ethnically homogeneous by using force or intimidation to remove from a given area persons of another ethnic or religious group." As a category, ethnic cleansing encompasses a continuum or spectrum of policies. In the words of Andrew Bell-Fialkoff, "ethnic cleansing ... defies easy definition. At one end it is virtually indistinguishable from forced emigration and population exchange while at the other it merges with deportation and genocide. At the most general level, however, ethnic cleansing can be understood as the expulsion of a population from a given territory."
Terry Martin has defined ethnic cleansing as "the forcible removal of an ethnically defined population from a given territory" and as "occupying the central part of a continuum between genocide on one end and nonviolent pressured ethnic emigration on the other end."
Gregory Stanton, the founder of Genocide Watch, has criticised the rise of the term and its use for events that he feels should be called "genocide": because "ethnic cleansing" has no legal definition, its media use can detract attention from events that should be prosecuted as genocide.
As a crime under international law
There is no international treaty that specifies a specific crime of ethnic cleansing; however, ethnic cleansing in the broad sense—the forcible deportation of a population—is defined as a crime against humanity under the statutes of both the International Criminal Court (ICC) and the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia (ICTY). The gross human rights violations integral to stricter definitions of ethnic cleansing are treated as separate crimes falling under public international law of crimes against humanity and in certain circumstances genocide. There are also situations, such as the expulsion of Germans after World War II, where ethnic cleansing has taken place without legal redress (see Preussische Treuhand v. Poland). Timothy v. Waters argues that similar ethnic cleansing could go unpunished in the future.
Mutual ethnic cleansing
Mutual ethnic cleansing occurs when two groups commit ethnic cleansing against minority members of the other group within their own territories. For instance in the 1920s, Turkey expelled its Greek minority and Greece expelled its Turkish minority following the Greco-Turkish War. Other examples where mutual ethnic cleansing occurred include the First Nagorno-Karabakh War and the population transfers by the Soviets of Germans, Poles, and Ukrainians after World War II.
Causes

According to Michael Mann, in The Dark Side of Democracy (2004), murderous ethnic cleansing is strongly related to the creation of democracies. He argues that murderous ethnic cleansing is due to the rise of nationalism, which associates citizenship with a specific ethnic group. Democracy, therefore, is tied to ethnic and national forms of exclusion. Nevertheless, it is not democratic states that are more prone to commit ethnic cleansing, because minorities tend to have constitutional guarantees. Neither are stable authoritarian regimes (except the nazi and communist regimes) which are likely perpetrators of murderous ethnic cleansing, but those regimes that are in process of democratization. Ethnic hostility appears where ethnicity overshadows social classes as the primordial system of social stratification. Usually, in deeply divided societies, categories such as class and ethnicity are deeply intertwined, and when an ethnic group is seen as oppressor or exploitative of the other, serious ethnic conflict can develop. Michael Mann holds that when two ethnic groups claim sovereignty over the same territory and can feel threatened, their differences can lead to severe grievances and danger of ethnic cleansing. The perpetration of murderous ethnic cleansing tends to occur in unstable geopolitical environments and in contexts of war. As ethnic cleansing requires high levels of organisation and is usually directed by states or other authoritative powers, perpetrators are usually state powers or institutions with some coherence and capacity, not failed states as it is generally perceived. The perpetrator powers tend to get support by core constituencies that favour combinations of nationalism, statism, and violence.
Ethnic cleansing was prevalent during the Age of Nationalism in Europe (19th and 20th centuries). Multi-ethnic European engaged in ethnic cleansing against minorities in order to pre-empt their secession and the loss of territory. Ethnic cleansing was particularly prevalent during periods of interstate war.
Genocide

Ethnic cleansing has been described as part of a continuum of violence whose most extreme form is genocide. Ethnic cleansing is similar to forced deportation or population transfer. While ethnic cleansing and genocide may share the same goal and methods (e.g., forced displacement), ethnic cleansing is intended to displace a persecuted population from a given territory, while genocide is intended to destroy a group.
Some academics consider genocide to be a subset of "murderous ethnic cleansing". Norman Naimark writes that these concepts are different but related, for "literally and figuratively, ethnic cleansing bleeds into genocide, as mass murder is committed in order to rid the land of a people." William Schabas states "ethnic cleansing is also a warning sign of genocide to come. Genocide is the last resort of the frustrated ethnic cleanser." Multiple genocide scholars have criticized distinguishing between ethnic cleansing and genocide, with Martin Shaw arguing that forced deportation necessarily results in the destruction of a group and this must be foreseen by the perpetrators.
As a military, political, and economic tactic





The foibe massacres (Italian: massacri delle foibe; Slovene: poboji v fojbah; Croatian: masakri fojbe), or simply "the foibe", refers to ethnic cleansing, mass killings and deportations both during and immediately after World War II, mainly committed by Yugoslav Partisans and OZNA in the then-Italian territories of Julian March (Karst Region and Istria), Kvarner and Dalmatia, against local Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) and Slavs, primarily members of fascist and collaborationist forces, and civilians opposed to the new Yugoslav authorities, and Italian, German, Croat and Slovene anti-communists against the regime of Josip Broz Tito, presumed to be associated with fascism, Nazism, collaboration with Axis and reventive purge of real, potential or presumed opponents of Titoism The foibe massacres were followed by the Istrian–Dalmatian exodus, which was the post-World War II exodus and departure of between 230,000 and 350,000 local ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) towards Italy, and in smaller numbers, towards the Americas, Australia and South Africa. From 1947, after the war, they were subject by Yugoslav authorities to less violent forms of intimidation, such as nationalization, expropriation, and discriminatory taxation, which gave them little option other than emigration. In 1953, there were 36,000 declared Italians in Yugoslavia, just about 16% of the original Italian population before World War II. According to the census organized in Croatia in 2001 and that organized in Slovenia in 2002, the Italians who remained in the former Yugoslavia amounted to 21,894 people (2,258 in Slovenia and 19,636 in Croatia).
The resettlement policy of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the 9th and 7th centuries BC is considered by some scholars to be one of the first cases of ethnic cleansing.
During the 1980s, in Lebanon, ethnic cleansing was common during all phases of the conflict, notable incidents were seen in the early phase of the war, such as the Damour massacre, the Karantina massacre, the Siege of the Tel al-Zaatar Palestinian refugee camp, and during the 1982 Lebanon War such as the Sabra and Shatila Massacre committed by Lebanese Maronite forces backed by Israel against Palestinian refugees and Lebanese Shia civilians. After the Israeli withdrawal from the Chouf, the Mountain War broke out, where ethnic cleansings (mostly in the form of tit-for-tat killings) occurred. During that time, the Syrian backed, mostly Druze dominated People's Liberation Army used a policy they called "territorial cleansing" to "drain" the Chouf of Maronite Christians in order to deny them of resisting the advance of the PSP. As a result, 163,670 Christian villagers were displaced due to these operations. In response to these massacres, the Lebanese Forces conducted a similar policy, which resulted in 20,000 Druze displaced.
Ethnic cleansing was a common phenomenon in the wars in Croatia, Kosovo, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. This entailed intimidation, forced expulsion, or killing of the unwanted ethnic group as well as the destruction of the places of worship, cemeteries and cultural and historical buildings of that ethnic group in order to alter the population composition of an area in the favour of another ethnic group which would become the majority.
According to numerous ICTY verdicts and indictments, Serb and Croat forces performed ethnic cleansing of their territories planned by their political leadership to create ethnically pure states (Republika Srpska and Republic of Serbian Krajina by the Serbs; and Herzeg-Bosnia by the Croats).
Survivors of the ethnic cleansing were left severely traumatized as a consequence of this campaign.
Israeli herders have engaged in a systemic displacement of Palestinian herders in Area C of the West Bank as a form of nationalist and economic warfare.
When enforced as part of a political settlement, as happened with the expulsion of Germans after World War II through the forced resettlement of ethnic Germans to Germany in its reduced borders after 1945, the forced population movements, constituting a type of ethnic cleansing, may contribute to long-term stability of a post-conflict nation. Some justifications may be made as to why the targeted group will be moved in the conflict resolution stages, as in the case of the ethnic Germans, some individuals of the large German population in Czechoslovakia and prewar Poland had encouraged Nazi jingoism before World War II, but this was forcibly resolved.
According to historian Norman Naimark, during an ethnic cleansing process, there may be destruction of physical symbols of the victims including temples, books, monuments, graveyards, and street names: "Ethnic cleansing involves not only the forced deportation of entire nations but the eradication of the memory of their presence." In many cases, the side perpetrating the alleged ethnic cleansing and its allies have fiercely disputed the charge.
Instances
For a more comprehensive list, see List of ethnic cleansing campaigns.See also
Main article: Outline of genocide studies- Cultural genocide
- Discrimination based on skin tone
- Ethnic conflict
- Ethnic violence
- Ethnocentrism
- Ethnocide
- Forced displacement
- Identity cleansing
- Identity politics
- Nativism (politics)
- Political cleansing of population
- Population cleansing
- Racial segregation
- Racism
- Redlining
- Religious persecution
- Religious discrimination
- Religious segregation
- Religious violence
- Sectarian violence
- Social cleansing
- Sundown town
- Supremacism
- Xenophobia
Explanatory notes
- "How could ‘forced deportation’ ever be achieved without extreme coercion, indeed violence? How, indeed, could deportation not be forced? How could people not resist? How could it not involve the destruction of a community, of the way of life that a group has enjoyed over a period of time? How could those who deported a group not intend this destruction? In what significant way is the forcible removal of a population from their homeland different from the destruction’ of a group? If the boundary between ‘cleansing’ and genocide is unreal, why police it?"
- Successively lost by Italy to Yugoslavia after the Treaty of Peace (1947).
Notes
- ^ "Ethnic cleansing". United Nations. United Nations Office on Genocide Prevention and the Responsibility to Protect. Retrieved December 20, 2020.
- Walling, Carrie Booth (2000). "The history and politics of ethnic cleansing". The International Journal of Human Rights. 4 (3–4): 47–66. doi:10.1080/13642980008406892. S2CID 144001685.
Most frequently, however, the aim of ethnic cleansing is to expel the despised ethnic group through either indirect coercion or direct force, and to ensure that return is impossible. Terror is the fundamental method used to achieve this end.
Methods of indirect coercion can include: introducing repressive laws and discriminatory measures designed to make minority life difficult; the deliberate failure to prevent mob violence against ethnic minorities; using surrogates to inflict violence; the destruction of the physical infrastructure upon which minority life depends; the imprisonment of male members of the ethnic group; threats to rape female members, and threats to kill. If ineffective, these indirect methods are often escalated to coerced emigration, where the removal of the ethnic group from the territory is pressured by physical force. This typically includes physical harassment and the expropriation of property. Deportation is an escalated form of direct coercion in that the forcible removal of 'undesirables' from the state's territory is organised, directed and carried out by state agents. The most serious of the direct methods, excluding genocide, is murderous cleansing, which entails the brutal and often public murder of some few in order to compel flight of the remaining group members.13 Unlike during genocide, when murder is intended to be total and an end in itself, murderous cleansing is used as a tool towards the larger aim of expelling survivors from the territory. The process can be made complete by revoking the citizenship of those who emigrate or flee. - Schabas, William A. (2003). "'Ethnic Cleansing' and Genocide: Similarities and Distinctions". European Yearbook of Minority Issues Online. 3 (1): 109–128. doi:10.1163/221161104X00075.
The Commission considered techniques of ethnic cleansing to include murder, torture, arbitrary arrest and detention, extrajudicial executions, sexual assault, confinement of civilian populations in ghetto areas, forcible removal, displacement and deportation of civilian populations, deliberate military attacks or threats of attacks on civilians and civilian areas, and wanton destruction of property.
- The danger of overstretching the term can be avoided...The goal of ethnic cleansing is to permanently remove a group from the area it inhabits...There is a popular dimension to ethnic cleansing because there are people needed to threaten with violence, to evict homes, organize mass transports, and to prevent the return of the unwanted...The main goal of ethnic cleansing was the removal of a group from a certain territory The Oxford Handbook of Postwar European History. (2012). United Kingdom: OUP Oxford.
- Joireman, Sandra Fullerton. Peace, preference, and property : return migration after violent conflict. University of Michigan. p. 49.
Violent conflict changes communities. "Returnees painfully discover that in their period of absence the homeland communities and their identities have undergone transformation, and these ruptures and changes have serious implications for their ability to reclaim a sense of home upon homecoming." The first issue in terms of returning home is usually the restoration of property, specifically the return or rebuilding of homes. People want their property restored, often before they return. But home means more than property, it also refers to the nature of the community. Anthropological literature emphasizes that time and the experience of violence changes people's sense of home and desire to return, and the nature of their communities of origin. To sum up, previous research has identified factors that influence decisions to return: time, trauma, family characteristics and economic opportunities.
- Bulutgil 2018, p. 1136.
- ^ Garrity, Meghan M (September 27, 2023). "'Ethnic Cleansing': An Analysis of Conceptual and Empirical Ambiguity". Political Science Quarterly. 138 (4): 469–489. doi:10.1093/psquar/qqad082.
- Kirby-McLemore, Jennifer (2021–2022). "Settling the Genocide v. Ethnic Cleansing Debate: Ending Misuse of the Euphemism Ethnic Cleansing". Denver Journal of International Law and Policy. 50: 115.
- "Who first coined the euphemism "ethnic cleansing" for racial murder and persecution? Surely it must have been a dictator? | Notes and Queries | guardian.co.uk". www.theguardian.com. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- Howe, Marvine (July 12, 1982). "Exodus of Serbians stirs province in Yugoslavia". The New York Times. p. 8. Archived from the original on March 17, 2018.
- Thum 2010, p. 75: way. Despite its euphemistic character and its origin in the language of the perpetrators, 'ethnic cleansing' is now the widely accepted scholarly term used to describe the systematic and violent removal of undesired ethnic groups from a given territory.
- Bulutgil, H. Zeynep (2018). "The state of the field and debates on ethnic cleansing". Nationalities Papers. 46 (6): 1136–1145. doi:10.1080/00905992.2018.1457018. S2CID 158519257.
- Jones, Adam (2012). "'Ethnic cleansing' and genocide". Crimes Against Humanity: A Beginner's Guide. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-78074-146-8.
- Schabas, William A. (2003). "'Ethnic Cleansing' and Genocide: Similarities and Distinctions". European Yearbook of Minority Issues Online. 3 (1): 109–128. doi:10.1163/221161104X00075.
'Ethnic cleansing' is probably better described as a popular or journalistic expression, with no recognized legal meaning in a technical sense... 'ethnic cleansing' is equivalent to deportation,' a grave breach of the Geneva Conventions as well as a crime against humanity, and therefore a crime within the jurisdiction of the Tribunal.
- Akçam, Taner (2011). "Demographic Policy and the Annihilation of the Armenians". The Young Turks' Crime Against Humanity: The Armenian Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing in the Ottoman Empire. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-15333-9.
The thesis being proposed here is that the Armenian Genocide was not implemented solely as demographic engineering, but also as destruction and annihilation, and that the 5 to 10 percent principle was decisive in achieving this goal. Care was taken so that the number of Armenians deported to Syria, and those who remained behind, would not exceed 5 to 10 percent of the population of the places in which they were found. Such a result could be achieved only through annihilation... According to official Ottoman statistics, it was necessary to reduce the prewar population of 1.3 million Armenians to approximately 200,000.
- Booth Walling, Carrie (2012). "The History and Politics of Ethnic Cleansing". In Booth, Ken (ed.). The Kosovo Tragedy: The Human Rights Dimensions. London: Routledge. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-13633-476-4.
- Saldanha, Arun (2012). Deleuze and Race. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 51, 70. ISBN 978-0-7486-6961-5.
- McDonnell, M. A.; Moses, A. D. (2005). "Raphael Lemkin as historian of genocide in the Americas". Journal of Genocide Research. 7 (4): 501–529. doi:10.1080/14623520500349951. S2CID 72663247.
- ^ Sousa, Ashley (2016). "Ethnic Cleansing and the Indian: The Crime That Should Haunt America by Gary Clayton Anderson". Journal of Southern History. 82 (1): 135–136. doi:10.1353/soh.2016.0023. ISSN 2325-6893. S2CID 159731284.
- Richmond, Walter (2013). "3: From War to Genocide". The Circassian Genocide. New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA: Rutgers University Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-8135-6068-7.
- Levene, Mark (2005). "6: Declining Powers". Genocide in the Age of the Nation-State Volume II: The Rise of the West and the Coming of Genocide. 175 Fifth Avenue, New York NY 10010. pp. 298–302. ISBN 1-84511-057-9.
- ^ Richmond, Walter (2013). "4: 1864". The Circassian Genocide. New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA: Rutgers University Press. pp. 96, 97. ISBN 978-0-8135-6068-7.
- Ther, Philipp (2004). "The Spell of the Homogeneous Nation State: Structural Factors and Agents of Ethnic Cleansing". In Munz, Rainer; Ohliger, Rainer (eds.). Diasporas and Ethnic Migrants: Germany, Israel and Russia in Comparative Perspective. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-13575-938-4. Archived from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- Akhund, Nadine (December 31, 2012). "The Two Carnegie Reports: From the Balkan Expedition of 1913 to the Albanian Trip of 1921". Balkanologie. Revue d'études pluridisciplinaires. XIVb (1–2). doi:10.4000/balkanologie.2365. Archived from the original on April 4, 2017. Retrieved April 3, 2017 – via balkanologie.revues.org.
- Fulbrooke, Mary (2004). A Concise History of Germany. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 197. ISBN 978-0-52154-071-1. Archived from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- Eichholtz, Dietrich (September 2004). "'Generalplan Ost' zur Versklavung osteuropäischer Völker" ['General Plan East' for the enslavement of Eastern European peoples]. Utopie Kreativ (in German). 167: 800–808 – via Rosa Luxemburg Foundation.
- Toal, Gerard; Dahlman, Carl T. (2011). Bosnia Remade: Ethnic Cleansing and Its Reversal. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-19-973036-0. Archived from the original on July 6, 2014. Retrieved March 1, 2016.
- West, Richard (1994). Tito and the Rise and Fall of Yugoslavia. New York: Carroll & Graf. p. 93. ISBN 978-0-7867-0332-6.
- Becirevic, Edina (2014). Genocide on the River Drina. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. pp. 22–23. ISBN 978-0-3001-9258-2. Archived from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved August 31, 2017.
- ^ Martin, Terry (1998). "The Origins of Soviet Ethnic Cleansing" Archived July 24, 2019, at the Wayback Machine. The Journal of Modern History 70 (4), 813–861. pg. 822
- "The Nakba did not start or end in 1948". Al Jazeera. May 23, 2017.
- Petrovic, Vladimir (2017). Ethnopolitical Temptations Reach Southeastern Europe: Wartime Policy Papers of Vasa Čubrilović and Sabin Manuilă. CEU Press.
- Allen, Tim, and Jean Seaton, eds. The media of conflict: War reporting and representations of ethnic violence. Zed Books, 1999. p. 152
- Feierstein, Daniel (April 4, 2023). "The Meaning of Concepts: Some Reflections on the Difficulties in Analysing State Crimes". HARM – Journal of Hostility, Aggression, Repression and Malice. 1. doi:10.46586/harm.2023.10453. ISSN 2940-3073.
The concept seems to have been borrowed from the Slavic expression etnicheskoye chishcheniye, first used by Soviet authorities in the 1980s to describe Azeri attempts to expel Armenians from the Nagorno-Karabakh area, and then immediately reappropriated by Serb nationalists to describe their policies in the central region of Yugoslavia.
- Cox, Caroline. "Nagorno Karabakh: Forgotten People in a Forgotten War." Contemporary Review 270 (1997): 8–13: "These operations were part of a policy designated `Operation Ring, comprising the proposed ethnic cleansing (a word used in relation to Azerbaijan's policy before it became familiar to the world in the context of the former Yugoslavia) of all Armenians from their ancient homeland of Karabakh."
- Gunkel, Christoph (October 31, 2010). "Ein Jahr, ein (Un-)Wort!" [One year, one (un)word!]. Spiegel Online (in German). Archived from the original on May 12, 2013. Retrieved February 17, 2013.
- "Final Report of the Commission of Experts Established Pursuant to United Nations Security Council Resolution 780 (1992)" (PDF). United Nations Security Council. May 27, 1994. p. 33. Paragraph 129
- "Final Report of the Commission of Experts Established Pursuant to United Nations Security Council Resolution 780 (1992)" (PDF). United Nations Security Council. May 27, 1994. p. 33. Archived from the original on May 14, 2011. Retrieved May 25, 2020.
Upon examination of reported information, specific studies and investigations, the Commission confirms its earlier view that 'ethnic cleansing' is a purposeful policy designed by one ethnic or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas. To a large extent, it is carried out in the name of misguided nationalism, historic grievances and a powerful driving sense of revenge. This purpose appears to be the occupation of territory to the exclusion of the purged group or groups. This policy and the practices of warring factions are described separately in the following paragraphs.
Paragraph 130. - Hayden, Robert M. (1996) "Schindler's Fate: Genocide, Ethnic Cleansing, and Population Transfers" Archived April 11, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. Slavic Review 55 (4), 727–48.
- Andrew Bell-Fialkoff, "A Brief History of Ethnic Cleansing" Archived February 3, 2004, at the Wayback Machine, Foreign Affairs 72 (3): 110, Summer 1993. Retrieved May 20, 2006.
- ^ Douglas Singleterry (April 2010), "Ethnic Cleansing and Genocidal Intent: A Failure of Judicial Interpretation?", Genocide Studies and Prevention 5, 1
- Ferdinandusse, Ward (2004). "The Interaction of National and International Approaches in the Repression of International Crimes" (PDF). The European Journal of International Law. 15 (5): 1042, note 7. doi:10.1093/ejil/15.5.1041. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 5, 2008.
- "Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court" Archived January 13, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Article 7; Updated Statute of the International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia Archived August 6, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Article 5.
- Shraga, Daphna; Zacklin, Ralph (2004). "The International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia". The European Journal of International Law. 15 (3). Archived from the original on September 27, 2007.
- Timothy V. Waters, "On the Legal Construction of Ethnic Cleansing" Archived November 6, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Paper 951, 2006, University of Mississippi School of Law. Retrieved on 2006, 12–13
- Pinxten, Rik; Dikomitis, Lisa (May 1, 2009). When God Comes to Town: Religious Traditions in Urban Contexts. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1-84545-920-8. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- Cornell, Svante E. (September 1998). "Religion as a factor in Caucasian conflicts". Civil Wars. 1 (3): 46–64. doi:10.1080/13698249808402381. ISSN 1369-8249.
- Snyder, Timothy (July 11, 2004). The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10586-5. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- Archived May 3, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Mann, Michael (2005), The Dark Side of Democracy: Explaining Ethnic Cleansing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, Ch. 1 "The Argument," pp. 1–33.
- ^ Müller-Crepon, Carl; Schvitz, Guy; Cederman, Lars-Erik (2024). ""Right-Peopling" the State: Nationalism, Historical Legacies, and Ethnic Cleansing in Europe, 1886–2020". Journal of Conflict Resolution. doi:10.1177/00220027241227897. hdl:20.500.11850/657611. ISSN 0022-0027.
- Mylonas, Harris (2013). The Politics of Nation-Building: Making Co-Nationals, Refugees, and Minorities. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9781139104005. ISBN 978-1-107-02045-0.
- International Association of Genocide Scholars (December 16, 2007). "Genocide Scholars Association Officially Recognizes Assyrian, Greek Genocides" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 1, 2011. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ^ Schabas, William (2000). Genocide in International Law. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 199–201. ISBN 9780521787901. Archived from the original on January 2, 2016. Retrieved October 29, 2015.
- Ethnic cleansing versus genocide:
- Lieberman, Benjamin (2010). "'Ethnic cleansing' versus genocide?". In Bloxham, Donald; Moses, A. Dirk (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-923211-6.
Explaining the relationship between ethnic cleansing and genocide has caused controversy. Ethnic cleansing shares with genocide the goal of achieving purity but the two can differ in their ultimate aims: ethnic cleansing seeks the forced removal of an undesired group or groups where genocide pursues the group's 'destruction'. Ethnic cleansing and genocide therefore fall along a spectrum of violence against groups with genocide lying on the far end of the spectrum.
- Martin, Terry (1998). "The Origins of Soviet Ethnic Cleansing". The Journal of Modern History. 70 (4): 813–861. doi:10.1086/235168. ISSN 0022-2801. JSTOR 10.1086/235168. S2CID 32917643.
When murder itself becomes the primary goal, it is typically called genocide... Ethnic cleansing is probably best understood as occupying the central part of a continuum between genocide on one end and nonviolent pressured ethnic emigration on the other end. Given this continuum, there will always be ambiguity as to when ethnic cleansing shades into genocide
- Schabas, William A. (2003). "'Ethnic Cleansing' and Genocide: Similarities and Distinctions". European Yearbook of Minority Issues Online. 3 (1): 109–128. doi:10.1163/221161104X00075.
The crime of genocide is aimed at the intentional destruction of an ethnic group. 'Ethnic cleansing' would seem to be targeted at something different, the expulsion of a group with a view to encouraging or at least tolerating its survival elsewhere. Yet ethnic cleansing may well have the effect of rendering the continued existence of a group impossible, thereby effecting its destruction. In other words, forcible deportation may achieve the same result as extermination camps.
- Walling, Carrie Booth (2000). "The history and politics of ethnic cleansing". The International Journal of Human Rights. 4 (3–4): 47–66. doi:10.1080/13642980008406892. S2CID 144001685.
These methods are a part of a wider continuum ranging from genocide at one extreme to emigration under pressure at the other... It is important - politically and legally - to distinguish between genocide and ethnic cleansing. The goal of the former is extermination: the complete annihilation of an ethnic, national or racial group. It contains both a physical element (acts such as murder) and a mental element (those acts are undertaken to destroy, in whole or in part, the said group). Ethnic cleansing involves population expulsions, sometimes accompanied by murder, but its aim is consolidation of power over territory, not the destruction of a complete people.
- Naimark, Norman M. (2002). Fires of Hatred. Harvard University Press. pp. 2–5. ISBN 978-0-674-00994-3.
A new term was needed because ethnic cleansing and genocide two different activities, and the differences between them are important. As in the case of determining first-degree murder, intentionality is a critical distinction. Genocide is the intentional killing off of part or all of an ethnic, religious, or national group; the murder of a people or peoples (in German, Völkermord) is the objective. The intention of ethnic cleansing is to remove a people and often all traces of them from a concrete territory. The goal, in other words, is to get rid of the "alien" nationality, ethnic, or religious group and to seize control of the territory it had formerly inhabited. At one extreme of its spectrum, ethnic cleansing is closer to forced deportation or what has been called "population transfer"; the idea is to get people to move, and the means are meant to be legal and semi-legal. At the other extreme, however, ethnic cleansing and genocide are distinguishable only by the ultimate intent. Here, both literally and figuratively, ethnic cleansing bleeds into genocide, as mass murder is committed in order to rid the land of a people.
- Hayden, Robert M. (1996). "Schindler's Fate: Genocide, Ethnic Cleansing, and Population Transfers". Slavic Review. 55 (4): 727–748. doi:10.2307/2501233. ISSN 0037-6779. JSTOR 2501233. S2CID 232725375.
Hitler wanted the Jews utterly exterminated, not simply driven from particular places. Ethnic cleansing, on the other hand, involves removals rather than extermination and is not exceptional but rather common in particular circumstances.
- Lieberman, Benjamin (2010). "'Ethnic cleansing' versus genocide?". In Bloxham, Donald; Moses, A. Dirk (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-923211-6.
- Mann, Michael (2005). The Dark Side of Democracy: Explaining Ethnic Cleansing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 17. ISBN 9780521538541. Archived from the original on January 2, 2016. Retrieved October 29, 2015.
- Naimark, Norman (November 4, 2007). "Theoretical Paper: Ethnic Cleansing". Online Encyclopedia of Mass Violence. Archived from the original on March 6, 2016.
- ^ Shaw, Martin (2015b), What is Genocide, Polity Press, ISBN 978-0-7456-8706-3 ‘Cleansing’ and genocide.
- Levene, Mark (2005). "6: Declining Powers". Genocide in the Age of the Nation-State Volume II: The Rise of the West and the Coming of Genocide. 175 Fifth Avenue, New York NY 10010. pp. 299–300. ISBN 1-84511-057-9.
- Jones, Adam (2016). Genocide: A Comprehensive Introduction. Taylor & Francis. pp. 108–110. ISBN 978-1-317-53386-3 – via Google Books.
- Richmond, Walter (2013). The Circassian Genocide. New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA: Rutgers University Press. pp. 97, 132. ISBN 978-0-8135-6068-7.
- Bloxham & Dirk Moses 2011.
- ^ Konrád, Barth & Mrňka 2021.
- Baracetti 2009, p. 664, "That fascists were specifically targeted by the repression is also confirmed by various Italian sources. A letter attached to the Hazarich report on the excavations carried out in the foibe in 1943 mentions corpses of fascists thrown there; another the extractions of the bodies of "our unfortunate squadristi (members of the fascist militia). An Italian report on "the grim fate of Pisino" (a city in istria) mentions only the killings of squadristi, which contrasts markedly with the subsequent report on the German offensive: random shootings of civilians, burning of houses and bombings".
- Baracetti 2009, "In 1947, British envoy W. J. Sullivan wrote of Italians arrested and deported by Yugoslav forces from around Trieste: "There is little doubt, while some of the persons deported may have been innocent, others were undoubtedly active fascists with more than mere party memberships on their conscience. Some of these have returned to Trieste but have kept well out of the Allied authorities, not participating in enquiries about the deportations for fear of arrest and trial 'for their former fascist activities'".
- Troha, Nevenka (2014). "Nasilje vojnih in povojnih dni". www.sistory.si (in Slovenian). Inštitut za novejšo zgodovino. Retrieved June 4, 2023.
By this definition, among the 601 victims , 475 were members of armed formations and 126 were civilians.
- Rumici 2002, p. 350.
- Italian-Slovene commission.
- "Il Giorno del Ricordo" (in Italian). February 10, 2014. Retrieved October 16, 2021.
- "L'esodo giuliano-dalmata e quegli italiani in fuga che nacquero due volte" (in Italian). February 5, 2019. Retrieved January 24, 2023.
- Pamela Ballinger (April 7, 2009). Genocide: Truth, Memory, and Representation. Duke University Press. p. 295. ISBN 978-0822392361. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- Tesser, L. (May 14, 2013). Ethnic Cleansing and the European Union – Page 136, Lynn Tesser. Springer. ISBN 9781137308771.
- Ballinger, Pamela (2003). History in Exile: Memory and Identity at the Borders of the Balkans. Princeton University Press. p. 103. ISBN 0691086974.
- Anna C. Bramwell, University of Oxford, UK (1988). Refugees in the Age of Total War. Unwin Hyman. pp. 139, 143. ISBN 9780044451945.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Matjaž Klemenčič, The Effects of the Dissolution of Yugoslavia on Minority Rights: the Italian Minority in Post-Yugoslav Slovenia and Croatia. See "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 24, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "12. Population by ethnicity, by towns/municipalities, census 2001". Census of Population, Households and Dwellings 2001. Zagreb: Croatian Bureau of Statistics. 2002. Retrieved June 10, 2017.
- "Popis 2002". Retrieved June 10, 2017.
- "Ethnic cleansing". Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- "Prosecutor v. Vujadin Popovic, Ljubisa Beara, Drago Nikolic, Ljubomir Borovcanin, Radivoje Miletic, Milan Gvero, and Vinko Pandurevic" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on December 11, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
In the Motion, the Prosecution submits that both the existence and implementation of the plan to create an ethnically pure Bosnian Serb state by Bosnian Serb political and military leaders are facts of common knowledge and have been held to be historical and accurate in a wide range of sources.
- "ICTY: Radoslav Brđanin judgement". Archived from the original on April 14, 2009.
- "Tadic Case: The Verdict". Archived from the original on October 14, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
Importantly, the objectives remained the same: to create an ethnically pure Serb State by uniting Serbs in Bosnia and Herzegovina and extending that State from the FRY to the Croatian Krajina along the important logistics and supply line that went through opstina Prijedor, thereby necessitating the expulsion of the non-Serb population of the opstina.
- "Prosecutor v. Jadranko Prlic, Bruno Stojic, Slobodan Praljak, Milivoj Petkovic, Valentin Coric and Berislav Pusic" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on September 5, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
Significantly, the Trial Chamber held that a reasonable Trial Chamber, could make a finding beyond any reasonable doubt that all of these acts were committed to carry out a plan aimed at changing the ethnic balance of the areas that formed Herceg-Bosna and mainly to deport the Muslim population and other non-Croat population out of Herceg-Bosna to create an ethnically pure Croatian territory within Herceg-Bosna.
- Weine et al. (1998), p. 147.
- Amira, Saad (2021). "The slow violence of Israeli settler-colonialism and the political ecology of ethnic cleansing in the West Bank". Settler Colonial Studies. 11 (4): 512–532. doi:10.1080/2201473X.2021.2007747. S2CID 244736676.
- Graham-Harrison, Emma; Kierszenbaum, Quique (October 21, 2023). "'The most successful land-grab strategy since 1967' as settlers push Bedouins off West Bank territory". The Guardian. Ein Rashash. Archived from the original on October 22, 2023.
- Ziv, Oren (October 19, 2023). "בעוד העיניים נשואות לדרום ולעזה, הטיהור האתני בגדה מואץ" [While the eyes are on the south and Gaza, the ethnic cleansing in the West Bank is accelerating]. Mekomit (in Hebrew). Archived from the original on October 22, 2023.
- ^ Judt, Tony (2005). Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945. Penguin Press.
- Naimark, Norman M. (September 19, 2002). Fires of Hatred: Ethnic Cleansing in Twentieth-Century Europe. Harvard University Press. pp. 209–211. ISBN 978-0-674-00994-3.
References
- Baracetti, Gaia (2009). "Foibe: Nationalism, Revenge and Ideology in Venezia Giulia and Istria, I943-5". Journal of Contemporary History. 44 (4): 657–674. doi:10.1177/0022009409339344. ISSN 0022-0094. JSTOR 40542981. S2CID 159919208.
- Bell-Fialkoff, Andrew (1993). "A Brief History of Ethnic Cleansing". Foreign Affairs. 72 (3): 110–121. doi:10.2307/20045626. JSTOR 20045626. Archived from the original on February 3, 2004.
- Bloxham, Donald; Dirk Moses, Anthony (2011). "Genocide and ethnic cleansing". In Bloxham, Donald; Gerwarth, Robert (eds.). Political Violence in Twentieth-Century Europe. Cambridge University Press. p. 125. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511793271.004. ISBN 9781107005037.
- "Period 1941–1945". Slovene-Italian Relations 1880–1956. Koper-Capodistria. July 25, 2000. Archived from the original on February 23, 2020.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Konrád, Ota; Barth, Boris; Mrňka, Jaromír, eds. (2021). Collective Identities and Post-War Violence in Europe, 1944–48. Springer International Publishing. p. 20. ISBN 9783030783860. Retrieved November 5, 2022.
- Petrovic, Drazen (1998). "Ethnic Cleansing – An Attempt at Methodology" (PDF). European Journal of International Law. 5 (4): 817.
- Thum, Gregor (2010). "Review: Ethnic Cleansing in Eastern Europe after 1945". Contemporary European History. 19 (1): 75–81. doi:10.1017/S0960777309990257. S2CID 145605508.
- Vladimir Petrović (2007), Etnicizacija čišćenja u reči i nedelu (Ethnicisation of Cleansing), Hereticus 1/2007, 11–36
- Rumici, Guido (2002). Infoibati (1943–1945). I Nomi, I Luoghi, I Testimoni, I Documenti (in Italian). Ugo Mursia. ISBN 978-88-425-2999-6.
- Weine, Stevan M.; Becker, Daniel F.; Vojvoda, Dolores; Hodzic, Emir (1998). "Individual change after genocide in Bosnian survivors of "ethnic cleansing": Assessing personality dysfunction". Journal of Traumatic Stress. 11 (1): 147–153. doi:10.1023/A:1024469418811. PMID 9479683. S2CID 31419500.
Further reading
Library resources aboutEthnic cleansing
- Basso, Andrew R. (2024). Destroy Them Gradually: Displacement as Atrocity. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-1-9788-3130-8.
- Bulutgil, H. Zeynep (2016). The Roots of Ethnic Cleansing in Europe. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-316-56528-5.
- Dahbour, Omar (2012). "National Rights, Minority Rights, and Ethnic Cleansing". Nationalism and Human Rights: In Theory and Practice in the Middle East, Central Europe, and the Asia-Pacific. Palgrave Macmillan US. pp. 97–122. ISBN 978-1-137-01202-9.
- Gordon, Neve; Ram, Moriel (2016). "Ethnic cleansing and the formation of settler colonial geographies" (PDF). Political Geography. 53: 20–29. doi:10.1016/j.polgeo.2016.01.010.
- Jenne, Erin K. (2016). "The causes and consequences of ethnic cleansing". The Routledge Handbook of Ethnic Conflict. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-315-72042-5.
- Lieberman, Benjamin (2013). Terrible Fate: Ethnic Cleansing in the Making of Modern Europe. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-3038-5.
- Pegorier, Clotilde (2013). Ethnic Cleansing: A Legal Qualification. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-06783-1.
- Rikhof, Joseph (2022). "Ethnic cleansing and exclusion". Serious International Crimes, Human Rights, and Forced Migration. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-003-09438-8.
- Ther, Philipp (2014). "The Dark Side of Nation-States: Ethnic Cleansing in Modern Europe". The Dark Side of Nation-States. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1-78238-303-1.
External links
| Nationalism | |
|---|---|
| Development | |
| By type |
|
| Organizations | |
| Related concepts |
|
| Segregation in countries by type (in some countries, categories overlap) | |
|---|---|
| Religious | |
| Ethnic and racial | |
| Gender | |
| Dynamics | |
| Related topics |
|
| Racism | |
|---|---|
| Types of racism | |
| Manifestations of racism | |
| Racism by region | |
| Racism by target | |
| Related topics |
|
| Discrimination | |
|---|---|
| Forms | |
| Attributes | |
| Social |
|
| Religious | |
| Ethnic/National |
|
| Manifestations |
|
| Discriminatory policies |
|
| Countermeasures |
|
| Related topics |
|
