| Revision as of 21:34, 22 December 2009 editBartholomewklick (talk | contribs)25 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:09, 23 December 2009 edit undoHighKing (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers27,836 edits RvNext edit → | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| ===Modern Tin Whistle=== | ===Modern Tin Whistle=== | ||
| The |
The manufactured tin whistle has it's origins, at least in part, in the flageolet, which under went a revival in the 19th century.<ref></ref> and a flageolet maker named Andrew Ellard was active in Dublin from 1819 to 1837, and Joseph and James Corbett in Limerick between 1801 and 1814. Tin whistles were popularized by Robert Clarke (1840 - 1882) in ] and later New Moston, ]. Up to 1900, they were also marketed as "Clarke London Flageolets" or "Clarke Flageolets".<ref name="Dannatt">Dannatt</ref> The whistle's ] system is similar to that of the six hole, "]" ("simple" in comparison to ] flutes). The six hole, diatonic system is also used on ] flutes, and was of course well known before Robert Clarke began producing his tin whistles circa 1843. Clarke's first whistle, the Meg, was pitched in high A and was later made in other keys suitable for Victorian parlour music. The company showed the whistles in ] of 1851.<ref name="DannattCollection">{{cite web | ||
| | author=Dannatt, Norman | | author=Dannatt, Norman | ||
| | title=Antique Clarke whistle collection | | title=Antique Clarke whistle collection | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 23 December 2009
| This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (October 2009) |
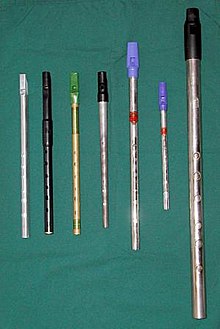
 Several high D tin whistles Several high D tin whistlesfrom left to right: Clarke Sweetone; Shaw (customised); O'Brien; Reyburn; Generation (customised); Copeland; Overton | |
| Woodwind instrument | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pennywhistle |
| Classification | |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 421.221.12 (Flute-like aerophone) |
| Related instruments | |
The tin whistle, also called the tinwhistle, penny whistle , English Flageolet, Tin Flageolet, Irish whistle and Clarke London Flageolet is a simple six-holed woodwind instrument. It is an end blown fipple flute flageolet, putting it in the same category as the recorder, Native American flute, and other woodwind instruments. A tin whistle player is called a tin whistler or whistler. The tin whistle is closely associated with Celtic music.
History
The penny whistle in its modern form stems from a wider family of fipple flutes that have been seen many forms and cultures throughout the world. In Europe such instruments that have a long and distinguished history and take various forms; most widely known of these are the recorder, tin whistle, Flabiol, Txistu and tabor pipe.
Almost all primitive cultures had a type of fipple flute and is most likely the first pitched flute-type instrument in existence. The oldest example includes of a Neanderthal fipple flute from Slovenia dates from 53.000-81.000 B.C., a German flute from 35.000 years ago, and flute made from sheeps bone in West Yorkshire dating to the Iron Age. Written sources that describe a fipple type-flute include the Roman and Greek aulos and tibia. In the early middle ages peoples of northern Europe were playing the instrument as seen in 3rd-century British bone flutes, and Irish Brehon Law describes flute like instrument. By the 12th century Italian flutes came in a variety of sizes, and fragments of 12th-century Norman bone whistles have been found in Ireland, and an intact 14cm Tusculum clay whistle from the 14th century in Scotland. In the 17th century whistles were called flageolets; a term to describe a whistle with a French made fipple headpiece (common to the modern penny whistle) and such instruments are linked to the development of the English flageolet, French flageolet and recorders of the renaissance and baroque period. The term flageolet is still preferred by some modern tin whistle makers as this characterises a wide variety of fipple flutes, including penny whistles, who feel this better describes the instrument.
Modern Tin Whistle
The manufactured tin whistle has it's origins, at least in part, in the flageolet, which under went a revival in the 19th century. and a flageolet maker named Andrew Ellard was active in Dublin from 1819 to 1837, and Joseph and James Corbett in Limerick between 1801 and 1814. Tin whistles were popularized by Robert Clarke (1840 - 1882) in Manchester and later New Moston, England. Up to 1900, they were also marketed as "Clarke London Flageolets" or "Clarke Flageolets". The whistle's fingering system is similar to that of the six hole, "simple system English flutes" ("simple" in comparison to Boehm system flutes). The six hole, diatonic system is also used on baroque flutes, and was of course well known before Robert Clarke began producing his tin whistles circa 1843. Clarke's first whistle, the Meg, was pitched in high A and was later made in other keys suitable for Victorian parlour music. The company showed the whistles in The Great Exhibition of 1851. The Clark tin whistle is voiced somewhat on an organ-pipe with a flattened tube forming the lip of the fipple mouthpeace and is usually made from rolled tin sheet or brass. Manufactured tin whistles became available no earlier than 1840, and were mass produced and widespread due to their relative affordability.
As the penny whistle was generally considered a toy it has been suggested that a children or street musicians were paid a penny from those who heard them playing the whistle. However in reality the instrument was so-called when it could be purchased for a penny. Clarke whistles were sold for a nominal fee (a British penny) and the acquired names of penny and tin whistle have endured to modern times. The word "tin-whistle" was also coined as early as 1825. but neither tin whistle or penny whistle word seems to have been common until the 20th century. The instrument became popular in several musical traditions namely; English , American , Scottish and Irish traditional music. The tin whistle due to its relative cheapness was a popular household instrument and was as ubiquitous as the harmonica. In the second half of the 19th century, some flute manufacturers such as Barnett Samuel and Joseph Wallis also sold whistles. These had a cylindrical brass tube. Like many old whistles, they had lead fipple plugs, and since lead is poisonous, caution should be exercised before playing an old whistle.
The Generation whistle was introduced in the first half of the 20th century, and also featured a brass tube with a lead fipple plug. The design was updated somewhat over the years, most notably the substitution of a plastic fipple for the lead plug design.
While whistles have most often been produced in higher pitches, the "low" whistle is not unknown historically. The Museum of Fine Arts, Boston has in its collection an example of a 19th-century low whistle from the famous Galpin collection. During the 1960s revival of traditional Irish music the low whistle was "recreated" by Bernard Overton at the request of Finbar Furey.
Contemporary whistles

Metal Tin Whistle with Wooden Stop Sample of music played on key of D metal tin whistle with wooden stop.
Metal Tin Whistle with Plastic Fipple Sample of music played on key of D metal tin whistle with plastic fipple.
Problems playing these files? See media help.
The most common whistles today are made of brass tubing, or nickel plated brass tubing, with a plastic fipple (mouthpiece). Generation, Feadóg, Oak, Acorn, Soodlum's (now Walton's), and other brands fall in this category. The next most common form is the conical sheet metal whistle with a wooden stop in the wide end to form the fipple, the Clarke's brand being the most prevalent. Other less common variants are the all-metal whistle, the PVC whistle, the Flanna square holed whistle, and the wooden whistle.
Gaining popularity as a folk instrument in the early 19th century in the Celtic music revivals, penny whistles now play an integral part of several folk traditions. Whistles are a prevalent starting instrument in English traditional music, Scottish traditional music and Irish traditional music, since they are often cheap (under US$10), relatively easy to start with (no tricky embouchure such as found with the flute), and the fingerings are nearly identical to those on the traditional six holed flute (Irish flute, baroque flute). The tin whistle is the most popular instrument in Irish traditional music today.
In recent years a number of instrument builders have started lines of "high-end," hand-made whistles, which can cost hundreds of dollars US each — expensive in comparison to cheap whistles, but nevertheless cheaper than most other instruments. These companies are typically either a single individual or a very small group of craftsmen who work closely together. It is common for builders of wooden flutes and Uilleann pipes to also build whistles. The instruments are distinguished from the inexpensive whistles in that each whistle is individually manufactured and "voiced" by a skilled person rather than made in a factory.
Tuning
Whistle keys
The whistle is tuned diatonically, which allows it to be used to easily play music in two major keys and their corresponding minor keys and modes. The whistle is identified by its lowest note, which is the tonic of the lowest major key. Note that this method of determining the key of the instrument is different from the method used to determine the key of a chromatic instrument, which is based on the relationship between notes on a score and sounded pitch. Whistles are available in a wide variety of different keys.
The most common whistles can easily play notes in the keys of D and G major. Since the D major key is lower these whistles are identified as D whistles. The next most common whistle tuning is a C whistle, which can easily play notes in the keys of C and F major. The C whistle is widely used in American folk music, whereas the D whistle is the most common choice for Irish and Scottish music.
Although the whistle is essentially a diatonic instrument, it is possible to get notes outside the principal major key of the whistle, either by half-holing (partially covering the highest open finger hole) or by cross-fingering (covering some holes while leaving some higher ones open). However, half-holing is somewhat more difficult to do correctly, and whistles are available in many keys, so for other keys a whistler will typically use a different whistle instead, reserving half-holing for accidentals. Some whistle designs allow a single fipple, or mouthpiece, to be used on differently keyed bodies.
Low whistles
Main article: Low whistleThere are larger whistles, which by virtue of being longer and wider produce tones an octave (or in rare cases two octaves) lower. Whistles in this category are likely to be made of metal or plastic tubing, with a tuning-slide head, and are almost always referred to as low whistles but sometimes called concert whistles. The low whistle operates on identical principles to the standard whistles, but musicians in the tradition may consider it a separate instrument.
The term soprano whistle is sometimes used for the higher-pitched whistles when it is necessary to distinguish them from low whistles.
Playing technique
Fingering and range
The notes are selected by opening or closing holes with the fingers. With all the holes closed, the whistle generates its lowest note, the tonic of a major scale. Successively opening holes from the bottom upward produces the rest of the notes of the scale in sequence: with the lowest hole open it generates the second, with the lowest two holes open, it produces the third and so on. With all six holes open, it produces the seventh.
As with a number of woodwind instruments, the tin whistle's second and higher registers are achieved by increasing the breath pressure or air velocity into the ducted flue windway. This increases the frequency of the air pressure waves created.(See Von Karman vortex street ) On a transverse flute this is generally done by narrowing the lip/embouchure. Since the size and direction of the tin whistle's windway, like that of the Recorder or fipple flute is fixed, it is necessary to increase the velocity of the air stream.( See overblowing ).
Fingering in the second register is generally the same as in the first/fundamental, though alternate fingerings are sometimes employed in the higher end of the registers to correct a flattening effect caused by higher aircolumn velocity. Also, the tonic note of the second register is usually played with the top hole of the whistle partially uncovered instead of covering all holes as with the tonic note of the first register; this makes it harder to accidentally drop into the first register and helps to correct pitch. Recorders perform this by "pinching" open the dorsal thumb hole.
Various other notes (relatively flat or sharp with respect to those of the major scale) can be accessed by cross fingering techniques, and all the notes (except the lowest of each octave/register) can be flattened by half holing. Perhaps the most effective and most used cross fingering is that which produces a flattened form of the seventh note (B flat instead of B on a C whistle, for example, or C natural instead of C sharp on a D whistle). This makes available another major scale (F on a C whistle, G on a D whistle).
The standard range of the whistle is two octaves. For a D whistle, this includes notes from the second D above middle C to the fourth D above middle C. It is possible to make sounds above this range, by blowing with sufficient force, but, in most musical contexts, the result will be loud and out of tune due to a cylindrical bore.
Ornamentation
Traditional Irish whistle playing uses a number of ornaments to embellish the music, including cuts, strikes and rolls. Most playing is legato with ornaments to create breaks between notes, rather than tongued. The Irish traditional music concept of the word "ornamentation" differs somewhat from that of European classical music in that ornaments are more commonly changes in how a note is articulated rather than the addition of separately-perceived notes to the piece.
Common ornaments and articulations include:
- Cuts
- Cuts are very briefly lifting a finger above the note being sounded without interrupting airflow into the whistle. For example, a player playing a low D on a D whistle can cut the note by very briefly lifting the first finger of his or her lower hand. This causes the pitch to briefly shift upward. The cut can be performed either at the very start of the note or after the note has begun to sound; some people call the latter a "double cut" or a "mid-note cut."
- Strikes
- Strikes or taps are similar to cuts except that a finger below the sounded note is briefly lowered to the whistle. For example, if a player is playing a low E on a D whistle the player could tap by quickly lowering and raising his or her bottom finger. Both cuts and taps are essentially instantaneous; the listener should not perceive them as separate notes.
- Rolls
- A roll is a note with first a cut and then a strike. Alternately, a roll can be considered as a group of notes of identical pitch and duration with different articulations. There are two common types of rolls:
- The long roll is a group of three slurred notes of equal pitch and duration, the first sounded without a cut or strike, the second sounded with a cut, and the third sounded with a strike.
- The short roll is a group of two slurred notes of equal pitch and duration, the first sounded with a cut and the second sounded with a strike.
- Cranns
- Cranns (or crans) are ornaments borrowed from the Uilleann piping tradition. They are similar to rolls except that only cuts are used, not taps or strikes. On the tin whistle they are generally only used for notes where a roll is impossible, such as the lowest note of the instrument.
- Slides
- Slides are similar to portamentos in classical music; a note below or above (usually below) the intended note is fingered, and then the fingering is gradually shifted in order to smoothly raise or lower the pitch to the intended note. The slide is generally a longer duration ornament than, for example, the cut or the tap and the listener should perceive the pitch changing.
- Tonguing
- Tonguing is used sparingly as a means of emphasizing certain notes, such as the first note in a tune. Tin whistle players usually do not tongue most notes. To tongue a note a player briefly touches their tongue to the front of the roof of the mouth at the start of the note (as if articulating a 't'), creating a percussive attack.
- Vibrato
- Vibrato can be achieved on most notes by opening and closing one of the open holes, or by variation of breath pressure. Of the two, fingered vibrato is much more common than diaphragmatic (breath) vibrato, except on notes like the lowest note on the whistle where fingered vibrato is much more difficult.
Some tricks
- Leading Tone
- Leading Tones are the seventh just before the tonic, so named because melodic styling often uses the seventh to lead into the tonic at the end of a phrase. On most tin whistles the leading tone to the lowest tonic can be played by using the little finger of the lower hand to partially cover the very end opening of the whistle, while keeping all other holes covered as usual for the tonic.
- Tone
- The tone of the tin whistle is largely determined by its manufacturing. Clarke style rolled metal whistles tend to have an airy "impure" sound, while Generation style cylindrical instruments tend to have clear or "pure" whistle sounds. Inexpensive rolled metal whistles, such as those from Cooperman Fife and Drum (which also produces high-end instruments) may be very airy in sound, and may be difficult to play in the upper register (second octave). Often placing a piece of tape over one edge of the fipple slot (just below the mouthpiece) to narrow the fipple will improve the instrument's tone and playability significantly.
- Scales
- While, as mentioned under Fingering, a player will usually play a given instrument only in its tonic key and possibly in the key beginning on the fourth (e.g. G on a D whistle), nearly any key is possible, becoming progressively more difficult to keep in tune as the player moves away from the whistle's tonic, according to the circle of fifths. Thus a D whistle is fairly apt for playing both G and A, and a C instrument can be used fairly easily for F and G.
Repertoire
A number of music genres commonly feature the tin whistle.
Irish and Scottish music

The Foggy Dew Instrumental version, featuring low whistle and viola da gamba, performed by Dancing Willow
Problems playing these files? See media help.
Traditional music from Ireland and Scotland is by far the most common music to play on the tin whistle, and comprises the vast majority of published scores suitable for whistle players. Musicians who play Irish and Scottish music on the tin whistle perform as members of bands. While the tin whistle is very common in Irish music to the point that it could be called characteristic of the genre and fairly common in Scottish music, it is not a "required" instrument in either one.
As ornamentation and improvisation around a simple melody is characteristic of both genres, many traditional musicians frown upon the use of musical scores, believing that learning "by ear," from recordings or live instruction, is the best way to learn these aspects of whistle performance. Hence, students of the tin whistle may be advised not to use musical scores, and will certainly be expected to spend a substantial amount of time listening to other performers even when scores are used. Scores are never used in live performances and usually discouraged in sessions. Nevertheless, it is a common practice to transcribe traditional tunes, both for the purpose of preserving melodies and as a learning tool. When traditional tunes are scored there are seldom if ever separate scores for individual instruments; hence, tin whistle players use the same score as all other musicians.
Kwela
Kwela is a genre of music created in South Africa in the 1950s, and characterised by an upbeat, jazzy tin whistle lead. Among all genres of music featuring the tin whistle, kwela is distinctive as the only one which is totally dominated by the instrument; the genre was created around the sound of the whistle. The low cost of the tin whistle made it an attractive instrument in the impoverished, apartheid-era townships; the Hohner tin whistle was especially popular in this genre. The kwela craze accounted for the sale of over a million tin whistles.
Kwela was mostly superseded in South Africa by the mbaqanga genre in the late fifties, and with it the saxophone largely supplanted the tin whistle as the lead instrument for music from the townships. However, kwela master Aaron "Big Voice Jack" Lerole continued to perform into the 1990s and a few kwela bands, such as London's The Positively Testcard continue to record kwela music today.
Kwela musical scores are rarely published and many of the recordings of founding kwela artists are out of print and hard to find. A representative compilation can be found on the following recording:
Other music
The tin whistle is used in many other types of music, though not to the extent that it could be called characteristic as with Irish music and kwela. It is not unusual to hear the tin whistle used in praise music and film soundtracks, and published scores suitable for tin whistle performance are available in both of these genres. The tin whistle also appears in "crossover" genres like world music, folk rock and folk metal.
Notation
Tin whistle music collections are generally notated in one of three different formats.
Standard musical notation
It is common to score music for the whistle using standard musical notation. The tin whistle is not a transposing instrument - for example, music for the D tin whistle is written in concert pitch, not transposed down a tone as would be normal for transposing instruments. Nevertheless, there is no real consensus on how tin whistle music should be written, or on how reading music onto the whistle should be taught. However, when music is scored for a soprano whistle it will be written an octave lower than it sounds, so avoiding use of ledger lines and making it much easier to read.
The traditional music of Ireland and Scotland constitutes the majority of published scores for the whistle. Since the majority of that music is written in D major, G major, or one of the corresponding musical modes, use of the D major or G major key signatures is a de facto standard. For example, the "C whistle" edition of Bill Ochs's popular The Clarke Tin Whistle Handbook is scored in D and differs from the D edition only in that the accompanying audio CD is played on a C whistle.
Reading directly onto the C whistle is popular for the obvious reason that its home key or name key is the all-natural major key (C major). Some musicians are encouraged to learn to read directly onto one whistle, while others are taught to read directly onto another.
The whistle player who wants music to read on to all whistles will need to learn the mechanics of written transposition, taking music with one key signature and rewriting it with another.
Tablature
Tablature notation for the tin whistle is a graphical representation of which tone holes the player should cover. The most common format is a vertical column of six circles, with holes to be covered for a given note shown filled with black, and a plus sign (+) at the top for notes in the second octave. Tablature is most commonly found in tutorial books for beginners.
Tonic solfa
The tonic solfa is found in Ireland and possibly Wales, especially in schools. Many schools have printed sheets with tunes notated in tonic solfa, although in Ireland more have teaching by rote. With the availability of good standard notation tutor books, teaching is possibly moving in this direction.
Abc notation
Since the majority of popular tin whistle music is traditional and out of copyright, it is common to share tune collections on the Internet. Abc notation is the most common means of electronic exchange of tunes. It is also designed to be easy to read by people, and many musicians learn to read it directly instead of using a computer program to transform it into a standard musical notation score.
Well-known performers
- In Irish traditional music
In 1973, Paddy Moloney (of The Chieftains) and Sean Potts released Tin Whistles, which helped to popularise the tin whistle in particular and Irish music in general. Mary Bergin's Feadóga Stáin (1979) and Feadóga Stáin 2 (1993) were similarly influential.
Other notable players include Carmel Gunning, Micho Russell, Joanie Madden, Brian Finnegan, and Seán Ryan. Many traditional pipers and flute players also play the whistle to a high standard. James Galway, the classical flautist, is also an outstanding whistler.
- In Scottish traditional music
Award winning singer and musician Julie Fowlis has recorded several tracks on the tin whistle, both in her solo work and with the band Dòchas.
- In kwela
Aaron "Big Voice Jack" Lerole and his band recorded a single called "Tom Hark" which sold five million copies worldwide and was used as the theme song for the BBC series The Killing Stones. But the most famous star of the kwela era was Spokes Mashiyane. Paul Simon's 1986 album Graceland draws heavily on South African music and includes pennywhistle solos in the traditional style.
- In popular music
The low whistle rose to public prominence thanks to its use by Davy Spillane in the stage show Riverdance (1995) and Tony Hinnigan on the soundtrack to the 1997 film Titanic.
Certain Irish punk bands use the tin whistle as well. Examples include The Cranberries, Dropkick Murphys, Bridget Regan from Flogging Molly or Spider Stacy (of The Pogues).
Andrea Corr from Irish pop/rock band The Corrs plays the tin whistle. Leroi Moore from the American/pop band the Dave Matthews Band played the tin whistle in a few of the songs in the band's repertoire.
Bob Hallett of the Canadian folk rock group Great Big Sea is also a renowned performer of the tin whistle, playing it during both traditional and original material.
Icelandic post-rock band Sigur Rós made use of the tin whistle in their song Hafsól when one of the members played a solo at the end.
Barry Privett of the Virginia based rock band Carbon Leaf performs several songs using the tin whistle.
The Unicorns use the penny whistle in the song Sea Ghost
- In jazz
Steve Buckley, a British jazz musician is known to have used the penny whistle as a serious instrument. His whistle playing can be heard on recordings with Loose Tubes, Django Bates and his album with Chris Batchelor Life As We Know It. Les Lieber is a celebrated American Jazz Tinwhistle player. Lieber has played with Paul Whiteman's Band and also with the Benny Goodman Sextet. Lieber made a record with Django Reinhardt in the AFN Studios in Paris in the post Second World War era and started an event called "Jazz at Noon" every Friday in a New York restaurant playing with a nucleus of advertising men, doctors, lawyers, and business executives who had been or could have been jazz musicians. Howard Johnson has also been known to play this instrument.
- In television
In Star Trek: The Next Generation the tin whistle called "The Ressikan Flute", is played by Jean-Luc Picard in the episodes titled The Inner Light, A Fistful of Datas, and Lessons.
References
- Oxford English Dictionary
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- The tin whistle tutor Edition: 3 - 1991 By Michael Raven
- The Essential Guide to Irish Flute and Tin Whistle By Grey Larsen
- The Neanderthal Flute, Crosscurrents #183 1997 Greenwich Publishing Canada
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- The Malham Iron-Age Pipe, by A. Raistrick, Professor Spaul and Eric Todd © 1952
- English Medieval Bone Flutes c.450 - c.1550 AD. By Helen Leaf
- The Cambridge Companion to the Recorder John Mansfield, Thomson et al, 1995 Cambridge
- Performance practice: a dictionary-guide for musicians By Roland John Jackson
- Whistler's Pocket Companion By Dona Gilliam, Mizzy McCaskill
- Mel Bays Complete Irish Tin Whistle Book By Mizzy McCaskill, Dona Gilliam
- The tin whistle tutor Edition: 3 - 1991 By Michael Raven
- The Essential Tin Whistle Toolbox By Grey Larsenis
- Dannatt
- Dannatt, Norman. "Antique Clarke whistle collection". Retrieved 10 July 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - The Oxford companion to musical instruments By Anthony Baines
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- Oxford English Dictionary online edition
- The words "tin whistle" and "pennywhistle" in any compound form do not generally appear in early-20th-century dictionaries, encyclopedias, or thesauri.
- The Essential Guide to Irish Flute and Tin Whistle By Grey Larsen
- The Essential Guide to Irish Flute and Tin Whistle By Grey Larsen
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- The Essential Guide to Irish Flute and Tin Whistle By Grey Larsen
- The Clarke Tin Whistle By Bill Ochs
- "Duct flute". Leslie Lindsey Mason Collection, Ex. coll. Francis W. Galpin. Retrieved 16 January 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Hannigan and Ledsam
- Vallely et al., p. 397
- Wisely
- Wolfe
- Gross
- ^ Larsen
- ^ Schaldach
- See, for example, the Open Directory's Tin whistle tune collections or the books published by online stores catering to tin whistle players.
- Ochs
- Open Directory
- http://chiffandfipple.com/
- Dannatt, Norman (1993). The Penny Whistle. The Clarke Tinwhistle Co.
- Dannatt, Norman (2005) The History of the Tinwhistle. The Clarke Tinwhistle Co. ISBN 0-9549693-2-4))
- Gatherer, Nigel. "History". The Scottish Whistle. Retrieved 30 January 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Gross, Richard. "Tinwhistle fingering chart". Tinwhistle Fingering Research Center. Retrieved 16 January 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Hannigan, Steáfán (2000). "Whistory: A Low Whistle History". The Low Whistle Book. Sin É Publications. ISBN 0-9525305-1-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Larsen, Grey. "A Guide to Grey Larsen's Notation System for Irish Ornamentation" (PDF). Retrieved 24 January 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - McCullough, L.E. (1976). "Historical Notes on the Tinwhistle". The Complete Irish Tin Whistle Tutor. Oak Publications. ISBN 0-8256-0340-4.
- Ochs, Bill (2001). The Clarke Tin Whistle: Deluxe Edition. The Pennywhistler's Press.
- "Tin Whistle Tune Collections". Open Directory. Retrieved 25 January 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Wisely, Dale (2000). "Deciphering Whistle Keys". Chiff and Fipple. Retrieved 22 March 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Wolfe, Joe. "Introduction to flute acoustics". UNSW Music Acoustics. Retrieved 16 January 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Vallely, Fintan (ed.), ed. (1999). The Companion to Irish Traditional Music. New York, NY: New York University Press. ISBN 0-8147-8802-5.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help) - http://www.volkangucer.com/winds.html
- Whistles at the whistle museum