| Revision as of 01:50, 10 December 2013 editMilesMoney (talk | contribs)3,474 edits Reverted good faith edits by 65.102.177.223 (talk): Lets discuss this removal on the talk page first, please, per brd. (TW)← Previous edit | Revision as of 05:43, 10 December 2013 edit undoRoccodrift (talk | contribs)682 edits Undid revision 585370805 by MilesMoney (talk) Don't hide behind BRD when you are clearly in violation of BRD.Next edit → | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
| ===Taxes=== | ===Taxes=== | ||
| Another cause is the rate at which ] coupled with the ] of the tax system. A ] is a tax by which the ] increases as the taxable base amount increases.<ref> (4b): increasing in rate as the base increases (a progressive tax)</ref><ref> (6). Increasing in rate as the taxable amount increases.</ref><ref>: Tax levied at a rate that increases as the quantity subject to taxation increases.</ref><ref>: (n) progressive tax (any tax in which the rate increases as the amount subject to taxation increases)</ref><ref name="Sommerfeld">Sommerfeld, Ray M., Silvia A. Madeo, Kenneth E. Anderson, Betty R. Jackson (1992), ''Concepts of Taxation'', Dryden Press: Fort Worth, TX</ref> |
Another cause is the rate at which ] coupled with the ] of the tax system. A ] is a tax by which the ] increases as the taxable base amount increases.<ref> (4b): increasing in rate as the base increases (a progressive tax)</ref><ref> (6). Increasing in rate as the taxable amount increases.</ref><ref>: Tax levied at a rate that increases as the quantity subject to taxation increases.</ref><ref>: (n) progressive tax (any tax in which the rate increases as the amount subject to taxation increases)</ref><ref name="Sommerfeld">Sommerfeld, Ray M., Silvia A. Madeo, Kenneth E. Anderson, Betty R. Jackson (1992), ''Concepts of Taxation'', Dryden Press: Fort Worth, TX</ref> There is debate between politicians and economists over the role of tax policy in mitigating or exacerbating wealth inequality. Economists such as ], ], and ] have argued that tax policy in the post World War II era has indeed increased income inequality by enabling the wealthiest Americans far greater access to capital than lower-income ones.<ref name=Piketty>Piketty, Thomas, and Emmanuel Saez. INCOME INEQUALITY IN THE UNITED STATES, 1913–1998. Tech. 1st ed. Vol. CXVIII. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 2003. Print.</ref> | ||
| There is debate between politicians and economists over the role of tax policy in mitigating or exacerbating wealth inequality. Economists such as ], ], and ] have argued that tax policy in the post World War II era has indeed increased income inequality by enabling the wealthiest Americans far greater access to capital than lower-income ones.<ref name=Piketty>Piketty, Thomas, and Emmanuel Saez. INCOME INEQUALITY IN THE UNITED STATES, 1913–1998. Tech. 1st ed. Vol. CXVIII. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 2003. Print.</ref> | |||
| ===Education=== | ===Education=== | ||
Revision as of 05:43, 10 December 2013
For the economic inequality among countries, see international inequality. For the United States, see Wealth inequality in the United States. For income inequality in the United States, see Income inequality in the United States.| It has been suggested that this article be split into articles titled Income inequality and Wealth concentration. (discuss) (February 2013) |

Economic inequality (also described as the gap between rich and poor, income inequality, wealth disparity, or wealth and income differences) is the difference between individuals or populations in the distribution of their assets, wealth, or income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality involves equity, equality of outcome, equality of opportunity, and life expectancy.
Opinions differ on the utility of inequality and its effects. A 2010 study considered it beneficial, while other recent studies consider it a growing social problem. While some inequality promotes investment, too much inequality is destructive. Income inequality can hinder long term growth. Statistical studies comparing inequality to year-over-year economic growth have been inconclusive; however in 2011, researchers from the International Monetary Fund published that income equality was more determinate of the duration of countries' growth spells than free trade, low government corruption, foreign investment, or low foreign debt.
Economic inequality varies between societies, historical periods, economic structures and systems (for example, capitalism or socialism), and between individuals' abilities to create wealth. The term can refer to cross sectional descriptions of the income or wealth at any particular period, and to the lifetime income and wealth over longer periods of time. There are various numerical indices for measuring economic inequality. A prominent one is the Gini coefficient, but there are also many other methods.
Measurement of inequality in the modern world
A study entitled "Divided we Stand: Why Inequality Keeps Rising” by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) reported its conclusions on the causes, consequences and policy implications for the ongoing intensification of the extremes of wealth and poverty across its 22 member nations (OECD 2011-12-05).
- "Income inequality in OECD countries is at its highest level for the past half century. The average income of the richest 10% of the population is about nine times that of the poorest 10% across the OECD, up from seven times 25 years ago."
- In the United States inequality has increased further from already high levels.
- "Other traditionally more egalitarian countries, such as Germany, Denmark and Sweden, have seen the gap between rich and poor expand from 5 to 1 in the 1980s, to 6 to 1 today."
A study by the World Institute for Development Economics Research at United Nations University reports that the richest 1% of adults alone owned 40% of global assets in the year 2000. The three richest people in the world possess more financial assets than the lowest 48 nations combined. The combined wealth of the "10 million dollar millionaires" grew to nearly $41 trillion in 2008. According to PolitiFact and others, the top 400 richest Americans "have more wealth than half of all Americans combined." In 2001, 46% of people in sub-Saharan Africa were living in extreme poverty. Nearly half of all Indian children are undernourished, however, even among the wealthiest fifth one third of children are malnourished.
Over the two decades prior to the onset of the global financial crisis, real disposable household incomes increased an average of 1.7% a year in its 34 member countries. However, the gap between rich and poor widened in most nations – the OECD journalist resource (2011-05) entitled "Growing Income Inequality in OECD Countries" states that with the exceptions of only France, Japan and Spain, wages of the 10% best-paid workers have risen relative to those of the 10% least-paid workers and the differential between the top and bottom 10% varies greatly from country to country: “While this ratio is much lower in the Nordic countries and in many continental European countries, it rises to around 14 to 1 in Israel, Turkey and the United States, to a high of 27 to 1 in Chile and Mexico.”
Although a discussion exists about the recent trends in global inequality, the issue is anything but clear, and this holds true for both the overall global inequality trend and for its between-country and within-country components. The existing data and estimates suggest a large increase in international (and more generally inter-macroregional) component between 1820 and 1960. It might have slightly decreased since that time at the expense of increasing inequality within countries.
Factors impacting economic inequality
There are many reasons for economic inequality within societies. Recent growth in overall income inequality, at least within the OECD countries, has been driven mostly by increasing inequality in wages and salaries.
Common factors thought to impact economic inequality include:
- labor market outcomes
- globalization
- technological changes
- policy reforms
- more regressive taxation
- computerization and increased technology
- racial discrimination
- gender discrimination
- nepotism
- variation in natural ability
The labor market
A major cause of economic inequality within modern market economies is the determination of wages by the market. Some small part of economic inequality is caused by the differences in the supply and demand for different types of work. However, where competition is imperfect; information unevenly distributed; opportunities to acquire education and skills unequal; and since many such imperfect conditions exist in virtually every market, there is in fact little presumption that markets are in general efficient. This means that there is an enormous potential role for government to correct these market failures. In a purely capitalist mode of production (i.e. where professional and labor organizations cannot limit the number of workers) the workers wages will not be controlled by these organizations, or by the employer, but rather by the market. Wages work in the same way as prices for any other good. Thus, wages can be considered as a function of market price of skill. And therefore, inequality is driven by this price. Under the law of supply and demand, the price of skill is determined by a race between the demand for the skilled worker and the supply of the skilled worker. "On the other hand, markets can also concentrate wealth, pass environmental costs on to society, and abuse workers and consumers." "Markets, by themselves, even when they are stable, often lead to high levels of inequality, outcomes that are widely viewed as unfair." Employers who offer a below market wage will find that their business is chronically understaffed. Their competitors will take advantage of the situation by offering a higher wage to snatch up the best of their labor. For a businessman who has the profit motive as the prime interest, it is a losing proposition to offer below or above market wages to workers.
A job where there are many workers willing to work a large amount of time (high supply) competing for a job that few require (low demand) will result in a low wage for that job. This is because competition between workers drives down the wage. An example of this would be jobs such as dish-washing or customer service. Competition amongst workers tends to drive down wages due to the expendable nature of the worker in relation to his or her particular job. A job where there are few able or willing workers (low supply), but a large need for the positions (high demand), will result in high wages for that job. This is because competition between employers for employees will drive up the wage. Examples of this would include jobs that require highly developed skills, rare abilities, or a high level of risk. Competition amongst employers tends to drive up wages due to the nature of the job, since there is a relative shortage of workers for the particular position. Professional and labor organizations may limit the supply of workers which results in higher demand and greater incomes for members. Members may also receive higher wages through collective bargaining, political influence, or corruption.
These supply and demand interactions result in a gradation of wage levels within society that significantly influence economic inequality. Polarization of wages does not explain the accumulation of wealth and very high incomes among the 1%. Joseph Stiglitz believes that "It is plain that markets must be tamed and tempered to make sure they work to the benefit of most citizens."
Taxes
Another cause is the rate at which income is taxed coupled with the progressivity of the tax system. A progressive tax is a tax by which the tax rate increases as the taxable base amount increases. There is debate between politicians and economists over the role of tax policy in mitigating or exacerbating wealth inequality. Economists such as Paul Krugman, Peter Orszag, and Emmanuel Saez have argued that tax policy in the post World War II era has indeed increased income inequality by enabling the wealthiest Americans far greater access to capital than lower-income ones.
Education
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (June 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

One important factor in the creation of inequality is variation in individuals' access to education. Education, especially in an area where there is a high demand for workers, creates high wages for those with this education however, increases in education first increase and then decrease growth as well as income inequality. As a result, those who are unable to afford an education, or choose not to pursue optional education, generally receive much lower wages. The justification for this is that a lack of education leads directly to lower incomes, and thus lower aggregate savings and investment. In particular, the increase in family income and wealth inequality leads to greater dispersion of educational attainment, primarily because those at the bottom of the educational distribution have fallen further below the average level of education. Conversely, education raises incomes and promotes growth because it helps to unleash the productive potential of the poor.
During the mass high school education movement from 1910–1940, there was an increase in skilled workers, which led to a decrease in the price of skilled labor. High school education during the period was designed to equip students with necessary skill sets to be able to perform at work. In fact, it differs from the present high school education, which is regarded as a stepping-stone to acquire college and advanced degrees. This decrease in wages caused a period of compression and decreased inequality between skilled and unskilled workers. Education is very important for the growth of the economy, however educational inequality in gender also influence towards the economy. Lagerlof and Galor stated that gender inequality in education can result to low economic growth, and continued gender inequality in education, thus creating a poverty trap. It is suggested that a large gap in male and female education may indicate backwardness and so may be associated with lower economic growth, which can explain why there is economic inequality between countries.
More of Barro studies also find that female secondary education is positively associated with growth. His findings show that countries with low female education; increasing it has little effect on economic growth, however in countries with high female education, increasing it significantly boosts economic growth. More and better education is a prerequisite for rapid economic development around the world. Education stimulates economic growth and improves people's lives through many channels.
By increasing the efficiency of the labour force it create better conditions for good governance, improving health and enhancing equality. Labor market success is linked to schooling achievement, the consequences of widening disparities in schooling is likely to be further increases in earnings inequality
Economic neoliberal views
John Schmitt and Ben Zipperer (2006) of the CEPR point to economic liberalism and the reduction of business regulation along with the decline of union membership as one of the causes of economic inequality. In an analysis of the effects of intensive Anglo-American neoliberal policies in comparison to continental European neoliberalism, where unions have remained strong, they concluded "The U.S. economic and social model is associated with substantial levels of social exclusion, including high levels of income inequality, high relative and absolute poverty rates, poor and unequal educational outcomes, poor health outcomes, and high rates of crime and incarceration. At the same time, the available evidence provides little support for the view that U.S.-style labor-market flexibility dramatically improves labor-market outcomes. Despite popular prejudices to the contrary, the U.S. economy consistently affords a lower level of economic mobility than all the continental European countries for which data is available."
Views on globalization
Trade liberalization may shift economic inequality from a global to a domestic scale. When rich countries trade with poor countries, the low-skilled workers in the rich countries may see reduced wages as a result of the competition, while low-skilled workers in the poor countries may see increased wages. Trade economist Paul Krugman estimates that trade liberalisation has had a measurable effect on the rising inequality in the United States. He attributes this trend to increased trade with poor countries and the fragmentation of the means of production, resulting in low skilled jobs becoming more tradeable. However, he concedes that the effect of trade on inequality in America is minor when compared to other causes, such as technological innovation, a view shared by other experts. Lawrence Katz estimates that trade has only accounted for 5-15% of rising income inequality. Robert Lawrence argues that technological innovation and automation has meant that low-skilled jobs have been replaced by machine labor in wealthier nations, and that wealthier countries no longer have significant numbers of low-skilled manufacturing workers that could be affected by competition from poor countries.
Impact of gender

In many countries, there is a gender income gap which favors males in the labor market. For example, the median full-time salary for U.S. women is 77% of that of U.S. men. Several factors other than discrimination may contribute to this gap. On average, women are more likely than men to consider factors other than pay when looking for work, and may be less willing to travel or relocate. Thomas Sowell, in his book Knowledge and Decisions, claims that this difference is due to women not taking jobs due to marriage or pregnancy, but income studies show that that does not explain the entire difference. A U.S. Census's report stated that in US once other factors are accounted for there is still a difference in earnings between women and men. The income gap in other countries ranges from 53% in Botswana to -40% in Bahrain.
Gender inequality and discrimination is argued to cause and perpetuate poverty and vulnerability in society as a whole. Gender Equity Indices seek to provide the tools to demonstrate this feature of equity.
Development patterns
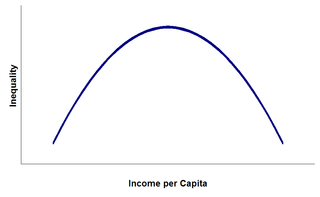
Economist Simon Kuznets argued that levels of economic inequality are in large part the result of stages of development. According to Kuznets, countries with low levels of development have relatively equal distributions of wealth. As a country develops, it acquires more capital, which leads to the owners of this capital having more wealth and income and introducing inequality. Eventually, through various possible redistribution mechanisms such as social welfare programs, more developed countries move back to lower levels of inequality. Plotting the relationship between level of income and inequality, Kuznets saw middle-income developing economies level of inequality bulging out to form what is now known as the Kuznets curve. Kuznets demonstrated this relationship using cross-sectional data. However, more recent testing of this theory with superior panel data has shown it to be very weak. Kuznets' curve predicts that income inequality will eventually decrease given time. As an example, income inequality did fall in the United States during its High School Movement in the 1940s and after. However, recent data shows that the level of income inequality began to rise after the 1970s. This does not necessarily disprove Kuznets' theory. It may be possible that another Kuznets' cycle is occurring, specifically the move from the manufacturing sector to the service sector. This implies that it may be possible for multiple Kuznets' cycles to be in effect at any given time.
Diversity of preferences
Related to cultural issues, diversity of preferences within a society may contribute to economic inequality. When faced with the choice between working harder to earn more money or enjoying more leisure time, equally capable individuals with identical earning potential may choose different strategies. The trade-off between work and leisure is particularly important in the supply side of the labor market in labor economics.
Likewise, individuals in a society often have different levels of risk aversion. When equally-able individuals undertake risky activities with the potential of large payoffs, such as starting new businesses, some ventures succeed and some fail. The presence of both successful and unsuccessful ventures in a society results in economic inequality even when all individuals are identical.
Wealth concentration
Main article: Wealth concentrationWealth concentration is a theoretical process by which, under certain conditions, newly created wealth concentrates in the possession of already-wealthy individuals or entities. According to this theory, those who already hold wealth have the means to invest in new sources of creating wealth or to otherwise leverage the accumulation of wealth, thus are the beneficiaries of the new wealth. Over time, wealth condensation can significantly contribute to the persistence of inequality within society.
Rent-seeking
Economist Joseph Stiglitz argues that rather than explaining concentrations of wealth and income, market forces should serve as a brake on such concentration, which may better be explained by the non-market force known as "rent-seeking". While the market will bid up compensation for rare and desired skills to reward wealth creation, greater productivity, etc., it will also prevent successful entrepreneurs from earning excess profits by fostering competition to cut prices, profits and large compensation. A better explainer of growing inequality, according to Stiglitz, is the use of political power generated by wealth by certain groups to shape government policies financially beneficial to them. This process, known to economists as rent-seeking, brings income not from creation of wealth but from "grabbing a larger share of the wealth that would otherwise have been produced without their effort"
Rent seeking is often thought to be the province of societies with weak institutions and weak rule of law, but Stiglitz believes there is no shortage of it in developed societies such as the United States. Examples of rent seeking leading to inequality include
- the obtaining of public resources by "rent-collectors" at below market prices (such as granting public land to railroads, or selling mineral resources for a nominal price in the US),
- selling services and products to the public at above market prices (medicare drug benefit in the US that prohibits government from negotiating prices of drugs with the drug companies, costing the US government an estimated $50 billion or more per year),
- securing government tolerance of monopoly power (The richest person in the world in 2011, Carlos Slim, controlled Mexico's newly privatized telecommunication industry).
Since rent seeking aims to "pluck the goose to obtain the largest amount of feathers with the least possible amount of hissing" – it is by nature obscure, avoiding public spotlight in legal fine print, or camouflaged its extraction with widely accepted rationalizations (markets are naturally competitive and so need no government regulation against monopolies).
Impact of finance sectors
Jamie Galbraith argues that countries with larger financial sectors have greater inequality, and the link is not an accident.
Mitigating factors
Countries with a left-leaning legislature have lower levels of inequality. Many factors constrain economic inequality – they may be divided into two classes: government sponsored, and market driven. The relative merits and effectiveness of each approach is a subject of debate.
Typical government initiatives to reduce economic inequality include:
- Public education: increasing the supply of skilled labor and reducing income inequality due to education differentials.
- Progressive taxation: the rich are taxed proportionally more than the poor, reducing the amount of income inequality in society if the change in taxation does not cause changes in income.
- Minimum wage legislation: raising the income of the poorest workers (for the ones that don't lose their jobs due to the minimum wage)
- Nationalization or subsidization of products: providing goods and services that everyone needs cheaply or freely (such as food, healthcare, and housing), governments can effectively raise the purchasing power of the poorer members of society.
- Unionization supportive legislation such as the Wagner Act.
These provisions may lower inequality, but have sometimes resulted in increased economic inequality (as in the Soviet Union, where the distribution of these government benefits was controlled by a privileged class). Political scientists have argued that public policy controlled by organizations of the wealthy have steadily eroded economic equality in the US since the 1970s.
Market forces outside of government intervention that can reduce economic inequality include:
- propensity to spend: with rising wealth & income, a person must spend more. In an extreme example, if one person owned everything, they would immediately need to hire people to maintain their properties, thus reducing the wealth concentration.
- Unionization: although not a market force, per se, labor organizations may reduce inequality by negotiating standard pay rates (though probably increasing unemployment). As union power has declined, and performance related pay has become more widespread, economic inequality has mirrored productive inequality.
Effects of inequality
Among the effects of inequality researchers have found include higher rates of health and social problems, and lower rates of social goods, a lower level of economic utility in society from resources devoted on high-end consumption, and even a lower level of economic growth when human capital is neglected for high-end consumption.
2013 Economics Nobel prize winner Robert J. Shiller said that rising inequality in the United States and elsewhere is the most important problem. Increasing inequality harms economic growth. High and persistent unemployment, in which inequality increases, has a negative effect on subsequent long-run economic growth. Unemployment can harm growth not only because it is a waste of resources, but also because it generates redistributive pressures and subsequent distortions, drives people to poverty, constrains liquidity limiting labor mobility, and erodes self-esteem promoting social dislocation, unrest and conflict. Policies aiming at controlling unemployment and in particular at reducing its inequality-associated effects support economic growth.
Health and social cohesion
British researchers Richard G. Wilkinson and Kate Pickett have found higher rates of health and social problems (obesity, mental illness, homicides, teenage births, incarceration, child conflict, drug use), and lower rates of social goods (life expectancy, educational performance, trust among strangers, women's status, social mobility, even numbers of patents issued) in countries and states with higher inequality. Using statistics from 23 developed countries and the 50 states of the US, they found social/health problems lower in countries like Japan and Finland and states like Utah and New Hampshire with high levels of equality, than in countries (US and UK) and states (Mississippi and New York) with large differences in household income.

For most of human history higher material living standards – full stomachs, access to clean water and warmth from fuel – led to better health and longer lives. This pattern of higher incomes-longer lives still holds among poorer countries, where life expectancy increases rapidly as per capita income increases, but in recent decades it has slowed down among middle income countries and plateaued among the richest thirty or so countries in the world. Americans live no longer on average (about 77 years in 2004) than Greeks (78 years) or New Zealanders (78), though the USA is almost twice as rich. Life expectancy in Sweden (80 years) and Japan (82) – where income was more equally distributed – was longer.
In recent years the characteristic that has strongly correlated with health in developed countries is income inequality. Creating an index of "Health and Social Problems" from nine factors, authors Richard Wilkinson and Kate Pickett found health and social problems "more common in countries with bigger income inequalities", and more common among states in the US with larger income inequalities. Other studies have confirmed this relationship. The UNICEF index of "child well-being in rich countries", studying 40 indicators in 22 countries, correlates with greater equality but not per capita income.
Pickett and Wilkinson argue that inequality and social stratification lead to higher levels of psychosocial stress and status anxiety which can lead to depression, chemical dependency, less community life, parenting problems and stress-related diseases.
Social cohesion
Further information: Social cohesionResearch has shown an inverse link between income inequality and social cohesion. In more equal societies, people are much more likely to trust each other, measures of social capital (the benefits of goodwill, fellowship, mutual sympathy and social connectedness among groups who make up a social units) suggest greater community involvement, and homicide rates are consistently lower.
Comparing results from the question "would others take advantage of you if they got the chance?" in U.S General Social Survey and statistics on income inequality, Eric Uslaner and Mitchell Brown found there is a high correlation between the amount of trust in society and the amount of income equality. A 2008 article by Andersen and Fetner also found a strong relationship between economic inequality within and across countries and tolerance for 35 democracies.
In two studies Robert Putnam established links between social capital and economic inequality. His most important studies established these links in both the United States and in Italy. His explanation for this relationship is that
Community and equality are mutually reinforcing... Social capital and economic inequality moved in tandem through most of the twentieth century. In terms of the distribution of wealth and income, America in the 1950s and 1960s was more egalitarian than it had been in more than a century... hose same decades were also the high point of social connectedness and civic engagement. Record highs in equality and social capital coincided. Conversely, the last third of the twentieth century was a time of growing inequality and eroding social capital... The timing of the two trends is striking: somewhere around 1965–70 America reversed course and started becoming both less just economically and less well connected socially and politically.
The economist Joseph Stiglitz has argued that economic inequality has led to distrust of business and government.
Crime
Crime rate has also been shown to be correlated with inequality in society. Most studies looking into the relationship have concentrated on homicides – since homicides are almost identically defined across all nations and jurisdictions. There have been over fifty studies showing tendencies for violence to be more common in societies where income differences are larger. Research has been conducted comparing developed countries with undeveloped countries, as well as studying areas within countries. Daly et al. 2001 found that among U.S States and Canadian Provinces there is a tenfold difference in homicide rates related to inequality. They estimated that about half of all variation in homicide rates can be accounted for by differences in the amount of inequality in each province or state. Fajnzylber et al. (2002) found a similar relationship worldwide. Among comments in academic literature on the relationship between homicides and inequality are:
- The most consistent finding in cross-national research on homicides has been that of a positive association between income inequality and homicides.
- Economic inequality is positively and significantly related to rates of homicide despite an extensive list of conceptually relevant controls. The fact that this relationship is found with the most recent data and using a different measure of economic inequality from previous research, suggests that the finding is very robust.
Social, cultural, and civic participation
Higher income inequality led to less of all forms of social, cultural, and civic participation among the less wealthy. When inequality is higher the poor do not shift to less expensive forms of participation.
Utility, economic welfare, and distributive efficiency
Following the utilitarian principle of seeking the greatest good for the greatest number – economic inequality is problematic. A house that provides less utility to a millionaire as a summer home than it would to a homeless family of five, is an example of reduced "distributive efficiency" within society, that decreases marginal utility of wealth and thus the sum total of personal utility. An additional dollar spent by a poor person will go to things providing a great deal of utility to that person, such as basic necessities like food, water, and healthcare; while, an additional dollar spent by a much richer person will very likely go to luxury items providing relatively less utility to that person. Thus, the marginal utility of wealth per person ("the additional dollar") decreases as a person becomes richer. From this standpoint, for any given amount of wealth in society, a society with more equality will have higher aggregate utility. Some studies have found evidence for this theory, noting that in societies where inequality is lower, population-wide satisfaction and happiness tend to be higher.
Economist Arthur Cecil Pigou argues that
... it is evident that any transference of income from a relatively rich man to a relatively poor man of similar temperament, since it enables more intense wants, to be satisfied at the expense of less intense wants, must increase the aggregate sum of satisfaction. The old "law of diminishing utility" thus leads securely to the proposition: Any cause which increases the absolute share of real income in the hands of the poor, provided that it does not lead to a contraction in the size of the national dividend from any point of view, will, in general, increase economic welfare.
Conservative economist Schmidtz argues that maximizing the sum of individual utilities will harm incentives to produce.
A society that takes Joe Rich’s second unit is taking that unit away from someone who . . . has nothing better to do than plant it and giving it to someone who . . . does have something better to do with it. That sounds good, but in the process, the society takes seed corn out of production and diverts it to food, thereby cannibalizing itself.
However, in addition to the diminishing marginal utility of unequal distribution, Pigou and others point out that a "keeping up with the Joneses" effect among the well off may lead to greater inequality and use of resources for no greater return in utility.
a larger proportion of the satisfaction yielded by the incomes of rich people comes from their relative, rather than from their absolute, amount. This part of it will not be destroyed if the incomes of all rich people are diminished together. The loss of economic welfare suffered by the rich when command over resources is transferred from them to the poor will, therefore, be substantially smaller relatively to the gain of economic welfare to the poor than a consideration of the law of diminishing utility taken by itself suggests.
When the goal is to own the biggest yacht – rather than a boat with certain features – there is no greater benefit from owning 100 metre long boat than a 20 m one as long as it is bigger than your rival. Economist Robert H. Frank compare the situation to that of male elks who use their antlers to spar with other males for mating rights.
The pressure to have bigger ones than your rivals leads to an arms race that consumes resources that could have been used more efficiently for other things, such as fighting off disease. As a result, every male ends up with a cumbersome and expensive pair of antlers, ... and "life is more miserable for bull elk as a group."
Economic incentives
Many people accept inequality as a given, and argue that an increased gap between rich and poor increases the incentives for competition and innovation within the world economy.
Some modern economic theories, such as the neoclassical school, have suggested that a functioning economy entails a certain level of unemployment. These theories argue that unemployment benefits must be below the wage level to provide an incentive to work, thereby mandating inequality and that additionally, it is impossible to lower unemployment down to zero.
Many economists believe that one of the main reasons that inequality might induce economic incentive is because material well-being and conspicuous consumption are related to status. In this view, high stratification of income (high inequality) creates high amounts of social stratification, leading to greater competition for status. One of the first writers to note this relationship was Adam Smith who recognized "regard" as one of the major driving forces behind economic activity. From The Theory of Moral Sentiments in 1759:
hat is the end of avarice and ambition, of the pursuit of wealth, of power, and pre-eminence? Is it to supply the necessities of nature? The wages of the meanest labourer can supply them... hy should those who have been educated in the higher ranks of life, regard it as worse than death, to be reduced to live, even without labour, upon the same simple fare with him, to dwell under the same lowly roof, and to be clothed in the same humble attire? From whence, then, arises that emulation which runs through all the different ranks of men, and what are the advantages which we propose by that great purpose of human life which we call bettering our condition? To be observed, to be attended to, to be taken notice of with sympathy, complacency, and approbation, are all the advantages which we can propose to derive from it. It is the vanity, not the ease, or the pleasure, which interests us
Modern sociologists and economists such as Juliet Schor and Robert H. Frank have studied the extent to which economic activity is fueled by the ability of consumption to represent social status. Schor, in The Overspent American, argues that the increasing inequality during the 1980s and 1990s strongly accounts for increasing aspirations of income, increased consumption, decreased savings, and increased debt.
In the book Luxury Fever, Robert H. Frank argues that satisfaction with levels of income is much more strongly affected by how someone's income compares with others than its absolute level. Frank gives the example of instructions to a yacht architect by a customer – shipping magnate Stavros Niarchos – to make Niarchos' new yacht 50 feet longer than that of rival magnate Aristotle Onassis – Niarchos not specifying or reportedly even aware of exactly how long Onassis's yacht was.
Inequality and economic growth
In the 1960s, economist Arthur Melvin Okun argued that pursuing equality could reduce efficiency (the total output produced with given resources) by reducing incentives to work, save, and invest and through the “leaky bucket” of wasteful government efforts to redistribute (such as a progressive tax code and minimum wages). Some resources “will simply disappear in transit, so the poor will not receive all the money that is taken from the rich”. Along the same lines, earlier writers had argued that wealthier individuals save proportionally more of their incomes, so that more inequality would lead to higher overall savings and thus capital accumulation and growth.
Cross-country evidence
Many authors have empirically examined the relationship between economic growth and income inequality in a large group of countries. Following the broader economic growth literature, the typical approach was to relate countries' real GDP per capita growth over a long period of time (e.g., 1965 through 1990) to the income distribution at the start of the period, simultaneously taking into account other standard determinants such as the initial level of real GDP per capita. A typical conclusion was that more unequal countries tend to grow slower (Alesina and Rodrik, 1994), though the evidence was contested.
Because of general dissatisfaction with the empirical approach, including difficulties in determining causality and capturing country-specific factors, attention turned to the analysis of how changes in the income distribution affected the growth rate in subsequent time period (usually five years) in a large group of countries. Forbes (2000) found that an increase in inequality tends to raise growth during the subsequent period. This literature did not go too far as Banerjee and Duflo (2003) found a complex relationship between inequality and growth, in which changes in inequality in either direction lowered growth subsequently. They interpreted this finding as supporting the notion that redistribution hurts growth, at least over the short- to medium-run, but also cautioned about interpreting income distribution-economic growth analysis of this type.
In recent years, the economic growth literature has recognized that growth in most countries does not follow a smooth path, but is characterized by sharp turning points – periods of sustained growth and stagnation. The interesting empirical questions, then, are about the determinants of the turning points (Pritchett, 2000).
Along these lines, Andrew Berg and Jonathan D. Ostry (2011) examined the question of what sustains long periods of strong growth, and found that one of the most robust and important determinants is the level of income inequality. In particular, they found that high 'growth spells' were much more likely to end in countries with less equal income distribution, and that the measured effect was large. For example, they estimate that closing half the inequality gap between Latin America and emerging Asia would more than double the expected duration of a 'growth spell.' Their findings were robust to the inclusion of other variables in the model, and to alternate definitions of growth spells. According to their study, which has featured prominently in the financial press, inequality is of course not the only thing that matters but it clearly belongs in the "pantheon" of well-established growth factors such as the quality of political institutions or trade openness.
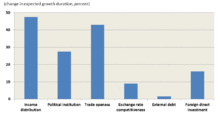
Berg and Ostry postulate that high levels of inequality might damage long term growth by amplifying the potential for financial crisis, discouraging investment because of political instability, making it more difficult for governments to make difficult choices (such as raising taxes or cutting public expenditure) in the face of shocks, or by discouraging investment in education and health for the poor.
Comparisons with the United States
Economic sociologist Lane Kenworthy has found no correlation between levels of inequality and economic growth among developed countries, among states of the US, or in the US over the years from 1947 to 2005. Nor did Jared Bernstein find a correlation, plotting yearly real GDP growth and the share of income going to the top 1%, 1929–2010
Mechanisms
According to economist Branko Milanovic, while traditionally economists thought inequality was good for growth
"The view that income inequality harms growth – or that improved equality can help sustain growth – has become more widely held in recent years. ... The main reason for this shift is the increasing importance of human capital in development. When physical capital mattered most, savings and investments were key. Then it was important to have a large contingent of rich people who could save a greater proportion of their income than the poor and invest it in physical capital. But now that human capital is scarcer than machines, widespread education has become the secret to growth."
"Broadly accessible education" is both difficult to achieve when income distribution is uneven and tends to reduce "income gaps between skilled and unskilled labor."
A study by Perotti (1996) examines of the channels through which inequality may affect economic growth. He shows that in accordance with the credit market imperfection approach, inequality is associated with lower level of human capital formation (education, experience, apprenticeship) and higher level of fertility, while lower level of human capital is associated with lower growth and lower levels of economic growth. In contrast, his examination of the political economy channel refutes the political economy mechanism. He demonstrates that inequality is associated with lower levels of taxation, while lower levels of taxation, contrary to the theories, are associated with lower level of economic growth
The credit market imperfection approach, developed by Galor and Zeira (1993), demonstrates that inequality in the presence of credit market imperfections has a long lasting detrimental effect on human capital formation and economic development.
The political economy approach, developed by Alesian and Rodrik (1994) and Persson and Tabellini (1994), argues that inequality is harmful for economic development because inequality generates a pressure to adopt redistributive policies that have an adverse effect on investment and economic growth.
The sovereign-debt economic problems of the late twenty-oughts do not seem to be correlated to redistribution policies in Europe. With the exception of Ireland, the countries at risk of default in 2011 (Greece, Italy, Spain, Portugal) were notable for their high Gini-measured levels of income inequality compared to other European countries. As measured by the Gini index, Greece as of 2008 had more income inequality than the economically healthy Germany.
Inequality and housing
A number of researchers (David Rodda, Jacob Vigdor, Janna Matlack, and Jacob Vigdor), argue that a shortage of affordable housing – at least in the US – is caused in part by income inequality. David Rodda noted that from 1984 and 1991, the number of quality rental units decreased as the demand for higher quality housing increased (Rhoda 1994:148). Through gentrification of older neighbourhoods, for example, in East New York, rental prices increased rapidly as landlords found new residents willing to pay higher market rate for housing and left lower income families without rental units. The ad valorem property tax policy combined with rising prices made it difficult or impossible for low income residents to keep pace.
Aspirational consumption and household risks
Firstly, certain costs are difficult to avoid and are shared by everyone, such as the costs of housing, pensions, education and health care. If the state does not provide these services, then for those on lower incomes, the costs must be borrowed and often those on lower incomes are those who are worse equipped to manage their finances. Secondly, aspirational consumption describes the process of middle income earners aspiring to achieve the standards of living enjoyed by their wealthier counterparts and one method of achieving this aspiration is by taking on debt. The result leads to even greater inequality and potential economic instability.
Perspectives regarding economic inequality
Marxism
Marxism favors an eventual society where distribution is based on an individual's needs rather than his ability to produce, inheritance, or other such factors. In such a system inequality would be minimal.
Marxists believe economic equality is necessary for political freedom – saying that when there is economic inequality then political inequality is assured – in such a society currency would be eliminated, the means of production owned in common and non-labor income eliminated (rent/profit or surplus value). Marxists believe that once the means of production are owned in common and worked for utility rather than profit, that all workers receive a voice in a democratic workplace and the money incentive removed, economic equality will be achieved.
Marxist Leninists believe that, during the transitional period between capitalism and socialism, workers will be paid based on "to each according to labour" as opposed to "to each according to need".
Meritocracy
Meritocracy favors an eventual society where an individual's success is a direct function of his merit, or contribution. Economic inequality would be a natural consequence of the wide range in individual skill, talent and effort in human population and, being the result of natural variation, individual effort and voluntary exchange, would not be considered ethically problematic in its own right.
Liberalism
Most modern social liberals, including centrist or left-of-center political groups, believe that the capitalist economic system should be fundamentally preserved, but the status quo regarding the income gap must be reformed. Most social liberals favor a capitalist system, Keynesian economics, neoliberalism, and progressive taxation.
However, classical liberals and libertarians generally do not take a stance on wealth inequality, but believe in equality under the law regardless of whether it leads to unequal wealth distribution. In 1966 Ludwig von Mises, a prominent figure in the Austrian School of economic thought, explains:
The liberal champions of equality under the law were fully aware of the fact that men are born unequal and that it is precisely their inequality that generates social cooperation and civilization. Equality under the law was in their opinion not designed to correct the inexorable facts of the universe and to make natural inequality disappear. It was, on the contrary, the device to secure for the whole of mankind the maximum of benefits it can derive from it. Henceforth no man-made institutions should prevent a man from attaining that station in which he can best serve his fellow citizens.
Libertarian Robert Nozick argued that government redistributes wealth by force (usually in the form of taxation), and that the ideal moral society would be one where all individuals are free from force. However, Nozick recognized that some modern economic inequalities were the result of forceful taking of property, and a certain amount of redistribution would be justified to compensate for this force but not because of the inequalities themselves. John Rawls argued in A Theory of Justice that inequalities in the distribution of wealth are only justified when they improve society as a whole, including the poorest members. Rawls does not discuss the full implications of his theory of justice. Some see Rawls's argument as a justification for capitalism since even the poorest members of society theoretically benefit from increased innovations under capitalism; others believe only a strong welfare state can satisfy Rawls's theory of justice.
Classical libertarian Milton Friedman believed that if government action is taken in pursuit of economic equality then political freedom would suffer. In a famous quote, he said:
- A society that puts equality before freedom will get neither. A society that puts freedom before equality will get a high degree of both.
Social justice arguments
Patrick Diamond and Anthony Giddens (professors of Economics and Sociology, respectively) hold that 'pure meritocracy is incoherent because, without redistribution, one generation's successful individuals would become the next generation's embedded caste, hoarding the wealth they had accumulated'.
They also state that social justice requires redistribution of high incomes and large concentrations of wealth in a way that spreads it more widely, in order to "recognise the contribution made by all sections of the community to building the nation's wealth." (Patrick Diamond and Anthony Giddens, 27 June 2005, New Statesman)
Claims that inequality lowers social welfare
In most western democracies, the desire to eliminate or reduce economic inequality is generally associated with the political left. One practical argument in favor of reduction is the idea that economic inequality reduces social cohesion and increases social unrest, thereby weakening the society.
There is evidence that this is true (see inequity aversion) and it is intuitive, at least for small face-to-face groups of people. Alberto Alesina, Rafael Di Tella, and Robert MacCulloch find that inequality negatively affects happiness in Europe but not in the United States.
It has also been argued that economic inequality invariably translates to political inequality, which further aggravates the problem. Even in cases where an increase in economic inequality makes nobody economically poorer, an increased inequality of resources is disadvantageous, as increased economic inequality can lead to a power shift due to an increased inequality in the ability to participate in democratic processes.
The capabilities approach
Further information: Capability approachThe capabilities approach – sometimes called the human development approach – looks at income inequality and poverty as form of “capability deprivation”. Unlike neoliberalism, which “defines well-being as utility maximization”, economic growth and income are considered a means to an end rather than the end itself. Its goal is to “wid people’s choices and the level of their achieved well-being” through increasing functionings (the things a person values doing), capabilities (the freedom to enjoy functionings) and agency (the ability to pursue valued goals).
When a person’s capabilities are lowered, they are in some way deprived of earning as much income as they would otherwise. An old, ill man cannot earn as much as a healthy young man; gender roles and customs may prevent a woman from receiving an education or working outside the home. There may be an epidemic that causes widespread panic, or there could be rampant violence in the area that prevents people from going to work for fear of their lives. As a result, income and economic inequality increases, and it becomes more difficult to reduce the gap without additional aid. To prevent such inequality, this approach believes it’s important to have political freedom, economic facilities, social opportunities, transparency guarantees, and protective security to ensure that people aren’t denied their functionings, capabilities, and agency and can thus work towards a better relevant income.
Policy responses intended to reduce economic inequality
Progressive taxation reduces absolute income inequality when the higher rates on higher-income individuals are paid and not evaded, and transfer payments and social safety nets result in progressive government spending. When income inequality is low, aggregate demand will be relatively high, because more people who want ordinary consumer goods and services will be able to afford them, while the labor force will not be as relatively monopolized by the wealthy. These principles have recently been confirmed by game theoretic economic models.
See also
- Equal opportunity
- Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index
- Income distribution
- Income inequality in the United States
- List of countries by income equality
- List of countries by distribution of wealth
- Occupy movement
- Plutocracy
- Poverty and Cycle of poverty
References
- Fletcher, Michael A. (March 10, 2013). "Research ties economic inequality to gap in life expectancy". Washington Post. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- U.S. Income Inequality: It’s Not So Bad By Thomas A. Garrett| Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis| Spring 2010
- Wilkinson, Richard (2009). The Spirit Level: Why More Equal Societies Almost Always Do Better. Allen Lane. p. 352. ISBN 978-1-84614-039-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Study covers years between 1950 and 2006. Berg, Andrew G.; Ostry, Jonathan D. (2011). "Equality and Efficiency". Finance and Development. 48 (3). International Monetary Fund. Retrieved September 10, 2012.
- World Trade Organization (May 2012). "Macroeconomic stability, inclusive growth and employment" (PDF). Thematic Think Piece. United Nations. p. 12. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Chapter 2: Inequality: Recent Trends in China and Experience in the OECD Area". CHINA IN FOCUS: LESSONS AND CHALLENGES (PDF). OECD. 2012. pp. 16–34. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- Vos, Rob (2012). "World Economic Situation and Prospects" (PDF). Development Policy and Analysis Division. New York: United Nations. p. 22. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ Banerjee, Abhijit V.; Duflo, Esther (2003). "Inequality And Growth: What Can The Data Say?". Journal of Economic Growth. 8 (3): 267–99. doi:10.1023/A:1026205114860. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- Wojciech Kopczuk, Emmanuel Saez, and Jae Song find that “most of the increase in the variance of (log) annual earnings is due to increases in the variance of (log) permanent earnings with modest increases in the variance of transitory (log) earnings.” Thus, in fact, the increase in earnings inequality is in lifetime income. Furthermore, they find that it remains difficult for someone to move up the earnings distribution (though they do find upward mobility for women in their lifetime). See their “Earnings Inequality and Mobility in the United States: Evidence from Social Security Data since 1937,” Quarterly Journal of Economics. 125, no. 1 (2010): 91–128.
- ^ Gurría, Angel (5 December 2011). Press Release for Divided We Stand: Why Inequality Keeps Rising (Report). OECD. doi:10.1787/9789264119536-en. Retrieved 2011-12-16.
- ""Inflation-Gap Persistence in the US". Timothy Cogley, Giorgio E. Primiceri and Thomas J. Sargent. American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics. Vol. 2, No. 1 (January 2010), pp. 43–69. Published by: American Economic Association". JSTOR 25760284.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - http://articles.moneycentral.msn.com/News/StudyRevealsOverwhelmingWealthGap.aspx
- "Growth of millionaires in India fastest in world ". Thaindian News. June 25, 2008.
- Kertscher, Tom; Borowski, Greg (March 10, 2011). "The Truth-O-Meter Says: True - Michael Moore says 400 Americans have more wealth than half of all Americans combined". PolitiFact. Retrieved August 11, 2013.
- Moore, Michael (March 6, 2011). "America Is Not Broke". Huffington Post. Retrieved August 11, 2013.
- Moore, Michael (March 7, 2011). "The Forbes 400 vs. Everybody Else". michaelmoore.com. Retrieved August 11, 2013.
{{cite web}}: External link in|work=|work=(help) - Pepitone, Julianne (September 22, 2010). "Forbes 400: The super-rich get richer". CNN. Retrieved August 11, 2013.
- Johnson, Dave (February 14, 2011). "9 Pictures That Expose This Country's Obscene Division of Wealth". Alternet. Retrieved August 11, 2013.
- "Birth rates 'must be curbed to win war on global poverty'". The Independent. January 31, 2007.
- "Half of India's children malnourished, says NGO report". Calcutta News. October 15, 2009.
- "Putting the smallest first: Why India makes a poor fist of feeding the young, and how it could do better". The Economist. 23 September 2010. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
Even the children of wealthier families suffer surprisingly high rates of malnutrition. Government data show that a third of children from the wealthiest fifth of India's population are malnourished.
(subscription required) - "Growing Income Inequality in OECD Countries". Journalist's Resource.org. 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - NOVOTNÝ, J. (2007): On the measurement of regional inequality: does spatial dimension of income inequality matter? The Annals of Regional Science, 41, 3, 563–580. http://web.natur.cuni.cz/~pepino/NOVOTNY2007AnnalsofRegionalScience.pdf
- ^ MÉSZÁROS, István (1995). Beyond Capital. London: Merlin Press. ISBN 978-85-7559-068-3.
- ^ Piketty, Thomas, and Emmanuel Saez. INCOME INEQUALITY IN THE UNITED STATES, 1913–1998. Tech. 1st ed. Vol. CXVIII. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 2003. Print.
- "Tackling Ethnic and Regional Inequalities" (PDF). Combating Poverty and Inequality: Structural Change, Social Polics, and Politi. United Nations Research Institute for Social Development. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- ^ U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Highlights of Women’s Earnings in 2009. Report 1025, June 2010.
- Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 8709080, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=8709080instead. - ^ Rawls, John (2005). A Theory of Justice. Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0674017726.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future (p. 34). Norton. Kindle Edition.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future . Norton. Kindle Edition. p. 9.
- Hazlitt, Henry (1988). "Chapter 20: Part 2". Economics in One Lesson. Three Rivers Press. ISBN 978-0-517-54823-3.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Hazlitt, Henry (1988). "Chapter 20: Part 1". Economics in One Lesson. Three Rivers Press. ISBN 978-0-517-54823-3.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future . Norton. Kindle Edition. p. 8.
- Webster (4b): increasing in rate as the base increases (a progressive tax)
- American Heritage (6). Increasing in rate as the taxable amount increases.
- Britannica Concise Encyclopedia: Tax levied at a rate that increases as the quantity subject to taxation increases.
- Princeton University WordNet: (n) progressive tax (any tax in which the rate increases as the amount subject to taxation increases)
- Sommerfeld, Ray M., Silvia A. Madeo, Kenneth E. Anderson, Betty R. Jackson (1992), Concepts of Taxation, Dryden Press: Fort Worth, TX
- Schmitt, John and Ben Zipperer. 2006. "Is the U.S. a Good Model for Reducing Social Exclusion in Europe?" Post-autistic Economics Review 40.
- ^ "Economic Focus:". The Economist. London: The Economist Group. 2008-04-19. p. 81.
- "Are Women Earning More Than Men?". Forbes. May 12, 2006.
- Lukas, Carrie (April 3, 2007). "A Bargain At 77 Cents To a Dollar". The Washington Post. Retrieved May 3, 2010.
- http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/censr-15.pdf
- Women 'earn less than men across the globe' | Vedior – Global Employment News
- ^ Nicola Jones, Rebecca Holmes, Jessica Espey 2008. Gender and the MDGs: A gender lens is vital for pro-poor results. London: Overseas Development Institute
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future (pp. 30–1, 35–6). Norton. Kindle Edition.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future (p. 32). Norton. Kindle Edition.
- Railroad land grants
- General Mining Law of 1872
- General Mining Act of 1872#The Mining Law of 1872
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality, p. 48.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality, p. 42.
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality, p. 44.
- James K. Galbraith, Inequality and Instability: A Study of the World Economy Just before the Great Crisis (New York: Oxford University Press, 2012).
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2012-06-04). The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future, p. 334. Norton. Kindle Edition.
- Bradley, David; Huber, Evelyne; Moller, Stephanie; Nielsen, François; Stephens, John D. (2003). "Distribution and Redistribution in Post-Industrial Democracies" (PDF). World Politics. 55 (2): 193–228. doi:10.1353/wp.2003.0009.
- Huber, Evelyne; Nielsen, François; Pribble, Jenny; Stephens, John D. (2006). "Politics and Inequality in Latin America and the Caribbean". American Sociological Review. 71 (6): 943–963. doi:10.1177/000312240607100604. JSTOR 25472438.
A strong record of democracy and a left-leaning legislative partisan balance are associated with lower levels of inequality.
-
Keller, K.R. (2010). "HOW CAN EDUCATION POLICY IMPROVE INCOME DISTRIBUTION? AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF EDUCATION STAGES AND MEASURES ON INCOME INEQUALITY". The Journal of Developing Areas. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
this study shows that income distribution improves by ensuring that expenditures per primary-school student are adequately kept up with increases in cohort size to prevent education quality from deteriorating.
-
"The impact of economic growth, tax policy and economic freedom on income inequality – Conclusions". Retrieved 2010-05-24.
While some degree of progressive income taxation may be a useful strategy for those who desire increased income equality, broader economic interventionism is not consistent with their desired goal.
-
Duncan, Denvil; Sabirianova Peter, K.S. (2008). "Tax Progressivity and Income Inequality". Andrew Young School of Policy Studies Research Paper Series. papers.ssrn.com: 30. doi:10.2139/ssrn.1260860. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
as taxes become more efficient, via lower progressivity, income inequality tends to increase
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Winner-Take-All Politics by Jacob S. Hacker, Paul Pierson
- García-Peñalosa (2006)
- Gross, D. (2007-06-10). "Income Inequality, Writ Larger". The New York Times. Retrieved 2010-05-23.
the rise of performance-based pay has accounted for 25 percent of the growth in wage inequality among male workers from 1976 to 1993.
- ^ Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, p. 5.
- ^ HAPPINESS: HAS SOCIAL SCIENCE A CLUE? Richard Layard 2003
- ^ More or Less| Branko Milanovic| Finance & Development| September 2011| Vol. 48, No. 3
- Christoffersen, John (October 14, 2013). "Rising inequality 'most important problem,' says Nobel-winning economist". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- Castells-Quintana, David (2012). "Unemployment and long-run economic growth: The role of income inequality and urbanisation" (PDF). Investigaciones Regionales. 12 (24): 153–173. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Statistics and graphs from Wilkinson and Pickett research.
- Sapolsky, Robert (2005). "Sick of Poverty". Scientific American. 293 (6): 92. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1205-92. Retrieved 2009-04-15.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, p. 82.
- (At the same time however, there is a strong connection between average income and health within countries. Example: Comparing average death rates in United States zip code areas organized by average income finds the highest income zip codes average a little over 90 deaths per 10,000, the poorest zip codes a little over 50 deaths and a "strikingly" regular gradient of death rates for income in between. source: Figure 1.4, Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, p. 13, Authors: "What is so striking about Figure 1.4 is how regular the health gradient is right across society". Data from G.D. Smith, J.D. Neaton, D. Wentworth, R. Stamler, J. Stamler, "Socioeconomic differentials in mortality risk among men screened for the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial: 1. White men.", American Journal of Public Health (2008) 98 (4): 486–96)
- Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, pp. 306–9. Figure 2.2 found on p. 20 and this page
- the authors found a Pearson Correlation Coefficient of 0.87 for the index and inequality among 20 developed countries for which data was available. Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, p. 310.
- a coefficient of 0.59 for 40 US states for which data was available (the index for US states did not include a component for mobility in its index). For both populations the statistical significance p-value was >0.01. Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, p. 310.
- compare figures 2.6 and 2.7 in Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level, 2011, pp. 23–4. Data from An overview of child well-being in rich countries The United Nations Children’s Fund, 2007
- The Spirit Level: how 'ideas wreckers' turned book into political punchbag| Robert Booth| The Guardian| 13 August 2010
- Inequality Trust and Political Engagement Eric Uslaner and Mitchell Brown, 2002
- Making Democracy Work: Civic Traditions in Modern Italy (Putnam, Leonardi, and Nanetti, 1993)
- Robert Putnam, Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community 2000
- Robert Putnam, Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community, 2000, pp. 359.
- The Price of Inequality: How Today's Divided Society Endangers Our Future, Stiglitz, J.E., (2012) W.W. Norton & Company, ISBN 978-0393088694
- Income inequality and homicide rates in Canada and The United
- Jerome L Neapolitana, "A comparative analysis of nations with low and high levels of violent crime", Journal of Criminal Justice, Volume 27, Issue 3, May–June 1999, pp. 260.
- political structure, economic inequality,and homicide: a cross-national analysis Deviant Behavior, Volume 20, Issue 1, 1999, pp. 50.
- Bram Lancee and Hermanvande Werfhorst (2011) "Income Inequality and Participation: A Comparison of 24 European Countries" GINI Discussion Paper No. 6 (Amsterdam Centre for Inequality Studies)
- The Equality Trust (2012) "Income Inequality and Participation" Research Update No. 4
- Blanchard and Oswald 2000, 2003
- ^ The Economics of Welfare| Arthur Cecil Pigou
- The Elements of Justice By David Schmidtz (2006)
- Whitfield, John (28 September 2011,). "Libertarians With Antlers". slate.com. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - Theory of Moral Sentiments, Part I, Section III, Chapter II
- Luxury Fever (excerpt)| milkeninstitute.org
- Economist Robert Frank at the Commonwealth Club MPR 06/26/2009, 12:00 p.m.
- Kaldor, Nicoals, 1955, Alternative Theories of Distribution,” Review of Economic Studies, 23(2), 83–100.
- ^ Alesina, Alberto and Dani Rodrik, 1994. "Distributive Politics and Economic Growth," Quarterly Journal of Economics, 109(2), 65–90
- Robert Barro, 2000, “Inequality and Growth in a Panel of Countries,” Journal of Economic Growth, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 5–32; K. Deininger, and L. Squire, 1998, “New Ways of Looking at Old Issues: Inequality and Growth,” Journal of Development Economics, Vol. 57, No. 2, pp. 259–87.
- Kristin Forbes, 2000, “A Reassessment of the Relationship between Inequality and Growth,” American Economic Review, Vol. 90, No. 4, pp. 869–87.
- Pritchett, L., 2000, “Understanding Patterns of Economic Growth,” World Bank Economic Review, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 221–50.
- ^ Andrew Berg and Jonathan D. Ostry, 2011, "Inequality and Unsustainable Growth: Two Sides of the Same Coin?" IMF Staff Discussion Note SDN/11/08, International Monetary Fund
- The Economist, October 13, 2012, Having Your Cake: Less Inequality Does Not Need To Mean Less Efficiency
- New York Times, October 16, 2012, “Income Inequality May Take Toll on Growth”
- New York Times, December 10, 2011, The 1 Percent Club’s Misguided Protectors
- Andrew Berg, Jonathan D. Ostry, and Jeromin Zettelmeyer, 2012, "What Makes Growth Sustained?" Journal of Development Economics, Vol. 98, No. 2, pp. 149–66.
- Andrew Berg, and Jonathan D. Ostry, “Warning! Inequality May be Hazardous to Your Growth.” iMF Direct. 8 April 2011.
- Does More Equality Mean Less Economic Growth?| Lane Kenworthy| December 3, 2007
- Does inequality prevent economic growth?| By Jared Bernstein, On the Economy| 1 October 2012
- Perotti, Roberto, 1996, “Growth, Income Distribution, and Democracy: What the Data Say” Journal of Economic Growth, 1(2), 149–87.
- Galor, Oded and Joseph Zeira, 1993, "Income Distribution and Macroeconomics," Review of Economic Studies, 60(1), 35–52.
- Persson, Torsten and Guido Tabellini, 1994, “Is Inequality Harmful for Growth?” American Economic Review, 84(3), 600–21.
- "Is Inequality Necessary?" by Timothy Noah, The New Republic December 20, 2011
- ^ David T Rodda (1994). Rich Man, Poor Renter: A Study of the Relationship Between the Income Distribution and Low Cost Rental Housing (Thesis). Harvard University. p. 148.
- Vigdor, Jacob (2002). "Does Gentrification Harm the Poor?". Brookings-Wharton Papers on Urban Affairs.
- Janna L. Matlack; Jacob L. Vigdor (2006). Do Rising Tides Lift All Prices? Income Inequality and Housing Affordability (PDF) (Report). Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER). Retrieved 6 June 2012.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)page 1 - (cited in Matlack Do Rising Tides Lift All Prices? Income Inequality and Housing Affordability, 2006)
- Pushed Out: The Hidden Costs of Gentrification: Displacement and Homelessness (PDF) (Report). Institute for Children and Poverty. 2009.
- ^ Milo Vandemoortele 2010. Equity: a key to macroeconomic stability. London: Overseas Development Institute
- New Statesman – NS Essay – 'Accumulation of wealth is unjust where it arises not from hard work and risk-taking enterprise, but from brute luck factors such as returns from property. Inheritance is a form of brute-luck inequality'
- Inequality and Happiness: Are Europeans and Americans Different?
- The relation between economic inequality and political inequality is explained by Robert Alan Dahl in the chapters The Presence of a Market Economy (pp. 63), The Distribution of Political Resources (pp. 84) und Market Capitalism and Human Dispositions (pp. 87) in On Political Equality, 2006, 120 pages, Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-12687-7
- ^ Amartya Sen (1999). "Poverty as Capability Deprivation". Development as Freedom. New York: Anchor Books.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) Cite error: The named reference "sen development as freedom" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Fukuda-Parr, Sakiko. 2003. “The Human Development Paradigm: Operationalizing Sen’s Ideas on Capabilities.” Feminist Economics 9(2/3): 301–17.
- , UNDP (1990) Human Deuelopment Report, Oxford University Press, New York
- Moyes, P. A note on minimally progressive taxation and absolute income inequality Social Choice and Welfare, Volume 5, Numbers 2-3 (1988), 227–234, DOI: 10.1007/BF00735763. Accessed: 19 May 2012.
- Pickett and Wilkinson, The Spirit Level: Why More Equal Societies Almost Always Do Better, 2011
- Duncan, Denvil, Klara Sabirianova Peter (October 2012). "Unequal Inequalities: Do Progressive Taxes Reduce Income Inequality?" (PDF). Institute for the Study of Labor.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Stewart, Alexander J. (2013-09-03). "From extortion to generosity, evolution in the Iterated Prisoner's Dilemma". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (38): 15348. doi:10.1073/pnas.1306246110. Retrieved 21 September 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) (popular treatment in university press release)
General references
- Books
- Wiemer Salverda, Brian Nolan, Timothy M. Smeeding (editors, 2009): The Oxford Handbook of Economic Inequality. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-923137-9
- von Braun, Joachim (2007). Globalization of Food and Agriculture and the Poor. Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Patrick Diamond and Anthony Giddens (2005), The New Egalitarianism, Polity Press
- A.B. Atkinsons and F. Bourguignon (1998), Handbook of Income Distribution, Elsevier
- Peter Lambert (2002). Distribution and Redistribution of Income. Manchester University Press, 3rd edition. ISBN 0-7190-5732-9
- Richard Lynn and Tatu Vanhanen (2002), IQ and the Wealth of Nations, University of Helsinki, Westport, CT: Praeger. ISBN 0-275-97510-X
- Arthur Cecil Pigou. The Economics of Welfare. I.VIII.3.
- Benjamin I. Page and Lawrence R. Jacobs (2009), Class War?: What Americans Really Think about Economic Inequality, University of Chicago Press ISBN 978-0-226-64455-4
- Schmidtz, David (2006). The Elements of Justice. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-53936-6.
- Amartya Sen and James Foster (1997). On Economic Inequality (Radcliffe Lectures). Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-828193-5.
- Richard G. Wilkinson (2005), The Impact of Inequality – how to make sick societies healthier, The New Press, ISBN 1-56584-925-6 (hc.)
- Richard G. Wilkinson and Kate Pickett (2009), The Spirit Level: Why more equal societies almost always do better, Allen Lane, ISBN 978-1-846-14039-6
- García-Peñalosa, Cecilia (2006). "Growth, Income Inequality, and Fiscal Policy: What are the Relevant Tradeoffs?" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-12-14.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - von Mises, Ludwig (1996). "chapter XXXV: The Welfare Principle versus the Market Principle". Human Action: A Treatise on Economics. Foundation for Economic Education. ISBN 1-57246-021-0.
- Séverine Deneulin and Lila Shahani (2009). An Introduction to the Human Development and Capability Approach. Sterling, VA: Earthscan.
- Amartya Sen (1999). Development as Freedom. New York: Anchor Books.
- Martin Gilens. Affluence & Influence: Economic Inequality and Political Power in America. Princeton University Press and the Russell Sage Foundation, 2012.
- Barro, R. 1991. "Economic Growth in a Cross-Section of Countries". Quarterly Journal of Economics 106: 407–43.
- Barro, R. and X. Sala-i-Martin. 1995. Economic Growth. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Dollar, D. and R. Gatti. 1999. Gender Inequality, Income, and Growth: Are Good Times good for Women? Washington DC: The World Bank.
- Lagerlöf, N. 1999. ‘'Gender Inequality, Fertility, and Growth’'. Department of Economics, University of Sydney
- Seguino, S. 1998. Gender Inequality and Economic Growth: A Cross-Country Analysis. University of Vermont.
- Solow, R. 1956. "A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth". Quarterly Journal of Economics 70: 65–94
- Papers
- Kaldor, N., 1955, "Alternative Theories of Distribution", Review of Economic Studies, 23(2), 83–100.
- Galor, O., and J., Zeira, 1993, "Income Distribution and Macroeconomics," Review of Economic Studies, 60(1), 35–52.
- Maavak, Mathew. "Class Warfare, Anarchy and the Future Society", Journal of Futures Studies, December 2012, 17(2): 15–36
- Alesina, A.; Di Tella, Rafael; MacCulloch, Robert (2004). "Inequality and Happiness: Are Americans and Europeans Different?". Journal of Public Economics. 88 (9–10): 2009–2042. doi:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2003.07.006..
- Andersen, Robert and Tina Fetner. 2008. "Economic Inequality and Intolerance: Attitudes toward Homosexuality in 35 Democracies", American Journal of Political Science, 52 (4): 942–58.
- Barro, Robert (2000). "Inequality and Growth in a Panel of Countries" (PDF). Journal of Economic Growth. 7 (1)..
- Ravallion, Martin (2005). World Bank, 5 May, Policy Research Working Paper no. WPS 3579, A poverty-inequality trade-off?
- Sala-Martin, Xavier (2006). "The World Distribution of Income: Falling Poverty and... Convergence, Period," Quarterly Journal of Economics, 121(2), May, pp. 351–397.
- Uslaner, Eric.; Mitchell, Brown. (2002). "Inequality, Trust, and Civic Engagement" (PDF).
- Fukuda-Parr, Sakiko. 2003. “The Human Development Paradigm: Operationalizing Sen’s Ideas on Capabilities.” Feminist Economics 9(2/3): 301–17.
- Kenworthy, Lane. "Rising Inequality, Public Policy, and America's Poor." Challenge 53.6 (2010): 93–109.
- Sawhill, Isabel. "Do We Face a Permanently Divided Society?" The Economics of Inequality, Poverty, and Discrimination in the 21st Century Ed. Robert S. Rycroft. The University of Mary Washington, 2012.
- Smeeding, Timothy and Thompson, Jeffrey. "Recent Trends in Income Inequality". Who Loses in the Downturn? Economic Crisis, Employment and Income Distribution (Research in Labor Economics, 32), Ed. Herwig Immervoll, Andreas Peichl, Konstantinos Tatsiramos. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2011. 1–50.
- Smeeding, Timothy and Thompson, Jeffrey. "Inequality in the Great Recession – The Case of the United States". FRDB International Income Inequality Project (July 2011). Working paper.
- Voitchovsky, Sarah. "The effects of inequality on growth: perspectives from the theoretical literature." Working paper.
External links
- Levy, Frank (2008). "Distribution of Income". In David R. Henderson (ed.) (ed.). Concise Encyclopedia of Economics (2nd ed.). Indianapolis: Library of Economics and Liberty. ISBN 978-0865976658. OCLC 237794267.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|editor=has generic name (help) - A portal dedicated to the topic of economic inequality
- Small Inequality Measures Calculus (and On-Line Calculator)
- The UC Atlas of Global Inequality explores some aspects of inequality using online, downloadable maps and graphics.
- Population Health Forum website – group seeking to improve health by addressing inequality.
- Russell Sage Foundation. "Social Inequality". Working Papers. Archived from the original (Web page) on May 29, 2006. Retrieved March 2, 2006.
- Leigh, A. and Jencks, C. (2005). "Inequality and Health: Long-Run Evidence from a Panel of Countries" (PDF). Retrieved November 30, 2005.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Clarkwest, A and Jencks, C. (2003). "Inequality and Mortality in Rich Countries: Who Owns the Null Hypothesis?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 28, 2006. Retrieved November 30, 2005.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - The Inequality Predicament United Nations Report on the World Social Situation 2005
- Two Americas: One Rich, One Poor? Understanding Income Inequality in the United States
- Has U.S. Income Inequality Really Increased? Accessed 2007-06-11.
- Measuring Trends in Leisure: The Allocation of Time Over Five Decades studies the trade-offs between earning income and enjoying leisure
- Data from the Inequality Survey
- Decreasing Inequality Under Latin America's "Social Democratic" and "Populist" Governments: Is the Difference Real? from the Center for Economic and Policy Research
- Wealth and Poverty: Center for Global Studies at the University of Illinois