| Revision as of 01:32, 4 December 2014 view source119.94.114.86 (talk) →Notable people← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:14, 27 December 2024 view source Naniwoofg (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,368 edits updated the infoboxTags: Mobile edit Mobile web editNext edit → | ||
| (411 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Highly urbanized city in South Cotabato, Philippines}} | |||
| <!-- Infobox begins --> | |||
| {{for|the person whom the city is named after|Paulino Santos}} | |||
| {{other uses}} | |||
| {{pp|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=July 2022}} | |||
| {{Use Philippine English|date=January 2023}} | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | {{Infobox settlement | ||
| |name |
| name = {{PH wikidata|name}} | ||
| | |
| translit_lang1 = Other | ||
| | translit_lang1_type1 = ] | |||
| |native_name = ''Heneral Santos'' | |||
| | translit_lang1_info1 = جنرل سنتوس | |||
| |settlement_type = ] | |||
| | |
| image_skyline = {{Photomontage | ||
| | photo1a = Gensan.jpg{{!}}Aerial view of urban GenSan | |||
| |image_skyline = Gensancity.jpg | |||
| | photo2a = Robinsons Place General Santos - panoramio.jpg{{!}}Robinsons Place GenSan | |||
| |image_caption = | |||
| | photo2b = Grill - BBQ in General Santos City.jpg{{!}}Barbecue grill stalls at Tiongson Arcade | |||
| |image_flag = | |||
| | |
| photo3a = | ||
| Gensan Dadiangas, Pioneer Avenue-Roxas (General Santos City; 08-11-2023).jpg | |||
| |image_seal = Ph seal gensan.png | |||
| | |
| size = 250 | ||
| | position = center | |||
| |image_map = {{#property:P242}} | |||
| | spacing = 2 | |||
| |map_caption = Map of South Cotabato with General Santos City highlighted | |||
| | |
| color = transparent | ||
| | border = 0 | |||
| |pushpin_map_caption = Location within the Philippines | |||
| | foot_montage = Aerial view of urban GenSan; Robinsons Place GenSan; Barbecue grill stalls at Tiongson Arcade; Dadiangas | |||
| |coordinates_region = PH | |||
| }} | |||
| |subdivision_type = Country | |||
| | image_caption = | |||
| |subdivision_name = ] | |||
| | image_flag = Flag_of_General_Santos,_South_Cotabato_(2022-present).png | |||
| |subdivision_type1 = Region | |||
| | flag_size = 120x80px | |||
| |subdivision_name1 = ] (Region XII) | |||
| | image_seal = General Santos City seal.jpg | |||
| |subdivision_type2 = Province | |||
| | seal_size = 100x80px | |||
| |subdivision_name2 = ] <small>(geographically only)</small> | |||
| | image_map = {{PH wikidata|image_map}} | |||
| |subdivision_type3 = Districts | |||
| | map_caption = Map of South Cotabato with {{PH wikidata|name}} highlighted | |||
| |subdivision_name3 = ] | |||
| | image_map1 = {{hidden begin|title=OpenStreetMap|ta1=center}}{{Infobox mapframe|frame-width=250}}{{hidden end}} | |||
| |parts_type = ]s | |||
| | |
| pushpin_map = Philippines | ||
| | pushpin_label_position = left | |||
| |p1 = 26 | |||
| | pushpin_map_caption = Location within the {{PH wikidata|country}} | |||
| |government_type = | |||
| | |
| coordinates = {{PH wikidata|coordinates}} | ||
| | settlement_type = {{PH wikidata|settlement_type}} | |||
| |leader_name = ] (]) | |||
| | subdivision_type = ] | |||
| |leader_title1 = Vice Mayor | |||
| | subdivision_name = ] | |||
| |leader_name1 = Shirlyn Bañas-Nograles (]) | |||
| | subdivision_type1 = ] | |||
| |leader_title2 = District Representative | |||
| | subdivision_name1 = {{PH wikidata|region}} | |||
| |leader_name2 = Pedro Acharon Jr. (]) | |||
| | subdivision_type2 = ] | |||
| |established_title = Incorporated | |||
| | subdivision_name2 = ] {{small|(geographically only)}} | |||
| |established_date = August 18, 1947 | |||
| | official_name = {{PH wikidata|official_name}} | |||
| |established_title1 = Cityhood | |||
| | etymology = | |||
| |established_date1 = 1968 | |||
| | |
| named_for = General ] | ||
| | |
| native_name = | ||
| | other_name = | |||
| |area_footnotes = <ref name=nscb>{{cite web |title=Province: South Cotabato |url=http://www.nscb.gov.ph/activestats/psgc/province.asp?provCode=126300000&provName=SOUTH%20COTABATO®Code=12®Name=REGION%20XII%20%28Soccsksargen%29 |work=PSGC Interactive |publisher=National Statistical Coordination Board |accessdate=14 May 2014 |location=Makati City, Philippines}}</ref> | |||
| | nickname = ''Tuna Capital of the Philippines''<ref name="PIAGovPH-DTI">{{cite news |title=DTI features 'best of the seas' at the IFEX PH 2018 |url=https://pia.gov.ph/news/articles/1008284 |access-date=April 17, 2019 |work=Philippine Information Agency|agency=DTI/PIA-NCR |date=May 26, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180526040813/https://pia.gov.ph/news/articles/1008284 |archive-date=May 26, 2018 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| |area_total_km2 = 492.86 | |||
| | |
| motto = | ||
| | anthem = ''Himno ng Heneral Santos''<br />{{small|(]: General Santos Hymn)}} | |||
| |area_water_km2 = | |||
| | subdivision_type3 = ] | |||
| |area_water_percent = | |||
| | subdivision_name3 = ] | |||
| |area_urban_km2 = | |||
| | established_title = ] | |||
| |area_metro_km2 = | |||
| | established_date = August 18, 1947 | |||
| |population_as_of = 2010 | |||
| | established_title1 = Cityhood | |||
| |population_footnotes = <ref name=2010PH_Census/> | |||
| | established_date1 = July 8, 1968 | |||
| |population_note = | |||
| | established_title2 = Highly urbanized city | |||
| |population_total = 538086 | |||
| | established_date2 = September 5, 1988 | |||
| |population_density_km2 = auto | |||
| | parts_type = ]s | |||
| |population_metro = | |||
| | parts_style = para | |||
| |population_density_metro_km2 = | |||
| | p1 = {{PH barangay count | {{wikidata|label|raw}} }} (see ]) | |||
| |population_urban = | |||
| | leader_title = ] | |||
| |population_density_urban_km2 = | |||
| | leader_name = Lorelie G. Pacquiao | |||
| |population_demonym = Generals, Heneral | |||
| | leader_title1 = ] | |||
| |population_blank2_title = ]s | |||
| | leader_name1 = Rosalita T. Nuñez | |||
| |population_blank2 = ], ], ], ] | |||
| | |
| leader_title2 = ] | ||
| | |
| leader_name2 = Loreto B. Acharon | ||
| | leader_title3 = ] | |||
| |timezone_DST = | |||
| | leader_name3 = {{PH Town Council | |||
| |utc_offset_DST = | |||
| | 1 = <div style="border-style:solid none;border-width:thin;border-color:Gainsboro;background-color:#e6e6e6;text-align:center;width:95%;font-variant:small-caps;"></div> | |||
| |latd = 06 |latm= 07 |latNS=N | |||
| | 2 = Jose Orlando R. Acharon | |||
| |longd = 125 |longm=10 |longEW=E | |||
| | 3 = Jose Edmar J. Yumang | |||
| |elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> tags--> | |||
| | 4 = Dominador S. Lagare Jr. | |||
| |elevation_m = 15.0 | |||
| | 5 = Maria Lourdes F. Casabuena | |||
| |postal_code_type = ] | |||
| | 6 = Vandyke B. Congson | |||
| |postal_code = {{#property:P281}} | |||
| | 7 = Elizabeth B. Bagonoc | |||
| |area_code_type = ] | |||
| | 8 = Richard L. Atendido | |||
| |area_code = {{#property:P473}} | |||
| | 9 = Jonathan T. Blando | |||
| |blank_info = ] | |||
| | 10 = Froebel Kan M. Balleque | |||
| |blank1_name = ] | |||
| | 11 = Virginia T. Llido | |||
| |blank1_info = 1st | |||
| | 12 = Jane G. Rivera | |||
| |website = {{URL|{{#property:P856}}}} | |||
| | 13 = Edgar C. Acharon | |||
| |footnotes = | |||
| }} | |||
| }} <!-- Infobox ends --> | |||
| | leader_title4 = ] | |||
| '''General Santos''' (]: ''Dakbayan sa Heneral Santos''; ]: ''Lungsod ng Heneral Santos''; previously known as ''Dadiangás'', and abbreviated ''G.S.C.'' or ''GenSan'') is the ] in the ].<ref name=Cities_of_the_Philippines_Most_extreme_points>]</ref> Classified as a ], General Santos is the 15th most populous city in the country with 538,086 inhabitants as per census data of 2010.<ref name=2010PH_Census>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov.ph/sites/default/files/attachments/hsd/pressrelease/Population%20and%20Annual%20Growth%20Rates%20for%20The%20Philippines%20and%20Its%20Regions%2C%20Provinces%2C%20and%20Highly%20Urbanized%20Cities%20Based%20on%201990%2C%202000%2C%20and%202010%20Censuses.pdf |title=Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities |work=2010 Census and Housing Population |publisher=National Statistics Office |accessdate=20 May 2014}}</ref> General Santos City is part of the ] region, and geographically in the province of ] but administered independent of it. | |||
| | leader_name4 = {{PH wikidata|electorate}} voters (]) | |||
| | government_type = {{PH wikidata|government_type}} | |||
| | government_footnotes = {{thinsp}}<ref>{{DILG detail}}</ref> | |||
| | elevation_m = {{PH wikidata|elevation_m}} | |||
| | elevation_max_m = 869 | |||
| | elevation_min_m = 0 | |||
| | elevation_max_rank = | |||
| | elevation_min_rank = | |||
| | elevation_footnotes = {{PH wikidata|elevation_footnotes}} | |||
| | elevation_max_footnotes = | |||
| | elevation_min_footnotes = | |||
| | area_rank = | |||
| | area_footnotes = {{PH area}} | |||
| | area_total_km2 = {{PH wikidata|area}} | |||
| | population_footnotes = {{PH census|current}} | |||
| | population_total = {{PH wikidata|population_total}} | |||
| | population_as_of = {{PH wikidata|population_as_of}} | |||
| | population_density_km2 = auto | |||
| | population_blank1_title = ]s | |||
| | population_blank1 = {{PH wikidata|household}} | |||
| | population_blank2_title = | |||
| | population_blank2 = | |||
| | population_demonym = Gensanon | |||
| | population_rank = | |||
| | population_note = | |||
| | timezone = ] | |||
| | utc_offset = +8 | |||
| | postal_code_type = ] | |||
| | postal_code = {{PH wikidata|postal_code}} | |||
| | postal2_code_type = {{PSGCstyle}} | |||
| | postal2_code = {{PSGC detail}} | |||
| | area_code_type = {{areacodestyle}} | |||
| | area_code = {{PH wikidata|area_code}} | |||
| | website = {{PH wikidata|website}} | |||
| | demographics_type1 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_title1 = ] (GDP) | |||
| | demographics1_info1 = ₱129.015 billion (2022)<ref name="gdpsoccsksargen2022">{{Cite web|title=City of General Santos Posts the Fastest Growth Among Economies in SOCCSKSARGEN in 2022|url=https://psa.gov.ph/statistics/ppa/node/1684061644}}</ref><br> | |||
| $2.279 billion (2022)<ref name="imfdec2022phptousd">{{Cite web|title=PH₱56.598 per dollar (per International Monetary Fund on Representative Exchange Rates for Selected Currencies for December 2022)|url=https://www.imf.org/external/np/fin/data/rms_mth.aspx?SelectDate=2022-12-31&reportType=REP|access-date=2023-12-09|website=]}}</ref> | |||
| | demographics1_title2 = {{PH wikidata|income_class_title}} | |||
| | demographics1_info2 = {{PH wikidata|income_class}} | |||
| | demographics1_title3 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_info3 = {{PH wikidata|poverty_incidence}}% ({{PH wikidata|poverty_incidence_point_in_time}}){{PH wikidata|poverty_incidence_footnotes}} | |||
| | demographics1_title4 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_info4 = {{PH wikidata|revenue}} {{PH wikidata|revenue_point_in_time}} | |||
| | demographics1_title5 = Revenue rank | |||
| | demographics1_info5 = | |||
| | demographics1_title6 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_info6 = {{PH wikidata|assets}} {{PH wikidata|assets_point_in_time}} | |||
| | demographics1_title7 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_info7 = | |||
| | demographics1_title8 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_info8 = {{PH wikidata|expenditure}} {{PH wikidata|expenditure_point_in_time}} | |||
| | demographics1_title9 = | |||
| | demographics1_info9 = | |||
| | demographics1_title10 = ] | |||
| | demographics1_info10 = {{PH wikidata|liabilities}} {{PH wikidata|liabilities_point_in_time}} | |||
| | demographics_type2 = Service provider | |||
| | demographics2_title1 = ] | |||
| | demographics2_info1 = {{PH electricity distribution | {{wikidata|label|raw}} }} | |||
| | demographics2_title2 = Water | |||
| | demographics2_info2 = | |||
| | demographics2_title3 = Telecommunications | |||
| | demographics2_info3 = | |||
| | demographics2_title4 = Cable TV | |||
| | demographics2_info4 = | |||
| | demographics2_title5 = | |||
| | demographics2_info5 = | |||
| | demographics2_title6 = | |||
| | demographics2_info6 = | |||
| | demographics2_title7 = | |||
| | demographics2_info7 = | |||
| | demographics2_title8 = | |||
| | demographics2_info8 = | |||
| | demographics2_title9 = | |||
| | demographics2_info9 = | |||
| | demographics2_title10 = | |||
| | demographics2_info10 = | |||
| | blank_name_sec1 = {{PH wikidata|climate_title}} | |||
| | blank_info_sec1 = {{PH wikidata|climate_type}} | |||
| | blank1_name_sec1 = ] | |||
| | blank1_info_sec1 = {{PH wikidata|language}} <br/> Maguindanaon | |||
| | blank2_name_sec1 = ] | |||
| | blank2_info_sec1 = | |||
| | blank3_name_sec1 = | |||
| | blank3_info_sec1 = | |||
| | blank4_name_sec1 = | |||
| | blank4_info_sec1 = | |||
| | blank5_name_sec1 = | |||
| | blank5_info_sec1 = | |||
| | blank6_name_sec1 = | |||
| | blank6_info_sec1 = | |||
| | blank7_name_sec1 = | |||
| | blank7_info_sec1 = | |||
| | blank1_name_sec2 = Major religions | |||
| | blank1_info_sec2 = | |||
| | blank2_name_sec2 = Feast date | |||
| | blank2_info_sec2 = | |||
| | blank3_name_sec2 = Catholic diocese | |||
| | blank3_info_sec2 = | |||
| | blank4_name_sec2 = Patron saint | |||
| | blank4_info_sec2 = | |||
| | blank5_name_sec2 = | |||
| | blank5_info_sec2 = | |||
| | blank6_name_sec2 = | |||
| | blank6_info_sec2 = | |||
| | blank7_name_sec2 = | |||
| | blank7_info_sec2 = | |||
| | short_description = | |||
| | footnotes = | |||
| }} | |||
| '''General Santos''', officially the '''City of General Santos'''{{NoteTag|{{langx|ceb|Dakbayan sa Heneral Santos}}; {{langx|hil|Dakbanwa sang Heneral Santos}}; ]: ''Ingud nu Heneral Santos''; ]: ''Banwe Dadiangas''; ]: ''Benwu Dadiangas''; ]: ''Lungsod ng Heneral Santos''}} and abbreviated as '''GenSan''', is a ] in the ] of ], ]. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 697,315 people making it the most populous city in Soccsksargen Region.{{PH census|current}} | |||
| It is located on the island of ], it is the ] and 15th-most populous city in the Philippines. It is the regional center for commerce and industry of the ] region, and it is also the only coastal as well as the largest city in the province of ] wherein it is geographically situated and grouped under the province by the ] but administered independently of it. | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| The city was named after Gen. ], a former ] and the settlement's leading pioneer. | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| The nomadic ] are the original inhabitants of General Santos, and traces of their early |
The nomadic ] are the original inhabitants of present-day General Santos, and traces of their early settlements of the area are found in the city's place names, which are derived from their vocabulary. Their name for the city, ''Dadiangas'', is from the '']'' tree that was once abundant in the area and is now a protected species under Republic Act 8371 or the Indigenous Peoples Right Act of 2007. The B'laan now lives alongside the city's new generation of settlers and other immigrants. | ||
| Beforehand, the B'laan would were forced upland into the surrounding hills after the Muslims settle in the area under the rule of the ]. | |||
| After the fall of Maguindanao, ] of ] expanded his domain south towards ]. Dadiangas remained as a port under the ] until the American era. | |||
| ===Waves of migration=== | ===Waves of migration=== | ||
| ] for whom the city is named after]] | |||
| Organized under the National Land Settlement Administration (NLSA) of the ] headed by ] ], General ] led the relocation of 62 Christian settlers from Luzon to the shores of Sarangani Bay aboard the ] “Basilan” of ''Compañia Maritima'' on February 27, 1939. The 62 pioneers, mostly agricultural and trade graduates, were the first large batch of settlers to land in the area with the mission to industriously cultivate the region. After this first influx of pioneers, thousands more Christians from ] and the ] have subsequently moved into the area, gradually driving some of the resident B'laan to the mountains and lost their livelihood. | |||
| Organized under the National Land Settlement Administration (NLSA) of the ] headed by ] ], General ] led the relocation of 62 Christian settlers from Luzon to the shores of Sarangani Bay aboard the ] “Basilan” of ''Compañia Maritima'' on February 27, 1939. The 62 pioneers, mostly agricultural and trade graduates, were the first large batch of settlers to land in the area with the mission to industriously cultivate the region. After this first influx of pioneers, more Christians from ] and ] subsequently migrated into the area, gradually driving some of the B'laan residents to the hills and mountains, where they have lost their livelihood and somewhat displaced ] living in the area. | |||
| In March 1939, the first formal settlement in the city was established in |
In March 1939, the first formal settlement in the city was established in Alagao, which is now known as Barangay Lagao. Lagao was known then as the "Municipal District of Buayan" under the jurisdiction of the deputy governor of the Municipal District of Glan, until it officially became an independent Municipal District of Buayan on October 1, 1940, appointing Datu Sharif Zainal Abedin, an Arab '']'' married to a daughter of a very influential '']'' of lower Buayan, as the first district municipal mayor. | ||
| ===Second World War=== | ===Second World War=== | ||
| During |
During ], the Municipal District of Buayan become one of the last frontiers between the combined American and Filipino forces and troops from the ]. Retreating Imperial Japanese forces made Klaja Karsts Land their last ground for defence, constructing round cement bunkers and tunnels. These bunkers can still be seen at Sitio Guadalupe; most of the tunnels, however, have since been damaged and even destroyed by treasure hunters and land developers. | ||
| ===Renaming and elevation to city status=== | ===Renaming and elevation to city status=== | ||
| {{main|Cities of the Philippines}} | |||
| A year after the Philippines regained full sovereignty from the United States on July 4, 1946, the Municipality of Buayan became a 4th class regular municipality by virtue of the Executive Order Number 82, dated August 18, 1947 by President ], absorbing the Municipal District of Glan whose low income bracket at the time disqualified it for the honour. Dadiangas was the seat of government for the Municipality of Buayan electing Irineo Santiago as its first Municipal Mayor on a local election that was held on November 11, 1947. Mayor Santiago was formally inducted on January 1, 1948.<ref></ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| A year after the Philippines regained full sovereignty from the United States on July 4, 1946, the Municipality of Buayan became a 4th class regular municipality by virtue of the Executive Order Number 82, dated August 18, 1947, by President ], absorbing the Municipal District of Glan, whose low income bracket at the time disqualified it for the honour. Dadiangas was the seat of government for the Municipality of Buayan electing Irineo Santiago as its first Municipal Mayor on a local election that was held on November 11, 1947. Mayor Santiago was formally inducted on January 1, 1948.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.generalsantosboard.com/history.php |title=History of General Santos City |access-date=December 10, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110711082830/http://www.generalsantosboard.com/history.php |archive-date=July 11, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Six years later, in June 1954, the Municipality of Buayan was renamed General Santos as a tribute to the leading pioneer via Act No. 1107<ref>{{cite web|url=http://lawph.com/statutes/ra1107-renaming-buayan,-cotabato-to-general-santos.html|title=An Act Changing the Name of the Municipality of Buayan, in the Province of Cotabato, to General Santos|publisher=LawPH.com| |
Six years later, in June 1954, the Municipality of Buayan was renamed General Santos as a tribute to the leading pioneer via Act No. 1107<ref>{{cite web |url=http://lawph.com/statutes/ra1107-renaming-buayan,-cotabato-to-general-santos.html |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120714205021/http://lawph.com/statutes/ra1107-renaming-buayan,-cotabato-to-general-santos.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=July 14, 2012 |title=An Act Changing the Name of the Municipality of Buayan, in the Province of Cotabato, to General Santos |publisher=LawPH.com |access-date=April 11, 2011}}</ref> authored by Congressman Luminog Mangelen of Cotabato Province. | ||
| From 1963 to 1967, the municipality's economy experienced a boom under Mayor Lucio A. Velayo, as several large agri-based and multinational firms such as ], General Milling Corporation and UDAGRI expanded into the area. Although it was then qualified to become a fourth class city from being a municipality, the residents rejected a move by Congressman Salipada Pendatun to convert the Municipality of Buayan into a city and to rename it ’’Rajah Buayan’’. | From 1963 to 1967, the municipality's economy experienced a boom under Mayor Lucio A. Velayo, as several large agri-based and multinational firms such as ], General Milling Corporation and UDAGRI expanded into the area. Although it was then qualified to become a fourth class city from being a municipality, the residents rejected a move by Congressman Salipada Pendatun to convert the Municipality of Buayan into a city and to rename it ’’Rajah Buayan’’. | ||
| On July 8, 1968, the Municipality of General Santos was converted into a city upon the approval of Republic Act No. 5412, authored by Congressman James L. Chiongbian. It was inaugurated on September 5 of that year, with Antonio C. Acharon became the new city's first mayor. |
On July 8, 1968, the Municipality of General Santos was converted into a city upon the approval of Republic Act No. 5412, authored by Congressman James L. Chiongbian. By this time, General Santos City had already established itself as a major economic and educational hub in the region. Three of the oldest educational institutions in the city — ] (1948), ] (1957), and ] (1961) — were established prior to the city’s official founding. It was inaugurated on September 5 of that year, with Antonio C. Acharon became the new city's first mayor. On September 5, 1988, a decade after its inauguration as a chartered city, GenSan was declared a highly urbanized city of South Cotabato. | ||
| Even after becoming a ] independent from South Cotabato in 1988, General Santos remained part of the province's congressional representation. The city only gained a separate representative with the passage of Republic Act No. 11243 on March 11, 2019,<ref name=ra11243>{{cite web|url=https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/downloads/2019/03mar/20190311-RA-11243-RRD.pdf|title=Republic Act No. 11243 - An Act Reapportioning the First Legislative District of the Province of South Cotabato, thereby creating the Lone Legislative District of General Santos City|date=March 11, 2019|accessdate=May 6, 2019|author=Congress of the Philippines}}</ref> which segregated General Santos from the ] of ] to be its ]. On September 15, 2021, House Bill No. 10021 authored by Representative Ferdinand Hernandez, that officially mandate General Santos as a lone district,<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/third_18/HBT10021.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=September 18, 2021 |archive-date=September 15, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210915182737/https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/third_18/HBT10021.pdf |url-status=dead}}</ref> separate from South Cotabato was passed on third and final reading. | |||
| In April 2001, Mayor Adelbert W. Antonino, an ally of deposed president ], coordinated with various mayors and governors to bring their respective constituents to ] in ] to ] the arrest of Estrada.<ref>{{cite news|last=Gloria|first=Glenda M.|title=Remembering the Iglesia-led EDSA 3|url=https://www.rappler.com/newsbreak/in-depth/104045-edsa-3-iglesia-ni-cristo/|access-date=March 7, 2024|work=]|publisher=Rappler Inc.|date=August 29, 2015|author-link=Newsbreak (magazine)|quote=This story on 'EDSA 3' was first published by ] in May 2001.}}</ref> | |||
| ==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| ] | |||
| General Santos lies at the southern part of the Philippines. The city is southeast of Manila, southeast of Cebu and southwest of Davao. | |||
| The city is bounded by municipalities of ], namely ] in the east, and ] in the south. General Santos is likewise bounded by the ] municipality of ] and ] municipality of ] in the north, and the municipality of ] in the west. | |||
| General Santos City lies at the southern part of the Philippines. It is located at 6°7'N 125°10'E latitude. The city is southeast of Manila, southeast of Cebu and southwest of Davao. | |||
| General Santos occupies the whole of South Cotabato's coastline. | |||
| The city is bounded by municipalities of ] namely ] in the east, and ] in the south. General Santos is likewise bounded by the ] municipality of ] and ] municipality of ] in the north, and the municipality of ] in the west. | |||
| {{clear left}} | |||
| ===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
| {{Weather box | |||
| General Santos City has a ] (] ''Aw''). | |||
| | location = General Santos (1991–2020, extremes 1949–2020) | |||
| | metric first = Yes | |||
| | single line = Yes | |||
| | width = auto | |||
| | Jan record high C = 37.5 | |||
| | Feb record high C = 38.0 | |||
| | Mar record high C = 38.9 | |||
| | Apr record high C = 39.0 | |||
| | May record high C = 39.4 | |||
| | Jun record high C = 38.5 | |||
| | Jul record high C = 37.0 | |||
| | Aug record high C = 37.0 | |||
| | Sep record high C = 36.5 | |||
| | Oct record high C = 37.0 | |||
| | Nov record high C = 37.0 | |||
| | Dec record high C = 37.5 | |||
| | year record high C = 39.0 | |||
| | Jan high C = 32.3 | |||
| | Feb high C = 32.9 | |||
| | Mar high C = 34.0 | |||
| | Apr high C = 34.3 | |||
| | May high C = 33.5 | |||
| | Jun high C = 32.2 | |||
| | Jul high C = 31.7 | |||
| | Aug high C = 31.7 | |||
| | Sep high C = 32.2 | |||
| | Oct high C = 32.6 | |||
| | Nov high C = 32.8 | |||
| | Dec high C = 32.6 | |||
| | year high C = 32.7 | |||
| | Jan mean C = 27.5 | |||
| | Feb mean C = 27.9 | |||
| | Mar mean C = 28.5 | |||
| | Apr mean C = 28.9 | |||
| | May mean C = 28.5 | |||
| | Jun mean C = 27.7 | |||
| | Jul mean C = 27.2 | |||
| | Aug mean C = 27.3 | |||
| | Sep mean C = 27.5 | |||
| | Oct mean C = 27.7 | |||
| | Nov mean C = 27.9 | |||
| | Dec mean C = 27.8 | |||
| | year mean C = 27.9 | |||
| | Jan low C = 22.6 | |||
| | Feb low C = 22.8 | |||
| | Mar low C = 23.0 | |||
| | Apr low C = 23.5 | |||
| | May low C = 23.6 | |||
| | Jun low C = 23.1 | |||
| | Jul low C = 22.8 | |||
| | Aug low C = 22.8 | |||
| | Sep low C = 22.8 | |||
| | Oct low C = 22.8 | |||
| | Nov low C = 23.0 | |||
| | Dec low C = 23.0 | |||
| | year low C = 23.0 | |||
| | Jan record low C = 17.1 | |||
| | Feb record low C = 17.2 | |||
| | Mar record low C = 16.9 | |||
| | Apr record low C = 18.3 | |||
| | May record low C = 18.7 | |||
| | Jun record low C = 17.9 | |||
| | Jul record low C = 17.2 | |||
| | Aug record low C = 17.5 | |||
| | Sep record low C = 18.0 | |||
| | Oct record low C = 18.2 | |||
| | Nov record low C = 18.3 | |||
| | Dec record low C = 18.0 | |||
| | year record low C = 16.9 | |||
| | rain colour = green | |||
| | Jan rain mm = 96.9 | |||
| | Feb rain mm = 53.0 | |||
| | Mar rain mm = 55.3 | |||
| | Apr rain mm = 54.1 | |||
| | May rain mm = 72.2 | |||
| | Jun rain mm = 101.9 | |||
| | Jul rain mm = 98.1 | |||
| | Aug rain mm = 91.3 | |||
| | Sep rain mm = 83.3 | |||
| | Oct rain mm = 99.6 | |||
| | Nov rain mm = 77.5 | |||
| | Dec rain mm = 74.9 | |||
| |year rain mm = 958.1 | |||
| | unit rain days = 0.1 mm | |||
| | Jan rain days = 9 | |||
| | Feb rain days = 7 | |||
| | Mar rain days = 6 | |||
| | Apr rain days = 6 | |||
| | May rain days = 8 | |||
| | Jun rain days = 12 | |||
| | Jul rain days = 11 | |||
| | Aug rain days = 11 | |||
| | Sep rain days = 10 | |||
| | Oct rain days = 10 | |||
| | Nov rain days = 8 | |||
| | Dec rain days = 8 | |||
| |year rain days = 106 | |||
| | Jan humidity = 79 | |||
| | Feb humidity = 76 | |||
| | Mar humidity = 75 | |||
| | Apr humidity = 75 | |||
| | May humidity = 78 | |||
| | Jun humidity = 82 | |||
| | Jul humidity = 83 | |||
| | Aug humidity = 82 | |||
| | Sep humidity = 81 | |||
| | Oct humidity = 81 | |||
| | Nov humidity = 80 | |||
| | Dec humidity = 79 | |||
| | year humidity = 79 | |||
| | source 1 = ]<ref name=PAGASAnormals>{{cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181013093404/https://data.gov.ph/?q=dataset/climatological-normal-values/resource/67484451-925e-4462-a3c2-44ab19c610db |archive-date=October 13, 2018 |url=https://data.gov.ph/?q=dataset/climatological-normal-values/resource/67484451-925e-4462-a3c2-44ab19c610db |title=General Santos City, South Cotabato Climatological Normal Values |publisher=Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration |access-date=October 13, 2018 |url-status=bot: unknown }}</ref><ref name=PAGASAextremes>{{cite web | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181013044610/https://pubfiles.pagasa.dost.gov.ph/pagasaweb/files/cad/CLIMATOLOGICAL%20EXTREMES%20(as%20of%202020)/General%20Santos.pdf |archive-date=October 13, 2018 |url=https://data.gov.ph/?q=dataset/climatological-extremes/resource/987ac3c3-12a3-40f5-8cbe-2d8df5b36059 |title=General Santos City, South Cotabato Climatological Extremes |publisher=Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration |access-date=October 13, 2018}}</ref>}} | |||
| General Santos has a ] (]). With an average annual rainfall of less than {{Convert|1000|mm}}, it is one of the driest places in the Philippines. | |||
| <!-- Start of Weatherbox --> | |||
| {{-}} | |||
| <center>{{Weather box | |||
| |location = General Santos City | |||
| |metric first = Yes | |||
| |single line = Yes | |||
| | Jan high C = 32.2 | |||
| | Feb high C = 32.5 | |||
| | Mar high C = 33.1 | |||
| | Apr high C = 33.4 | |||
| | May high C = 32.3 | |||
| | Jun high C = 31.4 | |||
| | Jul high C = 31 | |||
| | Aug high C = 31.1 | |||
| | Sep high C = 31.5 | |||
| | Oct high C = 31.9 | |||
| | Nov high C = 32.2 | |||
| | Dec high C = 32.1 | |||
| | Jan mean C = 26.8 | |||
| | Feb mean C = 27 | |||
| | Mar mean C = 27.4 | |||
| | Apr mean C = 27.9 | |||
| | May mean C = 27.5 | |||
| | Jun mean C = 26.9 | |||
| | Jul mean C = 26.5 | |||
| | Aug mean C = 26.5 | |||
| | Sep mean C = 26.8 | |||
| | Oct mean C = 27.1 | |||
| | Nov mean C = 27.1 | |||
| | Dec mean C = 26.9 | |||
| | Jan low C = 21.4 | |||
| | Feb low C = 21.5 | |||
| | Mar low C = 21.7 | |||
| | Apr low C = 22.4 | |||
| | May low C = 22.7 | |||
| | Jun low C = 22.4 | |||
| | Jul low C = 22 | |||
| | Aug low C = 22 | |||
| | Sep low C = 22.2 | |||
| | Oct low C = 22.3 | |||
| | Nov low C = 22 | |||
| | Dec low C = 21.8 | |||
| | Jan precipitation mm = 68 | |||
| | Feb precipitation mm = 69 | |||
| | Mar precipitation mm = 47 | |||
| | Apr precipitation mm = 57 | |||
| | May precipitation mm = 108 | |||
| | Jun precipitation mm = 118 | |||
| | Jul precipitation mm = 110 | |||
| | Aug precipitation mm = 93 | |||
| | Sep precipitation mm = 84 | |||
| | Oct precipitation mm = 113 | |||
| | Nov precipitation mm = 98 | |||
| | Dec precipitation mm = 87 | |||
| |source 1 = Climate-Data.org<ref>{{cite web|url=http://en.climate-data.org/location/4018/|title= Climate: General Santos - Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table|accessdate=2014-05-25}}</ref> | |||
| |date=May 2014 | |||
| }} | |||
| </center> | |||
| <!-- End of Weatherbox --> | |||
| ===Barangays=== | ===Barangays=== | ||
| ] | |||
| General Santos City is politically subdivided into 26 ]s.<ref name=nscb/> | |||
| General Santos is politically subdivided into 26 ]s.{{PSGC detail|area}} Each barangay consists of ]s while some have ]. | |||
| {{Div col| |
{{Div col|colwidth=15em}} | ||
| * Apopong | * Apopong | ||
| * Baluan | * Baluan | ||
| * Batomelong | * Batomelong | ||
| * Buayan | * ] | ||
| * Bula | * Bula | ||
| * Calumpang | * Calumpang | ||
| * City Heights | * City Heights | ||
| * Conel | * Conel | ||
| * Dadiangas East |
* Dadiangas East | ||
| * Dadiangas North | * Dadiangas North | ||
| * Dadiangas South | * Dadiangas South | ||
| * Dadiangas West | * Dadiangas West | ||
| * Fatima | * ] | ||
| * Katangawan | * Katangawan | ||
| * Labangal | * ] | ||
| * Lagao (1st & 3rd) | * Lagao (1st & 3rd) | ||
| * Ligaya | * Ligaya | ||
| Line 204: | Line 389: | ||
| * Tinagacan | * Tinagacan | ||
| * Upper Labay | * Upper Labay | ||
| {{ |
{{div col end}} | ||
| ==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| {{multiple image | |||
| {{Philippine Census |align=none | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | title= Population census of General Santos | |||
| | direction = vertical | |||
| | 1990= 250389 | |||
| | total_width = 200 | |||
| | 1995= 327173 | |||
| | image1 = The colorful and lively Kadsagayan Parade during Kalilangan.jpg | |||
| | 2000= 411822 | |||
| | caption1 = Kadsagayan Parade during Kalilangan Festival | |||
| | 2007= 529542 | |||
| | image2 = Tuna festival GenSan.jpg | |||
| | 2010= 538086 | |||
| | caption2 = Tuna Festival contingent | |||
| | footnote= Source: National Statistics Office<ref name=2010PH_Census/> | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Philippine Census | |||
| | align= left | |||
| | title = Population census of {{PH wikidata|name}} | |||
| | 1903 = {{PH census population|1903}} | |||
| | 1918 = {{PH census population|1918}} | |||
| | 1939 = {{PH census population|1939}} | |||
| | 1948 = {{PH census population|1948}} | |||
| | 1960 = {{PH census population|1960}} | |||
| | 1970 = {{PH census population|1970}} | |||
| | 1975 = {{PH census population|1975}} | |||
| | 1980 = {{PH census population|1980}} | |||
| | 1990 = {{PH census population|1990}} | |||
| | 1995 = {{PH census population|1995}} | |||
| | 2000 = {{PH census population|2000}} | |||
| | 2007 = {{PH census population|2007}} | |||
| | 2010 = {{PH census population|2010}} | |||
| | 2015 = {{PH census population|2015}} | |||
| | 2020 = {{PH census population|2020}} | |||
| | 2025 = | |||
| | 2030 = | |||
| | footnote = Source: ]{{PH census|2015}}{{PH census|2010}}{{PH census|2007}}{{LWUA population data}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| There are two major languages spoken in the city, with ] being widely spoken and being used by the local media outlets in the city (television, radio, and newspapers), followed by ], which is used mainly by settlers who came from the provinces of ], ], ] and ], as well as immigrants from the provinces of ], ] and ]. Other languages spoken within the city include ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ] is widely spoken but there are also Ilonggo settlers in the city and they are from South Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, North Cotabato and Maguindanao. | |||
| {{clear left}} | |||
| ===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
| {{bar box | |||
| The predominant religion in the city is ], with the largest denomination being the ], comprising about 80 percent of the population. Some eight percent self-identify as belonging to one of several ] churches, including the ], the ], ], and various Alliance, Baptist, Born Again, Church of God, Evangelical, Methodist and Pentecostal groups. Included also in this percentage is the ]. | |||
| | title = Religion in General Santos (2020)<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=Religious Affiliation in the Philippines (2020 Census of Population and Housing) {{!}} Philippine Statistics Authority {{!}} Republic of the Philippines |url=https://psa.gov.ph/content/religious-affiliation-philippines-2020-census-population-and-housing |access-date=2023-08-06 |website=psa.gov.ph}}</ref> | |||
| | titlebar = #ddd | |||
| The remaining 12 percent belong to non-Christian faiths, particularly ]. | |||
| | left1 = Religion | |||
| | right1 = percentage | |||
| | float = right | |||
| | bars = | |||
| {{bar percent|]|Gold|65}} | |||
| {{bar percent|Other Christian, including Protestants|Red|20.5}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|Green|9.8}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|Purple|3.3}} | |||
| {{bar percent|Others|Grey|1.4}} | |||
| }} | |||
| The predominant religion in the city is ], with the largest denomination being the ], comprising almost 90% of the population.{{citation needed|date=September 2018}} About 9% of the population belongs to ], mostly ].<ref name="PSA">{{cite web |title=Muslim Population in Mindanao (based on POPCEN 2015 |url=http://rssoarmm.psa.gov.ph/release/54739/factsheet/muslim-population-in-mindanao-%28based-on-popcen-2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180831174924/http://rssoarmm.psa.gov.ph/release/54739/factsheet/muslim-population-in-mindanao-%28based-on-popcen-2015 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 31, 2018 |author=Philippine Statistics Authority |access-date=August 31, 2018 |date=July 26, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| {{PH poverty incidence}} | |||
| The city's major economic activity is primarily anchored in two sectors namely the agro-industry and ]. | The city's major economic activity is primarily anchored in two sectors namely the agro-industry and ]. | ||
| *'''Agro-industry''': Endowed with rich volcanic soil, ample and well distributed rainfall all throughout the year and a typhoon-free climate, General Santos produces export quality high valued crops such as ], ], ], ], ] and ]. It also yields quality exotic fruits, vegetables and cut flowers. The city is also a top producer and exporter of quality livestock such as ], ], and ]. But with the continuing growth in population and economy in the passing of time, a number of the city's agricultural lands have gradually been converted into built up areas in order to address the relatively growing need of dwelling and viable spaces. | |||
| ] | |||
| *'''Agro-industry''': Endowed with rich volcanic soil, ample and well distributed rainfall all throughout the year and a typhoon-free climate, General Santos City produces export quality high valued crops such as ], ], ], ], ] and ]. It also yields quality exotic fruits, vegetables and cut flowers. The city is also a top producer and exporter of quality livestock such as ], ], and ]. But with the continuing growth in population and economy in the passing of time, a number of the city's agricultural lands have gradually been converted into built up areas in order to address the relatively growing need of dwelling and viable spaces. | |||
| *'''Fishing industry''': General Santos is the largest producer of ]-grade ] in the Philippines. Thus, as early as 1970, it was nicknamed "Tuna Capital of the Philippines". The city also accounts for the second-largest daily total catch of ] in the country after ] in the ]. The ] in yields a total daily capacity of 750 metric tons of fish catch, and employs about 7,800 workers. General Santos is home to seven tuna processing plants. The Fishport Complex in Barangay Tambler has a {{convert|750|m}} quay and a {{convert|300|m}} wharf for 2,000 GT reefer carriers. The fish port is equipped with modern facilities that comply with international standards on fish catch handling. Locals in the city boast that fish and seafood do not come fresher than what is found in their locality. | |||
| General Santos registered 1,365 new medium to large enterprises in 2011. An aggregate investment involved is estimated PHP 1.202 billion. Top industry for new investment in 2011 was as follows: Hotel and Restaurant-31%; Wholesale & Retail Trade-20%; Repair of Motor Vehicles, Motorcycles and Personal & Household Goods, Real Estate & Renting Business Activities-17%; Other Community, Social & Personal Services-8%; Financial Intermediation-5%; Manufacturing-5%; Fishing-3%; ICT-3 % | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| *'''Fishing industry''': General Santos City is the largest producer of ]-grade ] in the Philippines.Thus in as early as 1970, the title ''"Tuna Capital of the Philippines"'' has become a tag to it. GenSan also accounts for the second largest daily total catch of ] in the country after ] in the ]. Locals in the city boast that fishes and seafoods do not come fresher than what is found in their locality. The ] in GenSan yields a total daily capacity of 750 metric tons of fish catch alone and employs about 7,800 workers. Which is why General Santos City is home to seven (7) tuna processing plants in the country. The Fishport Complex in Barangay Tambler has a {{convert|750|m}} quay and a {{convert|300|m}} wharf for 2,000 GT reefer carriers. The fishport is equipped with modern facilities that comply with international standards on fish catch handling. | |||
| As of 2000, there are 59 banks serving the city. This composed of 46 commercial banks, 5 savings banks, 7 rural banks and 1 cooperative bank. Aside from this, there are 48 lending institutions as well as 49 pawnshops providing emergency loan assistance. | |||
| General Santos City has registered 1,365 new medium to large enterprises in 2011. An aggregate investment involved is estimated PHP 1.202 billion. Top industry for new investment in 2011 are as follows: Hotel and Restaurant-31%; Wholesale & Retail Trade-20%; Repair of Motor Vehicles, Motorcycles and Personal & Household Goods, Real Estate & Renting Business Activities-17%; Other Community, Social & Personal Services-8%; Financial Intermediation-5%; Manufacturing-5%; Fishing-3%; ICT-3 % | |||
| As of 2000, there are 59 banks serving the city. This composed of 46 commercial banks, 5 savings banks, 7 rural banks and 1 cooperative bank. Aside from this, there are 48 lending institutions as well as 49 pawnshops providing emergency loan assistance. | |||
| ===Shopping=== | ===Shopping=== | ||
| General Santos is the shopping capital of the ] region. Residents from nearby towns and provinces visit the city to do shopping and enjoy life and leisure activities. There are several huge shopping malls in the city, notable ones are ], ], Robinsons Place GenSan, Gaisano Mall of GenSan, RD Plaza (Fitmart), Veranza Mall, and the newest addition to the city which is RD City Mall located at Barangay Mabuhay, Unitop Shopping Mall in Barangay Dadingas West and AllHome (soon in Barangay Katangawan, Circumferential Road). SM Savemore has two branches in the city and another branch will be built within the downtown area. There are also news about building an Ayala Mall and Puregold. These malls are home to both national and international brands of retail merchandises as well as restaurants and cafes. There are many merchandise and large groceries owned by local and foreign Chinese, Taiwanese and Korean businessmen in the city. | |||
| General Santos City is the shopping capital of the SOCCSKSARGEN region. Residents from nearby towns and provinces visit the city to do shopping and enjoy life and leisure activities. | |||
| There are several huge shopping malls in the city, notable ones are KCC Mall of Gensan, ], Robinsons Place GenSan, Gaisano Mall of GenSan, RD Plaza (Fitmart), Veranza Mall, and the newest addition to the city which is RD City Mall located at Brgy. Calumpang. SM Savemore has a branch in the city and there are plans that they are building more in the city. There are also news about building an Ayala Mall and Puregold. These malls are home to both national and international brands of retail merchandises as well as restaurants and cafes. There are many merchandise and large groceries owned by local and foreign Chinese, Taiwanese and Korean businessmen in the city. | |||
| ==Tourist attractions== | |||
| There are a number of cultural-heritage sites in the city like ] in Notre Dame of Dadiangas University and the memorable statue of General Paulino Santos giving the way of the growing city. | |||
| ===Klaja Ecopark=== | |||
| An ecological preservation park located {{convert|15|km}} off the central business district on the north-east side of city in Barangay Conel. ''Klaja Karsts Land'' derived its name from ''“Kalaha”'' ("frying pot") as it looked like one due to the surrounding towers of ] formation naturally formed millions of years ago. It produced natural waterfalls and caves. Opposite is the ] and camping ground of Nopol Hills, which borders Barangays Conel and Mabuhay. Nopol Hills offers visitors a wide scenic overview of the entire city, as well as the ] and parts of ] and ] Province. | |||
| ===Mount Matutum=== | |||
| ] is an active volcano, approximately 5.7 km from Acmonan, Tupi, South Cotabato. Adjacent volcanic edifices are Landayao, Tampad, and Albulhek to the west of the volcano, and Magolo to the north. There is a well-preserved 320-metre wide crater at the volcano's summit. The crater is breached by three gorges and has a 120-metre deep, densely forested floor. The great view of Matutum is seen in Barangay Pagalungan, Polomolok, with some plantation of pineapples and Barangay Mabuhay and San Isidro in General Santos City. | |||
| ===Cuisine=== | |||
| Tuna is widely available in the city and is a part of the local cuisine along with a lot of other fresh seafood. Popular dishes include grilled tuna belly dipped in ] with onions and chili, and '']'' that comprises grilled meat mixed with ''Kinilaw'' (Filipino vinegar-based ]), while fried banana and '']'' is made from fresh local bananas. A wide range of dining establishments have popped up elsewhere in the city offering local and foreign cuisine. | |||
| ==Festivals== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ;Kalilangan Festival: General Santos City celebrates the Kalilangan every month of February. ''"Kalilangan"'' means festival, festivity or jubilation. It is a social gathering marked by exchanging of amenities among traditional leaders, elders, allies and subordinates in varying tones. In a broader perspective, Kalilangan projects a positive and dynamic meaning for it engulfs the artistic, humane and altruistic aspects of social interaction that takes place in any occasion or celebration. Kalilangan is a noble tradition. It is a complete work of art nourished and nurtured by rich cultural heritage that has withstand the test of time from generation to generation. The festival is being Spearheaded by the Mindanao State University upon which have garnered awards as the countries best native/local festival three years in succession. | |||
| ;Tuna Festival: Thanksgiving and festivities are being celebrated annually through its Tuna Festival during the Last week of August and the first week of September highlighting on its main industry which is the Tuna fishing. This is also in line with the celebration of the city's charter anniversary which falls every 5 September and is also being set as the culmination day for the Tuna Festival. Aside from parades and showcases, numerous culinary competitions are being held to promote sumptuous tuna based cuisines and other delectable meals made from fresh sea food | |||
| ;Yaman Gensan: Yaman Gensan is an annual event in Gensan that celebrates and promotes local entrepreneurs. It is also celebrates in Month of July. Tuna products, T'nalak, Malong and other tribal objects that show off and sell it, through manufacture. Yaman Gensan direves a good quality of highly urbanized. | |||
| ;Paskuhan sa Gensan: The city invites the way of Birth of Jesus christ, by honoring this event. This is actually celebrates in December 17 up to the countdown of New Year, Colorful lanterns, giant Christmas tree and Gensan Barangay Christmas House competition are in the event and also Paskuhan sa Gensan Street Dancing, choir group and Christmas Dance craze are joined also in the love and hope event. | |||
| ==Infrastructure== | ==Infrastructure== | ||
| ;Communication | ;Communication | ||
| Modern and state-of-the-art communication facilities at par with global standards are readily available and are provided in General Santos |
Modern and state-of-the-art communication facilities at par with global standards are readily available and are provided in General Santos by major telecommunication companies in the country. These include voice, data, internet and network solutions, among others, in both wired and mobile forms. | ||
| ===Transportation=== | ===Transportation=== | ||
| GenSan and the whole of Soccsksargen can be reached by air, land, or sea. | |||
| ] | |||
| GenSan and the whole of SOCCSKSARGEN region can be reached by air, land, or sea. | |||
| ;Air |
;Air transportation | ||
| ] | |||
| The ] is the largest airport in ].<ref>{{cite news |title=Demos in South get ugly; Ramos unfazed: Mindanao Council is good formula, FVR insists |author=Fel V. Maragay |work=Manila Standard|location=Philippines |date=July 4, 1996 |url=https://news.google.com/newspapers?id=4mUVAAAAIBAJ&pg=2659,557616&dq=the+largest+airport+in+mindanao&hl=en |access-date=October 9, 2011}}</ref> It has a 3,227-metre concrete runway<ref>{{cite web |title=General Santos International Airport |url=http://www.caap.gov.ph/web/airportsTambler.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100919142820/http://www.caap.gov.ph/web/airportsTambler.htm |archive-date=September 19, 2010 }}</ref> capable of handling wide-bodied jets like ] and ]. It was also called Rajah Buayan Airport in the 1990s, and Tambler Airport in 2008, before being renamed to its current name. Flights to and from ], ], and ] are currently being operated in the airport by ] and ]. General Santos International Airport is the second busiest airport in Mindanao and 9th busiest airport in the Philippines. | |||
| | title = Demos in South get ugly; Ramos unfazed: Mindanao Council is good formula, FVR insists | |||
| | author = Fel V. Maragay | |||
| | newspaper = Manila Standard. | |||
| | location = Philippines | |||
| | date = July 4, 1996 | |||
| | url = http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=4mUVAAAAIBAJ&sjid=0goEAAAAIBAJ&pg=2659,557616&dq=the+largest+airport+in+mindanao&hl=en | |||
| | accessdate = October 9, 2011 | |||
| }} | |||
| </ref> It has a 3,227-metre concrete runway<ref>{{cite web|title=General Santos International Airport|url=http://www.caap.gov.ph/web/airportsTambler.htm|work=http://www.caap.gov.ph}}</ref> capable of handling wide-bodied jets like ] and ]. It was also called Rajah Buayan Airport in the 1990s and Tambler Airport in year 2008 before it was renamed to its current name. Flights to and from ], ], and ] are currently being operated in the airport by ] and ]. General Santos International Airport is the second busiest airport in Mindanao and 9th busiest airport in the Philippines. | |||
| ;Sea |
;Sea transportation | ||
| ], the main international sea port of General Santos]] | |||
| The Makar Wharf is the main international sea port of the city and is one of the finest sea ports in the country. It is location in Barangay Labangal, away from the central business district. With a {{convert|740|m}} docking length and a {{convert|19|m}} width, the wharf can accommodate up to nine (9) ship berthing positions all at the same time.<ref>http://www.ictsi.com/operations.aspx?p_id=3&catg_id=&operation_id=132&id=152</ref> The port is complete with modern facilities like container yards, storage and weighing bridges to name a few.<ref>http://www.scipsi.com/equip.html</ref> Several shipping companies operate regular inter-island ferry service to and from other major ports in Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao. ], ] and ] provide these inter-island shipping routes while numerous ]n shipping lines operate international ferry service between General Santos City and neighboring ports in ] carrying both passenger and cargo loads. | |||
| The ] is the main international sea port of the city and is one of the finest sea ports in the country. It is located in Barangay Labangal, away from the central business district. With a {{convert|740|m}} docking length and a {{convert|19|m}} width, the wharf can accommodate up to nine ship berthing positions all at the same time.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ictsi.com/operations.aspx?p_id=3&catg_id=&operation_id=132&id=152 |title=International Container Terminal Services, Inc |access-date=February 27, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111003182515/http://www.ictsi.com/operations.aspx?p_id=3&catg_id=&operation_id=132&id=152 |archive-date=October 3, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The port is replete with modern facilities such as container yards, storage and weighing bridges.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.scipsi.com/equip.html |title=Archived copy |access-date=February 27, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110716015112/http://www.scipsi.com/equip.html |archive-date=July 16, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Several shipping companies operate regular inter-island ferry service to and from other major ports in Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao. ], ] and ] provide these inter-island shipping routes while numerous ]n shipping lines operate international ferry service between General Santos and neighboring ports in ] carrying both passenger and cargo loads. | |||
| ;Land transportation | |||
| ] | |||
| Commuting in and around General Santos is a fast and convenient ride. More than 400 passenger ], public utility vans and ] wield routes within the city and neighboring provinces like in ], ], ], ], ], ] and others. Three-wheeled motorized cabs known as ]s are the city's main mode of public transport and have been on the road since the pioneering times. Air-conditioned ]s also ply the city streets offering commuters a choice of a more comfortable mode of transportation. | |||
| ;Land Transportation | |||
| Commuting in and around General Santos City is a fast and convenient ride. More than 400 passenger ], public utility vans and ] wield routes within the city and neighboring provinces like in ], ], ], ], ], ] and others. Three-wheeled motorized cabs known as ]s are the city's main mode of public transport and have been on the road since the pioneering times. Air-conditioned ]s also ply the city streets offering commuters a choice of a more comfortable mode of transportation. | |||
| Maintained by the City Engineers' Office, the city's major road networks are paved and endowed with safety road marks, signs and signals to ensure a secure and efficient traffic flow within the city. |
Maintained by the City Engineers' Office, the city's major road networks are paved and endowed with safety road marks, signs and signals to ensure a secure and efficient traffic flow within the city. The ] links the city by land to other major cities in Mindanao and to the rest of the country. | ||
| The General Santos |
The General Santos Terminal—popularly known as Bulaong Terminal; located in Barangay Dadiangas North is the city's main integrated land transport terminal. The terminal serves as the city's gateway for land travelers. ]es and other forms of public mass transportation—to and from various parts of Mindanao such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | ||
| ===Utilities=== | ===Utilities=== | ||
| ;Power: Majority of the city's power supply is being serviced by the second district of South Cotabato Electric Cooperative ''(SOCOTECO-II)''. The said power distributor acquires the majority of its power needs for the city's consumption from the ] (TransCo) while other sources are drawn from various Independent Power Producers ''(IPP)'' from nearby power plants and barges. | ;Power: Majority of the city's power supply is being serviced by the second district of South Cotabato Electric Cooperative ''(SOCOTECO-II)''. The said power distributor acquires the majority of its power needs for the city's consumption from the ] (TransCo) while other sources are drawn from various Independent Power Producers ''(IPP)'' from nearby power plants and barges. | ||
| ;Water: Majority of the households and other entities in the city are provided and serviced with clean, safe and potable water supply from deep well sources by General Santos City Water District (GSCWD). |
;Water: Majority of the households and other entities in the city are provided and serviced with clean, safe and potable water supply from deep well sources by General Santos City Water District (GSCWD). Potable water sources in other far flung and remote parts of the city where cannot be reached by the local water utility service are being served by their individual Barangay Water And Sanitation systems. | ||
| ;Waste management: In a bid to achieve an efficient and sustainable management of non-hazardous waste the city produces every single day, the finalization and construction of the city's waste water treatment facility is currently underway at the corner of P. Acharon and I. Santiago Boulevards.<ref>http://www.gensantos.gov.ph/2010/05/construction-of-waste-treatment-facility-p-acharon-blvd-corner-santiago-blvd-general-santos-city/</ref> |
;Waste management: In a bid to achieve an efficient and sustainable management of non-hazardous waste the city produces every single day, the finalization and construction of the city's waste water treatment facility is currently underway at the corner of P. Acharon and I. Santiago Boulevards.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gensantos.gov.ph/2010/05/construction-of-waste-treatment-facility-p-acharon-blvd-corner-santiago-blvd-general-santos-city/ |title=Construction of Waste Treatment Facility, P. Acharon BLVD. Corner Santiago BLVD., General Santos City | General Santos City |access-date=March 4, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110726142040/http://www.gensantos.gov.ph/2010/05/construction-of-waste-treatment-facility-p-acharon-blvd-corner-santiago-blvd-general-santos-city/ |archive-date=July 26, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The said location is adjacent to the city public market and is the former site of the city's ''Fish Landing''. The facility will include settling ponds and anaerobic reactors, among others. | ||
| :Likewise is the finalization stage for the construction of a multi-million peso solid waste management and disposal system in Barangay Sinawal. |
:Likewise is the finalization stage for the construction of a multi-million peso solid waste management and disposal system in Barangay Sinawal. The new and modern solid waste management facility will replace the existing city dumpsite in Barangay Siguel.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gensantos.gov.ph/2011/02/11cs-gsc-001-contract-to-design-build-and-operate-a-sanitary-solid-waste-management-and-disposal-project-at-barangay-sinawal-city-of-general-santos-philippines/ |title=11CS-GSC-001 – Contract to Design, Build and Operate a Sanitary Solid Waste Management and Disposal Project at Barangay Sinawal, City of General Santos, Philippines. | General Santos City |access-date=March 4, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110308044036/http://www.gensantos.gov.ph/2011/02/11cs-gsc-001-contract-to-design-build-and-operate-a-sanitary-solid-waste-management-and-disposal-project-at-barangay-sinawal-city-of-general-santos-philippines/ |archive-date=March 8, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| ===Security and |
===Security and civil defense=== | ||
| The Philippine National Police, a military task force has been formed to protect the city from terrorist attacks and other crime. Task Force GenSan is affiliated with the Philippine Army and headed by an army colonel. 8 Police Stations are |
The Philippine National Police, a military task force has been formed to protect the city from terrorist attacks and other crime. Task Force GenSan is affiliated with the Philippine Army and headed by an army colonel. 8 Police Stations are built on each barangay to keep the safeness and a peaceful order in city. Agencies and Organizations are forming a good and peaceful will to group an order in a city. | ||
| ===Health |
===Health services=== | ||
| The average life expectancy of Gensanon is 70 for females and 65 for males. There are 19 hospitals, with |
The average life expectancy of Gensanon is 70 for females and 65 for males. There are 19 hospitals, with more than 2,200 beds in the city including General Santos Doctors Hospital, St. Elizabeth Hospital, ], Mindanao Medical Center, R.O Diagan Cooperative Hospital, GenSan Medical Center, Sarangani Bay Specialists Medical Center, General Santos City District Hospital and the newly inaugurated Dadiangas Medical Center servicing a care for the people. In addition, there is an ongoing construction of ACE Medical Center to add more hospital bed capacity and medical services in the city. | ||
| ==Education== | ==Education== | ||
| ] institution run by the ] or FMS (Fratres Maristae a Scholis)]] | ] institution run by the ] or FMS (Fratres Maristae a Scholis)]] | ||
| Aside from more than 50 Private Schools and more than 100 public schools, General Santos |
Aside from more than 50 Private Schools and Colleges, such as The Quantum Academy, and the Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Colleges, and more than 100 public schools, General Santos hosts three universities. These are the ], ], ]. | ||
| The ] of the country's oldest academic institution, ], located in Barangay Ligaya, officially opened its first operations in school year 2024-2025. | |||
| === Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Colleges === | |||
| In 1957, Atty. Eugenio Millado and Doña Aurora Millado established Mindanao Vocational School (MVS) on Pioneer Avenue. Over the years, ] (RMMC; formerly Magsaysay Memorial Colleges) acquired Southern Island Colleges (SIC) and became widely recognized for its contributions to education in the region. The institution has since become a cornerstone of higher education, offering affordable and comprehensive educational opportunities to students from various backgrounds. | |||
| The Millado family’s legacy remains central to the institution’s identity and mission. Their commitment to improving educational opportunities for the people of Mindanao, as well as their ongoing dedication to public service and community development, has helped ensure that RMMC remains not just an academic institution, but also a force for good in the region. | |||
| ===Notre Dame of St. Therese of the Child Jesus=== | |||
| Notre Dame of St. Therese of the Child Jesus (NDST; formerly Canonico Antonio Institute, Inc.) is a private educational institution. It offers ], ] and ], in adherence to the ] system as ]. The school is administered by the ] (DST), a Catholic religious congregation. The school's campus is located along Purok Nopol Road, Sitio Nupol, Barangay Conel in General Santos. | |||
| In 1992, Jovita Onez, a devout Catholic Christian from General Santos donated one hectare of land to the DST congregation. The Mother General at that time, accepted the donation and decided to establish a convent and school in the said place. The construction of the new convent started in 1999. Both buildings were finally established in 2001 with all its furnishings and were officially blessed and opened on January 3, 2001. By the following months, the DST Sisters were accepting enrollees for preschool and primary education. The school had officially set into operation on the opening of the academic year of the same year. | |||
| ==Media== | ==Media== | ||
| Notable media publications in the city |
Notable media publications in the city are the SusStar General Santos, Periodiko Banat, Sapol, and other local newspapers. ] is the most popular newspaper company in the city. | ||
| There are several television stations in the city that are owned and operated by broadcasting networks—] (now defunct), ], ], GMA News TV 26, ] (now defunct), ]. Most of these television networks reaches as far as Davao Region and Northern Mindanao; and caters the whole ]. Major and other minor cable and satellite television companies are also operating in the city. Most of the FM and AM radio stations are operating in the city 24 hours a day such as ] (now defunct), ], ], ], ], ], ] and others. | |||
| There are |
There are three local newscasts programs in General Santos: ''] (]) (now defunct), ] (GMA 8 Soccsksargen) now part as ] Flagship Newscast, Balita38 (EGTV Channel 46) and Ronda Brigada (]).'' | ||
| There are two local newscasts programs in General Santos: ] of ABS-CBN General Santos, Testigo Socsksargen of GMA SOCSKSARGEN and Ronda Brigada of Brigada News TV. Also, Aksyon Socsksargen of TV5 General Santos to be aired in the city soon. | |||
| ==Notable |
==Notable personalities== | ||
| {{see also|Category:People from General Santos}} | |||
| <!-- ONLY add people with WP article! --> | |||
| <!-- Only include people with WP articles as per ] --> | |||
| * ] (Baeby Baste) of '']'', child actor | |||
| * ], actor | * ], actor | ||
| * ], TV personality | * ], TV personality | ||
| * ], actress | * ], actress, host, big winner of '']'' | ||
| * ], professional boxer | * ], professional boxer | ||
| * ], professional boxer | * ], professional boxer | ||
| * ], politician | * ], politician | ||
| * ], professional boxer | * ], professional boxer | ||
| * ], head coach ] basketball of ] Blue Eagles | * ], head coach ] basketball of ] Blue Eagles | ||
| * ], 3rd Runner- |
* ], ] Pageant 3rd Runner-up and National Director of Miss Universe Philippines | ||
| * ], singer, ] | * ], singer, ] | ||
| * ], international artist | |||
| * ], dance group, Grand Champion, Showtime Season 1 | * ], dance group, Grand Champion, Showtime Season 1 | ||
| * Kolette Madelo, 3rd big placer of '']'' | |||
| * ], dance group, Grand Champion, Showtime Season 3 | |||
| ==Sister cities== | ==Sister cities== | ||
| ===Local=== | ===Local=== | ||
| *], since October 12, 1994<ref name="QuezonCityGovPH-SisterCities">{{cite web |title=Sister Cities |url=http://quezoncity.gov.ph/index.php/quezon-city-business-district/350-sister-cities |website=The Local Government of Quezon City |access-date=April 9, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171001010801/http://quezoncity.gov.ph/index.php/quezon-city-business-district/350-sister-cities |archive-date=October 1, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|PHI}} ''']''', Agusan del Norte | |||
| *], since 1980<ref name="PanayNews-SisterCities">{{cite news |last1=Tayona |first1=Glenda |last2=Silubrico |first2=Ruby |title=Iloilo to showcase culture to 'sister cities' tonight |url=https://www.panaynews.net/iloilo-to-showcase-culture-to-sister-cities-tonight/ |access-date=April 9, 2019 |work=Panay News |date=August 25, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190409192355/https://www.panaynews.net/iloilo-to-showcase-culture-to-sister-cities-tonight/ |archive-date=April 9, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|PHI}} ''']''', Cebu | |||
| *], Camarines Sur<ref name="SPGenSantosPH-Renewing">{{cite news|title=RESOLUTION RENEWING AND REVITALIZING THE EXISTING SISTER CITY TIES OF THE CITY GOVERNMENT OF GENERAL SANTOS WITH THE CITY OF NAGA, CAMARINES SUR|url=http://www.spgensantos.ph/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/PR181801827.pdf|access-date=April 17, 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190417083615/http://www.spgensantos.ph/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/PR181801827.pdf|archive-date=April 17, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|PHI}} ''']''', Metro Manila | |||
| *]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.facebook.com/1490359257650276/posts/2528916660461192|archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/iarchive/facebook/1490359257650276/2528916660461192|archive-date=February 26, 2022|url-access=limited|title=Resolution Sisterhood Cities in Region12|website=]}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|PHI}} ''']''', Capiz | |||
| * {{flagicon|PHI}} ''']''', Lanao del Norte | |||
| * {{flagicon|PHI}} '''], Camarines Sur | |||
| ===International=== | ===International=== | ||
| * {{flagicon|Australia}} ''']''', Australia<ref name="SisterCitiesAustralia">{{cite web |title=DIRECTORY OF AUSTRALIAN SISTER CITY AFFILIATIONS 2018 |url=http://www.sistercitiesaustralia.com/images/images_media/Documents/Aust_SCA_Affiliations.pdf |website=Sister Cities Australia |access-date=April 17, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180713192607/http://www.sistercitiesaustralia.com/images/images_media/Documents/Aust_SCA_Affiliations.pdf |archive-date=July 13, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagicon|Mexico}} ''']''', Mexico | |||
| * {{flagicon|USA}} ''']''', USA<ref name="GenSanMagazine-Jersey">{{cite news |title=GENSAN and JERSEY CITY to Sign SISTER CITY Agreement AUGUST 14 |url=https://gensan-magazine.com/2018/08/02/gensan-and-jersey-city-to-sign-sister-city-agreement-august-14/ |access-date=April 17, 2019 |work=Gensan Magazine |date=August 2, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190112082705/https://gensan-magazine.com/2018/08/02/gensan-and-jersey-city-to-sign-sister-city-agreement-august-14/ |archive-date=January 12, 2019 |language=en |quote=Come August 14, Jersey City will become Gensan's third international sister city (after Monterrey, Mexico and Hadano City, Japan), while Gensan becomes Jersey's second Philippine sister city (after Ozamiz City, Misamis Occidental).}}</ref><ref name="Inquirer-JerseyCity">{{cite news |title=Jersey City and GenSan now "sister cities" |url=https://usa.inquirer.net/15141/jersey-city-gensan-now-sister-cities |access-date=April 17, 2019 |newspaper=Philippine Daily Inquirer|agency=INQUIRER.net US Bureau |date=August 30, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180829213837/https://usa.inquirer.net/15141/jersey-city-gensan-now-sister-cities |archive-date=August 29, 2018 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagicon|Japan}} ''']''', Japan | |||
| * {{flagicon|Mexico}} ''']''', Mexico<ref name="GenSanMagazine-Jersey" /> | |||
| * {{flagicon|Japan}} ''']''', Japan<ref name="GenSanMagazine-Jersey" /> | |||
| ==Gallery== | |||
| <gallery widths="180" heights="150"> | |||
| File:City Hall, General Santos City, Philippines.JPG|General Santos City Hall | |||
| File:Amandari Cove lake - panoramio.jpg|Amarandi Cove Lake | |||
| File:KCC Mall of Gensan - panoramio.jpg|KCC Mall General Santos | |||
| File:Gen Santos city 4.jpg|Pioneer Avenue | |||
| File:Lagao, General Santos City, South Cotabato, Philippines - panoramio.jpg|SM City General Santos | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | {{portal|Philippines}} | ||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{NoteFoot}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{ |
{{reflist|colwidth=35em}} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category| |
{{Commons category|General Santos}} | ||
| {{Wikivoyage|General Santos}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{official website|http://GenSantos.gov.ph}} | |||
| {{Wikivoyage|General Santos City}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Geographic location |
{{Geographic location <!-- This geo box is for DIRECTLY ADJACENT municipalities as standardized for all other LGU's --> | ||
| |North= ] | | North = ] | ||
| |West= ]<br>] | | West = ]<br />] | ||
| |Center= General Santos |
| Center = General Santos | ||
| |East= ] | | East = ] | ||
| |Southeast = '']'' | | Southeast = '']'' | ||
| |Southwest= ] | | Southwest = ] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Navboxes | {{Navboxes | ||
| |title = Articles Related to General Santos | | title = Articles Related to General Santos | ||
| |list = | | list = | ||
| {{South Cotabato}} | {{South Cotabato}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Soccsksargen}} | ||
| {{Philippine cities}} | {{Philippine cities}} | ||
| {{Largest cities |
{{Largest cities and municipalities in Mindanao}} | ||
| {{Most populous cities in the Philippines}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 17:14, 27 December 2024
Highly urbanized city in South Cotabato, Philippines For the person whom the city is named after, see Paulino Santos. For other uses, see General Santos (disambiguation).Highly urbanized city in Soccsksargen, Philippines
| General Santos | |
|---|---|
| Highly urbanized city | |
| City of General Santos | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Jawi | جنرل سنتوس |
    Aerial view of urban GenSan; Robinsons Place GenSan; Barbecue grill stalls at Tiongson Arcade; Dadiangas
Aerial view of urban GenSan; Robinsons Place GenSan; Barbecue grill stalls at Tiongson Arcade; Dadiangas | |
 Flag Flag Seal Seal | |
| Nickname: Tuna Capital of the Philippines | |
| Anthem: Himno ng Heneral Santos (English: General Santos Hymn) | |
 Map of South Cotabato with General Santos highlighted Map of South Cotabato with General Santos highlighted | |
| OpenStreetMap | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 6°07′N 125°10′E / 6.12°N 125.17°E / 6.12; 125.17 | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Soccsksargen |
| Province | South Cotabato (geographically only) |
| District | Lone district of General Santos |
| Founded | August 18, 1947 |
| Cityhood | July 8, 1968 |
| Highly urbanized city | September 5, 1988 |
| Named for | General Paulino Santos |
| Barangays | 26 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod |
| • Mayor | Lorelie G. Pacquiao |
| • Vice Mayor | Rosalita T. Nuñez |
| • Representative | Loreto B. Acharon |
| • City Council |
Members
|
| • Electorate | 360,232 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 492.86 km (190.29 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 197 m (646 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 869 m (2,851 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 697,315 |
| • Density | 1,400/km (3,700/sq mi) |
| • Households | 175,345 |
| Demonym | Gensanon |
| Economy | |
| • Gross domestic product (GDP) | ₱129.015 billion (2022) $2.279 billion (2022) |
| • Income class | 1st city income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 9.90% (2021) |
| • Revenue | ₱ 2,931 million (2020) |
| • Assets | ₱ 8,093 million (2020) |
| • Expenditure | ₱ 3,557 million (2020) |
| • Liabilities | ₱ 1,983 million (2020) |
| Service provider | |
| • Electricity | South Cotabato 2 Electric Cooperative (SOCOTECO 2) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 9500 |
| PSGC | 126303000 |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)83 |
| Native languages | Hiligaynon Cebuano Tboli Blaan Tagalog Maguindanaon |
| Website | www |
General Santos, officially the City of General Santos and abbreviated as GenSan, is a highly urbanized city in the region of Soccsksargen, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 697,315 people making it the most populous city in Soccsksargen Region.
It is located on the island of Mindanao, it is the southernmost and 15th-most populous city in the Philippines. It is the regional center for commerce and industry of the Soccsksargen region, and it is also the only coastal as well as the largest city in the province of South Cotabato wherein it is geographically situated and grouped under the province by the Philippine Statistics Authority but administered independently of it.
Etymology
The city was named after Gen. Paulino Santos, a former Commanding General of the Philippine Army and the settlement's leading pioneer.
History
The nomadic B'laan people are the original inhabitants of present-day General Santos, and traces of their early settlements of the area are found in the city's place names, which are derived from their vocabulary. Their name for the city, Dadiangas, is from the Ziziphus spina-christi tree that was once abundant in the area and is now a protected species under Republic Act 8371 or the Indigenous Peoples Right Act of 2007. The B'laan now lives alongside the city's new generation of settlers and other immigrants.
Beforehand, the B'laan would were forced upland into the surrounding hills after the Muslims settle in the area under the rule of the Sultanate of Maguindanao.
After the fall of Maguindanao, Datu Uto of Buayan expanded his domain south towards Sarangani Bay. Dadiangas remained as a port under the Sultanate of Buayan until the American era.
Waves of migration

Organized under the National Land Settlement Administration (NLSA) of the Commonwealth Government headed by President Manuel L. Quezon, General Paulino Santos led the relocation of 62 Christian settlers from Luzon to the shores of Sarangani Bay aboard the steam ship “Basilan” of Compañia Maritima on February 27, 1939. The 62 pioneers, mostly agricultural and trade graduates, were the first large batch of settlers to land in the area with the mission to industriously cultivate the region. After this first influx of pioneers, more Christians from Visayas and Luzon subsequently migrated into the area, gradually driving some of the B'laan residents to the hills and mountains, where they have lost their livelihood and somewhat displaced Maguindanaon living in the area.
In March 1939, the first formal settlement in the city was established in Alagao, which is now known as Barangay Lagao. Lagao was known then as the "Municipal District of Buayan" under the jurisdiction of the deputy governor of the Municipal District of Glan, until it officially became an independent Municipal District of Buayan on October 1, 1940, appointing Datu Sharif Zainal Abedin, an Arab mestizo married to a daughter of a very influential datu of lower Buayan, as the first district municipal mayor.
Second World War
During World War II, the Municipal District of Buayan become one of the last frontiers between the combined American and Filipino forces and troops from the Empire of Japan. Retreating Imperial Japanese forces made Klaja Karsts Land their last ground for defence, constructing round cement bunkers and tunnels. These bunkers can still be seen at Sitio Guadalupe; most of the tunnels, however, have since been damaged and even destroyed by treasure hunters and land developers.
Renaming and elevation to city status
Main article: Cities of the Philippines
A year after the Philippines regained full sovereignty from the United States on July 4, 1946, the Municipality of Buayan became a 4th class regular municipality by virtue of the Executive Order Number 82, dated August 18, 1947, by President Manuel Roxas, absorbing the Municipal District of Glan, whose low income bracket at the time disqualified it for the honour. Dadiangas was the seat of government for the Municipality of Buayan electing Irineo Santiago as its first Municipal Mayor on a local election that was held on November 11, 1947. Mayor Santiago was formally inducted on January 1, 1948.
Six years later, in June 1954, the Municipality of Buayan was renamed General Santos as a tribute to the leading pioneer via Act No. 1107 authored by Congressman Luminog Mangelen of Cotabato Province.
From 1963 to 1967, the municipality's economy experienced a boom under Mayor Lucio A. Velayo, as several large agri-based and multinational firms such as Dole Philippines, General Milling Corporation and UDAGRI expanded into the area. Although it was then qualified to become a fourth class city from being a municipality, the residents rejected a move by Congressman Salipada Pendatun to convert the Municipality of Buayan into a city and to rename it ’’Rajah Buayan’’.
On July 8, 1968, the Municipality of General Santos was converted into a city upon the approval of Republic Act No. 5412, authored by Congressman James L. Chiongbian. By this time, General Santos City had already established itself as a major economic and educational hub in the region. Three of the oldest educational institutions in the city — Notre Dame Dadiangas University (1948), Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Colleges (1957), and Mindanao State University (1961) — were established prior to the city’s official founding. It was inaugurated on September 5 of that year, with Antonio C. Acharon became the new city's first mayor. On September 5, 1988, a decade after its inauguration as a chartered city, GenSan was declared a highly urbanized city of South Cotabato.
Even after becoming a highly urbanized city independent from South Cotabato in 1988, General Santos remained part of the province's congressional representation. The city only gained a separate representative with the passage of Republic Act No. 11243 on March 11, 2019, which segregated General Santos from the first congressional district of South Cotabato to be its 3rd congressional district. On September 15, 2021, House Bill No. 10021 authored by Representative Ferdinand Hernandez, that officially mandate General Santos as a lone district, separate from South Cotabato was passed on third and final reading.
In April 2001, Mayor Adelbert W. Antonino, an ally of deposed president Joseph Estrada, coordinated with various mayors and governors to bring their respective constituents to Epifanio delos Santos Avenue in Metro Manila to protest the arrest of Estrada.
Geography

General Santos lies at the southern part of the Philippines. The city is southeast of Manila, southeast of Cebu and southwest of Davao.
The city is bounded by municipalities of Sarangani Province, namely Alabel in the east, and Maasim in the south. General Santos is likewise bounded by the South Cotabato municipality of Polomolok and Sarangani Province municipality of Malungon in the north, and the municipality of T'boli in the west.
General Santos occupies the whole of South Cotabato's coastline.
Climate
| Climate data for General Santos (1991–2020, extremes 1949–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 37.5 (99.5) |
38.0 (100.4) |
38.9 (102.0) |
39.0 (102.2) |
39.4 (102.9) |
38.5 (101.3) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
36.5 (97.7) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
37.5 (99.5) |
39.0 (102.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.3 (90.1) |
32.9 (91.2) |
34.0 (93.2) |
34.3 (93.7) |
33.5 (92.3) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.8 (91.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.7 (90.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.5 (81.5) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.9 (84.0) |
28.5 (83.3) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22.6 (72.7) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.6 (74.5) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 17.1 (62.8) |
17.2 (63.0) |
16.9 (62.4) |
18.3 (64.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
17.9 (64.2) |
17.2 (63.0) |
17.5 (63.5) |
18.0 (64.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 96.9 (3.81) |
53.0 (2.09) |
55.3 (2.18) |
54.1 (2.13) |
72.2 (2.84) |
101.9 (4.01) |
98.1 (3.86) |
91.3 (3.59) |
83.3 (3.28) |
99.6 (3.92) |
77.5 (3.05) |
74.9 (2.95) |
958.1 (37.72) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 9 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 106 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 79 | 76 | 75 | 75 | 78 | 82 | 83 | 82 | 81 | 81 | 80 | 79 | 79 |
| Source: PAGASA | |||||||||||||
General Santos has a tropical wet and dry climate (Köppen climate classification). With an average annual rainfall of less than 1,000 millimetres (39 in), it is one of the driest places in the Philippines.
Barangays
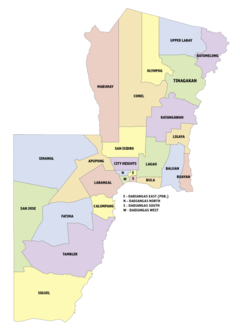
General Santos is politically subdivided into 26 barangays. Each barangay consists of puroks while some have sitios.
- Apopong
- Baluan
- Batomelong
- Buayan
- Bula
- Calumpang
- City Heights
- Conel
- Dadiangas East
- Dadiangas North
- Dadiangas South
- Dadiangas West
- Fatima
- Katangawan
- Labangal
- Lagao (1st & 3rd)
- Ligaya
- Mabuhay
- Olympog
- San Isidro (Lagao 2nd)
- San Jose
- Siguel
- Sinawal
- Tambler
- Tinagacan
- Upper Labay
Demographics
 Kadsagayan Parade during Kalilangan Festival
Kadsagayan Parade during Kalilangan Festival Tuna Festival contingent
Tuna Festival contingent
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 33 | — |
| 1918 | 9,787 | +46.15% |
| 1939 | 14,115 | +1.76% |
| 1948 | 32,019 | +9.53% |
| 1960 | 84,988 | +8.47% |
| 1970 | 85,861 | +0.10% |
| 1975 | 91,154 | +1.21% |
| 1980 | 149,396 | +10.38% |
| 1990 | 250,389 | +5.30% |
| 1995 | 327,173 | +5.14% |
| 2000 | 411,822 | +5.06% |
| 2007 | 529,542 | +3.53% |
| 2010 | 538,086 | +0.58% |
| 2015 | 594,446 | +1.92% |
| 2020 | 697,315 | +3.19% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority | ||
There are two major languages spoken in the city, with Cebuano being widely spoken and being used by the local media outlets in the city (television, radio, and newspapers), followed by Hiligaynon, which is used mainly by settlers who came from the provinces of South Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, North Cotabato and Maguindanao, as well as immigrants from the provinces of Negros Occidental, Iloilo and Guimaras. Other languages spoken within the city include B'laan, T'boli, Maguindanaon, Ilocano, and Kapampangan.
Religion
| Religion in General Santos (2020) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | percentage | |||
| Roman Catholic | 65% | |||
| Other Christian, including Protestants | 20.5% | |||
| Islam | 9.8% | |||
| Iglesia ni Cristo | 3.3% | |||
| Others | 1.4% | |||
The predominant religion in the city is Christianity, with the largest denomination being the Catholic Church, comprising almost 90% of the population. About 9% of the population belongs to Islam, mostly Sunnites.
Economy
Poverty incidence of General Santos
|
5
10
15
20
25
30
2006 16.70 2009 22.50 2012 19.30 2015 23.48 2018 14.74 2021 9.90 Source: Philippine Statistics Authority |
The city's major economic activity is primarily anchored in two sectors namely the agro-industry and fishing industry.
- Agro-industry: Endowed with rich volcanic soil, ample and well distributed rainfall all throughout the year and a typhoon-free climate, General Santos produces export quality high valued crops such as corn, coconut, pineapple, asparagus, banana and rice. It also yields quality exotic fruits, vegetables and cut flowers. The city is also a top producer and exporter of quality livestock such as poultry, hogs, and cattle. But with the continuing growth in population and economy in the passing of time, a number of the city's agricultural lands have gradually been converted into built up areas in order to address the relatively growing need of dwelling and viable spaces.

- Fishing industry: General Santos is the largest producer of sashimi-grade tuna in the Philippines. Thus, as early as 1970, it was nicknamed "Tuna Capital of the Philippines". The city also accounts for the second-largest daily total catch of fish in the country after Navotas in the National Capital Region. The fishing industry in yields a total daily capacity of 750 metric tons of fish catch, and employs about 7,800 workers. General Santos is home to seven tuna processing plants. The Fishport Complex in Barangay Tambler has a 750 metres (2,460 ft) quay and a 300 metres (980 ft) wharf for 2,000 GT reefer carriers. The fish port is equipped with modern facilities that comply with international standards on fish catch handling. Locals in the city boast that fish and seafood do not come fresher than what is found in their locality.
General Santos registered 1,365 new medium to large enterprises in 2011. An aggregate investment involved is estimated PHP 1.202 billion. Top industry for new investment in 2011 was as follows: Hotel and Restaurant-31%; Wholesale & Retail Trade-20%; Repair of Motor Vehicles, Motorcycles and Personal & Household Goods, Real Estate & Renting Business Activities-17%; Other Community, Social & Personal Services-8%; Financial Intermediation-5%; Manufacturing-5%; Fishing-3%; ICT-3 %
As of 2000, there are 59 banks serving the city. This composed of 46 commercial banks, 5 savings banks, 7 rural banks and 1 cooperative bank. Aside from this, there are 48 lending institutions as well as 49 pawnshops providing emergency loan assistance.
Shopping
General Santos is the shopping capital of the Soccksargen region. Residents from nearby towns and provinces visit the city to do shopping and enjoy life and leisure activities. There are several huge shopping malls in the city, notable ones are KCC Mall of Gensan, SM City General Santos, Robinsons Place GenSan, Gaisano Mall of GenSan, RD Plaza (Fitmart), Veranza Mall, and the newest addition to the city which is RD City Mall located at Barangay Mabuhay, Unitop Shopping Mall in Barangay Dadingas West and AllHome (soon in Barangay Katangawan, Circumferential Road). SM Savemore has two branches in the city and another branch will be built within the downtown area. There are also news about building an Ayala Mall and Puregold. These malls are home to both national and international brands of retail merchandises as well as restaurants and cafes. There are many merchandise and large groceries owned by local and foreign Chinese, Taiwanese and Korean businessmen in the city.
Infrastructure
- Communication
Modern and state-of-the-art communication facilities at par with global standards are readily available and are provided in General Santos by major telecommunication companies in the country. These include voice, data, internet and network solutions, among others, in both wired and mobile forms.
Transportation
GenSan and the whole of Soccsksargen can be reached by air, land, or sea.
- Air transportation

The General Santos International Airport is the largest airport in Mindanao. It has a 3,227-metre concrete runway capable of handling wide-bodied jets like Airbus A340 and Boeing 747. It was also called Rajah Buayan Airport in the 1990s, and Tambler Airport in 2008, before being renamed to its current name. Flights to and from Manila, Iloilo, and Cebu are currently being operated in the airport by Philippine Airlines and Cebu Pacific. General Santos International Airport is the second busiest airport in Mindanao and 9th busiest airport in the Philippines.
- Sea transportation

The Makar Wharf is the main international sea port of the city and is one of the finest sea ports in the country. It is located in Barangay Labangal, away from the central business district. With a 740 metres (2,430 ft) docking length and a 19 metres (62 ft) width, the wharf can accommodate up to nine ship berthing positions all at the same time. The port is replete with modern facilities such as container yards, storage and weighing bridges. Several shipping companies operate regular inter-island ferry service to and from other major ports in Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao. Negros Navigation, SuperFerry and Sulpicio Lines provide these inter-island shipping routes while numerous Indonesian shipping lines operate international ferry service between General Santos and neighboring ports in Indonesia carrying both passenger and cargo loads.
- Land transportation
Commuting in and around General Santos is a fast and convenient ride. More than 400 passenger buses, public utility vans and jeepneys wield routes within the city and neighboring provinces like in Koronadal, Cotabato, Davao, Tacurong, Pagadian, Cagayan de Oro and others. Three-wheeled motorized cabs known as tricycles are the city's main mode of public transport and have been on the road since the pioneering times. Air-conditioned taxis also ply the city streets offering commuters a choice of a more comfortable mode of transportation.
Maintained by the City Engineers' Office, the city's major road networks are paved and endowed with safety road marks, signs and signals to ensure a secure and efficient traffic flow within the city. The Pan-Philippine Highway links the city by land to other major cities in Mindanao and to the rest of the country.
The General Santos Terminal—popularly known as Bulaong Terminal; located in Barangay Dadiangas North is the city's main integrated land transport terminal. The terminal serves as the city's gateway for land travelers. Buses and other forms of public mass transportation—to and from various parts of Mindanao such as Koronadal, Tacurong, Cotabato, Davao, Kidapawan, Digos, Pagadian, and Cagayan de Oro.
Utilities
- Power
- Majority of the city's power supply is being serviced by the second district of South Cotabato Electric Cooperative (SOCOTECO-II). The said power distributor acquires the majority of its power needs for the city's consumption from the National Transmission Corporation (TransCo) while other sources are drawn from various Independent Power Producers (IPP) from nearby power plants and barges.
- Water
- Majority of the households and other entities in the city are provided and serviced with clean, safe and potable water supply from deep well sources by General Santos City Water District (GSCWD). Potable water sources in other far flung and remote parts of the city where cannot be reached by the local water utility service are being served by their individual Barangay Water And Sanitation systems.
- Waste management
- In a bid to achieve an efficient and sustainable management of non-hazardous waste the city produces every single day, the finalization and construction of the city's waste water treatment facility is currently underway at the corner of P. Acharon and I. Santiago Boulevards. The said location is adjacent to the city public market and is the former site of the city's Fish Landing. The facility will include settling ponds and anaerobic reactors, among others.
- Likewise is the finalization stage for the construction of a multi-million peso solid waste management and disposal system in Barangay Sinawal. The new and modern solid waste management facility will replace the existing city dumpsite in Barangay Siguel.
Security and civil defense
The Philippine National Police, a military task force has been formed to protect the city from terrorist attacks and other crime. Task Force GenSan is affiliated with the Philippine Army and headed by an army colonel. 8 Police Stations are built on each barangay to keep the safeness and a peaceful order in city. Agencies and Organizations are forming a good and peaceful will to group an order in a city.
Health services
The average life expectancy of Gensanon is 70 for females and 65 for males. There are 19 hospitals, with more than 2,200 beds in the city including General Santos Doctors Hospital, St. Elizabeth Hospital, SOCSARGEN County Hospital, Mindanao Medical Center, R.O Diagan Cooperative Hospital, GenSan Medical Center, Sarangani Bay Specialists Medical Center, General Santos City District Hospital and the newly inaugurated Dadiangas Medical Center servicing a care for the people. In addition, there is an ongoing construction of ACE Medical Center to add more hospital bed capacity and medical services in the city.
Education

Aside from more than 50 Private Schools and Colleges, such as The Quantum Academy, and the Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Colleges, and more than 100 public schools, General Santos hosts three universities. These are the Notre Dame of Dadiangas University, Mindanao State University – General Santos City, New Era University – General Santos Branch.
The General Santos campus of the country's oldest academic institution, University of Santo Tomas, located in Barangay Ligaya, officially opened its first operations in school year 2024-2025.
Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Colleges
In 1957, Atty. Eugenio Millado and Doña Aurora Millado established Mindanao Vocational School (MVS) on Pioneer Avenue. Over the years, Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Colleges (RMMC; formerly Magsaysay Memorial Colleges) acquired Southern Island Colleges (SIC) and became widely recognized for its contributions to education in the region. The institution has since become a cornerstone of higher education, offering affordable and comprehensive educational opportunities to students from various backgrounds.
The Millado family’s legacy remains central to the institution’s identity and mission. Their commitment to improving educational opportunities for the people of Mindanao, as well as their ongoing dedication to public service and community development, has helped ensure that RMMC remains not just an academic institution, but also a force for good in the region.
Notre Dame of St. Therese of the Child Jesus
Notre Dame of St. Therese of the Child Jesus (NDST; formerly Canonico Antonio Institute, Inc.) is a private educational institution. It offers primary education, junior high school and senior high school, in adherence to the K-12 education system as implemented in the Philippines. The school is administered by the Disciples of St. Therese of the Child Jesus (DST), a Catholic religious congregation. The school's campus is located along Purok Nopol Road, Sitio Nupol, Barangay Conel in General Santos.
In 1992, Jovita Onez, a devout Catholic Christian from General Santos donated one hectare of land to the DST congregation. The Mother General at that time, accepted the donation and decided to establish a convent and school in the said place. The construction of the new convent started in 1999. Both buildings were finally established in 2001 with all its furnishings and were officially blessed and opened on January 3, 2001. By the following months, the DST Sisters were accepting enrollees for preschool and primary education. The school had officially set into operation on the opening of the academic year of the same year.
Media
Notable media publications in the city are the SusStar General Santos, Periodiko Banat, Sapol, and other local newspapers. Brigada Newspaper General Santos is the most popular newspaper company in the city.
There are several television stations in the city that are owned and operated by broadcasting networks—ABS-CBN 3 Soccsksargen (now defunct), GMA 8 Soccsksargen, TV5 Channel 12 Gensan, GMA News TV 26, ABS-CBN Sports+Action Channel 36 (now defunct), Brigada News TV 39. Most of these television networks reaches as far as Davao Region and Northern Mindanao; and caters the whole Soccsksargen Region. Major and other minor cable and satellite television companies are also operating in the city. Most of the FM and AM radio stations are operating in the city 24 hours a day such as MOR 92.7 General Santos (now defunct), 89.5 Brigada News FM, iFM 91.9, 94.3 Yes! FM General Santos, Radyo5 97.5 News FM, K101.5 Love Radio GenSan, Barangay 102.3 GenSan and others.
There are three local newscasts programs in General Santos: TV Patrol Socsksargen (ABS-CBN 3 Soccsksargen) (now defunct), GMA Soccsksargen Flash Bulletin (GMA 8 Soccsksargen) now part as One Mindanao Flagship Newscast, Balita38 (EGTV Channel 46) and Ronda Brigada (Brigada News TV channel 39).
Notable personalities
See also: Category:People from General Santos- Sebastian Benedict (Baeby Baste) of Eat Bulaga!, child actor
- Gerald Anderson, actor
- Ethel Booba, TV personality
- Melai Cantiveros-Francisco, actress, host, big winner of Pinoy Big Brother: Double Up
- Nonito Donaire, professional boxer
- Rolando Navarrete, professional boxer
- Jinkee Pacquiao, politician
- Manny Pacquiao, professional boxer
- Bo Perasol, head coach UAAP basketball of Ateneo de Manila University Blue Eagles
- Shamcey Supsup, Miss Universe 2011 Pageant 3rd Runner-up and National Director of Miss Universe Philippines
- Zendee Rose Tenerefe, singer, YouTube personality
- Racso Jugarap, international artist
- XB Gensan, dance group, Grand Champion, Showtime Season 1
- Kolette Madelo, 3rd big placer of Pinoy Big Brother: Gen 11
Sister cities
Local
- Quezon City, since October 12, 1994
- Iloilo City, since 1980
- Naga, Camarines Sur
- Cotabato City
International
 Canberra, Australia
Canberra, Australia Jersey City, USA
Jersey City, USA Monterrey, Mexico
Monterrey, Mexico Hadano, Kanagawa, Japan
Hadano, Kanagawa, Japan
Gallery
-
General Santos City Hall
-
 Amarandi Cove Lake
Amarandi Cove Lake
-
 KCC Mall General Santos
KCC Mall General Santos
-
 Pioneer Avenue
Pioneer Avenue
-
 SM City General Santos
SM City General Santos
See also
Notes
- Cebuano: Dakbayan sa Heneral Santos; Hiligaynon: Dakbanwa sang Heneral Santos; Maguindanao: Ingud nu Heneral Santos; Blaan: Banwe Dadiangas; Tboli: Benwu Dadiangas; Filipino: Lungsod ng Heneral Santos
References
- "DTI features 'best of the seas' at the IFEX PH 2018". Philippine Information Agency. DTI/PIA-NCR. May 26, 2018. Archived from the original on May 26, 2018. Retrieved April 17, 2019.
- City of General Santos | (DILG)
- "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ Census of Population (2020). "Region XII (Soccsksargen)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- "City of General Santos Posts the Fastest Growth Among Economies in SOCCSKSARGEN in 2022".
- "PH₱56.598 per dollar (per International Monetary Fund on Representative Exchange Rates for Selected Currencies for December 2022)". IMF. Retrieved December 9, 2023.
- "PSA Releases the 2021 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. April 2, 2024. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- "History of General Santos City". Archived from the original on July 11, 2011. Retrieved December 10, 2018.
- "An Act Changing the Name of the Municipality of Buayan, in the Province of Cotabato, to General Santos". LawPH.com. Archived from the original on July 14, 2012. Retrieved April 11, 2011.
- Congress of the Philippines (March 11, 2019). "Republic Act No. 11243 - An Act Reapportioning the First Legislative District of the Province of South Cotabato, thereby creating the Lone Legislative District of General Santos City" (PDF). Retrieved May 6, 2019.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 15, 2021. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Gloria, Glenda M. (August 29, 2015). "Remembering the Iglesia-led EDSA 3". Rappler. Rappler Inc. Retrieved March 7, 2024.
This story on 'EDSA 3' was first published by Newsbreak in May 2001.
- "General Santos City, South Cotabato Climatological Normal Values". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on October 13, 2018. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - "General Santos City, South Cotabato Climatological Extremes" (PDF). Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on October 13, 2018. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
- "Province: South Cotabato". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved November 12, 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region XII (Soccsksargen)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region XII (Soccsksargen)" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region XII (Soccsksargen)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- "Province of South Cotabato". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- "Religious Affiliation in the Philippines (2020 Census of Population and Housing) | Philippine Statistics Authority | Republic of the Philippines". psa.gov.ph. Retrieved August 6, 2023.
- Philippine Statistics Authority (July 26, 2017). "Muslim Population in Mindanao (based on POPCEN 2015". Archived from the original on August 31, 2018. Retrieved August 31, 2018.
- "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. November 29, 2005.
- "2003 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. March 23, 2009.
- "City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates; 2006 and 2009" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. August 3, 2012.
- "2012 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. May 31, 2016.
- "Municipal and City Level Small Area Poverty Estimates; 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. July 10, 2019.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. December 15, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- "PSA Releases the 2021 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. April 2, 2024. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- Fel V. Maragay (July 4, 1996). "Demos in South get ugly; Ramos unfazed: Mindanao Council is good formula, FVR insists". Manila Standard. Philippines. Retrieved October 9, 2011.
- "General Santos International Airport". Archived from the original on September 19, 2010.
- "International Container Terminal Services, Inc". Archived from the original on October 3, 2011. Retrieved February 27, 2011.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved February 27, 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Construction of Waste Treatment Facility, P. Acharon BLVD. Corner Santiago BLVD., General Santos City | General Santos City". Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved March 4, 2011.
- "11CS-GSC-001 – Contract to Design, Build and Operate a Sanitary Solid Waste Management and Disposal Project at Barangay Sinawal, City of General Santos, Philippines. | General Santos City". Archived from the original on March 8, 2011. Retrieved March 4, 2011.
- "Sister Cities". The Local Government of Quezon City. Archived from the original on October 1, 2017. Retrieved April 9, 2019.
- Tayona, Glenda; Silubrico, Ruby (August 25, 2018). "Iloilo to showcase culture to 'sister cities' tonight". Panay News. Archived from the original on April 9, 2019. Retrieved April 9, 2019.
- "RESOLUTION RENEWING AND REVITALIZING THE EXISTING SISTER CITY TIES OF THE CITY GOVERNMENT OF GENERAL SANTOS WITH THE CITY OF NAGA, CAMARINES SUR" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on April 17, 2019. Retrieved April 17, 2019.
- "Resolution Sisterhood Cities in Region12". Facebook. Archived from the original on February 26, 2022.
- "DIRECTORY OF AUSTRALIAN SISTER CITY AFFILIATIONS 2018" (PDF). Sister Cities Australia. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 13, 2018. Retrieved April 17, 2019.
- ^ "GENSAN and JERSEY CITY to Sign SISTER CITY Agreement AUGUST 14". Gensan Magazine. August 2, 2018. Archived from the original on January 12, 2019. Retrieved April 17, 2019.
Come August 14, Jersey City will become Gensan's third international sister city (after Monterrey, Mexico and Hadano City, Japan), while Gensan becomes Jersey's second Philippine sister city (after Ozamiz City, Misamis Occidental).
- "Jersey City and GenSan now "sister cities"". Philippine Daily Inquirer. INQUIRER.net US Bureau. August 30, 2018. Archived from the original on August 29, 2018. Retrieved April 17, 2019.
External links
- Official website
- General Santos Profile at the DTI Cities and Municipalities Competitive Index
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Congregation of the Disciples of St. Therese of the Infant Jesus (DST)
| Places adjacent to General Santos | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
- General Santos
- 1939 establishments in the Philippines
- Cities in South Cotabato
- Highly urbanized cities in the Philippines
- Planned communities in the Philippines
- Political divisions established by Philippine executive order
- Populated places established in 1939
- Port cities and towns in the Philippines
- Private schools in the Philippines



