| Revision as of 20:26, 23 March 2016 editLiliCharlie (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users4,522 edits Reverted to revision 709429028 by 87.219.19.130 (talk): Against Maunal of Style and wrong tone. (TW)← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:45, 24 March 2016 edit undo209.66.197.28 (talk) correct tone, check the dictionaries. second tone not first.Next edit → | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
| | piccap = "Wuxi", as written in Chinese calligraphy | | piccap = "Wuxi", as written in Chinese calligraphy | ||
| | picsize = 117px | | picsize = 117px | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | t = 無錫 | | t = 無錫 | ||
| | |
| s = 无锡 | ||
| |bpmf =ㄨˊ ㄒㄧˊ | |||
| ⚫ | | w = Wu<sup>2</sup>-hsi<sup> |
||
| ⚫ | | p =wú xí | ||
| ⚫ | | w = Wu<sup>2</sup>-hsi<sup>2</sup> | ||
| | mi = {{IPAc-cmn|wu|2|x|i|1}} | | mi = {{IPAc-cmn|wu|2|x|i|1}} | ||
| | gr = Wushi | | gr = Wushi | ||
| Line 97: | Line 98: | ||
| | order = st | | order = st | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Wuxi''' ({{zh| |
'''Wuxi''' ({{zh|t=無錫|s=无锡|Hanyu Pinyin wú xí Tongyong Pinyin wú sí Wade–Giles Wu2-hsi2 IPA Gwoyeu Romatzyh Wushi Bopomofo ㄨˊ ㄒㄧˊ) is an old city in southern ] province, ]. | ||
| Split in half by ], Wuxi borders ] to the west and ] to the east. The ] lies between the northern half of Wuxi and ], while the southern half of the city borders the province of ]. Wuxi is also famous for being one of the birthplaces of China's modern industry and commerce, as well as the hometown of many important businessmen who have played essential roles in building commerce in ] since the early 20th century. | Split in half by ], Wuxi borders ] to the west and ] to the east. The ] lies between the northern half of Wuxi and ], while the southern half of the city borders the province of ]. Wuxi is also famous for being one of the birthplaces of China's modern industry and commerce, as well as the hometown of many important businessmen who have played essential roles in building commerce in ] since the early 20th century. | ||
Revision as of 21:45, 24 March 2016
"Wu Xi" redirects here. For the footballer, see Wu Xi (footballer). This article is about the city of Wuxi (无锡) in Jiangsu. For the county of Wuxi (巫溪) in Chongqing, see Wuxi County. Prefecture-level city in Jiangsu, China| Wuxi 无锡市 | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
 Clockwise from top: Wuxi National Software Park, Grand Buddha at Ling Shan, Kuatang Bridge, Downtown Wuxi, Nianqu Pagoda at the Plum Garden Clockwise from top: Wuxi National Software Park, Grand Buddha at Ling Shan, Kuatang Bridge, Downtown Wuxi, Nianqu Pagoda at the Plum Garden | |
| Official seal of WuxiSeal | |
| Motto(s): "Wuxi is full of warmth and water" | |
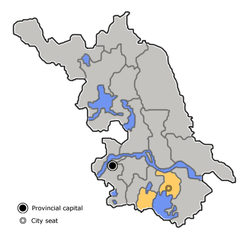 Location of Wuxi City jurisdiction in Jiangsu Location of Wuxi City jurisdiction in Jiangsu | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Jiangsu |
| County-level divisions | 9 |
| Township-level divisions | 73 |
| Government | |
| • CPC Municipal Secretary | Li Xiaomin (李小敏) |
| • Mayor | Wang Quan (汪泉) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,787.61 km (1,848.51 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 6,372,624 |
| • Density | 1,300/km (3,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | Urban center: 214000 Other Area: 214200, 214400 |
| Area code | 510 |
| License plate prefixes | 苏B |
| GDP (2012) | CNY 756.815 billion (USD 119.89 billion) |
| - per capita | CNY 117,400 (USD 18,700) |
| HDI | 0.909 - very high |
| Local Dialect | Wu: Wuxi dialect |
| Website | www |
| Wuxi | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File:Wuxi in Chinese.png"Wuxi", as written in Chinese calligraphy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 无锡 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 無錫 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wuxi ({{zh|t=無錫|s=无锡|Hanyu Pinyin wú xí Tongyong Pinyin wú sí Wade–Giles Wu2-hsi2 IPA Gwoyeu Romatzyh Wushi Bopomofo ㄨˊ ㄒㄧˊ) is an old city in southern Jiangsu province, China.
Split in half by Lake Tai, Wuxi borders Changzhou to the west and Suzhou to the east. The Yangtze River lies between the northern half of Wuxi and Taizhou, while the southern half of the city borders the province of Zhejiang. Wuxi is also famous for being one of the birthplaces of China's modern industry and commerce, as well as the hometown of many important businessmen who have played essential roles in building commerce in Shanghai since the early 20th century.
Name
The modern name consists of the Chinese characters 无 ("without, lacking") and 锡 ("tin") and simply means "No tin". According to a traditional story, during the warring states period, soldiers were stationed in Wuxi on Xishan ("tin hill"). While burying a pot to prepare food, a soldier found a stone plaque engraved with the words "If there is tin there is an army, conflict under heaven. If there is no tin (wuxi), there is peace, quiet under heaven." According to the story, Wuxi's name comes from this inscription.
However, some scholars believe the name may have originally been "吳墟" ("Ruins of Wu") from Meicun's role as the original capital of the region or from a Chinese transcription of an indigenous Baiyue name honoring a bird deity. Others believe that the name could be derived from an ancient pronunciation of the name Fu Xi.
Former spellings include Wu-shi, Wushi, and Wu-hsi. In Shanghainese, it is pronounced [ɦuɕiɪʔ].
History
Zhou Dynasty
According to traditional Chinese historians, two Zhou princes, Taibo and Zhongyong, founded the first Chinese state in the area of Wuxi around the 11th century BC. This state of Wu (吳) had its first capital at Meili, generally thought to be the village of Meicun in Wuxi (although some records indicate a location closer to Wu's later capitals around Suzhou). Taibo and Zhongyong helped develop Wu's agriculture and waterways and the area soon flourished. Taibo died without an heir, and Zhongyong succeeded him as King of Wu. His descendants were later officially enfeoffed by the Zhou court as vassals before declaring themselves full kings again during the Spring and Autumn Period.
A shrine to Taibo was set up in today's Meicun. Although the original wood structure was eventually destroyed in war, it has been rebuilt several times. A stone carved with sayings by Confucius can still be seen at the modern Taibo Shrine, whose architecture dates mostly to the Qing dynasty.
Spring and Autumn Period and Warring States Period
The State of Wu became one of the strongest kingdoms during the Spring and Autumn Period. Sunzi (Suntzu), who wrote the famous "the Art of War" came to Wu and helped the king with his military affairs. Wu was considered one of the seven strongest kingdoms during this period. Some of Sunzi's descendants still live in Sunxiang in Wuxi near the Plum Garden. However, Wu was later defeated by the State of Yue, today's Zhejiang and Fujian, which in turn was overthrown by the State of Chu and incorporated into Chu during the Warring States period.
Qin and Han dynasty
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The cultural and economic center of the "Wu" area shifted to Suzhou after the reign of the first Qin dynasty emperor, Qin Shi Huang, who united China; Wuxi at that time belonged to Suzhou. During the Han dynasty, Wuxi was set up as a county by emperor Han Wudi. Historic records show that tin was discovered during the early Han era, leading to conflicts in the area. Soon, however, the tin was depleted. This was once believed to be the origin of the name Wuxi, meaning "no tin." The name was changed to Youxi (有錫), meaning "having tin", during the Wang Mang conflicts period because Wang wanted to change the name.
Six dynasties, Tang and Song dynasties
Agriculture and the silk industry flourished in Wuxi and the town became a transportation center under the early Tang Dynasty after the construction of the Grand Canal. Although Suzhou became the center of the Wu area, Wuxi was also important in the county of Wu.
Yuan, Ming and Qing dynasties
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (December 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
During the Ming dynasty, Wuxi became a prosperous cultural center. During the late Ming and early Qing periods, Wuxi was a center for political discussion and public opinion. Agriculture, with rice and fish were major products in the Qing period.
During the Taiping Rebellion, Wuxi was devastated by the war's destruction, like other parts of the lower Yangtze valley. Warfare disrupted planting in the region.
During the late 19th century, Wuxi became a center of the textile industry in China and one of the four most important rice markets nationwide. By 1878, Wuxi was the leading silk-producing county in Jiangsu, outstripping even Suzhou, the traditional center of that industry. In the late 19th century, Wuxi was also the regional center for the waterborne transport of grain and a major commercial center.
20th century
Between 1900 and 1940, Wuxi was considered one of the most important counties in China. In dramatist Cao Yu's well-known drama "Thunderstorm", Wuxi was mentioned several times with the comment "Wuxi is a good place". After the China was set up by the communists in 1949, Wuxi continued to grow in importance, with an increases in textile production along with both light and heavy industry. This city was considered the second most important city in Jiangsu Province after the capital Nanjing. However, its developmental model has been criticized for the environmental deterioration caused. New strategies are now under consideration to ensure its sustainable development.
Geography

The city plan, as is typical of many older Chinese cities, is of a central city with a roughly circular plan, crisscrossed with older canals, the main canal still seeing heavy barge traffic.
Wuxi itself is on an alluvial plain of deep sedimentary deposits cut between limestone foothills, making it one of the sources for "scholar's rocks", the intricately weathered stones which were used as devices for contemplation.
Climate
Wuxi is hot and humid in summer and chilly and damp in winter, with an average annual temperature of 18 °C (64 °F) and very occasional snow. Because of its proximity to the East China Sea, it has a monsoon season and receives 100 centimetres (39 inches) of rain annually.
| Climate data for Wuxi | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7.4 (45.3) |
9.1 (48.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
20.0 (68.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
28.6 (83.5) |
31.8 (89.3) |
30.9 (87.6) |
27.0 (80.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
16.0 (60.8) |
9.9 (49.8) |
20.1 (68.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.3) |
1.8 (35.2) |
5.7 (42.3) |
11.1 (52.0) |
16.5 (61.7) |
21.3 (70.3) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
19.6 (67.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
7.3 (45.1) |
1.7 (35.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 47.3 (1.86) |
49.7 (1.96) |
82.5 (3.25) |
62.4 (2.46) |
79.8 (3.14) |
138.5 (5.45) |
121.8 (4.80) |
99.1 (3.90) |
53.7 (2.11) |
41.2 (1.62) |
39.5 (1.56) |
28.1 (1.11) |
843.6 (33.22) |
| Source: MSN Weather | |||||||||||||
Demographics
According to the 2010 Census, the prefecture-level of Wuxi has a population of 6,372,624, an increase of 1,192,777 from the 2000 census, giving it an annual population growth of 20.9% for the period 2000-2010.
Administration
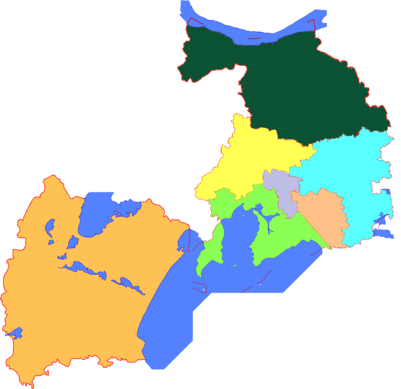
See also: List of administrative divisions of JiangsuThe prefecture-level city of Wuxi administers seven county-level divisions, including 5 districts and 2 county-level cities. The information here presented uses the metric system and data from 2010 Census.
These districts are sub-divided into 73 township-level divisions, including 59 towns and 24 subdistricts.
| Map | Subdivision | Hanzi | Pinyin | Population (2010) | Area (km) | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 1
Xinwu
Xishan
Huishan
Binhu
Jiangyin (city)
Yixing (city)
1. Liangxi
1
Xinwu
Xishan
Huishan
Binhu
Jiangyin (city)
Yixing (city)
1. Liangxi
| ||||||
| City Proper | ||||||
| Liangxi District | 梁溪区 | Liángxī Qū | 836,198 | 72 | 11,613 | |
| Suburban | ||||||
| Binhu District | 滨湖区 | Bīnhú Qū | 688,965 | 567 | 1,215 | |
| Xinwu District | 新吴区 | Xīnwú Qū | 536,807 | 219 | 2,451 | |
| Wuxi New Area | 无锡新区 | Wúxī Xīn Qū | see Xinwu District | |||
| Xishan District | 锡山区 | Xīshān Qū | 681,300 | 396 | 1,720 | |
| Huishan District | 惠山区 | Huìshān Qū | 691,059 | 327 | 1,215 | |
| Satellite cities (County-level cities) | ||||||
| Jiangyin | 江阴市 | Jiāngyīn Shì | 1,594,829 | 987 | 1,616 | |
| Yixing | 宜兴市 | Yíxīng Shì | 1,235,476 | 2,177 | 568 | |
| Total | 6,372,624 | 4,787 | 1,300 | |||
| Defunct: Chong'an District, Nanchang District, & Beitang District | ||||||
Economy
Currently Wuxi is designated as an investment grade city, and has two large industrial parks devoted to new industries. . While being the current manufacturing centers on textiles, there are projects to move to electric motor manufacturing and MRP software development. Wuxi is the solar technology hub in China as two major photovoltaic companies are based in the city. They are Suntech Power and Jetion Holdings Ltd which were listed on overseas stock exchanges.
In 2008 new energy industries were worth 37.8 Billion RMB, with the solar photovoltaic industry accounting for 30.2 Billion RMB of the total. The GDP per capita was ¥107,400 (US$17,050) in 2011, ranked first in Jiangsu, ahead of Nanjing and Suzhou.
Bicycle manufacturing for international brands is another industry, including bicycle assembly and bicycle component manufacturing. One of the two Chinese factories of Taiwan-based brake manufacturer Tektro is in Wuxi.
The center of the city is filled with modern high rise buildings and the market is being redeveloped in a postmodern style. Hynix completed a new chip plant in Wuxi.
Industry
- Wuxi New District
Since it was established in 1992, Wuxi New District (WND) has evolved to be one of the major industrial parks in China. A wide variety of components, sub-systems and original equipments are made in WND. Approximately 1200 enterprises have been registered in WND by the end of 2008. Wuxi New District provides strong support for international manufacturing operations. The Zone focuses on formation of the five pillar industries of electronic information, precision machinery and mechanical and electrical integration, bio-pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals and new materials.

- Wuxi Export Processing Zone
Established in 1992, Wuxi Export Processing Zone is located in Wuxi New District with a planned area of 2.98 km. The encouraged industries include electronic information, optical-mechanical-electronic-integration, precision machinery, and new materials. It is situated near to Wuxi Airport and Changzhou Port.
Culture


As an important city for the "Wu" area, its culture bears distinctive characteristics, which can be identified in its dialect, architecture, waterway transportation and various art types.
It was one of the art and cultural centers of "Jiangnan", with several famous Chinese authors claiming Wuxi as their home town. Among them, most recently, Qian Zhongshu, author of Fortress Besieged, a comedy of manners set in China in the 1930s. Wuxi was the birthplace of the famous Chinese (later American) artist Chen Chi (1912—2005), in whose honor a museum has been erected in the city.
One of the handicraft specialties of Wuxi is the production of Huishan clay figurines. and clay tea pots.
In modern times Wuxi has produced a number of cultural figures such as Hua Yanjun (1893–1950) also known as "Blind Abing" (瞎子阿炳), famous for his erhu and pipa music. Another famous musician is Liu Tianhua, who was the first to compile folk music using staff.
Transport
Railways
Wuxi is situated on the Shanghai–Nanjing Intercity High-Speed Railway, linking it directly with the provincial capital of Nanjing (1.5 hours) and China's economic hub, Shanghai (45 minutes train-ride) and the fifth biggest economic hub and tourist destination Suzhou (24 minutes). K-series trains all stop at Wuxi.
Air transport
Sunan Shuofang International Airport (IATA: WUX) opened in 2004 and serves the cities of Wuxi and Suzhou. It is situated 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) from the city centre and has direct flights to Beijing, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, Taipei, Singapore, and Osaka.
Expressways and highways
Expressways:
- Shanghai-Nanjing Expressway (Hu Ning Gao Su 沪宁高速)
- Wuxi-Yixing Expressway (Xi Yi Gao Su 锡宜高速)
National highways:
Provincial roads:
Metro
The Wuxi government has planned a network of 8 metro lines. Line 1 and line 2 of the Wuxi Metro began operation in 2014, on July 1 and December 28 respectively.
Tourism

Wuxi is a major tourist area of the Lower Yangtze Delta. It has both natural and man-made places of interest.
The city was built on the shore of Lake Tai with the lake providing a rich tourism resource. Noted spots include Yuantouzhu (the Islet of Turtlehead) and Taihu Xiandao (Islands of the Deities). Completed in 2008, this 115-metre (377 ft) tall Ferris wheel takes 18 minutes to complete one revolution. Passengers can enjoy the scenery of Lake Tai and the city center. At night, lighting effects are switched on around the wheel.
Literally "Tin Mountain" and "Kindhearted Mountain", Mount Xi and Mount Hui are two small hills located in the western part of the city. The classic royal Ji-chang-yuan Gardens are located at the foot of the hill as well as the Tianxia di er quan (天下第二泉), literally "the second spring under heaven"). Xi Shan is also a name for a tourist area located in Suzhou. Because two separate Chinese characters are both pronounced "Xi": one stands for "West", the other (in this case) is for the metal material tin.
The Grand Canal passes through the city. There are two canals: one is the old canal that has been there since it was excavated, the other is the new canal created after 1949.
Wuxi has many private gardens or parks built by learned scholars and rich people in the past. Among these, Li Yuan, Mei Yuan are good examples that have been well preserved. Xihui Gongyuan (Xihui Park), located at the foot of Xi Shan also houses historical relics, notably Jichang Garden. It is about 1,770 kilometres (5,810,000 ft) in length.
Located south of the Long Mountain, near Wuxi's Mashan Town, the 88 metres (289 ft) tall Grand Buddha at Ling Shan is one of the largest Buddha statues in China, and the ninth tallest statue worldwide.
Built during 16th - 19th century A.D., the town is located in the north-west part of Wuxi on the west bank of the Grand Canal and at the foot of Mount Hui. The town's buildings are mainly family ancestral halls.
Film and television District
Located in the western part of Wuxi, the district consists of Wuxi Three State City Park, Tang City, and Shuihu City. Established in 1987, it was the first Movie and TV film studio in China. The CCTV Wuxi Film/TV Studio used for the shooting of The Three Kingdoms and Water Margins is classified as a AAAAA scenic area by the China National Tourism Administration.
Shan Juan Cave
Located in Yixing (part of Wuxi), Shan Juan Cave is a 4-star scenic zone. The Chinese Romeo and Juliet, Liang Shanbo and Zhu Yingtai were said to study behind the cave.
Chen Chi Museum
This museum honoring the famous 20th century painter Chen Chi includes a small collection of his works.
Other historical places
The former Residence of Xue Fucheng, Former Residence of A Bin, Former Residence of Xu Xiake, Site of Luotuo Dun, Taibo Temple and Tomb, and Donglin Shuyuan. These historical places are protected by the city government.
Sports and stadiums
Wuxi has two stadiums. The old stadium is in the southern part of the city and has yet to reopen. The other is Wuxi New Stadium, which consists of a swimming stadium, soccer stadium and other facilities. It is located in the south-west part of the city, near Lake Tai. Major League Baseball has also had its main Chinese Development Center in Wuxi China since 2008. At the Development Center, Major League Baseball scouts and recruits the best players in all of China to play at the DC in the hopes that they will eventually play professional baseball in America.


Education
Universities and colleges
- Jiangnan University (江南大学)
- Wuxi Fisheries College,NAU (南京农业大学无锡渔业学院)
- Wuxi Professional College of Science and Technology (无锡科技职业技术学院)
- Wuxi Institute of Technology (无锡职业技术学院)
- Wuxi Institute of Commerce (无锡商业职业技术学院)
- Wuxi City College of Vocational Technology (无锡城市职业技术学院)
- Wuxi South Ocean College (无锡南洋职业技术学院)
- Jiangsu College of Information Technology (江苏信息职业技术学院)
- Wuxi Teachers' College (无锡高等师范学校)
- Jiangyin Polytechnic College (江阴职业技术学院)
- Wuxi Higher Health Vocational Technology School (无锡卫生高等职业技术学校,原无锡卫生学校)
High schools
- Wuxi No.1 High School (无锡市第一中学)
- Wuxi Big Bridge Experimental School (无锡市大桥实验中学)
- Wuxi Furen High School (No.2 Senior High School)] (无锡市辅仁中学/无锡市第二中学)
- Wuxi No.3 Senior High School (无锡市第三高级中学)
- Wuxi Shiei High School (无锡市市北高级中学)
- Wuxi Qingshan High School (无锡市青山高级中学)
- Jiangsu Tianyi High School (江苏省天一中学)
- Jiangsu Xishan Senior High School (江苏省锡山高级中学)
- Wuxi NO.1 Girls High School (无锡市第一女子中学,原东林中学)
- Jiangsu Meicun High School (江苏省梅村高级中学)
- Wuxi NO.6 High School(无锡市第六高级中学)
Notable people
- Gu Kaizhi (later half of the fourth century), a painter.
- Li Sheng (772–846), poet, who lived and was buried in Wuxi.
- Gu Xiancheng (顧憲成, 1550–1612), scholar and politician, especially well known in the "Dong Lin Movement".
- Xu Xiake (1587–1641), Ming Dynasty traveller and writer.
- Hua Hengfang (1833–1902), mathematics in late Qing Dynasty who did studies in various area of science and technology. He participated in designing the first streamer and the first steamboat in China.
- Xue Fucheng (薛福成, 1838–1894), well-known ideologist, diplomat and one of leading exponents for national bourgeoisie reform in the late Qing Dynasty.
- Rong Desheng (荣德生, 1875–1952), the largest national capitalist in the Republic of China era, most noted for his contribution to the Chinese textile industry.
- Cai Pei (1884–1960) a diplomat and politician in the Republic of China.
- Abing (1893–1950) folk musician, best known for his work "Er Quan Ying Yue" (moon reflected on Er stream) for the erhu.
- Xu Beihong (1895–1953), painter, most noted for his paintings of horses.
- Qian Zhongshu (钱锺书, 1910–1998), writer, best known for his comedy of manners Fortress Besieged.
- Chen Chi (1912–2005), internationally famous painter.
- Rong Yiren (1916–2005), Rong Desheng's son, the powerful "Red Capitalist", the capitalism-communist, Vice-President of the People's Republic of China from 1993 to 1998.
- Lu Yaochen (吕尧臣, born 1941), Chinese art master, famous Zisha (purple clay teapot) master, born in Yi Xing.
- Ding Junhui (born 1987), Snooker player.
- Zhou Yongkang (born 1942), senior Communist Party of China leader.
- Jimmy Wang Yu (born 1943), Chinese actor who appeared in the Shaw Brother's One Armed Swordsman. His movie, the Chinese Boxer (1969) is credited with being the first Hong Kong martial arts film that kick started the unarmed combat genre that took Asia by storm in the 1970s.
- Marie Lu (Born 1984)
Chinese American Author Notable for writing the Legend Series.
Gallery
-
 Liyuan Gardens
Liyuan Gardens
-
 Yuantouzhu peninsula, Sanshan Islands and Lake Tai, Wuxi
Yuantouzhu peninsula, Sanshan Islands and Lake Tai, Wuxi
-
 West part of Wuxi from temple of Mt. Qingshan
West part of Wuxi from temple of Mt. Qingshan
-
 Ling Shan giant buddha, Wuxi
Ling Shan giant buddha, Wuxi
-
 "The Light of Lihu lake", Wuxi
"The Light of Lihu lake", Wuxi
See also
- List of twin towns and sister cities in China
- Jiangnan
- List of cities in the People's Republic of China by population
References
- ^ City of Wuxi (2013-09-26). "【2012】无锡市国民经济和社会发展概况".
- "Origin of the name 'Wuxi'" ("“无锡”地名的由来"). Template:Zh icon
- "而今现在". Template:Zh icon
- "无锡市". Template:Zh icon
- "Wuxi" ("无锡"). Template:Zh icon
- "考“无锡”地名的由来". Template:Zh icon
- "无锡地名典故". Template:Zh icon
- 曾国藩(清):〈江西牙厘请照旧经收折〉,收于《曾文正公全集》(上海世界书局,1936年)奏疏卷20,页534-636。Template:Zh icon
- "MSN Weather". June 2011. Retrieved April 2, 2009.
- Template:Zh icon Compilation by LianXin website. Data from the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China
- China Business News http://thechinaperspective.com/articles/wuxicitywantsroleingreenenergy6391/index.html
- Hynix completes new chip plant in China
- RightSite.asia | Wuxi New District
- RightSite.asia | Wuxi Export Processing Zone
- synyan (2008-10-19). 梁溪漫志(07):蠡湖城太湖之星 (in Chinese). Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- "AAAAA Scenic Areas". China National Tourism Administration. 16 November 2008. Retrieved 9 April 2011.
External links
- Government website of Wuxi (available in Chinese, Japanese and English)
| Jiangsu topics | |
|---|---|
| Nanjing (capital) | |
| General | |
| Geography | |
| Education | |
| Culture |
|
| Visitor attractions | |
| Yangtze Delta metropolitan regions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Economic Zone | ||
| Shanghai Metropolitan Area |  | |
| Jiangsu Yangtze Metropolitan Belt | ||
| Zhejiang Hangzhou Greater Bay Area | ||
| Anhui | ||
| Metropolitan cities of China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major regions and cities of China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National megalopolises |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Administrative divisions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capitals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||