| Revision as of 16:03, 21 December 2023 view source39.62.134.237 (talk)No edit summaryTags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:31, 31 December 2024 view source RevolutionaryPatriot (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,278 editsNo edit summary | ||
| (200 intermediate revisions by 68 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description| |
{{Short description|Pashtun tribe}} | ||
| {{pp|small=yes}} | |||
| {{other uses}} | {{other uses}} | ||
| {{Infobox tribe | {{Infobox tribe | ||
| | name = Yūsufzai | | name = Yūsufzai | ||
| | local name = ايسپزی | | local name = ايسپزی | ||
| | type = | | type = | ||
| | image = | | image = A Eusofzye (adjusted).png | ||
| | alt = | | alt = | ||
| | caption = | | caption = Depiction of a Yusufzai warrior | ||
| | ethnicity = ] | | ethnicity = ] | ||
| | nisba = | | nisba = | ||
| | location = ], ] (]) | | location = ], ] (]) | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| | branches = ], Iliaszai, Akozai, Mandan, Isazai, Malizai | | branches = ], Iliaszai, Akozai, Mandan, Isazai, Malizai | ||
| | language = ] | | language = ] | ||
| | religion = ] ] | | religion = ] ] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | The '''Yusufzai''' or '''Yousafzai''' ({{langx|ps|یوسفزی}}, {{IPA|ps|jusəpˈzai|pron}}{{ref|a|1}}), also referred to as the '''Esapzai''' ({{lang|ps|ايسپزی}}, {{IPA|ps|iːsəpˈzai|pron}}), or '''Yusufzai Afghans''' historically, are one of the largest ] of ]. They are natively based in the northern part of ] (], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]), to which they migrated from ] during the 16th century, but they are also present in parts of ], including ], ], ] and ]. Outside of these countries, they can be found in ] District ] (]),<ref name="KhanRoshanKhan" /> Balochistan ] (]), ] (]) and ]. | ||
| ⚫ | The '''Yusufzai''' or '''Yousafzai''' ({{ |
||
| Most of the Yusufzai speak a ] of ] and some ] of ] (as in case of ]) and Afghan dialect ].<ref name="UND">{{Cite thesis |type=Master's thesis |last=Coyle|first=Dennis Walter|date=2014|title=Placing Wardak Among Pashto Varieties|url=https://commons.und.edu/theses/1635 |publisher=University of North Dakota}}</ref> | Most of the Yusufzai speak a ] of ] and some ] of ] (as in case of ]) and Afghan dialect ].<ref name="UND">{{Cite thesis |type=Master's thesis |last=Coyle|first=Dennis Walter|date=2014|title=Placing Wardak Among Pashto Varieties|url=https://commons.und.edu/theses/1635 |publisher=University of North Dakota}}</ref> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
| ==Mythical genealogy== | ==Mythical genealogy== | ||
| According to a popular mythical genealogy, recorded by 17th-century Mughal courtier ] in his book ''Tārīkh-i Khān Jahānī wa Makhzan-i Afghānī'', the Yusufzai tribe descended from their ]ous ancestor Yūsuf, who was son of Mand, who was son of Khashay (or Khakhay), who was son of Kand, who was son of Kharshbūn, who was son of Saṛban (progenitor of the ] tribal confederacy), who was son of ] (progenitor of all Pashtuns). Qais Abdur Rashid was a descendant of Afghana, who was described as a grandson of the ] king ] and commander-in-chief of the army of prophet ]. Qais was claimed to be a contemporary of the Islamic prophet ] and a kinsman of ] commander ]. When Khalid ibn al-Walid summoned Qais from ] to ], Qais accepted Islam and the prophet renamed him ''Abdur Rashīd'' (meaning "Servant of the Guide to the Right Path" or "Servant of God" in ]). Abdur Rashid returned to Ghor and introduced Islam there. The book stated that Yūsuf's grandfather (and Mand's father), Khashay, also had two other sons, Muk and Tarkalāṇī, who were the progenitors of the ] and ] tribes, respectively. Yūsuf had one brother, Umar, who was the progenitor of the ] tribe, which is closely related to Yusufzais. | According to a popular mythical genealogy, recorded by 17th-century Mughal courtier ] in his book '']'', the Yusufzai tribe descended from their ]ous ancestor Yūsuf, who was son of Mand, who was son of Khashay (or Khakhay), who was son of Kand, who was son of Kharshbūn, who was son of Saṛban (progenitor of the ] tribal confederacy), who was son of ] (progenitor of all Pashtuns). Qais Abdur Rashid was a descendant of Afghana, who was described as a grandson of the ] king ] and commander-in-chief of the army of prophet ]. Qais was claimed to be a contemporary of the Islamic prophet ] and a kinsman of ] commander ]. When Khalid ibn al-Walid summoned Qais from ] to ], Qais accepted Islam and the prophet renamed him ''Abdur Rashīd'' (meaning "Servant of the Guide to the Right Path" or "Servant of God" in ]). Abdur Rashid returned to Ghor and introduced Islam there. The book stated that Yūsuf's grandfather (and Mand's father), Khashay, also had two other sons, Muk and Tarkalāṇī, who were the progenitors of the ] and ] tribes, respectively. Yūsuf had one brother, Umar, who was the progenitor of the ] tribe, which is closely related to Yusufzais. | ||
| The 1595 Mughal account ''Ain-i-Akbari'' also mentioned the ] among Pashtuns, which shows that the tradition was already popular among 16th-century Pashtuns.<ref name="Nejatie"/> | The 1595 Mughal account ''Ain-i-Akbari'' also mentioned the ] among Pashtuns, which shows that the tradition was already popular among 16th-century Pashtuns.<ref name="Nejatie"/> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 45: | ||
| During the ], the Yusufzai tribe of Afghans was first explicitly mentioned in '']'' by ], a ] ruler from ] (in present-day ]) who captured ] in ].<ref>{{cite journal | last = Samrin | first = Farah | title = Yusufzais in Mughal History | year = 2006 | journal = Proceedings of the Indian History Congress| volume = 67 | pages = 292–300 | jstor = 44147949 }}</ref> On 21 January 1519, two weeks after his ], Babur wrote: "On Friday we marched for Sawad (]), with the intention of attacking the Yusufzai Afghans, and dismounted in between the water of ] and the united waters of Chandāwal (Jandul) and Bajaur. Shah Mansur Yusufzai had brought a few well-flavoured and quite ] ]."<ref name="babur">{{cite book |last=Beveridge |first=Annette Susannah |author-link=Annette Beveridge |date=7 January 2014 |title=The Bābur-nāma in English, Memoirs of Bābur|url=https://www.gutenberg.org/files/44608/44608-h/44608-h.htm |publisher=Project Gutenberg}}</ref> | During the ], the Yusufzai tribe of Afghans was first explicitly mentioned in '']'' by ], a ] ruler from ] (in present-day ]) who captured ] in ].<ref>{{cite journal | last = Samrin | first = Farah | title = Yusufzais in Mughal History | year = 2006 | journal = Proceedings of the Indian History Congress| volume = 67 | pages = 292–300 | jstor = 44147949 }}</ref> On 21 January 1519, two weeks after his ], Babur wrote: "On Friday we marched for Sawad (]), with the intention of attacking the Yusufzai Afghans, and dismounted in between the water of ] and the united waters of Chandāwal (Jandul) and Bajaur. Shah Mansur Yusufzai had brought a few well-flavoured and quite ] ]."<ref name="babur">{{cite book |last=Beveridge |first=Annette Susannah |author-link=Annette Beveridge |date=7 January 2014 |title=The Bābur-nāma in English, Memoirs of Bābur|url=https://www.gutenberg.org/files/44608/44608-h/44608-h.htm |publisher=Project Gutenberg}}</ref> | ||
| As part of a treaty with Yusufzai Afghans, Babur married ], daughter of Yusufzai chief Shah Mansur |
Due to the military and strategic strength of the Yousafzai, Babur needed security from their location in the hills that ] his empire and did not allow for a safe expansion to ]. As part of a treaty with Yusufzai Afghans to have family ties, Babur married ], daughter of Yusufzai chief Shah Mansur on 30 January 1519 for mutual security after failing to subdue the tribe. Shah Mansur had favoured peace while the faction of ] was against any forging of close ties.<ref>{{cite book|first=Radhey|last=Shyam|title=Babur|publisher=Janaki Prakashan|year=1978|pages=263}}</ref><ref>Arlinghaus, Joseph Theodore (1988) ''The Transformation of Afghan Tribal Society: Tribal Expansion, Mughal Imperialism and the Roshaniyya Insurrection, 1450-1600''</ref><ref>Elizabeth Moynihan '''' National Museum of Asian Art</ref> Bibi Mubarika played an important role in the establishment of friendly relations of Yusufzai Pashtun chiefs with Babur, who later founded the ] after defeating Pashtun Sultan ] at the ] in 1526.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Aftab|first1=Tahera|last2=edited|last3=Hiro|first3=introduced by Dilip|title=Inscribing South Asian Muslim women : an annotated bibliography & research guide|date=2008|publisher=Brill|location=Leiden|isbn=9789004158498|page=46|edition=.}}</ref> One of Mubarika's brothers, Mir Jamal Yusufzai, accompanied Babur to India in 1525 and later held high posts under Mughal Emperors ] and ]. Although suspicions existed on both sides and the Yusufzai had never paid taxes or tributes to Babur or any other ] Emperor.<ref>{{cite book|first=Soma|last=Mukherjee|title=Royal Mughal Ladies and Their Contributions|publisher=Gyan Books|year=2001|pages=118|isbn=978-8-121-20760-7}}</ref><ref>The News (2016) '''' by Dr. Himayatullah Yaqubi</ref> | ||
| ===Yusufzai Chieftaincy=== | |||
| ] conquered the land of Malakand division and Yusufzai remained the powerful and prominent tribe of Malakand Agency.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.thenews.com.pk/amp/38531-malik-ahmad-baba-yousafzais-lige-services-to-be-rembered | title=Malik Ahmad Baba Yousafzai's life, services to be rembered | date=4 May 2015 }}</ref> Major parts of the ] remained under the Yusufzai Chieftaincy and major Yusufzai chiefs are the following. | |||
| * ] ] (Reign; 1520 - 1535). | |||
| * ] (Reign; 1535 - 1553) | |||
| * Malak Misri Khan Ali Asghar Yusufzai (Reign; 1553 - 1580) | |||
| * Malak Ghazi Khan Yusufzai (Reign; 1580 - 1585) | |||
| * ] (Reign; 1585 - 1626).<ref>{{cite web | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gOFtAAAAMAAJ | title=History of the Pathans: The Sarabani Pathans | last1=Rashid | first1=Haroon | date=2002 }}</ref> | |||
| * Malak Bhaku Khan Yusufzai (Reign; 1626 - 1675).<ref>{{cite web | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m9otAAAAMAAJ&q=Bhaku+Khan | title=Muslim Rule in India & Pakistan, 711-1858 A.C.: A Political and Cultural History | last1=Ikram | first1=Sheikh Mohamad | date=1966 }}</ref> | |||
| After 1675, the Yusufzai Chieftaincy was divided into 32 areas which was remained under each Yusufzai tribal Mashar (Leader). | |||
| In 1586, ] tried to invade ] in the ] but failed and it become the greatest disaster to Mughal empire in the era of Akbar.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://archive.org/details/a-short-history-of-the-mughal-empire | title=''A Short History of the Mughal Empire'' | date=2016 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Skirmishes with Mughal forces=== | ===Skirmishes with Mughal forces=== | ||
| During the 1580s, many Yusufzais and ] |
During the 1580s, many Yusufzais and ] rebelled against the Mughals and joined the ] of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V19_154.gif|title=Imperial Gazetteer2 of India, Volume 19– Imperial Gazetteer of India |publisher=Digital South Asia Library|page=152|access-date=22 April 2015}}</ref> In late 1585, Moghul emperor ] sent military forces under ] and ] to crush the rebellion. In February 1586, about 8,000 Mughal soldiers, including Birbal, ] near the ] between ] and ] by the Yusufzai lashkar led by ]. This was the greatest disaster faced by the ] during Akbar's reign.<ref>{{cite book |first=John F. |last=Richards |author-link=John F. Richards |series=The New Cambridge History of India |title=The Mughal Empire |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1993 |pages=50–51 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HHyVh29gy4QC&pg=PA50|isbn=9780521566032 }}</ref> | ||
| In 1630, under the leadership of ]'s great-grandson, Abdul Qadir, thousands of Pashtuns from the Yusufzai, Mandanrs, ], ], ], ], and other tribes launched an attack on the Mughal Army in ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Misdaq |first=Nabi |date=2006 |title=Afghanistan: Political Frailty and External Interference|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hHmTAgAAQBAJ |isbn=1135990174|publisher=Routledge}}</ref> In 1667, the Yusufzai again revolted against the Mughals, with one of their chiefs in Swat proclaiming himself the king. Muhammad Amin Khan brought a 9,000 strong Mughal Army from ] to suppress the revolt.<ref>{{Cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HHyVh29gy4QC&q=yusufzai&pg=PA50 |title = The Mughal Empire|isbn = 9780521566032|last1 = Richards|first1 = John F.|year = 1995}}</ref> Although the Mughal Emperor ] was able to conquer the southern Yusufzai plains within the northern ], he failed to wrest Swat and the adjoining valleys from the control of the Yusufzai.<ref name="gommans"/> | In 1630, under the leadership of ]'s great-grandson, Abdul Qadir, thousands of Pashtuns from the Yusufzai, Mandanrs, ], ], ], ], and other tribes launched an attack on the Mughal Army in ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Misdaq |first=Nabi |date=2006 |title=Afghanistan: Political Frailty and External Interference|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hHmTAgAAQBAJ |isbn=1135990174|publisher=Routledge}}</ref> In 1667, the Yusufzai again revolted against the Mughals, with one of their chiefs in Swat proclaiming himself the king. Muhammad Amin Khan brought a 9,000 strong Mughal Army from ] to suppress the revolt.<ref>{{Cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HHyVh29gy4QC&q=yusufzai&pg=PA50 |title = The Mughal Empire|isbn = 9780521566032|last1 = Richards|first1 = John F.|year = 1995| publisher=Cambridge University Press }}</ref> Although the Mughal Emperor ] was able to conquer the southern Yusufzai plains within the northern ], he failed to wrest Swat and the adjoining valleys from the control of the Yusufzai.<ref name="gommans"/> | ||
| ===Durrani period=== | ===Durrani period=== | ||
| ], which was founded by ] Yusufzai in ], ]]] | ], which was founded by ] Yusufzai in ], ]]] | ||
| ] and ], marching on the left of ], who is riding a brown horse, during the ]]] | ] and ], marching on the left of ], who is riding a brown horse, during the ], which was the largest number of fatalities in a single day reported in a classic formation battle between two armies]] | ||
| ] (1747–1772), the founder of the Afghan ], categorized all ] into four ''ulūs'' (tribal confederacies) for administrative purposes: ], ], ], and |
] (1747–1772), the founder of the Afghan ], categorized all ] into four ''ulūs'' (tribal confederacies) for administrative purposes: ], ], ], and Bar Durrani ("Upper Durranis"). The Yusufzai were included in the Bar Durrani confederacy along with other eastern Pashtun tribes, including the ], ], ], and ].<ref name="Nejatie">The Pearl of Pearls: The Abdālī-Durrānī Confederacy and Its Transformation under Aḥmad Shāh, Durr-i Durrān by Sajjad Nejatie. https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/handle/1807/80750.</ref> The Bar Durrani comprised the bulk of those Pashtuns who settled in ], India where they were known as the ].<ref name="gommans">{{cite book|title=The Rise of the Indo-Afghan Empire: C. 1710-1780|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-2TH8UYeAaoC |last=Gommans|first=Jos J.L.|author-link=Jos Gommans|publisher=Brill|year=1995|pages=219|isbn=9004101098}}</ref> | ||
| ], who belonged to the Yusufzai tribe, was a prominent Rohilla chief. In the 1740s, he founded the city of ] in Rohilkhand. In 1757, he supported Ahmad Shah Durrani in his attack on Delhi. After his victory, Ahmad Shah Durrani re-installed the Mughal emperor ] on the Delhi throne as the titular Mughal head, but gave the actual control of Delhi to Najib ad-Daula. From 1757 to 1770, Najib ad-Daula served as the governor of ], also ruling over ]. In 1761, he took part in the ] and provided thousands of Rohilla troops and many guns to Ahmad Shah Durrani to defeat the ].<ref> ], 1909, v. 18, p. 334.</ref> He also convinced ], the ], to join the Durrani forces. Before his departure from Delhi, Ahmad Shah Durrani appointed Najib |
], who belonged to the Yusufzai tribe, was a prominent Afghan Rohilla chief. In the 1740s, he founded the city of ] in Rohilkhand. In 1757, he supported Ahmad Shah Durrani in his attack on Delhi. After his victory, Ahmad Shah Durrani re-installed the Mughal emperor ] on the Delhi throne as the titular Mughal head, but gave the actual control of Delhi to Najib ad-Daula. From 1757 to 1770, Najib ad-Daula served as the governor of ], also ruling over ]. In 1761, he took part in the ] and provided thousands of Rohilla troops and many guns to Ahmad Shah Durrani to defeat the ].<ref> ], 1909, v. 18, p. 334.</ref> He also convinced ], the ], to join the Durrani forces. Before his departure from Delhi, Ahmad Shah Durrani appointed Najib-ud-Daula as ''Mir Bakshi'' (paymaster-general) of the Mughal emperor ].<ref></ref> After his death in 1770, Najib ad-Dawlah was succeeded by his son, ], who was defeated in 1772 by a joint Mughal-Maratha force, forcing him to flee from Rohilkhand. However, the descendants of Najib ad-Dawlah continued to rule Najibabad area until they were defeated by the British at ] on 21 April 1858 during the ].<ref>{{cite EB1911 |wstitle=Bijnor |volume=3 |page=928}}</ref> | ||
| Today, many Yusufzais are settled in India, most notably in Rohilkhand region, as well as in ], which was founded in 1714 by Pashtun Nawab ].<ref name=Haleem2007>{{cite web|title=Study of the Pathan Communities in Four States of India|last=Haleem|first=Safia|url=http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130430071054/http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|url-status=usurped|archive-date=April 30, 2013|date=24 July 2007|publisher=Khyber Gateway|language=en|access-date=4 May 2014|quote=Farrukhabad has a mixed population of Pathans dominated by the Bangash and Yousafzais.}}</ref><ref name=Haleem>{{cite web|title=Study of the Pathan Communities in Four States of India|last=Haleem|first=Safia|date=24 July 2007|publisher=Khyber Gateway|language=en|access-date=4 May 2014|url=http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130430071054/http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|url-status=usurped|archive-date=April 30, 2013}}</ref> | Today, many Yusufzais are settled in India, most notably in Rohilkhand region, as well as in ], which was founded in 1714 by Pashtun Nawab ].<ref name=Haleem2007>{{cite web|title=Study of the Pathan Communities in Four States of India|last=Haleem|first=Safia|url=http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130430071054/http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|url-status=usurped|archive-date=April 30, 2013|date=24 July 2007|publisher=Khyber Gateway|language=en|access-date=4 May 2014|quote=Farrukhabad has a mixed population of Pathans dominated by the Bangash and Yousafzais.}}</ref><ref name=Haleem>{{cite web|title=Study of the Pathan Communities in Four States of India|last=Haleem|first=Safia|date=24 July 2007|publisher=Khyber Gateway|language=en|access-date=4 May 2014|url=http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130430071054/http://www.khyber.org/articles/2007/Study_of_the_Pathan_Communitie.shtml|url-status=usurped|archive-date=April 30, 2013}}</ref> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 87: | ||
| One of Iliaszai grandson through Taje, was a man named ], who had five sons: Hassan, Behram, Ali Sher, Hussain, and Ibrahim. The first four sons settled in present-day ], while Ibrahim was separated from them during the massacre of Yousafzai by ] in ]. Initially settling in ], Ibrahim's descendants eventually migrated to ] in present-day ]. | One of Iliaszai grandson through Taje, was a man named ], who had five sons: Hassan, Behram, Ali Sher, Hussain, and Ibrahim. The first four sons settled in present-day ], while Ibrahim was separated from them during the massacre of Yousafzai by ] in ]. Initially settling in ], Ibrahim's descendants eventually migrated to ] in present-day ]. | ||
| Ibrahim had only one son named Hassan Khan, and his family was known as Hassan Khel. However, after one of his descendant, Mughal Khan Yousafzai, his tribe came to be known as Mughal Khel. Mughal Khan's leadership and capabilities helped establish his tribe as one of the leading and honorable tribes of Bannu. Jaffar Khan Yousafzai, Mughal Khan's grandson, also earned a name and place for himself among the elders of the district. He also commissioned the construction of a beautiful mosque in ] in around 1820s.<ref name=":0" /> | Ibrahim had only one son named Hassan Khan, and his family was known as Hassan Khel. However, after one of his descendant, Mughal Khan Yousafzai, his tribe came to be known as ]. Mughal Khan's leadership and capabilities helped establish his tribe as one of the leading and honorable tribes of Bannu. Jaffar Khan Yousafzai, Mughal Khan's grandson, also earned a name and place for himself among the elders of the district. He also commissioned the construction of a beautiful mosque in ] in around 1820s.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The Mughal Khel tribe has the following sub-tribes: Qasim Khel, Jaffar Khel, Hakim Khel, and Muhammad Hassan Khel. The Mughal Khel have ruled and held the position of maliks in Ghoriwala for more than 300 years. Due to centuries of living in a land far away from their brethren, the Mughal Khels gradually assimilated in the local society, adopting the local elements and thus have transitioned from the ] pronunciations to ] but still in their speech and appearance their long lost characters can be identified.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Bannu :: History, Culture, LifeStyle, People, Food etc |url=https://pmru.kp.gov.pk/districts/bannu/ |access-date=2022-11-17 |website=pmru.kp.gov.pk}}</ref> | The ] tribe has the following sub-tribes: Qasim Khel, Jaffar Khel, Hakim Khel, and Muhammad Hassan Khel. The Mughal Khel have ruled and held the position of maliks in Ghoriwala for more than 300 years. Due to centuries of living in a land far away from their brethren, the Mughal Khels gradually assimilated in the local society, adopting the local elements and thus have transitioned from the ] pronunciations to ] but still in their speech and appearance their long lost characters can be identified.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Bannu :: History, Culture, LifeStyle, People, Food etc |url=https://pmru.kp.gov.pk/districts/bannu/ |access-date=2022-11-17 |website=pmru.kp.gov.pk}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Ibbetson |first=Sir Denzil |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dO0OAAAAQAAJ&dq=Mughal+Khel+Bannu&pg=PA82 |title=Panjab Castes: Being a Reprint of the Chapter on "The Races, Castes, and Tribes of the People" in the Report on the Census of the Panjab |date=1916 |publisher=Superintendent, Government Printing, Punjab |pages=82 |language=en}}</ref> | ||
| As the author of Bannu Gazetteer said: | As the author of Bannu Gazetteer said: | ||
| Line 139: | Line 151: | ||
| ==Subtribes== | ==Subtribes== | ||
| *] | |||
| * | |||
| *Azizkhel | *Azizkhel | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 153: | Line 163: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| * |
*Mahabatkhel | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| **] | |||
| **] | **] | ||
| **] | |||
| *]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Bannu :: Gazetteer |url=https://pmru.kp.gov.pk/districts/bannu/gazetteer.php#page/2 |access-date=2022-11-15 |website=pmru.kp.gov.pk}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=Khan Roshan Khan |url=http://archive.org/details/YousafzaiQaumKiSarguzasht |title=Yousafzai qaum ki sarguzasht |others=Nasir khan |pages=The Mughal Khels are mentioned on page no. 424 under Gadezai Heading |language=ur}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |first= |title=Leading Families in Bannu :: Khyber.ORG |url=http://www.khyber.org/publications/031-035/leadingfamilies.shtml#Jafar%20Khan%20of%20Ghoriwal |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070213055311/http://www.khyber.org/publications/031-035/leadingfamilies.shtml#Jafar%20Khan%20of%20Ghoriwal |url-status=usurped |archive-date=February 13, 2007 |access-date=2022-11-15 |website=www.khyber.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Khān |first=Muḥammad Ḥayāt |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hopEAQAAMAAJ |title=Afghanistan and Its Inhabitants |date=1981 |publisher=Sang-e-Meel Publications |pages=Mentioned on page no. 626 under the title of Khandane Ghoriwala |language=ur}}</ref> | *]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Bannu :: Gazetteer |url=https://pmru.kp.gov.pk/districts/bannu/gazetteer.php#page/2 |access-date=2022-11-15 |website=pmru.kp.gov.pk}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=Khan Roshan Khan |url=http://archive.org/details/YousafzaiQaumKiSarguzasht |title=Yousafzai qaum ki sarguzasht |others=Nasir khan |pages=The Mughal Khels are mentioned on page no. 424 under Gadezai Heading |language=ur}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |first= |title=Leading Families in Bannu :: Khyber.ORG |url=http://www.khyber.org/publications/031-035/leadingfamilies.shtml#Jafar%20Khan%20of%20Ghoriwal |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070213055311/http://www.khyber.org/publications/031-035/leadingfamilies.shtml#Jafar%20Khan%20of%20Ghoriwal |url-status=usurped |archive-date=February 13, 2007 |access-date=2022-11-15 |website=www.khyber.org}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Khān |first=Muḥammad Ḥayāt |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hopEAQAAMAAJ |title=Afghanistan and Its Inhabitants |date=1981 |publisher=Sang-e-Meel Publications |pages=Mentioned on page no. 626 under the title of Khandane Ghoriwala |language=ur}}</ref> | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 164: | Line 176: | ||
| == Notable Yusufzais/Yousafzais == | == Notable Yusufzais/Yousafzais == | ||
| * ], Pashtun Revolutionary and |
* ], Pashtun Revolutionary and ruler who once served under ] | ||
| * ], Journalist and ] leader | * ], Journalist and ] leader | ||
| * ], Lawyer and Chairman of ] (PTI) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], Chief advisor to the ] and lawyer for ] | |||
| * ], Empress Consort of the ] | |||
| * ], ''"Founder of Pakhtunkhwa"'' who fought for control of northern ] to expand the Yusufzai tribe | * ], ''"Founder of Pakhtunkhwa"'' who fought for control of northern ] to expand the Yusufzai tribe | ||
| * Bahaku Khan Yousafzai, Afghan Warrior who fought in the Sixth ] of 1667-1678<ref>We Mountains – Regional Website of North Pakistan (2020) '''' Jahandad Khan</ref><ref>] (2015) '''' Correspondents</ref><ref>'''' by Olaf Caroe (1958)</ref> | * Bahaku Khan Yousafzai, Afghan Warrior who fought in the Sixth ] of 1667-1678{{efn|''The War beginning with the Yusufzai attack of 1667, led by Bhaku/Bhagu Khan''}}<ref>We Mountains – Regional Website of North Pakistan (2020) '''' Jahandad Khan</ref><ref>] (2015) '''' Correspondents</ref><ref>'''' by Olaf Caroe (1958)</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Richards |first1=John F. |date=1993 |title=The Mughal Empire Part 1: Vol V|page=170 |publisher=Cambridge University Press; 1st edition |isbn=978-0521251198}}</ref> | ||
| * ] (16th Century), |
* ] (16th Century), Afghan chieftan leader who rallied his tribe and rebelled against ] emperor ] and inflicted one of their ] in 1586 | ||
| * ], Pashto Poet of the 18th Century | |||
| ⚫ | * ] (born 1997), Pashtun female education activist and Nobel Peace Prize laureate, from the Dalokhel Subclan | ||
| * ], Pashtun tribal leader martyr who refused to give up ground to the ] | |||
| ⚫ | * ] (born 1969), Pashtun education activist and father of Malala Yousafzai, from the Dalokhel Subclan | ||
| ⚫ | * ] (born 1997), Pashtun female education activist and Nobel Peace Prize laureate, from the Dalokhel Subclan | ||
| ⚫ | * ], Pashtun |
||
| ⚫ | * ] (born 1969), Pashtun education activist and father of Malala Yousafzai, from the Dalokhel Subclan | ||
| ⚫ | * ], Afghan |
||
| ⚫ | * ], Pashtun historian | ||
| ⚫ | * ], Military |
||
| ⚫ | * ], Afghan serviceman who fought with ] ] to Victory at ], 1761 | ||
| * ], dubbed the ''Afghan Napoleon'' who conquered northern ] battling the ] in the ], taking ] as their ] who were treated with mercy | |||
| * Malak Ghazi Khan Yusufzai, was the fourth ruler of Pakhtunkhwa State. Ghazi Khan was martyred in the battle against the Mughals | |||
| ⚫ | * ], Military officer who was martyred in the ] and decorated with the awarded ] for highest Wartime Gallantry of Pakistan | ||
| * ], Journalist who once interviewed ] | * ], Journalist who once interviewed ] | ||
| * ], |
* ], Afghan Journalist | ||
| ⚫ | * ], Socialist Revolutionary, decorated War Hero of the ] as well as a founding father for the nation of ] | ||
| * ], only female ] in ] history | |||
| * ], Afghan footballer representing the ] in the ] | |||
| * ], prominent member of the ], ] and served as President of the ] | |||
| * ], Afghan footballer who competed in the ] | |||
| ⚫ | * ], Socialist Revolutionary, |
||
| * ], Afghan |
* ], Afghan field hockey player | ||
| * ], Afghan football player who played for ] | |||
| * ], cricketer | |||
| * ], Poet and famous writer | * ], Poet and famous writer | ||
| * ], was a Pashtun tribal Yusufzai leader and a freedom fighter. The faqīr declared a ] against the British Empire, unsuccessfully in 1895, then successfully in ] | |||
| * ], specialised in ] |
* ], specialised in ] language and culture | ||
| ⚫ | * Jafar Khan Yusufzai,<ref>{{cite web | url=https://historyofpashtuns.blogspot.com/2016/05/yousafzais-of-ghoriwala-in-bannu.html?m=1 | title=History of Pashtuns: Yousafzais of Ghoriwala in Bannu }}</ref> |
||
| * ], Afghan warrior hero of the ] against the ] | |||
| * Malik Jamroz Khan, Pashtun tribal leader and among the founders of the ] | |||
| * ], Pashtun nationalist, ] affiliate and former provincial and federal minister of ] | |||
| * ], Pashtun nationalist, poet and writer who founded the ], refused offers to join government from President ] and was imprisoned by the military regime of ] | |||
| * ], Afghan judge, educator and a human rights activist during the ] regime | |||
| ⚫ | * Jafar Khan Yusufzai,<ref>{{cite web | url=https://historyofpashtuns.blogspot.com/2016/05/yousafzais-of-ghoriwala-in-bannu.html?m=1 | title=History of Pashtuns: Yousafzais of Ghoriwala in Bannu | date=23 May 2016 }}</ref> former Raes of ], ] | ||
| *], Indian Bollywood actress and superstar <ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.dawn.com/news/1157403 |title=Madhubala: From Peshawar with love ... |last=Khan |first=Javed |date=18 January 2015 |work=] |access-date=20 April 2018 |language=en-US |archive-date=20 April 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180420140131/https://www.dawn.com/news/1157403 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| * {{note|a|1}}In Pashto, "Yusufzai" ({{lang|ps|یوسفزی}}, ) is the masculine singular form of the word. Its feminine singular is "Yusufzey" ({{lang|ps|یوسفزۍ}}, ), while its plural is "Yusufzee" ({{lang|ps|یوسفزي}}, ). | * {{note|a|1}}In Pashto, "Yusufzai" ({{lang|ps|یوسفزی}}, ) is the masculine singular form of the word. Its feminine singular is "Yusufzey" ({{lang|ps|یوسفزۍ}}, ), while its plural is "Yusufzee" ({{lang|ps|یوسفزي}}, ). | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| {{Pashtun tribes}} | {{Pashtun tribes}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:31, 31 December 2024
Pashtun tribeFor other uses, see Yusufzai (disambiguation).
| Yūsufzai ايسپزی | |
|---|---|
 Depiction of a Yusufzai warrior Depiction of a Yusufzai warrior | |
| Ethnicity | Pashtun |
| Location | Afghanistan, Pakistan (Khyber Pakhtunkhwa) |
| Parent tribe | Sarbani |
| Branches | Mandanr, Iliaszai, Akozai, Mandan, Isazai, Malizai |
| Language | Pashto |
| Religion | |
The Yusufzai or Yousafzai (Pashto: یوسفزی, pronounced [jusəpˈzai]), also referred to as the Esapzai (ايسپزی, pronounced [iːsəpˈzai]), or Yusufzai Afghans historically, are one of the largest tribes of Pashtuns. They are natively based in the northern part of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Malakand, Dir, Swat, Shangla, Buner, Swabi, Mardan, Bajaur, Peshawar, Tor Ghar), to which they migrated from Kabul during the 16th century, but they are also present in parts of Afghanistan, including Kunar, Kabul, Kandahar and Farah. Outside of these countries, they can be found in Ghoriwala District Bannu (Mughal Khel), Balochistan Sibi (Akazai), Chagai (Hassanzai) and Rohilkandh.
Most of the Yusufzai speak a northern variety of Pashto and some southern variety of Pashto (as in case of Mughal Khel) and Afghan dialect Persian.
Etymology
In Pashto phonology, as /f/ is found only in loanwords and tends to be replaced by /p/, the name is usually pronounced as Yūsəpzay or Īsəpzay. The name literally means "descendant of Yusuf" in Pashto; Yūsuf (يوسف) is an Arabic and Aramaic masculine given name meaning "(God) shall add."
According to some scholars, including philologist J.W. McCrindle, the name Yūsəpzay or Īsəpzay is derived from the tribal names of Aspasioi and Assakenoi – the ancient inhabitants of the Kunar Valley and the Swat Valley who offered resistance when Alexander invaded their land in 327–326 BCE. According to historian R.C. Majumdar, the Assakenoi were either allied to or a branch of the larger Aspasioi, and both of these ancient tribal names were probably derived from the word Aśvaka, which literally means "horsemen", "horse breeders", or "cavalrymen" (from aśva or aspa, the Sanskrit and Avestan words for "horse").
McCrindle noted: "The name of the Aśvaka indicates that their country was renowned in primitive times, as it is at the present day, for its superior breed of horses. The fact that the Greeks translated their name into "Hippasioi" (from ἵππος, a horse) shows that they must have been aware of its etymological signification."
The name of the Aśvakan or Assakan is also the origin of the ethnonym Afghān, which has been historically used for all Pashtuns.
Mythical genealogy
According to a popular mythical genealogy, recorded by 17th-century Mughal courtier Nimat Allah al-Harawi in his book Tārīkh-i Khān Jahānī wa Makhzan-i Afghānī, the Yusufzai tribe descended from their eponymous ancestor Yūsuf, who was son of Mand, who was son of Khashay (or Khakhay), who was son of Kand, who was son of Kharshbūn, who was son of Saṛban (progenitor of the Sarbani tribal confederacy), who was son of Qais Abdur Rashid (progenitor of all Pashtuns). Qais Abdur Rashid was a descendant of Afghana, who was described as a grandson of the Israelite king Saul and commander-in-chief of the army of prophet Solomon. Qais was claimed to be a contemporary of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a kinsman of Arab commander Khalid ibn al-Walid. When Khalid ibn al-Walid summoned Qais from Ghor to Medina, Qais accepted Islam and the prophet renamed him Abdur Rashīd (meaning "Servant of the Guide to the Right Path" or "Servant of God" in Arabic). Abdur Rashid returned to Ghor and introduced Islam there. The book stated that Yūsuf's grandfather (and Mand's father), Khashay, also had two other sons, Muk and Tarkalāṇī, who were the progenitors of the Gigyani and Tarkani tribes, respectively. Yūsuf had one brother, Umar, who was the progenitor of the Mandanr tribe, which is closely related to Yusufzais.
The 1595 Mughal account Ain-i-Akbari also mentioned the tradition of Israelite descent among Pashtuns, which shows that the tradition was already popular among 16th-century Pashtuns.
History
Peace treaty with Babur

During the early modern period, the Yusufzai tribe of Afghans was first explicitly mentioned in Baburnama by Babur, a Timurid ruler from Fergana (in present-day Uzbekistan) who captured Kabul in 1504. On 21 January 1519, two weeks after his Bajaur massacre, Babur wrote: "On Friday we marched for Sawad (Swat), with the intention of attacking the Yusufzai Afghans, and dismounted in between the water of Panjkora and the united waters of Chandāwal (Jandul) and Bajaur. Shah Mansur Yusufzai had brought a few well-flavoured and quite intoxicating confections."
Due to the military and strategic strength of the Yousafzai, Babur needed security from their location in the hills that threatened his empire and did not allow for a safe expansion to India. As part of a treaty with Yusufzai Afghans to have family ties, Babur married Bibi Mubarika, daughter of Yusufzai chief Shah Mansur on 30 January 1519 for mutual security after failing to subdue the tribe. Shah Mansur had favoured peace while the faction of Malik Ahmad Khan was against any forging of close ties. Bibi Mubarika played an important role in the establishment of friendly relations of Yusufzai Pashtun chiefs with Babur, who later founded the Mughal Empire after defeating Pashtun Sultan Ibrahim Lodi at the First Battle of Panipat in 1526. One of Mubarika's brothers, Mir Jamal Yusufzai, accompanied Babur to India in 1525 and later held high posts under Mughal Emperors Humayun and Akbar. Although suspicions existed on both sides and the Yusufzai had never paid taxes or tributes to Babur or any other Mughal Emperor.
Yusufzai Chieftaincy
Malak Ahmad Khan Yusufzai conquered the land of Malakand division and Yusufzai remained the powerful and prominent tribe of Malakand Agency. Major parts of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa remained under the Yusufzai Chieftaincy and major Yusufzai chiefs are the following.
- Malak Ahmad Khan Yusufzai (Reign; 1520 - 1535).
- Malak Gaju Khan Yusufzai (Reign; 1535 - 1553)
- Malak Misri Khan Ali Asghar Yusufzai (Reign; 1553 - 1580)
- Malak Ghazi Khan Yusufzai (Reign; 1580 - 1585)
- Malak Kalu Khan Yousafzai (Reign; 1585 - 1626).
- Malak Bhaku Khan Yusufzai (Reign; 1626 - 1675).
After 1675, the Yusufzai Chieftaincy was divided into 32 areas which was remained under each Yusufzai tribal Mashar (Leader).
In 1586, Akbar the Great tried to invade Malakand in the Battle of the Malandari Pass (1586) but failed and it become the greatest disaster to Mughal empire in the era of Akbar.
Skirmishes with Mughal forces
During the 1580s, many Yusufzais and Mandanrs rebelled against the Mughals and joined the Roshani movement of Pir Roshan. In late 1585, Moghul emperor Akbar sent military forces under Zain Khan Koka and Birbal to crush the rebellion. In February 1586, about 8,000 Mughal soldiers, including Birbal, were killed near the Karakar Pass between Swat and Buner by the Yusufzai lashkar led by Kalu Khan. This was the greatest disaster faced by the Mughal Army during Akbar's reign.
In 1630, under the leadership of Pir Roshan's great-grandson, Abdul Qadir, thousands of Pashtuns from the Yusufzai, Mandanrs, Kheshgi, Mohmand, Afridi, Bangash, and other tribes launched an attack on the Mughal Army in Peshawar. In 1667, the Yusufzai again revolted against the Mughals, with one of their chiefs in Swat proclaiming himself the king. Muhammad Amin Khan brought a 9,000 strong Mughal Army from Delhi to suppress the revolt. Although the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb was able to conquer the southern Yusufzai plains within the northern Kabul valley, he failed to wrest Swat and the adjoining valleys from the control of the Yusufzai.
Durrani period

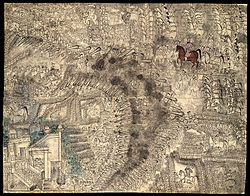
Ahmad Shah Durrani (1747–1772), the founder of the Afghan Durrani Empire, categorized all Afghan tribes into four ulūs (tribal confederacies) for administrative purposes: Durrani, Ghilji, Sur, and Bar Durrani ("Upper Durranis"). The Yusufzai were included in the Bar Durrani confederacy along with other eastern Pashtun tribes, including the Mohmand, Afridi, Bangash, and Khattak. The Bar Durrani comprised the bulk of those Pashtuns who settled in Rohilkhand, India where they were known as the Rohilla.
Najib-ud-Daula, who belonged to the Yusufzai tribe, was a prominent Afghan Rohilla chief. In the 1740s, he founded the city of Najibabad in Rohilkhand. In 1757, he supported Ahmad Shah Durrani in his attack on Delhi. After his victory, Ahmad Shah Durrani re-installed the Mughal emperor Alamgir II on the Delhi throne as the titular Mughal head, but gave the actual control of Delhi to Najib ad-Daula. From 1757 to 1770, Najib ad-Daula served as the governor of Saharanpur, also ruling over Dehradun. In 1761, he took part in the Third Battle of Panipat and provided thousands of Rohilla troops and many guns to Ahmad Shah Durrani to defeat the Marathas. He also convinced Shuja-ud-Daula, the Nawab of Awadh, to join the Durrani forces. Before his departure from Delhi, Ahmad Shah Durrani appointed Najib-ud-Daula as Mir Bakshi (paymaster-general) of the Mughal emperor Shah Alam II. After his death in 1770, Najib ad-Dawlah was succeeded by his son, Zabita Khan, who was defeated in 1772 by a joint Mughal-Maratha force, forcing him to flee from Rohilkhand. However, the descendants of Najib ad-Dawlah continued to rule Najibabad area until they were defeated by the British at Nagina on 21 April 1858 during the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Today, many Yusufzais are settled in India, most notably in Rohilkhand region, as well as in Farrukhabad, which was founded in 1714 by Pashtun Nawab Muhammad Khan Bangash.
State of Dir
Main article: Dir (princely state)
In Dir, descendants of 17th-century Akhund Ilyas Yusufzai, the founder of the city of Dir, laid the foundation of the state of Dir. In 1897, the British Raj annexed Dir and granted the title of the "Nawab of Dir" to Sharif Khan Akhundkhel, the ruler of Dir (1886–1904).
The princely state of Dir existed until 1969, after which they were merged into West Pakistan, and then in 1970 into the North-West Frontier Province (present-day Khyber Pakhtunkhwa) of Pakistan. Its area is part of the present-day Buner, Lower Dir and Upper Dir.
Yousafzai of Ghoriwala
Main article: Ghoriwala § Arrival of Mughal Khel
One of Iliaszai grandson through Taje, was a man named Gadezai, who had five sons: Hassan, Behram, Ali Sher, Hussain, and Ibrahim. The first four sons settled in present-day District Buner, while Ibrahim was separated from them during the massacre of Yousafzai by Ulugh Beg in Kabul. Initially settling in Kurram, Ibrahim's descendants eventually migrated to Ghoriwala in present-day District Bannu.
Ibrahim had only one son named Hassan Khan, and his family was known as Hassan Khel. However, after one of his descendant, Mughal Khan Yousafzai, his tribe came to be known as Mughal Khel. Mughal Khan's leadership and capabilities helped establish his tribe as one of the leading and honorable tribes of Bannu. Jaffar Khan Yousafzai, Mughal Khan's grandson, also earned a name and place for himself among the elders of the district. He also commissioned the construction of a beautiful mosque in Bannu Bazar in around 1820s.

The Mughal Khel tribe has the following sub-tribes: Qasim Khel, Jaffar Khel, Hakim Khel, and Muhammad Hassan Khel. The Mughal Khel have ruled and held the position of maliks in Ghoriwala for more than 300 years. Due to centuries of living in a land far away from their brethren, the Mughal Khels gradually assimilated in the local society, adopting the local elements and thus have transitioned from the Hard Pashto pronunciations to Soft Pashto but still in their speech and appearance their long lost characters can be identified.
As the author of Bannu Gazetteer said:
The most notable case of the sort is that of the Mughal Khels of Ghoriwala, a Yousafzai group, who conquered territory for themselves seven generations ago and still preserve in speech and physiognomy proof of their origin.
— Herbert Benjamin Edwardes, Gazetteer of the Bannu District 1883
Pashto dialect
Yusufzai Pashto, which is a variety of Northern Pashto, is the prestige variety of Pashto in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. Some of its consonants differ from the other dialects:
| Dialects | ښ | ږ | څ | ځ | ژ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yusufzai Pashto | |||||
| Ghilji Pashto | |||||
| Durrani Pashto |
Society
The Yusufzai Pashtun aristocracy was historically divided into several communities based on patrilineal segmentary groups:
- Khān
The khān referred to the Yusufzai landowners. In the 16th century, saint Sheikh Milli, a prominent Yusufzai dignitary, distributed the Yusufzai land among the major Yusufzai tribal clans (khēl). However, to avoid inequalities, he ordered that the lands should not become permanent property of the clans, but rather they should be realloted within the patrilineal clans periodically after every ten years or so. In this system (wēsh), each landowning khān would own shares (brakha) representing his proportion of the total area distributed. Through a regular rotation of ownership, the Yusufzai landowners would migrate for up to 30 miles for their new share after each cycle, although the tenants cultivating the land would stay on.
The wēsh system operated among the Yusufzai of Swat region until at least 1920s.
- Hamsāya
The hamsāya or "shade sharers" were the clients or dependents from other (non-Yusufzai) Pashtun tribes who became attached to the Yusufzai tribe over the years.
- Faqīr
The faqīr or "poor" were the non-Pashtun landless peasants who were assigned to the Yusufzai landowners. As dependent peasants, the faqīr used to pay rent for the land they cultivated.
In the 19th century, the distinction between hamsāya as a "dependent Pashtun tribe" and faqīr as "non-Pashtun landless peasants" became blurred. Both terms were then interchangeably used to simply refer to landless dependents or clients.
- Mlātəṛ
The mlātəṛ or "supporters" provided services to their patrons as artisans (kasabgar), musicians (ḍəm), herders, or commercial agents, mostly in return for a payment in grain or rice.
- Ghulām
The ghulām or "slaves" were more closely attached to their patron and his family and frequently entrusted with a variety of functions within their master's household. Although the ghulām were less free as compared to the hamsāya or the faqīr, they generally enjoyed a higher status in the society.
Subtribes
- Azizkhel
- Akazai
- Babuzai
- Shamozai
- Balarkhel
- Chagharzai
- Degankhel
- Hassanzai
- Kamalzai
- Khan Khel
- Khwaja Khel (Khwajgan)
- Madakhel
- Mahabatkhel
- Malizai
- Mandanr
- Mughal Khel
- Niamatkhel
- Nikpikhel
- Ranizai
- Tahirkheli
Notable Yusufzais/Yousafzais
- Gaju Khan, Pashtun Revolutionary and ruler who once served under Sher Shah Sur
- Shaukat Ali Yousafzai, Journalist and PTI leader
- Gohar Ali Khan, Lawyer and Chairman of Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI)
- Mashal Yousafzai, Chief advisor to the Chief Minister of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and lawyer for PTI
- Bibi Mubarika, Empress Consort of the Mughal Empire
- Malak Ahmad Khan Yusufzai, "Founder of Pakhtunkhwa" who fought for control of northern Khyber and Pakhtunkhwa to expand the Yusufzai tribe
- Bahaku Khan Yousafzai, Afghan Warrior who fought in the Sixth Afghan-Mughal War of 1667-1678
- Kalu Khan Yusufzai (16th Century), Afghan chieftan leader who rallied his tribe and rebelled against Mughal emperor Akbar the Great and inflicted one of their greatest defeats in 1586
- Hafiz Alpuri, Pashto Poet of the 18th Century
- Haji Musa Khan, Pashtun tribal leader martyr who refused to give up ground to the Taliban
- Malala Yousafzai (born 1997), Pashtun female education activist and Nobel Peace Prize laureate, from the Dalokhel Subclan
- Ziauddin Yousafzai (born 1969), Pashtun education activist and father of Malala Yousafzai, from the Dalokhel Subclan
- Khan Roshan Khan, Pashtun historian
- Najib ad-Dawlah Yousafzai, Afghan serviceman who fought with Ahmad Shāh's Durrani Empire to Victory at Panipat, 1761
- Malak Ghazi Khan Yusufzai, was the fourth ruler of Pakhtunkhwa State. Ghazi Khan was martyred in the battle against the Mughals
- Karnal Sher Khan, Military officer who was martyred in the Kargil War and decorated with the awarded Nishan-e-Haider for highest Wartime Gallantry of Pakistan
- Rahimullah Yusufzai, Journalist who once interviewed Osama Bin Laden
- Sami Yousafzai, Afghan Journalist
- Nisar Muhammad Yousafzai, Socialist Revolutionary, decorated War Hero of the Afghan War of Independence as well as a founding father for the nation of Tajikistan
- Abdul Ghafoor Yusufzai, Afghan footballer representing the Kingdom of Afghanistan in the 1948 Summer Olympic Games
- Mohammad Sarwar Yousafzai, Afghan footballer who competed in the 1948 Summer Olympics
- Ahmad Yusufzai, Afghan field hockey player
- Hamidullah Yousafzai, Afghan football player who played for Afghanistan national football team
- Abaseen Yousafzai, Poet and famous writer
- Sartor Faqir, was a Pashtun tribal Yusufzai leader and a freedom fighter. The faqīr declared a Jihād against the British Empire, unsuccessfully in 1895, then successfully in 1897
- Nisar Muhammad Khan, specialised in Pashto language and culture
- Azimullah Khan Yusufzai, Afghan warrior hero of the Great Revolt of 1857 against the British East India Company
- Malik Jamroz Khan, Pashtun tribal leader and among the founders of the Princely State of Swat
- Afzal Khan Lala, Pashtun nationalist, NAP affiliate and former provincial and federal minister of NWFP
- Kabir Stori, Pashtun nationalist, poet and writer who founded the Pashtuns Social Democratic Party, refused offers to join government from President Najibullah and was imprisoned by the military regime of Zia-ul-Haq
- Asmatullah Rohani, Afghan judge, educator and a human rights activist during the PDPA regime
- Jafar Khan Yusufzai, former Raes of Mughal Khel Tappa, Bannu
- Madhubala, Indian Bollywood actress and superstar
Notes
- ^1 In Pashto, "Yusufzai" (یوسفزی, ) is the masculine singular form of the word. Its feminine singular is "Yusufzey" (یوسفزۍ, ), while its plural is "Yusufzee" (یوسفزي, ).
References
- The War beginning with the Yusufzai attack of 1667, led by Bhaku/Bhagu Khan
- ^ Khan Roshan Khan. "Yousafzai qaum ki sarguzasht". Retrieved 2021-03-28.
- ^ Coyle, Dennis Walter (2014). Placing Wardak Among Pashto Varieties (Master's thesis). University of North Dakota.
- Tegey, Habibullah; Robson, Barbara (1996). A Reference Grammar of Pashto (PDF). Washington: Center for Applied Linguistics. p. 15.
- Majumdar, Ramesh Chandra (1977) . Ancient India (Reprinted ed.). Motilal Banarsidass. p. 99. ISBN 978-8-12080-436-4.
- John Watson McCrindle (1896). The Invasion of India by Alexander the Great: As Described by Arrian, Q. Curtius, Diodoros, Plutarch and Justin. University of Michigan: A. Constable. pp. 333–334.
- "The name Afghan has evidently been derived from Asvakan, the Assakenoi of Arrian... " (Megasthenes and Arrian, p 180. See also: Alexander's Invasion of India, p 38; J.W. McCrindle).
- "Even the name Afghan is Aryan being derived from Asvakayana, an important clan of the Asvakas or horsemen who must have derived this title from their handling of celebrated breeds of horses" (See: Imprints of Indian Thought and Culture abroad, p 124, Vivekananda Kendra Prakashan).
- cf: "Their name (Afghan) means "cavalier" being derived from the Sanskrit, Asva, or Asvaka, a horse, and shows that their country must have been noted in ancient times, as it is at the present day, for its superior breed of horses. Asvaka was an important tribe settled north to Kabul river, which offered a gallant resistance but ineffectual resistance to the arms of Alexander "(Ref: Scottish Geographical Magazine, 1999, p 275, Royal Scottish Geographical Society).
- "Afghans are Assakani of the Greeks; this word being the Sanskrit Ashvaka meaning 'horsemen' " (Ref: Sva, 1915, p 113, Christopher Molesworth Birdwood).
- Cf: "The name represents Sanskrit Asvaka in the sense of a cavalier, and this reappears scarcely modified in the Assakani or Assakeni of the historians of the expedition of Alexander" (Hobson-Jobson: A Glossary of Colloquial Anglo-Indian words and phrases, and of kindred terms, etymological..by Henry Yule, AD Burnell).
- ^ The Pearl of Pearls: The Abdālī-Durrānī Confederacy and Its Transformation under Aḥmad Shāh, Durr-i Durrān by Sajjad Nejatie. https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/handle/1807/80750.
- Samrin, Farah (2006). "Yusufzais in Mughal History". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 67: 292–300. JSTOR 44147949.
- Beveridge, Annette Susannah (7 January 2014). The Bābur-nāma in English, Memoirs of Bābur. Project Gutenberg.
- Shyam, Radhey (1978). Babur. Janaki Prakashan. p. 263.
- Arlinghaus, Joseph Theodore (1988) The Transformation of Afghan Tribal Society: Tribal Expansion, Mughal Imperialism and the Roshaniyya Insurrection, 1450-1600
- Elizabeth Moynihan V. A Passage to Kabul - An Unplanned Life: In Search of Mughal Gardens National Museum of Asian Art
- Aftab, Tahera; edited; Hiro, introduced by Dilip (2008). Inscribing South Asian Muslim women : an annotated bibliography & research guide (. ed.). Leiden: Brill. p. 46. ISBN 9789004158498.
{{cite book}}:|last2=has generic name (help) - Mukherjee, Soma (2001). Royal Mughal Ladies and Their Contributions. Gyan Books. p. 118. ISBN 978-8-121-20760-7.
- The News (2016) The forgotten Queen of Babur by Dr. Himayatullah Yaqubi
- "Malik Ahmad Baba Yousafzai's life, services to be rembered". 4 May 2015.
- Rashid, Haroon (2002). "History of the Pathans: The Sarabani Pathans".
- Ikram, Sheikh Mohamad (1966). "Muslim Rule in India & Pakistan, 711-1858 A.C.: A Political and Cultural History".
- "A Short History of the Mughal Empire". 2016.
- "Imperial Gazetteer2 of India, Volume 19– Imperial Gazetteer of India". Digital South Asia Library. p. 152. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- Richards, John F. (1993). The Mughal Empire. The New Cambridge History of India. Cambridge University Press. pp. 50–51. ISBN 9780521566032.
- Misdaq, Nabi (2006). Afghanistan: Political Frailty and External Interference. Routledge. ISBN 1135990174.
- Richards, John F. (1995). The Mughal Empire. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521566032.
- ^ Gommans, Jos J.L. (1995). The Rise of the Indo-Afghan Empire: C. 1710-1780. Brill. p. 219. ISBN 9004101098.
- Najibabad Tehsil & Town The Imperial Gazetteer of India, 1909, v. 18, p. 334.
- History of Modern India, 1707 A. D. to 2000 A. D
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Bijnor" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 3 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 928.
- Haleem, Safia (24 July 2007). "Study of the Pathan Communities in Four States of India". Khyber Gateway. Archived from the original on April 30, 2013. Retrieved 4 May 2014.
Farrukhabad has a mixed population of Pathans dominated by the Bangash and Yousafzais.
- Haleem, Safia (24 July 2007). "Study of the Pathan Communities in Four States of India". Khyber Gateway. Archived from the original on April 30, 2013. Retrieved 4 May 2014.
- Who's Who in the Dir, Swat and Chitral Agency – Corrected up to 1st September 1933 (PDF). New Delhi: The Manager Government of India Press. 1933. Retrieved 2013-07-31.
- Dir at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- Claus, Peter J.; Diamond, Sarah; Ann Mills, Margaret (2003). South Asian Folklore: An Encyclopedia : Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka. Taylor & Francis. p. 447. ISBN 978-0-41593-919-5.
- ^ Khan Roshan Khan. Yousafzai qaum ki sarguzasht (in Urdu). Nasir khan. pp. The Mughal Khels are mentioned on page no. 424 under Gadezai Heading.
- Muhammad Hayat Khan (1867). Hayat E Afghani By Muhammad Hayat Khan Published In 1867 Complete Book In Urdu.
- "Bannu :: History, Culture, LifeStyle, People, Food etc". pmru.kp.gov.pk. Retrieved 2022-11-17.
- Ibbetson, Sir Denzil (1916). Panjab Castes: Being a Reprint of the Chapter on "The Races, Castes, and Tribes of the People" in the Report on the Census of the Panjab. Superintendent, Government Printing, Punjab. p. 82.
- Gazetteer of the Bannu District: 1883. British Government. 1883. pp. Page number 58.
- Hallberg, Daniel G. 1992. Pashto, Waneci, Ormuri. Sociolinguistic Survey of Northern Pakistan, 4.
- Noelle, Christine (2012). State and Tribe in Nineteenth-Century Afghanistan: The Reign of Amir Dost Muhammad Khan (1826-1863). Routledge. p. 139. ISBN 978-1136603174.
- "Ancestor Database - Khan Khel -.-> خان خېل". www.khyber.org. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved 2021-03-28.
- "A Dictionary of the Pathan Tribes of the North West Frontier of India" (Part I. North of the Kabul River, including all Mohmands, and tribes west of the Indus), published by The General Staff Army Headquarter, Calcutta, India - (Originally Published 1910) :: The Khan Khel are mentioned on Page 26 (under ‘K’ -Khan Khel)
- "Bannu :: Gazetteer". pmru.kp.gov.pk. Retrieved 2022-11-15.
- "Leading Families in Bannu :: Khyber.ORG". www.khyber.org. Archived from the original on February 13, 2007. Retrieved 2022-11-15.
- Khān, Muḥammad Ḥayāt (1981). Afghanistan and Its Inhabitants (in Urdu). Sang-e-Meel Publications. pp. Mentioned on page no. 626 under the title of Khandane Ghoriwala.
- We Mountains – Regional Website of North Pakistan (2020) Akhund Salaak: The Soldier Saint Jahandad Khan
- International: The News (2015) Speakers recall life and sacrifices of Yousafzai tribe’s chief Correspondents
- The Pathans ~ 550 B.C. - AD 1957 by Olaf Caroe (1958)
- Richards, John F. (1993). The Mughal Empire Part 1: Vol V. Cambridge University Press; 1st edition. p. 170. ISBN 978-0521251198.
- "History of Pashtuns: Yousafzais of Ghoriwala in Bannu". 23 May 2016.
- Khan, Javed (18 January 2015). "Madhubala: From Peshawar with love ..." Dawn. Archived from the original on 20 April 2018. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
| Pashtun tribes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bettani |
| ||||||
| Gharghashti | |||||||
| Sarbani |
| ||||||
| Karlani | |||||||
| Allied tribes | |||||||
| Terminology | |||||||