| Revision as of 03:28, 13 March 2023 view sourceEvanBaldonado (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users12,231 editsm Replace hyphen with en-dash.Tag: Reverted← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 21:28, 3 January 2025 view source Super Dromaeosaurus (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users57,667 edits notable topic | ||
| (328 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Country in Eastern Europe}} | {{Short description|Country in Eastern Europe}} | ||
| {{About|the modern state|the historical principality|Moldavia|other uses|Moldova (disambiguation)}} | {{About|the modern state|the historical principality|Moldavia|other uses|Moldova (disambiguation)}} | ||
| {{pp- |
{{pp-move}} | ||
| {{Use British English|date=November 2023}} | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | |||
| {{pp-extended|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=May 2022}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=February 2024}} | |||
| {{Coord|47|N|29|E|type:country|display=title}} | |||
| {{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
| | conventional_long_name = Republic of Moldova | | conventional_long_name = Republic of Moldova | ||
| | common_name = Moldova | | common_name = Moldova | ||
| | native_name = {{native name|ro|Republica Moldova |
| native_name = {{native name|ro|Republica Moldova}} | ||
| | image_flag = Flag of Moldova.svg | | image_flag = Flag of Moldova.svg | ||
| | image_coat = Coat of arms of Moldova.svg | | image_coat = Coat of arms of Moldova.svg | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| | coordinates = {{Coord|47|0|N|28|55|E|type:city}} | | coordinates = {{Coord|47|0|N|28|55|E|type:city}} | ||
| | largest_city = capital | | largest_city = capital | ||
| | languages_type = Official language<br />{{nobold|and national language}} | |||
| | official_languages = ] (officially ])<!-- Law project voted on 2 March 2023 is still pending application. It will happen within 30 days as stated in the law. REMOVAL OF MOLDOVAN FROM THE INFOBOX WHILE THE LAW HAS NOT BEEN APPLIED WILL BE REVERTED AND THE PERSON REPORTED TO ADMINISTRATORS. --> <br> ] | |||
| | languages = ]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.parlament.md/CadrulLegal/Constitution/tabid/151/language/ro-RO/Default.aspx |title=Constituția Republicii Moldova, articolul 13: ''(1) Limba de stat a Republicii Moldova este limba română, funcționând pe baza grafiei latine.'' (pag.25) |publisher=Parlamentul Republicii Moldova |access-date=5 April 2023 |language=ro |archive-date=5 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230405142436/https://www.parlament.md/CadrulLegal/Constitution/tabid/151/language/ro-RO/Default.aspx |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.presedinte.md/app/webroot/Constitutia_RM/Constitutia_RM_RO.pdf |title=Constituția Republicii Moldova, articolul 13 (1), pag.25 |publisher=Preşedinţia Republicii Moldova |access-date=11 April 2023 |language=ro |archive-date=7 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230507121126/https://presedinte.md/app/webroot/Constitutia_RM/Constitutia_RM_RO.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | languages_type = Recognised minority<br />languages<!--Protected and/or co-official (regional) languages--><ref>{{cite web |url=https://deschide.md/ro/stiri/politic/78929/Pre%C8%99edintele-CCM-Constitu%C8%9Bia-nu-confer%C4%83-limbii-ruse-un-statut-deosebit-de-cel-al-altor-limbi-minoritare.htm |title= Președintele CCM: Constituția conferă limbii ruse un statut deosebit de cel al altor limbi minoritare |publisher=Deschide.md |access-date=22 January 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.moldpres.md/news/2021/01/21/21000400 |title=Chişinău, (21.01.2021) Judecătorii constituționali au decis că limba rusă nu va avea statutul de limbă de comunicare interetnică pe teritoriul Republicii Moldova |publisher=Moldpres.md |access-date=22 January 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://protv.md/politic/presedintele-cc-domnica-manole-explica-de-ce-a-fost-anulata-legea-cu-privire-la-statutul-special-pentru-limba-rusa-limba-de-stat-a-rm-este-limba-romana-video---2554643.html |title= Președintele CC Domnica Manole, explică de ce a fost anulată legea cu privire la statutul special pentru limbia rusă |publisher=ProTv.md |access-date=22 January 2021}}</ref> | |||
| | languages2_type = Recognised minority<br />languages<!--Protected and/or co-official (regional) languages--><ref>{{cite web |url=https://deschide.md/ro/stiri/politic/78929/Pre%C8%99edintele-CCM-Constitu%C8%9Bia-nu-confer%C4%83-limbii-ruse-un-statut-deosebit-de-cel-al-altor-limbi-minoritare.htm |title=Președintele CCM: Constituția conferă limbii ruse un statut deosebit de cel al altor limbi minoritare |publisher=Deschide.md |access-date=22 January 2021 |archive-date=29 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210129050215/https://deschide.md/ro/stiri/politic/78929/Pre%C8%99edintele-CCM-Constitu%C8%9Bia-nu-confer%C4%83-limbii-ruse-un-statut-deosebit-de-cel-al-altor-limbi-minoritare.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.moldpres.md/news/2021/01/21/21000400 |title=Chişinău, (21.01.2021) Judecătorii constituționali au decis că limba rusă nu va avea statutul de limbă de comunicare interetnică pe teritoriul Republicii Moldova |publisher=Moldpres.md |access-date=22 January 2021 |archive-date=23 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210123203429/https://www.moldpres.md/news/2021/01/21/21000400 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://protv.md/politic/presedintele-cc-domnica-manole-explica-de-ce-a-fost-anulata-legea-cu-privire-la-statutul-special-pentru-limba-rusa-limba-de-stat-a-rm-este-limba-romana-video---2554643.html |title=Președintele CC Domnica Manole, explică de ce a fost anulată legea cu privire la statutul special pentru limbia rusă |publisher=ProTv.md |access-date=22 January 2021 |archive-date=29 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210129092300/https://protv.md/politic/presedintele-cc-domnica-manole-explica-de-ce-a-fost-anulata-legea-cu-privire-la-statutul-special-pentru-limba-rusa-limba-de-stat-a-rm-este-limba-romana-video---2554643.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | languages = {{Collapsible list | |||
| | languages2 = {{Collapsible list | |||
| |titlestyle=background:transparent;text-align:left;font-weight:normal; | |titlestyle=background:transparent;text-align:left;font-weight:normal; | ||
| |title= ''See here'' | |title= ''See here'' | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| | |
|German | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |Russian | |||
| |] | |] | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| | ethnic_groups = 75% ]<br /> 7% ]{{efn|name=coeli|There is ] over the self-identification of Moldovans, with some authors considering them ethnic Romanians.}} <br />6.57% ]<br />4.57% ]<br />4.06% ]<br />1.88% ]<br />0.85% other | |||
| | ethnic_groups = 82.07% ] | |||
| <br />6.57% ]<br />4.57% ]<br />4.06% ]<br />1.88% ]<br />0.85% ''Other'' | |||
| | ethnic_groups_year = 2014; excl. ] | | ethnic_groups_year = 2014; excl. ] | ||
| | ethnic_groups_ref = <ref name="Recensamant2014">{{Cite web|url=https://statistica.gov.md/ro/recensamantul-populatiei-si-al-locuintelor-2014-122.html|title=Recensamântul Populației si al Locuințelor 2014|website=statistica.gov.md|date=2 August 2013 |
| ethnic_groups_ref = <ref name="Recensamant2014">{{Cite web|url=https://statistica.gov.md/ro/recensamantul-populatiei-si-al-locuintelor-2014-122.html|title=Recensamântul Populației si al Locuințelor 2014|website=statistica.gov.md|date=2 August 2013|access-date=30 November 2022|archive-date=2 December 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221202152706/https://statistica.gov.md/ro/recensamantul-populatiei-si-al-locuintelor-2014-122.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| | religion = {{ublist |item_style=white-space; |
| religion = {{ublist |item_style=white-space; | ||
| |{{Tree list}} | |{{Tree list}} | ||
| * 91.8% |
* 91.8% Christianity | ||
| ** 90.1% ] | ** 90.1% ] | ||
| ** 1.7% |
** 1.7% other ] | ||
| {{Tree list/end}} | {{Tree list/end}} | ||
| | 0.3% ] |5.5% ] |2.4% |
| 0.3% ] |5.5% ] |2.4% unspecified}} | ||
| | religion_year = 2014; excl. Transnistria | | religion_year = 2014; excl. Transnistria | ||
| | religion_ref = <ref name="Recensamant2014"/> | | religion_ref = <ref name="Recensamant2014"/> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 54: | ||
| | leader_title3 = ] | | leader_title3 = ] | ||
| | leader_name3 = ] | | leader_name3 = ] | ||
| | legislature = ] | | legislature = ] | ||
| | sovereignty_type = ] | | sovereignty_type = ] | ||
| | established_event1 = ] | | established_event1 = ] | ||
| Line 74: | Line 75: | ||
| | established_date9 = 29 July 1994 | | established_date9 = 29 July 1994 | ||
| | area_label = Incl. Transnistria | | area_label = Incl. Transnistria | ||
| | area_km2 = 33, |
| area_km2 = 33,843<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://moldova.md/ro/content/geografie|title=Republica Moldova – Geografie|website=Moldova.md|date=26 August 2016|access-date=23 June 2021|archive-date=24 June 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210624210341/https://moldova.md/ro/content/geografie|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| | area_rank = 135th <!-- Area rank should match ] --> | | area_rank = 135th <!-- Area rank should match ] --> | ||
| | area_sq_mi = 13,067 <!-- Do not remove per ] --> | | area_sq_mi = 13,067 <!-- Do not remove per ] --> | ||
| | area_label2 = Excl. Transnistria | | area_label2 = Excl. Transnistria | ||
| | area_data2 = {{convert|30,334|km2|abbr=on}} |
| area_data2 = {{convert|30,334|km2|abbr=on}}{{efn|The '']'' area, accepted by the Moldovan government and the ] authorities for ], is 3,509.6 square kilometers.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.citypopulation.de/en/moldova/transnistria/admin/|title=MOLDOVA: Transnistria (Pridnestrovie)|website=Citypopulation.de|access-date=23 June 2021|archive-date=25 March 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210325212647/https://www.citypopulation.de/en/moldova/transnistria/admin/|url-status=live}}</ref> The ''de facto'' area administered by Transnistria is 3,653 square kilometers, while the area claimed by Transnistria is 4,163 square kilometers.}} | ||
| | percent_water = 1.4 |
| percent_water = 1.4 (incl. Transnistria) | ||
| | population_estimate = 2, |
| population_estimate = 2,423,300<ref>{{cite web |url=https://statistica.gov.md/index.php/ro/numarul-populatiei-cu-resedinta-obisnuita-pe-sexe-si-grupe-9578_60448.html |title=Numărul populației cu reședință obișnuită, pe sexe şi grupe de vârstă, în profil teritorial la 1 Ianuarie 2023 |date=8 June 2023 |language=ro |publisher=Biroul Național de Statistică al Republicii Moldova (BNS) |access-date=9 June 2023 |archive-date=9 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230609093011/https://statistica.gov.md/index.php/ro/numarul-populatiei-cu-resedinta-obisnuita-pe-sexe-si-grupe-9578_60448.html |url-status=live }}</ref>{{efn|name=data1|Excludes data for ].}} | ||
| | population_estimate_year = January |
| population_estimate_year = January 2024 | ||
| | population_census = 2,804,801<ref name="Recensamant2014"/>{{efn|name=data1|Excludes data for ].}} | | population_census = 2,804,801<ref name="Recensamant2014"/>{{efn|name=data1|Excludes data for ].}} | ||
| | population_census_year = 2014 | | population_census_year = 2014 | ||
| | population_estimate_rank = |
| population_estimate_rank = 140th | ||
| | population_density_km2 = |
| population_density_km2 = 82.8 | ||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 234 <!-- Do not remove per ] --> | | population_density_sq_mi = 234 <!-- Do not remove per ] --> | ||
| | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $ |
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $45.407 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.MD">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/October/weo-report?c=921,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Moldova) |publisher=] |website=www.imf.org |date=22 October 2024 |access-date=9 November 2024}}</ref>{{efn|name=data1|Excludes data for ].}} | ||
| | GDP_PPP_year = |
| GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | ||
| | GDP_PPP_rank = |
| GDP_PPP_rank = 136th | ||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $ |
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $18,524<ref name="IMFWEO.MD" /> | ||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = |
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 91st | ||
| | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $18.062 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.MD" />{{efn|name=data1|Excludes data for ].}} | |||
| | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $14.048 billion<ref name="IMFWEORO">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2022/October/weo-report?c=512,914,612,171,614,311,213,911,314,193,122,912,313,419,513,316,913,124,339,638,514,218,963,616,223,516,918,748,618,624,522,622,156,626,628,228,924,233,632,636,634,238,662,960,423,935,128,611,321,243,248,469,253,642,643,939,734,644,819,172,132,646,648,915,134,652,174,328,258,656,654,336,263,268,532,944,176,534,536,429,433,178,436,136,343,158,439,916,664,826,542,967,443,917,544,941,446,666,668,672,946,137,546,674,676,548,556,678,181,867,682,684,273,868,921,948,943,686,688,518,728,836,558,138,196,278,692,694,962,142,449,564,565,283,853,288,293,566,964,182,359,453,968,922,714,862,135,716,456,722,942,718,724,576,936,961,813,726,199,733,184,524,361,362,364,732,366,144,146,463,528,923,738,578,537,742,866,369,744,186,925,869,746,926,466,112,111,298,927,846,299,582,487,474,754,698,&s=NGDPD,&sy=2020&ey=2027&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1|title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2022 |date=11 October 2022 |website=IMF.org |publisher=]|access-date=11 October 2022}}</ref>{{efn|name=data1|Excludes data for ].}} | |||
| | GDP_nominal_year = |
| GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | ||
| | GDP_nominal_rank = |
| GDP_nominal_rank = 130th | ||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $ |
| GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $7,368<ref name="IMFWEO.MD" /> | ||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = |
| GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 92nd | ||
| | Gini = |
| Gini = 25.7 <!-- number only --> | ||
| | Gini_year = |
| Gini_year = 2021 | ||
| | Gini_change = |
| Gini_change = decrease <!-- increase/decrease/steady --> | ||
| | Gini_ref = <ref |
| Gini_ref = <ref>{{cite web|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=MD |title=Gini index – Moldova |publisher=]|website=data.worldbank.org|access-date=23 September 2024 }}</ref> | ||
| | HDI = 0. |
| HDI = 0.763 <!-- number only --> | ||
| | HDI_year = |
| HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year --> | ||
| | HDI_change = |
| HDI_change = decrease <!-- increase/decrease/steady --> | ||
| | HDI_ref = <ref name="HDI">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2021/2022|language=en|publisher=]|date=8 September 2022|access-date=8 September 2022}}</ref> | | HDI_ref = <ref name="HDI">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2021/2022|language=en|publisher=]|date=8 September 2022|access-date=8 September 2022|archive-date=8 September 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220908114232/http://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2021-22pdf_1.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| | HDI_rank = |
| HDI_rank = 86th | ||
| | currency = ] | | currency = ] | ||
| | currency_code = MDL | | currency_code = MDL | ||
| Line 119: | Line 120: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Moldova''' |
'''Moldova''',{{efn|{{IPAc-en|audio=en-us-Moldova.ogg|m|ɒ|l|ˈ|d|oʊ|v|ə}} {{Respell|mol|DOH|və}}, {{small|sometimes }}{{IPAc-en|UK|ˈ|m|ɒ|l|d|ə|v|ə}} {{Respell|MOL|də|və}};{{refn|{{Cite encyclopedia |url=http://www.lexico.com/definition/Moldova |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200322182040/https://www.lexico.com/definition/moldova |url-status=dead |archive-date=22 March 2020 |title=Moldova |dictionary=] UK English Dictionary |publisher=]}} }}{{refn|{{Dictionary.com|access-date=30 January 2016|Moldova}}}}{{refn|The Free Dictionary: }} {{IPA|ro|molˈdova}}}} officially the '''Republic of Moldova''',{{efn|{{langx|ro|Republica Moldova}}}} is a ] country in ], on the northeastern corner of the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/|title=The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency|website=Cia.gov|language=en|access-date=14 December 2017|archive-date=5 January 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210105015457/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/|url-status=live}}</ref> The country spans a total of {{convert|33,483|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} and has a population of approximately 2.42 million as of January 2024.<ref>{{Cite news |date=3 April 2012 |title=Moldova country profile |language=en-GB |work=] |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17601580 |access-date=6 July 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707173359/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17601580 |url-status=live }}</ref> Moldova is bordered by ] to the west and ] to the north, east, and south.<ref name="CIA_World_Factbook_Moldova">{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |title=Moldova |work=] |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=5 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210105015457/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] of ] lies across the ] river on the country's eastern border with Ukraine. Moldova is a ] ] ] democratic republic with its capital in ], the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. | ||
| Most of Moldovan territory was a part of the ] from the 14th century until 1812, when it was ] to the ] by the ] (to which Moldavia was a ]) and became known as ]. In 1856, southern Bessarabia was returned to Moldavia, which three years later united with ] to form ], but Russian rule was restored over the whole of the region in 1878. During the 1917 ], Bessarabia briefly became an ] within the ]. In February 1918, it declared independence and then integrated into Romania later that year following a vote of its assembly. The decision was disputed by ], which in 1924 established, within the ], a so-called ] on partially Moldovan-inhabited territories to the east of Bessarabia. | Most of Moldovan territory was a part of the ] from the 14th century until 1812, when it was ] to the ] by the ] (to which Moldavia was a ]) and became known as ]. In 1856, southern Bessarabia was returned to Moldavia, which three years later united with ] to form ], but Russian rule was restored over the whole of the region in 1878. During the 1917 ], Bessarabia briefly became an ] within the ]. In February 1918, it declared independence and then integrated into Romania later that year following a vote of its assembly. The decision was disputed by ], which in 1924 established, within the ], a so-called ] on partially Moldovan-inhabited territories to the east of Bessarabia. In 1940, as a consequence of the ], Romania was ] to the ], leading to the creation of the ] (Moldavian SSR). | ||
| On 27 August 1991, as the ] was underway, the Moldavian SSR ] and took the name Moldova.<ref name="natura2000">{{cite web |url=http://www.natura2000oltenita-chiciu.ro/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Moldova-Pitoreasca-Picturesque-Moldavia-pdf-Vladimir-Toncea.pdf |title="Wine Road" in Republic of Moldova |access-date=18 May 2019 |archive-date=18 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190518103311/http://www.natura2000oltenita-chiciu.ro/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Moldova-Pitoreasca-Picturesque-Moldavia-pdf-Vladimir-Toncea.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> However, the strip of Moldovan territory on the east bank of the Dniester has been under the ''de facto'' control of the breakaway government of Transnistria since 1990. The ] was adopted in 1994, and the country became a ] with a ] as ] and a ] as ]. Under the presidency of ], ] on a pro-Western and anti-corruption ticket, Moldova has pursued membership of the ], and was granted candidate status in June 2022.<ref>{{Cite news |date=23 June 2022 |title=EU awards Ukraine and Moldova candidate status |language=en-GB |work=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-61891467 |access-date=16 August 2022 |archive-date=23 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220623000924/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-61891467 |url-status=live }}</ref> Accession talks to the EU began on 13 December 2023.<ref>{{Cite web |date=14 December 2023 |title=EU greenlights accession talks with Ukraine and Moldova |url=https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2023/12/14/eu-greenlights-accession-talks-with-ukraine-and-moldova |access-date=14 December 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=14 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231214175059/https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2023/12/14/eu-greenlights-accession-talks-with-ukraine-and-moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> Sandu has also suggested an end to ] in favour of a closer alliance with ] and strongly condemned ] of neighbouring ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Lynch |first=Suzanne |date=20 January 2023 |title=Time to join NATO? Moldova eyes joining 'a larger alliance' |url=https://www.politico.eu/article/maia-sandu-moldova-nato-alliance-joining-ukraine-war-russia-invasion/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=21 January 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230121000423/https://www.politico.eu/article/maia-sandu-moldova-nato-alliance-joining-ukraine-war-russia-invasion/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Moldova is the ] after Ukraine and much of its |
Moldova is the ] after Ukraine and much of its GDP is dominated by the ].<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2022/April/weo-report?c=967,921,926,&s=PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2022&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=GDP per capita, PPP (current international $) |access-date=27 July 2022 |archive-date=27 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220727115351/https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2022/April/weo-report?c=967,921,926,&s=PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2022&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> It has one of the lowest ]es in Europe, ranking 76th in the world (2022).<ref name="HDI"/> Moldova ranks 68th in the world on the ] {{as of|2024|lc=y}}.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/|title=Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship|access-date=2024-10-22|author=]|year=2024|isbn=978-92-805-3681-2|doi= 10.34667/tind.50062|location=Geneva|page=18}}</ref> Moldova is a member state of the United Nations, the ], the ], the ], the ], the ], and the ]. | ||
| ==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| {{main|Names of Moldavia and Moldova}} | {{main|Names of Moldavia and Moldova}} | ||
| The name ''Moldova'' is derived from the ] ({{ |
The name ''Moldova'' is derived from the ] ({{Langx|de|Moldau}}); the valley of this river served as a political centre at the time of the ] of the ] in 1359.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.moldova.md/en/istorie/ |title=History |publisher=Republic of Moldova |access-date=9 October 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131222142800/http://www.moldova.md/en/istorie/ |archive-date=22 December 2013}}</ref> The origin of the name of the river remains unclear. According to a legend recounted by Moldavian chroniclers ] and ], Prince ] named the river after hunting ]: following the chase, the prince's exhausted hound ''Molda (Seva)'' drowned in the river. The dog's name, given to the river, extended to the principality.<ref>{{cite book |last=King |first=Charles |author-link=Charles King (professor of international affairs) |title=The Moldovans: Romania, Russia, and the politics of culture |publisher=Hoover Press |year=2000 |chapter=From Principality to Province |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ldBFWtuv8DQC&pg=PA13 |page= |isbn=0-8179-9792-X |access-date=31 October 2010 |url=https://archive.org/details/moldovansromania00king_0/page/13 }}</ref> | ||
| For a short time in the 1990s, at the founding of the ], the name of the current Republic of Moldova was also spelled ''Moldavia''.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1991/12/23/world/end-soviet-union-text-accords-former-soviet-republics-setting-up-commonwealth.html?pagewanted=all |date=23 December 1991 |title=The End of the Soviet Union; Text of Accords by Former Soviet Republics Setting Up a Commonwealth |work=] |quote=...Republic of Kazakhstan, the Republic of Kirghizia, the Republic of Moldavia, the Russian Federation...}}</ref> After the ], the country began to use the Romanian name, |
For a short time in the 1990s, at the founding of the ], the name of the current Republic of Moldova was also spelled ''Moldavia''.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1991/12/23/world/end-soviet-union-text-accords-former-soviet-republics-setting-up-commonwealth.html?pagewanted=all |date=23 December 1991 |title=The End of the Soviet Union; Text of Accords by Former Soviet Republics Setting Up a Commonwealth |work=] |quote=...Republic of Kazakhstan, the Republic of Kirghizia, the Republic of Moldavia, the Russian Federation... |access-date=17 February 2017 |archive-date=9 March 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210309042542/https://www.nytimes.com/1991/12/23/world/end-soviet-union-text-accords-former-soviet-republics-setting-up-commonwealth.html?pagewanted=all |url-status=live }}</ref> After the ], the country began to use the Romanian name, {{lang|ro|Moldova}}. Officially, the name ''Republic of Moldova'' is designated by the United Nations. | ||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| {{More citations needed|section|date=March 2022}} | |||
| {{main|History of Moldova}} | {{main|History of Moldova}} | ||
| {{see also|History of Transnistria}} | {{see also|History of Transnistria|Founding of Moldavia}} | ||
| ], a ] ] and founder of the ], 19th-century depiction]] | |||
| The history of Moldova spans ], ] and ] empires, and periods of foreign rule and modern ]. | |||
| ===Prehistory=== | |||
| ], {{circa}} 4,000 BC]] | |||
| The prehistory of Moldova covers the period from the ] which begins with the presence of ] in the area of ] some 44,000 years ago and extends into the appearance of the first written records in ] in ]. In 2010, ] flint tools were discovered at Bayraki that are 800,000–1.2 million years old.<ref>{{cite web| url= http://paleogeo.org/article3.html|title= GEOARCHAEOLOGY OF THE EARLIEST PALEOLITHIC SITES (OLDOWAN) IN THE NORTH CAUCASUS AND THE EAST EUROPE| publisher= paleogeo.org|date= 2011| url-status= dead| archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20130520090413/http://paleogeo.org/article3.html| archive-date= 20 May 2013 | quote = Early Paleolithic cultural layers with tools of oldowan type was discovered in East Caucasus (Dagestan, Russia) by Kh. Amirkhanov (2006) and Dniester valley (Moldova) by N. Anisjutkin (2010).}}</ref> During the ], Moldova's territory stood at the centre of the large ] that stretched east beyond the ] in Ukraine and west up to and beyond the ] in Romania. The people of this civilization, which lasted roughly from 5500 to 2750 BC, practised agriculture, raised livestock, hunted, and made intricately designed pottery.<ref> | |||
| {{cite journal | |||
| | last1= Constantinescu| first1= Bogdan | |||
| | last2= Bugoi| first2= Roxana| last3= Pantos| first3= Emmanuel | |||
| | last4= Popovici| first4= Dragomir | |||
| | title= Phase and chemical composition analysis of pigments used in Cucuteni Neolithic painted ceramics | |||
| | journal= Documenta Praehistorica| volume= XXXIV| pages= 281–288 | |||
| | publisher= Department of Archaeology, Faculty of Arts, University of Ljubljana | |||
| | location= Ljubljana| year= 2007| issn= 1408-967X| oclc= 41553667 | |||
| | df= dmy-all | |||
| | doi= 10.4312/dp.34.21 | |||
| | doi-access= free}} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| Evidence of human habitation dates back 800,000–1.2 million years, with significant developments in ], ], and settlement during the ] and ]. In ], Moldova's location made it a crossroads for invasions by the ], ], ], and other tribes, followed by periods of ] and ] control. The medieval ] ], and was the medieval precursor of modern Moldova and ]. It reached prominence under rulers like ] before becoming a ] of the ] from 1538, until the 19th century. | |||
| ===Antiquity and the early Middle Ages=== | |||
| This area of present-day Moldova was inhabited by ancient ] and Moldovans identify themselves with their ancestors. ] tribes also inhabited Moldova's territory in the period of ]. Between the first and seventh centuries AD, the south came intermittently under the control of the ] and then the ]s. Due to its strategic location on a route between Asia and Europe, the territory of modern Moldova experienced many invasions in late antiquity and the ], notably by ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| In 1812, following ], the eastern half of the principality, ], was annexed by the ], marking the beginning of Russian influence in the region. In 1918, Bessarabia briefly became independent as the ] and, following the decision of the Parliament (Sfatul Țării), united with ]. During the Second World War it was occupied by the ] which reclaimed it from Romania. It joined the Union in 1940 as the ]. During this period, policies of ] and economic transformation deeply influenced the region. | |||
| In the 11th century, a ] by the name of Rodfos was possibly killed in the area by the ] who betrayed him.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.vikingart.com/VArt/PS_Sjonhem.htm |title=The Sjönhem Stone |access-date= 16 June 2006 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://archive.today/20060616225750/http://www.vikingart.com/VArt/PS_Sjonhem.htm |archive-date= 16 June 2006 }}</ref> In 1164, the future ] ], while attempting to reach the ], was taken prisoner by Vlachs, possibly in the area which now constitutes Moldova. | |||
| The ] in 1991 led to ], followed by the ] in 1992, a conflict that left the ] region as a de facto independent state. Moldova continues to navigate a complex relationship between pro-Western and pro-Russian factions. In recent years, it has pursued closer ties with the ], submitting a formal membership application in 2022. | |||
| The East Slavic ] (13th century) mentions the ] people, who resided on the eastern fringes of Moldovan territory and in the ] of ], ] and ]; their ethnic origin is disputed by historians. Archaeological research has identified the location of 13th-century fortified settlements in this region.<ref>A.V. Boldur, ''Istoria Basarabiei'', Editura V. Frunza, p 111-119</ref> The Bolohoveni disappeared from written chronicles after they were defeated in 1257 by ]. In the early 13th century, the ], a possible ]–] ] tribe of ], were also present in much of the region's territory. | |||
| In the ], the pro-European opposition candidate ] was elected as the new president of the republic, becoming the first female elected president of Moldova.<ref>{{Cite news|date=16 November 2020|title=Moldova election: Pro-EU candidate Maia Sandu wins presidency|language=en-GB|work=BBC News|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-54942847|access-date=27 July 2021|archive-date=24 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210424114019/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-54942847|url-status=live}}</ref> In the ], President Maia Sandu was re-elected with 55% of the vote in the run-off.<ref>{{cite news |title=Moldova election: Pro-EU leader wins despite alleged Russian meddling |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cz7w9dglzzlo |work=www.bbc.com}}</ref> | |||
| ===Founding of the Principality of Moldavia=== | |||
| {{main|Founding of Moldavia}} | |||
| ], a ] ] and founder of the ], 19th-century depiction]] | |||
| ==Politics== | |||
| The ] began when a ] ] (military leader), ], arrived in the region of the ]. His people from the ] at ] soon followed. Dragoș established a ] as a vassal to the ] in the 1350s. The independence of the ] of ] came when ], another Vlach voivode from Maramureș who had fallen out with the Hungarian king, crossed the ] in 1359 and took control of Moldavia, wresting the region from Hungary. The Principality of ] was bounded by the ] in the west, the ] River in the east, and the Danube River and ] to the south. Its territory comprised the present-day territory of the Republic of Moldova, the ] of Romania, and parts of the ] and ] region of present-day Ukraine. Locals referred to the principality as ''Moldova'' - like the present-day republic and Romania's north-eastern region. | |||
| {{main|Government of Moldova}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The Republic of Moldova is a ] with a ] ] of government and competitive, ]. The constitution provides for executive and ] branches as well as an independent ] and a clear ]. The ] serves as the ], is elected every four years, and can be re-elected once. The ] serves as the ], appointed by the president with ]'s support. The head of government in turn assembles a ], subject to parliamentary approval. Legislative authority is vested in the unicameral ] which has 101 seats and whose members are elected by popular vote on ] every four years. The president's official residence is the ]. | |||
| After the prime minister and government resigned in 2020 and the president and parliament failed to form a new government, early parliamentary elections were held in July 2021. According to ] observers, the ] were well-administered and competitive, and ] were largely respected.<ref>{{Cite web |date=22 December 2021 |title=Moldova early parliamentary elections 2021: OSCE/ODIHR election observation mission final report |url=https://www.osce.org/odihr/elections/508976 |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802094707/https://www.osce.org/odihr/elections/508976 |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] won 63 seats in the 101-seat parliament, enough to form a single-party majority.<ref>{{Cite web |title=2022 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Moldova |url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-country-reports-on-human-rights-practices/moldova/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=1 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230601190113/https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-country-reports-on-human-rights-practices/moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Between Poland and Hungary=== | |||
| The history of what is today Moldova has been intertwined with that of Poland for centuries. The Polish chronicler ] mentioned Moldavians as having joined a military expedition in 1342, under King ], against the ].<ref>''The Annals of Jan Długosz'', p. 273</ref> The Polish state was powerful enough to counter the ] which was consistently interested in bringing the area that would become Moldavia into its political orbit. | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| Ties between Poland and Moldavia expanded after the founding of the Moldavian state by ], a Vlach ] from ] who had fallen out with the Hungarian king. Crossing the ] in 1359, the voivode took control of Moldavia and succeeded in creating Moldavia as an independent political entity. Despite being disfavored by the brief union of ] and Hungary (the latter was still the country's overlord), Bogdan's successor ], the Moldavian ruler also likely allied himself with the ]. Lațcu also accepted ] to ] around 1370, but his gesture was to remain without consequences. | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | caption_align = center | |||
| | total_width = 150 | |||
| | image1 = Maia_Sandu_at_Batumi_International_Conference,_on_19_July_2021_(cropped).jpg | |||
| | image2 = | |||
| | caption1 = ], Moldova's ] since December 2020. | |||
| | caption2 = ]<br /><small>]<br />Since 2023</small> | |||
| | alt1 = | |||
| | alt2 = | |||
| }} | |||
| The 1994 ] sets the framework for the government of the country. A parliamentary majority of at least two-thirds is required to amend the ], which cannot be revised in times of war or national emergency. Amendments to the Constitution affecting the state's sovereignty, independence, or unity can only be made after a majority of voters support the proposal in a referendum. Furthermore, no revision can be made to limit the fundamental rights of people enumerated in the Constitution.<ref name="const2">{{cite web |title=The Constitution of the Republic of Moldova, 2000 |url=http://www.e-democracy.md/en/legislation/constitution/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200425182448/http://www.e-democracy.md/en/legislation/constitution/ |archive-date=25 April 2020 |access-date=9 October 2013 |publisher=E-democracy.md}}</ref> The 1994 constitution also establishes an ] ], composed of six judges (two appointed by the President, two by Parliament, and two by the Supreme Council of ]), serving six-year terms, during which they are irremovable and not subordinate to any power. The court is invested with the power of ] over all ], over ]s, and over ] signed by the country.<ref name="const2" /> | |||
| The head of state is the President of Moldova, who between 2001 and 2015 was elected by the Moldovan Parliament, requiring the support of three-fifths of the deputies (at least 61 votes). This system was designed to decrease executive authority in favour of the legislature. Nevertheless, the ] ruled on 4 March 2016 that this constitutional change adopted in 2000 regarding the presidential election was unconstitutional, thus reverting the election method of the president to a ] ].<ref>{{cite news |date=4 March 2016 |title=DECIS: Şeful statului va fi ales de popor; Modificarea din 2000 a Constituţiei privind alegerea preşedintelui de Parlament, NECONSTITUŢIONALĂ |language=ro |trans-title=DECIDED: The president will be elected by the people; The 2000 amendment of the Constitution concerning the election of the President by Parliament unconstitutional |newspaper=] |url=http://jurnal.md/ro/justitie/2016/3/4/decis-seful-statului-va-fi-ales-de-popor-modificarea-din-2000-a-constitutiei-privind-alegerea-presedintelui-de-parlament-neconstitutionala/ |url-status=live |access-date=4 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210225044414/https://www.jurnal.md/ro/justitie/2016/3/4/decis-seful-statului-va-fi-ales-de-popor-modificarea-din-2000-a-constitutiei-privind-alegerea-presedintelui-de-parlament-neconstitutionala/ |archive-date=25 February 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ====Polish influence grows==== | |||
| ] profited from the end of the Polish-Hungarian union and moved the country closer to the ], becoming a ] of king ] on 26 September 1387. This gesture was to have unexpected consequences: Petru supplied the Polish ruler with funds needed in the war against the ], and was granted control over ] until the debt was to be repaid; as this is not recorded to have been carried out, the region became disputed by the two states, until it was lost by Moldavia in the ] (1531). Prince Petru also expanded his rule southwards to the ]. His brother Roman I conquered the Hungarian-ruled ] in 1392, giving Moldavia an outlet to the ], before being toppled from the throne for supporting ] in his conflict with ] of ]. Under ], growing Polish influence was challenged by ], whose expedition was defeated at ] in 1385; however, Stephen disappeared in mysterious circumstances. | |||
| ===Foreign relations=== | |||
| Although ] was brought to the throne in 1400 by the Hungarians (with assistance from ]), this ruler shifted his allegiances towards Poland (notably engaging Moldavian forces on the Polish side in the ] and the ]), and placed his own choice of rulers in Wallachia. His reign was one of the most successful in Moldavia's history. | |||
| {{main|Foreign relations of Moldova|Moldovan neutrality|Moldova–European Union relations}} | |||
| After achieving independence from the Soviet Union, Moldova's foreign policy was designed with a view to establishing relations with other European countries, neutrality, and European Union integration. In May 1995, the country signed the ] Convention to become a member and was also admitted in July 1995 to the ]. | |||
| Moldova became a member state of the United Nations the ] (OSCE), the ], the ], the ] and the ] in 1992. 1994 saw Moldova become a participant in ]'s ] programme. Moldova joined the ] in 1996, the ] in 2001, and the ] in 2002. | |||
| ===Increasing Ottoman influence=== | |||
| ], several authors believed the ] was constructed on the site of a former ] fortress named ''Olhionia''.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.istoria.md/articol/103/Cetatea_Soroca_a_Moldovei| title=Cetatea Soroca a Moldovei (1499 – prezent)|publisher=Istoria.md| last=Bulat| first=Nicolae| language=ro}}</ref>]] | |||
| ] | |||
| For all of his success, it was under the reign of Alexander I that the first confrontation with the ] took place at Cetatea Albă in 1420. A deep crisis was to follow Alexander l's long reign, with his successors battling each other in a succession of wars that divided the country until the murder of ] and the accession of ] in 1451. Nevertheless, Moldavia was subject to further Hungarian interventions after that moment, as ] deposed Aaron and backed ] to the throne in ]. Peter Aaron's rule also signified the beginning of Moldavia's ] allegiance, as the ruler was the first to agree to pay ] to Sultan ]. | |||
| In 2005, Moldova and the European Union established an action plan that sought to improve cooperation between Moldova and the union. At the end of 2005, the ] (EUBAM) was established at the joint request of the presidents of Moldova and Ukraine. EUBAM assists the Moldovan and Ukrainian governments in approximating their border and customs procedures to EU standards and offers support in both countries' fight against cross-border crime. | |||
| ====Moldavia at its apogee==== | |||
| Peter Aaron was eventually ousted by his nephew, ] who would become the most important medieval Moldavian ruler who managed to uphold Moldavia's autonomy against Hungary, Poland and the Ottoman Empire.<ref name="Sedlar1994">{{cite book |last=Sedlar |first=Jean W. |title=East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000–1500 |publisher=University of Washington Press |year=1994 |page=396 |isbn=0-295-97290-4}}</ref><ref name="Pop1999">*{{cite book |last=Pop |first=Ioan-Aurel |title=Romanians and Romania: A Brief History |publisher=Boulder |year=1999 |page=64 |isbn=0-88033-440-1}}</ref> Under his rule, which lasted 47 years, Moldavia experienced a glorious political and cultural period.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Stephen-prince-of-Moldavia |title=Stephen - prince of Moldavia |author=<!--Not stated--> |website=britannica.com |publisher=] |access-date=25 June 2022}}</ref> | |||
| After the 1990–1992 ], Moldova sought a peaceful resolution to the conflict in the Transnistria region by working with Romania, Ukraine, and Russia, calling for international mediation, and co-operating with the OSCE and UN fact-finding and observer missions. The ], ], repeatedly stated that the Russian troops stationed in the breakaway region were there against the will of the Moldovan government and called on them to leave "completely and unconditionally".<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.easybourse.com/bourse-actualite/marches/moldova-calls-on-russian-troops-to-leave-transdniestr-574221|title=Moldova Calls on Russian Troops To Leave Transdniestr}}{{Dead link|date=March 2021 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> In 2012, a ] resulted in the death of a civilian, raising tensions with Russia.<ref>{{cite news |first=Ellen |last=Barry |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/01/04/world/europe/shooting-raises-tensions-between-moldova-and-russia.html |title=Shooting at Checkpoint Raises Tensions in a Disputed Region Claimed by Moldova |work=The New York Times |date=3 January 2012 |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=4 January 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120104091047/http://www.nytimes.com/2012/01/04/world/europe/shooting-raises-tensions-between-moldova-and-russia.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ====Age of Invasions==== | |||
| During this time, Moldavia was invaded repeatedly by ] and, beginning in the 15th century, by the ]. In 1538, the principality became a ] to the ], but it retained internal and partial external autonomy.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://countrystudies.us/moldova/3.htm|title=Moldova: Early History|publisher=]|date=June 1995|access-date=26 April 2018}}</ref> Nonetheless, the ] continued to strongly influence Moldavia both through national politics as well as on the local level through significant intermarriage between Moldavian nobility and the Polish ]. When in May 1600, ] removed ] from Moldavia's throne by winning the battle of ], briefly reuniting under his rule ], ], and ], a Polish army led by ] drove the Wallachians from Moldavia. Zamoyski reinstalled Ieremia Movilă to the throne, who put the country under the vassalage of the ]. Moldavia finally returned to Ottoman vassalage in 1621. | |||
| ], President of Moldova ], President of Ukraine ] and ] ] during the 2021 ] International Conference. In 2014, the EU signed ] with the three states.]] | |||
| ====Transnistria==== | |||
| While the region of ] was never politically part of the Principality of Moldavia, there were sizable areas which were owned by Moldavian boyars or the Moldavian rulers. The earliest surviving deeds referring to lands beyond the Dniester river date from the 16th century.<ref>Sava, p.4-6</ref>{{Full citation needed|date=May 2021}} Moldavian chronicler ] mentions that in 1584 some Moldavian villages from beyond the Dniester in the ] were attacked and plundered by ].<ref>] '']''</ref>{{Primary source inline|date=May 2021}} Many Moldavians were members of Cossacks units, with two of them, ] and ] becoming ]s of Ukraine. Ruxandra Lupu, the daughter of Moldavian voivode ] who married ], lived in ] according to Ukrainian tradition. | |||
| In September 2010, the ] approved a grant of €90 million to Moldova.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?language=en&type=IM-PRESS&reference=20100907IPR81460 |title=EU to grant €90 million to crisis-hit Moldova |publisher=Europarl.europa.eu |date=7 September 2010 |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=26 May 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130526045325/http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?language=en&type=IM-PRESS&reference=20100907IPR81460 |url-status=live }}</ref> The money was to supplement US$570 million in International Monetary Fund loans,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://en.rian.ru/exsoviet/20100130/157721106.html |title=Moldova to get $570 million in IMF loans |publisher=RIA Novosti|date=30 January 2010 |access-date=25 November 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121019012333/http://en.rian.ru/exsoviet/20100130/157721106.html |archive-date=19 October 2012}}</ref> World Bank and other bilateral support already granted to Moldova. In April 2010, Romania offered Moldova development aid worth of €100 million while the number of scholarships for Moldovan students doubled to 5,000.<ref>{{cite web |author=Chiriac |first=Marian |date=27 April 2010 |title=Romania, Moldova to Boost Relations |url=http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/romania-moldova-to-boost-relations |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130728223227/http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/romania-moldova-to-boost-relations |archive-date=28 July 2013 |access-date=9 October 2013 |publisher=]}}</ref> According to a lending agreement signed in February 2010, Poland provided US$15 million as a component of its support for Moldova in its European integration efforts.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.azi.md/en/story/9504 |title=Poland will support Moldova in its European integration efforts |publisher=Moldova Azi |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=27 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130827015717/http://www.azi.md/en/story/9504 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The first joint meeting of the Governments of Romania and Moldova, held in March 2012, concluded with several bilateral agreements in various fields.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.agerpres.ro/news-of-the-day/2012/03/04/first-meeting-of-romania-and-rep-of-moldova-governments-concluded-with-initialling-of-several-bilateral-agreements-13-27-18 |title=First meeting of Romania and Rep. of Moldova Governments, concluded with initialling of several bilateral agreements |publisher=agerpres.ro |date=4 March 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407072652/http://www.agerpres.ro/news-of-the-day/2012/03/04/first-meeting-of-romania-and-rep-of-moldova-governments-concluded-with-initialling-of-several-bilateral-agreements-13-27-18 |archive-date=7 April 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gov.ro/joint-meeting-of-the-government-of-romania-and-government-of-the-republic-of-moldova__l2a116286.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130208113857/http://www.gov.ro/joint-meeting-of-the-government-of-romania-and-government-of-the-republic-of-moldova__l2a116286.html |archive-date=8 February 2013 |title=Joint meeting of the Government of Romania and Government of the Republic of Moldova |language=ro |publisher=Guvernul Romaniei |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> The European orientation "has been the policy of Moldova in recent years and this is the policy that must continue," ] told lawmakers before ].<ref>], {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://thevotingnews.com/moldova-elects-pro-european-judge-timofti-as-president-ending-3-years-of-political-deadlock-the-washington-post/ |date=4 September 2015 }}</ref>{{full citation needed|date=December 2022}} | |||
| While most of today's Moldova came into the Ottoman orbit in the 16th century, a substantial part of Transnistria remained a part of the ] until the ] in 1793. | |||
| On 29 November 2013, at a summit in ], Moldova signed an ] with the European Union dedicated to the European Union's ']' with ex-Soviet countries.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://eeas.europa.eu/moldova/assoagreement/assoagreement-2013_en.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131207232619/http://www.eeas.europa.eu/moldova/assoagreement/assoagreement-2013_en.htm |archive-date=7 December 2013 |title=EU-Moldova Association Agreement |work=European Union External Action}}</ref> The ex-Romanian President ] stated that Romania will make all efforts for Moldova to join the EU as soon as possible. Likewise, Traian Băsescu declared that the ] is the next national project for Romania, as more than 75% of the population speaks Romanian.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.romanialibera.ro/politica/institutii/basescu--urmatorul-proiect-de-tara-al-romaniei--unirea-cu-basarabia-319094 |title=Băsescu: Următorul proiect de țară al României, unirea cu Basarabia |newspaper=România Liberă |date=27 November 2013 |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=4 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://www.romanialibera.ro/politica/institutii/basescu--urmatorul-proiect-de-tara-al-romaniei--unirea-cu-basarabia-319094 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Russian Empire=== | |||
| ] | |||
| In accordance with the ], and despite numerous protests by Moldavian nobles on behalf of the sovereignty of their principality, the ] (of which Moldavia was a ]) ceded to the ] the ] of the Principality of Moldavia along with ] and old Bessarabia (modern ]), which Russia had already conquered and annexed. The new Russian province was called ], and initially enjoyed a large degree of autonomy. After 1828 this autonomy was progressively restricted and in 1871 the Oblast was transformed into the Bessarabia Governorate, in a process of ], ]. As part of this process, the ] administration in Bessarabia gradually removed the ] from official and religious use.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://depts.washington.edu/cartah/text_archive/clark/bc_10.shtml#bc_10| title=Bessarabia, Chapter X: The Survival of Roumanian| first=Charles Upson| last=Clark| year=1927| publisher=Dodd, Mead & Company| website=Depts.washington.edu| access-date=9 October 2013| quote=Naturally, this system resulted not in acquisition of Russian by the Moldavians, but in their almost complete illiteracy in any language.| archive-date=9 December 2012| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121209212714/http://depts.washington.edu/cartah/text_archive/clark/bc_10.shtml#bc_10| url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ====Russia==== | |||
| ====Union with Romania and the return of the Russians==== | |||
| {{main |Moldova–Russia relations}} | |||
| The ] returned the ] (later organised as the ], Bolgrad and Ismail counties) to Moldavia, which remained an autonomous principality and, in 1859, ] with ] to form ]. In 1878, as a result of the ], Romania was forced to cede the three counties back to the Russian Empire. | |||
| A document written in 2021 by the Russia's FSB's Directorate for Cross-Border Cooperation, titled "Strategic objectives of the Russian Federation in the Republic of Moldova" sets out a 10-year plan to destabilise Moldova, using ], and political/elite sources in Moldova that are favourable to Russia and the Orthodox Church. Russia denies any such plan.<ref name="cnn163">{{cite web |title=Secret document reveals Russia's 10-year plan to destabilize Moldova |url=https://edition.cnn.com/2023/03/16/europe/russia-moldova-secret-document-intl-cmd/index.html |date=16 March 2023|publisher=]|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20230912123518/https://edition.cnn.com/2023/03/16/europe/russia-moldova-secret-document-intl-cmd/index.html|archive-date=12 September 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=How Russia Torpedoed Its Own Influence in Moldova|url=https://carnegieendowment.org/politika/89731|date=11 March 2023|publisher=]|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20230921170846/https://carnegieendowment.org/politika/89731|archive-date=21 September 2023}}</ref> | |||
| Religious leaders play a role in shaping foreign policy. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, the Russian Government has frequently used its connections with the ] to block and stymie the integration of former Soviet states like Moldova into the West.<ref>Andrew Higgins, "In Expanding Russian Influence, Faith Combines With Firepower," {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191110031305/https://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/14/world/europe/russia-orthodox-church.html |date=10 November 2019 }}</ref> | |||
| ====A multiethnic colonization==== | |||
| Over the 19th century, the Russian authorities encouraged the ] of Bessarabia or parts of it by ], ], ], ], ], and ], primarily in the northern and southern areas vacated by Turks and ], the latter having been expelled in the 1770s and 1780s, during the ];<ref>{{cite web |title=The Germans from Bessarabia |publisher=] |place= Edmonton, AB, Canada |website=Ualberta.ca |url=https://www.ualberta.ca/~german/PAA/Bessarabians.htm |access-date=9 October 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120926121442/http://www.ualberta.ca/~german/PAA/Bessarabians.htm |archive-date=26 September 2012 }}</ref><ref name="washington">{{cite book |author=Clark, Charles Upson |year=1927 |title=Bessarabia |chapter=Chapter VIII: Russia organizes the province |publisher=Dodd, Mead & Company |via=] (depts.washington.edu) |chapter-url=http://depts.washington.edu/cartah/text_archive/clark/bc_8.shtml#bc_8 |access-date=9 October 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-date=12 December 2012| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121212063455/http://depts.washington.edu/cartah/text_archive/clark/bc_8.shtml#bc_8}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=analele geo 2008 |format=PDF |website=fdocuments.in |url=https://fdocuments.in/document/analele-geo-2008.html}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Mennonite-Nogai Economic Relations, 1825–1860 |date=16 June 2000 |publisher=Goshen.edu |url=https://www.goshen.edu/mqr/2000/06/april-2000-staples/ |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> the inclusion of the province in the ] also allowed the immigration of more ].{{efn|name=fn1|The Jewish minority was more numerous in the past (228,620 Jews in Bessarabia in 1897, or 11.8% of the population).<ref>{{cite web |title = Moldova |website = The Jewish Virtual Library |publisher = American-Israeli Cooperative Enterprise |url = https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/vjw/moldova.html |access-date = 15 July 2015}}</ref>}} The Moldavian proportion of the population decreased from an estimated 86% in 1816,<ref>{{cite book |author=Nistor, Ion |author-link=Ion Nistor |year=1921 |title=Istoria Bassarabiei |publisher=Cernăuți}}</ref> to around 52% in 1905.<ref>{{cite book |author=Solomon, Flavius |section=Die Republik Moldau und ihre Minderheiten (Länderlexikon) |title=Ethnodoc-Datenbank für Minderheitenforschung in Südostosteuropa |language=de |page=52}}</ref> During this time there were anti-Semitic riots, leading to an exodus of thousands of Jews to the United States.<ref>{{cite web |author=Scheib, Ariel |date=23 July 1941 |title=Moldova |publisher=Jewishvirtuallibrary.org |url=https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/vjw/moldova.html |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> | |||
| In February 2023, Russia canceled a 2012 decree underpinning Moldova's sovereignty.<ref name="cnn163"/> In May 2023, the Moldovan government announced the immediate suspension of its participation in the Commonwealth of Independent States and its intentions to ultimately withdraw from the organization entirely.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Scotto di Santolo |first=Alessandra |date=15 May 2023 |title=Major blow for Putin as Moldova withdraws from Russia-led alliance |url=https://www.express.co.uk/news/world/1770254/putin-blow-maldova-cis-asembly-russia |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162327/https://www.express.co.uk/news/world/1770254/putin-blow-maldova-cis-asembly-russia |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Popusoi |first=Cristina |date=18 May 2023 |title=Moldova Is Distancing Itself From The CIS, But Leaving Might Not Be So Easy |language=en |work=Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-leaving-cis-russia/32417644.html |access-date=6 July 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162045/https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-leaving-cis-russia/32417644.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Goble |first=Paul |date=10 November 2022 |title=Moscow Working to Block Moldova from Leaving CIS |language=en-US |work=] |url=https://jamestown.org/program/moscow-working-to-block-moldova-from-leaving-cis/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162704/https://jamestown.org/program/moscow-working-to-block-moldova-from-leaving-cis/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In July 2023, Moldova passed a legislation removing it from membership in the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=PARLIAMENT ADOPTS IN FINAL READING LAW ON MOLDOVA'S WITHDRAWAL FROM CIS INTERPARLIAMENTARY ASSEMBLY |url=https://www.infotag.md/politics-en/309245/ |date=20 July 2023 |access-date=8 March 2024 |archive-date=29 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240129113439/http://www.infotag.md/politics-en/309245/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] between 1920 and 1940.]] | |||
| On 25 July 2023, the Moldovan government summoned the Russian ambassador Oleg Vasnetsov to Moldova after media reports of alleged spying devices on the rooftop of their embassy in Chişinău.<ref>{{Cite web |last2=Pokharel |first1=Josh |last1=Pennington |first2=Sugam |date=25 July 2023 |title=Moldova summons Russian ambassador after media reporting on alleged spy devices on embassy's rooftop |url=https://www.cnn.com/2023/07/25/europe/moldova-spying-allegations-intl/index.html |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801045016/https://www.cnn.com/2023/07/25/europe/moldova-spying-allegations-intl/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=26 July 2023 |title=Moldova expels 45 Russian diplomatic staff in spy row |language=en-GB |work=] |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-66320894 |access-date=1 August 2023 |archive-date=31 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230731183634/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-66320894 |url-status=live }}</ref> On 26 July 2023, the Moldovan government expelled 45 Russian diplomats and embassy staff due to "hostile actions" intended to destabilise the Republic of Moldova, according to Foreign Minister Nicu Popescu.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Bennetts |first=Marc |date=1 August 2023 |title=Moldova expels 45 Russian diplomats and embassy staff |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/moldova-expels-russian-diplomats-embassy-staff-5hjf56qjk |access-date=1 August 2023 |issn=0140-0460 |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801100849/https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/moldova-expels-russian-diplomats-embassy-staff-5hjf56qjk |url-status=live }}</ref> On 30 July, the Russian embassy announced that it would suspend consular appointments "for technical reasons".<ref>{{Cite news |last=Tanas |first=Alexander |date=30 July 2023 |title=Russian embassy in Moldova to suspend consular appointments |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/russian-embassy-moldova-suspend-consular-appointments-2023-07-30/ |access-date=1 August 2023 |archive-date=31 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230731211517/https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/russian-embassy-moldova-suspend-consular-appointments-2023-07-30/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ====Russian Revolution==== | |||
| ] brought in a rise in political and cultural (ethnic) awareness among the inhabitants of the region, as 300,000 Bessarabians were drafted into the ] formed in 1917; within bigger units several "Moldavian Soldiers' Committees" were formed. Following the ], a Bessarabian parliament, ] (a National Council), was ] and opened on {{OldStyleDate|December 3|1917|21 November}}. The Sfatul Țării proclaimed the ] ({{OldStyleDate|December 15|1917|2 December}}) within a federal Russian state, and formed a ] ({{OldStyleDate|21 December|1917|8 December}}). | |||
| The Moldovan ] (SIS) also ended all partnership agreements with Russia's ] after sending official notifications to the authorities in Moscow.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Necșuțu |first=Mădălin |date=1 August 2023 |title=Moldovan Secret Services Cancel Agreements with Russian Intelligence |work=] |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2023/08/01/moldovan-secret-services-cancel-agreements-with-russian-intelligence/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801154944/https://balkaninsight.com/2023/08/01/moldovan-secret-services-cancel-agreements-with-russian-intelligence/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Greater Romania === | |||
| After the ] ] in early January 1918 at the request of the National Council, Bessarabia proclaimed independence from Russia on {{OldStyleDate|February 6|1918|24 January}} and requested the assistance of the French army present in Romania (general ]) and of the Romanian Army.<ref>{{in lang|fr}} Anthony Babel: ''La Bessarabie (Bessarabia)'', Félix Alcan, Genève, Switzerland, 1931</ref> On {{OldStyleDate|April 9|1918|27 March}}, the Sfatul Țării decided with 86 votes for, 3 against and 36 abstaining, to ]. The union was conditional upon fulfilment of the ], autonomy, and respect for universal human rights.<ref>{{cite book |last=King |first=Charles |author-link=Charles King (professor of international affairs) |title=The Moldovans: Romania, Russia, and the politics of culture |publisher=Hoover Press |year=2000 |chapter=From Principality to Province |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ldBFWtuv8DQC&pg=PA33 |pages= |isbn=0-8179-9792-X |access-date=31 October 2010 |url=https://archive.org/details/moldovansromania00king_0/page/33 }}</ref> A part of the interim Parliament agreed to drop these conditions after ] and ] also joined the ], although historians note that they lacked the ] to do so.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.prm.md/search.php?id=2332&lang=rom| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071204070133/http://www.prm.md/search.php?id=2332&lang=rom |archive-date=4 December 2007 |title=Sfatul Țării ... proclaimed the Moldavian Democratic Republic |language=ro |publisher=Prm.md |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |first=Charles Upson |last=Clark |title=Bessarabia: Russia and Romania on the Black Sea – View Across Dniester From Hotin Castle |publisher=Dodd, Mead & Company |location=New York |year=1927 |chapter=24:The Decay of Russian Sentiment |chapter-url=http://depts.washington.edu/cartah/text_archive/clark/bc_17.shtml#bc_17 |access-date=31 October 2013}}</ref><ref>] (''Chronology'')</ref><ref>] (''Moldova'', pp. 240–245).</ref><ref>Cristina Petrescu, "Contrasting/Conflicting Identities:Bessarabians, Romanians, Moldovans" in'' Nation-Building and Contested Identities'', Polirom, 2001, pg. 156</ref> | |||
| ==== European Union Accession ==== | |||
| This union was recognized by most of the principal ] in the ], which however was not ratified by all of its signatories.<ref name="legal">{{cite journal |title=The Legal Status of the Bukovina and Bessarabia |author=Malbone W. Graham |journal=The American Journal of International Law |date=October 1944 |volume=38 |issue=4 |pages=667–673 |publisher=American Society of International Law |doi=10.2307/2192802 |jstor=2192802|s2cid=146890589 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Mitrasca |first=Marcel |title=Moldova: a Romanian province under Russian rule: diplomatic history from the archives of the great powers |publisher=Algora Publishing |year=2002 |chapter=Introduction |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mZogbSmBR-4C&pg=PA13 |page=13 |isbn=1-892941-86-4 |access-date=31 October 2010}}</ref> The ] did not recognize Romanian rule over Bessarabia, considering it an occupation of Russian territory.<ref>], ''Bessarabia'' In: '']'' (Crowell Collier and MacMillan Inc., 1967) vol. 4, p. 103</ref> Uprisings against Romanian rule took place in 1919 at ] and ], but were eventually suppressed by the Romanian Army. | |||
| {{main |Accession of Moldova to the European Union}} | |||
| ].|left]] | |||
| Moldova has set 2030 as the target date for EU Accession.<ref>{{cite web |title=Moldova sets 2030 as EU accession target at massive pro-EU rally in Chisinau |url=https://www.romania-insider.com/moldova-rally-eu-accession-may-2023 |date=22 May 2023 |access-date=8 March 2024 |archive-date=8 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231208090113/https://www.romania-insider.com/moldova-rally-eu-accession-may-2023 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In May 1919, the ] was proclaimed as a government in exile. After the failure of the ] in 1924, the Moldavian Autonomous Region, created earlier in the Transnistria region, was elevated to an ] within the ]. | |||
| Moldova signed the Association Agreement with the European Union in ] on 27 June 2014. The signing came after the accord was drafted in Vilnius in November 2013.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://eeas.europa.eu/top_stories/2014/270614_association_agreement_en.htm|title=European Union – EEAS (European External Action Service) – EU forges closer ties with Ukraine, Georgia and Moldova|website=Eeas.europa.eu|access-date=27 June 2014|archive-date=6 July 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160706211949/http://eeas.europa.eu/top_stories/2014/270614_association_agreement_en.htm|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_SPEECH-14-511_en.htm|title=European Commission – PRESS RELEASES – Press release – Remarks by President Barroso at the signing of the Association Agreements with Georgia, the Republic of Moldova and Ukraine|website=Europa.eu|access-date=27 June 2014|archive-date=30 June 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140630041046/http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_SPEECH-14-511_en.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===World War II and Soviet era=== | |||
| {{main|Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic}} | |||
| ], the village ], ].]] | |||
| Moldova signed the membership application to join the EU on 3 March 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Tanas |first=Alexander |date=3 March 2022 |title=With war on its doorstep, Moldova applies for EU membership |website=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldovan-president-says-moldova-applies-eu-membership-2022-03-03/ |access-date=3 March 2022 |archive-date=25 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220625000916/https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldovan-president-says-moldova-applies-eu-membership-2022-03-03/ |url-status=live }}</ref> On 23 June 2022, Moldova was officially granted ] by EU leaders.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.euractiv.com/section/europe-s-east/news/eu-leaders-grant-candidate-status-to-ukraine-and-moldova/ |title=EU leaders grant candidate status to Ukraine and Moldova |last=Brzozowski |first=Alexandra |date=23 June 2022 |website=euractiv.com |publisher=] |access-date=24 June 2022 |archive-date=23 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220623214851/https://www.euractiv.com/section/europe-s-east/news/eu-leaders-grant-candidate-status-to-ukraine-and-moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> The United Nations Development Programme is also providing assistance to Moldova in implementing the necessary reforms for full accession by 2030.<ref>{{Cite web |title=UNDP to support the Republic of Moldova to implement key reforms on its EU accession path {{!}} United Nations Development Programme |url=https://www.undp.org/moldova/press-releases/undp-support-republic-moldova-implement-key-reforms-its-eu-accession-path |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=UNDP |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802164623/https://www.undp.org/moldova/press-releases/undp-support-republic-moldova-implement-key-reforms-its-eu-accession-path |url-status=live }}</ref> The European Union's ] ] has confirmed that the pathway to accession does not depend upon a resolution of the ].<ref name="RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty">{{Cite news |date=1 June 2023 |title=Moldova's EU Path Independent Of Transdniester Developments, Says Borrell |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-eu-path-transdniester-borrell/32438431.html |access-date=2 August 2023 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802165031/https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-eu-path-transdniester-borrell/32438431.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ====Annexation by the USSR==== | |||
| In August 1939, the ] and its secret additional protocol were signed, by which ] recognized Bessarabia as being within the ], which led the latter to actively revive its claim to the region.<ref name="Olson 1994 483">{{cite book |last=Olson |first=James |title=An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires |year=1994 |page=483}}</ref> On 28 June 1940, the Soviet Union issued an ] requesting the cession of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, with which Romania complied the following day. Soon after, the ] (Moldavian SSR, MSSR) was established,<ref name="Olson 1994 483"/> comprising about 65% of Bessarabia, and 50% of the now-disbanded Moldavian ASSR (the present-day ]). Ethnic Germans ] in 1940. | |||
| On 27 June, Moldova signed a comprehensive free trade agreement with the ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=27 June 2023 |title=EFTA and Moldova sign a Free Trade Agreement {{!}} European Free Trade Association |url=https://www.efta.int/Free-Trade/news/EFTA-and-Moldova-sign-Free-Trade-Agreement-536291#:~:text=At%20the%20meeting,%20the%20EFTA,investment%20between%20the%20two%20sides. |access-date=5 July 2023 |website=] |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705130004/https://www.efta.int/Free-Trade/news/EFTA-and-Moldova-sign-Free-Trade-Agreement-536291#:~:text=At%20the%20meeting,%20the%20EFTA,investment%20between%20the%20two%20sides. |url-status=live }}</ref> On 28 June 2023, the European Union announced a €1.6 billion support and investment programme for Moldova, as well as confirming reductions in the price of mobile data and voice roaming charges in Moldova by European and Moldovan telecoms operators, as well as Moldova joining the EU's joint gas purchase platform.<ref>{{Cite web |date=28 June 2023 |title=The EU presents a Support Package for the Republic of Moldova |url=https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/home/en |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=21 June 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190621200951/https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/home/en |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ====Reincorporation into Romania and the Soviet occupation==== | |||
| As part of the 1941 ], Romania regained the territories of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, and seized a territory which became known as ]. Romanian forces, working with the Germans, ] about 300,000 Jews {{citation needed|date=October 2022}}, including 147,000 from Bessarabia and Bukovina. Of the latter, approximately 90,000 died.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.presidency.ro/static/ordine/RAPORT_FINAL_CPADCR.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080408193207/http://www.presidency.ro/static/ordine/RAPORT_FINAL_CPADCR.pdf |archive-date=8 April 2008 |title=Tismăneanu Report |pages=748–749 |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> Between 1941 and 1944 ] acted against the Romanian administration. The Soviet Army re-captured the region in February–August 1944, and re-established the Moldavian SSR. Between the end of the ] in August 1944 and the end of the war in May 1945, 256,800 inhabitants of the Moldavian SSR were drafted into the Soviet Army. 40,592 of them perished.<ref name="history">{{cite book |title=Istoria Republicii Moldova: din cele mai vechi timpuri pină în zilele noastre |trans-title=History of the Republic of Moldova: From Ancient Times to Our Days |editor=Asociația Oamenilor de știință din Moldova. H. Milescu-Spătaru. |edition=2nd |year=2002 |publisher=Elan Poligraf |location=Chișinău |language=ro |isbn=9975-9719-5-4 |pages=239–244}}</ref> | |||
| ] ] after the Soviet occupation of ] in 1940.]] | |||
| During the periods 1940–1941 and 1944–1953, ] to the northern ], to ], and northern ] occurred regularly, with the largest ones on 12–13 June 1941, and 5–6 July 1949, accounting from MSSR alone for 18,392{{efn|name=fn2|''Note:'' Further 11,844 were deported on 12–13 June 1941 from other Romanian territories occupied by the USSR a year earlier.}} and 35,796 deportees respectively.<ref name="tismrep">{{cite web |url=http://www.presidency.ro/static/ordine/RAPORT_FINAL_CPADCR.pdf |title=Tismăneanu Report |pages=747, 752 |language=ro |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> Other forms of Soviet persecution of the population included political arrests or, in 8,360 cases, execution. | |||
| ====Moldova in the USSR after World War II==== | |||
| In 1946, as a result of a severe drought and excessive delivery quota obligations and requisitions imposed by the Soviet government, the southwestern part of the USSR suffered from a major ].<ref>{{cite journal |first=Michael |last=Ellman |url=http://www.paulbogdanor.com/left/soviet/famine/ellman1947.pdf |title=The 1947 Soviet Famine and the Entitlement Approach to Famines |journal=Cambridge Journal of Economics |volume=39 |issue=24 |year=2000 |pages=603–630 |access-date=10 December 2015 |doi=10.1093/cje/24.5.603 |archive-date=25 March 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090325075851/http://www.paulbogdanor.com/left/soviet/famine/ellman1947.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |url=https://www.academia.edu/7785239 |title=Foametea din anii 1946–1947 din RSS Moldovenească: cauze și consecințe |journal=Capitol Din Lucrarea Duşmanul de Clasă. Represiuni Politice, Violenţă Şi Rezistenţă În R(A)Ss Moldovenească, 1924-1956, Chişinău, Cartier, 2015, Editia a Ii-A. Cartea Este Dispobilă În Librării |trans-title=The Mass Famine in the Moldavian SSR, 1946–1947: causes and consequences in Dusmanul de clasa. Represiuni politice, violenta si rezistenta in R(A)SS Moldoveneasca, 1924–1956 |access-date=19 October 2014|last1=Casu |first1=Igor }}</ref> In 1946–1947, at least 216,000 deaths and about 350,000 cases of ] were accounted by historians in the Moldavian SSR alone.<ref name="tismrep"/> Similar events occurred in the 1930s in the ].<ref name="tismrep"/> In 1944–53, there were several anti-Soviet resistance groups in Moldova; however the ] and later ] managed to eventually arrest, execute or deport their members.<ref name="tismrep"/> | |||
| In the postwar period, the Soviet government organized the immigration of working age Russian speakers (mostly Russians, ], and Ukrainians), into the new Soviet republic, especially into urbanized areas, partly to compensate for the demographic loss caused by the war and the emigration of 1940 and 1944.<ref>Pal Kolsto, ''National Integration and Violent Conflict in Post-Soviet Societies: The Cases of Estonia and Moldova'', ], 2002, {{ISBN|0-7425-1888-4}}, pg. 202</ref> In the 1970s and 1980s, the Moldavian SSR received substantial allocations from the budget of the USSR to develop industrial and scientific facilities and housing. In 1971, the ] adopted a decision "About the measures for further development of the city of ]" (modern Chișinău), that allotted more than one ] ]s (approximately 6.8 billion in 2018 US dollars) from the USSR budget for building projects.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.kishinev.info/architecture_en/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030210034311/http://www.kishinev.info/architecture_en/ |archive-date=10 February 2003 |title=Architecture of Chișinău |publisher=on Kishinev.info |access-date=12 October 2008}}</ref> | |||
| ] in ] in 1985]] | |||
| The Soviet government conducted a campaign to promote a Moldovan ethnic identity distinct from that of the Romanians, based on a theory developed during the existence of the ]. Official Soviet policy asserted that the language spoken by ] was distinct from the ] (see ]). To distinguish the two, during the Soviet period, Moldovan was written in the ], in contrast with Romanian, which since 1860 had been written in the ]. | |||
| All independent organizations were severely reprimanded, with the ] leaders being sentenced in 1972 to long prison terms.<ref>{{cite journal |url=https://www.academia.edu/4921186 |title=Political Repressions in the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic after 1956: Towards a Typology Based on KGB files Igor Casu |journal=Dystopia |volume=I |issue=1–2 |year=2014 |pages=89–127 |access-date=19 October 2014}}</ref> The ] is assessing the activity of the communist totalitarian regime. | |||
| ====Glasnost and Perestroika==== | |||
| In the 1980s, amid political conditions created by ] and ], a ] was formed, which in 1989 became known as the nationalist ] (FPM).<ref name="lang matei">{{in lang|ro}} Horia C. Matei, "State lumii. Enciclopedie de istorie." Meronia, București, 2006, p. 292-294</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://miris.eurac.edu/mugs2/do/blob.pdf?type=pdf&serial=1047909431571 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110719192119/http://miris.eurac.edu/mugs2/do/blob.pdf?type=pdf&serial=1047909431571 |archive-date=19 July 2011 |title=Romanian Nationalism in the Republic of Moldova |author=Andrei Panici |publisher=American University in Bulgaria |year=2002 |pages=40 and 41 |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> Along with several other Soviet republics, from 1988 onwards, Moldova started to move towards ]. On 27 August 1989, the FPM organized a mass demonstration in Chișinău that became known as the ]. The assembly pressured the authorities of the Moldavian SSR to adopt a language law on 31 August 1989 that proclaimed the Moldovan language written in the ] to be the state language of the MSSR. Its identity with the Romanian language was also established.<ref name="lang matei"/><ref name="lang law">{{cite web|format=DOC|url=http://www.iatp.md/ladom/downloads/M3.doc|title=Legea cu privire la functionarea limbilor vorbite pe teritoriul RSS Moldovenesti Nr.3465-XI din 01.09.89 Vestile nr.9/217, 1989|trans-title=The law on use of languages spoken in the Moldovan SSR No.3465-XI of 09/01/89|volume=9|issue=217|language=ro|work=Moldavian SSR News, Law regarding the usage of languages spoken on the territory of the Republic of Moldova|access-date=11 February 2006|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060219024839/http://www.iatp.md/ladom/downloads/M3.doc|archive-date=19 February 2006|quote='''''' Moldavian SSR supports the desire of the Moldovans that live across the borders of the Republic, and considering the existing linguistic Moldo-Romanian identity – of the Romanians that live on the territory of the USSR, of doing their studies and satisfying their cultural needs in their native language.}}</ref> In 1989, as opposition to the ] grew, there were ]. | |||
| ===Independence and aftermath=== | |||
| ] replaces the ] on the ] with the ] on 27 April 1990.]] | |||
| The ] for the local ] were held in February and March 1990. ] was elected as ], and ] as Prime Minister. On 23 June 1990, the Parliament adopted the Declaration of Sovereignty of the "Soviet Socialist Republic Moldova", which, among other things, stipulated the supremacy of Moldovan laws over those of the Soviet Union.<ref name="lang matei"/> After the failure of the ], ] on 27 August 1991. | |||
| On 21 December of the same year, Moldova, along with most of the other Soviet republics, signed the constitutive act that formed the post-Soviet ] (CIS). Moldova received official recognition on 25 December. On 26 December 1991, the Soviet Union ceased to exist. Declaring itself a ], Moldova did not join the military branch of the CIS. Three months later, on 2 March 1992, the country gained formal recognition as an independent state at the United Nations. In 1994, Moldova became a member of ]'s ] program, and a member of the Council of Europe on 29 June 1995.<ref name="lang matei"/> | |||
| ====Transnistria breaks away (1990 to present)==== | |||
| {{Further|Pridnestrovian Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic}} | |||
| In the region east of the ] river, ], which includes a large proportion of predominantly ] ] of Ukrainian (28%) and Russian (26%) descent (altogether 54% as of 1989), an independent ] was proclaimed on 16 August 1990, with its capital in ].<ref name="lang matei"/> The motives behind this move were fear of the rise of nationalism in Moldova.{{citation needed|date=April 2022}} In the winter of 1991–1992, clashes occurred between Transnistrian forces, ] by elements of the ], and the ]. Between 2 March and 26 July 1992, the conflict escalated into a ]. It was a brief war between Moldovan and separatist Transnistrian forces, with Russia intervening militarily on Transnistria's side. It ended with a ceasefire and the establishment of a security zone policed by a three-way peacekeeping force of Russian, Transnistrian, and Moldovan personnel.<ref>{{cite report |publisher=] |website=rand.org |title=Russia's Hostile Measures: Combating Russian gray zone aggression against NATO in the contact, blunt, and surge layers of competition |year=2020 |id=RR 2539 |url=http://www.rand.org/t/RR2539}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Market economy (1992) ==== | |||
| On 2 January 1992, Moldova introduced a ], liberalizing prices, which resulted in rapid inflation. From 1992 to 2001, the country suffered a serious economic crisis, leaving most of the population below the poverty line. In 1993, the ] introduced a new national currency, the ], to replace the ]. The ] began to change in 2001; and until 2008, the country saw a steady annual growth between 5% and 10%. The early 2000s also saw a considerable growth of emigration of Moldovans looking for work (mostly illegally) in Russia (especially the Moscow region), Italy, Portugal, Spain, and other countries; ]s from Moldovans abroad account for almost 38% of Moldova's ], the second-highest percentage in the world, after ] (45%).<ref>{{cite web|last1=Ratha|first1=Dilip|author-link=Dilip Ratha|url=http://peoplemove.worldbank.org/en/content/remittance-flows-to-developing-countries|title=Remittance flows to developing countries are estimated to exceed US$300 billion in 2008|publisher=peoplemove.worldbank.org |date=18 February 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090223020016/http://peoplemove.worldbank.org/en/content/remittance-flows-to-developing-countries |archive-date=23 February 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.iom.int/cms/en/sites/iom/home/news-and-views/press-briefing-notes/pbn-2008/pbn-listing/information-campaign-in-moldova-seeks-to.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407085911/https://www.iom.int/cms/en/sites/iom/home/news-and-views/press-briefing-notes/pbn-2008/pbn-listing/information-campaign-in-moldova-seeks-to.html |archive-date=7 April 2014 |title=Information Campaign to Increase the Efficiency of Remittance Flows |publisher=International Organization for Migration |date=9 December 2008}}</ref> | |||
| ====Elections: 1994–2009==== | |||
| In the ], the ] gained a majority of the seats, setting a turning point in Moldovan politics. With the nationalist Popular Front now in a parliamentary minority, new measures aiming to moderate the ethnic tensions in the country could be adopted. Plans for a ] were abandoned,<ref name="lang matei"/> and the new ] gave autonomy to the breakaway Transnistria and Gagauzia. On 23 December 1994, the Parliament of Moldova adopted a "Law on the Special Legal Status of Gagauzia", and in 1995, the latter was constituted. | |||
| ] outside the ] building in 2009]] | |||
| After winning the ], on 15 January 1997, ], the former First Secretary of the ] in 1989–91, became the country's second president (1997–2001), succeeding Mircea Snegur (1991–1996). In 2000, the Constitution was amended, transforming Moldova into a ], with the president being chosen through ] rather than direct popular vote. | |||
| ], the ] (reinstituted in 1993 after being outlawed in 1991), gained 71 of the 101 MPs, and on 4 April 2001, elected ] as the country's third president (re-elected in 2005). The country became the first post-Soviet state where a non-reformed Communist Party returned to power.<ref name="lang matei"/> New governments were formed by ] (19 April 2001 – 31 March 2008), and ] (31 March 2008 – 14 September 2009). In 2001–2003, ] improved, but then temporarily deteriorated in 2003–2006, in the wake of the failure of the ], culminating in the ]. The Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova managed to stay in power for eight years. | |||
| In the ], the Communist Party won 49.48% of the votes, followed by the ] with 13.14% of the votes, the ] with 12.43%, and the ] with 9.77%. The controversial results of this election sparked the ].<ref>{{cite web |first=Carmen |last=Fizesan |url=http://seventimes.ro/politics/supporting_actions_for_moldovas_riot.html |title=Supporting actions for Moldova's riot |publisher=SevenTimes.ro |date=8 April 2009 |access-date=9 October 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100121031517/http://seventimes.ro/politics/supporting_actions_for_moldovas_riot.html |archive-date=21 January 2010}}</ref><ref name="omg.md">{{cite web |url=http://archive.omg.md/Content.aspx?id=2437&lang=2|title=The protest initiative group: LDPM is the guilty one for the devastations in the Chișinău downtown |publisher=omg.md |date=8 April 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407125325/http://archive.omg.md/Content.aspx?id=2437&lang=2 |archive-date=7 April 2014}}</ref><ref name="unimedia.info">{{cite web |url=http://unimedia.info/stiri/-11183.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131023060456/http://unimedia.info/stiri/-11183.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=23 October 2013 |title=EU flags flying on the Presidency and Parliament, to calm the masses |date=2 June 2009 |publisher=Unimedia.info |access-date=9 October 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Stalemate 2009-2012 ==== | |||
| In August 2009, four Moldovan parties (Liberal Democratic Party, Liberal Party, ], and Our Moldova Alliance) agreed to create the ] that pushed the ] into opposition. On 28 August 2009, this coalition chose a new ] (]) in a vote that was boycotted by Communist legislators. ], who had been ] since 2001, eventually resigned on 11 September 2009, but the ]. The acting president Mihai Ghimpu instituted the ] to adopt a new version of the Constitution of Moldova. After the ] aimed to approve the reform failed in September 2010,<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/moldova-referendum-invalid-idUSLDE6840FD20100905 |title=Moldovan referendum appears to flop on low turnout |work=] |date=5 September 2010 |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> the parliament was dissolved again and a ] was scheduled for 28 November 2010.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-11430570|title=Moldova going to third election in two years |date=28 September 2010 |work=] |access-date=30 September 2010}}</ref> On 30 December 2010, Marian Lupu was elected as the Speaker of the Parliament and the acting President of the Republic of Moldova.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.allmoldova.com/en/moldova-news/1249049268.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120104191010/http://www.allmoldova.com/en/moldova-news/1249049268.html |archive-date=4 January 2012 |title=Marian Lupu elected Head of Parliament |date=30 November 2010 |publisher=allmoldova |access-date=27 October 2011}}</ref> In March 2012, ] was elected as president of Moldova in a parliamentary vote, becoming the first full-time president since Vladimir Voronin, a Communist, resigned in September 2009. Before the election of Timofti, Moldova had had three acting presidents in three years.<ref>{{cite news |title=Nicolae Timofti finally elected Moldova President |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17398641 |work=BBC News |date=16 March 2012}}</ref> After the Alliance for European Integration lost a no confidence vote, the ] was formed on 30 May 2013.<ref>{{cite news |title=New Moldavan pro-European coalition formed |url=https://www.europeanforum.net/headlines/new_moldavan_pro_european_coalition_formed |work=European Forum |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ====Banking crisis==== | |||
| In November 2014, Moldova's central bank took control of ''Banca de Economii'', the country's largest lender, and two smaller institutions, ''Banca Sociala'' and ''Unibank''. Investigations into activities at these three banks uncovered ] by means of fraudulent loans to business entities controlled by a Moldovan-Israeli ], ], of funds worth about 1 billion U.S. dollars.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.intellinews.com/audit-links-local-tycoon-to-1bn-moldovan-bank-fraud-500446512/?source=moldova&archive=bne |title=Audit links local tycoon to $1bn Moldovan bank fraud |publisher=Business New Europe |date=5 May 2015 |access-date=2 September 2015}}</ref> The large scale of the fraud compared to the size of the Moldovan economy is cited as tilting the country's politics in favour of the pro-Russian ].<ref>{{cite news |last1=Higgins |first1=Andrew |title=Moldova, Hunting Missing Millions, Finding Only Ash |date=4 June 2015 |work=] |access-date=10 March 2016 |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/05/world/europe/moldova-bank-theft.html?_r=0}}</ref> In 2015, Shor was still at large, after a period of house arrest. | |||
| ====Pavel Filip's government (2016-2019)==== | |||
| Following a period of political instability and massive public protests, a new government led by ] was invested in January 2016.<ref name="theguardian.com_2016-02-16">{{cite news | url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/jan/27/moldovan-prime-minister-pavel-filip-says-last-chance-to-end-national-crisis| title=Moldovan prime minister Pavel Filip says 'last chance' to end national crisis| newspaper=]| date=26 January 2016 | agency=]| access-date=10 March 2016}}</ref> Concerns over statewide corruption, the independence of the judiciary system, and the nontransparency of the banking system were expressed. Germany's broadcaster ] also raised concerns about the alleged influence of Moldovan oligarch ] over the Filip government.<ref name="Romania Curata_Deutsche Welle_2016-02-16">{{cite journal| url=http://www.romaniacurata.ro/ue-se-autosesizeaza-moldova-se-indreapta-spre-dictatura/| title=UE se autosesizează: Moldova se îndreaptă spre dictatură!| newspaper=Romania Curata| author=Deutsche Welle| access-date=10 March 2016| date=16 February 2016| language=ro| trans-title=EU Will Discuss the Matter: Moldova moving towards dictatorship!| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180621221405/http://www.romaniacurata.ro/ue-se-autosesizeaza-moldova-se-indreapta-spre-dictatura/| archive-date=21 June 2018| url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| In the ], Socialist, pro-Russian ] was elected as the new president of the republic.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Welle (www.dw.com) |first1=Deutsche |title=Pro-Russia candidate Igor Dodon to win Moldova presidential election {{!}} DW {{!}} 13 November 2016 |url=https://www.dw.com/en/pro-russia-candidate-igor-dodon-to-win-moldova-presidential-election/a-36379350 |work=DW.COM}}</ref> | |||
| ====2019 constitutional crisis==== | |||
| {{Main|2019 Moldovan constitutional crisis}} | |||
| In 2019, from 7 to 15 June, the Moldovan government went through a period of dual power in what is known as the ]. On 7 June, the Constitutional Court, which is largely believed to be controlled by Vladimir Plahotniuc<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://balkaninsight.com/2019/06/09/moldova-faces-turmoil-as-court-outlaws-new-govt/|title=Moldova Faces Turmoil as Court Outlaws New Govt|date=9 June 2019|website=Balkan Insight|language=en-US|access-date=20 June 2019}}</ref> from the ], announced that they had temporarily removed the sitting president, Igor Dodon, from power due to his ‘inability’ to call new parliamentary elections as the parliament did not form a coalition within three months of the validation of the election results. According to Moldovan constitutional law, the president may call snap elections if no government is formed after three months.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.presedinte.md/rom/titlul3|title=Titlul III. Autoritățile publice|website=www.presedinte.md|language=en|access-date=20 June 2019}}</ref> However, on 8 June, the ] reached an agreement with the ] forming a government led by Maia Sandu as the new prime minister, pushing the Democratic Party out of power.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.fairobserver.com/region/europe/moldova-constitutional-crisis-european-union-us-russia-news-18272/|title=A Constitutional Crisis in Moldova Produces an Unexpected Alliance|date=18 June 2019|website=Fair Observer|language=en-US|access-date=20 June 2019}}</ref> This new government was also supported by Igor Dodon. The new coalition and Igor Dodon argued that the president may call snap elections after consulting the parliament but is not obliged to do so. Additionally, because the election results were verified on 9 March, three months should be interpreted as three calendar months, not 90 days as was the case. The former prime minister, Pavel Filip from the Democratic Party, said that new parliamentary elections would be held on 6 September and refused to recognize the new coalition, calling it an illegal government. After a week of dual government meetings, some protest, and the international community mostly supporting the new government coalition, Pavel Filip stepped down as prime minister but still called for new elections.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/06/14/world/europe/moldova-new-government.html|title=Moldova Had Two Governments. One Has Finally Resigned.|last=Kingsley|first=Patrick|date=14 June 2019|work=The New York Times|access-date=20 June 2019|language=en-US|issn=0362-4331}}</ref> The Constitutional Court reversed the decision on 15 June, effectively ending the crisis.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://en.interfax.com.ua/news/general/594167.html|title=Moldova's Constitutional Court overturns all of its decisions that led to political crisis in country in 5 mins|website=en.interfax.com.ua|access-date=20 June 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ====COVID-19 pandemic==== | |||
| In March 2020, due to the ], the government called a "national red code alert" as the number of coronavirus cases in the country rose to six on 13 March 2020. Government "banned all gatherings of over 50 people until 1 April 2020 and closed all schools and kindergartens in an attempt to curb the spread of the virus". Flights were banned to Spain, Italy, France, Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Cyprus, Germany, Ireland, the U.K., Poland, Portugal and Romania.<ref name="sn1">{{cite news |title=Moldova calls national code red alert over coronavirus, bans flights |url=https://seenews.com/news/moldova-calls-national-code-red-alert-over-coronavirus-bans-flights-690722 |publisher=SeeNews |date=13 March 2020}}</ref> On 17 March, Parliament declared a ] for at least 60 days, suspended all international flights and closed borders with neighbours Romania and Ukraine. Moldova reported 29 cases of the disease on 17 March 2020.<ref name="sn2">{{cite news |title=Moldova declares state of emergency over coronavirus outbreak |url=https://seenews.com/news/moldova-declares-state-of-emergency-over-coronavirus-outbreak-691151 |publisher=SeeNews |date=17 March 2020}}</ref> The country reported its first death from the disease on 18 March 2020, when the total number of cases reached 30.<ref name="atr">{{cite news |title=Moldova reports first death from coronavirus, health ministry says |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-moldova/moldova-reports-first-death-from-coronavirus-health-ministry-says-idUSKBN2150U4 |publisher=Reuters |date=18 March 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Presidency of Maia Sandu since 2020 ==== | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | caption_align = center | |||
| | total_width = 300 | |||
| | image1 = Maia_Sandu_at_Batumi_International_Conference,_on_19_July_2021_(cropped).jpg | |||
| | image2 = Dorin Recean - février 2023.jpeg | |||
| | caption1 = ]<br /><small>]</small> | |||
| | caption2 = ]<br /><small>]</small> | |||
| | alt1 = | |||
| | alt2 = | |||
| }} | |||
| In the ], the pro-European opposition candidate ] was elected as the new president of the republic, defeating incumbent pro-Russian president Igor Dodon and thus becoming the first female elected president of Moldova.<ref>{{Cite news|date=16 November 2020|title=Moldova election: Pro-EU candidate Maia Sandu wins presidency|language=en-GB|work=BBC News|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-54942847|access-date=27 July 2021}}</ref> In December 2020, Prime Minister ], who had led a pro-Russian government since November 2019, resigned a day before Sandu was sworn in.<ref>{{Cite web|date=23 December 2020|title=Moldova's pro-Russian prime minister Ion Chicu resigns|url=https://www.euronews.com/2020/12/23/moldova-s-pro-russian-prime-minister-ion-chicu-resigns|access-date=27 July 2021|website=euronews|language=en}}</ref> The parliament, dominated by pro-Russian Socialists, did not accept any Prime Minister candidate proposed by the new president.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://balkaninsight.com/2021/03/25/moldova-parliament-rejects-proposed-pm-bringing-elections-nearer/|title=Moldova Parliament Rejects Proposed PM, Bringing Elections Nearer|date=25 March 2021}}</ref> On 28 April 2021, Sandu dissolved the ] after the ] ended Moldova's ] which had been brought about by the ].<ref>{{Cite web|date=28 April 2021|title=Moldovan leader dissolves parliament, sets July elections|url=https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20210428-moldovan-leader-dissolves-parliament-sets-july-elections|access-date=1 May 2021|website=France 24|language=en}}</ref> Parliamentary elections ] on 11 July 2021.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Moldova's president calls early election for July 11|url=https://apnews.com/article/elections-coronavirus-health-government-and-politics-0527c82d101cab326f3d96a3c3f4f54f|access-date=1 May 2021|website=AP NEWS|date=28 April 2021}}</ref> The snap parliamentary elections resulted in a landslide win for the pro-European ] (PAS).<ref>{{Cite web|date=12 July 2021|title=President Sandu's party wins landslide victory in Moldova's snap election|url=https://www.intellinews.com/president-sandu-s-party-wins-landslide-victory-in-moldova-s-snap-election-215371/|access-date=27 July 2021|website=www.intellinews.com|language=en}}</ref> On 6 August 2021, the ]-led ] was sworn in to office with 61 votes, all from the ] (PAS).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Natalia Gavriliţa, noul prim-ministru al Republicii Moldova. Guvernul a fost învestit în funcţie cu 61 de voturi |url=https://adevarul.ro/moldova/politica/natalia-gavrilita-noul-prim-ministru-republicii-moldova-guvernul-fost-investit-functie-61-voturi-1_610cf9ea5163ec4271d9951d/index.html |language=ro |website=Adevărul |access-date=6 August 2021 }}</ref> She resigned on 10 February 2023.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Criză politică în Republica Moldova. Premierul Natalia Gavrilița a demisionat |url=https://www.digi24.ro/stiri/externe/criza-politica-in-republica-moldova-premierul-natalia-gavrilita-a-demisionat-2247373 |access-date=2023-02-10 |website=www.digi24.ro |language=ro}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldovan government quits amid economic turmoil, Russia tensions |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldovan-prime-minister-announces-government-resignation-2023-02-10/ |website=Reuters |access-date=10 February 2023}}</ref> | |||
| === Russian invasion of neighbouring Ukraine === | |||
| {{Main|2022 Transnistria attacks|2022–2023 Moldovan energy crisis|2022–2023 Moldovan protests}} | |||
| In February 2022 Sandu condemned the ], calling it "a blatant breach of international law and of Ukrainian sovereignty and territorial integrity."<ref>{{Cite web|date=24 February 2022|title=The World Reacts to Russia's Invasion of Ukraine|url=https://www.lawfareblog.com/world-reacts-russias-invasion-ukraine|access-date=26 February 2022|website=Lawfare|language=en}}</ref> Prime Minister Natalia Gavrilita stated on 28 February 2022 that Moldova should rapidly move to become a member of the ];<ref>{{cite news |last1=VanderKlippe |first1=Nathan |title=Moldova vows to seek closer ties with Europe despite fears of provoking Russia |url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/world/article-moldova-vows-to-seek-closer-ties-with-europe-despite-fears-of/ |access-date=28 February 2022 |newspaper=] |date=28 February 2022 |language=en-CA}}</ref> the country submitted a formal application for EU membership on 3 March 2022,<ref>{{Cite web |date=3 March 2022 |title=With war on its doorstep, Moldova applies for EU membership |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldovan-president-says-moldova-applies-eu-membership-2022-03-03/ |website=Reuters}}</ref> and was subsequently granted the status of ] by the ] on 23 June 2022<ref>{{Cite web |date=3 March 2022 |title=European Council conclusions on Ukraine, the membership applications of Ukraine, the Republic of Moldova and Georgia, Western Balkans and external relations, 23 June 2022 |url=https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2022/06/23/european-council-conclusions-on-ukraine-the-membership-applications-of-ukraine-the-republic-of-moldova-and-georgia-western-balkans-and-external-relations-23-june-2022/ |website=European Council}}</ref> along with Ukraine. | |||
| On 26 April 2022, authorities from the Transnistria region said two transmitting antennas broadcasting Russian radio programs at ] broadcasting facility near the town of ] in the ] near the Ukrainian border ] and the previous evening, the premises of the ] had been attacked.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |last=tagesschau.de |title=Moldauische Konfliktregion Transnistrien meldet Explosionen |url=https://www.tagesschau.de/ausland/europa/transnistrien-expolsionen-101.html |access-date=26 April 2022 |website=tagesschau.de |language=de}}</ref> The Russian army has a military base and a large ammunition dump in the region. Russia has about 1,500 soldiers stationed in breakaway Transnistria. They are supposed to serve there as peacekeepers.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| On 24 May 2022, the former president of Moldova, Igor Dodon, was arrested. Dodon, leader of Moldova's main pro-Russian opposition, the Socialist Party, was accused of taking bribes. Moldova's pro-Western and pro-Russian factions became increasingly divided since Russia's invasion of Ukraine.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Welle (www.dw.com) |first1=Deutsche |title=Moldovan ex-president detained for alleged graft, treason {{!}} DW {{!}} 24.05.2022 |url=https://www.dw.com/en/moldovan-ex-president-detained-for-alleged-graft-treason/a-61913546 |work=DW.COM}}</ref> | |||
| On 31 October 2022, Moldova's Interior Ministry said that debris from a Russian missile landed in the northern village of ] after a Russian fusillade was intercepted by air defenses in neighboring Ukraine. The Ministry reported no people were hurt but the windows of several residential homes were shattered. The Russian strike was targeting a Ukrainian dam on the ] that runs through Moldova and Ukraine.<ref>{{cite news |date=October 31, 2022 |access-date=October 31, 2022 |title=Debris of Russian missile downed by Ukraine lands in Moldovan village |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/russian-missile-downed-by-ukraine-lands-moldovan-village-interior-ministry-2022-10-31/|work=reuters.com}}</ref> On 5 December, another missile fell near the city of ] as Russia launched another wave of missile strikes against Ukraine.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://unimedia.info/ro/news/3939e5b5b18ac88a/mai-cu-noi-detalii-despre-despre-racheta-cazuta-la-briceni-la-moment-nu-exista-niciun-risc-pentru-cetateni.html|title=MAI, cu noi detalii despre despre racheta căzută la Briceni: "La moment nu există niciun risc pentru cetățeni"|publisher=]|date=5 December 2022|language=ro}}</ref> Yet another missile fell into ] on 14 January 2023 as a result of another wave of missile strikes against Ukraine.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Tanas |first1=Alexander |last2=Holmes |first2=David |last3=Popeski |first3=Ron |last4=Oatis |first4=Jonathan |title=Moldova says missile debris found in north of the country |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldova-says-missile-debris-found-north-country-2023-01-14/ |website=reuters.com |date=14 January 2023 |agency=Reuters |access-date=15 January 2023}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Rocket debris found again in Moldova, from war next door |url=https://apnews.com/article/russia-ukraine-8d35f4ea80376c6e9828e79c7f195e22 |website=apnews.com |date=14 January 2023 |publisher=Associated Press |access-date=15 January 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ==Government== | |||
| {{main|Government of Moldova}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Moldova is a ] ] ] democratic ]. The 1994 Constitution of Moldova sets the framework for the government of the country. A parliamentary majority of at least two-thirds is required to amend the ], which cannot be revised in times of war or national emergency. Amendments to the Constitution affecting the state's sovereignty, independence, or unity can only be made after a majority of voters support the proposal in a referendum. Furthermore, no revision can be made to limit the fundamental rights of people enumerated in the Constitution.<ref name="const">{{cite web |url=http://www.e-democracy.md/en/legislation/constitution/ |title=The Constitution of the Republic of Moldova, 2000 |publisher=E-democracy.md |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> The country's central legislative body is the ] ] (''{{lang|ro|Parlament}}''), which has 101 seats, and whose members are elected by popular vote on ] every four years. | |||
| The head of state is the President of Moldova, who between 2001 and 2015 was elected by the Moldovan Parliament, requiring the support of three-fifths of the deputies (at least 61 votes). This system was designed to decrease executive authority in favour of the legislature. Nevertheless, the ] ruled on 4 March 2016, that this constitutional change adopted in 2000 regarding the presidential election was unconstitutional,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://jurnal.md/ro/justitie/2016/3/4/decis-seful-statului-va-fi-ales-de-popor-modificarea-din-2000-a-constitutiei-privind-alegerea-presedintelui-de-parlament-neconstitutionala/ |title=DECIS: Şeful statului va fi ales de popor; Modificarea din 2000 a Constituţiei privind alegerea preşedintelui de Parlament, NECONSTITUŢIONALĂ |newspaper=] |date=4 March 2016 |language=ro |trans-title=DECIDED: The president will be elected by the people; The 2000 amendment of the Constitution concerning the election of the President by Parliament unconstitutional }}</ref> thus reverting the election method of the president to a ] ]. The president appoints a ] who functions as the ], and who in turn assembles a ], both subject to parliamentary approval. | |||
| The 1994 constitution also establishes an ] ], composed of six judges (two appointed by the President, two by Parliament, and two by the Supreme Council of ]), serving six-year terms, during which they are irremovable and not subordinate to any power. The court is invested with the power of ] over all acts of parliament, over presidential decrees, and over international treaties signed by the country.<ref name="const"/> | |||
| ===Internal affairs=== | |||
| ], Chișinău]] | |||
| On 19 December 2016, Moldovan MPs approved raising the retirement age to 63 years<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cnbc.com/2016/12/19/europes-poorest-nation-passes-imf-backed-retirement-age-increase.html|title=Europe's poorest nation passes IMF-backed retirement age increase|last=CNBC|date=19 December 2016|website=Cnbc.com|access-date=3 August 2017}}</ref> from the current level of 57 for women and 62 for men, a reform that is part of a 3-year-old assistance program agreed with the ]. The retirement age will be lifted gradually by a few months every year until it is fully in effect in 2028. | |||
| Life expectancy in the ex-Soviet country is 67.5 years for men and 75.5 years for women, both among the poorest in Europe. In a country with a population of 3.5 million, of which 1 million are abroad, there are more than 700,000 pensioners. | |||
| ===Foreign relations=== | |||
| {{main|Foreign relations of Moldova|Moldova–European Union relations}}After achieving independence from the Soviet Union, Moldova's foreign policy was designed with a view to establishing relations with other European countries, neutrality, and European Union integration. In 1995 the country was admitted to the ]. | |||
| In addition to its participation in ]'s ] programme, Moldova is also a member state of the ], the ] (OSCE), the ], the ], the ], the ], the ] and the ].].|left]] | |||
| In 2005, Moldova and the European Union established an action plan that sought to improve cooperation between Moldova and the union. At the end of 2005, the ] (EUBAM) was established at the joint request of the presidents of Moldova and Ukraine. EUBAM assists the Moldovan and Ukrainian governments in approximating their border and customs procedures to EU standards and offers support in both countries' fight against cross-border crime. | |||
| After the 1990–1992 ], Moldova sought a peaceful resolution to the conflict in the Transnistria region by working with Romania, Ukraine, and Russia, calling for international mediation, and co-operating with the OSCE and UN fact-finding and observer missions. The ], ], repeatedly stated that the Russian troops stationed in the breakaway region were there against the will of the Moldovan government and called on them to leave "completely and unconditionally".<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.easybourse.com/bourse-actualite/marches/moldova-calls-on-russian-troops-to-leave-transdniestr-574221|title=Moldova Calls on Russian Troops To Leave Transdniestr}}{{Dead link|date=March 2021 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> In 2012, a ] resulted in the death of a civilian, raising tensions with Russia.<ref>{{cite news |first=Ellen |last=Barry |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/01/04/world/europe/shooting-raises-tensions-between-moldova-and-russia.html |title=Shooting at Checkpoint Raises Tensions in a Disputed Region Claimed by Moldova |work=The New York Times |date=3 January 2012 |access-date=2 September 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ], President of Moldova ], President of Ukraine ] and ] ] during the 2021 ] International Conference. In 2014, the EU signed ] with the three states.]] | |||
| Formal accession talks began on 13 December 2023.<ref>{{cite web |title=EU greenlights accession talks with Ukraine but Orbán vetoes €50-billion aid package |url=https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2023/12/14/eu-greenlights-accession-talks-with-ukraine-and-moldova |access-date=14 December 2023 |website=] |date=14 December 2023 |language=en |archive-date=14 December 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231214175059/https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2023/12/14/eu-greenlights-accession-talks-with-ukraine-and-moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> A referendum on joining the EU is planned for autumn 2024, there will be no voting stations in Transnistria, however residents there will be free to travel into other areas of Moldova to vote, should they wish to.<ref>{{cite web |title=Moldova will hold referendum on EU membership without Transnistria: Sandu |url=https://www.1lurer.am/en/2023/12/29/Moldova-will-hold-referendum-on-EU-membership-without-Transnistria-Sandhu/1054506 |date=29 December 2023 |access-date=8 March 2024 |archive-date=4 January 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240104013438/https://www.1lurer.am/en/2023/12/29/Moldova-will-hold-referendum-on-EU-membership-without-Transnistria-Sandhu/1054506 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In September 2010, the ] approved a grant of €90 million to Moldova.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.europarl.europa.eu/sides/getDoc.do?language=en&type=IM-PRESS&reference=20100907IPR81460 |title=EU to grant €90 million to crisis-hit Moldova |publisher=Europarl.europa.eu |date=7 September 2010 |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> The money was to supplement US$570 million in International Monetary Fund loans,<ref>{{cite news |url=http://en.rian.ru/exsoviet/20100130/157721106.html |title=Moldova to get $570 million in IMF loans |publisher=RIA Novosti|date=30 January 2010 |access-date=25 November 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121019012333/http://en.rian.ru/exsoviet/20100130/157721106.html |archive-date=19 October 2012}}</ref> World Bank and other bilateral support already granted to Moldova. In April 2010, Romania offered Moldova development aid worth of €100 million while the number of scholarships for Moldovan students doubled to 5,000.<ref>{{cite web |author=Marian Chiriac |url=http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/romania-moldova-to-boost-relations |title=Romania, Moldova to Boost Relations |date=27 April 2010 |publisher=Balkaninsight.com |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> According to a lending agreement signed in February 2010, Poland provided US$15 million as a component of its support for Moldova in its European integration efforts.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.azi.md/en/story/9504 |title=Poland will support Moldova in its European integration efforts |publisher=Moldova Azi |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=27 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130827015717/http://www.azi.md/en/story/9504 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The first joint meeting of the Governments of Romania and Moldova, held in March 2012, concluded with several bilateral agreements in various fields.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.agerpres.ro/news-of-the-day/2012/03/04/first-meeting-of-romania-and-rep-of-moldova-governments-concluded-with-initialling-of-several-bilateral-agreements-13-27-18 |title=First meeting of Romania and Rep. of Moldova Governments, concluded with initialling of several bilateral agreements |publisher=agerpres.ro |date=4 March 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407072652/http://www.agerpres.ro/news-of-the-day/2012/03/04/first-meeting-of-romania-and-rep-of-moldova-governments-concluded-with-initialling-of-several-bilateral-agreements-13-27-18 |archive-date=7 April 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gov.ro/joint-meeting-of-the-government-of-romania-and-government-of-the-republic-of-moldova__l2a116286.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130208113857/http://www.gov.ro/joint-meeting-of-the-government-of-romania-and-government-of-the-republic-of-moldova__l2a116286.html |archive-date=8 February 2013 |title=Joint meeting of the Government of Romania and Government of the Republic of Moldova |language=ro |publisher=Guvernul Romaniei |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> The European orientation "has been the policy of Moldova in recent years and this is the policy that must continue," ] told lawmakers before ].<ref>], </ref>{{full citation needed|date=December 2022}} | |||
| In Moldova's referendum on joining the EU, a narrow 50.17% voted "yes," with Maia Sandu alleging "unprecedented" outside interference. Sandu received 42% in the simultaneous presidential election, while her rival, Alexandr Stoianoglo, garnered 26%, leading to a run-off on 3 November 2024. The referendum was seen as a test of Moldova's commitment to EU integration, amid claims of vote manipulation by criminal groups.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Balmforth |first1=Tom |last2=Tanas |first2=Alexander |title=Moldova's EU referendum in tight finish; Sandu decries vote meddling |date=21 October 2024 |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldovas-eu-referendum-goes-wire-after-sandu-decries-vote-meddling-2024-10-21/ |website=Reuters |access-date=21 October 2024}}</ref> | |||
| On 29 November 2013, at a summit in Vilnius, Moldova signed an ] with the European Union dedicated to the European Union's ']' with ex-Soviet countries.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://eeas.europa.eu/moldova/assoagreement/assoagreement-2013_en.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131207232619/http://www.eeas.europa.eu/moldova/assoagreement/assoagreement-2013_en.htm |archive-date=7 December 2013 |title=EU-Moldova Association Agreement |work=European Union External Action}}</ref> The ex-Romanian President ] stated that Romania will make all efforts for Moldova to join the EU as soon as possible. Likewise, Traian Băsescu declared that the ] is the next national project for Romania, as more than 75% of the population speaks Romanian.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.romanialibera.ro/politica/institutii/basescu--urmatorul-proiect-de-tara-al-romaniei--unirea-cu-basarabia-319094 |title=Băsescu: Următorul proiect de țară al României, unirea cu Basarabia |newspaper=România Liberă |date=27 November 2013 |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=4 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://www.romanialibera.ro/politica/institutii/basescu--urmatorul-proiect-de-tara-al-romaniei--unirea-cu-basarabia-319094 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Security=== | |||
| Moldova signed the Association Agreement with the European Union in Brussels on 27 June 2014. The signing came after the accord was drafted in Vilnius in November 2013.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://eeas.europa.eu/top_stories/2014/270614_association_agreement_en.htm|title=European Union – EEAS (European External Action Service) – EU forges closer ties with Ukraine, Georgia and Moldova|website=Eeas.europa.eu}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_SPEECH-14-511_en.htm|title=European Commission – PRESS RELEASES – Press release – Remarks by President Barroso at the signing of the Association Agreements with Georgia, the Republic of Moldova and Ukraine|website=Europa.eu}}</ref> | |||
| The European Union created a ] through its ] on 24 April 2023. The mission seeks to support the government of Moldova in countering hybrid threats the country faces as a result of the ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://censor.net/en/news/3407322/eu_is_preparing_mission_to_moldova_to_make_it_more_resistant_to_hybrid_threats_borrell | title=EU is preparing mission to Moldova to make it more resistant to hybrid threats, – Borrell | date=22 March 2023 | access-date=8 March 2024 | archive-date=19 September 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230919235056/https://censor.net/en/news/3407322/eu_is_preparing_mission_to_moldova_to_make_it_more_resistant_to_hybrid_threats_borrell | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| A memorandum dated 29 March 2023 stated that the mission aims at "enhancing the resilience of Moldova's security sector in the area of crisis management as well as enhancing resilience to hybrid threats, including cybersecurity, and countering foreign information manipulation and interference".<ref>{{Cite web |last=Swaton |first=Chiara |date=8 June 2023 |title=Austria sends police officers, soldiers to EU Moldova mission |url=https://www.euractiv.com/section/politics/news/austria-sends-police-officers-soldiers-to-eu-moldova-mission/ |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-GB |archive-date=15 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230615060906/https://www.euractiv.com/section/politics/news/austria-sends-police-officers-soldiers-to-eu-moldova-mission/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The initial mandate of the mission is expected to be for two years and it will be made up of up to 40 police and customs officers and judicial officials.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Rettman |first=Andrew |date=31 March 2023 |title=EU sending anti-coup mission to Moldova in May |url=https://euobserver.com/world/156884 |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=4 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230604204657/https://euobserver.com/world/156884 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="thebriefing.eu">{{Cite web |url=https://www.thebriefing.eu/welt-eu-to-send-mission-to-moldova-to-consult-on-countrys-security/ |title=Welt: EU to Send Mission to Moldova to Consult on Country's Security – the Briefing |access-date=6 July 2023 |archive-date=5 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230405061021/https://www.thebriefing.eu/welt-eu-to-send-mission-to-moldova-to-consult-on-countrys-security/ |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=25 April 2023 |title=EU members look to support Moldova, send muntions to Ukraine to offset Russian expansionism |url=https://www.rfi.fr/en/international/20230425-eu-members-look-to-support-moldova-send-muntions-to-ukraine-to-offset-russian-expansionism |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=21 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230621175042/https://www.rfi.fr/en/international/20230425-eu-members-look-to-support-moldova-send-muntions-to-ukraine-to-offset-russian-expansionism |url-status=live }}</ref> ], ], ], Germany, ], Sweden, the ], ], ], and ] have all voiced support for the mission.<ref name="thebriefing.eu"/> | |||
| Religious leaders play a role in shaping foreign policy. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, the Russian Government has frequently used its connections with the ] to block and stymie the integration of former Soviet states like Moldova into the West.<ref>Andrew Higgins, "In Expanding Russian Influence, Faith Combines With Firepower," </ref> | |||
| On 2 February 2023 Moldova passed a law introducing criminal penalties for ], including prison terms. The law continues with penalties for financing and inciting separatism, plotting against Moldova, and collecting and stealing information that could harm the country's sovereignty, independence and integrity.<ref>{{cite web |last=Necșuțu |first=Mădălin |date=8 February 2023 |title=Moldova 'Separatism Law' Sparks Tensions With Breakaway Transnistria |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2023/02/08/moldova-separatism-law-sparks-tensions-with-breakaway-transnistria/ |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=30 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230730141431/https://balkaninsight.com/2023/02/08/moldova-separatism-law-sparks-tensions-with-breakaway-transnistria/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Moldova signed the membership application to join the EU on 3 March 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Tanas |first=Alexander |date=3 March 2022 |title=With war on its doorstep, Moldova applies for EU membership |website=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldovan-president-says-moldova-applies-eu-membership-2022-03-03/}}</ref> On 23 June 2022, Moldova was officially granted ] by EU leaders.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.euractiv.com/section/europe-s-east/news/eu-leaders-grant-candidate-status-to-ukraine-and-moldova/ |title=EU leaders grant candidate status to Ukraine and Moldova |last=Brzozowski |first=Alexandra |date=23 June 2022 |website=euractiv.com |publisher=] |access-date=24 June 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ===Military=== | ===Military=== | ||
| {{main|Military of Moldova}} | {{main|Military of Moldova}} | ||
| ] at the Joint Multinational Readiness |
] at the Joint Multinational Readiness Centre in ], Germany]] | ||
| The Moldovan armed forces consists of the ] and ]. | |||
| The Moldovan armed forces consists of the ] and ]. Moldova has accepted all relevant arms control obligations of the former Soviet Union. On 30 October 1992, Moldova ratified the ], which establishes comprehensive limits on key categories of conventional military equipment and provides for the destruction of weapons in excess of those limits. The country acceded to the provisions of the nuclear ] in October 1994 in ] It does not have nuclear, biological, chemical or radiological weapons. Moldova joined the ]'s ] on 16 March 1994. | |||
| Moldova maintains a standing army of just 6,500 soldiers, and spends just 0.4 percent of its GDP on defence, far behind its regional neighbours.<ref name="Necșuțu-2022" /> | |||
| Moldova accepted all relevant arms control obligations of the former Soviet Union. On 30 October 1992, Moldova ratified the ], which establishes comprehensive limits on key categories of conventional military equipment and provides for the destruction of weapons in excess of those limits. The country acceded to the provisions of the nuclear ] in October 1994 in Washington, D.C. It does not have nuclear, biological, chemical or radiological weapons. Moldova joined the ]'s ] on 16 March 1994. | |||
| Moldova is committed to a number of international and regional control of arms regulations such as the UN Firearms Protocol, Stability Pact Regional Implementation Plan, the UN Programme of Action (PoA) and the OSCE Documents on Stockpiles of Conventional Ammunition. | |||
| Moldova is committed to a number of international and regional control of arms regulations such as the ], ], the UN Programme of Action (PoA), and the ] Documents on Stockpiles of Conventional Ammunition.<ref>{{Cite web |date=19 November 2003 |title=OSCE Document on Stockpiles of Conventional Ammunition |url=https://www.osce.org/fsc/15792 |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162506/https://www.osce.org/fsc/15792 |url-status=live }}</ref> Since declaring independence in 1991, Moldova has participated in UN peacekeeping missions in ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Ministry of Defense of Republic of Moldova |url=https://www.army.md/?lng=3&action=show&cat=163 |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=www.army.md |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162330/https://www.army.md/?lng=3&action=show&cat=163 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=UNMIL |url=https://peacekeeping.un.org/en/mission/unmil |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=United Nations Peacekeeping |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162104/https://peacekeeping.un.org/en/mission/unmil |url-status=live }}</ref> On 12 November 2014, the US donated to Moldovan Armed Forces 39 ] and 10 trailers, with a value of US$700,000, to the 22nd Peacekeeping Battalion of the Moldovan National Army to "increase the capability of Moldovan peacekeeping contingents."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://moldova.usembassy.gov/111214.html |title=2014 – Embassy of the United States Chișinău, Moldova|website=Moldova.usembassy.gov |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://moldova.usembassy.gov/111214.html |archive-date=4 September 2015 }}</ref> | |||
| Since declaring independence in 1991, Moldova has participated in UN peacekeeping missions in Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire, Sudan and Georgia. | |||
| Moldova signed a military agreement with Romania to strengthen regional security. The agreement is part of Moldova's strategy to reform its military and cooperate with its neighbours.<ref>{{cite web|title=Moldova's military agreements to help strengthen regional security|url=http://www.turkishweekly.net/2013/12/21/news/moldovas-military-agreements-to-help-strengthen-regional-security/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://www.turkishweekly.net/2013/12/21/news/moldovas-military-agreements-to-help-strengthen-regional-security/|url-status=dead|archive-date=4 September 2015|access-date=21 December 2013}}</ref> | Moldova signed a military agreement with Romania to strengthen regional security in 2015. The agreement is part of Moldova's strategy to reform its military and cooperate with its neighbours.<ref>{{cite web|title=Moldova's military agreements to help strengthen regional security|url=http://www.turkishweekly.net/2013/12/21/news/moldovas-military-agreements-to-help-strengthen-regional-security/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://www.turkishweekly.net/2013/12/21/news/moldovas-military-agreements-to-help-strengthen-regional-security/|url-status=dead|archive-date=4 September 2015|access-date=21 December 2013}}</ref> | ||
| Since 2022, the army has begun a process of modernization, and has been provided with more than €87 million in support for the modernization of the defence sector and the strengthening of security through the ].<ref name="Necșuțu-2022">{{Cite web |last=Necșuțu |first=Mădălin |date=13 July 2022 |title=Moldova Weighs Mobility and Firepower in Military Overhaul |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2022/07/13/moldova-weighs-mobility-and-firepower-in-military-overhaul/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=19 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230919235054/https://balkaninsight.com/2022/07/13/moldova-weighs-mobility-and-firepower-in-military-overhaul/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=1 June 2023 |title=EU hands over first batch of modern equipment to Moldovan armed forces – EU NEIGHBOURS east |url=https://euneighbourseast.eu/news/latest-news/eu-hands-over-first-batch-of-modern-equipment-to-moldovan-armed-forces/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=euneighbourseast.eu |language=en-GB |archive-date=13 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230613215600/https://euneighbourseast.eu/news/latest-news/eu-hands-over-first-batch-of-modern-equipment-to-moldovan-armed-forces/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In October 2022, Defense Minister Anatolie Nosatii claimed that 90 percent of the country's military equipment is outdated and of Soviet origin, dating back to the 1960s and 1980s.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Defense Minister Says 90 Percent Of Moldova's Military Equipment Is Outdated |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-military-defense-outdated-underfunded/32095231.html |access-date=6 July 2023 |archive-date=31 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230531133442/https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-military-defense-outdated-underfunded/32095231.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In April 2023, Valeriu Mija, Secretary of State for Defence Policy and National Army Reform in the Defence Ministry, claimed that Moldova needed $275 million to modernize its armed forces, especially in light of ] and the presence of ].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Tanas |first=Alexander |date=13 April 2023 |title=Moldova needs $275 million to modernise armed forces, defence official says |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldova-needs-275-mln-modernise-armed-forces-defence-official-2023-04-13/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163741/https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldova-needs-275-mln-modernise-armed-forces-defence-official-2023-04-13/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In June 2023, Poland also sent a transport of military equipment worth €8 million (including ], laptops, ], and ultrasound equipment) to the ] to increase the country's internal security.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Poland sends military equipment to Moldovan police |url=https://www.thefirstnews.com/article/poland-sends-military-equipment-to-moldovan-police-38861 |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=www.thefirstnews.com |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162527/https://www.thefirstnews.com/article/poland-sends-military-equipment-to-moldovan-police-38861 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Poland hands over weapons and ammunition to the Moldovan police – Militarnyi |url=https://mil.in.ua/en/news/poland-hands-over-weapons-and-ammunition-to-the-moldovan-police/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=mil.in.ua |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162357/https://mil.in.ua/en/news/poland-hands-over-weapons-and-ammunition-to-the-moldovan-police/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Analysts at the Centre for European Policy Analysis have called for further western weapon donations.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Kirichenko |first=David |date=12 June 2023 |title=Moldova Needs Western Weapons |url=https://cepa.org/article/moldova-needs-western-weapons/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=Center for European Policy Analysis |language=en-US |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707161546/https://cepa.org/article/moldova-needs-western-weapons/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| On 12 November 2014, the US donated to Moldovan Armed Forces 39 ] and 10 trailers, with a value of US$700,000, to the 22nd Peacekeeping Battalion of the Moldovan National Army to "increase the capability of Moldovan peacekeeping contingents."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://moldova.usembassy.gov/111214.html |title=2014 – Embassy of the United States Chișinău, Moldova|website=Moldova.usembassy.gov |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150904002008/http://moldova.usembassy.gov/111214.html |archive-date=4 September 2015 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Human rights=== | ===Human rights=== | ||
| {{main|Human rights in Moldova}} | {{main|Human rights in Moldova}} | ||
| ] ranked Moldova as a "partly free" country with a score of 62/100 in 2023. They summarized their finds as follows: "Moldova has a competitive electoral environment, and ], ], and ] are mostly protected. Nonetheless, ], links between major political figures and powerful economic interests, and critical deficiencies in the justice sector and the rule of law all continue to hamper democratic governance."<ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldova: Freedom in the World 2023 Country Report |url=https://freedomhouse.org/country/moldova/freedom-world/2023 |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=27 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230727205636/https://freedomhouse.org/country/moldova/freedom-world/2023 |url-status=live }}</ref> According to ], Moldova's ] improved to 39 points in 2022 from 34 in 2020.<ref>{{Cite web |date=31 January 2023 |title=2022 Corruption Perceptions Index – Explore Moldova's results |url=https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2022 |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=16 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230416180715/https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2022 |url-status=live }}</ref> ] improved Moldova's ] ranking from 89th in 2020 to 40th in 2022, while cautioning that "Moldova's media are diverse but extremely polarised, like the country itself, which is marked by political instability and excessive influence by oligarchs."<ref>{{Cite web |date=13 April 2021 |title=Moldova {{!}} Free Press Unlimited |url=https://www.freepressunlimited.org/en/countries/moldova |access-date=5 July 2023 |website=Free Press Unlimited |language=en |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705135700/https://www.freepressunlimited.org/en/countries/moldova |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=23 July 2020 |title=Moldova {{!}} RSF |url=https://rsf.org/en/country/moldova |access-date=5 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705135655/https://rsf.org/en/country/moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| According to ], as of 2004 "Torture and other ill-treatment in police detention remained widespread; the state failed to carry out prompt and impartial investigations and police officers sometimes evaded penalties. Political dissidents from ] were released from arbitrary detention in the break-away Transdinester region only after an order of the ]."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://humanrightshouse.org/Articles/6039.html |title=Ilascu and Others vs. Moldova and Russia |publisher=Humanrightshouse.org |date=12 July 2004 |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=13 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180613032014/http://humanrightshouse.org/Articles/6039.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> In 2009, when Moldova experienced its most ] in a decade, several civilians, including ], were killed and many more injured.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.osac.gov/pages/ContentReportDetails.aspx?cid=10459 |title=Moldova 2011 Crime and Safety Report – Bureau of Diplomatic Security |publisher=Osac.gov |date=19 February 2011 |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> | |||
| According to ]'s 2022/23 report, "No visible progress was made in reducing instances of torture and other ill-treatment in detention. Impunity continued for past human rights violations by law enforcement agencies. New "temporary" restrictions on public assemblies were introduced. The rights of ] people were not fully realized, leading to cases of harassment, discrimination and violence. Some refugee reception centres turned away religious and ethnic minority refugees. In the breakaway Transdniestria region, prosecution and imprisonment for peaceful dissent continued."<ref>{{Cite web |title=Human rights in Moldova |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/location/europe-and-central-asia/moldova/report-moldova/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=Amnesty International |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707161740/https://www.amnesty.org/en/location/europe-and-central-asia/moldova/report-moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> On 18 June 2023, some 500 LGBT activists and supporters held a ] in the capital city of Chișinău which for the first time needed no heavy police cordons to protect them from protesters largely linked to the Orthodox church.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Tanas |first=Alexander |date=18 June 2023 |title=LGBT activists in Moldova hold march without police protection |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/lgbt-activists-moldova-hold-march-without-police-protection-2023-06-18/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802101756/https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/lgbt-activists-moldova-hold-march-without-police-protection-2023-06-18/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| According to ] of the ], released in April 2011, "In contrast to the previous year, there were no reports of killings by security forces. During the year reports of government exercising undue influence over the media substantially decreased." But "Transnistrian authorities continued to harass independent media and opposition lawmakers; restrict freedom of association, movement, and religion; and discriminate against Romanian speakers."<ref>{{cite web|url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2010/eur/154439.htm |title=2010 Human Rights Report: Moldova |publisher=United States Department of State |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> Moldova "has made noteworthy progress on religious freedom since the era of the Soviet Union, but it can still take further steps to foster diversity," said the ] ], in Chișinău, in September 2011.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=39500 |title=Moldova: UN human rights expert calls for more fostering of religious diversity |publisher=Un.org |date=9 September 2011 |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> Moldova improved its legislation by enacting the ''Law on Preventing and Combating Family Violence'', in 2008.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://sgdatabase.unwomen.org/uploads/Law%20on%20Preventing%20and%20Combating%20Family%20Violence%202007.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131029195628/http://sgdatabase.unwomen.org/uploads/Law%20on%20Preventing%20and%20Combating%20Family%20Violence%202007.pdf|archive-date=29 October 2013 |title=Law on Preventing and Combating Family Violence |publisher=UN Women |access-date=4 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| According to ] of the ], released in 2022, "While authorities investigated reports of human rights abuses and corruption committed by officials, the process was slow and burdensome. During the year, authorities indicted and detained several former high-level officials including former President Igor Dodon, former member of parliament Vladimir Andronachi, Shor Party member of parliament Marina Tauber and former director of Moldovan Railways Anatolie Topala. None of these cases resulted in conviction by a court at year's end. Authorities took some steps to identify, investigate, and prosecute officials for human rights abuses, but progress was slow."<ref name="United States Department of State">{{cite web |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2010/eur/154439.htm |title=2010 Human Rights Report: Moldova |publisher=United States Department of State |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=13 October 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191013183110/https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/2010/eur/154439.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In a meeting with the ] in October 2022, EU representatives "welcomed positive developments in Moldova such as the ratification of the ] on preventing and combating violence against women, the adoption of legislation on ], and the ongoing work to reform the Electoral Code. It encouraged Moldovan authorities to address shortcomings identified by OSCE/ODIHR and the ] across all areas and ensure effective and continuous implementation of human rights legislation."<ref>{{Cite web |date=20 October 2022 |title=Moldova: 13th EU-Moldova Human Rights Dialogue in Brussels {{!}} EEAS |url=https://www.eeas.europa.eu/eeas/moldova-13th-eu-moldova-human-rights-dialogue-brussels_en |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=Diplomatic Service of the European Union |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802101757/https://www.eeas.europa.eu/eeas/moldova-13th-eu-moldova-human-rights-dialogue-brussels_en |url-status=live }}</ref> The ]' 2016 recommendations on hate crimes were "largely reflected in amendments to the Criminal Code adopted by the Moldovan Parliament and published on 3 June 2022", but the report notes that Moldovan law enforcement officers often fail to record the bias motivations behind hate crimes, and additionally recommended "developing its victim support system to ensure effective access to justice, assistance, and protection services for hate crime victims".<ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldova {{!}} HCRW |url=https://hatecrime.osce.org/moldova |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=hatecrime.] |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802014001/https://hatecrime.osce.org/moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2021, 8 hate crimes were recorded, 7 of which reached a successful conviction, with one going to prosecution but without a conviction. | |||
| ===Administrative divisions=== | ===Administrative divisions=== | ||
| Line 372: | Line 254: | ||
| {{Map of administrative divisions of Moldova}} | {{Map of administrative divisions of Moldova}} | ||
| Moldova is divided into 32 districts (''raioane'', singular '']''), three municipalities and two ] (] and the ]).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://descentralizare.gov.md/regionmap.php?l=ro&idc=310|title=Autorități publice locale|publisher=Government of Moldova|access-date=12 October 2010}}</ref> The final status of Transnistria is ], as the central government does not control that territory. 10 other cities, including ] and ], the administrative seats of the two autonomous territories, also have ]. | Moldova is divided into 32 districts (''raioane'', singular '']''), three municipalities and two ] (] and the ]).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://descentralizare.gov.md/regionmap.php?l=ro&idc=310|title=Autorități publice locale|publisher=Government of Moldova|access-date=12 October 2010|archive-date=28 August 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100828065811/http://www.descentralizare.gov.md/regionmap.php?l=ro&idc=310|url-status=live}}</ref> The final status of Transnistria is ], as the central government does not control that territory. 10 other cities, including ] and ], the administrative seats of the two autonomous territories, also have ]. | ||
| Moldova has 66 cities (towns), including 13 with municipality status, and 916 communes. Another 700 villages are too small to have a separate administration and are administratively part of either cities (41 of them) or communes (659). This makes for a total of 1,682 localities in Moldova, two of which are uninhabited.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.statistica.md/public/files/Clasificatoare/CUATM_rom.zip|title=Clasificatorul unităţilor administrativ-teritoriale (CUATM)}}</ref> | Moldova has 66 cities (towns), including 13 with municipality status, and 916 communes. Another 700 villages are too small to have a separate administration and are administratively part of either cities (41 of them) or communes (659). This makes for a total of 1,682 localities in Moldova, two of which are uninhabited.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.statistica.md/public/files/Clasificatoare/CUATM_rom.zip|title=Clasificatorul unităţilor administrativ-teritoriale (CUATM)|access-date=20 May 2017|archive-date=8 May 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190508230025/http://www.statistica.md/public/files/Clasificatoare/CUATM_rom.zip|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| The largest city in Moldova is Chișinău with a population of approx. 695,400 people. The second largest city is Tiraspol at 129,500, part of the ] of ], followed by Bălți (146,900) and Bender (91,000). | |||
| {{Largest cities of Moldova}} | {{Largest cities of Moldova}} | ||
| The largest city in Moldova is Chișinău with a population of 635,994 people. | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| === Law enforcement and emergency services === | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| {{See also|Crime in Moldova|Healthcare in Moldova}}The Moldovan police force (]) reports to the ] (MAI) and is the primary law enforcement body, responsible for internal security, public order, traffic, and criminal investigations. Several agencies responsible for border management, emergency situations, migration and asylum also report to the ministry. Civilian authorities maintained effective control over the security forces.<ref name="United States Department of State" /> The Moldovan Police are divided into state and municipal organisations. State police provide law enforcement throughout Moldova while municipal police operate at the local ] level. National and municipal police forces often collaborate closely for law enforcement purposes. The ] is a specialized combat-ready police force primarily responsible for tackling organized crime, serious violent crime, and hostage situations. They are subordinate to the General Police Inspectorate and therefore under strict civilian control.<ref name="United States Department of State" /> | |||
| {{main|Geography of Moldova}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] near Vadul lui Vodă]] | |||
| There are also a number of more specialised police institutions including the Police Department of Chisinau Municipality and the General Directorate of Criminal Investigation. The ] are responsible for border security. It was a military branch until 2012 when it was put under the control of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. According to ''The Law on Police Use of Force Worldwide,'' "Moldova does not regulate and restrict the use of firearms by law enforcement officials as international law requires. Police use of a firearm can only be lawful where necessary to confront an imminent threat of death or serious injury or a grave and proximate threat to life."<ref>{{Cite web |date=10 May 2021 |title=Law on police use of force in Moldova |url=https://www.policinglaw.info/country/moldova |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=The Law on Police Use of Force |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802142316/https://www.policinglaw.info/country/moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Moldova lies between latitudes ] and ], and mostly between meridians ] and ] (a small area lies east of 30°). The total land area is {{convert|33851|km2|abbr=on}} | |||
| The ] (SIS) is a Moldovan state body specialized in ensuring ] by exercising all appropriate ] and ] measures, such as: collecting, processing, checking and capitalizing the information needed to identify, prevent and counteract any actions that according to law represent an internal or external threat to independence, sovereignty, unity, territorial integrity, constitutional order, democratic development, internal security of the state, society and citizens, the statehood of the Republic of Moldova, the stable functioning of vitally important branches of the national economy, both on the territory of the Republic of Moldova and abroad. | |||
| The largest part of the country (around 88% of the area) lies in ] region, between ] and ] rivers, while a narrow strip in the east is located in ] (east of the Dniester). The western border of Moldova is formed by the Prut river, which joins the ] before flowing into the ]. Moldova has access to the Danube for only about {{convert|480|m|ft|0|abbr=on}}, and ] is the only Moldovan port on the Danube. In the east, the Dniester is the main river, flowing through the country from north to south, receiving the waters of ], ], ], ]. ] flows into one of the Danube ], while ] into the Black Sea chain of limans. | |||
| Emergency services in Moldova consist of ], ] units, and a state ]. There are two hospitals in the capital city Chișinău, the primary being Medpark International Hospital, and general hospitals in ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Medical Assistance |url=https://md.usembassy.gov/u-s-citizen-services/doctors/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=U.S. Embassy in Moldova |language=en-US |archive-date=31 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230531171054/https://md.usembassy.gov/u-s-citizen-services/doctors/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=24 January 2023 |title=List of medical facilities in Moldova |url=https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/moldova-list-of-medical-facilities-and-practitioners/list-of-medical-facilities-in-moldova |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802142315/https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/moldova-list-of-medical-facilities-and-practitioners/list-of-medical-facilities-in-moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> Moldova has a universal healthcare system through a ] scheme. Casa Mariorei, founded in 2002, is a ] in Chișinău which provides shelter, healthcare, legal advice, and psychosocial support for native Moldovan, immigrant, and refugee women.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Burks |first=Roger |date=2 August 2022 |title=Moldovan GBV shelter offers safety and a community for refugees from Ukraine |work=] |url=https://www.unhcr.org/uk/news/stories/moldovan-gbv-shelter-offers-safety-and-community-refugees-ukraine |access-date=2 August 2023 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802142308/https://www.unhcr.org/uk/news/stories/moldovan-gbv-shelter-offers-safety-and-community-refugees-ukraine |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The country is landlocked, though it is close to the Black Sea; at its closest point it is separated from the ], an estuary of the Black Sea, by only 3 km of Ukrainian territory. While most of the country is hilly, elevations never exceed {{convert|430|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} – the highest point being the ]. Moldova's hills are part of the Moldavian Plateau, which geologically originate from the ]. Its subdivisions in Moldova include the Dniester Hills (Northern Moldavian Hills and ]), the Moldavian Plain (Middle Prut Valley and ]), and the Central Moldavian Plateau (], ]—] Massive, "Codri" meaning "forests"—], ], and ]). In the south, the country has a small flatland, the ]. The territory of Moldova east of the river Dniester is split between parts of the ], and parts of the ]. | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| {{main|Geography of Moldova}} | |||
| ] (''Dniester'')]] | |||
| Moldova is a landlocked country situated in Eastern Europe, on the northeastern corner of the ] in the ], between latitudes ] and ], and mostly between meridians ] and ] (a small area lies east of 30°). The country lies to the east of the ] and is bordered by ] to its west and by ] to its north, east, and south. The total length of the national boundaries is 1,389 km, including 939 km with Ukraine and 450 km with Romania. The country is separated from Romania on the west by the ] river and on the east from Ukraine by the ] river. The total land area is {{convert|33,843.5|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}}, of which {{convert|960|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} is water. The largest part of the country (around 88% of the area) lies in the ] region, while a narrow strip in the east is located in the ] of ] on the eastern bank of the Dniester. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Although the country is technically landlocked, in 1999 Moldova acquired from Ukraine (in exchange for ceding a stretch of contested road in the east of the country) a 0.45 kilometer river frontage to the Danube, on the confluence of the ] and Prut rivers. This has transformed the old village of ] (in the extreme south-west of the country) into a ], providing Moldova access to ] via the Danube and the ].<ref>NY Times report </ref> The Dniester river, which rises in Ukraine near the city of ], passes through Moldova, separating the main territory from its unrecognised breakaway region Transnistria, and empties into the Black Sea in Ukraine. At its closest point, Moldova is separated from the ], an estuary of the Black Sea, by only 3 km of Ukrainian territory. | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| ] | |||
| While most of the country is hilly, elevations never exceed {{convert|430|m|ft|abbr=on}}, the highest point being the ]. Moldova's hills are part of the ], which geologically originate from the Carpathian Mountains. Its subdivisions in Moldova include the Dniester Hills (Northern Moldavian Hills and Dniester Ridge), the Moldavian Plain (Middle Prut Valley and ]), and the Central Moldavian Plateau (Ciuluc-Soloneț Hills, Cornești Hills—] Massive, "Codri" meaning "forests"—Lower Dniester Hills, Lower Prut Valley, and Tigheci Hills). In the south, the country has a small flatland, the ]. The territory of Moldova east of the river Dniester is split between parts of the ], and parts of the ]. Moldova's exceptionally rich ] soil covers around three-quarters of the country's land area.<ref>{{Cite web |date=26 August 2016 |title=Geography – Republic of Moldova |url=https://moldova.md/en/content/geography |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=28 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230828051957/https://moldova.md/en/content/geography |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Moldova's capital and largest city is ], with approximately a third of the country's population residing in its metro area. Chișinău is Moldova's main industrial and commercial centre, and is located in the middle of the country, on the river ], a tributary of the ]. Moldova's second-largest city is ], which lies on the eastern bank of the Dniester and is the capital of the ] of ]. The country's third-largest city is ], often referred to as the 'northern capital'. It is situated {{convert|127|km|mi|abbr=off}} north of the capital Chișinău, and is located on the river ], a tributary of the Dniester, on a hilly landscape in the Bălți steppe. ] is the administrative centre of the ] of ]. | |||
| ===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
| ], part of the ] in the country]] | ], part of the ] in the country]] | ||
| Moldova has a climate which is moderately continental; its proximity to the ] leads to the climate being mildly cold in the autumn and winter and relatively cool in the spring and summer.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/climate/Moldova.htm |title=Moldova's Climate |publisher=Weatheronline.co.uk |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=14 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131014031249/http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/climate/Moldova.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| Moldova has a climate which is moderately continental; its proximity to the ] leads to the climate being mildly cold in the autumn and winter and relatively cool in the spring and summer.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.weatheronline.co.uk/reports/climate/Moldova.htm |title=Moldova's Climate |publisher=Weatheronline.co.uk |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> | |||
| The summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging about {{convert|20|°C|0|abbr=on}} and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging {{convert|-4|°C|0|abbr=on}}. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around {{convert|600|mm|0|abbr=on}} in the north to {{convert|400|mm|0|abbr=on}} in the south, can vary greatly; long dry spells are not unusual. The heaviest rainfall occurs in early summer and again in October; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common. Because of the irregular terrain, heavy summer rains often cause erosion and river silting. | The summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging about {{convert|20|°C|0|abbr=on}} and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging {{convert|-4|°C|0|abbr=on}}. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around {{convert|600|mm|0|abbr=on}} in the north to {{convert|400|mm|0|abbr=on}} in the south, can vary greatly; long dry spells are not unusual. The heaviest rainfall occurs in early summer and again in October; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common. Because of the irregular terrain, heavy summer rains often cause erosion and river silting. | ||
| The highest temperature ever recorded in Moldova was {{convert|41.5|°C|1|abbr=on}} on 21 July 2007 in ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Stînga Nistrului |url=http://www.weather-forecast.com/locations/Camenca |title=Camenca temperature |publisher=Weather-forecast.com |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> The lowest temperature ever recorded was {{convert|-35.5|°C|1|abbr=on}} on 20 January 1963 in Brătușeni, Edineț county.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.worldweatheronline.com/Bratuseni-weather/Gagauzia/MD.aspx |title=Bratuseni temperature |publisher=Worldweatheronline.com |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131020211429/http://www.worldweatheronline.com/Bratuseni-weather/Gagauzia/MD.aspx |archive-date=20 October 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | The highest temperature ever recorded in Moldova was {{convert|41.5|°C|1|abbr=on}} on 21 July 2007 in ].<ref>{{cite web |author=Stînga Nistrului |url=http://www.weather-forecast.com/locations/Camenca |title=Camenca temperature |publisher=Weather-forecast.com |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=5 June 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140605051834/http://www.weather-forecast.com/locations/Camenca |url-status=live }}</ref> The lowest temperature ever recorded was {{convert|-35.5|°C|1|abbr=on}} on 20 January 1963 in Brătușeni, Edineț county.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.worldweatheronline.com/Bratuseni-weather/Gagauzia/MD.aspx |title=Bratuseni temperature |publisher=Worldweatheronline.com |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131020211429/http://www.worldweatheronline.com/Bratuseni-weather/Gagauzia/MD.aspx |archive-date=20 October 2013 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin:auto;" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin:auto;" | ||
| |+Average daily maximum and minimum temperatures for the three largest cities in Moldova<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.weatherbase.com/weather/city.php3?c=MD&name=Moldova|title=Moldova climate information|publisher=Weatherbase|access-date=3 February 2016}}</ref> | |+Average daily maximum and minimum temperatures for the three largest cities in Moldova<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.weatherbase.com/weather/city.php3?c=MD&name=Moldova|title=Moldova climate information|publisher=Weatherbase|access-date=3 February 2016|archive-date=2 January 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102231617/http://www.weatherbase.com/weather/city.php3?c=MD&name=Moldova|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| !Location | !Location | ||
| Line 420: | Line 309: | ||
| ===Biodiversity=== | ===Biodiversity=== | ||
| {{see also|Protected areas in Moldova}} | {{see also|Protected areas in Moldova}} | ||
| ], Moldova is split between the ] and the ] of the ] within the ]. It is home to three terrestrial ecoregions: ], ], and ].<ref name="DinersteinOlson2017">{{cite journal |last1=Dinerstein |first1=Eric |last2=Olson |first2=David |last3=Joshi |first3=Anup |last4=Vynne |first4=Carly |last5=Burgess |first5=Neil D. |last6=Wikramanayake |first6=Eric |last7=Hahn |first7=Nathan |last8=Palminteri |first8=Suzanne |last9=Hedao |first9=Prashant |last10=Noss |first10=Reed |last11=Hansen |first11=Matt |last12=Locke |first12=Harvey |last13=Ellis |first13=Erle C. |last14=Jones |first14=Benjamin |last15=Barber |first15=Charles Victor |last16=Hayes |first16=Randy |last17=Kormos |first17=Cyril |last18=Martin |first18=Vance |last19=Crist |first19=Eileen |last20=Sechrest |first20=Wes |last21=Price |first21=Lori |last22=Baillie |first22=Jonathan E.M. |last23=Weeden |first23=Don |last24=Suckling |first24=Kierán |last25=Davis |first25=Crystal |last26=Sizer |first26=Nigel |last27=Moore |first27=Rebecca |last28=Thau |first28=Davi |last29=Birch |first29=Tanya |last30=Potapov |first30=Peter |last31=Turubanova |first31=Svetlana |last32=Tyukavina |first32=Alexandra |last33=de Souza |first33=Nadia |last34=Pintea |first34=Lilian |last35=Brito |first35=José C. |last36=Llewellyn |first36=Othman A. |last37=Miller |first37=Anthony G. |last38=Patzelt |first38=Annette |last39=Ghazanfar |first39=Shahina A. |last40=Timberlake |first40=Jonathan|last41=Klöser |first41=Heinz |last42=Shennan-Farpón |first42=Yara |last43=Kindt |first43=Roeland |last44=Lillesø |first44=Jens-Peter Barnekow |last45=van Breugel |first45=Paulo |last46=Graudal |first46=Lars |last47=Voge |first47=Maianna |last48=Al-Shammari |first48=Khalaf F. |last49=Saleem |first49=Muhammad |display-authors=6 |year=2017 |title=An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm |journal=BioScience |volume=67 |issue=6 |pages=534–545 |issn=0006-3568 |doi=10.1093/biosci/bix014 |doi-access=free |pmid=28608869 |pmc=5451287 |s2cid=13136188}}</ref> Forests currently cover only 11% of Moldova, though the state is making efforts to increase their range. It had a 2019 ] mean score of 2.2/10, ranking it 158th globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal |last1=Grantham |first1=H.S. |last2=Duncan|first2=A. |last3=Evans |first3=T.D. |last4=Jones |first4=K.R. |last5=Beyer |first5=H.L. |last6=Schuster |first6=R. |last7=Walston |first7=J. |last8=Ray|first8=J.C. |last9=Robinson |first9=J.G. |last10=Callow |first10=M. |last11=Clements |first11=T. |last12=Costa |first12=H.M. |last13=DeGemmis |first13=A. |last14=Elsen |first14=P.R. |last15=Ervin |first15=J. |last16=Franco|first16=P. |last17=Goldman|first17=E. |last18=Goetz |first18=S. |last19=Hansen |first19=A. |last20=Hofsvang |first20=E. |last21=Jantz |first21=P. |last22=Jupiter |first22=S. |last23=Kang |first23=A. |last24=Langhammer |first24=P. |last25=Laurance |first25=W.F. |last26=Lieberman |first26=S. |last27=Linkie |first27=M. |last28=Malhi |first28=Y. |last29=Maxwell |first29=S. |last30=Mendez |first30=M. |last31=Mittermeier |first31=R. |last32=Murray |first32=N.J. |last33=Possingham |first33=H. |last34=Radachowsky |first34=J. |last35=Saatchi |first35=S. |last36=Samper |first36=C.|last37=Silverman |first37=J. |last38=Shapiro |first38=A. |last39=Strassburg |first39=B. |last40=Stevens |first40=T. |last41=Stokes |first41=E. |last42=Taylor |first42=R. |last43=Tear |first43=T. |last44=Tizard |first44=R. |last45=Venter |first45=O. |last46=Visconti |first46=P. |last47=Wang |first47=S. |last48=Watson |first48=J.E.M. |display-authors=6 |year=2020 |title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity |type=Supplementary material |journal=Nature Communications |volume=11 |issue=1 |page=5978 |issn=2041-1723 |doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3 |doi-access=free |pmid=33293507 |pmc=7723057 |bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G |s2cid=228082162}}</ref> Game animals, such as ], ] and ] can be found in these wooded areas.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova">{{cite web |title=Environmental issues in Moldova |url=https://naturvernforbundet.no/international/environmental-issues-in-moldova/category940.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150409044105/http://naturvernforbundet.no/international/environmental-issues-in-moldova/category940.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=9 April 2015 |website=Naturvernforbundet |date=7 October 2009 |access-date=30 May 2020 }}</ref>], ]'s novel '']'' opens with a description of ] as a way to highlight the story's exotic setting.<ref>{{cite book |last=Sienkiewicz |first=Henryk |trans-title=With Fire and Sword |title=Ogniem i Mieczem |volume=1 |url=https://wolnelektury.pl/katalog/lektura/ogniem-i-mieczem-tom-pierwszy.html |access-date=7 May 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=O suhaku, który z suchych stepów przybył |trans-title=On the Suhaku of the arid steppes |date=6 October 2017 |website=Menażeria Etymologiczna |language=pl |via=wordpress.com |url=https://etymologicznamenazeria.wordpress.com/2017/10/06/o-suhaku-ktory-z-suchych-stepow-przybyl/ |access-date=7 May 2020}}</ref> Saigas are a ] ] that is now extinct in Moldova.]] | ], Moldova is split between the ] and the ] of the ] within the ]. It is home to three terrestrial ecoregions: ], ], and ].<ref name="DinersteinOlson2017">{{cite journal |last1=Dinerstein |first1=Eric |last2=Olson |first2=David |last3=Joshi |first3=Anup |last4=Vynne |first4=Carly |last5=Burgess |first5=Neil D. |last6=Wikramanayake |first6=Eric |last7=Hahn |first7=Nathan |last8=Palminteri |first8=Suzanne |last9=Hedao |first9=Prashant |last10=Noss |first10=Reed |last11=Hansen |first11=Matt |last12=Locke |first12=Harvey |last13=Ellis |first13=Erle C. |last14=Jones |first14=Benjamin |last15=Barber |first15=Charles Victor |last16=Hayes |first16=Randy |last17=Kormos |first17=Cyril |last18=Martin |first18=Vance |last19=Crist |first19=Eileen |last20=Sechrest |first20=Wes |last21=Price |first21=Lori |last22=Baillie |first22=Jonathan E.M. |last23=Weeden |first23=Don |last24=Suckling |first24=Kierán |last25=Davis |first25=Crystal |last26=Sizer |first26=Nigel |last27=Moore |first27=Rebecca |last28=Thau |first28=Davi |last29=Birch |first29=Tanya |last30=Potapov |first30=Peter |last31=Turubanova |first31=Svetlana |last32=Tyukavina |first32=Alexandra |last33=de Souza |first33=Nadia |last34=Pintea |first34=Lilian |last35=Brito |first35=José C. |last36=Llewellyn |first36=Othman A. |last37=Miller |first37=Anthony G. |last38=Patzelt |first38=Annette |last39=Ghazanfar |first39=Shahina A. |last40=Timberlake |first40=Jonathan|last41=Klöser |first41=Heinz |last42=Shennan-Farpón |first42=Yara |last43=Kindt |first43=Roeland |last44=Lillesø |first44=Jens-Peter Barnekow |last45=van Breugel |first45=Paulo |last46=Graudal |first46=Lars |last47=Voge |first47=Maianna |last48=Al-Shammari |first48=Khalaf F. |last49=Saleem |first49=Muhammad |display-authors=6 |year=2017 |title=An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm |journal=BioScience |volume=67 |issue=6 |pages=534–545 |issn=0006-3568 |doi=10.1093/biosci/bix014 |doi-access=free |pmid=28608869 |pmc=5451287 |s2cid=13136188}}</ref> Forests currently cover only 11% of Moldova, though the state is making efforts to increase their range. It had a 2019 ] mean score of 2.2/10, ranking it 158th globally out of 172 countries.<ref name="FLII-Supplementary">{{cite journal |last1=Grantham |first1=H.S. |last2=Duncan|first2=A. |last3=Evans |first3=T.D. |last4=Jones |first4=K.R. |last5=Beyer |first5=H.L. |last6=Schuster |first6=R. |last7=Walston |first7=J. |last8=Ray|first8=J.C. |last9=Robinson |first9=J.G. |last10=Callow |first10=M. |last11=Clements |first11=T. |last12=Costa |first12=H.M. |last13=DeGemmis |first13=A. |last14=Elsen |first14=P.R. |last15=Ervin |first15=J. |last16=Franco|first16=P. |last17=Goldman|first17=E. |last18=Goetz |first18=S. |last19=Hansen |first19=A. |last20=Hofsvang |first20=E. |last21=Jantz |first21=P. |last22=Jupiter |first22=S. |last23=Kang |first23=A. |last24=Langhammer |first24=P. |last25=Laurance |first25=W.F. |last26=Lieberman |first26=S. |last27=Linkie |first27=M. |last28=Malhi |first28=Y. |last29=Maxwell |first29=S. |last30=Mendez |first30=M. |last31=Mittermeier |first31=R. |last32=Murray |first32=N.J. |last33=Possingham |first33=H. |last34=Radachowsky |first34=J. |last35=Saatchi |first35=S. |last36=Samper |first36=C.|last37=Silverman |first37=J. |last38=Shapiro |first38=A. |last39=Strassburg |first39=B. |last40=Stevens |first40=T. |last41=Stokes |first41=E. |last42=Taylor |first42=R. |last43=Tear |first43=T. |last44=Tizard |first44=R. |last45=Venter |first45=O. |last46=Visconti |first46=P. |last47=Wang |first47=S. |last48=Watson |first48=J.E.M. |display-authors=6 |year=2020 |title=Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity |type=Supplementary material |journal=Nature Communications |volume=11 |issue=1 |page=5978 |issn=2041-1723 |doi=10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3 |doi-access=free |pmid=33293507 |pmc=7723057 |bibcode=2020NatCo..11.5978G |s2cid=228082162}}</ref> Game animals, such as ], ] and ] can be found in these wooded areas.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova">{{cite web |title=Environmental issues in Moldova |url=https://naturvernforbundet.no/international/environmental-issues-in-moldova/category940.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150409044105/http://naturvernforbundet.no/international/environmental-issues-in-moldova/category940.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=9 April 2015 |website=Naturvernforbundet |date=7 October 2009 |access-date=30 May 2020 }}</ref>] (''Dniester''), ]'s novel '']'' opens with a description of ] as a way to highlight the story's exotic setting.<ref>{{cite book |last=Sienkiewicz |first=Henryk |trans-title=With Fire and Sword |title=Ogniem i Mieczem |volume=1 |url=https://wolnelektury.pl/katalog/lektura/ogniem-i-mieczem-tom-pierwszy.html |access-date=7 May 2020 |archive-date=4 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200604162834/https://wolnelektury.pl/katalog/lektura/ogniem-i-mieczem-tom-pierwszy.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=O suhaku, który z suchych stepów przybył |trans-title=On the Suhaku of the arid steppes |date=6 October 2017 |website=Menażeria Etymologiczna |language=pl |via=wordpress.com |url=https://etymologicznamenazeria.wordpress.com/2017/10/06/o-suhaku-ktory-z-suchych-stepow-przybyl/ |access-date=7 May 2020 |archive-date=4 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200604162835/https://etymologicznamenazeria.wordpress.com/2017/10/06/o-suhaku-ktory-z-suchych-stepow-przybyl/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Saigas are a ] ] that is now extinct in Moldova.]] | ||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin:auto;" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin:auto;" | ||
| ! colspan="4" |] | ! colspan="4" |] | ||
| Line 434: | Line 323: | ||
| |{{convert|5177|ha|km2|0}} | |{{convert|5177|ha|km2|0}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Iagorlîc | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |1988 | |1988 | ||
| Line 444: | Line 333: | ||
| |{{convert|1691|ha|km2|0}} | |{{convert|1691|ha|km2|0}} | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |Plaiul Fagului | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |1992 | |1992 | ||
| Line 454: | Line 343: | ||
| |{{convert|6032|ha|km2|0}} | |{{convert|6032|ha|km2|0}} | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| The environment of Moldova suffered extreme degradation during the Soviet period, when industrial and agricultural development proceeded without regard for environmental protection.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova"/> Excessive use of pesticides resulted in heavily polluted topsoil, and industries lacked emission controls.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova"/> Founded in 1990, the ], a national, non-governmental, nonprofit organization which is a member of the ] has been working to restore Moldova's damaged natural environment.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova"/> The movement is national representative of the |
The environment of Moldova suffered extreme degradation during the Soviet period, when industrial and agricultural development proceeded without regard for environmental protection.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova"/> Excessive use of pesticides resulted in heavily polluted topsoil, and industries lacked emission controls.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova"/> Founded in 1990, the ], a national, non-governmental, nonprofit organization which is a member of the ] has been working to restore Moldova's damaged natural environment.<ref name="Environmental issues in Moldova"/> The movement is national representative of the Centre "Naturopa" of the ] and ] of the United Nations.<ref>{{cite conference | ||
| |title=Moldova participants & European participants |conference=European Partnership Fair for Civil Society Organizations in Moldova |date=15–16 June 2010 |place=Republican Palace, Chisinau, Moldova |page=25 |publisher=] |url=http://www.epd.eu/uploads/7a30d35a4a1fb6420184b7cdb9871f5a.pdf |access-date=24 July 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110720161119/http://www.epd.eu/uploads/7a30d35a4a1fb6420184b7cdb9871f5a.pdf |archive-date=20 July 2011 }}</ref> | |title=Moldova participants & European participants |conference=European Partnership Fair for Civil Society Organizations in Moldova |date=15–16 June 2010 |place=Republican Palace, Chisinau, Moldova |page=25 |publisher=] |url=http://www.epd.eu/uploads/7a30d35a4a1fb6420184b7cdb9871f5a.pdf |access-date=24 July 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110720161119/http://www.epd.eu/uploads/7a30d35a4a1fb6420184b7cdb9871f5a.pdf |archive-date=20 July 2011 }}</ref> | ||
| Once possessing a range from the ] through |
Once possessing a range from the ] through Central Asia over the ] into ] and Canada's ] as well as the ], ] survived in Moldova and Romania into the late 18th century. Deforestation, demographic pressure, as well as excessive hunting eradicated the native saiga herds which is ]. They were considered a characteristic animal of ] in antiquity. Historian ] referred to the saigas as the ''kolos'', describing it as "between the deer and ram in size" which (understandably but wrongly) was believed to drink through its nose.<ref>{{cite book |last=Strabo |title=] |trans-title=Geography |section=book VII, chapter 4, paragraph 8 |section-url=https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Strabo/7D*.html#4.7.9 |access-date=19 December 2012 }}{{dead link|date=August 2023|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> | ||
| Another animal which was extinct in Moldova since the 18th century until recently was the European Wood Bison or ]. The species was reintroduced with the arrival of three European bison from ] in Poland several days before ] on 27 August 2005.<ref>{{cite news |author=Autor invitat |date=27 August 2005 |title=The bison come back to Moldova |language=en |url=https://www.moldova.org/en/the-bison-come-back-to-moldova-4123-eng/ |access-date=30 May 2020 |publisher=Moldova.org}}</ref> Moldova is currently interested in expanding their wisent population, and began talks with Belarus in 2019 regarding a bison exchange program between the two countries.<ref>{{cite press release |title=Belarus, Moldova discuss bison exchange program |date=17 February 2019 |publisher=Ministry of Forestry of the Republic of Belarus |url=http://www.mlh.by/en/press-service/news/2584/ |access-date=30 May 2020 |archive-date=28 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200728032233/http://www.mlh.by/en/press-service/news/2584/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | Another animal which was extinct in Moldova since the 18th century until recently was the European Wood Bison or ]. The species was reintroduced with the arrival of three European bison from ] in Poland several days before ] on 27 August 2005.<ref>{{cite news |author=Autor invitat |date=27 August 2005 |title=The bison come back to Moldova |language=en |url=https://www.moldova.org/en/the-bison-come-back-to-moldova-4123-eng/ |access-date=30 May 2020 |publisher=Moldova.org |archive-date=16 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200616162621/https://www.moldova.org/en/the-bison-come-back-to-moldova-4123-eng/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Moldova is currently interested in expanding their wisent population, and began talks with Belarus in 2019 regarding a bison exchange program between the two countries.<ref>{{cite press release |title=Belarus, Moldova discuss bison exchange program |date=17 February 2019 |publisher=Ministry of Forestry of the Republic of Belarus |url=http://www.mlh.by/en/press-service/news/2584/ |access-date=30 May 2020 |archive-date=28 July 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200728032233/http://www.mlh.by/en/press-service/news/2584/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| ==Economy== | == Economy == | ||
| {{main|Economy of Moldova}} | {{main|Economy of Moldova}} | ||
| {{See also|Tourism in Moldova}} | |||
| {{Overly detailed|section|date=October 2016}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| === Overview === | |||
| After the breakup of the USSR in 1991, energy shortages, political uncertainty, trade obstacles and weak administrative capacity contributed to the decline of Moldova's economy. As a part of an ambitious economic liberalization effort, Moldova introduced a convertible currency, liberalized all prices, stopped issuing preferential credits to state enterprises, backed steady land privatization, removed export controls, and liberalized interest rates. The government entered into agreements with the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund to promote growth. | |||
| ], and ], 1980 to 2028]] | |||
| The economy subsequently declined from 1991 to 1999. Since 2000, however, the country's GDP (PPP) grew significantly:<ref name="CIA_World_Factbook_Moldova"/><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.indexmundi.com/g/g.aspx?c=md&v=65| title=Moldova – GDP (purchasing power parity) – Historical Data Graphs per Year| website=Indexmundi.com}}</ref> | |||
| The economy of Moldova is an ] upper-middle income economy, with a high ]. Since the country gained ] from the ] in 1992, it has steadily transitioned to a ]. According to the ], despite a strong economic performance over the past two decades, Moldova remains among the poorest nations in Europe. Growth has remained relatively high since the 1990s, with low levels of unemployment and falling levels of poverty, but a combination of demographic factors, especially an ] and significant levels of emigration, and recent regional events, especially ], have posed serious economic challenges to the Moldovan economy, particularly due to inflation and rising energy prices. Productivity growth has remained poor, and a significant proportion of the population are reliant on government pensions and social assistance.<ref>{{Cite web |date=7 April 2023 |title=The World Bank in Moldova |url=https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/moldova/overview |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=12 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230812104654/https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/moldova/overview |url-status=live }}</ref> Due to Moldova's historic reliance upon Russian oil and natural gas, the energy sector has posed a particular challenge to the country's economy. | |||
| ], and ].]] | |||
| ] has almost doubled from $2,749 (USD) in 2015 to $5,562 in 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |title=GDP Per Capita (current US$) – Moldova {{!}} Data |url=https://data.worldbank.org/ |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=26 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230526025607/https://data.worldbank.org/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Following the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns, annual GDP growth rebounded to 13.9% in 2021, before Russia's invasion of Ukraine, energy and refugee crises caused growth to collapse to −5.9%. {{as of|2022|lc=n}}, unemployment remains low at 2.3%, but inflation had dramatically increased to 28.7% due to the energy crisis caused by the invasion.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldova {{!}} Data |url=https://data.worldbank.org/ |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=26 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230526025607/https://data.worldbank.org/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In recent years the country has received significant economic assistance from the ], IMF, and World Bank, particularly after Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The ] predicts that in 2023 the economy will improve from a 1.5% contraction to a growth of 1.5%.<ref>{{Cite web |date=9 January 2023 |title=IMF Executive Board Concludes Second Reviews Under the Extended Credit Facility and Extended Fund Facility Arrangements for the Republic of Moldova |url=https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2023/01/09/pr2301-imf-executive-board-concludes-second-reviews-under-ecf-and-eff-for-moldova |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801213054/https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2023/01/09/pr2301-imf-executive-board-concludes-second-reviews-under-ecf-and-eff-for-moldova |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Moldova remains highly vulnerable to fluctuations in ]s from workers abroad (which constitute 25 percent of GDP), exports to the ] (CIS) and ] (EU) (88 per cent of total exports), and donor support (about 10 per cent of government spending).<ref name="Walker-2015">{{Cite news |last1=Walker |first1=Shaun |last2=Nardelli |first2=Alberto |date=18 January 2015 |title=Russia's rouble crisis poses threat to nine countries relying on remittances |language=en-GB |work=] |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/jan/18/russia-rouble-threat-nine-countries-remittances |access-date=1 August 2023 |issn=0261-3077 |archive-date=9 December 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161209201100/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/jan/18/russia-rouble-threat-nine-countries-remittances |url-status=live }}</ref> The main transmission channels through which adverse exogenous shocks could impact the Moldovan economy are remittances (also due to potentially returning migrants), external trade, and capital flows.<ref name="Walker-2015" /> | |||
| The economy's primary exports are agriculture, apparel, and sports equipments.<ref>{{Cite web |date=8 September 2022 |title=Moldova – Market Overview |url=https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/moldova-market-overview |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801213054/https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/moldova-market-overview |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2021, Moldova exported $140 million in wine and is the 21st largest exporter of wine in the world, with wine exports being the country's fifth largest export.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Wine in Moldova {{!}} OEC |url=https://oec.world/en/profile/bilateral-product/wine/reporter/mda |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=OEC – The Observatory of Economic Complexity |language=en |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801213056/https://oec.world/en/profile/bilateral-product/wine/reporter/mda |url-status=live }}</ref> With its 300 days of sunshine per year, the climate in Moldova is ideal for agriculture and particularly ]s. The wine industry is a major economic sector, representing three percent of Moldova's GDP and eight percent of the country's total exports, according to government data.<ref name="Five Things To Know About Moldova">{{Cite web |date=1 June 2023 |title=Five Things To Know About Moldova |url=https://www.barrons.com/news/five-things-to-know-about-moldova-d767674 |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707161910/https://www.barrons.com/news/five-things-to-know-about-moldova-d767674 |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2021, the EU became the main purchaser of Moldovan wines. ] (ICT) is one of the most promising economic sectors in Moldova, accounting for more than 10 percent of GDP. More than 2,000 students graduate with a degree in computing or a related field per year.<ref>{{Cite web |date=8 September 2022 |title=Moldova – Information and Communication Technology |url=https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/moldova-information-and-communication-technology |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801213100/https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/moldova-information-and-communication-technology |url-status=live }} {{pd-notice}}</ref> IT companies export about 80 percent of their total production to the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, the ], and ]. | |||
| {{col-begin}} | |||
| {{col-3}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| |+GDP per year (Source: World Bank)<ref>{{Cite web |title=World Bank Open Data |url=https://data.worldbank.org/ |access-date=1 August 2023 |website=World Bank Open Data |archive-date=26 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230526025607/https://data.worldbank.org/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| !Year | |||
| !GDP (Billions in US dollars) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2017 | |||
| ! 2005 !! 2006 !! 2007 !! 2008 !! 2009 !! 2010 !! 2011 !! 2012 !! 2013 !! 2014 !! 2015 | |||
| |9.52 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2018 | |||
| |8.41% || 9.07% || 9.76% || 10.67% || 10.13% || 10.99% || 6.80% || −0.70% || 8.90% || 1.80% || −1.10% | |||
| |11.25 | |||
| |} | |||
| Although estimates point to possible modest overvaluation of the real exchange rate, external competitiveness appears broadly adequate as reflected in strong sustained export performance.<ref name="imf.org">{{cite press release|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2014/cr14190.pdf |title=2014 Article IV consultation and first post-program monitoring discussions – Staff report; press release; and statement by the Executive Director for the Republic of Moldova |publisher=] |issue=IMF Country Report No. 14/190 |date=July 2014 |access-date=2 September 2015}}</ref> However, the near-term economic outlook is weak. Main risks to the near-term outlook relate to serious vulnerabilities and governance issues in the banking sector, policy slippages in the run up to the elections, intensification of geopolitical tensions in the region, and a further slowdown in activity in main trading partners. | |||
| Moldova remains highly vulnerable to fluctuations in remittances from workers abroad (which constitute 24 percent of GDP), exports to the ] (CIS) and ] (EU) (88 per cent of total exports), and donor support (about 10 per cent of government spending). The main transmission channels through which adverse exogenous shocks could impact the Moldovan economy are remittances (also due to potentially returning migrants), external trade, and capital flows. | |||
| Moldova largely achieved the main objectives of the combined ECF/EFF (IMF financial credit) supported program. The economy recovered from the drought-related contraction in 2012. | |||
| {| class="wikitable floatright" | |||
| ! Year | |||
| ! Economic<br />growth | |||
| ! Year | |||
| ! Economic<br />growth | |||
| ! Year | |||
| ! Economic<br />growth | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2019 | |||
| | 1991 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-7,5% </span>|| 2001 || <span style="color:#090">+6,1%</span> || 2011 || <span style="color:#090">+6,4%</span> | |||
| |11.74 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2020 | |||
| | 1992 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-29,0%</span> || 2002 || <span style="color:#090">+7,8% </span>|| 2012 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-0,7%</span> | |||
| |11.53 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2021 | |||
| | 1993 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-1,2% </span>|| 2003 || <span style="color:#090">+6,6% </span>|| 2013 || <span style="color:#090">+8,9%</span> | |||
| |13.69 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2022 | |||
| | 1994 || <span style="color:#e0584e">'''-30,9%'''</span> || 2004 || <span style="color:#090">+7,4% </span>|| 2014 || <span style="color:#090">+4,6%</span> | |||
| |14.51 | |||
| |} | |||
| {{col-3}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |+Imports per year (Source: World Bank) <ref name="worl923">{{Cite web |title=Indicators of economy in Moldova |url=https://www.worlddata.info/europe/moldova/economy.php |access-date=18 September 2023 |archive-date=16 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231016013233/https://www.worlddata.info/europe/moldova/economy.php |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| !Year | |||
| !Imports (Billions in US dollars) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2017 ||5.37 | |||
| | 1995 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-1,4% </span>|| 2005 || <span style="color:#090">+7,5%</span> || 2015 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-0,5%</span> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2018 ||6.39 | |||
| | 1996 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-5,9%</span> || 2006 || <span style="color:#090">+4,8%</span> || 2016 || <span style="color:#090">+2,0%</span> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2019 ||6.61 | |||
| | 1997 || <span style="color:#090">+1,6% </span>|| 2007 || <span style="color:#090">+3,0%</span> || 2017 || <span style="color:#090">+4,5%</span> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2020 ||5.92 | |||
| | 1998 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-6,5%</span> || 2008 || <span style="color:#090">+7,8%</span> || || | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2021||7.91 | |||
| | 1999 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-3,4%</span> || 2009 || <span style="color:#e0584e">-6,5% </span>|| || | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2022||10.91 | |||
| | 2000 || <span style="color:#090">+2,1% </span>|| 2010 || <span style="color:#090">+6,9%</span> || || | |||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="6" | Note:<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200521154828/https://businessday.ro/06/2011/cum-a-evoluat-economia-republicii-moldova-in-ultimii-20-de-ani-plus-o-comparatie-cu-romania/ |date=21 May 2020 }}. Accesat la 27 iunie 2011.</ref><ref>]: </ref><ref>BNS: . Accesat la 17 martie 2014.</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180725214653/https://unimedia.info/stiri/economia-moldovei-a-inregistrat-o-crestere-de-4-6--in-2014--si-constituie-111-miliarde-de-lei-90509.html |date=25 July 2018 }} Unimedia.info; Accesat la 17 February 2015</ref><ref name="Jurnal.md/ro/economic/2016/3/15/economia-republicii-moldova-in-scadere-in-2015-ultimele-cifre-de-la-statistica/_2018-09-28">{{Citation | url=http://jurnal.md/ro/economic/2016/3/15/economia-republicii-moldova-in-scadere-in-2015-ultimele-cifre-de-la-statistica/| title=Economia Republicii Moldova, în SCĂDERE în 2015; Ultimele cifre de la Statistică| newspaper=Jurnal.md/ro/economic/2016/3/15/economia-republicii-moldova-in-scadere-in-2015-ultimele-cifre-de-la-statistica/| access-date=28 September 2018}}</ref><ref name="adev2018-03-16">{{Citation | url=https://adevarul.ro/moldova/economie/bns-economia-republicii-moldova-crescut-45-anul-2017-1_5aaaf699df52022f759e95b5/index.html| title=BNS: Economia Republicii Moldova a crescut cu 4,5% în anul 2017| newspaper=Adevărul| date= 16 March 2018| author=Iurii Botnarenco| access-date=28 September 2018}}</ref> | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| {{col-3}} | |||
| The gross average monthly salary in the Republic of Moldova has registered a steady positive growth after 1999, being 5906 lei or 298 euros in 2018. | |||
| Corporate governance in the banking sector is a major concern. In line with FSAP recommendations, significant weaknesses in the legal and regulatory frameworks must be urgently addressed to ensure stability and soundness of the financial sector. Moldova has achieved a substantial degree of fiscal consolidation in recent years, but this trend is now reversing. Resisting pre-election pressures for selective spending increases and returning to the path of fiscal consolidation would reduce reliance on exceptionally high donor support. Structural fiscal reforms would help safeguard sustainability.<ref name="imf.org"/> Monetary policy has been successful in maintaining inflation within the NBM's target range. The implementation of structural reforms outlined in the National Development Strategy (NDS) Moldova 2020—especially in the business environment, physical infrastructure, and human resources development areas—would help boost potential growth and reduce poverty.<ref name="imf.org"/> Moldova's remarkable recovery from the severe recession of 2009 was largely the result of sound macroeconomic and financial policies and structural reforms. Despite a small contraction in 2012, Moldova's economic performance was among the strongest in the region during 2010–13. Economic activity grew cumulatively by about 24 percent; consumer price inflation was brought under control; and real wages increased cumulatively by about 13 percent. This expansion was made possible by adequate macroeconomic stabilization measures and ambitious structural reforms implemented in the wake of the crisis under a Fund-supported program. In November 2013, Moldova initialed an Association Agreement with the EU which includes provisions establishing a ] (DCFTA). | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| |+Exports per year (Source: World Bank) <ref name="worl923"/> | |||
| !The country | |||
| !Year | |||
| !Average monthly salary (euro) 2018 | |||
| !Exports (Billions in US dollars) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2017 ||3.12 | |||
| |Moldova<ref name="Monitorul.fisc.md/editorial/salariului-mediu-lunar-pe-economie-in-anul-2018-este-de-6150-lei.html_2018-09-28">{{Citation | url=https://monitorul.fisc.md/editorial/salariului-mediu-lunar-pe-economie-in-anul-2018-este-de-6150-lei.html| title=Salariului mediu lunar pe economie in anul 2018 este de 6150 lei / Editorial / Monitorul fiscal FISC.md| newspaper=Monitorul.fisc.md/editorial/salariului-mediu-lunar-pe-economie-in-anul-2018-este-de-6150-lei.html| access-date=28 September 2018}}</ref> | |||
| |€298 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2018 ||3.45 | |||
| |Romania<ref name="Mediafax_2018-08-07">{{Citation | url=https://www.mediafax.ro/social/ins-salariul-mediu-pe-economie-in-crestere-in-iunie-17388668| title=INS: Salariul mediu pe economie, în creştere în iunie| newspaper=Mediafax| date= 7 August 2018| author=Dan Straut| access-date=28 September 2018}}</ref> | |||
| |€966 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2019 ||3.66 | |||
| |Ukraine<ref name="Index.minfin.com_2018-09-28">{{Citation | url=https://index.minfin.com.ua/ua/labour/salary/average/2018-01| title=Середня заробітна плата (січень 2018)| newspaper=Index.minfin.com| access-date=28 September 2018}}</ref> | |||
| |€276 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2020 ||3.22 | |||
| |Russia<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://reconomica.ru/%d1%8d%d0%ba%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%be%d0%bc%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0/%d1%81%d1%82%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b8%d1%81%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0/%d1%81%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%bd%d1%8f%d1%8f-%d0%b7%d0%b0%d1%80%d0%bf%d0%bb%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b0-%d0%b2-%d1%80%d1%84-2018/,%20https://reconomica.ru/%d1%8d%d0%ba%d0%be%d0%bd%d0%be%d0%bc%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0/%d1%81%d1%82%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b8%d1%81%d1%82%d0%b8%d0%ba%d0%b0/%d1%81%d1%80%d0%b5%d0%b4%d0%bd%d1%8f%d1%8f-%d0%b7%d0%b0%d1%80%d0%bf%d0%bb%d0%b0%d1%82%d0%b0-%d0%b2-%d1%80%d1%84-2018/|title=Средняя зарплата в России в 2018 году по данным Росстата и ФБК — вы удивитесь! – Reconomica — истории из жизни реальных людей|first=Денис|last=Иванов}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |€534 | |||
| |2021||4.20 | |||
| |- | |||
| |2022||5.98 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| {{col-end}} | |||
| ] | |||
| A political crisis in early 2013 led to policy slippages in the fiscal and financial areas. The political crisis that broke out in early 2013 was resolved with the appointment of a government supported by a pro-European center-right/center coalition in May 2013. However, delays in policy implementation prevented completion of the final reviews under the ECF/EFF arrangements.{{citation needed|date=August 2016}} | |||
| ] shopping centre in Chișinău]] | |||
| Despite a sharp decline in poverty in recent years, Moldova remains one of the poorest countries in Europe and structural reforms are needed to promote sustainable growth. Based on the Europe and Central Asia (ECA) regional poverty line of US$5/day (PPP), 55 percent of the population was poor in 2011. While this was significantly lower than 94 percent in 2002, Moldova's poverty rate is still more than double the ECA average of 25 percent. The NDS—Moldova (National Development System) 2020, which was published in November 2012, focuses on several critical areas to boost economic development and reduce poverty. These include education, infrastructure, financial sector, business climate, energy consumption, pension system, and judicial framework. Following the ], Moldova has made significant progress towards achieving and retaining macroeconomic and financial stabilization. It has, furthermore, implemented many structural and institutional reforms that are indispensable for the efficient functioning of a market economy. These efforts have helped maintain macroeconomic and financial stability under difficult external circumstances, enabled the resumption of economic growth and contributed to establishing an environment conducive to the economy's further growth and development in the medium term.{{Citation needed|date=August 2016}} | |||
| The government's goal of ] has resulted in some market-oriented progress. Moldova experienced better than expected economic growth in 2013 due to increased agriculture production, to economic policies adopted by the Moldovan government since 2009, and to the receipt of EU trade preferences connecting Moldovan products to the world's largest market. Moldova has signed the ] and the Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Agreement with the European Union during summer 2014.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.gov.md/sites/default/files/document/attachments/7048451_en_acord_asociere.pdf |title=Association Agreement between the European Union and the European Atomic Energy Community and their Member States, of the one part, and the Republic of Moldova, of the other part |publisher=Government of the Republic of Moldova |date=26 November 2013 |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=24 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924024027/http://www.gov.md/sites/default/files/document/attachments/7048451_en_acord_asociere.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> Moldova has also achieved a Free Visa Regime<ref>{{cite web|url=http://eeas.europa.eu/delegations/moldova/travel_eu/index_en.htm|title=European Union|website=Eeas.europa.eu|access-date=26 November 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141202102356/http://eeas.europa.eu/delegations/moldova/travel_eu/index_en.htm|archive-date=2 December 2014|url-status=dead}}</ref> with the EU which represents the biggest achievement of Moldovan diplomacy since independence.<ref>{{cite press release|url=http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/jha/141491.pdf |title=Visa liberalisation for Moldova |publisher=Council of the European Union |date=14 March 2014 |access-date=2 September 2015}}</ref> Still, growth has been hampered by high prices for Russian natural gas, a Russian import ban on Moldovan wine, increased foreign scrutiny of Moldovan agricultural products, and by Moldova's large external debt. Over the longer term, Moldova's economy remains vulnerable to political uncertainty, weak administrative capacity, vested bureaucratic interests, corruption, higher fuel prices, Russian pressure, and the separatist regime in Moldova's Transnistria region.<ref name="indexmundi.com">{{cite web|url=http://www.indexmundi.com/moldova/economy_profile.html|title=Moldova Economy Profile 2014|website=Indexmundi.com}}</ref> | |||
| According to IMF World Economic Outlook April 2014, the Moldovan GDP (PPP) per capita is 3,927 International Dollars,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2014/02/weodata/download.aspx|title=Download entire World Economic Outlook database|website=Imf.org}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.gfmag.com/global-data/country-data/moldova-gdp-country-report|title=Moldova|work=Global Finance Magazine}}</ref> excluding grey economy and tax evasion. | |||
| ===Energy=== | ===Energy=== | ||
| {{ |
{{Excerpt|Energy in Moldova}} | ||
| === Tourism === | |||
| With few natural energy resources, Moldova imports almost all of its energy supplies from Russia and Ukraine. Moldova's dependence on Russian energy is underscored by a growing US$5 billion debt to Russian natural gas supplier Gazprom, largely the result of unreimbursed natural gas consumption in the separatist Transnistria region. In August 2013, work began on a new pipeline between Moldova and Romania that may eventually break Russia's monopoly on Moldova's gas supplies.<ref name="indexmundi.com"/> Moldova is a partner country of the EU ] energy programme, which has four key topics: enhancing ], ] of member state ]s on the basis of ] principles, supporting ] development, and attracting investment for energy projects of common and regional interest.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.inogate.org/|title=INOGATE|website=www.inogate.org}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Tourism in Moldova}} | |||
| Moldova is the among least visited countries in Europe, and tourism consequently plays a relatively minor role in the country's overall economy.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Petterson |first=Leif |date=2 July 2013 |title=Moldova: embracing its status as Europe's least-visited country |url=https://www.lonelyplanet.com/articles/moldova-embracing-its-status-as-europes-least-visited-country |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=15 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210815203959/https://www.lonelyplanet.com/articles/moldova-embracing-its-status-as-europes-least-visited-country |url-status=live }}</ref> Despite the impact of ], Moldova saw more foreign visitors in the first quarter of 2022 than pre-], going from 31,000 non-resident tourists in 2019 to 36,100 in 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Buckley |first=Julia |date=6 August 2022 |title=How the Ukraine invasion flattened Eastern European tourism |url=https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/ukraine-invasion-tourism-eastern-europe/index.html |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=CNN |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112942/https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/ukraine-invasion-tourism-eastern-europe/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref> This still makes it one of the least-visited countries in Europe, however in recent years a number of Western media outlets have begun to highlight Moldova and its capital city ] as an attractive tourism destination due to its picturesque natural landscapes, 300 days of sunshine per year, low prices, ancient wine culture, and mix of regional cultural influences.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Erizanu |first=Paula |date=1 June 2023 |title=I've come to love Chișinău: my home city in Moldova deserves the spotlight |language=en-GB |work=] |url=https://www.theguardian.com/travel/2023/jun/01/ive-come-to-love-chisinau-my-home-city-moldova-deserves-the-spotlight |access-date=2 August 2023 |issn=0261-3077 |archive-date=18 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231018234919/https://www.theguardian.com/travel/2023/jun/01/ive-come-to-love-chisinau-my-home-city-moldova-deserves-the-spotlight |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Cooper |first=Tim |date=30 September 2021 |title=Chisinau city guide: Where to eat, drink and stay in Moldova's capital |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/travel/europe/moldova/chisinau-travel-guide-best-hotels-city-restaurants-things-to-do-b1926513.html |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705202221/https://www.independent.co.uk/travel/europe/moldova/chisinau-travel-guide-best-hotels-city-restaurants-things-to-do-b1926513.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Smith |first=Jen Rose |date=8 May 2019 |title=Why you should go to the world's least-visited countries |url=https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/least-visited-countries-travel/index.html |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112942/https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/least-visited-countries-travel/index.html |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=27 August 2016 |title=25 quirky facts about Europe's least touristy country |language=en-GB |work=] |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/destinations/europe/articles/amazing-facts-about-moldova/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |issn=0307-1235 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112942/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/destinations/europe/articles/amazing-facts-about-moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Suri |first=Charu |date=12 February 2018 |title=This Enchanting Country May Be Eastern Europe's Best-Kept Secret |url=https://www.architecturaldigest.com/story/moldova-design-travel-guide |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112943/https://www.architecturaldigest.com/story/moldova-design-travel-guide |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Taylor |first=Chris |date=28 February 2019 |title=Moldova: exploring Europe's poorest and least visited nation |url=https://www.scmp.com/magazines/post-magazine/travel/article/2187876/exploring-moldova-europes-poorest-country-and-its |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112943/https://www.scmp.com/magazines/post-magazine/travel/article/2187876/exploring-moldova-europes-poorest-country-and-its |url-status=live }}</ref> Tourism in Moldova has focused on the country's natural landscapes, historical sites, and historic wine tradition. The government promotes international tourism within the country through its Moldova Travel brand.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldova.travel – the official tourist portal of Moldova |url=https://moldova.travel/en/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=Moldova Travel |language=en-US |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112944/https://moldova.travel/en/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Moldova is internationally connected by plane via ], with direct flights to and from many European destinations, including ], ], ], ], ]'s ], ], ], and ]. Rail links connect it via direct overnight trains to neighbouring ], ], ], and formerly Moscow.<ref name="www.seat61.com">{{Cite web |title=How to travel by train from London to Moldova |url=https://www.seat61.com/Moldova.htm |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=www.seat61.com |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112943/https://www.seat61.com/Moldova.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Moldovan citizens also enjoy visa-free travel across the ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=R |first=Bleona |date=30 April 2022 |title=Moldova Marks 8 Years of Visa-Free Travel to EU |url=https://www.schengenvisainfo.com/news/moldova-marks-8-years-of-visa-free-travel-to-eu/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=SchengenVisaInfo.com |language=en |archive-date=1 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220501073005/https://www.schengenvisainfo.com/news/moldova-marks-8-years-of-visa-free-travel-to-eu/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| As a major exporter of wine with more than 142 wineries and the largest wine cellar in the world, vineyard tours are offered to tourists across the country. Major sites include the ] winery, whose wine cellar stretches more than {{convert|120|km|mi|abbr=off}}; ], a 19th-century chateau with vineyards, a museum, art gallery, spa, hotel, and restaurant; and ], which boasts the world's largest collection of wine.<ref name="Guinness World Records" /> As a country with a deep history of ], the country also has more than 50 monasteries and 700 churches.<ref>{{Cite web |date=29 October 2019 |title=The world's least visited countries – have you been to any of them? |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/galleries/least-visited-countries-in-the-world/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=The Telegraph |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112944/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/galleries/least-visited-countries-in-the-world/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Among the most famous and well-visited are the ] ], carved into a cliff face in the 13th century and still in use today, and the 19th century ] in the centre of Chișinău. ] includes both the Old Orhei Archaeological Landscape, which features evidence of settlements dating back to at least the 12th century, and the typical ] soil on the ] of Moldova (the most arable soil on the planet) on its Tentative List of ]s.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Centre |first=UNESCO World Heritage |title=Orheiul Vechi Archaeological Landscape |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/6220/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=UNESCO World Heritage Centre |language=en |archive-date=9 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211109033906/https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/6220/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Centre |first=UNESCO World Heritage |title=The Typical Chernozem Soils of the Balti Steppe |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5647/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=UNESCO World Heritage Centre |language=en |archive-date=7 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211107092451/https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5647/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The capital city of ] hosts most of the country's national museums, including the ], ], Brancusi Gallery, the ] with over 236,000 exhibits, as well as bustling markets in the north of the city, including the house where ] once resided while in exile from the ], and which has since been turned into a museum. Every year on 3–4 October, the country celebrates National Wine Day, where wine producers open up their wineries to the general public and provide shuttle buses between locations.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Waller |first=John |date=9 October 2022 |title=Travel: Exploring Moldova – Europe's 'least known country' |url=https://www.thetelegraphandargus.co.uk/news/23034228.travel-exploring-moldova---europes-least-known-country/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802112944/https://www.thetelegraphandargus.co.uk/news/23034228.travel-exploring-moldova---europes-least-known-country/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Wine industry=== | ===Wine industry=== | ||
| {{main|Moldovan wine}} | {{main|Moldovan wine}} | ||
| ] is home to the world's biggest ].]] | ] is home to the world's biggest ].]] | ||
| With its 300 days of sunshine per year, the climate in Moldova is ideal for agriculture and particularly ]s. The wine industry is a major economic sector, representing three percent of Moldova's GDP and eight percent of the country's total exports, according to government data. Moldovan wine is being exported into over 70 states worldwide. Although Moldova is barely larger than ], the country has 122,000 hectares of vineyards and is among the 20 largest producers in the world, according to a report by the ] (OIV).<ref name="Five Things To Know About Moldova"/> | |||
| The country has a well-established ] industry. It has a vineyard area of {{convert|147000|ha}}, of which {{convert|102500|ha|abbr=on}} are used for commercial production. Most of the country's wine production is made for export. Many families have their own recipes and ] that have been passed down through the generations. There are 3 historical wine regions: Valul lui Traian (south west), Stefan Voda (south east) and ] (center), destined for the production of wines with protected geographic indication.<ref name="natura2000" /> ] is the home of the largest wine cellar in the world. It stretches for {{convert|200|km|abbr=on}} (though only {{convert|55|km|abbr=on}} is in use) and holds almost 2 million bottles of wine<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/article/worlds-largest-wine-cellar|title=This Massive Underground City is Filled With Wine|last=Bednarz|first=Christine|website=nationalgeographic.com|date=November 29, 2017|access-date=31 October 2022}}</ref> | |||
| Before ] and Moldova's pivot towards Europe, a majority of its wine exports went to Russia, but this has now changed: "Russia accounted for only 10 percent of Moldovan wine exports in 2021, down from 80 percent in the early 2000s, according to figures from the ]."<ref name="France 24-2022">{{Cite web |date=22 May 2022 |title=Moldova wine industry's EU focus pays off |url=https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20220522-moldova-wine-industry-s-eu-focus-pays-off |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162429/https://www.france24.com/en/live-news/20220522-moldova-wine-industry-s-eu-focus-pays-off |url-status=live }}</ref> The EU liberalized its market for Moldovan wines and has signed a bilateral free trade deal with Moldova, with the result that in 2021 the country exported more than 120 million litres of wine to European countries, compared to 8.6 million litres to Russia.<ref name="France 24-2022" /> | |||
| Many families have their own recipes and ] that have been passed down through the generations. There are 3 historical wine regions: Valul lui Traian (south west), Stefan Voda (south east) and ] (centre), destined for the production of wines with protected geographic indication.<ref name="natura2000" /> ] is the home of the largest wine cellar in the world. It stretches for {{convert|200|km|abbr=on}} (though only {{convert|55|km|abbr=on}} is in use) and holds some two million or more bottles of wine.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/article/worlds-largest-wine-cellar|title=This Massive Underground City is Filled With Wine|last=Bednarz|first=Christine|website=nationalgeographic.com|date=29 November 2017|access-date=31 October 2022|archive-date=1 November 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221101043548/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/article/worlds-largest-wine-cellar|url-status=dead}}</ref> It has retained the ] for largest wine cellar by number of bottles since 2005.<ref name="Guinness World Records">{{Cite web |title=Largest wine cellar by number of bottles |url=https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/largest-wine-cellar-by-number-of-bottles |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=Guinness World Records |language=en-gb |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707170559/https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/largest-wine-cellar-by-number-of-bottles |url-status=live }}</ref> The earliest wines in its collection date to 1969. ] in the south east is a winery and ], which was built at the end of the 19th century in the village of ] in the district ], and is thought to be the first winery in Bessarabia. It has since also become a tourist complex with a museum, art gallery, hotel, spa, and wine tasting rooms. | |||
| ===Agriculture=== | ===Agriculture=== | ||
| {{main|Agriculture in Moldova}} | {{main|Agriculture in Moldova}} | ||
| ] | |||
| Moldova's ] and ] ] (with warm summers and mild winters) have made the country one of the most productive agricultural regions since ancient times, and a major supplier of agricultural products in southeastern Europe. In agriculture, the economic reform started with the land cadastre reform.<ref name="cadastre law">{{cite web|url=http://lex.justice.md/md/295776/|title=Legea cu privire la secţiile pentru reforma agrară în cadrul organelor de autoadministrare locală ale Republicii Moldova Nr.129 din 02.03.92, Monitorul Oficial nr.3/80, 1992|trans-title=Law on Land Reform for the local self-administration of the Republic of Moldova Nr.129 from 02/03/92|issue=3|language=ro|work=Monitorul oficial|access-date=30 October 2016}}</ref> | |||
| Moldova is an agrarian-industrial state, with agricultural land occupying 2,499,000 hectares in a total area of 3,384,600 hectares.<ref name="Gerciu-2017">{{Cite web |last1=Gerciu |first1=Viorel |last2=Rundgren |first2=Gunnar |date=2017 |title=The Status and Potential of Organic Agriculture in the Republic of Moldova |url=https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/22962/The%20Status%20and%20Potential%20of%20Organic%20Agriculture%20in%20the%20Republic%20of%20Moldova.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y |website=UN Environment Programme |access-date=8 March 2024 |archive-date=5 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240205181552/https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/22962/The%20Status%20and%20Potential%20of%20Organic%20Agriculture%20in%20the%20Republic%20of%20Moldova.pdf?isAllowed=y&sequence=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> It is estimated that 1,810,500 of these hectares are ].<ref name="Gerciu-2017" /> It is among the most arable countries in Europe, with the Chernozem soil across the ] being among the most fertile soils anywhere in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldova |url=https://www.fao.org/3/y2722e/y2722e0x.htm#:~:text=Arable%20land%20and%20permanent%20crops,about%200.4%20million%20ha%20each. |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=www.fao.org |archive-date=18 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230818134915/https://www.fao.org/3/y2722e/y2722e0x.htm#:~:text=Arable%20land%20and%20permanent%20crops,about%200.4%20million%20ha%20each. |url-status=live }}</ref> With more than 300 days of sunshine per year supporting the cultivation of vineyards, Moldova is also one of the largest wine producers in the world. Moldova's agricultural sector benefits from a geographical proximity to large markets, especially the ].<ref name="Gerciu-2017" /> {{as of|2021|lc=n}}, agriculture made up 12% of Moldova's overall exports and 21% of overall employment.<ref>{{Cite web |title=REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA – Statistical Database – United Nations Economic Commission for Europe |url=https://w3.unece.org/CountriesInFigures/en/Home/Index?countryCode=498 |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=w3.unece.org |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802120023/https://w3.unece.org/CountriesInFigures/en/Home/Index?countryCode=498 |url-status=live }}</ref> Its most exported foods are maize, wheat, sunflower seeds, grapes, apples, sugar beets, milk, potatoes, barley, plums/sloes, while relevant and important domestic industries include sugar processing, vegetable oil, food processing, and agricultural machinery.<ref>{{Citation |title=Moldova |date=25 July 2023 |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |work=] |access-date=2 August 2023 |publisher=] |language=en |archive-date=5 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210105015457/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Between 2015 and 2022, agricultural production has almost doubled, particularly in vegetable and fruit production.<ref>{{Cite web |date=1 November 2022 |title=Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Moldova, editions 2002–2022 |url=https://statistica.gov.md/en/buletin-statistic-trimestrial-editiile-2005-2021-9877_59482.html |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Moldova, editions 2002–2022 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802131538/https://statistica.gov.md/en/buletin-statistic-trimestrial-editiile-2005-2021-9877_59482.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In July 2023, a network of 20 ] comprising over 1,000 seeds were created across Moldova with the assistance of ], ], and the ], with the aim is to improve local ], ], and the capacity of local government and farmers to respond effectively to changing environmental conditions.<ref>{{Cite web |date=27 July 2023 |title=Seed libraries were created as a first in Moldova, thanks to transfer Czech know-how |url=https://www.undp.org/moldova/press-releases/seed-libraries-were-created-first-moldova-thanks-transfer-czech-know-how |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802161617/https://www.undp.org/moldova/press-releases/seed-libraries-were-created-first-moldova-thanks-transfer-czech-know-how |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Moldova's agricultural products include vegetables, fruits, grapes, ], and grains.<ref>{{cite book |title=Family Reference Atlas of the World |date=2016 |publisher=National Geographic |location=Washington District of Columbia |edition=4 }}</ref> | |||
| Nevertheless, the country's agricultural sector faces serious long-term challenges. Despite having relatively modest per capita ], and lower than the world average, Moldova is highly vulnerable to ] and related environmental disasters which already cost the country 2.13% of annual GDP.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Climate change, environment & energy {{!}} Moldova |url=https://www.undp.org/moldova/climate-change-environment-energy |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=12 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230712144534/https://www.undp.org/moldova/climate-change-environment-energy |url-status=live }}</ref> According to Climate-KIC, run by the ], "The same region in Moldova can experience intense droughts and devastating floods in the course of a few months, which is the primary concern of local people when they talk about climate. But the irregular nature of these events made it difficult to sustain long term interest from Moldovan people or to channel money from donors."<ref>{{Cite web |date=7 May 2021 |title=Embracing a new approach to climate change in Moldova |url=https://www.climate-kic.org/news/moldova-climate-change-sida-undp/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=Climate-KIC |language=en |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802120023/https://www.climate-kic.org/news/moldova-climate-change-sida-undp/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Transport=== | |||
| {{main|Transport in Moldova|Rail transport in Moldova}} | |||
| ===Transport infrastructure=== | |||
| ].]] | |||
| {{main|Transport in Moldova|Rail transport in Moldova}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| The main means of transportation in Moldova are railways {{convert|1138|km|mi|abbr=on}} and a highway system ({{convert|12730|km|mi|0|abbr=on|disp=or}} overall, including {{convert|10937|km|mi|0|abbr=on|disp=or}} of paved surfaces). Rail links connect it via direct overnight trains to neighbouring ], ], ], and also Moscow.<ref name="www.seat61.com" /> | |||
| The ] terminal on the ] is compatible with small seagoing vessels. Shipping on the lower ] and ] rivers plays only a modest role in the country's transportation system. | |||
| The sole international air gateway of Moldova is the ]. with direct flights to and from many European destinations. | |||
| ==Telecommunications== | |||
| === Telecommunications === | |||
| {{main|Telecommunications in Moldova}} | {{main|Telecommunications in Moldova}} | ||
| Internet in Moldova is among the fastest and least expensive in the world {{as of|2023|lc=y}}.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Worldwide Broadband Price Research 2023 |url=https://www.cable.co.uk/broadband/pricing/worldwide-comparison/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=Cable.co.uk |language=en |archive-date=23 November 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171123001429/https://www.cable.co.uk/media-centre/release/new-worldwide-broadband-price-league-unveiled/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The country ranks 3rd in the world by gigabit coverage with around 90% of the population having the option to subscribe to a ] ] broadband plan.<ref name="International Trade Administration-2022">{{Cite web |date=8 September 2022 |title=Moldova – Information and Communication Technology |url=https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/moldova-information-and-communication-technology |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=1 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230801213100/https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/moldova-information-and-communication-technology |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] has judged it to have a highly developed digital infrastructure, with 98% 4G coverage of its territory.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Botezatu |first=Serghei |date=4 October 2021 |title=Digital Transformation of Moldova: there is no way back |url=https://www.undp.org/moldova/blog/digital-transformation-moldova-there-no-way-back |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707180255/https://www.undp.org/moldova/blog/digital-transformation-moldova-there-no-way-back |url-status=live }}</ref> By July 2022, there were more than 3 million internet users in Moldova, constituting some 76% of the population.<ref>{{Cite news |date=22 May 2023 |title=Moldova media guide – BBC News |language=en-GB |work=] |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17602346 |access-date=2 August 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163031/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17602346 |url-status=live }}</ref> Moldova is considering a bid to begin rolling out 5G in 2024, with testing beginning in 2019. ] launched in Moldova in August 2022.<ref>{{Cite tweet|number=1554975109907066880|user=SpaceX|title=Starlink is now live in Moldova → http://starlink.com/map|author-link=SpaceX|date=3 August 2022|access-date=3 August 2022}}</ref> ] (ICT) is one of the most promising economic sectors in Moldova, accounting for more than 10 percent of GDP. More than 2,000 Moldovan students per year graduate with a degree in ] or a related field.<ref name="International Trade Administration-2022" /> | |||
| The first million mobile telephone users were registered in September 2005. The number of mobile telephone users in Moldova increased by 47.3% in the first quarter of 2008 against the last year and exceeded 2.89 million.<ref name="2mil">{{in lang|ro}} – Agenția Naționala pentru Reglementare în Comunicații Electronice și Tehnologia Informației (])</ref> | |||
| The ]'s Global Cybersecurity Index ranks Moldova on the 33rd place in Europe and the 63rd place in the world. The country's joining in 2009 of the ] of the ] and adoption of the National Cyber Security Program for 2016–2020 have established the legislative parameters for a safer digital environment. Since Russia's invasion of neighbouring Ukraine and their campaign of ] against Moldova, the Moldovan government has invested significant money and resources in developing stronger ] practices and regulations with assistance from the European Union and United States.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Stupp |first=Catherine |date=27 July 2022 |title=Moldova Plans Cyber Overhauls Amid War in Neighboring Ukraine |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/moldova-plans-cyber-overhauls-amid-war-in-neighboring-ukraine-11658914202 |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802123752/https://www.wsj.com/articles/moldova-plans-cyber-overhauls-amid-war-in-neighboring-ukraine-11658914202 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Gallagher |first=Ryan |date=20 April 2023 |title=Cyberwar Descends on an Unprepared Moldova |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-04-20/russian-cyberattacks-target-moldova-amid-ukraine-war |access-date=2 August 2023}}</ref> The European Union has also set up and funded the Moldova Cybersecurity Rapid Assistance Unit to improve the cyber resilience of Moldova's public sector organisations and key critical infrastructure sectors. Moldova has adopted new legislation partially drafted by the unit which will go into effect on 1 January 2025.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Moldova Cybersecurity Rapid Assistance |url=https://eufordigital.eu/discover-eu/moldova-cybersecurity-rapid-assistance/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=EU4Digital |language=en-US |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802123758/https://eufordigital.eu/discover-eu/moldova-cybersecurity-rapid-assistance/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=17 May 2023 |title=Moldova adopts EU-backed Cybersecurity Law – EU NEIGHBOURS east |url=https://euneighbourseast.eu/news/latest-news/moldova-adopts-eu-backed-cybersecurity-law/ |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=euneighbourseast.eu |language=en-GB |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802123756/https://euneighbourseast.eu/news/latest-news/moldova-adopts-eu-backed-cybersecurity-law/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The country has also passed legislation in order to more closely align with the EU's ] regulations, and is currently mostly compliant.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2 October 2022 |title={{!}} Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of the Republic of Moldova |url=https://mfa.gov.md/en/content/new-data-protection-law-line-european-standards-provides-transparent-rules-benefitting |access-date=2 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802123804/https://mfa.gov.md/en/content/new-data-protection-law-line-european-standards-provides-transparent-rules-benefitting |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In September 2009, Moldova was the first country in the world to launch high-definition voice services (]) for mobile phones, and the first country in Europe to launch 14.4 Mbit/s mobile broadband on a national scale, with over 40% population coverage.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.theguardian.com/business/2009/dec/31/orange-launches-hd-mobile-phone-service|title=Orange launches HD mobile phone service|author=Katie Allen|date=31 December 2009|work=The Guardian|access-date=18 September 2010}}</ref> | |||
| ===Banking=== | |||
| {{As of|2010}}, there are around 1,295,000 ] with overall Internet penetration of 35.9%.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.itu.int/ITU-D/icteye/Reporting/ShowReportFrame.aspx?ReportName=%2FWTI%2FInformationTechnologyPublic&ReportFormat=HTML4.0&RP_intYear=2010&RP_intLanguageID=1&RP_bitLiveData=False |title=International Telecommunication Union |publisher=Itu.int |access-date=9 October 2013 |archive-date=3 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220303175647/https://www.itu.int/ITU-D/icteye/Reporting/ShowReportFrame.aspx?ReportName=%2FWTI%2FInformationTechnologyPublic&ReportFormat=HTML4.0&RP_intYear=2010&RP_intLanguageID=1&RP_bitLiveData=False |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| {{see also|List of banks in Moldova}} | |||
| The ] is responsible for the financial system and has a responsibility to the management and control of all banks in Moldova. It is accountable to the ]. | |||
| == Demographics == | |||
| On 6 June 2012, the Government approved the licensing of 4G / LTE for mobile operators.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://unimedia.info/stiri/doc-guvernul-da-unda-verde-pentru-acordarea-licentelor-4g-48577.html|title=the Government approved the licensing of 4G / LTE for mobile operators|author=UNIMEDIA|date=6 June 2013|work=UNIMEDIA|access-date=10 March 2013|archive-date=26 October 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121026012014/http://unimedia.info/stiri/doc-guvernul-da-unda-verde-pentru-acordarea-licentelor-4g-48577.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Demographics of Moldova}} | |||
| The most up-to-date and reliable information is available from the ]'s website which is continuously updated on a monthly and yearly basis. The most recent ] of Moldova was carried out in ] (not including ]). The next national census is due to be carried out in 2024.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Recensământul Populației și Locuințelor 2024 |url=https://statistica.gov.md/ro/recensamantul-populatiei-si-al-locuintelor-2024-9940.html |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=ro |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180409/https://statistica.gov.md/ro/recensamantul-populatiei-si-al-locuintelor-2024-9940.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| == |
=== Overview === | ||
| {{Pie chart|value1=75|value2=7|value3=6.57|value4=4.57|value5=4.06|value6=1.88|value7=0.34|value8=0.10|value9=0.06|value10=0.05|value11=0.03|value12=0.26|label1=]|label2=]|label3=]|label4=]|label5=]|label6=]|label7=]|label8=]|label9=Jews|label10=]|label11=]|label12=Others|caption=Population of Moldova according to ethnic group|footer=Source: ].}}Moldova has an estimated population of approx. 2,423,300 {{as of|2024|1|1|lc=y}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://statistica.gov.md/en/statistic_indicator_details/25 |title=Population |publisher=National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova |access-date=13 August 2024}}</ref> Moldova is relatively urbanised, with 43.4% of Moldovans living in urban areas {{as of|2022|lc=y}} and an urbanisation rate of 0.09%.<ref>{{Citation |title=Moldova |date=31 July 2023 |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |work=] |access-date=3 August 2023 |publisher=] |language=en |archive-date=5 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210105015457/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=World Bank Open Data |url=https://data.worldbank.org/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=World Bank Open Data |archive-date=26 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230526025607/https://data.worldbank.org/ |url-status=live }}</ref> About one-third of the Moldovan population live in the capital city ]'s ]. {{as of|2022|lc=n}}, the country's population density is 82.8 inhabitants per 1 km<sup>2</sup>, and average life expectancy was 71.5 years (67.2 for males, and 75.7 for females).<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova">{{Cite web |date= |title=Moldova in Figures, Statistical Summary: 2023 Edition |url=https://statistica.gov.md/files/files/publicatii_electronice/Moldova_in_cifre/2023/Moldova_cifre_eng_2023.pdf |access-date=3 August 2023 |publisher=] |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180408/https://statistica.gov.md/files/files/publicatii_electronice/Moldova_in_cifre/2023/Moldova_cifre_eng_2023.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> There are 100 women per 90 men in Moldova, and employed women have significantly higher levels of education, though women continued to earn 13.6% less than men on average.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> The number of elderly people (60 years and over) per 100 inhabitants in Moldova has increased year-on-year.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> The national language is ], a ], though approximately 15% of the Moldovan population also speak Russian {{as of|2014|lc=y}}. | |||
| {{Toomanycharts}}<!--As prose text is preferred overly detailed statistical charts and diagrams such as economic trends, weather boxes, historical population charts, and past elections results, etc, should be reserved for main sub articles on the topic as per WP:COUNTRYCHARTS---> | |||
| {{main|Demographics of Moldova}} | |||
| The country has been suffering from long-term population decline due to high levels of ] (in 2022, 43,000 more people left the country than came) as well as low fertility rates. According to ], the population has fallen by almost 33% since 1990, and by 2035 the total population may be half what it was in 1990.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Judah |first=Tim |date=16 January 2020 |title=Moldova Faces 'Existential' Population Crisis |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2020/01/16/moldova-faces-existential-population-crisis/ |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162502/https://balkaninsight.com/2020/01/16/moldova-faces-existential-population-crisis/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Since 2018, the number of deaths has exceeded the levels of live-births, though the gap has been reduced since 2021. {{as of|2022|lc=n}}, the average number of children per women of childbearing age was 1.69, well below the ] of 2.1, as compared to 1.78 in 2019. The total number of deaths fell by 20.5% in 2022 compared to 2019. Unemployment has remained low at about 3% in 2022.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> | |||
| ===Ethnic composition=== | |||
| As of the 2014 census, ] were the largest ethnic group of Moldova (75.1% of the population). In addition, 7.0% of the population declared themselves ], amid the ]. Although historical, the polarization based on ethnolinguistic criteria of the majority ethnic group reappeared with the national revival movement of the late 1980s, and, so far, there is no consensus regarding the mainstream identity in the Republic of Moldova (Moldovan or Romanian).<ref>{{cite report |authors=Iulian Groza, Mathias Jopp, ], Vadim Pistrinciuc, Andrei Popov, Adrian Popescu, Iulian Rusu |date=January 2018 |title=Strengthening Social Cohesion and a Common Identity in the Republic of Moldova |url=http://iep-berlin.de/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/Social-Cohesion-and-Common-Identity-EN.pdf |publisher=German Federal Foreign Office |pages=12–13 |access-date=5 December 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite conference |url=https://ecpr.eu/Filestore/PaperProposal/438e9bc3-a592-4200-99da-b6b89af0c1dc.pdf |title=The Construction, Deconstruction and Conflict of National Identities in Moldova |last=Cojocaru |first=Lee |date=August 2015 |location=Montreal |conference=ECPR General Conference}}</ref> | |||
| According to the ], ethnic ] made up approx. 75% of the country's population, while ] (7%), ] (6.57%), ] (4.57%), and ] (4.06%) made up the most substantial ethnic minorities. Smaller populations include ] (1.88%), ] (0.34%), ] (0.10%), Jews (0.06%), and ] (0.05%). | |||
| The country also has important minority ethnic communities, as shown in the table below. ], 4.4% of the population, are ] ] people. ], ], ], Ukrainians, although not numerous, were present as early as the 17th century, and have contributed cultural marks. The 19th century saw the arrival of many more Ukrainians from ] and ], as well as new communities, such as ], ], ], and ]. Most of Moldova's ] emigrated between 1979 and 2004. | |||
| === Language === | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| {{Further|Languages of Moldova}} | |||
| |+ | |||
| {{as of|2023|03|lc=n}}, the only ] of Moldova is Romanian, and all references to the Moldovan language in the ] and legal bills have been amended to refer to Romanian.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Fremer |first=Iana |date=24 April 2023 |title=Moldova: New Law Establishes Romanian as the State Language of the Country |url=https://www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2023-04-23/moldova-new-law-establishes-romanian-as-the-state-language-of-the-country/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180405/https://www.loc.gov/item/global-legal-monitor/2023-04-23/moldova-new-law-establishes-romanian-as-the-state-language-of-the-country/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=17 March 2023 |title=Moldovan Parliament Approves Final Reading Of Romanian Language Bill |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-parliament-approves-final-reading-romanian-language-bill/32321571.html |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=17 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230317223413/https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-parliament-approves-final-reading-romanian-language-bill/32321571.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The 2014 Moldovan census for the first time collected information about the languages spoken by residents in Moldova. There is a ] about whether or not ] and ] should be considered distinct languages, and the Moldovan government rejects any distinction, however the census allowed for respondents to respond with their preferred label. The results were ] (54.6%), ] (24.0%), Russian (14.5%), ] (2.7%), ] (2.7%), ] (1.7%), and Other (0.5%). | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| | colspan="19" align="center"|'''Population of Moldova according to ethnic group (Censuses 1959–2014)''' | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | Ethnic group | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 1959<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_59.php?reg=4|script-title=ru:№ 821 - 822: Всесоюзная перепись населения 1959 года. Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР: Молдовская ССР|trans-title=No. 821 - 822: 1959 All-Union Census. The national composition of the population in the republics of the USSR: Moldavian SSR|language=ru|journal=Demoscope Weekly|issn=1726-2887|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 1970<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_70.php?reg=9|script-title=ru:№ 821 - 822: Всесоюзная перепись населения 1970 года. Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР: Молдовская ССР|trans-title=No. 821 - 822: 1970 All-Union Population Census. The national composition of the population in the republics of the USSR: Moldavian SSR|language=ru|journal=Demoscope Weekly|issn=1726-2887|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 1979<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_79.php?reg=9|script-title=ru:№ 821 - 822: Всесоюзная перепись населения 1979 года. Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР: Молдовская ССР|trans-title=No. 821 - 822: 1979 All-Union Census. The national composition of the population in the republics of the USSR: Moldavian SSR|language=ru|journal=Demoscope Weekly|issn=1726-2887|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 1989<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/sng_nac_89.php?reg=9|script-title=ru:№ 821 - 822: Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года. Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР: Молдовская ССР|trans-title=No. 821 - 822: All-Union Population Census of 1989. The national composition of the population in the republics of the USSR: Moldavian SSR|language=ru|journal=Demoscope Weekly|issn=1726-2887|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2004'''**'''<ref name="statistica.md2017">{{cite web|url=http://www.statistica.md/public/files/publicatii_electronice/Anuar_Statistic/2017/2_AS.pdf|title=Statistical Yearbook of Moldova 2017: Results of the 2004 Population Census: 2. Population: 2.1: Population and the demographic structure|publisher=National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova|date=2017|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref><br />(without Transnistria) | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2014<ref>{{cite web|url=http://data.un.org/Data.aspx?d=POP&f=tableCode%3a26%3bcountryCode%3a498%3brefYear%3a2014%3bareaCode%3a0%3bsexCode%3a0&c=2,3,6,8,10,12,14,15,16&s=_countryEnglishNameOrderBy:asc,refYear:desc,areaCode:asc&v=1|title=Republic of Moldova 2014 - Census de facto complete tabulation|website=Data.un.org}}</ref><ref name="statistica.md2017"/><br />(without Transnistria) | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] '''*''' | |||
| | align="right" | 1,886,566 | |||
| | align="right" | 65.41 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,303,916 | |||
| | align="right" | 64.56 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,525,687 | |||
| | align="right" | 63.95 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,794,749 | |||
| | align="right" | 64.47 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,564,849 | |||
| | align="right" | 76.12 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,068,058 | |||
| | align="right" | 75.07 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] '''*''' | |||
| | align="right" | 1,663 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.06 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,581 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.04 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,657 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.04 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,477 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.06 | |||
| | align="right" | 73,276 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.17 | |||
| | align="right" | 192,800 | |||
| | align="right" | 7.00 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 420,820 | |||
| | align="right" | 14.59 | |||
| | align="right" | 506,560 | |||
| | align="right" | 14.19 | |||
| | align="right" | 560,679 | |||
| | align="right" | 14.20 | |||
| | align="right" | 600,366 | |||
| | align="right" | 13.85 | |||
| | align="right" | 282,406 | |||
| | align="right" | 8.38 | |||
| | align="right" | 181,035 | |||
| | align="right" | 6.57 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 95,856 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.32 | |||
| | align="right" | 124,902 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.50 | |||
| | align="right" | 138,000 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.49 | |||
| | align="right" | 153,458 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.54 | |||
| | align="right" | 147,500 | |||
| | align="right" | 4.38 | |||
| | align="right" | 126,010 | |||
| | align="right" | 4.57 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 292,930 | |||
| | align="right" | 10.16 | |||
| | align="right" | 414,444 | |||
| | align="right" | 11.61 | |||
| | align="right" | 505,730 | |||
| | align="right" | 12.81 | |||
| | align="right" | 562,069 | |||
| | align="right" | 12.97 | |||
| | align="right" | 201,218 | |||
| | align="right" | 5.97 | |||
| | align="right" | 111,726 | |||
| | align="right" | 4.06 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 61,652 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.14 | |||
| | align="right" | 73,776 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.07 | |||
| | align="right" | 80,665 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.04 | |||
| | align="right" | 88,419 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.04 | |||
| | align="right" | 65,662 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.95 | |||
| | align="right" | 51,867 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.88 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 7,265 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.25 | |||
| | align="right" | 9,235 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.26 | |||
| | align="right" | 10,666 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.27 | |||
| | align="right" | 11,571 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.27 | |||
| | align="right" | 12,271 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.36 | |||
| | align="right" | 9,323 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.34 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 5,977 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.21 | |||
| | align="right" | 10,327 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.29 | |||
| | align="right" | 13,874 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.35 | |||
| | align="right" | 19,608 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.45 | |||
| | align="right" | 5,059 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.15 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,828 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.10 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 95,107 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.30 | |||
| | align="right" | 98,072 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.75 | |||
| | align="right" | 80,124 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.03 | |||
| | align="right" | 65,836 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.52 | |||
| | align="right" | 3,628 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.11 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,597 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.06 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 4,783 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.17 | |||
| | align="right" | 4,899 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.14 | |||
| | align="right" | 4,961 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.13 | |||
| | align="right" | 4,739 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.11 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,383 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.07 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,404 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.05 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 3,843 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.13 | |||
| | align="right" | 9,399 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.26 | |||
| | align="right" | 11,374 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.29 | |||
| | align="right" | 7,335 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.17 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,616 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.05 | |||
| | align="right" | 914 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.03 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''Others'' | |||
| | align="right" | 7,947 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.28 | |||
| | align="right" | 11,734 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.33 | |||
| | align="right" | 16,049 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.41 | |||
| | align="right" | 24,590 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.57 | |||
| | align="right" | 9,444 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.28 | |||
| | align="right" | 7,157 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.26 | |||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="13" align="center"|'''*''' There is an ], in part involving linguisitic definition of ethnicity, over whether Moldovans' self-identification constitutes an ethnic group distinct and apart from Romanians, or a subset. | |||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="13" align="center"|'''**''' There were numerous allegations that the ethnic affiliation numbers were rigged: 7 out of 10 observer groups of the Council of Europe reported a significant number of cases where census-takers recommended respondents declare themselves Moldovans rather than Romanians. Complicating the interpretation of the results, 18.8% of respondents that identified themselves as Moldovans declared Romanian to be their native language.<ref>{{cite book |last=Protsyk |first=Oleh |others=Andrzej Marcin Suszycki, Ireneusz Pawel Karolewski |title=Nation and Nationalism. Political and Historical Studies |publisher=Oficyna Wydawnicza Atut Wrocawskie Wydawn. Oswiatowe |date=1 January 2007 |chapter=Nation-building in Moldova |isbn=978-83-7432-261-4 |url=http://www.policy.hu/protsyk/Publications/NationalisminMoldova.pdf}}</ref> | |||
| |} | |||
| === Diaspora and emigration === | |||
| According to the ] preliminary data, 2,998,235 inhabitants lived in Moldova (within the areas controlled by the central government), an 11.3% decrease from the figure recorded at the 2004 census. It is estimated that, as of 2022, 43.2% of the total population live in urban areas, and that the ] is 0.09%.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |work=The World Factbook | title=Moldova, geography |publisher=Central Intelligence Agency |date=12 June 2022 |access-date=12 June 2022 }}</ref> | |||
| {{Further|Moldovan diaspora}}{{See also|Emigration from Moldova}} | |||
| Emigration is a mass phenomenon in Moldova and has a major impact on the country's ] and economy. It is estimated that more than between 1.2 and 2 million Moldovan citizens (over 25% of the population) are living and working abroad.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Bunguri |first=Ernest |date=15 November 2020 |title=Moldova: How the diaspora keeps Europe's poorest nation afloat |url=https://www.euronews.com/2020/11/15/moldova-how-the-diaspora-of-europe-s-poorest-nation-keeps-its-economy-afloat |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180405/https://www.euronews.com/2020/11/15/moldova-how-the-diaspora-of-europe-s-poorest-nation-keeps-its-economy-afloat |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=17 May 2023 |title=Moldova: unleashing diaspora potential |url=https://www.mieux-initiative.eu/en/news-events/news/313-moldova-unlocking-diaspora-potential#:~:text=Furthermore%2C%20Moldova%20has%20some%20of,high%20priority%20for%20the%20government. |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=Mieux Initiative |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802105259/https://www.mieux-initiative.eu/en/news-events/news/313-moldova-unlocking-diaspora-potential#:~:text=Furthermore%2C%20Moldova%20has%20some%20of,high%20priority%20for%20the%20government. |url-status=dead }}</ref> The Moldovan economy is still heavily reliant on their remittance payments. Moldovans are found across the ] region, Western Europe, and North America. Among the most notable Moldovan ] populations are: 285,000 in ] (2020), 258,600 in ] (2002) 156,400 in Russia (2010), 188,923 in Italy (2019), 122,000 in Germany (2022), 26,300 in France (2019), and 20,470 in Canada (2021). | |||
| Current trends indicate that the population of Moldova will continue to fall with emigration remaining both chronic and higher than immigration or natural birth rates. In 2020, net emigration fell to a low of 7,000 {{Clarify|reason=Shouldn't there be some mention of the impact of the worldwide pandemic in 2020 on emigration numbers?|date=January 2025}}, but by 2022, 43,000 more people left the country than came, though this is slightly down from net emigration of 45,000 in 2021. ] of neighbouring Ukraine and the economic impact on Moldova may have been a key contributing factor in the rise from 2020 to 2022. However, there are indications that the invasion of Ukraine and the country's moves towards ] may have led to a rise in the number of Moldovan emigrants returning to their country of birth, seeking to help the country join the EU.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Ceapai |first1=Alla |last2=Jankowiak |first2=Celine |date=31 May 2023 |title=Returning Young Moldovan Diaspora Powers EU Membership Dream |url=https://www.barrons.com/news/returning-young-moldovan-diaspora-powers-eu-membership-dream-ac5f9935 |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180409/https://www.barrons.com/news/returning-young-moldovan-diaspora-powers-eu-membership-dream-ac5f9935 |url-status=live }}</ref> The Moldovan diaspora also had significant influence on recent Moldovan elections, voting overwhelmingly for ] as president in ] and for her ] in the ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Wemer |first=David |date=4 December 2020 |title=Moldova's diaspora flexes its political muscles |url=https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/moldovas-diaspora-flexes-its-political-muscles/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180406/https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/moldovas-diaspora-flexes-its-political-muscles/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| === Religion === | |||
| According to the last census in Transnistria (October 2015), the population of the region was 475,373, a 14.47% decrease from the figure recorded at the 2004 census. The ] rate was 69.9%. By ethnic composition, the population of Transnistria was distributed as follows: Russians - 29.1%, Moldovans - 28.6%, Ukrainians - 22.9%, Bulgarians - 2.4%, Gagauzians - 1.1%, Belarusians - 0.5%, Transnistrian - 0.2%, other nationalities - 1.4%. About 14% of the population did not declare their nationality. Also, for the first time, the population had the option to identify as "Transnistrian".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://newspmr.com/novosti-pmr/obshhestvo/15927|script-title=ru:Перепись населения ПМР|trans-title=Population census of PMR|language=ru|website=newspmr.com|date=9 March 2017|access-date=23 January 2021}}</ref> | |||
| {{Further|Religion in Moldova}} | |||
| ]. ].]] | |||
| Moldova's constitution provides for freedom of religion and complete separation of church and state, though the constitution cites the "exceptional importance" of ].<ref name="United States Department of State-2">{{Cite web |title=2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Moldova |url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/moldova/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803190415/https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> ] on the basis of religious affiliation is illegal, and ] was made illegal in May 2022.<ref name="United States Department of State-2" /> Religion in Moldova is dominated by the ] branch of Christianity. According to the 2014 Moldovan census, 90% of the country reported to be of the Eastern Orthodox Christian faith.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2 August 2013 |title=Population and Housing Census in the Republic of Moldova, May 12–25, 2014 |url=https://statistica.gov.md/en/population-and-housing-census-in-2014-122.html |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=17 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230917105214/https://statistica.gov.md/en/population-and-housing-census-in-2014-122.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Of this number, approx. 80–90% of Orthodox Moldovans belong to the Moldovan Orthodox Church (formally known as ]) which is subordinate to the ], and has played a powerful role in deepening Russia's influence in Moldova.<ref name="United States Department of State-2" /><ref>{{Cite web |last=Luchenko |first=Ksenia |date=31 January 2023 |title=Why the Russian Orthodox Church Supports the War in Ukraine |url=https://carnegieendowment.org/politika/88916 |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |archive-date=15 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230815200635/https://carnegieendowment.org/politika/88916 |url-status=live }}</ref> The remaining 10–20% of Orthodox Moldovans belong to the ], which is subordinate to the ].<ref name="United States Department of State-2" /> | |||
| Of the non-Orthodox population of Moldova, the ] estimates that {{as of|2022|lc=y}}, approx. 7% identify with no religion; ], ], and ] number between 15,000 and 30,000 each; the ] organisation estimates the Jewish population to be approx. 20,000; and the Islamic League of Moldova (an NGO recognised by the ] in 2011 as representing ]<ref>{{Cite news |date=28 April 2011 |title=Moldovan Muslim Leader 'Disappointed' By Anti-Islamic Remarks |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/moldovan_muslims_orthodox_church/16797096.html |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=10 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160310182825/http://www.rferl.org/content/moldovan_muslims_orthodox_church/16797096.html |url-status=live }}</ref>) estimates the number of Muslims to be approx. 15,000–17,000.<ref name="United States Department of State-2" /> There are six ] in ], one in ], one in ], and one in ], and one mosque in ]. The remaining less than 5% of the Moldovan population are ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="United States Department of State-2" /> The ] estimate that 80% of the population belong to the Moldovan Orthodox Church.<ref name="United States Department of State-2" /> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |+ | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| | colspan="5" align="center"|'''Population of ] according to ethnic group (Censuses 2004–2015)''' | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | Ethnic group | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2004<ref>{{cite web|last=Bespyatov|first=Tim|url=http://pop-stat.mashke.org/pmr-ethnic-loc2004.htm|title=Ethnic composition of Transnistria 2004|website=pop-stat.mashke.org|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2015<ref>{{cite web|format=ZIP|url=http://mer.gospmr.org/assets/files/zip/gss-pmr/doklad-byull.ezhegod/ezhegodnik-2017.zip|script-title=ru:Статистический ежегодник 2017|trans-title=Statistical Yearbook 2017|language=ru|website=Official Site of the Transnistrian Moldavian Republic|date=2017|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 168,678 | |||
| | align="right" | 30.37 | |||
| | align="right" | 161,300 | |||
| | align="right" | 34.0 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 177,382 | |||
| | align="right" | 31.94 | |||
| | align="right" | 156,600 | |||
| | align="right" | 33.0 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 160,069 | |||
| | align="right" | 28.82 | |||
| | align="right" | 126,700 | |||
| | align="right" | 26.7 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 13,858 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.50 | |||
| | align="right" | 13,300 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.8 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 4,096 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.74 | |||
| | align="right" | 5,700 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.2 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 3,811 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.69 | |||
| | align="right" | 2,800 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.6 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 2,071 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.37 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,400 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.3 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 1,791 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.32 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,000 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.2 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 1,259 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.23 | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 507 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.09 | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| |- | |||
| | Others | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| | align="right" | 5,700 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.2 | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! align="left" | Total | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 555,347 | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 474,500 | |||
| |} | |||
| === |
=== Health and fertility === | ||
| {{Further|Health in Moldova|Healthcare in Moldova}}{{Pie chart|value1=58|value2=15.8|value3=13.9|value4=7.5|value5=4.8|label1=]|label2=]|label3=Other causes|label4=]|label5=External causes|caption=Structure of deaths by major classes of causes of death in 2022}}Moldova provides ] through a ] scheme. According to the most recent 2022 official data, per 10,000 inhabitants there are 48.4 doctors and 91 units of average medical staff.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> Approx. 53% of those aged 16 and over in urban areas described their own health as 'good' or 'very good', compared to approx. 33% of people of the same age in rural areas.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> The country has 86 hospitals, 1,524 ] and branches, 12,600 physicians, 23,687 ]al personnel, and 17,293 ]s. Moldova spends 6% of its annual GDP on health care, up from 4.9% in 2019. | |||
| {{main|Languages of Moldova|Moldovan language|Romanian language}} | |||
| The official language of Moldova is ], a ].<ref>{{cite web| url=http://constcourt.md/libview.php?l=en&idc=7&id=512&t=/Overview/Press-Service/News/The-text-of-the-Declaration-of-Independence-prevails-over-the-text-of-the-Constitution| title=The text of the Declaration of Independence prevails over the text of the Constitution| publisher=Constitutional Court of Moldova| date=5 December 2013| access-date=13 June 2014}}</ref> | |||
| As of 2022 the average life expectancy was 71.5 years (67.2 for males, and 75.7 for females), slightly lower than comparable countries such as ], ], ], and Ukraine. The number of elderly people (aged 60 years and over) per 100 inhabitants in Moldova has increased year-on-year. The ] per woman in 2022 was 1.69, a fall from 1.78 in 2019, and below the replacement rate of 2.1. There were 10.6 ] per 1,000 inhabitants in 2022, a drop from 12.2 in 2019, and 14.2 deaths per 1,000 inhabitants, an increase from 13.7 in 2019 but a significant fall from 17.5 in 2019. ] per 1,000 live-births was 9.0, a slight increase on 8.7 in 2020. | |||
| The 1991 ] names the official language Romanian.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.moldova-suverana.md/index.php?start_from=&ucat=7&subaction=showfull&id=1156426235&archive=1156767681&|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080205095219/http://www.moldova-suverana.md/index.php?start_from=&ucat=7&subaction=showfull&id=1156426235&archive=1156767681&|archive-date=5 February 2008|title=Declarația de independența a Republicii Moldova, Moldova Suverană|language=ro|publisher=Moldova-suverana.md|date=5 February 2008|access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author=Bill Fraser|url=http://ec.europa.eu/translation/language_aids/recognition/field_guide_main_languages_of_europe_en.pdf|title=A Field Guide to the Main Languages of Europe – Spot that language and how to tell them apart|publisher=European Commission|date=11 December 2006|access-date=9 October 2013|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070224120109/http://ec.europa.eu/translation/language_aids/recognition/field_guide_main_languages_of_europe_en.pdf|archive-date=24 February 2007}}</ref> The ] stated that the national language of the Republic of Moldova was ], and its writing is based on the ].<ref name="Constitution">{{Cite web|url=http://www.e-democracy.md/en/legislation/constitution/|title=ADEPT : Laws of the Republic of Moldova : The Constitution of the Republic of Moldova|website=www.e-democracy.md}}</ref> | |||
| The overall number of deaths in 2022 fell by 20.5% compared to 2021.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> According to the National Agency for Public Health, the major causes of death in 2022 were ] (58%), ]s (15.8%), ] (7.5%), external causes (4.8%), and other causes (13.9%).<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> More specifically, the leading causes of death in 2019 were ], strokes, ], ] of the liver, and trachea, bronchus, and lung cancers.<ref>{{Cite web |date=9 December 2020 |title=Republic of Moldova data {{!}} World Health Organization |url=https://data.who.int/countries/498 |access-date=6 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162056/https://data.who.int/countries/498 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| In 2013, the Constitutional Court of Moldova ruled that the name "Romanian", as used in the Declaration of Independence to identify the official language, prevails over the name "Moldovan", given in Article 13 of the Constitution.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://constcourt.md/download.php?file=cHVibGljL2NjZG9jL2hvdGFyaXJpL3JvLWhfMzZfMjAxM19yby5wZGY%3D|title=Hotărâre Nr. 36 din 05.12.2013 privind interpretarea articolului 13 alin. (1) din Constituție în corelație cu Preambulul Constituției și Declarația de Independență a Republicii Moldova (Sesizările nr. 8b/2013 și 41b/2013)|trans-title=Decision No. 36 of 5 December 2013 regarding the interpretation of article 13 para. (1) of the Constitution in correlation with the Preamble of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence of the Republic of Moldova (References no. 8b / 2013 and 41b / 2013)|language=ro|date=5 December 2013|access-date=1 September 2019|publisher=Constitutional Court of the Republic of Moldova|quote=124. Prin urmare, Curtea consideră că prevederea conținută în Declarația de Independență referitoare la limba română ca limbă de stat a Republicii Moldova prevalează asupra prevederii referitoare la limba moldovenească conținute în articolul 13 al Constituției Therefore, the Court considers that the provision contained in the Declaration of Independence regarding the Romanian language as the state language of the Republic of Moldova prevails over the provision regarding the Moldovan language contained in Article 13 of the Constitution]}}</ref> | |||
| On 19 December 2016, the Moldovan parliament approved raising the retirement age to 63 years<ref>{{cite web |last=CNBC |date=19 December 2016 |title=Europe's poorest nation passes IMF-backed retirement age increase |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2016/12/19/europes-poorest-nation-passes-imf-backed-retirement-age-increase.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170803132504/https://www.cnbc.com/2016/12/19/europes-poorest-nation-passes-imf-backed-retirement-age-increase.html |archive-date=3 August 2017 |access-date=3 August 2017 |website=Cnbc.com}}</ref> from the current level of 57 for women and 62 for men, a reform that is part of a 3-year-old assistance program agreed with the ]. The retirement age will be lifted gradually by a few months every year until it is fully in effect in 2028.<ref>{{Cite news |date=19 December 2016 |title=Moldovan MPs approve IMF-backed retirement age increase |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-moldova-pensions-idUSKBN1481PE |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180408/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-moldova-pensions-idUSKBN1481PE |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |+ | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| | colspan="12" align="center"|'''Languages usually spoken in Moldova (Censuses 1989–2014)''' | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| | rowspan="16" align="center"| {{multiple image |align=left |direction=vertical |image1=Rep.Moldova - Lingvistic (2014-2).jpg | width1=170 |caption1=Romanian language (Moldovan) by district (2014) |alt1= |image2=Rep.Moldova - Lingvistic (2014-4).jpg |width2=170 |caption2=Russian language by district (2014)}} | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | First <br />language | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 1989<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/census.php?cy=6|script-title=ru:№ 821 - 822: Переписи населения Российской Империи, СССР, 15 новых независимых государств: Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года|trans-title=No. 821 - 822: Population Censuses of the Russian Empire, USSR, 15 Newly Independent States: 1989 All-Union Population Census|language=ru|journal=Demoscope Weekly|issn=1726-2887|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2004<ref>{{cite web|format=XLS|url=http://statistica.gov.md/public/files/Recensamint/Recensamintul_populatiei/vol_1/8_Nation_Limba_vorbita__materna_ro.xls|title=Population Census 2004: Population by main nationalities, mother tongue and language usually spoken|website=]|date=2004|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref><br />(without Transnistria) | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2014<ref>{{cite web|format=XLS|url=http://statistica.gov.md/public/files/Recensamint/Recensamint_pop_2014/Rezultate/Tabele/Caracteristici_populatie_RPL_2014_rom_rus_eng.xls|title=Structure of population by language usually used for communication and age groups on 2014 census|website=National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova|date=2014|access-date=1 September 2019}}</ref><br />(without Transnistria) | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! Number | |||
| ! % | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] '''*''' | |||
| | align="right" | 2,687,793 | |||
| | align="right" | 62.00 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,988,540 | |||
| | align="right" | 59.02 | |||
| | align="right" | 1,486,570 | |||
| | align="right" | 54.65 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] '''*''' | |||
| | align="right" | 790 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.02 | |||
| | align="right" | 554,814 | |||
| | align="right" | 16.47 | |||
| | align="right" | 652,394 | |||
| | align="right" | 23.98 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 1,003,563 | |||
| | align="right" | 23.15 | |||
| | align="right" | 540,990 | |||
| | align="right" | 16.06 | |||
| | align="right" | 394,133 | |||
| | align="right" | 14.49 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | ''140,000'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''3.2'' | |||
| | align="right" | 104,890 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.11 | |||
| | align="right" | 74,167 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.73 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | ''370,000'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''8.5'' | |||
| | align="right" | 130,114 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.86 | |||
| | align="right" | 73,802 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.71 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | ''70,000'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''1.6'' | |||
| | align="right" | 38,565 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.14 | |||
| | align="right" | 26,577 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.98 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | ''9,500'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''0.2'' | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| | align="right" | 5,764 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.21 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | ''17,000'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''0.4'' | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | ''2,300'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''0.05'' | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center" | - | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''Other languages'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''38,000'' | |||
| | align="right" | ''0.9'' | |||
| | align="right" | 11,318 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.34 | |||
| | align="right" | 6,970 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.26 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''Unspecified'' | |||
| | colspan="4" align="center" | - | |||
| | align="right" | 193,434 | |||
| | align="right" | 6.45 | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! align="left" | Total | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 4,335,360 | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 3,383,332 | |||
| ! colspan="2" | 2,998,235 | |||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="7" align="center"|* ''Moldovan language'' is one of the names used in the Republic of Moldova for the ''Romanian language''. | |||
| |} | |||
| === Education === | |||
| At the ] (which did not include data from the ]), 54.7% of the population named Moldovan whereas 24.0% named Romanian as their first language in daily use. Although only 4.1% are ethnic Russians, Russian is still used as the main language by 14.5% of the total population. Around 50% of ethnic Ukrainians, 33% of Gagauz, 33% of Bulgarians, and 5.7% of Moldovans declared Russian as their daily use language. | |||
| As of the academic year 2022/23, Moldova had 1,218 primary and secondary schools, 90 vocational schools, and 21 higher education institutions, as well as 12 ] higher education institutions.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /><ref>{{Cite web |title=Studying in Moldova |url=https://moldova-consulate.km.ua/en/about-moldova/studying-in-moldova/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=Honorary Consulate of the Republic of Moldova in Khmelnytsky |language=en-GB |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802102942/https://moldova-consulate.km.ua/en/about-moldova/studying-in-moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> There were a total of 437,000 pupils and students. {{as of|2015|lc=n}}, ] allocates 5,000 scholarships in high schools and universities for Moldovan students.<ref>{{cite web |date=22 June 2015 |title=România oferă tinerilor moldoveni 5.000 de burse în licee și universități |url=http://www.publika.md/romania-ofera-tinerilor-moldoveni-5000-de-burse-in-licee-si-universitati-_2337811.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150708164835/http://www.publika.md/romania-ofera-tinerilor-moldoveni-5000-de-burse-in-licee-si-universitati-_2337811.html |archive-date=8 July 2015 |access-date=7 July 2015 |work=PUBLIKA.MD |language=ro}}</ref> Likewise, more than half of preschool children in Moldova benefit from Romania funded program to renovate and equip ]s.<ref>{{cite web |date=7 July 2015 |title=Presedintele Klaus Iohannis l-a primit, la Suceava, pe Nicolae Timofti: "Republica Moldova isi poate implini destinul doar in Uniunea Europeana. Combaterea coruptiei, stabilitatea economica si intarirea institutiilor, singura cale catre succes" |url=http://www.hotnews.ro/stiri-esential-20282257-presedintele-klaus-iohannis-primit-suceava-nicolae-timofti.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150708175341/http://www.hotnews.ro/stiri-esential-20282257-presedintele-klaus-iohannis-primit-suceava-nicolae-timofti.htm |archive-date=8 July 2015 |access-date=7 July 2015 |work=HotNews.ro |language=ro}}</ref> Almost all the population is literate: the ] of the population aged 15 and over is estimated at 99.6%.<ref>{{Citation |title=Moldova – The World Factbook |date=31 July 2023 |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |work=] |access-date=3 August 2023 |publisher=] |language=en |archive-date=5 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210105015457/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ].]] | |||
| The main higher education institutions in Moldova are the ] (est. 1946) and the ] (est. 1961), both of which are located in ]. The ] (est. 1991) has featured on the ] and has educated a number of national leaders including current ] ] and leader of the opposition ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=21 October 2021 |title=Academy of Economic Studies of Moldova |url=https://www.timeshighereducation.com/world-university-rankings/academy-economic-studies-moldova |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=Times Higher Education (THE) |language=en}}</ref> Other important universities include the ] (est. 1940), ] (est. 1945), and the ] (est. 1964). Women account for 59.1% of students in higher education, and 70.1% of all foreign students in ] in Moldova. 32.3% of employed women in Moldova have received higher education, compared to 24.5% of men, and 16.9% specialised secondary education compared to 11.3% of men.<ref name="National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova" /> | |||
| === Regional differences and tensions === | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| {{See also|Transnistria conflict|Gagauzia|Unification of Moldova and Romania}} | |||
| |+ | |||
| ]]] | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! rowspan="2" | Rep. Moldova | |||
| ! colspan="2" | Native language | |||
| ! colspan="2" | Language of first use | |||
| |-bgcolor="#e0e0e0" | |||
| ! 2004 <br /> % | |||
| ! 2014 <br /> % | |||
| ! 2004 <br /> % | |||
| ! 2014 <br /> % | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 76.82 | |||
| | align="right" | 80.20 | |||
| | align="right" | 75.49 | |||
| | align="right" | 78.63 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 11.30 | |||
| | align="right" | 9.68 | |||
| | align="right" | 16.06 | |||
| | align="right" | 14.49 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 4.09 | |||
| | align="right" | 4.21 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.11 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.73 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 5.53 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.94 | |||
| | align="right" | 3.86 | |||
| | align="right" | 2.71 | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | align="right" | 1.61 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.53 | |||
| | align="right" | 1.14 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.98 | |||
| |- | |||
| | Other languages | |||
| | align="right" | 0.64 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.45 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.34 | |||
| | align="right" | 0.47 | |||
| |} | |||
| Since independence, Moldova characterised by a substantial range of profound regional differences across its internationally recognised territory. Since ], the country has struggled with issues of national identity, geopolitical strategy, and alliances, often torn between ] and the ] to the west and the ] to the east. Most notably, in eastern Moldova is the unrecognised breakaway state of ], which lies on the eastern bank of the ] river and borders ], which has pursued close diplomatic, military, and economic ties with Russia ], with more than a thousand Russian soldiers stationed in the region. This has proved particularly difficult following ] in 2022, as Transnistria's position on Ukraine's south-western flank and its hosting of more than a thousand Russian soldiers poses a potential threat to Ukraine's war efforts. The European Union's ] ] has confirmed that the pathway to accession does not depend upon a resolution of the ].<ref name="RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty"/> | |||
| Historically Russian was taught in schools as the first foreign language, because of the relationship with the Russian Empire and Soviet Union. In the 21st century, the primary foreign language taught in the schools is English. In 2013 more than 60% of schoolchildren took it as their first foreign language. This was followed by ], taken by less than 50% of students. Since 1996, the Republic of Moldova has been a full member of ]. ] was the third-ranked choice.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.moldova.org/english-the-most-preferred-foreign-language-among-moldovan-students-234764-eng/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140307214348/http://www.moldova.org/english-the-most-preferred-foreign-language-among-moldovan-students-234764-eng/|archive-date=7 March 2014 |title=English – the most preferred foreign language among Moldovan students |publisher=Moldova.org |access-date=7 March 2014}}</ref> | |||
| There is further the issue of the ] of ]. The ] are a ] people spread between southern Moldova and the south-west of Ukraine. While their exact origin is considered obscure, they have a strong sense of ethnic identity distinct from that of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine, with a ] and cultural traditions. They are nevertheless a heavily ] group.<ref name="Harrington-2023" /> Support for integration with Romania and the European Union is substantially lower among Gagauzians than among the broader Moldovan population. In 2014, shortly before the Republic of Moldova signed its EU Association Agreement, nearly 99 per cent of Gagauzians voted in a referendum "to reject closer links with Europe in favour of joining the Russian-led Eurasian Economic Union."<ref name="Harrington-2022">{{Cite news |last=Harrington |first=Keith |date=19 August 2022 |title=On 'Republic' Anniversary, Moldova's Gagauz Look to Moscow, and Chisinau |work=] |url=https://balkaninsight.com/2022/08/19/on-republic-anniversary-moldovas-gagauz-look-to-moscow-and-chisinau/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=6 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231106183510/https://balkaninsight.com/2022/08/19/on-republic-anniversary-moldovas-gagauz-look-to-moscow-and-chisinau/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2015, "just over half of Gagauzians voted for the Russian-backed socialist candidate ] as governor."<ref name="Harrington-2022" /> Gagauzia continues to represent a serious challenge both to Moldova's territorial sovereignty and political stability due to Russia's systemic involvement in the region, especially by backing pro-Russian local parties and leadership candidates.<ref name="Harrington-2023">{{Cite web |last=Harrington |first=Keith |date=6 April 2023 |title=ECMI Minorities Blog. Gagauzia's Response to Russia's Invasion of Ukraine |url=https://www.ecmi.de/infochannel/detail/gagauzias-response-to-russias-invasion-of-ukraine |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Chapple |first=Amos |date=24 March 2023 |title=In Moldova's Pro-Russian Gagauzia Region, Old Loyalties Die Hard |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/gagauzia-moldova-war-russia-ukraine/32329617.html |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=2 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802232122/https://www.rferl.org/a/gagauzia-moldova-war-russia-ukraine/32329617.html |url-status=live }}</ref> The ] has also highlighted the role of supposedly-neutral NGO groups in Gagauzia as a new front in Russia's ] against both Moldova and Ukraine.<ref name="Harrington-2023" /> The region's current local leader, ], in July 2023 thanked the fugitive Moldovan ] ], leader of the outlawed Moldovan pro-Russian opposition ], for his personal and financial support and his "willingness to do what it takes so that we may fulfil our election promises", and expressed a desire for deeper diplomatic ties with Russia.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Tanas |first=Alexander |date=20 July 2023 |title=New head of Moldovan region thanks exiled patron, backs Russia ties |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/new-leader-moldovan-region-thanks-exiled-patron-backs-ties-with-russia-2023-07-20/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803194444/https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/new-leader-moldovan-region-thanks-exiled-patron-backs-ties-with-russia-2023-07-20/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| There is also ] over ethnic and linguistic identity in Moldova concerning whether the ] and ] constitute separate linguistic and ethnic groups to the ] and Romanian people. The possibility of the ] has remained a popular topic in both countries since Moldova's independence in 1991. Romania and Moldova enjoy exceptionally strong ]. Romania supports Moldova's rapid accession to the European Union, provides vast economic assistance to Moldova's struggling economy, and provided up to 90% of Moldova's energy needs via discounted capped prices as Moldova sought to reduce its reliance on Russian oil and natural gas.<ref>{{Cite news |date=21 November 2022 |title=Romania provides 80%–90% of Moldova's energy needs- minister |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/romania-provides-80-90-moldovas-energy-needs-minister-2022-11-21/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180408/https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/romania-provides-80-90-moldovas-energy-needs-minister-2022-11-21/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Spaic-Kovacic |first=David |date=21 June 2023 |title=Romania supports Moldova's EU accession talks, expects 2023 start |url=https://www.euractiv.com/section/politics/news/romania-supports-moldovas-eu-accession-talks-expects-2023-start/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=] |language=en-GB |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180409/https://www.euractiv.com/section/politics/news/romania-supports-moldovas-eu-accession-talks-expects-2023-start/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Relations have strengthened further since Russia's invasion of Ukraine.<ref>{{Cite news |date=1 March 2023 |title=Moldova and Romania vow to boost ties amid war in Ukraine |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldova-romania-vow-boost-ties-amid-war-ukraine-2023-03-01/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705105229/https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/moldova-romania-vow-boost-ties-amid-war-ukraine-2023-03-01/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Up to 74% of the Romanian public and more than 40% of the Moldovan public would support Moldova being integrated into Romania in one form or another, though most in either country believe that 'now is not the right time'.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Sánchez |first=Wilder Alejandro |date=12 February 2023 |title=Opinion – Moldova and Romania's Unification is Not on the Horizon |url=https://www.e-ir.info/2023/02/12/opinion-moldova-and-romanias-unification-is-not-on-the-horizon/ |access-date=3 August 2023 |website=E-International Relations |language=en-US |archive-date=3 August 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803180406/https://www.e-ir.info/2023/02/12/opinion-moldova-and-romanias-unification-is-not-on-the-horizon/ |url-status=live }}</ref> A 2022 survey during the ] indicated that only 11% of Romania's population supports an immediate union, while over 42% think it is not the moment.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Nahoi |first1=Ovidiu |date=24 March 2022 |title=Sondaj: patriotismul românilor în context de război |language=ro |work=RFI România: Actualitate, informaţii, ştiri în direct |url=https://www.rfi.ro/social-143799-sondaj-patriotism-romani-context-razboi |access-date=28 March 2022 |archive-date=27 March 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220327101445/https://www.rfi.ro/social-143799-sondaj-patriotism-romani-context-razboi |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| {{bar box |float=right |title=Religion in Moldova |titlebar=#ddd | |||
| |left1 = Religion | |||
| |right1 = Percent | |||
| |bars = | |||
| {{bar percent|]|purple|93.34}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|blue|1.89}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|green|0.15}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|yellow|0.14}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|teal|0.11}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|orange|0.38}} | |||
| {{bar percent|]|red|0.98}} | |||
| {{bar percent|No answer|grey|2.24}} | |||
| {{bar percent|Other religion|black|0.88}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{main|Religion in Moldova}} | |||
| ] church in ].]] | |||
| The ] (the Moldovan Orthodox Church), autonomous and subordinated to the ], and the ] (the Bessarabian Orthodox Church), autonomous and subordinated to the ], both claim to be the national church of the country.<ref>{{cite journal |title= DN Carnevale - A Context-Grounded Approach to Religious Freedom: The Case of Orthodoxy in the Moldovan Republic |journal=Religions |date=May 2019 |volume=10 |issue=5 |page=314 |doi=10.3390/rel10050314 |doi-access=free |last1=Carnevale |first1=Davide N. }}</ref> For the 2004 census, ], who make up 93.3% of Moldova's population, were not required to declare the particular of the two main churches they belong to. As of 2020, the U.S. ] estimated that 90% of the Orthodox adherents belong to the Moldovan Orthodox Church.<ref>{{cite web |title=2020 Report on International Religious Freedom: Moldova |url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2020-report-on-international-religious-freedom/moldova/ |website=United States Department of State |publisher=Department of State |access-date=12 July 2021}}</ref> More than 2.0% of the population is Protestant including a growing number of Jehovah's Witnesses, 0.9% belongs to other religions, 1.0% is non-religious, 0.4% is atheist, and 2.2% did not answer the religion question at the census. | |||
| ===Education=== | |||
| {{main|Education in Moldova}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| There are 16 state and 15<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ond.vlaanderen.be/hogeronderwijs/bologna/links/National-reports-2007/National_Report_moldova2007.pdf |title=Bologna Process Template for National Reports: 2005–2007 (Moldova) |last=Moldovanu-Batrinac |first=Viorelia |date=18 December 2006 |work=] website |publisher=] |page=3 |access-date=2 July 2010}}</ref> private institutions of ] in Moldova, with a total of 126,100 students, including 104,300 in the state institutions and 21,700 in the private ones. The number of students per 10,000 inhabitants in Moldova has been constantly growing since the collapse of the Soviet Union, reaching 217 in 2000–2001, and 351 in 2005–2006. | |||
| The ] was founded in 1832. The ] and the ], the main scientific organizations of Moldova, were established in 1946. The Republic of Moldova was ranked 64th in the ] in 2021, down from 58th in 2019.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Innovation Index 2021 |url=https://www.wipo.int/global_innovation_index/en/2021/|work=]|publisher=]|access-date=5 March 2022 |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Global Innovation Index 2019|url=https://www.wipo.int/global_innovation_index/en/2019/index.html|access-date=2 September 2021|website=www.wipo.int|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=RTD - Item|url=https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/rtd/items/691898|access-date=2 September 2021|website=ec.europa.eu}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=28 October 2013|title=Global Innovation Index|url=https://knowledge.insead.edu/entrepreneurship-innovation/global-innovation-index-2930|access-date=2 September 2021|website=INSEAD Knowledge|language=en|archive-date=2 September 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210902101622/https://knowledge.insead.edu/entrepreneurship-innovation/global-innovation-index-2930|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| {{As of|2015}}, Romania allocates 5,000 scholarships in high schools and universities for Moldovan students.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.publika.md/romania-ofera-tinerilor-moldoveni-5000-de-burse-in-licee-si-universitati-_2337811.html |title=România oferă tinerilor moldoveni 5.000 de burse în licee și universități |work=PUBLIKA.MD |date=22 June 2015 |language=ro}}</ref> Likewise, more than half of preschool children in Moldova benefit from Romania funded program to renovate and equip ]s.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.hotnews.ro/stiri-esential-20282257-presedintele-klaus-iohannis-primit-suceava-nicolae-timofti.htm |title=Presedintele Klaus Iohannis l-a primit, la Suceava, pe Nicolae Timofti: "Republica Moldova isi poate implini destinul doar in Uniunea Europeana. Combaterea coruptiei, stabilitatea economica si intarirea institutiilor, singura cale catre succes" |work=HotNews.ro |date=7 July 2015 |language=ro}}</ref> Almost all the population is literate: the ] of the population aged 15 and over is estimated at 99.4% ({{As of|2015|lc=y}}).<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2103.html |title=The World Factbook |publisher=Cia.gov |date=2 September 2015 |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=24 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161124171442/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2103.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Crime=== | |||
| {{main|Crime in Moldova|2014 Moldovan bank fraud scandal}} | |||
| The ] lists widespread ] and underground economic activity among major issues in Moldova.<ref name="CIA_World_Factbook_Moldova"/> ] of Moldovan women and children to other parts of Europe is a serious problem.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.havocscope.com/women-victims-from-moldova-from-1991-through-2008/ |title=Women Victims from Moldova From 1991 through 2008 |publisher=Havocscope.com |access-date=4 November 2013}}</ref><ref>A ] report states: In terms of the citation index, eleven countries score '''very high''' as countries of origin. The countries are | |||
| (listed in alphabetical order, by sub-region): Belarus, the '''Republic of Moldova''', the Russian Federation and Ukraine (Commonwealth of Independent States); Albania, Bulgaria, Lithuania and Romania (Central and South Eastern Europe); China (Eastern Asia); Thailand (South-Eastern Asia); and Nigeria (Western Africa).(pg 58).</ref> | |||
| In 2014, US$1 billion disappeared from three of Moldova's leading banks.<ref name=bbc18615>"". ]. 18 June 2015.</ref> In two days, loans worth US$1 billion were transferred in to United Kingdom and ]-registered companies whose ultimate owners are unknown.<ref name=bbc18615/><ref>"". ]. 7 October 2015.</ref> Banks are administered by the ], so this loss was covered from state reserves.<ref name=bbc18615/> | |||
| ===Health and fertility=== | |||
| {{main|Health in Moldova}} | |||
| The ] (TFR) in Moldova was estimated in 2015 at 1.56 children/woman,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications//the-world-factbook/rankorder/2127rank.html|title=Country Comparison: Total Fertility Rate|publisher=cia.gov|date=2015|access-date=13 September 2016|archive-date=27 August 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160827092600/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2127rank.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> which is below the replacement rate of 2.1. In 2012, the average age of women at first birth was 23.9 years, with 75.2% of births being to women under 30, and 22.4% of births being to unmarried women.<ref>{{cite web| author=Biroul Naţional de Statistică|url=http://www.statistica.md/newsview.php?l=ro&idc=168&id=4096 |title=Biroul Național de Statistică – Comunicate de presă - Situaţia copiilor în Republica Moldova |publisher=Statistica.md |date=31 May 2013 |access-date=4 November 2013}}</ref> The ] was 41 deaths/100,000 live births (in 2010)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2223rank.html |title=The World Factbook – Moldova, rank |publisher=Cia.gov |date=2 September 2015 |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=18 April 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150418113820/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2223rank.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> and the ] was 12.59 deaths/1,000 live births (in 2015).<ref name="autogenerated4">{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |title=The World Factbook |publisher=Cia.gov |access-date=21 October 2013}}</ref> The ] in 2015 was estimated at 70.42 years (66.55 years male, 74.54 years female).<ref name="autogenerated4"/> | |||
| Public expenditure on health was 4.2% of the GDP and private expenditure on health 3.2%.<ref name="autogenerated1">{{cite web|url=http://hdrstats.undp.org/en/countries/data_sheets/cty_ds_MDA.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090429032404/http://hdrstats.undp.org/en/countries/data_sheets/cty_ds_MDA.html|archive-date=29 April 2009|title=Human Development Report 2009 – Moldova|publisher=Hdrstats.undp.org|access-date=7 October 2009}}</ref> There are about 264 physicians per 100,000 people.<ref name="autogenerated1"/> Health expenditure was US$138 (PPP) per capita in 2004.<ref name="autogenerated1"/> | |||
| Since the breakup of the Soviet Union, the country has seen a decrease in spending on health care and, as a result, the ] incidence rate in the country has grown.<ref name="autogenerated2">{{Cite web|url=https://pulitzercenter.org/stories/health-system-declined-tb-increased|title=As Health System Declined, TB Increased|website=Pulitzer Center|access-date=16 March 2021|archive-date=26 February 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210226040150/https://pulitzercenter.org/stories/health-system-declined-tb-increased|url-status=dead}}</ref> According to a 2009 study, Moldova was struggling with one of the highest incidence rates of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the world.<ref name="autogenerated3">{{Cite web|url=https://khn.org/morning-breakout/dr00058042/|title=Former Soviet Nations, China Face High MDR-TB Prevalence, Study Says|date=16 April 2009}}</ref> | |||
| The percentage of adults (aged 15–49) living with ] was estimated in 2009 at 0.40%.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2155rank.html |title=HIV/AIDS – Adult Prevalence Rate |publisher=Cia.gov |access-date=4 November 2013 |archive-date=21 December 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141221190412/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2155rank.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Emigration=== | |||
| {{main|Emigration from Moldova}} | |||
| Emigration is a mass phenomenon in Moldova and has a major impact on the country's ] and economy. The ] has estimated that 600,000 to one million Moldovan citizens (almost 25% of the population) are working abroad.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.outreachworld.org/Files/u_texas/Decision-Activity_Russia.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110514225142/http://www.outreachworld.org/Files/u_texas/Decision-Activity_Russia.pdf|archive-date=14 May 2011 |title=Understanding Migration, Emigration from Moldova |access-date=9 October 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| {{main|Culture of Moldova}} | {{main|Culture of Moldova}} | ||
| {{multiple image | {{multiple image | ||
| | align = right | |||
| | total_width = 300 | |||
| | image1 = Eminescu.jpg | |||
| | alt1 = Eminescu | |||
| | caption1 = ], the national poet of Moldova and Romania | |||
| | image2 = Dimitrie Cantemir - portrait from Descriptio Moldaviae, 1716.jpg | |||
| | alt2 = Cantemir | |||
| | caption2 = ], Moldavian scholar of the early Enlightenment | |||
| }} | |||
| Moldova's cultural tradition has been influenced primarily by the ] of its majority population, the roots of which go back to the second century AD, the period of ] colonization in ].<ref name="culture">{{cite web|url=http://countrystudies.us/moldova/18.htm|title=Moldova – Culture|website=Countrystudies.us|access-date=27 July 2018|archive-date=14 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171014093821/http://countrystudies.us/moldova/18.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> Located geographically at the crossroads of ], ] and other cultures, Moldova has enriched its own culture adopting and maintaining traditions of neighbouring regions and of other influential sources.<ref>{{cite web |author=Octavian Sofransky |url=http://www.bundesheer.at/pdf_pool/publikationen/wg3-sofransky.pdf |title=Ethno-Political Conflict in Moldova |publisher=European Centre in Moldova |access-date=2 September 2015 |archive-date=23 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923195357/http://www.bundesheer.at/pdf_pool/publikationen/wg3-sofransky.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> The largest ethnic group, which had come to identify itself widely as "Moldovan" by the 14th century, played a significant role in the shaping of ]. The culture has been also influenced by the ] culture, the neighbouring Magyar and Slavic populations, and later by the Ottoman Turks. A strong Western European influence in Moldovan literature and arts was prevalent in the 19th century. During the periods 1812–1917 and 1944–89, Moldovans were influenced by Russian and Soviet administrative control as well and by ethnic Russian immigration.<ref name="culture"/> | |||
| | image1 = Eminescu.jpg | |||
| | alt1 = Eminescu | |||
| | caption1 = ], the national poet of Moldova and Romania | |||
| | image2 =Dimitrie Cantemir - portrait from Descriptio Moldaviae, 1716.jpg | |||
| | alt2 = Cantemir | |||
| | caption2 = ], Moldavian scholar of the early Enlightenment | |||
| }} | |||
| Moldova's cultural tradition has been influenced primarily by the ] of its majority population, the roots of which go back to the second century AD, the period of ] colonization in ].<ref name="culture">{{cite web|url=http://countrystudies.us/moldova/18.htm|title=Moldova - Culture|website=Countrystudies.us|access-date=27 July 2018}}</ref> Located geographically at the crossroads of ], ] and other cultures, Moldova has enriched its own culture adopting and maintaining traditions of neighbouring regions and of other influential sources.<ref>{{cite web|author=Octavian Sofransky |url=http://www.bundesheer.at/pdf_pool/publikationen/wg3-sofransky.pdf |title=Ethno-Political Conflict in Moldova |publisher=European Centre in Moldova |access-date=2 September 2015}}</ref> The largest ethnic group, which had come to identify itself widely as "Moldovan" by the 14th century, played a significant role in the shaping of ]. The culture has been also influenced by the ] culture, the neighbouring Magyar and Slavic populations, and later by the Ottoman Turks. A strong Western European influence in Moldovan literature and arts was prevalent in the 19th century. During the periods 1812-1917 and 1944–89, Moldovans were influenced by Russian and Soviet administrative control as well and by ethnic Russian immigration.<ref name="culture"/> | |||
| ] in ]]] | ] in ]]] | ||
| The country's cultural heritage was marked by numerous churches and monasteries built by the Moldavian ruler ] in the 15th century, by the works of the later renaissance Metropolitans ] and ], and those of scholars such as ], ], ], ]{{efn|name=fn6|Prince ] was one of the most important figures of the Moldavian culture of the 18th century. He wrote the first geographical, ethnographic, and economic description of the country. {{in lang|la}} '']'', (Berlin, 1714), at Latin Wikisource.}} and ]. In the 19th century, Moldavians from the territories of the medieval Principality of ], divided into ], ], and ] (after 1859, Romania), made a significant contribution to the formation of the modern Romanian culture. Among these were many Bessarabians, such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]. | The country's cultural heritage was marked by numerous churches and monasteries built by the Moldavian ruler ] in the 15th century, by the works of the later renaissance Metropolitans ] and ], and those of scholars such as ], ], ], ]{{efn|name=fn6|Prince ] was one of the most important figures of the Moldavian culture of the 18th century. He wrote the first geographical, ethnographic, and economic description of the country. {{in lang|la}} '']'', (Berlin, 1714), ].}} and ]. In the 19th century, Moldavians from the territories of the medieval Principality of ], divided into ], ], and ] (after 1859, Romania), made a significant contribution to the formation of the modern Romanian culture. Among these were many Bessarabians, such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]. | ||
| ], a late ] poet, and ], a writer, are the most influential ] artists, considered national writers both in Romania and Moldova.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Catherine Lovatt|url=http://www.ce-review.org/00/3/lovatt3.html|title=2000: Year of Eminescu|journal=Central Europe Review|volume=2|issue=3|date=24 January 2000|access-date=10 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923201420/http://www.ce-review.org/00/3/lovatt3.html|archive-date=23 September 2015|url-status= |
], a late ] poet, and ], a writer, are the most influential ] artists, considered national writers both in Romania and Moldova.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Catherine Lovatt|url=http://www.ce-review.org/00/3/lovatt3.html|title=2000: Year of Eminescu|journal=Central Europe Review|volume=2|issue=3|date=24 January 2000|access-date=10 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923201420/http://www.ce-review.org/00/3/lovatt3.html|archive-date=23 September 2015|url-status=usurped}}</ref> | ||
| ===Cuisine=== | ===Cuisine=== | ||
| {{main|Moldovan cuisine}} | {{main|Moldovan cuisine}} | ||
| Moldova's fertile soil ('']'') produces plentiful ], ], vegetables, ], meat, and milk products, all of which have found their uses in the national cuisine. The fertile black soil combined with the use of traditional agricultural methods permits the growth of a wide range of foods in Moldova. Moldovan cuisine is similar to neighbouring ], ], and ], and the regions share many traditional dishes, often with regional variations. Moldovan cuisine has historically been particularly influenced by elements of ], ], and ]. Main dishes often include beef, pork, ], ], and a variety of ]. Popular alcoholic beverages are '']'' (Moldovan ]), beer, and ]—for which the country is known due to its high-quality offerings.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220912140913/https://www.sommeliers-international.com/en/breakaways-in-the-vineyards/wine-of-moldova|date=12 September 2022}} – Sommeliers International</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220912140908/https://vidawines.co.uk/moldovan-red-wines-the-best-red-wine-on-the-planet-you-have-never-heard-of/|date=12 September 2022}} – Vida Wines & Spirits</ref> | |||
| ] and ] porridge.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Moldovan cuisine is similar to neighbouring ], and has been influenced by elements of ], ], and ]. Main dishes include ], ], ], ], and a variety of ]. Popular alcoholic beverages are '']'' (Moldovan ]), ], and ]—of which the country is known for making high-quality offerings.<ref> – Sommeliers International</ref><ref> – Vida Wines & Spirits</ref> | |||
| There are several traditional Moldovan dishes. ] are stuffed and deep-fried pastries with fillings such as soft cheese (often ]), cabbage, potatoes, apples, sour cherries and others, both sweet and savoury.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Kieff |first=Leah |date=10 December 2015 |title=4 foods you must try in Moldova |url=https://www.peacecorps.gov/stories/4-foods-you-must-try-in-moldova/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163013/https://www.peacecorps.gov/stories/4-foods-you-must-try-in-moldova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> ] is a typical Moldovan dish usually consisting of cabbage leaves stuffed with rice, peppers, carrots, meat, and baked in oil. Regional variations can also be found in other former parts of the ]. ], a kind of ] made from yellow maize flour, is another staple. It is popular in other countries as ] and is often served with ] and ]. Another traditional dish, plachyndy, is a kind of flatbread often made with ] or ], wrapped around herbs, and pan-fried in oil.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Steafel |first=Eleanor |date=2 July 2021 |title=You need this easy flatbread recipe in your culinary arsenal |language=en-GB |work=The Telegraph |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/food-and-drink/features/need-easy-flatbread-recipe-culinary-arsenal/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |issn=0307-1235 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162852/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/food-and-drink/features/need-easy-flatbread-recipe-culinary-arsenal/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Zeamă is a thin chicken soup, typically consisting of homemade chicken broth prepared with a smaller whole chicken, water, thin homemade egg noodles (tăiței de casă), and a variety of finely chopped vegetables and herbs.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Zeama {{!}} Traditional Chicken Soup From Moldova {{!}} TasteAtlas |url=https://www.tasteatlas.com/zeama |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=www.tasteatlas.com |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162846/https://www.tasteatlas.com/zeama |url-status=live }}</ref> ] is a ] ]/] with a crumbly texture and tangy taste, mostly produced and popular in ], Romania, and Moldova, and often used in salads, pies, and dumplings.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Sikorsky |first=Dmytro |date=30 May 2016 |title=The Secret Of Bessarabia's Cuisine |url=http://odessareview.com/secret-bessarabias-cuisine/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=Odessa Review |language=en-US |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163012/http://odessareview.com/secret-bessarabias-cuisine/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ], a sour Eastern European soup made from beetroots, meat stock, and vegetables, is also popular and commonly served in Moldova. As with other parts of the region, ] (known as ''chiroște'' in Moldova) are another traditional staple and are often stuffed with a soft cheese in Moldova. The dough is made with ] and is boiled in salted water, pan-fried in oil, or baked in the oven.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Johnson |first=Doina |date=13 November 2019 |title=Moldovan Food – 14 Best Traditional Dishes as Recommended by a Local (with Recipes) – Nomad Paradise |url=https://nomadparadise.com/moldovan-food/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |language=en-US |archive-date=26 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200926041831/https://nomadparadise.com/moldovan-food/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=7 October 2009 |title=Hai la masa!: Coltunasi |url=https://kathrynannew.wordpress.com/2009/10/07/hai-la-masa-coltunasi/ |access-date=24 August 2016 |archive-date=16 March 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160316065912/https://kathrynannew.wordpress.com/2009/10/07/hai-la-masa-coltunasi/ |url-status=live }}</ref> ], a cake of Russian origin (and called Tort Smetanik in Moldova) is a popular layered cake with ] and ] (sour cream) or ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Goldstein |first1=Darra |title=The Oxford Companion to Sugar and Sweets |date=2015 |publisher=Oxford University Press}}</ref> | |||
| Traditional Moldovan dishes include ] (sweet and savoury pastries with fillings such as local cheese, cabbage, potatoes, apples, sour cherries and others), ], ], and a ] called zeamă. | |||
| Total recorded adult alcohol consumption is approximately evenly split between spirits, beer and wine. Notably, Moldova |
Total recorded adult alcohol consumption is approximately evenly split between spirits, beer, and wine. Notably, Moldova has among the highest alcohol consumption per capita in world, at {{convert|15.2|L|gal}} of pure alcohol imbibed in 2016.<ref>{{Cite magazine |title=How This Tiny European Country Got the World's Worst Drinking Problem |url=https://time.com/5654052/moldova-drinking-problem/ |url-status=live |magazine=Time |language=en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211221152612/https://time.com/5654052/moldova-drinking-problem/ |archive-date=21 December 2021 |access-date=21 December 2021}}</ref> This has fallen somewhat in recent years, but it remains a serious ongoing health concern.<ref>{{Cite web |date=30 June 2023 |title=Europeans are the world's heaviest drinkers: How do countries compare? |url=https://www.euronews.com/next/2023/06/30/so-long-dry-january-which-country-drinks-the-most-alcohol-in-europe |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=euronews |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162956/https://www.euronews.com/next/2023/06/30/so-long-dry-january-which-country-drinks-the-most-alcohol-in-europe |url-status=live }}</ref> | ||
| ===Holidays=== | === Holidays === | ||
| {{main|Public holidays in Moldova}} | {{main|Public holidays in Moldova}} | ||
| Most retail businesses close on |
Most retail businesses close on New Year's Day and ], but remain open on all other holidays. Christmas is celebrated either on 7 January, the traditional date in ] ]es, or on 25 December, with both dates being recognized as public holidays.<ref>{{cite news|title=Moldova Declares Western Christmas Day Official Holiday|newspaper=Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty |date=19 December 2013 |url=http://www.rferl.org/content/moldova-celebrates-western-christmas/25206410.html|access-date=20 December 2013|archive-date=19 December 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131219232059/http://www.rferl.org/content/moldova-celebrates-western-christmas/25206410.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | ||
| On 1 March features '']'' gifting, which is a tradition that females are gifted with a type of talisman that is given for good luck.<ref>{{Cite web|date=12 August 2014|title=Martisor, a Spring celebration for Eastern Europeans |
On 1 March features '']'' gifting, which is a tradition that females are gifted with a type of talisman that is given for good luck.<ref>{{Cite web|date=12 August 2014|title=Martisor, a Spring celebration for Eastern Europeans – FOREIGNERS IN UK|url=http://www.foreignersinuk.co.uk/community_news-community-martisor_a_spring_celebration_for_eastern_europeans_3823.html|access-date=29 August 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140812210746/http://www.foreignersinuk.co.uk/community_news-community-martisor_a_spring_celebration_for_eastern_europeans_3823.html|archive-date=12 August 2014}}</ref> | ||
| ===Music=== | ===Music=== | ||
| Line 1,133: | Line 564: | ||
| In the field of pop music, Moldova has produced the band ], who came to prominence in 2003, with their hit song "]", which topped multiple notable single charts. Moldova has been participating in the ] since 2005. Another popular band from Moldova is ] that represented the country in the ], finishing sixth, also in 2021, with a similar result. | In the field of pop music, Moldova has produced the band ], who came to prominence in 2003, with their hit song "]", which topped multiple notable single charts. Moldova has been participating in the ] since 2005. Another popular band from Moldova is ] that represented the country in the ], finishing sixth, also in 2021, with a similar result. | ||
| In May 2007, ] represented Moldova in Helsinki at the ] with her entry "]". Natalia squeezed into the final by a very small margin. She took tenth place with 109 points. | In May 2007, ] represented Moldova in Helsinki at the ] with her entry "]". Natalia squeezed into the final by a very small margin. She took tenth place with 109 points. | ||
| Then ] again represented Moldova in the ] finishing 12th. | Then ] again represented Moldova in the ] finishing 12th. | ||
| Line 1,144: | Line 575: | ||
| ===Media=== | ===Media=== | ||
| {{main|Media of Moldova|Television in Moldova|Cinema of Moldova|List of newspapers in Moldova}} | {{main|Media of Moldova|Television in Moldova|Cinema of Moldova|List of newspapers in Moldova}} | ||
| The right to ] and ] are guaranteed by the ]. ] improved Moldova's ] ranking to 28th in 2023 from 89th in 2020, partly due to government legal reforms which made it easier for journalists to access official information.<ref>{{Cite web |date=23 July 2020 |title=Moldova {{!}} RSF |url=https://rsf.org/en/country/moldova |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=5 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705135655/https://rsf.org/en/country/moldova |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Cojocari |first=Vitalie |title=Why Moldova is ahead of Romania in Media freedom |url=https://www.thomsonfoundation.org/latest/why-moldova-is-ahead-of-romania-in-media-freedom/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163121/https://www.thomsonfoundation.org/latest/why-moldova-is-ahead-of-romania-in-media-freedom/ |url-status=live }}</ref> However, they cautioned that "Moldova's media are diverse but extremely polarised, like the country itself, which is marked by political instability and excessive influence by oligarchs." Moldova's media are divided into pro-Russian and pro-Western camps and on party political lines.<ref name="BBC News-2022">{{Cite news |date=July 2022 |title=Moldova media guide |language=en-GB |work=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17602346 |access-date=7 July 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163031/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-17602346 |url-status=live }}</ref> Oligarchs and political leaders strongly influence their editorial stances. | |||
| In October 1939, '']'', a local station of the ], was the first radio station opened in Chișinău. Television in Moldova was ], within the framework of ]. Through cable, Moldovan viewers can receive a large number of ], a few ], and several ] versions of international channels in addition to several local channels.{{citation needed|date=June 2018}} One Russian and two local channels are aired.{{citation needed|date=June 2018}} Infotag is the state news agency. | |||
| Television remains the most popular and trusted medium, while online social media is exerting increasing influence. Most private ] rebroadcast output from Russian and Romanian stations.<ref name="BBC News-2022" /> The first ], ], has been broadcasting since 1939 from the capital city, Chişinău. ] is also widely available. Moldova's state-owned national radio-TV broadcaster is ] (TRM), which broadcasts the TV channel ]. | |||
| There were 3 million internet users by July 2022, approximately 76% of the population, and digital infrastructure is well-developed, with 98% ] coverage of territory. There are a number of daily and weekly newspapers published in Moldova, among the most popular being '']'' and ''],'' but print media has an overall small audience in Moldova''.'' ] are struggling to ensure financial sustainability in the face of diminishing advertisement revenues due to inflation, economic stagnation and uncertainty caused by Russia's invasion of Ukraine. | |||
| In 2022, the government removed the broadcasting licenses from six television stations for broadcasting ] and disinformation about ] in violation of the country's Audiovisual Services Code.<ref>{{Cite web |date=19 December 2022 |title=Six TV channels suspended amid 'misinformation' allegations |url=https://www.euronews.com/2022/12/19/six-tv-channels-suspended-in-moldova-amid-misinformation-allegations |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=euronews |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162747/https://www.euronews.com/2022/12/19/six-tv-channels-suspended-in-moldova-amid-misinformation-allegations |url-status=live }}</ref> The government stated that this was done in order to "prevent the risk of disinformation or attempts to manipulate public opinion".<ref>{{Cite web |date=17 December 2022 |title=Moldova suspends six channels over Ukraine 'disinformation' – DW – 12/17/2022 |url=https://www.dw.com/en/moldova-suspends-six-channels-over-ukraine-disinformation/a-64137437 |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=] |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162936/https://www.dw.com/en/moldova-suspends-six-channels-over-ukraine-disinformation/a-64137437 |url-status=live }}</ref> All six were either owned or affiliated with ], a fugitive pro-Russian politician and businessman who fled to Israel in 2019 after being convicted of fraud and money-laundering and sentenced to 15 years in prison ''in absentia''.<ref>{{Cite news |date=17 December 2022 |title=Moldovan Government Suspends Licenses Of Six TV Stations To 'Eliminate Propaganda' |language=en |work=] |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-ilan-shor-tv-stations-licenses-suspended-russia-war/32180842.html |access-date=7 July 2023 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162923/https://www.rferl.org/a/moldova-ilan-shor-tv-stations-licenses-suspended-russia-war/32180842.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In October 2023 Orizont TV, ITV, Prime, Publika TV, Canal 2 and Canal 3 were also banned for undermining the local elections as well as blocking a number of Russian media outlets which includes the news agencies TASS and Interfax.<ref>{{cite web |title=Moldova blocks more Russian media outlets |url=https://www.broadbandtvnews.com/2023/10/31/moldova-blocks-more-russian-media-outlets/ |date=31 October 2023 |access-date=7 June 2024 |archive-date=3 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231103191905/https://www.broadbandtvnews.com/2023/10/31/moldova-blocks-more-russian-media-outlets/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The ] developed in the 1960s during the Soviet period, nurturing a small but lively film industry.<ref name="Johnson-2018">{{Cite web |last=Johnson |first=Glen |date=5 August 2018 |title=Tiny Moldova was once a movie-making capital. A few diehards are trying to keep the tradition alive |url=https://www.latimes.com/world/europe/la-fg-moldova-film-20180805-story.html |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=] |language=en-US |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707161656/https://www.latimes.com/world/europe/la-fg-moldova-film-20180805-story.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Following the collapse of the Soviet Union and Moldova's independence, the country's economic stagnation and poverty has hampered the Moldovan film industry.<ref name="Johnson-2018" /><ref>{{Cite web |last=Clark |first=Marcus |date=8 November 2012 |title=Learn About Moldova's Brave Little Film Industry |url=https://theculturetrip.com/europe/moldova/articles/beyond-the-eastern-bloc-the-best-of-moldovan-film/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=Culture Trip |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163833/https://theculturetrip.com/europe/moldova/articles/beyond-the-eastern-bloc-the-best-of-moldovan-film/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Nevertheless, some films have seen some international success. Perhaps best-known are '']'' (1972), written and directed by Moldovan film-maker ], and '']'' (2009), which was co-produced by Romania, Moldova, and Luxembourg. In recent years Moldovan cinema has gained greater international attention. ''Carbon'' (2022), directed by Ion Borş, received positive acclaim by magazines such as Variety.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Vourlias |first=Christopher |date=15 June 2023 |title=Echoes of the Ukraine War Haunt the Moldovan Tragicomedy 'Carbon,' About a Post-Soviet Conflict Lost to History |url=https://variety.com/2023/film/global/urkaine-war-moldova-carbon-1235645182/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=Variety |language=en-US |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162900/https://variety.com/2023/film/global/urkaine-war-moldova-carbon-1235645182/ |url-status=live }}</ref> It was the winner of the ]'s Audience Award.<ref>{{Citation |title=Carbon |url=https://mubi.com/films/carbon-2022 |access-date=7 July 2023 |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707163008/https://mubi.com/films/carbon-2022 |url-status=live }}</ref> For the 37th edition of the ], Moldova was featured in its 'New Territory' section, which celebrates little-known film-making cultures.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Between irony and poetry: the Republic of Moldova at FIFF {{!}} Festival International de Films de Fribourg |url=https://www.fiff.ch/en/between-irony-and-poetry-republic-moldova-fiff |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=www.fiff.ch |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162742/https://www.fiff.ch/en/between-irony-and-poetry-republic-moldova-fiff |url-status=live }}</ref> In July 2022, the ] announced that it would be using state-of-the-art equipment to transfer more than 1,600 films from the ] archive for posterity and ]. The United States assisted by equipping in 2021 a ] laboratory to restore and preserve its archive feature and documentary films, representing an important part of Moldova's historical, cultural, and artistic heritage, and many of the films were broadcast on national TV with Romanian subtitles.<ref>{{Cite web |title=More than 1,600 films from Moldova Film archive will be digitized, with the support of the European Union and the U.S. Government {{!}} United Nations Development Programme |url=https://www.undp.org/moldova/press-releases/more-1600-films-moldova-film-archive-will-be-digitized-support-european-union-and-us-government |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=UNDP |language=en |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707180256/https://www.undp.org/moldova/press-releases/more-1600-films-moldova-film-archive-will-be-digitized-support-european-union-and-us-government |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Technical Difficulties |url=https://md.usembassy.gov/rediscovering-moldovas-cinema-heritage/ |access-date=7 July 2023 |website=md.usembassy.gov |date=25 February 2021 |archive-date=7 July 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230707162946/https://md.usembassy.gov/rediscovering-moldovas-cinema-heritage/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Sports=== | ===Sports=== | ||
| {{main|Sport in Moldova}} | {{main|Sport in Moldova}} | ||
| ] in 2015]] |
] in 2015]] Association football is the most popular team sport in Moldova. The governing body is the ], which belongs to ]. The ] played its first match in 1994, but never qualified to the ]. The most successful football club is ], the first and only Moldovan club to qualify for the group stage of the ] and the ]. Other winners of the ] include ], ], ] and ]. | ||
| '']'' (a form of ]) is the national sport in Moldova. ] is popular as well. More than 10,000 supporters turn out for home internationals. Since 2004, playing numbers at all levels have more than doubled to 3,200. Despite the hardships and deprivations the national team are ranked 34th in the world.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Souster|first=Mark|url=https://www.thetimes.co.uk/|title=Europe's poor relations show richness of spirit; Mark Souster visits Moldova and discovers a wealth of ambition at all levels in one of the game's new frontiers|date=27 October 2012|work=The Times (London, England)}}</ref> The most prestigious ] is the ], which was first run in 2004. In chess, the Republic of Moldova has several international masters, among which can be mentioned ], ], and ]. | '']'' (a form of ]) is the national sport in Moldova. ] is popular as well. More than 10,000 supporters turn out for home internationals. Since 2004, playing numbers at all levels have more than doubled to 3,200. Despite the hardships and deprivations the national team are ranked 34th in the world.<ref>{{Cite news|last=Souster|first=Mark|url=https://www.thetimes.co.uk/|title=Europe's poor relations show richness of spirit; Mark Souster visits Moldova and discovers a wealth of ambition at all levels in one of the game's new frontiers|date=27 October 2012|work=The Times (London, England)|access-date=13 February 2020|archive-date=30 March 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190330201402/https://www.thetimes.co.uk/|url-status=live}}</ref> The most prestigious ] is the ], which was first run in 2004. In chess, the Republic of Moldova has several international masters, among which can be mentioned ], ], and ]. | ||
| ] is one of the most successful Moldovan tennis players, with ] singles (]) and doubles (]) titles. | ] is one of the most successful Moldovan tennis players, with ] singles (]) and doubles (]) titles. | ||
| Athletes from Moldova have won European medals in ], ], ], and |
Athletes from Moldova have won European medals in ], ], ], and gymnastics; world medals in ], judo, swimming, and ]; as well as Olympic medals in ], ], ], ], and ]. Moldova made its Olympic debut at the ] in Lillehammer. Olympic medalists include ], ], ], ], and ]. ] represented the Soviet Union at the ], winning two medals. | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 1,165: | Line 604: | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| {{reflist|22em}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category|Moldova}} | {{Commons category|Moldova}} | ||
| {{Sister project links|Moldova|voy=Moldova}} | {{Sister project links|Moldova|voy=Moldova}} | ||
| * | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161018213138/https://www.congress.gov/bill/102nd-congress/senate-resolution/148/text?q=%7B%22search%22%3A%5B%22PL111-148%22%5D%7D&resultIndex=5 |date=18 October 2016 }} | ||
| *{{Official website|1=http://www.moldova.md/en}} | * {{Official website|1=http://www.moldova.md/en}} | ||
| *. '']''. ]. | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210105015457/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/moldova/ |date=5 January 2021 }}. '']''. ]. | ||
| * from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''. | * from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''. | ||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180721064530/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-17601580 |date=21 July 2018 }} from the ]. | |||
| *{{curlie|Regional/Europe/Moldova}} | |||
| * {{Wikiatlas|Moldova}} | |||
| * from the ]. | |||
| * {{osmrelation-inline|58974|bullet=no}} | |||
| *{{Wikiatlas|Moldova}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120426045144/http://www.ifs.du.edu/ifs/frm_CountryProfile.aspx?Country=MD |date=26 April 2012 }} from ]. | |||
| *{{osmrelation-inline|58974|bullet=no}} | |||
| * from ]. | |||
| {{Moldova topics |collapsed}} | {{Moldova topics |collapsed}} | ||
| {{Sovereign states of Europe}} | {{Sovereign states of Europe}} | ||
| {{Eastern Europe|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | {{Navboxes | ||
| |title = International organizations | |title = International organizations | ||
| Line 1,194: | Line 632: | ||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| {{Coord|47|N|29|E|type:country|display=title}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Line 1,207: | Line 646: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:28, 3 January 2025
Country in Eastern Europe This article is about the modern state. For the historical principality, see Moldavia. For other uses, see Moldova (disambiguation).
| Republic of MoldovaRepublica Moldova (Romanian) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Limba noastră "Our language" | |
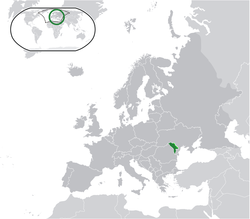 Location of Moldova in Europe (green) Location of Moldova in Europe (green)and its uncontrolled territory of Transnistria (light green) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Chișinău 47°0′N 28°55′E / 47.000°N 28.917°E / 47.000; 28.917 |
| Official language and national language | Romanian |
| Recognised minority languages | See here |
| Ethnic groups (2014; excl. Transnistria) | 75% Moldovans 7% Romanians 6.57% Ukrainians 4.57% Gagauzes 4.06% Russians 1.88% Bulgarians 0.85% other |
| Religion (2014; excl. Transnistria) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Moldovan |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| • President | Maia Sandu |
| • Prime Minister | Dorin Recean |
| • President of the Parliament | Igor Grosu |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Formation | |
| • Principality of Moldavia | 1346 |
| • Bessarabia Governorate | 1812 |
| • Moldavian Democratic Republic | 15 December 1917 |
| • Union with Romania | 9 April 1918 |
| • Moldavian ASSR | 12 October 1924 |
| • Moldavian SSR | 2 August 1940 |
| • Transnistria War | 2 November 1990 |
| • Independence from the Soviet Union | 27 August 1991 |
| • Constitution adopted | 29 July 1994 |
| Area | |
| • Incl. Transnistria | 33,843 km (13,067 sq mi) (135th) |
| • Water (%) | 1.4 (incl. Transnistria) |
| • Excl. Transnistria | 30,334 km (11,712 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • January 2024 estimate | 2,423,300 (140th) |
| • 2014 census | 2,804,801 |
| • Density | 82.8/km (214.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2021) | low inequality |
| HDI (2022) | high (86th) |
| Currency | Moldovan leu (MDL) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +373 |
| ISO 3166 code | MD |
| Internet TLD | .md |
| Website www | |
| |
Moldova, officially the Republic of Moldova, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, on the northeastern corner of the Balkans. The country spans a total of 33,483 km (12,928 sq mi) and has a population of approximately 2.42 million as of January 2024. Moldova is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised breakaway state of Transnistria lies across the Dniester river on the country's eastern border with Ukraine. Moldova is a unitary parliamentary representative democratic republic with its capital in Chișinău, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre.
Most of Moldovan territory was a part of the Principality of Moldavia from the 14th century until 1812, when it was ceded to the Russian Empire by the Ottoman Empire (to which Moldavia was a vassal state) and became known as Bessarabia. In 1856, southern Bessarabia was returned to Moldavia, which three years later united with Wallachia to form Romania, but Russian rule was restored over the whole of the region in 1878. During the 1917 Russian Revolution, Bessarabia briefly became an autonomous state within the Russian Republic. In February 1918, it declared independence and then integrated into Romania later that year following a vote of its assembly. The decision was disputed by Soviet Russia, which in 1924 established, within the Ukrainian SSR, a so-called Moldavian autonomous republic on partially Moldovan-inhabited territories to the east of Bessarabia. In 1940, as a consequence of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Romania was compelled to cede Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina to the Soviet Union, leading to the creation of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic (Moldavian SSR).
On 27 August 1991, as the dissolution of the Soviet Union was underway, the Moldavian SSR declared independence and took the name Moldova. However, the strip of Moldovan territory on the east bank of the Dniester has been under the de facto control of the breakaway government of Transnistria since 1990. The constitution of Moldova was adopted in 1994, and the country became a parliamentary republic with a president as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. Under the presidency of Maia Sandu, elected in 2020 on a pro-Western and anti-corruption ticket, Moldova has pursued membership of the European Union, and was granted candidate status in June 2022. Accession talks to the EU began on 13 December 2023. Sandu has also suggested an end to Moldova's constitutional commitment to military neutrality in favour of a closer alliance with NATO and strongly condemned Russia's invasion of neighbouring Ukraine.
Moldova is the second poorest country in Europe by GDP per official capita after Ukraine and much of its GDP is dominated by the service sector. It has one of the lowest Human Development Indexes in Europe, ranking 76th in the world (2022). Moldova ranks 68th in the world on the Global Innovation Index as of 2024. Moldova is a member state of the United Nations, the Council of Europe, the World Trade Organization, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, the GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development, the Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation, and the Association Trio.
Etymology
Main article: Names of Moldavia and MoldovaThe name Moldova is derived from the Moldova River (German: Moldau); the valley of this river served as a political centre at the time of the foundation of the Principality of Moldavia in 1359. The origin of the name of the river remains unclear. According to a legend recounted by Moldavian chroniclers Dimitrie Cantemir and Grigore Ureche, Prince Dragoș named the river after hunting aurochs: following the chase, the prince's exhausted hound Molda (Seva) drowned in the river. The dog's name, given to the river, extended to the principality.
For a short time in the 1990s, at the founding of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the name of the current Republic of Moldova was also spelled Moldavia. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country began to use the Romanian name, Moldova. Officially, the name Republic of Moldova is designated by the United Nations.
History
Main article: History of Moldova See also: History of Transnistria and Founding of Moldavia
The history of Moldova spans prehistoric cultures, ancient and medieval empires, and periods of foreign rule and modern independence.
Evidence of human habitation dates back 800,000–1.2 million years, with significant developments in agriculture, pottery, and settlement during the Neolithic and Bronze Ages. In antiquity, Moldova's location made it a crossroads for invasions by the Scythians, Goths, Huns, and other tribes, followed by periods of Roman and Byzantine control. The medieval Principality of Moldavia emerged in the 1350s, and was the medieval precursor of modern Moldova and Romania. It reached prominence under rulers like Stephen the Great before becoming a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire from 1538, until the 19th century.
In 1812, following one of several Russian–Turkish wars, the eastern half of the principality, Bessarabia, was annexed by the Russian Empire, marking the beginning of Russian influence in the region. In 1918, Bessarabia briefly became independent as the Moldavian Democratic Republic and, following the decision of the Parliament (Sfatul Țării), united with Romania. During the Second World War it was occupied by the Soviet Union which reclaimed it from Romania. It joined the Union in 1940 as the Moldavian SSR. During this period, policies of Russification and economic transformation deeply influenced the region.
The dissolution of the USSR in 1991 led to declared independence, followed by the Transnistria War in 1992, a conflict that left the Transnistrian region as a de facto independent state. Moldova continues to navigate a complex relationship between pro-Western and pro-Russian factions. In recent years, it has pursued closer ties with the European Union, submitting a formal membership application in 2022.
In the November 2020 presidential election, the pro-European opposition candidate Maia Sandu was elected as the new president of the republic, becoming the first female elected president of Moldova. In the November 2024 presidential election, President Maia Sandu was re-elected with 55% of the vote in the run-off.
Politics
Main article: Government of Moldova
The Republic of Moldova is a constitutional republic with a unicameral parliamentary system of government and competitive, multi-party elections. The constitution provides for executive and legislative branches as well as an independent judiciary and a clear separation of powers. The president serves as the head of state, is elected every four years, and can be re-elected once. The prime minister serves as the head of government, appointed by the president with parliament's support. The head of government in turn assembles a cabinet, subject to parliamentary approval. Legislative authority is vested in the unicameral Parliament of Moldova which has 101 seats and whose members are elected by popular vote on party lists every four years. The president's official residence is the Presidential Palace, Chișinău.
After the prime minister and government resigned in 2020 and the president and parliament failed to form a new government, early parliamentary elections were held in July 2021. According to Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe observers, the 2021 parliamentary elections were well-administered and competitive, and fundamental freedoms were largely respected. The Party of Action and Solidarity won 63 seats in the 101-seat parliament, enough to form a single-party majority.
 Maia Sandu, Moldova's President since December 2020.
Maia Sandu, Moldova's President since December 2020.
The 1994 Constitution of Moldova sets the framework for the government of the country. A parliamentary majority of at least two-thirds is required to amend the Constitution of Moldova, which cannot be revised in times of war or national emergency. Amendments to the Constitution affecting the state's sovereignty, independence, or unity can only be made after a majority of voters support the proposal in a referendum. Furthermore, no revision can be made to limit the fundamental rights of people enumerated in the Constitution. The 1994 constitution also establishes an independent Constitutional Court, composed of six judges (two appointed by the President, two by Parliament, and two by the Supreme Council of Magistrature), serving six-year terms, during which they are irremovable and not subordinate to any power. The court is invested with the power of judicial review over all acts of parliament, over presidential decrees, and over international treaties signed by the country.
The head of state is the President of Moldova, who between 2001 and 2015 was elected by the Moldovan Parliament, requiring the support of three-fifths of the deputies (at least 61 votes). This system was designed to decrease executive authority in favour of the legislature. Nevertheless, the Constitutional Court ruled on 4 March 2016 that this constitutional change adopted in 2000 regarding the presidential election was unconstitutional, thus reverting the election method of the president to a two-round system direct election.
Foreign relations
Main articles: Foreign relations of Moldova, Moldovan neutrality, and Moldova–European Union relationsAfter achieving independence from the Soviet Union, Moldova's foreign policy was designed with a view to establishing relations with other European countries, neutrality, and European Union integration. In May 1995, the country signed the CIS Interparliamentary Assembly Convention to become a member and was also admitted in July 1995 to the Council of Europe.
Moldova became a member state of the United Nations the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), the North Atlantic Cooperation Council, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development in 1992. 1994 saw Moldova become a participant in NATO's Partnership for Peace programme. Moldova joined the Francophonie in 1996, the World Trade Organization in 2001, and the International Criminal Court in 2002.
In 2005, Moldova and the European Union established an action plan that sought to improve cooperation between Moldova and the union. At the end of 2005, the European Union Border Assistance Mission to Moldova and Ukraine (EUBAM) was established at the joint request of the presidents of Moldova and Ukraine. EUBAM assists the Moldovan and Ukrainian governments in approximating their border and customs procedures to EU standards and offers support in both countries' fight against cross-border crime.
After the 1990–1992 War of Transnistria, Moldova sought a peaceful resolution to the conflict in the Transnistria region by working with Romania, Ukraine, and Russia, calling for international mediation, and co-operating with the OSCE and UN fact-finding and observer missions. The foreign minister of Moldova, Andrei Stratan, repeatedly stated that the Russian troops stationed in the breakaway region were there against the will of the Moldovan government and called on them to leave "completely and unconditionally". In 2012, a security zone incident resulted in the death of a civilian, raising tensions with Russia.

In September 2010, the European Parliament approved a grant of €90 million to Moldova. The money was to supplement US$570 million in International Monetary Fund loans, World Bank and other bilateral support already granted to Moldova. In April 2010, Romania offered Moldova development aid worth of €100 million while the number of scholarships for Moldovan students doubled to 5,000. According to a lending agreement signed in February 2010, Poland provided US$15 million as a component of its support for Moldova in its European integration efforts. The first joint meeting of the Governments of Romania and Moldova, held in March 2012, concluded with several bilateral agreements in various fields. The European orientation "has been the policy of Moldova in recent years and this is the policy that must continue," Nicolae Timofti told lawmakers before his election in 2012.
On 29 November 2013, at a summit in Vilnius, Moldova signed an association agreement with the European Union dedicated to the European Union's 'Eastern Partnership' with ex-Soviet countries. The ex-Romanian President Traian Băsescu stated that Romania will make all efforts for Moldova to join the EU as soon as possible. Likewise, Traian Băsescu declared that the unification of Moldova and Romania is the next national project for Romania, as more than 75% of the population speaks Romanian.
Russia
Main article: Moldova–Russia relationsA document written in 2021 by the Russia's FSB's Directorate for Cross-Border Cooperation, titled "Strategic objectives of the Russian Federation in the Republic of Moldova" sets out a 10-year plan to destabilise Moldova, using energy blackmail, and political/elite sources in Moldova that are favourable to Russia and the Orthodox Church. Russia denies any such plan.
Religious leaders play a role in shaping foreign policy. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, the Russian Government has frequently used its connections with the Russian Orthodox Church to block and stymie the integration of former Soviet states like Moldova into the West.
In February 2023, Russia canceled a 2012 decree underpinning Moldova's sovereignty. In May 2023, the Moldovan government announced the immediate suspension of its participation in the Commonwealth of Independent States and its intentions to ultimately withdraw from the organization entirely. In July 2023, Moldova passed a legislation removing it from membership in the CIS Interparliamentary Assembly.
On 25 July 2023, the Moldovan government summoned the Russian ambassador Oleg Vasnetsov to Moldova after media reports of alleged spying devices on the rooftop of their embassy in Chişinău. On 26 July 2023, the Moldovan government expelled 45 Russian diplomats and embassy staff due to "hostile actions" intended to destabilise the Republic of Moldova, according to Foreign Minister Nicu Popescu. On 30 July, the Russian embassy announced that it would suspend consular appointments "for technical reasons".
The Moldovan Security and Intelligence Service (SIS) also ended all partnership agreements with Russia's FSB after sending official notifications to the authorities in Moscow.
European Union Accession
Main article: Accession of Moldova to the European Union
Moldova has set 2030 as the target date for EU Accession.
Moldova signed the Association Agreement with the European Union in Brussels on 27 June 2014. The signing came after the accord was drafted in Vilnius in November 2013.
Moldova signed the membership application to join the EU on 3 March 2022. On 23 June 2022, Moldova was officially granted candidate status by EU leaders. The United Nations Development Programme is also providing assistance to Moldova in implementing the necessary reforms for full accession by 2030. The European Union's High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy Josep Borrell has confirmed that the pathway to accession does not depend upon a resolution of the Transnistria conflict.
On 27 June, Moldova signed a comprehensive free trade agreement with the European Free Trade Association. On 28 June 2023, the European Union announced a €1.6 billion support and investment programme for Moldova, as well as confirming reductions in the price of mobile data and voice roaming charges in Moldova by European and Moldovan telecoms operators, as well as Moldova joining the EU's joint gas purchase platform.
Formal accession talks began on 13 December 2023. A referendum on joining the EU is planned for autumn 2024, there will be no voting stations in Transnistria, however residents there will be free to travel into other areas of Moldova to vote, should they wish to.
In Moldova's referendum on joining the EU, a narrow 50.17% voted "yes," with Maia Sandu alleging "unprecedented" outside interference. Sandu received 42% in the simultaneous presidential election, while her rival, Alexandr Stoianoglo, garnered 26%, leading to a run-off on 3 November 2024. The referendum was seen as a test of Moldova's commitment to EU integration, amid claims of vote manipulation by criminal groups.
Security
The European Union created a Partnership Mission in Moldova through its Common Security and Defence Policy on 24 April 2023. The mission seeks to support the government of Moldova in countering hybrid threats the country faces as a result of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine.
A memorandum dated 29 March 2023 stated that the mission aims at "enhancing the resilience of Moldova's security sector in the area of crisis management as well as enhancing resilience to hybrid threats, including cybersecurity, and countering foreign information manipulation and interference". The initial mandate of the mission is expected to be for two years and it will be made up of up to 40 police and customs officers and judicial officials. Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Germany, Poland, Sweden, the Czech Republic, Portugal, Romania, and Denmark have all voiced support for the mission.
On 2 February 2023 Moldova passed a law introducing criminal penalties for separatism, including prison terms. The law continues with penalties for financing and inciting separatism, plotting against Moldova, and collecting and stealing information that could harm the country's sovereignty, independence and integrity.
Military
Main article: Military of Moldova
The Moldovan armed forces consists of the Ground Forces and Air Force. Moldova maintains a standing army of just 6,500 soldiers, and spends just 0.4 percent of its GDP on defence, far behind its regional neighbours.
Moldova accepted all relevant arms control obligations of the former Soviet Union. On 30 October 1992, Moldova ratified the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which establishes comprehensive limits on key categories of conventional military equipment and provides for the destruction of weapons in excess of those limits. The country acceded to the provisions of the nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in October 1994 in Washington, D.C. It does not have nuclear, biological, chemical or radiological weapons. Moldova joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's Partnership for Peace on 16 March 1994.
Moldova is committed to a number of international and regional control of arms regulations such as the UN Firearms Protocol, Stability Pact Regional Implementation Plan, the UN Programme of Action (PoA), and the OSCE Documents on Stockpiles of Conventional Ammunition. Since declaring independence in 1991, Moldova has participated in UN peacekeeping missions in Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire, Sudan, and Georgia. On 12 November 2014, the US donated to Moldovan Armed Forces 39 Humvees and 10 trailers, with a value of US$700,000, to the 22nd Peacekeeping Battalion of the Moldovan National Army to "increase the capability of Moldovan peacekeeping contingents."
Moldova signed a military agreement with Romania to strengthen regional security in 2015. The agreement is part of Moldova's strategy to reform its military and cooperate with its neighbours.
Since 2022, the army has begun a process of modernization, and has been provided with more than €87 million in support for the modernization of the defence sector and the strengthening of security through the European Peace Facility. In October 2022, Defense Minister Anatolie Nosatii claimed that 90 percent of the country's military equipment is outdated and of Soviet origin, dating back to the 1960s and 1980s. In April 2023, Valeriu Mija, Secretary of State for Defence Policy and National Army Reform in the Defence Ministry, claimed that Moldova needed $275 million to modernize its armed forces, especially in light of Russia's invasion of Ukraine and the presence of 1,500 Russian soldiers in Transnistria. In June 2023, Poland also sent a transport of military equipment worth €8 million (including drones, laptops, explosive ordnance disposal equipment, and ultrasound equipment) to the Moldovan police to increase the country's internal security. Analysts at the Centre for European Policy Analysis have called for further western weapon donations.
Human rights
Main article: Human rights in MoldovaFreedom House ranked Moldova as a "partly free" country with a score of 62/100 in 2023. They summarized their finds as follows: "Moldova has a competitive electoral environment, and freedoms of assembly, speech, and religion are mostly protected. Nonetheless, pervasive corruption, links between major political figures and powerful economic interests, and critical deficiencies in the justice sector and the rule of law all continue to hamper democratic governance." According to Transparency International, Moldova's Corruption Perceptions Index improved to 39 points in 2022 from 34 in 2020. Reporters Without Borders improved Moldova's Press Freedom Index ranking from 89th in 2020 to 40th in 2022, while cautioning that "Moldova's media are diverse but extremely polarised, like the country itself, which is marked by political instability and excessive influence by oligarchs."
According to Amnesty International's 2022/23 report, "No visible progress was made in reducing instances of torture and other ill-treatment in detention. Impunity continued for past human rights violations by law enforcement agencies. New "temporary" restrictions on public assemblies were introduced. The rights of LGBTI people were not fully realized, leading to cases of harassment, discrimination and violence. Some refugee reception centres turned away religious and ethnic minority refugees. In the breakaway Transdniestria region, prosecution and imprisonment for peaceful dissent continued." On 18 June 2023, some 500 LGBT activists and supporters held a Pride parade in the capital city of Chișinău which for the first time needed no heavy police cordons to protect them from protesters largely linked to the Orthodox church.
According to Human Rights Report of the United States Department of State, released in 2022, "While authorities investigated reports of human rights abuses and corruption committed by officials, the process was slow and burdensome. During the year, authorities indicted and detained several former high-level officials including former President Igor Dodon, former member of parliament Vladimir Andronachi, Shor Party member of parliament Marina Tauber and former director of Moldovan Railways Anatolie Topala. None of these cases resulted in conviction by a court at year's end. Authorities took some steps to identify, investigate, and prosecute officials for human rights abuses, but progress was slow."
In a meeting with the European Union in October 2022, EU representatives "welcomed positive developments in Moldova such as the ratification of the Istanbul Convention on preventing and combating violence against women, the adoption of legislation on hate crime, and the ongoing work to reform the Electoral Code. It encouraged Moldovan authorities to address shortcomings identified by OSCE/ODIHR and the Venice Commission across all areas and ensure effective and continuous implementation of human rights legislation." The Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights' 2016 recommendations on hate crimes were "largely reflected in amendments to the Criminal Code adopted by the Moldovan Parliament and published on 3 June 2022", but the report notes that Moldovan law enforcement officers often fail to record the bias motivations behind hate crimes, and additionally recommended "developing its victim support system to ensure effective access to justice, assistance, and protection services for hate crime victims". In 2021, 8 hate crimes were recorded, 7 of which reached a successful conviction, with one going to prosecution but without a conviction.
Administrative divisions
Main articles: Administrative divisions of Moldova, List of cities in Moldova, List of localities in Moldova, and Communes of Moldova Anenii Noi
Basarabeasca
Briceni
Cantemir
Călărași
Căușeni
Cimișlia
Dondușeni
Drochia
Dubăsari
Edineț
Fălești
Florești
Glodeni
Hîncești
Ialoveni
Leova
Nisporeni
Ocnița
Orhei
Rezina
Rîșcani
Sîngerei
Soroca
Șoldănești
Ștefan Vodă
Taraclia
Telenești
Ungheni
Strășeni
Cahul
CHIȘINĂU
Comrat
Bălți
Tiraspol
Romania
Ukraine
Anenii Noi
Basarabeasca
Briceni
Cantemir
Călărași
Căușeni
Cimișlia
Dondușeni
Drochia
Dubăsari
Edineț
Fălești
Florești
Glodeni
Hîncești
Ialoveni
Leova
Nisporeni
Ocnița
Orhei
Rezina
Rîșcani
Sîngerei
Soroca
Șoldănești
Ștefan Vodă
Taraclia
Telenești
Ungheni
Strășeni
Cahul
CHIȘINĂU
Comrat
Bălți
Tiraspol
Romania
Ukraine
Moldova is divided into 32 districts (raioane, singular raion), three municipalities and two autonomous regions (Gagauzia and the Left Bank of the Dniester). The final status of Transnistria is disputed, as the central government does not control that territory. 10 other cities, including Comrat and Tiraspol, the administrative seats of the two autonomous territories, also have municipality status.
Moldova has 66 cities (towns), including 13 with municipality status, and 916 communes. Another 700 villages are too small to have a separate administration and are administratively part of either cities (41 of them) or communes (659). This makes for a total of 1,682 localities in Moldova, two of which are uninhabited.
The largest city in Moldova is Chișinău with a population of approx. 695,400 people. The second largest city is Tiraspol at 129,500, part of the unrecognised breakaway region of Transnistria, followed by Bălți (146,900) and Bender (91,000).
| Largest cities in Moldova Source: Moldovan Census (2004); Note: 1. World Gazetteer. Moldova: largest cities 2004. 2. Pridnestrovie.net 2004 Census 2004. 3. National Bureau of Statistics of Moldova | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Pop. | Rank | Pop. | ||||||
 Chișinău  Tiraspol |
1 | Chișinău | 644,204 | 11 | Comrat | 20,113 |  Bălți  Bender | ||
| 2 | Tiraspol | 129,500 | 12 | Strășeni | 18,376 | ||||
| 3 | Bălți | 102,457 | 13 | Durlești | 17,210 | ||||
| 4 | Bender | 91,000 | 14 | Ceadîr-Lunga | 16,605 | ||||
| 5 | Rîbnița | 46,000 | 15 | Căușeni | 15,939 | ||||
| 6 | Ungheni | 30,804 | 16 | Codru | 15,934 | ||||
| 7 | Cahul | 30,018 | 17 | Edineț | 15,520 | ||||
| 8 | Soroca | 22,196 | 18 | Drochia | 13,150 | ||||
| 9 | Orhei | 21,065 | 19 | Ialoveni | 12,515 | ||||
| 10 | Dubăsari | 25,700 | 20 | Hîncești | 12,491 | ||||
Law enforcement and emergency services
See also: Crime in Moldova and Healthcare in MoldovaThe Moldovan police force (General Police Inspectorate) reports to the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MAI) and is the primary law enforcement body, responsible for internal security, public order, traffic, and criminal investigations. Several agencies responsible for border management, emergency situations, migration and asylum also report to the ministry. Civilian authorities maintained effective control over the security forces. The Moldovan Police are divided into state and municipal organisations. State police provide law enforcement throughout Moldova while municipal police operate at the local administrative level. National and municipal police forces often collaborate closely for law enforcement purposes. The Special Forces Brigade "Fulger" is a specialized combat-ready police force primarily responsible for tackling organized crime, serious violent crime, and hostage situations. They are subordinate to the General Police Inspectorate and therefore under strict civilian control.
There are also a number of more specialised police institutions including the Police Department of Chisinau Municipality and the General Directorate of Criminal Investigation. The Moldovan Border Police are responsible for border security. It was a military branch until 2012 when it was put under the control of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. According to The Law on Police Use of Force Worldwide, "Moldova does not regulate and restrict the use of firearms by law enforcement officials as international law requires. Police use of a firearm can only be lawful where necessary to confront an imminent threat of death or serious injury or a grave and proximate threat to life."
The Security and Intelligence Service (SIS) is a Moldovan state body specialized in ensuring national security by exercising all appropriate intelligence and counter-intelligence measures, such as: collecting, processing, checking and capitalizing the information needed to identify, prevent and counteract any actions that according to law represent an internal or external threat to independence, sovereignty, unity, territorial integrity, constitutional order, democratic development, internal security of the state, society and citizens, the statehood of the Republic of Moldova, the stable functioning of vitally important branches of the national economy, both on the territory of the Republic of Moldova and abroad.
Emergency services in Moldova consist of emergency medical services, search and rescue units, and a state firefighting service. There are two hospitals in the capital city Chișinău, the primary being Medpark International Hospital, and general hospitals in Bălți, Briceni, Cahul, and Călărași. Moldova has a universal healthcare system through a mandatory health insurance scheme. Casa Mariorei, founded in 2002, is a domestic violence shelter in Chișinău which provides shelter, healthcare, legal advice, and psychosocial support for native Moldovan, immigrant, and refugee women.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Moldova
Moldova is a landlocked country situated in Eastern Europe, on the northeastern corner of the Balkans in the Black Sea Basin, between latitudes 45° and 49° N, and mostly between meridians 26° and 30° E (a small area lies east of 30°). The country lies to the east of the Carpathian Mountains and is bordered by Romania to its west and by Ukraine to its north, east, and south. The total length of the national boundaries is 1,389 km, including 939 km with Ukraine and 450 km with Romania. The country is separated from Romania on the west by the Prut river and on the east from Ukraine by the Dniester river. The total land area is 33,843.5 km (13,067.0 sq mi), of which 960 km (370 sq mi) is water. The largest part of the country (around 88% of the area) lies in the Bessarabia region, while a narrow strip in the east is located in the unrecognised breakaway state of Transnistria on the eastern bank of the Dniester.

Although the country is technically landlocked, in 1999 Moldova acquired from Ukraine (in exchange for ceding a stretch of contested road in the east of the country) a 0.45 kilometer river frontage to the Danube, on the confluence of the Danube and Prut rivers. This has transformed the old village of Giurgiulești (in the extreme south-west of the country) into a river port, providing Moldova access to international waters via the Danube and the Black Sea. The Dniester river, which rises in Ukraine near the city of Drohobych, passes through Moldova, separating the main territory from its unrecognised breakaway region Transnistria, and empties into the Black Sea in Ukraine. At its closest point, Moldova is separated from the Dniester Liman, an estuary of the Black Sea, by only 3 km of Ukrainian territory.


While most of the country is hilly, elevations never exceed 430 m (1,410 ft), the highest point being the Bălănești Hill. Moldova's hills are part of the Moldavian Plateau, which geologically originate from the Carpathian Mountains. Its subdivisions in Moldova include the Dniester Hills (Northern Moldavian Hills and Dniester Ridge), the Moldavian Plain (Middle Prut Valley and Bălți Steppe), and the Central Moldavian Plateau (Ciuluc-Soloneț Hills, Cornești Hills—Codri Massive, "Codri" meaning "forests"—Lower Dniester Hills, Lower Prut Valley, and Tigheci Hills). In the south, the country has a small flatland, the Bugeac Plain. The territory of Moldova east of the river Dniester is split between parts of the Podolian Plateau, and parts of the Eurasian Steppe. Moldova's exceptionally rich Chernozem soil covers around three-quarters of the country's land area.
Moldova's capital and largest city is Chișinău, with approximately a third of the country's population residing in its metro area. Chișinău is Moldova's main industrial and commercial centre, and is located in the middle of the country, on the river Bîc, a tributary of the Dniester. Moldova's second-largest city is Tiraspol, which lies on the eastern bank of the Dniester and is the capital of the unrecognised breakaway region of Transnistria. The country's third-largest city is Bălți, often referred to as the 'northern capital'. It is situated 127 kilometres (79 miles) north of the capital Chișinău, and is located on the river Răut, a tributary of the Dniester, on a hilly landscape in the Bălți steppe. Comrat is the administrative centre of the autonomous region of Gagauzia.
Climate

Moldova has a climate which is moderately continental; its proximity to the Black Sea leads to the climate being mildly cold in the autumn and winter and relatively cool in the spring and summer.
The summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging about 20 °C (68 °F) and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging −4 °C (25 °F). Annual rainfall, which ranges from around 600 mm (24 in) in the north to 400 mm (16 in) in the south, can vary greatly; long dry spells are not unusual. The heaviest rainfall occurs in early summer and again in October; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common. Because of the irregular terrain, heavy summer rains often cause erosion and river silting.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Moldova was 41.5 °C (106.7 °F) on 21 July 2007 in Camenca. The lowest temperature ever recorded was −35.5 °C (−31.9 °F) on 20 January 1963 in Brătușeni, Edineț county.
| Location | July (°C) | July (°F) | January (°C) | January (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chișinău | 27/17 | 81/63 | 1/−4 | 33/24 |
| Tiraspol | 27/15 | 81/60 | 1/−6 | 33/21 |
| Bălți | 26/14 | 79/58 | −0/−7 | 31/18 |
Biodiversity
See also: Protected areas in MoldovaPhytogeographically, Moldova is split between the East European Plain and the Pontic–Caspian steppe of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. It is home to three terrestrial ecoregions: Central European mixed forests, East European forest steppe, and Pontic steppe. Forests currently cover only 11% of Moldova, though the state is making efforts to increase their range. It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 2.2/10, ranking it 158th globally out of 172 countries. Game animals, such as red deer, roe deer and wild boar can be found in these wooded areas.

| Scientific reserves in Moldova | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Location | Established | Area |
| Codru Reserve | Strășeni | 1971 | 5,177 hectares (52 km) |
| Iagorlîc | Dubăsari | 1988 | 836 hectares (8 km) |
| Lower Prut | Cahul | 1991 | 1,691 hectares (17 km) |
| Plaiul Fagului | Ungheni | 1992 | 5,642 hectares (56 km) |
| Pădurea Domnească | Glodeni | 1993 | 6,032 hectares (60 km) |
The environment of Moldova suffered extreme degradation during the Soviet period, when industrial and agricultural development proceeded without regard for environmental protection. Excessive use of pesticides resulted in heavily polluted topsoil, and industries lacked emission controls. Founded in 1990, the Ecological Movement of Moldova, a national, non-governmental, nonprofit organization which is a member of the International Union for Conservation of Nature has been working to restore Moldova's damaged natural environment. The movement is national representative of the Centre "Naturopa" of the Council of Europe and United Nations Environment Programme of the United Nations.
Once possessing a range from the British Isles through Central Asia over the Bering Strait into Alaska and Canada's Yukon as well as the Northwest Territories, saigas survived in Moldova and Romania into the late 18th century. Deforestation, demographic pressure, as well as excessive hunting eradicated the native saiga herds which is currently threatened with extinction. They were considered a characteristic animal of Scythia in antiquity. Historian Strabo referred to the saigas as the kolos, describing it as "between the deer and ram in size" which (understandably but wrongly) was believed to drink through its nose.
Another animal which was extinct in Moldova since the 18th century until recently was the European Wood Bison or wisent. The species was reintroduced with the arrival of three European bison from Białowieża Forest in Poland several days before Moldova's Independence Day on 27 August 2005. Moldova is currently interested in expanding their wisent population, and began talks with Belarus in 2019 regarding a bison exchange program between the two countries.
Economy
Main article: Economy of MoldovaOverview

The economy of Moldova is an emerging upper-middle income economy, with a high Human Development Index. Since the country gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1992, it has steadily transitioned to a market economy. According to the World Bank, despite a strong economic performance over the past two decades, Moldova remains among the poorest nations in Europe. Growth has remained relatively high since the 1990s, with low levels of unemployment and falling levels of poverty, but a combination of demographic factors, especially an ageing population and significant levels of emigration, and recent regional events, especially Russia's invasion of Ukraine, have posed serious economic challenges to the Moldovan economy, particularly due to inflation and rising energy prices. Productivity growth has remained poor, and a significant proportion of the population are reliant on government pensions and social assistance. Due to Moldova's historic reliance upon Russian oil and natural gas, the energy sector has posed a particular challenge to the country's economy.

GDP per capita has almost doubled from $2,749 (USD) in 2015 to $5,562 in 2022. Following the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns, annual GDP growth rebounded to 13.9% in 2021, before Russia's invasion of Ukraine, energy and refugee crises caused growth to collapse to −5.9%. As of 2022, unemployment remains low at 2.3%, but inflation had dramatically increased to 28.7% due to the energy crisis caused by the invasion. In recent years the country has received significant economic assistance from the European Union, IMF, and World Bank, particularly after Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The IMF predicts that in 2023 the economy will improve from a 1.5% contraction to a growth of 1.5%.
Moldova remains highly vulnerable to fluctuations in remittances from workers abroad (which constitute 25 percent of GDP), exports to the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and European Union (EU) (88 per cent of total exports), and donor support (about 10 per cent of government spending). The main transmission channels through which adverse exogenous shocks could impact the Moldovan economy are remittances (also due to potentially returning migrants), external trade, and capital flows.
The economy's primary exports are agriculture, apparel, and sports equipments. In 2021, Moldova exported $140 million in wine and is the 21st largest exporter of wine in the world, with wine exports being the country's fifth largest export. With its 300 days of sunshine per year, the climate in Moldova is ideal for agriculture and particularly vineyards. The wine industry is a major economic sector, representing three percent of Moldova's GDP and eight percent of the country's total exports, according to government data. In 2021, the EU became the main purchaser of Moldovan wines. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is one of the most promising economic sectors in Moldova, accounting for more than 10 percent of GDP. More than 2,000 students graduate with a degree in computing or a related field per year. IT companies export about 80 percent of their total production to the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, the Netherlands, and Romania.
|
|
|
Energy
This section is an excerpt from Energy in Moldova.
| This article needs to be updated. The reason given is: Russia stopped selling them gas https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cy8ymx50kz8o. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (January 2025) |
With few natural energy resources, Moldova imports almost all of its energy supplies. 50% of the country's national energy company, Moldovagaz, is owned by Russian oil and natural gas supplier Gazprom, the remaining 36% split between the Moldovan government (36.6%) and the unrecognised government of Transnistria (13.4%). Moldova's historic dependence on Russian energy is underscored by a debt of more than US$709 million to Gazprom as well as a further US$7 billion by Transnistria. Russia supplies the breakaway pro-Russian region with oil and natural gas without requiring them to pay, with the cost levied as debt against the Moldovan state as a form of economic warfare. The Moldovan government disputes the figures, and has identified more than US$100 million in fraudulent claims by Gazprom.
In August 2013, work began on a pipeline between Moldova and Romania that has now been completed and has broken Russia's monopoly on Moldova's gas supplies. Importing electricity from Romania began in 2022, breaking the need to buy electricity produced from Russian gas in Transnistria. Improved connectivity will be completed by 2025. As of June 2023, Moldova no longer imports oil or natural gas from Russia and has been granted access to the European Union's joint gas purchasing platform. Financial assistance was provided by the European Union, World Bank, and IMF in order to speed up this transition.
Moldova lacks domestic sources of fossil energy and must import substantial amounts of petroleum, coal, natural gas, and other energy resources. Primary energy supply in 2018 was about half natural gas, a quarter oil and solid biomass one-fifth.
Renewable energy has expanded rapidly and Moldova is seeking to diversify sources of energy and cease purchasing from Russia.Tourism
Main article: Tourism in MoldovaMoldova is the among least visited countries in Europe, and tourism consequently plays a relatively minor role in the country's overall economy. Despite the impact of Russia's invasion of neighbouring Ukraine, Moldova saw more foreign visitors in the first quarter of 2022 than pre-pandemic, going from 31,000 non-resident tourists in 2019 to 36,100 in 2022. This still makes it one of the least-visited countries in Europe, however in recent years a number of Western media outlets have begun to highlight Moldova and its capital city Chișinău as an attractive tourism destination due to its picturesque natural landscapes, 300 days of sunshine per year, low prices, ancient wine culture, and mix of regional cultural influences. Tourism in Moldova has focused on the country's natural landscapes, historical sites, and historic wine tradition. The government promotes international tourism within the country through its Moldova Travel brand. Moldova is internationally connected by plane via Chișinău International Airport, with direct flights to and from many European destinations, including Amsterdam Schiphol, Berlin Brandenburg, London Stansted, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Tel Aviv's Ben Gurion Airport, Rome–Fiumicino Airport, Istanbul Airport, and Dubai International Airport. Rail links connect it via direct overnight trains to neighbouring Bucharest, Kyiv, Odesa, and formerly Moscow. Moldovan citizens also enjoy visa-free travel across the Schengen Area.

As a major exporter of wine with more than 142 wineries and the largest wine cellar in the world, vineyard tours are offered to tourists across the country. Major sites include the Cricova winery, whose wine cellar stretches more than 120 kilometres (75 miles); Castel Mimi, a 19th-century chateau with vineyards, a museum, art gallery, spa, hotel, and restaurant; and Mileștii Mici, which boasts the world's largest collection of wine. As a country with a deep history of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, the country also has more than 50 monasteries and 700 churches. Among the most famous and well-visited are the Old Orhei Cave Monastery, carved into a cliff face in the 13th century and still in use today, and the 19th century Nativity Cathedral in the centre of Chișinău. UNESCO includes both the Old Orhei Archaeological Landscape, which features evidence of settlements dating back to at least the 12th century, and the typical Chernozem soil on the Bălți Steppe of Moldova (the most arable soil on the planet) on its Tentative List of World Heritage Sites. The capital city of Chișinău hosts most of the country's national museums, including the National Museum of Fine Arts, Moldova State University, Brancusi Gallery, the National Museum of History of Moldova with over 236,000 exhibits, as well as bustling markets in the north of the city, including the house where Alexander Pushkin once resided while in exile from the Russian Tsar, and which has since been turned into a museum. Every year on 3–4 October, the country celebrates National Wine Day, where wine producers open up their wineries to the general public and provide shuttle buses between locations.
Wine industry
Main article: Moldovan wine
With its 300 days of sunshine per year, the climate in Moldova is ideal for agriculture and particularly vineyards. The wine industry is a major economic sector, representing three percent of Moldova's GDP and eight percent of the country's total exports, according to government data. Moldovan wine is being exported into over 70 states worldwide. Although Moldova is barely larger than Belgium, the country has 122,000 hectares of vineyards and is among the 20 largest producers in the world, according to a report by the International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV).
Before Russia's invasion of Ukraine and Moldova's pivot towards Europe, a majority of its wine exports went to Russia, but this has now changed: "Russia accounted for only 10 percent of Moldovan wine exports in 2021, down from 80 percent in the early 2000s, according to figures from the Moldovan Ministry of Agriculture." The EU liberalized its market for Moldovan wines and has signed a bilateral free trade deal with Moldova, with the result that in 2021 the country exported more than 120 million litres of wine to European countries, compared to 8.6 million litres to Russia.
Many families have their own recipes and grape varieties that have been passed down through the generations. There are 3 historical wine regions: Valul lui Traian (south west), Stefan Voda (south east) and Codru (centre), destined for the production of wines with protected geographic indication. Mileștii Mici is the home of the largest wine cellar in the world. It stretches for 200 km (120 mi) (though only 55 km (34 mi) is in use) and holds some two million or more bottles of wine. It has retained the Guinness World Record for largest wine cellar by number of bottles since 2005. The earliest wines in its collection date to 1969. Mimi Castle in the south east is a winery and architectural monument, which was built at the end of the 19th century in the village of Bulboaca in the district Anenii Noi, and is thought to be the first winery in Bessarabia. It has since also become a tourist complex with a museum, art gallery, hotel, spa, and wine tasting rooms.
Agriculture
Main article: Agriculture in Moldova
Moldova is an agrarian-industrial state, with agricultural land occupying 2,499,000 hectares in a total area of 3,384,600 hectares. It is estimated that 1,810,500 of these hectares are arable. It is among the most arable countries in Europe, with the Chernozem soil across the Bălți Steppe being among the most fertile soils anywhere in the world. With more than 300 days of sunshine per year supporting the cultivation of vineyards, Moldova is also one of the largest wine producers in the world. Moldova's agricultural sector benefits from a geographical proximity to large markets, especially the European Union. As of 2021, agriculture made up 12% of Moldova's overall exports and 21% of overall employment. Its most exported foods are maize, wheat, sunflower seeds, grapes, apples, sugar beets, milk, potatoes, barley, plums/sloes, while relevant and important domestic industries include sugar processing, vegetable oil, food processing, and agricultural machinery. Between 2015 and 2022, agricultural production has almost doubled, particularly in vegetable and fruit production. In July 2023, a network of 20 seed libraries comprising over 1,000 seeds were created across Moldova with the assistance of Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic, NGOs, and the United Nations Development Programme, with the aim is to improve local agricultural biodiversity, climate resilience, and the capacity of local government and farmers to respond effectively to changing environmental conditions.
Nevertheless, the country's agricultural sector faces serious long-term challenges. Despite having relatively modest per capita greenhouse gas emissions, and lower than the world average, Moldova is highly vulnerable to climate change and related environmental disasters which already cost the country 2.13% of annual GDP. According to Climate-KIC, run by the European Institute of Innovation and Technology, "The same region in Moldova can experience intense droughts and devastating floods in the course of a few months, which is the primary concern of local people when they talk about climate. But the irregular nature of these events made it difficult to sustain long term interest from Moldovan people or to channel money from donors."
Transport infrastructure
Main articles: Transport in Moldova and Rail transport in Moldova
The main means of transportation in Moldova are railways 1,138 km (707 mi) and a highway system (12,730 km or 7,910 mi overall, including 10,937 km or 6,796 mi of paved surfaces). Rail links connect it via direct overnight trains to neighbouring Bucharest, Kyiv, Odesa, and also Moscow.
The Giurgiulești terminal on the Danube is compatible with small seagoing vessels. Shipping on the lower Prut and Nistru rivers plays only a modest role in the country's transportation system.
The sole international air gateway of Moldova is the Chișinău International Airport. with direct flights to and from many European destinations.
Telecommunications
Main article: Telecommunications in MoldovaInternet in Moldova is among the fastest and least expensive in the world as of 2023. The country ranks 3rd in the world by gigabit coverage with around 90% of the population having the option to subscribe to a gigabit-speed fibre-optic broadband plan. The United Nations Development Programme has judged it to have a highly developed digital infrastructure, with 98% 4G coverage of its territory. By July 2022, there were more than 3 million internet users in Moldova, constituting some 76% of the population. Moldova is considering a bid to begin rolling out 5G in 2024, with testing beginning in 2019. Starlink launched in Moldova in August 2022. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is one of the most promising economic sectors in Moldova, accounting for more than 10 percent of GDP. More than 2,000 Moldovan students per year graduate with a degree in computing or a related field.
The ITU's Global Cybersecurity Index ranks Moldova on the 33rd place in Europe and the 63rd place in the world. The country's joining in 2009 of the Convention on Cybercrime of the Council of Europe and adoption of the National Cyber Security Program for 2016–2020 have established the legislative parameters for a safer digital environment. Since Russia's invasion of neighbouring Ukraine and their campaign of cyberwarfare against Moldova, the Moldovan government has invested significant money and resources in developing stronger cybersecurity practices and regulations with assistance from the European Union and United States. The European Union has also set up and funded the Moldova Cybersecurity Rapid Assistance Unit to improve the cyber resilience of Moldova's public sector organisations and key critical infrastructure sectors. Moldova has adopted new legislation partially drafted by the unit which will go into effect on 1 January 2025. The country has also passed legislation in order to more closely align with the EU's GDPR regulations, and is currently mostly compliant.
Banking
See also: List of banks in MoldovaThe National Bank of Moldova is responsible for the financial system and has a responsibility to the management and control of all banks in Moldova. It is accountable to the Parliament of Moldova.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of MoldovaThe most up-to-date and reliable information is available from the National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova's website which is continuously updated on a monthly and yearly basis. The most recent national census of Moldova was carried out in 2014 (not including Transnistria). The next national census is due to be carried out in 2024.
Overview
Population of Moldova according to ethnic group
Moldovans (75%) Romanians (7%) Ukrainians (6.57%) Gagauzians (4.57%) Russians (4.06%) Bulgarians (1.88%) Romani (0.34%) Belarusians (0.10%) Jews (0.06%) Poles (0.05%) Germans (0.03%) Others (0.26%)Source: 2014 Moldovan census.
Moldova has an estimated population of approx. 2,423,300 as of 1 January 2024. Moldova is relatively urbanised, with 43.4% of Moldovans living in urban areas as of 2022 and an urbanisation rate of 0.09%. About one-third of the Moldovan population live in the capital city Chișinău's metropolitan area. As of 2022, the country's population density is 82.8 inhabitants per 1 km, and average life expectancy was 71.5 years (67.2 for males, and 75.7 for females). There are 100 women per 90 men in Moldova, and employed women have significantly higher levels of education, though women continued to earn 13.6% less than men on average. The number of elderly people (60 years and over) per 100 inhabitants in Moldova has increased year-on-year. The national language is Romanian, a Romance language, though approximately 15% of the Moldovan population also speak Russian as of 2014.
The country has been suffering from long-term population decline due to high levels of emigration (in 2022, 43,000 more people left the country than came) as well as low fertility rates. According to Balkan Insight, the population has fallen by almost 33% since 1990, and by 2035 the total population may be half what it was in 1990. Since 2018, the number of deaths has exceeded the levels of live-births, though the gap has been reduced since 2021. As of 2022, the average number of children per women of childbearing age was 1.69, well below the replacement rate of 2.1, as compared to 1.78 in 2019. The total number of deaths fell by 20.5% in 2022 compared to 2019. Unemployment has remained low at about 3% in 2022.
According to the 2014 national census, ethnic Moldovans made up approx. 75% of the country's population, while Romanians (7%), Ukrainians (6.57%), Gagauzians (4.57%), and Russians (4.06%) made up the most substantial ethnic minorities. Smaller populations include Bulgarians (1.88%), Romani (0.34%), Belarusians (0.10%), Jews (0.06%), and Poles (0.05%).
Language
Further information: Languages of MoldovaAs of March 2023, the only official language of Moldova is Romanian, and all references to the Moldovan language in the constitution and legal bills have been amended to refer to Romanian. The 2014 Moldovan census for the first time collected information about the languages spoken by residents in Moldova. There is a controversy about whether or not Moldovan and Romanian should be considered distinct languages, and the Moldovan government rejects any distinction, however the census allowed for respondents to respond with their preferred label. The results were Moldovan (54.6%), Romanian (24.0%), Russian (14.5%), Ukrainian (2.7%), Gagauz (2.7%), Bulgarian (1.7%), and Other (0.5%).
Diaspora and emigration
Further information: Moldovan diasporaSee also: Emigration from MoldovaEmigration is a mass phenomenon in Moldova and has a major impact on the country's demographics and economy. It is estimated that more than between 1.2 and 2 million Moldovan citizens (over 25% of the population) are living and working abroad. The Moldovan economy is still heavily reliant on their remittance payments. Moldovans are found across the Balkan region, Western Europe, and North America. Among the most notable Moldovan diaspora populations are: 285,000 in Romania (2020), 258,600 in Ukraine (2002) 156,400 in Russia (2010), 188,923 in Italy (2019), 122,000 in Germany (2022), 26,300 in France (2019), and 20,470 in Canada (2021).
Current trends indicate that the population of Moldova will continue to fall with emigration remaining both chronic and higher than immigration or natural birth rates. In 2020, net emigration fell to a low of 7,000 , but by 2022, 43,000 more people left the country than came, though this is slightly down from net emigration of 45,000 in 2021. Russia's invasion of neighbouring Ukraine and the economic impact on Moldova may have been a key contributing factor in the rise from 2020 to 2022. However, there are indications that the invasion of Ukraine and the country's moves towards accession to the European Union may have led to a rise in the number of Moldovan emigrants returning to their country of birth, seeking to help the country join the EU. The Moldovan diaspora also had significant influence on recent Moldovan elections, voting overwhelmingly for Maia Sandu as president in 2020 and for her Party of Action and Solidarity in the 2021 parliamentary election.
Religion
Further information: Religion in Moldova
Moldova's constitution provides for freedom of religion and complete separation of church and state, though the constitution cites the "exceptional importance" of Eastern Orthodox Christianity. Discrimination on the basis of religious affiliation is illegal, and incitement to religious and ethnic hatred was made illegal in May 2022. Religion in Moldova is dominated by the Eastern Orthodox branch of Christianity. According to the 2014 Moldovan census, 90% of the country reported to be of the Eastern Orthodox Christian faith. Of this number, approx. 80–90% of Orthodox Moldovans belong to the Moldovan Orthodox Church (formally known as Metropolis of Chișinău and All Moldova) which is subordinate to the Russian Orthodox Church, and has played a powerful role in deepening Russia's influence in Moldova. The remaining 10–20% of Orthodox Moldovans belong to the Metropolis of Bessarabia, which is subordinate to the Romanian Orthodox Church.
Of the non-Orthodox population of Moldova, the United States Department of State estimates that as of 2022, approx. 7% identify with no religion; Baptists, Jehovah's Witnesses, and Pentecostals number between 15,000 and 30,000 each; the Jewish Community of the Republic of Moldova organisation estimates the Jewish population to be approx. 20,000; and the Islamic League of Moldova (an NGO recognised by the Moldovan Ministry of Justice in 2011 as representing Moldovan Muslims) estimates the number of Muslims to be approx. 15,000–17,000. There are six synagogues in Chișinău, one in Orhei, one in Soroca, and one in Tiraspol, and one mosque in Chișinău. The remaining less than 5% of the Moldovan population are Seventh-day Adventists, Evangelical Christians, Roman Catholics, Lutherans, and atheists. The Transnistrian authorities estimate that 80% of the population belong to the Moldovan Orthodox Church.
Health and fertility
Further information: Health in Moldova and Healthcare in MoldovaStructure of deaths by major classes of causes of death in 2022
Diseases of the circulatory system (58%) Cancerous tumours (15.8%) Other causes (13.9%) Diseases of the digestive tract (7.5%) External causes (4.8%)Moldova provides universal healthcare through a mandatory health insurance scheme. According to the most recent 2022 official data, per 10,000 inhabitants there are 48.4 doctors and 91 units of average medical staff. Approx. 53% of those aged 16 and over in urban areas described their own health as 'good' or 'very good', compared to approx. 33% of people of the same age in rural areas. The country has 86 hospitals, 1,524 pharmacies and branches, 12,600 physicians, 23,687 paramedical personnel, and 17,293 hospital beds. Moldova spends 6% of its annual GDP on health care, up from 4.9% in 2019.
As of 2022 the average life expectancy was 71.5 years (67.2 for males, and 75.7 for females), slightly lower than comparable countries such as Albania, Bulgaria, Latvia, and Ukraine. The number of elderly people (aged 60 years and over) per 100 inhabitants in Moldova has increased year-on-year. The total fertility rate per woman in 2022 was 1.69, a fall from 1.78 in 2019, and below the replacement rate of 2.1. There were 10.6 live births per 1,000 inhabitants in 2022, a drop from 12.2 in 2019, and 14.2 deaths per 1,000 inhabitants, an increase from 13.7 in 2019 but a significant fall from 17.5 in 2019. Infant mortality per 1,000 live-births was 9.0, a slight increase on 8.7 in 2020.
The overall number of deaths in 2022 fell by 20.5% compared to 2021. According to the National Agency for Public Health, the major causes of death in 2022 were diseases of the circulatory system (58%), cancerous tumours (15.8%), diseases of the digestive tract (7.5%), external causes (4.8%), and other causes (13.9%). More specifically, the leading causes of death in 2019 were Ischaemic heart disease, strokes, hypertensive heart disease, cirrhosis of the liver, and trachea, bronchus, and lung cancers.
On 19 December 2016, the Moldovan parliament approved raising the retirement age to 63 years from the current level of 57 for women and 62 for men, a reform that is part of a 3-year-old assistance program agreed with the International Monetary Fund. The retirement age will be lifted gradually by a few months every year until it is fully in effect in 2028.
Education
As of the academic year 2022/23, Moldova had 1,218 primary and secondary schools, 90 vocational schools, and 21 higher education institutions, as well as 12 private higher education institutions. There were a total of 437,000 pupils and students. As of 2015, Romania allocates 5,000 scholarships in high schools and universities for Moldovan students. Likewise, more than half of preschool children in Moldova benefit from Romania funded program to renovate and equip kindergartens. Almost all the population is literate: the literacy rate of the population aged 15 and over is estimated at 99.6%.

The main higher education institutions in Moldova are the Moldova State University (est. 1946) and the Academy of Sciences of Moldova (est. 1961), both of which are located in Chișinău. The Academy of Economic Studies of Moldova (est. 1991) has featured on the Times Higher Education World University Rankings and has educated a number of national leaders including current President of Moldova Maia Sandu and leader of the opposition Igor Dodon. Other important universities include the Ion Creangă State Pedagogical University of Chișinău (est. 1940), Nicolae Testemițanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy (est. 1945), and the Technical University of Moldova (est. 1964). Women account for 59.1% of students in higher education, and 70.1% of all foreign students in doctoral programmes in Moldova. 32.3% of employed women in Moldova have received higher education, compared to 24.5% of men, and 16.9% specialised secondary education compared to 11.3% of men.
Regional differences and tensions
See also: Transnistria conflict, Gagauzia, and Unification of Moldova and Romania
Since independence, Moldova characterised by a substantial range of profound regional differences across its internationally recognised territory. Since independence, the country has struggled with issues of national identity, geopolitical strategy, and alliances, often torn between Romania and the European Union to the west and the Russian Federation to the east. Most notably, in eastern Moldova is the unrecognised breakaway state of Transnistria, which lies on the eastern bank of the Dniester river and borders Ukraine, which has pursued close diplomatic, military, and economic ties with Russia since 1992, with more than a thousand Russian soldiers stationed in the region. This has proved particularly difficult following Russia's invasion of Ukraine in 2022, as Transnistria's position on Ukraine's south-western flank and its hosting of more than a thousand Russian soldiers poses a potential threat to Ukraine's war efforts. The European Union's High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy Josep Borrell has confirmed that the pathway to accession does not depend upon a resolution of the Transnistria conflict. There is further the issue of the autonomous territorial unit of Gagauzia. The Gagauz people are a Turkic-speaking people spread between southern Moldova and the south-west of Ukraine. While their exact origin is considered obscure, they have a strong sense of ethnic identity distinct from that of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine, with a distinctive language and cultural traditions. They are nevertheless a heavily Russified group. Support for integration with Romania and the European Union is substantially lower among Gagauzians than among the broader Moldovan population. In 2014, shortly before the Republic of Moldova signed its EU Association Agreement, nearly 99 per cent of Gagauzians voted in a referendum "to reject closer links with Europe in favour of joining the Russian-led Eurasian Economic Union." In 2015, "just over half of Gagauzians voted for the Russian-backed socialist candidate Irina Vlakh as governor." Gagauzia continues to represent a serious challenge both to Moldova's territorial sovereignty and political stability due to Russia's systemic involvement in the region, especially by backing pro-Russian local parties and leadership candidates. The European Centre for Minority Issues has also highlighted the role of supposedly-neutral NGO groups in Gagauzia as a new front in Russia's hybrid-war against both Moldova and Ukraine. The region's current local leader, Evghenia Guțul, in July 2023 thanked the fugitive Moldovan oligarch Ilan Shor, leader of the outlawed Moldovan pro-Russian opposition Șor Party, for his personal and financial support and his "willingness to do what it takes so that we may fulfil our election promises", and expressed a desire for deeper diplomatic ties with Russia.
There is also substantial controversy over ethnic and linguistic identity in Moldova concerning whether the Moldovan language and Moldovan people constitute separate linguistic and ethnic groups to the Romanian language and Romanian people. The possibility of the unification of Moldova and Romania has remained a popular topic in both countries since Moldova's independence in 1991. Romania and Moldova enjoy exceptionally strong diplomatic relations. Romania supports Moldova's rapid accession to the European Union, provides vast economic assistance to Moldova's struggling economy, and provided up to 90% of Moldova's energy needs via discounted capped prices as Moldova sought to reduce its reliance on Russian oil and natural gas. Relations have strengthened further since Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Up to 74% of the Romanian public and more than 40% of the Moldovan public would support Moldova being integrated into Romania in one form or another, though most in either country believe that 'now is not the right time'. A 2022 survey during the Russian invasion of Ukraine indicated that only 11% of Romania's population supports an immediate union, while over 42% think it is not the moment.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Moldova Mihai Eminescu, the national poet of Moldova and Romania
Mihai Eminescu, the national poet of Moldova and Romania Dimitrie Cantemir, Moldavian scholar of the early Enlightenment
Dimitrie Cantemir, Moldavian scholar of the early Enlightenment
Moldova's cultural tradition has been influenced primarily by the Romanian origins of its majority population, the roots of which go back to the second century AD, the period of Roman colonization in Dacia. Located geographically at the crossroads of Latin, Slavic and other cultures, Moldova has enriched its own culture adopting and maintaining traditions of neighbouring regions and of other influential sources. The largest ethnic group, which had come to identify itself widely as "Moldovan" by the 14th century, played a significant role in the shaping of classical Romanian culture. The culture has been also influenced by the Byzantine culture, the neighbouring Magyar and Slavic populations, and later by the Ottoman Turks. A strong Western European influence in Moldovan literature and arts was prevalent in the 19th century. During the periods 1812–1917 and 1944–89, Moldovans were influenced by Russian and Soviet administrative control as well and by ethnic Russian immigration.

The country's cultural heritage was marked by numerous churches and monasteries built by the Moldavian ruler Stephen the Great in the 15th century, by the works of the later renaissance Metropolitans Varlaam and Dosoftei, and those of scholars such as Grigore Ureche, Miron Costin, Nicolae Milescu, Dimitrie Cantemir and Ion Neculce. In the 19th century, Moldavians from the territories of the medieval Principality of Moldavia, divided into Bessarabia, Bukovina, and Western Moldavia (after 1859, Romania), made a significant contribution to the formation of the modern Romanian culture. Among these were many Bessarabians, such as Alexandru Donici, Alexandru Hâjdeu, Bogdan Petriceicu Hasdeu, Constantin Stamati, Constantin Stamati-Ciurea, Costache Negruzzi, Alecu Russo, Constantin Stere.
Mihai Eminescu, a late Romantic poet, and Ion Creangă, a writer, are the most influential Romanian language artists, considered national writers both in Romania and Moldova.
Cuisine
Main article: Moldovan cuisineMoldova's fertile soil (chernozem) produces plentiful grapes, fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, and milk products, all of which have found their uses in the national cuisine. The fertile black soil combined with the use of traditional agricultural methods permits the growth of a wide range of foods in Moldova. Moldovan cuisine is similar to neighbouring Romania, Ukraine, and Poland, and the regions share many traditional dishes, often with regional variations. Moldovan cuisine has historically been particularly influenced by elements of Russian, Turkish, and Ukrainian cuisine. Main dishes often include beef, pork, potatoes, cabbage, and a variety of cereals. Popular alcoholic beverages are divin (Moldovan brandy), beer, and wine—for which the country is known due to its high-quality offerings.

There are several traditional Moldovan dishes. Plăcinte are stuffed and deep-fried pastries with fillings such as soft cheese (often Urdă), cabbage, potatoes, apples, sour cherries and others, both sweet and savoury. Sarmale is a typical Moldovan dish usually consisting of cabbage leaves stuffed with rice, peppers, carrots, meat, and baked in oil. Regional variations can also be found in other former parts of the Ottoman Empire. Mămăligă, a kind of porridge made from yellow maize flour, is another staple. It is popular in other countries as polenta and is often served with sheep's cheese and sour cream. Another traditional dish, plachyndy, is a kind of flatbread often made with kefir or buttermilk, wrapped around herbs, and pan-fried in oil. Zeamă is a thin chicken soup, typically consisting of homemade chicken broth prepared with a smaller whole chicken, water, thin homemade egg noodles (tăiței de casă), and a variety of finely chopped vegetables and herbs. Brynza is a soft sheep/goat cheese with a crumbly texture and tangy taste, mostly produced and popular in Slovakia, Romania, and Moldova, and often used in salads, pies, and dumplings.
Borscht, a sour Eastern European soup made from beetroots, meat stock, and vegetables, is also popular and commonly served in Moldova. As with other parts of the region, pierogi (known as chiroște in Moldova) are another traditional staple and are often stuffed with a soft cheese in Moldova. The dough is made with wheat flour and is boiled in salted water, pan-fried in oil, or baked in the oven. Medovik, a cake of Russian origin (and called Tort Smetanik in Moldova) is a popular layered cake with honey and smetana (sour cream) or condensed milk.
Total recorded adult alcohol consumption is approximately evenly split between spirits, beer, and wine. Notably, Moldova has among the highest alcohol consumption per capita in world, at 15.2 litres (4.0 US gal) of pure alcohol imbibed in 2016. This has fallen somewhat in recent years, but it remains a serious ongoing health concern.
Holidays
Main article: Public holidays in MoldovaMost retail businesses close on New Year's Day and Independence Day, but remain open on all other holidays. Christmas is celebrated either on 7 January, the traditional date in Old Calendarists Eastern Orthodox Churches, or on 25 December, with both dates being recognized as public holidays.
On 1 March features mărțișor gifting, which is a tradition that females are gifted with a type of talisman that is given for good luck.
Music
Main article: Music of Moldova
Among Moldova's most prominent composers are Gavriil Musicescu, Ștefan Neaga and Eugen Doga.
In the field of pop music, Moldova has produced the band O-Zone, who came to prominence in 2003, with their hit song "Dragostea Din Tei", which topped multiple notable single charts. Moldova has been participating in the Eurovision Song Contest since 2005. Another popular band from Moldova is Zdob și Zdub that represented the country in the 2005 Eurovision Song Contest, finishing sixth, also in 2021, with a similar result.
In May 2007, Natalia Barbu represented Moldova in Helsinki at the Eurovision Song Contest 2007 with her entry "Fight". Natalia squeezed into the final by a very small margin. She took tenth place with 109 points. Then Zdob și Zdub again represented Moldova in the 2011 Eurovision Song Contest finishing 12th.
The band SunStroke Project with Olia Tira represented the country in the 2010 Eurovision Song Contest with their hit song "Run Away". Their performance gained international notoriety as an internet meme due to the pelvic thrusting and dancing of Sergey Stepanov, the band saxophonist. He has been dubbed "Epic Sax Guy". SunStroke Project featured again in the 2017 Eurovision entry "Hey Mama" which got third place.
In 2015 a new musical project by the name of Carla's Dreams has risen in popularity around Moldova. Carla's Dreams reached the top charts in multiple countries in Europe with the release of their song "Sub Pielea Mea" in 2016. The song received a lot of airplay and reached number one place on the charts in Moldova as well as Russia. The group is still active and released their latest album in 2017. The theme of the musical group is "Anonymous" as they perform with painted faces, hoodies and sunglasses. The identity of the group members is still unknown.
Among most prominent classical musicians in Moldova are Maria Bieșu, one of the leading world's sopranos and the winner of the Japan International Competition; pianist Mark Zeltser, winner of the USSR National Competition, Long-Thibaud-Crespin Competition in Paris and Busoni Competition in Bolzano, Italy.
Media
Main articles: Media of Moldova, Television in Moldova, Cinema of Moldova, and List of newspapers in MoldovaThe right to freedom of speech and right to information are guaranteed by the Moldovan constitution. Reporters Without Borders improved Moldova's Press Freedom Index ranking to 28th in 2023 from 89th in 2020, partly due to government legal reforms which made it easier for journalists to access official information. However, they cautioned that "Moldova's media are diverse but extremely polarised, like the country itself, which is marked by political instability and excessive influence by oligarchs." Moldova's media are divided into pro-Russian and pro-Western camps and on party political lines. Oligarchs and political leaders strongly influence their editorial stances.
Television remains the most popular and trusted medium, while online social media is exerting increasing influence. Most private FM radio networks rebroadcast output from Russian and Romanian stations. The first publicly funded national radio broadcaster, Radio Moldova, has been broadcasting since 1939 from the capital city, Chişinău. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty is also widely available. Moldova's state-owned national radio-TV broadcaster is Teleradio-Moldova (TRM), which broadcasts the TV channel Moldova 1.
There were 3 million internet users by July 2022, approximately 76% of the population, and digital infrastructure is well-developed, with 98% 4G coverage of territory. There are a number of daily and weekly newspapers published in Moldova, among the most popular being Timpul de dimineață and Moldova Suverană, but print media has an overall small audience in Moldova. Independent media are struggling to ensure financial sustainability in the face of diminishing advertisement revenues due to inflation, economic stagnation and uncertainty caused by Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
In 2022, the government removed the broadcasting licenses from six television stations for broadcasting pro-Russian propaganda and disinformation about Russia's invasion of Ukraine in violation of the country's Audiovisual Services Code. The government stated that this was done in order to "prevent the risk of disinformation or attempts to manipulate public opinion". All six were either owned or affiliated with Ilan Șhor, a fugitive pro-Russian politician and businessman who fled to Israel in 2019 after being convicted of fraud and money-laundering and sentenced to 15 years in prison in absentia. In October 2023 Orizont TV, ITV, Prime, Publika TV, Canal 2 and Canal 3 were also banned for undermining the local elections as well as blocking a number of Russian media outlets which includes the news agencies TASS and Interfax.
The cinema of Moldova developed in the 1960s during the Soviet period, nurturing a small but lively film industry. Following the collapse of the Soviet Union and Moldova's independence, the country's economic stagnation and poverty has hampered the Moldovan film industry. Nevertheless, some films have seen some international success. Perhaps best-known are Lăutarii (1972), written and directed by Moldovan film-maker Emil Loteanu, and Wedding in Bessarabia (2009), which was co-produced by Romania, Moldova, and Luxembourg. In recent years Moldovan cinema has gained greater international attention. Carbon (2022), directed by Ion Borş, received positive acclaim by magazines such as Variety. It was the winner of the Transilvania International Film Festival's Audience Award. For the 37th edition of the Fribourg International Film Festival, Moldova was featured in its 'New Territory' section, which celebrates little-known film-making cultures. In July 2022, the United Nations Development Programme announced that it would be using state-of-the-art equipment to transfer more than 1,600 films from the Moldova-Film archive for posterity and cultural preservation. The United States assisted by equipping in 2021 a digitization laboratory to restore and preserve its archive feature and documentary films, representing an important part of Moldova's historical, cultural, and artistic heritage, and many of the films were broadcast on national TV with Romanian subtitles.
Sports
Main article: Sport in Moldova
Association football is the most popular team sport in Moldova. The governing body is the Moldovan Football Federation, which belongs to UEFA. The Moldova national football team played its first match in 1994, but never qualified to the UEFA European Championship. The most successful football club is Sheriff Tiraspol, the first and only Moldovan club to qualify for the group stage of the Champions League and the Europa League. Other winners of the Moldovan National Division include Zimbru Chișinău, Dacia Chișinău, FC Tiraspol and Milsami Orhei.
Trîntă (a form of wrestling) is the national sport in Moldova. Rugby union is popular as well. More than 10,000 supporters turn out for home internationals. Since 2004, playing numbers at all levels have more than doubled to 3,200. Despite the hardships and deprivations the national team are ranked 34th in the world. The most prestigious cycling race is the Moldova President's Cup, which was first run in 2004. In chess, the Republic of Moldova has several international masters, among which can be mentioned Viorel Iordăchescu, Dmitry Svetushkin, and Viorel Bologan.
Radu Albot is one of the most successful Moldovan tennis players, with ATP singles (2019 Delray Beach Open) and doubles (2015 Istanbul Open) titles.
Athletes from Moldova have won European medals in athletics, biathlon, football, and gymnastics; world medals in archery, judo, swimming, and taekwondo; as well as Olympic medals in boxing, canoeing, shooting, weightlifting, and wrestling. Moldova made its Olympic debut at the 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer. Olympic medalists include Sergei Mureiko, Oleg Moldovan, Vitalie Grușac, Veaceslav Gojan, and Serghei Tarnovschi. Nicolae Juravschi represented the Soviet Union at the 1988 Seoul Games, winning two medals.
See also
Notes
- There is a controversy over the self-identification of Moldovans, with some authors considering them ethnic Romanians.
- The de jure area, accepted by the Moldovan government and the Tiraspol authorities for Transnistria, is 3,509.6 square kilometers. The de facto area administered by Transnistria is 3,653 square kilometers, while the area claimed by Transnistria is 4,163 square kilometers.
- ^ Excludes data for Transnistria.
- /mɒlˈdoʊvə/ mol-DOH-və, sometimes UK: /ˈmɒldəvə/ MOL-də-və; Romanian pronunciation: [molˈdova]
- Romanian: Republica Moldova
- Prince Dimitrie Cantemir was one of the most important figures of the Moldavian culture of the 18th century. He wrote the first geographical, ethnographic, and economic description of the country. (in Latin) Descriptio Moldaviae, (Berlin, 1714), at Latin Wikisource.
References
- "Constituția Republicii Moldova, articolul 13: (1) Limba de stat a Republicii Moldova este limba română, funcționând pe baza grafiei latine. (pag.25)" (in Romanian). Parlamentul Republicii Moldova. Archived from the original on 5 April 2023. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- "Constituția Republicii Moldova, articolul 13 (1), pag.25" (PDF) (in Romanian). Preşedinţia Republicii Moldova. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 May 2023. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- "Președintele CCM: Constituția conferă limbii ruse un statut deosebit de cel al altor limbi minoritare". Deschide.md. Archived from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- "Chişinău, (21.01.2021) Judecătorii constituționali au decis că limba rusă nu va avea statutul de limbă de comunicare interetnică pe teritoriul Republicii Moldova". Moldpres.md. Archived from the original on 23 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- "Președintele CC Domnica Manole, explică de ce a fost anulată legea cu privire la statutul special pentru limbia rusă". ProTv.md. Archived from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ "Recensamântul Populației si al Locuințelor 2014". statistica.gov.md. 2 August 2013. Archived from the original on 2 December 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- "Republica Moldova – Geografie". Moldova.md. 26 August 2016. Archived from the original on 24 June 2021. Retrieved 23 June 2021.
- "MOLDOVA: Transnistria (Pridnestrovie)". Citypopulation.de. Archived from the original on 25 March 2021. Retrieved 23 June 2021.
- "Numărul populației cu reședință obișnuită, pe sexe şi grupe de vârstă, în profil teritorial la 1 Ianuarie 2023" (in Romanian). Biroul Național de Statistică al Republicii Moldova (BNS). 8 June 2023. Archived from the original on 9 June 2023. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Moldova)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- "Gini index – Moldova". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 23 September 2024.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2021/2022" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- "Moldova". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 22 March 2020.
- "Moldova". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- The Free Dictionary: Moldova
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- "Moldova country profile". BBC News. 3 April 2012. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Moldova". CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 5 January 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ^ ""Wine Road" in Republic of Moldova" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- "EU awards Ukraine and Moldova candidate status". BBC News. 23 June 2022. Archived from the original on 23 June 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- "EU greenlights accession talks with Ukraine and Moldova". Euronews. 14 December 2023. Archived from the original on 14 December 2023. Retrieved 14 December 2023.
- Lynch, Suzanne (20 January 2023). "Time to join NATO? Moldova eyes joining 'a larger alliance'". Politico. Archived from the original on 21 January 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "GDP per capita, PPP (current international $)". Archived from the original on 27 July 2022. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). Global Innovation Index 2024. Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship. Geneva. p. 18. doi:10.34667/tind.50062. ISBN 978-92-805-3681-2. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "History". Republic of Moldova. Archived from the original on 22 December 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- King, Charles (2000). "From Principality to Province". The Moldovans: Romania, Russia, and the politics of culture. Hoover Press. p. 13. ISBN 0-8179-9792-X. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- "The End of the Soviet Union; Text of Accords by Former Soviet Republics Setting Up a Commonwealth". The New York Times. 23 December 1991. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
...Republic of Kazakhstan, the Republic of Kirghizia, the Republic of Moldavia, the Russian Federation...
- "Moldova election: Pro-EU candidate Maia Sandu wins presidency". BBC News. 16 November 2020. Archived from the original on 24 April 2021. Retrieved 27 July 2021.
- "Moldova election: Pro-EU leader wins despite alleged Russian meddling". www.bbc.com.
- "Moldova early parliamentary elections 2021: OSCE/ODIHR election observation mission final report". Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. 22 December 2021. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "2022 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Moldova". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 1 June 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "The Constitution of the Republic of Moldova, 2000". E-democracy.md. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "DECIS: Şeful statului va fi ales de popor; Modificarea din 2000 a Constituţiei privind alegerea preşedintelui de Parlament, NECONSTITUŢIONALĂ" [DECIDED: The president will be elected by the people; The 2000 amendment of the Constitution concerning the election of the President by Parliament unconstitutional]. Jurnalul Național (in Romanian). 4 March 2016. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- "Moldova Calls on Russian Troops To Leave Transdniestr".
- Barry, Ellen (3 January 2012). "Shooting at Checkpoint Raises Tensions in a Disputed Region Claimed by Moldova". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 January 2012. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- "EU to grant €90 million to crisis-hit Moldova". Europarl.europa.eu. 7 September 2010. Archived from the original on 26 May 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Moldova to get $570 million in IMF loans". RIA Novosti. 30 January 2010. Archived from the original on 19 October 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Chiriac, Marian (27 April 2010). "Romania, Moldova to Boost Relations". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Poland will support Moldova in its European integration efforts". Moldova Azi. Archived from the original on 27 August 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "First meeting of Romania and Rep. of Moldova Governments, concluded with initialling of several bilateral agreements". agerpres.ro. 4 March 2012. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014.
- "Joint meeting of the Government of Romania and Government of the Republic of Moldova" (in Romanian). Guvernul Romaniei. Archived from the original on 8 February 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- The Washington Post, Moldova elected pro-European judge Timofti as president, ending 3 years of political deadlock Archived 4 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- "EU-Moldova Association Agreement". European Union External Action. Archived from the original on 7 December 2013.
- "Băsescu: Următorul proiect de țară al României, unirea cu Basarabia". România Liberă. 27 November 2013. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- ^ "Secret document reveals Russia's 10-year plan to destabilize Moldova". CNN. 16 March 2023. Archived from the original on 12 September 2023.
- "How Russia Torpedoed Its Own Influence in Moldova". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. 11 March 2023. Archived from the original on 21 September 2023.
- Andrew Higgins, "In Expanding Russian Influence, Faith Combines With Firepower," The New York Times, 13 September 2016 Archived 10 November 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- Scotto di Santolo, Alessandra (15 May 2023). "Major blow for Putin as Moldova withdraws from Russia-led alliance". The Daily Express. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- Popusoi, Cristina (18 May 2023). "Moldova Is Distancing Itself From The CIS, But Leaving Might Not Be So Easy". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- Goble, Paul (10 November 2022). "Moscow Working to Block Moldova from Leaving CIS". The Jamestown Foundation. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "PARLIAMENT ADOPTS IN FINAL READING LAW ON MOLDOVA'S WITHDRAWAL FROM CIS INTERPARLIAMENTARY ASSEMBLY". 20 July 2023. Archived from the original on 29 January 2024. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- Pennington, Josh; Pokharel, Sugam (25 July 2023). "Moldova summons Russian ambassador after media reporting on alleged spy devices on embassy's rooftop". CNN. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "Moldova expels 45 Russian diplomatic staff in spy row". BBC News. 26 July 2023. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- Bennetts, Marc (1 August 2023). "Moldova expels 45 Russian diplomats and embassy staff". The Times. ISSN 0140-0460. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- Tanas, Alexander (30 July 2023). "Russian embassy in Moldova to suspend consular appointments". Reuters. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- Necșuțu, Mădălin (1 August 2023). "Moldovan Secret Services Cancel Agreements with Russian Intelligence". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova sets 2030 as EU accession target at massive pro-EU rally in Chisinau". 22 May 2023. Archived from the original on 8 December 2023. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- "European Union – EEAS (European External Action Service) – EU forges closer ties with Ukraine, Georgia and Moldova". Eeas.europa.eu. Archived from the original on 6 July 2016. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- "European Commission – PRESS RELEASES – Press release – Remarks by President Barroso at the signing of the Association Agreements with Georgia, the Republic of Moldova and Ukraine". Europa.eu. Archived from the original on 30 June 2014. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- Tanas, Alexander (3 March 2022). "With war on its doorstep, Moldova applies for EU membership". Reuters. Archived from the original on 25 June 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- Brzozowski, Alexandra (23 June 2022). "EU leaders grant candidate status to Ukraine and Moldova". euractiv.com. Euractiv. Archived from the original on 23 June 2022. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- "UNDP to support the Republic of Moldova to implement key reforms on its EU accession path | United Nations Development Programme". UNDP. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Moldova's EU Path Independent Of Transdniester Developments, Says Borrell". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. 1 June 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "EFTA and Moldova sign a Free Trade Agreement | European Free Trade Association". European Free Trade Association. 27 June 2023. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- "The EU presents a Support Package for the Republic of Moldova". European Commission. 28 June 2023. Archived from the original on 21 June 2019. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "EU greenlights accession talks with Ukraine but Orbán vetoes €50-billion aid package". Euronews. 14 December 2023. Archived from the original on 14 December 2023. Retrieved 14 December 2023.
- "Moldova will hold referendum on EU membership without Transnistria: Sandu". 29 December 2023. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- Balmforth, Tom; Tanas, Alexander (21 October 2024). "Moldova's EU referendum in tight finish; Sandu decries vote meddling". Reuters. Retrieved 21 October 2024.
- "EU is preparing mission to Moldova to make it more resistant to hybrid threats, – Borrell". 22 March 2023. Archived from the original on 19 September 2023. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- Swaton, Chiara (8 June 2023). "Austria sends police officers, soldiers to EU Moldova mission". Euractiv. Archived from the original on 15 June 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- Rettman, Andrew (31 March 2023). "EU sending anti-coup mission to Moldova in May". EUobserver. Archived from the original on 4 June 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Welt: EU to Send Mission to Moldova to Consult on Country's Security – the Briefing". Archived from the original on 5 April 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "EU members look to support Moldova, send muntions to Ukraine to offset Russian expansionism". Radio France Internationale. 25 April 2023. Archived from the original on 21 June 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- Necșuțu, Mădălin (8 February 2023). "Moldova 'Separatism Law' Sparks Tensions With Breakaway Transnistria". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Necșuțu, Mădălin (13 July 2022). "Moldova Weighs Mobility and Firepower in Military Overhaul". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 19 September 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "OSCE Document on Stockpiles of Conventional Ammunition". OSCE. 19 November 2003. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Ministry of Defense of Republic of Moldova". www.army.md. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "UNMIL". United Nations Peacekeeping. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "2014 – Embassy of the United States Chișinău, Moldova". Moldova.usembassy.gov. Archived from the original on 4 September 2015.
- "Moldova's military agreements to help strengthen regional security". Archived from the original on 4 September 2015. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- "EU hands over first batch of modern equipment to Moldovan armed forces – EU NEIGHBOURS east". euneighbourseast.eu. 1 June 2023. Archived from the original on 13 June 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Defense Minister Says 90 Percent Of Moldova's Military Equipment Is Outdated". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 31 May 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- Tanas, Alexander (13 April 2023). "Moldova needs $275 million to modernise armed forces, defence official says". Reuters. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Poland sends military equipment to Moldovan police". www.thefirstnews.com. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Poland hands over weapons and ammunition to the Moldovan police – Militarnyi". mil.in.ua. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- Kirichenko, David (12 June 2023). "Moldova Needs Western Weapons". Center for European Policy Analysis. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Moldova: Freedom in the World 2023 Country Report". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "2022 Corruption Perceptions Index – Explore Moldova's results". Transparency International. 31 January 2023. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Moldova | Free Press Unlimited". Free Press Unlimited. 13 April 2021. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- "Moldova | RSF". Reporters Without Borders. 23 July 2020. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 5 July 2023.
- "Human rights in Moldova". Amnesty International. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Tanas, Alexander (18 June 2023). "LGBT activists in Moldova hold march without police protection". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "2010 Human Rights Report: Moldova". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 13 October 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Moldova: 13th EU-Moldova Human Rights Dialogue in Brussels | EEAS". Diplomatic Service of the European Union. 20 October 2022. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova | HCRW". hatecrime.osce.org. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Autorități publice locale". Government of Moldova. Archived from the original on 28 August 2010. Retrieved 12 October 2010.
- "Clasificatorul unităţilor administrativ-teritoriale (CUATM)". Archived from the original on 8 May 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2017.
- "Law on police use of force in Moldova". The Law on Police Use of Force. 10 May 2021. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Medical Assistance". U.S. Embassy in Moldova. Archived from the original on 31 May 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "List of medical facilities in Moldova". Government of the United Kingdom. 24 January 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Burks, Roger (2 August 2022). "Moldovan GBV shelter offers safety and a community for refugees from Ukraine". UNHCR. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- NY Times report
- "Geography – Republic of Moldova". Republic of Moldova. 26 August 2016. Archived from the original on 28 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Moldova's Climate". Weatheronline.co.uk. Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- Stînga Nistrului. "Camenca temperature". Weather-forecast.com. Archived from the original on 5 June 2014. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Bratuseni temperature". Worldweatheronline.com. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Moldova climate information". Weatherbase. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2016.
- Dinerstein, Eric; Olson, David; Joshi, Anup; Vynne, Carly; Burgess, Neil D.; Wikramanayake, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869. S2CID 13136188.
- Grantham, H.S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T.D.; Jones, K.R.; Beyer, H.L.; Schuster, R.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity". Nature Communications (Supplementary material). 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507. S2CID 228082162.
- ^ "Environmental issues in Moldova". Naturvernforbundet. 7 October 2009. Archived from the original on 9 April 2015. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- Sienkiewicz, Henryk. Ogniem i Mieczem [With Fire and Sword]. Vol. 1. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- "O suhaku, który z suchych stepów przybył" [On the Suhaku of the arid steppes]. Menażeria Etymologiczna (in Polish). 6 October 2017. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020 – via wordpress.com.
- Moldova participants & European participants (PDF). European Partnership Fair for Civil Society Organizations in Moldova. Republican Palace, Chisinau, Moldova: European Partnership for Democracy. 15–16 June 2010. p. 25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2010.
- Strabo. "book VII, chapter 4, paragraph 8". Geographica [Geography]. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- Autor invitat (27 August 2005). "The bison come back to Moldova". Moldova.org. Archived from the original on 16 June 2020. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- "Belarus, Moldova discuss bison exchange program" (Press release). Ministry of Forestry of the Republic of Belarus. 17 February 2019. Archived from the original on 28 July 2020. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- "The World Bank in Moldova". World Bank. 7 April 2023. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "GDP Per Capita (current US$) – Moldova | Data". World Bank. Archived from the original on 26 May 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "Moldova | Data". World Bank. Archived from the original on 26 May 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "IMF Executive Board Concludes Second Reviews Under the Extended Credit Facility and Extended Fund Facility Arrangements for the Republic of Moldova". IMF. 9 January 2023. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Walker, Shaun; Nardelli, Alberto (18 January 2015). "Russia's rouble crisis poses threat to nine countries relying on remittances". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 9 December 2016. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "Moldova – Market Overview". International Trade Administration. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "Wine in Moldova | OEC". OEC – The Observatory of Economic Complexity. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Five Things To Know About Moldova". Barron's. 1 June 2023. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Moldova – Information and Communication Technology". International Trade Administration. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "World Bank Open Data". World Bank Open Data. Archived from the original on 26 May 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Indicators of economy in Moldova". Archived from the original on 16 October 2023. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- Yafimava, Katja (5 November 2021). "Moldova's Gas Crisis and Its Lessons for Europe". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Archived from the original on 14 May 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Necșuțu, Mădălin (12 April 2022). "Moldovagaz Asks Gazprom for More Time on Debt Audit". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Jack, Victor (21 November 2022). "Putin puts the energy squeeze on pro-EU Moldova". Politico. Archived from the original on 29 July 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Gazprom dealt fresh blow as Moldova ditches Russian gas entirely". Yahoo News. 19 May 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Necșuțu, Mădălin (26 January 2023). "Moldova Audit Reveals Fraud Worth 100 Million Euros at Moldovagaz". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova Economy Profile 2014". Indexmundi.com. Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- "How Moldova Getting Ready to Cut off Gas to Transnistria and Consequences for Region". 26 June 2023. Archived from the original on 15 November 2023. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- "Moldova no longer using Russian natural gas, PM says". Reuters. 18 May 2023. Archived from the original on 9 July 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- "Moldova to get $570 million in IMF loans". RIA Novosti. 30 January 2010. Archived from the original on 19 October 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- Marian Chiriac (27 April 2010). "Romania, Moldova to Boost Relations". Balkaninsight.com. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- "Moldova energy profile – Analysis". IEA. Retrieved 21 October 2021.
- Petterson, Leif (2 July 2013). "Moldova: embracing its status as Europe's least-visited country". Lonely Planet. Archived from the original on 15 August 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Buckley, Julia (6 August 2022). "How the Ukraine invasion flattened Eastern European tourism". CNN. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Erizanu, Paula (1 June 2023). "I've come to love Chișinău: my home city in Moldova deserves the spotlight". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 18 October 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Cooper, Tim (30 September 2021). "Chisinau city guide: Where to eat, drink and stay in Moldova's capital". The Independent. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Smith, Jen Rose (8 May 2019). "Why you should go to the world's least-visited countries". CNN. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "25 quirky facts about Europe's least touristy country". The Daily Telegraph. 27 August 2016. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Suri, Charu (12 February 2018). "This Enchanting Country May Be Eastern Europe's Best-Kept Secret". Architectural Digest. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Taylor, Chris (28 February 2019). "Moldova: exploring Europe's poorest and least visited nation". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova.travel – the official tourist portal of Moldova". Moldova Travel. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "How to travel by train from London to Moldova". www.seat61.com. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- R, Bleona (30 April 2022). "Moldova Marks 8 Years of Visa-Free Travel to EU". SchengenVisaInfo.com. Archived from the original on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Largest wine cellar by number of bottles". Guinness World Records. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "The world's least visited countries – have you been to any of them?". The Telegraph. 29 October 2019. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Orheiul Vechi Archaeological Landscape". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "The Typical Chernozem Soils of the Balti Steppe". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 7 November 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Waller, John (9 October 2022). "Travel: Exploring Moldova – Europe's 'least known country'". Bradford Telegraph and Argus. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Moldova wine industry's EU focus pays off". France 24. 22 May 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- Bednarz, Christine (29 November 2017). "This Massive Underground City is Filled With Wine". nationalgeographic.com. Archived from the original on 1 November 2022. Retrieved 31 October 2022.
- ^ Gerciu, Viorel; Rundgren, Gunnar (2017). "The Status and Potential of Organic Agriculture in the Republic of Moldova" (PDF). UN Environment Programme. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- "Moldova". www.fao.org. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "REPUBLIC OF MOLDOVA – Statistical Database – United Nations Economic Commission for Europe". w3.unece.org. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova", The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, 25 July 2023, archived from the original on 5 January 2021, retrieved 2 August 2023
- "Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Moldova, editions 2002–2022". Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Moldova, editions 2002–2022. 1 November 2022. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Seed libraries were created as a first in Moldova, thanks to transfer Czech know-how". United Nations Development Programme. 27 July 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Climate change, environment & energy | Moldova". United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on 12 July 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Embracing a new approach to climate change in Moldova". Climate-KIC. 7 May 2021. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Worldwide Broadband Price Research 2023". Cable.co.uk. Archived from the original on 23 November 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Moldova – Information and Communication Technology". International Trade Administration. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Botezatu, Serghei (4 October 2021). "Digital Transformation of Moldova: there is no way back". UNDP. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- "Moldova media guide – BBC News". BBC News. 22 May 2023. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- @SpaceX (3 August 2022). "Starlink is now live in Moldova → http://starlink.com/map" (Tweet). Retrieved 3 August 2022 – via Twitter.
- Stupp, Catherine (27 July 2022). "Moldova Plans Cyber Overhauls Amid War in Neighboring Ukraine". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- Gallagher, Ryan (20 April 2023). "Cyberwar Descends on an Unprepared Moldova". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova Cybersecurity Rapid Assistance". EU4Digital. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Moldova adopts EU-backed Cybersecurity Law – EU NEIGHBOURS east". euneighbourseast.eu. 17 May 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "| Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of the Republic of Moldova". Government of Moldova. 2 October 2022. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- "Recensământul Populației și Locuințelor 2024". National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Population". National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. Retrieved 13 August 2024.
- "Moldova", The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, 31 July 2023, archived from the original on 5 January 2021, retrieved 3 August 2023
- "World Bank Open Data". World Bank Open Data. Archived from the original on 26 May 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ "Moldova in Figures, Statistical Summary: 2023 Edition" (PDF). National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Judah, Tim (16 January 2020). "Moldova Faces 'Existential' Population Crisis". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- Fremer, Iana (24 April 2023). "Moldova: New Law Establishes Romanian as the State Language of the Country". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Moldovan Parliament Approves Final Reading Of Romanian Language Bill". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. 17 March 2023. Archived from the original on 17 March 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Bunguri, Ernest (15 November 2020). "Moldova: How the diaspora keeps Europe's poorest nation afloat". Euronews. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Moldova: unleashing diaspora potential". Mieux Initiative. 17 May 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Ceapai, Alla; Jankowiak, Celine (31 May 2023). "Returning Young Moldovan Diaspora Powers EU Membership Dream". Barron's. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Wemer, David (4 December 2020). "Moldova's diaspora flexes its political muscles". Atlantic Council. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ "2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Moldova". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Population and Housing Census in the Republic of Moldova, May 12–25, 2014". National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. 2 August 2013. Archived from the original on 17 September 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Luchenko, Ksenia (31 January 2023). "Why the Russian Orthodox Church Supports the War in Ukraine". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Moldovan Muslim Leader 'Disappointed' By Anti-Islamic Remarks". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 28 April 2011. Archived from the original on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Republic of Moldova data | World Health Organization". World Health Organization. 9 December 2020. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- CNBC (19 December 2016). "Europe's poorest nation passes IMF-backed retirement age increase". Cnbc.com. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- "Moldovan MPs approve IMF-backed retirement age increase". Reuters. 19 December 2016. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Studying in Moldova". Honorary Consulate of the Republic of Moldova in Khmelnytsky. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "România oferă tinerilor moldoveni 5.000 de burse în licee și universități". PUBLIKA.MD (in Romanian). 22 June 2015. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- "Presedintele Klaus Iohannis l-a primit, la Suceava, pe Nicolae Timofti: "Republica Moldova isi poate implini destinul doar in Uniunea Europeana. Combaterea coruptiei, stabilitatea economica si intarirea institutiilor, singura cale catre succes"". HotNews.ro (in Romanian). 7 July 2015. Archived from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- "Moldova – The World Factbook", The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, 31 July 2023, archived from the original on 5 January 2021, retrieved 3 August 2023
- "Academy of Economic Studies of Moldova". Times Higher Education (THE). 21 October 2021. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Harrington, Keith (6 April 2023). "ECMI Minorities Blog. Gagauzia's Response to Russia's Invasion of Ukraine". European Centre for Minority Issues. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Harrington, Keith (19 August 2022). "On 'Republic' Anniversary, Moldova's Gagauz Look to Moscow, and Chisinau". Balkan Insight. Archived from the original on 6 November 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Chapple, Amos (24 March 2023). "In Moldova's Pro-Russian Gagauzia Region, Old Loyalties Die Hard". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Tanas, Alexander (20 July 2023). "New head of Moldovan region thanks exiled patron, backs Russia ties". Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Romania provides 80%–90% of Moldova's energy needs- minister". Reuters. 21 November 2022. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Spaic-Kovacic, David (21 June 2023). "Romania supports Moldova's EU accession talks, expects 2023 start". Euractiv. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- "Moldova and Romania vow to boost ties amid war in Ukraine". Reuters. 1 March 2023. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Sánchez, Wilder Alejandro (12 February 2023). "Opinion – Moldova and Romania's Unification is Not on the Horizon". E-International Relations. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- Nahoi, Ovidiu (24 March 2022). "Sondaj: patriotismul românilor în context de război". RFI România: Actualitate, informaţii, ştiri în direct (in Romanian). Archived from the original on 27 March 2022. Retrieved 28 March 2022.
- ^ "Moldova – Culture". Countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- Octavian Sofransky. "Ethno-Political Conflict in Moldova" (PDF). European Centre in Moldova. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
- Catherine Lovatt (24 January 2000). "2000: Year of Eminescu". Central Europe Review. 2 (3). Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- Wine of Moldova Archived 12 September 2022 at the Wayback Machine – Sommeliers International
- Moldovan Red Wines: The Best Red Wine on the Planet You Have Never Heard Of Archived 12 September 2022 at the Wayback Machine – Vida Wines & Spirits
- Kieff, Leah (10 December 2015). "4 foods you must try in Moldova". Peace Corps. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Steafel, Eleanor (2 July 2021). "You need this easy flatbread recipe in your culinary arsenal". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Zeama | Traditional Chicken Soup From Moldova | TasteAtlas". www.tasteatlas.com. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Sikorsky, Dmytro (30 May 2016). "The Secret Of Bessarabia's Cuisine". Odessa Review. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Johnson, Doina (13 November 2019). "Moldovan Food – 14 Best Traditional Dishes as Recommended by a Local (with Recipes) – Nomad Paradise". Archived from the original on 26 September 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Hai la masa!: Coltunasi". 7 October 2009. Archived from the original on 16 March 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
- Goldstein, Darra (2015). The Oxford Companion to Sugar and Sweets. Oxford University Press.
- "How This Tiny European Country Got the World's Worst Drinking Problem". Time. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- "Europeans are the world's heaviest drinkers: How do countries compare?". euronews. 30 June 2023. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Moldova Declares Western Christmas Day Official Holiday". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 19 December 2013. Archived from the original on 19 December 2013. Retrieved 20 December 2013.
- "Martisor, a Spring celebration for Eastern Europeans – FOREIGNERS IN UK". 12 August 2014. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 29 August 2021.
- "2017 Grand Final Scoreboard". Eurovision.tv. European Broadcasting Union. Archived from the original on 27 March 2019. Retrieved 14 May 2016.
- "Moldova | RSF". Reporters Without Borders. 23 July 2020. Archived from the original on 5 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Cojocari, Vitalie. "Why Moldova is ahead of Romania in Media freedom". Thomson Foundation. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- ^ "Moldova media guide". BBC News. July 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Six TV channels suspended amid 'misinformation' allegations". euronews. 19 December 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Moldova suspends six channels over Ukraine 'disinformation' – DW – 12/17/2022". Deutsche Welle. 17 December 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Moldovan Government Suspends Licenses Of Six TV Stations To 'Eliminate Propaganda'". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. 17 December 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Moldova blocks more Russian media outlets". 31 October 2023. Archived from the original on 3 November 2023. Retrieved 7 June 2024.
- ^ Johnson, Glen (5 August 2018). "Tiny Moldova was once a movie-making capital. A few diehards are trying to keep the tradition alive". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Clark, Marcus (8 November 2012). "Learn About Moldova's Brave Little Film Industry". Culture Trip. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Vourlias, Christopher (15 June 2023). "Echoes of the Ukraine War Haunt the Moldovan Tragicomedy 'Carbon,' About a Post-Soviet Conflict Lost to History". Variety. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Carbon, archived from the original on 7 July 2023, retrieved 7 July 2023
- "Between irony and poetry: the Republic of Moldova at FIFF | Festival International de Films de Fribourg". www.fiff.ch. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "More than 1,600 films from Moldova Film archive will be digitized, with the support of the European Union and the U.S. Government | United Nations Development Programme". UNDP. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- "Technical Difficulties". md.usembassy.gov. 25 February 2021. Archived from the original on 7 July 2023. Retrieved 7 July 2023.
- Souster, Mark (27 October 2012). "Europe's poor relations show richness of spirit; Mark Souster visits Moldova and discovers a wealth of ambition at all levels in one of the game's new frontiers". The Times (London, England). Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 13 February 2020.
External links
- S.Res.148 – A resolution to express the sense of the Senate that the United States should support the right to self-determination of the people of the Republic of Moldavia and northern Bucovina Archived 18 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Official website
- Moldova Archived 5 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Moldova, Republic of from UCB Libraries GovPubs.
- Moldova profile Archived 21 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine from the BBC News.
 Wikimedia Atlas of Moldova
Wikimedia Atlas of Moldova Geographic data related to Moldova at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Moldova at OpenStreetMap- Key Development Forecasts for Moldova Archived 26 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine from International Futures.
| Moldova articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |  | ||||
| Geography |
| ||||
| Politics | |||||
| Economy | |||||
| Society |
| ||||
| Eastern Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |
| States with limited recognition | |
| History |
|
| International organizations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
47°N 29°E / 47°N 29°E / 47; 29
Categories:- Moldova
- Landlocked countries
- Countries and territories where Romanian is an official language
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States
- Member states of the Council of Europe
- Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- Member states of the United Nations
- Republics
- States and territories established in 1991
- 1991 establishments in Europe
- Countries in Europe