| Revision as of 17:32, 22 May 2011 view sourceWikitanvirBot (talk | contribs)144,145 editsm r2.7.1) (robot Modifying: si:බුරුමය (රට)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:46, 26 December 2024 view source GreekApple123 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users8,660 edits →Sport: Changed linkTag: Visual edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Country in Southeast Asia}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=August 2010}} | |||
| {{ |
{{Redirect|Burma}} | ||
| {{pp-semi-indef}} | |||
| {{Lead too short|date=March 2011}} | |||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| {{Infobox Country | |||
| {{Use British English|date=May 2020}} | |||
| |native_name = ]<br>''Pyidaunzu Thanmăda Myăma Nainngandaw'' | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=February 2021}} | |||
| |conventional_long_name =Republic of the Union of Myanmar | |||
| {{Infobox country | |||
| |common_name = Burma | |||
| | |
| conventional_long_name = Republic of the Union of Myanmar | ||
| | |
| common_name = Myanmar | ||
| | native_name = {{ubl|{{native name|my|ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံ|italics=off<wbr/>}}|{{small|{{translit|my|Pyidaungzu thămăda myama naingngandaw}}}}}} | |||
| |symbol_type = State seal | |||
| | |
| image_flag = Flag of Myanmar.svg | ||
| | image_coat = State seal of Myanmar.svg | |||
| |map_caption = Location of Burma <small>(green)</small> in ] <small>dark grey</small> | |||
| | coa_size = 95 | |||
| |capital = ] | |||
| | symbol_type = State Seal | |||
| |national_motto = | |||
| |national_anthem = |
| national_anthem = {{lang|my|ကမ္ဘာမကျေ}}<br />{{transliteration|my|Kaba Ma Kyei}}<br />"]"{{parabr}}{{centre|]}} | ||
| | image_map = {{Switcher|]|Show globe|]|Show map of ASEAN|default=1}} | |||
| |official_languages = ] | |||
| | map_caption = {{map caption |location_color=green |region=] |region_color=dark grey |legend=Location Burma (Myanmar) ASEAN.svg}} | |||
| |languages_type = ]s | |||
| | |
| image_map2 = | ||
| | capital = ]{{Efn|Officially spelled "Nay Pyi Taw"}} | |||
| |regional_languages = ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | |||
| | coordinates = {{Coord|21|00|N|96|00|E|type:city}} | |||
| |demonym = Burmese/Myanma | |||
| | largest_city = ]{{Efn|Formerly known as "Rangoon"}} | |||
| |military_ capital = ] (<sup>2</sup>) | |||
| | languages_type = Official language | |||
| |business capital_= ] | |||
| | languages = ] | |||
| |largest_city = ] (Rangoon) | |||
| | languages2_type = {{nobold|Recognised regional languages}}<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.ethnologue.com/country/MM/ | title=Myanmar | Ethnologue Free | access-date=20 July 2023 | archive-date=9 March 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230309065715/https://www.ethnologue.com/country/MM/ | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |latd=19 |latm=45 |latNS=N |longd=96 |longm=6 |longEW=E | |||
| | languages2 = {{hlist| ] | ] | ] | ] | ] | ] | ]}} | |||
| |government_type = ] | |||
| | ethnic_groups = {{unbulleted list | |||
| |leader_title1 = ] | |||
| | 68.78% ] | |||
| |leader_name1 = ] | |||
| | 6.69% ] | |||
| |leader_title2 = ] | |||
| | 4.61% ] | |||
| |leader_name2 = ]<br>] | |||
| | 4.51% ] | |||
| |leader_title3 = | |||
| | 2.19% ] | |||
| |leader_name3 = | |||
| | 2.09% ] | |||
| |sovereignty_type = Formation | |||
| | 1.50% ] | |||
| |established_event1 = ] | |||
| | 0.39% ] | |||
| |established_date1 = 23 December 849 | |||
| | 9.24% ] | |||
| |established_event2 = ] | |||
| |established_date2 = 16 October 1510 | |||
| |established_event3 = ] | |||
| |established_date3 = 21 March 1752 | |||
| |established_event4 = ] | |||
| |established_date4 = 4 January 1948 (from ]) | |||
| |established_event5=] | |||
| |established_date5=2 March 1962 | |||
| |legislature=] | |||
| |upper_house=] | |||
| |lower_house=] | |||
| |area_rank = 40th | |||
| |area_magnitude = 1 E11 | |||
| |area_km2 = 676,578 | |||
| |area_sq_mi = 261,227 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |percent_water = 3.06 | |||
| |population_estimate = 55,400,000<ref name=unpop>{{cite journal | url=http://countryoffice.unfpa.org/myanmar/2009/10/30/1474/indicators/ | title=Population, Reproductive Health and Gender Statistics| version=2009 | publisher=United Nations | author=UNFPA | |||
| Population Division | year=2009 | accessdate= 12 March 2009}}</ref> | |||
| |population_estimate_year = 2009 | |||
| |population_estimate_rank = 24th | |||
| |population_census = 33,234,000 (<sup>3</sup>) | |||
| |population_census_year = 1983 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = 73.9 | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi = 191.5 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |population_density_rank = 119th | |||
| |GDP_PPP_year = 2010 | |||
| |GDP_PPP = $76.473 billion<ref name=imf2>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2008&ey=2011&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=518&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=54&pr.y=7 |title=Burma (Myanmar) |publisher=International Monetary Fund|accessdate=6 May 2011}}</ref> | |||
| |GDP_PPP_rank = | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $1,250<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |||
| |GDP_nominal = $42.953 billion<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| |GDP_nominal_year = 2010 | |||
| |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $702<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| |HDI_year = 2010 <!-- Please use the year that the data refers and not the publication year--> | |||
| |HDI = {{decrease}} 0.451<ref name="UN">{{cite web|url=http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDR_2010_EN_Table1.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2010|year=2010|publisher=United Nations|accessdate=5 November 2010}}</ref> | |||
| |HDI_rank = 132nd | |||
| |HDI_category =<span style="color:#e0584e;">low</span> | |||
| |FSI = 97.0 {{increase}} 0.5 | |||
| |FSI_year = 2007 | |||
| |FSI_rank = 14th | |||
| |FSI_category = <span style="colour:red;">Alert</span> | |||
| |currency = ] (K) | |||
| |currency_code = MMK | |||
| |Official exchange rate = 6 Kyat | |||
| |Exchange rate = 1350 Kyat | |||
| |time_zone = ] | |||
| |utc_offset = +6:30 | |||
| |drives_on = right<ref>Road infrastructure is still for driving on the left.</ref> | |||
| |cctld = ] | |||
| |calling_code = ] | |||
| |footnote1 = Some governments recognise ] as the national capital.<ref></ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | ethnic_groups_year = 2019<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.idea.int/sites/default/files/publications/chapters/deciphering-myanmars-ethnic-landscape/deciphering-myanmars-ethnic-landscape-CH2.pdf|title=Overview of Myanmar's diversity|access-date=25 May 2024|archive-date=21 May 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240521163711/https://www.idea.int/sites/default/files/publications/chapters/deciphering-myanmars-ethnic-landscape/deciphering-myanmars-ethnic-landscape-CH2.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://ispmyanmar.com/event/party-mergers-falling-short-of-expectation-ymg-season-2-episode-2/|title=ISP Myanmar talk shows|date=15 December 2020 |access-date=25 May 2024|archive-date=10 May 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240510125921/https://ispmyanmar.com/event/party-mergers-falling-short-of-expectation-ymg-season-2-episode-2/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ponyate.org/ethnic-population-dashboard-740399e|title=PonYate ethnic population dashboard|access-date=25 May 2024|archive-date=21 May 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240521163715/https://www.ponyate.org/ethnic-population-dashboard-740399e|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {{Contains Burmese text}} | |||
| | religion = {{unbulleted list | |||
| '''Burma''' ({{IPAc-en|En-us-Burma.ogg|ˈ|b|ɜr|m|ə}}), officially the '''Republic of the Union of Myanmar''' ({{IPAc-en|En-us-Myanmar.ogg|ˌ|m|j|ɑː|n|ˈ|m|ɑr}}; {{lang-my|ပြည်တော်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်}}, ''Pyidaunzu Thanmăda Myăma Nainngandaw'', {{IPA-my|pjìdà̀uɴzṵ θà̀ɴməda̯ mjəmà nàiɴŋàɴdɔ̀|pron}}) is a country in ]. The country is bordered by the ] on the northeast, ] on the east, ] on the southeast, ] on the west, ] on the northwest, and the ] to the southwest, with the ] defining its southern periphery. One-third of Burma's total perimeter of {{convert|1930|km|adj=off}} forms an uninterrupted coastline. Burma is the second largest country by geographical area in ].<ref>Asian Development Bank - Myanmar Fact Sheet, <http://www.adb.org/Documents/Fact_Sheets/MYA.pdf>. Retrieved 8 July 2010.</ref> | |||
| | 89.8% ] (])<ref>{{cite web|title=Myanmar's Constitution of 2008|url=https://constituteproject.org/constitution/Myanmar_2008.pdf?lang=en|website=constituteproject.org|access-date=29 October 2017|archive-date=20 September 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160920113951/https://constituteproject.org/constitution/Myanmar_2008.pdf?lang=en|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | 6.2% ] | |||
| | 2.3% ] | |||
| | 1.6% ]<ref>{{cite web |title=The 2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census- The Union Report: Religion |url=https://myanmar.unfpa.org/sites/default/files/pub-pdf/UNION_2-C_religion_EN_0.pdf |website=myanmar.unfpa.org |publisher=Department of Population Ministry of Labour, Immigration and Population MYANMAR |access-date=3 February 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180329011235/http://myanmar.unfpa.org/sites/default/files/pub-pdf/UNION_2-C_religion_EN_0.pdf |archive-date=29 March 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| | demonym = {{hlist|]|Myanmarian}}<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.health.act.gov.au/sites/default/files/ACT%20Health%20Community%20Profile%20-%20Burma%20%282014%29.pdf|title=ACT Health Community Profile, pg. 1|publisher=Multicultural Health Policy Unit|access-date=5 August 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150411161154/http://www.health.act.gov.au/sites/default/files/ACT%20Health%20Community%20Profile%20-%20Burma%20%282014%29.pdf|archive-date=11 April 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| | government_type = Unitary ] republic under a ] | |||
| | leader_title1 = ], ], and ] | |||
| | leader_name1 = ] | |||
| | leader_title2 = ] and ] | |||
| | leader_name2 = ]{{efn|Soe Win is the only vice chairman of the SAC, but he is one of five deputy prime ministers. The others are ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite news |title=Myanmar Junta Reshuffles Governing Body |url=https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-junta-reshuffles-governing-body.html |access-date=6 February 2023 |work=] |date=2 February 2023 |archive-date=7 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230207093226/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-junta-reshuffles-governing-body.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Myanmar reshuffle of generals suggests 'instability,' experts say |url=https://www.rfa.org/english/news/myanmar/reshuffle-09262023154048.html |access-date=2 October 2023 |work=] |date=26 September 2023 |archive-date=29 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230929044657/https://www.rfa.org/english/news/myanmar/reshuffle-09262023154048.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Myanmar Junta Leader Reshuffles Cabinet Days After Extending Emergency Rule |url=https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/politics/myanmar-junta-leader-reshuffles-cabinet-days-after-extending-emergency-rule.html |access-date=14 February 2024 |work=] |date=4 August 2023 |archive-date=22 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231122220805/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/politics/myanmar-junta-leader-reshuffles-cabinet-days-after-extending-emergency-rule.html |url-status=live }}</ref>}} | |||
| | legislature = ] | |||
| | sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| | established_event1 = ] | |||
| | established_date1 = 23 December 849 | |||
| | established_event3 = ] | |||
| | established_date3 = 16 October 1510 | |||
| | established_event4 = ] | |||
| | established_date4 = 29 February 1752 | |||
| | established_event5 = ] | |||
| | established_date5 = 1 January 1886 | |||
| | established_event6 = ] from the ] | |||
| | established_date6 = 4 January 1948 | |||
| | established_event7 = ] | |||
| | established_date7 = 2 March 1962 | |||
| | established_event8 = ] | |||
| | established_date8 = 18 September 1988 | |||
| | established_event9 = ] | |||
| | established_date9 = 31 January 2011 | |||
| | established_event10 = ] | |||
| | established_date10 = 1 February 2021 | |||
| | area_rank = 39th <!--should be same as listed on ]--> | |||
| | area_km2 = 676,579 | |||
| | area_sq_mi = 261,227 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | percent_water = 3.06 | |||
| | population_estimate = 55,770,232<ref>{{cite web|url=https://myanmar.unfpa.org/sites/default/files/pub-pdf/4F_Population%20Projections.pdf|title=The 2014 Myanmar Populations and Housing Census|access-date=29 May 2024|archive-date=24 September 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200924221152/https://myanmar.unfpa.org/sites/default/files/pub-pdf/4F_Population%20Projections.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | population_estimate_year = 2022 | |||
| | population_estimate_rank = 26th | |||
| | population_density_km2 = <!--auto calculate--><!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 196.8 | |||
| | population_density_rank = 125th | |||
| | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $283.572 billion<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/April/weo-report?c=512,914,612,171,614,311,213,911,314,193,122,912,313,419,513,316,913,124,339,638,514,218,963,616,223,516,918,748,618,624,522,622,156,626,628,228,924,233,632,636,634,238,662,960,423,935,128,611,321,243,248,469,253,642,643,939,734,644,819,172,132,646,648,915,134,652,174,328,258,656,654,336,263,268,532,944,176,534,536,429,433,178,436,136,343,158,439,916,664,826,542,967,443,917,544,941,446,666,668,672,946,137,546,674,676,548,556,678,181,867,682,684,273,868,921,948,943,686,688,518,728,836,558,138,196,278,692,694,962,142,449,564,565,283,853,288,293,566,964,182,359,453,968,922,714,862,135,716,456,722,942,718,724,576,936,961,813,726,199,733,184,524,361,362,364,732,366,144,146,463,528,923,738,578,537,742,866,369,744,186,925,869,746,926,466,112,111,298,927,846,299,582,487,474,754,698,&s=PPPGDP,&sy=2024&ey=2025&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=Report for Selected Countries and Subjects }}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | |||
| | GDP_PPP_rank = 64th | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $5,200<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/MMR }}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 146th | |||
| | GDP_nominal = {{decrease}} $68.006 billion<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/MMR }}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | |||
| | GDP_nominal_rank = 87th | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{decrease}} $1,250<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/MMR }}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 167th | |||
| | Gini = 30.7 | |||
| | Gini_year = 2017 | |||
| | Gini_change = decrease<!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | Gini_ref = <ref>{{cite web |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=MM |title=GINI index (World Bank estimate) |publisher=] |website=data.worldbank.org |access-date=13 July 2021 |archive-date=6 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190306111516/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=MM |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | Gini_rank = 106th | |||
| | HDI = 0.608<!--number only--> | |||
| | HDI_year = 2022<!--Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> | |||
| | HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2023/24|language=en|publisher=]|date=13 March 2024|page=289|access-date=13 March 2024|archive-date=13 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313164319/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI_rank = 144th | |||
| | currency = ] (K) | |||
| | currency_code = MMK | |||
| | time_zone = ] | |||
| | utc_offset = +06:30 | |||
| | drives_on = right | |||
| | calling_code = ] | |||
| | iso3166code = {{ISO 3166-1|MM}} | |||
| | cctld = ] | |||
| | today = | |||
| | time_zone_DST = | |||
| | established_event13 = | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Contains special characters|Burmese}} | |||
| '''Myanmar''',{{efn|{{Lang-my-name-MLCTS|MLCTS=Mranma|MY=မြန်မာ}}, {{IPA-my|mjəmà|pron}}}} officially the '''Republic of the Union of Myanmar'''{{efn|{{lang-my-name-MLCTS|MLCTS=Pranyhtaungcu. Sa.ma.ta. Mranma Nuingngamtau|MY=ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်}}; {{IPA-my|pjìdàʊɴzṵ θàɴməda̰ mjəmà nàɪɴŋàɴdɔ̀|pron}})}} and also rendered as '''Burma''' (the official English form until 1989), is a country in northwest ]. It is the largest country by area in ] and has a population of about 55 million.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Myanmar Population 2024 (Live) |url=https://worldpopulationreview.com/countries/myanmar-population |access-date=2024-08-10 |website=worldpopulationreview.com}}</ref> It is bordered by ] and ] to its northwest, ] to its northeast, ] and ] to its east and southeast, and the ] and the ] to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is ], and its largest city is ] (formerly Rangoon).<ref name="World Factbook">{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/burma/ |work=The World Factbook |title=Burma |date=8 August 2023 |publisher=U.S. Central Intelligence Agency |access-date=23 January 2021 |archive-date=10 February 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210210200835/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/burma/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Early civilisations in the area included the ]-speaking ] in ] and the ] in ].<ref>{{cite book | title=Early civilizations of Southeast Asia | publisher=Altamira Press | author=O'Reilly, Dougald JW | year=2007 | location=United Kingdom | isbn=978-0-7591-0279-8}}</ref> In the 9th century, the ] entered the upper ] valley, and following the establishment of the ] in the 1050s, the ], ], and ] slowly became dominant in the country. The ] fell to ], and several warring states emerged. In the 16th century, reunified by the ], the country became the largest empire in the ] for a short period.<ref>], p. 152</ref> The early 19th-century ] ruled over an area that included modern Myanmar and briefly controlled ], the ], and ] as well. The British ] seized control of the administration of Myanmar after three ] in the 19th century, and the country became a ]. After a brief ], Myanmar was reconquered by the Allies. On 4 January 1948, Myanmar declared ] under the terms of the ]. | |||
| The country's culture, heavily influenced by those of its neighbours, is based on ] ] intertwined with ]. Burma's diverse population has played a major role in defining its politics, history, and demographics in modern times, and the country continues to struggle to overcome its ]. The ] has dominated government since ] led a ] in 1962 that toppled the civilian government of ]. From that point, Burma's leadership went under the control of the military-led ]. It remained so until 2011, when the council was dissolved following the ] and subsequent inauguration of Burma's civilian government. | |||
| Myanmar's post-independence history has been checkered by continuing unrest and conflict to this day. The ] resulted in a ] under the ]. On 8 August 1988, the ] then resulted in a nominal transition to a ] two years later, but the country's ] refused to cede power, and has continued to rule the country through to the present. The country remains riven by ethnic strife among its ] and has one of the world's ]. The ] and several other organisations have reported consistent and systemic ] violations in the country.<ref name=UNHR>{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/burma |title=Burma |publisher=Human Rights Watch |access-date=6 July 2013 |archive-date=1 December 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111201235346/https://www.hrw.org/burma |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite web |url=http://www.amnestyusa.org/our-work/countries/asia-and-the-pacific/myanmar |title=Myanmar Human Rights |publisher=Amnesty International USA |access-date=6 July 2013 |archive-date=29 May 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110529055701/http://www.amnestyusa.org/our-work/countries/asia-and-the-pacific/myanmar |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/world-report-2012/world-report-2012-burma |title=World Report 2012: Burma |publisher=Human Rights Watch |access-date=6 July 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130630121229/http://www.hrw.org/world-report-2012/world-report-2012-burma |archive-date=30 June 2013 |date=22 January 2012 }}</ref> In 2011, the ] was officially dissolved following a ], and a nominally ] was installed. ] and ]s were released and the ] was held, leading to improved ] and eased ],<ref name=Easing>{{cite news |last=Madhani |first=Aamer |title=Obama administration eases Burma sanctions before visit |url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/theoval/2012/11/16/obama-lifts-sanctions-burma-visit/1710253/ |newspaper=USA Today |date=16 November 2012 |access-date=22 August 2017 |archive-date=13 January 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130113090007/http://www.usatoday.com/story/theoval/2012/11/16/obama-lifts-sanctions-burma-visit/1710253/ |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite news |last1=Fuller |first1=Thomas |last2=Geitner |first2=Paul |title=European Union Suspends Most Myanmar Sanctions |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/24/world/asia/eu-suspends-sanctions-on-myanmar.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120424015447/http://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/24/world/asia/eu-suspends-sanctions-on-myanmar.html |archive-date=2012-04-24 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |newspaper=] |date=23 April 2012 }}</ref> although the country's treatment of its ], particularly in connection with the ], continued to be a source of international tension and consternation.<ref name=MinorityTreatment>{{cite web |author=Greenwood, Faine |url=http://www.undispatch.com/the-8-stages-of-genocide-against-burmas-rohingya |title=The 8 Stages of Genocide Against Burma's Rohingya {{pipe}} UN DispatchUN Dispatch |publisher=Undispatch.com |date=27 May 2013 |access-date=13 April 2014 |archive-date=18 June 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130618062450/http://www.undispatch.com/the-8-stages-of-genocide-against-burmas-rohingya |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite news | url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-myanmar-violence-idUSBRE85A01C20120611 | title=EU welcomes "measured" Myanmar response to rioting | work=Reuters | date=11 June 2012 | access-date=1 July 2017 | archive-date=6 August 2012 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120806072509/http://www.reuters.com/article/2012/06/11/us-myanmar-violence-idUSBRE85A01C20120611 | url-status=live }}<br />{{cite news | url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-18395788 | title=Q&A: Communal violence in Burma | publisher=BBC | access-date=14 October 2013 | archive-date=16 April 2019 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190416191015/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-18395788 | url-status=live }}</ref> Following the ], in which ] won a clear majority in both houses, the ] again seized power ].<ref name=":3">{{cite news|date=1 February 2021|title=Myanmar military takes control of country after detaining Aung San Suu Kyi|language=en-GB|publisher=BBC News|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-55882489|access-date=1 February 2021|archive-date=31 January 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210131232954/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-55882489|url-status=live}}</ref> The coup, which was widely condemned by the ], led to ] and has been marked by violent ] by the military, as well as a larger outbreak of the ].<ref>{{Cite news|title=Fatalities Reported After Military Truck Rams Protesters in Myanmar|first=Sui-Lee|last=Wee|newspaper=The New York Times|date=5 December 2021|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2021/12/05/world/asia/myanmar-car-protesters-killed.html|access-date=7 December 2021|archive-date=7 December 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211207224710/https://www.nytimes.com/2021/12/05/world/asia/myanmar-car-protesters-killed.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The military also arrested Aung San Suu Kyi in order to remove her from public life, and charged her with crimes ranging from ] to violation of ] protocols; all of the charges against her are "politically motivated" according to independent observers.<ref>{{Cite news|title=Myanmar's junta condemned over guilty verdicts in Aung San Suu Kyi trial|first=Rebecca|last=Ratcliffe|newspaper=The Guardian|date=6 December 2021|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/dec/06/aung-san-suu-kyi-sentenced-to-four-years-in-prison-for-incitement|access-date=7 December 2021|archive-date=7 December 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211207123547/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/dec/06/aung-san-suu-kyi-sentenced-to-four-years-in-prison-for-incitement|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] and several other organizations have reported consistent and systematic ] violations in the country, including ], ] and a lack of ]. However, since the dispersion of the country's ], some groups within Burma have attempted to adopt a new constitution in hopes of creating a more modern, democratic nation. | |||
| Myanmar is a member of the ], ], ], and ], but it is not a member of the ] despite once being part of the ]. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the ]. The country is very rich in ]s, such as ], ], ], ], ] and other ]s, as well as also endowed with ], having the highest ] potential compared to other countries of the Great ] Subregion.<ref>Vakulchuk, Roman; Kyaw Kyaw Hlaing; Edward Ziwa Naing; Indra Overland; Beni Suryadi and Sanjayan Velautham (2017). Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI) and Myanmar Institute of Strategic and International Studies (MISIS) Report. p. 8.</ref> However, Myanmar has long suffered from ], factional violence, ], poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of ] with little regard to ].<ref>{{cite journal |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/25773443 |title=Why Has Myanmar not Developed Like East Asia? |last=Wong |first=John |journal=ASEAN Economic Bulletin |volume=13 |number=3 |date=March 1997 |pages=344–358 |doi=10.1355/AE13-3E |doi-broken-date=22 November 2024 |jstor=25773443 |access-date=8 May 2023 |archive-date=8 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230508191403/https://www.jstor.org/stable/25773443 |url-status=live |issn=0217-4472}}</ref> In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (]) at US$221.5 billion.<ref name=imf2>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2017/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2017&ey=2019&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&pr1.x=64&pr1.y=6&c=518&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a=|title=Burma (Myanmar)|work=World Economic Outlook Database|publisher=International Monetary Fund|access-date=19 May 2017|archive-date=29 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210329175838/https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2017/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2017&ey=2019&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&pr1.x=64&pr1.y=6&c=518&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a=|url-status=live}}</ref> The ] in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the ] is controlled by ] of the ].<ref name=IncomeGap>{{cite news |url=http://www.nationmultimedia.com/aec/Income-gap-worlds-widest-30214106.html |title=Income Gap 'world's widest' |work=The Nation |access-date=15 September 2014 |author=Eleven Media |date=4 September 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140915230853/http://www.nationmultimedia.com/aec/Income-gap-worlds-widest-30214106.html |archive-date=15 September 2014 }}<br />{{cite news | url=https://www.dvb.no/analysis/income-inequality-in-burma/33726 | title=Income inequality in Burma | publisher=Democratic Voice of Burma | access-date=15 September 2014 | last=McCornac |first=Dennis | date=22 October 2013 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140915230920/https://www.dvb.no/analysis/income-inequality-in-burma/33726 | archive-date=15 September 2014 | url-status=dead | df=dmy-all }}</ref> Myanmar is one of the ]; as of 2022, according to the ], it ranks 144 out of 193 countries in terms of ].<ref name="UNHDR"/> Since 2021, more than 600,000 people were displaced across Myanmar due to the surge in violence post-coup, with more than three million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance.<ref>{{cite web| url=https://reliefweb.int/report/myanmar/issue-brief-dire-consequences-addressing-humanitarian-fallout-myanmar-s-coup| title=Issue Brief: Dire Consequences: Addressing the Humanitarian Fallout from Myanmar's Coup - Myanmar| work=ReliefWeb| date=21 October 2021| access-date=9 August 2022| archive-date=2 February 2022| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220202220333/https://reliefweb.int/report/myanmar/issue-brief-dire-consequences-addressing-humanitarian-fallout-myanmar-s-coup| url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| {{Main|Names of Burma}} | |||
| "Burma" is derived from the Burmese word "Bamar" (]), which in turn is the colloquial form of Myanmar (]) (or Mranma in old ]), both of which historically referred to the majority ] (or the Bamar). Depending on the ] used the pronunciation would be "Bama" ({{IPA-my|bəmà|pron}}), or "Myamah" ({{IPA-my|mjəmà|pron}}). The name "Burma" has been in use in English since the time of ]. | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| In 1989, the military government ] the English translations of many colonial-era names, including the name of the country to "Myanmar". This prompted one scholar to coin the term "Myanmarification" to refer to the top-down programme of political and cultural reform in the context of which the renaming was done. The renaming remains a contested issue.<ref name="Houtman">{{cite book |url=http://homepages.tesco.net/~ghoutman |title=Mental culture in Burmese crisis politics |last=Houtman |first=Gustaaf |year=1999 |series=ILCAA Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa Monograph Series No. 33|publisher= Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa |pages=43–47 |isbn=978-4872977486}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Names of Myanmar}} | |||
| The name of the country has been a matter of dispute and disagreement, particularly in the early 21st century, focusing mainly on the political legitimacy of those using ''Myanmar'' versus ''Burma''.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.usip.org/blog/2018/06/whats-name-burma-or-myanmar|title=What's in a Name: Burma or Myanmar?|website=United States Institute of Peace|language=en|access-date=27 April 2020|archive-date=19 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200719221651/https://www.usip.org/blog/2018/06/whats-name-burma-or-myanmar|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7013943.stm|title=Should it be Burma or Myanmar?|date=26 September 2007|access-date=27 April 2020|language=en-GB|archive-date=18 May 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200518145013/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/7013943.stm|url-status=live}}</ref> Both names derive from the earlier ] ''Mranma'' or ''Mramma'', an ] for the majority ] ethnic group, of uncertain etymology.<ref name=dgeh>{{cite book | title=Burma | last=Hall | first=DGE | chapter=Pre-Pagan Burma | year=1960 | edition=3 | page=13}}</ref> The terms are also popularly thought to derive from ] ''Brahma Desha'', 'land of ]'.<ref>{{Cite book|url={{GBurl|id=bV3shLzx0B4C|p=352}}|title=Mental Culture in Burmese Crisis Politics: Aung San Suu Kyi and the National League for Democracy|last=Houtman|first=Gustaaf|date=1999|publisher=ILCAA|isbn=9784872977486|page=352}}</ref> | |||
| In 1989, the ] ] the English translations of many names dating back to ] or earlier, including that of the country itself: ''Burma'' became ''Myanmar''. The renaming remains a contested issue.<ref name="Houtman1999">{{cite book |url={{GBurl|id=bV3shLzx0B4C|p=45}} |title=Mental culture in Burmese crisis politics |last=Houtman |first=Gustaaf |year=1999 |series=ILCAA Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa Monograph Series No. 33 |publisher=Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa |pages=43–54 |isbn=978-4-87297-748-6}}</ref> Many political and ethnic opposition groups and countries continue to use ''Burma'' because they do not recognise the legitimacy or authority of the military government.<ref name="steinberg">{{cite book |last=Steinberg |first=David I. |date=2002 |title=Burma: The State of Myanmar |url={{GBurl|id=CSTuWZ0BMmMC}} |publisher=Georgetown University Press |page=xi |isbn=978-1-58901-285-1}}</ref> | |||
| While most of the name changes are closer to their actual Burmese pronunciations, many opposition groups and countries continue to oppose their use in English because they recognise neither the legitimacy of the ruling military government nor its authority to rename the country or towns in English.<ref name="steinberg">{{cite book |last=Steinberg |first=David L. |year=2002 |month=February |title=Burma: The State of Myanmar |publisher=] |id=ISBN}}</ref> Various non-Burman ethnic groups choose not to recognise the name because the term Myanmar has historically been used as a label for the majority ethnic group, the ], rather than for the country.<ref name="thantmyintu2001">{{cite book | first=Thant | last=Myint-U | year=2001 | title=The Making of Modern Burma | isbn=0-521-79914-7 | publisher=Cambridge Univ. Press | location=Cambridge}}</ref><ref name="msmith"/><ref>''The Burma Road from the Union of Burma to Myanmar'', Mya Maung, Asian Survey, Vol. 30, No. 6, June 1990, p 602</ref> | |||
| The country's official full name is "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" ({{langx|my|ပြည်ထောင်စုသမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်}}, ''{{transliteration|my|Pyihtaungsu Thamada Myanma Naingngantaw}}'', {{IPA-my|pjìdàʊɴzṵ θàɴməda̰ mjəmà nàɪɴŋàɴdɔ̀|pron}}). Countries that do not officially recognise that name use the long form "Union of Burma" instead.{{r|World Factbook}}<ref name="NCGUB">{{cite web |url=http://www.ncgub.net/ |title=NCGUB |publisher=National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma |access-date=3 May 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150909080518/http://ncgub.net/ |archive-date=9 September 2015 |url-status=dead }}</ref> In English, the country is popularly known as either ''Burma'' or ''Myanmar''. In Burmese, the pronunciation depends on the ] used and is either ''{{transliteration|my|Bama}}'' ({{IPA-my|bəmà|pron}}) or ''{{transliteration|my|Myamah}}'' ({{IPA-my|mjəmà|pron}}).<ref name="Houtman1999" /> | |||
| Various world entities have chosen to accept or reject the name change. The United Nations, of which Burma (under the name Myanmar) is a member, endorsed the name change five days after its announcement by the junta.<ref name="Scrivener">{{cite news | |||
| |url=http://www.thestar.com/article/264116 |title=The Burma question |last=Scrivener |first=Leslie |date=6 October 2007 |work=TheStar.com | location=Toronto}}</ref> However, governments of many countries including Australia, Canada, France,<ref name="www.diplomatie.gouv.fr">{{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.diplomatie.gouv.fr/fr/pays-zones-geo_833/birmanie_551/index.html|title= Birmanie|publisher=France Diplomatie}}</ref> the United Kingdom and the United States<ref>"Background Notes: Burma." Electronic Information and Publications Office. Dec 2008. Bureau of Public Affairs. Accessed 5 Jul 2009. http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm</ref> still refer to the country as "Burma", with varying levels of recognition of the validity of the name change itself. Others, including the ] and the governments of ], ], ],<ref name="BBC">{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/magazine/7013943.stm | |||
| |title=Should it be Burma or Myanmar?|date=26 September 2007|work=Magazine|publisher=]|accessdate=2 July 2008}}</ref> Russia<ref name="Singer">{{cite news|url=http://jordanispalestine.blogspot.com/2008/08/myanmar-and-israel-fighting-semantic.html|title=Myanmar and Israel – Fighting the Semantic Wars|last=Singer|first=David|date=2 October 2007|accessdate=24 November 2008}}</ref> and the People's Republic of China recognise "Myanmar" as the official name. | |||
| Official ] retains ''Burma'' as the country's name although the ]'s website lists the country as ''Burma (Myanmar)''.<ref name="USNaming">{{cite news |title=Burma or Myanmar? Obama calls it both on visit |url=http://asiancorrespondent.com/92211/burma-or-myanmar-obama-calls-it-both-on-visit// |agency=] |newspaper=] |publisher=Hybrid News Limited |location=Bristol, England |date=19 November 2012 |access-date=19 November 2012 |quote=Yangon, Burma (AP) – Officially at least, America still calls this Southeast Asian nation Burma, the favoured appellation of dissidents and pro-democracy activists who opposed the former military junta's move to summarily change its name 23 years ago. |archive-date=21 November 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121121120002/http://asiancorrespondent.com/92211/burma-or-myanmar-obama-calls-it-both-on-visit/ |url-status=dead }}<br />{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/nov/19/burma-myanmar-obama-name-visit|date=19 November 2012|newspaper=The Guardian|title=Burma v Myanmar – what's in a name? Obama plays it safe during historic visit|author=Jason Burke}}<br />{{cite web |url=https://travel.state.gov/travel/cis_pa_tw/cis/cis_1077.html |title=Burma (Myanmar) |publisher=] |access-date=13 April 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131020073109/http://travel.state.gov/travel/cis_pa_tw/cis/cis_1077.html |archive-date=20 October 2013 }}</ref> The ] uses ''Myanmar'', as does the ] and as do ],<ref>{{cite web |title=Countries, economies and regions – Myanmar |url=http://dfat.gov.au/geo/myanmar/Pages/myanmar.aspx |publisher=Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Australian Government |access-date=14 September 2016 |archive-date=20 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170920180542/http://dfat.gov.au/geo/myanmar/Pages/myanmar.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref> ], ],<ref>{{cite news |title=Burma vs. Myanmar: What's in a Name |url=http://www.dw.de/burma-vs-myanmar-whats-in-a-name/a-2804762 |access-date=2 August 2013 |newspaper=DW |date=1 September 2007 |archive-date=22 March 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150322193443/http://www.dw.de/burma-vs-myanmar-whats-in-a-name/a-2804762 |url-status=live }}</ref> ], ], ], ],<ref>{{cite news |last=Mudditt |first=Jessica |date=19 November 2012 |title=Burma or Myanmar: Will the US make the switch? |url=http://www.mmtimes.com/index.php/special-features/153-sanctions-to-sucess/3187-burma-or-myanmar-will-the-us-make-the-switch.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130321003449/http://mmtimes.com/index.php/special-features/153-sanctions-to-sucess/3187-burma-or-myanmar-will-the-us-make-the-switch.html |archive-date=21 March 2013 |access-date=2 August 2013}}</ref> ],<ref name="Dittmer">{{cite book |title=Burma Or Myanmar? The Struggle for National Identity |last=Dittmer |first=Lowell |year=2010 |page=2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=aoHP2Q2I1p4C&q=9789814313643&pg=PA2 |publisher=World Scientific |isbn=9789814313643 |access-date=9 August 2023 |archive-date=10 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230810233429/https://books.google.com/books?id=aoHP2Q2I1p4C&pg=PA2&q=9789814313643 |url-status=live }}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web |title=Representations and travel advice – Myanmar |url=https://www.eda.admin.ch/eda/en/home/laender-reise-information/myanmar.html |publisher=Federal Department of Foreign Affairs |access-date=14 September 2016 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010114231/https://www.eda.admin.ch/eda/en/home/laender-reise-information/myanmar.html |url-status=live }}</ref> ]<ref>{{cite web|website=Government of Canada – Global Affairs Canada|access-date=15 November 2018|title=Canada and Myanmar relations|url=http://international.gc.ca/world-monde/myanmar/relations.aspx?lang=eng|archive-date=20 November 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181120040924/http://international.gc.ca/world-monde/myanmar/relations.aspx?lang=eng|url-status=dead}}</ref> and ].<ref>{{Cite web |last= |title=Кабінет Міністрів України - МЗС: Відбувся перший в історії українсько-м'янманських відносин офіційний візит до Республіки Союз М'янма |url=https://www.kmu.gov.ua/news/249653997 |access-date=2024-10-27 |website=www.kmu.gov.ua |language=uk}}</ref> Most English-speaking international news media refer to the country by the name ''Myanmar'', including the ],<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-12990563 | publisher=BBC News | title=Myanmar profile | date=16 July 2013 | access-date=22 June 2018 | archive-date=26 June 2014 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140626082954/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-12990563 | url-status=live }}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news | url=http://edition.cnn.com/2013/07/30/world/asia/myanmar-fast-facts | publisher=CNN | title=Myanmar Fast Facts | date=30 July 2013 | access-date=17 March 2014 | archive-date=29 May 2017 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170529211524/http://edition.cnn.com/2013/07/30/world/asia/myanmar-fast-facts | url-status=live }}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia-pacific/2013/07/201372271935496428.html |title=Myanmar blast hits anti-Muslim monk's event – Asia-Pacific |publisher=Al Jazeera |date=22 July 2013 |access-date=17 March 2014 |archive-date=20 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170920015012/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia-pacific/2013/07/201372271935496428.html |url-status=live }}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news|url=http://uk.reuters.com/places/myanmar |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121027012001/http://uk.reuters.com/places/myanmar |url-status=dead |archive-date=27 October 2012 |title=Myanmar |work=Reuters |date=9 February 2009}}</ref> and the ] (])/].<ref name="ABCRA">{{cite news |last1=Woodley |first1=Naomi |title=Carr apprehensive about Rohingyas' future in Myanmar |url=http://www.abc.net.au/am/content/2013/s3801497.htm |access-date=14 September 2016 |work=AM |publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |date=12 July 2013 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010115947/http://www.abc.net.au/am/content/2013/s3801497.htm |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite news |title=Aung San Suu Kyi arrives in Thailand for official visit |url=http://www.radioaustralia.net.au/international/2016-06-23/aung-san-suu-kyi-arrives-in-thailand-for-official-visit/1593108 |access-date=14 September 2016 |publisher=Radio Australia |date=23 June 2016 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010114241/http://www.radioaustralia.net.au/international/2016-06-23/aung-san-suu-kyi-arrives-in-thailand-for-official-visit/1593108 |url-status=live }}</ref> Myanmar is known by a name deriving from ''Burma'' in ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ambafrance-mm.org/Birmanie-ou-Myanmar-Le-vrai-faux |title='Birmanie ou Myanmar ? Le vrai faux débat francophone' – La France en Birmanie |publisher=Ambafrance-mm.org |access-date=13 April 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140408202934/http://www.ambafrance-mm.org/Birmanie-ou-Myanmar-Le-vrai-faux |archive-date=8 April 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> French-language media consistently use ''Birmanie''.<ref>{{cite magazine |url=http://tempsreel.nouvelobs.com/topnews/20170904.AFP9687/birmanie-87-000-rohingyas-refugies-au-bangladesh-en-dix-jours-selon-l-onu.html |title=Birmanie: 87.000 Rohingyas réfugiés au Bangladesh en dix jours, selon l'ONU |magazine=L'Obs |date=4 September 2017 |access-date=9 September 2017 |archive-date=9 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170909131747/http://tempsreel.nouvelobs.com/topnews/20170904.AFP9687/birmanie-87-000-rohingyas-refugies-au-bangladesh-en-dix-jours-selon-l-onu.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://tempsreel.nouvelobs.com/tag/birmanie|title=L'actualité sur Birmanie par L'Obs|website=L'Obs|access-date=5 September 2017|archive-date=12 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171212170716/http://tempsreel.nouvelobs.com/tag/birmanie|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Media usage is also mixed. In spite of the usage by the United States government, some American news outlets including '']'', '']'', The '']'' and '']'', and international news agencies the '']'', '']'' and '']'' have adopted the name "Myanmar". The name "Burma" is still widely used by other news outlets, including '']'', '']'', the '']'', '']'', most British newspapers<!--See the Reuters citation at the end of the sentence-->, '']'' and '']''. Other sources often use combined terms such as "Burma, also known as Myanmar." Some media outlets that use "Myanmar" refer to "Burma" as the nation's "colonial name."<ref>Klotz, Irene, , Malaysia Star, 28 July 2005</ref><ref>Shenon, Philip, , New York Times, 20 Aug 1995</ref><ref>, Reuters editorial comment, 23 October 2007</ref> | |||
| There are at least nine different pronunciations of the English name ''Myanmar'', and no single one is standard. Pronunciations with two syllables are found most often in major British and American dictionaries.<ref group=pronunciations>examples of two-syllable pronunciations: {{IPAc-en|ˌ|m|j|æ|n|ˈ|m|ɑːr}}, {{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|j|æ|n|m|ɑːr}}, {{IPAc-en|audio=En-us-Myanmar.ogg|ˌ|m|j|ɑː|n|ˈ|m|ɑːr}}, or {{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|j|ɑː|n|m|ɑːr}}</ref> Dictionaries—such as ]—and other sources also report pronunciations with three syllables.<ref group=pronunciations>examples of three-syllable pronunciations: {{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|iː|ə|n|m|ɑːr}}, {{IPAc-en|m|i|ˈ|æ|n|m|ɑːr}}, {{IPAc-en|ˌ|m|aɪ|ə|n|ˈ|m|ɑːr}}, {{IPAc-en|m|aɪ|ˈ|ɑː|n|m|ɑːr}}, or {{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|aɪ|æ|n|m|ɑːr}}</ref><ref name="Myanmar">{{cite web|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/magazinemonitor/2007/09/how_to_say_myanmar.shtml|title=How to say Myanmar|work=Magazine Monitor|series=An occasional guide to the words and names in the news from Martha Figueroa-Clark of the ] Pronunciation Unit|publisher=BBC|date=26 September 2007|author=Martha Figueroa-Clark|access-date=23 December 2019|archive-date=10 July 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190710185740/https://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/magazinemonitor/2007/09/how_to_say_myanmar.shtml|url-status=live}}<br />{{cite web |url=https://www.lexico.com/definition/myanmar |title=Definition of MYANMAR by Oxford Dictionary on Lexico.com (British & World English) |publisher=Oxford Dictionaries |access-date=29 April 2021 |archive-date=29 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210429132905/https://www.lexico.com/definition/myanmar |url-status=dead }}<br />{{cite web |url=https://www.ahdictionary.com/word/search.html?q=Myanmar |title=Myanmar |publisher=American Heritage Dictionary |access-date=29 April 2021 |archive-date=29 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210429132314/https://www.ahdictionary.com/word/search.html?q=Myanmar |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite encyclopedia |author=Thackrah, J. R. |url=http://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/myanmar |title=Definition of Myanmar |dictionary=Collins English Dictionary |access-date=1 September 2012 |archive-date=26 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181226082844/https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/myanmar |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite web |url=http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/myanmar?show=0&t=1345589109 |title=Myanmar – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary |publisher=Merriam-webster.com |access-date=1 September 2012 |archive-date=26 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181226082847/https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/Myanmar |url-status=live }}<br />{{cite book | title=Sociolinguistics: An International Handbook of the Science of Language and Society | last=Ammon | first=Ulrich | year=2004 | edition=2nd | volume=3/3 | isbn=978-3-11-018418-1 | publisher=] | url={{GBurl|id=LMZm0w0k1c4C|p=2012}} | page=2012 }}</ref> | |||
| Uncertainty among English speakers on how to pronounce "Myanmar" gives rise to pronunciations such as {{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|j|ɑː|n|.|m|ɑr}}, {{IPAc-en|m|aɪ|.|ən|ˈ|m|ɑr}}, {{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|iː|.|ən|.|m|ɑr}} and {{IPAc-en|m|iː|ˈ|æ|n|.|m|ɑr}}. The BBC recommends {{IPAc-en|m|j|æ|n|ˈ|m|ɑr}}.<ref>{{cite news | |||
| |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/magazinemonitor/2007/09/how_to_say_myanmar.shtml | |||
| |title=How to Say: Myanmar | |||
| |date=26 September 2007 | |||
| |publisher=BBC News Magazine Monitor | |||
| |accessdate = 1 October 2007}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.onelook.com/?loc=bm3&w=myanmar | |||
| |title=Dictionary Search | |||
| |publisher=onelook.com | |||
| |accessdate = 1 October 2007}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url=http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/cgi-bin/cmudict?in=myanmar&stress=-s#lookup | |||
| |title=The CMU Pronouncing Dictionary | |||
| |publisher=Carnegie Mellon University | |||
| |accessdate = 1 October 2007}}</ref> The common pronunciation in Burmese is {{IPA-my|mjəmà|}}. | |||
| As ] explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a ], in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: {{IPA|}}. So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as {{IPA|}} by some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a ] based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. However, ''Burma'' is pronounced {{IPA|}} by rhotic speakers of English due to a ] constraint, as {{IPA|/ɜː/}} occurs only before {{IPA|/r/}} in those accents. | |||
| On 21 October 2010 some media reported that the government changed the official name to ''Republic of the Union of Myanmar'', which was established as part of the ].<ref name="r2010-10-21">{{cite news|url=http://ca.reuters.com/article/topNews/idCATRE69K2HM20101021|title=Myanmar gets new flag, official name, anthem|date=2010-10-21|publisher=Reuters|accessdate=23 October 2010}}</ref> But this information was not confirmed by any Burmese government sources nor any other credible sources till 30 March 2011 – the new name ''Republic of the Union of Myanmar'' is in effect as of inaugration of new government.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.myanmar.com/newspaper/nlm/index.html|title=Republic of the Union of Myanmar|date=30 March 2011|work=]|publisher=Myanmar.com|accessdate=2011-04-04}}</ref> Prior to this, the country was known formally as the ''Union of Myanmar'' since 1989. This had itself replaced the previous designation of the ''Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma'' used in the ], which in turn had replaced the ] adopted following independence, which had referred simply to the ''Union of Burma''.{{citation needed|date=December 2010|reason=Reuters informed about this new name, but still no confirmation in official (Burmese or others) sources – maybe Reuters is wrong, so please give an official source for this information (also see discussion page)}} | |||
| == |
== History == | ||
| {{ |
{{main|History of Myanmar}} | ||
| {{More citations needed|section|date=August 2022}} | |||
| ], which is approximately {{convert|50400|km2|sqmi|0|abbr=on}} in area, is largely used for rice cultivation.<ref name="myatthein">{{cite book | first=Myat | last=Thein | year=2005 | title=Economic Development of Myanmar | isbn=9-8123-0211-5 | publisher=Inst. of Southeast Asian Studies | location=Singapore}}</ref>]] | |||
| ] southwest of ]]] | |||
| === Prehistory === | |||
| Burma, which has a total area of {{convert|678500|km2}}, is the largest country in mainland ], and the 40th-largest in the world. It lies between latitudes ] and ], and longitudes ] and ]. | |||
| {{main|Prehistory of Myanmar|Migration period of ancient Burma}} | |||
| ], {{circa|8th century}}]] | |||
| Archaeological evidence shows that '']'' lived in the region now known as Myanmar as early as 750,000 years ago, with no more ''erectus'' finds after 75,000 years ago.<ref name="BLibConfOBMS2015">{{cite web|author1=Win Naing Tun|title=Prehistory to Protohistory of Myanmar: A Perspective of Historical Geography|url=http://www.burmalibrary.org/docs21/History/Win-Naing-Tun-2015-Prehistory_to_Protohistory_of_Myanmar_A_Perspective_of_Historical_Geography-en.pdf|publisher=Myanmar Environment Institute|access-date=22 November 2016|page=1|date=24 July 2015|quote=Homo erectus had lived in Myanmar 750,000 years ago|archive-date=26 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211026014002/https://www.burmalibrary.org/docs21/History/Win-Naing-Tun-2015-Prehistory_to_Protohistory_of_Myanmar_A_Perspective_of_Historical_Geography-en.pdf|url-status=live}}<br />{{cite book|last=Bowman|first=John Stewart Bowman|title=Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture|year=2013|publisher=Columbia University Press|isbn=978-0-231-50004-3|page=476|url={{GBurl|id=cYoHOqC7Yx4C}}}}</ref> The first evidence of '']'' is dated to about 25,000 BP with discoveries of stone tools in central Myanmar.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Schaarschmidt|first1=Maria|last2=Fu|first2=Xiao|last3=Li|first3=Bo|last4=Marwick|first4=Ben|last5=Khaing|first5=Kyaw|last6=Douka|first6=Katerina|last7=Roberts|first7=Richard G.|title=pIRIR and IR-RF dating of archaeological deposits at Badahlin and Gu Myaung Caves – First luminescence ages for Myanmar|journal=Quaternary Geochronology|volume=49|pages=262–270|date=January 2018|doi=10.1016/j.quageo.2018.01.001|s2cid=133664286|url=https://ro.uow.edu.au/smhpapers1/425|access-date=21 January 2020|archive-date=25 June 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220625002707/https://ro.uow.edu.au/smhpapers1/425/|url-status=live}}</ref> Evidence of ] age domestication of plants and animals and the use of polished stone tools dating to sometime between 10,000 and 6,000 BCE has been discovered in the form of ]s in ].<ref>{{cite web | last=Cooler | first=Richard M. | title=The Art and Culture of Burma (Chapter 1) | year=2002 | url=http://www.seasite.niu.edu/burmese/cooler/BurmaArt_TOC.htm | publisher=Northern Illinois University | location=DeKalb | access-date=22 March 2012 | archive-date=26 December 2016 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161226041623/http://www.seasite.niu.edu/burmese/cooler/BurmaArt_TOC.htm | url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| It is bordered to the northwest by ] of ] and ], ], ] and ] of India to the northwest. Its north and northeast border straddles the ] and ] regions of China for a Sino-Burman border total of {{convert|2185|km|mi}}. It is bounded by ] and ] to the southeast. Burma has {{convert|1930|km|mi}} of contiguous coastline along the ] and ] to the southwest and the south, which forms one quarter of its total perimeter.<ref name="CIA">{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/bm.html |title=Burma |accessdate = 13 January 2007 |work=The World Factbook | publisher=Central Intelligence Agency }}{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}</ref> | |||
| The ] arrived {{circa|1500 BCE}} when people in the region were turning copper into bronze, growing rice and domesticating poultry and pigs; they were among the first people in the world to do so.<ref>], p. 37</ref> Human remains and artefacts from this era were discovered in ] in the ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar-travel/myanmar-mandalay/monywa.htm |title=Skeletal Remains of Nyaunggan, Budalin Township, Monywa District, Sagaing Division |author=Yee Yee Aung |publisher=Perspective July 2002 |access-date=7 October 2008 |archive-date=28 December 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081228204723/http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar-travel/myanmar-mandalay/monywa.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> The ] began around 500 BCE with the emergence of iron-working settlements in an area south of present-day ].<ref>], p. 45</ref> Evidence also shows the presence of rice-growing settlements of large villages and small towns that traded with their surroundings as far as China between 500 BCE and 200 CE.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Hudson|first=Bob|title=A Pyu Homeland in the Samon Valley: a new theory of the origins of Myanmar's early urban system|url=http://acl.arts.usyd.edu.au/~hudson/BH2005Jan.pdf|journal=Myanmar Historical Commission Golden Jubilee International Conference|date=March 2005|page=1|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131126021929/http://acl.arts.usyd.edu.au/~hudson/BH2005Jan.pdf|archive-date=26 November 2013}}</ref> Iron Age Burmese cultures also had influences from outside sources such as ] and ], as seen in their funerary practices concerning child burials. This indicates some form of communication between groups in Myanmar and other places, possibly through trade.<ref>Coupey, A. S. (2008). Infant and child burials in the Samon valley, Myanmar. In Archaeology in Southeast Asia, from Homo Erectus to the living traditions: choice of papers from the 11th International Conference of the European Association of Southeast Asian Archaeologists, 25–29 September 2006, Bougon, France</ref> | |||
| In the north, the ] mountains form the border with China. ], located in ], at an elevation of {{convert|5881|m|ft|0}}, is the highest point in Burma.<ref>{{cite book | editor = Dr. Patrick Hesp et al. | year=2000 | title=Geographica's World Reference | publisher =Random House Australia | pages =738, 741}}</ref> Three mountain ranges, namely the Rakhine Yoma, the Bago Yoma, and the ] exist within Burma, all of which run north-to-south from the ].<ref name="myathan">{{cite book | first=Mya | last=Than | year=2005 | title=Myanmar in ASEAN: Regional Co-operation Experience | isbn=9-8123-0210-7 | publisher=Institute of Southeast Asian Studies | location=Singapore}}</ref> The mountain chains divide Burma's three river systems, which are the ], ], and the ] rivers.<ref name="myatthein"/> The Irrawaddy River, Burma's longest river, nearly {{convert|2170|km|mi|0}} long, flows into the ]. Fertile plains exist in the valleys between the mountain chains.<ref name="myathan"/> The majority of Burma's population lives in the Irrawaddy valley, which is situated between the Rakhine Yoma and the Shan Plateau. | |||
| === |
=== Early city-states === | ||
| {{main|Pyu city-states|Mon kingdoms}} | |||
| {{Main|Climate of Burma}} | |||
| Around the second century BCE the first-known ]s emerged in central Myanmar. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu people, the earliest inhabitants of Myanmar of whom records are extant, from present-day ].<ref name=EarlyYunnan>{{cite book|last=Hall|first=D.G.E.|title=Burma|edition=3rd|year=1960|publisher=Hutchinson University Library|isbn=978-1-4067-3503-1|pages=8–10}}<br />{{cite book|last=Moore|first=Elizabeth H.|title=Early Landscapes of Myanmar|year=2007|publisher=River Books|location=Bangkok|isbn=978-974-9863-31-2|page=236}}</ref> The Pyu culture was heavily influenced by trade with India, importing Buddhism as well as other cultural, architectural and political concepts, which would have an enduring influence on later Burmese culture and political organisation.<ref>], pp. 51–52</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Much of the country lies between the ] and the ]. It lies in the ] region of Asia, with its coastal regions receiving over {{convert|5000|mm|in|1|abbr=on}} of rain annually. Annual ] in the ] region is approximately {{convert|2500|mm|in|1|abbr=on}}, while average annual rainfall in the Dry Zone, which is located in central Burma, is less than {{convert|1000|mm|in|1|abbr=on}}. Northern regions of the country are the coolest, with average temperatures of {{convert|21|C|F}}. Coastal and delta regions have an average maximum temperature of {{convert|32|C|F|1}}.<ref name="myatthein"/> | |||
| By the 9th century, several city-states had sprouted across the land: the Pyu in the central dry zone, Mon along the southern coastline and Arakanese along the western littoral. The balance was upset when the Pyu came under repeated attacks from ] between the 750s and the 830s. In the mid-to-late 9th century the ] founded a small settlement at ]. It was one of several competing city-states until the late 10th century, when it grew in authority and grandeur.<ref>], pp. 90–91</ref> | |||
| ===Wildlife=== | |||
| The country's slow economic growth has contributed to the preservation of much of its environment and ]s. Forests, including dense tropical growth and valuable ] in lower Burma, cover over 49% of the country, including areas of ], ], ] and ]. ] and ] and ] have been introduced. In the highlands of the north, ], ] and various ]s cover much of the land.<ref name="BRMLIB">{{cite web |url=http://www.burmalibrary.org/reg.burma/archives/199909/msg00690.html |title=Myanmar's Forest Law and Rules |publisher=BurmaLibrary.org |accessdate=15 July 2006}}</ref> Heavy logging since the new 1995 forestry law went into effect has seriously reduced forest acreage and wildlife habitat.<ref>Reid, Robert; Bindloss, Joseph and Butler, Stuart (2009) "Environment: National Parks" ''Myanmar (Burma)'' (10<sup>th</sup> edition) Lonely Planet, Footscray, Victoria, Australia, page 85, ISBN 978-1-74104-718-9</ref> The lands along the coast support all varieties of ]s and once had large areas of ] although much of the protective mangroves have disappeared. In much of central Burma (the Dry Zone), vegetation is sparse and stunted. | |||
| === Pagan Kingdom === | |||
| Typical ] animals, particularly ]s and ]s, occur sparsely in Burma. In upper Burma, there are ], wild ], ]s, ], ], and ]s, which are also tamed or bred in captivity for use as work animals, particularly in the ]. Smaller ]s are also numerous, ranging from ]s and ]s to ]es and ]s. The abundance of birds is notable with over 800 species, including ]s, ], ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]birds. Among ] species there are ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]s. Hundreds of species of ] ] are wide-ranging, plentiful and are very important food sources.<ref name="MNET">{{cite web|url=http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar-culture/myanmar-flora-fauna.htm |title="Flora and Fauna" at |publisher=Myanmars.net |date= |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> For a list of protected areas, see ]. | |||
| {{main|Pagan Kingdom|Toungoo dynasty|Konbaung dynasty}} | |||
| {{see also|Kingdom of Ava|Hanthawaddy Kingdom|Kingdom of Mrauk U|Shan States}} | |||
| ]s and ]s in present-day ], the capital of the ]]] | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ] gradually grew to absorb its surrounding states until the 1050s–1060s when ] founded the Pagan Kingdom, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Pagan Empire and the ] were two main powers in mainland Southeast Asia.<ref>], p. 24</ref> The ] and culture gradually became dominant in the upper Irrawaddy valley, eclipsing the ], ] and ] norms{{clarify|date=January 2023}} by the late 12th century.<ref name=mha-63-65>{{cite book |last=Htin Aung |first=Maung |title=A History of Burma |url=https://archive.org/details/historyofburma00htin |url-access=registration |publisher=] |location=New York / London |year=1967 |pages=}}</ref> Theravada ] slowly began to spread to the village level, although ], ], ], and ] remained heavily entrenched. Pagan's rulers and wealthy built over 10,000 ] temples in the Pagan capital zone alone. Repeated Mongol invasions in the late 13th century toppled the four-century-old kingdom in 1287.<ref name="mha-63-65" /> | |||
| {{Main|History of Burma}} | |||
| After the ], the ] kingdom ceded the provinces of ], Tenassarim, and Arakan to the British.<ref name="thantmyintu"/> ] and southern Burma were incorporated into ] in 1853. All of Burma came directly or indirectly under ] in 1886 after the ] and the fall of Mandalay.<ref name="thantmyintu"/> Burma was administered as a province of ] until 1937 when it became a separate, self-governing colony. The country became independent from the United Kingdom on 4 January 1948, as the ''"Union of Burma"''. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| It became the ''"Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma"'' on 4 January 1974, before reverting to the ''"Union of Burma"'' on 23 September 1988. On 18 June 1989, the ] (SLORC) adopted the name ''"Union of Myanmar"'' for English transliteration. This controversial name change in English, while accepted in the UN and in many countries, is not recognised by the Burmese democracy movement and by nations such as Canada, the United Kingdom and the United States.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm|work=US Department of State|title= Profile: Union of Burma}}</ref> | |||
| Pagan's collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier, ] migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing ] came to dominate the entire northwestern to eastern arc surrounding the Irrawaddy valley. The valley too was beset with petty states until the late 14th century when two sizeable powers, ] and ], emerged. In the west, a politically fragmented Arakan was under competing influences of its stronger neighbours until the ] unified the Arakan coastline for the first time in 1437. The kingdom was a protectorate of the ] at different time periods.<ref name=kh-2-25>Maung Maung Tin, Vol. 2, p. 25</ref> | |||
| In the 14th and 15th centuries, Ava fought ] but could never quite reassemble the lost empire. Having held off Ava, the ]-speaking Hanthawaddy entered its golden age, and Arakan went on to become a power in its own right for the next 350 years. In contrast, constant warfare left Ava greatly weakened, and it slowly disintegrated from 1481 onward. In 1527, the Confederation of Shan States conquered Ava and ruled Upper Myanmar until 1555. | |||
| ===Early history=== | |||
| {{Main|Early History of Burma}} | |||
| Like the Pagan Empire, Ava, ] and the Shan states were all ] polities. Despite the wars, cultural synchronisation continued. This period is considered a golden age for ]. ] "grew more confident, popular, and stylistically diverse", and the second generation of Burmese law codes as well as the earliest ] emerged.<ref>], p. 134</ref> Hanthawaddy monarchs introduced religious reforms that later spread to the rest of the country.<ref>], pp. 64–65</ref> | |||
| Archaeological evidence suggests that civilisation in the region which now forms Burma is quite old. The oldest archaeological find was of ]s and a ] assemblage in a ] cave site in ] in Shan State.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lib.washington.edu/asp/myanmar/pdfs/AR0001A.pdf |author= U Aung Thaw |publisher=Burma Research Society; Yangon University, Yangon, Myanmar |title=Mon history |accessdate=25 February 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |url=http://books.google.com/?id=gxM0k5lGupAC&pg=PT320&lpg=PT320&dq=Padah+lin |author= John N. Miksic |publisher= NUS Press; National University of Singapore, Singapore |title=Earthernware in Southeast Asia |accessdate=25 February 2009 |isbn=9789971692711 |year=2003}}</ref> | |||
| === Taungoo and Konbaung === | |||
| The ] are thought to be the earliest group to migrate into the lower ] valley, and by the mid-10th century BC were dominant in southern Burma.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.albany.edu/~gb661/monhist1.html |author=George Aaron Broadwell |publisher=Dept. of Anthropology; University at Albany, Albany, New York |title=Mon history |accessdate=11 July 2006}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] under ] in 1580]] | |||
| ]. '']'']] | |||
| Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, through the efforts of ], a former vassal state of Ava. Taungoo's young, ambitious King ] defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in the ]. His successor ] went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states, ], Manipur, ], the ], ] and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Ayutthaya seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established ] at ] (Syriam). | |||
| The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing ], ], ], ] and upper ]. The restored Toungoo kings created a legal and political framework whose basic features continued well into the 19th century. The crown completely replaced the hereditary chieftainships with appointed governorships in the entire Irrawaddy valley and greatly reduced the hereditary rights of Shan chiefs. Its trade and secular administrative reforms built a prosperous economy for more than 80 years. From the 1720s onward, the kingdom was beset with repeated ] raids into Upper Myanmar and a nagging rebellion in Lan Na. In 1740, the Mon of Lower Myanmar founded the ]. Hanthawaddy forces sacked Ava in 1752, ending the 266-year-old Toungoo Dynasty.] shows British occupation during the ].]] | |||
| The ] speaking ] arrived later in the 1st century BC, and established several city states – of which ] was the most powerful – in central Irrawaddy valley. The Mon and Pyu kingdoms were an active overland ] between India and China. The Pyu kingdoms entered a period of rapid decline in early 9th century AD when the powerful kingdom of ] (in present-day ]) invaded the Irrawaddy valley several times. | |||
| After the fall of Ava, the ] involved one resistance group under ] defeating the Restored Hanthawaddy, and by 1759 he had reunited all of Myanmar and Manipur and driven out the French and the British, who had provided arms to Hanthawaddy. By 1770, Alaungpaya's heirs had subdued much of Laos and fought and won the ] against ] and the ] against ].<ref>], pp. 184–187</ref> | |||
| With Burma preoccupied by the Chinese threat, Ayutthaya recovered its territories by 1770 and went on to capture Lan Na by 1776. Burma and Siam went to war until 1855, but all resulted in a stalemate, exchanging ] (to Burma) and Lan Na (to Ayutthaya). Faced with a powerful China and a resurgent Ayutthaya in the east, King ] turned west, acquiring Arakan (1785), Manipur (1814) and Assam (1817). It was the second-largest empire in Burmese history but also one with a long ill-defined border with ].<ref>], p. 109</ref> | |||
| ===Bagan (1044–1287)=== | |||
| {{main|Pagan Kingdom}} | |||
| Tibeto-Burman speaking ], or the ], began migrating to the Irrawaddy valley from present-day ]'s Nanzhao kingdom starting in 7th century AD. Filling the power gap left by the Pyu, the Burmans established a small kingdom centred in ] in 849. But it was not until the reign of King ] (1044–1077) that Bagan's influence expanded throughout much of present-day Burma. | |||
| In 1826, Burma lost Arakan, ], Assam and Tenasserim to the British in the ]. In 1852, the British easily seized Lower Burma in the ]. King ] tried to modernise the kingdom and in 1875 narrowly avoided annexation by ceding the ]. The British, alarmed by the consolidation of ], annexed the remainder of the country in the ] in 1885. | |||
| After Anawrahta's capture of the Mon capital of ] in 1057, the Burmans adopted Theravada Buddhism from the Mons. The ] was created, based on the ], during the reign of King ] (1084–1112). Prosperous from trade, Bagan kings built many magnificent temples and ]s throughout the country – many of which can still be seen today. | |||
| Konbaung kings extended Restored Toungoo's administrative reforms and achieved unprecedented levels of internal control and external expansion. For the first time in history, the Burmese language and culture came to predominate the entire Irrawaddy valley. The evolution and growth of Burmese literature and theatre continued, aided by an extremely high adult male literacy rate for the era (half of all males and 5% of females).<ref>], pp. 202–206</ref> Nonetheless, the extent and pace of reforms were uneven and ultimately proved insufficient to stem the advance of British colonialism. | |||
| Bagan's power slowly waned in the 13th century. ]'s ] forces ] northern Burma starting in 1277, and sacked Bagan city itself in 1287. Bagan's over two century reign of Irrawaddy valley and its periphery was over. | |||
| === British Burma (1885–1948) === | |||
| ].]] | |||
| {{main|British rule in Burma|Burma campaign}} | |||
| ]s, which resulted in the abdication of the last Burmese monarch, King ]]] | |||
| ] on the ] road, July 1944]] | |||
| In the 19th century, Burmese rulers sought to maintain their traditional influence in the western areas of Assam, Manipur and Arakan. Pressing them, however, was the ] Company, which was expanding its interests eastwards over the same territory. Over the next 60 years, diplomacy, raids, treaties and compromises, known collectively as the ], continued until Britain proclaimed control over most of Burma.<ref>{{cite book |last=Baten |first=Jörg |title=A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present |publisher=Cambridge University Press |date=2016 |page=287 |isbn=978-1-107-50718-0}}</ref> With the fall of Mandalay, all of Burma came under British rule, being ] on 1 January 1886. | |||
| ===Small kingdoms (1287–1531)=== | |||
| The Mongols could not stay for long in the searing Irrawaddy valley. But the ] from Yunnan who came down with the ]s fanned out to the ] valley, Shan states, ], ] and ], and became powerful players in ]. | |||
| Throughout the colonial era, many Indians arrived as soldiers, civil servants, construction workers and traders and, along with the ] community, dominated commercial and civil life in Burma. ] became the capital of British Burma and an important port between ] and ]. Burmese resentment was strong, and was vented in violent riots that periodically paralysed Rangoon until the 1930s.<ref>{{cite book |last=Collis |first=Maurice |title=Trials in Burma |year=1945}}</ref> Some of the discontent was caused by a disrespect for Burmese culture and traditions. ] became the vanguards of the independence movement. ], an activist monk, died in prison after a 166-day hunger strike.<ref>{{cite book |first=Heinz |last=Bechert |author-link=Heinz Bechert |title=The World of Buddhism-Buddhist Monks and Nuns in Society and Culture |url=https://archive.org/details/worldofbuddhismb00bech |publisher=Facts on File |location=New York City |year=1984 |isbn=978-0-87196-982-8}}</ref> | |||
| The Bagan empire was irreparably broken up into several small kingdoms: | |||
| * The Burman kingdom of ] (1364–1555), the ] to three smaller kingdoms founded by Burmanised ] kings, controlling ] (without the ]s) | |||
| * The Mon kingdom of Hanthawady ] (1287–1540), founded by a Mon-ised Shan King Wareru (1287–1306), controlling ] (without ]). | |||
| * The Rakhine kingdom of ] (1434–1784), in the west. | |||
| * Several ]s in the Shan hills in the east and the ] in the north while the north-western frontier of present ] still disconnected yet. | |||
| On 1 April 1937, Burma became a separately administered colony of Britain, and ] became the first Prime Minister and Premier of Burma. Ba Maw was an outspoken advocate for Burmese self-rule, and he opposed the participation of Britain, and by extension Burma, in ]. He resigned from the Legislative Assembly and was arrested for sedition. In 1940, before ], ] formed the ] in Japan. | |||
| This period was characterised by constant warfare between Ava and Bago, and to a lesser extent, Ava and the Shans. Ava briefly controlled Rakhine (1379–1430) and came close to defeating Bago a few times, but could never quite reassemble the lost empire. Nevertheless, Burmese culture entered a golden age. Hanthawady Bago prospered. Bago's Queen Shin Saw Bu (1453–1472) raised the gilded ] to its present height. | |||
| As a major battleground, Burma was devastated during World War II by the ]. Within months after they entered the war, Japanese troops had advanced on Rangoon, and the British administration had collapsed. A ] headed by Ba Maw was established by the Japanese in August 1942. ]'s British ] were formed into ] groups trained to operate deep behind Japanese lines.<ref>{{cite news|author=Bennett, Will |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/chindits-remember-their-fallen-comrades-1597019.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220618/https://www.independent.co.uk/news/chindits-remember-their-fallen-comrades-1597019.html |archive-date=18 June 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |title=Chindits remember their fallen comrades |work=The Independent |date=20 August 1995 |access-date=20 November 2012 |location=London}}</ref> A similar American unit, ], followed the Chindits into the Burmese jungle in 1943.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.loc.gov/vets/stories/cbi-marauders.html |title=China-Burma-India: Merrill's Marauders. Veterans History Project, Library of Congress |publisher=Loc.gov |date=14 November 2012 |access-date=20 November 2012 |archive-date=28 March 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130328063322/http://www.loc.gov/vets/stories/cbi-marauders.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| By the late-15th century, constant warfare had left Ava greatly weakened. Its peripheral areas became either independent or autonomous. In 1486, King ] (1486–1531) of ] broke away from Ava and established a small independent kingdom. In 1527, ''Mohnyin'' (Shan: Mong Yang) ] finally captured Ava, upsetting the delicate power balance that had existed for nearly two centuries. The Shans would rule Upper Burma until 1555. | |||
| Beginning in late 1944, allied troops launched a ] that led to the ] in July 1945. The battles were intense with much of Burma laid waste by the fighting. Overall, the Japanese lost some 150,000 men in Burma with 1,700 prisoners taken.<ref>{{cite book |author1=Towle, Philip |author-link1 = Philip Towle |author2=Kosuge, Margaret |author3=Kibata, Yōichi |year=2000 |url={{GBurl|id=ktCv32ysz0AC|p=48}}|title=Japanese prisoners of war |publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group |page=48 |isbn=978-1-85285-192-7}}</ref> Although many Burmese fought initially for the Japanese as part of the Burma Independence Army, many Burmese, mostly from the ethnic minorities, served in the British Burma Army.<ref>{{cite book|first=Ian|last=Fellowes-Gordon|year=1971|title=The Battle For Naw Seng's Kingdom: General Stilwel}}</ref> The ] and the Arakan National Army fought with the Japanese from 1942 to 1944 but switched allegiance to the Allied side in 1945. Overall, 170,000 to 250,000 Burmese civilians died during World War II.<ref>Micheal Clodfelter. Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1500–2000. 2nd Ed. 2002 {{ISBN|0-7864-1204-6}}. p. 556<br />Werner Gruhl, Imperial Japan's World War Two, 1931–1945 Transaction 2007 {{ISBN|978-0-7658-0352-8}} (Werner Gruhl is former chief of NASA's Cost and Economic Analysis Branch with a lifetime interest in the study of the First and Second World Wars.)</ref> | |||
| ===Taungoo (1531–1752)=== | |||
| {{main|Taungoo Dynasty}} | |||
| Reinforced by fleeing Burmans from Ava, the minor Burman ] under its young, ambitious king ] (1531–1551) defeated the more powerful Mon kingdom at ], reunifying all of ] by 1540. Tabinshwehti's successor King ] (1551–1581) would go on to conquer ] (1556), ] (1557), ] (1557), ] (1564, 1569) and ] (1574), bringing most of western South East Asia under his rule. Preparing to invade ], a maritime power controlling the entire coastline west of Rakhine Yoma, up to ] province in ]. | |||
| Following World War II, ] negotiated the ] with ethnic leaders that guaranteed the independence of Myanmar as a unified state. ], Pe Khin, ], Sir Maung Gyi, Sein Mya Maung, ] were among the negotiators of the historic ] negotiated with Bamar leader General Aung San and other ethnic leaders in 1947. In 1947, Aung San became Deputy Chairman of the Executive Council of Myanmar, a transitional government. But in July 1947, political rivals<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/interview/author-discusses-martyrs-day-assassination-of-aung-san.html|title=Author Discusses Martyrs' Day Assassination of Aung San|work=The Irrawaddy|author=Moe, Kyaw Zwa|date=August 1977|access-date=20 October 2013|archive-date=7 November 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131107153638/http://www.irrawaddy.org/interview/author-discusses-martyrs-day-assassination-of-aung-san.html|url-status=live}}</ref> ] and several cabinet members.<ref>{{cite book|first=Gustaaf|last=Houtman|year=1999|title=Mental Culture in Burmese Crisis Politics: Aung San Suu Kyi and the National League for Democracy|isbn=978-4-87297-748-6|publisher=Tokyo University of Foreign Studies, Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa|location=Tokyo}}</ref> | |||
| Bayinnaung's massive empire unravelled soon after his death in 1581. Ayutthaya ] had driven out the Burmese by 1593 and went on to take ]. In 1599, Rakhine forces aided by ] mercenaries sacked the kingdom's capital ]. Chief ] mercenary ] (Burmese: ''Nga Zinga'') promptly rebelled against his Rakhine masters and established ] rule in ] (Syriam), then the most important seaport in Burma. The country was in chaos. | |||
| === Independence (1948–1962) === | |||
| The Burmese under King ] (1605–1628) regrouped and defeated the ] in 1611. Anaukpetlun reestablished a smaller reconstituted kingdom based in Ava covering Upper Burma, Lower Burma and Shan states (but without Rakhine or Taninthayi). After the reign of King Thalun (1629–1648), who rebuilt the war-torn country, the kingdom experienced a slow and steady decline for the next 100 years. The Mons successfully rebelled starting in 1740 with French help and ] encouragement, broke away Lower Burma by 1747, and finally put an end to the House of Taungoo in 1752 when they took ]. | |||
| {{main|Post-independence Burma (1948–1962)}}{{See also|Independence Day (Myanmar)}} | |||
| On 4 January 1948, the nation became an independent republic, under the terms of the ]. The new country was named the ''Union of Burma'', with ] as its first president and ] as its first prime minister. Unlike most other former British colonies and overseas territories, Burma did not become a member of the ]. A ] parliament was formed, consisting of a ] and a ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://english.dvb.no/e_docs/511947_con.htm|title=The Constitution of the Union of Burma|access-date=7 July 2006|year=1947|publisher=DVB| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060615072018/http://english.dvb.no/e_docs/511947_con.htm|archive-date=15 June 2006}}</ref> and ] elections were held in ], ] and ]. | |||
| The geographical area Burma encompasses today can be traced to the ], which combined Burma Proper, which consisted of Lower Burma and Upper Burma, and the Frontier Areas, which had been administered separately by the British.<ref>{{cite book |first=Martin |last=Smith |year=1991 |title=Burma -Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity |publisher=Zed Books |location=London and New Jersey |pages=42–43}}</ref> | |||
| ===Konbaung (1752–1885)=== | |||
| {{main|Konbaung Dynasty}} | |||
| ] reveals early British occupation in Burma during the ].]] | |||
| In 1961, ], the Union of Burma's Permanent Representative to the United Nations and former secretary to the prime minister, was elected ], a position he held for ten years.<ref>{{cite journal|volume=14|issue=9|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=7610 | |||
| King ] (1752–1760), established the ] in ] in 1752.<ref>{{cite book| url=http://dlxs.library.cornell.edu/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=sea;cc=sea;view=toc;subview=short;idno=sea328| title=An Account of An Embassy to the Kingdom of Ava by Michael Symes,1795}}</ref> He founded ] in 1755. By his death in 1760, Alaungpaya had reunified the country. In 1767, King ] (1763–1777) sacked ]. The ] of China ] from 1765 to 1769 without success. The Chinese invasions allowed the new Siamese kingdom based in Bangkok to repel the Burmese out of ] by the late 1770s. | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120314141301/http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=7610 | |||
| |archive-date=14 March 2012 | |||
| |author=Zaw, Aung | |||
| |title=Can Another Asian Fill U Thant's Shoes?|journal=The Irrawaddy |date=September 2006}}</ref> | |||
| When the non-Burman ethnic groups pushed for autonomy or federalism, alongside having a weak civilian government at the centre, the military leadership staged a coup d'état in 1962. Though incorporated in the 1947 Constitution, successive military governments construed the use of the term ']' as being anti-national, anti-unity and pro-disintegration.<ref>{{Cite news |url=http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-united-states-of-myanmar/article18525853.ece |title=The united states of Myanmar? |newspaper=The Hindu |date=23 May 2017 |access-date=9 September 2017 |last1=Kipgen |first1=Nehginpao |archive-date=13 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200613230526/https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-united-states-of-myanmar/article18525853.ece |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| King ] (1782–1819) failed repeatedly to reconquer Siam in 1780s and 1790s. Bodawpaya did manage to capture the western kingdom of ], which had been largely independent since the fall of Bagan, in 1784. Bodawpaya also formally annexed ], a rebellion-prone protectorate, in 1813. | |||
| === Military rule (1962–2011) === | |||
| King ]'s (1819–1837) general ] put down a rebellion in ] in 1819 and captured then independent kingdom of ] in 1819 (again in 1821). The new conquests brought the Burmese adjacent to the British India. The British defeated the Burmese in the ] (1824–1826). Burma had to cede ], ], ] (Arakan) and ] (Tenessarim). | |||
| On 2 March 1962, the military led by General ] ], and the government had been under direct or indirect control by the military since then. Between 1962 and 1974, Myanmar was ruled by a ] headed by the general. Almost all aspects of society (business, media, production) were ] or brought under government control under the ],<ref name="thantmyintu">]</ref> which combined Soviet-style nationalisation and ]. | |||
| A ] of the ] was adopted in 1974. Until 1988, the country was ruled as a ], with the general and other military officers resigning and ruling through the ] (BSPP).<ref name="christinafink">{{cite book |first=Christina |last=Fink |year=2001 |title=Living Silence: Burma under Military Rule |isbn=978-1-85649-926-2 |publisher=White Lotus |location=Bangkok |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/livingsilence00chri }}</ref> During this period, Myanmar became one of the world's most impoverished countries.<ref name="ruin">{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2007/sep/28/burma.uk |title=The Burma road to ruin |work=The Guardian |location=London |first=Mark |last=Tallentire |date=28 September 2007 |access-date=12 December 2016 |archive-date=4 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304081122/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2007/sep/28/burma.uk |url-status=live }}</ref> There were sporadic protests against military rule during the Ne Win years, and these were almost always violently suppressed. On 7 July 1962, the government broke up ], killing 15 students.<ref name="thantmyintu" /> In 1974, the military violently suppressed ] at the funeral of U Thant. Student protests in 1975, 1976, and 1977 were quickly suppressed by overwhelming force.<ref name="christinafink" /> | |||
| In 1852, the British attacked a much weakened Burma during a Burmese palace power struggle. After the ], which lasted 3 months, the British had captured the remaining coastal provinces: ], ] and ], naming the territories as ]. | |||
| In 1988, unrest over economic mismanagement and political oppression by the government led to widespread pro-democracy demonstrations throughout the country known as the ]. Security forces killed thousands of demonstrators, and General ] staged a coup d'état and formed the ] (SLORC). In 1989, SLORC declared martial law after widespread protests. The military government finalised plans for People's Assembly elections on 31 May 1989.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/pyithu_hluttaw_election_law.htm |title=Pyithu Hluttaw Election Law |access-date=11 July 2006 |date=31 May 1989 |work=State Law and Order Restoration Council |publisher=iBiblio.org |archive-date=16 September 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190916133423/http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/pyithu_hluttaw_election_law.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> SLORC changed the country's official English name from the "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma" to the "Union of Myanmar" on 18 June 1989 by enacting the adaptation of the expression law. | |||
| King ] (1853–1878) founded ] in 1859 and made it his capital. He skilfully navigated the growing threats posed by the competing interests of Britain and France. In the process, Mindon had to renounce ] (Karenni) states in 1875. His successor, King ] (1878–1885), was largely ineffectual. In 1885, the British, alarmed by the French conquest of neighbouring ], occupied ]. The ] (1885) lasted a mere one month insofar as capturing the capital ] was concerned. The ] was exiled to ], India. British forces spent at least another four years pacifying the country – not only in the Burmese heartland but also in the Shan, ] and ] hill areas. By some accounts, minor insurrections did not end until 1896. | |||
| In May 1990, the government held free multiparty elections for the first time in almost 30 years, and the ] (NLD), the party of Aung San Suu Kyi, won<ref name="burmese_vote_1990_05_29_nytimes_com">Erlanger, Steven: | |||
| ===Colonial era (1886–1948)=== | |||
| {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210215085252/https://www.nytimes.com/1990/05/29/world/burmese-vote-rejects-army-rule-with-big-victory-for-opposition.html |date=15 February 2021 }}, 29 May 1990, ''The New York Times'', retrieved 1 March 2021</ref> ] (i.e., 80% of the seats). However, the military junta refused to cede power<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/Elections-02.htm |title=1990 Multi-party Democracy General Elections |author=Han, Khin Kyaw |date=1 February 2003 |work=National League for Democracy |publisher=iBiblio.org |access-date=12 July 2006 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010114240/http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/Elections-02.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> and continued to rule the nation, first as SLORC and, from 1997, as the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) until its dissolution in March 2011. General ] took over the Chairmanship – effectively the position of Myanmar's top ruler – from General Saw Maung in 1992 and held it until 2011.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Horn|first=Robert|date=2011-04-11|title=Is Burma's Strongman Really Retiring?|magazine=Time|url=http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,2064470,00.html|access-date=2011-09-01|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110901055649/http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0%2C8599%2C2064470%2C00.html|archive-date=2011-09-01}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|British rule in Burma}} | |||
| ]s, which resulted in the abdication of the last Burmese monarch, King ].]] | |||
| The British conquest of Burma began in 1824 in response to a Burmese attempt to invade India. By 1886, and after two further wars, Britain had incorporated the entire country into the ]. "The dawn of 1886 saw the addition of still further territory to that vast expanse which owns the sovereignty of the Queen. The King of Burmah having persistently violated treaties, war was declared against him, and the Burmese capital of Mandalay was entered by the British forces, under ], on November 28th, 1885".<ref>{{cite book | first=Cornelius | last=Brown | year=1897 | title=True Stories of the Reign of Queen Victoria 1837-1897}}</ref> Burma was administered as a province of ] until 1937 when it became a separate, self-governing colony. To stimulate trade and facilitate changes, the British brought in ] and ], who quickly displaced the Burmese in urban areas. To this day ] and ] have large ] populations. Railways and schools were built, as well as a large number of prisons, including the infamous ], then and now used for ]s. Burmese resentment was strong and was vented in violent riots that paralysed Yangon on occasion all the way until the 1930s.<ref>{{cite book | first=Maurice | last=Collis | year=1945 | title=Trials in Burma}}</ref> | |||
| On 23 June 1997, Myanmar was admitted into the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. On 27 March 2006, the military junta, which had moved the national capital from Yangon to a site near ] in November 2005, officially named the new capital ], meaning "city of the kings".<ref>{{cite news |title=Burma's new capital stages parade |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/4848408.stm |publisher=BBC News |date=27 March 2006 |access-date=24 June 2006 |archive-date=3 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181203065423/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/4848408.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Much of the discontent was caused by a disrespect for ] and traditions, for example, what the British termed the Shoe Question: the colonisers' refusal to remove their shoes upon entering Buddhist temples or other holy places. In October 1919, ] in Mandalay was the scene of violence when tempers flared after scandalised Buddhist monks attempted to physically expel a group of shoe-wearing British visitors. The leader of the monks was later sentenced to life imprisonment for attempted murder. Such incidents inspired the Burmese resistance to use ] as a rallying point for their cause. Buddhist monks became the vanguards of the independence movement, and many died while protesting. One monk-turned-martyr was ], who died in prison after a 166-day hunger strike to protest a rule that forbade him from wearing his Buddhist robes while imprisoned.<ref>{{cite book | first=Heinz | last=Bechert | year=1984 | title=The World of Buddhism-Buddhist Monks and Nuns in Society and Culture | isbn=978-0871969828 | publisher=Facts on File | location=New York, N.Y.}}</ref> | |||
| ] during the ] with a banner that reads ''non-violence: national movement'' in ]. In the background is ].]] | |||
| ]) in downtown Rangoon, which was developed and expanded by the British to serve as ]'s capital.]] | |||
| ] in southern Myanmar, May 2008]] | |||
| During the colonial period, intermarriage between European male settlers and Burmese women, as well as between Anglo-Indians (who arrived with the British) and Burmese caused the birth of the ] community. This influential community was to dominate the country during colonial rule and through the mid-1960s. On 1 April 1937, Burma became a separately administered territory, independent of the Indian administration. The vote for keeping Burma in India, or as a separate colony "khwe-yay-twe-yay" divided the populace, and laid the groundwork for the insurgencies to come after independence. In the 1940s, the ], commanded by ], founded the ]. The Thirty Comrades received training in Japan.<ref name="aungsan">{{cite book | first=Gustaaf | last=Houtman | year=1999 | title=Mental Culture in Burmese Crisis Politics: Aung San Suu Kyi and the National League for Democracy | isbn=4-87297-748-3 | publisher=Tokyo University of Foreign Studies, Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa | location=Tokyo}}</ref> | |||
| In August 2007, an increase in the price of fuel led to the ] led by Buddhist monks that were dealt with harshly by the government.<ref name=PetrolSaffronRevolution>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/6947251.stm|title=Burma leaders double fuel prices|publisher=BBC News|date=15 August 2007|access-date=20 November 2012|archive-date=30 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170530110116/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/6947251.stm|url-status=live}}<br />{{cite news|url=http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/asia/article2521951.ece|title=Military junta threatens monks in Burma|location=London|work=The Times|date=24 September 2007|access-date=27 April 2010|first1=Jenny|last1=Booth|archive-date=10 October 2008|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081010194752/http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/asia/article2521951.ece|url-status=dead}}<br />{{cite web|url=http://www.novinite.com/view_news.php?id=85644|title=100,000 Protestors Flood Streets of Rangoon in "Saffron Revolution"|access-date=15 February 2009|archive-date=17 October 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201017022614/https://www.novinite.com/view_news.php?id=85644|url-status=live}}<br />{{cite book|author=Fink, Christina|chapter=The Moment of the Monks: Burma, 2007|editor-link=Adam Roberts (scholar)|editor=Adam Roberts|editor2=Timothy Garton Ash|title=Civil Resistance and Power Politics: The Experience of Non-violent Action from Gandhi to the Present|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=2009|isbn=978-0-19-955201-6|pages=354–70|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BxOQKrCe7UUC&q=Civil+resistance+and+power+politics|access-date=9 August 2023|archive-date=20 August 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230820072155/https://books.google.com/books?id=BxOQKrCe7UUC&q=Civil+resistance+and+power+politics|url-status=live}}<br />{{cite news|url=http://english.aljazeera.net/NR/exeres/4081D23F-F1A4-46AF-BA50-D47FA2B7A4AE.htm|title=UN envoy warns of Myanmar crisis|publisher=English.aljazeera.net|access-date=20 November 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080228090420/http://english.aljazeera.net/NR/exeres/4081D23F-F1A4-46AF-BA50-D47FA2B7A4AE.htm|archive-date=28 February 2008}}</ref> The government cracked down on them on 26 September 2007, with reports of barricades at the ] and monks killed. There were also rumours of disagreement within the Burmese armed forces, but none was confirmed. The military crackdown against unarmed ]ers was widely condemned as part of the ] and led to an increase in economic sanctions against the ]. | |||
| In May 2008, ] caused extensive damage in the densely populated rice-farming delta of the ].<ref>{{cite news|last=Fountain |first=Henry |url=http://www.iht.com/articles/ap/2008/05/06/asia/AS-GEN-Myanmar-Cyclone.php |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081011025523/http://www.iht.com/articles/ap/2008/05/06/asia/AS-GEN-Myanmar-Cyclone.php |archive-date=11 October 2008 |title=Aid arrives in Myanmar as death toll passes 22,000, but worst-hit area still cut off – |work=International Herald Tribune |date=6 May 2008}}</ref> It was the worst natural disaster in Burmese history with reports of an estimated 200,000 people dead or missing, damages totalled to 10 billion US dollars, and as many as 1 million were left homeless.<ref>{{cite news | |||
| During World War II, Burma became a major front-line in the ]. The British administration collapsed ahead of the advancing Japanese troops, jails and asylums were opened and Rangoon was deserted except for the many ] and Indians who remained at their posts. A stream of some 300,000 refugees fled across the jungles into India; known as 'The Trek', all but 30,000 of those 300,000 arrived in India. Initially the Japanese-led ] succeeded and the British were expelled from most of Burma, but the British counter-attacked using primarily troops of the ]. By July 1945, the British had retaken the country. | |||
| |url=http://www.deseretnews.com/article/695277601/Official-UN-planes-land-in-Myanmar-with-aid-after-cyclone.html?pg=all | |||
| |title=Official: UN plane lands in Myanmar with aid after cyclone | |||
| |agency=Associated Press | |||
| |access-date=6 August 2015 | |||
| |archive-date=6 September 2015 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150906080826/http://www.deseretnews.com/article/695277601/Official-UN-planes-land-in-Myanmar-with-aid-after-cyclone.html?pg=all | |||
| |url-status=dead | |||
| }}</ref> In the critical days following this disaster, Myanmar's ] government was accused of hindering United Nations recovery efforts.<ref>{{cite news |author1=Stevenson, Rachel |author2=Borger, Julian |author3=MacKinnon, Ian |name-list-style=amp |title=Burma snubs foreign aid workers |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2008/may/09/cyclonenargis.burma4 |work=The Guardian |location=London |date=9 May 2008 |access-date=12 December 2016 |archive-date=2 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130902085545/http://www.theguardian.com/world/2008/may/09/cyclonenargis.burma4 |url-status=live }}</ref> ] was requested, but concerns about foreign military or intelligence presence in the country delayed the entry of United States military planes delivering medicine, food, and other supplies.<ref>{{cite web|title=Burma: imperialists exploit natural disaster to promote regime change|url=http://www.cpgb-ml.org/index.php?art=410&secName=proletarian&subName=display|publisher=Proletarian Online|date=June 2008|access-date=13 November 2013|archive-date=13 November 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131113132830/http://www.cpgb-ml.org/index.php?art=410&secName=proletarian&subName=display|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In early August 2009, ] in Shan State in northern Myanmar. For several weeks, junta troops fought against ethnic minorities including the ],<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nbcnews.com/id/wbna32596296 |title=Fighting forces up to 30,000 to flee Myanmar |work=NBC News |date=28 August 2009 |access-date=20 November 2012 |archive-date=23 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200923230219/http://www.nbcnews.com/id/32596296 |url-status=live }}</ref> ], and ].<ref name="BangkokPost">{{cite news |date=27 August 2009 |title=More fighting feared as thousands flee Burma |work=] |agency=] |url=https://mg.co.za/article/2009-08-27-more-fighting-feared-as-thousands-flee-burma |access-date=28 August 2009 |archive-date=3 March 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170303122522/https://mg.co.za/article/2009-08-27-more-fighting-feared-as-thousands-flee-burma |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="NYTrefugees">{{cite news |work=The New York Times |last=Fuller |first=Thomas |date=28 August 2009 |access-date=28 August 2009 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/29/world/asia/29myanmar.html |title=Refugees Flee to China as Fighting Breaks Out in Myanmar |archive-date=13 February 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120213153527/http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/29/world/asia/29myanmar.html |url-status=live }}</ref> During 8–12 August, the first days of the conflict, as many as 10,000 Burmese civilians fled to Yunnan in neighbouring China.<ref name="BangkokPost" /><ref name="NYTrefugees" /><ref>{{cite news |publisher=BBC News |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/8223430.stm |title=Thousands Flee Burma Violence |date=26 August 2009 |access-date=28 August 2009 |archive-date=29 August 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090829215715/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/8223430.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] on the ] road, July 1944.]] | |||
| Although many Burmese fought initially for the Japanese, some Burmese, mostly from the ethnic minorities, also served in the British Burma Army.<ref>{{cite book | first=Ian | last=Fellowes-Gordon | year=1971 | title=The Battle For Naw Seng's Kingdom: General Stilwel}}</ref> In 1943, the Chin Levies and ] were formed in the border districts of Burma still under British administration. The Burma Rifles fought as part of the ]s under ] from 1943 to 1945. Later in the war, the Americans created ] who also fought against the Japanese. Many others fought with the British ]. The ] under the command of ] and the Arakan National Army fought with the Japanese from 1942–1944, but switched allegiance to the Allied side in 1945. | |||
| === Civil wars === | |||
| British soldiers waged a guerrilla war against ] forces in Burma. ] were formed into ] groups trained to operate deep behind Japanese lines.<ref>"". The Independent. 20 August 1995.</ref> A similar American unit, ], followed the Chindits into the jungle in 1943.<ref>"". Veterans History Project, Library of Congress.</ref> Overall, the Japanese lost some 150,000 men in Burma. Only 1,700 prisoners were taken.<ref>"''''". Philip Towle, Margaret Kosuge, Yōichi Kibata (2000). ]. p.48. ISBN 1852851929</ref> | |||
| {{main|Internal conflict in Myanmar}} | |||
| ]s have been a constant feature of Myanmar's socio-political landscape since the attainment of independence in 1948. These wars are predominantly struggles for ethnic and sub-national autonomy, with the areas surrounding the ethnically Bamar central districts of the country serving as the primary geographical setting of conflict. Foreign journalists and visitors require a special travel permit to visit the areas in which Myanmar's civil wars continue.<ref>{{cite web|title=Restricted Areas in Burma|url=http://www.tourismburma.com/restricted-areas-in-burma/|publisher=Tourism Burma|access-date=27 March 2013|year=2013|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130102230338/http://www.tourismburma.com/restricted-areas-in-burma/|archive-date=2 January 2013}}</ref> | |||
| In October 2012, the ongoing conflicts in Myanmar included the ],<ref>{{cite news |title=Ethnic Rifts Strain Myanmar as It Moves Toward Democracy |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2013/04/05/world/asia/ethnic-rifts-strain-myanmar-as-it-moves-toward-democracy.html |newspaper=The New York Times |date=4 April 2013 |author=Fuller, Thomas |access-date=25 February 2017 |archive-date=22 July 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160722151744/http://www.nytimes.com/2013/04/05/world/asia/ethnic-rifts-strain-myanmar-as-it-moves-toward-democracy.html |url-status=live }}</ref> between the Pro-Christian ] and the government;<ref name=ChristianVsGovt>{{cite news|title=Displaced by fighting, villagers take shelter in Hpakant|url=http://www.dvb.no/news/displaced-by-fighting-villagers-take-shelter-in-hpakant/23955|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121127023044/http://www.dvb.no/news/displaced-by-fighting-villagers-take-shelter-in-hpakant/23955|url-status=dead|archive-date=27 November 2012|access-date=27 March 2013|newspaper=Democratic Voice of Burma|date=25 September 2012|author=Nadi, Nang Mya}}<br />{{cite news|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/peopleandpower/2012/10/20121031172469210.html|title=Blood and Gold: Inside Burma's Hidden War|publisher=Al Jazeera|date=4 October 2012|access-date=5 January 2013|archive-date=1 January 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190101175348/https://www.aljazeera.com/programmes/peopleandpower/2012/10/20121031172469210.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> a civil war between the ] Muslims,<ref name="lan">{{cite book |last=Simpson |first=Andrew |title=Language and National Identity in Asia |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-19-922648-1 |location=United Kingdom |page=267}}</ref> and the government and non-government groups in ];<ref>{{cite news|title=About 75,000 Rohingyas in Myanmar camps: Refugee International|url=http://www.thehindu.com/news/international/about-75000-rohingyas-in-myanmar-camps-refugee-international/article3948606.ece|access-date=27 March 2013|newspaper=The Hindu|date=29 September 2012|location=Chennai, India|archive-date=8 February 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180208141327/http://www.thehindu.com/news/international/about-75000-rohingyas-in-myanmar-camps-refugee-international/article3948606.ece|url-status=live}}</ref> and a conflict between the ],<ref name=ShanVsGovt>{{cite web|title=Supporting Human Rights in Burma|url=https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/blog/2012/11/09/supporting-human-rights-burma|access-date=27 March 2013|author=Power, Samantha|via=]|work=]|date=9 November 2012|archive-date=22 January 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170122060757/https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/blog/2012/11/09/supporting-human-rights-burma|url-status=live}}<br />{{cite news|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/features/2012/10/201210285232434409.html|title=Myanmar Shan refugees struggle at Thai border|publisher=Al Jazeera|date=2 October 2012|access-date=5 January 2013|archive-date=22 April 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190422154430/https://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/features/2012/10/201210285232434409.html|url-status=live}}</ref> ], and ]<ref>{{cite news|title=Karen fighters and Burma Army soldiers killed over ceasefire breach|url=http://karennews.org/2012/03/karen-fighters-and-burma-army-soldiers-killed-over-ceasefire-breech.html/|access-date=27 March 2013|newspaper=Karen News|date=16 March 2012|author=Saw Khar Su Nyar (KIC)|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130615153917/http://karennews.org/2012/03/karen-fighters-and-burma-army-soldiers-killed-over-ceasefire-breech.html/|archive-date=15 June 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.irinnews.org/report/95008/MYANMAR-Karen-groups-cautious-on-peace-initiative |title=Myanmar: Karen groups cautious on peace initiative |agency=] |date=5 March 2012 |access-date=5 January 2013 |archive-date=1 January 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160101072043/http://www.irinnews.org/report/95008/myanmar-karen-groups-cautious-on-peace-initiative |url-status=live }}</ref> minority groups, and the government in the eastern half of the country. In addition, ] signalled an intention to become involved in Myanmar.<ref>{{cite news|title=Concern in India as Al Qaeda announces new India front|url=http://www.myanmarnews.net/index.php/sid/225407619|date=4 September 2014|access-date=6 September 2014|publisher=Myanmar News.Net|archive-date=6 April 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160406002614/http://www.myanmarnews.net/index.php/sid/225407619|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In 1947, Aung San became Deputy Chairman of the Executive Council of Burma, a transitional government. But in July 1947, political rivals assassinated ] and several cabinet members.<ref name="aungsan"/> | |||
| Armed conflict between ] and the ] resulted in the ] in February 2015. The conflict had forced 40,000 to 50,000 civilians to flee their homes and seek shelter on the Chinese side of the border.<ref>{{cite web |date=12 February 2015 |title=Tens of thousands flee war, airstrikes in Kokang region |url=http://www.dvb.no/news/tens-thousands-flee-war-airstrikes-kokang-region/48271 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150328223618/http://www.dvb.no/news/tens-thousands-flee-war-airstrikes-kokang-region/48271 |archive-date=28 March 2015 |access-date=31 March 2015 |work=]}}</ref> During the incident, the government of China was accused of giving military assistance to the ] rebels.<ref>" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190511065757/http://www.rfa.org/english/news/myanmar/kokang-02132015185129.html |date=11 May 2019 }}". ].</ref> Clashes between Burmese troops and local insurgent groups have continued, fuelling tensions between China and Myanmar.<ref>{{cite web |last=Lintner |first=Bertil |author-link=Bertil Lintner |date=2017-04-05 |title=A Chinese war in Myanmar |url=https://asiatimes.com/2017/04/chinese-war-myanmar/ |access-date=2022-07-05 |website=Asia Times |language=en-US |archive-date=21 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220621214332/https://asiatimes.com/2017/04/chinese-war-myanmar/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Democratic republic (1948–1962)=== | |||
| {{Main|Post-independence Burma, 1948–1962}} | |||
| On 4 January 1948, the nation became an independent ], named the ''Union of Burma'', with ] as its first President and ] as its first Prime Minister. Unlike most other former British colonies and overseas territories, it did not become a member of the ]. A ] ] was formed, consisting of a ] and a ],<ref name="1947con">{{cite web|url=http://english.dvb.no/e_docs/511947_con.htm |title=The Constitution of the Union of Burma |accessdate=7 July 2006 |year=1947 |publisher=DVB| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20060615072018/http://english.dvb.no/e_docs/511947_con.htm| archivedate = 15 June 2006}}</ref> and ] elections were held in ], ] and ]. | |||
| === Period of liberalisation, 2011–2021 === | |||
| The geographical area Burma encompasses today can be traced to the ], which combined Burma Proper, which consisted of ] and ], and the ], which had been administered separately by the British.<ref name="msmith">{{cite book|first=Martin| last=Smith|year=1991| title=Burma -Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity|publisher=Zed Books|location=London and New Jersey|pages=42–43}}</ref> | |||
| {{See also|2011–2015 Myanmar political reforms}} | |||
| The military-backed Government had promulgated a ] in 1993, but the process appeared to stall several times, until 2008 when the Government published a new draft national constitution, and organised a (flawed) national referendum which adopted it. The new constitution provided for election of a national assembly with powers to appoint a president, while practically ensuring army control at all levels.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Steinberg|first=David I.|url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/318409825|title=Burma/Myanmar : what everyone needs to know|date=2010|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-539067-4|location=Oxford|pages=142–147|oclc=318409825}}</ref> | |||
| ] and Secretary of State ] with ] and her staff at her home in Yangon, 2012]] | |||
| A ] - the first for twenty years - was boycotted by the ]. The military-backed ] declared victory, stating that it had been favoured by 80 per cent of the votes; fraud, however, was alleged.<ref name="tni.org">{{cite web|date=14 December 2010|title=A Changing Ethnic Landscape: Analysis of Burma's 2010 Polls|url=http://www.tni.org/briefing/changing-ethnic-landscape-analysis-burmas-2010-polls|access-date=27 March 2013|work=Transnational Institute – Burma Project|publisher=TNI|archive-date=2 April 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402140616/http://www.tni.org/briefing/changing-ethnic-landscape-analysis-burmas-2010-polls|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=MacFarquhar |first=Neil |title=U.N. Doubts Fairness of Election in Myanmar |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/22/world/asia/22nations.html |work=The New York Times |date=21 October 2010 |access-date=25 February 2017 |archive-date=15 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170715200353/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/22/world/asia/22nations.html |url-status=live }}</ref> A nominally civilian government was then formed, with retired general ] as president.<ref>{{cite web|date=2018-09-03|title=Myanmar profile - Timeline|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-pacific-12992883|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210326180520/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-pacific-12992883|archive-date=2021-03-26|access-date=2021-09-25|website=BBC News}}</ref> | |||
| In 1961, ], then the Union of Burma's Permanent Representative to the United Nations and former Secretary to the Prime Minister, was elected ]; he was the first non-Westerner to head any international organisation and would serve as UN Secretary-General for ten years.<ref name="az">{{cite web|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=7610|author=Aung Zaw|title=Can Another Asian Fill U Thant's Shoes?|work=] September 2006|accessdate=12 September 2006}}</ref> Among the Burmese to work at the UN when he was Secretary-General was a young ], who went on to become winner of the 1991 ]. | |||
| A series of liberalising political and economic actions – or reforms – then took place. By the end of 2011 these included the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest, the establishment of the ], the granting of general amnesties for more than 200 political prisoners, new labour laws that permitted labour unions and strikes, a relaxation of press censorship, and the regulation of currency practices.<ref>{{cite news|author=Loyn, David|date=19 November 2011|title=Obstacles lie ahead in Burma's bid for reform|publisher=BBC|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-15303968|access-date=20 November 2011|archive-date=18 November 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111118122129/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-15303968|url-status=live}}</ref> In response, ] ] visited Myanmar in December 2011 – the first visit by a US Secretary of State in more than fifty years<ref>{{cite news|author=Hepler, Lauren|author2=Voorhees, Josh|date=1 December 2011|title=Budding Friendship on Display as Clinton, Burma's Suu Kyi Meet Again|newspaper=]|agency=]|url=http://slatest.slate.com/posts/2011/11/18/hillary_clinton_to_visit_myanmar_burma_first_trip_by_secretary_of_state_in_more_than_50_years.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130617073614/http://slatest.slate.com/posts/2011/11/18/hillary_clinton_to_visit_myanmar_burma_first_trip_by_secretary_of_state_in_more_than_50_years.html|archive-date=17 June 2013|quote=Wrapping up a historic three-day visit to Myanmar , the first by a secretary of state to the Southeast Asian nation in more than 50 years}}</ref> – meeting both President Thein Sein and opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi.<ref name="Clinton">{{cite news|author=Myers, Steven Lee|date=2 December 2011|title=Clinton Says U.S. Will Relax Some Restrictions on Myanmar|page=A6|newspaper=The New York Times|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/02/world/asia/us-will-relax-curbs-on-aid-to-myanmar.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111201172242/http://www.nytimes.com/2011/12/02/world/asia/us-will-relax-curbs-on-aid-to-myanmar.html |archive-date=2011-12-01 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live|access-date=15 May 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ===Rule by military junta (1962–2011)=== | |||
| {{Main|1962 Burmese coup d'état}} | |||
| ]'s ] party participated in the 2012 by-elections, facilitated by the government's abolition of the laws that previously barred it.<ref>{{cite news|date=18 November 2011|title=US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton to visit Burma|publisher=BBC|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-15787052|access-date=25 November 2011|archive-date=20 November 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111120053747/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-15787052|url-status=live}}</ref> In the April 2012 ], the NLD won 43 of the 45 available seats. The 2012 by-elections were also the first time that international representatives were allowed to monitor the voting process in Myanmar.<ref>{{cite news|last=Golluoglu|first=Esmer|date=4 February 2012|title=Aung San Suu Kyi hails 'new era' for Burma after landslide victory|newspaper=The Guardian|location=London|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/apr/02/aung-san-suu-kyi-new-era-burma?newsfeed=true}}</ref> | |||
| ====Ne Win years==== | |||
| ] rule ended in 1962 when ] ] led a military ]. He ruled for nearly 26 years and pursued policies under the rubric of the ]. Between 1962 and 1974, Burma was ruled by a revolutionary council headed by the general, and almost all aspects of society (business, media, production) were ] or brought under government control (even the ]).<ref name="thantmyintu">{{cite book | first=Thant | last=Myint-U | year=2006 | title=The River of Lost Footsteps | isbn=0-374-16342-1 | publisher=Farra, Strauss and Giroux | location=New York}}</ref> In an effort to consolidate power, Ne Win and many other top generals resigned from the military and took civilian posts and, from 1974, instituted elections in a ]. | |||
| Myanmar's improved international reputation was indicated by ]'s approval of Myanmar's bid for the position of ASEAN chair in 2014.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Cabellero-Anthony|first1=Mely|date=March 2014|title="Myanmar's Chairmanship of ASEAN: Challenges and Opportunities", Myanmar's Growing Regional Role|url=http://www.nbr.org/publications/element.aspx?id=741|journal=NBR Special Report|access-date=4 August 2014|archive-date=10 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010114243/http://www.nbr.org/publications/element.aspx?id=741|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Between 1974 and 1988, Burma was effectively ruled by Ne Win through the ] (BSPP),<ref name="christinafink">{{cite book | first=Christina | last=Fink | year=2001 | title=Living Silence:Burma under Military Rule | isbn=1-8564-9926-X | publisher=White Lotus | location=Bankok}}</ref> which from 1964 until 1988 was the sole political party. During this period, Burma became one of the world's most impoverished countries. The Burmese Way to Socialism<ref name="ruin">{{cite news|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2007/sep/28/burma.uk|title=The Burma road to ruin|publisher=The Guardian | location=London | first=Mark | last=Tallentire | date=28 September 2007 | accessdate=27 April 2010}}</ref> combined ]-style nationalisation and ] with the governmental implementation of ] beliefs.{{Citation needed|date=July 2010}} Criticism was scathing, such as an article published in a February 1974 issue of '']'' magazine describing the Burmese Way to Socialism as 'an amalgam of Buddhist and Marxist illogic'.<ref name="ms">{{cite book|author=Martin Smith|title=Burma – Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity|year=1991|publisher=Zed Books|location=London and New Jersey|pages=124,200,20,130}}</ref> | |||
| ], ], ] and ]]] | |||
| Almost from the beginning, there were sporadic protests against the military rule, many of which were organised by students, and these were almost always violently suppressed by the government. On 7 July 1962, the government broke up demonstrations at ], killing 15 students.<ref name="thantmyintu"/> In 1974, the military violently suppressed anti-government protests at the funeral of ]. Student protests in 1975, 1976 and 1977 were quickly suppressed by overwhelming force.<ref name="christinafink"/> | |||
| ==== 2015 general elections ==== | |||
| Ne Win's rise to power in 1962 and his relentless persecution of "resident aliens" (immigrant groups not recognised as citizens of the ''Union of Burma'') led to an exodus/expulsion of some 300,000 ].<ref>{{cite book|author=Martin Smith|year=1991|title=Burma – Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity|publisher=Zed Books|location=London,New Jersey|pages=43–44,98,56–57,176}}</ref> They migrated to escape ] and wholesale nationalisation of private enterprise a few years later in 1964.<ref>. TIME. 17 July 1964.</ref> The Anglo-Burmese at this time either fled the country or changed their names and blended in with the broader Burmese society. | |||
| General elections ]. These were the first openly contested elections held in Myanmar since the 1990 general election (which was annulled<ref name="landmark_elections_2015_12_03_bbc"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210321181407/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-33547036 |date=21 March 2021 }} 3 December 2015, BBC News, retrieved 1 March 2021</ref>). The results gave the NLD an ] of seats in both chambers of the ], enough to ensure that its candidate would become president, while NLD leader ] is constitutionally barred from the presidency.<ref name="landmark_elections_2015_12_03_bbc" /><ref name="national_league_wins_2015_11_13_bbc">{{cite news |title=Suu Kyi's National League for Democracy Wins Majority in Myanmar |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-34805806 |access-date=13 November 2015 |publisher=BBC News |date=13 November 2015 |archive-date=13 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151113070516/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-34805806 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The new parliament convened on 1 February 2016,<ref>{{cite web|title = Suu Kyi's novice MPs learn ropes in outgoing Myanmar parliament|url = http://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asiapacific/suu-kyi-s-novice-mps/2464054.html|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160127170900/http://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asiapacific/suu-kyi-s-novice-mps/2464054.html|url-status=dead|archive-date = 27 January 2016|publisher = Channel NewsAsia|access-date = 28 January 2016}}</ref> and on 15 March 2016, ] was elected as the first non-military president since the military coup of 1962.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Moe|first1=Wae|last2=Ramzy|first2=Austin|title=Myanmar Lawmakers Name Htin Kyaw President, Affirming Civilian Rule|date=15 March 2016|newspaper=The New York Times|url=http://nyti.ms/1M4ac5P}}</ref> On 6 April 2016, ] assumed the newly created role of ], a role akin to a ].<ref>Daniel Combs, ''Until the World Shatters: Truth, Lies, and the Looting of Myanmar'' (2021).</ref> | |||
| A new ] was adopted in 1974. | |||
| === Coup d'état and civil war === | |||
| Hundreds of thousands of ] Muslims fled Burma and many refugees inundated neighbouring ] including 200,000 in 1978 as a result of the ].<ref>. Marwaan Macan-Markar. IPS.</ref> | |||
| {{main|2021 Myanmar coup d'état|Myanmar civil war (2021–present)}} | |||
| {{See also|Myanmar protests (2021–present)}} | |||
| In Myanmar's 2020 parliamentary election, the ostensibly ruling ], the party of State Counsellor ], competed with various other smaller parties – particularly the military-affiliated ].<ref name="myanmar_election_2020_11_11_nytimes_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210301062240/https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/11/world/asia/myanmar-election-aung-san-suu-kyi-results.html |date=1 March 2021 }} 11 November 2020, ''The New York Times'', retrieved 18 December 2020</ref> Suu Kyi's NLD won the ] on 8 November in a landslide.<ref name="myanmar_election_2020_11_11_nytimes_com" /><ref name="suu_kyis_party_wins_2020_11_13_bbc"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230329220822/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-54899170 |date=29 March 2023 }} 11 November 2020, BBC News, retrieved 18 December 2020</ref><ref name="commission_rejects_2021_01_29_apnews_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210203131321/https://apnews.com/article/aung-san-suu-kyi-elections-myanmar-cc1b225b806c27dda748d3ab51d0e47f |date=3 February 2021 }} 29 January 2021, ], retrieved 28 February 2021</ref> The USDP, regarded as a proxy for the military, suffered a "humiliating" defeat<ref name="crisis_in_myanmar_2021_01_31_reuters"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210228221918/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-myanmar-politics-explainer/explainer-crisis-in-myanmar-after-army-alleges-election-fraud-idUSKBN2A113H |date=28 February 2021 }} 31 January 2021, updated 1 February 2021, ], retrieved 28 February 2021</ref><ref name="defeated_2020_11_12_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210301160653/https://www.irrawaddy.com/elections/military-backed-usdp-leaders-defeated-nld-myanmar-election.html |date=1 March 2021 }} 12 November 2020, '']'', retrieved 28 February 2021</ref> – even worse than in 2015<ref name="defeated_2020_11_12_irrawaddy_com" /> – capturing only 33 of the 476 elected seats.<ref name="commission_rejects_2021_01_29_apnews_com" /><ref name="crisis_in_myanmar_2021_01_31_reuters" /> | |||
| ====Uprising of 1988 and the SPDC==== | |||
| ] | |||
| In 1988, unrest over economic mismanagement and political oppression by the government led to widespread pro-democracy demonstrations throughout the country known as the ]. Security forces killed thousands of demonstrators, and General ] staged a ] and formed the ] (SLORC). In 1989, SLORC declared ] after widespread protests. The military government finalised plans for People's Assembly elections on 31 May 1989.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/pyithu_hluttaw_election_law.htm |title=PYITHU HLUTTAW ELECTION LAW |accessdate=11 July 2006 |date=31 May 1989 |work=State Law and Order Restoration Council |publisher=iBiblio.org}}</ref> SLORC changed the country's official English name from the "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma" to the "Union of Myanmar" in 1989. | |||
| As the election results began emerging, the USDP rejected them, urging a new election with the military as observers.<ref name="myanmar_election_2020_11_11_nytimes_com" /><ref name="defeated_2020_11_12_irrawaddy_com" /> More than 90 other smaller parties contested the vote, including more than 15 who complained of irregularities. However, election observers declared there were no major irregularities.<ref name="crisis_in_myanmar_2021_01_31_reuters" /><ref name="commission_rejects_2021_01_29_apnews_com" /><ref name="myanmar_election_body_2021_01_28_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210301124627/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-election-body-rejects-military-allegations-electoral-fraud.html |date=1 March 2021 }} 28 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 6 February 2021</ref> However, despite the election commission validating the NLD's overwhelming victory,<ref name="myanmar_election_body_2021_01_28_irrawaddy_com" /> the USDP and Myanmar's military persistently alleged fraud.<ref name="military_condemns_2021_01_15_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210310112448/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-military-condemns-speakers-refusal-probe-election-fraud-claims.html |date=10 March 2021 }} 15 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 7 February 2021</ref><ref name="military_demands_2021_01_21_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210310112448/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-military-condemns-speakers-refusal-probe-election-fraud-claims.html |date=10 March 2021 }} 21 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 7 February 2021</ref><ref name="crisis_in_myanmar_2021_01_31_reuters" /><ref name="Myanmar_military_2021_01_26_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210301142916/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-military-refuses-rule-coup-presses-claim-fraud-nov-election.html |date=1 March 2021 }} 26 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 7 February 2021</ref><ref name="military_threats channelnewsasia_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210130124925/https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/military-threats--coup-fears-overshadow-myanmar-parliament-opening-14068508 |date=30 January 2021 }} '']'',</ref><ref name="military_chief_warns_2021_01_28_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210301124634/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmar-military-chief-warns-constitution-revoked-laws-not-followed.html |date=1 March 2021 }} 28 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 7 February 2021</ref><ref name="coup_talk_2021_01_28_bangkokpost_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210224030219/https://www.bangkokpost.com/world/2059323/un-embassies-fret-over-myanmar-coup-talk |date=24 February 2021 }} 28 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 30 January 2021</ref>{{overcite|date=July 2024}} | |||
| In May 1990, the government held ]s for the first time in almost 30 years. The ] (NLD), the party of ], ](i.e., 80% of the seats), but the election results were annulled by SLORC, which refused to step down.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/Elections-02.htm |title=1990 MULTI-PARTY DEMOCRACY GENERAL ELECTIONS |author=Khin Kyaw Han |accessdate=11 July 2006 |date=1 February 2003 |work=National League for Democracy |publisher=iBiblio.org}}</ref> Led by ] since 1992, the military regime has made cease-fire agreements with most ethnic guerilla groups. In 1992, SLORC unveiled plans to create a ] through the National Convention, which began 9 January 1993. In 1997, the State Law and Order Restoration Council was renamed the ] (SPDC). | |||
| In January, 2021, just before the new parliament was to be sworn in, the NLD announced that Suu Kyi would retain her State Counsellor role in the upcoming government. | |||
| <ref name="suu_kyi_to_keep_2021_01_25_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210301124641/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/myanmars-daw-aung-san-suu-kyi-keep-state-counselor-position-nld-says.html |date=1 March 2021 }} 25 January 2021, '']'', retrieved 6 February 2021</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| On 23 June 1997, Burma was admitted into the ] (ASEAN). The National Convention continues to convene and adjourn. Many major political parties, particularly the NLD, have been absent or excluded, and little progress has been made.{{Citation needed|date=June 2008}} On 27 March 2006, the military junta, which had moved the national capital from ] to a site near ] in November 2005, officially named the new capital ], meaning "city of the kings".<ref name="newcapital">{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/4848408.stm |title=Burma's new capital stages parade |publisher=BBC News|date=27 March 2006 |accessdate=24 June 2006 }}</ref> The '']'', however, still considers the capital to be Rangoon.<ref name="Rangooncapital">{{cite web | author = Central Intelligence Agency | title = CIA – The World Factbook – Field Listing – Capital | date= 9 April 2009 | url = https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2057.html | accessdate = 21 April 2009 }}</ref> | |||
| In the early morning of 1 February 2021, the day parliament was set to convene, the ], Myanmar's military, detained Suu Kyi and other members of the ruling party.<ref name="crisis_in_myanmar_2021_01_31_reuters" /><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021-02-01_bbc"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210131232954/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-55882489 |date=31 January 2021 }} 1 February 2021, BBC News, retrieved 1 February 2021</ref><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210302033544/https://asia.nikkei.com/Spotlight/Myanmar-Coup/Myanmar-coup-Week-of-Feb.1-to-Feb.-21-EU-action-in-focus-as-foreign-ministers-set-to-meet |date=2 March 2021 }} (reverse chronology) 1 February through 21 February 2021, '']'', retrieved 1 March 2021</ref> The military handed power to military chief ] and declared a state of emergency for one year<ref name="suu_kyi_detained_2021_01_31_bloomberg_com">{{cite news|url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-01-31/myanmar-s-suu-kyi-detained-in-early-morning-raid-reuters-says|title=Myanmar Military Takes Power for One Year, Suu Kyi in Detention|newspaper=Bloomberg.com|date=31 January 2021|via=www.bloomberg.com|access-date=1 February 2021|archive-date=1 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210201050819/https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-01-31/myanmar-s-suu-kyi-detained-in-early-morning-raid-reuters-says|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021-02-01_bbc" /> and began closing the borders, restricting travel and electronic communications nationwide.<ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> The military announced it would replace the existing election commission with a new one, and a military media outlet indicated new elections would be held in about one year – though the military avoided making an official commitment to that.<ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> The military expelled NLD party Members of Parliament from the capital city, ].<ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> By 15 March 2021 the military leadership continued to extend martial law into more parts of Yangon, while security forces killed 38 people in a single day of violence.<ref>{{cite news|first=Helen|last=Regan|title=Chinese factories set on fire in Myanmar in deadliest day since coup|url=https://www.cnn.com/2021/03/15/asia/myanmar-deaths-chinese-factories-intl-hnk/index.html|access-date=2021-03-15|website=CNN|archive-date=15 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210315111827/https://www.cnn.com/2021/03/15/asia/myanmar-deaths-chinese-factories-intl-hnk/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In November 2006, the ] (ILO) announced it will be seeking at the ]<ref>.</ref> "to prosecute members of the ruling Myanmar junta for crimes against humanity" over the continuous ] of its citizens by the military. According to the ILO, an estimated 800,000 people are subject to forced labour in Myanmar.<ref>.</ref> | |||
| ] are highlighted in {{highlight|red|#EBC0B3}}.]] | |||
| By the second day of the coup, thousands of protesters were marching in the streets of Yangon, and other protests erupted nationwide, largely halting commerce and transportation. Despite the military's arrests and killings of protesters, the first weeks of the coup found growing public participation, including groups of civil servants, teachers, students, workers, monks and religious leaders – even normally disaffected ethnic minorities.<ref name="teachers_join_2021_02_05_bbc"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210222185331/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-55944482 |date=22 February 2021 }} 5 February 2021, BBC News, retrieved 28 February 2021</ref><ref name="tens_of_thousands_2021_02_07_irrawaddy_com"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211227061633/https://www.irrawaddy.com/news/burma/tens-thousands-take-streets-myanmar-protest-military-regime.html |date=27 December 2021 }} 12 November 2020, '']'', retrieved 28 February 2021</ref><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> | |||
| The coup was immediately condemned by the ], and leaders of democratic nations. The U.S. threatened sanctions on the military and its leaders, including a "freeze" of US$1 billion of their assets in the U.S.<ref name="teachers_join_2021_02_05_bbc" /><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> ], ], ], ], ], ], the ] and ] refrained from criticizing the military coup.<ref>{{cite news |title=On Bloodiest Day for Myanmar Civilians, India Attends Military Parade by Coup Leaders |url=https://thewire.in/diplomacy/india-china-russia-pakistan-attend-myanmar-armed-forces-day-parade |work=] |date=28 March 2021 |access-date=15 June 2021 |archive-date=28 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210328071814/https://thewire.in/diplomacy/india-china-russia-pakistan-attend-myanmar-armed-forces-day-parade |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=China Responds to Bloodshed in Myanmar With Deafening Silence |url=https://thediplomat.com/2021/03/china-responds-to-bloodshed-in-myanmar-with-deafening-silence/ |work=The Diplomat |date=2 March 2021 |access-date=15 June 2021 |archive-date=16 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210616043203/https://thediplomat.com/2021/03/china-responds-to-bloodshed-in-myanmar-with-deafening-silence/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=India has a history of involvement in its neighbours' affairs. Why has it not condemned the Myanmar coup? |url=https://www.scmp.com/week-asia/opinion/article/3122841/india-has-history-involvement-its-neighbours-affairs-why-has-it |work=South China Morning Post |date=24 February 2021 |access-date=15 June 2021 |archive-date=16 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210616043304/https://www.scmp.com/week-asia/opinion/article/3122841/india-has-history-involvement-its-neighbours-affairs-why-has-it |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Myanmar coup: ASEAN split over the way forward |url=https://www.dw.com/en/myanmar-coup-asean-ties/a-57042503 |work=Deutsche Welle |date=29 March 2021 |access-date=15 June 2021 |archive-date=10 June 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210610152119/https://www.dw.com/en/myanmar-coup-asean-ties/a-57042503 |url-status=live }}</ref> A ] resolution called for the release of Aung San Suu Kyi and the other detained leaders<ref name="teachers_join_2021_02_05_bbc" /><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> – a position shared by the ].<ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> | |||
| The ] were a campaign of ].<ref>Christina Fink, “The Moment of the Monks: Burma, 2007”, in ] and ] (eds.), ''Civil Resistance and Power Politics: The Experience of Non-violent Action from Gandhi to the Present'', Oxford University Press, 2009, ISBN 978-0-19-955201-6, pp. 354-70. </ref> The main immediate cause of the protests was an event in mid-August: the unannounced decision of the ruling ], the State Peace and Development Council, to remove ] which caused the price of ] and ] to suddenly rise as much as double, and the price of ] for buses to increase fivefold in less than a week.<ref name="Fuel">.</ref> The protest demonstrations were at first dealt with quickly and harshly by the junta, with dozens of protesters arrested and detained. Starting 18 September, the protests were led by thousands of ], and those protests were allowed to proceed until a renewed government crackdown on September 26.<ref name="Monks">.</ref> During the crack-down, there were rumours of disagreement within the Burmese armed forces, but none were confirmed. Some news reports referred to the protests as the ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/asia/article2521951.ece|title=Military junta threatens monks in Burma | location=London | work=The Times | date=24 September 2007 | accessdate=27 April 2010 | first1=Jenny | last1=Booth}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.novinite.com/view_news.php?id=85644|title=100,000 Protestors Flood Streets of Rangoon in "Saffron Revolution"}}</ref> | |||
| ] with a banner that reads ''non-violence: national movement'' in ], in the background is ]]] | |||
| International development and aid partners – business, non-governmental, and governmental – hinted at suspension of partnerships with Myanmar. Banks were closed and ] communications platforms, including ] and ], removed Tatmadaw postings. Protesters appeared at Myanmar embassies in foreign countries.<ref name="teachers_join_2021_02_05_bbc" /><ref name="myanmar_coup_2021_02_21_nikkei_com" /> The National Unity Government then declared the formation of an armed wing on 5 May 2021, a date that is often cited as the start of a ]. This armed wing was named the ] (PDF) to protect its supporters from military junta attacks and as a first step towards a Federal Union Army. The civil war is ongoing as of 2024.<ref>{{cite news |title=Can Myanmar's New 'People's Defense Force' Succeed? |url=https://thediplomat.com/2021/05/can-myanmars-new-peoples-defense-force-succeed/ |agency=The Diplomat |date=26 April 2021 |access-date=3 June 2021 |archive-date=9 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210509135933/https://thediplomat.com/2021/05/can-myanmars-new-peoples-defense-force-succeed/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.brookings.edu/articles/the-civil-war-in-myanmar-no-end-in-sight/ | title=The civil war in Myanmar: No end in sight | access-date=6 October 2023 | archive-date=13 October 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231013033325/https://www.brookings.edu/articles/the-civil-war-in-myanmar-no-end-in-sight/ | url-status=live }}</ref><ref name=":3" /> | |||
| During the 2007 anti-government protests a significant role was played by ], the leader of the opposition to the Burmese military government. Aung San Suu Kyi was under periods of house arrest from 1989-2010. In September 2007, hundreds of monks paid respects to her at the gate of her home, which was the first time in four years that people were able to see her in public. She was then given a second public appearance on 29 September, when she was allowed to leave house arrest briefly and meet with a UN envoy trying to persuade the junta to ease its crackdown against a pro-democracy uprising, to which the Myanmar government reluctantly agreed. | |||
| == Geography == | |||
| On 7 February 2008, SPDC announced that a referendum for the Constitution would be held and Elections by 2010. The ] was held on 10 May and promised a "discipline-flourishing democracy" for the country in the future. | |||
| {{main|Geography of Myanmar}} | |||
| Myanmar has a total area of {{convert|678500|km2}}. It lies between latitudes ] and ], and longitudes ] and ]. Myanmar is bordered in the northwest by the ] of ] and the ], Manipur, ] and ] states of India. Its north and northeast border is with the ] and ] for a Sino-Myanmar border total of {{convert|2185|km|abbr=on}}. It is bounded by ] and ] to the southeast. Myanmar has {{convert|1930|km|abbr=on}} of contiguous coastline along the ] and ] to the southwest and the south, which forms one quarter of its total perimeter.{{r|World Factbook}} | |||
| World governments remain divided on how to deal with the military junta. Calls for further sanctions by Canada, the United Kingdom, the United States and France are opposed by neighbouring countries; in particular, China has stated its belief that "sanctions or pressure will not help to solve the issue".<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/7035946.stm |title=Burma party rejects junta's terms |publisher=BBC News|date=9 October 2007|accessdate=9 October 2007 }}</ref> There is some disagreement over whether sanctions are the most effective approach to dealing with the junta, such as from a Cato Institute study and from prominent Burmese such as ] (a former senior UN official and Cambridge historian), who have opined that sanctions may have caused more harm than good to the Burmese people.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cato.org/pubs/trade/tpa-001.html |title=U.S. Sanctions on Burma-A Failure on All Fronts |publisher=Cato Institute}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.lrb.co.uk/v29/n03/than01_.html |title=What to Do About Burma |author=Thant Myint-U}}</ref> | |||
| In the north, the ] form the border with China. ], located in ], at an elevation of {{convert|5881|m|ft|0}}, is the highest point in Myanmar.<ref>{{cite book| editor = Patrick Hesp | year=2000 | title=Geographica's World Reference | publisher=Random House Australia | pages =738, 741|display-editors=etal}}</ref> Many mountain ranges, such as the ], the ], the ] and the ] exist within Myanmar, all of which run north-to-south from the ].<ref name="myathan">{{cite book | first=Mya | last=Than | year=2005 | title=Myanmar in ASEAN: Regional Co-operation Experience | isbn=978-9812302106 | publisher=Institute of Southeast Asian Studies | location=Singapore}}</ref> The mountain chains divide Myanmar's three river systems, which are the ], ], and the ] rivers.<ref name="myatthein">{{cite book | first=Myat | last=Thein | year=2005 | title=Economic Development of Myanmar | isbn=978-9812302113 | publisher=Inst. of Southeast Asian Studies | location=Singapore}}</ref> The Irrawaddy River, Myanmar's longest river at nearly {{convert|2170|km|mi|0}}, flows into the ]. Fertile plains exist in the valleys between the ]s.<ref name="myathan" /> The majority of Myanmar's population lives in the ] valley, which is situated between the ] and the ]. | |||
| In 1950, the ] became the largest of 20 minority groups participating in an insurgency against the government of Burma. The conflict continues as of 2009.<ref>{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}, Refugees International</ref> In 2004, the BBC, citing ], estimates that up to 200,000 Karen have been driven from their homes during decades of war, with 120,000 more refugees from Burma, mostly Karen, living in ]s on the Thai side of the border. Many accuse the military government of Burma of ].<ref>. 16 May 2006. BBC News.</ref> As a result of the ] in minority group areas, more than two million people have fled Burma to ].<ref>. Spiegel Online. 11 May 2007.</ref> | |||
| === Administrative divisions === | |||
| On 3 May 2008, ] devastated the country when winds of up to 215 km/h (135 mph)<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.cnn.com/2008/WORLD/asiapcf/05/07/myanmar.aidcyclone/#cnnSTCText | work=CNN}} {{Dead link|date=August 2010|bot=RjwilmsiBot}}</ref> touched land in the densely populated, rice-farming delta of the ].<ref>.</ref> It was the worst ] in Burmese history. Reports estimated that more than 200,000 people were dead or missing, and damage totaled to 10 billion dollars (USD). The ] reported, "Some villages have been almost totally eradicated and vast rice-growing areas are wiped out."<ref>{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}.</ref> The United Nations projects that as many as 1 million were left homeless; and the ] "has received reports of malaria outbreaks in the worst-affected area."<ref name="autogenerated2">{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}.</ref> Yet in the critical days following this disaster, Burma's isolationist regime hindered recovery efforts by delaying the entry of United Nations planes delivering medicine, food, and other supplies. The government's action was described by the United Nations as "unprecedented."<ref>{{cite news|coauthors=Rachel Stevenson, Julian Borger, Ian MacKinnon |title=Burma snubs foreign aid workers |url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2008/may/09/cyclonenargis.burma4 |work=The Guardian |date=9 May 2008 |accessdate=9 May 2008 | location=London}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Administrative divisions of Myanmar}} | |||
| {{Burma Administrative Divisions Image Map}} | |||
| On 4 May 2009, an American, ], allegedly swam across the lake uninvited to the house of Aung San Suu Kyi and remained there for two nights, resulting in the arrest of Yettaw and Suu Kyi, who were held in ] near Yangon.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://edition.cnn.com/2009/WORLD/asiapcf/05/15/myanmar.swimmer/ |title=American who swam to Suu Kyi's home faces 3 charges |work=CNN |date=14 May 2009}} {{Dead link|date=August 2010|bot=RjwilmsiBot}}</ref> As a result, Suu Kyi is being charged with violating the terms of her house arrest, and faces a sentence of up to five years.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.smartbrief.com/news/un_wire/storyDetails.jsp?issueid=E9C04503-313D-486E-A6C0-43F8AE6BBFE5©id=8C9EBF00-335A-44C5-AA9C-B72E8E4AB8EF |title=UN calls on Myanmar to release Suu Kyi |date=15 May 2009}}</ref> Suu Kyi's house arrest was due to end on 27 May 2009.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2009/05/16/world/asia/16myanmar.html?_r=1&hpw |work=The New York Times |author=Seth Mydans |date=15 May 2009 | title=After Years of Isolation, a Dissident Still Torments Her Tormentors}}</ref> On 11 August 2009, Suu Kyi was sentenced to an additional 18 months of house arrest following conviction on charges of violating the terms of her previous incarceration.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.reuters.com/article/topNews/idUSTRE57A04C20090811 |title=Myanmar's Suu Kyi ordered back into house detention |author=Aung Hla Tun |work=Reuters |date=11 August 2009}}</ref> ] ] stated, "This is a purely political sentence designed to prevent her from taking part in the regime's planned elections next year." On August 12, 2009, U.S. Senator ] negotiated Yettaw's release on humanitarian grounds because of Yettaw's health. Myanmar authorities commuted Yettaw's sentence in half, suspending the remaining three-and-a-half years upon Yettaw's deportation. On August 14, Senator Webb flew with Yettaw to Thailand. | |||
| Myanmar is divided into seven states ({{lang|my|ပြည်နယ်}}) and seven regions ({{lang|my|တိုင်းဒေသကြီး}}), formerly called divisions.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar/index.htm |title=Myanmar. States & Regions |publisher=Myanmar's NET |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131104160039/http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar/index.htm |archive-date=4 November 2013 }}</ref> Regions are predominantly Bamar (that is, mainly inhabited by Myanmar's dominant ethnic group). States, in essence, are regions that are home to particular ethnic minorities. The administrative divisions are further subdivided into ], which are further subdivided into townships, ], and villages. | |||
| Below are the number of districts, townships, cities/towns, wards, village groups and villages in each division and state of Myanmar as of 31 December 2001:<ref>''List of Districts, Townships, Cities/Towns, Wards, Village Groups and Villages in Union of Myanmar'' published by Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of Union of Myanmar on 31 December 2001</ref> | |||
| In early August 2009, a conflict known as the ] broke out in ] in northern Burma. For several weeks, junta troops fought against ethnic minorities including the ],<ref>. Msnbc.com. 28 August 2009.</ref> ], and ].<ref name=BangkokPost>{{cite web | url=http://www.bangkokpost.com/news/asia/152806/more-fighting-feared-as-thousands-flee-burma | title=More fighting feared as thousands flee Burma | publisher=] | author=] | date=27 August 2009 | accessdate=28 August 2009}}</ref><ref name=NYTrefugees>{{cite news | work=The New York Times | last=Fuller | first=Thomas | date=28 August 2009 | accessdate=28 August 2009 | url=http://www.nytimes.com/2009/08/29/world/asia/29myanmar.html?ref=world | title=Refugees Flee to China as Fighting Breaks Out in Myanmar}}</ref> From 8–12 August, the first days of the conflict, as many as 10,000 Burmese civilians fled to ] province in neighbouring China.<ref name=BangkokPost/><ref name=NYTrefugees/><ref name=BBCrefugees>{{cite news | work=BBC News | url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/8223430.stm | title='Thousands Flee Burma Violence' | date=26 August 2009 | accessdate=28 August 2009}}</ref> | |||
| On 13 August 2010, Junta announces the election date for 2010 is 7 November. | |||
| Opposition forces in conflict zones were given an ultimatum till 1 September 2010 to either surrender or integrate their troops into Border Guard Forces under ] control. Five ethnic ceasfire groups and 4 local militia have agreed to this, eight refused.<ref>page 5 of the of the ]</ref> | |||
| In October, 2010, a new flag was adopted and the official name of the country changed to "Republic of the Union of Myanmar", replacing the old "Union of Myanmar" from 1989. | |||
| Observers described the election day of 2010 as mostly peaceful, though there were alleged irregularities in polling stations. There was an official turnout of 77%.<ref name="tni.org"> Burma Policy Briefing 4. of the ] and Burma Centrum Nederland</ref> | |||
| On November 9, 2010, Myanmar's ruling junta stated that the ] won 80% of the votes. This claim is widely disputed by pro-democracy opposition groups, asserting that the military regime engaged in rampant fraud to achieve its result.<ref name="tni.org"/> | |||
| On November 13, 2010 the military authorities in Burma released the pro-democracy leader, Aung San Suu Kyi. | |||
| There is now worry among the UN and other nations that skirmishes, due to discontent with the elections, could erupt into civil war. (see ]). | |||
| On March 24, 2011, an ] hit eastern Burma, about 70 miles (110 km) from ]. | |||
| ===List of historical capitals=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| *{{Columns | |||
| |col1= | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| |col2= | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| }} | |||
| ==Government and politics== | |||
| {{Main|Politics of Burma}} | |||
| Burma is governed in the form of a ] with the head of state being ], who was inaugurated as ] on 30 March 2011. He previously served as Prime Minister upon the death of General Soe Win on 2 October 2007. General ] was ] until 19 October 2004, when he was replaced by ] ], after the purge of ] sections within the ]. The majority of ministry and cabinet posts are held by military officers, with the exceptions being the Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Labour, and the Ministry of National Planning and Economic Development, posts which are held by civilians.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/chiefs/chiefs29.html |title=Chiefs of State and Cabinet Members of Foreign Governments: Burma |accessdate=11 July 2006 |date=2 June 2006 |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency}}</ref><!--]--> | |||
| Elected delegates in the 1990 People's Assembly election formed the ] (NCGUB), a ] since December 1990, with the mission of restoring democracy.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ncgub.net/NCGUB/index%20of%20NCGUB.htm |title= The Birth Of The NCGUB |accessdate=19 July 2006 |publisher=National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20060718073929/http://ncgub.net/NCGUB/index+of+NCGUB.htm| archivedate = 18 July 2006}}</ref> Dr. ], a first cousin of ], has held the position of prime minister of the NCGUB since its inception. The NCGUB has been outlawed by the military government. | |||
| Major political parties in the country are the ] and the ], although their activities are heavily regulated and suppressed by the military government. Many other parties, often representing ethnic minorities, exist.{{Citation needed|date=October 2009}} The military government allows little room for political organisations and has outlawed many political parties and underground student organisations. The military supported the ] in the 1990 elections and, more recently, an organisation named the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nationalreview.com/comment/comment-mccain061103.asp |title= Crisis in Rangoon |accessdate=14 July 2006 |last=McCain |first=John | authorlink=John McCain |date=11 May 2003 |publisher=National Review Online}}</ref> | |||
| ] and the people, cooperate and crush all those harming the union."]] | |||
| In 1988, the army violently repressed protests against economic mismanagement and political oppression. On 8 August 1988, the military opened fire on demonstrators in what is known as ] and imposed martial law. However, the 1988 protests paved way for the 1990 People's Assembly elections. The election results were subsequently annulled by ]'s government. The ], led by ], won over 60% of the vote and over 80% of parliamentary seats in the 1990 election, the first held in 30 years. The military-backed ] won less than 2% of the seats. | |||
| Aung San Suu Kyi has earned international recognition as an activist for the return of democratic rule, winning the ] in 1991. The ruling regime has repeatedly placed her under ]. Despite a direct appeal by former UN Secretary General ] to ] and pressure by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (]), the military junta extended Aung San Suu Kyi's house arrest for another year on 27 May 2006 under the 1975 State Protection Act, which grants the government the right to detain any persons on the grounds of protecting peace and stability in the country.<ref>{{cite news|author=] |url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=5797&z=154 |title=Suu Kyi's Detention Extended, Supporters likely to Protest |publisher=]|date= 27 May 2006 |accessdate=27 May 2006 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|author=] |url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=5798&z=154 |title=Opposition Condemns Extension of Suu Kyi's Detention |publisher=]|date= 27 May 2006 |accessdate=27 May 2006 }}</ref> She was sentenced again to 18 months imprisonment starting in May 2009. She was released on November 12, 2010.<ref>http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2010/nov/12/aung-san-suu-kyi-burma-release''Guardian'' report on Aung's release from house arrest.</ref> | |||
| The junta faces increasing pressure from the United States and the United Kingdom. Burma's situation was referred to the ] for the first time in December 2005 for an informal consultation. In September 2006, ten of the United Nations Security Council's 15 members voted to place Myanmar on the council's formal agenda.<ref>{{cite news|author=] |url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=6176 |title=UN Security Council Puts Burma on Agenda |first=Kim|last=Gamel|work=], 16 September 2006|accessdate=11 October 2006}}</ref> On ], 4 January 2007, the government released 40 ]s, under a general amnesty, in which 2,831 prisoners were released.<ref name="CNN2007">{{cite news |title= Myanmar frees political prisoners |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2007/WORLD/asiapcf/01/11/myanmar.release.ap/ |work=CNN |date=11 January 2007 |accessdate=13 January 2007 }} {{Dead link|date=August 2010|bot=RjwilmsiBot}}</ref> On 8 January 2007, UN Secretary-General ] urged the national government to free all political prisoners, including Aung San Suu Kyi.<ref>{{cite news |title=Ban Ki-moon calls on Myanmar to release all political prisoners |url=http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=21182&Cr=myanmar&Cr1= |work=UN News Centre |publisher=United Nations |date=8 January 2007 |accessdate=13 January 2007 }}</ref> Three days later, on 11 January, five additional prisoners were released from prison.<ref name="CNN2007"/> | |||
| ] has also stated its frustration with the Union of Myanmar's government. It has formed the ASEAN Inter-Parliamentary Myanmar Caucus to address the lack of democratisation in the country.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.aseanmp.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=1&Itemid=10 |title=About Us |accessdate=9 July 2006 | publisher=ASEAN Inter-Parliamentary Myanmar Caucus}}{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}</ref> Dramatic change in the country's political situation remains unlikely, due to support from major regional powers such as India, Russia, and, in particular, China.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs2/Chinese_MM_Eco.pdf |title=The Political Economy of China-Myanmar Relations: Strategic and Economic Dimensions |accessdate=14 July 2006 |last=Poon |first=Khim Shee |date= |year=2002 | format=PDF |publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nwc.navy.mil/press/review/2002/spring/art3-sp2.htm|title=Burma and Superpower Rivalries in the Asia-Pacific|accessdate=16 July 2006|last=Selth|first=Andrew|year=Spring 2002|publisher=Naval War College Review}}{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}</ref> | |||
| In the annual ] in January 2007, held in ], Philippines, member countries failed to find common ground on the issue of Burma's lack of political reform.<ref>{{cite news |first=Carlos H. |last=Conde |title=Southeast Asians Agree to Trade Zone |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2007/01/14/world/asia/14asean.html |work=New York Times |date=14 January 2007 |accessdate=13 January 2007 }}</ref> During the summit, ASEAN foreign ministers asked Burma to make greater progress on its roadmap toward democracy and national reconciliation.<ref name="reutersASEAN">{{cite news |first=Bill |last=Tarrant |title=ASEAN leaders weigh charter, wrangle over Myanmar |url=http://in.today.reuters.com/news/newsArticle.aspx?type=worldNews&storyID=2007-01-13T143522Z_01_NOOTR_RTRJONC_0_India-283431-2.xml |work= |publisher=Reuters |date=13 January 2007 |accessdate=13 January 2007 }}</ref> Some member countries contend that Burma's ] issues are the country's own domestic affairs, while others contend that its poor human rights record is an international issue.<ref name="reutersASEAN"/> | |||
| Burma's army-drafted constitution was overwhelmingly approved (by 92.4% of the 22 million voters with alleged voter turnout of 99%) on 10 May in the first phase of a two-stage ] amid ]. It was the first national vote since the 1990 election. Multi-party elections in 2010 would end 5 decades of military rule, as the new charter gives the military an automatic 25% of seats in parliament. NLD spokesman ], inter alia, criticised the referendum: "This referendum was full of cheating and fraud across the country; In some villages, authorities and polling station officials ticked the ballots themselves and did not let the voters do anything."<ref>{{cite news|url=http://in.reuters.com/article/topNews/idINIndia-33587120080515 |title=Reuters, Cyclone-hit Myanmar says 92 percent back charter |publisher=In.reuters.com |date=15 May 2008 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> The constitution would bar ] from public office. 5 million citizens will vote 24 May in ] and the ] delta, worst hit by ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.gmanews.tv/story/95378/Myanmar-OKs-charter-amid-cyclone-disaster |title=www.gmanews.tv, Myanmar OKs charter amid cyclone disaster |publisher=Gmanews.tv |date= |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Burma has a high level of ], and ranks 176th out of 180 countries worldwide on the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.transparency.org/news_room/in_focus/2008/cpi2008/cpi_2008_table |title=cpi 2008 table /cpi2008/2008/in focus/news room |publisher=Transparency.org |date= |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| ==Human rights== | |||
| {{Main|Human rights in Burma}} | |||
| {{See|Internal conflict in Burma|Health in Burma|HIV/AIDS in Burma}} | |||
| ] are a long-standing concern for the international community and human rights organisations. There is consensus that the military regime in Burma is one of the world's most repressive and abusive regimes.<ref>{{Cite document | contribution = A Special Report to the 59th Session of the United Nations | title = A Special Report to the 59th Session of the United Nations | publisher = Freedom House | place = Geneva | pages = vii-7 | year = 2003| id = | contribution-url = http://www.middle-east-info.org/gateway/mostrepressiveregimes.pdf | accessdate = 2010-11-07 | quote = ruled by one of the world’s most repressive regimes | postscript = <!-- Bot inserted parameter. Either remove it; or change its value to "." for the cite to end in a ".", as necessary. -->{{inconsistent citations}}}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | title = Are EU Trade Sanctions On Burma Compatible With WTO Law? | journal = Are EU Trade Sanctions on Burma Compatible with WTO Law? | first = Robert | last = Howse | coauthors = Jared M. Genser | pages = 166+| id = | url = http://students.law.umich.edu/mjil/article-pdfs/v29n2-howse-genser.pdf | accessdate = 2010-11-07 | quote = repressive and abusive military regime}}</ref> | |||
| Several human rights organisations, including ] and ], and the ] have reported on human rights abuses by the military government.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hrw.org/english/docs/2004/09/01/burma9290.htm |title=Statement to the EU Development Committee |accessdate=11 July 2006 |author=Brad Adams |publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://sciencemode.com/2007/09/28/satellite-images-verify-myanmar-forced-relocations-mounting-military-presence/ |title=Satellite Images Verify Myanmar Forced Relocations, Mounting Military Presence |accessdate=1 October 2007 |publisher=]}}</ref> They have claimed that there is no independent ] in Burma. The military government restricts ] through software-based censorship that limits the material citizens can access on-line.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.opennetinitiative.net/studies/burma/ |title=Internet Filtering in Burma in 2005: A Country Study |publisher=OpenNet Initiative}}</ref><ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.burmanet.org/news/2006/06/27/mizzima-news-burma-bans-google-and-gmail-mungpi/#more-4642|title=Burma bans Google and gmail | publisher=BurmaNet News|date=27 June 2006| accessdate=28 June 2006}}</ref> ], ], and ] are common.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://web.amnesty.org/library/index/ENGASA160201998 |title=Myanmar: 10th anniversary of military repression |accessdate=14 July 2006 |date=7 August 1998 |publisher=]|archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20060824024228/http://web.amnesty.org/library/index/ENGASA160201998 |archivedate = 24 August 2006}}</ref> The military is also notorious for rampant use of sexual violence as an instrument of control, including allegations of systematic rapes and taking of ] as porters for the military. A strong women's pro-democracy movement has formed in exile, largely along the Thai border and in Chiang Mai. There is a growing international movement to defend women's human rights issues.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.womenofburma.org/Statement&Release/state_of_terror_report.pdf |format=PDF |title=State of Terror report |accessdate=21 May 2007 |date=1 February 2007 |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| The ''Freedom in the World 2004'' report by ] notes that "The junta rules by decree, controls the judiciary, suppresses all basic rights, and commits human rights abuses with ]. Military officers hold all cabinet positions, and active or retired officers hold all top posts in all ministries. ] is reportedly rampant both at the higher and local levels."<ref>{{Dead link|date=July 2009}}</ref> | |||
| Brad Adams, director of Human Rights Watch's Asia division, in a 2004 address described the human rights situation in the country as appalling: "Burma is the textbook example of a ]. Government informants and spies are omnipresent. Average Burmese people are afraid to speak to foreigners except in most superficial of manners for fear of being hauled in later for questioning or worse. There is no ], assembly or association."<ref>{{cite web|author=Brad Adams, Director, Human Rights Watch Asia Division |url=http://hrw.org/english/docs/2004/09/01/burma9290.htm |title=Statement to the EU Development Committee | Human Rights Watch |publisher=Hrw.org |date=30 August 2004 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Evidence has been gathered suggesting that the Burmese regime has marked certain ethnic minorities such as the ] for extermination or 'Burmisation'.<ref> – Anton La Guardia, Telegraph, 24 June 2005</ref> This, however, has received little attention from the international community since it has been more subtle and indirect than the mass killings in places like ].<ref> – Mike Thomson, Telegraph, 4 March 2006</ref> | |||
| In April 2007, the U.S. ] (GAO) identified financial and other restrictions that the military government places on international humanitarian assistance. The GAO report, entitled "Assistance Programs Constrained in Burma", outlined the specific efforts of the government to hinder the humanitarian work of international organisations, including restrictions on the free movement of international staff within the country. The report notes that the regime has tightened its control over assistance work since former Prime Minister ] was purged in October 2004. The military junta passed guidelines in February 2006, which formalised these restrictive policies. According to the report, the guidelines require that programs run by humanitarian groups "enhance and safeguard the national interest" and that international organisations coordinate with state agents and select their Burmese staff from government-prepared lists of individuals. United Nations officials have declared these restrictions unacceptable. | |||
| Burma's government spends the least percentage of its GDP on health care of any country in the world, and international donor organisations give less to Burma, per capita, than any other country except India.<ref name=autogenerated1>http://www.msf.org/source/countries/asia/myanmar/2008/PreventableFate/PreventableFatereport.pdf</ref> According to the report named "Preventable Fate", published by ], 25,000 Burmese AIDS patients died in 2007, deaths that could largely have been prevented by Anti Retroviral Therapy drugs and proper treatment.<ref name=autogenerated1 /> | |||
| ==Regions and states== | |||
| {{Main|Administrative divisions of Burma}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The country is divided into seven states ({{my|ပြည်နယ်}}) and seven regions ({{my|တိုင်းဒေသကြီး}}), formerly called divisions.<ref name="2008constbur">{{my|ပြည်တောင်စုသမတမြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်ဖွဲ့စည်းပုံ အခြေခံဥပဒဒေ (၂၀၀၈ ခုနစ်)|}} (in Burmese) </ref> The announcement on the renaming of division to regions was made on 20 August 2010.<ref>{{cite news |title=တိုင်းခုနစ်တိုင်းကို တိုင်းဒေသကြီးများအဖြစ် လည်းကောင်း၊ ကိုယ်ပိုင်အုပ်ချုပ်ခွင့်ရ တိုင်းနှင့် ကိုယ်ပိုင်အပ်ချုပ်ခွင့်ရ ဒေသများ ရုံးစိုက်ရာ မြို့များကို လည်းကောင်း ပြည်ထောင်စုနယ်မြေတွင်ခရိုင်နှင့်မြို့နယ်များကို လည်းကောင်း သတ်မှတ်ကြေညာ |newspaper=] |date=2010-08-20 |url=http://www.news-eleven.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=4375:2010-08-20-12-39-51&catid=42:2009-11-10-07-36-59&Itemid=112 |accessdate=2010-08-23 |language=Burmese}}</ref> Regions are predominantly ] (that is, mainly inhabited by the dominant ethnic group). States, in essence, are regions which are home to particular ethnic minorities. The administrative divisions are further subdivided into ], which are further subdivided into ]s, ]s, and villages. | |||
| Below are the number of districts, townships, cities/towns, wards, village Groups and villages in each divisions and states of Burma as of 31 December 2001:<ref>''List of Districts, Townships, Cities/Towns, Wards, Village Groups and Villages in Union of Myanmar'' published by Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of Union of Myanmar on 31 December 2001</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! No. | ! No. | ||
| ! ] | ! ] | ||
| ! |
! Districts | ||
| ! Town<br />ships | |||
| ! ] | |||
| ! |
! Cities/<br />Towns | ||
| ! ] | ! ] | ||
| ! |
! Village<br />groups | ||
| ! |
! Villages | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | 1 | | 1 | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | |
| 4 | ||
| | 18 | | 18 | ||
| | 20 | | 20 | ||
| Line 502: | Line 450: | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| === Climate === | |||
| ==Foreign relations and military== | |||
| {{ |
{{main|Climate of Myanmar}} | ||
| The country's ], particularly with Western nations, have been strained. The United States has placed a ban on new investments by U.S. firms, an import ban, and an arms embargo on the Union of Myanmar, as well as frozen military assets in the United States because of the military regime's ongoing human rights abuses, the ongoing detention of Nobel Peace Prize recipient ], and refusal to honour the election results of the 1990 People's Assembly election.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.congress.gov/cgi-bin/bdquery/z?d108:SN01182:@@@L&summ2=m& | title=Burma Freedom and Democracy Act of 2003 | publisher=United States Library of Congress |accessdate=4 February 2007 |date=4 June 2003}}</ref> Similarly, the European Union has placed sanctions on Burma, including an arms embargo, cessation of ]s, and suspension of all aid with the exception of ].<ref name="EU">{{cite web|url=http://ec.europa.eu/comm/external_relations/myanmar/intro/index.htm|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060725000750/http://ec.europa.eu/comm/external_relations/myanmar/intro/index.htm|archivedate=2006-07-25 |title= The EU's relations with Burma / Myanmar |accessdate=13 July 2006 |publisher=European Union}}</ref> U.S. and European government sanctions against the military government, coupled with boycotts and other direct pressure on corporations by supporters of the democracy movement, have resulted in the withdrawal from the country of most U.S. and many European companies. However, several Western companies remain due to loopholes in the sanctions{{Citation needed|date=September 2009}}. | |||
| ] | |||
| Despite Western isolation, Asian corporations have generally remained willing to continue investing in the country and to initiate new investments, particularly in ] extraction. The country has close relations with neighbouring India and China with several Indian and Chinese companies operating in the country. There remains active debate as to the extent to which the American-led sanctions have had adverse effects on the civilian population or on the military rulers.<ref>{{cite news|last=Hiatt |first=Fred |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/ac2/wp-dyn?pagename=article&contentId=A21505-2003Jun22 |title=How Best to Rid the World of Monsters |publisher=Washington Post|date=23 June 2003 |accessdate=24 May 2006 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/reg.burma/archives/199905/msg00184.html |title=Reuters Belgian group seeks Total boycott over Myanmar |work=Ibiblio |publisher=Reuters |date=10 May 1999 |accessdate=24 June 2006 }}</ref> Burma has also received extensive military aid from India and China in the past.<ref>{{cite news|author=View all comments that have been posted about this article. |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/09/27/AR2007092702382_pf.html |title=Caution by Junta's Asian Neighbors Reflects Their Self-Interest – |publisher=Washingtonpost.com |date=27 September 2007 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> According to some estimates, Burma has received more than US$200 million in military aid from India.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.businessweek.com/globalbiz/content/oct2007/gb20071019_332887_page_2.htm |title=India's Role in Burma's Crisis |publisher=Businessweek.com |date=19 October 2007 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> Under India's ], fields of cooperation between India and Burma include ],<ref>{{cite news|url=http://nl.newsbank.com/nl-search/we/Archives?p_product=NewsLibrary&p_multi=BBAB&d_place=BBAB&p_theme=newslibrary2&p_action=search&p_maxdocs=200&p_topdoc=1&p_text_direct-0=11045BA04AFDFED0&p_field_direct-0=document_id&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&s_trackval=GooglePM |title=NewsLibrary.com – newspaper archive, clipping service – newspapers and other news sources |publisher=Nl.newsbank.com |date=9 March 2006 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> oil and gas exploration,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0426/p04s01-wosc.html |title=India looks to Burma to slake growing thirst for gas |publisher=csmonitor.com |date=26 April 2006 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2008-08/04/content_8953269.htm |title=Myanmar, India to build IT centres in Myanmar_English_Xinhua |publisher=News.xinhuanet.com |date=4 August 2008 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://steelguru.com/news/index/2008/08/01/NTY5MDg%3D/India_to_develop_two_hydel_power_projects_in_Myanmar.html |title=SteelGuru – News |publisher=Steelguru.com |date=1 August 2008 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> and construction of ports and buildings.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/mobile/bbc_news/world/asia_pacific/716/71684/story7168492.shtml |title=BBC News |publisher=BBC News |date=2 January 2008 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> In 2008, India suspended military aid to Burma over the issue of human rights abuses by the ruling junta, although it has preserved extensive commercial ties which provide the regime with much needed revenue.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hrw.org/english/docs/2008/01/14/india17739_txt.htm |title=India and Burma: time to choose (Human Rights Watch, 14-1-2008) |publisher=Hrw.org |date= |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Much of the country lies between the ] and the ]. It lies in the ] region of Asia, with its coastal regions receiving over {{convert|5000|mm|in|1|abbr=on}} of rain annually. Annual ] in the ] region is approximately {{convert|2500|mm|in|1|abbr=on}}, while average annual rainfall in the dry zone in central Myanmar is less than {{convert|1000|mm|in|1|abbr=on}}. The northern regions of Myanmar are the coolest, with average temperatures of {{convert|21|C|F}}. Coastal and delta regions have an average maximum temperature of {{convert|32|C|F|1}}.<ref name="myatthein" /> | |||
| The country's armed forces are known as the ], which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the ], the ], and the ]. The country ] in the world for its number of active troops in service.<ref name="CIA"/> The military is very influential in the country, with top cabinet and ministry posts held by ]s. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but military spending is very high.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.commondreams.org/headlines05/0607-03.htm |title= World Military Spending Topped ]1 ] in 2004 |accessdate=19 July 2006 |last=Starck |first=Peter |date=7 June 2005 |work=Reuters |publisher=Common Dreams NewsCenter }}</ref> The country imports most of its weapons from Russia, ], China and India. | |||
| Previously and currently analysed data, as well as future projections on changes caused by ] predict serious consequences to development for all economic, productive, social, and environmental sectors in Myanmar.<ref name=":1">{{cite web|title=Impact of Climate Change and the Case of Myanmar {{!}} Myanmar Climate Change Alliance|url=https://myanmarccalliance.org/en/climate-change-basics/impact-of-climate-change-and-the-case-of-myanmar/|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181205141140/https://myanmarccalliance.org/en/climate-change-basics/impact-of-climate-change-and-the-case-of-myanmar/|archive-date=5 December 2018|access-date=2 December 2018|website=myanmarccalliance.org|language=en-GB}}</ref> In order to combat the hardships ahead and do its part to help ] Myanmar has displayed interest in expanding its use of renewable energy and lowering its level of carbon emissions. Groups involved in helping Myanmar with the transition and move forward include the ], Myanmar Climate Change Alliance, and the ] which directed in producing the final draft of the Myanmar national climate change policy that was presented to various sectors of the Myanmar government for review.<ref name=":2">{{Cite news|title=National climate change policy finalised|language=en|work=The Myanmar Times|url=https://www.mmtimes.com/national-news/yangon/25824-national-climate-change-policy-finalised.html|access-date=18 October 2018|archive-date=15 December 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181215224221/https://www.mmtimes.com/national-news/yangon/25824-national-climate-change-policy-finalised.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In April 2015, it was announced that the ] and Myanmar would enter a full partnership framework aimed to better access to electricity and other basic services for about six million people and expected to benefit three million pregnant woman and children through improved health services.<ref name=":4">{{Cite news|title=Millions to Benefit from Myanmar's New Partnership Framework With the World Bank Group|language=en|publisher=World Bank|url=http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2015/04/23/millions-benefit-myanmar-new-partnership-framework-world-bank-group|access-date=2 December 2018|archive-date=23 September 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180923051600/http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2015/04/23/millions-benefit-myanmar-new-partnership-framework-world-bank-group|url-status=live}}</ref> Acquired funding and proper planning has allowed Myanmar to better prepare for the impacts of climate change by enacting programs which teach its people new farming methods, rebuild its infrastructure with materials resilient to natural disasters, and transition various sectors towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions.<ref name=":5">{{cite web|title=Myanmar Climate Change Policy|url=http://myanmarccalliance.org/mcca/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/National-Myanmar-Climate-Change-Policy-DRAFT-1_for-website.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200322094917/http://myanmarccalliance.org/mcca/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/National-Myanmar-Climate-Change-Policy-DRAFT-1_for-website.pdf|archive-date=22 March 2020|website=myanmarccalliance.org}}</ref> | |||
| The country is building a research ] near May Myo (Pyin Oo Lwin) with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear ] pact since 1992 and a member of the ] (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor. The research reactor outbuilding frame was built by ELE steel industries limited of Yangon and water from Anisakhan/BE water fall will be used for the reactor cavity cooling system. | |||
| === Biodiversity === | |||
| ] will not defend the country in any international forum following the military regime's refusal to restore democracy. In April 2007, the Malaysian Foreign Ministry parliamentary secretary ] said ] and other ASEAN members had decided not to defend Burma if the country's issue was raised for discussion at any international conference. "Now Myanmar has to defend itself if it is bombarded in any international forum", he said when winding up a debate at committee stage for the Foreign Ministry. He was replying to queries from opposition leader ] on the next course of action to be taken by Malaysia and ASEAN with the military junta. Lim had said Malaysia must play a proactive role in pursuing regional initiatives to bring about a change in Burma and support efforts to bring the situation in Burma to the ]'s attention.<ref>{{cite news|title=Asean Will Not Defend Myanmar at International Fora – Ahmad Shabery |publisher=Bernama|date=19 April 2007 |accessdate=23 April 2007 }}</ref> In November 2008, Burma's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal.<ref>{{cite news|author=Randeep Ramesh, South Asia correspondent |url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2008/nov/05/bangladesh-burma-bengal-gas |title=Bangladesh sends warship to Burma in gas row | World news |publisher=The Guardian |date= 5 November 2008|accessdate=17 April 2010 | location=London}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Wildlife of Myanmar}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| {{further|Deforestation in Myanmar|List of protected areas of Myanmar}} | |||
| Myanmar is a ] country with more than 16,000 ], 314 ], 1131 ], 293 ], and 139 ] species, and 64 terrestrial ] including tropical and subtropical vegetation, seasonally inundated wetlands, shoreline and tidal systems, and alpine ecosystems. Myanmar houses some of the largest intact natural ecosystems in ], but the remaining ecosystems are under threat from land use intensification and over-exploitation. According to the ] categories and criteria more than a third of Myanmar's land area has been converted to ] over the last 2–3 centuries, and nearly half of its ecosystems are threatened. Despite large gaps in information for some ecosystems, there is a large potential to develop a comprehensive ] that protects its terrestrial biodiversity.<ref>{{cite journal| last1 = Murray | first1 = Nicholas J.| last2 = Keith | first2 = David A.| last3 = Duncan | first3 = Adam| last4 = Tizard | first4 = Robert| last5 = Ferrer-Paris | first5 = Jose R.| last6 = Worthington | first6 = Thomas A.| last7 = Armstrong | first7 = Kate| last8 = Nyan Hlaing | last9 = Win Thuya Htut | last10 = Aung Htat Oo | last11 = Kyaw Zay Ya | last12 = Grantham | first12 = Hedley | date = 2020 | title = Myanmar's terrestrial ecosystems: Status, threats and conservation opportunities | |||
| Until 2005, the ] annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Burma by consensus.<ref name = "UN-5483030"> | |||
| | journal = Biological Conservation | volume = 252 | page = 108834 | doi = 10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108834 | s2cid = 228850408| doi-access = free | bibcode = 2020BCons.25208834M| hdl = 1959.4/unsworks_73305 | hdl-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| {{UN document |docid=A-54-PV.83 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=54 |meeting=83 |page=30 |anchor=pg030-bk03 |date=17 December 1999 |meetingtime=10:00 |speakername=The President |accessdate=25 September 2007 }} | |||
| </ref><ref name = "UN-5483030"/><ref> | |||
| {{UN document |docid=A-55-PV.81 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=55 |meeting=81 |page=22 |anchor=pg022-bk01 |date=4 December 2000 |meetingtime=15:00 |speakername=The President |accessdate=25 September 2007 }} | |||
| </ref><ref> | |||
| {{UN document |docid=A-56-PV.92 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=56 |meeting=92 |page=7 |anchor=pg007-bk04 |date=24 December 2001 |meetingtime=11:00 |accessdate=25 September 2007 }} | |||
| </ref><ref> | |||
| {{UN document |docid=A-60-PV.69 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=60 |meeting=69 |page=19 |anchor=pg019-bk05 |date=23 December 2005 |meetingtime=10:00 |speakername=The President |accessdate=25 September 2007 }}</ref> But in 2006 a divided ] voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Burma to end its systematic violations of human rights.<ref>{{UN document |docid=A-61-PV.84 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=61 |meeting=84 |page=14 |anchor=pg014-bk07 |date=22 December 2006 |meetingtime=10:00 |accessdate=25 September 2007 }}</ref> In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the ]<ref name="UN_S200714">{{UN document |docid=S-2007-14 |type=Document |body=Security Council |year=2007 |document_number=14 |accessdate=25 September 2007| date=12 January 2007}}</ref> calling on the government of Myanmar to respect human rights and begin a democratic transition. South Africa also voted against the resolution.<ref>{{UN document |docid=S-PV-5619 |body=Security Council |type=Verbotim Report |meeting=5619 |page=3 |anchor=pg003-bk01 |date=12 January 2007 |meetingtime=16:00 |speakername=Mr. Kumalo | speakernation=South Africa |accessdate=25 September 2007 }}</ref> | |||
| Myanmar continues to perform badly in the global ] (EPI) with an overall ranking of 153 out of 180 countries in 2016, among the worst in the ]n region. The environmental areas where Myanmar performs worst (i.e. highest ranking) are ] (174), health impacts of ] (143) and ] and ] (142). Myanmar performs best (i.e. lowest ranking) in ] (21) but with declining ]s. Despite several issues, Myanmar also ranks 64 and scores very good (i.e. a high percentage of 93.73%) in environmental effects of the agricultural industry because of an excellent management of the ].<ref>{{Cite journal|url=http://epi.yale.edu/reports/2016-report|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160204021925/http://epi.yale.edu/reports/2016-report|url-status=dead|archive-date=4 February 2016|title=2016 Report|journal=EPI Report|access-date=17 December 2016}}</ref><ref>EPI (2016): {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170424221820/http://epi.yale.edu/country/myanmar |date=24 April 2017 }}</ref> Myanmar is one of the most highly vulnerable countries to ]; this poses a number of social, political, economic and foreign policy challenges to the country.<ref>Overland, I. et al. (2017). {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200728065717/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320622312_Impact_of_Climate_Change_on_ASEAN_International_Affairs_Risk_and_Opportunity_Multiplier |date=28 July 2020 }}. Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI) and Myanmar Institute of International and Strategic Studies (MISIS).</ref> The country had a 2019 ] mean score of 7.18/10, ranking it 49th globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal|last1=Grantham|first1=H. S.|last2=Duncan|first2=A.|last3=Evans|first3=T. D.|last4=Jones|first4=K. R.|last5=Beyer|first5=H. L.|last6=Schuster|first6=R.|last7=Walston|first7=J.|last8=Ray|first8=J. C.|last9=Robinson|first9=J. G.|last10=Callow|first10=M.|last11=Clements|first11=T.|last12=Costa|first12=H. M.|last13=DeGemmis|first13=A.|last14=Elsen|first14=P. R.|last15=Ervin|first15=J.|last16=Franco|first16=P.|last17=Goldman|first17=E.|last18=Goetz|first18=S.|last19=Hansen|first19=A.|last20=Hofsvang|first20=E.|last21=Jantz|first21=P.|last22=Jupiter|first22=S.|last23=Kang|first23=A.|last24=Langhammer|first24=P.|last25=Laurance|first25=W. F.|last26=Lieberman|first26=S.|last27=Linkie|first27=M.|last28=Malhi|first28=Y.|last29=Maxwell|first29=S.|last30=Mendez|first30=M.|last31=Mittermeier|first31=R.|last32=Murray|first32=N. J.|last33=Possingham|first33=H.|last34=Radachowsky|first34=J.|last35=Saatchi|first35=S.|last36=Samper|first36=C.|last37=Silverman|first37=J.|last38=Shapiro|first38=A.|last39=Strassburg|first39=B.|last40=Stevens|first40=T.|last41=Stokes|first41=E.|last42=Taylor|first42=R.|last43=Tear|first43=T.|last44=Tizard|first44=R.|last45=Venter|first45=O.|last46=Visconti|first46=P.|last47=Wang|first47=S.|last48=Watson|first48=J. E. M.|display-authors=1|title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material|journal=Nature Communications|volume=11|issue=1|year=2020|page=5978|issn=2041-1723|doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3|pmid=33293507|pmc=7723057|bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G }}</ref> | |||
| The country is a corner of the ] of ] production. In 1996 the ] in Rangoon released a "Country Commercial Guide", which states "Exports of opiates alone appear to be worth about as much as all legal exports." It goes on to say that investments in infrastructure and hotels are coming from major opiate-growing and opiate-exporting organisations and from those with close ties to these organisations.<ref name='BurmaNation'>{{cite news | first=Dennis | last=Bernstein | coauthors= Leslie Kean | title=People of the Opiate – Burma's dictatorship of drugs | date=16 January 1996 | publisher= | url =http://nick.assumption.edu/WebVAX/Nation/Bernstein16Dec96.html | work =] | pages = | accessdate = 6 July 2008 | language = }}</ref> A four-year investigation concluded that Burma's national company ] (MOGE) was "the main channel for laundering the revenues of ] produced and exported under the control of the ]." The main player in the country's drug market is the ], ethnic fighters who control areas along the country's eastern border with Thailand, part of the infamous Golden Triangle. The ], an ally of Burma's ruling military junta, was once the militant arm of the Beijing-backed ]. Burma has been a significant cog in the transnational drug trade since World War II.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.worldnetdaily.com/news/article.asp?ARTICLE_ID=26063 |title=Afghan war lifts Burma's opium trade |work=] |date=16 January 2002 |author=LoBaido, Anthony C |publisher=WorldNetDaily.com Inc}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gluckman.com/BurmaBorder.html |title=Where has all the opium gone? |author=Gluckman, Ron |publisher=Ron Gluckman}}</ref> The land area devoted to opium production increased 29% in 2007. A United Nations report cites corruption, poverty and a lack of government control as causes for the jump.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.voanews.com/english/archive/2007-10/2007-10-12-voa10.cfm?CFID=156804067&CFTOKEN=33443232 |title=Opium Cultivation Blossoms in Burma |first=Chad |last=Bouchard |work=] |date=12 October 2007}}{{dead link|date=November 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Myanmar's slow economic growth has contributed to the preservation of much of its environment and ecosystems. ]s, including dense tropical growth and valuable ] in lower Myanmar, cover over 49% of the country, including areas of ], ], ] and '']''. ] and ] and rubber have been introduced. In the ]s of the north, oak, pine and various rhododendrons cover much of the land.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.burmalibrary.org/reg.burma/archives/199909/msg00690.html |title=Myanmar's Forest Law and Rules n |publisher=BurmaLibrary.org |access-date=15 July 2006 |archive-date=11 October 2006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20061011134623/http://www.burmalibrary.org/reg.burma/archives/199909/msg00690.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In 2010 as part of the Wikileaks leaked cables, Burma was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified Surface-to-Air Missile facility.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://wikileaks.ch/cable/2004/08/04RANGOON1100.html |title=ALLEGED NORTH KOREAN INVOLVEMENT IN MISSILE ASSEMBLY AND UNDERGROUND FACILITY CONSTRUCTION IN BURMA |date=27 August 2004 |publisher=Wikileaks.ch}}</ref> | |||
| Heavy logging since the new 1995 forestry law went into effect has seriously reduced forest area and wildlife habitat.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Reid |first1=Robert |last2=Bindloss |first2=Joseph |last3=Butler |first3=Stuart |year=2009 |chapter=Environment: National Parks |title=Myanmar (Burma) |edition=10th |publisher=Lonely Planet |location=Footscray, Victoria, Australia |page= |isbn=978-1-74104-718-9 |chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/lonelyplanetmyan00joeb |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/lonelyplanetmyan00joeb/page/85 }}</ref> The lands along the coast support all varieties of tropical fruits and once had large areas of ] although much of the protective mangroves have disappeared. In much of central Myanmar (the dry zone), ] is sparse and stunted. | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| {{Main|Economy of Burma}} | |||
| {{See|Agriculture in Burma|Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia)|Tourism in Burma|Transport in Burma}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Typical jungle animals, particularly ]s, occur sparsely in Myanmar. In upper Myanmar, there are ], ], ], ]s, ], ], and ]s, which are also tamed or bred in captivity for use as work animals, particularly in the ]. Smaller mammals are also numerous, ranging from ]s and ]s to ]. The abundance of ]s is notable with over 800 species, including ], ], ], ], ], ]s, ]s, and ]. Among reptile species there are ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]s. Hundreds of species of freshwater fish are wide-ranging, plentiful and are very important food sources.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar-culture/myanmar-flora-fauna.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060923162044/http://www.myanmars.net/myanmar-culture/myanmar-flora-fauna.htm |archive-date=23 September 2006 |url-status=dead |title="Flora and Fauna" at |publisher=Myanmars.net |access-date=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| The country is one of the poorest nations in Southeast Asia, suffering from decades of stagnation, mismanagement and isolation. Based on the Economist, IMF: ] for the period 2001-2010 was 10.3 percent. | |||
| == Government and politics == | |||
| Under British administration, Burma was the second-wealthiest country in South-East Asia; second only to the Philippines. It had been the world's largest exporter of ]. During British administration, Burma supplied oil through the ]. Burma also had a wealth of natural and labour resources. It produced 75% of the world's ] (although the land-clearing involved led to the creation of vast dust-bowl) and had a highly literate population.<ref name="steinberg"/> The country was believed to be on the fast track to development.<ref name="steinberg"/> | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | perrow = 3 | |||
| | total_width = 350 | |||
| | image1 = Senior General Min Aung Hlaing 2017 (cropped).jpg | |||
| | image2 = Soe Win.jpg | |||
| | image3 = | |||
| | footer = Head of Government, Deputy Head of Government, and acting Head of State | |||
| * ], ] and ] | |||
| * ], ] and ] | |||
| * ], acting ] | |||
| | align = | |||
| | direction = | |||
| | alt1 = | |||
| | caption1 = | |||
| | caption2 = | |||
| }} | |||
| Myanmar operates ''de jure'' as a ] ] ] under its ]. But in February 2021, the civilian government led by ], was deposed by the ]. In February 2021, ] declared a one-year state emergency and First Vice President ] became the ] and handed the power to the ] ] and he assumed the role ], then ]. The ] acts as the ] ] and the ] acts as the ] ].<ref>{{cite web | last=Phillips | first=Kimberley | title=The last thing the Myanmar people need is false hope | website=The Canberra Times | date=20 February 2021 | url=https://www.canberratimes.com.au/story/7133580/the-last-thing-the-myanmar-people-need-is-false-hope/ | access-date=23 February 2021 | archive-date=21 February 2021 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210221102954/https://www.canberratimes.com.au/story/7133580/the-last-thing-the-myanmar-people-need-is-false-hope/ | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister ] disastrously attempted to make Burma a ] and adopted central planning. Rice exports fell by two thirds and mineral exports by over 96%. Plans were partly financed by printing money, which led to inflation.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www2.sjsu.edu/faculty/watkins/burma.htm |title=Political and Economic History of Myanmar (Burma) Economics |accessdate=8 July 2006|last=Watkins |first=Thayer |publisher=San José State University}}</ref> The 1962 coup d'état was followed by an economic scheme called the ], a plan to nationalise all industries, with the exception of agriculture. The catastrophic program turned Burma into one of the world's most impoverished countries.<ref name="ruin"/> Burma's admittance to ] status by the UN in 1987 highlighted its economic bankruptcy.<ref>{{cite web|year=2005 |url=http://www.un.org/special-rep/ohrlls/ldc/list.htm |title=List of Least Developed Countries |publisher=UN-OHRLLS }}</ref> | |||
| ] (Pyidaungsu Hluttaw)]] | |||
| After 1988, the regime retreated from totalitarian rule. It permitted modest expansion of the private sector, allowed some foreign investment, and received needed foreign exchange.<ref>{{cite book | author=Stephen Codrington | year=2005 | title=Planet geography | publisher =Solid Star Press | page=559 | isbn=0-9579-8193-7}}</ref> The economy is currently rated as ] (one up from ]).<ref name="freedom">{{cite web|url=http://www.heritage.org/index/country/Burma|title=Index of Economic Freedom: Burma|year=2009}}</ref> All fundamental market institutions are suppressed.<ref name="freedom"/><ref name="turnell"/> Private enterprises are often co-owned or indirectly owned by state. The corruption watchdog organisation ] in its 2007 ] released on 26 September 2007 ranked Burma the most corrupt country in the world, tied with ].<ref>2007 CPI http://www.transparency.org/policy_research/surveys_indices/cpi/2007</ref> | |||
| The constitution of Myanmar, its third since independence, was drafted by its military rulers and published in September 2008. The country is governed as a ] with a ] (with an executive ] accountable to the legislature), with 25% of the legislators appointed by the military and the rest elected in general elections. | |||
| The legislature, called the ], is bicameral and made up of two houses: The 224-seat upper ] and the 440-seat lower ]. The upper house consists 168 members who are directly elected and 56 who are appointed by the ]. The lower house consists of 330 members who are directly elected and 110 who are appointed by the armed forces. | |||
| The national currency is ]. Burma has a dual exchange rate system similar to Cuba.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://search.japantimes.co.jp/cgi-bin/eo20080502a1.html|title=The rape of Burma: where did the wealth go?|date=2 May 2008|author=Sean Turnell|publisher=The Japan Times}}</ref> The market rate was around two hundred times below the government-set rate in 2006.<ref name="turnell">{{cite web|url=http://uscampaignforburma.org/contact-resources/TurnellCongressTestimony.pdf|title=Burma's Economic Prospects – Testimony before the Senate Foreign Relations Subcommittee on East Asian and Pacific Affairs|author=Sean Turnell|date=29 March 2006}}{{dead link|date=November 2010}}</ref> Inflation averaged 30.1% between 2005 and 2007.<ref name="freedom"/> ] is a serious problem for the economy. In April 2007, the ] organised a two-day workshop on the economy. The workshop concluded that skyrocketing inflation was impeding economic growth. "Basic commodity prices have increased from 30 to 60 percent since the military regime promoted a salary increase for government workers in April 2006", said Soe Win, the moderator of the workshop. "Inflation is also correlated with corruption." Myint Thein, an NLD spokesperson, added: "Inflation is the critical source of the current economic crisis."<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=7064|title=High Inflation Impeding Burma's Economy, Says NLD |publisher=]|date=30 April 2007|accessdate=30 April 2007}}</ref> | |||
| === Political culture === | |||
| In recent years, both China and India have attempted to strengthen ties with the government for economic benefit. Many nations, including the United States and Canada, and the European Union, have imposed investment and trade sanctions on Burma. The United States has banned all imports from Burma.<ref name="turnell"/> Foreign investment comes primarily from People's Republic of China, ], South Korea, India, and ].<ref>{{cite news | first =David | last =Fullbrook | url =http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/FK04Ae03.html | title =So long US, hello China, India | publisher =Asia Times |date=4 November 2004 | accessdate =14 July 2006}}</ref> | |||
| The major political parties are the ] and the ]. | |||
| Myanmar's army-drafted constitution was approved in a ] in May 2008. The results, 92.4% of the 22 million voters with an official turnout of 99%, are considered suspect by many international observers and by the National League of Democracy with reports of widespread ], ballot stuffing, and voter intimidation.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://in.reuters.com/article/topNews/idINIndia-33587120080515 |title=Reuters, Cyclone-hit Myanmar says 92 percent back charter |work=Reuters |date=15 May 2008 |access-date=17 April 2010 |archive-date=10 January 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090110185048/http://in.reuters.com/article/topNews/idINIndia-33587120080515 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] resulted in a victory for the military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party. Various foreign observers questioned the fairness of the elections.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/22/world/asia/22nations.html|date=22 October 2010|work=The New York Times|first=Neil|last=MacFarquhar|title=U.N. Doubts Fairness of Election in Myanmar|access-date=25 February 2017|archive-date=15 July 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170715200353/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/22/world/asia/22nations.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |author=Jha, Lalit K |url=http://www2.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=15692 |title=2010 Burmese Election may be Illegitimate: Clinton |work=The Irrawaddy |date=21 May 2009 |access-date=15 May 2013 |archive-date=10 November 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131110164549/http://www2.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=15692 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-11707294 |title=Western states dismiss Burma's election |publisher=BBC |date=8 November 2010 |access-date=11 November 2010 |archive-date=11 November 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101111021602/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-11707294 |url-status=live }}</ref> One criticism of the election was that only government-sanctioned political parties were allowed to contest in it and the popular ] was declared illegal.<ref name=guardianASSK>{{cite news|last=Tisdall|first=Simon|title=Aung San Suu Kyi has to tread softly – but governments must tell it like it is|date=4 July 2011|work=The Guardian |location=UK|url=https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2011/jul/04/aung-san-suu-kyi-burmese}}</ref> However, immediately following the elections, the government ended the house arrest of the democracy advocate and leader of the National League for Democracy, ],<ref>{{cite news|author=Walker, Peter |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2010/nov/12/aung-san-suu-kyi-burma-release |title=Guardian report on Aung's release from house arrest |work=The Guardian |access-date=1 September 2012 |location=London |date=12 November 2010}}</ref> and her ability to move freely around the country is considered an important test of the military's movement toward more openness.<ref name=guardianASSK /> | |||
| The major agricultural product is rice which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the ] 52 modern ] varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas.<ref>{{PDFlink|{{dead link|date=November 2010}}|21.2 KB}}, Facts About Cooperation, International Rice Research Institute. Retrieved on 25 September 2007.</ref> | |||
| Myanmar rates as a corrupt nation on the ] with a rank of 130th out of 180 countries worldwide, with 1st being least corrupt, {{As of|2019||lc=y}}.<ref>{{cite web|title=Corruption Perceptions Index 2019|url=https://www.transparency.org/en/countries/myanmar|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200623134205/https://www.transparency.org/en/countries/myanmar|archive-date=23 June 2020|access-date=14 August 2020|publisher=Transparency.org}}</ref> | |||
| The lack of an educated workforce skilled in modern technology contributes to the growing problems of the economy.<ref>{{cite book | first=Ian | last=Brown | year=2005 | title=A Colonial Economy In Crisis | publisher =Routledge | isbn=0-4153-0580-2}}</ref> | |||
| === Foreign relations === | |||
| Today, the country lacks adequate infrastructure. Goods travel primarily across the ] border, where most illegal drugs are exported and along the ]. Railways are old and rudimentary, with few repairs since their construction in the late 19th century.<ref name="idea">{{cite web|url=http://www.idea.int/asia_pacific/burma/upload/chap3.pdf |title=Challenges to Democratization in Burma |accessdate=12 July 2006 |year=2001 |month=November |format=PDF |publisher=International IDEA}}</ref> Highways are normally unpaved, except in the major cities.<ref name="idea"/> Energy shortages are common throughout the country including in ]. | |||
| {{main|Foreign relations of Myanmar}} | |||
| Though the country's foreign relations, particularly with ], have historically been strained, the situation has markedly improved since the reforms following the 2010 elections. After years of diplomatic isolation and economic and military sanctions,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.congress.gov/cgi-bin/bdquery/z?d108:SN01182:@@@L&summ2=m& |title=Burma Freedom and Democracy Act of 2003 |publisher=United States Library of Congress |access-date=4 February 2007 |date=4 June 2003 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040125044621/http://www.congress.gov/cgi-bin/bdquery/z?d108%3ASN01182%3A%40%40%40L&summ2=m& |archive-date=25 January 2004 }}</ref> the United States relaxed curbs on foreign aid to Myanmar in November 2011<ref name="Clinton" /> and announced the resumption of diplomatic relations on 13 January 2012<ref>{{cite news | author1=Myers, Steven Lee |author2=Mydans, Seth | url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/01/14/world/asia/united-states-resumes-diplomatic-relations-with-myanmar.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120113174407/http://www.nytimes.com/2012/01/14/world/asia/united-states-resumes-diplomatic-relations-with-myanmar.html |archive-date=2012-01-13 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live | work=The New York Times | title=U.S. to Renew Myanmar Ties in Light of Reforms | date=13 January 2012 |access-date=15 May 2013}}</ref> The ] has placed sanctions on Myanmar, including an ], cessation of ]s, and suspension of all aid with the exception of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ec.europa.eu/comm/external_relations/myanmar/intro/index.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060725000750/http://ec.europa.eu/comm/external_relations/myanmar/intro/index.htm|archive-date=25 July 2006 |title= The EU's relations with Burma / Myanmar |access-date=13 July 2006 |publisher=European Union}}</ref> | |||
| Sanctions imposed by the United States and European countries against the former military government, coupled with boycotts and other direct pressure on corporations by supporters of the democracy movement, have resulted in the withdrawal from the country of most U.S. and many European companies.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/8195956.stm |title=Overview of Burma sanctions |publisher=BBC News |access-date=12 November 2011 |date=18 December 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110812181932/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/8195956.stm |archive-date=12 August 2011}}</ref> Despite Western isolation, Asian corporations have generally remained willing to continue investing in the country and to initiate new investments, particularly in natural resource extraction. The country has close relations with neighbouring India and China with several Indian and Chinese companies operating in the country. Under India's ], fields of co-operation between India and Myanmar include ],<ref>{{cite news |url=http://nl.newsbank.com/nl-search/we/Archives?p_product=NewsLibrary&p_multi=BBAB&d_place=BBAB&p_theme=newslibrary2&p_action=search&p_maxdocs=200&p_topdoc=1&p_text_direct-0=11045BA04AFDFED0&p_field_direct-0=document_id&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&s_trackval=GooglePM |title=Burma, India to sign accord on use of India's remote sensing satellite data |publisher=NewsLibrary.com |date=9 March 2006 |access-date=17 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110501183947/http://nl.newsbank.com/nl-search/we/Archives?p_product=NewsLibrary&p_multi=BBAB&d_place=BBAB&p_theme=newslibrary2&p_action=search&p_maxdocs=200&p_topdoc=1&p_text_direct-0=11045BA04AFDFED0&p_field_direct-0=document_id&p_perpage=10&p_sort=YMD_date:D&s_trackval=GooglePM |archive-date=1 May 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> oil and gas exploration,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0426/p04s01-wosc.html |title=India looks to Burma to slake growing thirst for gas |work=The Christian Science Monitor |date=26 April 2006 |access-date=17 April 2010 |archive-date=8 July 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100708035039/http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0426/p04s01-wosc.html |url-status=live }}</ref> information technology,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2008-08/04/content_8953269.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090111015855/http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2008-08/04/content_8953269.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=11 January 2009 |title=Myanmar, India to build IT centres in Myanmar_English_Xinhua |agency=Xinhua News Agency |date=4 August 2008 |access-date=17 April 2010}}</ref> hydropower<ref>{{cite web |url=http://steelguru.com/news/index/2008/08/01/NTY5MDg%3D/India_to_develop_two_hydel_power_projects_in_Myanmar.html |title=India to develop two hydel power projects in Myanmar – 56908 |publisher=Steelguru.com |date=1 August 2008 |access-date=20 November 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090116032246/http://steelguru.com/news/index/2008/08/01/NTY5MDg%3D/India_to_develop_two_hydel_power_projects_in_Myanmar.html |archive-date=16 January 2009}}</ref> and construction of ports and buildings.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/mobile/bbc_news/world/asia_pacific/716/71684/story7168492.shtml |title=India urges Burma reconciliation |publisher=BBC News |date=2 January 2008 |access-date=17 April 2010 |archive-date=2 December 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101202013907/http://news.bbc.co.uk/mobile/bbc_news/world/asia_pacific/716/71684/story7168492.shtml |url-status=live }}</ref> Myanmar also has close political relations with Vietnam<ref>{{Cite web |last=] |date=2019-12-17 |title=PM calls for stronger Vietnam-Myanmar parliamentary ties |url=https://en.vietnamplus.vn/pm-calls-for-stronger-vietnammyanmar-parliamentary-ties/165624.vnp |access-date=2023-04-03 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=3 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230403185621/https://en.vietnamplus.vn/pm-calls-for-stronger-vietnammyanmar-parliamentary-ties/165624.vnp |url-status=live }}</ref> and Japan.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Michimi Muranushi |date=2019-10-22 |title=Japan's Defense of Myanmar and the Rohingya Genocide |url=https://www.mei.edu/publications/japans-defense-myanmar-and-rohingya-genocide |access-date=2023-04-03 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=20 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230320170843/https://www.mei.edu/publications/japans-defense-myanmar-and-rohingya-genocide |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=2021-05-26 |title=Japan should not follow the Western policy on Myanmar - Diplomat op-ed |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/japan-should-not-follow-western-policy-myanmar-diplomat-op-ed-2021-05-26/ |access-date=2023-04-03 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20220803021638/https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/japan-should-not-follow-western-policy-myanmar-diplomat-op-ed-2021-05-26/ |archive-date=2022-08-03}}</ref> | |||
| Burma is also the world's second largest producer of ], accounting for 8% of entire world production and is a major source of ]s, including ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unodc.org/pdf/myanmar/myanmar_country_profile_2005.pdf |title=Myanmar Country Profile |accessdate=9 July 2006 |year=2005 |month=December |format=PDF |work=Office on Drugs and Crime | pages=5–6 | publisher=United Nations}}</ref> | |||
| Opium bans implemented since 2002 after international pressure have left ex-poppy farmers without sustainable sources of income in the Kokang and Wa regions. They depend on casual labour for income.<ref> of the ]</ref> | |||
| In May 2013, Thein Sein became the first Myanmar president to visit the ] in 47 years. President ] praised the former general for political and economic reforms and the cessation of tensions between Myanmar and the United States. Political activists objected to the visit because of concerns over human rights abuses in Myanmar, but Obama assured Thein Sein that Myanmar will receive U.S. support. The two governments agreed to sign a ] and investment framework agreement on 21 May 2013.<ref>{{cite news|title=Obama Vows US Support As Myanmar Leader Visits|url=https://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=185449969|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130521150924/http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=185449969|archive-date=21 May 2013|publisher=NPR|date=20 May 2013|agency=Associated Press}}</ref> | |||
| Chinese investors are welcomed to cultivate monoplantations of rubber, sugarcane and tea. | |||
| Other industries include agricultural goods, textiles, wood products, construction materials, gems, metals, oil and natural gas. The Norwegian company Seadrill owned by John Fredriksen is involved in offshore oildrilling, expected to give the Burmese Military Junta oil and oil export revenues. | |||
| In June 2013, Myanmar held its first ever summit, the ] on East Asia 2013. A regional spinoff of the annual ] in ], Switzerland, the summit was held on 5–7 June and attended by 1,200 participants, including 10 heads of state, 12 ministers and 40 senior directors from around the world.<ref>{{cite web|title={{As written|Pheo|nix}} Voyages appointed travel manager for Myanmar's first major summit|url=http://www.ttgmice.com/article/pheonix-voyages-appointed-travel-manager-for-myanmars-first-major-summit/|publisher=TTGmice|access-date=29 April 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131110163809/http://www.ttgmice.com/article/pheonix-voyages-appointed-travel-manager-for-myanmars-first-major-summit/|archive-date=10 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| The Union of Myanmar's rulers depend on sales of precious stones such as ], ] and ] to fund their regime. ] are the biggest earner; 90% of the world's ] come from the country, whose red stones are prized for their purity and ]. ] buys the majority of the country's ]. Burma's "''Valley of Rubies''", the mountainous ] area, {{convert|200|km|mi|abbr=on}} north of ], is noted for its rare pigeon's blood rubies and blue ].<ref>.</ref> Many U.S. and European jewellery companies, including Bulgari, Tiffany, and Cartier, refuse to import these stones based on reports of deplorable working conditions in the mines. Human Rights Watch has encouraged a complete ban on the purchase of Burmese gems based on these reports and because nearly all profits go to the ruling junta, as the majority of mining activity in the country is government-run.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.hrw.org/en/news/2007/11/11/burma-gem-trade-bolsters-military-regime-fuels-atrocities |title=Burma: Gem Trade Bolsters Military Regime, Fuels Atrocities |publisher=Human Rights Watch |date=11 November 2007}}</ref> | |||
| === Military === | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|Armed forces of Myanmar}}Since the late 1950s, Myanmar's military has had major roles in Myanmar's politics.<ref name=":Han">{{Cite book |last=Han |first=Enze |title=The Ripple Effect: China's Complex Presence in Southeast Asia |date=2024 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-19-769659-0 |location=New York, NY}}</ref>{{Rp|page=23}}] ] multirole fighter]] | |||
| Myanmar has received extensive military aid from China in the past.<ref>{{cite news |author=Cody, Edward |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/09/27/AR2007092702382_pf.html |title=Caution by Junta's Asian Neighbors Reflects Their Self-Interest |newspaper=The Washington Post |date=27 September 2007 |access-date=17 April 2010 |archive-date=7 July 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130707052329/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/09/27/AR2007092702382_pf.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Myanmar has been a member of ASEAN since 1997. Though it gave up its turn to hold the ASEAN chair and host the ] in 2006, it chaired the forum and hosted the summit in 2014.<ref>{{cite press release |url=http://www.asean.org/?static_post=24th-asean-summit |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160416074423/http://www.asean.org/?static_post=24th-asean-summit |url-status=dead |archive-date=16 April 2016 |work=ASEAN | title=24th ASEAN Summit, Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar, 10–11 May 2014 | date=4 April 2014}}</ref> In November 2008, Myanmar's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.asean.org/?static_post=24th-asean-summit |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160416074423/http://www.asean.org/?static_post=24th-asean-summit |url-status=dead |archive-date=16 April 2016 |title=24th ASEAN Summit, Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar, 10–11 May 2014 |work=ASEAN |date= 4 April 2014|access-date=1 April 2016 }}</ref> Controversy surrounding the Rohingya population also remains an issue between Bangladesh and Myanmar.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1966621,00.html | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100220230847/http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1966621,00.html | url-status=dead | archive-date=20 February 2010 | magazine=Time | title=For Rohingya in Bangladesh, No Place is Home | date=19 February 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Myanmar's armed forces are known as the ], which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the ], the ], and the ]. The country ] in the world for its number of active troops in service.<ref name="NCGUB" /> The military is very influential in Myanmar, with all top cabinet and ministry posts usually held by military officials. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but Myanmar's military forces' expenses are high.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.commondreams.org/headlines05/0607-03.htm |title=World Military Spending Topped US$1 trillion in 2004 |access-date=19 July 2006 |last=Starck |first=Peter |date=7 June 2005 |agency=Reuters |publisher=Common Dreams NewsCenter |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060620161837/http://www.commondreams.org/headlines05/0607-03.htm |archive-date=20 June 2006 }}</ref> Myanmar imports most of its weapons from Russia, Ukraine, China and India. | |||
| Since 1992, the government has encouraged ]. However, fewer than 750,000 tourists enter the country annually.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.channelviewpublications.net/cit/006/0097/cit0060097.pdf |format=PDF |title=The Politics of Tourism in Myanmar |accessdate=8 July 2006|last=Henderson |first=Joan C. |publisher=]}}</ref> ] has requested that international tourists not visit Burma. The junta's forced labour programmes were focused around tourist destinations which have been heavily criticised for their human rights records. Burma's Minister of Hotels and Tourism ] has stated that the government receives a significant percentage of the income of private sector tourism services.<ref>{{cite web|author=tayza thuria |url=http://www.tayzathuria.org.uk/bd/2006/12/24/re.htm |title=Burma Digest |publisher=Tayzathuria.org.uk |date=24 December 2006 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> Much of the country is completely off-limits to tourists, and the military very tightly controls interactions between foreigners and the people of Burma, particularly the border regions.<ref>{{cite web | title=Cycling Burma (Myanmar) | url=http://7ride.com/rides/myanmar-%28burma%29-2006.aspx | work=Cycling Burma (Myanmar) | date=1900-1-0 | accessdate=2010-05-21}}</ref> They are not to discuss politics with foreigners, under penalty of imprisonment, and in 2001, the Myanmar Tourism Promotion Board issued an order for local officials to protect tourists and limit "unnecessary contact" between foreigners and ordinary Burmese people.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.burmacampaign.org.uk/action_holiday.html |title=The Tourism Campaign – Campaigns – The Burma Campaign UK |publisher=Burmacampaign.org.uk |date= |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Myanmar is building a research ] near ] with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear ] pact since 1992 and a member of the ] (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor.<ref>{{cite news|publisher=BBC |title=Russia and Burma in Nuclear Deal |date=15 May 2007 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/6658713.stm |access-date=28 September 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070819190144/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/6658713.stm |archive-date=19 August 2007 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|work=The Telegraph|title=Nuclear Watchdog asks Burma to Open Up Suspect Sites|date=14 January 2011|last=Moore|first=Malcolm|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/burmamyanmar/8259803/Nuclear-watchdog-asks-Burma-to-open-up-suspect-sites.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220110/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/burmamyanmar/8259803/Nuclear-watchdog-asks-Burma-to-open-up-suspect-sites.html |archive-date=10 January 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live|access-date=28 September 2011|location=London}}{{cbignore}}</ref> In 2010 as part of the ], Myanmar was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified surface-to-air missile facility.<ref>{{cite news |title=Myanmar 'building nuclear sites' |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2010/12/10/myanmar-building-nuclear-sites |access-date=3 June 2024 |work=Al Jazeera |date=10 December 2010 |language=en |archive-date=3 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240603015912/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2010/12/10/myanmar-building-nuclear-sites |url-status=live }}</ref> As of 2019, the United States ] assessed that Myanmar is not in violation of its obligations under the ] but that the Myanmar government had a history of non-transparency on its nuclear programs and aims.<ref name="ACVC">{{cite web|last1=Bureau of Arms Control, Verification and Compliance|title=Adherence to and Compliance with Arms Control, Non-Proliferation, and Disarmament Agreements and Commitments|url=https://www.state.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Compliance-Report-2019-August-19-Unclassified-Final.pdf|access-date=2 January 2020|website=2019 Compliance Report|publisher=United States Department of State|archive-date=22 January 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210122040233/https://www.state.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Compliance-Report-2019-August-19-Unclassified-Final.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The M9 gas field in Burma is expected to go online in 2012.<ref name="atimes.com">{{cite web|author=Jul 10, 2008 |url=http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/JG10Ae01.html |title=Asia Times Online :: Southeast Asia news and business from Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, Malaysia and Vietnam |publisher=Atimes.com |date=10 July 2008 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Until 2005, the ] annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Myanmar by consensus.<ref name="UN-5483030">{{UN document |docid=A-54-PV.83 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=54 |meeting=83 |page=30 |anchor=pg030-bk03 |date=17 December 1999 |meetingtime=10:00 |speakername=The President |access-date=25 September 2007 }}</ref><ref>{{UN document |docid=A-55-PV.81 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=55 |meeting=81 |page=22 |anchor=pg022-bk01 |date=4 December 2000 |meetingtime=15:00 |speakername=The President |access-date=25 September 2007 }}</ref><ref>{{UN document |docid=A-56-PV.92 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=56 |meeting=92 |page=7 |anchor=pg007-bk04 |date=24 December 2001 |meetingtime=11:00 |access-date=25 September 2007 }}</ref><ref>{{UN document |docid=A-60-PV.69 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=60 |meeting=69 |page=19 |anchor=pg019-bk05 |date=23 December 2005 |meetingtime=10:00 |speakername=The President |access-date=25 September 2007 }}</ref> But in 2006 a divided United Nations General Assembly voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Myanmar to end its systematic violations of human rights.<ref>{{UN document |docid=A-61-PV.84 |body=General Assembly |type=Verbotim Report |session=61 |meeting=84 |page=14 |anchor=pg014-bk07 |date=22 December 2006 |meetingtime=10:00 |access-date=25 September 2007 }}</ref> In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the ]<ref>{{UN document |docid=S-2007-14 |type=Document |body=Security Council |year=2007 |document_number=14 |date=12 January 2007 |access-date=25 September 2007}}</ref> calling on the government of Myanmar to respect human rights and begin a democratic transition. South Africa also voted against the resolution.<ref>{{UN document |docid=S-PV-5619 |body=Security Council |type=Verbotim Report |meeting=5619 |page=3 |anchor=pg003-bk01 |date=12 January 2007 |meetingtime=16:00 |speakername=Mr. Kumalo |speakernation=South Africa |access-date=25 September 2007}}</ref> | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| {{Main|Demographics of Burma}} | |||
| ]. Much of Yangon's urban population resides in densely populated flats.]] | |||
| === Human rights and internal conflicts === | |||
| Burma has a population of about 56 million.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unescap.org/esid/psis/population/popin/profiles/myn.asp |title= POPULATION AND SOCIAL INTEGRATION SECTION (PSIS) |publisher=UN Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific }}</ref> Population figures are rough estimates because the last partial census, conducted by the Ministry of Home and Religious Affairs under the control of the military junta, was taken in 1983.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/obl/docs/Considered_responses-2.pdf | title=Conflict and Displacement in Karenni: The Need for Considered Responses |accessdate=13 July 2006 |year=2000 | month=May | format=PDF |publisher=Burma Ethnic Research Group}}</ref> No trustworthy nationwide census has been taken in Burma since 1931. There are over 600,000 registered ]s from Burma in ], and millions more work illegally. Burmese migrant workers account for 80% of Thailand's migrant workers.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://web.amnesty.org/library/index/ENGASA390012005 |title=Thailand: The Plight of Burmese Migrant Workers |accessdate=13 July 2006 |date=8 June 2006 |publisher=Amnesty International |archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20060626102346/http://web.amnesty.org/library/index/ENGASA390012005 |archivedate = 26 June 2006}}</ref> Burma has a ] of {{convert|75|/km2}}, one of the lowest in ]. Refugee camps exist along Indian, Bangladeshi and Thai borders while several thousand are in ]. Conservative estimates state that there are over 295,800 refugees from Burma, with the majority being ], ], and ] and are principally located along the Thai-Burma border.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/publ/opendoc.pdf?tbl=PUBL&id=449676844 | title=Myanmar Refugees in South East Asia |accessdate=13 July 2006 |year=2006 | month=April | format=PDF |publisher=UNHCR}}</ref> There are nine permanent refugee camps along the Thai-Burma border, most of which were established in the mid-1980s. The refugee camps are under the care of the . | |||
| {{main|Human rights in Myanmar|Internal conflict in Myanmar}} | |||
| {{undue weight section|date=November 2020}} | |||
| ] and regions affected by fighting during and after 1995 are highlighted in yellow.]] | |||
| There is consensus that the former military regime in Myanmar (1962–2010) was one of the world's most repressive and abusive regimes.<ref>{{cite web |title=The World's Most Repressive Regimes 2013 |url=http://www.middle-east-info.org/gateway/mostrepressiveregimes.pdf |publisher=Freedom House |location=Geneva |year=2003 |pages=vii–7 |quote=Burma continues to be ruled by one of the world's most repressive regimes. |access-date=7 November 2010 |archive-date=30 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191030032649/http://www.middle-east-info.org/gateway/mostrepressiveregimes.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | title = Are EU Trade Sanctions on Burma Compatible With WTO Law? | journal=Are EU Trade Sanctions on Burma Compatible with WTO Law? | first = Robert | last = Howse |author2=Jared M. Genser | pages = 166 ff| url = http://students.law.umich.edu/mjil/article-pdfs/v29n2-howse-genser.pdf| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100607153959/http://students.law.umich.edu/mjil/article-pdfs/v29n2-howse-genser.pdf| archive-date = 7 June 2010| access-date =7 November 2010 | quote = repressive and abusive military regime}}</ref> In November 2012, ], Barack Obama's Special Assistant to the President on Human Rights, wrote on the White House blog that "Serious human rights abuses against civilians in several regions continue, including against women and children."<ref name=ShanVsGovt /> Members of the United Nations and major international human rights organisations have issued repeated and consistent reports of widespread and systematic human rights violations in Myanmar. The United Nations General Assembly has repeatedly<ref>{{cite web|title=List of UN General Assembly Resolutions on Burma|url=http://www.altsean.org/Research/UN%20Dossier/UNGA.htm|access-date=4 January 2010|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161104120635/http://www.altsean.org/Research/UN%20Dossier/UNGA.htm|archive-date=4 November 2016}}</ref> called on the Burmese military junta to respect human rights and in November 2009 the General Assembly adopted a resolution "strongly condemning the ongoing systematic violations of human rights and fundamental freedoms" and calling on the Burmese military regime "to take urgent measures to put an end to violations of international human rights and humanitarian law."<ref>{{Cite press release|title=UN General Assembly Resolution: Time for Concrete Action|publisher=International Federation for Human Rights|date=20 November 2009|url=http://www.fidh.org/UN-General-Assembly-Resolution-time-for-concrete|access-date=4 January 2010|archive-date=29 January 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100129215628/http://www.fidh.org/UN-General-Assembly-Resolution-time-for-concrete|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| International human rights organisations including ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://hrw.org/english/docs/2004/09/01/burma9290.htm|title=Statement to the EU Development Committee|date=1 September 2004|author=Adams, Brad|publisher=]|access-date=12 July 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060620074005/http://hrw.org/english/docs/2004/09/01/burma9290.htm|archive-date=20 June 2006|url-status=dead}}</ref> and ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://report2009.amnesty.org/en/regions/asia-pacific/myanmar|title=Amnesty International 2009 Report on Human Rights in Myanmar|access-date=4 January 2010 |author=Adams, Brad|publisher=]|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090912013419/http://report2009.amnesty.org/en/regions/asia-pacific/myanmar|archive-date=12 September 2009}}</ref> have repeatedly documented and condemned widespread human rights violations in Myanmar. The ''Freedom in the World 2011'' report by ] notes, "The military junta has ... suppressed nearly all basic rights; and committed human rights abuses with impunity." In July 2013, the ] indicated that there were approximately 100 political prisoners being held in Burmese prisons.<ref name="mmtimes1">{{cite news|date=24 July 2013|title=Myanmar set to release some 70 prisoners|newspaper=The Myanmar Times|url=http://www.mmtimes.com/index.php/national-news/7577-myanmar-set-to-release-some-70-prisoners.html|access-date=24 July 2013|archive-date=2 November 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131102003228/http://www.mmtimes.com/index.php/national-news/7577-myanmar-set-to-release-some-70-prisoners.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="irrawaddy1">{{cite news|last=Weng|first=Lawi|date=24 July 2013|title=Burma Govt Releases 73 Political Prisoners|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/burma/burma-govt-releases-73-political-prisoners.html|access-date=24 July 2013|archive-date=30 October 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131030200045/http://www.irrawaddy.org/burma/burma-govt-releases-73-political-prisoners.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Myanmar: Final push on political prisoners needed|url=http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/docid/50659a382.html|access-date=19 March 2013|date=27 September 2012|archive-date=18 December 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191218083935/http://www.refworld.org/docid/50659a382.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Burma Frees 56 Political Prisoners|url=http://www.voanews.com/content/burma-frees-fifty-six-political-prisoners-day-after-sanctions-dropped/1647578.html|access-date=26 April 2013|publisher=Voice of America|date=22 April 2013|archive-date=26 April 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130426052937/http://www.voanews.com/content/burma-frees-fifty-six-political-prisoners-day-after-sanctions-dropped/1647578.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Evidence gathered by a British researcher was published in 2005 regarding the extermination or "Burmisation" of certain ethnic minorities, such as the ], ] and ].<ref>{{cite news|last=Guardia |first=Anton La |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/Myanmarmyanmar/1492726/Myanmar%27s-%27slow-genocide%27-is-revealed-through-the-eyes-of-its-child-victims.html |title=Myanmar's 'slow genocide' is revealed through the eyes of its child victims |newspaper=The Telegraph |date=24 June 2005 |access-date=20 November 2012 |location=London}}{{dead link|date=July 2021|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> | |||
| ], ], Thailand, one of the largest of nine ] camps in Thailand<ref>{{cite web |title=2013 UNHCR country operations profile – Thailand |url=http://www.unhcr.org/pages/49e489646.html |access-date=15 May 2013 |archive-date=24 April 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130424075211/http://www.unhcr.org/pages/49e489646.html |url-status=live }}</ref>]] | |||
| Based on the evidence gathered by Amnesty photographs and video of the ongoing armed conflict between the Myanmar military and the ] (AA), attacks escalated on civilians in Rakhine State. Ming Yu Hah, ]'s Deputy Regional Director for Campaigns said, the ] must urgently refer the situation in Myanmar to the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/latest/news/2020/10/myanmar-villages-burned-civilians-injured-rakhine-state-conflict/|title=Myanmar: Villages burned, civilians injured and killed as Rakhine State conflict escalates|access-date=12 October 2020|website=Amnesty International|date=12 October 2020|archive-date=15 October 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201015014929/https://www.amnesty.org/en/latest/news/2020/10/myanmar-villages-burned-civilians-injured-rakhine-state-conflict/|url-status=live}}</ref> The military is notorious for rampant use of sexual violence.<ref name="UNHR" /> | |||
| ==== Child soldiers ==== | |||
| Child soldiers were reported in 2012 to have played a major part in the Burmese Army.<ref name=":6">{{cite web |last=Rodion Ebbighausen, Shamil Shams |date=2012-03-19 |title=MTV and Burmese pop stars campaign to end human trafficking |url=https://www.dw.com/en/mtv-and-burmese-pop-stars-campaign-to-end-human-trafficking/a-15817535 |access-date=2022-06-01 |website=] |language=en-GB |archive-date=1 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220601031101/https://www.dw.com/en/mtv-and-burmese-pop-stars-campaign-to-end-human-trafficking/a-15817535 |url-status=live }}</ref> ''The Independent'' reported in June 2012 that "Children are being sold as conscripts into the Burmese military for as little as $40 and a bag of rice or a can of petrol."<ref>{{cite news|title=Two Burmese children a week conscripted into military|newspaper=The Independent|author=Taylor, Jerome|date=19 June 2012|url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/two-burmese-children-a-week-conscripted-into-military-7858858.html|access-date=15 May 2013|location=London|archive-date=26 October 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141026003058/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/two-burmese-children-a-week-conscripted-into-military-7858858.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> In September 2012, the Myanmar Armed Forces released 42 child soldiers, and the ] met with representatives of the government as well as the ] to secure the release of more child soldiers.<ref>{{cite news|title=ILO in Talks with Kachins over Child Soldiers|author=Weng, Lawi|work=The Irrawaddy|date=5 September 2012|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/archives/13354|access-date=15 May 2013|archive-date=5 January 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130105023630/http://www.irrawaddy.org/archives/13354|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Slavery and human trafficking ==== | |||
| {{Further|Sex trafficking in Myanmar}} | |||
| ] and ] are common in Myanmar.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Kieran Guilbert |date=2018-06-26 |title=Exclusive: Women most at risk from traffickers in India, Libya, Myanmar - poll |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-women-dangerous-poll-trafficking-excl-idUSKBN1JM02M |access-date=2022-06-01 |archive-date=1 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220601031101/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-women-dangerous-poll-trafficking-excl-idUSKBN1JM02M |url-status=live }}</ref> Human trafficking happens mostly to women who are unemployed and have low incomes. They are deceived by brokers that better opportunities and wages exist for them abroad.<ref>{{cite web |title=Myanmar UN ACT |url=http://un-act.org/myanmar/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190506104746/http://un-act.org/myanmar/ |archive-date=6 May 2019 |access-date=6 May 2019 |website=UN ACT}}</ref> In 2017, the government reported 185 trafficking cases. The government of Burma makes little effort to eliminate human trafficking. The ] reported that both the government and ] were complicit in sex and labour trafficking.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.state.gov/j/tip/rls/tiprpt/countries/2018/282623.htm|title=Burma|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180725003051/https://www.state.gov/j/tip/rls/tiprpt/countries/2018/282623.htm|archive-date=25 July 2018|url-status=dead}}</ref> Women and girls from all ] and foreigners have been victims of sex trafficking in Myanmar.<ref name=":6" /> They are forced into prostitution, marriages or pregnancies.<ref name=":7">{{cite web |date=2009 |title=Nowhere else to go: An examination of sexual trafficking and related human rights abuses in Southern Burma |url=https://sherloc.unodc.org/cld/es/bibliography/2009/nowhere_else_to_go_an_examination_of_sexual_trafficking_and_related_human_rights_abuses_in_southern_burma.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220601030016/https://sherloc.unodc.org/cld/es/bibliography/2009/nowhere_else_to_go_an_examination_of_sexual_trafficking_and_related_human_rights_abuses_in_southern_burma.html |archive-date=2022-06-01 |website=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.hrw.org/report/2019/03/21/give-us-baby-and-well-let-you-go/trafficking-kachin-brides-myanmar-china|title=Give Us a Baby and We'll Let You Go: Trafficking of Kachin Brides from Myanmar to China|date=21 March 2019|website=Human Rights Watch|access-date=28 March 2020|archive-date=31 July 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210731213631/https://www.hrw.org/report/2019/03/21/give-us-baby-and-well-let-you-go/trafficking-kachin-brides-myanmar-china|url-status=live}}</ref> Sex trafficking in Myanmar has been fuelled by factors like ], political instability, land confiscation,<ref name="autogenerated3">{{cite web |date=July 12, 2018 |title=Thousands of Myanmar women forced into marriages in China |url=https://www.dw.com/en/thousands-of-myanmar-women-forced-into-marriages-in-china/a-46625465 |website=DW News |access-date=16 August 2023 |archive-date=25 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200325143450/https://www.dw.com/en/thousands-of-myanmar-women-forced-into-marriages-in-china/a-46625465 |url-status=live }}</ref> poor border management,<ref>{{cite web |date=December 20, 2019 |title=NGO Report: Malaysia Now a Destination for Sex-Trafficking of Rohingya Girls |url=https://www.benarnews.org/english/news/malaysian/malaysia-rohingya-12202019174632.html |website=Benar News |access-date=16 August 2023 |archive-date=21 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211021215842/https://www.benarnews.org/english/news/malaysian/malaysia-rohingya-12202019174632.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="autogenerated7">{{cite web |date=August 23, 2017 |title=Trafficked to China to marry, a Myanmar woman hopes to save others from same fate |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-myanmar-trafficking-marriage/trafficked-to-china-to-marry-a-myanmarwoman-hopes-to-save-others-from-same-fate-idUSKCN1B402K |website=Reuters |access-date=16 August 2023 |archive-date=16 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230816073900/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-myanmar-trafficking-marriage/trafficked-to-china-to-marry-a-myanmarwoman-hopes-to-save-others-from-same-fate-idUSKCN1B402K |url-status=live }}</ref> and government restrictions on providing travel documents.<ref name=":7" /> | |||
| A cyber-scam industry in Myanmar's borderlands has involved human trafficking, forced labour and other abuses.<ref name=":8">{{Cite web |date=2023-10-05 |title=Myanmar's cyber-scam industry limps on amid regional crackdown |url=https://www.frontiermyanmar.net/en/myanmars-cyber-scam-industry-limps-on-amid-regional-crackdown/ |access-date=2023-11-29 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=5 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231205145610/https://www.frontiermyanmar.net/en/myanmars-cyber-scam-industry-limps-on-amid-regional-crackdown/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Many of the scam centres are in territories controlled by junta allies like the ].<ref name=":8" /> In August 2023, a report from the ] noted that at least 120,000 people in Myanmar were trapped in such centres by criminal gangs.<ref>{{Cite web |date=October 10, 2023 |title=#trending: Chinese netizens afraid of Southeast Asia travel after hit movie No More Bets shows human trafficking scams |url=https://www.todayonline.com/world/no-more-bets-movie-chinese-tourists-2271816 |access-date=2023-11-29 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=5 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231205145607/https://www.todayonline.com/world/no-more-bets-movie-chinese-tourists-2271816 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Genocide allegations and crimes against Rohingya people ==== | |||
| ] of Myanmar<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/dec/20/Myanmar-rohingya-muslim-refugee-camps | title=Trapped inside Myanmar's refugee camps, the Rohingya people call for recognition | work=The Guardian | date=20 December 2012 | access-date=10 February 2015}}{{dead link|date=September 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=US Holocaust Museum highlights plight of Myanmar's downtrodden Rohingya Muslims|url=https://www.foxnews.com/us/us-holocaust-museum-highlights-plight-of-myanmars-downtrodden-rohingya-muslims|date=6 November 2013|agency=]|publisher=]|access-date=6 June 2015|archive-date=19 October 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151019125757/http://www.foxnews.com/us/2013/11/06/us-holocaust-museum-highlights-plight-myanmar-downtrodden-rohingya-muslims/|url-status=live}}</ref> |alt=]] | |||
| {{See also|Rohingya conflict|2013 Myanmar anti-Muslim riots|Rohingya genocide}} | |||
| The ] have consistently faced human rights abuses by the Burmese regime that has refused to acknowledge them as Burmese citizens (despite some of them having lived in Burma for over three generations)—the Rohingya have been denied Burmese citizenship since the enactment of a ].<ref name=rohingya>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/7872635.stm |title=What drive the Rohingya to sea? |publisher=BBC |date=5 February 2009 |access-date=29 July 2012 |author=Head, Jonathan |archive-date=1 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191001062936/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/7872635.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> The Burmese regime has attempted to forcibly expel Rohingya and bring in non-Rohingyas to replace them<ref name="South East Asia pg. 342">{{cite book |title=A Handbook of Terrorism and Insurgency in South East Asia| editor=Tan, Andrew T. H.| chapter=Chapter 16, State Terrorism in Arakan|author1=Islam, Syed |author2=Islam, Serajul |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-84542-543-2 |page=342 |year=2007}}</ref>—this policy has resulted in the expulsion of approximately half of the 800,000<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/burmas-monks-call-for-muslim-community-to-be-shunned-7973317.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220618/https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/burmas-monks-call-for-muslim-community-to-be-shunned-7973317.html |archive-date=18 June 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live | title=Burma's monks call for Muslim community to be shunned | work=The Independent | access-date=15 September 2014 | author=Hindstrom, Hanna | date=25 July 2012}}</ref> Rohingya from Burma, while the Rohingya people have been described as "among the world's least wanted"<ref>{{cite news | url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8521280.stm | title=Bangladesh accused of 'crackdown' on Rohingya refugees | publisher=BBC | date=18 February 2010 | access-date=29 July 2012 | author=Dummett, Mark | archive-date=27 October 2012 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121027120525/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8521280.stm | url-status=live }}</ref> and "one of the world's most persecuted minorities."<ref name="South East Asia pg. 342" /><ref>{{cite news | url=http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/refdaily?pass=463ef21123&id=4fe952205 | title=Myanmar, Bangladesh leaders 'to discuss Rohingya' | agency=] | date=25 June 2012 | access-date=15 September 2014 | archive-date=15 September 2014 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140915184608/http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/refdaily?pass=463ef21123&id=4fe952205 | url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=https://thediplomat.com/asean-beat/2012/10/09/the-rohingyas-place-in-a-democratic-burma/ |title=The Rohingya: Unwanted at Home, Unwelcome Abroad |work=] |date=9 October 2012 |author1=Bento, Lucas |author2=Yusuf, Guled |name-list-style=amp |access-date=12 February 2021 |archive-date=29 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029204931/http://thediplomat.com/asean-beat/2012/10/09/the-rohingyas-place-in-a-democratic-burma/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Rohingya are not allowed to travel without official permission, are banned from owning land, and are required to sign a commitment to have no more than two children.<ref name=rohingya /> As of July 2012, the Myanmar government does not include the Rohingya minority group—classified as ] Bengali Muslims from Bangladesh since 1982—on the government's list of more than 130 ethnic races and, therefore, the government states that they have no claim to Myanmar citizenship.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.thehindu.com/news/international/article3703383.ece| title=Rohingyas are not citizens: Myanmar minister| date=30 July 2012| location=Chennai, India| work=]| access-date=1 November 2012| archive-date=7 January 2016| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107231250/http://www.thehindu.com/news/international/article3703383.ece| url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Since the democratic transition began in 2011, there has been continuous violence as 280 people have been killed and 140,000 forced to flee from their homes in the Rakhine state in 2014.<ref>{{cite news|title=Exodus grows as Muslim Rohingya flee persecution in Myanmar homeland|url=http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2014/11/18/asia-pacific/crime-legal-asia-pacific/exodus-grows-muslim-rohigya-flee-persecution-myanmar-homeland/|access-date=14 December 2014|newspaper=Japan Times|date=18 November 2014|archive-date=17 December 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141217232601/http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2014/11/18/asia-pacific/crime-legal-asia-pacific/exodus-grows-muslim-rohigya-flee-persecution-myanmar-homeland/|url-status=live}}</ref> A UN envoy reported in March 2013 that unrest had re-emerged between Myanmar's ] and ] communities, with violence spreading to towns that are located closer to Yangon.<ref>{{cite news|title='Brutal efficiency' in Myanmar attacks: UN|url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/breaking-news/brutal-efficiency-in-myanmar-attacks-un/story-fn3dxix6-1226607261777|access-date=27 March 2013|newspaper=The Australian|date=27 March 2013|agency=Australian Associated Press|archive-date=27 March 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130327001952/http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/breaking-news/brutal-efficiency-in-myanmar-attacks-un/story-fn3dxix6-1226607261777|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===== Organ trading ===== | |||
| The military forces took over Myanmar in 2021. A yearlong investigation conducted by ] reveals that half of Myanmar's 54 million population lives below poverty line. This drives many of them to the extreme measures such as online organ trade. This illegal action of selling their personal organs can earn them a payment equal to a two-year salary. Many advertise the organ they wish to donate on social media, this is a endless cycle as families time and again find themselves online to trade their organs as money runs out.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Rebane |first=Teele |date=2024-08-30 |title=Myanmar's poorest are so desperate they're turning to social media to sell their kidneys |url=https://edition.cnn.com/2024/08/30/asia/myanmar-organ-selling-coup-poverty-intl-hnk/index.html |access-date=2024-09-01 |website=CNN |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Government reforms ==== | |||
| According to the ],<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.crisisgroup.org/en/regions/asia/south-east-asia/burma-myanmar/B127-myanmar-major-reform-underway.aspx | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121202223754/http://www.crisisgroup.org/en/regions/asia/south-east-asia/burma-myanmar/B127-myanmar-major-reform-underway.aspx | archive-date=2 December 2012 | title=Major Reform Underway | publisher=Crisis Group | date=22 September 2011 | access-date=29 August 2011}}</ref> since Myanmar transitioned to a new government in August 2011, the country's human rights record has been improving. Previously giving Myanmar its lowest rating of 7, the 2012 ''Freedom in the World'' report also notes improvement, giving Myanmar a 6 for improvements in civil liberties and political rights, the release of political prisoners, and a loosening of restrictions.<ref>{{cite web|title=Freedom in the World 2012: Burma|url=http://www.freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2012/burma-0|publisher=Freedom House|access-date=4 February 2012|archive-date=11 November 2013|archive-url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20131111164649/http://www.freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2012/burma-0|url-status=dead}}</ref> In 2013, Myanmar improved yet again, receiving a score of 5 in civil liberties and 6 in political freedoms.<ref>{{cite web|title=Burma|url=http://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2013/burma|access-date=22 November 2013|author=Freedom House|year=2013|archive-date=2 December 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131202232101/http://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2013/burma|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The government has assembled a ] that consists of 15 members from various backgrounds.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://australianetworknews.com/stories/201109/3312219.htm?desktop |title=Burma gets rights commission |publisher=Australia Network News |date=7 September 2011 |access-date=29 August 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110926011538/http://australianetworknews.com/stories/201109/3312219.htm?desktop |archive-date=26 September 2011 }}</ref> Several activists in exile, including Thee Lay Thee Anyeint members, have returned to Myanmar after President Thein Sein's invitation to expatriates to return home to work for national development.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.mmtimes.com/2011/news/593/news59307.html |title=Anyeint group returns from exile in Thailand |publisher=MM Times |date=19–25 September 2011 |access-date=29 August 2011 |author=Kyaw Hsu |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110930085339/http://www.mmtimes.com/2011/news/593/news59307.html |archive-date=30 September 2011 }}</ref> In an address to the United Nations Security Council on 22 September 2011, Myanmar's Foreign Minister ] confirmed the government's intention to release prisoners in the near future.<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.smh.com.au/world/burma-flags-mass-release-of-political-prisoners-20110928-1kx9d.html | title=Burma flags mass release of political prisoners | work=The Sydney Morning Herald | date=29 September 2011 | access-date=29 August 2011 | author=Murdoch, Lindsay | archive-date=30 September 2011 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110930155712/http://www.smh.com.au/world/burma-flags-mass-release-of-political-prisoners-20110928-1kx9d.html | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The government has also relaxed reporting laws, but these remain highly restrictive.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.dawn.com/2011/09/20/free-press-is-the-key-to-myanmar-reform.htmldawn |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120729234619/http://www.dawn.com/2011/09/20/free-press-is-the-key-to-myanmar-reform.htmldawn |url-status=dead |archive-date=29 July 2012 |title=Free press is the key to Myanmar reform |agency=Agence France-Presse |date=20 September 2011 |access-date=29 August 2011 }}</ref> In September 2011, several banned websites, including YouTube, ] and ], were unblocked.<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/burmese-junta-relaxes-access-to-foreign-websites-2356125.html | title=Burmese junta relaxes access to foreign websites | work=The Independent | location=London | date=17 September 2011 | access-date=29 August 2011 | author=Buncombe, Andrew | archive-date=20 October 2011 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111020142656/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/burmese-junta-relaxes-access-to-foreign-websites-2356125.html | url-status=dead }}</ref> A 2011 report by the ] found that, while contact with the Myanmar government was constrained by donor restrictions, international humanitarian non-governmental organisations (NGOs) see opportunities for effective advocacy with government officials, especially at the local level. At the same time, international NGOs are mindful of the ethical quandary of how to work with the government without bolstering or appeasing it.<ref>. Soubhik Ronnie Saha The Hauser Center for Nonprofit Organizations Harvard University September 2011</ref> ] | |||
| Following Thein Sein's first ever visit to the UK and a meeting with Prime Minister ], the Myanmar president declared that all of his nation's political prisoners will be released by the end of 2013, in addition to a statement of support for the well-being of the Rohingya Muslim community. In a speech at ], he revealed that "We are reviewing all cases. I guarantee to you that by the end of this year, there will be no prisoners of conscience in Myanmar."<ref>{{cite news|title=No more political prisoners: Myanmar|url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/breaking-news/no-more-political-prisoners-myanmar/story-fn3dxix6-1226679907770?net_sub_uid=44933799|access-date=16 July 2013|newspaper=The Australian|date=16 July 2013|author=Woodcock, Andrew }}</ref> | |||
| Homosexual acts are ] and can be punishable by life imprisonment.<ref>{{cite news |url= https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/gay-lesbian-bisexual-relationships-illegal-in-74-countries-a7033666.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220618/https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/gay-lesbian-bisexual-relationships-illegal-in-74-countries-a7033666.html |archive-date=18 June 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |title= LGBT relationships are illegal in 74 countries, research finds | work = The Independent| date=17 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=State Sponsored Homophobia 2016: A world survey of sexual orientation laws: criminalisation, protection and recognition|url=http://ilga.org/downloads/02_ILGA_State_Sponsored_Homophobia_2016_ENG_WEB_150516.pdf|work=]|date=17 May 2016|access-date=9 July 2018|archive-date=2 September 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170902183618/http://ilga.org/downloads/02_ILGA_State_Sponsored_Homophobia_2016_ENG_WEB_150516.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In 2016, Myanmar leader ] was accused of failing to protect Myanmar's ] minority.<ref>" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170827102057/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/asia/rohingya-muslims-burma-myanmar-aung-san-suu-kyi-legitimising-genocide-a7439151.html |date=27 August 2017 }}". ''The Independent''. 25 November 2016.</ref> Since August 2017 ] have treated 113 Rohingya refugee females for sexual assault with all but one describing military assailants.<ref>AP News. (12 December 2017). "Army's rape of Rohingya women sweeping, methodical: AP". {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171212214500/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/2017/12/rape-rohingya-women-sweeping-methodical-ap-171211063236832.html |date=12 December 2017 }}. Retrieved 12 December 2017.</ref> | |||
| == Economy == | |||
| {{main|Economy of Myanmar}} | |||
| {{further|Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia)|Transport in Myanmar|Oil and gas industry in Myanmar}} | |||
| Myanmar's ] is one of the ] in the world with a nominal GDP of US$76.09 billion in 2019 and an estimated purchasing power adjusted GDP of US$327.629 billion in 2017 according to the World Bank.<ref>{{cite news|title=world bank indicator|work=World Bank|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD?locations=MM|access-date=30 January 2021|archive-date=15 November 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191115104355/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD?locations=MM|url-status=live}}</ref>{{synthesis inline|date=June 2021}} Foreigners are able to legally lease but not own property.<ref name="aht">{{cite news|last=Aung Hla Htun|date=16 March 2012|title=Exclusive: Myanmar drafts new foreign investment rules|work=Reuters|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-myanmar-investment-idUSBRE82F0IY20120316|access-date=17 March 2012|archive-date=16 March 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120316160225/https://www.reuters.com/article/2012/03/16/us-myanmar-investment-idUSBRE82F0IY20120316|url-status=live}}</ref> In December 2014, Myanmar set up its first stock exchange, the ].<ref>{{cite news|date=25 March 2016|title=Yangon Stock Exchange Formally Opens for Business|work=The New York Times|url=https://www.nytimes.com/aponline/2016/03/25/world/asia/ap-as-myanmar-stock-exchange.html|access-date=25 March 2016}}</ref> | |||
| The informal economy's share in Myanmar is one of the biggest in the world and is closely linked to corruption, smuggling and illegal trade activities.<ref>{{cite book | first=Ian | last=Brown | year=2005 | title=A Colonial Economy in Crisis | publisher=Routledge | isbn=978-0-415-30580-8}}</ref><ref>Stokke, Kristian; Vakulchuk, Roman and Indra Overland (2018) {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200728150758/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323018961_Myanmar_A_Political_Economy_Analysis |date=28 July 2020 }}. Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI). Report commissioned by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs.</ref> In addition, decades of civil war and unrest have contributed to Myanmar's current levels of poverty and lack of economic progress. Myanmar lacks adequate ]. Goods travel primarily across the Thai border (where most illegal drugs are exported) and along the Irrawaddy River.<ref name="idea">{{cite web |url=http://www.idea.int/asia_pacific/burma/upload/chap3.pdf |title=Challenges to Democratization in Burma |access-date=12 July 2006 |date=November 2001 |publisher=International IDEA |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060723083624/http://www.idea.int/asia_pacific/burma/upload/chap3.pdf |archive-date=23 July 2006 }}</ref> Notably, opium production in Myanmar is the world's second-largest source of ] after ], producing some 25% of the world's opium, forming part of the Golden Triangle. While opium poppy cultivation in Myanmar had declined year-on-year since 2015, cultivation area increased by 33% totalling 40,100 hectares alongside an 88% increase in yield potential to 790 tonnes in 2022 according to latest data from the ] (UNODC) Myanmar Opium Survey 2022.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.unodc.org/roseap/myanmar/2023/01/myanmar-opium-survey-report/story.html|title=Myanmar Opium Survey 2021: Cultivation, Production and Implications|date=February 2022|access-date=18 April 2023|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426044556/https://www.unodc.org/roseap/myanmar/2023/01/myanmar-opium-survey-report/story.html|url-status=live}}</ref> With that said, the ] (UNODC) has also warned that opium production in Myanmar may rise again if the economic crunch brought on by COVID-19 and the country's February 1 military coup persists, with significant public health and security consequences for much of Asia.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.voanews.com/a/east-asia-pacific_myanmars-economic-meltdown-likely-push-opium-output-says-un/6206434.html|title=Myanmar's Economic Meltdown Likely to Push Opium Output Up, Says UN|date=31 May 2021|accessdate=15 October 2021|archive-date=18 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211018182910/https://www.voanews.com/a/east-asia-pacific_myanmars-economic-meltdown-likely-push-opium-output-says-un/6206434.html|url-status=live}}</ref> At the same time, the Golden Triangle, and specifically Shan State of Myanmar, is believed to be the largest ] producing area in the world. The growing signs of an intensification of methamphetamine manufacturing activity within and around the Golden Triangle, and a corresponding decrease in the number of production facilities dismantled in other parts of the region, suggests that methamphetamine manufacture in East and Southeast Asia is now consolidated into the lower Mekong region.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cnn.com/2018/11/14/opinions/asia-organized-crime-intl/index.html|title=Parts of Asia are slipping into the hands of organized crime|first=Jeremy|last=Douglas|website=CNN|date=15 November 2018|access-date=18 April 2023|archive-date=18 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230418083136/https://www.cnn.com/2018/11/14/opinions/asia-organized-crime-intl/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Countries in East and Southeast Asia have collectively witnessed sustained increases in seizures of methamphetamine over the last decade, totalling over 171 tons and a record of over 1 billion methamphetamine tablets in 2021 according to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, more than any other part of the world.<ref>{{Cite web|date=May 2022|title=Synthetic Drugs in East and Southeast Asia: Latest Developments and Challenges 2022|url=https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/scientists/2022-regional-synthetic-drugs-in-east-and-southeast-asia.html|access-date=18 April 2023|archive-date=26 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230426145938/https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/scientists/2022-regional-synthetic-drugs-in-east-and-southeast-asia.html|url-status=live}}</ref> In April and May 2020, Myanmar authorities reported Asia's largest ever drug operation in ] totalling what was believed to be 193 million methamphetamine tablets, hundreds of kilogrammes of crystal methamphetamine as well as some heroin, and over 162,000 litres and 35.5 tons of drug precursors as well as sophisticated production equipment and several staging and storage facilities.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/myanmar-drugs-exclusive-idINKBN22U0PH|title=Huge fentanyl haul seized in Asia's biggest-ever drugs bust|newspaper=Reuters|date=18 May 2020|via=www.reuters.com|access-date=18 April 2023|archive-date=28 February 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230228092412/https://www.reuters.com/article/myanmar-drugs-exclusive-idINKBN22U0PH|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Both China and India have attempted to strengthen ties with the government for economic benefit in the early 2010s. Many Western nations, including the United States and Canada, and the ], historically imposed investment and trade sanctions on Myanmar. The United States and European Union eased most of their sanctions in 2012.<ref>{{cite news |last=Hargreaves |first=Steve |url=https://money.cnn.com/2013/06/18/news/economy/myanmar-business/index.html?iid=HP_LN |title=Myanmar: Tales from the last business frontier |publisher=CNN |date=18 June 2013 |access-date=6 July 2013 |archive-date=22 June 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130622080534/http://money.cnn.com/2013/06/18/news/economy/myanmar-business/index.html?iid=HP_LN |url-status=live }}</ref> From May 2012 to February 2013, the United States began to lift its economic sanctions on Myanmar "in response to the historic reforms that have been taking place in that country."<ref>{{cite web|date=18 March 2013|title=Frequently Asked Questions and Answers|url=http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/faqs/Sanctions/Pages/answer.aspx#268|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130727011638/http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/faqs/Sanctions/Pages/answer.aspx|archive-date=27 July 2013|access-date=4 August 2013|publisher=U.S. Department of the Treasury}}</ref> Foreign investment comes primarily from China, Singapore, the Philippines, South Korea, India, and Thailand.<ref>{{cite news |first=David |last=Fullbrook |url=http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/FK04Ae03.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20041106012133/http://atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/FK04Ae03.html |url-status=unfit |archive-date=6 November 2004 |title=So long US, hello China, India |work=Asia Times |date=4 November 2004 |access-date=14 July 2006}}</ref> The military has stakes in some major industrial corporations of the country (from oil production and consumer goods to transportation and tourism).<ref name="mccartan">{{cite news|last=McCartan|first=Brian|date=28 February 2012|title=Myanmar military in the money|work=Asia Times|url=http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/NB28Ae02.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120227154915/http://atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/NB28Ae02.html|url-status=unfit|archive-date=27 February 2012|access-date=30 September 2012}}</ref><ref name="brady">{{cite news|last=Brady|first=Brendan|date=7 September 2012|title=Boom Days in Burma|work=Newsweek|url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/newsweek/2012/09/16/boom-days-in-burma.html|url-status=dead|access-date=30 September 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120929192043/http://www.thedailybeast.com/newsweek/2012/09/16/boom-days-in-burma.html|archive-date=29 September 2012}}</ref> | |||
| === Economic history === | |||
| ] to ] takes about 7.5 hours ({{convert|179|km|mi|abbr=on|disp=or}}).]]Under the ] administration, the people of Burma were at the bottom of the social hierarchy, with ] at the top, Indians, Chinese, and Christianized minorities in the middle, and Buddhist Burmese at the bottom.<ref name=":0">{{cite book|last=Myint-U|first=Thant|title=The river of lost footsteps: histories of Burma|date=2006|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-374-16342-6|edition=1st|location=New York|oclc=65064707}}</ref> Forcefully integrated into the world economy, Burma's economy grew by involving itself with extractive industries and ] agriculture. However, much of the wealth was concentrated in the hands of Europeans. The country became the world's largest exporter of ], mainly to European markets, while other colonies like India suffered mass starvation.<ref>{{cite book|last=Davis|first=Mike|title=Late Victorian holocausts: El Niño famines and the making of the third world|date=2001|publisher=Verso|isbn=1-85984-739-0|location=London|oclc=45636958}}</ref> Being a follower of free market principles, the British opened up the country to large-scale immigration with Rangoon exceeding New York City as the greatest immigration port in the world in the 1920s. Historian ] states, "This was out of a total population of only 13 million; it was equivalent to the United Kingdom today taking 2 million people a year." By then, in most of Burma's largest cities, ], ], ] and ], the Indian immigrants formed a majority of the population. The Burmese under British rule felt helpless, and reacted with a "racism that combined feelings of superiority and fear".<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| Crude oil production, an indigenous industry of ], was taken over by the British and put under ] monopoly. British Burma began exporting crude oil in 1853.<ref>{{cite web|author=Total|title=Oil and Gas in Myanmar |url=http://burma.total.com/myanmar-en/oil-and-gas-in-myanmar/oil-and-gas-in-myanmar-900130.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150415084151/http://burma.total.com/myanmar-en/oil-and-gas-in-myanmar/oil-and-gas-in-myanmar-900130.html|archive-date=15 April 2015}}</ref> European firms produced 75% of the world's teak.<ref name="steinberg" /> The wealth was, however, mainly concentrated in the hands of Europeans. In the 1930s, agricultural production fell dramatically as international rice prices declined and did not recover for several decades.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Booth, Anne|date=Spring 2003|title=The Burma Development Disaster in Comparative Historical Perspective|url=http://www.soas.ac.uk/sbbr/editions/file64274.pdf|journal=SOAS Bulletin of Burma Research|volume=1|issue=1|issn=1479-8484|access-date=2 October 2012|archive-date=9 August 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070809043455/http://www.soapy-massage.com/thai-soapy-massage-turkish-bath-house.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> During the Japanese invasion of Burma in World War II, the British followed a ] policy. They destroyed major government buildings, oil wells and mines that developed for tungsten (]), tin, lead and silver to keep them from the Japanese. Myanmar was bombed extensively by the Allies.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} | |||
| After independence, the country was in ruins with its major infrastructure completely destroyed. With the loss of India, Burma lost relevance and obtained independence from the British. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister ] embarked upon a policy of nationalisation and the state was declared the owner of all of the land in Burma. The government tried to implement an eight-year plan partly financed by injecting money into the economy, but this caused inflation to rise.<ref>{{cite web|last=Watkins|first=Thayer|title=Political and Economic History of Myanmar (Burma) Economics|url=http://www2.sjsu.edu/faculty/watkins/burma.htm|access-date=8 July 2006|publisher=San Jose State University|archive-date=26 May 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060526144053/http://www2.sjsu.edu/faculty/watkins/burma.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> The ] was followed by an economic scheme called the ], a plan to nationalise all industries, with the exception of ]. While the economy continued to grow at a slower rate, the country eschewed a Western-oriented development model, and by the 1980s, was left behind capitalist powerhouses like ] which were integrated with Western economies.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor, Robert H.|title=General Ne Win : a political biography|date=25 May 2015|isbn=978-981-4620-13-0|location=Singapore|oclc=934623309}}</ref><ref name="ruin" /> Myanmar asked for admittance to a ] status in 1987 to receive debt relief.<ref>{{cite web|year=2005|title=List of Least Developed Countries|url=https://www.un.org/special-rep/ohrlls/ldc/list.htm|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131026045553/http://www.un.org/special-rep/ohrlls/ldc/list.htm|archive-date=26 October 2013|publisher=UN-OHRLLS}}</ref> | |||
| === Agriculture === | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Further|Agriculture in Myanmar}} | |||
| The major agricultural product is ], which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the ], 52 modern rice varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.irri.org/media/facts/pdfs/myanmar.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050907011925/http://www.irri.org/media/facts/pdfs/myanmar.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=7 September 2005 |title=Myanmar and IRRI }} {{small|(21.2 KB)}}, Facts About Cooperation, International Rice Research Institute. Retrieved 25 September 2007.</ref> In 2008 rice production was estimated at 50 million tons.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx |title=Faostat |publisher=Faostat.fao.org |access-date=17 August 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110713020710/http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx |archive-date=13 July 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| === Extractive industries === | |||
| Myanmar produces precious stones such as ], ]s, ]s, and ]. ] are the biggest earner; 90% of the world's rubies come from the country, whose red stones are prized for their purity and hue. Thailand buys the majority of the country's gems. Myanmar's "Valley of Rubies", the mountainous ] area, {{convert|200|km|mi|abbr=on}} north of ], is noted for its rare pigeon's blood rubies and blue sapphires.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.uvm.edu/envnr/gemecology/index.html|title=Gems of Burma and their Environmental Impact |publisher=Uvm.edu |access-date=20 November 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100526104410/http://www.uvm.edu/envnr/gemecology/index.html |archive-date=26 May 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Many ] and ] jewellery companies, including Bulgari, Tiffany and Cartier, refuse to import these stones based on reports of deplorable working conditions in the mines. ] has encouraged a complete ban on the purchase of Burmese gems based on these reports and because nearly all profits go to the ruling junta, as the majority of mining activity in the country is government-run.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.hrw.org/en/news/2007/11/11/burma-gem-trade-bolsters-military-regime-fuels-atrocities |title=Burma: Gem Trade Bolsters Military Regime, Fuels Atrocities |publisher=Human Rights Watch |date=11 November 2007 |access-date=22 August 2017 |archive-date=3 September 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140903143133/http://www.hrw.org/en/news/2007/11/11/burma-gem-trade-bolsters-military-regime-fuels-atrocities |url-status=live }}</ref> The government of Myanmar controls the gem trade by direct ownership or by joint ventures with private owners of mines.<ref>{{cite news |author=Ferro, Shane |date=19 July 2011 |url=http://www.blouinartinfo.com/news/story/38144/burmese-gem-emporium-rakes-in-15-billion-despite-human-rights-abuse-concerns/ |title=Burmese Gem Emporium Rakes in $1.5 Billion Despite Human Rights Abuse Concerns |publisher=Blouin ARTINFO |access-date=15 May 2013 |archive-date=5 February 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160205180522/http://www.blouinartinfo.com/news/story/38144/burmese-gem-emporium-rakes-in-15-billion-despite-human-rights-abuse-concerns |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ] are also a significant export, as Myanmar supplies around 10% of the world's rare earths.<ref>{{cite web |title=U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries, January 2021 |url=https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2021/mcs2021-rare-earths.pdf |website=usgs.gov |publisher=USGS |access-date=9 October 2021 |archive-date=27 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211127021048/https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2021/mcs2021-rare-earths.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Conflict in Kachin State has threatened the operations of its mines as of February 2021.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Subramanian |first1=Sribala |title=Rare Earths in Myanmar: Unobtanium? |url=https://thediplomat.com/2021/06/rare-earths-in-myanmar-unobtanium/ |website=The Diplomat |access-date=9 October 2021 |archive-date=9 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211009133352/https://thediplomat.com/2021/06/rare-earths-in-myanmar-unobtanium/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=Daly |first1=Tom |title=China rare earths extend surge on worries over Myanmar supply, inspection threat |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-rare-earths-myanmar-idUSKBN2BI1HR |website=Reuters |date=26 March 2021 |access-date=9 October 2021 |archive-date=9 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211009133347/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-rare-earths-myanmar-idUSKBN2BI1HR |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Other industries include agricultural goods, textiles, wood products, construction materials, gems, metals, oil and natural gas. ] has identified at least 39 locations capable of geothermal power production and some of these hydrothermal reservoirs lie quite close to Yangon which is a significant underutilised resource for electrical production.<ref>{{citation |last=DuByne |first=David |title=Geothermal Energy in Myanmar Securing Electricity for Eastern Border Development |url=http://www.oilseedcrops.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Geothermal-Energy-in-Myanmar-Securing-Electricity-for-Eastern-Border-Development-David-DuByne.pdf |journal=Myanmar Business Today Magazine |date=November 2015 |pages=6–8 |access-date=20 November 2015 |archive-date=20 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151120104918/http://www.oilseedcrops.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Geothermal-Energy-in-Myanmar-Securing-Electricity-for-Eastern-Border-Development-David-DuByne.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Tourism === | |||
| {{main|Tourism in Myanmar}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] in Mandalay]] | |||
| The government receives a significant percentage of the income of private-sector tourism services.<ref>{{cite web |last=Enescu, Raluca |url=http://www.tayzathuria.org.uk/bd/2006/12/24/re.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110430235921/http://www.tayzathuria.org.uk/bd/2006/12/24/re.htm |archive-date=30 April 2011 |title=Burma Digest |publisher=Tayzathuria.org.uk |date=24 December 2006}}</ref> The most popular available tourist destinations in Myanmar include big cities such as ] and ]; religious sites in ], ], ] and ]; nature trails in ], ], ], ]; ancient cities such as ] and ]; as well as beaches in ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.southernmyanmar.com/beaches-2/|title=Southern Myanmar|page=Tourist Destinations|website=southernmyanmar.com|access-date=20 May 2015|archive-date=11 May 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150511103149/http://www.southernmyanmar.com/beaches-2/|url-status=dead}}</ref> ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://birma.com/destinations-in-myanmar |title=Myanmar Travel Agency |page=Tourist Destinations |website=birma.com |access-date=20 October 2013 |archive-date=20 October 2013 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20131020180639/http://birma.com/destinations-in-myanmar |url-status=live }}</ref> Nevertheless, much of the country is off-limits to tourists, and interactions between foreigners and the people of Myanmar, particularly in the border regions, are subject to police scrutiny. They are not to discuss politics with foreigners, under penalty of imprisonment and, in 2001, the Myanmar Tourism Promotion Board issued an order for local officials to protect tourists and limit "unnecessary contact" between foreigners and ordinary Burmese people.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.burmacampaign.org.uk/action_holiday.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090429173300/http://www.burmacampaign.org.uk/action_holiday.html |archive-date=29 April 2009 |title=The Tourism Campaign – Campaigns |publisher=The Burma Campaign UK |access-date=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| The most common way for travellers to enter the country is by air.<ref name="LP1">{{cite web|title=Getting there & away|url=http://www.lonelyplanet.com/myanmar-burma/transport/getting-there-away|publisher=lonelyplanet.com|access-date=4 August 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130801235500/http://www.lonelyplanet.com/myanmar-burma/transport/getting-there-away|archive-date=1 August 2013}}</ref> According to the website '']'', getting into Myanmar is problematic: "No bus or train service connects Myanmar with another country, nor can you travel by car or motorcycle across the border – you must walk across." They further state that "It is not possible for foreigners to go to/from Myanmar by sea or river."<ref name="LP1" /> There are a few border crossings that allow the passage of private vehicles, such as the border between ] (China) to ], the border between ] (Myanmar) and ] (Thailand)—the most direct border between ] and ], and the border between ] and ], Thailand. At least one tourist company has successfully run commercial overland routes through these borders since 2013.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dragoman.com/holidays/details/south-east-asia-between-kunming-and-bangkok-via-burma|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150129052459/http://www.dragoman.com/holidays/details/south-east-asia-between-kunming-and-bangkok-via-burma|url-status=dead|title=Dragoman|archive-date=29 January 2015}}</ref> | |||
| Flights are available from most countries, though direct flights are limited to mainly Thai and other ] airlines. According to '']'' magazine, "In the past, there were only 15 international airlines and increasing numbers of airlines have begun launching direct flights from Japan, Qatar, Taiwan, South Korea, Germany and Singapore."<ref name="11.1">{{cite web|title=International airlines to open direct flights to Myanmar|url=http://elevenmyanmar.com/business/2945-international-airlines-to-open-direct-flights-to-myanmar|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131110164418/http://elevenmyanmar.com/business/2945-international-airlines-to-open-direct-flights-to-myanmar|archive-date=10 November 2013|date=2 August 2013}}</ref> | |||
| == Demographics == | |||
| {{main|Demographics of Myanmar}} | |||
| ]. Much of Yangon's urban population resides in densely populated flats.]] | |||
| {|class="wikitable" style="float: right; margin-left: 10px" | |||
| ! colspan="4" style="text-align:center; background:#cfb;"|Population{{UN Population|ref}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="background:#cfb;"|Year | |||
| ! style="background:#cfb;"|Million | |||
| |- | |||
| |style="text-align:left;"|1950 ||style="text-align:right;"|17.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| |style="text-align:left;"|2000 ||style="text-align:right;"|46.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| |style="text-align:left;"|{{UN Population|Year}} ||style="text-align:right;"|{{#expr:{{formatnum:{{UN Population|Myanmar}}|R}}/1e6 round 1}} | |||
| |} | |||
| The provisional results of the ] showed that the total population was 51,419,420.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Spoorenberg |first1=Thomas |year=2015 |title=Provisional results of the 2014 census of Myanmar: The surprise that wasn't |journal=Asian Population Studies |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=4–6 |doi=10.1080/17441730.2014.972084 |s2cid=154114929 }}</ref> This figure includes an estimated 1,206,353 persons in parts of northern ], ] and ] who were not counted.<ref name="spoor">{{cite journal |last1=Spoorenberg |first1=Thomas |year=2015 |title=Myanmar's first census in more than 30 years: A radical revision of the official population count |journal=Population & Societies |volume=527 |issue=November |pages=1–4 |url=http://www.ined.fr/fichier/s_rubrique/24592/population.societies.2015.527.census.birma.en.en.pdf |access-date=9 December 2015 |archive-date=8 August 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190808043519/https://www.ined.fr/fichier/s_rubrique/24592/population.societies.2015.527.census.birma.en.en.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> People who were out of the country at the time of the census are not included in these figures. There are over 600,000 registered ]s from Myanmar in ], and millions more work illegally. Burmese citizens account for 80% of all migrant workers in Thailand.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://web.amnesty.org/library/index/ENGASA390012005 |title=Thailand: The Plight of Burmese Migrant Workers |access-date=13 July 2006 |date=8 June 2006 |publisher=Amnesty International |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20060626102346/http://web.amnesty.org/library/index/ENGASA390012005 |archive-date = 26 June 2006}}</ref> At the beginning of the 20th century, Burma's ] was approximately 10 million.<ref>{{cite book|last=Maung|first=M. Ismael Khin|title=The population of Burma: An analysis of the 1973 Census|publisher=East-West Population Institute|date=April 1986|isbn=0866380779}}</ref> The national population density is {{convert|76|/km2}}, among the lowest in Southeast Asia. | |||
| Myanmar's fertility rate in 2011 was 2.23, slightly above the ]<ref name="jon" /> and low compared to ] of similar economic standing.<ref name="jon" /> There has been a significant decline in fertility in the 2000s, from a rate of 4.7 children per woman in 1983, down to 2.4 in 2001, despite the absence of any national population policy.<ref name="jon">{{cite journal |last1=Jones |first1=Gavin W. |year=2007 |title=Delayed Marriage and Very Low Fertility in Pacific Asia |journal=Population and Development Review |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=453–478 |url=http://dahuang.dhxy.info/population/Delayed_Marriage_Fertility09.pdf |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/5x361pgmm?url=http://dahuang.dhxy.info/population/Delayed_Marriage_Fertility09.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=9 March 2011 |doi=10.1111/j.1728-4457.2007.00180.x |access-date=5 January 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Spoorenberg |first1=Thomas |year=2013 |title=Demographic changes in Myanmar since 1983: An examination of official data |journal=Population and Development Review |volume=39 |issue=2 |pages=309–324 |doi=10.1111/j.1728-4457.2013.00593.x }}</ref><ref name="mya">{{cite journal |author=Mon, Myat |year=2000 |title=The Economic Position of Women in Burma |journal=Asian Studies Review |volume=24 |issue=2 |pages=243–255 |doi=10.1080/10357820008713272 |s2cid=144323033 |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/1467-8403.00076 |access-date=21 January 2020 |archive-date=27 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727060044/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/1467-8403.00076 |url-status=live }}</ref> The fertility rate is much lower in urban areas. | |||
| The relatively rapid decline in fertility is attributed to several factors, including extreme delays in marriage (almost unparalleled among developing countries in the region), the prevalence of illegal abortions, and the high proportion of single, unmarried women of reproductive age, with 25.9% of women aged 30–34 and 33.1% of men and women aged 25–34 being single.<ref name="mya" /><ref name=mar> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20031225072830/https://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/worldmarriage/worldmarriagepatterns2000.pdf |date=25 December 2003 }}. United Nations</ref> | |||
| These patterns stem from economic dynamics, including high income inequality, which results in residents of reproductive age opting for delay of marriage and family-building in favour of attempting to find employment and establish some form of wealth;<ref name="mya" /> the average age of marriage in Myanmar is 27.5 for men, 26.4 for women.<ref name="mya" /><ref name=mar /> | |||
| === Largest cities === | |||
| {{further|List of cities and largest towns in Myanmar}} | |||
| {{Largest cities | |||
| | country = Myanmar | |||
| | stat_ref = | |||
| | list_by_pop = | |||
| | div_name = Division | |||
| | div_link = | |||
| | city_1 = Yangon | |||
| | div_1 = Yangon Region{{!}}Yangon | |||
| | pop_1 = 5,211,431 | |||
| | img_1 = Yangoon-south.jpg | |||
| | city_2 = Mandalay | |||
| | div_2 = Mandalay Region{{!}}Mandalay | |||
| | pop_2 = 1,225,546 | |||
| | img_2 = Mandeley vue panoramique.JPG | |||
| | city_3 = Naypyidaw | |||
| | div_3 = Naypyidaw Union Territory {{!}}Naypyidaw | |||
| | pop_3 = 1,160,242 | |||
| | img_3 = Uppatasanti Pagoda, view from west, closeup.jpg | |||
| | city_4 = Bago, Burma{{!}}Bago | |||
| | div_4 = Bago Region{{!}}Bago | |||
| | pop_4 = 491,434 | |||
| | img_4 = Bago,_Myanmar_(15168477180).jpg | |||
| | city_5 = Hpa-An | |||
| | div_5 = Kayin State{{!}}Kayin | |||
| | pop_5 = 421,575 | |||
| | city_6 = Taunggyi | |||
| | div_6 = Shan State{{!}}Shan | |||
| | pop_6 = 381,636 | |||
| | city_7 = Monywa | |||
| | div_7 = Sagaing Region{{!}}Sagaing | |||
| | pop_7 = 372,095 | |||
| | city_8 = Myitkyina | |||
| | div_8 = Kachin State{{!}}Kachin | |||
| | pop_8 = 306,949 | |||
| | city_9 = Mawlamyine | |||
| | div_9 = Mon State{{!}}Mon | |||
| | pop_9 = 289,388 | |||
| | city_10 = Magway, Burma{{!}}Magway | |||
| | div_10 = Magway Region{{!}}Magway | |||
| | pop_10 = 289,247 | |||
| }} | |||
| ===Ethnic groups=== | === Ethnic groups === | ||
| {{ |
{{main|List of ethnic groups in Myanmar}} | ||
| {{bar box | {{bar box | ||
| |title=Ethnic Composition in Burma |
|title=Ethnic Composition in Burma/Myanmar<br />(rough estimate) | ||
| |titlebar=#ddd | |titlebar=#ddd | ||
| |width= |
|width= | ||
| |left1= |
|left1=Ethnic group | ||
| |right1= |
|right1=Per cent | ||
| |float= |
|float=right | ||
| |bars= | |bars= | ||
| {{bar percent|]|orange|68}} | {{bar percent|]|orange|68}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]|blue| |
{{bar percent|]|blue|10}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]|green|7}} | {{bar percent|]|green|7}} | ||
| {{bar percent|Other groups|cyan|4.5}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|yellow|3.5}} | {{bar percent|]|yellow|3.5}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]|purple| |
{{bar percent|]|purple|3}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]|red|2}} | {{bar percent|]|red|2}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]|violet|2}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|black|1.5}} | {{bar percent|]|black|1.5}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]|brown|1}} | {{bar percent|]|brown|1}} | ||
| {{bar percent|]| |
{{bar percent|]|lime|0.8}} | ||
| {{bar percent| |
{{bar percent|Other groups|cyan|5}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] minority, one of the many ethnic groups that make up Burma's population.]] | |||
| Myanmar is ]. The government recognises ]. There are at least 108 different ethnolinguistic groups in Myanmar, consisting mainly of distinct ] peoples, but with sizeable populations of ], ], and Austroasiatic (Mon–Khmer) peoples.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=MM |title=Languages of Myanmar |access-date=13 January 2007 |last=Gordon |first=Raymond G. Jr. |year=2005 |work=Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition |publisher=SIL International |archive-date=7 December 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121207085517/http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=MM |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The ] form an estimated 68% of the population.<ref name="statedept">{{cite web |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm |title=Background Note: Burma |access-date=7 July 2006 |date=August 2005 |work=] |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170122194342/https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm |archive-date=22 January 2017 |url-status=dead }}</ref>{{irrelevant citation|date=July 2024|reason=the source doesn't mention ethnic composition in Myanmar}} 10% of the population are ].<ref name="statedept" /> The Kayin make up 7% of the population.<ref name="statedept" /> The ] constitute 4% of the population. ] form approximately 3% of the population.<ref name="statedept" /><ref>{{cite book | author=Than, Mya | editor=Suryadinata, Leo | year=1997 | title=Ethnic Chinese As Southeast Asians}}</ref> Myanmar's ethnic ] groups prefer the term "ethnic nationality" over "ethnic minority" as the term "minority" furthers their sense of insecurity in the face of what is often described as "Burmanisation"—the proliferation and domination of the dominant ] over minority cultures. | |||
| According to the ] Institute of Statistics, Burma's official ] as of 2000 was 89.9%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.uis.unesco.org/TEMPLATE/html/Exceltables/education/Literacy_Regional_April2006.xls |title=Adult (15+) Literacy Rates and Illiterate Population by Region and Gender for |accessdate=13 July 2006 |year=2006 |month=April |format=XLS |publisher=UNESCO Institute of Statistics}}</ref> Historically, Burma has had high literacy rates. To qualify for ] status by the UN in order to receive debt relief, Burma lowered its official literacy rate from 78.6% to 18.7% in 1987.<ref>{{cite book | editor=Robert I Rotberg | year=1998 | title=Burma: Prospects for a Democratic Future }}</ref> | |||
| ], who form 2% of the population, are ethno-linguistically related to the ].<ref name="statedept" /> ] are 2%.<ref name="statedept" /> The remainder are ], ], ], ]s, ], ] and other ethnic minorities. Included in this group are the ]. Once forming a large and influential community, the Anglo-Burmese left the country in steady streams from 1958 onwards, principally to Australia and the United Kingdom. It is estimated that 52,000 Anglo-Burmese remain in Myanmar. {{As of|2009}}, 110,000 Burmese ]s were living in refugee camps in Thailand.<ref>{{cite news |last=Kato |first=Mariko |url=http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2009/02/18/national/myanmar-refugees-to-try-resettling/ |title=Myanmar refugees to try resettling |work=Japan Times |date=18 February 2009 |access-date=6 August 2014 |archive-date=8 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140808052623/http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2009/02/18/national/myanmar-refugees-to-try-resettling/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Burma is ethnically diverse. The government recognises ]. While it is extremely difficult to verify this statement, there are at least 108 different ethnolinguistic groups in Burma, consisting mainly of distinct Tibeto-Burman peoples, but with sizeable populations of Daic, Hmong-Mien, and Austroasiatic (Mon-Khmer) peoples.<ref name="ethnologue_myanmar">{{cite web|url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=MM |title=Languages of Myanmar |accessdate=13 January 2007 |last=Gordon |first=Raymond G., Jr. |year=2005 |work=Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition |publisher=SIL International}}</ref> The ] form an estimated 68% of the population.<ref name="statedept">{{cite web |url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm |title=Background Note: Burma |accessdate = 7 July 2006 |year=2005 |month=August |work=] |publisher=]}}</ref> 10% of the population are ].<ref name="statedept"/> The ] make up 7% of the population.<ref name="statedept"/> The ] constitute 4% of the population. ] form approximately 3% of the population.<ref name="statedept"/><ref>{{cite book | author=Mya Than | editor=Leo Suryadinata | year=1997 | title=Ethnic Chinese As Southeast Asians | id=ISBN}}</ref> Burma's ethnic minority groups prefer the term "ethnic nationality" over "ethnic minority" as the term "minority" furthers their sense of insecurity in the face of what is often described as "Burmanisation"--the proliferation and domination of the dominant Bamar culture over minority cultures. | |||
| Refugee camps exist along Indian, Bangladeshi and Thai borders while several thousand are in ]. Conservative estimates state that there are over 295,800 minority refugees from Myanmar, with the majority being ], ], and ] are principally located along the Thai-Myanmar border.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/publ/opendoc.pdf?tbl=PUBL&id=449676844 |title=Myanmar Refugees in South East Asia |access-date=13 July 2006 |date=April 2006 |format=PDF |publisher=UNHCR |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060621015621/http://www.unhcr.org/cgi-bin/texis/vtx/publ/opendoc.pdf?tbl=PUBL&id=449676844 |archive-date=21 June 2006 }}</ref> There are nine permanent refugee camps along the Thai-Myanmar border, most of which were established in the mid-1980s. The refugee camps are under the care of the Thai-Burma Border Consortium (TBBC). Since 2006,<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/from-tropical-burma-to-syracuse-refugees-adjust/ |title=From tropical Burma to Syracuse, refugees adjust |work=CBS News |date=25 April 2012 |access-date=20 November 2012 |archive-date=5 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120705231358/http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-18563_162-57420502/from-tropical-burma-to-syracuse-refugees-adjust |url-status=live }}</ref> over 55,000 Burmese ]s have been resettled in the United States.<ref>"". U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.</ref> | |||
| ], who form 2% of the population, are ethno-linguistically related to the ].<ref name="statedept"/> ] comprise 2%.<ref name="statedept"/> The remainder are ], ], ]s and other ethnic minorities. Included in this group are the ]. Once forming a large and influential community, the Anglo-Burmese left the country in steady streams from 1958 onwards, principally to Australia and the U.K.. Today, it is estimated that only 52,000 Anglo-Burmese remain in the country. There are 110,000 Burmese ]s in Thai border camps.<ref>. The Japan Times Online. 18 February 2009.</ref> | |||
| The persecution of ], ] and other ethnic groups after the military coup headed by General ] in 1962 led to the expulsion or emigration of 300,000 people.<ref>{{cite book|author=Smith, Martin |year=1991|title=Burma – Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity|publisher=Zed Books|location=London, New Jersey|pages=43–44, 98, 56–57, 176}}</ref> They migrated to escape ] and the wholesale nationalisation of private enterprise that took place in 1964.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,875949,00.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081208073731/http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,875949,00.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=8 December 2008 |title=Asians v. Asians.|magazine=Time |date=17 July 1964 |access-date=20 November 2012}}{{subscription required}}</ref> The Anglo-Burmese at this time either fled the country or changed their names and blended in with the broader Burmese society. | |||
| 89% of the country's population are Buddhist, according to a report on ABC World News Tonight in May 2008 and the Buddha Dharma Education Association.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.buddhanet.net/e-learning/buddhistworld/burma-txt.htm | title = Buddhanet.net | accessdate = 2011-02-17}}</ref> | |||
| Many ] Muslims have fled Myanmar. Many refugees headed to neighbouring Bangladesh, including 200,000 in 1978 as a result of the ].<ref>{{cite news |last=Macan-Markar |first=Marwaan |title=Burma's Muslim Rohingyas – The New Boat People. |url=http://ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=45850 |publisher=Ipsnews.net |access-date=6 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090311004334/http://www.ipsnews.net/news.asp?idnews=45850 |archive-date=11 March 2009}}</ref> 250,000 more left in 1991.<ref>{{cite news |last=Ford |first=Peter |title=Why deadly race riots could rattle Myanmar's fledgling reforms |url=http://www.csmonitor.com/World/Asia-Pacific/2012/0612/Why-deadly-race-riots-could-rattle-Myanmar-s-fledgling-reforms |work=The Christian Science Monitor |date=12 June 2012 |access-date=6 August 2014 |archive-date=5 January 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150105222644/http://www.csmonitor.com/World/Asia-Pacific/2012/0612/Why-deadly-race-riots-could-rattle-Myanmar-s-fledgling-reforms |url-status=live }}</ref> Since August 2017, an estimated 23,000-43,700 Rohingya have been killed<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Habib |first1=Mohshin |url=http://nla.gov.au/nla.obj-748001039 |title=Forced migration of Rohingya : the untold experience |last2=Ahmad |first2=Salahuddin |last3=Jubb |first3=Christine |last4=Pallard |first4=Henri |last5=Rahman |first5=Masudur |last6=Ontario International Development Agency (issuing body) |publisher=Ontario International Development Agency, Canada |year=2018 |isbn=9780986681516 |page=69 |access-date=30 October 2024}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Barron |first=Laignee |date=8 March 2018 |title=More Than 43,000 Rohingya Parents May Be Missing. Experts Fear They Are Dead |url=https://time.com/5187292/rohingya-crisis-missing-parents-refugees-bangladesh/ |access-date=30 October 2024 |work=]}}</ref> in the ongoing ], and another 730,000 have fled to Bangladesh.<ref>{{Cite web |date=24 August 2022 |title=Myanmar: No Justice, No Freedom for Rohingya 5 Years On |url=https://www.hrw.org/news/2022/08/24/myanmar-no-justice-no-freedom-rohingya-5-years |access-date=30 October 2024 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| ==Culture== | |||
| {{Main|Culture of Burma}} | |||
| ] is one of the many coming-of-age ceremonies in Burmese culture.]] | |||
| === Languages === | |||
| A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Burma, the majority culture is primarily ] and ]. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries. This is manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of ] ]. Considered the national epic of Burma, the '']'', an adaptation of India's '']'', has been influenced greatly by ], ], and ] versions of the play.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.goldenlandpages.com/hotspots/rama/rama.htm |title=Ramayana in Myanmar's heart |accessdate=13 July 2006 |date=13 September 2003 |publisher=Goldenland Pages}}</ref> Buddhism is practised along with ] which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.<ref>{{cite book | first=R.C. | last=Temple| year=1906 | title=The Thirty-seven Nats-A Phase of Spirit-Worship prevailing in Burma}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://myanmartravelinformation.com/mti-myanmar-religion/nats.htm|title=The Worshipping of Nats – The Special Festival of Mount Popa}}{{dead link|date=November 2010}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Languages of Myanmar}} | |||
| Myanmar is home to four major language families: ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |last=Gordon |first=Raymond G. Jr. |title=Languages of Myanmar |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=MM |publisher=SIL International |year=2005 |access-date=14 July 2006 |archive-date=7 December 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121207085517/http://www.ethnologue.com/show_country.asp?name=MM |url-status=live }}</ref> Sino-Tibetan languages are most widely spoken. They include ], ], ], ], and Chinese (mainly ]). The primary Tai–Kadai language is ]. ], ], and ] are the major Austroasiatic languages spoken in Myanmar. The two major Indo-European languages are ], the liturgical language of Theravada Buddhism, and English.<ref name="ethno">{{cite web |last=Gordon |first=Raymond G. Jr. |title=Language Family Trees: Sino-Tibetan |url=http://www.ethnologue.com/show_family.asp?subid=90150 |work=Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition |publisher=SIL International |year=2005 |access-date=9 July 2006 |archive-date=11 August 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080811202503/http://www.ethnologue.com/show_family.asp?subid=90150 |url-status=live }}</ref> More than a hundred languages are spoken in total. Since many of them are known only within small tribes around the country, they may have been lost (many if not all) after a few generations. | |||
| ], rice noodles in fish soup, is widely considered to be Burma's national dish.]] | |||
| In a traditional village, the monastery is the centre of cultural life. Monks are venerated and supported by the lay people. A novitiation ceremony called ] is the most important ] events for a boy when he enters the monastery for a short period of time.<ref name="kmc">{{cite book | author=Khin Myo Chit | authorlink=Khin Myo Chit | year=1980 | title=Flowers and Festivals Round the Burmese Year }}</ref> All boys of Buddhist family need to be a novice (beginner for Buddhism) before the age of twenty and to be a monk after the age of twenty. It is compulsory for all boys of Buddhism. The duration can be as little as one week. Girls have ear-piercing ceremonies (]) at the same time.<ref name="kmc" /> Burmese culture is most evident in villages where local festivals are held throughout the year, the most important being the pagoda festival.<ref name="Myam-ma">{{cite book | author=Tsaya | year=1886 | title=Myam-ma, the home of the Burman | publisher =Thacker, Spink and Co. | location =Calcutta | pages = 36–37 }}</ref><ref name="sy">{{cite book|author=Shway Yoe|year=1882|title=The Burman – His Life and Notions|publisher=Norton Library 1963|location=New York|pages=211–216, 317–319}}</ref> Many villages have a guardian nat, and superstition and taboos are commonplace. | |||
| ], the mother tongue of the Bamar and official language of Myanmar, is related to ] and Chinese.<ref name="ethno" /> It is written in a ] consisting of circular and semi-circular letters, which were adapted from the ], which in turn was developed from a southern Indian script in the 5th century. The earliest known inscriptions in the Burmese script date from the 11th century. It is also used to write ], the sacred language of Theravada Buddhism, as well as several ethnic minority languages, including Shan, several Karen dialects, and Kayah (Karenni), with the addition of specialised characters and ]s for each language.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://lwinmoe.friendsofburma.org/doc/myanmar_extension.pdf |title=Proposal for encoding characters for Myanmar minority languages in the UCS |access-date=9 July 2006 |date=2 April 2006 |publisher=International Organization for Standardization |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060723083627/http://lwinmoe.friendsofburma.org/doc/myanmar_extension.pdf |archive-date=23 July 2006}}</ref> | |||
| British colonial rule also introduced Western elements of culture to Burma. Burma's educational system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as ].<ref>{{cite news | first =Steven | last =Martin | url =http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/3578993.stm | title =Burma maintains bygone buildings | publisher =BBC News |date= March 2004 | accessdate =9 July 2006 }}</ref> Many ethnic minorities, particularly the ] in the southeast, and the Kachin and ] who populate the north and north-east, practice ].<ref>{{cite book|url=http://www.archive.org/details/TheSilkenEast|title=The Silken East – A Record of Life and Travel in Burma|first=V. C.|last=Scott O'Connor|year=1904|publisher=Kiscadale|location= Scotland 1993|page=32}}</ref> According to CIA World Factbook, the Burman population is 68%, and the Ethnic groups comprise of 32%. However, the exiled leaders and organisations claims that Ethnic population is 40% which is implicitly contrasted with CIA report (official U.S report). | |||
| === |
=== Religion === | ||
| {{ |
{{main|Religion in Myanmar}} | ||
| ], the mother tongue of the Bamar and official language of Burma, is related to ] and to the ]s.<ref name="ethno"/> It is written in a ] consisting of circular and semi-circular letters, which were adapted from the ], which in turn was developed from a southern Indian script in the 8th century. The earliest known inscriptions in the Burmese script date from the 11th century. It is also used to write ], the sacred language of ], as well as several ethnic minority languages, including Shan, several Karen dialects, and Kayah (Karenni), with the addition of specialised characters and ]s for each language.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://lwinmoe.friendsofburma.org/doc/myanmar_extension.pdf |title=Proposal for encoding characters for Myanmar minority languages in the UCS |accessdate=9 July 2006 |date=2 April 2006 |format=PDF |publisher=International Organization for Standardization}}</ref> The Burmese language incorporates widespread usage of ]s and is age-oriented.<ref name="Myam-ma" /> Burmese society has traditionally stressed the importance of education. In villages, secular schooling often takes place in ]. ] and ] take place at government schools. | |||
| Many religions are practised in Myanmar. Religious edifices and orders have been in existence for many years. The Christian and Muslim populations do, however, face religious persecution and it is hard, if not impossible, for non-Buddhists to join the army or get government jobs, the main route to success in the country.<ref>"Ethnic and Religious Diversity: Myanmar's Unfolding Nemesis", Matthews, Bruce, Institute of South East Asian Studies, Visiting Researcher Series, Volume 2001, No. 3. 2001.</ref> Such persecution and targeting of civilians is particularly notable in eastern Myanmar, where over 3,000 villages have been destroyed in the past ten years.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://tbbc.org/resources.html#reports |title=Internal Displacement in Eastern Burma 2006 Survey |access-date=4 February 2007 |author=Thailand Burma Border Consortium |year=2007| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070515121040/http://www.tbbc.org/resources.html |archive-date=15 May 2007}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Harry |last=Priestly |url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=5380 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120119160146/http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=5380 |archive-date=19 January 2012 |title=The Outsiders |work=] |date=17 January 2006}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://isrc.payap.ac.th/document/papers/paper23.pdf |title=The Encounter of Missionary Christianity and Resurgent Buddhism in Post-colonial Myanmar |access-date=14 July 2006 |author=Ling, Samuel Ngun |year=2003 |publisher=Payap University |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060302235658/http://isrc.payap.ac.th/document/papers/paper23.pdf |archive-date=2 March 2006}}</ref> More than 200,000 Muslims have fled to Bangladesh by 2007 to escape persecution.<ref>{{cite book |last=Zatko |first=Martin |title=The Rough Guide to Myanmar|date=2015|page=357}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Dummett |first=Mark |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/7019882.stm |title=Burmese exiles in desperate conditions |publisher=BBC News |date=29 September 2007 |access-date=20 November 2012 |archive-date=1 September 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170901205917/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/asia-pacific/7019882.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| {{Main|Religion in Burma|Buddhism in Burma|Hinduism in Burma|Christianity in Burma|Islam in Burma|History of the Jews in Burma}} | |||
| ] are venerated throughout Burma, which is one of the most predominantly ] countries in the world.]] | |||
| {{bar box | |||
| |title=Religion in Burma | |||
| |titlebar=#ddd | |||
| |width=30% | |||
| |left1=religion | |||
| |right1=percent | |||
| |float=left | |||
| |bars= | |||
| {{bar percent|]|yellow|89}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|blue|4}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|green|4}} | |||
| {{bar percent|Others including ] and ]|purple|2}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|black|1}} | |||
| }} | |||
| A large majority of the population practices Buddhism; estimates range from 80%<ref name="pew"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010114310/http://www.globalreligiousfutures.org/countries/burma-myanmar/religious_demography#/?affiliations_religion_id=0&affiliations_year=2010 |date=10 October 2017 }}. ]. 2010.</ref> to 89%.<ref name=Buddhanet>{{cite web | url = http://www.buddhanet.net/e-learning/buddhistworld/burma-txt.htm | title = Buddhanet.net | access-date = 17 February 2011 | archive-date = 31 March 2017 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170331000030/http://www.buddhanet.net/e-learning/buddhistworld/burma-txt.htm | url-status = live }}</ref><ref name="COTM">{{cite web | url = https://www.childrenofthemekong.org/in-myanmar-the-worst-is-yet-to-come-an-exclusive-interview/ | title = Children of the Mekong | date = 2 March 2023 | access-date = 14 March 2023 | archive-date = 14 March 2023 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230314154216/https://www.childrenofthemekong.org/in-myanmar-the-worst-is-yet-to-come-an-exclusive-interview/ | url-status = live }}</ref> According to ], 87.9% of the population identifies as Buddhists.<ref name="TUR" /> ] Buddhism is the most widespread.<ref name=Buddhanet /> There are some 500,000 Buddhist monks and 75,000 nuns in this country of 54 million.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Pyone |first1=Taung |title=Monks in Myanmar have a new target |url=https://www.economist.com/asia/2019/11/14/monks-in-myanmar-have-a-new-target |access-date=17 November 2019 |newspaper=The Economist |date=14 November 2019 |archive-date=17 November 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191117122716/https://www.economist.com/asia/2019/11/14/monks-in-myanmar-have-a-new-target |url-status=live }}</ref> Other religions are practised largely without obstruction, with the notable exception of some religious minorities such as the Rohingya people, who have continued to have their citizenship status denied and treated as illegal immigrants instead,<ref name=rohingya /> and Christians in Chin State.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://2001-2009.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2007/90131.htm |title=Burma-International Religious Freedom Report 2007 |publisher=U.S. Department of State |date=14 September 2007 |access-date=22 May 2019 |archive-date=8 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200508105248/https://2001-2009.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2007/90131.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Many religions are practised in Burma. Religious edifices and orders have been in existence for many years. Festivals can be held on a grand scale. The Christian and Muslim populations do, however, face religious persecution and it is hard, if not impossible, for non-Buddhists to join the army or get government jobs, the main route to success in the country.<ref>"Ethnic and Religious Diversity: Myanmar's Unfolding Nemesis", Matthews, Bruce, Institute of South East Asian Studies, Visiting Researcher Series, Volume 2001, No. 3. 2001.</ref> Such persecution and targeting of civilians is particularly notable in Eastern Burma, where over 3000 villages have been destroyed in the past ten years.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://tbbc.org/resources.html#reports |title=Internal Displacement in Eastern Burma 2006 Survey | accessdate=4 February 2007 | author=Thailand Burma Border Consortium | year=2007| archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20070515121040/http://www.tbbc.org/resources.html| archivedate = 15 May 2007}}</ref><ref name=priestly>{{cite news |first=Harry |last=Priestly |url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/article.php?art_id=5380 |title=The Outsiders |publisher=] |date=17 January 2006 |accessdate=7 July 2006}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://isrc.payap.ac.th/document/papers/paper23.pdf |title=The Encounter of Missionary Christianity and Resurgent Buddhism in Post-colonial Myanmar |accessdate=14 July 2006 |author=Samuel Ngun Ling |year=2003 |format=PDF |publisher=Payap University | archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20060302235658/http://isrc.payap.ac.th/document/papers/paper23.pdf| archivedate = 2 March 2006}}</ref> More than 200,000 ] Muslims have settled in Bangladesh, to escape persecution, over the past 20 years.<ref>. BBC News. 29 September 2007.</ref> | |||
| According to 2014 census, 6.2% of the population identifies as Christian; 4.3% as Muslim; 0.8% as followers of tribal religions; 0.5% as ]; 0.2% as followers of other religions; and 0.1% follow no religion.<ref name="TUR">{{cite book | title=The 2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census Report Volume 2-C | publisher=Department of Population Ministry of Labour, Immigration and Population| date=July 2016 | pages=12–15}}</ref> According to the 2010 estimates of the ], 7% of the population is Christian; 4% is Muslim; 1% follows traditional ] beliefs; and 2% follow other religions, including ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://2001-2009.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2007/90131.htm |title=International Religious Freedom Report 2007 – Burma |publisher=State.gov |access-date=17 April 2010 |date=14 September 2007 |archive-date=8 May 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200508105248/https://2001-2009.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2007/90131.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm |title=Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs – Background Note: Burma |publisher=State.gov |access-date=17 April 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170122194342/https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/35910.htm |archive-date=22 January 2017 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Jehovah's Witnesses have been present since 1914<ref>{{cite book |title=2013 Yearbook of Jehovah's Witnesses |publisher=Watchtower Bible and Tract Society of New York, Inc. |year=2013 |page=85}}</ref> and have about 80 congregations around the country and a branch office in Yangon publishing in 16 languages.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.jw.org/en/jehovahs-witnesses/offices/myanmar |title=Office and Tour Information |publisher=jw.org |access-date=6 November 2015 |archive-date=9 October 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151009050318/http://www.jw.org/en/jehovahs-witnesses/offices/myanmar/ |url-status=live }}</ref> A tiny Jewish community in Yangon had a synagogue but no resident rabbi.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2010/148859.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101121191852/http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2010/148859.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=21 November 2010 |title=Burma—International Religious Freedom Report 2010 |publisher=U.S. Department of State |date=17 November 2010 |access-date=22 February 2011}}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Although Hinduism is practised by 0.5% of the population, it was a major religion in Myanmar's past.<ref>{{cite book |last=Aung-Thwin |first=Michael A. |title=The Mists of Rāmañña: The Legend that was Lower Burma |publisher=University of Hawai'i Press |location=Honolulu |edition=illustrated |year=2005 |pages=31–34 |isbn=978-0-8248-2886-8}}</ref><ref>], pp. 115–116</ref> ] is practised by many ] alongside Buddhism. | |||
| ===Education=== | |||
| {{Main|Education in Burma}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| === Health === | |||
| The educational system of Burma is operated by the government Ministry of Education. Universities and professional institutes from upper Burma and lower Burma are run by two separate entities, the Department of Higher Education of Upper Burma and the Department of Higher Education of Lower Burma. Headquarters are based in Yangon and Mandalay respectively. The education system is based on the United Kingdom's system, due to nearly a century of British and Christian presences in Burma. Nearly all schools are government-operated, but there has been a recent increase in privately funded English language schools. Schooling is compulsory until the end of elementary school, probably about 9 years old, while the compulsory schooling age is 15 or 16 at international level. | |||
| {{main|Health in Myanmar}} | |||
| The general state of ] in Myanmar is poor. The government spends anywhere from 0.5% to 3% of the country's GDP on health care, consistently ranking among the lowest in the world.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.ppionline.org/ppi_ci.cfm?knlgAreaID=108&subsecID=900003&contentID=254167 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110427103224/http://www.ppionline.org/ppi_ci.cfm?knlgAreaID=108&subsecID=900003&contentID=254167 |archive-date=27 April 2011 |title=PPI: Almost Half of All World Health Spending is in the United States |date=17 January 2007}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Anwar |first=Yasmin |title=Myanmar junta faulted for rampant diseases |url=http://www.berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2007/06/28_Myanmar.shtml |publisher=UC Berkeley News |date=28 June 2007}}{{dead link|date=September 2016}}</ref> Although ] is nominally free, in reality, patients have to pay for medicine and treatment, even in public clinics and hospitals. Public hospitals lack many of the basic facilities and equipment. The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Myanmar is 240. This is compared with 219.3 in 2008 and 662 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate, per 1,000 births is 73 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality is 47. According to Doctors without Borders, 25,000 Burmese AIDS patients died in 2007, deaths that could largely have been prevented by ] drugs and proper treatment.<ref name="autogenerated1">. ]. November 2008</ref> | |||
| HIV/AIDS, recognised as a disease of concern by the ], is most prevalent among ]s and ] users. In 2005, the estimated adult ] was 1.3% (200,000–570,000 people), according to ], and early indicators of any progress against the HIV epidemic are inconsistent.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/myanmar_statistics.html#25 |title=At a glance: Myanmar – statistics |access-date=9 January 2007 |work=UNICEF |archive-date=1 September 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100901015340/http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/myanmar_statistics.html#25 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://data.unaids.org/UNA-docs/REPORT_ICAAP_01July05_en.pdf |title=A scaled-up response to AIDS in Asia and the Pacific |access-date=10 January 2007 |date=1 July 2005 |work=UNAIDS |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070223010935/http://data.unaids.org/UNA-docs/report_icaap_01july05_en.pdf |archive-date=23 February 2007 }}</ref><ref name="06decUNAIDS">{{cite web|url=http://data.unaids.org/pub/EpiReport/2006/05-Asia_2006_EpiUpdate_eng.pdf |title=Asia |access-date=9 January 2007 |work=UNAIDS |date=December 2006 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070116033206/http://data.unaids.org/pub/EpiReport/2006/05-Asia_2006_EpiUpdate_eng.pdf |archive-date=16 January 2007 }}</ref> However, the National AIDS Programme Myanmar found that 32% of sex workers and 43% of intravenous drug users in Myanmar have HIV.<ref name="06decUNAIDS" /> | |||
| There are 101 universities, 12 institutes, 9 degree colleges and 24 colleges in Burma, a total of 146 higher education institutions.<ref>Chronicle of National Development Comparison Between Period Preceding 1988 and after (up to 31.12.2006)</ref> | |||
| ], ], Myanmar]] | |||
| There are 10 Technical Training Schools, 23 nursing training schools, 1 sport academy and 20 midwifery schools. | |||
| With a score of 15.7 in the 2024 Global Hunger Index, '''Myanmar''' has a level of hunger that is moderate.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Hunger Index Scores by 2024 GHI Rank |url=https://www.globalhungerindex.org/ranking.html |access-date=2024-12-25 |website=Global Hunger Index (GHI) - peer-reviewed annual publication designed to comprehensively measure and track hunger at the global, regional, and country levels |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| There are 2047 Basic Education High Schools, 2605 Basic Education Middle Schools, 29944 Basic Education Primary Schools and 5952 Post Primary Schools. 1692 multimedia classrooms exist within this system. | |||
| === Education === | |||
| There are four international schools which are acknowledged by WASC and College Board – ] (ISY), ] (CISM), ] (YIS) and ] (ISM) in Yangon. | |||
| {{main|Education in Myanmar}} | |||
| ], ], Myanmar]] | |||
| ===Units of measure=== | |||
| {{Main|Burmese units of measurement}} | |||
| Burma is one of three countries that still predominantly uses a non-metric system of measure, according to the CIA Factbook.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/appendix/print_appendix-g.html |title=The World Factbook, Appendix G: Weights and Measures |year=2010 |work=Web Pages |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |accessdate=10 May 2010}}</ref> The common units of measure are unique to Burma but the government web pages use both imperial units<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.moai.gov.mm/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&layout=blog&id=16&Itemid=2 |title=Ministry of Agriculture and Information |date=2009-2010 |work=Web Page |publisher=Myanmar Agriculture |accessdate=10 May 2010}}</ref> and metric units.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.mofa.gov.mm/aboutmyanmar/geography.html |title=About Myanmar : Geography |year=2009 |work=Web Page |publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs |accessdate=10 May 2010}}</ref> | |||
| According to the ] Institute of Statistics, Myanmar's official ] as of 2000 was 90%.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.uis.unesco.org/TEMPLATE/html/Exceltables/education/Literacy_Regional_April2006.xls|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070625071529/http://www.uis.unesco.org/TEMPLATE/html/Exceltables/education/Literacy_Regional_April2006.xls|archive-date=25 June 2007|title=Adult (15+) Literacy Rates and Illiterate Population by Region and Gender for |access-date=13 July 2006 |date=April 2006 |format=XLS |publisher=UNESCO Institute of Statistics}}</ref> Historically, Myanmar has had high literacy rates. The educational system of Myanmar is operated by the government agency, the ]. The education system is based on the United Kingdom's system after nearly a century of British and Christian presences in Myanmar. Nearly all schools are government-operated, but there has been an increase in privately funded English language schools in the early 21st century. Schooling is compulsory until the end of elementary school, approximately 9 years old, while the compulsory schooling age is 15 or 16 at international level. | |||
| ==Media== | |||
| {{Main|Media of Burma}} | |||
| ] | |||
| There are 101 universities, 12 institutes, 9 degree colleges and 24 colleges in Myanmar, a total of 146 higher education institutions.<ref>Chronicle of National Development Comparison Between Period Preceding 1988 and after (up to 31 December 2006).</ref> There are 10 technical training schools, 23 nursing training schools, 1 sport academy and 20 midwifery schools. There are four international schools acknowledged by WASC and College Board—], ], Yangon International School, and International School of Myanmar in Yangon. Myanmar was ranked 125th in the ] in 2024.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/|title=Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship|access-date=2024-10-22|author=]|year=2024|isbn=978-92-805-3681-2|doi= 10.34667/tind.50062|website=www.wipo.int|location=Geneva|page=18}}</ref> | |||
| Due to Burma's political climate, there are not many media companies in relation to the country's population, although a certain number exists. Some are privately owned, but all programming must meet with the approval of the ] board. | |||
| === Crime === | |||
| Burma is the primary subject of a 2007 graphic novel titled '']'' by ] author and animator, ]. The graphic novel was translated into English under the title '']'' in 2008. In 2009, a documentary about Burmese ]s called '']'' was released.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://burmavjmovie.com/ |title=Burma VJ – Academy Award Nominee – Best Documentary Feature |publisher=Burmavjmovie.com |date= |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> This film was nominated for ] at the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://dannyfisher.org/2010/02/02/burma-vj-nominated-for-a-2010-academy-award-for-best-documentary-feature/ |title=Burma VJ Nominated for the 2010 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature " Rev. Danny Fisher |publisher=Dannyfisher.org |date=2 February 2010 |accessdate=17 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| {{Further|Crime in Myanmar}} | |||
| Myanmar had a murder rate of 15.2 per 100,000 population with a total of 8,044 murders in 2012.<ref name=UNODC>{{cite web|url=https://www.unodc.org/gsh/en/index.html|title=UNODC: Global Study on Homicide|author=agt|access-date=5 January 2015|archive-date=2 June 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190602171852/http://www.unodc.org/gsh/en/index.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Factors influencing Myanmar's high murder rate include communal violence and armed conflict.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://investvine.com/asean-as-safe-as-we-think/|title=ASEAN: As safe as we think?|first=Justin|last=Calderon|work=Inside Investor|date=3 July 2013|access-date=7 July 2013|archive-date=22 June 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190622190043/http://investvine.com/asean-as-safe-as-we-think/|url-status=dead}}</ref> Myanmar is one of the world's most corrupt nations. The 2012 ] ] ranked the country at number 171, out of 176 countries in total.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.trust.org/item/?map=myanmar-still-near-bottom-of-corruption-rankings-in-2012-despite-reforms%2F |publisher=] |title=Myanmar still near bottom of corruption rankings in 2012 despite reforms |date=5 December 2012 |access-date=5 January 2015 |archive-date=5 January 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150105214224/http://www.trust.org/item/?map=myanmar-still-near-bottom-of-corruption-rankings-in-2012-despite-reforms%2F |url-status=dead }}</ref> Myanmar is the world's second largest producer of ] after ], producing some 25% of the world's opium, and forms part of the ]. The opium industry was a monopoly during colonial times and has since been illegally operated by corrupt officials in the Burmese military and rebel fighters,<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-20150082 |title=UN report: Opium cultivation rising in Burma |publisher=BBC News |date=31 October 2012 |access-date=10 June 2013 |archive-date=15 July 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130715114536/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-20150082 |url-status=live }}</ref> primarily as the basis for heroin manufacture. Myanmar is the largest producer of methamphetamines in the world, with the majority of '']'' found in Thailand produced in Myanmar, particularly in the Golden Triangle and northeastern Shan State, which borders Thailand, Laos and China.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.bangkokpost.com/news/investigation/279434/myanmar-reforms-mask-meteoric-rise-in-drug-trade|title=Myanmar's rising drug trade|last=Thornton|first=Phil|date=12 February 2012|work=Bangkok Post|access-date=19 February 2012}}</ref> Burmese-produced ''ya ba'' is typically trafficked to Thailand via Laos, before being transported through the northeastern Thai region of ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/LG13Ae01.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100715054055/http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/LG13Ae01.html|url-status=unfit|archive-date=15 July 2010|title=Holes in Thailand's drug fences|last=McCartan|first=Brian|date=13 July 2010|work=Asia Times|access-date=19 February 2012}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Main|Outline of Burma}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| == |
== Culture == | ||
| {{main|Culture of Myanmar}} | |||
| {{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| ] dance]] | |||
| A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Myanmar, with majority culture primarily Buddhist and ]. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries, manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of Theravada Buddhism. Considered the national epic of Myanmar, the '']'', an adaptation of India's '']'', has been influenced greatly by Thai, Mon, and Indian versions of the play.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.goldenlandpages.com/hotspots/rama/rama.htm |title=Ramayana in Myanmar's heart |access-date=13 July 2006 |date=13 September 2003 |publisher=Goldenland Pages |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060426233452/http://www.goldenlandpages.com/hotspots/rama/rama.htm |archive-date=26 April 2006}}</ref> Buddhism is practised along with ], which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.<ref>{{cite book |last=Temple |first=R.C. |title=The Thirty-seven Nats-A Phase of Spirit-Worship prevailing in Burma |year=1906}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://myanmartravelinformation.com/mti-myanmar-religion/nats.htm |title=The Worshipping of Nats – The Special Festival of Mount Popa |publisher=Myanmar Travel Information |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060623011500/http://myanmartravelinformation.com/mti-myanmar-religion/nats.htm | |||
| |archive-date=23 June 2006 |access-date=10 January 2012}}</ref> | |||
| ] ceremony in ]]] | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Sister project links}} | |||
| {{Wikinews}} | |||
| ; Government | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ; General information | |||
| * | |||
| *{{CIA World Factbook link|bm|Burma}} | |||
| * from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| *{{wikiatlas|Myanmar}} | |||
| *{{Wikitravel|Myanmar}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| In a traditional village, the monastery is the centre of cultural life. Monks are venerated and supported by the lay people. A novitiation ceremony called ] is the most important ] events for a boy, during which he enters the monastery for a short time.<ref name="kmc">{{cite book |author=Chit, Khin Myo |author-link=Khin Myo Chit |year=1980 |title=Flowers and Festivals Round the Burmese Year }}</ref> All male children in Buddhist families are encouraged to be a novice (beginner for Buddhism) before the age of twenty and to be a monk after the age of twenty. Girls have ear-piercing ceremonies ({{lang|my|နားသ}}) at the same time.<ref name="kmc" /> Burmese culture is most evident in villages where local festivals are held throughout the year, the most important being the ].<ref name="Myam-ma">{{cite book |author=Tsaya |year=1886 |title=Myam-ma, the home of the Myanmarn |publisher=Thacker, Spink and Co. |location=Calcutta |pages=36–37}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Yoe, Shway |year=1882|title=The Myanmarn – His Life and Notions |publisher=Norton Library 1963 |location=New York |pages=211–216, 317–319}}</ref> Many villages have a guardian nat, and superstition and taboos are commonplace. | |||
| {{Burma (Myanmar) topics}} | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| ] (Rakhine) girl pours water at revellers during the Burmese New Year ] Water Festival in Yangon.]] | |||
| |title = Geographic locale | |||
| British colonial rule introduced Western elements of culture to Myanmar. Myanmar's education system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as Yangon.<ref>{{cite news |first=Steven |last=Martin |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/3578993.stm |title=Burma maintains bygone buildings |publisher=BBC News |date=March 2004 |access-date=9 July 2006 |archive-date=8 April 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080408162817/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/3578993.stm |url-status=live }}</ref> Many ethnic minorities, particularly the Karen in the southeast and the Kachin and Chin who populate the north and northeast, practice Christianity.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/TheSilkenEast |title=The Silken East – A Record of Life and Travel in Burma |author=Scott O'Connor |year=1904 |publisher=Kiscadale |location=Scotland |page=}}</ref> According to '']'', the Burman population is 68% and the ethnic groups constitute 32%. In contrast, the exiled leaders and organisations claim the country is 40% ethnic. | |||
| === Cuisine === | |||
| {{main|Burmese cuisine}} | |||
| ] is characterised by extensive use of fish products such as ], ] (fermented seafood) and dried prawn. ] is the traditional breakfast dish and is Myanmar's national dish. Seafood is a common ingredient in coastal cities, while meat and poultry are more commonly used in landlocked cities like Mandalay. Freshwater fish and shrimp have been incorporated into inland cooking as a primary source of protein and are used in a variety of ways, fresh, salted whole or filleted, salted and dried, made into a salty paste, or fermented sour and pressed. Burmese cuisine also includes a variety of salads ('']''), centred on one major ingredient, ranging from starches like rice, wheat and rice noodles, glass noodles and vermicelli, to potato, ginger, tomato, ], long bean, and ] (pickled tea leaves). | |||
| === Sport === | |||
| {{Main|Sport in Myanmar}} | |||
| The ], ], ], and ] martial arts and ] are traditional sports in Myanmar.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://factsanddetails.com/southeast-asia/Myanmar/sub5_5e/entry-3098.html|title=SPORTS IN MYANMAR: SOCCER, OLYMPICS AND TRADITIONAL SPORTS|last=Hays|first=Jeffrey|website=Facts and Details|access-date=5 June 2017|archive-date=2 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170602070755/http://factsanddetails.com/southeast-asia/Myanmar/sub5_5e/entry-3098.html|url-status=live}}</ref> Football is played all over the country, even in villages, and its ] is ruled by the ]. The ] took place in Naypyidaw, Yangon, Mandalay and ] in December representing the third occasion that the event has been staged in Myanmar. Myanmar previously hosted the games in ] and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.betweenonline.com/2011/12/28/myanmar-prepares-for-the-2013-southeast-asian-games/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180624150410/http://www.betweenonline.com/2011/12/28/myanmar-prepares-for-the-2013-southeast-asian-games/|url-status=dead|archive-date=24 June 2018|title=Myanmar prepares for the 2013 Southeast Asian Games|access-date=5 January 2012}}</ref> | |||
| === Art === | |||
| {{main|Art of Myanmar|Myanmar architecture}} | |||
| Burmese traditional art concepts are popular and respected by the Burmese people and people from abroad. Burmese contemporary art has developed quite rapidly on its own terms. Artists born after the 1980s have had greater chances of art practice outside the country. | |||
| One of the first to study western art was ]. Together with ] and a handful of other artists, they were the pioneers of western painting style. Later on most young children learned the concepts from them. Some well known contemporary artists are ], Aung Kyaw Htet, ], Myint Swe, Min Wai Aung, ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| === Media and communications === | |||
| {{main|Media of Myanmar}} | |||
| Because of Myanmar's political climate, there are not many media companies in relation to the country's population. Some are privately owned. All programming must meet with the approval of the censorship board. The Burmese government announced on 20 August 2012 that it would stop censoring media before publication. Following the announcement, newspapers and other outlets no longer required approved by state censors; however, journalists in the country can still face consequences for what they write and say.<ref>{{cite news|title=Burma Abolishes Censorship|url=http://www.thedailybeast.com/cheats/2012/08/20/burma-abolishes-censorship.html|work=The Daily Beast|access-date=20 August 2012|archive-date=21 August 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120821034757/http://www.thedailybeast.com/cheats/2012/08/20/burma-abolishes-censorship.html|url-status=live}}</ref> In April 2013, international media reports were published to relay the enactment of the media liberalisation reforms that we announced in August 2012. For the first time in numerous decades, the publication of privately owned newspapers commenced in the country.<ref>{{cite news |last=Sukri |first=Azhar |title=Myanmar shows new signs of press freedom |url=http://www.aljazeera.com/video/asia/2013/04/201341115227284132.html |publisher=Al Jazeera |date=1 April 2013 |access-date=24 April 2013 |archive-date=4 April 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130404121722/http://www.aljazeera.com/video/asia/2013/04/201341115227284132.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Internet ==== | |||
| {{main|Internet in Myanmar}} | |||
| ] women in a village near ], 2010]] | |||
| Internet use is estimated to be relatively low compared to other countries.<ref name="Calderaro">{{cite journal |last1=Calderaro |first1=Andrea |title=Internet Governance Capacity Building in Post-Authoritarian Contexts. Telecom Reform and Human Rights in Myanmar |journal=SSRN |date=1 May 2015 |doi=10.2139/ssrn.2686095 |url=http://orca.cf.ac.uk/90938/1/SSRN-id2686095-2.pdf |access-date=22 February 2021 |archive-date=10 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210310112035/http://orca.cf.ac.uk/90938/1/SSRN-id2686095-2.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.opentechfund.org/files/reports/otf_myanmar_access_openness_public.pdf |title=Internet Access and Openness: Myanmar 2012 |access-date=18 July 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140414221004/https://www.opentechfund.org/files/reports/otf_myanmar_access_openness_public.pdf |archive-date=14 April 2014 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Myanmar's internet used to be subject to censorship, and authorities viewed e-mails and posts on Internet blogs until 2012 when the government removed media censorship. During the strict censorship days, activity at internet cafes was regulated, and one blogger named ] was sentenced to prison for publishing a video of destruction caused by ] in 2008; Zarganar was released in October 2011. | |||
| In regards to communications infrastructure, Myanmar is the last ranked Asian country in the World Economic Forum's ] (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. With 139 countries reported on, Myanmar ranked number 133 overall in the 2016 NRI ranking.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://reports.weforum.org/global-information-technology-report-2016/networked-readiness-index/?doing_wp_cron=1577930341.6168849468231201171875 | title=NRI Overall Ranking 2016 | publisher=World Economic Forum | access-date=1 January 2020 | archive-date=28 May 2020 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200528133139/https://reports.weforum.org/global-information-technology-report-2016/networked-readiness-index/?doing_wp_cron=1577930341.6168849468231201171875 | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Film === | |||
| {{main|Cinema of Myanmar}} | |||
| Myanmar's first film was a documentary of the funeral of Tun Shein—a leading politician of the 1910s, who campaigned for Burmese independence in London. The first Burmese ] ''Myitta Ne Thuya'' ('']'') in 1920 which proved a major success, despite its poor quality. During the 1920s and 1930s, many Burmese-owned film companies made and produced several films. The first Burmese ] was produced in 1932 in ], India with the title Ngwe Pay Lo Ma Ya (Money Can't Buy It). After World War II, Burmese cinema continued to address political themes. Many of the films produced in the early Cold War era had a strong propaganda element. | |||
| In the era that followed the political events of 1988, the film industry has been increasingly controlled by the government. Film stars who had been involved in the political activities were banned from appearing in films. The government issues strict rules on censorship and largely determines who produces films, as well as who gets academy awards.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Zaw, Aung |title=Celluloid Disillusions|url=http://www.irrawaddy.org/database/2004/vol12.3/cover.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050213182520/http://www.irrawaddy.org/database/2004/vol12.3/cover.html|archive-date=13 February 2005|journal=Irrawaddy|volume= 12|issue=3|date=March 2004}}</ref> | |||
| Over the years, the movie industry has also shifted to producing many lower-budget ] films. Most of the movies produced nowadays are ].<ref>Kyi Soe Tun quoted in the Bangkok Post, 11 August 2006</ref> In 2008, only 12 films worthy of being considered for an ] were made, although at least 800 VCDs were produced.<ref>. ''Irrawaddy''. 16 January 2009</ref> Myanmar is the primary subject of a 2007 graphic novel titled ''Chroniques Birmanes'' by ] author and animator, ]. The graphic novel was translated into English under the title '']'' in 2008. In 2009, a documentary about Burmese ]s called '']'' was released.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://burmavjmovie.com/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090521155756/http://burmavjmovie.com/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=21 May 2009 |title=Burma VJ – Academy Award Nominee – Best Documentary Feature |publisher=Burmavjmovie.com |access-date=17 April 2010 }}</ref> This film was nominated for ] at the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://dannyfisher.org/2010/02/02/burma-vj-nominated-for-a-2010-academy-award-for-best-documentary-feature/ |title=Burma VJ Nominated for the 2010 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature, Rev. Danny Fisher |publisher=Dannyfisher.org |date=2 February 2010 |access-date=17 April 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110429004750/http://dannyfisher.org/2010/02/02/burma-vj-nominated-for-a-2010-academy-award-for-best-documentary-feature/ |archive-date=29 April 2011 }}</ref> '']'' had its world premiere on 12 September 2011 at the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.indiewire.com/2011/09/tiff-list-2011-a-complete-guide-to-the-toronto-international-film-festival-52378/|title=TIFF List 2011: A Complete Guide To The Toronto International Film Festival|last1=Knegt|first1=Peter|date=12 September 2011|website=IndieWire|language=en|access-date=31 December 2018|archive-date=27 October 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181027185622/https://www.indiewire.com/2011/09/tiff-list-2011-a-complete-guide-to-the-toronto-international-film-festival-52378/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{portal|Myanmar|Asia|Countries}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| {{reflist|group=nb}} | |||
| ==Pronunciations of ''Myanmar''== | |||
| {{reflist|group=pronunciations}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| == Bibliography == | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * Cameron, Ewan. "The State of Myanmar", ''History Today'', May 2020, vol. 70, issue 4, pp. 90–93. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Charney |first=Michael W. |title=History of Modern Burma |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1999}} | |||
| * Combs, Daniel. ''Until the World Shatters: Truth, Lies, and the Looting of Myanmar'' (2021). | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lieberman |first=Victor B. |title=Strange Parallels: Southeast Asia in Global Context, c. 800–1830, volume 1, Integration on the Mainland |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-521-80496-7 |ref=Lieberman}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Maclean |first=Rory |title=Under the Dragon-A Journey through Burma |publisher=] |year=2008 |isbn=978-1-84511-622-4 |ref=Maclean}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Myint-U |first=Thant |title=The River of Lost Footsteps—Histories of Burma |publisher=] |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-374-16342-6 |ref=Myint-U}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kemp |first=Hans |title= |publisher=Visionary World |edition=illustrated with text by Tom Vater |year=2013 |isbn=978-9628563708}} | |||
| * by Aye Chan | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Sister project links|voy=Myanmar|commons=မြန်မာပြည်|d=Q836}} | |||
| '''Government''' | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210603041202/http://www.president-office.gov.mm/en/ |date=3 June 2021 }} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160101072042/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/world-leaders-1/BM.html |date=1 January 2016 }} from the ] (CIA) | |||
| '''General information''' | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151016011526/http://mingalapar.com/ |date=16 October 2015 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130622160420/http://myanma.com/ |date=22 June 2013 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211201171209/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/burma/ |date=1 December 2021 }}. '']''. ]. | |||
| * from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140626082954/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-12990563 |date=26 June 2014 }} from ] | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150428155257/http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/400119/Myanmar |date=28 April 2015 }} at '']'' | |||
| * {{OSM relation|50371}} | |||
| * {{wikiatlas|Myanmar}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140825021158/http://www.pbs.org/wnet/wideangle/episodes/eyes-of-the-storm/turning-points-in-burmese-history/5363/ |date=25 August 2014 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121011100735/http://www.ifs.du.edu/ifs/frm_CountryProfile.aspx?Country=MM |date=11 October 2012 }} from ] | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060716151155/http://www.burmalibrary.org/ |date=16 July 2006 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220701134450/https://sea.lib.niu.edu/seadl/islandora/object/SEAImages:ds5276p4861900zacollection#page/1/mode/1up |date=1 July 2022 }} | |||
| {{Burma (Myanmar) topics|state=expanded}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title =Related articles | |||
| |list = | |list = | ||
| {{Countries and territories of Southeast Asia}} | {{Countries and territories of Southeast Asia}} | ||
| {{Countries and Territories of South Asia}} | |||
| {{Austronesian-speaking}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Template group | |||
| |title = International membership and history | |||
| |list = | |||
| {{Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)}} | |||
| {{East Asia Summit (EAS)}} | |||
| {{Countries of Asia}} | {{Countries of Asia}} | ||
| {{Shanghai Cooperation Organization}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| <!--Metadata--> | |||
| {{Coord|22|N|96|E|type:country_region:MM|display=title}} | |||
| {{Coord|22|N|96|E|type:country_region:MM|display=title|name=Myanmar (Burma)}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link GA|lt}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|hr}} | |||
| ] | |||
| <!--Interwikis--> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:46, 26 December 2024
Country in Southeast Asia "Burma" redirects here. For other uses, see Burma (disambiguation).
Republic of the Union of Myanmar
| |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 State Seal
State Seal
| |
| Anthem: ကမ္ဘာမကျေ Kaba Ma Kyei "Till the End of the World" | |
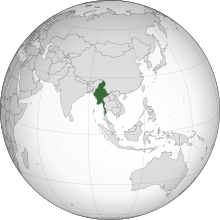 Show globe Show globe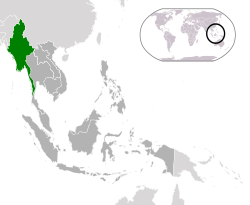 Show map of ASEANLocation of Myanmar (green) Show map of ASEANLocation of Myanmar (green) | |
| Capital | Naypyidaw 21°00′N 96°00′E / 21.000°N 96.000°E / 21.000; 96.000 |
| Largest city | Yangon |
| Official language | Burmese |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2019) | |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary assembly-independent republic under a military junta |
| • Acting President, SAC Chairman, and Prime Minister | Min Aung Hlaing |
| • SAC Vice Chairman and Deputy Prime Minister | Soe Win |
| Legislature | State Administration Council |
| Formation | |
| • Pagan era | 23 December 849 |
| • Taungoo era | 16 October 1510 |
| • Konbaung era | 29 February 1752 |
| • Colonial era | 1 January 1886 |
| • Independence from the United Kingdom | 4 January 1948 |
| • 1962 coup d'état | 2 March 1962 |
| • 1988 coup d'état | 18 September 1988 |
| • Current constitution | 31 January 2011 |
| • 2021 coup d'état | 1 February 2021 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 676,579 km (261,229 sq mi) (39th) |
| • Water (%) | 3.06 |
| Population | |
| • 2022 estimate | 55,770,232 (26th) |
| • Density | 196.8/sq mi (76.0/km) (125th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2017) | medium inequality (106th) |
| HDI (2022) | medium (144th) |
| Currency | Kyat (K) (MMK) |
| Time zone | UTC+06:30 (MMT) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +95 |
| ISO 3166 code | MM |
| Internet TLD | .mm |
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar and also rendered as Burma (the official English form until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by India and Bangladesh to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (formerly Rangoon).
Early civilisations in the area included the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu city-states in Upper Myanmar and the Mon kingdoms in Lower Myanmar. In the 9th century, the Bamar people entered the upper Irrawaddy valley, and following the establishment of the Pagan Kingdom in the 1050s, the Burmese language, culture, and Theravada Buddhism slowly became dominant in the country. The Pagan Kingdom fell to Mongol invasions, and several warring states emerged. In the 16th century, reunified by the Taungoo dynasty, the country became the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia for a short period. The early 19th-century Konbaung dynasty ruled over an area that included modern Myanmar and briefly controlled Assam, the Lushai Hills, and Manipur as well. The British East India Company seized control of the administration of Myanmar after three Anglo-Burmese Wars in the 19th century, and the country became a British colony. After a brief Japanese occupation, Myanmar was reconquered by the Allies. On 4 January 1948, Myanmar declared independence under the terms of the Burma Independence Act 1947.
Myanmar's post-independence history has been checkered by continuing unrest and conflict to this day. The coup d'état in 1962 resulted in a military dictatorship under the Burma Socialist Programme Party. On 8 August 1988, the 8888 Uprising then resulted in a nominal transition to a multi-party system two years later, but the country's post-uprising military council refused to cede power, and has continued to rule the country through to the present. The country remains riven by ethnic strife among its myriad ethnic groups and has one of the world's longest-running ongoing civil wars. The United Nations and several other organisations have reported consistent and systemic human rights violations in the country. In 2011, the military junta was officially dissolved following a 2010 general election, and a nominally civilian government was installed. Aung San Suu Kyi and political prisoners were released and the 2015 Myanmar general election was held, leading to improved foreign relations and eased economic sanctions, although the country's treatment of its ethnic minorities, particularly in connection with the Rohingya conflict, continued to be a source of international tension and consternation. Following the 2020 Myanmar general election, in which Aung San Suu Kyi’s party won a clear majority in both houses, the Burmese military (Tatmadaw) again seized power in a coup d'état. The coup, which was widely condemned by the international community, led to continuous ongoing widespread protests in Myanmar and has been marked by violent political repression by the military, as well as a larger outbreak of the civil war. The military also arrested Aung San Suu Kyi in order to remove her from public life, and charged her with crimes ranging from corruption to violation of COVID-19 protocols; all of the charges against her are "politically motivated" according to independent observers.
Myanmar is a member of the East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the Commonwealth of Nations despite once being part of the British Empire. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The country is very rich in natural resources, such as jade, gems, oil, natural gas, teak and other minerals, as well as also endowed with renewable energy, having the highest solar power potential compared to other countries of the Great Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from instability, factional violence, corruption, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of colonial exploitation with little regard to human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (PPP) at US$221.5 billion. The income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the economy is controlled by cronies of the military junta. Myanmar is one of the least developed countries; as of 2022, according to the Human Development Index, it ranks 144 out of 193 countries in terms of human development. Since 2021, more than 600,000 people were displaced across Myanmar due to the surge in violence post-coup, with more than three million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance.
Etymology
Main article: Names of MyanmarThe name of the country has been a matter of dispute and disagreement, particularly in the early 21st century, focusing mainly on the political legitimacy of those using Myanmar versus Burma. Both names derive from the earlier Burmese Mranma or Mramma, an ethnonym for the majority Burman ethnic group, of uncertain etymology. The terms are also popularly thought to derive from Sanskrit Brahma Desha, 'land of Brahma'.
In 1989, the military government officially changed the English translations of many names dating back to Burma's colonial period or earlier, including that of the country itself: Burma became Myanmar. The renaming remains a contested issue. Many political and ethnic opposition groups and countries continue to use Burma because they do not recognise the legitimacy or authority of the military government.
The country's official full name is "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" (Burmese: ပြည်ထောင်စုသမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်, Pyihtaungsu Thamada Myanma Naingngantaw, pronounced [pjìdàʊɴzṵ θàɴməda̰ mjəmà nàɪɴŋàɴdɔ̀]). Countries that do not officially recognise that name use the long form "Union of Burma" instead. In English, the country is popularly known as either Burma or Myanmar. In Burmese, the pronunciation depends on the register used and is either Bama (pronounced [bəmà]) or Myamah (pronounced [mjəmà]).
Official United States foreign policy retains Burma as the country's name although the State Department's website lists the country as Burma (Myanmar). The United Nations uses Myanmar, as does the ASEAN and as do Australia, Russia, Germany, China, India, Bangladesh, Norway, Japan, Switzerland, Canada and Ukraine. Most English-speaking international news media refer to the country by the name Myanmar, including the BBC, CNN, Al Jazeera, Reuters, and the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC)/Radio Australia. Myanmar is known by a name deriving from Burma in Spanish, Italian, Romanian, and Greek. French-language media consistently use Birmanie.
There are at least nine different pronunciations of the English name Myanmar, and no single one is standard. Pronunciations with two syllables are found most often in major British and American dictionaries. Dictionaries—such as Collins—and other sources also report pronunciations with three syllables.
As John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: . So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as by some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. However, Burma is pronounced by rhotic speakers of English due to a phonotactic constraint, as /ɜː/ occurs only before /r/ in those accents.
History
Main article: History of Myanmar| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Myanmar" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Prehistory
Main articles: Prehistory of Myanmar and Migration period of ancient Burma
Archaeological evidence shows that Homo erectus lived in the region now known as Myanmar as early as 750,000 years ago, with no more erectus finds after 75,000 years ago. The first evidence of Homo sapiens is dated to about 25,000 BP with discoveries of stone tools in central Myanmar. Evidence of Neolithic age domestication of plants and animals and the use of polished stone tools dating to sometime between 10,000 and 6,000 BCE has been discovered in the form of cave paintings in Padah-Lin Caves.
The Bronze Age arrived c. 1500 BCE when people in the region were turning copper into bronze, growing rice and domesticating poultry and pigs; they were among the first people in the world to do so. Human remains and artefacts from this era were discovered in Monywa District in the Sagaing Region. The Iron Age began around 500 BCE with the emergence of iron-working settlements in an area south of present-day Mandalay. Evidence also shows the presence of rice-growing settlements of large villages and small towns that traded with their surroundings as far as China between 500 BCE and 200 CE. Iron Age Burmese cultures also had influences from outside sources such as India and Thailand, as seen in their funerary practices concerning child burials. This indicates some form of communication between groups in Myanmar and other places, possibly through trade.
Early city-states
Main articles: Pyu city-states and Mon kingdomsAround the second century BCE the first-known city-states emerged in central Myanmar. The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu people, the earliest inhabitants of Myanmar of whom records are extant, from present-day Yunnan. The Pyu culture was heavily influenced by trade with India, importing Buddhism as well as other cultural, architectural and political concepts, which would have an enduring influence on later Burmese culture and political organisation.
By the 9th century, several city-states had sprouted across the land: the Pyu in the central dry zone, Mon along the southern coastline and Arakanese along the western littoral. The balance was upset when the Pyu came under repeated attacks from Nanzhao between the 750s and the 830s. In the mid-to-late 9th century the Bamar people founded a small settlement at Bagan. It was one of several competing city-states until the late 10th century, when it grew in authority and grandeur.
Pagan Kingdom
Main articles: Pagan Kingdom, Toungoo dynasty, and Konbaung dynasty See also: Kingdom of Ava, Hanthawaddy Kingdom, Kingdom of Mrauk U, and Shan States
Pagan gradually grew to absorb its surrounding states until the 1050s–1060s when Anawrahta founded the Pagan Kingdom, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. In the 12th and 13th centuries, the Pagan Empire and the Khmer Empire were two main powers in mainland Southeast Asia. The Burmese language and culture gradually became dominant in the upper Irrawaddy valley, eclipsing the Pyu, Mon and Pali norms by the late 12th century. Theravada Buddhism slowly began to spread to the village level, although Tantric, Mahayana, Hinduism, and folk religion remained heavily entrenched. Pagan's rulers and wealthy built over 10,000 Buddhist temples in the Pagan capital zone alone. Repeated Mongol invasions in the late 13th century toppled the four-century-old kingdom in 1287.

Pagan's collapse was followed by 250 years of political fragmentation that lasted well into the 16th century. Like the Burmans four centuries earlier, Shan migrants who arrived with the Mongol invasions stayed behind. Several competing Shan States came to dominate the entire northwestern to eastern arc surrounding the Irrawaddy valley. The valley too was beset with petty states until the late 14th century when two sizeable powers, Ava Kingdom and Hanthawaddy Kingdom, emerged. In the west, a politically fragmented Arakan was under competing influences of its stronger neighbours until the Kingdom of Mrauk U unified the Arakan coastline for the first time in 1437. The kingdom was a protectorate of the Bengal Sultanate at different time periods.
In the 14th and 15th centuries, Ava fought wars of unification but could never quite reassemble the lost empire. Having held off Ava, the Mon-speaking Hanthawaddy entered its golden age, and Arakan went on to become a power in its own right for the next 350 years. In contrast, constant warfare left Ava greatly weakened, and it slowly disintegrated from 1481 onward. In 1527, the Confederation of Shan States conquered Ava and ruled Upper Myanmar until 1555.
Like the Pagan Empire, Ava, Hanthawaddy and the Shan states were all multi-ethnic polities. Despite the wars, cultural synchronisation continued. This period is considered a golden age for Burmese culture. Burmese literature "grew more confident, popular, and stylistically diverse", and the second generation of Burmese law codes as well as the earliest pan-Burma chronicles emerged. Hanthawaddy monarchs introduced religious reforms that later spread to the rest of the country.
Taungoo and Konbaung



Political unification returned in the mid-16th century, through the efforts of Taungoo, a former vassal state of Ava. Taungoo's young, ambitious King Tabinshwehti defeated the more powerful Hanthawaddy in the Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War. His successor Bayinnaung went on to conquer a vast swath of mainland Southeast Asia including the Shan states, Lan Na, Manipur, Mong Mao, the Ayutthaya Kingdom, Lan Xang and southern Arakan. However, the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia unravelled soon after Bayinnaung's death in 1581, completely collapsing by 1599. Ayutthaya seized Tenasserim and Lan Na, and Portuguese mercenaries established Portuguese rule at Thanlyin (Syriam).
The dynasty regrouped and defeated the Portuguese in 1613 and Siam in 1614. It restored a smaller, more manageable kingdom, encompassing Lower Myanmar, Upper Myanmar, Shan states, Lan Na and upper Tenasserim. The restored Toungoo kings created a legal and political framework whose basic features continued well into the 19th century. The crown completely replaced the hereditary chieftainships with appointed governorships in the entire Irrawaddy valley and greatly reduced the hereditary rights of Shan chiefs. Its trade and secular administrative reforms built a prosperous economy for more than 80 years. From the 1720s onward, the kingdom was beset with repeated Meithei raids into Upper Myanmar and a nagging rebellion in Lan Na. In 1740, the Mon of Lower Myanmar founded the Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom. Hanthawaddy forces sacked Ava in 1752, ending the 266-year-old Toungoo Dynasty.

After the fall of Ava, the Konbaung–Hanthawaddy War involved one resistance group under Alaungpaya defeating the Restored Hanthawaddy, and by 1759 he had reunited all of Myanmar and Manipur and driven out the French and the British, who had provided arms to Hanthawaddy. By 1770, Alaungpaya's heirs had subdued much of Laos and fought and won the Burmese–Siamese War against Ayutthaya and the Sino-Burmese War against Qing China.
With Burma preoccupied by the Chinese threat, Ayutthaya recovered its territories by 1770 and went on to capture Lan Na by 1776. Burma and Siam went to war until 1855, but all resulted in a stalemate, exchanging Tenasserim (to Burma) and Lan Na (to Ayutthaya). Faced with a powerful China and a resurgent Ayutthaya in the east, King Bodawpaya turned west, acquiring Arakan (1785), Manipur (1814) and Assam (1817). It was the second-largest empire in Burmese history but also one with a long ill-defined border with British India.
In 1826, Burma lost Arakan, Manipur, Assam and Tenasserim to the British in the First Anglo-Burmese War. In 1852, the British easily seized Lower Burma in the Second Anglo-Burmese War. King Mindon Min tried to modernise the kingdom and in 1875 narrowly avoided annexation by ceding the Karenni States. The British, alarmed by the consolidation of French Indochina, annexed the remainder of the country in the Third Anglo-Burmese War in 1885.
Konbaung kings extended Restored Toungoo's administrative reforms and achieved unprecedented levels of internal control and external expansion. For the first time in history, the Burmese language and culture came to predominate the entire Irrawaddy valley. The evolution and growth of Burmese literature and theatre continued, aided by an extremely high adult male literacy rate for the era (half of all males and 5% of females). Nonetheless, the extent and pace of reforms were uneven and ultimately proved insufficient to stem the advance of British colonialism.
British Burma (1885–1948)
Main articles: British rule in Burma and Burma campaign

In the 19th century, Burmese rulers sought to maintain their traditional influence in the western areas of Assam, Manipur and Arakan. Pressing them, however, was the British East India Company, which was expanding its interests eastwards over the same territory. Over the next 60 years, diplomacy, raids, treaties and compromises, known collectively as the Anglo-Burmese Wars, continued until Britain proclaimed control over most of Burma. With the fall of Mandalay, all of Burma came under British rule, being annexed on 1 January 1886.
Throughout the colonial era, many Indians arrived as soldiers, civil servants, construction workers and traders and, along with the Anglo-Burmese community, dominated commercial and civil life in Burma. Rangoon became the capital of British Burma and an important port between Calcutta and Singapore. Burmese resentment was strong, and was vented in violent riots that periodically paralysed Rangoon until the 1930s. Some of the discontent was caused by a disrespect for Burmese culture and traditions. Buddhist monks became the vanguards of the independence movement. U Wisara, an activist monk, died in prison after a 166-day hunger strike.
On 1 April 1937, Burma became a separately administered colony of Britain, and Ba Maw became the first Prime Minister and Premier of Burma. Ba Maw was an outspoken advocate for Burmese self-rule, and he opposed the participation of Britain, and by extension Burma, in World War II. He resigned from the Legislative Assembly and was arrested for sedition. In 1940, before Japan formally entered the war, Aung San formed the Burma Independence Army in Japan.
As a major battleground, Burma was devastated during World War II by the Japanese invasion. Within months after they entered the war, Japanese troops had advanced on Rangoon, and the British administration had collapsed. A Burmese Executive Administration headed by Ba Maw was established by the Japanese in August 1942. Wingate's British Chindits were formed into long-range penetration groups trained to operate deep behind Japanese lines. A similar American unit, Merrill's Marauders, followed the Chindits into the Burmese jungle in 1943.
Beginning in late 1944, allied troops launched a series of offensives that led to the end of Japanese rule in July 1945. The battles were intense with much of Burma laid waste by the fighting. Overall, the Japanese lost some 150,000 men in Burma with 1,700 prisoners taken. Although many Burmese fought initially for the Japanese as part of the Burma Independence Army, many Burmese, mostly from the ethnic minorities, served in the British Burma Army. The Burma National Army and the Arakan National Army fought with the Japanese from 1942 to 1944 but switched allegiance to the Allied side in 1945. Overall, 170,000 to 250,000 Burmese civilians died during World War II.
Following World War II, Aung San negotiated the Panglong Agreement with ethnic leaders that guaranteed the independence of Myanmar as a unified state. Aung Zan Wai, Pe Khin, Bo Hmu Aung, Sir Maung Gyi, Sein Mya Maung, Myoma U Than Kywe were among the negotiators of the historic Panglong Conference negotiated with Bamar leader General Aung San and other ethnic leaders in 1947. In 1947, Aung San became Deputy Chairman of the Executive Council of Myanmar, a transitional government. But in July 1947, political rivals assassinated Aung San and several cabinet members.
Independence (1948–1962)
Main article: Post-independence Burma (1948–1962)See also: Independence Day (Myanmar)On 4 January 1948, the nation became an independent republic, under the terms of the Burma Independence Act 1947. The new country was named the Union of Burma, with Sao Shwe Thaik as its first president and U Nu as its first prime minister. Unlike most other former British colonies and overseas territories, Burma did not become a member of the Commonwealth. A bicameral parliament was formed, consisting of a Chamber of Deputies and a Chamber of Nationalities, and multi-party elections were held in 1951–1952, 1956 and 1960.
The geographical area Burma encompasses today can be traced to the Panglong Agreement, which combined Burma Proper, which consisted of Lower Burma and Upper Burma, and the Frontier Areas, which had been administered separately by the British.
In 1961, U Thant, the Union of Burma's Permanent Representative to the United Nations and former secretary to the prime minister, was elected Secretary-General of the United Nations, a position he held for ten years.
When the non-Burman ethnic groups pushed for autonomy or federalism, alongside having a weak civilian government at the centre, the military leadership staged a coup d'état in 1962. Though incorporated in the 1947 Constitution, successive military governments construed the use of the term 'federalism' as being anti-national, anti-unity and pro-disintegration.
Military rule (1962–2011)
On 2 March 1962, the military led by General Ne Win took control of Burma through a coup d'état, and the government had been under direct or indirect control by the military since then. Between 1962 and 1974, Myanmar was ruled by a revolutionary council headed by the general. Almost all aspects of society (business, media, production) were nationalised or brought under government control under the Burmese Way to Socialism, which combined Soviet-style nationalisation and central planning.
A new constitution of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma was adopted in 1974. Until 1988, the country was ruled as a one-party system, with the general and other military officers resigning and ruling through the Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP). During this period, Myanmar became one of the world's most impoverished countries. There were sporadic protests against military rule during the Ne Win years, and these were almost always violently suppressed. On 7 July 1962, the government broke up demonstrations at Rangoon University, killing 15 students. In 1974, the military violently suppressed anti-government protests at the funeral of U Thant. Student protests in 1975, 1976, and 1977 were quickly suppressed by overwhelming force.
In 1988, unrest over economic mismanagement and political oppression by the government led to widespread pro-democracy demonstrations throughout the country known as the 8888 Uprising. Security forces killed thousands of demonstrators, and General Saw Maung staged a coup d'état and formed the State Law and Order Restoration Council (SLORC). In 1989, SLORC declared martial law after widespread protests. The military government finalised plans for People's Assembly elections on 31 May 1989. SLORC changed the country's official English name from the "Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma" to the "Union of Myanmar" on 18 June 1989 by enacting the adaptation of the expression law.
In May 1990, the government held free multiparty elections for the first time in almost 30 years, and the National League for Democracy (NLD), the party of Aung San Suu Kyi, won earning 392 out of a total 492 seats (i.e., 80% of the seats). However, the military junta refused to cede power and continued to rule the nation, first as SLORC and, from 1997, as the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC) until its dissolution in March 2011. General Than Shwe took over the Chairmanship – effectively the position of Myanmar's top ruler – from General Saw Maung in 1992 and held it until 2011.
On 23 June 1997, Myanmar was admitted into the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. On 27 March 2006, the military junta, which had moved the national capital from Yangon to a site near Pyinmana in November 2005, officially named the new capital Naypyidaw, meaning "city of the kings".


In August 2007, an increase in the price of fuel led to the Saffron Revolution led by Buddhist monks that were dealt with harshly by the government. The government cracked down on them on 26 September 2007, with reports of barricades at the Shwedagon Pagoda and monks killed. There were also rumours of disagreement within the Burmese armed forces, but none was confirmed. The military crackdown against unarmed protesters was widely condemned as part of the international reactions to the Saffron Revolution and led to an increase in economic sanctions against the Burmese Government.
In May 2008, Cyclone Nargis caused extensive damage in the densely populated rice-farming delta of the Irrawaddy Division. It was the worst natural disaster in Burmese history with reports of an estimated 200,000 people dead or missing, damages totalled to 10 billion US dollars, and as many as 1 million were left homeless. In the critical days following this disaster, Myanmar's isolationist government was accused of hindering United Nations recovery efforts. Humanitarian aid was requested, but concerns about foreign military or intelligence presence in the country delayed the entry of United States military planes delivering medicine, food, and other supplies.
In early August 2009, a conflict broke out in Shan State in northern Myanmar. For several weeks, junta troops fought against ethnic minorities including the Han Chinese, Wa, and Kachin. During 8–12 August, the first days of the conflict, as many as 10,000 Burmese civilians fled to Yunnan in neighbouring China.
Civil wars
Main article: Internal conflict in MyanmarCivil wars have been a constant feature of Myanmar's socio-political landscape since the attainment of independence in 1948. These wars are predominantly struggles for ethnic and sub-national autonomy, with the areas surrounding the ethnically Bamar central districts of the country serving as the primary geographical setting of conflict. Foreign journalists and visitors require a special travel permit to visit the areas in which Myanmar's civil wars continue.
In October 2012, the ongoing conflicts in Myanmar included the Kachin conflict, between the Pro-Christian Kachin Independence Army and the government; a civil war between the Rohingya Muslims, and the government and non-government groups in Rakhine State; and a conflict between the Shan, Lahu, and Karen minority groups, and the government in the eastern half of the country. In addition, al-Qaeda signalled an intention to become involved in Myanmar.
Armed conflict between ethnic Chinese rebels and the Myanmar Armed Forces resulted in the Kokang offensive in February 2015. The conflict had forced 40,000 to 50,000 civilians to flee their homes and seek shelter on the Chinese side of the border. During the incident, the government of China was accused of giving military assistance to the ethnic Chinese rebels. Clashes between Burmese troops and local insurgent groups have continued, fuelling tensions between China and Myanmar.
Period of liberalisation, 2011–2021
See also: 2011–2015 Myanmar political reformsThe military-backed Government had promulgated a "Roadmap to Discipline-flourishing Democracy" in 1993, but the process appeared to stall several times, until 2008 when the Government published a new draft national constitution, and organised a (flawed) national referendum which adopted it. The new constitution provided for election of a national assembly with powers to appoint a president, while practically ensuring army control at all levels.

A general election in 2010 - the first for twenty years - was boycotted by the NLD. The military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party declared victory, stating that it had been favoured by 80 per cent of the votes; fraud, however, was alleged. A nominally civilian government was then formed, with retired general Thein Sein as president.
A series of liberalising political and economic actions – or reforms – then took place. By the end of 2011 these included the release of pro-democracy leader Aung San Suu Kyi from house arrest, the establishment of the National Human Rights Commission, the granting of general amnesties for more than 200 political prisoners, new labour laws that permitted labour unions and strikes, a relaxation of press censorship, and the regulation of currency practices. In response, United States Secretary of State Hillary Clinton visited Myanmar in December 2011 – the first visit by a US Secretary of State in more than fifty years – meeting both President Thein Sein and opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi.
Aung San Suu Kyi's NLD party participated in the 2012 by-elections, facilitated by the government's abolition of the laws that previously barred it. In the April 2012 by-elections, the NLD won 43 of the 45 available seats. The 2012 by-elections were also the first time that international representatives were allowed to monitor the voting process in Myanmar.
Myanmar's improved international reputation was indicated by ASEAN's approval of Myanmar's bid for the position of ASEAN chair in 2014.

2015 general elections
General elections were held on 8 November 2015. These were the first openly contested elections held in Myanmar since the 1990 general election (which was annulled). The results gave the NLD an absolute majority of seats in both chambers of the national parliament, enough to ensure that its candidate would become president, while NLD leader Aung San Suu Kyi is constitutionally barred from the presidency.
The new parliament convened on 1 February 2016, and on 15 March 2016, Htin Kyaw was elected as the first non-military president since the military coup of 1962. On 6 April 2016, Aung San Suu Kyi assumed the newly created role of state counsellor, a role akin to a prime minister.
Coup d'état and civil war
Main articles: 2021 Myanmar coup d'état and Myanmar civil war (2021–present) See also: Myanmar protests (2021–present)In Myanmar's 2020 parliamentary election, the ostensibly ruling National League for Democracy (NLD), the party of State Counsellor Aung San Suu Kyi, competed with various other smaller parties – particularly the military-affiliated Union Solidarity and Development Party (USDP). Suu Kyi's NLD won the 2020 Myanmar general election on 8 November in a landslide. The USDP, regarded as a proxy for the military, suffered a "humiliating" defeat – even worse than in 2015 – capturing only 33 of the 476 elected seats.
As the election results began emerging, the USDP rejected them, urging a new election with the military as observers. More than 90 other smaller parties contested the vote, including more than 15 who complained of irregularities. However, election observers declared there were no major irregularities. However, despite the election commission validating the NLD's overwhelming victory, the USDP and Myanmar's military persistently alleged fraud. In January, 2021, just before the new parliament was to be sworn in, the NLD announced that Suu Kyi would retain her State Counsellor role in the upcoming government.

In the early morning of 1 February 2021, the day parliament was set to convene, the Tatmadaw, Myanmar's military, detained Suu Kyi and other members of the ruling party. The military handed power to military chief Min Aung Hlaing and declared a state of emergency for one year and began closing the borders, restricting travel and electronic communications nationwide. The military announced it would replace the existing election commission with a new one, and a military media outlet indicated new elections would be held in about one year – though the military avoided making an official commitment to that. The military expelled NLD party Members of Parliament from the capital city, Naypyidaw. By 15 March 2021 the military leadership continued to extend martial law into more parts of Yangon, while security forces killed 38 people in a single day of violence.

By the second day of the coup, thousands of protesters were marching in the streets of Yangon, and other protests erupted nationwide, largely halting commerce and transportation. Despite the military's arrests and killings of protesters, the first weeks of the coup found growing public participation, including groups of civil servants, teachers, students, workers, monks and religious leaders – even normally disaffected ethnic minorities.
The coup was immediately condemned by the United Nations Secretary General, and leaders of democratic nations. The U.S. threatened sanctions on the military and its leaders, including a "freeze" of US$1 billion of their assets in the U.S. India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Russia, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines and China refrained from criticizing the military coup. A United Nations Security Council resolution called for the release of Aung San Suu Kyi and the other detained leaders – a position shared by the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights.
International development and aid partners – business, non-governmental, and governmental – hinted at suspension of partnerships with Myanmar. Banks were closed and social media communications platforms, including Facebook and Twitter, removed Tatmadaw postings. Protesters appeared at Myanmar embassies in foreign countries. The National Unity Government then declared the formation of an armed wing on 5 May 2021, a date that is often cited as the start of a full-scale civil war. This armed wing was named the People's Defence Force (PDF) to protect its supporters from military junta attacks and as a first step towards a Federal Union Army. The civil war is ongoing as of 2024.
Geography
Main article: Geography of MyanmarMyanmar has a total area of 678,500 square kilometres (262,000 sq mi). It lies between latitudes 9° and 29°N, and longitudes 92° and 102°E. Myanmar is bordered in the northwest by the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh and the Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh states of India. Its north and northeast border is with the Tibet Autonomous Region and Yunnan for a Sino-Myanmar border total of 2,185 km (1,358 mi). It is bounded by Laos and Thailand to the southeast. Myanmar has 1,930 km (1,200 mi) of contiguous coastline along the Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea to the southwest and the south, which forms one quarter of its total perimeter.
In the north, the Hengduan Mountains form the border with China. Hkakabo Razi, located in Kachin State, at an elevation of 5,881 metres (19,295 ft), is the highest point in Myanmar. Many mountain ranges, such as the Rakhine Yoma, the Bago Yoma, the Shan Hills and the Tenasserim Hills exist within Myanmar, all of which run north-to-south from the Himalayas. The mountain chains divide Myanmar's three river systems, which are the Irrawaddy, Salween (Thanlwin), and the Sittaung rivers. The Irrawaddy River, Myanmar's longest river at nearly 2,170 kilometres (1,348 mi), flows into the Gulf of Martaban. Fertile plains exist in the valleys between the mountain chains. The majority of Myanmar's population lives in the Irrawaddy valley, which is situated between the Rakhine Yoma and the Shan Plateau.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions of Myanmar
Myanmar is divided into seven states (ပြည်နယ်) and seven regions (တိုင်းဒေသကြီး), formerly called divisions. Regions are predominantly Bamar (that is, mainly inhabited by Myanmar's dominant ethnic group). States, in essence, are regions that are home to particular ethnic minorities. The administrative divisions are further subdivided into districts, which are further subdivided into townships, wards, and villages.
Below are the number of districts, townships, cities/towns, wards, village groups and villages in each division and state of Myanmar as of 31 December 2001:
| No. | State/Region | Districts | Town ships |
Cities/ Towns |
Wards | Village groups |
Villages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kachin State | 4 | 18 | 20 | 116 | 606 | 2630 |
| 2 | Kayah State | 2 | 7 | 7 | 29 | 79 | 624 |
| 3 | Kayin State | 3 | 7 | 10 | 46 | 376 | 2092 |
| 4 | Chin State | 2 | 9 | 9 | 29 | 475 | 1355 |
| 5 | Sagaing Region | 8 | 37 | 37 | 171 | 1769 | 6095 |
| 6 | Tanintharyi Region | 3 | 10 | 10 | 63 | 265 | 1255 |
| 7 | Bago Region | 4 | 28 | 33 | 246 | 1424 | 6498 |
| 8 | Magway Region | 5 | 25 | 26 | 160 | 1543 | 4774 |
| 9 | Mandalay Region | 7 | 31 | 29 | 259 | 1611 | 5472 |
| 10 | Mon State | 2 | 10 | 11 | 69 | 381 | 1199 |
| 11 | Rakhine State | 4 | 17 | 17 | 120 | 1041 | 3871 |
| 12 | Yangon Region | 4 | 45 | 20 | 685 | 634 | 2119 |
| 13 | Shan State | 11 | 54 | 54 | 336 | 1626 | 15513 |
| 14 | Ayeyarwady Region | 6 | 26 | 29 | 219 | 1912 | 11651 |
| Total | 63 | 324 | 312 | 2548 | 13742 | 65148 |
Climate
Main article: Climate of Myanmar
Much of the country lies between the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator. It lies in the monsoon region of Asia, with its coastal regions receiving over 5,000 mm (196.9 in) of rain annually. Annual rainfall in the delta region is approximately 2,500 mm (98.4 in), while average annual rainfall in the dry zone in central Myanmar is less than 1,000 mm (39.4 in). The northern regions of Myanmar are the coolest, with average temperatures of 21 °C (70 °F). Coastal and delta regions have an average maximum temperature of 32 °C (89.6 °F). Previously and currently analysed data, as well as future projections on changes caused by climate change predict serious consequences to development for all economic, productive, social, and environmental sectors in Myanmar. In order to combat the hardships ahead and do its part to help combat climate change Myanmar has displayed interest in expanding its use of renewable energy and lowering its level of carbon emissions. Groups involved in helping Myanmar with the transition and move forward include the UN Environment Programme, Myanmar Climate Change Alliance, and the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Conservation which directed in producing the final draft of the Myanmar national climate change policy that was presented to various sectors of the Myanmar government for review.
In April 2015, it was announced that the World Bank and Myanmar would enter a full partnership framework aimed to better access to electricity and other basic services for about six million people and expected to benefit three million pregnant woman and children through improved health services. Acquired funding and proper planning has allowed Myanmar to better prepare for the impacts of climate change by enacting programs which teach its people new farming methods, rebuild its infrastructure with materials resilient to natural disasters, and transition various sectors towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Biodiversity
Main article: Wildlife of Myanmar
Myanmar is a biodiverse country with more than 16,000 plant, 314 mammal, 1131 bird, 293 reptile, and 139 amphibian species, and 64 terrestrial ecosystems including tropical and subtropical vegetation, seasonally inundated wetlands, shoreline and tidal systems, and alpine ecosystems. Myanmar houses some of the largest intact natural ecosystems in Southeast Asia, but the remaining ecosystems are under threat from land use intensification and over-exploitation. According to the IUCN Red List of Ecosystems categories and criteria more than a third of Myanmar's land area has been converted to anthropogenic ecosystems over the last 2–3 centuries, and nearly half of its ecosystems are threatened. Despite large gaps in information for some ecosystems, there is a large potential to develop a comprehensive protected area network that protects its terrestrial biodiversity.
Myanmar continues to perform badly in the global Environmental Performance Index (EPI) with an overall ranking of 153 out of 180 countries in 2016, among the worst in the South Asian region. The environmental areas where Myanmar performs worst (i.e. highest ranking) are air quality (174), health impacts of environmental issues (143) and biodiversity and habitat (142). Myanmar performs best (i.e. lowest ranking) in environmental impacts of fisheries (21) but with declining fish stocks. Despite several issues, Myanmar also ranks 64 and scores very good (i.e. a high percentage of 93.73%) in environmental effects of the agricultural industry because of an excellent management of the nitrogen cycle. Myanmar is one of the most highly vulnerable countries to climate change; this poses a number of social, political, economic and foreign policy challenges to the country. The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.18/10, ranking it 49th globally out of 172 countries.
Myanmar's slow economic growth has contributed to the preservation of much of its environment and ecosystems. Forests, including dense tropical growth and valuable teak in lower Myanmar, cover over 49% of the country, including areas of acacia, bamboo, ironwood and Magnolia champaca. Coconut and betel palm and rubber have been introduced. In the highlands of the north, oak, pine and various rhododendrons cover much of the land.
Heavy logging since the new 1995 forestry law went into effect has seriously reduced forest area and wildlife habitat. The lands along the coast support all varieties of tropical fruits and once had large areas of mangroves although much of the protective mangroves have disappeared. In much of central Myanmar (the dry zone), vegetation is sparse and stunted.
Typical jungle animals, particularly tigers, occur sparsely in Myanmar. In upper Myanmar, there are rhinoceros, wild water buffalo, clouded leopard, wild boars, deer, antelope, and elephants, which are also tamed or bred in captivity for use as work animals, particularly in the lumber industry. Smaller mammals are also numerous, ranging from gibbons and monkeys to flying foxes. The abundance of birds is notable with over 800 species, including parrots, myna, peafowl, red junglefowl, weaverbirds, crows, herons, and barn owl. Among reptile species there are crocodiles, geckos, cobras, Burmese pythons, and turtles. Hundreds of species of freshwater fish are wide-ranging, plentiful and are very important food sources.
Government and politics

 Head of Government, Deputy Head of Government, and acting Head of State
Head of Government, Deputy Head of Government, and acting Head of State
- Min Aung Hlaing, Prime Minister and Chairman of the State Administration Council
- Soe Win, Deputy Prime Minister and Vice Chairman of the State Administration Council
- Myint Swe, acting President of Myanmar
Myanmar operates de jure as a unitary assembly-independent republic under its 2008 constitution. But in February 2021, the civilian government led by Aung San Suu Kyi, was deposed by the Tatmadaw. In February 2021, Myanmar military declared a one-year state emergency and First Vice President Myint Swe became the Acting President of Myanmar and handed the power to the Commander-in-Chief of Defence Services Min Aung Hlaing and he assumed the role Chairman of the State Administration Council, then Prime Minister. The President of Myanmar acts as the de jure head of state and the Chairman of the State Administration Council acts as the de facto head of government.

The constitution of Myanmar, its third since independence, was drafted by its military rulers and published in September 2008. The country is governed as a parliamentary system with a bicameral legislature (with an executive president accountable to the legislature), with 25% of the legislators appointed by the military and the rest elected in general elections.
The legislature, called the Assembly of the Union, is bicameral and made up of two houses: The 224-seat upper House of Nationalities and the 440-seat lower House of Representatives. The upper house consists 168 members who are directly elected and 56 who are appointed by the Burmese Armed Forces. The lower house consists of 330 members who are directly elected and 110 who are appointed by the armed forces.
Political culture
The major political parties are the National League for Democracy and the Union Solidarity and Development Party.
Myanmar's army-drafted constitution was approved in a referendum in May 2008. The results, 92.4% of the 22 million voters with an official turnout of 99%, are considered suspect by many international observers and by the National League of Democracy with reports of widespread fraud, ballot stuffing, and voter intimidation.
The elections of 2010 resulted in a victory for the military-backed Union Solidarity and Development Party. Various foreign observers questioned the fairness of the elections. One criticism of the election was that only government-sanctioned political parties were allowed to contest in it and the popular National League for Democracy was declared illegal. However, immediately following the elections, the government ended the house arrest of the democracy advocate and leader of the National League for Democracy, Aung San Suu Kyi, and her ability to move freely around the country is considered an important test of the military's movement toward more openness.
Myanmar rates as a corrupt nation on the Corruption Perceptions Index with a rank of 130th out of 180 countries worldwide, with 1st being least corrupt, as of 2019.
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of MyanmarThough the country's foreign relations, particularly with Western nations, have historically been strained, the situation has markedly improved since the reforms following the 2010 elections. After years of diplomatic isolation and economic and military sanctions, the United States relaxed curbs on foreign aid to Myanmar in November 2011 and announced the resumption of diplomatic relations on 13 January 2012 The European Union has placed sanctions on Myanmar, including an arms embargo, cessation of trade preferences, and suspension of all aid with the exception of humanitarian aid.
Sanctions imposed by the United States and European countries against the former military government, coupled with boycotts and other direct pressure on corporations by supporters of the democracy movement, have resulted in the withdrawal from the country of most U.S. and many European companies. Despite Western isolation, Asian corporations have generally remained willing to continue investing in the country and to initiate new investments, particularly in natural resource extraction. The country has close relations with neighbouring India and China with several Indian and Chinese companies operating in the country. Under India's Look East policy, fields of co-operation between India and Myanmar include remote sensing, oil and gas exploration, information technology, hydropower and construction of ports and buildings. Myanmar also has close political relations with Vietnam and Japan.
In May 2013, Thein Sein became the first Myanmar president to visit the White House in 47 years. President Barack Obama praised the former general for political and economic reforms and the cessation of tensions between Myanmar and the United States. Political activists objected to the visit because of concerns over human rights abuses in Myanmar, but Obama assured Thein Sein that Myanmar will receive U.S. support. The two governments agreed to sign a bilateral trade and investment framework agreement on 21 May 2013.
In June 2013, Myanmar held its first ever summit, the World Economic Forum on East Asia 2013. A regional spinoff of the annual World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, the summit was held on 5–7 June and attended by 1,200 participants, including 10 heads of state, 12 ministers and 40 senior directors from around the world.
Military
Main article: Armed forces of MyanmarSince the late 1950s, Myanmar's military has had major roles in Myanmar's politics.

Myanmar has received extensive military aid from China in the past. Myanmar has been a member of ASEAN since 1997. Though it gave up its turn to hold the ASEAN chair and host the ASEAN Summit in 2006, it chaired the forum and hosted the summit in 2014. In November 2008, Myanmar's political situation with neighbouring Bangladesh became tense as they began searching for natural gas in a disputed block of the Bay of Bengal. Controversy surrounding the Rohingya population also remains an issue between Bangladesh and Myanmar.
Myanmar's armed forces are known as the Tatmadaw, which numbers 488,000. The Tatmadaw comprises the Army, the Navy, and the Air Force. The country ranked twelfth in the world for its number of active troops in service. The military is very influential in Myanmar, with all top cabinet and ministry posts usually held by military officials. Official figures for military spending are not available. Estimates vary widely because of uncertain exchange rates, but Myanmar's military forces' expenses are high. Myanmar imports most of its weapons from Russia, Ukraine, China and India.
Myanmar is building a research nuclear reactor near Pyin Oo Lwin with help from Russia. It is one of the signatories of the nuclear non-proliferation pact since 1992 and a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) since 1957. The military junta had informed the IAEA in September 2000 of its intention to construct the reactor. In 2010 as part of the leaked diplomatic cables, Myanmar was suspected of using North Korean construction teams to build a fortified surface-to-air missile facility. As of 2019, the United States Bureau of Arms Control assessed that Myanmar is not in violation of its obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty but that the Myanmar government had a history of non-transparency on its nuclear programs and aims.
Until 2005, the United Nations General Assembly annually adopted a detailed resolution about the situation in Myanmar by consensus. But in 2006 a divided United Nations General Assembly voted through a resolution that strongly called upon the government of Myanmar to end its systematic violations of human rights. In January 2007, Russia and China vetoed a draft resolution before the United Nations Security Council calling on the government of Myanmar to respect human rights and begin a democratic transition. South Africa also voted against the resolution.
Human rights and internal conflicts
Main articles: Human rights in Myanmar and Internal conflict in Myanmar| This section may lend undue weight to certain ideas, incidents, or controversies. Please help to create a more balanced presentation. Discuss and resolve this issue before removing this message. (November 2020) |

There is consensus that the former military regime in Myanmar (1962–2010) was one of the world's most repressive and abusive regimes. In November 2012, Samantha Power, Barack Obama's Special Assistant to the President on Human Rights, wrote on the White House blog that "Serious human rights abuses against civilians in several regions continue, including against women and children." Members of the United Nations and major international human rights organisations have issued repeated and consistent reports of widespread and systematic human rights violations in Myanmar. The United Nations General Assembly has repeatedly called on the Burmese military junta to respect human rights and in November 2009 the General Assembly adopted a resolution "strongly condemning the ongoing systematic violations of human rights and fundamental freedoms" and calling on the Burmese military regime "to take urgent measures to put an end to violations of international human rights and humanitarian law."
International human rights organisations including Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International have repeatedly documented and condemned widespread human rights violations in Myanmar. The Freedom in the World 2011 report by Freedom House notes, "The military junta has ... suppressed nearly all basic rights; and committed human rights abuses with impunity." In July 2013, the Assistance Association for Political Prisoners indicated that there were approximately 100 political prisoners being held in Burmese prisons. Evidence gathered by a British researcher was published in 2005 regarding the extermination or "Burmisation" of certain ethnic minorities, such as the Karen, Karenni and Shan.

Based on the evidence gathered by Amnesty photographs and video of the ongoing armed conflict between the Myanmar military and the Arakan Army (AA), attacks escalated on civilians in Rakhine State. Ming Yu Hah, Amnesty International's Deputy Regional Director for Campaigns said, the UN Security Council must urgently refer the situation in Myanmar to the International Criminal Court. The military is notorious for rampant use of sexual violence.
Child soldiers
Child soldiers were reported in 2012 to have played a major part in the Burmese Army. The Independent reported in June 2012 that "Children are being sold as conscripts into the Burmese military for as little as $40 and a bag of rice or a can of petrol." In September 2012, the Myanmar Armed Forces released 42 child soldiers, and the International Labour Organization met with representatives of the government as well as the Kachin Independence Army to secure the release of more child soldiers.
Slavery and human trafficking
Further information: Sex trafficking in MyanmarForced labour and human trafficking are common in Myanmar. Human trafficking happens mostly to women who are unemployed and have low incomes. They are deceived by brokers that better opportunities and wages exist for them abroad. In 2017, the government reported 185 trafficking cases. The government of Burma makes little effort to eliminate human trafficking. The U.S. State Department reported that both the government and Tatmadaw were complicit in sex and labour trafficking. Women and girls from all ethnic groups and foreigners have been victims of sex trafficking in Myanmar. They are forced into prostitution, marriages or pregnancies. Sex trafficking in Myanmar has been fuelled by factors like internal conflict, political instability, land confiscation, poor border management, and government restrictions on providing travel documents.
A cyber-scam industry in Myanmar's borderlands has involved human trafficking, forced labour and other abuses. Many of the scam centres are in territories controlled by junta allies like the Border Guard Force. In August 2023, a report from the Office of the U.N. High Commissioner for Human Rights noted that at least 120,000 people in Myanmar were trapped in such centres by criminal gangs.
Genocide allegations and crimes against Rohingya people

The Rohingya people have consistently faced human rights abuses by the Burmese regime that has refused to acknowledge them as Burmese citizens (despite some of them having lived in Burma for over three generations)—the Rohingya have been denied Burmese citizenship since the enactment of a 1982 citizenship law. The Burmese regime has attempted to forcibly expel Rohingya and bring in non-Rohingyas to replace them—this policy has resulted in the expulsion of approximately half of the 800,000 Rohingya from Burma, while the Rohingya people have been described as "among the world's least wanted" and "one of the world's most persecuted minorities."
Rohingya are not allowed to travel without official permission, are banned from owning land, and are required to sign a commitment to have no more than two children. As of July 2012, the Myanmar government does not include the Rohingya minority group—classified as stateless Bengali Muslims from Bangladesh since 1982—on the government's list of more than 130 ethnic races and, therefore, the government states that they have no claim to Myanmar citizenship.
Since the democratic transition began in 2011, there has been continuous violence as 280 people have been killed and 140,000 forced to flee from their homes in the Rakhine state in 2014. A UN envoy reported in March 2013 that unrest had re-emerged between Myanmar's Buddhist and Muslim communities, with violence spreading to towns that are located closer to Yangon.
Organ trading
The military forces took over Myanmar in 2021. A yearlong investigation conducted by CNN reveals that half of Myanmar's 54 million population lives below poverty line. This drives many of them to the extreme measures such as online organ trade. This illegal action of selling their personal organs can earn them a payment equal to a two-year salary. Many advertise the organ they wish to donate on social media, this is a endless cycle as families time and again find themselves online to trade their organs as money runs out.
Government reforms
According to the Crisis Group, since Myanmar transitioned to a new government in August 2011, the country's human rights record has been improving. Previously giving Myanmar its lowest rating of 7, the 2012 Freedom in the World report also notes improvement, giving Myanmar a 6 for improvements in civil liberties and political rights, the release of political prisoners, and a loosening of restrictions. In 2013, Myanmar improved yet again, receiving a score of 5 in civil liberties and 6 in political freedoms.
The government has assembled a National Human Rights Commission that consists of 15 members from various backgrounds. Several activists in exile, including Thee Lay Thee Anyeint members, have returned to Myanmar after President Thein Sein's invitation to expatriates to return home to work for national development. In an address to the United Nations Security Council on 22 September 2011, Myanmar's Foreign Minister Wunna Maung Lwin confirmed the government's intention to release prisoners in the near future.
The government has also relaxed reporting laws, but these remain highly restrictive. In September 2011, several banned websites, including YouTube, Democratic Voice of Burma and Voice of America, were unblocked. A 2011 report by the Hauser Center for Nonprofit Organizations found that, while contact with the Myanmar government was constrained by donor restrictions, international humanitarian non-governmental organisations (NGOs) see opportunities for effective advocacy with government officials, especially at the local level. At the same time, international NGOs are mindful of the ethical quandary of how to work with the government without bolstering or appeasing it.

Following Thein Sein's first ever visit to the UK and a meeting with Prime Minister David Cameron, the Myanmar president declared that all of his nation's political prisoners will be released by the end of 2013, in addition to a statement of support for the well-being of the Rohingya Muslim community. In a speech at Chatham House, he revealed that "We are reviewing all cases. I guarantee to you that by the end of this year, there will be no prisoners of conscience in Myanmar."
Homosexual acts are illegal in Myanmar and can be punishable by life imprisonment.
In 2016, Myanmar leader Aung San Suu Kyi was accused of failing to protect Myanmar's Muslim minority. Since August 2017 Doctors Without Borders have treated 113 Rohingya refugee females for sexual assault with all but one describing military assailants.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Myanmar Further information: Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia), Transport in Myanmar, and Oil and gas industry in MyanmarMyanmar's economy is one of the fastest growing economies in the world with a nominal GDP of US$76.09 billion in 2019 and an estimated purchasing power adjusted GDP of US$327.629 billion in 2017 according to the World Bank. Foreigners are able to legally lease but not own property. In December 2014, Myanmar set up its first stock exchange, the Yangon Stock Exchange.
The informal economy's share in Myanmar is one of the biggest in the world and is closely linked to corruption, smuggling and illegal trade activities. In addition, decades of civil war and unrest have contributed to Myanmar's current levels of poverty and lack of economic progress. Myanmar lacks adequate infrastructure. Goods travel primarily across the Thai border (where most illegal drugs are exported) and along the Irrawaddy River. Notably, opium production in Myanmar is the world's second-largest source of opium after Afghanistan, producing some 25% of the world's opium, forming part of the Golden Triangle. While opium poppy cultivation in Myanmar had declined year-on-year since 2015, cultivation area increased by 33% totalling 40,100 hectares alongside an 88% increase in yield potential to 790 tonnes in 2022 according to latest data from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) Myanmar Opium Survey 2022. With that said, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has also warned that opium production in Myanmar may rise again if the economic crunch brought on by COVID-19 and the country's February 1 military coup persists, with significant public health and security consequences for much of Asia. At the same time, the Golden Triangle, and specifically Shan State of Myanmar, is believed to be the largest methamphetamine producing area in the world. The growing signs of an intensification of methamphetamine manufacturing activity within and around the Golden Triangle, and a corresponding decrease in the number of production facilities dismantled in other parts of the region, suggests that methamphetamine manufacture in East and Southeast Asia is now consolidated into the lower Mekong region. Countries in East and Southeast Asia have collectively witnessed sustained increases in seizures of methamphetamine over the last decade, totalling over 171 tons and a record of over 1 billion methamphetamine tablets in 2021 according to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, more than any other part of the world. In April and May 2020, Myanmar authorities reported Asia's largest ever drug operation in Shan State totalling what was believed to be 193 million methamphetamine tablets, hundreds of kilogrammes of crystal methamphetamine as well as some heroin, and over 162,000 litres and 35.5 tons of drug precursors as well as sophisticated production equipment and several staging and storage facilities.
Both China and India have attempted to strengthen ties with the government for economic benefit in the early 2010s. Many Western nations, including the United States and Canada, and the European Union, historically imposed investment and trade sanctions on Myanmar. The United States and European Union eased most of their sanctions in 2012. From May 2012 to February 2013, the United States began to lift its economic sanctions on Myanmar "in response to the historic reforms that have been taking place in that country." Foreign investment comes primarily from China, Singapore, the Philippines, South Korea, India, and Thailand. The military has stakes in some major industrial corporations of the country (from oil production and consumer goods to transportation and tourism).
Economic history

Under the British administration, the people of Burma were at the bottom of the social hierarchy, with Europeans at the top, Indians, Chinese, and Christianized minorities in the middle, and Buddhist Burmese at the bottom. Forcefully integrated into the world economy, Burma's economy grew by involving itself with extractive industries and cash crop agriculture. However, much of the wealth was concentrated in the hands of Europeans. The country became the world's largest exporter of rice, mainly to European markets, while other colonies like India suffered mass starvation. Being a follower of free market principles, the British opened up the country to large-scale immigration with Rangoon exceeding New York City as the greatest immigration port in the world in the 1920s. Historian Thant Myint-U states, "This was out of a total population of only 13 million; it was equivalent to the United Kingdom today taking 2 million people a year." By then, in most of Burma's largest cities, Rangoon, Akyab, Bassein and Moulmein, the Indian immigrants formed a majority of the population. The Burmese under British rule felt helpless, and reacted with a "racism that combined feelings of superiority and fear".
Crude oil production, an indigenous industry of Yenangyaung, was taken over by the British and put under Burmah Oil monopoly. British Burma began exporting crude oil in 1853. European firms produced 75% of the world's teak. The wealth was, however, mainly concentrated in the hands of Europeans. In the 1930s, agricultural production fell dramatically as international rice prices declined and did not recover for several decades. During the Japanese invasion of Burma in World War II, the British followed a scorched earth policy. They destroyed major government buildings, oil wells and mines that developed for tungsten (Mawchi), tin, lead and silver to keep them from the Japanese. Myanmar was bombed extensively by the Allies.
After independence, the country was in ruins with its major infrastructure completely destroyed. With the loss of India, Burma lost relevance and obtained independence from the British. After a parliamentary government was formed in 1948, Prime Minister U Nu embarked upon a policy of nationalisation and the state was declared the owner of all of the land in Burma. The government tried to implement an eight-year plan partly financed by injecting money into the economy, but this caused inflation to rise. The 1962 coup d'état was followed by an economic scheme called the Burmese Way to Socialism, a plan to nationalise all industries, with the exception of agriculture. While the economy continued to grow at a slower rate, the country eschewed a Western-oriented development model, and by the 1980s, was left behind capitalist powerhouses like Singapore which were integrated with Western economies. Myanmar asked for admittance to a least developed country status in 1987 to receive debt relief.
Agriculture

The major agricultural product is rice, which covers about 60% of the country's total cultivated land area. Rice accounts for 97% of total food grain production by weight. Through collaboration with the International Rice Research Institute, 52 modern rice varieties were released in the country between 1966 and 1997, helping increase national rice production to 14 million tons in 1987 and to 19 million tons in 1996. By 1988, modern varieties were planted on half of the country's ricelands, including 98 percent of the irrigated areas. In 2008 rice production was estimated at 50 million tons.
Extractive industries
Myanmar produces precious stones such as rubies, sapphires, pearls, and jade. Rubies are the biggest earner; 90% of the world's rubies come from the country, whose red stones are prized for their purity and hue. Thailand buys the majority of the country's gems. Myanmar's "Valley of Rubies", the mountainous Mogok area, 200 km (120 mi) north of Mandalay, is noted for its rare pigeon's blood rubies and blue sapphires.
Many U.S. and European jewellery companies, including Bulgari, Tiffany and Cartier, refuse to import these stones based on reports of deplorable working conditions in the mines. Human Rights Watch has encouraged a complete ban on the purchase of Burmese gems based on these reports and because nearly all profits go to the ruling junta, as the majority of mining activity in the country is government-run. The government of Myanmar controls the gem trade by direct ownership or by joint ventures with private owners of mines.
Rare-earth elements are also a significant export, as Myanmar supplies around 10% of the world's rare earths. Conflict in Kachin State has threatened the operations of its mines as of February 2021.
Other industries include agricultural goods, textiles, wood products, construction materials, gems, metals, oil and natural gas. Myanmar Engineering Society has identified at least 39 locations capable of geothermal power production and some of these hydrothermal reservoirs lie quite close to Yangon which is a significant underutilised resource for electrical production.
Tourism
Main article: Tourism in Myanmar

The government receives a significant percentage of the income of private-sector tourism services. The most popular available tourist destinations in Myanmar include big cities such as Yangon and Mandalay; religious sites in Mon State, Pindaya, Bago and Hpa-An; nature trails in Inle Lake, Kengtung, Putao, Pyin Oo Lwin; ancient cities such as Bagan and Mrauk-U; as well as beaches in Nabule, Ngapali, Ngwe-Saung, and Mergui. Nevertheless, much of the country is off-limits to tourists, and interactions between foreigners and the people of Myanmar, particularly in the border regions, are subject to police scrutiny. They are not to discuss politics with foreigners, under penalty of imprisonment and, in 2001, the Myanmar Tourism Promotion Board issued an order for local officials to protect tourists and limit "unnecessary contact" between foreigners and ordinary Burmese people.
The most common way for travellers to enter the country is by air. According to the website Lonely Planet, getting into Myanmar is problematic: "No bus or train service connects Myanmar with another country, nor can you travel by car or motorcycle across the border – you must walk across." They further state that "It is not possible for foreigners to go to/from Myanmar by sea or river." There are a few border crossings that allow the passage of private vehicles, such as the border between Ruili (China) to Mu-se, the border between Htee Kee (Myanmar) and Phu Nam Ron (Thailand)—the most direct border between Dawei and Kanchanaburi, and the border between Myawaddy and Mae Sot, Thailand. At least one tourist company has successfully run commercial overland routes through these borders since 2013.
Flights are available from most countries, though direct flights are limited to mainly Thai and other ASEAN airlines. According to Eleven magazine, "In the past, there were only 15 international airlines and increasing numbers of airlines have begun launching direct flights from Japan, Qatar, Taiwan, South Korea, Germany and Singapore."
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Myanmar
| Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Million | ||
| 1950 | 17.1 | ||
| 2000 | 46.1 | ||
| 2021 | 53.8 | ||
The provisional results of the 2014 Myanmar Census showed that the total population was 51,419,420. This figure includes an estimated 1,206,353 persons in parts of northern Rakhine State, Kachin State and Kayin State who were not counted. People who were out of the country at the time of the census are not included in these figures. There are over 600,000 registered migrant workers from Myanmar in Thailand, and millions more work illegally. Burmese citizens account for 80% of all migrant workers in Thailand. At the beginning of the 20th century, Burma's population was approximately 10 million. The national population density is 76 per square kilometre (200/sq mi), among the lowest in Southeast Asia.
Myanmar's fertility rate in 2011 was 2.23, slightly above the replacement level and low compared to Southeast Asian countries of similar economic standing. There has been a significant decline in fertility in the 2000s, from a rate of 4.7 children per woman in 1983, down to 2.4 in 2001, despite the absence of any national population policy. The fertility rate is much lower in urban areas.
The relatively rapid decline in fertility is attributed to several factors, including extreme delays in marriage (almost unparalleled among developing countries in the region), the prevalence of illegal abortions, and the high proportion of single, unmarried women of reproductive age, with 25.9% of women aged 30–34 and 33.1% of men and women aged 25–34 being single.
These patterns stem from economic dynamics, including high income inequality, which results in residents of reproductive age opting for delay of marriage and family-building in favour of attempting to find employment and establish some form of wealth; the average age of marriage in Myanmar is 27.5 for men, 26.4 for women.
Largest cities
Further information: List of cities and largest towns in Myanmar| Largest cities or towns in Myanmar geohive.com | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Division | Pop. | ||||||
 Yangon  Mandalay |
1 | Yangon | Yangon | 5,211,431 |  Naypyidaw  Bago | ||||
| 2 | Mandalay | Mandalay | 1,225,546 | ||||||
| 3 | Naypyidaw | Naypyidaw | 1,160,242 | ||||||
| 4 | Bago | Bago | 491,434 | ||||||
| 5 | Hpa-An | Kayin | 421,575 | ||||||
| 6 | Taunggyi | Shan | 381,636 | ||||||
| 7 | Monywa | Sagaing | 372,095 | ||||||
| 8 | Myitkyina | Kachin | 306,949 | ||||||
| 9 | Mawlamyine | Mon | 289,388 | ||||||
| 10 | Magway | Magway | 289,247 | ||||||
Ethnic groups
Main article: List of ethnic groups in Myanmar| Ethnic Composition in Burma/Myanmar (rough estimate) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnic group | Per cent | |||
| Bamar | 68% | |||
| Shan | 10% | |||
| Karen | 7% | |||
| Rakhine | 3.5% | |||
| Han-Chinese | 3% | |||
| Mon | 2% | |||
| Indians | 2% | |||
| Kachin | 1.5% | |||
| Chin | 1% | |||
| Kayah | 0.8% | |||
| Other groups | 5% | |||

Myanmar is ethnically diverse. The government recognises 135 distinct ethnic groups. There are at least 108 different ethnolinguistic groups in Myanmar, consisting mainly of distinct Tibeto-Burman peoples, but with sizeable populations of Tai–Kadai, Hmong–Mien, and Austroasiatic (Mon–Khmer) peoples.
The Bamar form an estimated 68% of the population. 10% of the population are Shan. The Kayin make up 7% of the population. The Rakhine people constitute 4% of the population. Overseas Chinese form approximately 3% of the population. Myanmar's ethnic minority groups prefer the term "ethnic nationality" over "ethnic minority" as the term "minority" furthers their sense of insecurity in the face of what is often described as "Burmanisation"—the proliferation and domination of the dominant Bamar culture over minority cultures.
Mon, who form 2% of the population, are ethno-linguistically related to the Khmer. Overseas Indians are 2%. The remainder are Kachin, Chin, Rohingya, Anglo-Indians, Gurkha, Nepali and other ethnic minorities. Included in this group are the Anglo-Burmese. Once forming a large and influential community, the Anglo-Burmese left the country in steady streams from 1958 onwards, principally to Australia and the United Kingdom. It is estimated that 52,000 Anglo-Burmese remain in Myanmar. As of 2009, 110,000 Burmese refugees were living in refugee camps in Thailand.
Refugee camps exist along Indian, Bangladeshi and Thai borders while several thousand are in Malaysia. Conservative estimates state that there are over 295,800 minority refugees from Myanmar, with the majority being Rohingya, Karen, and Karenni are principally located along the Thai-Myanmar border. There are nine permanent refugee camps along the Thai-Myanmar border, most of which were established in the mid-1980s. The refugee camps are under the care of the Thai-Burma Border Consortium (TBBC). Since 2006, over 55,000 Burmese refugees have been resettled in the United States.
The persecution of Burmese Indians, Burmese Chinese and other ethnic groups after the military coup headed by General Ne Win in 1962 led to the expulsion or emigration of 300,000 people. They migrated to escape racial discrimination and the wholesale nationalisation of private enterprise that took place in 1964. The Anglo-Burmese at this time either fled the country or changed their names and blended in with the broader Burmese society.
Many Rohingya Muslims have fled Myanmar. Many refugees headed to neighbouring Bangladesh, including 200,000 in 1978 as a result of the King Dragon operation in Arakan. 250,000 more left in 1991. Since August 2017, an estimated 23,000-43,700 Rohingya have been killed in the ongoing Rohingya genocide, and another 730,000 have fled to Bangladesh.
Languages
Main article: Languages of MyanmarMyanmar is home to four major language families: Sino-Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, Austroasiatic, and Indo-European. Sino-Tibetan languages are most widely spoken. They include Burmese, Karen, Kachin, Chin, and Chinese (mainly Hokkien). The primary Tai–Kadai language is Shan. Mon, Palaung, and Wa are the major Austroasiatic languages spoken in Myanmar. The two major Indo-European languages are Pali, the liturgical language of Theravada Buddhism, and English. More than a hundred languages are spoken in total. Since many of them are known only within small tribes around the country, they may have been lost (many if not all) after a few generations.
Burmese, the mother tongue of the Bamar and official language of Myanmar, is related to Tibetan and Chinese. It is written in a script consisting of circular and semi-circular letters, which were adapted from the Mon script, which in turn was developed from a southern Indian script in the 5th century. The earliest known inscriptions in the Burmese script date from the 11th century. It is also used to write Pali, the sacred language of Theravada Buddhism, as well as several ethnic minority languages, including Shan, several Karen dialects, and Kayah (Karenni), with the addition of specialised characters and diacritics for each language.
Religion
Main article: Religion in MyanmarMany religions are practised in Myanmar. Religious edifices and orders have been in existence for many years. The Christian and Muslim populations do, however, face religious persecution and it is hard, if not impossible, for non-Buddhists to join the army or get government jobs, the main route to success in the country. Such persecution and targeting of civilians is particularly notable in eastern Myanmar, where over 3,000 villages have been destroyed in the past ten years. More than 200,000 Muslims have fled to Bangladesh by 2007 to escape persecution.
A large majority of the population practices Buddhism; estimates range from 80% to 89%. According to 2014 Myanmar Census, 87.9% of the population identifies as Buddhists. Theravāda Buddhism is the most widespread. There are some 500,000 Buddhist monks and 75,000 nuns in this country of 54 million. Other religions are practised largely without obstruction, with the notable exception of some religious minorities such as the Rohingya people, who have continued to have their citizenship status denied and treated as illegal immigrants instead, and Christians in Chin State.
According to 2014 census, 6.2% of the population identifies as Christian; 4.3% as Muslim; 0.8% as followers of tribal religions; 0.5% as Hindus; 0.2% as followers of other religions; and 0.1% follow no religion. According to the 2010 estimates of the Pew Research Center, 7% of the population is Christian; 4% is Muslim; 1% follows traditional animistic beliefs; and 2% follow other religions, including Mahayana Buddhism, Hinduism, and East Asian religions. Jehovah's Witnesses have been present since 1914 and have about 80 congregations around the country and a branch office in Yangon publishing in 16 languages. A tiny Jewish community in Yangon had a synagogue but no resident rabbi.

Although Hinduism is practised by 0.5% of the population, it was a major religion in Myanmar's past. Burmese folk religion is practised by many Bamars alongside Buddhism.
Health
Main article: Health in MyanmarThe general state of health care in Myanmar is poor. The government spends anywhere from 0.5% to 3% of the country's GDP on health care, consistently ranking among the lowest in the world. Although health care is nominally free, in reality, patients have to pay for medicine and treatment, even in public clinics and hospitals. Public hospitals lack many of the basic facilities and equipment. The 2010 maternal mortality rate per 100,000 births for Myanmar is 240. This is compared with 219.3 in 2008 and 662 in 1990. The under 5 mortality rate, per 1,000 births is 73 and the neonatal mortality as a percentage of under 5's mortality is 47. According to Doctors without Borders, 25,000 Burmese AIDS patients died in 2007, deaths that could largely have been prevented by antiretroviral therapy drugs and proper treatment.
HIV/AIDS, recognised as a disease of concern by the Myanmar Ministry of Health, is most prevalent among sex workers and intravenous drug users. In 2005, the estimated adult HIV prevalence rate in Myanmar was 1.3% (200,000–570,000 people), according to UNAIDS, and early indicators of any progress against the HIV epidemic are inconsistent. However, the National AIDS Programme Myanmar found that 32% of sex workers and 43% of intravenous drug users in Myanmar have HIV.
With a score of 15.7 in the 2024 Global Hunger Index, Myanmar has a level of hunger that is moderate.
Education
Main article: Education in Myanmar
According to the UNESCO Institute of Statistics, Myanmar's official literacy rate as of 2000 was 90%. Historically, Myanmar has had high literacy rates. The educational system of Myanmar is operated by the government agency, the Ministry of Education. The education system is based on the United Kingdom's system after nearly a century of British and Christian presences in Myanmar. Nearly all schools are government-operated, but there has been an increase in privately funded English language schools in the early 21st century. Schooling is compulsory until the end of elementary school, approximately 9 years old, while the compulsory schooling age is 15 or 16 at international level.
There are 101 universities, 12 institutes, 9 degree colleges and 24 colleges in Myanmar, a total of 146 higher education institutions. There are 10 technical training schools, 23 nursing training schools, 1 sport academy and 20 midwifery schools. There are four international schools acknowledged by WASC and College Board—The International School Yangon, Myanmar International School, Yangon International School, and International School of Myanmar in Yangon. Myanmar was ranked 125th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
Crime
Further information: Crime in MyanmarMyanmar had a murder rate of 15.2 per 100,000 population with a total of 8,044 murders in 2012. Factors influencing Myanmar's high murder rate include communal violence and armed conflict. Myanmar is one of the world's most corrupt nations. The 2012 Transparency International Corruption Perceptions Index ranked the country at number 171, out of 176 countries in total. Myanmar is the world's second largest producer of opium after Afghanistan, producing some 25% of the world's opium, and forms part of the Golden Triangle. The opium industry was a monopoly during colonial times and has since been illegally operated by corrupt officials in the Burmese military and rebel fighters, primarily as the basis for heroin manufacture. Myanmar is the largest producer of methamphetamines in the world, with the majority of Ya ba found in Thailand produced in Myanmar, particularly in the Golden Triangle and northeastern Shan State, which borders Thailand, Laos and China. Burmese-produced ya ba is typically trafficked to Thailand via Laos, before being transported through the northeastern Thai region of Isan.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Myanmar
A diverse range of indigenous cultures exist in Myanmar, with majority culture primarily Buddhist and Bamar. Bamar culture has been influenced by the cultures of neighbouring countries, manifested in its language, cuisine, music, dance and theatre. The arts, particularly literature, have historically been influenced by the local form of Theravada Buddhism. Considered the national epic of Myanmar, the Yama Zatdaw, an adaptation of India's Ramayana, has been influenced greatly by Thai, Mon, and Indian versions of the play. Buddhism is practised along with nat worship, which involves elaborate rituals to propitiate one from a pantheon of 37 nats.

In a traditional village, the monastery is the centre of cultural life. Monks are venerated and supported by the lay people. A novitiation ceremony called shinbyu is the most important coming of age events for a boy, during which he enters the monastery for a short time. All male children in Buddhist families are encouraged to be a novice (beginner for Buddhism) before the age of twenty and to be a monk after the age of twenty. Girls have ear-piercing ceremonies (နားသ) at the same time. Burmese culture is most evident in villages where local festivals are held throughout the year, the most important being the pagoda festival. Many villages have a guardian nat, and superstition and taboos are commonplace.

British colonial rule introduced Western elements of culture to Myanmar. Myanmar's education system is modelled after that of the United Kingdom. Colonial architectural influences are most evident in major cities such as Yangon. Many ethnic minorities, particularly the Karen in the southeast and the Kachin and Chin who populate the north and northeast, practice Christianity. According to The World Factbook, the Burman population is 68% and the ethnic groups constitute 32%. In contrast, the exiled leaders and organisations claim the country is 40% ethnic.
Cuisine
Main article: Burmese cuisineBurmese cuisine is characterised by extensive use of fish products such as fish sauce, ngapi (fermented seafood) and dried prawn. Mohinga is the traditional breakfast dish and is Myanmar's national dish. Seafood is a common ingredient in coastal cities, while meat and poultry are more commonly used in landlocked cities like Mandalay. Freshwater fish and shrimp have been incorporated into inland cooking as a primary source of protein and are used in a variety of ways, fresh, salted whole or filleted, salted and dried, made into a salty paste, or fermented sour and pressed. Burmese cuisine also includes a variety of salads (a thoke), centred on one major ingredient, ranging from starches like rice, wheat and rice noodles, glass noodles and vermicelli, to potato, ginger, tomato, kaffir lime, long bean, and lahpet (pickled tea leaves).
Sport
Main article: Sport in MyanmarThe Lethwei, Bando, Banshay, and Pongyi thaing martial arts and chinlone are traditional sports in Myanmar. Football is played all over the country, even in villages, and its national team is ruled by the Myanmar Football Federation. The 2013 Southeast Asian Games took place in Naypyidaw, Yangon, Mandalay and Ngwesaung Beach in December representing the third occasion that the event has been staged in Myanmar. Myanmar previously hosted the games in 1961 and 1969.
Art
Main articles: Art of Myanmar and Myanmar architectureBurmese traditional art concepts are popular and respected by the Burmese people and people from abroad. Burmese contemporary art has developed quite rapidly on its own terms. Artists born after the 1980s have had greater chances of art practice outside the country.
One of the first to study western art was Ba Nyan. Together with Ngwe Gaing and a handful of other artists, they were the pioneers of western painting style. Later on most young children learned the concepts from them. Some well known contemporary artists are Lun Gywe, Aung Kyaw Htet, MPP Yei Myint, Myint Swe, Min Wai Aung, Aung Myint, Kin Maung Yin, Po Po and Zaw Zaw Aung.
Media and communications
Main article: Media of MyanmarBecause of Myanmar's political climate, there are not many media companies in relation to the country's population. Some are privately owned. All programming must meet with the approval of the censorship board. The Burmese government announced on 20 August 2012 that it would stop censoring media before publication. Following the announcement, newspapers and other outlets no longer required approved by state censors; however, journalists in the country can still face consequences for what they write and say. In April 2013, international media reports were published to relay the enactment of the media liberalisation reforms that we announced in August 2012. For the first time in numerous decades, the publication of privately owned newspapers commenced in the country.
Internet
Main article: Internet in Myanmar
Internet use is estimated to be relatively low compared to other countries. Myanmar's internet used to be subject to censorship, and authorities viewed e-mails and posts on Internet blogs until 2012 when the government removed media censorship. During the strict censorship days, activity at internet cafes was regulated, and one blogger named Zarganar was sentenced to prison for publishing a video of destruction caused by Cyclone Nargis in 2008; Zarganar was released in October 2011.
In regards to communications infrastructure, Myanmar is the last ranked Asian country in the World Economic Forum's Networked Readiness Index (NRI) – an indicator for determining the development level of a country's information and communication technologies. With 139 countries reported on, Myanmar ranked number 133 overall in the 2016 NRI ranking.
Film
Main article: Cinema of MyanmarMyanmar's first film was a documentary of the funeral of Tun Shein—a leading politician of the 1910s, who campaigned for Burmese independence in London. The first Burmese silent film Myitta Ne Thuya (Love and Liquor) in 1920 which proved a major success, despite its poor quality. During the 1920s and 1930s, many Burmese-owned film companies made and produced several films. The first Burmese sound film was produced in 1932 in Bombay, India with the title Ngwe Pay Lo Ma Ya (Money Can't Buy It). After World War II, Burmese cinema continued to address political themes. Many of the films produced in the early Cold War era had a strong propaganda element.
In the era that followed the political events of 1988, the film industry has been increasingly controlled by the government. Film stars who had been involved in the political activities were banned from appearing in films. The government issues strict rules on censorship and largely determines who produces films, as well as who gets academy awards.
Over the years, the movie industry has also shifted to producing many lower-budget direct-to-video films. Most of the movies produced nowadays are comedies. In 2008, only 12 films worthy of being considered for an Academy Award were made, although at least 800 VCDs were produced. Myanmar is the primary subject of a 2007 graphic novel titled Chroniques Birmanes by Québécois author and animator, Guy Delisle. The graphic novel was translated into English under the title Burma Chronicles in 2008. In 2009, a documentary about Burmese videojournalists called Burma VJ was released. This film was nominated for Best Documentary Feature at the 2010 Academy Awards. The Lady had its world premiere on 12 September 2011 at the 36th Toronto International Film Festival.
See also
Notes
- Formerly known as "Rangoon"
- Officially spelled "Nay Pyi Taw"
- Soe Win is the only vice chairman of the SAC, but he is one of five deputy prime ministers. The others are Mya Tun Oo, Tin Aung San, Win Shein, and Than Swe.
- Burmese: မြန်မာ; MLCTS: Mranma, pronounced [mjəmà]
- Burmese: ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်; MLCTS: Pranyhtaungcu. Sa.ma.ta. Mranma Nuingngamtau; pronounced [pjìdàʊɴzṵ θàɴməda̰ mjəmà nàɪɴŋàɴdɔ̀])
Pronunciations of Myanmar
- examples of two-syllable pronunciations: /ˌmjænˈmɑːr/, /ˈmjænmɑːr/, /ˌmjɑːnˈmɑːr/ , or /ˈmjɑːnmɑːr/
- examples of three-syllable pronunciations: /ˈmiːənmɑːr/, /miˈænmɑːr/, /ˌmaɪənˈmɑːr/, /maɪˈɑːnmɑːr/, or /ˈmaɪænmɑːr/
References
- "Myanmar | Ethnologue Free". Archived from the original on 9 March 2023. Retrieved 20 July 2023.
- "Overview of Myanmar's diversity" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 25 May 2024.
- "ISP Myanmar talk shows". 15 December 2020. Archived from the original on 10 May 2024. Retrieved 25 May 2024.
- "PonYate ethnic population dashboard". Archived from the original on 21 May 2024. Retrieved 25 May 2024.
- "Myanmar's Constitution of 2008" (PDF). constituteproject.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2017.
- "The 2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census- The Union Report: Religion" (PDF). myanmar.unfpa.org. Department of Population Ministry of Labour, Immigration and Population MYANMAR. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 March 2018. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- "ACT Health Community Profile, pg. 1" (PDF). Multicultural Health Policy Unit. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 April 2015. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- "Myanmar Junta Reshuffles Governing Body". The Irrawaddy. 2 February 2023. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- "Myanmar reshuffle of generals suggests 'instability,' experts say". Radio Free Asia. 26 September 2023. Archived from the original on 29 September 2023. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- "Myanmar Junta Leader Reshuffles Cabinet Days After Extending Emergency Rule". The Irrawaddy. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 22 November 2023. Retrieved 14 February 2024.
- "The 2014 Myanmar Populations and Housing Census" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects".
- https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/MMR.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/MMR.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/MMR.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - "GINI index (World Bank estimate)". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 13 July 2021.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. p. 289. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- "Myanmar Population 2024 (Live)". worldpopulationreview.com. Retrieved 10 August 2024.
- ^ "Burma". The World Factbook. U.S. Central Intelligence Agency. 8 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2021.
- O'Reilly, Dougald JW (2007). Early civilizations of Southeast Asia. United Kingdom: Altamira Press. ISBN 978-0-7591-0279-8.
- Lieberman, p. 152
- ^ "Burma". Human Rights Watch. Archived from the original on 1 December 2011. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
"Myanmar Human Rights". Amnesty International USA. Archived from the original on 29 May 2011. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
"World Report 2012: Burma". Human Rights Watch. 22 January 2012. Archived from the original on 30 June 2013. Retrieved 6 July 2013. - Madhani, Aamer (16 November 2012). "Obama administration eases Burma sanctions before visit". USA Today. Archived from the original on 13 January 2013. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
Fuller, Thomas; Geitner, Paul (23 April 2012). "European Union Suspends Most Myanmar Sanctions". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 24 April 2012. - Greenwood, Faine (27 May 2013). "The 8 Stages of Genocide Against Burma's Rohingya | UN DispatchUN Dispatch". Undispatch.com. Archived from the original on 18 June 2013. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
"EU welcomes "measured" Myanmar response to rioting". Reuters. 11 June 2012. Archived from the original on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
"Q&A: Communal violence in Burma". BBC. Archived from the original on 16 April 2019. Retrieved 14 October 2013. - ^ "Myanmar military takes control of country after detaining Aung San Suu Kyi". BBC News. 1 February 2021. Archived from the original on 31 January 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- Wee, Sui-Lee (5 December 2021). "Fatalities Reported After Military Truck Rams Protesters in Myanmar". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- Ratcliffe, Rebecca (6 December 2021). "Myanmar's junta condemned over guilty verdicts in Aung San Suu Kyi trial". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 7 December 2021. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- Vakulchuk, Roman; Kyaw Kyaw Hlaing; Edward Ziwa Naing; Indra Overland; Beni Suryadi and Sanjayan Velautham (2017). Myanmar's Attractiveness for Investment in the Energy Sector. A Comparative International Perspective. Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI) and Myanmar Institute of Strategic and International Studies (MISIS) Report. p. 8.
- Wong, John (March 1997). "Why Has Myanmar not Developed Like East Asia?". ASEAN Economic Bulletin. 13 (3): 344–358. doi:10.1355/AE13-3E (inactive 22 November 2024). ISSN 0217-4472. JSTOR 25773443. Archived from the original on 8 May 2023. Retrieved 8 May 2023.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - "Burma (Myanmar)". World Economic Outlook Database. International Monetary Fund. Archived from the original on 29 March 2021. Retrieved 19 May 2017.
- Eleven Media (4 September 2013). "Income Gap 'world's widest'". The Nation. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
McCornac, Dennis (22 October 2013). "Income inequality in Burma". Democratic Voice of Burma. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014. - "Issue Brief: Dire Consequences: Addressing the Humanitarian Fallout from Myanmar's Coup - Myanmar". ReliefWeb. 21 October 2021. Archived from the original on 2 February 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "What's in a Name: Burma or Myanmar?". United States Institute of Peace. Archived from the original on 19 July 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- "Should it be Burma or Myanmar?". 26 September 2007. Archived from the original on 18 May 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- Hall, DGE (1960). "Pre-Pagan Burma". Burma (3 ed.). p. 13.
- Houtman, Gustaaf (1999). Mental Culture in Burmese Crisis Politics: Aung San Suu Kyi and the National League for Democracy. ILCAA. p. 352. ISBN 9784872977486.
- ^ Houtman, Gustaaf (1999). Mental culture in Burmese crisis politics. ILCAA Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa Monograph Series No. 33. Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa. pp. 43–54. ISBN 978-4-87297-748-6.
- ^ Steinberg, David I. (2002). Burma: The State of Myanmar. Georgetown University Press. p. xi. ISBN 978-1-58901-285-1.
- ^ "NCGUB". National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma. Archived from the original on 9 September 2015. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- "Burma or Myanmar? Obama calls it both on visit". Asian Correspondent. Bristol, England: Hybrid News Limited. Associated Press. 19 November 2012. Archived from the original on 21 November 2012. Retrieved 19 November 2012.
Yangon, Burma (AP) – Officially at least, America still calls this Southeast Asian nation Burma, the favoured appellation of dissidents and pro-democracy activists who opposed the former military junta's move to summarily change its name 23 years ago.
Jason Burke (19 November 2012). "Burma v Myanmar – what's in a name? Obama plays it safe during historic visit". The Guardian.
"Burma (Myanmar)". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 13 April 2014. - "Countries, economies and regions – Myanmar". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Australian Government. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- "Burma vs. Myanmar: What's in a Name". DW. 1 September 2007. Archived from the original on 22 March 2015. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- Mudditt, Jessica (19 November 2012). "Burma or Myanmar: Will the US make the switch?". Archived from the original on 21 March 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- Dittmer, Lowell (2010). Burma Or Myanmar? The Struggle for National Identity. World Scientific. p. 2. ISBN 9789814313643. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- "Representations and travel advice – Myanmar". Federal Department of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- "Canada and Myanmar relations". Government of Canada – Global Affairs Canada. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 15 November 2018.
- "Кабінет Міністрів України - МЗС: Відбувся перший в історії українсько-м'янманських відносин офіційний візит до Республіки Союз М'янма". www.kmu.gov.ua (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 27 October 2024.
- "Myanmar profile". BBC News. 16 July 2013. Archived from the original on 26 June 2014. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- "Myanmar Fast Facts". CNN. 30 July 2013. Archived from the original on 29 May 2017. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- "Myanmar blast hits anti-Muslim monk's event – Asia-Pacific". Al Jazeera. 22 July 2013. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- "Myanmar". Reuters. 9 February 2009. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012.
- Woodley, Naomi (12 July 2013). "Carr apprehensive about Rohingyas' future in Myanmar". AM. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
"Aung San Suu Kyi arrives in Thailand for official visit". Radio Australia. 23 June 2016. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2016. - "'Birmanie ou Myanmar ? Le vrai faux débat francophone' – La France en Birmanie". Ambafrance-mm.org. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- "Birmanie: 87.000 Rohingyas réfugiés au Bangladesh en dix jours, selon l'ONU". L'Obs. 4 September 2017. Archived from the original on 9 September 2017. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- "L'actualité sur Birmanie par L'Obs". L'Obs. Archived from the original on 12 December 2017. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
- Martha Figueroa-Clark (26 September 2007). "How to say Myanmar". Magazine Monitor. An occasional guide to the words and names in the news from Martha Figueroa-Clark of the BBC Pronunciation Unit. BBC. Archived from the original on 10 July 2019. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
"Definition of MYANMAR by Oxford Dictionary on Lexico.com (British & World English)". Oxford Dictionaries. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
"Myanmar". American Heritage Dictionary. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
Thackrah, J. R. "Definition of Myanmar". Collins English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
"Myanmar – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary". Merriam-webster.com. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
Ammon, Ulrich (2004). Sociolinguistics: An International Handbook of the Science of Language and Society. Vol. 3/3 (2nd ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 2012. ISBN 978-3-11-018418-1. - Win Naing Tun (24 July 2015). "Prehistory to Protohistory of Myanmar: A Perspective of Historical Geography" (PDF). Myanmar Environment Institute. p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 October 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
Homo erectus had lived in Myanmar 750,000 years ago
Bowman, John Stewart Bowman (2013). Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture. Columbia University Press. p. 476. ISBN 978-0-231-50004-3. - Schaarschmidt, Maria; Fu, Xiao; Li, Bo; Marwick, Ben; Khaing, Kyaw; Douka, Katerina; Roberts, Richard G. (January 2018). "pIRIR and IR-RF dating of archaeological deposits at Badahlin and Gu Myaung Caves – First luminescence ages for Myanmar". Quaternary Geochronology. 49: 262–270. doi:10.1016/j.quageo.2018.01.001. S2CID 133664286. Archived from the original on 25 June 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- Cooler, Richard M. (2002). "The Art and Culture of Burma (Chapter 1)". DeKalb: Northern Illinois University. Archived from the original on 26 December 2016. Retrieved 22 March 2012.
- Myint-U, p. 37
- Yee Yee Aung. "Skeletal Remains of Nyaunggan, Budalin Township, Monywa District, Sagaing Division". Perspective July 2002. Archived from the original on 28 December 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- Myint-U, p. 45
- Hudson, Bob (March 2005). "A Pyu Homeland in the Samon Valley: a new theory of the origins of Myanmar's early urban system" (PDF). Myanmar Historical Commission Golden Jubilee International Conference: 1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 November 2013.
- Coupey, A. S. (2008). Infant and child burials in the Samon valley, Myanmar. In Archaeology in Southeast Asia, from Homo Erectus to the living traditions: choice of papers from the 11th International Conference of the European Association of Southeast Asian Archaeologists, 25–29 September 2006, Bougon, France
- Hall, D.G.E. (1960). Burma (3rd ed.). Hutchinson University Library. pp. 8–10. ISBN 978-1-4067-3503-1.
Moore, Elizabeth H. (2007). Early Landscapes of Myanmar. Bangkok: River Books. p. 236. ISBN 978-974-9863-31-2. - Myint-U, pp. 51–52
- Lieberman, pp. 90–91
- Lieberman, p. 24
- ^ Htin Aung, Maung (1967). A History of Burma. New York / London: Cambridge University Press. pp. 63–65.
- Maung Maung Tin, Vol. 2, p. 25
- Lieberman, p. 134
- Myint-U, pp. 64–65
- Lieberman, pp. 184–187
- Myint-U, p. 109
- Lieberman, pp. 202–206
- Baten, Jörg (2016). A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. p. 287. ISBN 978-1-107-50718-0.
- Collis, Maurice (1945). Trials in Burma.
- Bechert, Heinz (1984). The World of Buddhism-Buddhist Monks and Nuns in Society and Culture. New York City: Facts on File. ISBN 978-0-87196-982-8.
- Bennett, Will (20 August 1995). "Chindits remember their fallen comrades". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- "China-Burma-India: Merrill's Marauders. Veterans History Project, Library of Congress". Loc.gov. 14 November 2012. Archived from the original on 28 March 2013. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- Towle, Philip; Kosuge, Margaret; Kibata, Yōichi (2000). Japanese prisoners of war. Continuum International Publishing Group. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-85285-192-7.
- Fellowes-Gordon, Ian (1971). The Battle For Naw Seng's Kingdom: General Stilwel.
- Micheal Clodfelter. Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1500–2000. 2nd Ed. 2002 ISBN 0-7864-1204-6. p. 556
Werner Gruhl, Imperial Japan's World War Two, 1931–1945 Transaction 2007 ISBN 978-0-7658-0352-8 (Werner Gruhl is former chief of NASA's Cost and Economic Analysis Branch with a lifetime interest in the study of the First and Second World Wars.) - Moe, Kyaw Zwa (August 1977). "Author Discusses Martyrs' Day Assassination of Aung San". The Irrawaddy. Archived from the original on 7 November 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- Houtman, Gustaaf (1999). Mental Culture in Burmese Crisis Politics: Aung San Suu Kyi and the National League for Democracy. Tokyo: Tokyo University of Foreign Studies, Institute for the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa. ISBN 978-4-87297-748-6.
- "The Constitution of the Union of Burma". DVB. 1947. Archived from the original on 15 June 2006. Retrieved 7 July 2006.
- Smith, Martin (1991). Burma -Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity. London and New Jersey: Zed Books. pp. 42–43.
- Zaw, Aung (September 2006). "Can Another Asian Fill U Thant's Shoes?". The Irrawaddy. 14 (9). Archived from the original on 14 March 2012.
- Kipgen, Nehginpao (23 May 2017). "The united states of Myanmar?". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ^ Myint-U
- ^ Fink, Christina (2001). Living Silence: Burma under Military Rule. Bangkok: White Lotus. ISBN 978-1-85649-926-2.
- ^ Tallentire, Mark (28 September 2007). "The Burma road to ruin". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Pyithu Hluttaw Election Law". State Law and Order Restoration Council. iBiblio.org. 31 May 1989. Archived from the original on 16 September 2019. Retrieved 11 July 2006.
- Erlanger, Steven: "Burmese Vote Rejects Army Rule With Big Victory for Opposition," Archived 15 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine, 29 May 1990, The New York Times, retrieved 1 March 2021
- Han, Khin Kyaw (1 February 2003). "1990 Multi-party Democracy General Elections". National League for Democracy. iBiblio.org. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 12 July 2006.
- Horn, Robert (11 April 2011). "Is Burma's Strongman Really Retiring?". Time. Archived from the original on 1 September 2011. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- "Burma's new capital stages parade". BBC News. 27 March 2006. Archived from the original on 3 December 2018. Retrieved 24 June 2006.
- "Burma leaders double fuel prices". BBC News. 15 August 2007. Archived from the original on 30 May 2017. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
Booth, Jenny (24 September 2007). "Military junta threatens monks in Burma". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 October 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
"100,000 Protestors Flood Streets of Rangoon in "Saffron Revolution"". Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 15 February 2009.
Fink, Christina (2009). "The Moment of the Monks: Burma, 2007". In Adam Roberts; Timothy Garton Ash (eds.). Civil Resistance and Power Politics: The Experience of Non-violent Action from Gandhi to the Present. Oxford University Press. pp. 354–70. ISBN 978-0-19-955201-6. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
"UN envoy warns of Myanmar crisis". English.aljazeera.net. Archived from the original on 28 February 2008. Retrieved 20 November 2012. - Fountain, Henry (6 May 2008). "Aid arrives in Myanmar as death toll passes 22,000, but worst-hit area still cut off –". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 11 October 2008.
- "Official: UN plane lands in Myanmar with aid after cyclone". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- Stevenson, Rachel; Borger, Julian & MacKinnon, Ian (9 May 2008). "Burma snubs foreign aid workers". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 2 September 2013. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- "Burma: imperialists exploit natural disaster to promote regime change". Proletarian Online. June 2008. Archived from the original on 13 November 2013. Retrieved 13 November 2013.
- "Fighting forces up to 30,000 to flee Myanmar". NBC News. 28 August 2009. Archived from the original on 23 September 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ "More fighting feared as thousands flee Burma". Mail & Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 27 August 2009. Archived from the original on 3 March 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Fuller, Thomas (28 August 2009). "Refugees Flee to China as Fighting Breaks Out in Myanmar". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- "Thousands Flee Burma Violence". BBC News. 26 August 2009. Archived from the original on 29 August 2009. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- "Restricted Areas in Burma". Tourism Burma. 2013. Archived from the original on 2 January 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- Fuller, Thomas (4 April 2013). "Ethnic Rifts Strain Myanmar as It Moves Toward Democracy". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 July 2016. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- Nadi, Nang Mya (25 September 2012). "Displaced by fighting, villagers take shelter in Hpakant". Democratic Voice of Burma. Archived from the original on 27 November 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
"Blood and Gold: Inside Burma's Hidden War". Al Jazeera. 4 October 2012. Archived from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2013. - Simpson, Andrew (2007). Language and National Identity in Asia. United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. p. 267. ISBN 978-0-19-922648-1.
- "About 75,000 Rohingyas in Myanmar camps: Refugee International". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 29 September 2012. Archived from the original on 8 February 2018. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- ^ Power, Samantha (9 November 2012). "Supporting Human Rights in Burma". whitehouse.gov. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 27 March 2013 – via National Archives.
"Myanmar Shan refugees struggle at Thai border". Al Jazeera. 2 October 2012. Archived from the original on 22 April 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2013. - Saw Khar Su Nyar (KIC) (16 March 2012). "Karen fighters and Burma Army soldiers killed over ceasefire breach". Karen News. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- "Myanmar: Karen groups cautious on peace initiative". IRIN. 5 March 2012. Archived from the original on 1 January 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- "Concern in India as Al Qaeda announces new India front". Myanmar News.Net. 4 September 2014. Archived from the original on 6 April 2016. Retrieved 6 September 2014.
- "Tens of thousands flee war, airstrikes in Kokang region". Democratic Voice of Burma. 12 February 2015. Archived from the original on 28 March 2015. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "Myanmar Kokang Rebels Deny Receiving Chinese Weapons Archived 11 May 2019 at the Wayback Machine". Radio Free Asia.
- Lintner, Bertil (5 April 2017). "A Chinese war in Myanmar". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 21 June 2022. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- Steinberg, David I. (2010). Burma/Myanmar : what everyone needs to know. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 142–147. ISBN 978-0-19-539067-4. OCLC 318409825.
- "A Changing Ethnic Landscape: Analysis of Burma's 2010 Polls". Transnational Institute – Burma Project. TNI. 14 December 2010. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- MacFarquhar, Neil (21 October 2010). "U.N. Doubts Fairness of Election in Myanmar". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- "Myanmar profile - Timeline". BBC News. 3 September 2018. Archived from the original on 26 March 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- Loyn, David (19 November 2011). "Obstacles lie ahead in Burma's bid for reform". BBC. Archived from the original on 18 November 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- Hepler, Lauren; Voorhees, Josh (1 December 2011). "Budding Friendship on Display as Clinton, Burma's Suu Kyi Meet Again". Slate. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 17 June 2013.
Wrapping up a historic three-day visit to Myanmar , the first by a secretary of state to the Southeast Asian nation in more than 50 years
- ^ Myers, Steven Lee (2 December 2011). "Clinton Says U.S. Will Relax Some Restrictions on Myanmar". The New York Times. p. A6. Archived from the original on 1 December 2011. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- "US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton to visit Burma". BBC. 18 November 2011. Archived from the original on 20 November 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- Golluoglu, Esmer (4 February 2012). "Aung San Suu Kyi hails 'new era' for Burma after landslide victory". The Guardian. London.
- Cabellero-Anthony, Mely (March 2014). ""Myanmar's Chairmanship of ASEAN: Challenges and Opportunities", Myanmar's Growing Regional Role". NBR Special Report. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- ^ "Myanmar's 2015 landmark elections explained," Archived 21 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 3 December 2015, BBC News, retrieved 1 March 2021
- "Suu Kyi's National League for Democracy Wins Majority in Myanmar". BBC News. 13 November 2015. Archived from the original on 13 November 2015. Retrieved 13 November 2015.
- "Suu Kyi's novice MPs learn ropes in outgoing Myanmar parliament". Channel NewsAsia. Archived from the original on 27 January 2016. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- Moe, Wae; Ramzy, Austin (15 March 2016). "Myanmar Lawmakers Name Htin Kyaw President, Affirming Civilian Rule". The New York Times.
- Daniel Combs, Until the World Shatters: Truth, Lies, and the Looting of Myanmar (2021).
- ^ "Myanmar Election Delivers Another Decisive Win for Aung San Suu Kyi," Archived 1 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 11 November 2020, The New York Times, retrieved 18 December 2020
- "Myanmar: Aung San Suu Kyi's party wins majority in election," Archived 29 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine 11 November 2020, BBC News, retrieved 18 December 2020
- ^ "Myanmar election commission rejects military's fraud claims," Archived 3 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine 29 January 2021, Associated Press, retrieved 28 February 2021
- ^ "Explainer: Crisis in Myanmar after army alleges election fraud," Archived 28 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine 31 January 2021, updated 1 February 2021, Reuters News Service, retrieved 28 February 2021
- ^ "Military-Backed USDP Leaders Defeated by NLD in Myanmar Election," Archived 1 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 12 November 2020, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 28 February 2021
- ^ "Myanmar Election Body Rejects Military Allegations of Electoral Fraud," Archived 1 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 28 January 2021, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 6 February 2021
- "Myanmar Military Condemns Speaker's Refusal to Probe Election Fraud Claims," Archived 10 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 15 January 2021, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 7 February 2021
- "Myanmar Military Demands Proof November Election Was Fair," Archived 10 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 21 January 2021, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 7 February 2021
- "Myanmar Military Refuses to Rule Out Coup as It Presses Claim of Fraud in Nov Election," Archived 1 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 26 January 2021, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 7 February 2021
- "Military Thrests: Coup Fears Overshadow Myanmar Parliament Opening," Archived 30 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine Channel NewsAsia,
- "Myanmar Military Chief Warns Constitution Should Be Revoked If Laws Not Followed," Archived 1 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 28 January 2021, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 7 February 2021
- "UN, embassies fret over Myanmar coup talk," Archived 24 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine 28 January 2021, Bangkok Post, retrieved 30 January 2021
- "Myanmar's Daw Aung San Suu Kyi to Keep State Counselor Position NLD Says," Archived 1 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine 25 January 2021, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 6 February 2021
- ^ "Myanmar coup: Aung San Suu Kyi detained as military seizes control," Archived 31 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine 1 February 2021, BBC News, retrieved 1 February 2021
- ^ "Myanmar coup: Week(s) of Feb.1 to Feb. 21, EU action in focus as foreign ministers set to meet; Candlelight vigil held in Yangon; Facebook removes military's 'True News' page," Archived 2 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine (reverse chronology) 1 February through 21 February 2021, Nikkei Asia, retrieved 1 March 2021
- "Myanmar Military Takes Power for One Year, Suu Kyi in Detention". Bloomberg.com. 31 January 2021. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2021 – via www.bloomberg.com.
- Regan, Helen. "Chinese factories set on fire in Myanmar in deadliest day since coup". CNN. Archived from the original on 15 March 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ "Myanmar coup: Teachers join growing protests against military," Archived 22 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine 5 February 2021, BBC News, retrieved 28 February 2021
- "Tens of Thousands Take to Streets in Myanmar to Protest Military Regime," Archived 27 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine 12 November 2020, The Irrawaddy, retrieved 28 February 2021
- "On Bloodiest Day for Myanmar Civilians, India Attends Military Parade by Coup Leaders". The Wire. 28 March 2021. Archived from the original on 28 March 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- "China Responds to Bloodshed in Myanmar With Deafening Silence". The Diplomat. 2 March 2021. Archived from the original on 16 June 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- "India has a history of involvement in its neighbours' affairs. Why has it not condemned the Myanmar coup?". South China Morning Post. 24 February 2021. Archived from the original on 16 June 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- "Myanmar coup: ASEAN split over the way forward". Deutsche Welle. 29 March 2021. Archived from the original on 10 June 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- "Can Myanmar's New 'People's Defense Force' Succeed?". The Diplomat. 26 April 2021. Archived from the original on 9 May 2021. Retrieved 3 June 2021.
- "The civil war in Myanmar: No end in sight". Archived from the original on 13 October 2023. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- Patrick Hesp; et al., eds. (2000). Geographica's World Reference. Random House Australia. pp. 738, 741.
- ^ Than, Mya (2005). Myanmar in ASEAN: Regional Co-operation Experience. Singapore: Institute of Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN 978-9812302106.
- ^ Thein, Myat (2005). Economic Development of Myanmar. Singapore: Inst. of Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN 978-9812302113.
- "Myanmar. States & Regions". Myanmar's NET. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013.
- List of Districts, Townships, Cities/Towns, Wards, Village Groups and Villages in Union of Myanmar published by Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of Union of Myanmar on 31 December 2001
- "Impact of Climate Change and the Case of Myanmar | Myanmar Climate Change Alliance". myanmarccalliance.org. Archived from the original on 5 December 2018. Retrieved 2 December 2018.
- "National climate change policy finalised". The Myanmar Times. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- "Millions to Benefit from Myanmar's New Partnership Framework With the World Bank Group". World Bank. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 2 December 2018.
- "Myanmar Climate Change Policy" (PDF). myanmarccalliance.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 March 2020.
- Murray, Nicholas J.; Keith, David A.; Duncan, Adam; Tizard, Robert; Ferrer-Paris, Jose R.; Worthington, Thomas A.; Armstrong, Kate; Nyan Hlaing; Win Thuya Htut; Aung Htat Oo; Kyaw Zay Ya; Grantham, Hedley (2020). "Myanmar's terrestrial ecosystems: Status, threats and conservation opportunities". Biological Conservation. 252: 108834. Bibcode:2020BCons.25208834M. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108834. hdl:1959.4/unsworks_73305. S2CID 228850408.
- "2016 Report". EPI Report. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- EPI (2016): Myanmar Archived 24 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Overland, I. et al. (2017). Impact of Climate Change on ASEAN International Affairs: Risk and Opportunity Multiplier Archived 28 July 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI) and Myanmar Institute of International and Strategic Studies (MISIS).
- Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- "Myanmar's Forest Law and Rules n". BurmaLibrary.org. Archived from the original on 11 October 2006. Retrieved 15 July 2006.
- Reid, Robert; Bindloss, Joseph; Butler, Stuart (2009). "Environment: National Parks". Myanmar (Burma) (10th ed.). Footscray, Victoria, Australia: Lonely Planet. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-74104-718-9.
- ""Flora and Fauna" at". Myanmars.net. Archived from the original on 23 September 2006. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- Phillips, Kimberley (20 February 2021). "The last thing the Myanmar people need is false hope". The Canberra Times. Archived from the original on 21 February 2021. Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- "Reuters, Cyclone-hit Myanmar says 92 percent back charter". Reuters. 15 May 2008. Archived from the original on 10 January 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- MacFarquhar, Neil (22 October 2010). "U.N. Doubts Fairness of Election in Myanmar". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 15 July 2017. Retrieved 25 February 2017.
- Jha, Lalit K (21 May 2009). "2010 Burmese Election may be Illegitimate: Clinton". The Irrawaddy. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- "Western states dismiss Burma's election". BBC. 8 November 2010. Archived from the original on 11 November 2010. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ^ Tisdall, Simon (4 July 2011). "Aung San Suu Kyi has to tread softly – but governments must tell it like it is". The Guardian. UK.
- Walker, Peter (12 November 2010). "Guardian report on Aung's release from house arrest". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
- "Corruption Perceptions Index 2019". Transparency.org. Archived from the original on 23 June 2020. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- "Burma Freedom and Democracy Act of 2003". United States Library of Congress. 4 June 2003. Archived from the original on 25 January 2004. Retrieved 4 February 2007.
- Myers, Steven Lee; Mydans, Seth (13 January 2012). "U.S. to Renew Myanmar Ties in Light of Reforms". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 13 January 2012. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- "The EU's relations with Burma / Myanmar". European Union. Archived from the original on 25 July 2006. Retrieved 13 July 2006.
- "Overview of Burma sanctions". BBC News. 18 December 2009. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Burma, India to sign accord on use of India's remote sensing satellite data". NewsLibrary.com. 9 March 2006. Archived from the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- "India looks to Burma to slake growing thirst for gas". The Christian Science Monitor. 26 April 2006. Archived from the original on 8 July 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- "Myanmar, India to build IT centres in Myanmar_English_Xinhua". Xinhua News Agency. 4 August 2008. Archived from the original on 11 January 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- "India to develop two hydel power projects in Myanmar – 56908". Steelguru.com. 1 August 2008. Archived from the original on 16 January 2009. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- "India urges Burma reconciliation". BBC News. 2 January 2008. Archived from the original on 2 December 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- Vietnam News Agency (17 December 2019). "PM calls for stronger Vietnam-Myanmar parliamentary ties". VietnamPlus. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- Michimi Muranushi (22 October 2019). "Japan's Defense of Myanmar and the Rohingya Genocide". Middle East Institute. Archived from the original on 20 March 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- "Japan should not follow the Western policy on Myanmar - Diplomat op-ed". Reuters. 26 May 2021. Archived from the original on 3 August 2022. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- "Obama Vows US Support As Myanmar Leader Visits". NPR. Associated Press. 20 May 2013. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013.
- "Pheonix Voyages appointed travel manager for Myanmar's first major summit". TTGmice. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- Han, Enze (2024). The Ripple Effect: China's Complex Presence in Southeast Asia. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-769659-0.
- Cody, Edward (27 September 2007). "Caution by Junta's Asian Neighbors Reflects Their Self-Interest". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 7 July 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- "24th ASEAN Summit, Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar, 10–11 May 2014". ASEAN (Press release). 4 April 2014. Archived from the original on 16 April 2016.
- "24th ASEAN Summit, Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar, 10–11 May 2014". ASEAN. 4 April 2014. Archived from the original on 16 April 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- "For Rohingya in Bangladesh, No Place is Home". Time. 19 February 2010. Archived from the original on 20 February 2010.
- Starck, Peter (7 June 2005). "World Military Spending Topped US$1 trillion in 2004". Common Dreams NewsCenter. Reuters. Archived from the original on 20 June 2006. Retrieved 19 July 2006.
- "Russia and Burma in Nuclear Deal". BBC. 15 May 2007. Archived from the original on 19 August 2007. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- Moore, Malcolm (14 January 2011). "Nuclear Watchdog asks Burma to Open Up Suspect Sites". The Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- "Myanmar 'building nuclear sites'". Al Jazeera. 10 December 2010. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- Bureau of Arms Control, Verification and Compliance. "Adherence to and Compliance with Arms Control, Non-Proliferation, and Disarmament Agreements and Commitments" (PDF). 2019 Compliance Report. United States Department of State. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- United Nations General Assembly Session 54 Verbotim Report 83. A/54/PV.83 page 30. The President 17 December 1999 at 10:00.
- United Nations General Assembly Session 55 Verbotim Report 81. A/55/PV.81 page 22. The President 4 December 2000 at 15:00.
- United Nations General Assembly Session 56 Verbotim Report 92. A/56/PV.92 page 7. 24 December 2001 at 11:00.
- United Nations General Assembly Session 60 Verbotim Report 69. A/60/PV.69 page 19. The President 23 December 2005 at 10:00.
- United Nations General Assembly Session 61 Verbotim Report 84. A/61/PV.84 page 14. 22 December 2006 at 10:00.
- United Nations Security Council Document 14. S/2007/14 12 January 2007.
- United Nations Security Council Verbotim Report 5619. S/PV/5619 page 3. Mr. Kumalo South Africa 12 January 2007 at 16:00.
- "The World's Most Repressive Regimes 2013" (PDF). Geneva: Freedom House. 2003. pp. vii–7. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 October 2019. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
Burma continues to be ruled by one of the world's most repressive regimes.
- Howse, Robert; Jared M. Genser. "Are EU Trade Sanctions on Burma Compatible With WTO Law?" (PDF). Are EU Trade Sanctions on Burma Compatible with WTO Law?: 166 ff. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2010. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
repressive and abusive military regime
- "List of UN General Assembly Resolutions on Burma". Archived from the original on 4 November 2016. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "UN General Assembly Resolution: Time for Concrete Action" (Press release). International Federation for Human Rights. 20 November 2009. Archived from the original on 29 January 2010. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- Adams, Brad (1 September 2004). "Statement to the EU Development Committee". Human Rights Watch. Archived from the original on 20 June 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2006.
- Adams, Brad. "Amnesty International 2009 Report on Human Rights in Myanmar". Amnesty International. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "Myanmar set to release some 70 prisoners". The Myanmar Times. 24 July 2013. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
- Weng, Lawi (24 July 2013). "Burma Govt Releases 73 Political Prisoners". Archived from the original on 30 October 2013. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
- "Myanmar: Final push on political prisoners needed". 27 September 2012. Archived from the original on 18 December 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- "Burma Frees 56 Political Prisoners". Voice of America. 22 April 2013. Archived from the original on 26 April 2013. Retrieved 26 April 2013.
- Guardia, Anton La (24 June 2005). "Myanmar's 'slow genocide' is revealed through the eyes of its child victims". The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- "2013 UNHCR country operations profile – Thailand". Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- "Myanmar: Villages burned, civilians injured and killed as Rakhine State conflict escalates". Amnesty International. 12 October 2020. Archived from the original on 15 October 2020. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- ^ Rodion Ebbighausen, Shamil Shams (19 March 2012). "MTV and Burmese pop stars campaign to end human trafficking". Deutsche Welle. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- Taylor, Jerome (19 June 2012). "Two Burmese children a week conscripted into military". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 26 October 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- Weng, Lawi (5 September 2012). "ILO in Talks with Kachins over Child Soldiers". The Irrawaddy. Archived from the original on 5 January 2013. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- Kieran Guilbert (26 June 2018). "Exclusive: Women most at risk from traffickers in India, Libya, Myanmar - poll". Reuters. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- "Myanmar UN ACT". UN ACT. Archived from the original on 6 May 2019. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- "Burma". Archived from the original on 25 July 2018.
- ^ "Nowhere else to go: An examination of sexual trafficking and related human rights abuses in Southern Burma". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 2009. Archived from the original on 1 June 2022.
- "Give Us a Baby and We'll Let You Go: Trafficking of Kachin Brides from Myanmar to China". Human Rights Watch. 21 March 2019. Archived from the original on 31 July 2021. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- "Thousands of Myanmar women forced into marriages in China". DW News. 12 July 2018. Archived from the original on 25 March 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- "NGO Report: Malaysia Now a Destination for Sex-Trafficking of Rohingya Girls". Benar News. 20 December 2019. Archived from the original on 21 October 2021. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- "Trafficked to China to marry, a Myanmar woman hopes to save others from same fate". Reuters. 23 August 2017. Archived from the original on 16 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "Myanmar's cyber-scam industry limps on amid regional crackdown". Frontier Myanmar. 5 October 2023. Archived from the original on 5 December 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- "#trending: Chinese netizens afraid of Southeast Asia travel after hit movie No More Bets shows human trafficking scams". Today (Singapore newspaper). 10 October 2023. Archived from the original on 5 December 2023. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- "Trapped inside Myanmar's refugee camps, the Rohingya people call for recognition". The Guardian. 20 December 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- "US Holocaust Museum highlights plight of Myanmar's downtrodden Rohingya Muslims". Fox News Channel. Associated Press. 6 November 2013. Archived from the original on 19 October 2015. Retrieved 6 June 2015.
- ^ Head, Jonathan (5 February 2009). "What drive the Rohingya to sea?". BBC. Archived from the original on 1 October 2019. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- ^ Islam, Syed; Islam, Serajul (2007). "Chapter 16, State Terrorism in Arakan". In Tan, Andrew T. H. (ed.). A Handbook of Terrorism and Insurgency in South East Asia. Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 342. ISBN 978-1-84542-543-2.
- Hindstrom, Hanna (25 July 2012). "Burma's monks call for Muslim community to be shunned". The Independent. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- Dummett, Mark (18 February 2010). "Bangladesh accused of 'crackdown' on Rohingya refugees". BBC. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- "Myanmar, Bangladesh leaders 'to discuss Rohingya'". Agence France-Presse. 25 June 2012. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- Bento, Lucas & Yusuf, Guled (9 October 2012). "The Rohingya: Unwanted at Home, Unwelcome Abroad". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- "Rohingyas are not citizens: Myanmar minister". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 30 July 2012. Archived from the original on 7 January 2016. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
- "Exodus grows as Muslim Rohingya flee persecution in Myanmar homeland". Japan Times. 18 November 2014. Archived from the original on 17 December 2014. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- "'Brutal efficiency' in Myanmar attacks: UN". The Australian. Australian Associated Press. 27 March 2013. Archived from the original on 27 March 2013. Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- Rebane, Teele (30 August 2024). "Myanmar's poorest are so desperate they're turning to social media to sell their kidneys". CNN. Retrieved 1 September 2024.
- "Major Reform Underway". Crisis Group. 22 September 2011. Archived from the original on 2 December 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- "Freedom in the World 2012: Burma". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- Freedom House (2013). "Burma". Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 22 November 2013.
- "Burma gets rights commission". Australia Network News. 7 September 2011. Archived from the original on 26 September 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- Kyaw Hsu (19–25 September 2011). "Anyeint group returns from exile in Thailand". MM Times. Archived from the original on 30 September 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- Murdoch, Lindsay (29 September 2011). "Burma flags mass release of political prisoners". The Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 30 September 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- "Free press is the key to Myanmar reform". Agence France-Presse. 20 September 2011. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- Buncombe, Andrew (17 September 2011). "Burmese junta relaxes access to foreign websites". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 20 October 2011. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- Working Through Ambiguity: International NGOs in Myanmar. Soubhik Ronnie Saha The Hauser Center for Nonprofit Organizations Harvard University September 2011
- Woodcock, Andrew (16 July 2013). "No more political prisoners: Myanmar". The Australian. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- "LGBT relationships are illegal in 74 countries, research finds". The Independent. 17 May 2016. Archived from the original on 18 June 2022.
- "State Sponsored Homophobia 2016: A world survey of sexual orientation laws: criminalisation, protection and recognition" (PDF). International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association. 17 May 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 September 2017. Retrieved 9 July 2018.
- "Burma's Aung San Suu Kyi accused of 'legitimising genocide of Rohingya Muslims' Archived 27 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine". The Independent. 25 November 2016.
- AP News. (12 December 2017). "Army's rape of Rohingya women sweeping, methodical: AP". Al Jazeera website Archived 12 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- "world bank indicator". World Bank. Archived from the original on 15 November 2019. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- Aung Hla Htun (16 March 2012). "Exclusive: Myanmar drafts new foreign investment rules". Reuters. Archived from the original on 16 March 2012. Retrieved 17 March 2012.
- "Yangon Stock Exchange Formally Opens for Business". The New York Times. 25 March 2016. Retrieved 25 March 2016.
- Brown, Ian (2005). A Colonial Economy in Crisis. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-30580-8.
- Stokke, Kristian; Vakulchuk, Roman and Indra Overland (2018) Myanmar: A Political Economy Analysis Archived 28 July 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Norwegian Institute of International Affairs (NUPI). Report commissioned by the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- "Challenges to Democratization in Burma" (PDF). International IDEA. November 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2006.
- "Myanmar Opium Survey 2021: Cultivation, Production and Implications". February 2022. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 18 April 2023.
- "Myanmar's Economic Meltdown Likely to Push Opium Output Up, Says UN". 31 May 2021. Archived from the original on 18 October 2021. Retrieved 15 October 2021.
- Douglas, Jeremy (15 November 2018). "Parts of Asia are slipping into the hands of organized crime". CNN. Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 18 April 2023.
- "Synthetic Drugs in East and Southeast Asia: Latest Developments and Challenges 2022". May 2022. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 18 April 2023.
- "Huge fentanyl haul seized in Asia's biggest-ever drugs bust". Reuters. 18 May 2020. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 18 April 2023 – via www.reuters.com.
- Hargreaves, Steve (18 June 2013). "Myanmar: Tales from the last business frontier". CNN. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
- "Frequently Asked Questions and Answers". U.S. Department of the Treasury. 18 March 2013. Archived from the original on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 4 August 2013.
- Fullbrook, David (4 November 2004). "So long US, hello China, India". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 6 November 2004. Retrieved 14 July 2006.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - McCartan, Brian (28 February 2012). "Myanmar military in the money". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - Brady, Brendan (7 September 2012). "Boom Days in Burma". Newsweek. Archived from the original on 29 September 2012. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ Myint-U, Thant (2006). The river of lost footsteps: histories of Burma (1st ed.). New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-16342-6. OCLC 65064707.
- Davis, Mike (2001). Late Victorian holocausts: El Niño famines and the making of the third world. London: Verso. ISBN 1-85984-739-0. OCLC 45636958.
- Total. "Oil and Gas in Myanmar". Archived from the original on 15 April 2015.
- Booth, Anne (Spring 2003). "The Burma Development Disaster in Comparative Historical Perspective". SOAS Bulletin of Burma Research. 1 (1). ISSN 1479-8484. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Watkins, Thayer. "Political and Economic History of Myanmar (Burma) Economics". San Jose State University. Archived from the original on 26 May 2006. Retrieved 8 July 2006.
- Taylor, Robert H. (25 May 2015). General Ne Win : a political biography. Singapore. ISBN 978-981-4620-13-0. OCLC 934623309.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "List of Least Developed Countries". UN-OHRLLS. 2005. Archived from the original on 26 October 2013.
- "Myanmar and IRRI" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2005. (21.2 KB), Facts About Cooperation, International Rice Research Institute. Retrieved 25 September 2007.
- "Faostat". Faostat.fao.org. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- "Gems of Burma and their Environmental Impact". Uvm.edu. Archived from the original on 26 May 2010. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- "Burma: Gem Trade Bolsters Military Regime, Fuels Atrocities". Human Rights Watch. 11 November 2007. Archived from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- Ferro, Shane (19 July 2011). "Burmese Gem Emporium Rakes in $1.5 Billion Despite Human Rights Abuse Concerns". Blouin ARTINFO. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- "U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries, January 2021" (PDF). usgs.gov. USGS. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- Subramanian, Sribala. "Rare Earths in Myanmar: Unobtanium?". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 9 October 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- Daly, Tom (26 March 2021). "China rare earths extend surge on worries over Myanmar supply, inspection threat". Reuters. Archived from the original on 9 October 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- DuByne, David (November 2015), "Geothermal Energy in Myanmar Securing Electricity for Eastern Border Development" (PDF), Myanmar Business Today Magazine: 6–8, archived (PDF) from the original on 20 November 2015, retrieved 20 November 2015
- Enescu, Raluca (24 December 2006). "Burma Digest". Tayzathuria.org.uk. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011.
- "Southern Myanmar". southernmyanmar.com. p. Tourist Destinations. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- "Myanmar Travel Agency". birma.com. p. Tourist Destinations. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- "The Tourism Campaign – Campaigns". The Burma Campaign UK. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- ^ "Getting there & away". lonelyplanet.com. Archived from the original on 1 August 2013. Retrieved 4 August 2013.
- "Dragoman". Archived from the original on 29 January 2015.
- "International airlines to open direct flights to Myanmar". 2 August 2013. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013.
- "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- Spoorenberg, Thomas (2015). "Provisional results of the 2014 census of Myanmar: The surprise that wasn't". Asian Population Studies. 11 (1): 4–6. doi:10.1080/17441730.2014.972084. S2CID 154114929.
- Spoorenberg, Thomas (2015). "Myanmar's first census in more than 30 years: A radical revision of the official population count" (PDF). Population & Societies. 527 (November): 1–4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2019. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- "Thailand: The Plight of Burmese Migrant Workers". Amnesty International. 8 June 2006. Archived from the original on 26 June 2006. Retrieved 13 July 2006.
- Maung, M. Ismael Khin (April 1986). The population of Burma: An analysis of the 1973 Census. East-West Population Institute. ISBN 0866380779.
- ^ Jones, Gavin W. (2007). "Delayed Marriage and Very Low Fertility in Pacific Asia" (PDF). Population and Development Review. 33 (3): 453–478. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2007.00180.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 March 2011. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- Spoorenberg, Thomas (2013). "Demographic changes in Myanmar since 1983: An examination of official data". Population and Development Review. 39 (2): 309–324. doi:10.1111/j.1728-4457.2013.00593.x.
- ^ Mon, Myat (2000). "The Economic Position of Women in Burma". Asian Studies Review. 24 (2): 243–255. doi:10.1080/10357820008713272. S2CID 144323033. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ^ WorldMarriage Patterns 2000 Archived 25 December 2003 at the Wayback Machine. United Nations
- Gordon, Raymond G. Jr. (2005). "Languages of Myanmar". Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. SIL International. Archived from the original on 7 December 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2007.
- ^ "Background Note: Burma". Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs. U.S. Department of State. August 2005. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2006.
- Than, Mya (1997). Suryadinata, Leo (ed.). Ethnic Chinese As Southeast Asians.
- Kato, Mariko (18 February 2009). "Myanmar refugees to try resettling". Japan Times. Archived from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- "Myanmar Refugees in South East Asia" (PDF). UNHCR. April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 June 2006. Retrieved 13 July 2006.
- "From tropical Burma to Syracuse, refugees adjust". CBS News. 25 April 2012. Archived from the original on 5 July 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- "Office Of Refugee Resettlement: Data". U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Smith, Martin (1991). Burma – Insurgency and the Politics of Ethnicity. London, New Jersey: Zed Books. pp. 43–44, 98, 56–57, 176.
- "Asians v. Asians". Time. 17 July 1964. Archived from the original on 8 December 2008. Retrieved 20 November 2012.(subscription required)
- Macan-Markar, Marwaan. "Burma's Muslim Rohingyas – The New Boat People". Ipsnews.net. Archived from the original on 11 March 2009. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- Ford, Peter (12 June 2012). "Why deadly race riots could rattle Myanmar's fledgling reforms". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on 5 January 2015. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- Habib, Mohshin; Ahmad, Salahuddin; Jubb, Christine; Pallard, Henri; Rahman, Masudur; Ontario International Development Agency (issuing body) (2018). Forced migration of Rohingya : the untold experience. Ontario International Development Agency, Canada. p. 69. ISBN 9780986681516. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- Barron, Laignee (8 March 2018). "More Than 43,000 Rohingya Parents May Be Missing. Experts Fear They Are Dead". TIME Magazine. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- "Myanmar: No Justice, No Freedom for Rohingya 5 Years On". Human Rights Watch. 24 August 2022. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- Gordon, Raymond G. Jr. (2005). "Languages of Myanmar". SIL International. Archived from the original on 7 December 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2006.
- ^ Gordon, Raymond G. Jr. (2005). "Language Family Trees: Sino-Tibetan". Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. SIL International. Archived from the original on 11 August 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2006.
- "Proposal for encoding characters for Myanmar minority languages in the UCS" (PDF). International Organization for Standardization. 2 April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2006. Retrieved 9 July 2006.
- "Ethnic and Religious Diversity: Myanmar's Unfolding Nemesis", Matthews, Bruce, Institute of South East Asian Studies, Visiting Researcher Series, Volume 2001, No. 3. 2001.
- Thailand Burma Border Consortium (2007). "Internal Displacement in Eastern Burma 2006 Survey". Archived from the original on 15 May 2007. Retrieved 4 February 2007.
- Priestly, Harry (17 January 2006). "The Outsiders". The Irrawaddy. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012.
- Ling, Samuel Ngun (2003). "The Encounter of Missionary Christianity and Resurgent Buddhism in Post-colonial Myanmar" (PDF). Payap University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 March 2006. Retrieved 14 July 2006.
- Zatko, Martin (2015). The Rough Guide to Myanmar. p. 357.
- Dummett, Mark (29 September 2007). "Burmese exiles in desperate conditions". BBC News. Archived from the original on 1 September 2017. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project: Burma Archived 10 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Pew Research Center. 2010.
- ^ "Buddhanet.net". Archived from the original on 31 March 2017. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- "Children of the Mekong". 2 March 2023. Archived from the original on 14 March 2023. Retrieved 14 March 2023.
- ^ The 2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census Report Volume 2-C. Department of Population Ministry of Labour, Immigration and Population. July 2016. pp. 12–15.
- Pyone, Taung (14 November 2019). "Monks in Myanmar have a new target". The Economist. Archived from the original on 17 November 2019. Retrieved 17 November 2019.
- "Burma-International Religious Freedom Report 2007". U.S. Department of State. 14 September 2007. Archived from the original on 8 May 2020. Retrieved 22 May 2019.
- "International Religious Freedom Report 2007 – Burma". State.gov. 14 September 2007. Archived from the original on 8 May 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- "Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs – Background Note: Burma". State.gov. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- 2013 Yearbook of Jehovah's Witnesses. Watchtower Bible and Tract Society of New York, Inc. 2013. p. 85.
- "Office and Tour Information". jw.org. Archived from the original on 9 October 2015. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- "Burma—International Religious Freedom Report 2010". U.S. Department of State. 17 November 2010. Archived from the original on 21 November 2010. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- Aung-Thwin, Michael A. (2005). The Mists of Rāmañña: The Legend that was Lower Burma (illustrated ed.). Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press. pp. 31–34. ISBN 978-0-8248-2886-8.
- Lieberman, pp. 115–116
- "PPI: Almost Half of All World Health Spending is in the United States". 17 January 2007. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011.
- Anwar, Yasmin (28 June 2007). "Myanmar junta faulted for rampant diseases". UC Berkeley News.
- A preventable fate: The failure of ART scale-up in Myanmar. Médecins Sans Frontières. November 2008
- "At a glance: Myanmar – statistics". UNICEF. Archived from the original on 1 September 2010. Retrieved 9 January 2007.
- "A scaled-up response to AIDS in Asia and the Pacific" (PDF). UNAIDS. 1 July 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 February 2007. Retrieved 10 January 2007.
- ^ "Asia" (PDF). UNAIDS. December 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2007. Retrieved 9 January 2007.
- "Global Hunger Index Scores by 2024 GHI Rank". Global Hunger Index (GHI) - peer-reviewed annual publication designed to comprehensively measure and track hunger at the global, regional, and country levels. Retrieved 25 December 2024.
- "Adult (15+) Literacy Rates and Illiterate Population by Region and Gender for". UNESCO Institute of Statistics. April 2006. Archived from the original (XLS) on 25 June 2007. Retrieved 13 July 2006.
- Chronicle of National Development Comparison Between Period Preceding 1988 and after (up to 31 December 2006).
- World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. Geneva. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - agt. "UNODC: Global Study on Homicide". Archived from the original on 2 June 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- Calderon, Justin (3 July 2013). "ASEAN: As safe as we think?". Inside Investor. Archived from the original on 22 June 2019. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
- "Myanmar still near bottom of corruption rankings in 2012 despite reforms". Thomson Reuters Foundation. 5 December 2012. Archived from the original on 5 January 2015. Retrieved 5 January 2015.
- "UN report: Opium cultivation rising in Burma". BBC News. 31 October 2012. Archived from the original on 15 July 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
- Thornton, Phil (12 February 2012). "Myanmar's rising drug trade". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- McCartan, Brian (13 July 2010). "Holes in Thailand's drug fences". Asia Times. Archived from the original on 15 July 2010. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - "Ramayana in Myanmar's heart". Goldenland Pages. 13 September 2003. Archived from the original on 26 April 2006. Retrieved 13 July 2006.
- Temple, R.C. (1906). The Thirty-seven Nats-A Phase of Spirit-Worship prevailing in Burma.
- "The Worshipping of Nats – The Special Festival of Mount Popa". Myanmar Travel Information. Archived from the original on 23 June 2006. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ^ Chit, Khin Myo (1980). Flowers and Festivals Round the Burmese Year.
- Tsaya (1886). Myam-ma, the home of the Myanmarn. Calcutta: Thacker, Spink and Co. pp. 36–37.
- Yoe, Shway (1882). The Myanmarn – His Life and Notions. New York: Norton Library 1963. pp. 211–216, 317–319.
- Martin, Steven (March 2004). "Burma maintains bygone buildings". BBC News. Archived from the original on 8 April 2008. Retrieved 9 July 2006.
- Scott O'Connor (1904). The Silken East – A Record of Life and Travel in Burma. Scotland: Kiscadale. p. 32.
- Hays, Jeffrey. "SPORTS IN MYANMAR: SOCCER, OLYMPICS AND TRADITIONAL SPORTS". Facts and Details. Archived from the original on 2 June 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2017.
- "Myanmar prepares for the 2013 Southeast Asian Games". Archived from the original on 24 June 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2012.
- "Burma Abolishes Censorship". The Daily Beast. Archived from the original on 21 August 2012. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- Sukri, Azhar (1 April 2013). "Myanmar shows new signs of press freedom". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 4 April 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- Calderaro, Andrea (1 May 2015). "Internet Governance Capacity Building in Post-Authoritarian Contexts. Telecom Reform and Human Rights in Myanmar" (PDF). SSRN. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2686095. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 March 2021. Retrieved 22 February 2021.
- "Internet Access and Openness: Myanmar 2012" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- "NRI Overall Ranking 2016". World Economic Forum. Archived from the original on 28 May 2020. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- Zaw, Aung (March 2004). "Celluloid Disillusions". Irrawaddy. 12 (3). Archived from the original on 13 February 2005.
- Kyi Soe Tun quoted in the Bangkok Post, 11 August 2006
- Through the Director's Lens. Irrawaddy. 16 January 2009
- "Burma VJ – Academy Award Nominee – Best Documentary Feature". Burmavjmovie.com. Archived from the original on 21 May 2009. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- "Burma VJ Nominated for the 2010 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature, Rev. Danny Fisher". Dannyfisher.org. 2 February 2010. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
- Knegt, Peter (12 September 2011). "TIFF List 2011: A Complete Guide To The Toronto International Film Festival". IndieWire. Archived from the original on 27 October 2018. Retrieved 31 December 2018.
Bibliography
- Cameron, Ewan. "The State of Myanmar", History Today, May 2020, vol. 70, issue 4, pp. 90–93.
- Charney, Michael W. (1999). History of Modern Burma. Cambridge University Press.
- Combs, Daniel. Until the World Shatters: Truth, Lies, and the Looting of Myanmar (2021).
- Lieberman, Victor B. (2003). Strange Parallels: Southeast Asia in Global Context, c. 800–1830, volume 1, Integration on the Mainland. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-80496-7.
- Maclean, Rory (2008). Under the Dragon-A Journey through Burma. Tauris Parke. ISBN 978-1-84511-622-4.
- Myint-U, Thant (2006). The River of Lost Footsteps—Histories of Burma. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-16342-6.
- Kemp, Hans (2013). (illustrated with text by Tom Vater ed.). Visionary World. ISBN 978-9628563708.
- "Burma's Western Border as Reported by the Diplomatic Correspondence(1947–1975)" by Aye Chan
External links
Government
- Republic of the Union of Myanmar – President's Office Archived 3 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- Myanmar National Portal
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members Archived 1 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine from the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
General information
- General information about Myanmar Archived 16 October 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- Burma Myanmar search Engine Archived 22 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Burma Archived 1 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Burma from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Burma profile Archived 26 June 2014 at the Wayback Machine from BBC News
- Myanmar Archived 28 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine at Encyclopædia Britannica
 Geographic data related to Myanmar at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Myanmar at OpenStreetMap Wikimedia Atlas of Myanmar
Wikimedia Atlas of Myanmar- Interactive timeline of turning points in Burmese history Archived 25 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- Key Development Forecasts for Myanmar Archived 11 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine from International Futures
- Online Burma/Myanmar Library: Classified and annotated links to more than 17,000 full-text documents on Burma/Myanmar Archived 16 July 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- Historical Photographs of Burma | Southeast Asia Digital Library Archived 1 July 2022 at the Wayback Machine
| Related articles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
22°N 96°E / 22°N 96°E / 22; 96 (Myanmar (Burma))
Categories: