| Revision as of 08:29, 22 May 2011 editMaterialscientist (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Checkusers, Administrators1,994,292 editsm Reverted edits by 196.13.185.253 (talk) to last version by CanadianLinuxUser← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:50, 26 May 2011 edit undoCurb Chain (talk | contribs)18,691 edits →Jewelry: Palladium#Jewelry says "Like platinum, it will develop a hazy patina over time." but this article does not mention anything about a patinaNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{about|the chemical element|other uses|Platinum (disambiguation)}} | {{about|the chemical element|other uses|Platinum (disambiguation)}} | ||
| {{contradict-other|Palladium}} | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | {{pp-move-indef}} | ||
| {{Infobox platinum}} | {{Infobox platinum}} | ||
Revision as of 05:50, 26 May 2011
This article is about the chemical element. For other uses, see Platinum (disambiguation).| This article appears to contradict the article Palladium. Please discuss at the talk page and do not remove this message until the contradictions are resolved. |
Platinum (/ˈplæt.n.əm/ or /ˈplæt.nəm/) is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal. Even though it has six naturally occurring isotopes, platinum is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust and has an average abundance of approximately 0.005 mg/kg. It occurs in some nickel and copper ores along with some native deposits, mostly in South Africa, which accounts for 80% of the world production.
As a member of the platinum group of elements, as well as of the group 10 of the periodic table of elements, platinum is generally unreactive. It exhibits a remarkable resistance to corrosion, even at high temperatures, and as such is considered a noble metal. As a result, platinum is often found chemically uncombined as native platinum. Because it occurs naturally in the alluvial sands of various rivers, it was first used by pre-Columbian South American natives to produce artifacts. It was referenced in European writings as early as 16th century, but it was not until Antonio de Ulloa published a report on a new metal of Colombian origin in 1748 that it became investigated by scientists.
Platinum is used in catalytic converters, laboratory equipment, electrical contacts and electrodes, platinum resistance thermometers, dentistry equipment, and jewelry. Because only a few hundred tonnes are produced annually, it is a scarce material, and is highly valuable and is a major precious metal commodity. Being a heavy metal, it leads to health issues upon exposure to its salts, but due to its corrosion resistance it is not toxic as a metal. Some of its compounds, most notably cisplatin, are applied in chemotherapy against certain types of cancer.
Characteristics
Physical
As a pure metal, platinum is silvery-white, lustrous, ductile, and malleable. It does not oxidize at any temperature, although it is corroded by halogens, cyanides, sulfur, and caustic alkalis. Platinum is insoluble in hydrochloric and nitric acid, but dissolves in aqua regia to form chloroplatinic acid, H2PtCl6. Platinum's resistance to wear and tarnish is well suited for making fine jewelry. The metal has an excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperature and has stable electrical properties. All of these characteristics have been exploited for industrial applications.
Chemical
See also: Platinum group
The most common oxidation states of platinum are +2 and +4. The +1 and +3 oxidation states are less common, and are often stabilized by metal bonding in bimetallic (or polymetallic) species. As is expected, tetracoordinate platinum(II) compounds tend to adopt 16-electron square planar geometries. While elemental platinum is generally unreactive, it dissolves in aqua regia to give soluble hexachloroplatinic acid ("H2PtCl6", formally (H3O)2PtCl6·nH2O ):
- Pt + 4 HNO3 + 6 HCl → H2PtCl6 + 4 NO2 + 4 H2O
As a soft acid, platinum has a great affinity for sulfur, such as on dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); numerous DMSO complexes have been reported and care should be taken in the choice of reaction solvent.
Isotopes
Main article: Isotopes of platinumPlatinum has six naturally occurring isotopes: Pt, Pt, Pt, Pt, Pt, and Pt. The most abundant of these is Pt, comprising 33.83% of all platinum. It is the only stable isotope with a non-zero spin; with a spin of /2, Pt satellite peaks are often observed in H and P NMR spectroscopy (i.e. Pt-phosphine and Pt-alkyl complexes). Pt is the least abundant at only 0.01%. Of the naturally occurring isotopes, only Pt is unstable, though it decays with a half-life of 6.5×10 years. Pt undergoes alpha decay, but because its half-life is estimated at longer than 3.2×10 years, it is considered stable. Platinum also has 31 synthetic isotopes ranging in atomic mass from 166 to 202, making the total number of known isotopes 37. The least stable of these is Pt with a half-life of 300 µs, while the most stable is Pt with a half-life of 50 years. Most platinum isotopes decay by some combination of beta decay and alpha decay. Pt, Pt, and Pt decay primarily by electron capture. Pt and Pt have double beta decay paths.
Occurrence


Platinum is an extremely rare metal, occurring at a concentration of only 0.005 ppm in the Earth's crust. It is sometimes mistaken for silver (Ag). Platinum is often found chemically uncombined as native platinum and alloyed with iridium as platiniridium. Most often the native platinum is found in secondary deposits; platinum is combined with the other platinum group metals in alluvial deposits. The alluvial deposits used by pre-Columbian people in the Chocó Department, Colombia are still a source for platinum group metals. Another large alluvial deposit is in the Ural Mountains, Russia, and it is still mined.
In nickel and copper deposits, platinum group metals occur as sulfides (e.g., (Pt,Pd)S), tellurides (e.g., PtBiTe), antimonides (PdSb), and arsenides (e.g., PtAs2), and as end alloys with nickel or copper. Platinum arsenide, sperrylite (PtAs2), is a major source of platinum associated with nickel ores in the Sudbury Basin deposit in Ontario, Canada. At Platinum, Alaska, about 545,000 troy ounces had been mined between 1927 and 1975. The mine ceased operations in 1990. The rare sulfide mineral cooperite, (Pt,Pd,Ni)S, contains platinum along with palladium and nickel. Cooperite occurs in the Merensky Reef within the Bushveld complex, Gauteng, South Africa.
In 1865, chromites were identified in the Bushveld region of South Africa, followed by the discovery of platinum in 1906. The largest known primary reserves are in the Bushveld complex in South Africa. The large copper–nickel deposits near Norilsk in Russia, and the Sudbury Basin, Canada, are the two other large deposits. In the Sudbury Basin, the huge quantities of nickel ore processed make up for the fact platinum is present as only 0.5 ppm in the ore. Smaller reserves can be found in the United States, for example in the Absaroka Range in Montana. In 2009, South Africa was the top producer of platinum, with an almost 80% share, followed by Russia at 11%.
Platinum exists in higher abundances on the Moon and in meteorites. Correspondingly, platinum is found in slightly higher abundances at sites of bolide impact on the Earth that are associated with resulting post-impact volcanism, and can be mined economically; the Sudbury Basin is one such example.
Compounds
Halides
Hexachloroplatinic acid mentioned above is probably the most important platinum compound, as it serves as the precursor for many other platinum compounds. By itself, it has various applications in photography, zinc etchings, indelible ink, plating, mirrors, porcelain coloring, and as a catalyst.
Treatment of hexachloroplatinic acid with an ammonium salt, such as ammonium chloride, gives ammonium hexachloroplatinate, which is relatively insoluble in ammonium solutions. Heating this ammonium salt in the presence of hydrogen reduces it to elemental platinum. Potassium hexachloroplatinate is similarly insoluble, and hexachloroplatinic acid has been used in the determination of potassium ions by gravimetry.
When hexachloroplatinic acid is heated, it decomposes through platinum(IV) chloride and platinum(II) chloride to elemental platinum, although the reactions do not occur stepwise:
- (H3O)2PtCl6·nH2O ⇌ PtCl4 + 2 HCl + (n + 2) H2O
- PtCl4 ⇌ PtCl2 + Cl2
- PtCl2 ⇌ Pt + Cl2
All three reactions are reversible. Platinum(II) and platinum(IV) bromides are known as well. Platinum hexafluoride is a strong oxidizer capable of oxidizing oxygen.
Oxides
Platinum(IV) oxide, PtO2, also known as Adams' catalyst, is a black powder which is soluble in KOH solutions and concentrated acids. PtO2 and the less common PtO both decompose upon heating. Platinum(II,IV) oxide, Pt3O4, is formed in the following reaction:
- 2 Pt + Pt + 4 O → Pt3O4
Platinum also forms a trioxide, where it is present in the +4 oxidation state.
Other compounds
Unlike palladium acetate, platinum(II) acetate is not commercially available. Where a base is desired, the halides have been used in conjunction with sodium acetate. The use of platinum(II) acetylacetonate has also been reported.
Several barium platinides have been synthesized in which platinum exhibits negative oxidation states ranging from −1 to −2. These include BaPt, Ba
3Pt
2, and Ba
2Pt. Caesium platinide, Cs
2Pt, has been shown to contain Pt
anions. Platinum also exhibits negative oxidation states at surfaces reduced electrochemically. The negative oxidation states exhibited by platinum are unusual for metallic elements, and they are attributed to the relativistic stabilization of the 6s orbitals.
Zeise's salt, containing an ethylene ligand, was one of the first organometallic compounds discovered. Dichloro(cycloocta-1,5-diene)platinum(II) is a commercially available olefin complex, which contains easily displaceable cod ligands ("cod" being an abbreviation of 1,5-cyclooctadiene). The cod complex and the halides are convenient starting points to platinum chemistry.
Cisplatin, or cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) is the first of a series of square planar platinum(II)-containing chemotherapy drugs, including carboplatin and oxaliplatin. These compounds are capable of crosslinking DNA, and kill cells by similar pathways to alkylating chemotherapeutic agents.
-
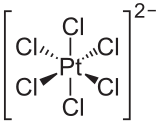 The hexachloroplatinate ion
The hexachloroplatinate ion
-
 The anion of Zeise's salt
The anion of Zeise's salt
-
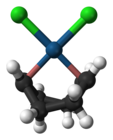 Dichloro(cycloocta-1,5-diene)platinum(II)
Dichloro(cycloocta-1,5-diene)platinum(II)
-
 Cisplatin
Cisplatin
History
Platinum occurs naturally in the alluvial sands of various rivers, though there is little evidence of its use by ancient people. However, the metal was used by pre-Columbian Americans near modern-day Esmeraldas, Ecuador to produce artifacts of a white gold-platinum alloy. The first European reference to platinum appears in 1557 in the writings of the Italian humanist Julius Caesar Scaliger as a description of an unknown noble metal found between Darién and Mexico, "which no fire nor any Spanish artifice has yet been able to liquefy."

In 1741, Charles Wood, a British metallurgist, found various samples of Colombian platinum in Jamaica, which he sent to William Brownrigg for further investigation. Antonio de Ulloa, also credited with the discovery of platinum, returned to Spain from the French Geodesic Mission in 1746 after having been there for eight years. His historical account of the expedition included a description of platinum as being neither separable nor calcinable. Ulloa also anticipated the discovery of platinum mines. After publishing the report in 1748, Ulloa did not continue to investigate the new metal. In 1758, he was sent to superintend mercury mining operations in Huancavelica.
In 1750, after studying the platinum sent to him by Wood, Brownrigg presented a detailed account of the metal to the Royal Society, mentioning that he had seen no mention of it in any previous accounts of known minerals. Brownrigg also made note of platinum's extremely high melting point and refractoriness toward borax. Other chemists across Europe soon began studying platinum, including Torbern Bergman, Jöns Jakob Berzelius, William Lewis, and Pierre Macquer. In 1752, Henrik Scheffer published a detailed scientific description of the metal, which he referred to as "white gold", including an account of how he succeeded in fusing platinum ore with the aid of arsenic. Scheffer described platinum as being less pliable than gold, but with similar resistance to corrosion.
Carl von Sickingen researched platinum extensively in 1772. He succeeded in making malleable platinum by alloying it with gold, dissolving the alloy in aqua regia, precipitating the platinum with ammonium chloride, igniting the ammonium chloroplatinate, and hammering the resulting finely divided platinum to make it cohere. Franz Karl Achard made the first platinum crucible in 1784. He worked with the platinum by fusing it with arsenic, then later volatilizing the arsenic.
In 1786, Charles III of Spain provided a library and laboratory to Pierre-François Chabaneau to aid in his research of platinum. Chabaneau succeeded in removing various impurities from the ore, including gold, mercury, lead, copper, and iron. This led him to believe he was working with a single metal, but in truth the ore still contained the yet-undiscovered platinum group metals. This led to inconsistent results in his experiments. At times, the platinum seemed malleable, but when it was alloyed with iridium, it would be much more brittle. Sometimes the metal was entirely incombustible, but when alloyed with osmium, it would volatilize. After several months, Chabaneau succeeded in producing 23 kilograms of pure, malleable platinum by hammering and compressing the sponge form while white-hot. Chabeneau realized the infusibility of platinum would lend value to objects made of it, and so started a business with Joaquín Cabezas producing platinum ingots and utensils. This started what is known as the "platinum age" in Spain.
In 2007, Gerhard Ertl won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for determining the detailed molecular mechanisms of the catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over platinum (catalytic converter).
Production

Platinum, along with the rest of the platinum metals is, obtained commercially as a by-product from nickel and copper mining and processing. During electrorefining of copper, noble metals, such as silver, gold and the platinum group metals, as well as selenium and tellurium, settle to the bottom of the cell as "anode mud", which forms the starting point for the extraction of the platinum group metals.
If pure platinum is found in placer deposits or other ores, it is isolated from them by various methods of subtracting impurities. Because platinum is significantly denser than many of its impurities, the lighter impurities can be removed by simply floating them away in a liquid. Platinum is also nonmagnetic, while nickel and iron are both magnetic. These two impurities are thus removed by running an electromagnet over the mixture. Because platinum has a higher melting point than most other substances, many impurities can be burned or melted away without melting the platinum. Finally, platinum is resistant to hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, while other substances are readily attacked by them. Metal impurities can be removed by stirring the mixture in either of the two acids and recovering the remaining platinum.
One suitable method for purification for the raw platinum, which contains platinum, gold, and the other platinum group metals, is to process it with aqua regia, in which palladium, gold and platinum are dissolved, while osmium, iridium, ruthenium and rhodium stay unreacted. The gold is precipitated by the addition of iron(III) chloride and after filtering off the gold, the platinum is precipitated by the addition of ammonium chloride as ammonium chloroplatinate. Ammonium chloroplatinate can be converted to the metal by heating.
Applications

Of the 239 tonnes of platinum sold in 2006, 130 tonnes were used for vehicle emissions control devices, 49 tonnes for jewelry, 13.3 tonnes in electronics, and 11.2 tonnes in the chemical industry as a catalyst. The remaining 35.5 tonnes went to various other minor applications, such as electrodes, anticancer drugs, oxygen sensors, spark plugs and turbine engines.
Catalysis
The most common use of platinum is as a catalyst in chemical reactions, many times as platinum black. It has been employed in this application since the early 19th century, when platinum powder was used to catalyze the ignition of hydrogen. Its most important application is in automobiles as a catalytic converter, which allows the complete combustion of low concentrations of unburned hydrocarbons from the exhaust into carbon dioxide and water vapor. Platinum is also used in the petroleum industry as a catalyst in a number of separate processes, but especially in catalytic reforming of straight run naphthas into higher-octane gasoline which becomes rich in aromatic compounds. PtO2, also known as Adams' catalyst, is used as a hydrogenation catalyst, specifically for vegetable oils. Platinum metal also strongly catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas.
Standard

From 1889 to 1960, the meter was defined as the length of a platinum-iridium (90:10) alloy bar, known as the International Prototype Meter bar. The previous bar was made of platinum in 1799. The International Prototype Kilogram remains defined by a cylinder of the same platinum-iridium alloy made in 1879.
The standard hydrogen electrode also uses a platinized platinum electrode due to its corrosion resistance, and other attributes.
Precious metal

Platinum is a precious metal commodity; its bullion has the ISO currency code of XPT. Coins, bars, and ingots are traded or collected. Platinum finds use in jewelry, usually as a 90–95% alloy, due to its inertness and shine. In watchmaking, Vacheron Constantin, Patek Philippe, Rolex, Breitling, and other companies use platinum for producing their limited edition watch series. Watchmakers appreciate the unique properties of platinum, as it neither tarnishes nor wears out (relative to gold).

The price of platinum, like other industrial commodities, is more volatile than that of gold. In 2008, the price of platinum ranged from $774 to $2,252 per oz.
During periods of sustained economic stability and growth, the price of platinum tends to be as much as twice the price of gold, whereas during periods of economic uncertainty, the price of platinum tends to decrease due to reduced industrial demand, falling below the price of gold. Gold prices are more stable in slow economic times, as gold is considered a safe haven and gold demand is not driven by industrial uses. In the 18th century, platinum's rarity made King Louis XV of France declare it the only metal fit for a king.
Other uses
In the laboratory, platinum wire is used for electrodes; platinum pans and supports are used in thermogravimetric analysis because of the stringent requirements of chemical inertness upon heating to high temperatures (~1000°C). Platinum is used as an alloying agent for various metal products, including fine wires, noncorrosive laboratory containers, medical instruments, dental prostheses, electrical contacts, and thermocouples. Platinum-cobalt, an alloy of roughly three parts platinum and one part cobalt, is used to make relatively strong permanent magnets. Platinum-based anodes are used in ships, pipelines, and steel piers.
Symbol of prestige
See also: Platinum album and Platinum (color)
Platinum's rarity as a metal has caused advertisers to associate it with exclusivity and wealth. "Platinum" debit cards have greater privileges than do "gold" ones. "Platinum awards" are the second highest possible, ranking above "gold", "silver" and "bronze", but below diamond. For example, in the United States, a musical album that has sold more than 1 million copies, will be credited as "platinum", whereas an album that sold more than 10 million copies will be certified as “diamond”. Some products, such as blenders and vehicles, with a silvery-white color are identified as "platinum". Platinum is considered a precious metal, although its use is not as common as the use of gold or silver. The frame of the Crown of Queen Elizabeth the Queen Mother, manufactured for her coronation as Consort of King George VI, is made of platinum. It was the first British crown to be made of this particular metal.
Health issues
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, short-term exposure to platinum salts may cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, and long-term exposure may cause both respiratory and skin allergies. The current OSHA standard is 2 micrograms per cubic meter of air averaged over an 8-hour work shift.
Certain platinum complexes are used in chemotherapy, and show good activity against some tumors. Cisplatin is particularly effective against testicular cancer; the cure rate was improved from 10% to 85%. However, the side effects are severe. Cisplatin causes cumulative, irreversible kidney damage and deafness. As with other ototoxic agents, deafness may be secondary to interactions with melanin in the stria vascularis.
As platinum is a catalyst in the manufacture of the silicone rubber and gel components of several types of medical implants (breast implants, joint replacement prosthetics, artificial lumbar discs, vascular access ports, etc.), the possibility platinum could enter the body and cause adverse effects has merited study. The Food and Drug Administration and other institutions have reviewed the issue and found no evidence to suggest toxicity in vivo.
See also
- Platinum, Alaska
- Platinum black
- Platinum coin
- Platinum group
- Mixed metal oxide
- Platinum in Africa
- Merensky Reef
- Precious metal
- 2000s commodities boom
- Palladium
- Platinum nanoparticles
- Platinum color
References
- "Standard Atomic Weights: Platinum". CIAAW. 2005.
- Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (2022-05-04). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ Arblaster, John W. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- Woods, Ian (2004). The Elements: Platinum. The Elements. Benchmark Books. ISBN 978-0761415503.
- ^ Lagowski, J. J., ed. (2004). Chemistry Foundations and Applications. Vol. 3. Thomson Gale. pp. 267–268. ISBN 0-02-865724-1.
- ^ CRC contributors (2007–2008). "Platinum". In Lide, David R. (ed.). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Vol. 4. New York: CRC Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-8493-0488-0.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - Craig, Bruce D; Anderson, David S; International, A.S.M. (1995-01). "Platinum". Handbook of corrosion data. pp. 8–9. ISBN 9780871705181.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Kauffman, George B.; Thurner, Joseph J.; Zatko, David A. (1967). "Ammonium Hexachloroplatinate(IV)". Inorganic Syntheses. 9: 182–185. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch51.
- ^ Han, Y.; Huynh, H. V.; Tan, G. K. (2007). "Mono- vs Bis(carbene) Complexes: A Detailed Study on Platinum(II)−Benzimidazolin-2-ylidenes". Organometallics. 26: 4612. doi:10.1021/om700543p.
- Audi, G. (2003). "The NUBASE Evaluation of Nuclear and Decay Properties". Nuclear Physics A. 729. Atomic Mass Data Center: 3–128. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001.
- Earth's natural wealth: an audit. New Scientist. May 23, 2007.
- Stellman, Jeanne Mager (1998). Encyclopaedia of Occupational Health and Safety: Chemical, industries and occupations. International Labour Organization. p. 141. ISBN 9221098168.
- Murata, K. J. (1958). in Symposium on Spectrocemical Analysis for Trace Elements. ASTM International. p. 71.
- "The History of Platinum". Alaska Community Database Online. ExploreNorth. Retrieved April 12, 2011.
Platinum is located on the Bering Sea coast, below Red Mountain on the south spit of Goodnews Bay.
- Xiao, Z.; Laplante, A. R. (2004). "Characterizing and recovering the platinum group minerals—a review". Minerals Engineering. 17: 961–979. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2004.04.001.
- Dan Oancea: Platinum In South Africa http://www.infomine.com/publications/docs/Mining.com/Sep2008e.pdf
- ^ Seymour, R. J. (2001). "Platinum-group metals". Kirk Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1612012019052513.a01.pub2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Mining Platinum in Montana". New York Times. 1998-08-13. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
- "Platinum–Group Metals" (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries. 2010. Retrieved 2010-09-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Koeberl, Christian (1998). "Identification of meteoritic components in imactites". Meteorites: flux with time and impact effects. pp. 133–155. ISBN 9781862390171.
- ^ Krebs, Robert E. (1998). "Platinum". The History and Use of our Earth's Chemical Elements. Greenwood Press. pp. 124–127. ISBN 0-313-30123-9.
- Smith, G. F.; Gring, J. L. (1933). "The Separation and Determination of the Alkali Metals Using Perchloric Acid. V. Perchloric Acid and Chloroplatinic Acid in the Determination of Small Amounts of Potassium in the Presence of Large Amounts of Sodium". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 55 (10): 3957–3961. doi:10.1021/ja01337a007.
- Schweizer, A. E.; Kerr, G. T. (1978). "Thermal Decomposition of Hexachloroplatinic Acid". Inorganic Chemistry. 17 (8): 2326–2327. doi:10.1021/ic50186a067.
- Perry, D. L. (1995). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. pp. 296–298. ISBN 0849386713.
- Ahrens, Sebastian; Strassner, Thomas (2006). "Detour-free synthesis of platinum-bis-NHC chloride complexes, their structure and catalytic activity in the CH activation of methane". Inorganica Chimica Acta. 359: 4789. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2006.05.042.
- Karpov, Andrey; Konuma, Mitsuharu; Jansen, Martin (2006). "An experimental proof for negative oxidation states of platinum: ESCA-measurements on barium platinides". Chemical Communications (8): 838–840. doi:10.1039/b514631c. PMID 16479284.
- ^ Jansen, Martin (2005). "Effects of relativistic motion of electrons on the chemistry of gold and platinum". Solid State Sciences. 7: 1464. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2005.06.015.
- Ghilane, J.; Lagrost, C.; Guilloux-Viry, M.; Simonet, J.; Delamar, M.; Mangeney, C.; Hapiot, P. (2007). "Spectroscopic Evidence of Platinum Negative Oxidation States at Electrochemically Reduced Surfaces". Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 111: 5701. doi:10.1021/jp068879d.
- Richards, A.D.; Rodger, A. (2007). "Synthetic metallomolecules as agents for the control of DNA structure". Chemical Society Reviews. 36 (3): 471–483. doi:10.1039/b609495c. PMID 17325786.
- ^ Weeks, M. E. (1968). Discovery of the Elements (7 ed.). Journal of Chemical Education. pp. 385–407. ISBN 0848685792. OCLC 23991202.
- Ertl, Gerhard (2008). "Reactions at Surfaces: From Atoms to Complexity (Nobel Lecture)". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 47 (19): 385–407. doi:10.1002/anie.200800480. PMID 18357601.
- George, M. W. (2008). "Platinum-group metals" (pdf). U.S. Geological Survey Mineral Commodity Summaries. USGS Mineral Resources Program.
- George, M. W. 2006 Minerals Yearbook: Platinum-Group Metals (PDF). United States Geological Survey USGS.
- Heiserman, David L. (1992). Exploring Chemical Elements and their Compounds. TAB Books. pp. 272–274. ISBN 0-8306-3018-X.
- Hunt, L. B.; Lever, F. M. (1969). "Platinum Metals: A Survey of Productive Resources to industrial Uses" (PDF). Platinum Metals Review. 13 (4): 126–138. Retrieved 2009-10-02.
- George, Micheal W. "Mineral Yearbook 2006: Platinum-Group Metals" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-09-25.
- Petrucci, Ralph H. (2007). General Chemistry: Principles & Modern Applications (9th ed.). Prentice Hall. p. 606. ISBN 0131493302.
- Gupta, S. V. (2010). "Chapter 4. Metre Convention and Evolution of Base Units". Springer Series in Materials Science, Volume 122. p. 47. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-00738-5_4.
- Feltham, A. M.; Spiro, Michael (1971). "Platinized platinum electrodes". Chemical Reviews. 71: 177. doi:10.1021/cr60270a002.
- "Unknown Facts about Platinum". watches.infoniac.com. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
- "Fixing Statistics". The London Platinum and Palladium Market. Retrieved 2010-06-13.
- "One Year Platinum". Kitco. Retrieved 2009-01-12.
- "Platinum versus Gold". The Speculative Invertor.
- "Platinum". Minerals Zone. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
- Gwin, John (1986). "Pricing Financial Institution Products". Journal of Professional Services Marketing. 1: 91. doi:10.1300/J090v01n03_07.
- Crouse, Richard (2000-05-01). Big Bang Baby: The Rock Trivia Book. p. 126. ISBN 9780888822192.
- Gauding, Madonna (2009-10-06). The Signs and Symbols Bible: The Definitive Guide to Mysterious Markings. ISBN 9781402770043.
- "Occupational Health Guideline for Soluble Platinum Salts (as Platinum)" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
- Einhorn LH. (1 November 1990). "Treatment of testicular cancer: a new and improved model". J. Clin. Oncol. 8 (11): 1777–81. PMID 1700077.
- Von Hoff DD; et al. (1979). "Toxic effects of cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) in man". Cancer Treat. Rep. 63 (9–10): 1527–31. PMID 387223.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - "FDA Backgrounder on Platinum in Silicone Breast Implants". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
- Brook, Michael (2006). "Platinum in silicone breast implants". Biomaterials. 27 (17): 3274–3286. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.027. PMID 16483647.
External links
- Nuclides and Isotopes Fourteenth Edition: Chart of the Nuclides, General Electric Company, 1989.
- "The Platinum Group Metals Database".
- "A balanced historical account of the sequence of discoveries of platinum; illustrated".
- "Platinum Metals Review E-Journal".
- "Platinum-Group Metals Statistics and Information". United States Geological Survey.
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jewellery | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forms | |||||||||||||
| Making |
| ||||||||||||
| Materials |
| ||||||||||||
| Terms |
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Categories:

