| Revision as of 18:48, 6 January 2016 view sourceRapido (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,154 edits "the tenets of those operations still live in the hearts of some politicians" and the example is original research and not in source.← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:06, 6 January 2016 view source Poeticbent (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers29,717 edits it's all there unless you really don't want to see it per WP:NOTGETTINGITNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{about|the controversy over the use of the term| |
{{about|the controversy over the use of the term|real camps|German camps in occupied Poland during World War II}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=May 2014}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=May 2014}} | ||
| ] were located on the prewar territories of many European countries including ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]; nevertheless, ] of ] were built by Nazi Germany only in ] for logistical reasons]] | ] were located on the prewar territories of many European countries including ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]; nevertheless, ] of ] were built by Nazi Germany only in ] for logistical reasons]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| After the fall of Nazism, the wartime alliances ended and the Cold War began. Numerous war criminals, protected by chancellor ],<ref name="Simon Wiesenthal Center">{{cite web |url=http://www.wiesenthal.com/site/pp.asp?c=lsKWLbPJLnF&b=4441293#.UokrCZHKJZY |title=About Simon Wiesenthal |year=2013 |website=Simon Wiesenthal Center |accessdate=17 November 2013 |at=Section 11 }}</ref><ref name="Hartmann">{{cite web |url=http://www.sopos.org/aufsaetze/4bdfd55e42f57/1.phtml |title=Der Alibiprozeß |publisher=Ossietzky 9/2010 |work=Den Aufsatz kommentieren |year=2010 |accessdate=19 November 2013 |last=Hartmann |first= Ralph |language=German}}</ref> joined domestic counter-intelligence in order to spy on the Soviet agents within the American-occupied zone. The ] turned to ] previously in the ] for assistance.<ref name="Eichner/Schramm">Klaus Eichner, Gotthold Schramm, et al (2007). ''Angriff und Abwehr: die deutschen Geheimdienste nach 1945'', Berlin: Edition Ost (Reinhard Gehlen) p. 42. {{OCLC|91785168}}.</ref> The West German intelligence formed ] ({{lang-de|Dienststelle 114}}) within the ]; headed by Alfred Benzinger (a Nazi ''Abwehrpolizei''), who in 1956 launched a coordinated action to move the blame away from the war criminals under various investigations. Benzinger adopted the ] "Polish death camps" in the mid 1960s in order to suggest, contrarily to the facts, that Poles, not Germans, were responsible for the mass genocide during World War II.<ref name="Wręcz">{{cite web |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20120425051227/http://wprostp.pl/artykul/polskie-obozy-koncentracyjne%E2%80%9D-wymyslily-niemieckie-tajne-sluzby |title="Polskie obozy koncentracyjne" wymyśliły niemieckie tajne służby ("Polish death camps" invented by German secret service) |publisher=Wręcz Przeciwnie (]) |year=2011 |author=W.P.}}</ref> | After the fall of Nazism, the wartime alliances ended and the Cold War began. Numerous war criminals, protected by chancellor ],<ref name="Simon Wiesenthal Center">{{cite web |url=http://www.wiesenthal.com/site/pp.asp?c=lsKWLbPJLnF&b=4441293#.UokrCZHKJZY |title=About Simon Wiesenthal |year=2013 |website=Simon Wiesenthal Center |accessdate=17 November 2013 |at=Section 11 }}</ref><ref name="Hartmann">{{cite web |url=http://www.sopos.org/aufsaetze/4bdfd55e42f57/1.phtml |title=Der Alibiprozeß |publisher=Ossietzky 9/2010 |work=Den Aufsatz kommentieren |year=2010 |accessdate=19 November 2013 |last=Hartmann |first= Ralph |language=German}}</ref> joined domestic counter-intelligence in order to spy on the Soviet agents within the American-occupied zone. The ] turned to ] previously in the ] for assistance.<ref name="Eichner/Schramm">Klaus Eichner, Gotthold Schramm, et al (2007). ''Angriff und Abwehr: die deutschen Geheimdienste nach 1945'', Berlin: Edition Ost (Reinhard Gehlen) p. 42. {{OCLC|91785168}}.</ref> The West German intelligence formed ] ({{lang-de|Dienststelle 114}}) within the ]; headed by Alfred Benzinger (a Nazi ''Abwehrpolizei''), who in 1956 launched a coordinated action to move the blame away from the war criminals under various investigations. Benzinger adopted the ] "Polish death camps" in the mid 1960s in order to suggest, contrarily to the facts, that Poles, not Germans, were responsible for the mass genocide during World War II.<ref name="Wręcz">{{cite web |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20120425051227/http://wprostp.pl/artykul/polskie-obozy-koncentracyjne%E2%80%9D-wymyslily-niemieckie-tajne-sluzby |title="Polskie obozy koncentracyjne" wymyśliły niemieckie tajne służby ("Polish death camps" invented by German secret service) |publisher=Wręcz Przeciwnie (]) |year=2011 |author=W.P.}}</ref> | ||
| At the height of the Cold War, the clandestine Agency 114 had been merged into the ], the successor of the Gehlen Org. It was located in Karlsruhe and the Zimmerle & Co. which served as the front, ostensibly specializing in roller blinds. Aside from Soviet counter-intelligence activities, the agency also began monitoring domestic leftists and pacifists. Alfred Benzinger, a well-experienced former officer of the secret Nazi military police '']'' remained in charge. Among the former Nazis who also worked in the agency were: Konrad Fiebig, and Walter Kurreck.<ref name="Eichner/Schramm"/> It was Benzinger who coordinated the action to propagate a deceitful term "Polish Concentration Camps" in popular media.<ref name="Wręcz"/> | At the height of the Cold War, the clandestine Agency 114 had been merged into the ], the successor of the Gehlen Org. It was located in Karlsruhe and the Zimmerle & Co. which served as the front, ostensibly specializing in roller blinds. Aside from Soviet counter-intelligence activities, the agency also began monitoring domestic leftists and pacifists. Alfred Benzinger, a well-experienced former officer of the secret Nazi military police '']'' remained in charge. Among the former Nazis who also worked in the agency were: Konrad Fiebig, and Walter Kurreck.<ref name="Eichner/Schramm"/> It was Benzinger who coordinated the action to propagate a deceitful term "Polish Concentration Camps" in popular media.<ref name="Wręcz"/> Notably, the tenets of those operations attempting to make Poles, not Germans, responsible for the genocide, still live in the hearts of some politicians including ], the recipient of the ] Award,<ref>John Mann (7 May 2009). "British MP, John Mann, accepts Jan Karski Award". American Jewish Committee. Retrieved 2010-02-05. Speech transcript.</ref> who in his interview for the Jewish Chronicle.com proclaimed, without mentioning ] by the Germans in Poland, that Poles were the perpetrators of the Holocaust, and that claiming victimhood by Poland is a "revisionist angle" similar to that of Lithuania and Latvia.<ref name="thejc.com">{{cite web |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100727145846/http://www.thejc.com/comment/comment/21392/europe-must-focus-baltic-hate |title=Europe must focus on Baltic hate |work=The Jewish Chronicle |date=29 October 2009 |accessdate=22 August 2014 |author=John Mann}}</ref> | ||
| ==Use and reactions== | ==Use and reactions== | ||
Revision as of 20:06, 6 January 2016
This article is about the controversy over the use of the term. For real camps, see German camps in occupied Poland during World War II.



Polish death camp and Polish concentration camp are terms that have been used in international media, and by public figures, in reference to concentration camps built and run by Nazi Germany in the General Government and other parts of occupied Poland during the Holocaust. The use of these terms has been described as insulting by the Polish foreign minister Adam Daniel Rotfeld (himself a Jewish Holocaust survivor) in 2005, who also alleged that – intentionally or unintentionally – it shifted the responsibility for the construction or operation of the camps from the German to the Polish people. The use of these terms, explicitly mentioning "Poland" or "Polish", has been discouraged by the Polish and Israeli governments, Polish diaspora organizations around the world, and Jewish organizations such as the American Jewish Committee.
Historical context
Main articles: List of Nazi concentration camps, German camps in occupied Poland during World War II, The Holocaust in Poland, and Occupation of Poland (1939–1945)After the German invasion of Poland, unlike in most European countries occupied by Nazi Germany, where the Germans sought and found true collaborators among the locals, in occupied Poland there was no official collaboration either at the political or at the economic level. Poland never officially surrendered to the Germans and instead, maintained a government-in-exile along with its own military force abroad fighting against them. Historians generally agree that there was little collaboration with the Nazis by individual Poles in comparison with other German-occupied countries.
The prewar Polish government and administration were able to partially evacuate to France and United Kingdom in 1939 to continue their struggle against the Nazis from the West, with a formal Polish Army quickly rebuilt. The Polish government based in Paris (until 1940) and in London thereafter, was represented in the occupied territories by a vast structure of the Polish Underground State, and its military arm, Armia Krajowa. The AK formed the major part of the Polish resistance movement, which was the largest resistance movement in occupied Europe, engaged in fighting the occupiers.
A large part of the former territory of the invaded Second Polish Republic was ostensibly annexed by the Third Reich and another part used to create the so-called General Government with the total German administration. The General Government had no international recognition of any kind. The territories administered by the Nazis were never in whole nor in part intended as a Polish state within a German-dominated Europe either. The ethnic Poles were not allowed to become Reich citizens. The Nazi claim that the Polish state ceased to exist was blatantly false, because Poland's legislative or executive agencies along with Poland's constitution kept functioning in form and fact through occupation until the end of the war.
Operations to whitewash German responsibility for WWII
After the fall of Nazism, the wartime alliances ended and the Cold War began. Numerous war criminals, protected by chancellor Konrad Adenauer, joined domestic counter-intelligence in order to spy on the Soviet agents within the American-occupied zone. The United States Army turned to Reinhard Gehlen previously in the Wehrmacht for assistance. The West German intelligence formed Agency 114 (Template:Lang-de) within the Gehlen Organization; headed by Alfred Benzinger (a Nazi Abwehrpolizei), who in 1956 launched a coordinated action to move the blame away from the war criminals under various investigations. Benzinger adopted the loaded phrase "Polish death camps" in the mid 1960s in order to suggest, contrarily to the facts, that Poles, not Germans, were responsible for the mass genocide during World War II.
At the height of the Cold War, the clandestine Agency 114 had been merged into the BND, the successor of the Gehlen Org. It was located in Karlsruhe and the Zimmerle & Co. which served as the front, ostensibly specializing in roller blinds. Aside from Soviet counter-intelligence activities, the agency also began monitoring domestic leftists and pacifists. Alfred Benzinger, a well-experienced former officer of the secret Nazi military police Geheime Feldpolizei remained in charge. Among the former Nazis who also worked in the agency were: Konrad Fiebig, and Walter Kurreck. It was Benzinger who coordinated the action to propagate a deceitful term "Polish Concentration Camps" in popular media. Notably, the tenets of those operations attempting to make Poles, not Germans, responsible for the genocide, still live in the hearts of some politicians including John Mann, the recipient of the Jan Karski Award, who in his interview for the Jewish Chronicle.com proclaimed, without mentioning the 3 million Polish Jews murdered by the Germans in Poland, that Poles were the perpetrators of the Holocaust, and that claiming victimhood by Poland is a "revisionist angle" similar to that of Lithuania and Latvia.
Use and reactions

Before the end of World War II, an early appearance in print of the term "Polish death camp" as a geographic reference was in the 1944 article published in Collier's and written by the Polish resistance fighter Jan Karski, titled "Polish Death Camp." Similar early postwar uses of this double entendre can be found in the 1945 archives of several magazines including Contemporary Jewish Record, The Jewish Veteran, and the The Palestine Yearbook and Israeli Annual, as well as in the 1947 work Beyond the Last Path by Hungarian-born Jew and Belgian resistance fighter Eugene Weinstock who referred to Auschwitz as "the Polish death camp".
Over time, many non-Polish media and notable figures have been known to make references to the German-run extermination program in Nazi-occupied Poland by the use of phrases such as the "Polish death/concentration/extermination camp", "Polish ghetto", "Polish Holocaust", "Nazi Poland", and so on, instead of Nazi Germany's WWII ghetto, German Holocaust of the Jews, Nazi Germany, etc.
A common explanation for the use of the phrase "Polish death camp" is that the infamous Nazi death camps (i.e. the extermination camps of the Schutzstaffel) including Auschwitz, Treblinka, Majdanek, Chełmno, Belzec and Sobibor were built in Poland occupied at that particular time. However, two of the mentioned death camps (Auschwitz and Chełmno) were situated in lands annexed by Germany (Germany proper by Germany's own account) and also, most Nazi concentration camps were located in the territory of Nazi Germany anyway. A complete list, drawn up in 1967 by the German Ministry of Justice, names about 1,200 camps and subcamps in numerous countries occupied by Nazi Germany.
Opponents of the use of these terms argue that they are inaccurate, as they may imply that the camps—located in Nazi-occupied Poland—might have been a responsibility of the Poles (i.e., Polish), when in fact they were designed, constructed and run by Nazi Germany and used to exterminate millions of Poles alongside Polish Jews, as well as Jews transported by the Nazis from across Europe.
The use of terms of this kind, explicitly mentioning "Poland" or "Polish", has been discouraged by the Polish government and the Polish diaspora organizations around the world since 1989. Specifically the Polish Ministry of Foreign Affairs monitors and catalogs the use of the term and is involved in the actions asking for correction and apology. In 2005, the Polish Foreign Minister Adam Daniel Rotfeld suggested that there are instances of "bad will, saying that under the pretext that "it's only a geographic reference", attempts are made to distort history and conceal the truth." Adding adjective "Polish" when referring to concentration camps or ghettos located in occupied Poland, or to the world Holocaust in general, can suggest, often unintentionally and always counter factually, that the atrocities in question were perpetrated by the Poles, or that the Poles were active participants in the Nazi rule of Poland during World War II.
In 2008, due to the continued usage of the term Polish in regards to atrocities committed and camps built and operated by the German state under Nazi leadership, the chairman of the Polish Institute of National Remembrance (IPN) issued a letter to local administrations with a call to add German before Nazi in all monuments and tables that commemorate the victims of Nazi Germany. As stated by the IPN official, while in Poland 'Nazi' is definitely connected to 'German' this is not the case everywhere in the world, and the change will help avoid any misinterpretation that the responsibility for the crimes against humanity committed in war-torn Poland wasn't specifically German. At the time several places of martyrology underwent renovations, and the new plaques were to clearly indicate the nationality of the people responsible for atrocities. Additionally, IPN requested to better document and commemorate the crimes perpertated by the Soviet Union as well.
The American Jewish Committee has also rejected the usage, stating that:
Auschwitz-Birkenau and the other death camps, including Belzec, Chelmno, Majdanek, Sobibor and Treblinka, were conceived, built and operated by Nazi Germany and its allies. The camps were located in German-occupied Poland, the European country with by far the largest Jewish population, but they were most emphatically not "Polish camps". This is not a mere semantic matter. Historical integrity and accuracy hang in the balance.
The government of Israel has also deprecated the usage of this phrase.
Concerns about the use of the term Polish death camp led the Polish government to request that UNESCO change the official name of Auschwitz from "Auschwitz Concentration Camp" to "former Nazi German concentration camp Auschwitz-Birkenau" in order to make clearer that the concentration camp was built and operated by Nazi Germany. On 28 June 2007 at its meeting in Christchurch, New Zealand, the World Heritage Committee of UNESCO changed the name of the camp to "Auschwitz Birkenau. German Nazi Concentration and Extermination Camp (1940–1945)." Previously, some media, including Der Spiegel in Germany, had called the camp "Polish". The New York Times regularly refers to Auschwitz as Polish rather than German.
An example of the controversy occurred when an April 30, 2004 CTV News report made reference to "the Polish camp in Treblinka". The Polish embassy in Canada lodged a complaint with CTV. Robert Hurst of CTV, however, argued that the term "Polish" was used throughout North America in a geographical sense, and declined to issue a correction. The Polish Ambassador to Ottawa then complained to the National Specialty Services Panel of the Canadian Broadcast Standards Council. The Council did not accept Hurst's argument and ruled that the word "'Polish'—similarly to such adjectives as 'English', 'French' and 'German'—had connotations that clearly extended beyond geographic context. Its use with reference to Nazi extermination camps was misleading and improper".
Polish newspaper Rzeczpospolita has criticized international media outlets, including Haaretz from Israel, as "holocaust deniers" over usage of the term. However, all foreign media articles so criticized by Rzeczpospolita (as of November 2008) make clear that the perpetrators were German, and none claim Poles built the camps.
The incorrect phrase Polish concentration camps is used in some school textbooks outside Poland to refer to the Nazi German concentration camps on occupied Polish territory.
On December 23, 2009, writing in The Guardian, Timothy Garton Ash said:
Watching a German television news report on the trial of John Demjanjuk a few weeks ago, I was amazed to hear the announcer describe him as a guard in "the Polish extermination camp Sobibor". What times are these, when one of the main German TV channels thinks it can describe Nazi camps as "Polish"? In my experience, the automatic equation of Poland with Catholicism, nationalism and antisemitism – and thence a slide to guilt by association with the Holocaust – is still widespread. This collective stereotyping does no justice to the historical record.
In 2009 Zbigniew Osewski, grandson of a Stutthof prisoner, announced he was suing Axel Springer AG for calling Majdanek a 'former Polish concentration camp' in article from November 2008 published in the German newspaper Die Welt. The case started in 2012. In 2010, The Polish-American Kosciuszko Foundation launched a petition demanding that four major U.S. news organizations endorse the use of the term "German concentration camps in Nazi-occupied Poland".
The Globe and Mail reported on 23 September 2011 about "Polish concentration camps". Canadian MP Ted Opitz and Minister of Citizenship Jason Kenney supported Polish protests.
In May 2012, U.S. President Barack Obama referred to "a Polish death camp" while posthumously awarding the Presidential Medal of Freedom to Jan Karski. After complaints from Poles, including Polish Foreign Minister Radosław Sikorski and Alex Storozynski, president of the Kosciuszko Foundation, a representative of the Obama administration said the President misspoke and "was referring to Nazi death camps in German-occupied Poland."
In 2013, Karol Tendera who was a prisoner at Auschwitz-Birkenau, and is the secretary of the association of former prisoners of German concentration camps, has sued the German television network ZDF, demanding formal apology and 50,000 PLN to be donated for charitable causes for the use of the expression "Polish concentration camps".
-
 Poland was invaded in 1939 from both sides and divided between Nazi Germany and the USSR
Poland was invaded in 1939 from both sides and divided between Nazi Germany and the USSR
-
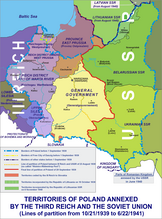 Occupied Poland, 1939–41
Occupied Poland, 1939–41
-
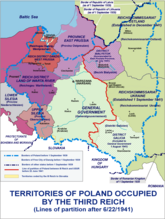 Occupied Poland, 1944, after Operation Barbarossa
Occupied Poland, 1944, after Operation Barbarossa
See also
- Anti-Polish sentiment
- Nazi crimes against the Polish nation
- Polenlager
- Polish League Against Defamation
- Bereza Kartuska prison
References
- Carla Tonini, The Polish underground press and the issue of collaboration with the Nazi occupiers, 1939-1944, European Review of History: Revue Europeenne d'Histoire, Volume 15, Issue 2 April 2008, pages 193-205.
- Klaus-Peter Friedrich. Collaboration in a "Land without a Quisling": Patterns of Cooperation with the Nazi German Occupation Regime in Poland during World War II. Slavic Review, Vol. 64, No. 4, (Winter, 2005), pp. 711-746.
- Adam Galamaga (21 May 2011). Great Britain and the Holocaust: Poland’s Role in Revealing the News. GRIN Verlag. p. 15. ISBN 978-3-640-92005-1. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- Carla Tonini, The Polish underground press and the issue of collaboration with the Nazi occupiers, 1939-1944, European Review of History: Revue Europeenne d'Histoire, Volume 15, Issue 2 April 2008 , pages 193 - 205
- Klaus-Peter Friedrich. Collaboration in a "Land without a Quisling": Patterns of Cooperation with the Nazi German Occupation Regime in Poland during World War II. Slavic Review, Vol. 64, No. 4, (Winter, 2005), pp. 711-746. JSTOR
- John Connelly, Why the Poles Collaborated so Little: And Why That Is No Reason for Nationalist Hubris, Slavic Review, Vol. 64, No. 4 (Winter, 2005), pp. 771-781, JSTOR
- Steven J. Zaloga; Richard Hook (21 January 1982). The Polish Army 1939-45. Osprey Publishing. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-85045-417-8. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- Józef Garliński (April 1975). "The Polish Underground State 1939–1945". Journal of Contemporary History. 10 (2). Sage Publications, Ltd.: 219–259. doi:10.1177/002200947501000202. JSTOR 260146.
- Norman Davies (28 February 2005). God's Playground: 1795 to the present. Columbia University Press. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-231-12819-3. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- Majer, Diemut (1981). Non-Germans under the Third Reich: The Nazi Judicial and Administrative System in Germany and Occupied Eastern Europe with Special Regard to Occupied Poland. Harold Bold Verlag, p. 256 (236–237 reprint, Johns Hopkins University Press 2003). OCLC 45821002
- "About Simon Wiesenthal". Simon Wiesenthal Center. 2013. Section 11. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- Hartmann, Ralph (2010). "Der Alibiprozeß". Den Aufsatz kommentieren (in German). Ossietzky 9/2010. Retrieved 19 November 2013.
- ^ Klaus Eichner, Gotthold Schramm, et al (2007). Angriff und Abwehr: die deutschen Geheimdienste nach 1945, Berlin: Edition Ost (Reinhard Gehlen) p. 42. OCLC 91785168.
- ^ W.P. (2011). ""Polskie obozy koncentracyjne" wymyśliły niemieckie tajne służby ("Polish death camps" invented by German secret service)". Wręcz Przeciwnie (Internet Archive).
- John Mann (7 May 2009). "British MP, John Mann, accepts Jan Karski Award". American Jewish Committee. Retrieved 2010-02-05. Speech transcript.
- John Mann (29 October 2009). "Europe must focus on Baltic hate". The Jewish Chronicle. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- Karski, Jan (1944). "Polish Death Camp." Collier's, 14 October, pp. 18–19, 60–61.
- Contemporary Jewish Record (American Jewish Committee), 1945, vol. 8, p. 69. Quote: "Most of the 27,000 Jews of Thrace ... were deported to Polish death camps."
- The Jewish Veteran (Jewish War Veterans of the United States of America) 1945, vol. 14, no. 12. Quote: "2,000 Greek Jews repatriated from Polish death camps."
- The Palestine Yearbook and Israeli Annual (Zionist Organization of America) 1945, p. 337. Quote: "3,000,000 were foreign Jews brought to Polish death camps."
- Weinstock, Eugene. 1947. Beyond the Last Path. New York: Boni & Gaer, p. 43.
- Polish Embassy in Spain protests against "Nazi Poland"
- A. H. Foxman: "Poland And The Death Camps: Setting The Record Straight". The Jewish Week, June 12, 2012.
- ^ Piotr Zychowicz, Interview with the Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Poland, Prof. Adam Daniel Rotfeld Rzeczpospolita daily, 25 January 2005.
- ^ Canadian CTV Television censured
- List of concentration camps and their outposts Template:De icon
- Piotrowski, Tadeusz (2005). "Project InPosterum: Poland WWII Casualties". Archived from the original on 18 April 2007. Retrieved 15 March 2007.
- Łuczak, Czesław (1994). "Szanse i trudności bilansu demograficznego Polski w latach 1939–1945". Dzieje Najnowsze (1994/2).
- Interwencje. MSZ
- ^ Government information on the Polish foreign policy presented by the Minister of Foreign Affairs, Prof. Adam Daniel Rotfeld, at the session of the Sejm on 21st January 2005
- ^ Template:Pl icon Akcja IPN: Mordowali "Niemcy", nie "naziści" (IPN initiative: "the Nazi Germans" committed Holocaust, not "the Nazis.") Fakty. Interia.pl, December 9, 2008.
- American Jewish Committee. (2005-01-30). "Statement on Poland and the Auschwitz Commemoration." Press release.
- David Peleg. "Two nations fed with the same suffering". Against "Polish camps", The "Rzeczpospolita" daily campaign. Rzeczpospolita.pl. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- Tran, Mark. The Guardian. (2007-06-27). "Poles claim victory in battle to rename Auschwitz."
- Auschwitz Might Get Name Change, The Jewish Journal, 27 April 2006.
- Yad Vashem for renaming Auschwitz, The Jerusalem Post, 12 May 2006.
- "UNESCO approves Poland's request to rename Auschwitz". The Europe Channel. 27 June 2007. Archived from the original on 8 July 2007.
- UNESCO World Heritage Committee. (2007-06-28). World Heritage Committee approves Auschwitz name change". Press release. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
- Nicholas Watt (1 April 2006). "Auschwitz may be renamed to reinforce link with Nazi era". The Guardian. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- BBC News. (2006-03-31). "Poland seeks Auschwitz renaming."
- Mark Tran (27 June 2007). "Poles claim victory in battle to rename Auschwitz". The Guardian. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- Frank Milewski (1 January 2010). "Will the N.Y. Times ever get it straight". Canada Free Press.
- "Polskie czy niemieckie obozy zagłady?" (in Polish). Państwowe Muzeum Auschwitz-Birkenau w Oświęcimiu. 23 July 2004.
- Thomas Urban: "Populisten lassen googeln" Template:De icon]
- Thenews.pl :: News from Poland (soft redirect) http://www.thenews.pl/international/artykul122671_poland-in-foreign-eyes.html
- "As at Auschwitz, the gates of hell are built and torn down by human hearts". The Guardian. London. 23 December 2009. Archived from the original on 26 December 2009. Retrieved 18 April 2010.
- Marcin Wawrzyńczak, "'Polish Camps' in Polish Court," Gazeta Wyborcza, 2009-08-14, at http://wyborcza.pl/1,76842,6928930,_Polish_Camps__in_Polish_Court.html
- Ruszył proces wobec "Die Welt" o "polski obóz koncentracyjny"
- Petition against "Polish concentration camps," Warsaw Business Journal, November 3, 2010, at http://www.wbj.pl/article-51918-petition-against-polish-concentration-camps.html?typ=ise
- Petition against "Polish death camps" The Kosciuszko Foundation
- "Canadian MPs defend Poland over 'Polish concentration camp' slur". Rzeczpospolita, Openparliament.ca. Polskie Radio S.A. 10 June 2011. Retrieved 27 July 2012.
- "White House: Obama misspoke by referring to 'Polish death camp' while honoring Polish war hero". The Washington Post. 29 May 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- Why the words ‘Polish death camps’ cut so deep
- "Były więzień Auschwitz skarży ZDF za "polskie obozy"". interia.pl. 22 July 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
External links
- Truth About Camps. A page dedicated to the "German death camps and concentration camps in Nazi occupied Poland 1939-45" at the Institute of National Remembrance
- Polish minister's speeches on the phenomenon
- Appeal against "Polish death camps" in Rzeczpospolita
- Polish Ministry of Foreign Affairs - Against "Polish Camps"
- Article on Irena Sendler but discusses issue of calling German camps as Polish
- Article which discusses irresponsible accusation against Poland including reference to German death camps as "Polish" death camps.
- Template:Pl icon Report of the Polish ministry on foreign usage of "Polish death camp" argument