| Revision as of 04:45, 18 May 2021 editTol (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors28,863 editsm Rollback edit(s) by HistoricalNameisPersianSea (talk): Unexplained content removal (RW 16.1)Tags: Removed redirect Rollback← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 21:23, 24 December 2024 edit undoMaxeto0910 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users93,004 edits →Environment and wildlife: period (only) after sentenceTag: Visual edit | ||
| (390 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{ |
{{Short description|Marginal sea of the northern Indian Ocean}} | ||
| {{Infobox body of water | {{Infobox body of water | ||
| | name = Arabian Sea | | name = Arabian Sea | ||
| | native_name = |
| native_name = {{native name|ar| بَحرُ ٱلْعَرَبْ}} | ||
| | |
| pushpin_map = | ||
| | pushpin_map_alt = | |||
| | image = Arabian Sea - n22e70.jpg | |||
| | alt = center | |||
| | caption = | |||
| | pushpin_map = | |||
| | pushpin_map_alt = | |||
| | pushpin_map_caption = | | pushpin_map_caption = | ||
| | image_bathymetry = Arabian Sea |
| image_bathymetry = Arabian Sea in its region.svg | ||
| | alt_bathymetry = | | alt_bathymetry = | ||
| | caption_bathymetry = | | caption_bathymetry = The Arabian Sea as defined by the ] | ||
| | location = ], ] and ] | | location = ], ] and ] | ||
| | coordinates = {{coord|14|N|65|E|type:waterbody_scale:10000000|display=inline,title}} | | coordinates = {{coord|14|N|65|E|type:waterbody_scale:10000000|display=inline,title}} | ||
| | type = ] | | type = ] | ||
| | part_of = ] | | part_of = ] | ||
| | inflow = | | inflow = | ||
| | rivers = | | rivers = | ||
| | outflow = | | outflow = | ||
| | catchment = | | catchment = | ||
| | basin_countries = |
| basin_countries = India<br>Iran<br>Maldives<br>Oman<br>Pakistan<br>Seychelles<br>Somalia<br>Sri Lanka<br>Yemen | ||
| | agency = | | agency = | ||
| | designation = | | designation = | ||
| | length = | | length = | ||
| | width = {{convert|2400|km|mi|abbr=on}} | | width = {{convert|2400|km|mi|abbr=on}} | ||
| | area = {{convert|3862000|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} (3,600,000 to 4,600,000 km2 in various sources) | | area = {{convert|3862000|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} (3,600,000 to 4,600,000 km2 in various sources) | ||
| | depth = | | depth = | ||
| | max-depth = {{convert|4652|m|ft|abbr=on}} | | max-depth = {{convert|4652|m|ft|abbr=on}} | ||
| | volume = | | volume = | ||
| | residence_time = | | residence_time = | ||
| | salinity = | | salinity = | ||
| | shore = | | shore = | ||
| | elevation = | | elevation = | ||
| | frozen = | | frozen = | ||
| | islands = ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | | islands = ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | ||
| | sections = | | sections = | ||
| | islands_category = | | islands_category = | ||
| | trenches = | | trenches = | ||
| | benches = | | benches = | ||
| | cities = | | cities = | ||
| | website = | | website = | ||
| | reference = | | reference = | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ] | |||
| The '''Arabian Sea''' ({{ |
The '''Arabian Sea''' ({{langx|ar| بَحرُ ٱلْعَرَبْ|baḥr al-ʿarab}})<ref>{{Cite web|title=Arabian Sea|url=https://metadata.un.org/thesaurus/1000357?lang=en|access-date=28 December 2023|website=UNBIS Thesaurus}}</ref> is a region of ] in the northern ], bounded on the west by the ], ] and ], on the northwest by ] and ], on the north by ], on the east by ], and on the southeast by the ]<ref>Banse, Karl, and Charles R. McClain. "Winter blooms of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea as observed by the Coastal Zone Color Scanner." Marine Ecology Progress Series (1986): 201-211.</ref> and the ], on the southwest by ].<ref>Pham, J. Peter. "Putting Somali piracy in context." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 28.3 (2010): 325-341.</ref> Its total area is {{convert|3,862,000|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} and its maximum depth is {{convert|5395|m|ft|abbr=off|sp=us}}. The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the ] through the strait of ], and the ] is in the northwest, connecting it to the ]. | ||
| The Arabian Sea has been crossed by many important marine trade routes since the 3rd or 2nd millennium BCE. Major seaports include ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], | |||
| ] and ] in India, the ], ], and the ] in Pakistan, ] in Iran and the ] in ], ]. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include ] (]), ] (Oman), ] (India) and ] (Pakistan). | |||
| There are about 10 ancient maps from Greeks, which named the Mokran Sea and Persian Gulf together as the Pars Sea. But after Arabs raid to Iran, and because Iranian have lost their previous political powers, many changes have been made in geographical names of Iran’s Sea.<ref></ref> | |||
| ==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| The Arabian Sea's surface area is about {{convert|3862000|km2|sqmi|-1|abbr=on}}.<ref name="Britannica">, Encyclopædia Britannica</ref> The maximum width of the sea is approximately {{convert|2400|km|mi|-1|abbr=on}}, and its maximum depth is {{convert| |
The Arabian Sea's surface area is about {{convert|3862000|km2|sqmi|-1|abbr=on}}.<ref name="Britannica">, Encyclopædia Britannica</ref> The maximum width of the sea is approximately {{convert|2400|km|mi|-1|abbr=on}}, and its maximum depth is {{convert|5395|m|ft|0}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=NOAA Bathymetric Data Viewer |url=https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/maps/bathymetry/ |publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration}}</ref> The biggest river flowing into the sea is the ]. | ||
| The Arabian Sea has two important branches — the Gulf of Aden in the southwest, connecting with the Red Sea through the strait of ]; and the Gulf of Oman to the northwest, connecting with the Persian Gulf. There are also the gulfs of ] and ] on the ]. | |||
| The Arabian Sea has two important branches: the Gulf of Aden in the southwest, connecting with the Red Sea through the strait of ]; and the Gulf of Oman to the northwest, connecting with the Persian Gulf. There are also the gulfs of ] and ] on the ]. | |||
| The Arabian Sea has been crossed by many important marine trade routes since the 3rd or 2nd millennium BCE. Major seaports include ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] in India, the ], ], and the ] in Pakistan, ] in Iran and the ] in ], ]. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include ] (]), ] (Oman), ] (India) and ] (Pakistan). | |||
| The countries with coastlines on the Arabian Sea are Yemen, Oman, Pakistan, Iran, India and the ].<ref name="Britannica"/> | The countries with coastlines on the Arabian Sea are Yemen, Oman, Pakistan, Iran, India and the ].<ref name="Britannica"/> | ||
| ===Limits=== | ===Limits=== | ||
| The ] defines the limits of the Arabian Sea as follows:<ref>{{cite web |url=https://iho.int/uploads/user/pubs/standards/s-23/S-23_Ed3_1953_EN.pdf |title=Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition |year=1953 |publisher=International Hydrographic Organization |access-date=28 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171207191813/https://www.iho.int/iho_pubs/standard/S-23/S-23_Ed3_1953_EN.pdf |archive-date=7 December 2017 }}</ref> | The ] defines the limits of the Arabian Sea as follows:<ref>{{cite web |url=https://iho.int/uploads/user/pubs/standards/s-23/S-23_Ed3_1953_EN.pdf |title=Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition |year=1953 |publisher=International Hydrographic Organization |access-date=28 December 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171207191813/https://www.iho.int/iho_pubs/standard/S-23/S-23_Ed3_1953_EN.pdf |archive-date=7 December 2017 |pages=20–21}}</ref> | ||
| *On the west: the eastern limit of the Gulf of Aden. | *On the west: the eastern limit of the Gulf of Aden. | ||
| Line 68: | Line 58: | ||
| *On the east: the western limit of the Laccadive Sea a line running from ] on the west coast of India ({{coord|14|48|N|74|07|E}}) to ] ({{coord|13|42|N|72|10|E}}) and thence down the west side of the ] and Maldive archipelagos to the most southerly point of ] in the Maldives. | *On the east: the western limit of the Laccadive Sea a line running from ] on the west coast of India ({{coord|14|48|N|74|07|E}}) to ] ({{coord|13|42|N|72|10|E}}) and thence down the west side of the ] and Maldive archipelagos to the most southerly point of ] in the Maldives. | ||
| ===Hydrography=== | |||
| ==Border and Basin countries== | |||
| The ] in 1959 was among the first to perform hydrographic surveys of the Arabian Sea. Significant bathymetric surveys were also conducted by the ] during the 1960s.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hall |first1=John K. |last2=Levenson |first2=Shahar |title=Compilation of a 100m bathymetric grid for the Arabian Plate; Red Sea, Arabian and Oman Seas and Persian Gulf |journal=U.S. HYDRO 2017 Conference |date=March 20, 2017 }}</ref> | |||
| Border and Basin countries:<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/iran/|title=Middle East :: Iran — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency|website=www.cia.gov}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.wildlifeofpakistan.com/IntroductiontoPakistan/coastlineofPakistan.htm|title=Introduction to Pakistan: Section 5: Coastline|website=www.wildlifeofpakistan.com}}</ref> | |||
| ====Hydrographic features==== | |||
| Significant features in the northern Arabian Sea include the ], the second largest fan system in the world. The De Covilhao Trough, named after the 15th century ] explorer ], reaches depths of {{convert|4400|m|ft|0}} and separates the Indus Fan region from the Oman Abyssal Plain, which eventually leads to the ]. | |||
| The southern limits are dominated by the ], a deep basin reaching depths over {{convert|4200|m|ft|0}}. The northern sections of the ] flank the southern edge of the Arabian Basin. | |||
| The deepest parts of the Arabian Sea are in the Alula-Fartak Trough on the western edge of the Arabian Sea off the Gulf of Aden. The trough, reaching depths over {{convert|5360|m|ft|0}}, traverses the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea. The deepest known point is in the Arabian Sea limits at a depth of {{convert|5395|m|ft|0}}. Other significant deep points are part of the Arabian Basin, which include a {{convert|5358|m|ft|0}} deep point off the northern limit of Calrsberg Ridge.<ref>{{cite web |title=NOAA Bathymetric Data Viewer |url=https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/maps/bathymetry/ |publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration}}</ref> | |||
| ====Seamounts==== | |||
| Prominent ] off the Indian west coast include Raman Seamount named after ], Panikkar Seamount, named after ], and the Wadia ], named after ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Wadia Guyot |url=https://www.marineregions.org/gazetteer.php?p=details&id=5802 |website=Marine Regions Gazetteer |access-date=14 September 2024}}</ref> | |||
| Sind'Bad Seamount, named after the fictional explorer ], Zheng He Seamount, and the Mount Error Guyot are some notable sea mounts in western Arabian Sea.<ref>{{cite web |title=Sind'Bad Seamount |url=https://www.marineregions.org/gazetteer.php?p=details&id=5795 |website=Marine Regions Gazetteer}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Mount Error Guyot |url=https://www.marineregions.org/gazetteer.php?p=details&id=5790 |website=Marine Regions Gazetteer |access-date=14 September 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ==Border and basin countries== | |||
| Border and basin countries:<ref>{{Cite CIA World Factbook|country=Iran}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.wildlifeofpakistan.com/IntroductiontoPakistan/coastlineofPakistan.htm|title=Introduction to Pakistan: Section 5: Coastline|website=www.wildlifeofpakistan.com|access-date=2020-08-28|archive-date=2020-06-26|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200626173333/http://www.wildlifeofpakistan.com/IntroductiontoPakistan/coastlineofPakistan.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| #{{IND}} - 2,500 km coastline | #{{IND}} - 2,500 km coastline | ||
| #{{PAK}} - 1,050 km coastline | #{{PAK}} - 1,050 km coastline | ||
| Line 77: | Line 82: | ||
| #{{YEM}} | #{{YEM}} | ||
| #{{SOM}} | #{{SOM}} | ||
| About 70 percent of coastline and 90 percent of population of Arabian Sea area is not Arab. | |||
| <gallery mode="packed"> | |||
| File:Bandra Sea Link aerial.jpg|right|Arabian Sea above Bombay/Mumbai | |||
| File:Arabian Sea - October 2012.jpg|right|Arabian Sea seen from space | |||
| File:Arabian Sea in Karachi.jpg|right|Arabian Sea in Karachi, Pakistan | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==Alternative names== | ==Alternative names== | ||
| {{Expert needed|geography|talk=Alternative_names|reason=This article possibly contains ] of material and claims which does not ] relate to the topic|date=April 2023}} | |||
| The Arabian Sea historically and geographically has been referred to with many different names by ], ], European geographers and travelers, including : | |||
| The Arabian Sea historically and geographically has been referred to with different names by ] and European geographers and travelers, including ], Indian Sea, ],<ref name=Kamat>{{cite web|url=http://www.kamat.com/indica/geography/arabian_sea.htm|title=Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea|work=kamat.com}}</ref> Erythraean, Persian Sea in para No 34-35 of the Voyage.<ref name=Periplus>{{cite web|url=http://depts.washington.edu/silkroad/texts/periplus/periplus.html|title=The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea|work=washington.edu}}</ref> In Indian folklore, it is referred to as Darya, Sindhu Sagar, Arab Samudra.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.kamat.com/indica/geography/arabian_sea.htm|title=Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea|website=www.kamat.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://depts.washington.edu/silkroad/texts/periplus/periplus.html|title=The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea|website=depts.washington.edu}}</ref><ref name="auto">{{Cite web |url=http://www.scribd.com/doc/8583367/The-Periplus-of-the-Erythraean-Sea |title=The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea |access-date=2012-04-03 |archive-date=2013-12-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131202223335/http://www.scribd.com/doc/8583367/The-Periplus-of-the-Erythraean-Sea |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| # ] | |||
| Indian Sea, ]u Sagar,<ref name=Kamat>{{cite web|url=http://www.kamat.com/indica/geography/arabian_sea.htm|title=Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea|work=kamat.com}}</ref> Darya, and Arab Samudra,<ref name=Kamat /> Erythraean Sea,<ref name=Periplus>{{cite web|url=http://depts.washington.edu/silkroad/texts/periplus/periplus.html|title=The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea|work=washington.edu}}</ref> Sindh Sea, and Akhzar Sea, In Indian folklore,it is referred to as Dariya, and Arab Samudra,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.kamat.com/indica/geography/arabian_sea.htm|title=Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea|website=www.kamat.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://depts.washington.edu/silkroad/texts/periplus/periplus.html|title=The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea|website=depts.washington.edu}}</ref><ref name="auto">{{Cite web |url=http://www.scribd.com/doc/8583367/The-Periplus-of-the-Erythraean-Sea |title=Archived copy |access-date=2012-04-03 |archive-date=2013-12-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131202223335/http://www.scribd.com/doc/8583367/The-Periplus-of-the-Erythraean-Sea |url-status=dead }}</ref> ], .<ref>http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یا دریای عرب </ref> in Turkish language they call arabinan sea as Oman sea, this name was used by most of the ottoman geographer such as ] and ] in the Tuḥfat al-kibār fī asfār al-Bihār'' ({{lang|ar| أسفار البحار}}) ('A Gift to the Great concerning Naval Expeditions') (1656) –''The History of the Maritime Wars of the Turks''{{sfn|Mitchell|1831|p=}} (1831) English translation by James Mitchell.<ref> in the MuslimHeritage.com</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131014092439/http://www.muslimheritage.com/topics/default.cfm?ArticleID=658 |date=2013-10-14 }} in the MuslimHeritage.com</ref> refered as oman sea and also persian sea and some other ] maps were using Bahre Ajam (persian sea). ] and some of the geographers of ] were using the word Bahre Fars (persian sea) to mention the current body of water in the north of ]. | |||
| <ref>http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یا دریای عرب </ref> ] | |||
| Arab geographers, sailors and nomads used to call this sea by different names, including the Akhdar (Green) Sea, Bahre Fars (Persian Sea), the Ocean Sea, the Hindu sea, the Makran Sea, the sea of Oman; among them ], ], ] and ]. They wrote: "The green sea and Indian sea and Persian sea are all one sea and in this sea there are strange creatures." in Iran and Turkey people call it Oman sea.<ref name=MFA>{{cite web|url=https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536034|title=Ministry of MoFA Iran: Introducing a Book and Atlas|work=mfa.gov.ir}}</ref> | |||
| ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] had mentioned the sea as Persian sea and sea of Mokran.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://parssea.org/?p=298 |title= Documents on the Persian Gulf's name: the eternal heritage of ancient time Author:Ajam, Muḥammad|year=2010 |publisher=Parssea Organization |access-date=7 February 2010 }}</ref> some of the midival map including the map by ], 1693 had mentioned the Persian sea and also Makran.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://fa.wikipedia.org/search/?title=%D8%AF%D8%B1%DB%8C%D8%A7%DB%8C_%D8%B9%D8%B1%D8%A8&oldid=29950720|title=دریای عرب|date=September 14, 2020|via=Misplaced Pages}}</ref> Cornelius Le Brun's Year 1718 Map. On this map, the name of the Oman Sea is recorded as "Gulf of Hormuz". The name "Arabian Sea" has been informed of a sea off the coast of Yemen, and you can rename it the Arabian Sea, as the "Indian Sea" church. Map of Iran in the 16th century by ] in which the name of the Persian Sea and the Indian Sea appear.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://catdir.loc.gov/catdir/toc/fy11pdf02/2010344035.pdf |title= List|website= catdir.loc.gov|access-date=2020-09-19}}</ref> | |||
| In the ], as well as in some ancient maps, Erythraean Sea refers to the whole area of the northwestern Indian Ocean, including the Arabian Sea.<ref>{{cite web| url = http://commons.wikimedia.org/File:1794_Anville_Map_of_the_Ancient_World_-_Geographicus_-_AncientWorld-anville-1794.jpg| title = 1794, Orbis Veteribus Notus by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville| year = 1794}}</ref> | |||
| Arab sailors and nomads used to call this sea by different names, including the green sea, the ocean sea, the Hindu sea,the persian sea, the Makran Sea, the sea of Oman, but none of them mentioned Arabian sea until 19 century , among them the ], ] and ]. They wrote: “The green sea in the east and the sea of darkness in the west is the sea of strange creatures (]) And the enchanted islands (]) (]). Abdullah bin Lotf bin Abdul Rashid, a geographic historian and tourist mentioned in the book History of Islam and Iran, explains the Green Sea and says: “It is also called the Sea of India and it connects with the Persian Sea.” <ref>{{Cite web|url=https://ar.wikipedia.org/search/?title=%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1_%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%B1%D8%A8&oldid=50091160|title=بحر العرب|date=August 28, 2020|via=Misplaced Pages}}</ref>. There is no historical map of more than 300 years with the Arabian Sea name.<ref>https://www.britannica.com/place/Arabian-Sea</ref><ref>https://www.jstor.org/stable/20078849?seq=1</ref> | |||
| Arabian Sea was first used on European maps in the colonial period .<ref></ref> | |||
| Among historians, travellers and geographers of the Islamic era, many of them writing in Arabic or persian from the 9th to the 17th century, ],<ref>"Al-Massalek wa al-Mamalek", Leiden edition, 1889. p. 233</ref> ],<ref>The abrdiged "Al-Buldan", Leiden, 1885, p. 8</ref> ],<ref>Ibn Rustah, Kitāb al-A'lāk an-Nafīsa, ed. M. J. De Goeje, Bibliotheca Geographorum Arabicorum , Leiden, E. J. Brill, 1891/1892. p. 81</ref> Sohrab,<ref>Ajayeb al-Aqalim al-Saba ila Nehayate al-Mara, (Vienne: 1929), p. 59. 9th century AD.</ref> Ramhormozi,<ref>Nakhoda Bozorg ibn Shahriyar Ramhormozi was another Persian geographer of the classical Islamic era, "Ajayeb al-Hind", ed: M. Davis, Leiden 1886, p. 41</ref> ],<ref>"Massalek al-Mamalek", ed.: De M.J. Goeje, Leiden 1927, p. 28</ref> ],<ref>"Muruj adh-dhahab wa ma'adin al-jawhar (The Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems)", English Translation by Aloys Sprenger, Vol I, (London: 1841), p. 259</ref> Al-Mutahhar ibn Tahir al-Maqdisi (d. 966),<ref>al-Bad’ wa-l Tarikh, (Paris: 1907) Tom IV, p. 58.</ref> ],<ref>"The Oriental Geography of Ebn Hawkal", Translated by Sir Williams Ouseley (London: 1800) p. 62; "Surat al-Arḍ"(Leiden 1938), Vol I, p. 42.</ref> ],<ref>Ahsan al-Taqasim fi Ma’rifat al-Aqalim. Ed: De A.J. Goeje, (Leiden 1906), p. 17.</ref> ], Mohammad ibn Najub Bekiran,<ref>"Jahan Nama", Vol I. p. 44. .</ref> ],<ref>"Al-Tafhim le-awa’el Sena al-Tanjim" ed.: Jalal al-Din Homai (Tehran: 1318 Hijri Sola Calendar), p. 167. Also in "Qanun Masudi"(Heydarabad, 1955), Vol. II. p. 558.</ref> ],<ref>"Geographic d’Edirisi" traduite de l’Arabe en Francais par P. Amedee Jaulert (Recueil des voyages et des memoires publiees par la Societe de Geographie), (Paris: 1840), Vols. VI and VI. "Nuzhat al-Mushtaq fi Ikhtraq al-Afar", (Rome : 1878). p. 9</ref> ],<ref>"mu’jam al-Buldan",(Cairo: 1906), Vol. 2, p. 68.</ref> ],<ref>"Athar al-Bilad" (Gutingen: 1848), p. 104.</ref> ],<ref>"Taqwim al-Buldan", Geographie d’Aboulfeda traduite de l’Arab par M. Reinaud, 2 Vols. (Paris: 1848), Vol 1, p. 23.</ref> ],<ref name="Quotedalso"> | |||
| Quoted also in Mohammad Javad Mashkoor in an article titled "Nam-i Khalij Fars" in the proceeding of the "Seminar on Khalij-e-Fars" (Tehran: 1964). p. 46. | |||
| </ref> ],<ref>"Nuzhat al-Qolub", ed: Mohammad Dabir Sayaqi, (Tehran: 1336 Hijri Solar Year), p. 164. | |||
| </ref> ],<ref name="Quotedalso" /> ],<ref>"The Travels of Ibn Babutta", translated from the abrdiged Arabic MMS of Cambridge by the Rev. Samuel Lee(Cambridgde: 1824), p. 56</ref> ] and other sources have used the terms, "Bahr-i Mohit", "Bahr-i Mohit i ]", "Bahr-al-'Ajami", "Bahr-i-Fars", "Dera-i-Fars"(Persian), and "Bahr-i Mokran/Mecran", "Bahr-i Al Akhzar" (green) to refer to the current Arabian sea. ("Bahr-in Arabic means Sea" and Mohit means ocean) none of them referred to as Arabian sea. | |||
| <ref>http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یا دریای عرب </ref> | |||
| <gallery mode="packed"> | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
| File: |
File:Soulier, E.; Andriveau-Goujon, J. Anciens Empires Jusqua Alexandre. 1838.jpg|] 1838. | ||
| File:1658 Jansson Map of the Indian Ocean (Erythrean Sea) in Antiquity - Geographicus - ErythraeanSea-jansson-1658.jpg|1658 ] Map of the Indian Ocean (]) | |||
| File:Basra-ps64.JPG|Persian Sea. | |||
| File:The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693, from his system of global gores the south.jpg|The western part of the Indian Ocean,1693 | |||
| File:Asia in the shape of the mythical winged horse Pegasus..jpg|thumb|Asia. Sinus Persicus and the Mare Persicum in a very famous map published in many atlases in recent years]] | |||
| File:PeriplusAncientMap.jpg|17th century map depicting the locations of the '']'' | |||
| File:Basra bahrefars.jpg|thumb|Bahrefars | |||
| File:A horizontal Malabar Coast miniature, a reprint by Petrus Bertius, 1630.jpg|A horizontal Malabar Coast miniature, a reprint by ], 1630 | |||
| File:Soulier, E.; Andriveau-Goujon, J. Anciens Empires Jusqua Alexandre. 1838.jpg|Soulier, E.; Andriveau-Goujon, MER ERYTHREE 1838. | |||
| File:Basra-ps64.JPG|Persian Sea | |||
| File:Periplous of the Erythraean Sea.svg|upright=1.8|Names, routes and locations of the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' | |||
| File:Asia in the shape of the mythical winged horse Pegasus..jpg|Asia. ] and the Mare Persicum | |||
| File:1658 Jansson Map of the Indian Ocean (Erythrean Sea) in Antiquity - Geographicus - ErythraeanSea-jansson-1658.jpg|1658 Jansson Map of the Indian Ocean (Erythrean Sea) | |||
| File:A horizontal Malabar Coast miniature, a reprint by Petrus Bertius, 1630.jpg|A horizontal Malabar Coast miniature, a reprint by Petrus Bertius, 1630 | |||
| File:The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693, from his system of global gores the south.jpg|The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693, from his system of global gores the south | |||
| File:The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 from his system of global gores the Makran coast.jpg|The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 from the Makran coast | |||
| File:Map of persia.jpg|thumb| Persian Sea | |||
| </gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| ==Trade routes== | ==Trade routes== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The Arabian Sea has been an important ] ] since the era of the ''coastal sailing vessels'' from possibly as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, certainly the late 2nd millennium BCE through the later days known as the ]. By the time of ], several well-established combined land-sea trade routes depended upon ] through the sea around the rough inland ]s to its north. | The Arabian Sea has been an important ] ] since the era of the ''coastal sailing vessels'' from possibly as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, certainly the late 2nd millennium BCE through the later days known as the ]. By the time of ], several well-established combined land-sea trade routes depended upon ] through the sea around the rough inland ]s to its north. | ||
| Line 124: | Line 113: | ||
| This southern coastal route past the rough country in the ] was significant, and the ]ian ]s built several shallow canals to service the trade, one more or less along the route of today's ], and another from the Red Sea to the ], both shallow works that were swallowed up by huge ]s in antiquity. Later the ] arose in ] to rule a mercantile empire rooted in the trade with Europe via Alexandria. | This southern coastal route past the rough country in the ] was significant, and the ]ian ]s built several shallow canals to service the trade, one more or less along the route of today's ], and another from the Red Sea to the ], both shallow works that were swallowed up by huge ]s in antiquity. Later the ] arose in ] to rule a mercantile empire rooted in the trade with Europe via Alexandria. | ||
| <ref> |
<ref>{{cite web| url = https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536033| title = Documents on the Persian Gulf's name the eternal heritage ancient time by Dr. Mohammad Ajam<!-- -->}}</ref> | ||
| ===Major ports=== | ===Major ports=== | ||
| ] in ] is the largest port in the Arabian Sea, and the largest container port in India. | ] in ] is the largest port in the Arabian Sea, and the largest container port in India. | ||
| Major Indian ports in the Arabian Sea are ], ], ], ] |
Major Indian ports in the Arabian Sea are ], ], ], ], ], ] and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://shipping.gov.in/writereaddata/l892s/7yearsTRAFFIC-42175832.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://shipping.gov.in/writereaddata/l892s/7yearsTRAFFIC-42175832.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=TRAFFIC HANDLED AT MAJOR PORTS (LAST 7 YEARS)|website=shipping.gov.in}}{{Dead link|date=October 2019 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://aapa.files.cms-plus.com/PDFs/WORLD%20PORT%20RANKINGS%202009.pdf |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/http://aapa.files.cms-plus.com/PDFs/WORLD%20PORT%20RANKINGS%202009.pdf |archive-date=2022-10-09 |url-status=live|title=WORLD PORT RANKINGS|year=2009|website=aapa.files.cms-plus.com}}</ref> | ||
| ] |
] at Kochi Port in India]] | ||
| The ], Pakistan's largest and busiest seaport lies on the coast of the sea. It is located between the ] towns of ] and ]. | The ], Pakistan's largest and busiest seaport lies on the coast of the sea. It is located between the ] towns of ] and ]. | ||
| The ] of Pakistan is a warm-water, deep-sea port situated at ] in ] at the apex of the Arabian Sea and at the entrance of the Persian Gulf, about 460 km west of Karachi and approximately 75 |
The ] of Pakistan is a warm-water, deep-sea port situated at ] in ] at the apex of the Arabian Sea and at the entrance of the Persian Gulf, about 460 km west of Karachi and approximately {{convert|75|km|mi|abbr=on}} east of Pakistan's border with Iran. The port is located on the eastern bay of a natural hammerhead-shaped peninsula jutting out into the Arabian Sea from the coastline. | ||
| ] in Salalah, Oman is also a major port in the area. The International Task Force often uses the port as a base. There is a significant number of warships of all nations coming in and out of the port, which makes it a very safe bubble. The port handled just under 3.5m ] in 2009.<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121025024826/http://www.portofsalalah.com/port_news_item.aspx?id=16655 |date=October 25, 2012 }}, Port of Salalah</ref> | ] in Salalah, Oman is also a major port in the area. The International Task Force often uses the port as a base. There is a significant number of warships of all nations coming in and out of the port, which makes it a very safe bubble. The port handled just under 3.5m ] in 2009.<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121025024826/http://www.portofsalalah.com/port_news_item.aspx?id=16655 |date=October 25, 2012 }}, Port of Salalah</ref> | ||
| == Season names of shipping weather== | |||
| === Bat furan === | |||
| The winter, when ]n anticyclone makes monsoon winds favourable to shipping. | |||
| === Bat hiddan === | |||
| The summer, when off-shore winds from ] causes storms and shipping decrease as the result of them. | |||
| ==Islands== | ==Islands== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| There are several islands in the Arabian Sea, with the most important ones being ] (India), ] (Yemen), ] (Oman) and ] (Pakistan). | There are several islands in the Arabian Sea, with the most important ones being ] (India), ] (Yemen), ] (Oman) and ] (Pakistan). | ||
| The Lakshadweep Islands (formerly known as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Aminidivi Islands) is a group of islands in the Laccadive Sea region of Arabian Sea, 200 |
The Lakshadweep Islands (formerly known as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Aminidivi Islands) is a group of islands in the Laccadive Sea region of Arabian Sea, {{convert|200|to|440|km|mi|abbr=on}} off the southwestern coast of India. The archipelago is a ] and is governed by the ]. The islands form the smallest union territory of India with their total surface area being just {{convert|32|km2|abbr=on}}. Next to these islands are the Maldives islands. These islands are all part of the ] group of islands. | ||
| ] was an island which was around for only a few years. After the 2013 earthquake in Pakistan, the mud island was formed. By 2016 the island had completely submerged.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.dawn.com/news/1305482/gwadars-quake-island-disappears | title=Gwadar's quake island disappears | date=31 December 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| Astola Island, also known as ''Jezira Haft Talar'' in ], or 'Island of the Seven Hills', is a small, uninhabited island in the northern tip of the Arabian Sea in Pakistan's territorial waters. | Astola Island, also known as ''Jezira Haft Talar'' in ], or 'Island of the Seven Hills', is a small, uninhabited island in the northern tip of the Arabian Sea in Pakistan's territorial waters. | ||
| Line 155: | Line 139: | ||
| Socotra, also spelled ''Soqotra'', is the largest island, being part of a small archipelago of four islands. It lies some {{convert|240|km|mi|abbr=on}} east of the ] and {{convert|380|km|mi|abbr=on}} south of the Arabian Peninsula. | Socotra, also spelled ''Soqotra'', is the largest island, being part of a small archipelago of four islands. It lies some {{convert|240|km|mi|abbr=on}} east of the ] and {{convert|380|km|mi|abbr=on}} south of the Arabian Peninsula. | ||
| Masirah |
Masirah and the five ] are islands off the southeastern coast of Oman. | ||
| == Major cities == | |||
| There are many major cities and towns in the coast of Arabian Sea. Some of the major cities are ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ==Oxygen |
==Oxygen minimum zone== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The Arabian Sea has one of the world's three largest oceanic ]s (OMZ), or “dead zones,” along with the eastern tropical North Pacific and the eastern tropical South Pacific. OMZs have very low levels of ], sometimes undetectable by standard equipment.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Lüke|first1=Claudia|last2=Speth|first2=Daan R.|last3=Kox|first3=Martine A. R.|last4=Villanueva|first4=Laura|last5=Jetten|first5=Mike S. M.|date=2016-04-07|title=Metagenomic analysis of nitrogen and methane cycling in the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone |
The Arabian Sea has one of the world's three largest oceanic ]s (OMZ), or “dead zones,” along with the eastern tropical North Pacific and the eastern tropical South Pacific. OMZs have very low levels of ], sometimes so low as to be undetectable by standard equipment.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Lüke|first1=Claudia|last2=Speth|first2=Daan R.|last3=Kox|first3=Martine A. R.|last4=Villanueva|first4=Laura|last5=Jetten|first5=Mike S. M.|date=2016-04-07|title=Metagenomic analysis of nitrogen and methane cycling in the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone|journal=PeerJ|language=en|volume=4|pages=e1924|doi=10.7717/peerj.1924|issn=2167-8359|pmc=4830246|pmid=27077014 |doi-access=free }}</ref> The Arabian Sea's OMZ has the lowest levels of oxygen in the world, especially in the Gulf of Oman.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Queste|first1=Bastien Y.|last2=Vic|first2=Clément|last3=Heywood|first3=Karen J.|last4=Piontkovski|first4=Sergey A.|date=2018|title=Physical Controls on Oxygen Distribution and Denitrification Potential in the North West Arabian Sea|journal=Geophysical Research Letters|language=en|volume=45|issue=9|pages=4143–4152|doi=10.1029/2017GL076666|bibcode=2018GeoRL..45.4143Q|issn=1944-8007|doi-access=free}}</ref> Causes of the OMZ may include untreated sewage as well as high temperatures on the Indian subcontinent, which increase winds blowing towards India, bringing up nutrients and reducing oxygen in the Arabian Sea's waters. In winter, phytoplankton suited to low-oxygen conditions turn the OMZ bright green.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Bhanoo|first=S.N.|title=A Green Blanket on the Arabian Sea|work=The New York Times}}</ref> | ||
| == Natural resorces== | |||
| == Environment and wildlife == | |||
| The wildlife of the Arabian sea is diverse, and entirely unique because of the geographic distribution. | |||
| <gallery mode="packed"> | |||
| File:The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 from his system of global gores the Makran coast.jpg|The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 from his system of global gores the Makran coast | |||
| File:Karachi Mangroves.jpg|Mangrove forests are abundant south of Karachi, Pakistan. | |||
| File:Nakhl-Minoo.jpg|] and ] in ], Iran | |||
| File:The-Worlds-Most-Isolated-and-Distinct-Whale-Population-Humpback-Whales-of-the-Arabian-Sea-pone.0114162.s001.tif|Critically endangered | |||
| File:Dugong.jpg|] mother and her offspring in shallow waters | |||
| File:Makran sea .makoran coast in Iran.jpg|Makran coast | |||
| File:Makoran sea .Makoran coast in Iran.jpg|Makran sea. Makoran coast in Iran. | |||
| File:Red Coast of Makoran sea Iran.jpg|Makran coast | |||
| File:Arabian or Makoran sea .Makoran red coast in Iran.jpg|Iran | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==Arabian Sea warming== | |||
| Recent studies<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Roxy |first1=Mathew Koll |last2=Ritika |first2=Kapoor |last3=Terray |first3=Pascal |last4=Murtugudde |first4=Raghu |last5=Ashok |first5=Karumuri |last6=Goswami |first6=B. N. |title=Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid Indian Ocean warming and a weakening land-sea thermal gradient |journal=Nature Communications |date=16 June 2015 |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=7423 |doi=10.1038/ncomms8423 |pmid=26077934 |bibcode=2015NatCo...6.7423R |s2cid=7061499 |language=en |issn=2041-1723|doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Pratik |first1=Kad |last2=Parekh |first2=Anant |last3=Karmakar |first3=Ananya |last4=Chowdary |first4=Jasti S. |last5=Gnanaseelan |first5=C. |title=Recent changes in the summer monsoon circulation and their impact on dynamics and thermodynamics of the Arabian Sea |journal=Theoretical and Applied Climatology |date=1 April 2019 |volume=136 |issue=1 |pages=321–331 |doi=10.1007/s00704-018-2493-6 |bibcode=2019ThApC.136..321P |s2cid=126114281 |url=https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00704-018-2493-6 |language=en |issn=1434-4483}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Roxy |first1=M. K. |last2=Gnanaseelan |first2=C. |last3=Parekh |first3=Anant |last4=Chowdary |first4=Jasti S. |last5=Singh |first5=Shikha |last6=Modi |first6=Aditi |last7=Kakatkar |first7=Rashmi |last8=Mohapatra |first8=Sandeep |last9=Dhara |first9=Chirag |last10=Shenoi |first10=S. C. |last11=Rajeevan |first11=M. |title=Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region: A Report of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India |date=2020 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-981-15-4327-2 |pages=191–206 |chapter-url=https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-15-4327-2_10 |language=en |chapter=Indian Ocean Warming|doi=10.1007/978-981-15-4327-2_10 |s2cid=226643638 }}</ref> by the ] confirmed that the Arabian Sea is warming monotonously; it possibly is due to global warming. The intensification and northward shift of the summer monsoon low-level jet over the Arabian Sea from 1979 to 2015, led to increased upper ocean heat content due to enhanced downwelling and reduced southward heat transport.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Pratik |first1=Kad |last2=Parekh |first2=Anant |last3=Karmakar |first3=Ananya |last4=Chowdary |first4=Jasti S. |last5=Gnanaseelan |first5=C. |title=Recent changes in the summer monsoon circulation and their impact on dynamics and thermodynamics of the Arabian Sea |journal=Theoretical and Applied Climatology |date=1 April 2019 |volume=136 |issue=1 |pages=321–331 |doi=10.1007/s00704-018-2493-6 |bibcode=2019ThApC.136..321P |s2cid=126114281 |url=https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00704-018-2493-6 |language=en |issn=1434-4483}}</ref> | |||
| ==Native names== | |||
| Regional ]s for the Arabian sea in languages of the coastal regions surrounding it. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| ! Language | |||
| ! Name | |||
| !Romanized | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | بَحرُ ٱلْعَرَبْ | |||
| |''baḥr al-ʿarab'' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |ޢަރަބި ކަނޑު | |||
| |''arabi kanḍu'' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |અરબી સમુદ્ર | |||
| |''arabī samudra'' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |अरब सागर | |||
| |''arab sāgar'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |ಅರಬ್ಬೀ ಸಮುದ್ರ | |||
| |''arabbī samudra'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |अरबी दर्या | |||
| |''arabī daryā'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |അറബിക്കടൽ | |||
| |''aṟabikkaḍal'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | अरबी समुद्र | |||
| |''arabī samudra'' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |دریای عرب | |||
| |''darya-i-arab'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |عربي سمنڊ | |||
| |''arabī samaṇḍ'' | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | Bada Carbeed | |||
| |Bada Arbeed | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| |அரபிகடல் | |||
| |''aṟabikkaḍal'' | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |{{Nastaliq|بحیرہ عرب}} | |||
| |''bahīrā arab'' | |||
| |} | |||
| ] Critically endangered ]s off ] Oman. | |||
| ] Iran | |||
| ] | |||
| ] mother and her offspring in shallow waters.]] | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Portal|Oceans}} | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| Line 176: | Line 237: | ||
| ==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
| {{EB1911 |wstitle=Arabian Sea}} | {{EB1911 |wstitle=Arabian Sea}} | ||
| * | |||
| *Documents on the Persian Gulf's name | |||
| *A book and Atlas | |||
| *Arabian sea and persian sea | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons}} | |||
| {{commons category-inline|Arabian Sea}} | |||
| * | * | ||
| Line 186: | Line 246: | ||
| {{Waters of South Asia}} | {{Waters of South Asia}} | ||
| {{Countries bordering the Arabian Sea}} | {{Countries bordering the Arabian Sea}} | ||
| {{portalbar|Oceans}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:23, 24 December 2024
Marginal sea of the northern Indian Ocean| Arabian Sea | |
|---|---|
| بَحرُ ٱلْعَرَبْ (Arabic) | |
 The Arabian Sea as defined by the International Hydrographic Organization The Arabian Sea as defined by the International Hydrographic Organization | |
| Location | East Africa, West Asia and South Asia |
| Coordinates | 14°N 65°E / 14°N 65°E / 14; 65 |
| Type | Sea |
| Part of | Indian Ocean |
| Basin countries | India Iran Maldives Oman Pakistan Seychelles Somalia Sri Lanka Yemen |
| Max. width | 2,400 km (1,500 mi) |
| Surface area | 3,862,000 km (1,491,000 sq mi) (3,600,000 to 4,600,000 km2 in various sources) |
| Max. depth | 4,652 m (15,262 ft) |
| Islands | Astola island, Basavaraj Durga Island, Bundal Island, Charna Island, Clifton Oyster Rocks, Khiprianwala Island, Lakshadweep, Malan Island, Manora Island, Masirah Island, Piram Island, Pirotan, Shams Pir, Socotra Archipelago |
The Arabian Sea (Arabic: بَحرُ ٱلْعَرَبْ, romanized: baḥr al-ʿarab) is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea and the Maldives, on the southwest by Somalia. Its total area is 3,862,000 km (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 5,395 meters (17,700 feet). The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.
Geography
The Arabian Sea's surface area is about 3,862,000 km (1,491,130 sq mi). The maximum width of the sea is approximately 2,400 km (1,490 mi), and its maximum depth is 5,395 metres (17,700 ft). The biggest river flowing into the sea is the Indus River.
The Arabian Sea has two important branches: the Gulf of Aden in the southwest, connecting with the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb; and the Gulf of Oman to the northwest, connecting with the Persian Gulf. There are also the gulfs of Khambhat and Kutch on the Indian Coast. The Arabian Sea has been crossed by many important marine trade routes since the 3rd or 2nd millennium BCE. Major seaports include Kandla Port, Mundra Port, Pipavav Port, Dahej Port, Hazira Port, Mumbai Port, Nhava Sheva Port (Navi Mumbai), Mormugão Port (Goa), New Mangalore Port and Kochi Port in India, the Port of Karachi, Port Qasim, and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan, Chabahar Port in Iran and the Port of Salalah in Salalah, Oman. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include Socotra (Yemen), Masirah Island (Oman), Lakshadweep (India) and Astola Island (Pakistan). The countries with coastlines on the Arabian Sea are Yemen, Oman, Pakistan, Iran, India and the Maldives.
Limits
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Arabian Sea as follows:
- On the west: the eastern limit of the Gulf of Aden.
- On the north: a line joining Ràs al Hadd, east point of the Arabian Peninsula (22°32'N) and Ràs Jiyùni (61°43'E) on the coast of Pakistan.
- On the south: a line running from the southern extremity of Addu Atoll in the Maldives, to the eastern extremity of Ràs Hafun (the easternmost point of Africa, 10°26'N).
- On the east: the western limit of the Laccadive Sea a line running from Sadashivgad on the west coast of India (14°48′N 74°07′E / 14.800°N 74.117°E / 14.800; 74.117) to Cora Divh (13°42′N 72°10′E / 13.700°N 72.167°E / 13.700; 72.167) and thence down the west side of the Laccadive and Maldive archipelagos to the most southerly point of Addu Atoll in the Maldives.
Hydrography
The International Indian Ocean Expedition in 1959 was among the first to perform hydrographic surveys of the Arabian Sea. Significant bathymetric surveys were also conducted by the Soviet Union during the 1960s.
Hydrographic features
Significant features in the northern Arabian Sea include the Indus Fan, the second largest fan system in the world. The De Covilhao Trough, named after the 15th century Portuguese explorer Pero de Covilhăo, reaches depths of 4,400 metres (14,436 ft) and separates the Indus Fan region from the Oman Abyssal Plain, which eventually leads to the Gulf of Oman.
The southern limits are dominated by the Arabian Basin, a deep basin reaching depths over 4,200 metres (13,780 ft). The northern sections of the Carlsberg Ridge flank the southern edge of the Arabian Basin.
The deepest parts of the Arabian Sea are in the Alula-Fartak Trough on the western edge of the Arabian Sea off the Gulf of Aden. The trough, reaching depths over 5,360 metres (17,585 ft), traverses the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea. The deepest known point is in the Arabian Sea limits at a depth of 5,395 metres (17,700 ft). Other significant deep points are part of the Arabian Basin, which include a 5,358 metres (17,579 ft) deep point off the northern limit of Calrsberg Ridge.
Seamounts
Prominent sea mounts off the Indian west coast include Raman Seamount named after C. V. Raman, Panikkar Seamount, named after N. K. Panikkar, and the Wadia Guyot, named after D. N. Wadia.
Sind'Bad Seamount, named after the fictional explorer Sinbad the Sailor, Zheng He Seamount, and the Mount Error Guyot are some notable sea mounts in western Arabian Sea.
Border and basin countries
Border and basin countries:
Alternative names
| This article needs attention from an expert in geography. The specific problem is: This article possibly contains synthesis of material and claims which does not verifiably relate to the topic. See the talk page for details. WikiProject Geography may be able to help recruit an expert. (April 2023) |
The Arabian Sea historically and geographically has been referred to with different names by Arabian and European geographers and travelers, including Erythraean Sea, Indian Sea, Oman sea, Erythraean, Persian Sea in para No 34-35 of the Voyage. In Indian folklore, it is referred to as Darya, Sindhu Sagar, Arab Samudra.
Arab geographers, sailors and nomads used to call this sea by different names, including the Akhdar (Green) Sea, Bahre Fars (Persian Sea), the Ocean Sea, the Hindu sea, the Makran Sea, the sea of Oman; among them Zakariya al-Qazwini, Al-Masudi, Ibn Hawqal and Hafiz-i Abru. They wrote: "The green sea and Indian sea and Persian sea are all one sea and in this sea there are strange creatures." in Iran and Turkey people call it Oman sea. In the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, as well as in some ancient maps, Erythraean Sea refers to the whole area of the northwestern Indian Ocean, including the Arabian Sea.
-
 Erythraean Sea 1838.
Erythraean Sea 1838.
-
 1658 Jansson Map of the Indian Ocean (Erythraean Sea)
1658 Jansson Map of the Indian Ocean (Erythraean Sea)
-
 The western part of the Indian Ocean,1693
The western part of the Indian Ocean,1693
-
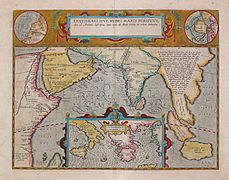 17th century map depicting the locations of the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
17th century map depicting the locations of the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
-
 A horizontal Malabar Coast miniature, a reprint by Petrus Bertius, 1630
A horizontal Malabar Coast miniature, a reprint by Petrus Bertius, 1630
-
Persian Sea
-
 Asia. Sinus Persicus and the Mare Persicum
Asia. Sinus Persicus and the Mare Persicum
Trade routes

The Arabian Sea has been an important marine trade route since the era of the coastal sailing vessels from possibly as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, certainly the late 2nd millennium BCE through the later days known as the Age of Sail. By the time of Julius Caesar, several well-established combined land-sea trade routes depended upon water transport through the sea around the rough inland terrain features to its north.
These routes usually began in the Far East or down river from Madhya Pradesh, India with transshipment via historic Bharuch (Bharakuccha), traversed past the inhospitable coast of modern-day Iran, then split around Hadhramaut, Yemen into two streams north into the Gulf of Aden and thence into the Levant, or south into Alexandria via Red Sea ports such as Axum. Each major route involved transhipping to pack animal caravan, travel through desert country and risk of bandits and extortionate tolls by local potentates.
This southern coastal route past the rough country in the southern Arabian Peninsula was significant, and the Egyptian Pharaohs built several shallow canals to service the trade, one more or less along the route of today's Suez Canal, and another from the Red Sea to the Nile River, both shallow works that were swallowed up by huge sand storms in antiquity. Later the kingdom of Axum arose in Ethiopia to rule a mercantile empire rooted in the trade with Europe via Alexandria.
Major ports
Jawaharlal Nehru Port in Mumbai is the largest port in the Arabian Sea, and the largest container port in India. Major Indian ports in the Arabian Sea are Mundra Port, Kandla Port, Nava Sheva, Kochi Port, Mumbai Port, Vizhinjam International Seaport Thiruvananthapuram and Mormugão.

The Port of Karachi, Pakistan's largest and busiest seaport lies on the coast of the sea. It is located between the Karachi towns of Kiamari and Saddar.
The Gwadar Port of Pakistan is a warm-water, deep-sea port situated at Gwadar in Balochistan at the apex of the Arabian Sea and at the entrance of the Persian Gulf, about 460 km west of Karachi and approximately 75 km (47 mi) east of Pakistan's border with Iran. The port is located on the eastern bay of a natural hammerhead-shaped peninsula jutting out into the Arabian Sea from the coastline.
Port of Salalah in Salalah, Oman is also a major port in the area. The International Task Force often uses the port as a base. There is a significant number of warships of all nations coming in and out of the port, which makes it a very safe bubble. The port handled just under 3.5m teu in 2009.
Islands

There are several islands in the Arabian Sea, with the most important ones being Lakshadweep Islands (India), Socotra (Yemen), Masirah (Oman) and Astola Island (Pakistan).
The Lakshadweep Islands (formerly known as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Aminidivi Islands) is a group of islands in the Laccadive Sea region of Arabian Sea, 200 to 440 km (120 to 270 mi) off the southwestern coast of India. The archipelago is a union territory and is governed by the Union Government of India. The islands form the smallest union territory of India with their total surface area being just 32 km (12 sq mi). Next to these islands are the Maldives islands. These islands are all part of the Lakshadweep-Maldives-Chagos group of islands.
Zalzala Koh was an island which was around for only a few years. After the 2013 earthquake in Pakistan, the mud island was formed. By 2016 the island had completely submerged.
Astola Island, also known as Jezira Haft Talar in Balochi, or 'Island of the Seven Hills', is a small, uninhabited island in the northern tip of the Arabian Sea in Pakistan's territorial waters.
Socotra, also spelled Soqotra, is the largest island, being part of a small archipelago of four islands. It lies some 240 km (150 mi) east of the Horn of Africa and 380 km (240 mi) south of the Arabian Peninsula.
Masirah and the five Khuriya Muriya Islands are islands off the southeastern coast of Oman.
Major cities
There are many major cities and towns in the coast of Arabian Sea. Some of the major cities are Mumbai, Muscat, Karachi, Aden, Salalah, Thiruvananthapuram, Kochi, Kozhikode, Alappuzha, Kollam, Mangalore, Bhavnagar, Jamnagar, Mogadishu, Gwadar, Abu Dhabi, Mundra, Dubai, Kannur, Panaji, Karwar, Udupi, Ratnagiri, Murdeshwar, Veraval, Colombo, Takamaka, and Dhiffushi.
Oxygen minimum zone

The Arabian Sea has one of the world's three largest oceanic oxygen minimum zones (OMZ), or “dead zones,” along with the eastern tropical North Pacific and the eastern tropical South Pacific. OMZs have very low levels of oxygen, sometimes so low as to be undetectable by standard equipment. The Arabian Sea's OMZ has the lowest levels of oxygen in the world, especially in the Gulf of Oman. Causes of the OMZ may include untreated sewage as well as high temperatures on the Indian subcontinent, which increase winds blowing towards India, bringing up nutrients and reducing oxygen in the Arabian Sea's waters. In winter, phytoplankton suited to low-oxygen conditions turn the OMZ bright green.
Environment and wildlife
The wildlife of the Arabian sea is diverse, and entirely unique because of the geographic distribution.
-
 The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 from his system of global gores the Makran coast
The western part of the Indian Ocean, by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 from his system of global gores the Makran coast
-
 Mangrove forests are abundant south of Karachi, Pakistan.
Mangrove forests are abundant south of Karachi, Pakistan.
-
 Palm and sunset in Minoo Island, Iran
Palm and sunset in Minoo Island, Iran
-
 Critically endangered
Critically endangered
-
 Dugong mother and her offspring in shallow waters
Dugong mother and her offspring in shallow waters
-
 Makran coast
Makran coast
-
 Makran sea. Makoran coast in Iran.
Makran sea. Makoran coast in Iran.
-
 Makran coast
Makran coast
-
 Iran
Iran
Arabian Sea warming
Recent studies by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology confirmed that the Arabian Sea is warming monotonously; it possibly is due to global warming. The intensification and northward shift of the summer monsoon low-level jet over the Arabian Sea from 1979 to 2015, led to increased upper ocean heat content due to enhanced downwelling and reduced southward heat transport.
Native names
Regional endonyms for the Arabian sea in languages of the coastal regions surrounding it.
| Language | Name | Romanized |
|---|---|---|
| Arabic | بَحرُ ٱلْعَرَبْ | baḥr al-ʿarab |
| Divehi | ޢަރަބި ކަނޑު | arabi kanḍu |
| Gujarati | અરબી સમુદ્ર | arabī samudra |
| Hindi | अरब सागर | arab sāgar |
| Kannada | ಅರಬ್ಬೀ ಸಮುದ್ರ | arabbī samudra |
| Konkani | अरबी दर्या | arabī daryā |
| Malayalam | അറബിക്കടൽ | aṟabikkaḍal |
| Marathi | अरबी समुद्र | arabī samudra |
| Persian | دریای عرب | darya-i-arab |
| Sindhi | عربي سمنڊ | arabī samaṇḍ |
| Somali | Bada Carbeed | Bada Arbeed |
| Tamil | அரபிகடல் | aṟabikkaḍal |
| Urdu | بحیرہ عرب | bahīrā arab |
See also
References
- "Arabian Sea". UNBIS Thesaurus. Retrieved 28 December 2023.
- Banse, Karl, and Charles R. McClain. "Winter blooms of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea as observed by the Coastal Zone Color Scanner." Marine Ecology Progress Series (1986): 201-211.
- Pham, J. Peter. "Putting Somali piracy in context." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 28.3 (2010): 325-341.
- ^ Arabian Sea, Encyclopædia Britannica
- "NOAA Bathymetric Data Viewer". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. pp. 20–21. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2017. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- Hall, John K.; Levenson, Shahar (March 20, 2017). "Compilation of a 100m bathymetric grid for the Arabian Plate; Red Sea, Arabian and Oman Seas and Persian Gulf". U.S. HYDRO 2017 Conference.
- "NOAA Bathymetric Data Viewer". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- "Wadia Guyot". Marine Regions Gazetteer. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- "Sind'Bad Seamount". Marine Regions Gazetteer.
- "Mount Error Guyot". Marine Regions Gazetteer. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- "Iran". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- "Introduction to Pakistan: Section 5: Coastline". www.wildlifeofpakistan.com. Archived from the original on 2020-06-26. Retrieved 2020-08-28.
- "Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea". kamat.com.
- "The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea". washington.edu.
- "Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea". www.kamat.com.
- "The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea". depts.washington.edu.
- "The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea". Archived from the original on 2013-12-02. Retrieved 2012-04-03.
- "Ministry of MoFA Iran: Introducing a Book and Atlas". mfa.gov.ir.
- "1794, Orbis Veteribus Notus by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville". 1794.
- "Documents on the Persian Gulf's name the eternal heritage ancient time by Dr. Mohammad Ajam".
- "TRAFFIC HANDLED AT MAJOR PORTS (LAST 7 YEARS)" (PDF). shipping.gov.in. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- "WORLD PORT RANKINGS" (PDF). aapa.files.cms-plus.com. 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- Salalah’s versatility beats the slump Archived October 25, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Port of Salalah
- "Gwadar's quake island disappears". 31 December 2016.
- Lüke, Claudia; Speth, Daan R.; Kox, Martine A. R.; Villanueva, Laura; Jetten, Mike S. M. (2016-04-07). "Metagenomic analysis of nitrogen and methane cycling in the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone". PeerJ. 4: e1924. doi:10.7717/peerj.1924. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 4830246. PMID 27077014.
- Queste, Bastien Y.; Vic, Clément; Heywood, Karen J.; Piontkovski, Sergey A. (2018). "Physical Controls on Oxygen Distribution and Denitrification Potential in the North West Arabian Sea". Geophysical Research Letters. 45 (9): 4143–4152. Bibcode:2018GeoRL..45.4143Q. doi:10.1029/2017GL076666. ISSN 1944-8007.
- Bhanoo, S.N. "A Green Blanket on the Arabian Sea". The New York Times.
- Roxy, Mathew Koll; Ritika, Kapoor; Terray, Pascal; Murtugudde, Raghu; Ashok, Karumuri; Goswami, B. N. (16 June 2015). "Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid Indian Ocean warming and a weakening land-sea thermal gradient". Nature Communications. 6 (1): 7423. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7423R. doi:10.1038/ncomms8423. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 26077934. S2CID 7061499.
- Pratik, Kad; Parekh, Anant; Karmakar, Ananya; Chowdary, Jasti S.; Gnanaseelan, C. (1 April 2019). "Recent changes in the summer monsoon circulation and their impact on dynamics and thermodynamics of the Arabian Sea". Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 136 (1): 321–331. Bibcode:2019ThApC.136..321P. doi:10.1007/s00704-018-2493-6. ISSN 1434-4483. S2CID 126114281.
- Roxy, M. K.; Gnanaseelan, C.; Parekh, Anant; Chowdary, Jasti S.; Singh, Shikha; Modi, Aditi; Kakatkar, Rashmi; Mohapatra, Sandeep; Dhara, Chirag; Shenoi, S. C.; Rajeevan, M. (2020). "Indian Ocean Warming". Assessment of Climate Change over the Indian Region: A Report of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India. Springer. pp. 191–206. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-4327-2_10. ISBN 978-981-15-4327-2. S2CID 226643638.
- Pratik, Kad; Parekh, Anant; Karmakar, Ananya; Chowdary, Jasti S.; Gnanaseelan, C. (1 April 2019). "Recent changes in the summer monsoon circulation and their impact on dynamics and thermodynamics of the Arabian Sea". Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 136 (1): 321–331. Bibcode:2019ThApC.136..321P. doi:10.1007/s00704-018-2493-6. ISSN 1434-4483. S2CID 126114281.
Sources
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Arabian Sea". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Arabian Sea". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
| Hydrography of the Indian subcontinent | |
|---|---|
| Inland rivers | |
| Inland lakes, deltas, etc. | |
| Coastal | |
| Categories |
|
| Countries bordering the Arabian Sea | |
|---|---|
- Arabian Sea
- Arabian Peninsula
- Marine ecoregions
- Bodies of water of Iran
- Bodies of water of the Maldives
- Bodies of water of Pakistan
- Bodies of water of Oman
- Bodies of water of Somalia
- Seas of Africa
- Seas of Asia
- Seas of India
- Seas of the Indian Ocean
- Seas of Iran
- Seas of Yemen
- India–Pakistan border
- Oman–Yemen border


