| Revision as of 08:22, 29 December 2024 editScsbot (talk | contribs)Bots239,977 edits edited by robot: archiving December 13← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 00:05, 5 January 2025 edit undoScsbot (talk | contribs)Bots239,977 edits edited by robot: adding date header(s) | ||
| (99 intermediate revisions by 34 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| = December 15 = | |||
| == help to identify ] == | |||
| ] in New South Wales Australia]] Did I get species right? Thanks. ] (], ]) 06:56, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :related: https://species.wikimedia.org/Wikispecies:Village_Pump#help_to_identify_species ] (], ]) 06:57, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :FWIW, I can't detect any visible differences between the plant in this photo and the ones illustrated in the ] and the ] articles. However, the latter makes it clear that ''Polygala'' is a large genus, and is cultivated, with hybrids, so it's possible that this one could be a close relative that differs in ways not visible here, such as in the bark or roots. That may or may not matter for your purposes. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 10:11, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == How to address changes to taxonomy == | |||
| Hi all, | |||
| I am a biology student brand new to wiki editing who is interested in cleaning up small articles/stubs for less known taxa. One that I've encountered is a mushroom that occurs in the pacific northwest ('']''). The article mentions that this fungus is occasionally mistaken for another fungus, '']''. <br> | |||
| However, the issue I've run into is that ''F. pinicola'' used to be considered a single species found around the world, but relatively recently was split into a few different species. The original name was given to the one that occurs in Europe, and the one in the pacific northwest (and thus could be mistaken for ''F. ochracea'') was given the name '']''. | |||
| <br> | |||
| The wiki page says <blockquote><p>Historically, this fungus has been misidentified as ''F. pinicola.'' When both species are immature, they can look very similar, but can be distinguished by lighting a match next to the surface of the fungus. ''F. pinicola'' will boil and melt in heat, while F. ochracea will not.</p></blockquote> | |||
| <br>Since the source says ''pinicola'' (as likely do most/all other sources of this info given the change was so recent), and since technically it's true that they used to be mistaken for it... what would be the most appropriate way to modernize that section? | |||
| <br> | |||
| <B>My questions are</b>: | |||
| Should I replace ''F. pinicola'' with ''F. mounceae''? Or is that wrong because the source doesn't refer to it by that name? Would it be better to write something like (now known as/considered ''F. mounceae'') next to the first mention of the species? Or is that a poor choice because it implies all the members of ''F. pinicola'' were renamed ''F. mounceae''? | |||
| <br> | |||
| Any advice on how to go about updating this section is incredibly appreciated | |||
| <br> | |||
| ] (]) 10:21, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::First, take these sorts of questions to the relevant Wikiproject, in this case ]. I am not as familiar with the consensus at ], but it seems like they defer to '']'' and ] to decide. Those sources presently seem to consider '']'' a good species. Also, be careful about "replacing", there are rules to ensure the continuity of the article history. By the way, there is a hilarious but unencyclopedic/copyvio recipe appended to the '']'' article. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 11:09, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Thanks for the tips, I didn't know about projects so I'll go read up on that. And thanks for the warnings about replacing things. I've been reading a lot of help pages, but I'm still in the process of learning the all conventions and what mechanics break if you do things the wrong way. | |||
| ::::I actually saw the recipe ages ago before I made my account and completely forgot about it... it was one of many things that prompted me to get into wiki editing. ] (]) 23:12, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == Does stopping masturbation lead to sperm DNA damage? == | |||
| I'm looking for information on the potential link between the frequency of ejaculation (specifically through masturbation) and sperm DNA damage. I've come across some conflicting information and would appreciate it if someone could point me towards reliable scientific studies or reviews that address this topic. | |||
| Specifically, I'm interested in whether prolonged periods of abstinence from ejaculation might have any negative effects on sperm DNA integrity. Any insights or links to relevant research would be greatly appreciated. ] (]) 17:08, 15 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Only males may abstain from sperm-releasing ] that serves to flush the genital tract of old sperm that in any case will eventually dissipate. No causal relationship between masturbation and any form of mental or physical disorder has been found but abstinence may be thought or taught]]] to increase the chance of wanted conception during subsequent intercourse. ] (]) 00:51, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::There's many rumors about that topic. One is that not ejaculating frequently increases the risk of developing ]. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 01:02, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Nothing really conclusive but there's some evidence that short periods are associated with lower DNA fragmentation, see<small> | |||
| :* {{Cite journal |last=Du |first=Chengchao |last2=Li |first2=Yi |last3=Yin |first3=Chongyang |last4=Luo |first4=Xuefeng |last5=Pan |first5=Xiangcheng |date=10 January 2024 |title=Association of abstinence time with semen quality and fertility outcomes: a systematic review and dose–response meta‐analysis |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/andr.13583 |journal=Andrology |language=en |volume=12 |issue=6 |pages=1224–1235 |doi=10.1111/andr.13583 |issn=2047-2919}} | |||
| :* {{Cite journal |last=Hanson |first=Brent M. |last2=Aston |first2=Kenneth I. |last3=Jenkins |first3=Tim G. |last4=Carrell |first4=Douglas T. |last5=Hotaling |first5=James M. |date=16 November 2017 |title=The impact of ejaculatory abstinence on semen analysis parameters: a systematic review |url=https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5845044/ |journal=Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics |language=en |volume=35 |issue=2 |pages=213 |doi=10.1007/s10815-017-1086-0 |issn=2047-2919 |pmc=5845044 |pmid=29143943}} | |||
| :* {{Cite journal |last=Ayad |first=Bashir M. |last2=Horst |first2=Gerhard Van der |last3=Plessis |first3=Stefan S. Du |last4=Carrell |first4=Douglas T. |last5=Hotaling |first5=James M. |date=14 October 2017 |title=Revisiting The Relationship between The Ejaculatory Abstinence Period and Semen Characteristics |url=https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5641453/ |journal=International Journal of Fertility & Sterility |language=en |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=238 |doi=10.22074/ijfs.2018.5192 |issn=2047-2919 |pmc=5641453 |pmid=29043697}} | |||
| :</small> | |||
| :for example. ] (] • ]) 02:12, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Mature sperm cells do not have ] capability.<sup></sup> Inevitably, as sperm cells get older, they will naturally and unavoidably be subject to more and more ]. Obviously, freshly produced spermatozoa will, on average, have less DNA damage. It is reasonable to assume that the expected amount of damage is proportional to the age of the cells, which is consistent with what studies appear to find. Also, obviously, the more the damage is to a spermatozoon fertilizing an oocyte, the larger the likelihood that the ] in the resulting zygote, which does have DNA repair capability, will be incomplete. The studies I've looked at did not allow me to assess how much this is of practical significance. --] 09:40, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 16 = | |||
| == ] == | |||
| Thanks to those who answered my ], I think it should be added to a disambiguation page. If anyone wants to help me write that, reach out. | |||
| A sandpile seems disorganized and inert, but these are critically self-organizing. Do the frequency and size of disturbances on sand dunes and snowy peaks follow power law distribution? | |||
| ] (]) 01:18, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Shouldn't this be at the Math Desk? <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 05:12, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::If the question is not about the model mentioned in the heading but about the physical properties of sand dunes and snowy peaks, this here is the right section of the Reference desk. --] 08:51, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::I await a non-mathematical answer. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 09:23, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::It depends is probably a fairly reasonable non-mathematical answer for these kinds of systems. For sand dunes anyway, sometimes avalanche frequency is irregular and the size distribution follows a power law, and sometimes it's close to periodic and the avalanches span the whole system. It seems there are multiple regimes, and these kinds of systems switch between them. ] (]) 09:35, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::Thank you! I'm impressed this seems so casual, but surely you read this somewhere that might have a URL? | |||
| :::::] (]) 22:29, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Hi, this is an interesting and somewhat open question! A lot of work is done on these models but much less on careful analyses of real dunes. I did find that is freely accessible and describes some physical experiments and how well they fit various models. The general answer seems to be that the power law models are highly idealized, and determining the degree to which any real system's behavior is predicted by the model ahead of time is very difficult. Update: and it does include discussion of how well the model fits experiments.] (]) 17:21, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::That dissertation is great! | |||
| ::] (]) 22:30, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == Polar night == | |||
| Are there any common or scientific names for types of polar night? The types that I use are: | |||
| * ''polar night'' - meaning a day when sun's altitude remains below horizon entire day (there is no daylight at solar noon, only civil twilight), occurring poleward from 67°24′ north or south | |||
| * ''civil polar night'' - meaning a day when sun's altitude remains below -6° entire day (there is no civil twilight at solar noon, only nautical twilight), occurring poleward from 72°34′ north or south | |||
| * ''nautical polar night'' - meaning a day when sun's altitude remains below -12° entire day (there is no nautical twilight at solar noon, only astronomical twilight), occurring poleward from 78°34′ north or south | |||
| * ''astronomical polar night'' - meaning a day when sun's altitude remains below -18° entire day (there is no astronomical twilight at solar noon, only night), occurring poleward from 84°34′ north or south | |||
| These names were changed on ] article, and I wnat to know whether these named I listed are in use in any scientific papers, or in common language. (And I posted that question here and not in language desk because I think that this is not related to language very tightly.) | |||
| --] (]) 18:56, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Some definitions at from the ]. ] (]) 22:55, 16 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::These seem to be generalizable as: X polar night is a period, lasting not less than 24 hours, during which the sun remains below the horizon and there is no X twilight. The specific definitions depend then on the specific definitions of ]/]/]. These can be defined with a subjective observational standard or with an (originally experimentally determined) objective standard. --] 10:36, 17 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::FWIW, I as a former amateur astronomer have never previously thought about the question of ''Polar'' twilight and night nomenclatures, but immediately and completely understood what the (previously unencountered) terms used in the query must mean without having to read the attached descriptions. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 16:34, 17 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 17 = | |||
| == differential equations with complex coefficients == | |||
| In an intro ODE class one basically studies the equation <math>\dot x=Ax</math> where x is a real vector and A is a real matrix. A typically has complex eigenvalues, giving a periodic or oscillating solution to the equation. That is very important in physics, which has various sorts of harmonic oscillators everywhere. If A and x are complex instead of real, mathematically the ODE theory works out about the same way. I don't know what happens with PDE's since I haven't really studied them. | |||
| My question is whether the complex case is important in physics the way the real case is. Can one arrive at it through straightforward coordinate transformations? Do the complex eigenvalues "output" from one equation find their way into the "input" of some other equation? Does the distance metric matter? I.e. in math and old-fashioned physics we use the Euclidean metric, but in realtivity one uses the Minkowski metric, so I'm wondering if that leads to complex numbers. This is all motivated partly by wondering where all the complex numbers in quantum mechanics come from. Thanks. ] (]) 22:54, 17 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Perhaps I don't understand what you are getting at but simple harmonic motion is xdot=j*w*x where w is angular frequency and j is i ] (]) 00:35, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :If PDEs count, the ] and the ] are examples of differential equations in the complex domain. A linear differential equation of the form <math>\dot x=Ax</math> on the complex vector space <math>\mathbb{C}^n</math> can be turned into one on the real vector space <math>\mathbb{R}^{2n}</math>. For a very simple example, using <math>n=1,</math> the equation <math>\begin{bmatrix}\dot z\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}i\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}z\end{bmatrix}</math> can be replaced by | |||
| ::<math>\begin{bmatrix}\dot x\\\dot y\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}0&-1\\1&0\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}x\\y\end{bmatrix}.</math> | |||
| : --] 01:11, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Shouldn't this be at the Math Desk? It almost seems like the IP could be trolling, given the same question just above. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 14:49, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::The question whether the complex case is important <u>in physics</u> the way the real case is, is not a maths issue. IMO the Science section is the best choice. I do not see another post that asks the same or even a related question. --] 21:51, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::Just as above, I await a non-mathematical answer to this question. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 07:01, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| Thanks all. Greglocock, your SHO example is 1-dimensional but of course you can have a periodic oscillator (such as a planetary orbit) in any orientation in space, you can have damped or forced harmonic oscillators, etc. Those are all described by the same matrix equation. The periodic case means that the matrix eigenvalues are purely imaginary. The damped and forced cases are where there is a real part that is negative or positive respectively. Abductive, of course plenty of science questions (say about how to calculate an electron's trajectory using Maxwell's equations) will have mathematical answers, and the science desk is clearly still the right place for them, as they are things you would study in science class rather than math class. Lambiam, thanks, yes, PDE's are fine, and of course quantum mechanics uses complex PDE's. What I was hoping to see was a situation where you start out with real-valued DEs in some complicated system, and then through some coupling or something, you end up with complex-valued DEs due to real matrices having complex eigenvalues. Also I think the Minkowski metric can be treated like the Euclidean one where the time coordinate is imaginary. But I don't know how this really works, and Misplaced Pages's articles about such topics always make me first want to go learn more math (Lie algebras in this case). Maybe someday. ] (]) 07:25, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 18 = | |||
| == Why don't all mast radiators have top hats? == | |||
| ]Our ] article describes a device called a "top hat" which increases the range for mast radiators that can't be built tall enough. | |||
| So, why would you bother building a mast radiator without a top hat? Couldn't you just build it shorter with the top hat, and save steel? ] (]) 15:00, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :The main source cited in our article states, "{{tq|Top loading is less desirable than increased tower height but is useful where towers must be electrically short due to either extremely low carrier frequencies or to aeronautical limitations. Top loading increases the base resistance and lowers the capacitive base reactance, thus reducing the ''Q'' and improving the bandwidth of towers less than 90° high.}}"<sup></sup> If "reducing the {{serif|''Q''}}" is an undesirable effect, this is a trade-off design issue in which height seems to be favoured if circumstances permit. --] 21:41, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == Name of our solar system == | |||
| Is our star system officially called "Sol", or is that just something that came from science fiction and then became ubiquitous? ] (]) 22:06, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :It's called the ], and its star is called Sol, from Latin via French. Hence terms like "solstice", which means "sun stands still" in its apparent annual "sine wave" shaped path through the sky. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 23:31, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Via French? According to the OED, it came direct from Latin.<sup></sup> --] 11:45, 19 December 2024 (UTC)}} | |||
| ::::Old French plus Latin. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 14:25, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::Also in Old French, the word meaning "sun" was '']''. --] 23:42, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::Let's say {{fact}} to that claim. The star is indeed called Sol if you're speaking Latin, but in English it's the Sun (or sun). Of course words like "solar" and "solstice" derive from the Latin name, but using "Sol" to mean "the Sun" does seem to be something from science fiction. --] (]) 06:04, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::"Sol" is occasionally used to mean the Sun by astronomers. I feel like it is used in contexts where it is necessary to distinguish our experience with the Sun here on Earth, such as sunsets, from more "sterile" aspects of the Sun one might experience off the Earth. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 08:56, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Being an astronomer myself, I don't think I've ever heard anyone use "Sol" outside of a science fiction context. --] (]) 09:06, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::Scientific articles that use the term Sol; and . These are rather speculative but as I mentioned, the usage is for off-planet situations. <span style="font-family: Cambria;"> ] (])</span> 13:05, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::Using Sol, Terra and Luna to refer to the Sun, Earth and Moon only happens if you write your entire article in Latin and in science fiction, not in regular science articles. They are capitalised though. Just as people write about a galaxy (one of many) or the Galaxy (the Milky Way Galaxy, that's our galaxy). The Solar System is also capitalised. ] (]) 10:38, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::The article says "Sol" is the "personification" of the sun. Google Image the term "old Sol" and you'll see plenty of images of the sun with a face, not just Sci-Fi stuff. And "Luna" is obviously the basis for a number of words not connected with Sci-Fi. Lunar orbit, lunar module, etc. And the term "terra firma" has often been used in everyday usage. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 11:34, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::: And yet, if you ask 1,000 people "What's that big yellow thing up in the sky called?", you'll get 1,000 "the Sun"s and zero "Sol"s. Yes, in specialised contexts, Sol is used; but that doesn't justify saying our solar system's star "is called Sol" without any qualification, as if that were the normal, default term. It's not. -- ] </sup></span>]] 12:16, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::::And after you've gotten that response, ask them why it isn't the "Sunner System". And why a sun room attached to a house isn't called a "sunarium". And why those energy-gathering plates on some roofs are not called "sunner panels". ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 14:22, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::::What does that have to do with anything? The question was 'Is our star system ''officially'' called "Sol"?' (my emphasis). The answer is it is not. And that does not preclude other terms being derived from Latin ''sol'' (or, often enough, from Greek ''helios''), nobody denies that, it is irrelevant to the question. --] (]) 14:52, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::::::The problem is that the OP's question contains false premises. One is the question of what the "official" name is. There is no "official" name. It's the "conventional" name. And the second part, claiming that "Sol" comes from Sci-fi, is demonstrably false. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 15:05, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::::::Then demonstrate (that the usage of "Sol" as a name for the Sun, in English, not its use to derive adjectives, originated outside of SF), with references. The original question does not even include any premises, with maybe the exception of "ubiquitous". --] (]) 15:18, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::::::::"Is our star system officially called "Sol" , or is that just something that came from science fiction and then became ubiquitous? ". And the wording of your own question, just above, does not make sense. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 15:24, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::::::::Looking at Newspapers.com (pay site), I'm seeing colloquial references to "old Sol" (meaning the sun) as far back as the 1820s. No hint of sci-fi derivation. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 15:32, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::::::::::Great! Well done. --] (]) 15:41, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::::::::::Feel free to box up this section. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 15:52, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::::::::The 1933 OED entry for ''Sol'', linked to above, gives several pre-SF uses, the earliest from 1450. --] 23:48, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::::::::Yes, of course, but that's not surprising, is it? 15th century humanists, astrologers and pre-Victorian poets liked to sprinkle their texts with Latin words. But I don't think this is what the question is about. It's a matter of context, but it should be up to OP to clarify that. --] (]) 08:48, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::::::::::::It's not surprising, but the discussion was not whether the use of ''Sol'' in English texts is surprising, but whether it originated outside of SF. --] 10:52, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::::::::::In my view, the question has a clear scifi bent, and that particular usage ("Where shall we go for our vacation? Alpha Centauri or Sol?") does not originate in the 15th century. The word is much older, of course it is, but the usage is not. In the 15th century people didn't even know that the Sun is just an ordinary star and could do with a particular name to distinguish it from the others. The connotations of ''sol'' were vastly different from what they are today and from what is implied in OP's question. Incidentally, the ] doesn't even define a name , although they recommend using capitalised "Sun". Certainly no "Sol" anywhere. --] (]) 12:04, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::{{small|Does that make it a Sol-ecism? ] (]) 12:19, 19 December 2024 (UTC)}} | |||
| :::::::::<small>More like a ]. Meaning a factory where suns are made. From Sol = sun, and ipso = facto. Thus endeth the entymogology lesson for today. Go in peace to love and serve whomsoever. -- ] </sup></span>]] 19:37, 19 December 2024 (UTC) </small> | |||
| == Mountains == | |||
| Why there are no mountains on Earth with a height above 10,000 m? As the death zone is about at 8,000 m, and above 19,000 m, there is an Armstrong limit, where water boils at normal human body temperature, it is good that there are no more mountains higher than 8,000 km than just 14, but if there were hundreds of mountains above 9,000 m, then these were bad to climb. If there were different limits for death zone and Armstrong limit, would then there be possible to have higher mountains? I have just thought that, it is not a homework? --] (]) 22:29, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :There are ] that are over 20km high. Given that some of those are on airless worlds, I don't think the air pressure has any bearing on it. ] (]) 22:57, 18 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Multiple sources from web searching suggest the ''theoretical'' maximum height for mountains on Earth is around 15,000 m – the limiting factor is ]; the higher (therefore more voluminous) a mountain is, the more its weight causes the crust beneath it to sink. The actual heights of mountains are a trade-off between how fast tectonic movements can raise them versus isostatic sinking ''and'' how quickly they are eroded, and tectonic movements do not last for ever. See also ]. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 00:25, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::And erosion goes faster as the mountain gets higher, in particular when it's high enough to support glaciers – one reason why mountains can get higher on an airless world. Now it gets interesting for a mountain high enough to reach into the stratosphere, as it would be too dry to have anything but bare rock. I suppose it would locally raise the tropopause, preventing that. ] (]) 11:13, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 19 = | |||
| == Does human DNA become weaker with each generation? == | |||
| As with photocopying something over and over, the text becomes less clear each time. | |||
| Does human DNA become weaker with each generation? ] (]) 21:22, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Sure, DNA replication is not perfect, although ] reduces the error rate to about 1 mistake per 10<sup>9</sup> nucleotides (see our article on ]). But that is per generation of cells, not of the whole organisms. Many mutations will be neutral in effect (because much of our DNA is redundant), some will be deleterious, and a few might be advantageous. It is the process of natural selection that hinders the spread of deleterious mutations: sometimes this aspect is called ]. One thus usually expects a stable ] over time rather than that "DNA becomes weaker with each generation". Medical science is reducing the selection pressure against some mutations, which consequently may become more common. One of the problems for asexual organisms is referred to as ]; assuming that reverse mutations are rare, each generation has at least the mutational load of its predecessor. In contrast, in sexual organisms ] generates the variation that, combined with selection, can repair the situation. Sexual organisms consequently have a lighter genetic load. ] (]) 22:42, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::So ] won't work properly in case of ] ? ] (]) 23:16, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::The larger the degree of inbreeding, the larger the chance that deleterious traits are expressed. But this very expression of traits leading to decreased biological fitness of their bearers is what actually enables purifying selection in the longer term. --] 23:36, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::@] so ] won't stop these deleterious traits to get expressed? ] (]) 14:11, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::No, this is not an issue of ]. The genes involved are faithfully reproduced and passed on from generation to generation. --] 15:53, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Or stronger e.g. "", and those guys live for centuries and have much more DNA than us. ] (]) 15:21, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::@] If not due to DNA damage, why do babies from inbreeding appear like DNA-damaged species? ] (]) 17:29, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Inbred offspring of species that normally outcross may show abnormalities because they are more likely than outcrossed offspring to be ] for ] that are deleterious. In individuals that are heterozygous at these loci, the recessive alleles will not be expressed (because the other wild-type dominant allele is sufficient to do their job adequately). See our article on ]. ] (]) 19:26, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == Larvae going south == | |||
| In a novel I've just finished ('']'' by ]) he writes: | |||
| * '' leave the body in an orderly fashion, following each other in a neat procession that always heads south. South-east or south-west sometimes, but never north. No-one knows why''. | |||
| The author has done considerable international research on the science of forensic identification of decayed bodies and I assume his details can be trusted. | |||
| I've looked online for any verification of this surprising statement, but found only , which seems to debunk it. | |||
| Is there any truth to this? -- ] </sup></span>]] 23:38, 19 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Can't speak to its truth, but . . . | |||
| :* Does Beckett state this in his own auctorial voice (i.e. as an ])? If so, he might be genuinely mistaken. | |||
| :* The book was published nearly 20 years ago, what was the accepted wisdom ''then''? | |||
| :* What specific species (if any) is the book describing? – your linked Quora discussion refers only to "maggots" (which can be of numerous species and are a kind of larva, but there are many others, including for example ]). | |||
| :*Alternatively, if the statement is made by a character in the book, is that character meant to be infallible, or is he portrayed as less than omniscient, or an ']'? | |||
| :Regarding the statement, in the Northern hemisphere the arc of South-east to South-west is predominently where the Sun is found well above the horizon, the North never, so the larvae involved might simply be seeking maximum warmth or light. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 02:18, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :: This appears in the very first paragraph of Chapter I, which starts out: | |||
| ::* ''A human body starts to decompose four minutes after death. Once the encapsulation of life, it now undergoes its final metamorphoses. It begins to digest itself. Cells dissolve from the inside out. Tissue turns to liquid, then to gas. No longer animate, the body becomes an immovable feast for other organisms. Bacteria first, then insects. Flies. Eggs are laid, then hatched. The larvae feed on the nutrient-rich broth, and then migrate. They leave the body in an orderly fashion ...'' (then the quote above completes the paragraph). | |||
| :: It's not until para 2 that he starts talking about any human characters, and not until para 4 that he invokes the first person. | |||
| :: That's as much as I know. But I find it hard to believe he'd just make up a detail and put it in such a prominent place if it could so easily be debunked if it were not true. -- ] </sup></span>]] 02:39, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::I wonder how they would measure the migratory path of maggots within a sealed coffin. ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 02:51, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::: The context of the novel is about finding decaying corpses that have been dumped in a forest. No coffins involved. -- ] </sup></span>]] 06:08, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::], see also ] research facilities. ] (]) 13:44, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::Could it be that the larvae are setting off in search of another corpse? The prevailing wind in the UK is from the south-west, so by heading into the wind they won't be distracted by the frangrance of the one they've just left. ]|] 09:30, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| If you can, have a look at 'Heinrich, Bernd. “Coordinated Mass Movements of Blow Fly Larvae (Diptera: Calliphoridae).” Northeastern Naturalist, vol. 20, no. 4, 2013, pp. N23–27. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/43288173.' Here are some extracts | |||
| * On the fourth day, after a cooling night with dew on the grass, a stream of tens of thousands of larvae exited from beneath the carcass within 1 h after sunrise, and proceeded in a single 1-2-cm-wide column directly toward the rising sun... | |||
| * However, in this case, the larvae left at night, within 1 h after a cloudburst (at 21 :00 hours). But, unlike before, this nocturnal larval exodus in the rain was diffuse; thousands of larvae spread out in virtually all directions over an 8 m2area. Apparently, the sudden moisture had cued and facilitated the mass exodus, but the absence of sun had prevented a unidirectional, en masse movement. | |||
| * However, on the following morning as the sun was starting to illuminate the carcass on the dewy grass, masses of larvae gathered at the east end of the carcass at 07:00 hours. In one half hour later, they started streaming in a column directly (within one degree) toward the rising sun, and the carcass was then nearly vacated. | |||
| It goes on. Maggot migration appears to be a bit more complicated than the novel suggests. ] (]) 09:39, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| I suppose you could try to address it from the other direction and look at the technology your average maggot has access to in terms of light detection, heat detection, olfactory systems, orientation in magnetic fields (like many arthropods) etc. They presumably have quite a lot of tools. ] (]) 10:13, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :If orderly migrating maggots tend to move towards the sun, they should display a northward tendency in Oztralia. --] 10:31, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :: Maybe, but the novel is set in England. | |||
| :: I must say, as soon as I read the quoted para for the first time, my immediate thought was that it might have something to do with the magnetic field of the earth. -- ] </sup></span>]] 10:42, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Prime suspect might be the Bolwig organ, the photoreceptor cluster many fly larvae have. ] (]) 10:49, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Obviously, Jack, you need to create a corpse, place it in a nearby forest, and carefully observe which way the maggots go. For Science! And Literary Criticism! {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 21:01, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 20 = | |||
| == Winter solstice and time of sunrise? == | |||
| How is it that despite December 21st supposedly being the shortest day of the year, sunrise here happens later and later until December 26 and only on January 05 starts to turn around to occur earlier and earlier. On December 25 it takes place at about 08:44, between December 26 and January 04 it takes place at about 08:45, and on January 05 it takes place again at about 08:44. (Google rounds out the seconds). Is it Google's fault? Is it everywhere the same? Confused in Brussels, Belgium. ] (]) 12:06, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :The pertinent article is ], start with the section ]. The details are not that simple to understand, but it's basically due to the ellipticity of Earth's orbit and its axial tilt. --] (]) 12:22, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::Also note that sunset begins to be later on 22 December so that the time between sunrise and sunset is a few seconds longer than on 21 December (3 seconds longer on 22/12/24 in Brussels according to ). ] (]) 13:33, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::Also see ]. The obliquity of the ecliptic (that is, the Earth's axial tilt) is the main component and hardest to understand. But the idea is that the time when the Sun is exactly south (that is, the true noon) moves some minutes back and forth throughout the year and it moves quite rapidly to later times in late December. ] (]) 19:05, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| == Three unit questions == | |||
| # Why territorial waters are defined by nautical miles instead of kilometers? | |||
| # Why GDP is usually measured in US dollars rather than euros? Euro would be better because it is not tied into any country. | |||
| # Are there any laws in United States that are defined by metric units? | |||
| --] (]) 23:30, 20 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :#There were nautical miles in use before there were kilometers. | |||
| :#There were US dollars in use before there were Euros. | |||
| :#Yes. | |||
| :The questions all reduce to Why can't millions of people make a change of historically widely accepted units that continue to serve their purpose, and convert to different units that would have no substantive difference, because someone has an opinion. ] (]) 00:52, 21 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::Do any people use metric units in marine and air navigation like "The ship is 10 kilometers from the port", "The plane is 10 kilometers from the destination? And is there any European country with metric flight levels? --] (]) 07:22, 21 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Inland shipping (rivers, canals and lakes) in Europe (except the UK) is fully metric. Ships going for example ] – ] may have to switch units along the way. Gliders and ultralight aircraft in Europe often use metric instruments and airport dimensions are also metric (including runway length). Countries are free to define their territorial waters in whatever way they deem fit, so with nautical miles having no legal status in a fully metric country, they may define their territorial waters as extending 22224 metres. ] (]) 11:23, 21 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Our ] article says: {{xt|"In 1929 the international nautical mile was defined by the First International Extraordinary Hydrographic Conference in Monaco as exactly 1,852 metres (which is 6,076.12 ft). The United States did not adopt the international nautical mile until 1954. Britain adopted it in 1970..."}} | |||
| ::As the US customary units are actually defined in terms that relate them to metric units, any US law based on measurements is technically defined by metric units.--] (]) (]) 01:55, 21 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::The US dollar has been the world's dominant ] for about 75 years. As for the metric system in the US, it is standard in scientific, medical, electronics, auto manufacturing and other highly technical industries. By law, all packaged foods and beverages have metric quantities as well as customary quantities. See ]. ] (]) 02:28, 21 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| The Wikipaedia article on the Nautical Mile talks about how the term originated, it was originally defined in terms of latitude not as a number of meters ] (]) 10:03, 24 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| The euro is tied to multiple specific countries is it not? If you use euros you're just changing from one "dependency" to a "dependency" on the ] countries. A statement of the problem or problems intended to be addressed would be useful. Currency values are interconvertible in any case. Economics does sometimes use the "]" for certain things, which is intended to adjust for differences in ] between countries and over time. But since it's not an actual "real" currency it's not something one can easily "visualize" in their heads, which is likely why it's not used more. --] (]) 05:41, 26 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 24 = | = December 24 = | ||
| Line 315: | Line 84: | ||
| :Yes, the dissolved hydrogen will exit the water just as quickly (even faster, because of its low ] and complete lack of ] or capability for ]), and even if it does enter the bloodstream, it will likewise get back out in short order before it can actually do anything (which, BTW, is why ]s use it in their breathing mixes -- because it gets out of the bloodstream so much faster and therefore doesn't ]) -- so, I don't think it will do much! ] (]) 01:50, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | :Yes, the dissolved hydrogen will exit the water just as quickly (even faster, because of its low ] and complete lack of ] or capability for ]), and even if it does enter the bloodstream, it will likewise get back out in short order before it can actually do anything (which, BTW, is why ]s use it in their breathing mixes -- because it gets out of the bloodstream so much faster and therefore doesn't ]) -- so, I don't think it will do much! ] (]) 01:50, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | ||
| ::It's conceivable it might take out the chloramine, I guess. I don't think there's very much of it, but it tastes awful, which is why I add a tiny bit of vitamin C when I drink tap water. It seems to take very little. Of course it's hard to tell whether it's just being masked by the taste of the vitamin C. --] (]) 02:12, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | ::It's conceivable it might take out the chloramine, I guess. I don't think there's very much of it, but it tastes awful, which is why I add a tiny bit of vitamin C when I drink tap water. It seems to take very little. Of course it's hard to tell whether it's just being masked by the taste of the vitamin C. --] (]) 02:12, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | ||
| :If you just want to split water into hydrogen and oxygen all you need is ]. You don't say where you saw this ad but if it was on a socia media site forget it. ]|] 11:47, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::If this so-called hydrogen water was emitting hydrogen bubbles, would it be possible to set it afire? ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 14:03, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :We once had an article on this topic, but see ]. ] (]) 22:27, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::I don't know if it is rubbish or not but a quick look on the web indicates to me it is notable enough for Misplaced Pages. I didn't see anything indicating it definitely did anything useful so such an article should definitely have caveats. I haven't seen any expression of a potential worry either so it isn't like we'd be saying bleach is a good medicine for covid. ] (]) 23:07, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :'']'' does not sound of exceptionally high quality. ] (]) 01:05, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| = December 29 = | = December 29 = | ||
| == Potential energy vs. kinetic energy. Why not also "]" vs. "]"? E.g. in the following case: == | |||
| In a ], reaching the highest point involves - both a minimal kinetic energy - along with a maximal potential energy, whereas reaching the lowest point involves - both a maximal kinetic energy - along with a minimal potential energy. Thus the mechanical energy becomes the sum of kinetic energy + potential energy, and ''is a conserved quantity''. | |||
| So I wonder if it's reasonable to define also "potential velocity" vs. "kinetic velocity", and claim that in a harmonic oscillator, reaching the highest point involves - both a ''minimal'' "kinetic velocity" (i.e. involves what we usually call ''a rest'') - along with a ''maximal'' "potential velocity", whereas reaching the lowest point involves - both a ''maximal'' "kinetic velocity" (i.e. involves what we usually call ''the actual velocity'') - along with a ''minimal'' "potential velocity". Thus we can also define "mechanical velocity" as the sum of "kinetic velocity" + "potential velocity", and ''claim that the mechanical velocity is a conserved quantity'' - at least as far as a harmonic oscillator is concerned. | |||
| Reasonable? | |||
| Note that I could also ask an analogous question - as to the concept of "potential momentum", but this term is already used in the theory of ] for another meaning, so for the time being I'm focusing on velocity. | |||
| ] (]) 12:26, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| : 'kinetic velocity' is just 'velocity'. 'potential velocity' has no meaning. ] (]) 13:56, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::Per my suggestion, the ratio between distance and time is not called "velocity" but rather "kinetic velocity". | |||
| ::Further, per my suggestion, if you don't indicate whether the "velocity" you're talking about is a "kinetic velocity" or a "potential velocity" or a "mechanical velocity", the very concept of "velocity" alone has no meaning! | |||
| ::On the other hand, "potential velocity" is defined as the difference between the "mechanical velocity" and the "kinetic velocity"! Just as, this is the case if we replace "velocity" by "energy". For more details, see the example above, about the harmonic oscillator. ] (]) 15:14, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::You could define the ''potential velocity'' of a body at a particular height as the velocity it would hit the ground at if dropped from that height. But the sum of the potential and kinetic velocities would not be conserved; rather <math>v_{\mathrm{tot}} = \sqrt{v_{p}^{2} + v_{k}^{2}}</math> would be constant. ] (]) 18:54, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Thank you. ] (]) 20:07, 29 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::: 'Potential velocity' has no meaning. You seem to be arguing that in a system where energy is conserved, but is transforming between kinetic and potential energy, (You might also want to compare this to ].) then you can express that instead through a new conservation law based on velocity. But this doesn't work. There's no relation between velocity and potential energy. | |||
| ::: In a harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is typically coming from some central restoring force with a relationship to ''position'', nothing at all to do with velocity. Where some axiomatic external rule (such as ] applying, because the system is a mass on a spring) ''happens'' to relate the position and velocity through a suitable relation, then the system will then (]) behave as a harmonic oscillator. But a different system (swap the spring for a ]) doesn't have this, thus won't oscillate. ] (]) 00:00, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Let me quote a sentence from my original post: {{tq|Thus we can also...claim that the mechanical velocity is a conserved quantity - '''at least as far as a harmonic oscillator is concerned'''.}} | |||
| ::::What's wrong in this quotation? ] (]) 07:52, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::::It is true, not only for harmonic oscillators, provided that you define {{math|1='''v'''<sub>pot</sub> = − '''v'''<sub>kin</sub>}}. --] 09:07, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::* You have defined some arbitrary values for new 'velocities', where their ''only'' definition is that they then demonstrate some new conservation law. Which is really the conservation of energy, but you're refusing to use that term for some reason. | |||
| ::::: As Catslash pointed out, the conserved quantity here is proportional to the square of velocity, so your conservation equation has to include that. It's simply wrong that any linear function of velocity would be conserved here. Not merely we can't prove that, but we can prove (the sum of the squares diverges from the sum) that it's actually contradicted. For any definition of 'another velocity' which is a linear function of velocity. | |||
| ::::: Lambiam's definition isn't a conservation law, it's merely a ]. The sum of any value and its ] is always ]. ] (]) 14:04, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::{{small|It is a law of conservation of ''sanity''. Lacking a definition of potential energy, other than by having been informed that kinetic energy + potential energy is a conserved quantity, there is not much better we can do.}} --] 11:20, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::: We have a perfectly viable definition of potential energy. For a pendulum it's based on the change in height of the pendulum bob against gravity. For some other oscillators it would involve the work done against a spring. ] (]) 16:33, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::::::Oops, I mistyped. I meant to write: | |||
| :::::::::"{{small|Lacking a definition of potential velocity, other than by having been informed that kinetic velocity + potential velocity is a conserved quantity, there is not much better we can do.}}" | |||
| :::::::: --] 23:32, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 30 = | |||
| == Saltiness comparison == | |||
| Is there some test one might easily perform in a home ] to compare the ] (due to the concentration of ] ]s) of two liquid preparations, without involving biological ]s? --] 09:22, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Put two equally sized drops, one of each liquid, on a warm surface, wait for them to evaporate, and compare how much salt residue each leaves? Not very precise or measurable, but significant differences should be noticeable. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 10:21, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::The principle is sound, but the residue from one drop won't be measurable using kitchen equipment -- better to put equal amounts of each liquid in two warm pans (use enough liquid to cover the bottom of each pan with a thin layer), wait for them to evaporate and then weigh the residue! Or, if you're not afraid of doing some ], you could also try an indirect method -- bring both liquids to a boil, measure the temperature of both, and then use the formula for ] to calculate the saltiness of each! ] (]) 18:22, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::Presumably the ''liquid preparations'' are not simple saline solutions, but contain other solutes - or else one could simply use a hydrometer. It is unlikely that Lambian is afraid of doing some algebra. ] (]) 18:57, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :<s>Assuming the liquid preparations are water-based and don't contain alcohols and/or detergents one can measure their rates of dispersion. Simply add a drop of food dye to each liquid and then time how rapidly droplets of each liquid disperse in distilled water. Materials needed: food dye, eye dropper, distilled water, small clear containers and a timer.</s> ] (]) 21:09, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::The ] of a solution will indicate its molarity, but not identify the solute. ''Liquid preparations'' that might be found in a kitchen are likely to contain both salt and sugar. Electrical conductivity is a property that will be greatly affected by the salt but not the sugar (this does not help in distinguishing Na<sup>+</sup> from K<sup>+</sup> ions though). ] (]) 22:23, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::That's what I'm thinking too -- use an ] to measure the ] of the preparation, and compare to that of solutions with known NaCl concentration (using a ]-type method). ] (]) 20:18, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Quantitative urine test-strips for sodium seem to be available. They're probably covering the concentration range of tens to hundreds millimolar. ] (]) 00:58, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::Thanks, test strips seem more practical in the kitchen setting than an ohmmeter (why not call it a "]meter"?), for which I'd need to devise a way (or so I think) to keep the terminals apart at a steady distance. Test strips require a colour comparison, but I expect that a significant difference in salinity will result in a perceptible colour difference when one strip is placed across the other. Only experiment can tell whether this expectation will come true. Salinity is usually measured in g/L; for kitchen preparations a ballpark figure is 1 g/L. If I'm not mistaken this corresponds to {{nowrap|1=(1 g/L) / (58.443 g/mol) ≈}} {{nowrap|1=0.017 M = 17 ].}} I also see offers for salinity test strips, 0–1000 ppm, for "Science Education". --] 11:40, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::Test strips surely come with a printed color-chart. But if all you are trying to do is determine which is more salty, then that's even easier than quantifying each separately. Caveat for what you might find for sale: some "salinity" tests are based on the chloride not the sodium, so a complex matrix that has components other than NaCl could fool it. ] (]) 18:44, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| == The (uncommon?) terms "relativistic length", and "relativistic time". == | |||
| 1. In Misplaced Pages, the page ] is automatically redirected to our article ], ''which actually doesn't mention the term "relativistic length" at all''. '''I wonder if there is an accepted term for the concept of relativistic length'''. | |||
| 2. A similar qusestion arises, at to the concept of relativistic time: The page ], is automatically redirected to our article ], which prefers the abbreviated term "time dilation" (59 times) to the term "relativistic time dilation" (8 times only), and ''nowhere'' mentions the term "relativistic time" alone (i.e. without the third word "dilation") - although it does mention the term "proper time" for the shortest time. Further, this article doesn't even mention the term "dilated time" either. It does mention, though, another term: ], but regardless of time dilation in ''Special'' relativity. '''To sum up, I wonder what's the accepted term used for the dilated time (mainly is Special relativity): Is it "coordinate time"? "Relativistic time"?''' | |||
| ] (]) 09:32, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :Are you reading these things as "contraction of relativistic length" etc.? It is "relativistic contraction of length" and "relativistic dilation of time". --] (]) 09:37, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::When I wrote: {{tq|The page ] is automatically redirected to our article ] which...nowhere mentions the term "relativistic time" alone (i.e. without the third word "dilation")}}, I had already guessed that the term "dilation of relativistic time" (i.e, with the word "dilation" preceding the words "relativistic time") existed nowhere (at least in Misplaced Pages), and that this redirected page actually meant "relativistic dilation of time". The same is true for the redirected page "relativistic length contraction": I had already gussed it didn't mean "contraction of relativistic length", because (as I had already written): {{tq|the article ]...doesn't mention the term "relativistic length" at all}}. | |||
| ::Anyway, I'm still waiting for an answer to my original question: Are there accepted terms for the concepts, of relativistic length - as opposed to ], and of relativistic time - as opposed to ]? ] (]) 10:12, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :::A term that will be understood in the context of relativistic length contraction is ''relative length'' – that is, length relative to an observer.<sup></sup> --] 10:55, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Thank you. The middle source uses the term "comparative length", rather than "relative length". I couldn't open the third source. ] (]) 08:04, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::::The text under the graph labelled '''Comparative length''' on page 20 of the middle source reads: | |||
| ::::::Graph of the relative length of a stationary rod on earth, as observed from the reference frame of a traveling rod of 100cm proper length. | |||
| :::::A similar use of "relative length" can be seen on the preceding page. --] 10:23, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| == What did Juan Maldacena say after "Geometry of" in this video? == | |||
| I was watching this video ] and ] as they explore a wealth of developments connecting black holes, string theory etc, ] said something right after "'''Geometry of'''" Here is the spot: https://www.youtube.com/live/yNNXia9IrZs?si=G7S90UT4C8Bb-OnG&t=4484 What is that? ] (]) 20:46, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| :]. --] (]) 21:05, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| ::Thank you, its the ]'s accent which made me post here. ] (]) 21:18, 30 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = December 31 = | |||
| == Brightest spot of a discharge tube == | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| What causes the discharge tubes to have their brightest spots at different positions? ] (]) 13:12, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| : See also the pictures at ]. --] (]) 13:26, 31 December 2024 (UTC) | |||
| = January 1 = | |||
| == Two unit questions == | |||
| #Is there any metric unit whose ratio is not power of 10, and is divisible by 3? Is there any common use for things like "{{frac|2|3}} km", "{{frac|5|12}} kg", "{{frac|3|1|6}} m"? | |||
| #Is a one-tenth of nautical mile (185.2 m) used in English-speaking countries? Is there a name for it? | |||
| --] (]) 10:41, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :1 not that I know of (engineer who has worked with SI for 50 years) | |||
| :2 not that I know of (yacht's navigator for many years on and off) | |||
| :] (]) 11:35, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::In Finland, ''kaapelinmitta'' is 185.2 m. Is there an English equivalent? --] (]) 18:11, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::]. --] (]) 18:26, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::::Good article. I was wrong ] (]) 22:26, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::The answer can be found by looking up '']'' on Wiktionary. --] 00:14, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| == What is more physiological (for a right-hander) left-hand drive or right-hand drive? == | |||
| Has anyone determined whether it is better for a right-hander to have the left hand on the steering wheel and the right hand on the gear shift stick, or the other way round? Are there other tests of whether left-hand drive or right-hand drive is physiologically better (for a right-hander at least)? ] (]) 12:03, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :<small>Supplementary question: I've only driven right-hand-drive vehicles (being in the UK) where the light stalk is on the left of the steering column and the wiper & washer controls are (usually) on the right. On a l-h-drive vehicle, is this usually the same, or reversed? {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 12:12, 2 January 2025 (UTC)</small> | |||
| ::<small>Modern cars are designed for mass production in RH- and LH-drive versions with a minimum difference of parts. Steering columns with attached controls are therefore unchanged between versions. ] (]) 12:29, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::In the UK nowadays, are cars still mostly manual transmission, or has automatic become the norm? ←] <sup>'']''</sup> ]→ 12:38, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::::In the UK, sales of new automatics have just recently overtaken manuals - so probably still more manuals than automatics on the road. ] (]) 14:37, 2 January 2025 (UTC)</small> | |||
| :::::<small>This may be tied to the rise of EVs, since they have automatic transmissions by default. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 05:29, 3 January 2025 (UTC)</small> | |||
| :::In Australia, we drive on the left, and the indicator and wiper stalks are the opposite way to the UK. Having moved back from the UK after 30 years, it took me a while to stop indicating with wipers. ] (]) 05:08, 3 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::I've driven different (automatic) left-hand-drive vehicles with the light stalk on each side, but left side has been more common. Perhaps because the right hand is more likely to be busy with the gear shift? (Even in the US, where automatic has been heavily dominant since before I learned to drive.) -- ] (]) 17:32, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :It's better for a right-hander to have both hands on the steering wheel regardless of where the gear lever is. See . I suspect the same goes for a left-hander. ] (]) 14:39, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::I suppose that the question is whether right-handers have an easier time operating the gear stick when changing gears in manual-transmission cars designed for left-hand traffic, with the steering wheel on the right (like in the UK) or right-hand traffic, with the steering wheel on the left (like in most of continental Europe). Obviously, drivers will use their hand at the side where the gear stick is, so if it is in the middle and the driver, behind the wheel, sits in the right front seat, they'll use their left hand, regardless of their handedness. But this may be more awkward for a rightie. Or not. | |||
| ::--] 16:30, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::In my personal experience (more than 10 years driving on each side of the road, in all four combinations of car handedness and road handedness) the question which hand to use for shifting gears is fairly insignificant. Switching from one type of car to the other is a bit awkward though. —] (]) 18:33, 2 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::::My first car, a ], had the gearstick on the left and the handbreak on the right, which was a bit of a juggle in traffic. ] (]) 19:13, 3 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| == Distinguishing a picture of a sunset from the picture of a sunrise? == | |||
| Is there a way (if you don't know which way is west and which way is east in a particular location) to distinguish a picture of a sunset from the picture of a sunrise? ] (]) 12:08, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :Generally, no, but there are a few tricks that sometimes work. In dry sunny weather, there's more dust in the air at sunset (due to thermals) than at sunrise, making the sky around the sun redder at sunset. But in moist weather, mist has the same effect at sunrise. If the picture is good enough to see ], comparing the distribution of sunspots to the known distribution of that day (this is routinely monitored) tells you where the North Pole of the sun is. At sunset, the North Pole points somewhat to the right; at sunrise, to the left. If you see any ] or ] clouds in the picture, it was a sunset, as such clouds form during the day and disappear around sunset, but absence of such clouds doesn't mean the picture was taken at sunrise. A very large cumulonimbus may survive the night. ] clouds are often very large, expanding into ], in the evening, but are much smaller at dawn as there's more air traffic during the day than at night, making the upper troposphere more moist towards the end of the day. Cirrostratus also contributes to red sunsets and (to lesser extend, as there's only natural cirrostratus) red sunrises. ], ], flowers and flocks of birds may also give an indication. And of course human activity: the beach is busier at sunset than at sunrise. ] (]) 13:41, 1 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::Supposing the photograph has high enough resolution to show ]s it can be helpful to know that the pattern of spots at sunrise is reversed left-right at sunset. ] (]) 13:21, 3 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::At the equinox, the disk of the Sun with its pattern of sunspots appears to rotate clockwise from sunrise to sunset by 180 degrees minus twice your latitude (taking north positive). At my place, that's 75 degrees. Other times of the year it's less; at the start and end of polar day and polar night, there's no rotation. Sunset and sunrise merge then. | |||
| :::And I forgot to mention: cirrostratus clouds will turn red just after sunset or just before sunrise. At the exact moment of sunrise or sunset, they appear pretty white. ] (]) 17:06, 3 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| ::::I differ: the same rotation is involved everywhere on Earth. If you stand on tiptoe at a N. or S. pole to take a picture of the Sun it is you who must pirouette 15 degrees per hour to keep facing the Sun. The Earth rotates you at this rate at all non-polar locations. If you stand within the arctic or antarctic circles, for parts of the year the 24-hour night or 24-hour daylight seem to prevent photographs of sunrise or sunset. However the terms "sunrise" and "sunset" can then be interpreted as times that are related to particular timezones which are generally assigned by longitude. In photographing the 24-hour Sun the equatorial rise and set times for your own longitude are significant elevation maxima worth mentioning even though the minimum elevation remains above the horizon. I maintain that the sunspot pattern observed from any location on Earth rotates 360 degrees per 24 hours and that "night", the darkness from sunset to sunrise, is when the Earth's bulk interrupts one's view of the rotation but not the rotation itself which is continuous. | |||
| ::::The questioner asks for interpretation of a single picture. It is beside the point that more would be revealed by a picture sequence such as of changing cloud colours. ] (]) 12:41, 4 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| :::::In my experience (Southern England) they tend to be pinker at dawn and oranger(!) at dusk. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} ] (]) 03:23, 4 January 2025 (UTC) | |||
| = January 5 = | |||
Latest revision as of 00:05, 5 January 2025
Welcome to the science sectionof the Misplaced Pages reference desk. skip to bottom Select a section: Shortcut Want a faster answer?
Main page: Help searching Misplaced Pages
How can I get my question answered?
- Select the section of the desk that best fits the general topic of your question (see the navigation column to the right).
- Post your question to only one section, providing a short header that gives the topic of your question.
- Type '~~~~' (that is, four tilde characters) at the end – this signs and dates your contribution so we know who wrote what and when.
- Don't post personal contact information – it will be removed. Any answers will be provided here.
- Please be as specific as possible, and include all relevant context – the usefulness of answers may depend on the context.
- Note:
- We don't answer (and may remove) questions that require medical diagnosis or legal advice.
- We don't answer requests for opinions, predictions or debate.
- We don't do your homework for you, though we'll help you past the stuck point.
- We don't conduct original research or provide a free source of ideas, but we'll help you find information you need.
How do I answer a question?
Main page: Misplaced Pages:Reference desk/Guidelines
- The best answers address the question directly, and back up facts with wikilinks and links to sources. Do not edit others' comments and do not give any medical or legal advice.
December 24
Unknown species of insect
Am I correct in inferring that  this guy is an oriental beetle? I was off-put by the green head at first, but the antennae seem to match. JayCubby 03:00, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
this guy is an oriental beetle? I was off-put by the green head at first, but the antennae seem to match. JayCubby 03:00, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
(reference: https://www.genesdigest.com/macro/image.php?imageid=168&apage=0&ipage=1)
It looks like one of the invasive Japanese beetles that happens to like my blackberries in the summer.Modocc (talk) 13:11, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
- I would say not necessarily a Japanese beetle, but almost certainly one of the other Scarab beetles, though with 35,000 species that doesn't help a lot. Looking at the infobox illustration in that article, 16. & 17., "Anisoplia segetum" looks very similar, but evidently we either don't have an article or (if our Anisoplia article is a complete list) it's been renamed. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} 94.1.223.204 (talk) 14:18, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
- Yes, it's not the Japanese beetle for this beetle appears to lack its white-dotted fringe although its condition is deteriorated. Its shape is also more or less more slender; and not as round. Modocc (talk) 15:02, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
- Perhaps it is the shining leaf chafer Strigoderma pimalis. Shown here. Modocc (talk) 16:09, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
- That looks like easily the best match I've seen so far, and likely correct. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} 94.1.223.204 (talk) 17:09, 24 December 2024 (UTC)
December 25
Mass of oscillating neutrino
From the conservation of energy and momentum it follows that a particle that is not subject to external forces must have constancy of mass.
If I am right, this means that the mass of the neutrino cannot change during the neutrino oscillation, although its flavoring may. Is this written down somewhere? Thank you. Hevesli (talk) 19:24, 25 December 2024 (UTC)
- Any (flavored) neutrino that is really observed is a superposition of two or three mass eigenstates. This is actually the cause of neutrino oscillations. So, the answer to your question is complicated. Ruslik_Zero 19:40, 25 December 2024 (UTC)
- Important note: particle physicists today generally only ever use "mass" to mean "invariant mass" and never anything else: . Like the term says, invariant mass is well, invariant, it never changes ever, no matter what "external forces" may or may not be involved. Being proper particle-icans and following the standard practice in the field, then, the three neutrino masses are constant values. ..."Wait, three?" Yeah sure, turns out neutrinos come in three "flavors" but each flavor is a mixture of the three possible mass "states". As mentioned, due to Quantum Weirdness we aren't able to get these different states "alone by themselves" to measure each by itself, so we only know the differences of the squares of the masses. Yeah welcome to quantum mechanics.
- Richard Feynman: "Quantum mechanics describes nature as absurd from the point of view of common sense. And yet it fully agrees with experiment. So I hope you can accept nature as She is – absurd." --Slowking Man (talk) 06:06, 26 December 2024 (UTC)
- The equation uses invariant mass m0 which is constant if E and p are constant. The traveling neutrino has a varying mass mixture of different flavors with different masses. If a mixture of different masses changes, you would expect the resulting mass to change with it. But somehow this does not happen as the neutrino mass mixture changes. These mixture changes cannot be any changes. The changes must be such that the resulting mass of the traveling neutrino remains constant. My question is whether this is described somewhere. Hevesli (talk) 11:16, 26 December 2024 (UTC)
- I freely confess I'm uncertain exactly what's being "asked for" or "gotten at" here. Have you looked at the neutrino oscillation article? From it:
That is, the three neutrino states that interact with the charged leptons in weak interactions are each a different superposition of the three (propagating) neutrino states of definite mass. Neutrinos are emitted and absorbed in weak processes in flavor eigenstates but travel as mass eigenstates.
- What is it that we're "doing" with the energy–momentum relation here? For the neutrino, we don't have a single value of "mass" to plug in for , because we can't "see" the individual mass eigenstates, only some linear combination of them. What you want for describing neutrino interactions is quantum field theory, which is special relativity + QM. (Remember, relativity is a "classical" theory, which presumes everything always has single well-defined values of everything. Which isn't true in quantum-world.) --Slowking Man (talk) 18:41, 26 December 2024 (UTC)
- Not all potential evolutions of a linear combination of unequal values produce constant results. Constancy can only be guaranteed by a constraint on the evolutions. Does the fact that this constraint is satisfied in the case of neutrino oscillation follow from the mathematical formulation of the Standard Model, or does this formulation allow evolutions of the mass mixture for which the combination is not constant? If the unequal values are unknown, I have no idea of how such a constraint might be formulated. I think the OP is asking whether this constraint is described somewhere. --Lambiam 00:51, 27 December 2024 (UTC)
- I freely confess I'm uncertain exactly what's being "asked for" or "gotten at" here. Have you looked at the neutrino oscillation article? From it:
- The equation uses invariant mass m0 which is constant if E and p are constant. The traveling neutrino has a varying mass mixture of different flavors with different masses. If a mixture of different masses changes, you would expect the resulting mass to change with it. But somehow this does not happen as the neutrino mass mixture changes. These mixture changes cannot be any changes. The changes must be such that the resulting mass of the traveling neutrino remains constant. My question is whether this is described somewhere. Hevesli (talk) 11:16, 26 December 2024 (UTC)
December 27
Low-intensity exercise
If you exercise at a low intensity for an extended period of time, does the runner's high still occur if you do it for long enough? Or does it only occur above a certain threshold intensity of exercise? 2601:646:8082:BA0:CDFF:17F5:371:402F (talk) 20:13, 27 December 2024 (UTC)
- Hows about you try it and report back? :) ←Baseball Bugs carrots→ 21:31, 27 December 2024 (UTC)
- I wanted to try it just today, but I had to exchange the under-desk elliptical trainer I got for Christmas for a different model with more inclined treadles because with the one I got, my knees would hit the desk at the top of every cycle. Anyway, I was hoping someone else tried it first (preferably as part of a formal scientific study) so I would know if I could control whether I got a runner's high from exercise or not? 2601:646:8082:BA0:9052:E6AF:23C7:7CAF (talk) 03:09, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
Also, sorry for adding to my own question, but here's a related one: is it known whether the length of a person's dopamine receptor D4 (which is inversely correlated with its sensitivity) influences whether said person gets a runner's high from exercise (and especially from low-intensity exercise)? 2601:646:8082:BA0:9052:E6AF:23C7:7CAF (talk) 03:14, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
fastidious organism vs auxotroph
Hi,
What is the difference between an auxotroph and a fastidious organism? It seems to me the second one would have more requirements than the first one, but the limit between the two definitions is rather unclear to me.
Thank you 212.195.231.13 (talk) 23:17, 27 December 2024 (UTC)
- I'm not 100% sure, but it seems to me that an auxotroph is a specific type of a fastidious organism. 2601:646:8082:BA0:9052:E6AF:23C7:7CAF (talk) 03:02, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
- Symbiosis aside, it would seem that most auxotrophs would be fastidious organisms, but there could be many more fastidious organisms that aren't auxotrophs. Auxotrophs specifically can't produce organic compounds on their own. There are a LOT of organisms that rely on the availability of non-organic nutrients, such as specific elements/minerals. For instance, vertebrates require access to calcium. Calcium is an element; our inability to produce it does not make us auxotrophs.
- But perhaps symbiosis would allow an organism to be an auxotroph without being a fastidious organism? For instance, mammals tend to have bacteria in our guts that can digest nutrients that our bodies can't on their own. Perhaps some of those bacteria also assemble certain nutrients that our bodies can't? -- Avocado (talk) 14:27, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
December 28
Paper with wrong enantiomer in a figure
In the following reference:
- Quack, Martin; Seyfang, Georg; Wichmann, Gunther (2022). "Perspectives on parity violation in chiral molecules: theory, spectroscopic experiment and biomolecular homochirality". Chemical Science. 13 (36): 10598–10643. doi:10.1039/d2sc01323a. PMID 36320700.
it is stated in the caption of Fig. 8 that S–bromochlorofluoromethane is predicted to be lower in energy due to parity violation, but in the figure the wrong enantiomer is shown on this side. Which enantiomer is more stable, according to the original sources for this data? –LaundryPizza03 (dc̄) 08:18, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
Where can I find data on the circulation and citation rates of these journals?
Hello everyone, To write an article about a scientist, you need to know, where can I find data on circulation and citation rates of journals from this list? Vyacheslav84 (talk) 09:58, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
So-called “Hydrogen water”
I saw an ad promoting a device which presumable splits water into hydrogen and oxygen and infuses water with extra hydrogen, to a claimed surplus of perhaps 5 ppm, which doesn’t seem like much. I found a review article which looked at several dozen related studies that found benefits:https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10816294/ .
I’ve noticed that carbon dioxide or chlorine (chloramine?) dissolved in water work their way out pretty easily, so I wonder if dissolved hydrogen could similarly exit hydrogen enriched water and be burped or farted out, rather than entering the blood stream and having health benefits. is it more than the latest snake oil? Edison (talk) 23:01, 28 December 2024 (UTC)
- Yes, the dissolved hydrogen will exit the water just as quickly (even faster, because of its low molecular mass and complete lack of polarity or capability for ionic dissociation), and even if it does enter the bloodstream, it will likewise get back out in short order before it can actually do anything (which, BTW, is why deep-sea divers use it in their breathing mixes -- because it gets out of the bloodstream so much faster and therefore doesn't build up and form bubbles like nitrogen does) -- so, I don't think it will do much! 2601:646:8082:BA0:209E:CE95:DB32:DD64 (talk) 01:50, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- It's conceivable it might take out the chloramine, I guess. I don't think there's very much of it, but it tastes awful, which is why I add a tiny bit of vitamin C when I drink tap water. It seems to take very little. Of course it's hard to tell whether it's just being masked by the taste of the vitamin C. --Trovatore (talk) 02:12, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- If you just want to split water into hydrogen and oxygen all you need is a battery and two bits of wire. You don't say where you saw this ad but if it was on a socia media site forget it. Shantavira| 11:47, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- If this so-called hydrogen water was emitting hydrogen bubbles, would it be possible to set it afire? ←Baseball Bugs carrots→ 14:03, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- We once had an article on this topic, but see Misplaced Pages:Articles for deletion/Hydrogen water. Graeme Bartlett (talk) 22:27, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- I don't know if it is rubbish or not but a quick look on the web indicates to me it is notable enough for Misplaced Pages. I didn't see anything indicating it definitely did anything useful so such an article should definitely have caveats. I haven't seen any expression of a potential worry either so it isn't like we'd be saying bleach is a good medicine for covid. NadVolum (talk) 23:07, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- International Journal of Molecular Sciences does not sound of exceptionally high quality. DMacks (talk) 01:05, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
December 29
Potential energy vs. kinetic energy. Why not also "potential velocity" vs. "kinetic velocity"? E.g. in the following case:
In a harmonic oscillator, reaching the highest point involves - both a minimal kinetic energy - along with a maximal potential energy, whereas reaching the lowest point involves - both a maximal kinetic energy - along with a minimal potential energy. Thus the mechanical energy becomes the sum of kinetic energy + potential energy, and is a conserved quantity.
So I wonder if it's reasonable to define also "potential velocity" vs. "kinetic velocity", and claim that in a harmonic oscillator, reaching the highest point involves - both a minimal "kinetic velocity" (i.e. involves what we usually call a rest) - along with a maximal "potential velocity", whereas reaching the lowest point involves - both a maximal "kinetic velocity" (i.e. involves what we usually call the actual velocity) - along with a minimal "potential velocity". Thus we can also define "mechanical velocity" as the sum of "kinetic velocity" + "potential velocity", and claim that the mechanical velocity is a conserved quantity - at least as far as a harmonic oscillator is concerned.
Reasonable?
Note that I could also ask an analogous question - as to the concept of "potential momentum", but this term is already used in the theory of hidden momentum for another meaning, so for the time being I'm focusing on velocity.
HOTmag (talk) 12:26, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- 'kinetic velocity' is just 'velocity'. 'potential velocity' has no meaning. Andy Dingley (talk) 13:56, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- Per my suggestion, the ratio between distance and time is not called "velocity" but rather "kinetic velocity".
- Further, per my suggestion, if you don't indicate whether the "velocity" you're talking about is a "kinetic velocity" or a "potential velocity" or a "mechanical velocity", the very concept of "velocity" alone has no meaning!
- On the other hand, "potential velocity" is defined as the difference between the "mechanical velocity" and the "kinetic velocity"! Just as, this is the case if we replace "velocity" by "energy". For more details, see the example above, about the harmonic oscillator. HOTmag (talk) 15:14, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- You could define the potential velocity of a body at a particular height as the velocity it would hit the ground at if dropped from that height. But the sum of the potential and kinetic velocities would not be conserved; rather would be constant. catslash (talk) 18:54, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- Thank you. HOTmag (talk) 20:07, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
- 'Potential velocity' has no meaning. You seem to be arguing that in a system where energy is conserved, but is transforming between kinetic and potential energy, (You might also want to compare this to conservation of momentum.) then you can express that instead through a new conservation law based on velocity. But this doesn't work. There's no relation between velocity and potential energy.
- In a harmonic oscillator, the potential energy is typically coming from some central restoring force with a relationship to position, nothing at all to do with velocity. Where some axiomatic external rule (such as Hooke's Law applying, because the system is a mass on a spring) happens to relate the position and velocity through a suitable relation, then the system will then (and only then) behave as a harmonic oscillator. But a different system (swap the spring for a dashpot) doesn't have this, thus won't oscillate. Andy Dingley (talk) 00:00, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- Let me quote a sentence from my original post:
Thus we can also...claim that the mechanical velocity is a conserved quantity - at least as far as a harmonic oscillator is concerned.
- What's wrong in this quotation? HOTmag (talk) 07:52, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- It is true, not only for harmonic oscillators, provided that you define vpot = − vkin. --Lambiam 09:07, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- You have defined some arbitrary values for new 'velocities', where their only definition is that they then demonstrate some new conservation law. Which is really the conservation of energy, but you're refusing to use that term for some reason.
- As Catslash pointed out, the conserved quantity here is proportional to the square of velocity, so your conservation equation has to include that. It's simply wrong that any linear function of velocity would be conserved here. Not merely we can't prove that, but we can prove (the sum of the squares diverges from the sum) that it's actually contradicted. For any definition of 'another velocity' which is a linear function of velocity.
- Lambiam's definition isn't a conservation law, it's merely a mathematical identity. The sum of any value and its additive inverse is always zero. Andy Dingley (talk) 14:04, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- It is a law of conservation of sanity. Lacking a definition of potential energy, other than by having been informed that kinetic energy + potential energy is a conserved quantity, there is not much better we can do. --Lambiam 11:20, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- We have a perfectly viable definition of potential energy. For a pendulum it's based on the change in height of the pendulum bob against gravity. For some other oscillators it would involve the work done against a spring. Andy Dingley (talk) 16:33, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- Oops, I mistyped. I meant to write:
- "Lacking a definition of potential velocity, other than by having been informed that kinetic velocity + potential velocity is a conserved quantity, there is not much better we can do."
- --Lambiam 23:32, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- Oops, I mistyped. I meant to write:
- We have a perfectly viable definition of potential energy. For a pendulum it's based on the change in height of the pendulum bob against gravity. For some other oscillators it would involve the work done against a spring. Andy Dingley (talk) 16:33, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- It is a law of conservation of sanity. Lacking a definition of potential energy, other than by having been informed that kinetic energy + potential energy is a conserved quantity, there is not much better we can do. --Lambiam 11:20, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- Let me quote a sentence from my original post:
- You could define the potential velocity of a body at a particular height as the velocity it would hit the ground at if dropped from that height. But the sum of the potential and kinetic velocities would not be conserved; rather would be constant. catslash (talk) 18:54, 29 December 2024 (UTC)
December 30
Saltiness comparison
Is there some test one might easily perform in a home test kitchen to compare the saltiness (due to the concentration of Na cations) of two liquid preparations, without involving biological taste buds? --Lambiam 09:22, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- Put two equally sized drops, one of each liquid, on a warm surface, wait for them to evaporate, and compare how much salt residue each leaves? Not very precise or measurable, but significant differences should be noticeable. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} 94.1.223.204 (talk) 10:21, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- The principle is sound, but the residue from one drop won't be measurable using kitchen equipment -- better to put equal amounts of each liquid in two warm pans (use enough liquid to cover the bottom of each pan with a thin layer), wait for them to evaporate and then weigh the residue! Or, if you're not afraid of doing some algebra, you could also try an indirect method -- bring both liquids to a boil, measure the temperature of both, and then use the formula for boiling point elevation to calculate the saltiness of each! 2601:646:8082:BA0:BD1B:60D8:96CA:C5B0 (talk) 18:22, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- Presumably the liquid preparations are not simple saline solutions, but contain other solutes - or else one could simply use a hydrometer. It is unlikely that Lambian is afraid of doing some algebra. catslash (talk) 18:57, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
Assuming the liquid preparations are water-based and don't contain alcohols and/or detergents one can measure their rates of dispersion. Simply add a drop of food dye to each liquid and then time how rapidly droplets of each liquid disperse in distilled water. Materials needed: food dye, eye dropper, distilled water, small clear containers and a timer.Modocc (talk) 21:09, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- The colligative properties of a solution will indicate its molarity, but not identify the solute. Liquid preparations that might be found in a kitchen are likely to contain both salt and sugar. Electrical conductivity is a property that will be greatly affected by the salt but not the sugar (this does not help in distinguishing Na from K ions though). catslash (talk) 22:23, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- That's what I'm thinking too -- use an ohmmeter to measure the electrical conductivity of the preparation, and compare to that of solutions with known NaCl concentration (using a calibration curve-type method). 73.162.165.162 (talk) 20:18, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- Quantitative urine test-strips for sodium seem to be available. They're probably covering the concentration range of tens to hundreds millimolar. DMacks (talk) 00:58, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- Thanks, test strips seem more practical in the kitchen setting than an ohmmeter (why not call it a "mhometer"?), for which I'd need to devise a way (or so I think) to keep the terminals apart at a steady distance. Test strips require a colour comparison, but I expect that a significant difference in salinity will result in a perceptible colour difference when one strip is placed across the other. Only experiment can tell whether this expectation will come true. Salinity is usually measured in g/L; for kitchen preparations a ballpark figure is 1 g/L. If I'm not mistaken this corresponds to (1 g/L) / (58.443 g/mol) ≈ 0.017 M = 17 mM. I also see offers for salinity test strips, 0–1000 ppm, for "Science Education". --Lambiam 11:40, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- Test strips surely come with a printed color-chart. But if all you are trying to do is determine which is more salty, then that's even easier than quantifying each separately. Caveat for what you might find for sale: some "salinity" tests are based on the chloride not the sodium, so a complex matrix that has components other than NaCl could fool it. DMacks (talk) 18:44, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- Thanks, test strips seem more practical in the kitchen setting than an ohmmeter (why not call it a "mhometer"?), for which I'd need to devise a way (or so I think) to keep the terminals apart at a steady distance. Test strips require a colour comparison, but I expect that a significant difference in salinity will result in a perceptible colour difference when one strip is placed across the other. Only experiment can tell whether this expectation will come true. Salinity is usually measured in g/L; for kitchen preparations a ballpark figure is 1 g/L. If I'm not mistaken this corresponds to (1 g/L) / (58.443 g/mol) ≈ 0.017 M = 17 mM. I also see offers for salinity test strips, 0–1000 ppm, for "Science Education". --Lambiam 11:40, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
The (uncommon?) terms "relativistic length", and "relativistic time".
1. In Misplaced Pages, the page relativistic length contraction is automatically redirected to our article length contraction, which actually doesn't mention the term "relativistic length" at all. I wonder if there is an accepted term for the concept of relativistic length.
2. A similar qusestion arises, at to the concept of relativistic time: The page relativistic time dilation, is automatically redirected to our article time dilation, which prefers the abbreviated term "time dilation" (59 times) to the term "relativistic time dilation" (8 times only), and nowhere mentions the term "relativistic time" alone (i.e. without the third word "dilation") - although it does mention the term "proper time" for the shortest time. Further, this article doesn't even mention the term "dilated time" either. It does mention, though, another term: coordinate time, but regardless of time dilation in Special relativity. To sum up, I wonder what's the accepted term used for the dilated time (mainly is Special relativity): Is it "coordinate time"? "Relativistic time"?
HOTmag (talk) 09:32, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- Are you reading these things as "contraction of relativistic length" etc.? It is "relativistic contraction of length" and "relativistic dilation of time". --Wrongfilter (talk) 09:37, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- When I wrote:
The page relativistic time dilation is automatically redirected to our article time dilation which...nowhere mentions the term "relativistic time" alone (i.e. without the third word "dilation")
, I had already guessed that the term "dilation of relativistic time" (i.e, with the word "dilation" preceding the words "relativistic time") existed nowhere (at least in Misplaced Pages), and that this redirected page actually meant "relativistic dilation of time". The same is true for the redirected page "relativistic length contraction": I had already gussed it didn't mean "contraction of relativistic length", because (as I had already written):the article length contraction...doesn't mention the term "relativistic length" at all
. - Anyway, I'm still waiting for an answer to my original question: Are there accepted terms for the concepts, of relativistic length - as opposed to proper length, and of relativistic time - as opposed to proper time? HOTmag (talk) 10:12, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- A term that will be understood in the context of relativistic length contraction is relative length – that is, length relative to an observer. --Lambiam 10:55, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- Thank you. The middle source uses the term "comparative length", rather than "relative length". I couldn't open the third source. HOTmag (talk) 08:04, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- The text under the graph labelled Comparative length on page 20 of the middle source reads:
- Graph of the relative length of a stationary rod on earth, as observed from the reference frame of a traveling rod of 100cm proper length.
- A similar use of "relative length" can be seen on the preceding page. --Lambiam 10:23, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- The text under the graph labelled Comparative length on page 20 of the middle source reads:
- Thank you. The middle source uses the term "comparative length", rather than "relative length". I couldn't open the third source. HOTmag (talk) 08:04, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- A term that will be understood in the context of relativistic length contraction is relative length – that is, length relative to an observer. --Lambiam 10:55, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- When I wrote:
What did Juan Maldacena say after "Geometry of" in this video?
I was watching this video Brian Greene and Juan Maldacena as they explore a wealth of developments connecting black holes, string theory etc, Juan Maldacena said something right after "Geometry of" Here is the spot: https://www.youtube.com/live/yNNXia9IrZs?si=G7S90UT4C8Bb-OnG&t=4484 What is that? HarryOrange (talk) 20:46, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- Schwarzschild solution. --Wrongfilter (talk) 21:05, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
- Thank you, its the Juan Maldacena's accent which made me post here. HarryOrange (talk) 21:18, 30 December 2024 (UTC)
December 31
Brightest spot of a discharge tube

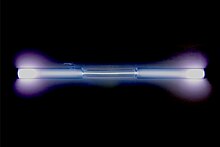
What causes the discharge tubes to have their brightest spots at different positions? Nucleus hydro elemon (talk) 13:12, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
- See also the pictures at Gas-filled tube #Gases in use. --CiaPan (talk) 13:26, 31 December 2024 (UTC)
January 1
Two unit questions
- Is there any metric unit whose ratio is not power of 10, and is divisible by 3? Is there any common use for things like "2⁄3 km", "5⁄12 kg", "3+1⁄6 m"?
- Is a one-tenth of nautical mile (185.2 m) used in English-speaking countries? Is there a name for it?
--40bus (talk) 10:41, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- 1 not that I know of (engineer who has worked with SI for 50 years)
- 2 not that I know of (yacht's navigator for many years on and off)
- Greglocock (talk) 11:35, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- In Finland, kaapelinmitta is 185.2 m. Is there an English equivalent? --40bus (talk) 18:11, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- Good article. I was wrong Greglocock (talk) 22:26, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- The answer can be found by looking up kaapelinmitta on Wiktionary. --Lambiam 00:14, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
What is more physiological (for a right-hander) left-hand drive or right-hand drive?
Has anyone determined whether it is better for a right-hander to have the left hand on the steering wheel and the right hand on the gear shift stick, or the other way round? Are there other tests of whether left-hand drive or right-hand drive is physiologically better (for a right-hander at least)? 178.51.7.23 (talk) 12:03, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- Supplementary question: I've only driven right-hand-drive vehicles (being in the UK) where the light stalk is on the left of the steering column and the wiper & washer controls are (usually) on the right. On a l-h-drive vehicle, is this usually the same, or reversed? {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} 94.6.84.253 (talk) 12:12, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- Modern cars are designed for mass production in RH- and LH-drive versions with a minimum difference of parts. Steering columns with attached controls are therefore unchanged between versions. Philvoids (talk) 12:29, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- In the UK nowadays, are cars still mostly manual transmission, or has automatic become the norm? ←Baseball Bugs carrots→ 12:38, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- In the UK, sales of new automatics have just recently overtaken manuals - so probably still more manuals than automatics on the road. catslash (talk) 14:37, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- This may be tied to the rise of EVs, since they have automatic transmissions by default. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} 94.6.84.253 (talk) 05:29, 3 January 2025 (UTC)
- In the UK, sales of new automatics have just recently overtaken manuals - so probably still more manuals than automatics on the road. catslash (talk) 14:37, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- In Australia, we drive on the left, and the indicator and wiper stalks are the opposite way to the UK. Having moved back from the UK after 30 years, it took me a while to stop indicating with wipers. TrogWoolley (talk) 05:08, 3 January 2025 (UTC)
- In the UK nowadays, are cars still mostly manual transmission, or has automatic become the norm? ←Baseball Bugs carrots→ 12:38, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- I've driven different (automatic) left-hand-drive vehicles with the light stalk on each side, but left side has been more common. Perhaps because the right hand is more likely to be busy with the gear shift? (Even in the US, where automatic has been heavily dominant since before I learned to drive.) -- Avocado (talk) 17:32, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- Modern cars are designed for mass production in RH- and LH-drive versions with a minimum difference of parts. Steering columns with attached controls are therefore unchanged between versions. Philvoids (talk) 12:29, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- It's better for a right-hander to have both hands on the steering wheel regardless of where the gear lever is. See Rule 160. I suspect the same goes for a left-hander. Bazza 7 (talk) 14:39, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- I suppose that the question is whether right-handers have an easier time operating the gear stick when changing gears in manual-transmission cars designed for left-hand traffic, with the steering wheel on the right (like in the UK) or right-hand traffic, with the steering wheel on the left (like in most of continental Europe). Obviously, drivers will use their hand at the side where the gear stick is, so if it is in the middle and the driver, behind the wheel, sits in the right front seat, they'll use their left hand, regardless of their handedness. But this may be more awkward for a rightie. Or not.
- --Lambiam 16:30, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- In my personal experience (more than 10 years driving on each side of the road, in all four combinations of car handedness and road handedness) the question which hand to use for shifting gears is fairly insignificant. Switching from one type of car to the other is a bit awkward though. —Kusma (talk) 18:33, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
- My first car, a Hillman Minx, had the gearstick on the left and the handbreak on the right, which was a bit of a juggle in traffic. Alansplodge (talk) 19:13, 3 January 2025 (UTC)
- In my personal experience (more than 10 years driving on each side of the road, in all four combinations of car handedness and road handedness) the question which hand to use for shifting gears is fairly insignificant. Switching from one type of car to the other is a bit awkward though. —Kusma (talk) 18:33, 2 January 2025 (UTC)
Distinguishing a picture of a sunset from the picture of a sunrise?
Is there a way (if you don't know which way is west and which way is east in a particular location) to distinguish a picture of a sunset from the picture of a sunrise? 178.51.7.23 (talk) 12:08, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- Generally, no, but there are a few tricks that sometimes work. In dry sunny weather, there's more dust in the air at sunset (due to thermals) than at sunrise, making the sky around the sun redder at sunset. But in moist weather, mist has the same effect at sunrise. If the picture is good enough to see sunspots, comparing the distribution of sunspots to the known distribution of that day (this is routinely monitored) tells you where the North Pole of the sun is. At sunset, the North Pole points somewhat to the right; at sunrise, to the left. If you see any cumulus or cumulonimbus clouds in the picture, it was a sunset, as such clouds form during the day and disappear around sunset, but absence of such clouds doesn't mean the picture was taken at sunrise. A very large cumulonimbus may survive the night. Cirrus aviaticus clouds are often very large, expanding into cirrostratus, in the evening, but are much smaller at dawn as there's more air traffic during the day than at night, making the upper troposphere more moist towards the end of the day. Cirrostratus also contributes to red sunsets and (to lesser extend, as there's only natural cirrostratus) red sunrises. Dew, rime, flowers and flocks of birds may also give an indication. And of course human activity: the beach is busier at sunset than at sunrise. PiusImpavidus (talk) 13:41, 1 January 2025 (UTC)
- Supposing the photograph has high enough resolution to show Sunspots it can be helpful to know that the pattern of spots at sunrise is reversed left-right at sunset. Philvoids (talk) 13:21, 3 January 2025 (UTC)
- At the equinox, the disk of the Sun with its pattern of sunspots appears to rotate clockwise from sunrise to sunset by 180 degrees minus twice your latitude (taking north positive). At my place, that's 75 degrees. Other times of the year it's less; at the start and end of polar day and polar night, there's no rotation. Sunset and sunrise merge then.
- And I forgot to mention: cirrostratus clouds will turn red just after sunset or just before sunrise. At the exact moment of sunrise or sunset, they appear pretty white. PiusImpavidus (talk) 17:06, 3 January 2025 (UTC)
- I differ: the same rotation is involved everywhere on Earth. If you stand on tiptoe at a N. or S. pole to take a picture of the Sun it is you who must pirouette 15 degrees per hour to keep facing the Sun. The Earth rotates you at this rate at all non-polar locations. If you stand within the arctic or antarctic circles, for parts of the year the 24-hour night or 24-hour daylight seem to prevent photographs of sunrise or sunset. However the terms "sunrise" and "sunset" can then be interpreted as times that are related to particular timezones which are generally assigned by longitude. In photographing the 24-hour Sun the equatorial rise and set times for your own longitude are significant elevation maxima worth mentioning even though the minimum elevation remains above the horizon. I maintain that the sunspot pattern observed from any location on Earth rotates 360 degrees per 24 hours and that "night", the darkness from sunset to sunrise, is when the Earth's bulk interrupts one's view of the rotation but not the rotation itself which is continuous.
- The questioner asks for interpretation of a single picture. It is beside the point that more would be revealed by a picture sequence such as of changing cloud colours. Philvoids (talk) 12:41, 4 January 2025 (UTC)
- In my experience (Southern England) they tend to be pinker at dawn and oranger(!) at dusk. {The poster formerly known as 87.81.230.195} 94.6.84.253 (talk) 03:23, 4 January 2025 (UTC)
- Supposing the photograph has high enough resolution to show Sunspots it can be helpful to know that the pattern of spots at sunrise is reversed left-right at sunset. Philvoids (talk) 13:21, 3 January 2025 (UTC)
 uses invariant mass m0 which is constant if E and p are constant. The traveling neutrino has a varying mass mixture of different flavors with different masses. If a mixture of different masses changes, you would expect the resulting mass to change with it. But somehow this does not happen as the neutrino mass mixture changes. These mixture changes cannot be any changes. The changes must be such that the resulting mass of the traveling neutrino remains constant. My question is whether this is described somewhere.
uses invariant mass m0 which is constant if E and p are constant. The traveling neutrino has a varying mass mixture of different flavors with different masses. If a mixture of different masses changes, you would expect the resulting mass to change with it. But somehow this does not happen as the neutrino mass mixture changes. These mixture changes cannot be any changes. The changes must be such that the resulting mass of the traveling neutrino remains constant. My question is whether this is described somewhere.  , because we can't "see" the individual mass eigenstates, only some
, because we can't "see" the individual mass eigenstates, only some  would be constant.
would be constant.