| Revision as of 11:49, 16 April 2022 editCrafterNova (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users16,639 edits fixed acronym of the compound in lead sentenceTag: 2017 wikitext editor← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 09:16, 24 January 2024 edit undoMaxim Masiutin (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, IP block exemptions, Pending changes reviewers30,659 edits Used lowercase "cite" template everywhere for consistency. | ||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| | verifiedrevid = 477191825 | | verifiedrevid = 477191825 | ||
| | ImageFile = 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazin.svg | | ImageFile = 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazin.svg | ||
| | ImageSize = 110px | | ImageSize = 110px | ||
| | ImageFileL1 = 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine-from-xtal-3D-balls.png | | ImageFileL1 = 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine-from-xtal-3D-balls.png | ||
| | ImageFileR1 = 24dnp3d.png | | ImageFileR1 = 24dnp3d.png | ||
| | PIN = (2,4-Dinitrophenyl)hydrazine | | PIN = (2,4-Dinitrophenyl)hydrazine | ||
| | OtherNames = 2,4-DNPH<br />2,4-DNP<br />Brady's reagent<br />Borche's reagent | | OtherNames = 2,4-DNPH<br />2,4-DNP<br />DNPH<br />Brady's reagent<br />Borche's reagent | ||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 3001507 | | ChemSpiderID = 3001507 | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| | SMILES = c1cc(c(cc1(=O))(=O))NN | | SMILES = c1cc(c(cc1(=O))(=O))NN | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| | Formula = C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>N<sub>4</sub>O<sub>4</sub> | | Formula = C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>N<sub>4</sub>O<sub>4</sub> | ||
| | MolarMass = 198.14 g/mol | | MolarMass = 198.14 g/mol | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| | Solubility = Slight | | Solubility = Slight | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section7={{Chembox Hazards | | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| | ExternalSDS = | | ExternalSDS = | ||
| | MainHazards = Flammable, possibly carcinogenic | | MainHazards = Flammable, possibly carcinogenic | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine''' ('''2,4-DNPH''') is the ] C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NHNH<sub>2</sub>. |
'''2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine''' ('''2,4-DNPH''' or '''DNPH''') is the ] C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NHNH<sub>2</sub>. DNPH is a red to orange solid. It is a substituted ]. The solid is relatively sensitive to ] and ]. For this reason DNPH is usually handled as a wet powder. DNPH is a precursor to the drug ]. | ||
| ==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis== | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
| ==DNP test== | ==DNP test== | ||
| DNPH is a reagent in instructional laboratories on ]. |
DNPH is a reagent in instructional laboratories on ]. '''Brady's reagent''' or '''Borche's reagent''', is prepared by dissolving DNPH in a solution containing ] and some concentrated ]. This solution is used to ] ]s and ]s. A positive test is signalled by the formation of a yellow, orange or red ] of the dinitrophenylhydrazone. Aromatic carbonyls give red precipitates whereas ] carbonyls give more yellow color.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Mohrig |first1=Jerry R. |last2=Hammond |first2=Christina Noring |last3=Morrill |first3=Terence C. |last4=Neckers |first4=Douglas C. |title=Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Balanced Approach, Macroscale and Microscale |date=1998 |publisher=W.H. Freeman and Company |location=New York |isbn=0-7167-2818-4 |url=https://archive.org/details/experimentalorga00mohr/page/n5/mode/2up |page=530 |url-access=registration}}</ref> The reaction between DNPH and a generic ketone to form a ] is shown below: | ||
| :RR'C=O + C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NHNH<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NHN=CRR' + H<sub>2</sub>O | :RR'C=O + C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NHNH<sub>2</sub> → C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(NO<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NHN=CRR' + H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| This reaction is, overall, a ] as two molecules joining together with loss of water. |
This reaction is, overall, a ] as two molecules joining together with loss of water. Mechanistically, it is an example of ]: nucleophilic addition of the -NH<sub>2</sub> group to the C=O carbonyl group, followed by the elimination of a H<sub>2</sub>O molecule:<ref>Adapted from ''Chemistry in Context'', 4th Edition, 2000, Graham Hill and John Holman</ref> | ||
| :]. Selected parameters: C=N, 128 pm; N-N, 1.38 pm, N-N-C(Ar), 119<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1107/S1600536806048112|title=Benzophenone 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone|year=2006|last1=Tameem|first1=Abdassalam Abdelhafiz|last2=Salhin|first2=Abdussalam|last3=Saad|first3=Bahruddin|last4=Rahman|first4=Ismail Ab.|last5=Saleh|first5=Muhammad Idiris|last6=Ng|first6=Shea-Lin|last7=Fun|first7=Hoong-Kun|journal=Acta Crystallographica Section E|volume=62|issue=12|pages=o5686–o5688}}</ref>]] | :]. Selected parameters: C=N, 128 pm; N-N, 1.38 pm, N-N-C(Ar), 119<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1107/S1600536806048112|title=Benzophenone 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone|year=2006|last1=Tameem|first1=Abdassalam Abdelhafiz|last2=Salhin|first2=Abdussalam|last3=Saad|first3=Bahruddin|last4=Rahman|first4=Ismail Ab.|last5=Saleh|first5=Muhammad Idiris|last6=Ng|first6=Shea-Lin|last7=Fun|first7=Hoong-Kun|journal=Acta Crystallographica Section E|volume=62|issue=12|pages=o5686–o5688}}</ref>]] | ||
| ] is added to a solution of 2,4-DNPH and heated, an orange-red precipitate forms.]] | ] is added to a solution of 2,4-DNPH and heated, an orange-red precipitate forms.]] | ||
| DNP-derived hydrazones have characteristic melting points, facilitating identification of the carbonyl. In particular, the use of |
DNP-derived hydrazones have characteristic melting points, facilitating identification of the carbonyl. In particular, the use of DNPH was developed by Brady and Elsmie.<ref>{{cite journal | author1 = Brady, Oscar L. | author2 = Elsmie, Gladys V. | title = The use of 2:4-dinitrophenylhydrazine as a reagent for aldehydes and ketones | journal = ] | volume = 51 | pages = 77–78 | year = 1926 | doi = 10.1039/AN9265100077 | issue = 599 | bibcode = 1926Ana....51...77B}}</ref> Modern spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques have superseded these techniques. | ||
| DNPH does not react with other carbonyl-containing functional groups such as ], ]s, and ], for which there is resonance-associated stability as a lone-pair of electrons interacts with the ] of the carbonyl carbon resulting in increased delocalization in the molecule. This stability would be lost by addition of a reagent to the carbonyl group. Hence, these compounds are more resistant to addition reactions. Also, with carboxylic acids, there is the effect of the compound acting as a base, leaving the resulting carboxylate negatively charged and hence no longer vulnerable to nucleophilic attack. | |||
| ==Safety== | ==Safety== | ||
| Dry DNPH is friction and shock sensitive. For this reason, it’s supplied damp or ‘wetted’ when a school purchases it from a chemical supplier.<ref>{{cite web |title=What is 2,4-DNPH and Why Are Schools Carrying Out Controlled Explosions? |url=https://www.compoundchem.com/2016/11/07/24-dnp/ |accessdate=26 October 2022 |website=Compound Interest|date=7 November 2016 }}</ref> If DNPH is stored improperly and left to dry out, it can become explosive. | |||
| It is an artificial uncoupler of the electron transport chain (ETC).<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/education/2016/nov/02/bomb-disposal-squads-detonate-chemical-stocks-english-schools-a-level-chemistry-24-dnp |newspaper=The Guardian |title=Bomb disposal squads detonate chemical stocks in British schools |date=2 November 2016 |accessdate=19 March 2018 }}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 87: | Line 88: | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Dinitrophenylhydrazine, 2, 4-}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Dinitrophenylhydrazine, 2, 4-}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:16, 24 January 2024

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (2,4-Dinitrophenyl)hydrazine | |||
| Other names
2,4-DNPH 2,4-DNP DNPH Brady's reagent Borche's reagent | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.918 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C6H6N4O4 | ||
| Molar mass | 198.14 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Red or orange powder | ||
| Melting point | 198 to 202 °C (388 to 396 °F; 471 to 475 K) dec. | ||
| Solubility in water | Slight | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
| Main hazards | Flammable, possibly carcinogenic | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Warning | ||
| Hazard statements | H228, H302, H319 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P240, P241, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P305+P351+P338, P330, P337+P313, P370+P378, P501 | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH or DNPH) is the organic compound C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2. DNPH is a red to orange solid. It is a substituted hydrazine. The solid is relatively sensitive to shock and friction. For this reason DNPH is usually handled as a wet powder. DNPH is a precursor to the drug Sivifene.
Synthesis
It can be prepared by the reaction of hydrazine sulfate with 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene:
DNP test
DNPH is a reagent in instructional laboratories on qualitative organic analysis. Brady's reagent or Borche's reagent, is prepared by dissolving DNPH in a solution containing methanol and some concentrated sulfuric acid. This solution is used to detect ketones and aldehydes. A positive test is signalled by the formation of a yellow, orange or red precipitate of the dinitrophenylhydrazone. Aromatic carbonyls give red precipitates whereas aliphatic carbonyls give more yellow color. The reaction between DNPH and a generic ketone to form a hydrazone is shown below:
- RR'C=O + C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 → C6H3(NO2)2NHN=CRR' + H2O
This reaction is, overall, a condensation reaction as two molecules joining together with loss of water. Mechanistically, it is an example of addition-elimination reaction: nucleophilic addition of the -NH2 group to the C=O carbonyl group, followed by the elimination of a H2O molecule:
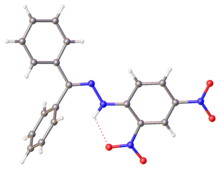
X-ray structure of DNP-derived hydrazone of benzophenone. Selected parameters: C=N, 128 pm; N-N, 1.38 pm, N-N-C(Ar), 119

DNP-derived hydrazones have characteristic melting points, facilitating identification of the carbonyl. In particular, the use of DNPH was developed by Brady and Elsmie. Modern spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques have superseded these techniques.
DNPH does not react with other carbonyl-containing functional groups such as carboxylic acids, amides, and esters, for which there is resonance-associated stability as a lone-pair of electrons interacts with the p orbital of the carbonyl carbon resulting in increased delocalization in the molecule. This stability would be lost by addition of a reagent to the carbonyl group. Hence, these compounds are more resistant to addition reactions. Also, with carboxylic acids, there is the effect of the compound acting as a base, leaving the resulting carboxylate negatively charged and hence no longer vulnerable to nucleophilic attack.
Safety
Dry DNPH is friction and shock sensitive. For this reason, it’s supplied damp or ‘wetted’ when a school purchases it from a chemical supplier. If DNPH is stored improperly and left to dry out, it can become explosive. It is an artificial uncoupler of the electron transport chain (ETC).
See also
References
- Allen, C. F. H. (1933). "2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine". Organic Syntheses. 13: 36. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.013.0036.
- Mohrig, Jerry R.; Hammond, Christina Noring; Morrill, Terence C.; Neckers, Douglas C. (1998). Experimental Organic Chemistry: A Balanced Approach, Macroscale and Microscale. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. p. 530. ISBN 0-7167-2818-4.
- Adapted from Chemistry in Context, 4th Edition, 2000, Graham Hill and John Holman
- Tameem, Abdassalam Abdelhafiz; Salhin, Abdussalam; Saad, Bahruddin; Rahman, Ismail Ab.; Saleh, Muhammad Idiris; Ng, Shea-Lin; Fun, Hoong-Kun (2006). "Benzophenone 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 62 (12): o5686–o5688. doi:10.1107/S1600536806048112.
- Brady, Oscar L.; Elsmie, Gladys V. (1926). "The use of 2:4-dinitrophenylhydrazine as a reagent for aldehydes and ketones". Analyst. 51 (599): 77–78. Bibcode:1926Ana....51...77B. doi:10.1039/AN9265100077.
- "What is 2,4-DNPH and Why Are Schools Carrying Out Controlled Explosions?". Compound Interest. 7 November 2016. Retrieved 26 October 2022.
- "Bomb disposal squads detonate chemical stocks in British schools". The Guardian. 2 November 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2018.


