| Revision as of 18:24, 8 December 2023 editAmitchell125 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users96,666 editsm →Overview: space← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:12, 26 December 2024 edit undoXTOC6 (talk | contribs)74 edits Added short descriptionTags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit Android app edit App description add | ||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Territorial administrative divisions or designations in Ukraine}} <!-- "none" is preferred when the title is sufficiently descriptive; see ] --> | |||
| {{pp-protect|small=yes}} | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | {{Ukraine subdivisions sidebar}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2022}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2022}} | ||
| ⚫ | {{Ukraine subdivisions sidebar}} | ||
| ⚫ | The '''administrative divisions of Ukraine''' ({{ |
||
| {{Politics of Ukraine}} | |||
| ⚫ | The '''administrative divisions of Ukraine''' ({{langx|uk|Адміністративний устрій України|translit=Administratyvnyi ustrii Ukrainy}}) are under the jurisdiction of the ]. Ukraine is a ] with three levels of administrative divisions: 27 regions (24 ], two ] and one ]), 136 ]s (districts) and 1469 ]s.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111226134808/http://w1.c1.rada.gov.ua/pls/z7502/a002|date=2011-12-26}}. ] website.</ref><ref>], ], and ] (1999). ''''. ]. p. 292. {{ISBN|0-8133-3538-8}}</ref> | ||
| The administrative reform of July 2020 merged most of the 490 raions and 118 ] into 136 raions. The next level below raions are ]s.<ref>{{Cite web |last=LiWebRadaAdmin |date=2015-05-22 |title=Реформа територіального устрою України |url=https://silrada.org/reforma-terytorialnogo-ustroyu-ukrayiny/ |access-date=2022-10-20 |website=Silrada.org |language=uk}}</ref> | The administrative reform of July 2020 merged most of the 490 legacy raions and 118 pre-2020 ] into 136 reorganized raions, or districts of Ukraine. The next level below raions are ]s.<ref>{{Cite web |last=LiWebRadaAdmin |date=2015-05-22 |title=Реформа територіального устрою України |url=https://silrada.org/reforma-terytorialnogo-ustroyu-ukrayiny/ |access-date=2022-10-20 |website=Silrada.org |language=uk}}</ref> | ||
| Following the ] and ], ] and ] as well as portions of ], ], ] and ] |
Following the ] and ], ] and ] as well as portions of ], ], ] and ] oblasts came under the '']'' administration of the ]. Internationally, most states have not recognized the Russian claims.<ref>{{Cite news |date=2022-09-30 |title=Putin signs documents to illegally annex four Ukrainian regions, in drastic escalation of Russia's war |language=en-CA |work=The Globe and Mail |url=https://www.theglobeandmail.com/world/article-putin-signs-documents-to-unlawfully-claim-4-ukrainian-regions-in/ |access-date=2023-05-05}}</ref> | ||
| ==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| {{See also|Local government in Ukraine}}According to Article 133 of the ], the system of administrative and territorial organization of Ukraine consists of: |
{{See also|Local government in Ukraine}}According to Article 133 of the ] as amended, the system of administrative and territorial organization of Ukraine consists of: | ||
| * the ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]s | |||
| * ] (], rural settlements, villages) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]s (communities)<ref>{{Cite web |date=2019-04-02 |title=Конституція України {{!}} від 28.06.1996 № 254к/96-ВР (Сторінка 3 з 4) |url=https://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80/page3 |access-date=2023-05-05 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190402062117/https://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80/page3 |archive-date=2 April 2019 }}</ref> | |||
| In |
In an administrative reform in 2020, all populated places in the country (except for two cities with special status, Kyiv and ]) were resubordinated to raions.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Офіційний портал Верховної Ради України|url=http://static.rada.gov.ua/zakon/new/NEWSAIT/ADM/zmist.html|website=static.rada.gov.ua|access-date=2020-12-12}}</ref> The new figure of 136 raions includes 10 in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and ]; since September 2023, the Crimean raions are functional.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-08-23 |title=Про внесення змін до деяких законодавчих актів України щодо вирішення окремих питань адміністративно-територіального устрою Автономної Республіки Крим |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/go/3334-20 |access-date=2024-03-28 |website=Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України |language=uk}}</ref> | ||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| ⚫ | |+ Administrative divisions of Ukraine | ||
| ! Level of subdivision !! Territory !! Total | ! Level of subdivision !! Territory !! Total | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 25: | Line 32: | ||
| | 2 | | 2 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | | ] (regions) | ||
| | 24 | | 24 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | Second | | Second | ||
| | ] | | ] (districts) | ||
| | 136 | | 136 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | Third | | Third | ||
| | ]s | | ]s (territorial communities) | ||
| | 1469 | | 1469 | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 50: | Line 57: | ||
| == First level == | == First level == | ||
| There are three types of first-level administrative divisions: 24 oblasts, 1 autonomous republic and 2 cities with special status. | There are three types of first-level administrative divisions: 24 oblasts (regions), 1 autonomous republic and 2 cities with special status. | ||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| ! Colour | ! Colour | ||
| Line 56: | Line 63: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | {{legend|#FFEC77|24 ]|up=yes}} | | {{legend|#FFEC77|24 ]|up=yes}} | ||
| | An '''oblast''' in ], sometimes translated as '''region''' or '''province''', is the main type of first-level administrative division of the country. Ukraine is a unitary state, thus the oblasts do not have much legal scope of competence other than that which is established in the ] and by law. Articles 140–146 of Chapter XI of the constitution deal directly with local authorities and their competency. | | An '''oblast''' in ], sometimes translated as '''region''' or '''province''', is the main type of first-level administrative division of the country. Ukraine is a ], thus the oblasts do not have much legal scope of competence other than that which is established in the ] and by law. Articles 140–146 of Chapter XI of the constitution deal directly with local authorities and their competency. | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | {{legend|#FFC125|1 ]}} | | {{legend|#FFC125|1 ]}} | ||
| | The administrative status of the ] is recognized in the Ukrainian Constitution in Chapter X: Autonomous Republic of Crimea and is governed in accordance with laws passed by Ukraine's parliament. |
| The administrative status of the ] is recognized in the Ukrainian Constitution in Chapter X: Autonomous Republic of Crimea and is governed in accordance with laws passed by Ukraine's parliament. In 2014, the autonomous republic was ] as the ].<ref>{{Cite news |date=2014-03-18 |title=Putin signs Crimea treaty as Ukraine serviceman dies in attack |language=en |work=Reuters |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-ukraine-crisis-idUSBREA1Q1E820140318 |first1=Steve |last1=Gutterman |first2=Pavel |last2=Polityuk |access-date=2023-06-18}}</ref> | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | {{legend|#00FF7F|2 ]|up=yes}} | | {{legend|#00FF7F|2 ]|up=yes}} | ||
| | There are two cities with special status: ] and ] (occupied since 2014). Their administrative status is recognized in the Ukrainian Constitution in Chapter IX: Territorial Structure of Ukraine.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Конституція України |language=uk |work=Законодавство України |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80 |access-date=2023-06-18 |archive-date=29 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190529034958/https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80 |url-status= |
| There are two cities with special status: ] and ] (occupied since 2014). Their administrative status is recognized in the Ukrainian Constitution in Chapter IX: Territorial Structure of Ukraine.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Конституція України |language=uk |work=Законодавство України |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80 |access-date=2023-06-18 |archive-date=29 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190529034958/https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80 |url-status=live }}</ref> Unlike the oblasts and the autonomous republic, the cities with special status only have ] and are not subdivided into hromadas. | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| Line 219: | Line 226: | ||
| |{{Nts|2121322}} | |{{Nts|2121322}} | ||
| |79.50 | |79.50 | ||
| |]<br>{{small|(de jure)}}<br>]<br>{{small|(de facto) |
|]<br>{{small|(de jure)}}<br>]<br>{{small|(de facto, 2014–2022)}} | ||
| |8 | |8 | ||
| |37 | |37 | ||
| Line 408: | Line 415: | ||
| {{Main|Autonomous Republic of Crimea}} | {{Main|Autonomous Republic of Crimea}} | ||
| The Autonomous Republic of Crimea ({{ |
The Autonomous Republic of Crimea ({{langx|uk|Автономна Республіка Крим}}) geographically encompasses the major portion of the Crimean peninsula in southern Ukraine. Its capital is ]. The Autonomous Republic of Crimea is the only region within Ukraine that has its own constitution. | ||
| On 16 March 2014, after the occupation of Crimea by the Russian military, a referendum on joining the Russian Federation was held. A majority of votes supported the measure. On 21 March 2014, the Russian Duma voted to annex Crimea as a ] into the Russian Federation. The Ukrainian government does not recognize the referendum or annexation of Crimea as legitimate. On 27 March, the UN General Assembly passed ] by 100 to 11 votes, recognizing the referendum as invalid and denying any legal change in the status of Crimea and Sevastopol. | On 16 March 2014, after the occupation of Crimea by the Russian military, a referendum on joining the Russian Federation was held. A majority of votes supported the measure. On 21 March 2014, the Russian Duma voted to annex Crimea as a ] into the Russian Federation. The Ukrainian government does not recognize the referendum or annexation of Crimea as legitimate. On 27 March, the UN General Assembly passed ] by 100 to 11 votes, recognizing the referendum as invalid and denying any legal change in the status of Crimea and Sevastopol. | ||
| ===Oblasts=== | ===Oblasts=== | ||
| {{Main|Oblasts of Ukraine}} | {{Main|Oblasts of Ukraine}} | ||
| An oblast ({{ |
An oblast ({{langx|uk|область}}; {{plural form|{{langx|uk|області|label=none}}}}) is on the first level of the administrative division of Ukraine. | ||
| Most oblasts are named after their administrative center. Volyn and Zakarpattia, whose respective capitals are Lutsk and Uzhhorod, are named after the historic regions ] and ]. | Most oblasts are named after their administrative center. Volyn and Zakarpattia oblasts, whose respective capitals are Lutsk and Uzhhorod, are named after the historic regions ] and ]. | ||
| ===Cities with special status=== | ===Cities with special status=== | ||
| {{Main|City with special status}} | {{Main|City with special status}} | ||
| Two cities have special status ({{ |
Two cities have special status ({{langx|uk|міста зі спеціальним статусом}}): ] and ]. Their special status puts them on the same administrative level as the oblasts, and thus under the direct supervision of the state via their respective ], which constitute the executive bodies of the cities. Following the ], Sevastopol is controlled by Russia and is incorporated as a ].<ref>{{cite web |title=About the capital of Ukraine – the hero city of Kyiv (Vidomosti Verkhovnoi Rady Ukrainy (VVR), 1999, № 11, p. 79) |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/401-14#Text |access-date=4 October 2021 |website=GOV.UA |publisher=Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine |ref=VRA}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2022-12-14 |title=Russia's annexation of Crimea |url=https://kyivindependent.com/russias-annexation-of-crimea/ |access-date=2023-05-04 |website=Kyiv Independent |language=en}}</ref> | ||
| == Second level == | == Second level == | ||
| Line 428: | Line 435: | ||
| ===Raions=== | ===Raions=== | ||
| {{Main|Raions of Ukraine}} | {{Main|Raions of Ukraine}} | ||
| Raions ({{ |
Raions ({{langx|uk|район}}; {{plural form|{{langx|uk|райони|label=none}}}}) are smaller territorial units of subdivision in Ukraine. There are 136 raions.<ref>{{cite news |title=The council reduced the number of districts in Ukraine: 136 instead of 490|url= https://www.pravda.com.ua/news/2020/07/17/7259715/|work=] |date=17 July 2020|language=uk}}</ref> Following the December 2019 draft ] changes submitted to the Verkhovna Rada by President ], 136 new raions have replaced the former 490 raions of Ukraine.<ref name="50808046decentralizationAdU">{{cite news |title=Zelensky's decentralization: without features of Donbas, but with districts and prefects|url=https://www.bbc.com/ukrainian/features-50808046|work=]|date=16 December 2019|language=uk}}</ref> | ||
| ===Urban |
===Urban districts=== | ||
| {{Main|Urban districts of Ukraine}}An urban |
{{Main|Urban districts of Ukraine}}An urban district is subordinate to the city administration.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Конституція України |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/go/254%D0%BA/96-%D0%B2%D1%80 |access-date=2023-05-03 |website=Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України |language=uk}}</ref> | ||
| == Third level == | == Third level == | ||
| Line 437: | Line 444: | ||
| === Hromadas === | === Hromadas === | ||
| {{Further|List of hromadas of Ukraine}} | {{Further|List of hromadas of Ukraine}} | ||
| The territorial hromadas ({{ |
The territorial hromadas ({{langx|uk|територіальна громада}}; <small>]</small> 'territorial community'; {{Plural form|територіальні громади}}), or simply hromadas ({{langx|uk|громада}}; {{Plural form|громади}}) were established by the ] on 12 June 2020 as a part of administrative reform that started in 2015.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Автор |title=Те, чого ніколи не було в Україні: Уряд затвердив адмінтерустрій базового рівня, що забезпечить повсюдність місцевого самоврядування |url=https://decentralization.gov.ua/admin/articles/12533.html |access-date=2022-10-20 |website=decentralization.gov.ua}}</ref> | ||
| There are three types of hromadas: ''rural'' ({{ |
There are three types of hromadas: ''rural'' ({{langx|uk|сільська громада}}), ''settlement'' ({{langx|uk|селищна громада}}) and ''urban'' ({{langx|uk|міська громада}}). There are 1469 hromadas in total (as of November 1, 2023).<ref>{{Cite web |last=Автор |title=Децентралізація в Україні |url=https://decentralization.gov.ua/newgromada |access-date=2023-05-03 |website=decentralization.gov.ua}}</ref> | ||
| == History == | == History == | ||
| Line 454: | Line 461: | ||
| === Ukrainian People's Republic === | === Ukrainian People's Republic === | ||
| ] | |||
| According to the ], the country was divided into zemlias (lands), volosts and hromadas (communities). This law was not fully implemented as on 29 April 1918 there was the anti-socialist coup in Kyiv, after which ] reverted the reform back to the ]-type administration.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Конституція Української Народньої Республіки (Статут про державний устрій, права і вільності УНР) |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/go/n0002300-18 |access-date=2023-11-13 |website=Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України |language=uk}}</ref> | According to the ], the country was divided into zemlias (lands), volosts and hromadas (communities). This law was not fully implemented as on 29 April 1918 there was the anti-socialist coup in Kyiv, after which ] reverted the reform back to the ]-type administration.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Конституція Української Народньої Республіки (Статут про державний устрій, права і вільності УНР) |url=https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/go/n0002300-18 |access-date=2023-11-13 |website=Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України |language=uk}}</ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 05:12, 26 December 2024
Territorial administrative divisions or designations in Ukraine
| Part of a series on the |
| Subdivisions of Ukraine |
|---|
 |
| First level |
| Second level |
| Third level |
| This sidebar: |
| Politics of Ukraine |
|---|
 |
| Constitution |
| Presidency |
| Executive |
| Legislature |
| Judiciary |
Local government
|
| Elections |
|
Foreign relations
|
| See also |
|
|
The administrative divisions of Ukraine (Ukrainian: Адміністративний устрій України, romanized: Administratyvnyi ustrii Ukrainy) are under the jurisdiction of the Ukrainian Constitution. Ukraine is a unitary state with three levels of administrative divisions: 27 regions (24 oblasts, two cities with special status and one autonomous republic), 136 raions (districts) and 1469 hromadas.
The administrative reform of July 2020 merged most of the 490 legacy raions and 118 pre-2020 cities of regional significance into 136 reorganized raions, or districts of Ukraine. The next level below raions are hromadas.
Following the annexations of Crimea and southeastern Ukraine by the Russian Federation, Autonomous Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol as well as portions of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts came under the de facto administration of the Russian Federation. Internationally, most states have not recognized the Russian claims.
Overview
See also: Local government in UkraineAccording to Article 133 of the Constitution of Ukraine as amended, the system of administrative and territorial organization of Ukraine consists of:
- the Autonomous Republic of Crimea
- oblasts
- raions
- populated places (cities, rural settlements, villages)
- urban districts
- hromadas (communities)
In an administrative reform in 2020, all populated places in the country (except for two cities with special status, Kyiv and Sevastopol) were resubordinated to raions. The new figure of 136 raions includes 10 in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol; since September 2023, the Crimean raions are functional.
| Level of subdivision | Territory | Total |
|---|---|---|
| First | autonomous republic | 1 |
| cities with special status | 2 | |
| oblasts (regions) | 24 | |
| Second | raions (districts) | 136 |
| Third | hromadas (territorial communities) | 1469 |
First level
There are three types of first-level administrative divisions: 24 oblasts (regions), 1 autonomous republic and 2 cities with special status.
| Colour | Description |
|---|---|
| 24 oblasts | An oblast in Ukraine, sometimes translated as region or province, is the main type of first-level administrative division of the country. Ukraine is a unitary state, thus the oblasts do not have much legal scope of competence other than that which is established in the Ukrainian Constitution and by law. Articles 140–146 of Chapter XI of the constitution deal directly with local authorities and their competency. |
| 1 autonomous republic | The administrative status of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea is recognized in the Ukrainian Constitution in Chapter X: Autonomous Republic of Crimea and is governed in accordance with laws passed by Ukraine's parliament. In 2014, the autonomous republic was illegally annexed by Russia as the Republic of Crimea. |
| 2 cities with special status | There are two cities with special status: Kyiv and Sevastopol (occupied since 2014). Their administrative status is recognized in the Ukrainian Constitution in Chapter IX: Territorial Structure of Ukraine. Unlike the oblasts and the autonomous republic, the cities with special status only have urban districts and are not subdivided into hromadas. |
List
| Flag | Coat of arms | No. | Name | Area (km) | Population (2021 estimate) |
Population density (people/km, 2021) |
Capital | No. of raions | No. of hromadas | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Autonomous Republic of Crimea |
26,081 | 1,967,259 | 75.43 | Simferopol | 10 | — | 
| ||

|
2 | Vinnytsia Oblast | 26,513 | 1,529,123 | 57.67 | Vinnytsia | 6 | 63 | 
| |

|
3 | Volyn Oblast | 20,144 | 1,027,397 | 51.00 | Lutsk | 4 | 54 | 
| |
| 4 | Dnipropetrovsk Oblast | 31,974 | 3,142,035 | 98.27 | Dnipro | 7 | 86 | 
| ||

|
5 | Donetsk Oblast | 26,517 | 4,100,280 | 154.63 | Donetsk (de jure) Kramatorsk (de facto) |
8 | 66 | 
| |
| 6 | Zhytomyr Oblast | 29,832 | 1,195,495 | 40.07 | Zhytomyr | 4 | 65 | 
| ||
| 7 | Zakarpattia Oblast | 12,777 | 1,250,129 | 97.84 | Uzhhorod | 6 | 64 | 
| ||
| 8 | Zaporizhzhia Oblast | 27,180 | 1,666,515 | 61.31 | Zaporizhzhia | 5 | 67 | 
| ||

|
9 | Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast | 13,928 | 1,361,109 | 97.72 | Ivano-Frankivsk | 6 | 62 | 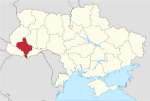
| |

|
10 | Kyiv Oblast | 28,131 | 1,788,530 | 63.58 | Kyiv | 7 | 69 | 
| |
| 11 | Kirovohrad Oblast | 24,588 | 920,128 | 37.42 | Kropyvnytskyi | 4 | 49 | 
| ||
| 12 | Luhansk Oblast | 26,684 | 2,121,322 | 79.50 | Luhansk (de jure) Sievierodonetsk (de facto, 2014–2022) |
8 | 37 | 
| ||
| 13 | Lviv Oblast | 21,833 | 2,497,750 | 114.40 | Lviv | 7 | 73 | 
| ||
| 14 | Mykolaiv Oblast | 24,598 | 1,108,394 | 45.06 | Mykolaiv | 4 | 52 | 
| ||
| 15 | Odesa Oblast | 33,310 | 2,368,107 | 71.09 | Odesa | 7 | 91 | 
| ||
| 16 | Poltava Oblast | 28,748 | 1,371,529 | 47.71 | Poltava | 4 | 60 | 
| ||
| 17 | Rivne Oblast | 20,047 | 1,148,456 | 57.29 | Rivne | 4 | 64 | 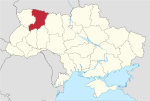
| ||
| 18 | Sumy Oblast | 23,834 | 1,053,452 | 44.20 | Sumy | 5 | 51 | 
| ||
| 19 | Ternopil Oblast | 13,823 | 1,030,562 | 74.55 | Ternopil | 3 | 55 | 
| ||
| 20 | Kharkiv Oblast | 31,415 | 2,633,834 | 83.84 | Kharkiv | 7 | 56 | 
| ||
| 21 | Kherson Oblast | 28,461 | 1,016,707 | 35.72 | Kherson | 5 | 49 | 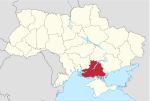
| ||
| 22 | Khmelnytskyi Oblast | 20,645 | 1,243,787 | 60.25 | Khmelnytskyi | 3 | 60 | 
| ||
| 23 | Cherkasy Oblast | 20,900 | 1,178,266 | 56.38 | Cherkasy | 4 | 66 | 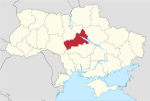
| ||
| 24 | Chernivtsi Oblast | 8,097 | 896,566 | 110.73 | Chernivtsi | 3 | 52 | 
| ||
| 25 | Chernihiv Oblast | 31,865 | 976,701 | 30.65 | Chernihiv | 5 | 57 | 
| ||
| 26 | Kyiv | 839 | 2,962,180 | 3530.61 | Kyiv | 10 | — | 
| ||
| 27 | Sevastopol | 864 | 385,870 | 446.61 | Sevastopol | 4 | — | 
|
Autonomous republic
Main article: Autonomous Republic of CrimeaThe Autonomous Republic of Crimea (Ukrainian: Автономна Республіка Крим) geographically encompasses the major portion of the Crimean peninsula in southern Ukraine. Its capital is Simferopol. The Autonomous Republic of Crimea is the only region within Ukraine that has its own constitution.
On 16 March 2014, after the occupation of Crimea by the Russian military, a referendum on joining the Russian Federation was held. A majority of votes supported the measure. On 21 March 2014, the Russian Duma voted to annex Crimea as a subject into the Russian Federation. The Ukrainian government does not recognize the referendum or annexation of Crimea as legitimate. On 27 March, the UN General Assembly passed Resolution 68/262 by 100 to 11 votes, recognizing the referendum as invalid and denying any legal change in the status of Crimea and Sevastopol.
Oblasts
Main article: Oblasts of UkraineAn oblast (Ukrainian: область; pl. області) is on the first level of the administrative division of Ukraine.
Most oblasts are named after their administrative center. Volyn and Zakarpattia oblasts, whose respective capitals are Lutsk and Uzhhorod, are named after the historic regions Volhynia and Transcarpathia.
Cities with special status
Main article: City with special statusTwo cities have special status (Ukrainian: міста зі спеціальним статусом): Kyiv and Sevastopol. Their special status puts them on the same administrative level as the oblasts, and thus under the direct supervision of the state via their respective local state administrations, which constitute the executive bodies of the cities. Following the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, Sevastopol is controlled by Russia and is incorporated as a federal subject of Russia.
Second level
Raions
Main article: Raions of UkraineRaions (Ukrainian: район; pl. райони) are smaller territorial units of subdivision in Ukraine. There are 136 raions. Following the December 2019 draft constitutional changes submitted to the Verkhovna Rada by President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, 136 new raions have replaced the former 490 raions of Ukraine.
Urban districts
Main article: Urban districts of UkraineAn urban district is subordinate to the city administration.
Third level
Hromadas
Further information: List of hromadas of UkraineThe territorial hromadas (Ukrainian: територіальна громада; lit. 'territorial community'; pl. територіальні громади), or simply hromadas (Ukrainian: громада; pl. громади) were established by the Government of Ukraine on 12 June 2020 as a part of administrative reform that started in 2015.
There are three types of hromadas: rural (Ukrainian: сільська громада), settlement (Ukrainian: селищна громада) and urban (Ukrainian: міська громада). There are 1469 hromadas in total (as of November 1, 2023).
History
Main articles: Development of the administrative divisions of Ukraine and Historical regions in present-day UkraineCossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate was divided into military-administrative districts known as regimental districts (polks) whose number fluctuated with the size of the Hetmanate's territory. In 1649, when the Hetmanate controlled both the right and left banks, it included 16 such districts. After the loss of Right-bank Ukraine, this number was reduced to ten. The regimental districts were further divided into companies (sotnias), which were administered by captains (sotnyk). The lowest division was the kurin.
Ukrainian People's Republic

According to the Constitution of the Ukrainian People's Republic, the country was divided into zemlias (lands), volosts and hromadas (communities). This law was not fully implemented as on 29 April 1918 there was the anti-socialist coup in Kyiv, after which Pavlo Skoropadskyi reverted the reform back to the governorate-type administration.
Soviet Ukraine
Before the introduction of oblasts in 1932, Soviet Ukraine comprised 40 okruhas, which had replaced the former Russian Imperial governorate subdivisions.
In 1932 the territory of the Soviet Ukraine was re-established based on oblasts. At the same time, most of the Western Ukraine at the time formed part of the Second Polish Republic and shared in the Polish form of administrative division based on voivodeships.
See also
References
- Regions of Ukraine and their composition Archived 2011-12-26 at the Wayback Machine. Verkhovna Rada website.
- Paul D'Anieri, Robert Kravchuk, and Taras Kuzio (1999). Politics and society in Ukraine. Westview Press. p. 292. ISBN 0-8133-3538-8
- LiWebRadaAdmin (22 May 2015). "Реформа територіального устрою України". Silrada.org (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- "Putin signs documents to illegally annex four Ukrainian regions, in drastic escalation of Russia's war". The Globe and Mail. 30 September 2022. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- "Конституція України | від 28.06.1996 № 254к/96-ВР (Сторінка 3 з 4)". 2 April 2019. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- "Офіційний портал Верховної Ради України". static.rada.gov.ua. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- "Про внесення змін до деяких законодавчих актів України щодо вирішення окремих питань адміністративно-територіального устрою Автономної Республіки Крим". Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України (in Ukrainian). 23 August 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- Gutterman, Steve; Polityuk, Pavel (18 March 2014). "Putin signs Crimea treaty as Ukraine serviceman dies in attack". Reuters. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- "Конституція України". Законодавство України (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 29 May 2019. Retrieved 18 June 2023.
- "About the capital of Ukraine – the hero city of Kyiv (Vidomosti Verkhovnoi Rady Ukrainy (VVR), 1999, № 11, p. 79)". GOV.UA. Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- "Russia's annexation of Crimea". Kyiv Independent. 14 December 2022. Retrieved 4 May 2023.
- "The council reduced the number of districts in Ukraine: 136 instead of 490". Ukrainska Pravda (in Ukrainian). 17 July 2020.
- "Zelensky's decentralization: without features of Donbas, but with districts and prefects". BBC Ukrainian (in Ukrainian). 16 December 2019.
- "Конституція України". Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- Автор. "Те, чого ніколи не було в Україні: Уряд затвердив адмінтерустрій базового рівня, що забезпечить повсюдність місцевого самоврядування". decentralization.gov.ua. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- Автор. "Децентралізація в Україні". decentralization.gov.ua. Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- Magocsi, Paul Robert (2010). "The Cossack State, 1648–1711". History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples (2nd ed.). Toronto: U of Toronto. p. 235. ISBN 978-1442610217. Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- "Конституція Української Народньої Республіки (Статут про державний устрій, права і вільності УНР)". Офіційний вебпортал парламенту України (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 13 November 2023.
- "Адміністративно-територіальний устрій України". ВУЕ (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- "Збірник законів та розпоряджень робітничо-селянського уряду України (1935–1936)". 17 January 2020. Archived from the original on 17 January 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- "Ustawa Konstytucyjna z dnia 15 lipca 1920 r. zawierająca statut organiczny Województwa Śląskiego". isap.sejm.gov.pl. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
External links
- "Regions of Ukraine and their composition". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 26 December 2011. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- "Ukraine Raions". Statoids. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- "Ukrainian cities and regions in alphabetical order". UkraineTrek. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- "Administrative territorial composition of Ukraine" (PDF). Ministry of Regional Development, Construction, and Communal Living. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2014. Retrieved 5 April 2015.
| Administrative divisions of Ukraine | |
|---|---|
| Capital: Kyiv | |
| Oblasts | |
| Cities with special status | |
| Autonomous republic | |
| Administrative centers | |
| Claimed and controlled by Russia as the Republic of Crimea and the Federal City of Sevastopol Claimed and partially controlled by Russia as the Republics Donetsk People's Republic, Lugansk People's Republic and Zaporozhye and Kherson oblasts Partially claimed and partially controlled by Russia as a part of Kherson oblast Partially controlled by Russia, but not claimed as its part. | |
| Oblasts | |
|---|---|
| Autonomous republic | |
| Cities with special status | |
| Claimed and controlled by Russia as the Republic of Crimea and the Federal City of Sevastopol | |
| First-level administrative divisions in European countries | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
Table of administrative divisions by country
| |




