| Revision as of 23:26, 11 March 2009 view sourceQuantumobserver (talk | contribs)Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers6,447 editsm Reverted edits by Colinharley to last revision by 91.153.79.142 (HG)← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:00, 14 March 2009 view source Redking7 (talk | contribs)1,992 edits consistency with UK article and accuracy.Next edit → | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
| | url=http://www.paclii.org/pg/legis/consol_act/cotisopng534/ | accessdate= 2005-07-16}}</ref> and for active steps to be taken in their preservation. The PNG legislature has enacted various laws in which a type of tenure called "]" is recognised, meaning that the traditional lands of the ] have some legal basis to inalienable tenure. This customary land notionally covers most of the usable land in the country (some 97% of total land area);<ref>{{cite web | title=Customary Land Tenure in Papua New Guinea: Status and Prospects | author=Lynne Armitage |publisher=Queensland University of Technology | url=http://dlc.dlib.indiana.edu/archive/00001043/00/armitage.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate= 2005-07-15}}</ref> alienated land is either held privately under State Lease or is government land. Freehold Title (also known as ]) can only be held by Papua New Guinea citizens.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mj.gov.tl/dntp/rel/DATA/LLP%20I/ARD%20Reports%20and%20studies/Compartive%20Study/Comparative%20study%20by%20HBW%20Inc.pdf|title=Facilitating Foreign Investment through Property Lease Options|format=PDF|author=HBW International Inc.|accessdate=2007-08-28|pages=9|date=September 10, 2003}} See footnote 30 which explains that the precise reference in legislation was not found.</ref> | | url=http://www.paclii.org/pg/legis/consol_act/cotisopng534/ | accessdate= 2005-07-16}}</ref> and for active steps to be taken in their preservation. The PNG legislature has enacted various laws in which a type of tenure called "]" is recognised, meaning that the traditional lands of the ] have some legal basis to inalienable tenure. This customary land notionally covers most of the usable land in the country (some 97% of total land area);<ref>{{cite web | title=Customary Land Tenure in Papua New Guinea: Status and Prospects | author=Lynne Armitage |publisher=Queensland University of Technology | url=http://dlc.dlib.indiana.edu/archive/00001043/00/armitage.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate= 2005-07-15}}</ref> alienated land is either held privately under State Lease or is government land. Freehold Title (also known as ]) can only be held by Papua New Guinea citizens.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mj.gov.tl/dntp/rel/DATA/LLP%20I/ARD%20Reports%20and%20studies/Compartive%20Study/Comparative%20study%20by%20HBW%20Inc.pdf|title=Facilitating Foreign Investment through Property Lease Options|format=PDF|author=HBW International Inc.|accessdate=2007-08-28|pages=9|date=September 10, 2003}} See footnote 30 which explains that the precise reference in legislation was not found.</ref> | ||
| The country's geography is similarly diverse and, in places, extremely rugged. A spine of mountains runs the length of the island of New Guinea, forming a populous ] region. Dense ]s can be found in the lowland and coastal areas. This terrain has made it difficult for the country to develop transportation infrastructure. In some areas, planes are the only mode of transport. After being ruled by three external powers since 1884, Papua New Guinea gained its ] from ] in 1975. |
The country's geography is similarly diverse and, in places, extremely rugged. A spine of mountains runs the length of the island of New Guinea, forming a populous ] region. Dense ]s can be found in the lowland and coastal areas. This terrain has made it difficult for the country to develop transportation infrastructure. In some areas, planes are the only mode of transport. After being ruled by three external powers since 1884, Papua New Guinea gained its ] from ] in 1975. Papua New Guinea is a ] with ] as the ]. | ||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 14 March 2009
For other uses, see Papua New Guinea (disambiguation).| Independent State of Papua New GuineaPapua Niugini | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: Unity in diversity | |
| Anthem: O Arise, All You Sons | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Port Moresby |
| Official languages | English, Tok Pisin, Hiri Motu |
| Demonym(s) | Papua New Guinean |
| Government | Constitutional monarchy |
| • Queen | Elizabeth II |
| • Governor-General | Sir Paulias Matane |
| • Prime Minister | Sir Michael Somare |
| Independence From Australia | |
| • Self-governing | December 1, 1973 |
| • Independence | September 16, 1975 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 462,840 km (178,700 sq mi) (54th) |
| • Water (%) | 2 |
| Population | |
| • 2007 estimate | 6,300,000 (104th) |
| • Density | 13/km (33.7/sq mi) (201st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate |
| • Total | $11.953 billion (132nd) |
| • Per capita | $1,973 (140th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate |
| • Total | $6.001 billion (132nd) |
| • Per capita | $991 (130th) |
| Gini (1996) | 50.9 high inequality |
| HDI (2008) | Error: Invalid HDI value (149th) |
| Currency | Papua New Guinean kina (PGK) |
| Time zone | UTC+10 (AEST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+10 (not observed (as of 2005)) |
| Drives on | Left |
| Calling code | 675 |
| ISO 3166 code | PG |
| Internet TLD | .pg |
Papua New Guinea (/ˈpæpuːə njuː ˈgɪni/, also /ˈpɑːpuːə/ or /ˈpæpjuːə/; Tok Pisin: Papua Niugini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands (the western portion of the island is a part of Indonesian provinces of Papua and West Papua). It is located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, in a region defined since the early 19th century as Melanesia. Its capital, and one of its few major cities, is Port Moresby. It is one of the most diverse countries on Earth, with over 850 indigenous languages and at least as many traditional societies, out of a population of just under 6 million. It is also one of the most rural, with only 18 per cent of its people living in urban centres. The country is also one of the world's least explored, culturally and geographically, and many undiscovered species of plants and animals are thought to exist in the interior of Papua New Guinea.
The majority of the population live in traditional societies and practise subsistence-based agriculture. These societies and clans have some explicit acknowledgement within the nation's constitutional framework. The PNG Constitution (Preamble 5(4)) expresses the wish for traditional villages and communities to remain as viable units of Papua New Guinean society, and for active steps to be taken in their preservation. The PNG legislature has enacted various laws in which a type of tenure called "customary land title" is recognised, meaning that the traditional lands of the indigenous peoples have some legal basis to inalienable tenure. This customary land notionally covers most of the usable land in the country (some 97% of total land area); alienated land is either held privately under State Lease or is government land. Freehold Title (also known as fee simple) can only be held by Papua New Guinea citizens.
The country's geography is similarly diverse and, in places, extremely rugged. A spine of mountains runs the length of the island of New Guinea, forming a populous highlands region. Dense rainforests can be found in the lowland and coastal areas. This terrain has made it difficult for the country to develop transportation infrastructure. In some areas, planes are the only mode of transport. After being ruled by three external powers since 1884, Papua New Guinea gained its independence from Australia in 1975. Papua New Guinea is a constitutional monarchy with Queen Elizabeth II as the head of state.
History
Main article: History of Papua New GuineaHuman remains have been found which have been dated to about 50,000 years ago. These ancient inhabitants probably had their origins in Southeast Asia. Agriculture was independently developed in the New Guinea highlands around 9,000 years ago, making it one of the few areas of original plant domestication in the world. A major migration of Austronesian speaking peoples came to coastal regions roughly 2,500 years ago, and this is correlated with the introduction of pottery, pigs, and certain fishing techniques. More recently, some 300 years ago, the sweet potato entered New Guinea having been introduced to the Moluccas from South America by the then-locally dominant colonial power, Portugal. The far higher crop yields from sweet potato gardens radically transformed traditional agriculture; sweet potato largely supplanted the previous staple, taro, and gave rise to a significant increase in population in the highlands.
Little was known in the West about the island until the nineteenth century, although traders from Southeast Asia had been visiting New Guinea as long as 5,000 years ago collecting bird of paradise plumes, and Spanish and Portuguese explorers had encountered it as early as the sixteenth century (1526 and 1527 Dom Jorge de Meneses). The country's dual name results from its complex administrative history before Independence. The word papua is derived from a Malay word describing the frizzy Melanesian hair, and "New Guinea" (Nueva Guinea) was the name coined by the Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez, who in 1545 noted the resemblance of the people to those he had earlier seen along the Guinea coast of Africa.
The northern half of the country came into German hands in 1884 as German New Guinea. During World War I, it was occupied by Australia, which had begun administering British New Guinea, the southern part, as the re-named Papua in 1904 once Britain was assured by the federation of the Australian colonies that Queensland, with its equivocal history of race relations, would not have a direct hand in the administration of the territory. After World War I, Australia was given a mandate to administer the former German New Guinea by the League of Nations. Papua, by contrast, was deemed to be an External Territory of the Australian Commonwealth, though as a matter of law it remained a British possession, an issue which had significance for the country's post-Independence legal system after 1975. This difference in legal status meant that Papua and New Guinea had entirely separate administrations, both controlled by Australia.
The two territories were combined into the Territory of Papua and New Guinea after World War II, which later was simply referred to as "Papua New Guinea". The Administration of Papua was now also open to United Nations oversight. However, certain statutes continued (and continue) to have application only in one of the two territories, a matter considerably complicated today by the adjustment of the former boundary among contiguous provinces with respect to road access and language groups, so that such statutes apply on one side only of a boundary which no longer exists.
Peaceful independence from Australia, the de facto metropolitan power, occurred on September 16, 1975, and close ties remain (Australia remains the largest bilateral aid donor to Papua New Guinea).
A secessionist revolt in 1975-76 on the island of Bougainville resulted in an eleventh-hour modification of the draft Constitution of Papua New Guinea to allow for Bougainville and the other eighteen districts of pre-Independence Papua New Guinea to have quasi-federal status as provinces. The revolt recurred and claimed 20,000 lives from 1988 until it was resolved in 1997. Autonomous Bougainville recently elected Joseph Kabui as president but his death from a heart attack has meant deputy John Tabinaman is now its leader.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Papua New GuineaPapua New Guinea is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations and Queen Elizabeth II is the head of state. It had been expected by the constitutional convention, which prepared the draft constitution, and by Australia, the outgoing metropolitan power, that Papua New Guinea would choose not to retain its link with the British monarchy. The founders, however, considered that imperial honours had a cachet that the newly independent state would not be able to confer with a purely indigenous honours system — the Monarchy was thus maintained. The Queen is represented in Papua New Guinea by the Governor-General, currently Sir Paulias Matane. Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands are unusual among Commonwealth realms in that their Governors-General are effectively selected by the legislature rather than by the executive, as in some parliamentary democracies within or formerly within the Commonwealth whose non-executive ceremonial president is similarly chosen and as would have been the case had the link with the monarchy been severed at independence such that the governor-general was an autochthonous head of state.
Actual executive power lies with the Prime Minister, who heads the cabinet. The unicameral National Parliament has 109 seats, of which 20 are occupied by the governors of the 19 provinces and the NCD. Candidates for members of parliament are voted upon when the prime minister calls a national election, a maximum of five years after the previous national election. In the early years of independence, the instability of the party system led to frequent votes of no-confidence in Parliament with resulting falls of the government of the day and the need for national elections, in accordance with the conventions of parliamentary democracy. In recent years, successive governments have passed legislation preventing such votes sooner than 18 months after a national election. This has arguably resulted in greater stability though, perhaps, at a cost of reducing the accountability of the executive branch of government.
Elections in PNG attract large numbers of candidates. After independence in 1975, members were elected by the first past the post system, with winners frequently gaining less than 15% of the vote. Electoral reforms in 2001 introduced the Limited Preferential Vote system (LPV), a version of the Alternative Vote. The 2007 general election was the first to be conducted using LPV.
Law
Main article: Law of Papua New GuineaThe unicameral Parliament enacts legislation in the same manner as in other jurisdictions having "cabinet," "responsible government," or "parliamentary democracy": it is introduced by the executive government to the legislature, debated and, if passed, becomes law when it receives royal assent by the Governor-General. Most legislation is actually regulation implemented by the bureaucracy under enabling legislation previously passed by Parliament.
All ordinary statutes enacted by Parliament must be consistent with the Constitution and the courts have jurisdiction to rule on the constitutionality of statutes, both in disputes before them and on a reference where there is no dispute but only an abstract question of law. Unusual among developing countries, the judicial branch of government in Papua New Guinea has remained remarkably independent and successive executive governments have continued to respect its authority.
The "underlying law" — that is, the common law of Papua New Guinea — consists of Australian common law as it stood on September 16, 1975 (the date of Independence), and thereafter the decisions of PNG’s own courts. The courts are directed by the Constitution and, latterly, the Underlying Law Act, to take note of the "custom" of traditional communities, with a view to determining which customs are common to the whole country and may be declared also to be part of the underlying law. In practice, this has proved extremely difficult and has been largely neglected. Statutes are largely adapted from overseas jurisdictions, primarily Australia and England. Advocacy in the courts follows the adversarial pattern of other common law countries.
Regions, provinces and districts
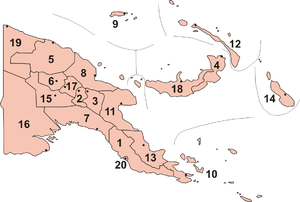
Main articles: Regions of Papua New Guinea, Provinces of Papua New Guinea, and Districts and LLGs of Papua New GuineaPapua New Guinea is divided into four regions, which are not the primary administrative divisions, but are quite significant in many aspects of government, commercial, sporting and other activities.
The nation has 20 province-level divisions: eighteen provinces, the Autonomous Region of Bougainville and the National Capital District. Each province is divided into one or more districts, which in turn are divided into one or more Local Level Government areas.
Provinces are the primary administrative divisions of the country. Provincial governments are branches of the national government — Papua New Guinea is not a federation of provinces. The province-level divisions are as follows:
 |
Geography

At 462,840 km (178,704 sq mi), Papua New Guinea is the world's fifty-fourth largest country (after Cameroon). It is comparable in size to Sweden, and somewhat larger than the US state of California.
Papua New Guinea is mostly mountainous (highest peak: Mount Wilhelm at 4,509 m; 14,793 ft) and mostly covered with tropical rainforest, as well as very large wetland areas surrounding the Sepik and Fly rivers. Papua New Guinea is surrounded by coral reefs which are under close watch to preserve them.
The country is situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, at the point of collision of several tectonic plates. There are a number of active volcanoes and eruptions are frequent. Earthquakes are relatively common, sometimes accompanied by tsunamis.
The mainland of the country is the eastern half of New Guinea island, where the largest towns are also located, including the capital Port Moresby and Lae; other major islands within Papua New Guinea include New Ireland, New Britain, Manus and Bougainville.
Papua New Guinea is one of the few regions close to the equator that experience snowfall, which occurs in the most elevated parts of the mainland.
Ecology
Papua New Guinea is part of the Australasia ecozone, which also includes Australia, New Zealand, eastern Indonesia, and several Pacific island groups, including the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu.
Geologically, the island of New Guinea is a northern extension of the Indo-Australian tectonic plate, forming part of a single landmass Australia-New Guinea (also called Sahul or Meganesia). It is connected to the Australian segment by a shallow continental shelf across the Torres Strait, which in former ages had lain exposed as a land bridge — particularly during ice ages when sea levels were lower than at present.

Consequently, many species of birds and mammals found on New Guinea have close genetic links with corresponding species found in Australia. One notable feature in common for the two landmasses is the existence of several species of marsupial mammals, including some kangaroos and possums, which are not found elsewhere.
Many of the other islands within PNG territory, including New Britain, New Ireland, Bougainville, the Admiralty Islands, the Trobriand Islands, and the Louisiade Archipelago, were never linked to New Guinea by land bridges, and they lack many of the land mammals and flightless birds that are common to New Guinea and Australia.
Australia and New Guinea are portions of the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana, which started to break into smaller continents in the Cretaceous era, 130–65 million years ago. Australia finally broke free from Antarctica about 45 million years ago. All the Australasian lands are home to the Antarctic flora, descended from the flora of southern Gondwana, including the coniferous podocarps and Araucaria pines, and the broadleafed southern beech (Nothofagus). These plant families are still present in Papua New Guinea.
As the Indo-Australian Plate (which includes landmasses of India, Australia, and the Indian Ocean floor in-between) drifts north, it collides with the Eurasian Plate, and the collision of the two plates pushed up the Himalayas, the Indonesian islands, and New Guinea's Central Range. The Central Range is much younger and higher than the mountains of Australia, so high that it is home to rare equatorial glaciers. New Guinea is part of the humid tropics, and many Indomalayan rainforest plants spread across the narrow straits from Asia, mixing together with the old Australian and Antarctic floras.

PNG includes a number of terrestrial ecoregions:
- Admiralty Islands lowland rain forests
- Central Range montane rain forests
- Huon Peninsula montane rain forests
- Louisiade Archipelago rain forests
- New Britain-New Ireland lowland rain forests
- New Britain-New Ireland montane rain forests
- New Guinea mangroves
- Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests
- Northern New Guinea montane rain forests
- Solomon Islands rain forests (includes Bougainville and Buka)
- Southeastern Papuan rain forests
- Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests
- Southern New Guinea lowland rain forests
- Trobriand Islands rain forests
- Trans Fly savanna and grasslands
- Central Range sub-alpine grasslands
Economy
Main article: Economy of Papua New GuineaPapua New Guinea is richly endowed with natural resources, but exploitation has been hampered by rugged terrain, the high cost of developing infrastructure, serious law and order problems and the system of land title, which makes identifying the owners of land for the purpose of negotiating appropriate agreements problematic. Agriculture provides a subsistence livelihood for 85% of the population. Mineral deposits, including oil, copper, and gold, account for 72% of export earnings. Former Prime Minister Sir Mekere Morauta tried to restore integrity to state institutions, stabilize the kina, restore stability to the national budget, privatize public enterprises where appropriate, and ensure ongoing peace on Bougainville following the 1997 agreement which ended Bougainville's secessionist unrest. The Morauta government had considerable success in attracting international support, specifically gaining the backing of the IMF and the World Bank in securing development assistance loans. Significant challenges face the current Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare, including gaining further investor confidence, continuing efforts to privatize government assets, and maintaining the support of members of Parliament. The third quarter (September, 2004) Reserve Bank Report by the Governor of Bank of PNG showed positive economic stance by the Government, with inflation at zero.
In March 2006 the United Nations Committee for Development Policy called for Papua New Guinea's designation of developing country to be downgraded to least-developed country because of protracted economic and social stagnation. However, an evaluation by the International Monetary Fund in late 2008 found that "a combination of prudent fiscal and monetary policies, and high global prices for mineral commodity exports, have underpinned Papua New Guinea's recent buoyant economic growth and macroeconomic stability. Real GDP growth, at over 6 percent in 2007, was broad-based and is expected to continue to be strong in 2008."
Land tenure
Only some 3% of the land of Papua New Guinea is in private hands; it is privately held under 99 year State Lease, or it is held by the State. There is virtually no freehold title; the few existing freeholds are automatically converted to State Lease when they are transferred between vendor and purchaser. Unalienated land is owned under customary title by traditional landowners. The precise nature of the seisin varies from one culture to another. Many writers portray land as in the communal ownership of traditional clans; however, closer studies usually show that the smallest portions of land whose ownership cannot be further divided are held by the individual heads of extended families and their descendants, or their descendants alone if they have recently died. This is a matter of vital importance because a problem of economic development is identifying the membership of customary landowning groups, and the owners. Disputes between mining and forestry companies and landowner groups often devolve on the issue of whether the companies entered into contractual relations for the use of land with the true owners. Customary property — usually land — cannot be devised by will; it can only be inherited according to the custom of the deceased's people.
Demographics

Papua New Guinea is one of the most heterogeneous nations in the world. There are hundreds of ethnic groups indigenous to Papua New Guinea, the majority being from the group known as Papuans, whose ancestors arrived in the New Guinea region tens of thousands of years ago. The others are Austronesians, their ancestors having arrived in the region less than four thousand years ago. There are also numerous people from other parts of the world now resident, including Chinese, Europeans, Australians, Filipinos, Polynesians and Micronesians.
Papua New Guinea has more languages than any other country, with over 820 indigenous languages, representing twelve percent of the world's total. Indigenous languages are classified into two large groups: Austronesian languages and non-Austronesian (or Papuan languages). There are three official languages for Papua New Guinea. English is an official language, and is the language of government and the education system, but it is not widely spoken. The primary lingua franca of the country is Tok Pisin (commonly known in English as New Guinea Pidgin or Melanesian Pidgin), in which much of the debate in Parliament is conducted, many information campaigns and advertisements are presented, and until recently a national newspaper, Wantok, was published. The only area where Tok Pisin is not prevalent is the southern region of Papua, where people often use the third official language, Hiri Motu. Although it lies in the Papua region, Port Moresby has a highly diverse population which primarily uses Tok Pisin, and to a lesser extent English, with Motu spoken as the indigenous language in outlying villages. With an average of only 7,000 speakers per language, Papua New Guinea has a greater density of languages than any other nation on earth except Vanuatu.
PNG has the highest incidence of HIV and AIDS in the Pacific region and is the fourth country in the Asia Pacific region to fit the criteria for a generalised HIV/AIDS epidemic. Lack of HIV/AIDS awareness is a major problem, especially in rural areas. HIV/AIDS in Papua New Guinea
Religion

The courts and government practice uphold the constitutional right to freedom of speech, thought, and belief, and no legislation to curb those rights has been adopted, though Sir Arnold Amet, the immediately previous Chief Justice of Papua New Guinea and an outspoken proponent of Pentecostal Christianity, frequently urged legislative and other curbs on the activities of Muslims in the country.
The 2000 census showed 96 percent of citizens were members of a Christian church; however, many citizens combine their Christian faith with some pre-Christian traditional indigenous practices. The census percentages were as follows:
- Roman Catholic Church (27.0%)
- Evangelical Lutheran Church of Papua New Guinea (19.5%)
- United Church (11.5%)
- Seventh-day Adventist Church (10.0%)
- Pentecostal (8.6%)
- Evangelical Alliance (5.2%)
- Anglican Church of Papua New Guinea (3.2%)
- Members Church of God International (2.0%)
- Baptist (0.5%)
- Church of Christ (0.4%)
- Jehovah's Witnesses (0.3%)
- Salvation Army (0.2%)
- Other Christian (8.0%)
Minority religions include the Bahá'í Faith (15,000 or 0.3%), while Islam in Papua New Guinea accounts for approximately 1,000 to 2,000 or about 0.04%, (largely foreign residents of African and Southeast Asian origin, but with some Papua New Guinean converts in the towns). Non-traditional Christian churches and non-Christian religious groups are active throughout the country. The Papua New Guinea Council of Churches has stated that both Muslim and Confucian missionaries are active, and foreign missionary activity in general is high.
Traditional religions were often animist and some also tended to have elements of ancestor worship though generalisation is suspect given the extreme heterogeneity of Melanesian societies. Prevalent among traditional tribes is the belief in masalai, or evil spirits, which are blamed for "poisoning" people, causing calamity and death. For a discussion of one (West Papuan) society's traditional religion by way of example, see the article on the Korowai of West Papua.
Culture
Main articles: Culture of Papua New Guinea and Music of Papua New Guinea

The culture of Papua New Guinea is multi-faceted and complex. It is estimated that more than a thousand different cultural groups exist in PNG. Because of this diversity, many different styles of cultural expression have emerged; each group has created its own expressive forms in art, dance, weaponry, costumes, singing, music, architecture and much more.
Most of these different cultural groups have their own language. People typically live in villages that rely on subsistence farming. In some areas people hunt and collect wild plants (such as yam roots) to supplement their diets. Those who become skilled at hunting, farming and fishing earn a great deal of respect.
On the Sepik river, there is a famous tradition of wood carving, often in the form of plants or animals, representing ancestor spirits.
Sea shells are no longer the currency of Papua New Guinea, as they were in some regions — sea shells were abolished as currency in 1933. However, this heritage is still present in local customs; in some cultures, to get a bride, a groom must bring a certain number of golden-edged clam shells as a bride price. In other regions, bride price is paid in lengths of shell money, pigs, cassowaries or cash; elsewhere, bride price is unknown and it is brides who must pay dowry.
People of the highlands engage in colourful local rituals that are called "sing sings". They paint themselves, and dress up with feathers, pearls and animal skins to represent birds, trees or mountain spirits. Sometimes an important event, such as a legendary battle, is enacted at such a musical festival. (See also Music of Papua New Guinea.)
Education
The University of Papua New Guinea based in the National Capital District offers various degrees to national and international students. Teaching language is English. The Papua New Guinea University of Technology is based outside of Lae, in Morobe Province.
Sport
Main article: Sport in Papua New Guinea See also: Rugby league in Papua New Guinea
Sport is an important part of PNG culture. The national sport, although not official, is considered to be rugby league. In a nation where communities are far apart and many people live at a minimal subsistence level, rugby league has been described as a replacement for tribal warfare as a way of explaining the local enthusiasm for the game (a matter of life and death). Many Papua New Guineans have become instant celebrities by representing their country or playing in an overseas professional league. Even Australian rugby league players who have played in the annual (Australian) State of Origin clash, which is celebrated feverishly every year in PNG, are among the most well known identities throughout the nation. The Papua New Guinea national rugby league team usually play against the Australian national rugby league team each year in Port Moresby. It is such a popular fixture that thousands of people can't get into the ground once it's full, causing people to climb onto the stadium roof or up trees outside the ground in order to see the match. The limited capacity of the stadium for this fixture often sparks riots. Spectators clashed with riot police during this fixture in 2006.
Australian Rules Football has experienced considerable growth over the past decade, now being Papua New Guinea's second most popular sport. They also boast the second highest number of players in the world. The Papua New Guinea national Australian rules football team competed at both the 2002 and 2005 International Cups and were runners-up both times (to Ireland and New Zealand respectively). The 2008 Australian Football International Cup saw Papua New Guinea win the competition for the first time defeating New Zealand 7.12. 54 to 7.4. 46 in the Final at the Melbourne Cricket Ground. AFL-PNG is the governing body of the sport in Papua New Guinea. Mal Michael is a famous Papua New Guinean footballer in the AFL, and his popularity has helped increase awareness of the game in his homeland.
Other major sports which have a part in the PNG sporting landscape are soccer, rugby union and, in eastern Papua, cricket. The national rugby union team have in the past attempted to qualify for the Rugby World Cup, but have yet to debut.
Transport
Main article: Transport in Papua New GuineaTransport in Papua New Guinea is heavily limited by the country's mountainous terrain. Port Moresby is not linked by road to any of the other major towns and many remote villages can only be reached by light aircraft or on foot. As a result, air travel is the single most important form of transport. Papua New Guinea has 578 airstrips, with 557 of them being unpaved.
See also
- Awards system of Papua New Guinea
- Biodiversity protection efforts in Papua New Guinea
- Communications in Papua New Guinea
- Education in Papua New Guinea
- Foreign relations of Papua New Guinea
- List of diplomatic missions in Papua New Guinea
- List of Papua New Guineans
- Lists of cities & towns in Papua New Guinea by population
- List of Districts and Local Level Governments of Papua New Guinea
- Military of Papua New Guinea
- Tourism of Papua New Guinea
Notes
- Sir Michael Somare (2004-12-06). "Stable Government, Investment Initiatives, and Economic Growth". Keynote address to the 8th Papua New Guinea Mining and Petroleum Conference (Google cache). Retrieved 2007-08-09.
- "Never more to rise". The National (February 6, 2006). Retrieved 2005-01-19.
- "BBC Country profile: Papua New Guinea", news.bbc.co.uk, 20 April 2008. Link accessed 2008-04-20.
- ^ "Papua New Guinea". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2008-10-09.
- "World Bank data on urbanisation". World Development Indicators. World Bank. 2005. Retrieved 2005-07-15.
- "Constitution of Independent State of Papua New Guinea (consol. to amendment #22)". Pacific Islands Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 2005-07-16.
- Lynne Armitage. "Customary Land Tenure in Papua New Guinea: Status and Prospects" (PDF). Queensland University of Technology. Retrieved 2005-07-15.
- HBW International Inc. (September 10, 2003). "Facilitating Foreign Investment through Property Lease Options" (PDF). p. 9. Retrieved 2007-08-28. See footnote 30 which explains that the precise reference in legislation was not found.
- Swaddling (1996) p. 282
- Swaddling (1996) "Such trade links and the nominal claim of the Sultan of Ceram over New Guinea constituted the legal basis for the Netherlands' claim over West New Guinea and ultimately that of Indonesia over what is new West Papua"
- For example, the Creditors Remedies Act (Papua), Ch 47 of the Revised Laws of Papua New Guinea.
- Bradford, Sarah (1997). Elizabeth: A Biography of Britain's Queen. Riverhead Books. ISBN 1-57322-600-9.
- The Constitution of Papua New Guinea sets out the names of the 19 provinces at the time of Independence. Several provinces have changed their names; such changes are not strictly speaking official without a formal constitutional amendment, though "Oro," for example, is universally used in reference to that province.
- "Overcoming economic vulnerability and creating employment" (PDF). Committee for Development Policy. 20–24 March 2006. p. 29. Retrieved 2008-12-24.
{{cite web}}:|chapter=ignored (help)CS1 maint: date format (link) - http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2008/pr08107.htm "Statement of an IMF Mission at the Conclusion of the Staff Visit to Papua New Guinea"
- "HIV/AIDS in Papua New Guinea". Australia's Aid Program (AusAID). Retrieved 2005-12-16.
- "Amazon.com listing for the "Four Corners: A Journey into the Heart of Papua New Guinea"".
- Salak, Kira. "Nonfiction book "Four Corners: A Journey into the Heart of Papua New Guinea"".
- "Papua New Guinea — culture". Datec Pty Ltd. Retrieved 2005-12-16. (Web archive)
- University of Papua New Guinea at www.upng.ac.pg
- PNG National Sport
- "Papua New Guinea". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2007-12-13.
References
- Swaddling, Pamela (1996). Plumes from Paradise. Papua New Guinea National Museum. ISBN 9980-85-103-1.
External links
- Government
- Government of Papua New Guinea
- Prime Minister of Papua New Guinea
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- General information
- "Papua New Guinea". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Papua New Guinea at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Papua New Guinea
Wikimedia Atlas of Papua New Guinea- Template:Wikitravel
- Papua New Guinea, an external wiki
- Papua New Guinea focused wiki
- Papua New Guinea Business Directory
| Countries and territories of Oceania | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
| ||||||||||
| Associated states | |||||||||||
| Dependencies and other territories |
| ||||||||||
| Islands of Papua New Guinea | |
|---|---|
| Bismarck Archipelago | |
| Louisiade Archipelago | |
| North Solomon Islands | |
Template:Austronesian-speaking
| Commonwealth realms and dominions | |
|---|---|
| Current |
|
| Former |
|
| |
| Countries of the Malay Archipelago | |
|---|---|