| Revision as of 09:58, 26 December 2024 editMinhaj Rafif (talk | contribs)27 edits ←Created page with '== Shape and Structure == Earth is an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. Its internal structure consists of the crust, mantle, outer core (liquid), and inner core (solid).<br><br> == Tectonic plates == Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. Plate movements cause earthquakes, mountain formation, and volcanic activity.<br><br> == Surface == Earth’s surface...' | Latest revision as of 10:08, 26 December 2024 edit undoMinhaj Rafif (talk | contribs)27 editsNo edit summary | ||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| <gallery> | |||
| The Blue Marble.jpg | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Shape and Structure == | == Shape and Structure == | ||
| Earth is an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. Its internal structure consists of the crust, mantle, outer core (liquid), and inner core (solid).<br><br> | Earth is an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the ]. Its internal structure consists of the crust, mantle, outer core (liquid), and inner core (solid).<br><br> | ||
| <gallery> | |||
| Tectonic plates (empty).svg | |||
| </gallery> | |||
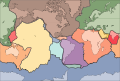
| == Tectonic plates == | == Tectonic plates == | ||
| Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. Plate movements cause earthquakes, mountain formation, and volcanic activity.<br><br> | Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. Plate movements cause ], mountain formation, and volcanic activity.<br><br> | ||
| <gallery> | |||
| Global View of the Arctic and Antarctic.jpg | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Surface == | == Surface == | ||
| Earth’s surface is 70% water and 30% land, consisting of continents, islands, oceans, rivers, and deserts. Its diverse terrain supports life.<br><br> | Earth’s surface is 70% water and 30% land, consisting of continents, islands, oceans, rivers, and deserts. Its diverse terrain supports life.<br><br> | ||
| <gallery> | |||
| Top of Atmosphere.jpg | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Atmosphere == | == Atmosphere == | ||
| Earth’s atmosphere is a layer of gases, primarily nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), which protects life from harmful solar radiation and maintains temperature.<br><br> | Earth’s atmosphere is a layer of gases, primarily nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), which protects life from harmful solar ] and maintains temperature.<br><br> | ||
| <gallery> | |||
| HydrologicalCycle1.png | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Weather, Climate, and Water Cycle == | == Weather, Climate, and Water Cycle == | ||
| Weather describes short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to long-term patterns. The water cycle involves evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, regulating life-supporting processes.<br><br> | Weather describes short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to long-term patterns. The water cycle involves evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, regulating life-supporting processes.<br><br> | ||
| <gallery> | |||
| HydrologicalCycle1.png | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == Orbit and Rotation == | == Orbit and Rotation == | ||
| Earth orbits the Sun in an elliptical path, completing one revolution in 365.25 days. Its 24-hour axial rotation causes day and night. The tilt of its axis results in seasons.<br><br> | Earth orbits the Sun in an elliptical path, completing one revolution in 365.25 days. Its 24-hour axial rotation causes day and night. The tilt of its axis results in seasons.<br><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 10:08, 26 December 2024
Shape and Structure
Earth is an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. Its internal structure consists of the crust, mantle, outer core (liquid), and inner core (solid).
Tectonic plates
Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere. Plate movements cause earthquakes, mountain formation, and volcanic activity.
Surface
Earth’s surface is 70% water and 30% land, consisting of continents, islands, oceans, rivers, and deserts. Its diverse terrain supports life.
Atmosphere
Earth’s atmosphere is a layer of gases, primarily nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), which protects life from harmful solar radiation and maintains temperature.
Weather, Climate, and Water Cycle
Weather describes short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to long-term patterns. The water cycle involves evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, regulating life-supporting processes.
Orbit and Rotation
Earth orbits the Sun in an elliptical path, completing one revolution in 365.25 days. Its 24-hour axial rotation causes day and night. The tilt of its axis results in seasons.
Reference
National Geographic: Earth Science - https://www.nationalgeographic.com/
USGS: Plate Tectonics - https://www.usgs.gov/
NASA Earth Observatory - https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/
Britannica: Atmosphere - https://www.britannica.com/
NOAA: Weather & Climate - https://www.noaa.gov/
NASA: Earth Facts - https://www.nasa.gov/