| Revision as of 17:57, 18 February 2007 edit83.135.18.111 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:51, 17 October 2024 edit undoDzulfi Ramadhan (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users5,318 edits →ChannelsTags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit Android app edit | ||
| (397 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|none}} <!-- "none" is preferred when the title is sufficiently descriptive; see ] --> | |||
| As the world's third largest economy and with the largest ] in the ], ] today offers a vast diversity of television stations. | |||
| {{Culture of Germany}} | |||
| '''Television in Germany''' began in ] on 22 March 1935, broadcasting for 90 minutes three times a week. It was home to the first regular television service in the world,<ref name="dw">{{cite web|title=22.3.1935: Erstes Fernsehprogramm der Welt|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230306070242/http://www.kalenderblatt.de/index.php?what=thmanu&lang=de&manu_id=1737&sdt=20090322&maca=de-podcast_kalenderblatt-1086-xml-mrss|publisher=]|accessdate=9 March 2024}}</ref> named '']''. | |||
| In 2000, the German television market had approximately 36.5 million television households, making it the largest television market in ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ec.europa.eu/information_society/topics/telecoms/regulatory/studies/documents/dtv_euro2000.pdf|title=Digital Single Market|website=Digital Single Market|publisher=European Commission}}</ref> Nowadays, 95% of German households have at least one television receiver.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.destatis.de/DE/ZahlenFakten/GesellschaftStaat/EinkommenKonsumLebensbedingungen/AusstattungGebrauchsguetern/Tabellen/Unterhaltungselektronik_D.html|title=Staat & Gesellschaft - Ausstattung mit Gebrauchsgütern - Ausstattung privater Haushalte mit Unterhaltungselektronik - Deutschland - Statistisches Bundesamt (Destatis)|website=www.destatis.de|access-date=2016-11-18}}</ref> All the main German TV channels are ]. | |||
| ==History of German TV== | |||
| ===Before World War II=== | |||
| ==History== | |||
| The first regular electronic television service began in ] on ], ], using a 180-line system, and broadcasting 90 minutes three times a week. Very few receivers were ever privately owned, and viewers went instead to ''Fernsehstuben'' (television parlors). During the ], broadcasts, up to eight hours a day, took place in ] and ]. The ]s intended to use television as a medium for their ], but it was able to reach only a small number of viewers, in contrast to ]. By 1939 and the start of ] plans for an expansion of television programming were soon changed in favor of radio. Nevertheless, the Berlin station, along with one in occupied Paris, remained on the air for most of ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|History of television in Germany|Deutscher Fernsehfunk}} | |||
| In 1948 the British occupation forces allowed ] to broadcast television programmes for the British zone. Other regional networks also started to launch television in their own areas. Meanwhile, the GDR was launching its own television service, ] (DFF), based on the ] model. | |||
| A regular schedule began through the cooperation of all ] members in 1954. Basic principles in the central areas of entertainment, information and enlightenment were established and television plays developed as the medium's own specific art form. Improvements in technology and programming, as well as reduced prices, led to a steady increase in licence holders, and the number of licenses passed the 1-million mark in October 1957. | |||
| ===1950s=== | |||
| On 1 April 1963, the long-promised second TV network, the ] (Second German Television) started. Unlike ARD, which was regionalized and had its roots in radio, ZDF was a centrally organized channel devoted solely to television. On 25 August 1967, at 9:30 a.m. on both ARD and ZDF, vice chancellor ] started the era of colour TV in ] by pressing a symbolic launch button at the International Radio and TV Fair in West Berlin. | |||
| After ] it took several years until a TV program was broadcasted again. Directly after the war, newspapers and radio were the only available mass media and they were under direct control of the Allied government. In the West, the ], ] and ] had founded the ], the ''Arbeitsgemeinschaft der öffentlich-rechtlichen Rundfunkanstalten Deutschlands'' (''Cooperative association of the public broadcasters in Germany''). In the East, the ] founded its own radio and later TV stations, known as ''Deutscher Fernsehfunk'' (DFF). Many parts of Germany (particularly the GDR) received both channels. | |||
| ] started DFF2 in 1969, and introduced colour programming on both channels. In 1972, the DFF was renamed, dropping the pretense of being an all-Germany service and becoming Fernsehen der DDR (GDR Television) or DDR-FS. Its two channels became known as DDR1 and DDR2. | |||
| In ] both the ''ARD'' and the ''DFF'' made their first broadcasts. But at that time, only few West Germans and even fewer East Germans owned a TV set. Radios were still cheaper and a lot more popular. One of the events that enhanced the popularity of TV among the West Germans was the broadcast of the ] finals from ], which many followed on TV screens in shop windows. | |||
| The first two privately financed TV networks, ] (short for Radio Television Luxemburg) and ], started their programming in West Germany in 1984. (Previously RTL broadcast from ] but was only received in parts of Southwestern Germany). | |||
| ===1960s=== | |||
| After ], the TV stations of the ] were dissolved and the remnants were used to found new regional networks, e.g. the ] (Central German Broadcasting), as part of the ARD. In addition, more private TV stations opened, becoming available through cable, satellite and in some cases, over the airwaves. | |||
| In the ] TV became much more popular and was finally available for the vast part of the population. In ], a second TV network, the '']'' (''Second German Television'') started. In ], vice chancellor ] started the era of color TV in West Germany. Also, in the ], several member networks of the ''ARD'' started broadcasting their own regional television programs, known colloquially as ''Die Dritten'' (''The Third Networks'') In 1969 East Germany started DFF2, and introduced color programming on both channels. | |||
| == |
==Market== | ||
| Today, with almost 40 million TV households, 365 TV channels licensed in Germany and a total market volume of €9,615 million in 2008, Germany represents one of the biggest and most diversified TV markets in the world. The strongest revenue segment in Germany is public funding (€4,430 million in 2008), followed by advertising (€4,035 million) and subscription (1,150 € million).<ref name="international-television1"> International Television Expert Group</ref> This dominant market position of public and advertisement funded free TV channels in Germany explains why the German pay TV segment is significantly underperforming in an international comparison.<ref> International Television Expert Group</ref> | |||
| In 1972, the DFF was renamed, dropping the pretense of being an all-German service and becoming Fernsehen der DDR (GDR Television) or DDR-FS. Its two channels became known as DDR1 and DDR2. | |||
| In terms of total TV viewing market share Germany's market leaders in 2023 were again the two biggest ] channels (ZDF with 14.6% and Das Erste with 11.9%) and the two leading commercial channels (RTL with 7.9% and Sat.1 with 4.7%).<ref name=dwdl /> The leading pay TV provider was ] (see below). The biggest teleshopping providers in Germany are QVC and HSE24. | |||
| ===1980s=== | |||
| With 18.1 million TV households satellite is the dominant TV infrastructure in Germany, followed by cable (17.9 million TV households) and terrestrial (3.8 million TV households).<ref>{{cite web|title=Satellitenfernsehen in Deutschland|url=http://www.kabelfernsehen-kabelanschluss.de/artikel/satellitenfernsehen-in-deutschland|publisher=kabelfernsehen-kabelanschluss.de|access-date=2016-04-05}}</ref> In a 2010 survey half of German television viewers said they often found nothing to watch on television.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111119162745/http://www.v-net.tv/NewsDisplay.aspx?id=555 |date=2011-11-19}}</ref> | |||
| Until the early ], the average German TV viewer could choose only between usually three TV channels, all of them publicly financed through license fees. These broadcast only in the afternoon and evening and not always in color. In Western Germany this changed in ], as the first two privately financed TV networks, ''RTL plus'' (short for ''Radio Tele Luxemburg'') and ''SAT 1'', started their programming (previously ] had transmitted from Luxembourg into southwestern Germany). In contrast to the national public TV services, these new stations were only able to show their programs in the bigger cities via satellite or via broadband cable. But as the new stations introduced some very different kinds of programs (especially ''RTL plus'', which in its first years was known for its erotic programs in the late evening), their popularity increased and more people invested in broadband cable access or satellite antennas. | |||
| The ] sphere is the largest market for ] in Europe. Foreign TV shows and other formats are often dubbed into German, while ] formats with the original language are also becoming more popular.<ref>{{cite web|title=Hollywood dubbing: The German Bruce Willis and other invisible stars|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-21523643|publisher=BBC|date=21 February 2013|access-date=14 April 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ===1990s-2000s=== | |||
| ==Channels== | |||
| After reunification, the TV stations of the ] were dissolved and the remnants were used to found new regional networks, e.g. the '']'' (''Central German Broadcasting''), as part of the ''ARD''. In addition, more private TV stations opened, becoming available through cable, satellite, and in some cases, over the airwaves. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| {{Main|List of television stations in Germany}} | |||
| The channels with the largest viewing share in 2023 are:<ref name="dwdl">{{cite web|url=https://www.dwdl.de/zahlenzentrale/96184/rtl_legt_zu_prosieben_groesster_verlierer_kabel_eins_klar_im_plus/page_0.html |title=RTL legt zu, ProSieben größter Verlierer, Kabel Eins klar im Plus |website=dwdl.de |access-date=2024-01-03}}</ref> | |||
| As the millennium approached, Germany began airing new channels. The second programmes (], ] and ]) gained a huge stake in viewer ratings. The normal ratings chain is: ARD, RTL, ZDF, Sat1.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} RTL and ProSieben started buying international television series, mainly from the United States and United Kingdom (like ], ], ], ], ]). ARD and ZDF continued to produce their own content by investing in their own production companies and not buying international shows. In contrast, ARD and ZDF exported some show concepts to the USA, UK and China; for example "]". In ], a German law (Rundfunkstaatsvertrag) required channels to switch from analogue signals to digital signals by ]. Many regions can already receive the high-definition signals like Berlin, Lower-Saxony or the Ruhr valley. The programme diversity is by far the largest in Europe; with Germany being in the middle of Europe it can receive satellite channels like ], ], ], ], ], ] and other pan-European or Asian-African channels. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style= | |||
| ==Subscription channels== | |||
| |- | |||
| {{main|Arena (pay television network)}} | |||
| ! Position !! Channel !! Owner !! Share of<br/>total viewing (%)<br/>in 2023 !! Share of<br/>total viewing (%)<br/>in 2011<ref name="agf">{{cite web|url=https://www.agf.de/daten/tvdaten/marktanteile/ |title=AGF - Marktanteile |website=agf.de |access-date=2015-04-10}}</ref> !! Comparison<br/>2023/2011 | |||
| {{main|Premiere (pay television network)}} | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1 || ]|| ] || 14.6 || 12.1 || {{increase}} <small>(2.5)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | 2 || ] || ] || 11.9 || 12.4 || {{decrease}} <small>(0.5)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | 3 || ] || ] || 7.9 || 14.1 || {{decrease}} <small>(6.2)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | rowspan="2"| 4 || ] || ] || 4.7 || 10.1 || {{decrease}} <small>(5.4)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | ]|| RTL Group || 4.7 || 5.6 || {{decrease}} <small>(0.9)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | 5 || ] || ProSiebenSat.1 Media || 3.2 || 4.1 || {{decrease}} <small>(0.9)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | 6 || ] || ProSiebenSat.1 Media || 3.0 || 6.2 || {{decrease}} <small>(3.2)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | rowspan="2"| 7 || ]|| ZDF || 2.6 || 0.4 || {{increase}} <small>(2.2)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| | ]|| ]/] || 2.6 || 2.5 || {{increase}} <small>(0.1)</small> | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| The combined share of ARD's so called Third Programmes (regional broadcasters ], ], ], etc.) was 13.8% in 2023<ref name="dritte">{{cite web|url=https://www.dwdl.de/zahlenzentrale/96237/rekordjahr_fuer_nitro_zdfneo_disney_und_comedy_central/ |title=So lief 2023 für die Spartensender |publisher=dwdl.de |access-date=2024-01-03}}</ref> | |||
| ===Subscription channels=== | |||
| Also around the millennium was the heyday of Germany's sole subscription channel Premiere. Premiere offered telecasts of Germany's soccer ]. The "Bundesliga" was Premiere's cash-cow, but they lost the broadcasting rights in ] to a newly formed competitor, ]. Furthermore, Premiere was the brainchild of the former television czar, ]. Kirch went into insolvency after a struggling decade of losing viewers from his preceding subscription channel, DF1 (Digital TV 1). The company gained ground with its new manager ] and now tries to get viewers back with buying new international shows from overseas and introduce them to the German audience (]'s ] was first shown on Premiere). Also Kofler and Kirch bought international movies from American films studios in advance so they can broadcast them one year after their release. Normally, American movies are shown on non-subscription (free-TV) channels after three years of their release, so Premiere benefitted from that advantage. Premiere highlights a combination of multiple channels featuring ], ], ] and several themed channels for music, crime and sport. | |||
| {{Main|HD+|Sky Deutschland|Kabel Deutschland}} | |||
| Germany's sole subscription channel Premiere had its heyday around the millennium. Premiere offered telecasts of the German football league – the ], but they lost the broadcasting rights in 2006 to a newly formed competitor – ]. Premiere was the brainchild of the former television czar, ]. He went into insolvency after a decade of losing viewers from his subscription channel, DF1 (Digital TV 1). The company regained some ground with its new manager ].{{Citation needed|date=November 2018}} | |||
| Around ], several German cable companies created a new challenger to Premiere, ARENA. The participating companies are ] (]) and ] (North Rhine-Westphalia) through their combined partnership called "]". Arena, a rather small company tried to buy the pay-TV rights to the German Bundesliga and won by a decision of the marketing directorate of the ]. The Bundesliga is a cash-cow on the German television market, so previous rights holders Premiere got a big blow into their concept of broadcasting. Arena holds the rights from 2006 to ]. In 2008 there will be further negotiations for the broadcasting of the ]. | |||
| In 2005, several German cable companies created a new challenger to Premiere - ARENA. The participating companies are ] (Hesse) and ] (North Rhine-Westphalia) through their combined partnership called "]". Arena, a rather small company, wanted to buy the pay-TV rights to the German Bundesliga and won by a decision of the marketing directorate of the ]. The rights to broadcast the Bundesliga is regarded as lucrative in the German television market, so previous rights holders Premiere suffered a wounding blow to their business model. Arena held the rights from 2006 to 2008. Further negotiations were due in 2008 for the broadcasting of the ]. | |||
| ==ARD - Das Erste== | |||
| ==Public broadcasters== | |||
| As stated above, the ''ARD'' was the first German broadcasting station. It has a very federally oriented structure. Currently, nine regional TV stations cooperate together to produce programs for the TV network known as ''Das Erste'' (''The First''): | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|ARD (broadcaster)|ZDF}} | |||
| As stated above, the ARD was the first German broadcasting station. It has a federally orientated structure. At present, nine regional public broadcasters cooperate to produce programs for the TV network known as '']'' (''The First''): | |||
| * ] – ''North German Broadcasting'' – ], ], ] and ] | |||
| * ] – also a television broadcaster – ] | |||
| * ] – ''Berlin-Brandenburg Broadcasting'' – ] and ] | |||
| * ] – ''Central German Broadcasting'' – ], ] and ] | |||
| * ] – ''West German Broadcasting'' – ] | |||
| * ] – ''Hessian Broadcasting'' – ] | |||
| * ] – ''South Western Broadcasting'' – ] and ] | |||
| * ] – ''Saarland Broadcasting'' – ] | |||
| * ] – ''Bavarian Broadcasting'' – ] | |||
| Seven of these broadcasters run their own regional TV programs (''The Third''), most of them use several frequencies and show local opt-outs. | |||
| (''The fact that small regions like Bremen or the Saarland have their own broadcasting stations has mainly historical reasons. They only contribute to the nationwide TV program ''Das Erste'' and only have limited regional TV programs.'') | |||
| While multi-state-broadcasters ], ], ] and ] have state versions (e.g. RBB Berlin, MDR Sachsen, NDR Hamburg and SWR Baden-Württemberg), ] and ] have regional opt-outs below state level (BR: North and South, WDR: 11 versions). | |||
| Two small regions, ] (]) and the ] (]), have their own broadcasting stations, mainly for historical reasons. They only contribute to the national TV channel ''Das Erste'' and produce a state opt-out for their neighbour broadcaster (] on SWR, ] on NDR). | |||
| ==Teletext== | |||
| ''Das Erste'' is a network which consists of programming oriented for the whole family. Especially well-known and respected are its TV news, e.g. the ], produced by the NDR and broadcast nightly at 8 p.m. The Tagesschau is a national institution since its inception 1952. Until the early ], it was considered taboo by some to call someone else between 8:00 and 8:15, as everybody was supposedly watching the "Tagesschau" then. As of today there is news available around the clock. Other famous programs are ] (a crime series, which is located in several different cities and produced by all the partners of the ARD in turn). ''Das Erste'' also shows children's programs like ], daily soap operas like ] or ], Germany's longest running weekly soap opera ], sport events (though extremely popular sports like soccer or car racing are also shown on the private broadcasting stations) and also TV shows for senior citizens, often featuring German folk music. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Germany has run a regular ] service (often called Videotext) since 1 June 1980 on the public broadcasting channels. Almost all German TV stations have teletext.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ard-text.de/|title=Teletext im Ersten|work=Das Erste|access-date=10 April 2017}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.sevenonemedia.de/teletext-viewer|title=Teletext Viewer|work=SevenOne Media|access-date=10 April 2017}}</ref> Even with the advent of digital television, teletext is still widely used.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://mmm.verdi.de/medienwirtschaft/teletext-nicht-totzukriegen-52483|title = Teletext: Nicht totzukriegen| date=3 August 2018 }}</ref> | |||
| Teletext pages are selected via a three-digit number, ranging from 100 to 899. While every station is free to organize their teletext pages in any way, most adhere to the following de facto standard: | |||
| The ''ARD'' is not only responsible for ''Das Erste''. There are seven regional networks, called ''Die Dritten'' (''The Third Networks''). Only RB and SR do not have their own full-time third networks, but mostly broadcast the programming of the NDR and the SWR, respectively. The third networks feature documentaries, older movies and regional news programs, often shown for only one federal state or only parts of it. For example the NDR every evening at 19:30 stops broadcasting its common program and broadcasts instead regional news bulletins for Schleswig-Holstein (''Schleswig-Holstein-Magazin''), Hamburg (''Hamburg Journal''), Mecklenburg-West Pomerania (''Nordmagazin''), Bremen (''Buten & Binnen'') and Lower Saxony (''Hallo, Niedersachsen!'')). | |||
| * 100 Main page | |||
| Since the ], the ''ARD'' also produces several niche channels. The first one was ''EinsPlus'', which was intended as a culture niche channel and was broadcasted from ] till ]. Afterwards, the ''ARD'' co-produced ''3sat'', in cooperation with the ''ZDF'', the Austrian Broadcasting network ''ORF'' and the Swiss Broadcasting network ''DRS''. A second culture niche channel is ''arte'', which is co-produced with the French Broadcasting Service ''LaSept''. | |||
| * 110 News | |||
| * 120 News / Weather | |||
| * 200 Sports / Soccer | |||
| * 300 TV schedule | |||
| * 333 On air now | |||
| * 600 Advertising, chats, phone sex (commercial channels only) | |||
| The teletext system is also used to transmit subtitles on a special, transparent page (usually 149, 150 or 777), so that both text and the normal picture are visible. With the advent of digital television however, a few stations discarded teletext subtitles and are now using the subtitles feature of the ] (DVB) system. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| ==Reception== | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{update section|date=October 2021}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Technology !! Total households !! Relative households | |||
| |- | |||
| | Satellite || 17,779,000 || 46.1% | |||
| |- | |||
| | Cable (digital) || 11,229,000 || 29.1% | |||
| |- | |||
| | Cable (analogue)|| 6,630,000 || 9.9% | |||
| |- | |||
| | DVB-T || 3,865,000 || 10.0% | |||
| |- | |||
| | DSL-TV || 1,899,000 || 4.9% | |||
| |- | |||
| | '''All''' || '''38,557,000''' || '''100%''' | |||
| |} | |||
| ===Satellite=== | |||
| Digital satellite television has been officially available in Germany since 1996. Prior to May 2012, most of the 30+ TV stations broadcast their ''satellite'' signal using both analogue and digital (DVB-S); however, all analogue satellite broadcasts ceased on 30 April 2012. | |||
| There is currently a single pay TV satellite operator in Germany - ]. Prior to being known as Sky, the service was named Premiere;<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.spiegel.de/wirtschaft/0,1518,623512,00.html|title=Premiere soll künftig Sky Deutschland heißen|date=13 February 2010|publisher=spiegel-online.de}}</ref> it (along with its former owner ]) got into serious financial trouble due to its early and proprietary usage of encryption (Betacrypt, D-box). Subsequently, Premiere was bought by ] and renamed Sky, in keeping with their satellite services elsewhere in Europe (] and ]). | |||
| ;HDTV via satellite | |||
| In late 2004 German channel group ] showed a ] documentary and a self-produced TV movie in ] via ] ], followed by the Hollywood films '']'' and '']'' in March 2005. These were intended to be a test for future commercial HD services. | |||
| Regular ] broadcast of the HD versions of ] and ] began on 26 October 2005. Unlike the test broadcasts, ] and ] were used. Both ProSieben HD and Sat.1 HD ceased their unencrypted broadcasts in 2008; encrypted HD broadcasting of both channels resumed under the ] brand (which also included other commercial channels; see below) in January 2010. | |||
| Premiere, after several delays, started broadcasting three HD channels — one each dedicated to ]s, ]s and ] — in November 2005, although there were virtually no suitable, certified receivers available on the market. The content was also sparse and thus often repeated. Sky (formerly Premiere) reuses its proprietary ] system embedded into its content scrambling system (]) from SD broadcasts<!--probably not 100% correct--> to block analogue output of the movie channel from the receiving ] altogether, only allowing ]-secured transmissions; the other channels are less restricted. | |||
| On 1 November 2009 the premium ] service launched with two channels, RTL HD and Vox HD, with Sat.1 HD, ProSieben HD and ] HD joining the service in January 2010. DSF HD (now called Sport1 HD) began test broadcasts in August 2010 and launched fully on HD+ on 1 November 2010, followed by Sixx HD and RTL2 HD on 1 December 2010. In June 2011, Comedy Central HD, Nickelodeon HD and N24 HD joined service, bringing the number of channels offered to 11. In April 2011, HD+ became available to Sky Deutschland subscribers without the need for an HD+ ] and viewing card (although an additional subscription is still required). | |||
| Currently (as of May 2012) all satellite HDTV channels are broadcast using the ] codec. As of July 2014, most material is upscaled SD content. | |||
| ;Free-to-air HDTV via satellite | |||
| Prior to 30 April 2012 there were eight free-to-air HDTV channels originating in Germany broadcast via satellite: Das Erste HD, ZDF HD, Arte HD, Anixe HD,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.engadgethd.com/2008/02/16/sat-1-hd-and-prosieben-hd-go-offline-til-2010-in-germany/|title=Sat.1 HD and ProSieben HD go offline until 2010 in Germany - Engadget HD|work=Engadget HD|date=16 February 2008}}</ref> EinsFestival HD,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.einsfestival.de/was_ist_einsfestival/hdtv_in_einsfestival.jsp|title=HDTV in Einsfestival {{!}} Einsfestival|language=de|access-date=8 April 2012|publisher=ARD|work=EinsFestival|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120509224155/http://www.einsfestival.de/was_ist_einsfestival/hdtv_in_einsfestival.jsp|archive-date=2012-05-09|url-status=dead}}</ref> ] HD, QVC HD and HSE24 HD.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.digitalfernsehen.de/Astra-Sonnenklar-TV-ab-September-in-HD-frei-empfangbar.64105.0.html|title=Astra: Sonnenklar TV ab September in HD frei empfangbar - DIGITALFERNSEHEN.de|trans-title=Astra: Sonnenklar TV available in HD for free from September - DIGITALFERNSEHEN.de|language=de|date=19 August 2011|access-date=8 April 2012|work=Digitalfernsehen.de}}</ref> After 30 April 2012, when all analogue satellite broadcasts ceased, ten additional FTA HD channels became available (all of which are ] channels): ] HD, ] HD, ] HD, ] HD, ] HD, ] HD, ] HD, ] HD, ] HD and ] HD.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.kabel-internet-telefon.de/news/36645-zdfneo-3sat-br-ndr-swr-wdr-phoenix-kika-starten-hd-kanaele|title=ZDFneo, 3sat, BR, NDR, SWR, WDR, Phoenix, KiKa starten HD Kanäle|language=de|trans-title=ZDFneo, 3sat, BR, NDR, SWR, WDR, Phoenix, KiKa launch HD channels|date=13 March 2012|access-date=8 April 2012|work=kabel-internet-telefon.de}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://digital.t-online.de/hdtv-neue-hd-kanaele-von-ard-und-zdf-ab-30-april-2012/id_53311006/index|title=HDTV: Neue HD-Kanäle von ARD und ZDF ab 30. April 2012|language=de|trans-title=HDTV: New HD channels from ARD and ZDF after 30 April 2012|date=20 January 2012|access-date=8 April 2012|work=T-online.de}}</ref> | |||
| From December 2013 on all PSB channels except ], ] and ] are available in HD. | |||
| ===Cable=== | |||
| DVB-C transmission started in 2004 with ] Premiere and digital versions of the analogue channels. | |||
| The rather late changeover to DVB was caused both by the long process of selling the infrastructure of former monopolist ] to others and the fact that the cable network ends at the curb or property, with the in-house cable in large apartment buildings being operated by a different company. Due to this, the new owners of Deutsche Telekom's cable network were in many cases not able to offer new products directly to the viewer. | |||
| By 2006, there were three major cable operators, Unity Media in ], ] and ] and by far the largest, ] in the other 13 states. Today, all companies offer about 200 TV channels by DVB-C, which includes some 70 channels at no extra charge as well as a number of ] offers and subscription-based packages (like the HD-broadcasts of privately owned channels, comparable to HD+ on satellite). In addition to that pay TV broadcaster ] is also available. | |||
| In some very large apartment complexes a number of local and national companies operate an in-house cable network which is fed solely by its own satellite antenna on the building, not the local cable operator. The satellite channels are either transcoded into analogue transmission, receivable by any TV set without extra equipment, or into DVB-C. | |||
| As of 2014, still 17.2% of Germany transmits television with analogue cable signals, compared to 29.1% of digital cable; this similar to the situation in the ], ] and ], where analogue cable is also still widely used.<ref>http://www.die-medienanstalten.de/fileadmin/Download/Publikationen/Digitalisierungsbericht/2014/Digitalisierungsbericht_2014_Daten_und_Fakten.pdf Digitalisierungsbericht 2014 - Daten und Fakten</ref> | |||
| ===Terrestrial=== | |||
| Terrestrial reception had lost most of its users by the 1990s{{Citation needed|date=November 2008}} due to extensive cable and satellite coverage. In a two step process analogue terrestrial TV broadcasting in the states of ] and ] was switched off in 2003 and replaced by ], in 2005, about two-thirds of Germany's states began to replace analogue transmission. By 2006, all metropolitan and most rural areas had moved to digital transmission. Today, only foreign army bases and some local TV stations still broadcast on analogue. | |||
| While the public broadcasters ] and ] transmit throughout Germany, commercial stations often are only available within metropolitan areas, so the number of available channels varies between about 10 and 30. All DVB-T1 channels were ] and the broadcasters rented transmission services directly from a transmitter operator, usually ]. ARD stations also use their own transmitters. | |||
| In June 2016, a gradual switch-over from ] with ] encoding to ] with ] encoding has commenced. The first phase included one new multiplex broadcasting six channels in selected urban areas, in addition to the old DVB-T standard.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.media-broadcast.com/uploads/media/Tabelle_Senderstandorte_DVB-T2HD_Erste-Stufe_22032016.pdf|title=List of sites for the DVB-T2 HD preview mux}}</ref> The DVB-T2 channels are broadcasting in 1080p50.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.digitalfernsehen.de/DVB-T2-HD-ARD-vorerst-nur-hochskaliertes-Full-HD.138903.0.html|title=DVB-T2 HD: ARD vorerst nur hochskaliertes Full HD|access-date=2016-10-24}}</ref> The commercial channels are encrypted and part of the "Freenet TV"-Package.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.teltarif.de/dvb-t2-freenet-tv-start/news/63743.html|title=DVB-T2: Private Programme werden als Freenet-TV vermarktet|last=Weidner|first=Markus|access-date=2016-10-24}}</ref> The final switch-over to DVB-T2 occurred in steps, starting with major metropolitan areas who switched on 29 March 2017. The last transmitter is planned to switch in 2019.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.dvb-t2hd.de/programme|title=DVB-T2 HD - offizielles Informationsportal|newspaper=DVB-T2 HD - offizielles Informationsportal|access-date=2016-10-24}}</ref> | |||
| ==Series== | |||
| Almost all fictional programs on German television are regular TV series. While the public broadcaster(s) predominantly own(s) the productions that are broadcast, the private stations/networks often put on series licensed from abroad, mainly the United States. Peaking in the 1990s, the private channels had aired self-produced series such as '']'' (1996–2000), '']'' (Alarm for Cobra 11 - The Motorway Police) (since 1996), ''The Sentinel'' (1994–1996), '']'' (1996–2005) or '']'' (mainly from 1992 to 2006) with great success. Since the late 2000s, the amount of original series on the private broadcasters has markedly declined. | |||
| The highest-rated series is the crime drama {{Lang|de|]}}, which airs almost every Sunday on public broadcaster ]. It has run since 1970 and has featured several casts, that are not related to each other. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * {{section link|Dubbing (filmmaking)|Germany, Austria and Switzerland}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist|2}} | |||
| {{Television in Germany}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Television in Europe}} | |||
| {{Germany topics}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:51, 17 October 2024
Television in Germany began in Berlin on 22 March 1935, broadcasting for 90 minutes three times a week. It was home to the first regular television service in the world, named Fernsehsender Paul Nipkow.
In 2000, the German television market had approximately 36.5 million television households, making it the largest television market in Europe. Nowadays, 95% of German households have at least one television receiver. All the main German TV channels are free-to-air.
History

In 1948 the British occupation forces allowed NWDR to broadcast television programmes for the British zone. Other regional networks also started to launch television in their own areas. Meanwhile, the GDR was launching its own television service, Deutscher Fernsehfunk (DFF), based on the Soviet model.
A regular schedule began through the cooperation of all ARD members in 1954. Basic principles in the central areas of entertainment, information and enlightenment were established and television plays developed as the medium's own specific art form. Improvements in technology and programming, as well as reduced prices, led to a steady increase in licence holders, and the number of licenses passed the 1-million mark in October 1957.
On 1 April 1963, the long-promised second TV network, the Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen (Second German Television) started. Unlike ARD, which was regionalized and had its roots in radio, ZDF was a centrally organized channel devoted solely to television. On 25 August 1967, at 9:30 a.m. on both ARD and ZDF, vice chancellor Willy Brandt started the era of colour TV in West Germany by pressing a symbolic launch button at the International Radio and TV Fair in West Berlin.
East Germany started DFF2 in 1969, and introduced colour programming on both channels. In 1972, the DFF was renamed, dropping the pretense of being an all-Germany service and becoming Fernsehen der DDR (GDR Television) or DDR-FS. Its two channels became known as DDR1 and DDR2.
The first two privately financed TV networks, RTL plus (short for Radio Television Luxemburg) and SAT 1, started their programming in West Germany in 1984. (Previously RTL broadcast from Luxembourg but was only received in parts of Southwestern Germany).
After reunification, the TV stations of the German Democratic Republic were dissolved and the remnants were used to found new regional networks, e.g. the Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (Central German Broadcasting), as part of the ARD. In addition, more private TV stations opened, becoming available through cable, satellite and in some cases, over the airwaves.
Market
Today, with almost 40 million TV households, 365 TV channels licensed in Germany and a total market volume of €9,615 million in 2008, Germany represents one of the biggest and most diversified TV markets in the world. The strongest revenue segment in Germany is public funding (€4,430 million in 2008), followed by advertising (€4,035 million) and subscription (1,150 € million). This dominant market position of public and advertisement funded free TV channels in Germany explains why the German pay TV segment is significantly underperforming in an international comparison.
In terms of total TV viewing market share Germany's market leaders in 2023 were again the two biggest public-service channels (ZDF with 14.6% and Das Erste with 11.9%) and the two leading commercial channels (RTL with 7.9% and Sat.1 with 4.7%). The leading pay TV provider was Sky Deutschland (see below). The biggest teleshopping providers in Germany are QVC and HSE24.
With 18.1 million TV households satellite is the dominant TV infrastructure in Germany, followed by cable (17.9 million TV households) and terrestrial (3.8 million TV households). In a 2010 survey half of German television viewers said they often found nothing to watch on television.
The Germanophone sphere is the largest market for dubbing in Europe. Foreign TV shows and other formats are often dubbed into German, while subtitled formats with the original language are also becoming more popular.
Channels

The channels with the largest viewing share in 2023 are:
| Position | Channel | Owner | Share of total viewing (%) in 2023 |
Share of total viewing (%) in 2011 |
Comparison 2023/2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZDF | ZDF | 14.6 | 12.1 | |
| 2 | Das Erste | ARD | 11.9 | 12.4 | |
| 3 | RTL | RTL Group | 7.9 | 14.1 | |
| 4 | Sat.1 | ProSiebenSat.1 Media | 4.7 | 10.1 | |
| Vox | RTL Group | 4.7 | 5.6 | ||
| 5 | Kabel Eins | ProSiebenSat.1 Media | 3.2 | 4.1 | |
| 6 | ProSieben | ProSiebenSat.1 Media | 3.0 | 6.2 | |
| 7 | ZDFneo | ZDF | 2.6 | 0.4 | |
| NDR Fernsehen | NDR/RB | 2.6 | 2.5 |
The combined share of ARD's so called Third Programmes (regional broadcasters WDR, NDR, SWR, etc.) was 13.8% in 2023
Subscription channels
Main articles: HD+, Sky Deutschland, and Kabel DeutschlandGermany's sole subscription channel Premiere had its heyday around the millennium. Premiere offered telecasts of the German football league – the Bundesliga, but they lost the broadcasting rights in 2006 to a newly formed competitor – Arena. Premiere was the brainchild of the former television czar, Leo Kirch. He went into insolvency after a decade of losing viewers from his subscription channel, DF1 (Digital TV 1). The company regained some ground with its new manager Georg Kofler.
In 2005, several German cable companies created a new challenger to Premiere - ARENA. The participating companies are iesy (Hesse) and ish (TV) (North Rhine-Westphalia) through their combined partnership called "Unity Media". Arena, a rather small company, wanted to buy the pay-TV rights to the German Bundesliga and won by a decision of the marketing directorate of the DFL. The rights to broadcast the Bundesliga is regarded as lucrative in the German television market, so previous rights holders Premiere suffered a wounding blow to their business model. Arena held the rights from 2006 to 2008. Further negotiations were due in 2008 for the broadcasting of the Bundesliga.
Public broadcasters
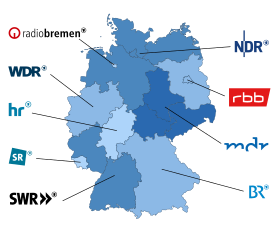
As stated above, the ARD was the first German broadcasting station. It has a federally orientated structure. At present, nine regional public broadcasters cooperate to produce programs for the TV network known as Das Erste (The First):
- Norddeutscher Rundfunk – North German Broadcasting – Hamburg, Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Radio Bremen – also a television broadcaster – Bremen
- Rundfunk Berlin-Brandenburg – Berlin-Brandenburg Broadcasting – Berlin and Brandenburg
- Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk – Central German Broadcasting – Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia
- Westdeutscher Rundfunk – West German Broadcasting – North Rhine-Westphalia
- Hessischer Rundfunk – Hessian Broadcasting – Hesse
- Südwestrundfunk – South Western Broadcasting – Baden-Württemberg and Rhineland-Palatinate
- Saarländischer Rundfunk – Saarland Broadcasting – Saarland
- Bayerischer Rundfunk – Bavarian Broadcasting – Bavaria
Seven of these broadcasters run their own regional TV programs (The Third), most of them use several frequencies and show local opt-outs. While multi-state-broadcasters NDR, RBB, MDR and SWR have state versions (e.g. RBB Berlin, MDR Sachsen, NDR Hamburg and SWR Baden-Württemberg), BR and WDR have regional opt-outs below state level (BR: North and South, WDR: 11 versions). Two small regions, Bremen (RB) and the Saarland (SR), have their own broadcasting stations, mainly for historical reasons. They only contribute to the national TV channel Das Erste and produce a state opt-out for their neighbour broadcaster (SR Fernsehen on SWR, Radio Bremen TV on NDR).
Teletext

Germany has run a regular Teletext service (often called Videotext) since 1 June 1980 on the public broadcasting channels. Almost all German TV stations have teletext. Even with the advent of digital television, teletext is still widely used.
Teletext pages are selected via a three-digit number, ranging from 100 to 899. While every station is free to organize their teletext pages in any way, most adhere to the following de facto standard:
- 100 Main page
- 110 News
- 120 News / Weather
- 200 Sports / Soccer
- 300 TV schedule
- 333 On air now
- 600 Advertising, chats, phone sex (commercial channels only)
The teletext system is also used to transmit subtitles on a special, transparent page (usually 149, 150 or 777), so that both text and the normal picture are visible. With the advent of digital television however, a few stations discarded teletext subtitles and are now using the subtitles feature of the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) system.
Reception
| This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (October 2021) |
| Technology | Total households | Relative households |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite | 17,779,000 | 46.1% |
| Cable (digital) | 11,229,000 | 29.1% |
| Cable (analogue) | 6,630,000 | 9.9% |
| DVB-T | 3,865,000 | 10.0% |
| DSL-TV | 1,899,000 | 4.9% |
| All | 38,557,000 | 100% |
Satellite
Digital satellite television has been officially available in Germany since 1996. Prior to May 2012, most of the 30+ TV stations broadcast their satellite signal using both analogue and digital (DVB-S); however, all analogue satellite broadcasts ceased on 30 April 2012.
There is currently a single pay TV satellite operator in Germany - Sky Deutschland. Prior to being known as Sky, the service was named Premiere; it (along with its former owner Leo Kirch) got into serious financial trouble due to its early and proprietary usage of encryption (Betacrypt, D-box). Subsequently, Premiere was bought by News Corporation and renamed Sky, in keeping with their satellite services elsewhere in Europe (Sky (UK and Ireland) and Sky Italia).
- HDTV via satellite
In late 2004 German channel group ProSieben showed a BBC documentary and a self-produced TV movie in 1080i via MPEG-2 DVB-S, followed by the Hollywood films Spider-Man and Men in Black II in March 2005. These were intended to be a test for future commercial HD services.
Regular free to air broadcast of the HD versions of ProSieben and Sat.1 began on 26 October 2005. Unlike the test broadcasts, DVB-S2 and MPEG-4 AVC were used. Both ProSieben HD and Sat.1 HD ceased their unencrypted broadcasts in 2008; encrypted HD broadcasting of both channels resumed under the HD+ brand (which also included other commercial channels; see below) in January 2010.
Premiere, after several delays, started broadcasting three HD channels — one each dedicated to films, sports and documentaries — in November 2005, although there were virtually no suitable, certified receivers available on the market. The content was also sparse and thus often repeated. Sky (formerly Premiere) reuses its proprietary digital rights management system embedded into its content scrambling system (Nagravision) from SD broadcasts to block analogue output of the movie channel from the receiving set-top box altogether, only allowing HDCP-secured transmissions; the other channels are less restricted.
On 1 November 2009 the premium HD+ service launched with two channels, RTL HD and Vox HD, with Sat.1 HD, ProSieben HD and Kabel eins HD joining the service in January 2010. DSF HD (now called Sport1 HD) began test broadcasts in August 2010 and launched fully on HD+ on 1 November 2010, followed by Sixx HD and RTL2 HD on 1 December 2010. In June 2011, Comedy Central HD, Nickelodeon HD and N24 HD joined service, bringing the number of channels offered to 11. In April 2011, HD+ became available to Sky Deutschland subscribers without the need for an HD+ CAM and viewing card (although an additional subscription is still required).
Currently (as of May 2012) all satellite HDTV channels are broadcast using the h.264 codec. As of July 2014, most material is upscaled SD content.
- Free-to-air HDTV via satellite
Prior to 30 April 2012 there were eight free-to-air HDTV channels originating in Germany broadcast via satellite: Das Erste HD, ZDF HD, Arte HD, Anixe HD, EinsFestival HD, sonnenklar.TV HD, QVC HD and HSE24 HD. After 30 April 2012, when all analogue satellite broadcasts ceased, ten additional FTA HD channels became available (all of which are public service channels): Phoenix HD, NDR HD, WDR HD, BR HD, SWR HD, ZDFneo HD, ZDFinfo HD, ZDFkultur HD, 3sat HD and KiKa HD. From December 2013 on all PSB channels except ARD-alpha, SR Fernsehen and Radio Bremen TV are available in HD.
Cable
DVB-C transmission started in 2004 with pay TV Premiere and digital versions of the analogue channels.
The rather late changeover to DVB was caused both by the long process of selling the infrastructure of former monopolist Deutsche Telekom to others and the fact that the cable network ends at the curb or property, with the in-house cable in large apartment buildings being operated by a different company. Due to this, the new owners of Deutsche Telekom's cable network were in many cases not able to offer new products directly to the viewer.
By 2006, there were three major cable operators, Unity Media in Hesse, North Rhine-Westphalia and Baden-Württemberg and by far the largest, Kabel Deutschland in the other 13 states. Today, all companies offer about 200 TV channels by DVB-C, which includes some 70 channels at no extra charge as well as a number of pay-per-view offers and subscription-based packages (like the HD-broadcasts of privately owned channels, comparable to HD+ on satellite). In addition to that pay TV broadcaster Sky Deutschland is also available.
In some very large apartment complexes a number of local and national companies operate an in-house cable network which is fed solely by its own satellite antenna on the building, not the local cable operator. The satellite channels are either transcoded into analogue transmission, receivable by any TV set without extra equipment, or into DVB-C.
As of 2014, still 17.2% of Germany transmits television with analogue cable signals, compared to 29.1% of digital cable; this similar to the situation in the Netherlands, Sweden and Belgium, where analogue cable is also still widely used.
Terrestrial
Terrestrial reception had lost most of its users by the 1990s due to extensive cable and satellite coverage. In a two step process analogue terrestrial TV broadcasting in the states of Berlin and Brandenburg was switched off in 2003 and replaced by DVB-T, in 2005, about two-thirds of Germany's states began to replace analogue transmission. By 2006, all metropolitan and most rural areas had moved to digital transmission. Today, only foreign army bases and some local TV stations still broadcast on analogue.
While the public broadcasters ARD and ZDF transmit throughout Germany, commercial stations often are only available within metropolitan areas, so the number of available channels varies between about 10 and 30. All DVB-T1 channels were free-to-air and the broadcasters rented transmission services directly from a transmitter operator, usually Media Broadcast. ARD stations also use their own transmitters.
In June 2016, a gradual switch-over from DVB-T with MPEG-2 encoding to DVB-T2 with HEVC encoding has commenced. The first phase included one new multiplex broadcasting six channels in selected urban areas, in addition to the old DVB-T standard. The DVB-T2 channels are broadcasting in 1080p50. The commercial channels are encrypted and part of the "Freenet TV"-Package. The final switch-over to DVB-T2 occurred in steps, starting with major metropolitan areas who switched on 29 March 2017. The last transmitter is planned to switch in 2019.
Series
Almost all fictional programs on German television are regular TV series. While the public broadcaster(s) predominantly own(s) the productions that are broadcast, the private stations/networks often put on series licensed from abroad, mainly the United States. Peaking in the 1990s, the private channels had aired self-produced series such as Der Clown (1996–2000), Alarm für Cobra 11 – Die Autobahnpolizei (Alarm for Cobra 11 - The Motorway Police) (since 1996), The Sentinel (1994–1996), Alpha Team - The Lifesaver in OP (1996–2005) or Wolff's Turf (mainly from 1992 to 2006) with great success. Since the late 2000s, the amount of original series on the private broadcasters has markedly declined.
The highest-rated series is the crime drama Tatort, which airs almost every Sunday on public broadcaster ARD. It has run since 1970 and has featured several casts, that are not related to each other.
See also
- Telecommunications in Germany
- List of television stations in Germany
- List of German language television channels
- List of German television series
- German television comedy
- International Television Expert Group
- Media of Germany
- Dubbing (filmmaking) § Germany, Austria and Switzerland
References
- "22.3.1935: Erstes Fernsehprogramm der Welt". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 9 March 2024.
- "Digital Single Market" (PDF). Digital Single Market. European Commission.
- "Staat & Gesellschaft - Ausstattung mit Gebrauchsgütern - Ausstattung privater Haushalte mit Unterhaltungselektronik - Deutschland - Statistisches Bundesamt (Destatis)". www.destatis.de. Retrieved 2016-11-18.
- German TV Market Report 2009 International Television Expert Group
- Global TV Market Report 2009 International Television Expert Group
- ^ "RTL legt zu, ProSieben größter Verlierer, Kabel Eins klar im Plus". dwdl.de. Retrieved 2024-01-03.
- "Satellitenfernsehen in Deutschland". kabelfernsehen-kabelanschluss.de. Retrieved 2016-04-05.
- Operators need an EPG+ strategy for content discovery Archived 2011-11-19 at the Wayback Machine
- "Hollywood dubbing: The German Bruce Willis and other invisible stars". BBC. 21 February 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2015.
- "AGF - Marktanteile". agf.de. Retrieved 2015-04-10.
- "So lief 2023 für die Spartensender". dwdl.de. Retrieved 2024-01-03.
- "Teletext im Ersten". Das Erste. Retrieved 10 April 2017.
- "Teletext Viewer". SevenOne Media. Retrieved 10 April 2017.
- "Teletext: Nicht totzukriegen". 3 August 2018.
- "Premiere soll künftig Sky Deutschland heißen". spiegel-online.de. 13 February 2010.
- "Sat.1 HD and ProSieben HD go offline until 2010 in Germany - Engadget HD". Engadget HD. 16 February 2008.
- "HDTV in Einsfestival | Einsfestival". EinsFestival (in German). ARD. Archived from the original on 2012-05-09. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- "Astra: Sonnenklar TV ab September in HD frei empfangbar - DIGITALFERNSEHEN.de" [Astra: Sonnenklar TV available in HD for free from September - DIGITALFERNSEHEN.de]. Digitalfernsehen.de (in German). 19 August 2011. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- "ZDFneo, 3sat, BR, NDR, SWR, WDR, Phoenix, KiKa starten HD Kanäle" [ZDFneo, 3sat, BR, NDR, SWR, WDR, Phoenix, KiKa launch HD channels]. kabel-internet-telefon.de (in German). 13 March 2012. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- "HDTV: Neue HD-Kanäle von ARD und ZDF ab 30. April 2012" [HDTV: New HD channels from ARD and ZDF after 30 April 2012]. T-online.de (in German). 20 January 2012. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- http://www.die-medienanstalten.de/fileadmin/Download/Publikationen/Digitalisierungsbericht/2014/Digitalisierungsbericht_2014_Daten_und_Fakten.pdf Digitalisierungsbericht 2014 - Daten und Fakten
- "List of sites for the DVB-T2 HD preview mux" (PDF).
- "DVB-T2 HD: ARD vorerst nur hochskaliertes Full HD". Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- Weidner, Markus. "DVB-T2: Private Programme werden als Freenet-TV vermarktet". Retrieved 2016-10-24.
- "DVB-T2 HD - offizielles Informationsportal". DVB-T2 HD - offizielles Informationsportal. Retrieved 2016-10-24.
| ARD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZDF | |||||
| ARD & ZDF | |||||
| RTL Deutschland |
| ||||
| ProSiebenSat.1 Media |
| ||||
| Paramount Global |
| ||||
| Warner Bros. Discovery |
| ||||
| Disney Germany |
| ||||
| High View Group |
| ||||
| WeltN24 |
| ||||
| Acun Medya |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Regional channels |
| ||||
| Sky Deutschland |
| ||||
| NBCUniversal |
| ||||
| Mainstream Media |
| ||||
| A&E Networks |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Lists | |||||
| Television in Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
