| Revision as of 12:39, 28 June 2007 editAdavidb (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers121,630 edits Undid revision 141157596 by 24.250.238.237 (talk) sarcastic chapter references; take any edit debate to talk page← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 21:49, 25 December 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,407,495 edits Added date. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Dominic3203 | #UCB_webform 36/3850 | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Autonomous Christian congregations}} | |||
| {{redirect|Church of Christ}} | |||
| {{about|a specific fellowship of Christian congregations|Churches of Christ that do not agree with congregational support of church or ]s|Churches of Christ (non-institutional)|groups of autonomous congregations in Europe using the name "church of Christ" that have unclear association with the Restoration Movement|Churches of Christ in Europe|other uses|Church of Christ}} | |||
| :''The Churches of Christ discussed in this article are not part of the ]; the ]; the ]; the ] (Christian Science); the ] or any other ] within the ]; the ]; the ] in the United Kingdom; the ]; or the ]-based ].'' | |||
| {{Infobox Christian denomination | |||
| {{christianity}} | |||
| | name = Churches of Christ | |||
| The '''Churches of Christ''' are ], ] ] ]. These churches comprise about 2,000,000 members in over 40,000 individual congregations worldwide. <ref>"". This is a live country-by-country tabulation, and is known to under-represent certain developing countries. </ref> | |||
| | image = Old Bethany Church of Christ, Bethany, West Virginia.jpg | |||
| |imagewidth = 300px | |||
| |alt = Old Bethany Church of Christ Building, Bethany, West Virginia | |||
| | caption = ], Bethany, West Virginia | |||
| |main_classification=] ]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Churches of Christ (1906 - Present) - Religious Group |url=https://www.thearda.com/us-religion/group-profiles/groups?D=226 |access-date=2023-05-16 |website=www.thearda.com}}</ref><ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Protestant Reformation">"Though some in the Movement have been reluctant to label themselves Protestants, the Stone-Campbell Movement is in the direct lineage of the Protestant Reformation. Especially shaped by Reformed theology through its Presbyterian roots, the Movement also shares historical and theological traits with Anglican and Anabaptist forebears." Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, "Protestant Reformation", in ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}.</ref> | |||
| | orientation = ] | |||
| | polity = ] | |||
| | separations = {{plainlist| | |||
| *] (1906) | |||
| *] (1960s) | |||
| *] (1993) | |||
| }} | |||
| | fellowships = | |||
| | associations = | |||
| | area = | |||
| |founded_date=| congregations = 41,498 (worldwide)<br />11,790 (U.S.)<ref name="who">{{cite web | |||
| |url = http://churchzip.com/statisticalsummary.htm | |||
| |title = Church numbers listed by country | |||
| |access-date = 2014-12-05 | |||
| |publisher = ChurchZip | |||
| |archive-date = August 13, 2011 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110813145619/http://churchzip.com/statisticalsummary.htm | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| }} This is a country-by-country tabulation, based on the enumeration of specific individual church locations and leaders. While it is known to under-represent certain developing countries, it is the largest such enumeration, and improves significantly on earlier broad-based estimates having no supporting detail.</ref> | |||
| | members = 2,000,000 (approx.) worldwide;<ref>{{cite web |url=https://church-of-christ.org/how-many-churches-of-christ-are-there.html |title=How Many churches of Christ Are There? |website=The churches of Christ |access-date=March 20, 2020 }}</ref> 1,113,362 in the United States (2020)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.21stcc.com/pdfs/ccusa_stats_sheet.pdf |title=Churches of Christ in the United States |website=21st Century Christian |date=June 2020 |first=Carl H. |last=Royster |access-date=August 26, 2020 |archive-date=July 29, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200729184935/https://www.21stcc.com/pdfs/ccusa_stats_sheet.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| | footnotes = | |||
| |publications={{ubl | |||
| |''Christian Courier''<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.christiancourier.com/faqs |title=Frequently Asked Questions |website=Christian Courier |access-date=March 20, 2020 |archive-date=May 6, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200506060742/https://www.christiancourier.com/faqs |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| |WVBS (videos, educ. material)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://video.wvbs.org/about |title=About World Video Bible School |website=WBVS |access-date=March 20, 2020 }}</ref> | |||
| |''The Christian Chronicle'' (news)<ref>{{cite web |url=https://christianchronicle.org/about/ |title=About The Christian Chronicle |website=The Christian Chronicle |access-date=March 31, 2021 }}</ref> | |||
| |''The Christian Worker'' (]) | |||
| |Apologetics Press<ref>{{cite web |url=https://apologeticspress.org/AboutAP.aspx |title=What We Believe |website=Apologetics Press |access-date=March 20, 2020 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://apologeticspress.org/apcontent.aspx?category=11&article=1191 |title=Who Are These People |website=Apologetics Press |first=Dave |last=Miller |date=31 December 2002 |access-date=March 23, 2020 }}</ref> | |||
| |House to House Heart to Heart<ref>{{cite web |url=https://my.housetohouse.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/RTL-2019-July-Edition.pdf#page=2 |title=Reaching the Lost |website=House to House |publisher=Jacksonville church of Christ |date=July 2019 |page=2 |access-date=March 20, 2020 |quote=under the oversight of the elders }}</ref>}} | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''Churches of Christ''', also commonly known as the '''Church of Christ''', is a loose association of autonomous ] congregations located around the world. Typically, their distinguishing beliefs are that of the necessity of baptism for salvation and the prohibition of musical instruments in worship. Many such congregations identify themselves as being ].<ref name="Hughes2001">{{cite book |last1=Hughes |first1=Richard Thomas |title=The Churches of Christ |date=2001 |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-275-97074-1 |page=5 |language=English}}</ref> The Churches of Christ arose in the United States from the ] of 19th-century Christians who declared independence from denominations and traditional ]. They sought "the unification of all Christians in a single body patterned after the original church described in the ]."<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian">], ''I Just Want to Be a Christian'', 20th Century Christian, Nashville, Tennessee 1984, {{ISBN|0-89098-021-7}}.</ref>{{rp|54}} | |||
| ==Overview== | |||
| Churches of Christ generally emphasize their intent simply to be part of the church established by Jesus Christ in his death, burial, and resurrection, which became evident on the Day of Pentecost as described in the New Testament in Acts 2. Churches of Christ emphasize the use of the New Testament only to find doctrine, ecclesiastical structure, and moral beliefs, while maintaining that the Old Testament is also the inspired Word of God, is historically accurate, and that its principles remain true and beneficial (although its laws are not binding under the new covenant in Christ unless otherwise taught in the New Testament). | |||
| Modern Churches of Christ have their historical roots in the ], which was a convergence of Christians across ] lines in search of a return to an original "pre-denominational" form of Christianity.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988">C. Leonard Allen and Richard T. Hughes, "Discovering Our Roots: The Ancestry of the Churches of Christ," Abilene Christian University Press, 1988, {{ISBN|0-89112-006-8}}.</ref>{{rp|108}} Participants in this movement sought to base their doctrine and practice on the ] alone, rather than recognizing the traditional ] and denominational hierarchies that had come to define ] since the first century A.D.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|82,104,105}} Members of the Churches of Christ believe that ] founded only one church, that the current divisions among Christians do not express God's will, and that the only basis for restoring Christian unity is the Bible.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/> They simply identify themselves as "Christians", without using any other forms of religious or denominational identification.<ref>{{cite book |title=What Is the Church of Christ? |first=V. E. |last=Howard |author-link=V. E. Howard |year=1971 |edition=4th (revised) |page=29 |publisher=Central Printers & Publishers |asin=B001EM1NHM |quote= The church of Jesus Christ is non-denominational. It is neither Catholic, Jewish nor Protestant. It was not founded in 'protest' of any institution, and it is not the product of the 'Restoration' or 'Reformation.' It is the product of the seed of the kingdom (Luke 8:11ff) grown in the hearts of men.}}</ref><ref name="Neither Catholic, Protestant nor Jew">Batsell Barrett Baxter and Carroll Ellis, ''Neither Catholic, Protestant nor Jew'', Church of Christ (1960) ASIN: B00073CQPM. According to Richard Thomas Hughes in ''Reviving the Ancient Faith: The Story of Churches of Christ in America'', ], 1996, {{ISBN|0-8028-4086-8}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-4086-8}}, this is "arguably the most widely distributed tract ever published by the churches of Christ or anyone associated with that tradition."</ref><ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South">Samuel S. Hill, Charles H. Lippy, Charles Reagan Wilson, ''Encyclopedia of Religion in the South'', Mercer University Press, 2005, {{ISBN|0-86554-758-0}}, {{ISBN|978-0-86554-758-2}}.</ref>{{rp|213}} They aspire to be the New Testament church as established by Christ.<ref>"On the cornerstone of the Southside Church of Christ in ], is this inscription: 'Church of Christ, Founded in Jerusalem, A.D. 33. This building erected in 1953.' This is not an unusual claim; for similar wording can be found on buildings of churches of Christ in many parts of the United States. The Christians who use such cornerstones reason that the church of Jesus Christ began on Pentecost, A.D. 33. Therefore, to be true to the New Testament, the twentieth-century church must trace its origins to the first century." Robert W. Hooper, ''A Distinct People: A History of the Churches of Christ in the 20th Century'', p. 1, Simon and Schuster, 1993, {{ISBN|1-878990-26-8}}, {{ISBN|978-1-878990-26-6}}.</ref><ref>"Traditional Churches of Christ have pursued the restorationist vision with extraordinary zeal. Indeed, the cornerstones of many Church of Christ buildings read 'Founded, A.D. 33.' " Jill, et al. (2005), "Encyclopedia of Religion", p. 212.</ref><ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|106}} | |||
| {{blockquote|Members of the church of Christ do not conceive of themselves as a new church started near the beginning of the 19th century. Rather, the whole movement is designed to reproduce in contemporary times the church originally established on ], A.D. 33. The strength of the appeal lies in the restoration of Christ's original church.|]<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/>}} | |||
| Churches of Christ in the United States are historically linked to the ] championed by ] preachers/theologians of the late ] and early ], most notably ] and his son ], Walter Scott, and ]. These and other leaders from various denominations were seeking original Christianity as they were independently finding several beliefs, practices, and restrictive dogmas in their respective church traditions to have no biblical basis. | |||
| Churches of Christ generally share the following theological beliefs and practices:<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ">{{cite web |author-link=Batsell Barrett Baxter |last=Baxter |first=Batsell Barrett |title=Who are the churches of Christ and what do they believe in? |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060616071601/http://woodsonchapel.com/coc.cfm |url=http://woodsonchapel.com/coc.cfm |archive-date=June 16, 2006 }} Also available via these links to {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140209022100/http://church-of-christ.org/who.html |date=2014-02-09 }}, (archived June 22, 2006) and (archived July 13, 2006).</ref> | |||
| Members of the Church of Christ point out that throughout church history many have sought a return to the simple, original Christianity that is "pre-denominational" and unbound by the decisions of councils or denominational hierarchies.{{Fact|date=May 2007}} Rather than basing doctrine on the interpretations of post-first century church fathers, ecclesiastical councils, or more modern denominational synods or conventions, they use only the Bible as their official source of doctrine.<ref>Lemmons, Reuel. "". BELIEVE Religious Information Service. Retrieved on ] ].</ref> This also allows for the Bible to be open for continual examination and interpretation from congregation to congregation and from Christian to Christian. | |||
| * ], ] church organization without denominational oversight;<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|238}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} | |||
| These views are based on the conviction that the church is a spiritual body, rather than a secular or political one. Furthermore, that God demonstrates in the New Testament how a person may become a Christian, thus a part of the church, and how Christians may collectively organize and carry out the purposes of the church which Christ established. Also realized is that Christians can do this without any prior knowledge of other Churches of Christ as different groups practicing this form of Christianity have discovered one another without any prior connection (e.g., different segments of what became known as the Restoration Movement; early, ante-Nicene churches). | |||
| * Refusal to hold to any formal ]s or informal "doctrinal statements" or "statements of faith", stating instead a reliance on the Bible alone for doctrine and practice;<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|103}}<ref name="Unauthorized Guide">Carmen Renee Berry, ''The Unauthorized Guide to Choosing a Church'', Brazos Press, 2003, {{ISBN|1-58743-036-3}}.</ref>{{rp|238,240}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|123}} | |||
| * Local governance<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|238}} by a ] of male ];<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}}<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|47–54}} | |||
| * ] by ] of ]<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|238}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} in the Name of the Father, Son, and ] for the forgiveness of sins;<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|103}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} | |||
| * Weekly observance of the ]<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} on Sunday<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|107}}<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|238}} | |||
| **In British congregations, the term "breaking of bread" is commonly used. | |||
| **In American congregations, the terms "Communion" or "body and blood" are used. | |||
| **Churches of Christ typically offer ] on the first day of each week, offering the bread and fruit of the vine to all present at each person's self-examination. | |||
| * Practice of ''a cappella'' singing is the norm in worship,<ref>{{cite AV media |url=https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/eschatological-weeds/id1291144720?i=1000475406662 |title= Eschatological Weeds |website=The Remnant |via=Apple Podcasts |access-date=June 6, 2020 |first=Jonah |last=Goldberg }}</ref> based on New Testament passages teaching to sing for worship, with no mention of instrumental music (and also that worship in church assemblies for centuries in the early Church practiced a cappella singing).<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|240}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|125}} | |||
| In keeping with their history, the Churches of Christ claim the ] as their sole rule of faith and practice in deciding matters of doctrine and ecclesiastical structure.<ref>{{bibleverse|Col.|2:14}}.</ref> They view the ] as divinely ]<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|103}} and historically accurate, but they do not consider its laws to be binding under the ] in ] (unless they are repeated in the New Testament) (Hebrews 8: 7–13).<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Hermeneutics"/>{{rp|388}}<ref name="Wharton 1997"/>{{rp|23–37}}<ref name="Pharr 2000">David Pharr, ''The Beginning of Our Confidence: Seven Weeks of Daily Lessons for New Christians'', 21st Century Christian, 2000, {{ISBN|0-89098-374-7}}.</ref>{{rp|65–67}} They believe that the New Testament demonstrates how a person may become a Christian (and thus a part of the universal Church of Christ) and how a church should be collectively organized and carry out its scriptural purposes.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/> | |||
| Today, Churches of Christ usually have these distinctive traits: the refusal to hold to any ]s other than the ] itself (i.e., 2 Tim 3:16-17, '']''); the practice of repentance and water baptism by ] in Christ's name as the response to receive forgiveness of sins and the Holy Spirit (e.g., Mark 16:16; Acts 2:38; Acts 22:16); autonomous, ] congregational church organization, congregational oversight by a ] (Titus 1:5) of male ] (Titus 1:6); the weekly observance (Acts 20:7) of communion/eucharist (i.e., ]); and the practice by most congregations of ''a cappella'' worship singing (although several related congregations use instruments while keeping these other practices - also known as Christian Churches). | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=July 2022}} | |||
| ==Church Population in the U.S.== | |||
| There are approximately 13,000 congregations in the United States with about 1.3 million members (''Churches of Christ in the United States'', ).] | |||
| ===Demographics=== | |||
| ==Self-identification== | |||
| In 2022, the total membership of Churches of Christ is estimated to be between 1,700,000 and 2,000,000,<ref>{{cite web | |||
| Members do not consider themselves either Catholic, Orthodox, or Protestant. They hold to the biblical and historical reality that the church was founded by Jesus Christ, and that its doctrines and practices were established long before these other traditions, movements, structures, councils, etc. The church therefore biblically, historically and spiritually transcends these other entities that developed later within Christendom. Members also do not typically consider themselves to be members of a ], but prefer to simply be known as "Christians" (in contrast to, for example, a Catholic Christian, a Presbyterian Christian, a Baptist Christian, etc.), with no other religious title needed or preferred. Thus, a collective group of Christians is a church of Christ (e.g., Romans 16:16). | |||
| |url=https://www.christianity.com/church/denominations/churches-of-christ-10-things-to-know-about-their-history-and-beliefs.html | |||
| |title=Churches of Christ - 10 Things to Know about their History and Beliefs | |||
| |date=November 1, 2018 | |||
| |publisher= | |||
| |access-date=July 27, 2022 | |||
| |quote=}}</ref><ref name="churchzip"/> with over 40,000 individual congregations worldwide.<ref name="churchzip">{{cite web | |||
| |url = http://churchzip.com/statisticalsummary.htm | |||
| |title = Church numbers listed by country | |||
| |access-date = July 27, 2022 | |||
| |publisher = ChurchZip | |||
| |archive-date = August 13, 2011 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110813145619/http://churchzip.com/statisticalsummary.htm | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| }} This is a country-by-country tabulation, based on the enumeration of specific individual church locations and leaders. While it is known to under-represent certain developing countries, it is the largest such enumeration, and improves significantly on earlier broad-based estimates having no supporting detail.</ref> In the United States, there are approximately 1,087,559 members and 11,776 congregations.<ref name="churchzip"/> Overall U.S. membership was approximately 1.3 million in 1990 and 1.3 million in 2008.<ref name="ARIS 2008">Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar, {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090407053149/http://b27.cc.trincoll.edu/weblogs/AmericanReligionSurvey-ARIS/reports/ARIS_Report_2008.pdf|date=April 7, 2009}}, ], March 2009.</ref>{{rp|5}} Estimates of the proportion of the US adult population associated with the Churches of Christ vary from 0.8% to 1.5%.<ref name="ARIS 2008"/>{{rp|5}}<ref> ''U.S. Religious Landscape Survey: Chapter 1'', Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life, ], February 2008.</ref>{{rp|12,16}} Approximately 1,240 congregations, with 172,000 members, are predominantly ]; 240 congregations with 10,000 members are ]-speaking.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, "Churches of Christ", in ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}.</ref>{{rp|213}} The average congregation size is approximately 100 members, with larger congregations reporting over 1,000 members.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|213}} In 2000, the Churches of Christ were the 12th largest religious group in the U.S. based on the number of members, but the 4th largest in number of congregations.<ref name="Yeakley PPT 2008"/> | |||
| Within the U.S., membership in the Churches of Christ has declined by approximately 12% over the period from 1980 through 2007. The current retention rate of young adults graduating from high school appears to be approximately 60%. Membership is concentrated, with 70% of the U.S. membership, in thirteen states. Churches of Christ had a presence in 2,429 counties, placing them fifth behind the ], ], ] and ] – but the average number of adherents per county was approximately 677. The divorce rate was 6.9%, much lower than national averages.<ref name="Yeakley PPT 2008">Flavil Yeakley, ''Good News and Bad News: A Realistic Assessment of Churches of Christ in the United States: 2008''; an mp3 of the author presenting some of the results at the 2009 East Tennessee School of Preaching and Ministry lectureship on March 4, 2009, is available {{Dead link|date=July 2019 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} and a PowerPoint presentation from the 2008 CMU conference using some of the survey results posted on the Campus Ministry United website is available .</ref> | |||
| ==History in America== | |||
| ===Restoration Movement=== | |||
| The American ] of the 18th and 19th centuries was an emergence of seekers who perpetuated ideals that have existed throughout church history regarding inspired truth over ecclesiastic tradition or dogma. This movement was in some ways similar to the Reformation and was sometimes referred to as "the new Reformation." The Restoration Movement promoted a return to the purposes of the first century churches as described in the ] and is considered by some historians to be part of the ]. One major impetus of the movement was the Kentucky Cane Ridge Revival in 1801, which resulted in many from various traditions no longer holding to their denominational ties and referring to themselves simply as "Christians" or "Disciples." Several Churches of Christ were established as a result of this revival, with some denominational congregations even dropping their traditional titles in favor of "Church of Christ," "Disciples of Christ," or "Christian Church." While ever emphasizing that the Bible is the only source to seek doctrine, an acceptance of diverse opinions was the norm in the quest for truth. "]" was an oft-quoted slogan of the period.<ref>{{cite news|publisher=Restoration Movement Quarterly, '''39''':3. Abilene, Texas: ]|title=In Essentials Unity: The Pre-history of a Restoration Movement Slogan|author=Rollmann, Hans|url=http://www.acu.edu/sponsored/restoration_quarterly/archives/1990s/vol_39_no_3_contents/rollmann.html}}</ref> | |||
| ==Name== | |||
| The movement was actually the result of several smaller groups converging because of the same truths and ideals each were independently seeking. It solidified as a historical phenomenon in ] when ] from two major movements championed by ] and Alexander Campbell merged (historians thus often refer to it as the "Stone-Campbell Movement"). Following Stone's death in ], Alexander Campbell served as the most influential surviving voice. | |||
| ]]]"Church of Christ" is the most common name used by this group. In keeping with their focus of not being a denomination, using Ephesians 1:22–23 as reference to the church being the body of Christ and a body cannot be divided, congregations have identified themselves primarily as community churches and secondarily as Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|219–220}} A much earlier tradition is to identify a congregation as "the church" at a particular location, with no other description or qualifiers.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|220}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells">Monroe E. Hawley, ''Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity'', Quality Publications, Abilene, Texas, 1976, {{ISBN|0-89137-512-0}} (paper), {{ISBN|0-89137-513-9}} (cloth)</ref>{{rp|136–137}} A primary motivation behind the name is the desire to use a scriptural or Biblical name – to identify the church using a name that is found in the New Testament.<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian"/><ref name="Howard 1971">V. E. Howard, ''What Is the Church of Christ?'' 4th Edition (Revised) Central Printers & Publishers, West Monroe, Louisiana, 1971.</ref>{{rp|163,164}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/><ref name="Shepherd 1929">J. W. Shepherd, ''The Church, the Falling Away, and the Restoration'', Gospel Advocate Company, Nashville, Tennessee, 1929 (reprinted in 1973)</ref>{{rp|7–8}} Adherents are also referred to as ] by academics<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/> and other denominations<ref name="Faith Defenders"> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150109233529/http://www.faithdefenders.com/articles/cults/campbellism.html |date=2015-01-09 }} Morey 2014.</ref> because it is assumed that they are followers of the teachings of Alexander Campbell, similar to ] or ]. Campbell himself refuted the idea that a denomination was started by him or that he was the head of one in ''The Christian Baptist'' publication in 1826 and 1828, stating: "Some religious editors in Kentucky call those who are desirous of seeing the ancient order of things restored, 'the Restorationers', 'the Campbellites'... This may go well with some; but all who fear God and keep his commands will pity and deplore the weakness and folly of those who either think to convince or to persuade by such means" (''The Christian Baptist'', Vol. IV, 88–89) and: "It is a nickname of reproach invented and adopted by those whose views, feelings and desires are all sectarian – who cannot conceive of Christianity in any other light than an ISM" (''The Christian Baptist'', Vol. V, 270). He was also associated with the Baptist denomination until 1820. The term "''Campbellite''" is usually offensive to members of the churches of Christ because members claim no allegiance to anyone except Jesus Christ and teach only what is presented in biblical texts.<ref name="Merriam-Webster">The Merriam-Webster Collegiate Dictionary describes the term as "sometimes offensive." Merriam-Webster, I. (2003). Merriam-Webster's collegiate dictionary. (Eleventh ed.). Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster, Inc. Entry on "Campbellite."</ref> | |||
| ] said the "calling of Bible things by Bible names" was important in the reformation.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.scrollpublishing.com/store/Alexander-Campbell-Communion.html |title=On the Breaking of Bread |first=Alexander |last=Campbell |editor-first=Joseph A. |editor-last=Walters |publisher=Scroll Publishing |access-date=November 21, 2024}}</ref> This became an early slogan of the Restorationist Movement.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Slogans"/>{{rp|688}} These congregations generally avoid names that associate the church with a particular man (other than Christ) or a particular doctrine or theological point of view (e.g., ], ], ]).<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian"/><ref name="Neither Catholic, Protestant nor Jew"/> They believe that Christ established only one church, and that the use of denominational names serves to foster division among Christians.<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|23,24}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/><ref name="Declaration and Address">], ], 1809, available on-line </ref><ref name="Shields 1945">O. E. Shields, ''The ]'', VOL. XXXIX, No. 9, September 1945.</ref><ref name="Kurfees October 14, 1920">M. C. Kurfees, "Bible Things by Bible Names – The General and Local Senses of the Term 'Church'", '']'' (October 14, 1920):1104–1105, as reprinted in ''Appendix II: Restoration Documents'' of ''I Just Want to Be a Christian'', ] (1984)</ref><ref name="McQuiddy November 11, 1920">J. C. McQuiddy, "The New Testament Church", '']'' (November 11, 1920):1097–1098, as reprinted in ''Appendix II: Restoration Documents'' of ''I Just Want to Be a Christian'', ] (1984)</ref> ] expressed an ideal of unity in his '']'': "The church of Jesus Christ on earth is essentially, intentionally, and constitutionally one."<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Slogans">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, "Slogans", in ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}},</ref>{{rp|688}} This statement essentially echoes the words of Jesus Christ in John 17:21, 23. | |||
| {{see also|Restoration Movement}} | |||
| Other terms are derived from their use in the New Testament: "church of God", "church of the Lord", "churches of Christ", "church of the first-born", "church of the living God", "the house of God", and "the people of God",<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/><ref name="Kurfees September 30, 1920">M. C. Kurfees, "Bible Things by Bible Names – Different Designations of the Church Further Considered", '']'' (September 30, 1920):958–959, as reprinted in ''Appendix II: Restoration Documents'' of ''I Just Want to Be a Christian'', ] (1984)</ref> while terms recognized as scriptural, such as ], are avoided to prevent confusion or identification with other groups that use those designations.<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian"/><ref name="Redigging the Wells"/><ref>Within the Restoration Movement, congregations that do not use musical instruments in worship use the name "Church of Christ" almost exclusively; congregations that do use musical instruments most often use the term "Christian Church." Monroe E. Hawley, ''Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity'', 1976, page 89.</ref> As a practical matter, use of a common term is seen as a way to help individual Christians find congregations with a similar approach to the scriptures.<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/><ref>As, ''e.g.'', for listings in the ].</ref> Members understand that a scriptural name can be used in a "denominational" or "sectarian" way.<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian"/>{{rp|31}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|83–94,134–136}}<ref name="Kurfees September 30, 1920"/> Using the term "Church of Christ" exclusively has been criticized as identifying a denomination.<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian"/>{{rp|31}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|83–94,134–136}}<ref name="Kurfees September 30, 1920"/> Many congregations and individuals do not capitalize the word "church" in the phrases "church of Christ" and "churches of Christ".<ref name="Garrett 2002">Leroy Garrett, ''The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement'', College Press, 2002, {{ISBN|0-89900-909-3}}, {{ISBN|978-0-89900-909-4}}, 573 pages</ref>{{rp|382}}<ref>Examples of this usage include the ] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090208030801/http://stores.homestead.com/GospelAdvocateCompany/StoreFront.bok |date=February 8, 2009 }} ("Serving the church of Christ since 1855" – accessed October 26, 2008); the ] ("Classes in every area are taught in a faith-informed approach by highly qualified faculty who represent the range of perspectives that exist among churches of Christ." – accessed October 26, 2008); the ] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081009223324/http://web.fhu.edu/NR/exeres/D115CB7C-F50A-482C-84B3-DAEA305A7854,frameless.htm |date=2008-10-09 }} ("Freed-Hardeman University is a private institution, associated with churches of Christ, dedicated to moral and spiritual values, academic excellence, and service in a friendly, supportive environment... The university is governed by a self-perpetuating board of trustees who are members of churches of Christ and who hold the institution in trust for its founders, alumni, and supporters." – accessed October 26, 2008); ], ''Who are the churches of Christ and what do they believe in?'' (Available on-line {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080619130916/http://www.woodsonchapel.com/coc.php |date=2008-06-19 }}, , {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140209022100/http://church-of-christ.org/who.html |date=2014-02-09 }}, {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080509163609/http://www.cris.com/~mmcoc/coc.html |date=2008-05-09 }} and {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101130131444/http://scripturessay.com/article.php?cat=&id=6 |date=2010-11-30 }}); Batsell Barrett Baxter and Carroll Ellis, ''Neither Catholic, Protestant nor Jew'', tract, Church of Christ (1960); Monroe E. Hawley, ''Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity'', Quality Publications, Abilene, Texas, 1976; ], ''I Just Want to Be a Christian'', 20th Century Christian, Nashville, Tennessee 1984; and V. E. Howard, ''What Is the Church of Christ?'' 4th Edition (Revised), 1971; Website of the ("Welcome to the Home page for the Frisco church of Christ in Frisco, Texas." – accessed October 27, 2008); website of the church of Christ ("The purpose of this Web Site is to unite the churches of Christ in one accord." – accessed October 27, 2008) {{cite web |url=http://www.woodsonchapel.com/coc.php |title=The Church of Christ at Woodson Chapel : Welcome! |access-date=2009-05-21 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080502001629/http://www.woodsonchapel.com/coc.php |archive-date=May 2, 2008 }}</ref> This is based on the understanding that the term "church of Christ" is used in the New Testament as a descriptive phrase, indicating that the church belongs to ], rather than as a proper name.<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|91}} | |||
| ===Historical Connection to Christian Churches and Disciples of Christ=== | |||
| Modern Churches of Christ and Christian Churches are very similar (the primary difference being ''a cappella'' worship in Churches of Christ) and, depending on the tenor of each local congregation, maintain communication and fellowship. | |||
| ==Church organization== | |||
| In contrast, what is today known as ] is very different, having developed into a denominational entity which no longer embraces Restoration Movement ideology (although its evolution has obvious historical roots in the Restoration Movement). | |||
| ===Congregational autonomy and leadership=== | |||
| During the first century of the Restoration Movement, all three of these titles were commonly used for congregations. As interpretations, convictions, and preferences regarding ''a cappella'' and instrumental music distinguished congregations, the ''a cappella'' churches typically used "Church of Christ" to identify themselves while instrumental churches used "Disciples of Christ" or "Christian Church" as designations. In 1906, the U.S. Census for the first time made a distinction of two groups between the ''a cappella'' and instrumental churches (this was also the result of other issues related to the Civil War). | |||
| Church government is congregational rather than denominational. Churches of Christ purposefully have no central headquarters, councils, or other organizational structure above the local church level.<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|214}}<ref name="Perfect Stranger">Stuart M. Matlins, Arthur J. Magida, J. Magida, ''How to Be a Perfect Stranger: A Guide to Etiquette in Other People's Religious Ceremonies'', Wood Lake Publishing Inc., 1999, {{ISBN|1-896836-28-3}}, {{ISBN|978-1-896836-28-7}}, Chapter 6 – Churches of Christ.</ref>{{rp|103}}<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|238}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005">Ron Rhodes, ''The Complete Guide to Christian Denominations'', Harvest House Publishers, 2005, {{ISBN|0-7369-1289-4}}.</ref>{{rp|124}}<ref>"Churches of Christ from the beginning have maintained no formal organization structures larger than the local congregations and no official journals or vehicles declaring sanctioned positions. Consensus views do, however, often emerge through the influence of opinion leaders who express themselves in journals, at lectureships, or at area preacher meetings and other gatherings" page 213, Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages</ref> Rather, the independent congregations are a network with each congregation participating at its own discretion in various means of service and fellowship with other congregations (see ]).<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}}<ref>"Churches of Christ adhere to a strict congregationalism that cooperates in various projects overseen by one congregation or organized as parachurch enterprises, but many congregations hold themselves apart from such cooperative projects." Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, page 206, entry on ''Church, Doctrine of the''</ref><ref>"It is nothing less than phenomenal that the Churches of Christ get so much done without any centralized planning or structure. Everything is ''ad hoc''. Most programs emerge from the inspiration and commitment of a single congregation or even a single person. Worthwhile projects survive and prosper by the voluntary cooperation of other individuals and congregations." Page 449, Leroy Garrett, ''The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement'', College Press, 2002, {{ISBN|0-89900-909-3}}, {{ISBN|978-0-89900-909-4}}, 573 pages</ref> Churches of Christ are linked by their shared commitment to Biblical restoration principles.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|106}} Congregations which do not participate with other church congregations and which refuse to pool resources in order to support outside causes (such as mission work, orphanages, Bible colleges, etc.) are sometimes called "]." | |||
| Congregations are generally overseen by a plurality of ] who are sometimes assisted in the administration of various works by ]s.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}}<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|47,54–55}} Elders are generally seen as responsible for the spiritual welfare of the congregation, while deacons are seen as responsible for the non-spiritual needs of the church.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Ministry"/>{{rp|531}} Deacons serve under the supervision of the elders, and are often assigned to specific ministries.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Ministry"/>{{rp|531}} Successful service as a deacon is often seen as preparation for the eldership.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Ministry"/>{{rp|531}} Elders and deacons are appointed by the congregation based on the qualifications found in {{Bibleref2|1Timothy|3||1 Timothy 3}} and {{Bibleref2|Titus|1}}, including that the persons must be male (female elders and deaconesses are not recognized, as these are not found in Scripture).<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|53,48–52}}<ref name="Ferguson 1975">], , {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080516205017/http://www.acu.edu/sponsored/restoration_quarterly/archives/1970s/vol_18_no_3_contents/Ferguson.html |date=2008-05-16 }} '']'', Vol. 18 No. 3 (1975): 142–150</ref><ref name="Ferguson 1996">], ''The Church of Christ: A Biblical Ecclesiology for Today'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 1996, {{ISBN|0-8028-4189-9}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-4189-6}}, 443 pages</ref>{{rp|323,335}} Congregations look for elders who have a mature enough understanding of scripture to enable them to supervise the minister and to teach, as well as to perform "governance" functions.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Elders">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Elders, Eldership''</ref>{{rp|298}} In the absence of willing men who meet these qualifications, congregations are sometimes overseen by the congregation's men in general.<ref>"Where elderships do not exist, most congregations function through a 'business meeting' system that may include any member of the congregation or, in other cases, the men of the church." Page 531, Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Ministry''</ref> | |||
| The development of the Disciples of Christ denomination was the later result of some within the instrumental church embracing liberal Protestant ideologies that many others would not accept. Thus, those who refused to accept such separated and typically refer to themselves as Christian Churches, leaving the Disciples of Christ designation to the others who eventually organized into that named denomination which exists today. While "Disciples of Christ" is often used as a designation in history books for all churches within the Restoration Movement of the 19th and early 20th centuries, modern Churches of Christ and Christian Churches more accurately reflect the Restoration Movement ideals of that era. | |||
| While the early Restoration Movement had a tradition of itinerant ]s rather than "located Preachers", during the 20th century a long-term, formally trained congregational ] became the norm among Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Ministry">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Ministry''</ref>{{rp|532}} Ministers are understood to serve under the oversight of the elders<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Elders"/>{{rp|298}} and may or may not also be qualified as an elder. While the presence of a long-term professional minister has sometimes created "significant ''de facto'' ministerial authority" and led to conflict between the minister and the elders, the eldership has remained the "ultimate locus of authority in the congregation".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Ministry"/>{{rp|531}} There is, however, a small segment of Churches of Christ who oppose the "located minister" concept (see below). | |||
| {{see also|Restoration Movement#Churches of Christ/Disciples of Christ split}} | |||
| Churches of Christ hold to the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Roberts |first=Price |title=Studies for New Converts |place=Cincinnati |publisher=The Standard Publishing Company |year=1979 |pages=53–56}}</ref> No special titles are used for preachers or ministers that would identify them as "]".<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|106}}<ref name="Wharton 1997"/>{{rp|112–113}} Many ministers have undergraduate or graduate education in religion, or specific training in preaching through a non-college school of preaching.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|215}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Ministry"/>{{rp|531}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Preaching">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Preaching''</ref>{{rp|607}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Schools of Preaching">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Schools of Preaching''</ref>{{rp|672,673}} Churches of Christ emphasize that there is no distinction between "clergy" and "]" and that every member has a gift and a role to play in accomplishing the work of the church.<ref>R. B. Sweet, ''Now That I'm a Christian'', Sweet Publishing, 1948 (revised 2003), {{ISBN|0-8344-0129-0}}</ref>{{rp|38–40}} | |||
| ====Variations within Churches of Christ==== | |||
| Since Churches of Christ are not denominational and purposefully do not maintain an ecclesiastical hierarchy or doctrinal council (as the Bible alone is held as the only source to find doctrine), it is not unusual to find variations from congregation to congregation. For example, some allow for more open interpretations regarding worship and other church practices, while others hold to more strict interpretations. The level of fellowship and cooperation that will exist between those of varying opinions will depend on each member and local congregation. Congregations and members are free to study the Scriptures and to the best of their abilities determine God's revealed will. Yet, most Churches of Christ have the similarities mentioned in the prior introduction. | |||
| ===Variations within Churches of Christ=== | |||
| Differences between local congregations of churches of Christ include institutionalism<ref>{{cite web | |||
| While there is an identifiable mainstream within the Churches of Christ, there are also significant variations within the fellowship.<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|212}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|213}}<ref name="All People, All Times">Jeffery S. Stevenson, ''All People, All Times Rethinking Biblical Authority in Churches of Christ'', Xulon Press, 2009, {{ISBN|1-60791-539-1}}, {{ISBN|978-1-60791-539-3}}</ref>{{rp|31,32}}<ref name="Hughes and Roberts, 2001"/>{{rp|4}}<ref name="Hawkins 2008">Ralph K. Hawkins, ''A Heritage in Crisis: Where We've Been, Where We Are, and Where We're Going in the Churches of Christ'', University Press of America, 2008, 147 pages, {{ISBN|0-7618-4080-X}}, 9780761840800</ref>{{rp|1,2}} The approach taken to restoring the New Testament church has focused on "methods and procedures" such as church organization, the form of worship, and how the church should function. As a result, most divisions among Churches of Christ have been the result of "methodological" disputes. These are meaningful to members of this movement because of the seriousness with which they take the goal of "restoring the form and structure of the primitive church".<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|212}} | |||
| | last = | |||
| | first = | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = What Is Institutionalism? | |||
| | work = | |||
| | publisher = The Good Fight | |||
| | date = | |||
| | url = http://www.goodfight.com/notes/Institutionalism.html | |||
| | format = | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | accessdate = 2007-06-13 }}</ref> (using organizations outside the local congregation to evangelize and provide general benevolence), whether the local church can raise money for its work by any means other than the free will offerings of its members,<ref>{{cite web | |||
| | last = Bronger | |||
| | first = J. R. | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = The Church, Part 8 | |||
| | work = What Is Written | |||
| | publisher = Traders Point Church of Christ | |||
| | date = ] | |||
| | url = http://www.traderspointchurch.org/articles/wiw990613.html | |||
| | format = | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | accessdate = 2007-06-13 }}</ref> | |||
| and varied beliefs regarding the scriptural legitimacy of church-maintained fellowship halls<ref>{{cite web | |||
| | last = | |||
| | first = | |||
| | authorlink = | |||
| | coauthors = | |||
| | title = Is it ok to eat in the Church building, fellowship hall, multi-purpose room or any room purchased with offering money? | |||
| | work = Frequently Asked Questions | |||
| | publisher = Rivermont Church of Christ | |||
| | date = | |||
| | url = http://www.rmcoc.com/faq/faq5.htm | |||
| | format = | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | accessdate = 2007-06-13 }}</ref> | |||
| and recreational facilities. | |||
| Three-quarters of the congregations and 87% of the membership are described by ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone–Campbell Movement'' as "mainstream", sharing a general consensus on practice and theology.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|213}} | |||
| ====Church of Christ Emergent==== | |||
| It appears that the response of some congregations to ] thought has produced another movement within the main group, though this is not a formally distinguished body. See the article on ]. | |||
| Congregational a cappella music from hymnals (perhaps pitched from a pitch pipe), but directed by any capable song-leader motioning the time signature, is notably characteristic of the Churches of Christ.<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|240}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Instrumental Music">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Instrumental Music''</ref>{{rp|417}}<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.christianchronicle.org/article555~Nation%27s_largest_Church_of_Christ_adding_instrumental_service |title=Nation's largest Church of Christ adding instrumental service |last=Ross |first=Bobby Jr |access-date=2008-09-19 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130516174443/http://www.christianchronicle.org/article555~Nation%27s_largest_Church_of_Christ_adding_instrumental_service |archive-date=May 16, 2013 |work=christianchronicle.org |publisher=The Christian Chronicle |date=January 2007 }}</ref> Few congregations clap hands or use musical instruments during "formal" weekly convocations. | |||
| ==Church organization== | |||
| ===Congregational autonomy=== | |||
| Church leadership is congregational rather than denominational. The Churches of Christ have no formally recognized headquarters, councils, or hierarchal church government. Rather, the independent congregations are a network with each congregation participating at its own discretion in various means of service and fellowship with other congregations. | |||
| The remaining congregations may be grouped into four categories which generally differ from the mainstream consensus in specific practices, rather than in theological perspectives, and tend to have smaller congregations on average.<ref name = "Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ" />{{rp |213}} | |||
| ===Congregational leadership=== | |||
| Congregations are individually overseen by a plurality of ] (also known as shepherds, pastors, overseers, or bishops) who are assisted in the administration of various works by ]s. Elders and deacons are chosen in congregations based on the qualifications found in I Timothy 3 and Titus 1. | |||
| The largest of these four categories is ]. This group is notable for opposing congregational support of institutions such as orphanages and Bible colleges. Similarly, non-institutional congregations also oppose the use of church facilities for non-church activities (such as fellowship dinners or recreation); as such, they oppose the construction of "fellowship halls", gymnasiums, and similar structures. In both cases, opposition is based on the belief that support of institutions and non-church activities are not proper functions of the local congregation. Approximately 2,055 congregations fall into this category.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|213}}<ref name=Who>{{cite web |url=http://www.christianchronicle.org/article621~Who_are_we%3F |title=Who are we? |access-date=2020-08-26 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111219042030/http://www.christianchronicle.org/article621~Who_are_we |archive-date=December 19, 2011 |last=Ross |first=Bobby Jr |work=Features |publisher=The Christian Chronicle }}</ref> | |||
| While Churches of Christ promote the biblical concept of the priesthood of all believers, congregations generally pay well-trained and educated preachers and staff. Churches of Christ also emphasize that each member is a minister, that no believer is more important than anyone else, and that all should use the gifts he or she has to serve others. Often, the elders and ministers have duties, within the local congregation, that are similar to clergy duties in other religious bodies. | |||
| The remaining three groups, whose congregations are generally considerably smaller than those of the mainstream or non-institutional groups, also oppose institutional support as well as "fellowship halls" and similar structures (for the same reasons as the non-institutional groups), but differ by other beliefs and practices (the groups often overlap, but in all cases hold to more conservative views than even the non-institutional groups):<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|213}} | |||
| ==Hermeneutics== | |||
| Churches of Christ believe in ]. Interpretive approaches to scripture may vary somewhat from congregation to congregation as Churches of Christ are not bound to a creed, catechism or denominational council. The emphasis is to find doctrine only in the Bible. Regarding biblical historicity and literalism, Churches of Christ are quite conservative and generally see the Bible as historically accurate and literal, unless scriptural context obviously indicates otherwise. Regarding church practices, worship, and doctrine, there is great liberty from congregation to congregation in interpreting what is biblically permissible, as congregations are not controlled by a denominational hierarchy. | |||
| *One group opposes separate "]" classes for children or gender-separated (the groups thus meet only as a whole assembly in one area); this group consists of approximately 1,100 congregations. The no Sunday School group generally overlaps with the "one-cup" group and may overlap with the "mutual edification" group as defined below. | |||
| Some believe God only binds people to the explicit commands of New Testament scripture, meaning that anything commanded must be obeyed in its proper and obvious context but that anything not expressly forbidden is allowable and open to interpretation and preference. Others have a more stringent view of Scripture, believing that only what is expressly commanded, given as an approved example, or indicated as obvious by inference is allowable as a practice in the church. The latter view means that if something is not specifically mentioned and approved of in the New Testament, then the church should not take the liberty of doing it. There is much variety that exists from congregation to congregation between these two ideologies. This approach, which is related to the non-denominational/autonomous nature of the church, allows open interpretation for the uninhibited search and discovery of the original meanings of biblical texts. Yet, Churches of Christ tend to be uncannily similar in their biblical interpretations regarding salvation, morality, and the seriousness of worshiping God. The liturgy or form of worship is also strikingly similar in congregations, although the style might vary in different locales. | |||
| *Another group opposes the use of multiple ] cups (the term "one-cup" is often used, sometimes pejoratively as "one-cuppers", to describe this group); there are approximately 550 congregations in this group. Congregations in this group differ as to whether "the wine" should be fermented or unfermented, whether the cup can be refilled if during the service it runs dry (or even if it is accidentally spilled), and whether "the bread" can be broken ahead of time or must be broken by the individual participant during Lord's Supper time. | |||
| *The last and smallest group "emphasize mutual edification by various leaders in the churches and oppose one person doing most of the preaching" (the term "mutual edification" is often used to describe this group); there are approximately 130 congregations in this grouping. | |||
| ==Beliefs== | |||
| ===Doctrine of Salvation (Soteriology)=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Churches of Christ teach the biblical doctrine that is common in most ] churches—that humans (of accountable age) are lost in sin (Romans 3:23) but can be redeemed because Jesus Christ, the Son of God, offered Himself as the atoning sacrifice (Romans 6:23.) | |||
| Churches of Christ seek to practice the principle of the ] being the only source to find doctrine (known elsewhere as '']'').<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|123}}<ref>"Whenever there are disagreements in the Churches of Christ, a 'reference to the scriptures is made in settling every religious question. A pronouncement from the scripture is considered the final word.'" page 240, Carmen Renee Berry, ''The Unauthorized Guide to Choosing a Church'', ], 2003</ref> The Bible is generally regarded as ] and ].<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|123}} Churches of Christ generally see the Bible as historically accurate and literal, unless scriptural context obviously indicates otherwise. Regarding church practices, worship, and doctrine, there is great liberty from congregation to congregation in interpreting what is biblically permissible, as congregations are not controlled by a denominational hierarchy.<ref>See F. LaGard Smith, "The Cultural Church", 20th Century Christian, 1992, 237 pages, {{ISBN|978-0-89098-131-3}}</ref> Their approach to the Bible is driven by the "assumption that the Bible is sufficiently plain and simple to render its message obvious to any sincere believer".<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|212}} Related to this is an assumption that the Bible provides an understandable "blueprint" or "constitution" for the church.<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|213}} | |||
| {{blockquote|'''If it's not in the Bible, then these folks aren't going to do it'''.|Carmen Renee Berry|''The Unauthorized Guide to Choosing a Church''<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|240}}}} | |||
| The difference between Churches of Christ and most other evangelical churches is the teaching on how one receives this salvation. Churches of Christ adhere to the biblical teaching that salvation occurs when one obeys Christ in baptism. This is based on scriptures such as Mark 16:16, John 3:3-5, Acts 2:38, Acts 22:16 and I Peter 3:21. In contrast, most Protestant churches and evangelicals today teach that mental belief in Christ with no response, quoting a "sinner's prayer," or "asking Jesus into one's heart" will suffice. Churches of Christ almost unanimously reject these notions based on these doctrines not being found in Scripture and because of the New Testament scriptures regarding the purposes of baptism. Baptism is performed only by immersion (the New Testament Greek term ''baptizo'' always meant "to immerse") and only upon those capable of believing in Christ and repenting of sin (i.e., no ]). | |||
| Historically, three ] approaches have been used among Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Hermeneutics">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, entry on ''Hermeneutics.''</ref>{{rp|387}}<ref name="Olbricht 1995">Thomas H. Olbricht, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080922142001/http://www.acu.edu/sponsored/restoration_quarterly/archives/1990s/vol_37_no_1_contents/olbricht.html |date=2008-09-22 }} '']'', Vol. 37/No. 1 (1995)</ref> | |||
| ==Other Theological Tendencies== | |||
| * Analysis of commands, examples, and necessary inferences; | |||
| Some would label Churches of Christ as typically ], although members do not usually embrace this term and often disagree with certain tenets. The Catholic concept of ] and the Calvinistic ideas of ], ], etc. are generally rejected as doctrines that are not found in Scripture but were later innovations. Election and predestination are functions of the exercise of free will. Those who choose God's way through Christ are elect and therefore saved while those who reject Christ are lost in their sin. Furthermore, the popular notion of "]" is rejected. It is generally held that, although not the norm, a Christian can consciously elect to cease following Christ and hence be lost ("fallen from grace"). (2 Peter 2:20-22) | |||
| * ] analysis distinguishing between Patriarchal, Mosaic and Christian dispensations (however, Churches of Christ are ] and generally hold ] views); and | |||
| * ] analysis. | |||
| The relative importance given to each of these three strategies has varied over time and between different contexts.<ref name="Olbricht 1995"/> The general impression in the current Churches of Christ is that the group's hermeneutics are entirely based on the command, example, inference approach.<ref name="Olbricht 1995"/> In practice, interpretation has been deductive, and heavily influenced by the group's central commitment to ] and ].<ref name="Olbricht 1995"/> ] has been used as well, as when all of the conversion accounts from the book of ] are collated and analyzed to determine the steps necessary for ].<ref name="Olbricht 1995"/> One student of the movement summarized the traditional approach this way: "In most of their theologizing, however, my impression is that spokespersons in the Churches of Christ reason from Scripture in a ] manner, arguing from one premise or hypothesis to another so as to arrive at a conclusion. In this regard the approach is much like that of science which, in practice moves deductively from one hypothesis to another, rather than in a ] inductive manner."<ref name="Olbricht 1995"/> In recent years, changes in the degree of emphasis placed on ecclesiology and soteriology has spurred a reexamination of the traditional hermeneutics among some associated with the Churches of Christ.<ref name="Olbricht 1995"/> | |||
| Regarding eschatology, Churches of Christ are generally ], although a few congregations hold ] interpretations. | |||
| A debate arose during the 1980s over the use of the command, example, necessary inference model for identifying the "essentials" of the ] faith. Some argued that it fostered ], and advocated instead a hermeneutic based on the character of ], ] and the ]. Traditionalists urged the rejection of this "new hermeneutic".<ref>Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, page 219</ref> Use of this ] formula has declined as congregations have shifted to an increased "focus on 'spiritual' issues like discipleship, servanthood, family and praise".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Hermeneutics"/>{{rp|388}} Relatively greater emphasis has been given to ] studies in congregational Bible classes and at affiliated colleges in recent decades. While it is still not seen as authoritative for Christian worship, church organization, or regulating the Christian's life, some have argued that it is theologically authoritative.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Hermeneutics"/>{{rp|388}} | |||
| ===Basis of ''a cappella'' worship practice=== | |||
| There is no evidence to indicate that the first century church used instruments in worship, and because all New Testament scriptures that command or refer to worship in song only mention singing, the Churches of Christ have historically followed this tradition. It is also pointed out that in all of church history, instrumental music in worship was not practiced until the sixth century, hence the Italian word ''a cappella'' (as the chapel). The level of conviction regarding ''a cappella'' only worship varies from church to church. To some this is a preference, a good interpretation, or an embraced tradition but is not binding on others because there is no command in Scripture that forbids instruments in worship. To others, to use instruments in worship would equate with adding to the Bible since instruments are not mentioned, making the ''a cappella'' practice a strong matter of doctrine or dogma. | |||
| Many scholars associated with the Churches of Christ embrace the methods of modern ] but not the associated anti-supernaturalistic views. More generally, the classical grammatico-historical method is prevalent, which provides a basis for some openness to alternative approaches to understanding the scriptures.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Hermeneutics"/>{{rp|389}} | |||
| ==Notable members of Churches of Christ== | |||
| *See list at | |||
| ===Doctrine of salvation (soteriology)=== | |||
| Churches of Christ are strongly anti-] and anti-] in their understanding of ] and generally present conversion as "obedience to the proclaimed facts of the gospel rather than as the result of an emotional, Spirit-initiated conversion".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|215}} Churches of Christ hold the view that humans of accountable age are lost because they have committed ].<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} These lost souls can be redeemed because ], the Son of God, offered himself as the ].<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} Children too young to understand right from wrong and make a conscious choice between the two are believed to be innocent of sin.<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|107}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} There is no set age for this to occur; it is only when the child learns the difference between right and wrong that they are accountable ({{bibleverse|James|4:17}}). Congregations differ in their interpretation of the age of accountability.<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|107}} | |||
| Churches of Christ generally teach that the process of salvation involves the following steps:<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/> | |||
| # One must be properly taught, and hear ({{Bibleref|Romans|10:14-17}}); | |||
| # One must ] or have ] ({{Bibleref|Hebrews|11:6}}, {{Bibleref|Mark|16:16}}); | |||
| # One must ], which means turning from one's former lifestyle and choosing God's ways ({{Bibleref|Acts|17:30}}); | |||
| # One must ] belief that Jesus is the son of God ({{Bibleref|Acts|8:36–37}}); | |||
| # One must be ] in the name of Jesus Christ ({{Bibleref|Acts|2:38}}); and | |||
| # One must live faithfully as a Christian ({{Bibleverse|1|Peter|2:9}}). | |||
| Beginning in the 1960s, many preachers began placing more emphasis on the role of ] in salvation, instead of focusing exclusively on implementing all of the New Testament commands and examples.<ref name="Hughes and Roberts, 2001">Richard Thomas Hughes and R. L. Roberts, ''The Churches of Christ'', 2nd Edition, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2001, {{ISBN|0-313-23312-8}}, {{ISBN|978-0-313-23312-8}}, 345 pages</ref>{{rp|152,153}} This was not an entirely new approach, as others had actively "affirmed a theology of free and unmerited grace", but it did represent a change of emphasis with grace becoming "a theme that would increasingly define this tradition".<ref name="Hughes and Roberts, 2001"/>{{rp|153}} | |||
| ====Baptism==== | |||
| {{see also|Baptism in early Christianity}} | |||
| ]]]] has been recognized as the important initiatory rite throughout the ] of the ],<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|11}} but Christian groups differ over the manner and time in which baptism is administered,<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|11}} the meaning and significance of baptism,<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|11}} its role in salvation,<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|12}} and who is a candidate for baptism.<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|12}} | |||
| Baptism in Churches of Christ is performed only by ],<ref name="Perfect Stranger"/>{{rp|107}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} based on the New Testament's use of the ] verb ''βαπτίζω'' (baptizō) which is understood to mean to dip, immerse, submerge or plunge.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|313–314}}<ref name="Wharton 1997">Edward C. Wharton, ''The Church of Christ: The Distinctive Nature of the New Testament Church'', ] Co., 1997, {{ISBN|0-89225-464-5}}.</ref>{{rp|45–46}}<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism">Tom J. Nettles, Richard L. Pratt, Jr., John H. Armstrong, Robert Kolb, ''Understanding Four Views on Baptism'', ], 2007, {{ISBN|0-310-26267-4}}, {{ISBN|978-0-310-26267-1}}, 222 pages</ref>{{rp|139}}<ref name="Baptism, Why Wait?">Rees Bryant, ''Baptism, Why Wait?: Faith's Response in Conversion'', College Press, 1999, {{ISBN|0-89900-858-5}}, {{ISBN|978-0-89900-858-5}}, 224 pages</ref>{{rp|22}} Immersion is seen as more closely conforming to the death, burial, and resurrection of Jesus than other modes of baptism.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|314–316}}<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|140}} Churches of Christ argue that historically immersion was the mode used in the ], and that pouring and sprinkling emerged later.<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|140}} Over time these secondary modes came to replace immersion, in the State Churches of Europe.<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|140}} Only those mentally capable of belief and repentance are baptized (e.g., infant baptism is not practiced).<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}}<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|318–319}}<ref name="Ferguson 1996"/>{{rp|195}} | |||
| Churches of Christ have historically had the most conservative position on baptism among the various branches of the ], understanding that repentance and baptism by immersion are necessary parts of conversion.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Baptism''</ref>{{rp|61}} The most significant disagreements concerned the extent to which a correct understanding of the role of baptism is necessary for its validity.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|61}} ] argued that if a believer was baptized out of a desire to obey God, the baptism was valid, even if the individual did not fully understand the role baptism plays in salvation.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|61}} ] argued that to be valid, the convert must also understand that baptism is for the forgiveness of sins.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|62}} McGary's view became the prevailing one in the early 20th century, but the approach advocated by Lipscomb never totally disappeared.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|62}} More recently, the rise of the ], who "reimmersed some who came into their fellowship, even those previously immersed 'for remission of sins' in a Church of Christ," has caused some to reexamine the question of ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|66}} | |||
| Churches of Christ consistently teach that in baptism a believer surrenders his life in faith and obedience to God, and that God "by the merits of Christ's blood, cleanses one from sin and truly changes the state of the person from an alien to a citizen of God's kingdom. Baptism is not a human work; it is the place where God does the work that only God can do."<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|66}} The term "alien" is used in reference to sinners as in {{bibleverse|Eph|2:12|NKJV}}. Members consider baptism a passive act of faith rather than a meritorious work; it "is a confession that a person has nothing to offer God".<ref name="Theology Matters"/>{{rp|112}} While Churches of Christ do not describe baptism as a "sacrament", their view of it can legitimately be described as "sacramental".<ref name="Baptism, Why Wait?"/>{{rp|186}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|66}} They see the power of baptism coming from God, who uses baptism as a vehicle, rather than from the water or the act itself,<ref name="Baptism, Why Wait?"/>{{rp|186}} and understand baptism to be an integral part of the conversion process, rather than as only a symbol of conversion.<ref name="Baptism, Why Wait?"/>{{rp|184}} A recent trend is to emphasize the transformational aspect of baptism: instead of describing it as nothing more than a legal requirement or sign of something that happened in the past, it is seen as "the event that places the believer 'into Christ' where God does the ongoing work of transformation".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|66}} There is a minority that downplays the importance of baptism in order to avoid sectarianism, but the broader trend is to "reexamine the richness of the Biblical teaching of baptism and to reinforce its central and essential place in Christianity".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Baptism"/>{{rp|66}} | |||
| Because of the belief that baptism is a necessary part of ], some ] hold that the Churches of Christ endorse the doctrine of ].<ref name="Foster">Douglas A. Foster, {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100520041454/http://www.acu.edu/sponsored/restoration_quarterly/archives/2000s/vol_43_no_2_contents/foster.html |date=May 20, 2010 }} '']'', Volume 43/Number 2 (2001)</ref> However members of the Churches of Christ reject this, arguing that since ] and ] are necessary, and that the cleansing of sins is by the blood of ] through the grace of God, baptism is not an inherently redeeming ritual.<ref name="Understanding Four Views on Baptism"/>{{rp|133}}<ref name="Foster"/><ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Regeneration">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Regeneration''</ref>{{rp|630,631}} One author describes the relationship between faith and baptism this way, "''Faith'' is the ''reason why'' a person is a child of God; ''baptism'' is the ''time at which'' one is incorporated into Christ and so becomes a child of God" (italics are in the source).<ref name="Ferguson 1996"/>{{rp|170}} Baptism is understood as a confessional expression of faith and repentance,<ref name="Ferguson 1996"/>{{rp|179–182}} rather than a "work" that earns salvation.<ref name="Ferguson 1996"/>{{rp|170}} | |||
| ===''A cappella'' singing=== | |||
| ] The Churches of Christ generally combine the lack of any historical evidence that the early church used ] in its ] assemblies<ref name="I Just Want to Be a Christian"/>{{rp|47}}<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|237–238}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Instrumental Music"/>{{rp|415}} with the New Testament's lack of scriptures authorizing the use of instruments in worship assemblies<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|244–246}} to conclude that instruments should not be used today in corporate worship. Thus, they have typically practiced '']'' music in their worship assemblies.<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|240}}<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|124}} | |||
| The tradition of ''a cappella'' congregational singing in the Churches of Christ is deep rooted and the rich history of the practice stimulated the creation of many ] in the early 20th century. Notable Churches of Christ hymn writers have included ] ("]") and ] ("Worthy Art Thou"). More traditional Church of Christ hymns commonly are in the style of ]. The ] '']'', which was first published in 1921 and has had many subsequent editions, is widely used in Churches of Christ.<ref name=WakefieldGrove/> | |||
| Scriptures cited to support the practice of ''a cappella'' worship include: | |||
| * {{bibleverse|Matt|26:30|rsv}}: "And when they had sung a ], they went out to the ]."<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|236}} | |||
| * {{bibleverse|Rom|15:9|rsv}}: "Therefore I will praise thee among the ], and sing to thy name";<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|236}} | |||
| * {{bibleverse|Eph|5:18–19|rsv}}: "... be filled with the Spirit, addressing one another in ] and hymns and spiritual songs, singing and making melody to the Lord with all your heart,"<ref name="Who Are the churches of Christ"/><ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|236}} | |||
| * {{bibleverse|1 Cor|14:15|rsv}}: "I will sing with the Spirit, and I will sing with the understanding also."<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|236}} | |||
| * {{bibleverse|Col|3:16|rsv}}: "Let the word of Christ dwell in you richly; in all wisdom teaching and admonishing one another with ] and ] and spiritual songs, singing with grace in your hearts unto God."<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|237}} | |||
| * {{bibleverse|Heb|2:12|rsv}}: "I will declare thy name unto my brethren, in the midst of the church will I sing praise unto thee."<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|237}} | |||
| * {{bibleverse|Heb|13:15|rsv}}: By him therefore let us offer the sacrifice of praise to God continually, that is, the fruit of our lips giving thanks to his name. | |||
| The use of musical instruments in worship was a divisive topic within the ] from its earliest years, when some adherents opposed the practice on traditional grounds, while others may have relied on ''a cappella'' simply because they lacked access to musical instruments. Alexander Campbell opposed the use of instruments in worship. As early as 1855, some Restoration Movement churches were using ]s or ]s, ultimately leading the Churches of Christ to separate from the groups that condoned instrumental music.<ref name=WakefieldGrove>{{cite web|first=John C. |last=Wakefield |title=Stone-Campbell tradition, the |work=The Grove Dictionary of American Music, 2nd edition |publisher=Grove Music Online |date=31 Jan 2014}}</ref> However, since the early 2000's, an increasing number of congregations within the Churches of Christ have begun using musical instruments in their worship assemblies. Some of these latter describe themselves as a "Church of Christ (Instrumental)".<ref name="Unauthorized Guide"/>{{rp|240}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Instrumental Music"/>{{rp|417}}<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.christianchronicle.org/article555~Nation%27s_largest_Church_of_Christ_adding_instrumental_service |title=Nation's largest Church of Christ adding instrumental service |last=Ross |first=Bobby Jr |access-date=2008-09-19 |work=christianchronicle.org |publisher=The Christian Chronicle |date=January 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130516174443/http://www.christianchronicle.org/article555~Nation%27s_largest_Church_of_Christ_adding_instrumental_service |archive-date=2013-05-16 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Local Church of Christ adds Instruments to Worship|url=http://www.dnj.com/story/life/2015/04/16/local-church-christ-adds-instruments-worship/25891291/|access-date=January 6, 2017|newspaper=Daily News Journal|date=April 16, 2015|location=Murfreesboro|first=Nancy|last=De Gennaro}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Hall|first1=Heidi|title=Church of Christ opens door to musical instruments|url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2015/03/06/church-of-christ-instrumental-music/24499691/|access-date=January 6, 2017|publisher=The Tennessean|date=March 6, 2015|newspaper=USA Today|quote=About 20 of 12,000 Church of Christ congregations nationwide offer instrumental music}}</ref><ref name="Hawkins 2008"/>{{rp|667}} | |||
| ===Other theological tendencies=== | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Many leaders argue that the Churches of Christ only follow the Bible and have no "theology".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Theology">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Theology''</ref>{{rp|737}} ] as classically understood – the systematic development of the classical doctrinal topics – is relatively recent and rare among this movement.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Theology"/>{{rp|737}} Because Churches of Christ reject all formalized ]s on the basis that they add to or detract from Scripture, they generally reject most conceptual doctrinal positions out of hand.<ref>"Creeds are rejected because they are believed to generate schisms in the body of Christ. As well, theological paradigms (such as ] and ]) are avoided because the New Testament alone is the proper guide to doctrinal belief." Ron Rhodes, ''The Complete Guide to Christian Denominations'', ], 2005, {{ISBN|0-7369-1289-4}}, page 123.</ref> Churches of Christ do tend to elaborate certain "driving motifs".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Theology"/>{{rp|737}} These are scripture (]), the church (]) and the "plan of salvation" (]).<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Theology"/>{{rp|737}} The importance of theology, understood as teaching or "doctrine", has been defended on the basis that an understanding of doctrine is necessary to respond intelligently to questions from others, to promote spiritual health, and to draw the believer closer to God.<ref name="Theology Matters">Harold Hazelip, Gary Holloway, Randall J. Harris, Mark C. Black, ''Theology Matters: In Honor of Harold Hazelip: Answers for the Church Today'', College Press, 1998, {{ISBN|0-89900-813-5}}, {{ISBN|978-0-89900-813-4}}, 368 pages</ref>{{rp|10–11}} | |||
| {{blockquote|Churches of Christ avoid the term "theology", preferring instead the term "doctrine": theology is what humans say about the Bible; doctrine is simply what the Bible says.|''Encyclopedia of Religion in the South''<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|213}}}} | |||
| ====Eschatology==== | |||
| Regarding ] (a branch of theology concerned with the final events in the history of the world or of humankind), Churches of Christ are generally ], their originally prevalent ] (evident in ]'s '']'') having dissipated around the era of the ]. Before then, many leaders were "moderate historical premillennialists" who did not advocate specific historical interpretations. Churches of Christ have moved away from ] as ] ] has come more to fore in Protestant ] circles.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|219}}<ref>Dispensational premillennialism is characterized by an emphasis on the ], the restoration of Israel, ] and related ideas.</ref> ] and ] are the prevailing views today.<ref name="Rhodes 2005"/>{{rp|125}} | |||
| Premillennialism was a focus of controversy during the first half of the 20th century.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|219}} One of the most influential advocates for that point of view was ],<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Boll, Robert Henry">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Boll, Robert Henry''</ref>{{rp|96–97}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Eschatology">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Eschatology''</ref>{{rp|306}} whose eschatological views came to be most singularly opposed by ]<ref>Robert E. Hooper, ''A Distinct People: A History of the Churches of Christ in the 20th Century'' (West Monroe, LA: ], 1994), pp. 131–180 ''et passim'', {{ISBN|1-878990-26-8}}.</ref> By the end of the 20th century, however, the divisions caused by the debate over premillennialism were diminishing, and in the 2000 edition of the directory ''Churches of Christ in the United States'', published by Mac Lynn, congregations holding premillennial views were no longer listed separately.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Boll, Robert Henry"/>{{rp|97}}<ref>Mac Lynn, ''Churches of Christ in the United States: inclusive of her commonwealth and territories'', Twentieth Century Christian Books, 2000, {{ISBN|0-89098-172-8}}, {{ISBN|978-0-89098-172-6}}, 682 pages</ref> | |||
| ====Work of the Holy Spirit==== | |||
| During the late 19th century, the prevailing view in the Restoration Movement was that the ] currently acts only through the influence of inspired scripture.<ref name="Foster 2003">Douglas A. Foster, {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927110838/http://www.acu.edu/sponsored/restoration_quarterly/documents/451/Foster-451.pdf |date=2011-09-27 }} '']'', 45:1, 2003</ref> This ] view was associated with ], who was "greatly affected by what he viewed as the excesses of the emotional camp meetings and revivals of his day".<ref name="Foster 2003"/> He believed that the Spirit draws people towards salvation but understood the Spirit to do this "in the same way any person moves another—by persuasion with words and ideas". This view came to prevail over that of ], who believed the Spirit had a more direct role in the life of the Christian.<ref name="Foster 2003"/> Since the early 20th century, many, but not all, among the Churches of Christ have moved away from this "word-only" theory of the operation of the Holy Spirit.<ref>See for example, Harvey Floyd, ''Is the Holy Spirit for me?: A search for the meaning of the Spirit in today's church'', 20th Century Christian, 1981, {{ISBN|978-0-89098-446-8}}, 128 pages</ref> As one scholar of the movement puts it, "or better or worse, those who champion the so-called word-only theory no longer have a hold on the minds of the constituency of Churches of Christ. Though relatively few have adopted outright charismatic and third wave views and remained in the body, apparently the spiritual waves have begun to erode that rational rock."<ref name="Foster 2003"/> The Churches of Christ hold a ] perspective on the ].{{citation needed|date=March 2022}}<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Olbricht |first=Thomas H |date=1 January 2004 |title=Barton W. Stone and Walter Scott on the Holy Spirit and Ministry |url=https://digitalcommons.pepperdine.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1398&context=leaven |journal=Leaven |volume=12 |issue=3 |pages=1–6 |via=Google Scholar}}</ref> | |||
| ==== The Trinity ==== | |||
| Alexander Campbell and Barton W. Stone are recognized as two of the major Reformers of the so-called "Stone–Campbell Movement." Barton Stone was staunchly non-trinitarian as he elucidates in his, "An Address to the Christian Churches in Kentucky, Tennessee, & Ohio On Several Important Doctrines of Religion<ref>{{Cite web |title=An Address to the Christian Churches, Second Edition (1821) |url=https://webfiles.acu.edu/departments/Library/HR/restmov_nov11/www.mun.ca/rels/restmov/texts/bstone/ADDR-2ND.HTM |access-date=2024-07-05 |website=webfiles.acu.edu}}</ref>." Alexander Campbell, "rejected the term 'Trinity,' but Campbell did not reject the theological idea of the tri-unity of the Christian God."<ref>{{Cite web |date=2013-03-18 |title=Alexander Campbell on Trinity and Christology |url=https://johnmarkhicks.com/2013/03/18/alexander-campbell-on-trinity-and-christology/ |access-date=2024-07-05 |website=John Mark Hicks |language=en-US}}</ref> The fact that these two movements merged into one shows that this was not a major point of contention, even if it was a point of disagreement.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://focusonthekingdom.org/The%20Christologies%20of%20Stone%20and%20Campbell.pdf |title=The Christologies of Barton Stone and Alexander Campbell |website=Restoration Fellowship |first=Greg |last=Demmitt |access-date=July 5, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ====Church history==== | |||
| {{see also|Restorationism}} | |||
| The fundamental idea of "restoration" or "Christian Primitivism" is that problems or deficiencies in the ] can be corrected by using the ] as a "normative model."<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Models of Restoration">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, 9780802838988, 854 pages, entry on ''Restoration, Historical Models of''</ref>{{Rp|635}} The call for restoration is often justified on the basis of a "falling away" that corrupted the original purity of the church.<ref name="Shepherd 1929"/><ref name="Ward 1965">Roy B. Ward, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131211224629/http://www.acu.edu/sponsored/restoration_quarterly/archives/1960s/vol_8_no_4_contents/ward.html |date=2013-12-11 }} '']'', Vol. 8, No. 4, 1965</ref><ref name="Garrett 1980">Leroy Garrett (editor), ''Restoration Review'', Volume 22, Number 4, April 1980</ref> This falling away is identified with the development of ] and ].<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|56–66,103–138}}<ref name="Shepherd 1929"/>{{rp|54–73}}<ref name="Ward 1965"/><ref name="Garrett 1980"/> New Testament verses that discuss future apostasy ({{bibleverse|2|Thessalonians|2:3}}) and heresy (e.g., {{bibleverse||Acts|20:29}}, {{bibleverse|1|Timothy|4:1}}, {{bibleverse|2|Tim|4:1-4:4}}) are understood to predict this falling away.<ref name="Ward 1965"/> The logic of "restoration" could imply that the "true" church completely disappeared and thus lead towards exclusivism.<ref name="Garrett 1980"/> Another view of restoration is that the "true Church ... has ''always'' existed by grace and not by human engineering" (italics in the original).<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Meaning of Restoration">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, 9780802838988, 854 pages, entry on ''"Restoration," Meanings of Within the Movement''</ref>{{Rp|640}} In this view the goal is to "help Christians realize the ''ideal'' of the church in the New Testament – to restore the church ''as conceived in the mind of Christ''" (italics in the original).<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Meaning of Restoration"/>{{Rp|640}} Early Restoration Movement leaders did not believe that the church had ceased to exist, but instead sought to reform and reunite the church.<ref name="Garrett 1980"/><ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Meaning of Restoration"/>{{Rp|638}}<ref name="Garrett 1984">Leroy Garrett (editor), ''Restoration Review'', Volume 26, Number 8, October 1984</ref><ref name="Garrett 1992">Leroy Garrett (editor), ''Restoration Review'', Volume 34, Number 9, November 1992</ref> A number of congregations' web sites explicitly state that the true church never disappeared.<ref>For example: | |||
| *, Church of Christ of Genesee County , (accessed 12/04/2013); | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141205052216/http://www.westendcofc.org/a-missing-chapter-in-church.html |date=2014-12-05 }}, West End Church of Christ {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141205052256/http://www.westendcofc.org/what-to-expect.html |date=2014-12-05 }} (accessed 12/04/2013); | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131210040835/http://woodbridgechurchofchrist.com/aboutus.html |date=December 10, 2013 }}, Woodbridge Church of Christ {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131210034928/http://woodbridgechurchofchrist.com/home.html |date=December 10, 2013 }} (accessed 12/04/2013); | |||
| *John Telgren, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150403165115/http://lcofc.org/aboutmore.html |date=2015-04-03 }}, Leavenworth Church of Christ {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150403161530/http://lcofc.org/index.html |date=2015-04-03 }} (accessed 12/04/2013); | |||
| *, Glendale church of Christ (accessed 12/04/2013).</ref> The belief in a general falling away is not seen as inconsistent with the idea that a faithful remnant of the church never entirely disappeared.<ref name="Howard 1971"/>{{rp|153}}<ref name="Shepherd 1929"/>{{rp|5}}<ref name="Lyon 2006">Mack Lyon, ''Churches of Christ: Who Are They?'', Publishing Designs, Inc., Huntsville, Alabama, 2006</ref>{{rp|41}} Some have attempted to trace this remnant through the intervening centuries between the New Testament and the beginning of the Restoration Movement in the early 1800s.<ref name="Grimm 1963">{{cite book|title=Tradition and History of the Early Churches of Christ In Central Europe|year=1963|publisher=Firm Foundation Publishing House|url=http://www.netbiblestudy.net/history/index.htm|author=Hans Godwin Grimm.|others=Translated by H.L. Schug|asin=B0006WF106}}</ref><ref>Keith Sisman, , 2nd edition, 2011, {{ISBN|978-0-9564937-1-2}}.</ref> | |||
| One effect of the emphasis placed on the New Testament church is a "sense of historylessness" that sees the intervening history between the 1st century and the modern church as "irrelevant or even abhorrent."<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|152}} Authors within the brotherhood have recently argued that a greater attention to history can help guide the church through modern-day challenges.<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|151–157}}<ref>Jeff. W. Childers, Douglas A. Foster and Jack R. Reese, ''The Crux of the Matter'', ACU Press, 2002, {{ISBN|0-89112-036-X}}</ref>{{rp|60–64}} | |||
| ====Contemporary social and political views==== | |||
| The churches of Christ maintain a significant proportion of political diversity.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/02/23/u-s-religious-groups-and-their-political-leanings/|title=U.S. religious groups and their political leanings|website=Pew Research Center|date=February 23, 2016 |language=en-US|access-date=2020-03-20}}</ref> According to the Pew Research Center in 2016, 50% of adherents of the churches of Christ identify as Republican or lean Republican, 39% identify as Democratic or lean Democratic and 11% have no preference.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://christianchronicle.org/elephant-in-the-church-is-the-gop-the-party-of-churches-of-christ/|title=Elephant in the pews: Is the GOP the party of Churches of Christ?|last=bobbyross|date=2016-02-25|website=The Christian Chronicle|language=en-US|access-date=2020-03-20}}</ref> Despite this, the ''Christian Chronicle'' says that the vast majority of adherents maintain a conservative view on modern social issues. This is evident when the Research Center questioned adherents' political ideology. In the survey, 51% identified as "conservative", 29% identified as "moderate" and just 12% identified as "liberal", with 8% not knowing.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.pewforum.org/religious-landscape-study/|title=Political ideology among members of the Churches of Christ - Religion in America: U.S. Religious Data, Demographics and Statistics|website=Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project|language=en-US|access-date=2020-03-20}}</ref> In contemporary society, the vast majority of adherents of the churches of Christ view homosexuality as a sin.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://apologeticspress.org/APContent.aspx?category=7&article=1011|title=Homosexuality and Transgenderism: The Science Supports the Bible|website=apologeticspress.org|language=en|access-date=2020-03-20}}</ref> They cite Leviticus 18:22 and Romans 1:26–27 for their position. Most don't view same-sex attraction as a sin; however, they condemn "acting on same-sex desires".<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.christiancourier.com/articles/1225-straight-talk-about-homosexuality|title=Straight Talk About Homosexuality|website=Christian Courier|language=en|access-date=2020-03-20|archive-date=March 20, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200320203438/https://www.christiancourier.com/articles/1225-straight-talk-about-homosexuality|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{see also|Restoration Movement}} | |||
| ] at Cane Ridge, Kentucky]] | |||
| ===Early Restoration Movement history=== | |||
| {{see also|Christianity in the 19th century}} | |||
| The Restoration Movement originated with the convergence of several independent efforts to go back to ].<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|101}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|27}} Two were of particular importance to the development of the movement.<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|101–106}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|27}} The first, led by ], began at ], ] and called themselves simply "]". The second began in western ] and was led by ] and his son, ]; they used the name "]". Both groups sought to restore the whole Christian church on the pattern set forth in the ], and both believed that ]s kept Christianity divided.<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|101–106}}<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|27–32}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The Campbell movement was characterized by a "systematic and rational reconstruction" of the early church, in contrast to the Stone movement which was characterized by radical freedom and lack of ].<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|106–108}} Despite their differences, the two movements agreed on several critical issues.<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|108}} Both saw restoring the early church as a route to Christian freedom, and both believed that unity among Christians could be achieved by using apostolic Christianity as a model.<ref name="Allen & Hughes 1988"/>{{rp|108}} The commitment of both movements to restoring the early church and to uniting Christians was enough to motivate a union between many in the two movements.<ref name="Hughes and Roberts, 2001"/>{{rp|8,9}} While emphasizing that the Bible is the only source to seek doctrine, an acceptance of Christians with diverse opinions was the norm in the quest for truth. "In essentials, unity; in non-essentials, liberty; in all things, love" was an oft-quoted slogan of the period.<ref>Hans Rollmann, '']'', Volume 39/Number 3 (1997)</ref> The Stone and Campbell movements merged in 1832.<ref name="Redigging the Wells"/>{{rp|28}}<ref name="Garrison & DeGroot, 1948">Garrison, Winfred Earnest and DeGroot, Alfred T. (1948). ''The Disciples of Christ, A History'', St Louis, Missouri: The Bethany Press</ref>{{rp|212}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Survey and Analysis">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ], Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, Introductory section entitled ''Stone-Campbell History Over Three Centuries: A Survey and Analysis''</ref>{{rp|xxi}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Chronology">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, Introductory Chronology</ref>{{rp|xxxvii}} | |||
| The Restoration Movement began during, and was greatly influenced by, the ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Awakenings">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Great Awakenings''</ref>{{rp|368}} While the Campbells resisted what they saw as the spiritual manipulation of the camp meetings, the Southern phase of the Awakening "was an important matrix of ]'s reform movement" and shaped the evangelistic techniques used by both Stone and the Campbells.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Awakenings"/>{{rp|368}} | |||
| ===Christian Churches and Churches of Christ separation=== | |||
| In 1906, the U.S. Religious Census listed the ] and the Churches of Christ as separate and distinct groups for the first time.<ref name="McAlister & Tucker, 1975">McAlister, Lester G. and Tucker, William E. (1975), Journey in Faith: A History of the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) – St. Louis, Chalice Press, {{ISBN|978-0-8272-1703-4}}</ref>{{rp|251}} This was the recognition of a division that had been growing for years under the influence of conservatives such as ], with reports of the division having been published as early as 1883.<ref name="McAlister & Tucker, 1975"/>{{rp|252}} The most visible distinction between the two groups was the rejection of musical instruments in the Churches of Christ. The controversy over musical instruments began in 1860 with the introduction of ] in some churches. More basic were differences in the underlying approach to Biblical interpretation. For the Churches of Christ, any practices not present in accounts of New Testament worship were not permissible in the church, and they could find no New Testament documentation of the use of instrumental music in worship. For the Christian Churches, any practices not expressly forbidden could be considered.<ref name="McAlister & Tucker, 1975"/>{{rp|242–247}} Another specific source of controversy was the role of missionary societies, the first of which was the ], formed in October 1849.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missionary Societies Controversy"/><ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: American Christian Missionary Society">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''American Christian Missionary Society'', pages 24-26</ref> While there was no disagreement over the need for ], many believed that missionary societies were not authorized by scripture and would compromise the autonomy of local congregations.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missionary Societies Controversy">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Missionary Societies, Controversy Over'', pp. 534-537</ref> This disagreement became another important factor leading to the separation of the Churches of Christ from the ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missionary Societies Controversy"/> Cultural factors arising from the ] also contributed to the division.<ref name="Dictionary of Christianity in America: Churches of Christ (Non-Instrumental)">Reid, D. G., Linder, R. D., Shelley, B. L., & Stout, H. S. (1990). Dictionary of Christianity in America. Downers Grove, IL: InterVarsity Press. Entry on ''Churches of Christ (Non-Instrumental)''</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| {{blockquote|Nothing in life has given me more pain in heart than the separation from those I have heretofore worked with and loved|]|1899<ref>], 1899, as quoted by Leroy Garrett on page 104 of ''The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement'', College Press, 2002, {{ISBN|0-89900-909-3}}, {{ISBN|978-0-89900-909-4}}, 573 pages</ref>}} | |||
| In 1968, at the International Convention of Christian Churches (]), those Christian Churches that favored a denominational structure, wished to be more ecumenical, and also accepted more of the modern liberal theology of various denominations, adopted a new "provisional design" for their work together, becoming the ].<ref name="Garrett 2002"/>{{rp|495}} Those congregations that chose not to be associated with the new denominational organization continued as undenominational ], completing a separation that had begun decades before.<ref name="Garrett 2002"/>{{rp|407–409}} The instrumental Christian Churches and Churches of Christ in some cases have both organizational and hermeneutical differences with the Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|186}} For example, they have a loosely organized convention and view scriptural silence on an issue more permissively,<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|186}} but they are more closely related to the Churches of Christ in their theology and ecclesiology than they are with the Disciples of Christ denomination.<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|186}} Some see divisions in the movement as the result of the tension between the goals of restoration and ecumenism, with the a cappella Churches of Christ and Christian churches and churches of Christ resolving the tension by stressing Bible authority, while the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) resolved the tension by stressing ecumenism.<ref name="Encyclopedia of Religion in the South"/>{{rp|210}}<ref name="Garrett 2002"/>{{rp|383}} | |||
| ===Race relations=== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Early Restoration Movement leaders varied in their views of ], reflecting the range of positions common in the ]<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Race Relations''</ref>{{rp|619}} ] was a strong opponent of ], arguing that there was no Biblical justification for the form of slavery then being practiced in the ] and calling for immediate ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|619}} ] represented a more "]" opposition to slavery, writing of it as more of a political problem than as a religious or moral one.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|619}} Having seen ] and ] divide over the issue of ], Campbell argued that scripture regulated slavery rather than prohibited it, and that ] should not be allowed to become an issue over which Christians would break fellowship with each other.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|619}} Like the country as a whole, the assumption of white racial superiority was almost universal among those on all sides of the issue, and it was common for congregations to have separate seating for black members.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|619}} | |||
| After the ], black Christians who had been worshiping in mixed-race Restoration Movement congregations formed their own congregations.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|619}} White members of Restoration Movement congregations shared many of the racial prejudices of the times.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|620}} Among the Churches of Christ, ] became a prominent ] evangelist. He estimated that by January 1919 he had "traveled 23,052 miles, preached 1,161 sermons, and baptized 457 converts".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|620}} | |||
| {{blockquote|To object to any child of God participating in the service on account of his race, social or civil state, his color or ], is to object to ] and to cast him from our association. It is a fearful thing to do. I have never attended a church that negroes did not attend. |]|1907<ref>], ], '''49''' (1 August 1907): 488–489.</ref>}} | |||
| During the ] of the 1950s and 1960s the Churches of Christ struggled with changing racial attitudes.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|621}} Some leaders, such as ], and ] of ] railed against racial integration, saying that racial segregation was the Divine Order.<ref name="no to integration">{{cite news |last1=Brown |first1=Michael D |title=Despite school sentiment, Harding's leader said no to integration |url=https://www.arktimes.com/arkansas/despite-school-sentiment-hardings-leader-said-no-to-integration/Content?oid=2276428 |access-date=29 December 2018 |publisher=Arkansas Times |date=6 June 2012}}</ref><ref name=Wallace>"The manner in which the brethren in some quarters are going in for the negro meetings leads one to wonder whether they are trying to make white folks out of the negroes or negroes out of the white folks. The trend of the general mix-up seems to be toward the latter. Reliable reports have come to me of white women, members of the church, becoming so animated over a ] as to go up to him after a sermon and shake hands with him holding his hand in both of theirs. That kind of thing will turn the head of most white preachers, and sometimes affect their conduct, and anybody ought to know that it will make fools out of the negroes. For any woman in the church to so far forget her dignity, and lower herself so, just because a negro has learned enough about the gospel to preach it to his race, is pitiable indeed. Her husband should take her in charge unless he has gone crazy, too. In that case somebody ought to take both of them in charge." ], Vol. 3, No. 8 March 1941, "Negro Meetings for White People," in the ''Bible Banner''.</ref> Schools and colleges associated with the movement were at the center of the debate.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|621}} N.B. Hardeman, the president of ], was adamant that the black and white races should not mingle, and refused to shake hands with black Christians.<ref name=Wallace /> ] first admitted black undergraduate students in 1962 (graduate students had been admitted in 1961).<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|621}} Desegregation of other campuses followed.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|621}}<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://webfiles.acu.edu/departments/Library/HR/restmov_nov11/www.mun.ca/rels/restmov/texts/race/haymes22.html|title=Abilene Christian College Desegregates its Graduate School|journal=]|pages=1, 6|series=18|date=June 9, 1961|author=Don Haymes}}</ref> | |||
| Efforts to address racism continued through the following decades.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|622}} A national meeting of prominent leaders from the Churches of Christ was held in June 1968.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|622}} Thirty-two participants signed a set of proposals intended to address discrimination in local congregations, church affiliated activities and the lives of individual Christians.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|622}} An important symbolic step was taken in 1999 when the president of Abilene Christian University "confessed the sin of racism in the school's past segregationist policies" and asked black Christians for forgiveness during a lectureship at ], a historically black school affiliated with the Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Race Relations"/>{{rp|622}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Southwestern Christian College">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Southwestern Christian College''</ref>{{rp|695}} | |||
| ===Institutional controversy=== | |||
| After ], Churches of Christ began sending ministers and humanitarian relief to war-torn ] and ]. | |||
| Though there was agreement that separate para-church "missionary societies" could not be established (on the belief that such work could only be performed through local congregations), a doctrinal conflict ensued about how this work was to be done. Eventually, the funding and control of outreach programs in the United States such as homes for orphans, nursing homes, mission work, setting up new congregations, Bible colleges or seminaries, and large-scale radio and television programs became part of the controversy. | |||
| Congregations which supported and participated in pooling funds for these institutional activities are said to be "]" congregations. Congregations which have traditionally opposed these organized sponsorship activities are said to be "]" congregations. The institutional controversy resulted in the largest division among Churches of Christ in the 20th century.<ref>Randy Harshbarger, "A history of the institutional controversy among Texas Churches of Christ: 1945 to the present," M.A. thesis, Stephen F. Austin State University, 2007, 149 pages; AAT 1452110</ref> | |||
| ===Separation of the International Churches of Christ=== | |||
| The ] had their roots in a "discipling" movement that arose among the mainline Churches of Christ during the 1970s.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''International Churches of Christ''</ref>{{rp|418}} This discipling movement developed in the campus ministry of Chuck Lucas.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418}} | |||
| In 1967, Chuck Lucas was minister of the 14th Street Church of Christ in ], ] (later renamed the Crossroads Church of Christ). That year he started a new project known as Campus Advance (based on principles borrowed from the ] and the ]). Centered on the ], the program called for a strong evangelical outreach and an intimate religious atmosphere in the form of ''soul talks'' and ''prayer partners. Soul talks'' were held in student residences and involved prayer and sharing overseen by a leader who delegated authority over group members. ''Prayer partners'' referred to the practice of pairing a new Christian with an older guide for personal assistance and direction. Both procedures led to "in-depth involvement of each member in one another's lives", and critics accused Lucas of fostering cultism.<ref name="alt religions">{{cite book | last = Paden | first = Russell | editor = Timothy Miller | title = America's Alternative Religions | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=og_u0Re1uwUC&q=%22international+churches+of+christ%22%7C%22boston+church+of+christ%22 | access-date = 2007-08-07 |date=July 1995 | publisher = State University of New York Press | location = Albany | isbn = 978-0-7914-2397-4 | pages = 133–36 | chapter = The Boston Church of Christ | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=og_u0Re1uwUC&q=%22international+churches+of+christ%22%7C%22boston+church+of+christ%22&pg=PA133}}</ref> | |||
| The Crossroads Movement later spread into some other Churches of Christ. One of Lucas' converts, ], moved to the Boston area in 1979 and began working with "would-be disciples" in the Lexington Church of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418}} He asked them to "redefine their commitment to Christ," and introduced the use of discipling partners. The congregation grew rapidly, and was renamed the Boston Church of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418}} In the early 1980s, the focus of the movement moved to Boston, Massachusetts where ] and the Boston Church of Christ became prominently associated with the trend.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418}}<ref name="alt religions"/>{{rp|133,134}} With the national leadership located in ], during the 1980s it commonly became known as the "Boston movement".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418}}<ref name="alt religions"/>{{rp|133,134}} A formal break was made from the mainline Churches of Christ in 1993 with the organization of the International Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418}} This new designation formalized a division that was already in existence between those involved with the Crossroads/Boston Movement and "mainline" Churches of Christ.<ref name="Garrett 2002"/>{{rp|442}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|418,419}} Other names that have been used for this movement include the "Crossroads movement," "Multiplying Ministries," the "Discipling Movement" and the "Boston Church of Christ".<ref name="alt religions"/>{{rp|133}} | |||
| Kip McKean resigned as the "World Mission Evangelist" in November 2002.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|419}} Some ICoC leaders began "tentative efforts" at reconciliation with the Churches of Christ during the Abilene Christian University Lectureship in February 2004.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: ICOC"/>{{rp|419}} | |||
| ===Restoration Movement timeline=== | |||
| {{Restoration Movement Timeline graphical timeline|state=plain}} | |||
| ==Churches of Christ outside the United States== | ==Churches of Christ outside the United States== | ||
| Most members of the Churches of Christ live outside the ]. Although there is no reliable counting system, it is anecdotally believed there may be more than 1,000,000 members of the Churches of Christ in ], approximately 1,000,000 in ], and 50,000 in ] and ]. Total worldwide membership is over 3,000,000, with approximately 1,000,000 in the U.S.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|212}} | |||
| The ] are the ]n Stone-Campbell group, and are named after the movement's name at the time of its founding. Of the three current US groups, they are closest in belief and practice to the Disciples of Christ. A similar ] group is the ]. | |||
| ===Africa=== | |||
| Most of the Association of Churches of Christ in the UK became part of the ] in 1981. Most of the remaining became the ]. The latter group, together with Australian and New Zealand Churches have pursued a "Missional" emphasis and had an ideal of "Five Fold Leadership." These ideas have been imported from Pentecostal groupings and many churches within the Fellowship bear little resemblance to the original churches. The main grouping of Churches of Christ in Britain is that which supports the Christian Worker magazine. Other churches are supporters of the Scripture Standard magazine. A history of the Association of Churches of Christ, Let Sects and Parties Fall, was written by David M Thompson. | |||
| Although there is no reliable counting system, it is anecdotally believed to be 1,000,000 or more members of the Churches of Christ in ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|212}} The total number of congregations is approximately 14,000.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Africa">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Africa, Missions in''</ref>{{rp|7}} The most significant concentrations are in ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Africa"/>{{rp|7}} | |||
| ===Asia=== | |||
| The Australian and New Zealand groups planted churches throughout the ], (although the American groups are credited with establishing churches in American Samoa, two major island groups within the Kingdom of Tonga and Fiti Levu, the main island within the Fijian Islands), the United Kingdom group planted churches throughout the ], and the American groups planted churches throughout the ] and the rest of the world. These groups often used the name "Church of Christ" and were affiliated with the other churches of that name. While a few such churches still exist, many have merged with other groups. | |||
| Estimates are that there are 2,000 or more Restoration Movement congregations in India,<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Asia">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Asia, Missions in''</ref>{{rp|37,38}} with a membership of approximately 1,000,000.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Churches of Christ"/>{{rp|212}} More than 100 congregations exist in the ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Asia"/>{{rp|38}} Growth in other Asian countries has been smaller but is still significant.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Asia"/>{{rp|38}} | |||
| ===Australia=== | |||
| {{see also|Churches of Christ in Australia}} | |||
| Historically, Restoration Movement groups from ] were more influential than those from the United States in the early development of the movement in ]. Churches of Christ grew up independently in several locations.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Australia"/>{{rp|47}} While early Churches of Christ in Australia saw ]s as divisive, towards the end of the 19th century they began viewing "summary statements of belief" as useful in tutoring second generation members and converts from other religious groups.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Australia"/>{{rp|50}} The period from 1875 through 1910 also saw debates over the use of musical instruments in worship, Christian Endeavor Societies and Sunday Schools. Ultimately, all three found general acceptance in the movement.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Australia"/>{{rp|51}} Currently, the Restoration Movement is not as divided in Australia as it is in the ].<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Australia">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Australia, The Movement in''</ref>{{rp|53}} There have been strong ties with the ], but many conservative ministers and congregations associate with the ] instead.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Australia"/>{{rp|53}} Others have sought support from non-instrumental Churches of Christ, particularly those who felt that "conference" congregations had "departed from the restoration ideal".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Australia"/>{{rp|53}} | |||
| ===Canada=== | |||
| A relatively small proportion of total membership comes from ]. A growing portion of the Canadian demographic is made up of ] members of the church. This is partly the result of Canadian demographics as a whole, and partly due to decreased interest amongst late generation Canadians.<ref>Wayne Turner, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100301020515/http://www.gospelherald.org/Magazine/2007/2007-02/Strangers.htm |date=March 1, 2010 }} ''Gospel Herald'', February 2007</ref> The largest concentration of active congregations in Canada are in Southern Ontario, with notable congregations gathering in Beamsville, Bramalea, Niagara Falls, Vineland, Toronto (several), and Waterloo. However, many congregations of various sizes (typically under 300 members) meet all across Canada.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130927193038/http://www.gospelherald.org/churchdirectory.htm |date=2013-09-27 }} ''Gospel Herald'' (accessed December 6, 2013)</ref> | |||
| ===Great Britain=== | |||
| {{see also|Churches of Christ in Europe}} | |||
| In the early 1800s, ] were influenced by the writings of ] in the '']'' and '']''.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/> A group in Nottingham withdrew from the Scotch Baptist church in 1836 to form a Church of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Great Britain and Ireland, Churches of Christ in''</ref>{{rp|369}} James Wallis, a member of that group, founded a magazine named '']'' in 1837.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} In 1842 the first Cooperative Meeting of Churches of Christ in Great Britain was held in Edinburgh.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} Approximately 50 congregations were involved, representing a membership of 1,600.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} The name "Churches of Christ" was formally adopted at an annual meeting in 1870.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} ] influenced the British Restoration Movement indirectly through his writings; he visited Britain for several months in 1847, and "presided at the Second Cooperative Meeting of the British Churches at Chester".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} At that time the movement had grown to encompass 80 congregations with a total membership of 2,300.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} Annual meetings were held after 1847.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|369}} | |||
| The use of instrumental music in worship was not a source of division among the Churches of Christ in Great Britain before World War I. More significant was the issue of ]; a national conference was established in 1916 for congregations that opposed the war.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|371}} A conference for "Old Paths" congregations was first held in 1924.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|371}} The issues involved included concern that the Christian Association was compromising traditional principles in seeking ] ties with other organizations and a sense that it had abandoned Scripture as "an all-sufficient rule of faith and practice".<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|371}} Two "Old Paths" congregations withdrew from the Association in 1931; an additional two withdrew in 1934, and nineteen more withdrew between 1943 and 1947.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|371}} | |||
| Membership declined rapidly during and after the First World War.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|372}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Europe">Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, ''The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, {{ISBN|0-8028-3898-7}}, {{ISBN|978-0-8028-3898-8}}, 854 pages, entry on ''Europe, Missions in''</ref>{{rp|312}} The Association of Churches of Christ in Britain disbanded in 1980.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|372}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Europe"/>{{rp|312}} Most Association congregations (approximately 40) united with the ] in 1981.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|372}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Europe"/>{{rp|312}} In the same year, twenty-four other congregations formed a Fellowship of Churches of Christ.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|372}} The Fellowship developed ties with the ] during the 1980s.<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Great Britain and Ireland"/>{{rp|372}}<ref name="Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Missions in Europe"/>{{rp|312}} | |||
| The Fellowship of Churches of Christ and some Australian and New Zealand Churches advocate a "missional" emphasis with an ideal of "Five Fold Leadership". Many people in more traditional Churches of Christ see these groups as having more in common with ] churches. The main publishing organs of traditional Churches of Christ in Britain are ''The Christian Worker'' magazine and the ''Scripture Standard'' magazine. A history of the Association of Churches of Christ, ''Let Sects and Parties Fall'', was written by David M Thompson.<ref>David M. Thompson, ''Let Sects and Parties Fall: A Short History of the Association of Churches of Christ in Great Britain and Ireland'', Berean Publishing Trust (January 1980), {{ISBN|978-0-85050-012-7}}, 160 pages</ref> Further information can be found in the ''Historical Survey of Churches of Christ in the British Isles'', edited by Joe Nisbet.<ref>Joe Nisbet, gen. ed. ''Historical Survey of Churches of Christ in the British Isles''. Aberdeen, Scotland, 1995. 580 pages</ref> | |||
| ===South America=== | |||
| In ] there are above 600 congregations and 100,000 members from the Restoration Movement. Most of them were established by Lloyd David Sanders.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.movimentoderestauracao.com/index.php/quem-somos/90-as-igrejas-de-cristo-cristas-e-o-movimento-de-restauracao |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180429102608/http://www.movimentoderestauracao.com/index.php/quem-somos/90-as-igrejas-de-cristo-cristas-e-o-movimento-de-restauracao |url-status=dead |archive-date=April 29, 2018 |publisher=Movimento de Restauração |title=As Igrejas de Cristo / Cristās e o Movimento de Restauroção |trans-title=The Churches of Christ / Christians and the Restoration Movement |work=www.movimentoderestauracao.com |access-date=June 17, 2019 |language=pt}} (English and various other translations available)</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{portal|Christianity}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] – a television network affiliated with the Churches of Christ | |||
| * ] – a printed outreach affiliated with the Churches of Christ | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] – an annual gathering of students of missions, missionaries, and professors of missions associated with Churches of Christ | |||
| '''Categories''' | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == References == | |||
| === Citations === | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| == |
=== Sources === | ||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| <!--See http://en.wikipedia.org/Wikipedia:Footnotes for an explanation of how to generate footnotes using the <ref(erences/)> tags--> | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Allen | first = Crawford Leonard | title = Discovering Our Roots: The Ancestry of Churches of Christ | publisher = ] | year = 1988 | location = Abilene, Texas | page = 161 | isbn = 0-89112-008-4 }} | |||
| <div class="references-small"><references/></div> | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Brownlow | first = Leroy | title = Why I Am a Member of the Church of Christ | publisher = L. Brownlow Publishing Co. | year = 1973 | location = Fort Worth, Texas | page = 192 | oclc = 213866131 }} | |||
| {{more sources|April 2007}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Cartwright | first = Colbert S. | title = People of the Chalice | publisher = Chalice Press| year = 1987 | location = St, Louis, Missouri | isbn = 978-0-8272-2938-9 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last=Ferguson | first=Everett | title = The Church of Christ: A Biblical Ecclesiology for Today | publisher=Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing | year = 1996 | page = 443 | isbn = 978-0-8028-4189-6 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last1=Foster | first1=Douglas Allen | last2=Dunnavant | first2= Anthony L. | title = The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ | publisher = Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing | year = 2004 | page = 854 | isbn = 978-0-8028-3898-8 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last =Garrett| first = Leroy | title = The Stone-Campbell Movement | publisher = College Press | year = 1983 | location = Joplin | isbn = 0-89900-059-2 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Garrett | first = Leroy | title = The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement | publisher = College Press | year = 2002 | page = 573 | isbn=978-0-89900-909-4 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Hawley | first = Monroe E. | title = Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity | publisher = Quality Publications | year = 1976| location = Abilene, Texas | isbn=978-0-89137-513-5 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Holloway |first = Gary |author2=Foster, Douglas A. | |||
| | title = Renewing God's People | publisher = ] | year = 2001 | location = Abilene, TX | page = 151 | isbn = 978-0-89112-010-0 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Hughes | first = Richard T. | title = Reviving the Ancient Faith: The Story of Churches of Christ in America | publisher = ] | year = 1996 | location = ] | page = 448 | isbn = 978-0-8028-4086-8 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last1 = Hughes | first1 = Richard |author2=Hatch, Nathan O. |author3=] | title = American Origins of the Churches of Christ | publisher = ] | year = 2000| location = ] | page = 118 |isbn = 978-0-89112-009-4 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = McMillon | first = Lynn A. | title = Restoration Roots | publisher = Gospel Teachers Publications, Inc. |year = 1983 | location = Dallas | page = 97 | oclc = 10950221 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Murch | first = James DeForest | title = Christians Only, A history of the Restoration Movement | publisher = The Standard Publishing Company | year = 1962 | location = Cincinnati | oclc = 3047672 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Shelly | first = Rubel | title = I Just Want to Be a Christian | publisher = 20th Century Christian | year = 1984 | location = Nashville, Tennessee | isbn = 978-0-89098-021-7 }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{wiktionary|βαπτίζω}} | |||
| <!--Please refer to http://en.wikipedia.org/Talk:Churches_of_Christ/Link_Policy prior to posting links.--> | <!--Please refer to http://en.wikipedia.org/Talk:Churches_of_Christ/Link_Policy prior to posting links.--> | ||
| {{Prone to spam|date=July 2013}} | |||
| {{external links}} | |||
| <!-- {{No more links}} | |||
| Please be cautious adding more external links. | |||
| ===General websites=== | |||
| *- Sharing the Truth of the Gospel. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * - Written & multimedia material by members of churches of Christ. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *- Training program for youth. | |||
| * - A portal for churches of Christ. | |||
| Misplaced Pages is not a collection of links and should not be used for advertising. | |||
| ===Online print media=== | |||
| * - Publishes materials defending a literal interpretation of creation in the Bible. | |||
| * - A newspaper of the Churches of Christ. | |||
| * - Investigating biblical apologetics, religious doctrine, and ethical issues. | |||
| * - Publisher of Think magazine. Discusses modern day issues. | |||
| * - An online/printed magazine used to teach both Christians and non-Christians. | |||
| * - Online articles, sermon outlines, and discussion forum. | |||
| * - Magazine devoted to study of the Restoration Movement and Churches of Christ. | |||
| * - An online/printed magazine used to defend the Truth and teach others. | |||
| * - A monthly publication from what would be regarded as a "conservative" or "non-institutional" viewpoint. | |||
| * - A publication representing the "one cup" brotherhood. | |||
| Excessive or inappropriate links will be removed. | |||
| ===Online TV/Radio stations=== | |||
| * | |||
| * - "A satellite network, broadcasting the truth and nothing but the truth, 24 hours a day, seven days a week."'' | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *'' | |||
| *'' | |||
| See ] and ] for details. | |||
| ===Directories=== | |||
| * - Global Directory of 40,031 Churches of Christ with maps, web-sites, contact names, and geographical search capabilities." | |||
| * - Locate local US Church Websites with Thumbnail views by State. Just click on the map. | |||
| * - An Online directory of US Churches of Christ web pages | |||
| * - | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| If there are already suitable links, propose additions or replacements on | |||
| ===History and sources=== | |||
| the article's talk page, or submit your link to the relevant category at | |||
| * | |||
| the Open Directory Project (dmoz.org) and link there using {{Dmoz}}. | |||
| * | |||
| --> | |||
| ===Church of Christ search engines=== | |||
| * | * | ||
| * – Online news source of the Churches of Christ | |||
| * | |||
| * – A newspaper of the Churches of Christ. | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160717191540/http://www.christiancourier.com/ |date=July 17, 2016 }} – A religious journal associated with the Churches of Christ. | |||
| * – A Church of Christ Ministry Website, providing Sound Doctrine Teaching Content from Sound Churches of Christ. | |||
| * | |||
| * {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120615004742/http://www.mun.ca/rels/restmov/subs/texts.html |date=June 15, 2012 |title=''Restoration Movement Texts'' }} | |||
| * {{Citation | url = https://webfiles.acu.edu/departments/Library/HR/restmov_nov11/www.mun.ca/rels/restmov/index.html | title = The Restoration Movement Pages | publisher = ] | type = historical texts, images, biographies and other resources | url-status=dead | archive-url = https://archive.today/20131123194700/https://webfiles.acu.edu/departments/Library/HR/restmov_nov11/www.mun.ca/rels/restmov/index.html | archive-date = 2013-11-23 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211022055506/http://archives.soas.ac.uk/CalmView/Record.aspx?src=CalmView.Catalog&id=CoC&pos=1 |date=October 22, 2021 }} – archive papers of the Missionary Committee of Churches of Christ Great Britain and Ireland | |||
| {{Restoration Movement}} | |||
| ===Miscellaneous=== | |||
| {{Church of Christ Colleges}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Evangelicalism in the United States}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Presbyterian Church in the United States of America}} | |||
| *] | |||
| {{authority control}} | |||
| * | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Churches Of Christ}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:49, 25 December 2024
Autonomous Christian congregations This article is about a specific fellowship of Christian congregations. For Churches of Christ that do not agree with congregational support of church or parachurch organizations, see Churches of Christ (non-institutional). For groups of autonomous congregations in Europe using the name "church of Christ" that have unclear association with the Restoration Movement, see Churches of Christ in Europe. For other uses, see Church of Christ.| Churches of Christ | |
|---|---|
 Old Bethany Church of Christ Building, Bethany, West Virginia Old Bethany Church of Christ Building, Bethany, West Virginia | |
| Classification | Evangelical Protestant |
| Orientation | Restorationist |
| Polity | Congregationalist |
| Separations | |
| Congregations | 41,498 (worldwide) 11,790 (U.S.) |
| Members | 2,000,000 (approx.) worldwide; 1,113,362 in the United States (2020) |
| Publications |
|
The Churches of Christ, also commonly known as the Church of Christ, is a loose association of autonomous Christian congregations located around the world. Typically, their distinguishing beliefs are that of the necessity of baptism for salvation and the prohibition of musical instruments in worship. Many such congregations identify themselves as being nondenominational. The Churches of Christ arose in the United States from the Restoration Movement of 19th-century Christians who declared independence from denominations and traditional creeds. They sought "the unification of all Christians in a single body patterned after the original church described in the New Testament."
Overview
Modern Churches of Christ have their historical roots in the Restoration Movement, which was a convergence of Christians across denominational lines in search of a return to an original "pre-denominational" form of Christianity. Participants in this movement sought to base their doctrine and practice on the Bible alone, rather than recognizing the traditional councils and denominational hierarchies that had come to define Christianity since the first century A.D. Members of the Churches of Christ believe that Jesus founded only one church, that the current divisions among Christians do not express God's will, and that the only basis for restoring Christian unity is the Bible. They simply identify themselves as "Christians", without using any other forms of religious or denominational identification. They aspire to be the New Testament church as established by Christ.
Members of the church of Christ do not conceive of themselves as a new church started near the beginning of the 19th century. Rather, the whole movement is designed to reproduce in contemporary times the church originally established on Pentecost, A.D. 33. The strength of the appeal lies in the restoration of Christ's original church.
— Batsell Barrett Baxter
Churches of Christ generally share the following theological beliefs and practices:
- Autonomous, congregational church organization without denominational oversight;
- Refusal to hold to any formal creeds or informal "doctrinal statements" or "statements of faith", stating instead a reliance on the Bible alone for doctrine and practice;
- Local governance by a plurality of male elders;
- Baptism by immersion of consenting believers in the Name of the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit for the forgiveness of sins;
- Weekly observance of the Lord's Supper on Sunday
- In British congregations, the term "breaking of bread" is commonly used.
- In American congregations, the terms "Communion" or "body and blood" are used.
- Churches of Christ typically offer open communion on the first day of each week, offering the bread and fruit of the vine to all present at each person's self-examination.
- Practice of a cappella singing is the norm in worship, based on New Testament passages teaching to sing for worship, with no mention of instrumental music (and also that worship in church assemblies for centuries in the early Church practiced a cappella singing).
In keeping with their history, the Churches of Christ claim the New Testament as their sole rule of faith and practice in deciding matters of doctrine and ecclesiastical structure. They view the Old Testament as divinely inspired and historically accurate, but they do not consider its laws to be binding under the New Covenant in Christ (unless they are repeated in the New Testament) (Hebrews 8: 7–13). They believe that the New Testament demonstrates how a person may become a Christian (and thus a part of the universal Church of Christ) and how a church should be collectively organized and carry out its scriptural purposes.
Demographics
In 2022, the total membership of Churches of Christ is estimated to be between 1,700,000 and 2,000,000, with over 40,000 individual congregations worldwide. In the United States, there are approximately 1,087,559 members and 11,776 congregations. Overall U.S. membership was approximately 1.3 million in 1990 and 1.3 million in 2008. Estimates of the proportion of the US adult population associated with the Churches of Christ vary from 0.8% to 1.5%. Approximately 1,240 congregations, with 172,000 members, are predominantly African-American; 240 congregations with 10,000 members are Spanish-speaking. The average congregation size is approximately 100 members, with larger congregations reporting over 1,000 members. In 2000, the Churches of Christ were the 12th largest religious group in the U.S. based on the number of members, but the 4th largest in number of congregations.
Within the U.S., membership in the Churches of Christ has declined by approximately 12% over the period from 1980 through 2007. The current retention rate of young adults graduating from high school appears to be approximately 60%. Membership is concentrated, with 70% of the U.S. membership, in thirteen states. Churches of Christ had a presence in 2,429 counties, placing them fifth behind the United Methodist Church, Catholic Church, Southern Baptist Convention and Assemblies of God – but the average number of adherents per county was approximately 677. The divorce rate was 6.9%, much lower than national averages.
Name

"Church of Christ" is the most common name used by this group. In keeping with their focus of not being a denomination, using Ephesians 1:22–23 as reference to the church being the body of Christ and a body cannot be divided, congregations have identified themselves primarily as community churches and secondarily as Churches of Christ. A much earlier tradition is to identify a congregation as "the church" at a particular location, with no other description or qualifiers. A primary motivation behind the name is the desire to use a scriptural or Biblical name – to identify the church using a name that is found in the New Testament. Adherents are also referred to as Campbellites by academics and other denominations because it is assumed that they are followers of the teachings of Alexander Campbell, similar to Lutherans or Calvinists. Campbell himself refuted the idea that a denomination was started by him or that he was the head of one in The Christian Baptist publication in 1826 and 1828, stating: "Some religious editors in Kentucky call those who are desirous of seeing the ancient order of things restored, 'the Restorationers', 'the Campbellites'... This may go well with some; but all who fear God and keep his commands will pity and deplore the weakness and folly of those who either think to convince or to persuade by such means" (The Christian Baptist, Vol. IV, 88–89) and: "It is a nickname of reproach invented and adopted by those whose views, feelings and desires are all sectarian – who cannot conceive of Christianity in any other light than an ISM" (The Christian Baptist, Vol. V, 270). He was also associated with the Baptist denomination until 1820. The term "Campbellite" is usually offensive to members of the churches of Christ because members claim no allegiance to anyone except Jesus Christ and teach only what is presented in biblical texts.
Alexander Campbell said the "calling of Bible things by Bible names" was important in the reformation. This became an early slogan of the Restorationist Movement. These congregations generally avoid names that associate the church with a particular man (other than Christ) or a particular doctrine or theological point of view (e.g., Lutheran, Wesleyan, Reformed). They believe that Christ established only one church, and that the use of denominational names serves to foster division among Christians. Thomas Campbell expressed an ideal of unity in his Declaration and Address: "The church of Jesus Christ on earth is essentially, intentionally, and constitutionally one." This statement essentially echoes the words of Jesus Christ in John 17:21, 23.
Other terms are derived from their use in the New Testament: "church of God", "church of the Lord", "churches of Christ", "church of the first-born", "church of the living God", "the house of God", and "the people of God", while terms recognized as scriptural, such as Church of God, are avoided to prevent confusion or identification with other groups that use those designations. As a practical matter, use of a common term is seen as a way to help individual Christians find congregations with a similar approach to the scriptures. Members understand that a scriptural name can be used in a "denominational" or "sectarian" way. Using the term "Church of Christ" exclusively has been criticized as identifying a denomination. Many congregations and individuals do not capitalize the word "church" in the phrases "church of Christ" and "churches of Christ". This is based on the understanding that the term "church of Christ" is used in the New Testament as a descriptive phrase, indicating that the church belongs to Christ, rather than as a proper name.
Church organization
Congregational autonomy and leadership
Church government is congregational rather than denominational. Churches of Christ purposefully have no central headquarters, councils, or other organizational structure above the local church level. Rather, the independent congregations are a network with each congregation participating at its own discretion in various means of service and fellowship with other congregations (see Sponsoring church (Churches of Christ)). Churches of Christ are linked by their shared commitment to Biblical restoration principles. Congregations which do not participate with other church congregations and which refuse to pool resources in order to support outside causes (such as mission work, orphanages, Bible colleges, etc.) are sometimes called "non-institutional."
Congregations are generally overseen by a plurality of elders who are sometimes assisted in the administration of various works by deacons. Elders are generally seen as responsible for the spiritual welfare of the congregation, while deacons are seen as responsible for the non-spiritual needs of the church. Deacons serve under the supervision of the elders, and are often assigned to specific ministries. Successful service as a deacon is often seen as preparation for the eldership. Elders and deacons are appointed by the congregation based on the qualifications found in 1 Timothy 3 and Titus 1, including that the persons must be male (female elders and deaconesses are not recognized, as these are not found in Scripture). Congregations look for elders who have a mature enough understanding of scripture to enable them to supervise the minister and to teach, as well as to perform "governance" functions. In the absence of willing men who meet these qualifications, congregations are sometimes overseen by the congregation's men in general.
While the early Restoration Movement had a tradition of itinerant preachers rather than "located Preachers", during the 20th century a long-term, formally trained congregational minister became the norm among Churches of Christ. Ministers are understood to serve under the oversight of the elders and may or may not also be qualified as an elder. While the presence of a long-term professional minister has sometimes created "significant de facto ministerial authority" and led to conflict between the minister and the elders, the eldership has remained the "ultimate locus of authority in the congregation". There is, however, a small segment of Churches of Christ who oppose the "located minister" concept (see below).
Churches of Christ hold to the priesthood of all believers. No special titles are used for preachers or ministers that would identify them as "clergy". Many ministers have undergraduate or graduate education in religion, or specific training in preaching through a non-college school of preaching. Churches of Christ emphasize that there is no distinction between "clergy" and "laity" and that every member has a gift and a role to play in accomplishing the work of the church.
Variations within Churches of Christ
While there is an identifiable mainstream within the Churches of Christ, there are also significant variations within the fellowship. The approach taken to restoring the New Testament church has focused on "methods and procedures" such as church organization, the form of worship, and how the church should function. As a result, most divisions among Churches of Christ have been the result of "methodological" disputes. These are meaningful to members of this movement because of the seriousness with which they take the goal of "restoring the form and structure of the primitive church".
Three-quarters of the congregations and 87% of the membership are described by The Encyclopedia of the Stone–Campbell Movement as "mainstream", sharing a general consensus on practice and theology.
Congregational a cappella music from hymnals (perhaps pitched from a pitch pipe), but directed by any capable song-leader motioning the time signature, is notably characteristic of the Churches of Christ. Few congregations clap hands or use musical instruments during "formal" weekly convocations.
The remaining congregations may be grouped into four categories which generally differ from the mainstream consensus in specific practices, rather than in theological perspectives, and tend to have smaller congregations on average.
The largest of these four categories is the "non-institutional" Churches of Christ. This group is notable for opposing congregational support of institutions such as orphanages and Bible colleges. Similarly, non-institutional congregations also oppose the use of church facilities for non-church activities (such as fellowship dinners or recreation); as such, they oppose the construction of "fellowship halls", gymnasiums, and similar structures. In both cases, opposition is based on the belief that support of institutions and non-church activities are not proper functions of the local congregation. Approximately 2,055 congregations fall into this category.
The remaining three groups, whose congregations are generally considerably smaller than those of the mainstream or non-institutional groups, also oppose institutional support as well as "fellowship halls" and similar structures (for the same reasons as the non-institutional groups), but differ by other beliefs and practices (the groups often overlap, but in all cases hold to more conservative views than even the non-institutional groups):
- One group opposes separate "Sunday School" classes for children or gender-separated (the groups thus meet only as a whole assembly in one area); this group consists of approximately 1,100 congregations. The no Sunday School group generally overlaps with the "one-cup" group and may overlap with the "mutual edification" group as defined below.
- Another group opposes the use of multiple communion cups (the term "one-cup" is often used, sometimes pejoratively as "one-cuppers", to describe this group); there are approximately 550 congregations in this group. Congregations in this group differ as to whether "the wine" should be fermented or unfermented, whether the cup can be refilled if during the service it runs dry (or even if it is accidentally spilled), and whether "the bread" can be broken ahead of time or must be broken by the individual participant during Lord's Supper time.
- The last and smallest group "emphasize mutual edification by various leaders in the churches and oppose one person doing most of the preaching" (the term "mutual edification" is often used to describe this group); there are approximately 130 congregations in this grouping.
Beliefs

Churches of Christ seek to practice the principle of the Bible being the only source to find doctrine (known elsewhere as sola scriptura). The Bible is generally regarded as inspired and inerrant. Churches of Christ generally see the Bible as historically accurate and literal, unless scriptural context obviously indicates otherwise. Regarding church practices, worship, and doctrine, there is great liberty from congregation to congregation in interpreting what is biblically permissible, as congregations are not controlled by a denominational hierarchy. Their approach to the Bible is driven by the "assumption that the Bible is sufficiently plain and simple to render its message obvious to any sincere believer". Related to this is an assumption that the Bible provides an understandable "blueprint" or "constitution" for the church.
If it's not in the Bible, then these folks aren't going to do it.
— Carmen Renee Berry, The Unauthorized Guide to Choosing a Church
Historically, three hermeneutic approaches have been used among Churches of Christ.
- Analysis of commands, examples, and necessary inferences;
- Dispensational analysis distinguishing between Patriarchal, Mosaic and Christian dispensations (however, Churches of Christ are amillennial and generally hold preterist views); and
- Grammatico-historical analysis.
The relative importance given to each of these three strategies has varied over time and between different contexts. The general impression in the current Churches of Christ is that the group's hermeneutics are entirely based on the command, example, inference approach. In practice, interpretation has been deductive, and heavily influenced by the group's central commitment to ecclesiology and soteriology. Inductive reasoning has been used as well, as when all of the conversion accounts from the book of Acts are collated and analyzed to determine the steps necessary for salvation. One student of the movement summarized the traditional approach this way: "In most of their theologizing, however, my impression is that spokespersons in the Churches of Christ reason from Scripture in a deductive manner, arguing from one premise or hypothesis to another so as to arrive at a conclusion. In this regard the approach is much like that of science which, in practice moves deductively from one hypothesis to another, rather than in a Baconian inductive manner." In recent years, changes in the degree of emphasis placed on ecclesiology and soteriology has spurred a reexamination of the traditional hermeneutics among some associated with the Churches of Christ.
A debate arose during the 1980s over the use of the command, example, necessary inference model for identifying the "essentials" of the New Testament faith. Some argued that it fostered legalism, and advocated instead a hermeneutic based on the character of God, Christ and the Holy Spirit. Traditionalists urged the rejection of this "new hermeneutic". Use of this tripartite formula has declined as congregations have shifted to an increased "focus on 'spiritual' issues like discipleship, servanthood, family and praise". Relatively greater emphasis has been given to Old Testament studies in congregational Bible classes and at affiliated colleges in recent decades. While it is still not seen as authoritative for Christian worship, church organization, or regulating the Christian's life, some have argued that it is theologically authoritative.
Many scholars associated with the Churches of Christ embrace the methods of modern Biblical criticism but not the associated anti-supernaturalistic views. More generally, the classical grammatico-historical method is prevalent, which provides a basis for some openness to alternative approaches to understanding the scriptures.
Doctrine of salvation (soteriology)
Churches of Christ are strongly anti-Lutheran and anti-Calvinist in their understanding of salvation and generally present conversion as "obedience to the proclaimed facts of the gospel rather than as the result of an emotional, Spirit-initiated conversion". Churches of Christ hold the view that humans of accountable age are lost because they have committed sins. These lost souls can be redeemed because Jesus Christ, the Son of God, offered himself as the atoning sacrifice. Children too young to understand right from wrong and make a conscious choice between the two are believed to be innocent of sin. There is no set age for this to occur; it is only when the child learns the difference between right and wrong that they are accountable (James 4:17). Congregations differ in their interpretation of the age of accountability.
Churches of Christ generally teach that the process of salvation involves the following steps:
- One must be properly taught, and hear (Romans 10:14–17);
- One must believe or have faith (Hebrews 11:6, Mark 16:16);
- One must repent, which means turning from one's former lifestyle and choosing God's ways (Acts 17:30);
- One must confess belief that Jesus is the son of God (Acts 8:36–37);
- One must be baptized in the name of Jesus Christ (Acts 2:38); and
- One must live faithfully as a Christian (1 Peter 2:9).
Beginning in the 1960s, many preachers began placing more emphasis on the role of grace in salvation, instead of focusing exclusively on implementing all of the New Testament commands and examples. This was not an entirely new approach, as others had actively "affirmed a theology of free and unmerited grace", but it did represent a change of emphasis with grace becoming "a theme that would increasingly define this tradition".
Baptism
See also: Baptism in early Christianity
Baptism has been recognized as the important initiatory rite throughout the history of the Christian Church, but Christian groups differ over the manner and time in which baptism is administered, the meaning and significance of baptism, its role in salvation, and who is a candidate for baptism.
Baptism in Churches of Christ is performed only by bodily immersion, based on the New Testament's use of the Koine Greek verb βαπτίζω (baptizō) which is understood to mean to dip, immerse, submerge or plunge. Immersion is seen as more closely conforming to the death, burial, and resurrection of Jesus than other modes of baptism. Churches of Christ argue that historically immersion was the mode used in the first century, and that pouring and sprinkling emerged later. Over time these secondary modes came to replace immersion, in the State Churches of Europe. Only those mentally capable of belief and repentance are baptized (e.g., infant baptism is not practiced).
Churches of Christ have historically had the most conservative position on baptism among the various branches of the Restoration Movement, understanding that repentance and baptism by immersion are necessary parts of conversion. The most significant disagreements concerned the extent to which a correct understanding of the role of baptism is necessary for its validity. David Lipscomb argued that if a believer was baptized out of a desire to obey God, the baptism was valid, even if the individual did not fully understand the role baptism plays in salvation. Austin McGary argued that to be valid, the convert must also understand that baptism is for the forgiveness of sins. McGary's view became the prevailing one in the early 20th century, but the approach advocated by Lipscomb never totally disappeared. More recently, the rise of the International Churches of Christ, who "reimmersed some who came into their fellowship, even those previously immersed 'for remission of sins' in a Church of Christ," has caused some to reexamine the question of rebaptism.
Churches of Christ consistently teach that in baptism a believer surrenders his life in faith and obedience to God, and that God "by the merits of Christ's blood, cleanses one from sin and truly changes the state of the person from an alien to a citizen of God's kingdom. Baptism is not a human work; it is the place where God does the work that only God can do." The term "alien" is used in reference to sinners as in Eph 2:12. Members consider baptism a passive act of faith rather than a meritorious work; it "is a confession that a person has nothing to offer God". While Churches of Christ do not describe baptism as a "sacrament", their view of it can legitimately be described as "sacramental". They see the power of baptism coming from God, who uses baptism as a vehicle, rather than from the water or the act itself, and understand baptism to be an integral part of the conversion process, rather than as only a symbol of conversion. A recent trend is to emphasize the transformational aspect of baptism: instead of describing it as nothing more than a legal requirement or sign of something that happened in the past, it is seen as "the event that places the believer 'into Christ' where God does the ongoing work of transformation". There is a minority that downplays the importance of baptism in order to avoid sectarianism, but the broader trend is to "reexamine the richness of the Biblical teaching of baptism and to reinforce its central and essential place in Christianity".
Because of the belief that baptism is a necessary part of salvation, some Baptists hold that the Churches of Christ endorse the doctrine of baptismal regeneration. However members of the Churches of Christ reject this, arguing that since faith and repentance are necessary, and that the cleansing of sins is by the blood of Christ through the grace of God, baptism is not an inherently redeeming ritual. One author describes the relationship between faith and baptism this way, "Faith is the reason why a person is a child of God; baptism is the time at which one is incorporated into Christ and so becomes a child of God" (italics are in the source). Baptism is understood as a confessional expression of faith and repentance, rather than a "work" that earns salvation.
A cappella singing

The Churches of Christ generally combine the lack of any historical evidence that the early church used musical instruments in its worship assemblies with the New Testament's lack of scriptures authorizing the use of instruments in worship assemblies to conclude that instruments should not be used today in corporate worship. Thus, they have typically practiced a cappella music in their worship assemblies.
The tradition of a cappella congregational singing in the Churches of Christ is deep rooted and the rich history of the practice stimulated the creation of many hymns in the early 20th century. Notable Churches of Christ hymn writers have included Albert Brumley ("I'll Fly Away") and Tillit S. Teddlie ("Worthy Art Thou"). More traditional Church of Christ hymns commonly are in the style of gospel hymnody. The hymnal Great Songs of the Church, which was first published in 1921 and has had many subsequent editions, is widely used in Churches of Christ.
Scriptures cited to support the practice of a cappella worship include:
- Matt 26:30: "And when they had sung a hymn, they went out to the Mount of Olives."
- Rom 15:9: "Therefore I will praise thee among the Gentiles, and sing to thy name";
- Eph 5:18–19: "... be filled with the Spirit, addressing one another in psalms and hymns and spiritual songs, singing and making melody to the Lord with all your heart,"
- 1 Cor 14:15: "I will sing with the Spirit, and I will sing with the understanding also."
- Col 3:16: "Let the word of Christ dwell in you richly; in all wisdom teaching and admonishing one another with psalms and hymns and spiritual songs, singing with grace in your hearts unto God."
- Heb 2:12: "I will declare thy name unto my brethren, in the midst of the church will I sing praise unto thee."
- Heb 13:15: By him therefore let us offer the sacrifice of praise to God continually, that is, the fruit of our lips giving thanks to his name.
The use of musical instruments in worship was a divisive topic within the Stone–Campbell Movement from its earliest years, when some adherents opposed the practice on traditional grounds, while others may have relied on a cappella simply because they lacked access to musical instruments. Alexander Campbell opposed the use of instruments in worship. As early as 1855, some Restoration Movement churches were using organs or pianos, ultimately leading the Churches of Christ to separate from the groups that condoned instrumental music. However, since the early 2000's, an increasing number of congregations within the Churches of Christ have begun using musical instruments in their worship assemblies. Some of these latter describe themselves as a "Church of Christ (Instrumental)".
Other theological tendencies
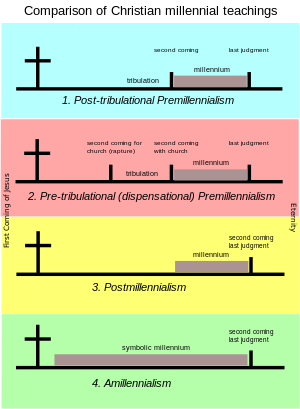
Many leaders argue that the Churches of Christ only follow the Bible and have no "theology". Christian theology as classically understood – the systematic development of the classical doctrinal topics – is relatively recent and rare among this movement. Because Churches of Christ reject all formalized creeds on the basis that they add to or detract from Scripture, they generally reject most conceptual doctrinal positions out of hand. Churches of Christ do tend to elaborate certain "driving motifs". These are scripture (hermeneutics), the church (ecclesiology) and the "plan of salvation" (soteriology). The importance of theology, understood as teaching or "doctrine", has been defended on the basis that an understanding of doctrine is necessary to respond intelligently to questions from others, to promote spiritual health, and to draw the believer closer to God.
Churches of Christ avoid the term "theology", preferring instead the term "doctrine": theology is what humans say about the Bible; doctrine is simply what the Bible says.
— Encyclopedia of Religion in the South
Eschatology
Regarding eschatology (a branch of theology concerned with the final events in the history of the world or of humankind), Churches of Christ are generally amillennial, their originally prevalent postmillennialism (evident in Alexander Campbell's Millennial Harbinger) having dissipated around the era of the First World War. Before then, many leaders were "moderate historical premillennialists" who did not advocate specific historical interpretations. Churches of Christ have moved away from premillennialism as dispensational millennialism has come more to fore in Protestant evangelical circles. Amillennialism and postmillennialism are the prevailing views today.
Premillennialism was a focus of controversy during the first half of the 20th century. One of the most influential advocates for that point of view was Robert Henry Boll, whose eschatological views came to be most singularly opposed by Foy E. Wallace Jr. By the end of the 20th century, however, the divisions caused by the debate over premillennialism were diminishing, and in the 2000 edition of the directory Churches of Christ in the United States, published by Mac Lynn, congregations holding premillennial views were no longer listed separately.
Work of the Holy Spirit
During the late 19th century, the prevailing view in the Restoration Movement was that the Holy Spirit currently acts only through the influence of inspired scripture. This rationalist view was associated with Alexander Campbell, who was "greatly affected by what he viewed as the excesses of the emotional camp meetings and revivals of his day". He believed that the Spirit draws people towards salvation but understood the Spirit to do this "in the same way any person moves another—by persuasion with words and ideas". This view came to prevail over that of Barton W. Stone, who believed the Spirit had a more direct role in the life of the Christian. Since the early 20th century, many, but not all, among the Churches of Christ have moved away from this "word-only" theory of the operation of the Holy Spirit. As one scholar of the movement puts it, "or better or worse, those who champion the so-called word-only theory no longer have a hold on the minds of the constituency of Churches of Christ. Though relatively few have adopted outright charismatic and third wave views and remained in the body, apparently the spiritual waves have begun to erode that rational rock." The Churches of Christ hold a cessationist perspective on the gifts of the Spirit.
The Trinity
Alexander Campbell and Barton W. Stone are recognized as two of the major Reformers of the so-called "Stone–Campbell Movement." Barton Stone was staunchly non-trinitarian as he elucidates in his, "An Address to the Christian Churches in Kentucky, Tennessee, & Ohio On Several Important Doctrines of Religion." Alexander Campbell, "rejected the term 'Trinity,' but Campbell did not reject the theological idea of the tri-unity of the Christian God." The fact that these two movements merged into one shows that this was not a major point of contention, even if it was a point of disagreement.
Church history
See also: RestorationismThe fundamental idea of "restoration" or "Christian Primitivism" is that problems or deficiencies in the church can be corrected by using the primitive church as a "normative model." The call for restoration is often justified on the basis of a "falling away" that corrupted the original purity of the church. This falling away is identified with the development of Catholicism and denominationalism. New Testament verses that discuss future apostasy (2 Thessalonians 2:3) and heresy (e.g., Acts 20:29, 1 Timothy 4:1, 2 Tim 4:1–4:4) are understood to predict this falling away. The logic of "restoration" could imply that the "true" church completely disappeared and thus lead towards exclusivism. Another view of restoration is that the "true Church ... has always existed by grace and not by human engineering" (italics in the original). In this view the goal is to "help Christians realize the ideal of the church in the New Testament – to restore the church as conceived in the mind of Christ" (italics in the original). Early Restoration Movement leaders did not believe that the church had ceased to exist, but instead sought to reform and reunite the church. A number of congregations' web sites explicitly state that the true church never disappeared. The belief in a general falling away is not seen as inconsistent with the idea that a faithful remnant of the church never entirely disappeared. Some have attempted to trace this remnant through the intervening centuries between the New Testament and the beginning of the Restoration Movement in the early 1800s.
One effect of the emphasis placed on the New Testament church is a "sense of historylessness" that sees the intervening history between the 1st century and the modern church as "irrelevant or even abhorrent." Authors within the brotherhood have recently argued that a greater attention to history can help guide the church through modern-day challenges.
Contemporary social and political views
The churches of Christ maintain a significant proportion of political diversity. According to the Pew Research Center in 2016, 50% of adherents of the churches of Christ identify as Republican or lean Republican, 39% identify as Democratic or lean Democratic and 11% have no preference. Despite this, the Christian Chronicle says that the vast majority of adherents maintain a conservative view on modern social issues. This is evident when the Research Center questioned adherents' political ideology. In the survey, 51% identified as "conservative", 29% identified as "moderate" and just 12% identified as "liberal", with 8% not knowing. In contemporary society, the vast majority of adherents of the churches of Christ view homosexuality as a sin. They cite Leviticus 18:22 and Romans 1:26–27 for their position. Most don't view same-sex attraction as a sin; however, they condemn "acting on same-sex desires".
History
See also: Restoration Movement
Early Restoration Movement history
See also: Christianity in the 19th centuryThe Restoration Movement originated with the convergence of several independent efforts to go back to apostolic Christianity. Two were of particular importance to the development of the movement. The first, led by Barton W. Stone, began at Cane Ridge, Kentucky and called themselves simply "Christians". The second began in western Pennsylvania and was led by Thomas Campbell and his son, Alexander Campbell; they used the name "Disciples of Christ". Both groups sought to restore the whole Christian church on the pattern set forth in the New Testament, and both believed that creeds kept Christianity divided.

The Campbell movement was characterized by a "systematic and rational reconstruction" of the early church, in contrast to the Stone movement which was characterized by radical freedom and lack of dogma. Despite their differences, the two movements agreed on several critical issues. Both saw restoring the early church as a route to Christian freedom, and both believed that unity among Christians could be achieved by using apostolic Christianity as a model. The commitment of both movements to restoring the early church and to uniting Christians was enough to motivate a union between many in the two movements. While emphasizing that the Bible is the only source to seek doctrine, an acceptance of Christians with diverse opinions was the norm in the quest for truth. "In essentials, unity; in non-essentials, liberty; in all things, love" was an oft-quoted slogan of the period. The Stone and Campbell movements merged in 1832.
The Restoration Movement began during, and was greatly influenced by, the Second Great Awakening. While the Campbells resisted what they saw as the spiritual manipulation of the camp meetings, the Southern phase of the Awakening "was an important matrix of Barton Stone's reform movement" and shaped the evangelistic techniques used by both Stone and the Campbells.
Christian Churches and Churches of Christ separation
In 1906, the U.S. Religious Census listed the Christian Churches and the Churches of Christ as separate and distinct groups for the first time. This was the recognition of a division that had been growing for years under the influence of conservatives such as Daniel Sommer, with reports of the division having been published as early as 1883. The most visible distinction between the two groups was the rejection of musical instruments in the Churches of Christ. The controversy over musical instruments began in 1860 with the introduction of organs in some churches. More basic were differences in the underlying approach to Biblical interpretation. For the Churches of Christ, any practices not present in accounts of New Testament worship were not permissible in the church, and they could find no New Testament documentation of the use of instrumental music in worship. For the Christian Churches, any practices not expressly forbidden could be considered. Another specific source of controversy was the role of missionary societies, the first of which was the American Christian Missionary Society, formed in October 1849. While there was no disagreement over the need for evangelism, many believed that missionary societies were not authorized by scripture and would compromise the autonomy of local congregations. This disagreement became another important factor leading to the separation of the Churches of Christ from the Christian Church. Cultural factors arising from the American Civil War also contributed to the division.

Nothing in life has given me more pain in heart than the separation from those I have heretofore worked with and loved
— David Lipscomb, 1899
In 1968, at the International Convention of Christian Churches (Disciples of Christ), those Christian Churches that favored a denominational structure, wished to be more ecumenical, and also accepted more of the modern liberal theology of various denominations, adopted a new "provisional design" for their work together, becoming the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ). Those congregations that chose not to be associated with the new denominational organization continued as undenominational Christian churches and churches of Christ, completing a separation that had begun decades before. The instrumental Christian Churches and Churches of Christ in some cases have both organizational and hermeneutical differences with the Churches of Christ. For example, they have a loosely organized convention and view scriptural silence on an issue more permissively, but they are more closely related to the Churches of Christ in their theology and ecclesiology than they are with the Disciples of Christ denomination. Some see divisions in the movement as the result of the tension between the goals of restoration and ecumenism, with the a cappella Churches of Christ and Christian churches and churches of Christ resolving the tension by stressing Bible authority, while the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) resolved the tension by stressing ecumenism.
Race relations

Early Restoration Movement leaders varied in their views of slavery, reflecting the range of positions common in the Pre-Civil-War U.S. Barton W. Stone was a strong opponent of slavery, arguing that there was no Biblical justification for the form of slavery then being practiced in the United States and calling for immediate emancipation. Alexander Campbell represented a more "Jeffersonian" opposition to slavery, writing of it as more of a political problem than as a religious or moral one. Having seen Methodists and Baptists divide over the issue of slavery, Campbell argued that scripture regulated slavery rather than prohibited it, and that abolition should not be allowed to become an issue over which Christians would break fellowship with each other. Like the country as a whole, the assumption of white racial superiority was almost universal among those on all sides of the issue, and it was common for congregations to have separate seating for black members.
After the Civil War, black Christians who had been worshiping in mixed-race Restoration Movement congregations formed their own congregations. White members of Restoration Movement congregations shared many of the racial prejudices of the times. Among the Churches of Christ, Marshall Keeble became a prominent African-American evangelist. He estimated that by January 1919 he had "traveled 23,052 miles, preached 1,161 sermons, and baptized 457 converts".
To object to any child of God participating in the service on account of his race, social or civil state, his color or race, is to object to Jesus Christ and to cast him from our association. It is a fearful thing to do. I have never attended a church that negroes did not attend.
— David Lipscomb, 1907
During the Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s the Churches of Christ struggled with changing racial attitudes. Some leaders, such as Foy E. Wallace Jr., and George S. Benson of Harding University railed against racial integration, saying that racial segregation was the Divine Order. Schools and colleges associated with the movement were at the center of the debate. N.B. Hardeman, the president of Freed-Hardeman, was adamant that the black and white races should not mingle, and refused to shake hands with black Christians. Abilene Christian College first admitted black undergraduate students in 1962 (graduate students had been admitted in 1961). Desegregation of other campuses followed.
Efforts to address racism continued through the following decades. A national meeting of prominent leaders from the Churches of Christ was held in June 1968. Thirty-two participants signed a set of proposals intended to address discrimination in local congregations, church affiliated activities and the lives of individual Christians. An important symbolic step was taken in 1999 when the president of Abilene Christian University "confessed the sin of racism in the school's past segregationist policies" and asked black Christians for forgiveness during a lectureship at Southwestern Christian College, a historically black school affiliated with the Churches of Christ.
Institutional controversy
After World War II, Churches of Christ began sending ministers and humanitarian relief to war-torn Europe and Asia.
Though there was agreement that separate para-church "missionary societies" could not be established (on the belief that such work could only be performed through local congregations), a doctrinal conflict ensued about how this work was to be done. Eventually, the funding and control of outreach programs in the United States such as homes for orphans, nursing homes, mission work, setting up new congregations, Bible colleges or seminaries, and large-scale radio and television programs became part of the controversy.
Congregations which supported and participated in pooling funds for these institutional activities are said to be "sponsoring church" congregations. Congregations which have traditionally opposed these organized sponsorship activities are said to be "non-institutional" congregations. The institutional controversy resulted in the largest division among Churches of Christ in the 20th century.
Separation of the International Churches of Christ
The International Churches of Christ had their roots in a "discipling" movement that arose among the mainline Churches of Christ during the 1970s. This discipling movement developed in the campus ministry of Chuck Lucas.
In 1967, Chuck Lucas was minister of the 14th Street Church of Christ in Gainesville, Florida (later renamed the Crossroads Church of Christ). That year he started a new project known as Campus Advance (based on principles borrowed from the Campus Crusade and the Shepherding Movement). Centered on the University of Florida, the program called for a strong evangelical outreach and an intimate religious atmosphere in the form of soul talks and prayer partners. Soul talks were held in student residences and involved prayer and sharing overseen by a leader who delegated authority over group members. Prayer partners referred to the practice of pairing a new Christian with an older guide for personal assistance and direction. Both procedures led to "in-depth involvement of each member in one another's lives", and critics accused Lucas of fostering cultism.
The Crossroads Movement later spread into some other Churches of Christ. One of Lucas' converts, Kip McKean, moved to the Boston area in 1979 and began working with "would-be disciples" in the Lexington Church of Christ. He asked them to "redefine their commitment to Christ," and introduced the use of discipling partners. The congregation grew rapidly, and was renamed the Boston Church of Christ. In the early 1980s, the focus of the movement moved to Boston, Massachusetts where Kip McKean and the Boston Church of Christ became prominently associated with the trend. With the national leadership located in Boston, during the 1980s it commonly became known as the "Boston movement". A formal break was made from the mainline Churches of Christ in 1993 with the organization of the International Churches of Christ. This new designation formalized a division that was already in existence between those involved with the Crossroads/Boston Movement and "mainline" Churches of Christ. Other names that have been used for this movement include the "Crossroads movement," "Multiplying Ministries," the "Discipling Movement" and the "Boston Church of Christ".
Kip McKean resigned as the "World Mission Evangelist" in November 2002. Some ICoC leaders began "tentative efforts" at reconciliation with the Churches of Christ during the Abilene Christian University Lectureship in February 2004.
Restoration Movement timeline
| Timeline of the Restoration Movement | |
|---|---|
|
↓Union↓Thomas Campbell dies↓Int'l Conv. includes Canada↓Disciples Restructure↓Cane Ridge Revival↓Stone dies↓Alexander Campbell dies↓NCMC organized by Black Disciples↓NCMC merges w/ CC(DOC)↓Last Will & Testament↓Walter Scott dies↓NACC organized as protest of Int'l Conv.↓Declaration & Address↓First use of organs↓Census Bureau recognizes Churches of Christ↓ICoC formalize splitGeneral ConventionInternational ConventionGeneral AssemblyAmerican Christian Missionary SocietyChristian Churches (DoC)The Christian ChurchChr. Woman's Board of MissionsUnited Christian Missionary Soc.(Disciples of Christ)ChristiansForeign Chr. Missionary Soc.Nat'l Christian Missionary Conv.Christian churches and churches of ChristUnited MovementNorth American Christian ConventionDisciplesChurches of ChristICoCICC│1800│1820│1840│1860│1880│1900│1920│1940│1960│1980│2000│2020 |
Churches of Christ outside the United States
Most members of the Churches of Christ live outside the United States. Although there is no reliable counting system, it is anecdotally believed there may be more than 1,000,000 members of the Churches of Christ in Africa, approximately 1,000,000 in India, and 50,000 in Central and South America. Total worldwide membership is over 3,000,000, with approximately 1,000,000 in the U.S.
Africa
Although there is no reliable counting system, it is anecdotally believed to be 1,000,000 or more members of the Churches of Christ in Africa. The total number of congregations is approximately 14,000. The most significant concentrations are in Nigeria, Malawi, Ghana, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Ethiopia, South Africa, South Sudan and Kenya.
Asia
Estimates are that there are 2,000 or more Restoration Movement congregations in India, with a membership of approximately 1,000,000. More than 100 congregations exist in the Philippines. Growth in other Asian countries has been smaller but is still significant.
Australia
See also: Churches of Christ in AustraliaHistorically, Restoration Movement groups from Great Britain were more influential than those from the United States in the early development of the movement in Australia. Churches of Christ grew up independently in several locations. While early Churches of Christ in Australia saw creeds as divisive, towards the end of the 19th century they began viewing "summary statements of belief" as useful in tutoring second generation members and converts from other religious groups. The period from 1875 through 1910 also saw debates over the use of musical instruments in worship, Christian Endeavor Societies and Sunday Schools. Ultimately, all three found general acceptance in the movement. Currently, the Restoration Movement is not as divided in Australia as it is in the United States. There have been strong ties with the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), but many conservative ministers and congregations associate with the Christian churches and churches of Christ instead. Others have sought support from non-instrumental Churches of Christ, particularly those who felt that "conference" congregations had "departed from the restoration ideal".
Canada
A relatively small proportion of total membership comes from Canada. A growing portion of the Canadian demographic is made up of immigrant members of the church. This is partly the result of Canadian demographics as a whole, and partly due to decreased interest amongst late generation Canadians. The largest concentration of active congregations in Canada are in Southern Ontario, with notable congregations gathering in Beamsville, Bramalea, Niagara Falls, Vineland, Toronto (several), and Waterloo. However, many congregations of various sizes (typically under 300 members) meet all across Canada.
Great Britain
See also: Churches of Christ in EuropeIn the early 1800s, Scottish Baptists were influenced by the writings of Alexander Campbell in the Christian Baptist and Millennial Harbinger. A group in Nottingham withdrew from the Scotch Baptist church in 1836 to form a Church of Christ. James Wallis, a member of that group, founded a magazine named The British Millennial Harbinger in 1837. In 1842 the first Cooperative Meeting of Churches of Christ in Great Britain was held in Edinburgh. Approximately 50 congregations were involved, representing a membership of 1,600. The name "Churches of Christ" was formally adopted at an annual meeting in 1870. Alexander Campbell influenced the British Restoration Movement indirectly through his writings; he visited Britain for several months in 1847, and "presided at the Second Cooperative Meeting of the British Churches at Chester". At that time the movement had grown to encompass 80 congregations with a total membership of 2,300. Annual meetings were held after 1847.
The use of instrumental music in worship was not a source of division among the Churches of Christ in Great Britain before World War I. More significant was the issue of pacifism; a national conference was established in 1916 for congregations that opposed the war. A conference for "Old Paths" congregations was first held in 1924. The issues involved included concern that the Christian Association was compromising traditional principles in seeking ecumenical ties with other organizations and a sense that it had abandoned Scripture as "an all-sufficient rule of faith and practice". Two "Old Paths" congregations withdrew from the Association in 1931; an additional two withdrew in 1934, and nineteen more withdrew between 1943 and 1947.
Membership declined rapidly during and after the First World War. The Association of Churches of Christ in Britain disbanded in 1980. Most Association congregations (approximately 40) united with the United Reformed Church in 1981. In the same year, twenty-four other congregations formed a Fellowship of Churches of Christ. The Fellowship developed ties with the Christian churches and churches of Christ during the 1980s.
The Fellowship of Churches of Christ and some Australian and New Zealand Churches advocate a "missional" emphasis with an ideal of "Five Fold Leadership". Many people in more traditional Churches of Christ see these groups as having more in common with Pentecostal churches. The main publishing organs of traditional Churches of Christ in Britain are The Christian Worker magazine and the Scripture Standard magazine. A history of the Association of Churches of Christ, Let Sects and Parties Fall, was written by David M Thompson. Further information can be found in the Historical Survey of Churches of Christ in the British Isles, edited by Joe Nisbet.
South America
In Brazil there are above 600 congregations and 100,000 members from the Restoration Movement. Most of them were established by Lloyd David Sanders.
See also
- Christian churches and churches of Christ
- Christianity in the United States
- Christian primitivism
- Churches of Christ (non-institutional)
- Congregationalist polity
- Gospel Broadcasting Network (GBN) – a television network affiliated with the Churches of Christ
- House to House Heart to Heart – a printed outreach affiliated with the Churches of Christ
- List of universities and colleges affiliated with the Churches of Christ
- Regulative principle of worship
- Sponsoring church (Churches of Christ)
- World Convention of Churches of Christ
- World Mission Workshop – an annual gathering of students of missions, missionaries, and professors of missions associated with Churches of Christ
Categories
References
Citations
- "Churches of Christ (1906 - Present) - Religious Group". www.thearda.com. Retrieved May 16, 2023.
- "Though some in the Movement have been reluctant to label themselves Protestants, the Stone-Campbell Movement is in the direct lineage of the Protestant Reformation. Especially shaped by Reformed theology through its Presbyterian roots, the Movement also shares historical and theological traits with Anglican and Anabaptist forebears." Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, "Protestant Reformation", in The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8.
- "Church numbers listed by country". ChurchZip. Archived from the original on August 13, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2014. This is a country-by-country tabulation, based on the enumeration of specific individual church locations and leaders. While it is known to under-represent certain developing countries, it is the largest such enumeration, and improves significantly on earlier broad-based estimates having no supporting detail.
- "How Many churches of Christ Are There?". The churches of Christ. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- Royster, Carl H. (June 2020). "Churches of Christ in the United States" (PDF). 21st Century Christian. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 29, 2020. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "Frequently Asked Questions". Christian Courier. Archived from the original on May 6, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- "About World Video Bible School". WBVS. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- "About The Christian Chronicle". The Christian Chronicle. Retrieved March 31, 2021.
- "What We Believe". Apologetics Press. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- Miller, Dave (December 31, 2002). "Who Are These People". Apologetics Press. Retrieved March 23, 2020.
- "Reaching the Lost" (PDF). House to House. Jacksonville church of Christ. July 2019. p. 2. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
under the oversight of the elders
- Hughes, Richard Thomas (2001). The Churches of Christ. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-275-97074-1.
- ^ Rubel Shelly, I Just Want to Be a Christian, 20th Century Christian, Nashville, Tennessee 1984, ISBN 0-89098-021-7.
- ^ Baxter, Batsell Barrett. "Who are the churches of Christ and what do they believe in?". Archived from the original on June 16, 2006. Also available via these links to church-of-christ.org Archived 2014-02-09 at the Wayback Machine, cris.com/~mmcoc (archived June 22, 2006) and scriptureessay.com (archived July 13, 2006).
- ^ C. Leonard Allen and Richard T. Hughes, "Discovering Our Roots: The Ancestry of the Churches of Christ," Abilene Christian University Press, 1988, ISBN 0-89112-006-8.
- Howard, V. E. (1971). What Is the Church of Christ? (4th (revised) ed.). Central Printers & Publishers. p. 29. ASIN B001EM1NHM.
The church of Jesus Christ is non-denominational. It is neither Catholic, Jewish nor Protestant. It was not founded in 'protest' of any institution, and it is not the product of the 'Restoration' or 'Reformation.' It is the product of the seed of the kingdom (Luke 8:11ff) grown in the hearts of men.
- ^ Batsell Barrett Baxter and Carroll Ellis, Neither Catholic, Protestant nor Jew, Church of Christ (1960) ASIN: B00073CQPM. According to Richard Thomas Hughes in Reviving the Ancient Faith: The Story of Churches of Christ in America, William B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 1996, ISBN 0-8028-4086-8, ISBN 978-0-8028-4086-8, this is "arguably the most widely distributed tract ever published by the churches of Christ or anyone associated with that tradition."
- ^ Samuel S. Hill, Charles H. Lippy, Charles Reagan Wilson, Encyclopedia of Religion in the South, Mercer University Press, 2005, ISBN 0-86554-758-0, ISBN 978-0-86554-758-2.
- "On the cornerstone of the Southside Church of Christ in Springfield, Missouri, is this inscription: 'Church of Christ, Founded in Jerusalem, A.D. 33. This building erected in 1953.' This is not an unusual claim; for similar wording can be found on buildings of churches of Christ in many parts of the United States. The Christians who use such cornerstones reason that the church of Jesus Christ began on Pentecost, A.D. 33. Therefore, to be true to the New Testament, the twentieth-century church must trace its origins to the first century." Robert W. Hooper, A Distinct People: A History of the Churches of Christ in the 20th Century, p. 1, Simon and Schuster, 1993, ISBN 1-878990-26-8, ISBN 978-1-878990-26-6.
- "Traditional Churches of Christ have pursued the restorationist vision with extraordinary zeal. Indeed, the cornerstones of many Church of Christ buildings read 'Founded, A.D. 33.' " Jill, et al. (2005), "Encyclopedia of Religion", p. 212.
- ^ Stuart M. Matlins, Arthur J. Magida, J. Magida, How to Be a Perfect Stranger: A Guide to Etiquette in Other People's Religious Ceremonies, Wood Lake Publishing Inc., 1999, ISBN 1-896836-28-3, ISBN 978-1-896836-28-7, Chapter 6 – Churches of Christ.
- ^ Carmen Renee Berry, The Unauthorized Guide to Choosing a Church, Brazos Press, 2003, ISBN 1-58743-036-3.
- ^ Ron Rhodes, The Complete Guide to Christian Denominations, Harvest House Publishers, 2005, ISBN 0-7369-1289-4.
- ^ V. E. Howard, What Is the Church of Christ? 4th Edition (Revised) Central Printers & Publishers, West Monroe, Louisiana, 1971.
- Goldberg, Jonah. Eschatological Weeds. The Remnant. Retrieved June 6, 2020 – via Apple Podcasts.
- Col. 2:14.
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, entry on Hermeneutics.
- ^ Edward C. Wharton, The Church of Christ: The Distinctive Nature of the New Testament Church, Gospel Advocate Co., 1997, ISBN 0-89225-464-5.
- David Pharr, The Beginning of Our Confidence: Seven Weeks of Daily Lessons for New Christians, 21st Century Christian, 2000, ISBN 0-89098-374-7.
- "Churches of Christ - 10 Things to Know about their History and Beliefs". November 1, 2018. Retrieved July 27, 2022.
- ^ "Church numbers listed by country". ChurchZip. Archived from the original on August 13, 2011. Retrieved July 27, 2022. This is a country-by-country tabulation, based on the enumeration of specific individual church locations and leaders. While it is known to under-represent certain developing countries, it is the largest such enumeration, and improves significantly on earlier broad-based estimates having no supporting detail.
- ^ Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar, American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS 2008) Archived April 7, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Trinity College, March 2009.
- "The Religious Composition of the United States," U.S. Religious Landscape Survey: Chapter 1, Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life, Pew Research Center, February 2008.
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, "Churches of Christ", in The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8.
- ^ Flavil Yeakley, Good News and Bad News: A Realistic Assessment of Churches of Christ in the United States: 2008; an mp3 of the author presenting some of the results at the 2009 East Tennessee School of Preaching and Ministry lectureship on March 4, 2009, is available here and a PowerPoint presentation from the 2008 CMU conference using some of the survey results posted on the Campus Ministry United website is available here.
- ^ Monroe E. Hawley, Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity, Quality Publications, Abilene, Texas, 1976, ISBN 0-89137-512-0 (paper), ISBN 0-89137-513-9 (cloth)
- ^ J. W. Shepherd, The Church, the Falling Away, and the Restoration, Gospel Advocate Company, Nashville, Tennessee, 1929 (reprinted in 1973)
- "Campbellism and the Church of Christ" Archived 2015-01-09 at the Wayback Machine Morey 2014.
- The Merriam-Webster Collegiate Dictionary describes the term as "sometimes offensive." Merriam-Webster, I. (2003). Merriam-Webster's collegiate dictionary. (Eleventh ed.). Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster, Inc. Entry on "Campbellite."
- Campbell, Alexander. Walters, Joseph A. (ed.). "On the Breaking of Bread". Scroll Publishing. Retrieved November 21, 2024.
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, "Slogans", in The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8,
- Thomas Campbell, Declaration and Address, 1809, available on-line here
- O. E. Shields, "The Church of Christ," The Word and Work, VOL. XXXIX, No. 9, September 1945.
- M. C. Kurfees, "Bible Things by Bible Names – The General and Local Senses of the Term 'Church'", Gospel Advocate (October 14, 1920):1104–1105, as reprinted in Appendix II: Restoration Documents of I Just Want to Be a Christian, Rubel Shelly (1984)
- J. C. McQuiddy, "The New Testament Church", Gospel Advocate (November 11, 1920):1097–1098, as reprinted in Appendix II: Restoration Documents of I Just Want to Be a Christian, Rubel Shelly (1984)
- ^ M. C. Kurfees, "Bible Things by Bible Names – Different Designations of the Church Further Considered", Gospel Advocate (September 30, 1920):958–959, as reprinted in Appendix II: Restoration Documents of I Just Want to Be a Christian, Rubel Shelly (1984)
- Within the Restoration Movement, congregations that do not use musical instruments in worship use the name "Church of Christ" almost exclusively; congregations that do use musical instruments most often use the term "Christian Church." Monroe E. Hawley, Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity, 1976, page 89.
- As, e.g., for listings in the yellow pages.
- ^ Leroy Garrett, The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement, College Press, 2002, ISBN 0-89900-909-3, ISBN 978-0-89900-909-4, 573 pages
- Examples of this usage include the Gospel Advocate website Archived February 8, 2009, at the Wayback Machine ("Serving the church of Christ since 1855" – accessed October 26, 2008); the Lipscomb University website ("Classes in every area are taught in a faith-informed approach by highly qualified faculty who represent the range of perspectives that exist among churches of Christ." – accessed October 26, 2008); the Freed-Hardeman University website Archived 2008-10-09 at the Wayback Machine ("Freed-Hardeman University is a private institution, associated with churches of Christ, dedicated to moral and spiritual values, academic excellence, and service in a friendly, supportive environment... The university is governed by a self-perpetuating board of trustees who are members of churches of Christ and who hold the institution in trust for its founders, alumni, and supporters." – accessed October 26, 2008); Batsell Barrett Baxter, Who are the churches of Christ and what do they believe in? (Available on-line here Archived 2008-06-19 at the Wayback Machine, here, here Archived 2014-02-09 at the Wayback Machine, here Archived 2008-05-09 at the Wayback Machine and here Archived 2010-11-30 at the Wayback Machine); Batsell Barrett Baxter and Carroll Ellis, Neither Catholic, Protestant nor Jew, tract, Church of Christ (1960); Monroe E. Hawley, Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity, Quality Publications, Abilene, Texas, 1976; Rubel Shelly, I Just Want to Be a Christian, 20th Century Christian, Nashville, Tennessee 1984; and V. E. Howard, What Is the Church of Christ? 4th Edition (Revised), 1971; Website of the Frisco church of Christ ("Welcome to the Home page for the Frisco church of Christ in Frisco, Texas." – accessed October 27, 2008); website of the church of Christ Internet Ministries ("The purpose of this Web Site is to unite the churches of Christ in one accord." – accessed October 27, 2008) "The Church of Christ at Woodson Chapel : Welcome!". Archived from the original on May 2, 2008. Retrieved May 21, 2009.
- "Churches of Christ from the beginning have maintained no formal organization structures larger than the local congregations and no official journals or vehicles declaring sanctioned positions. Consensus views do, however, often emerge through the influence of opinion leaders who express themselves in journals, at lectureships, or at area preacher meetings and other gatherings" page 213, Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages
- "Churches of Christ adhere to a strict congregationalism that cooperates in various projects overseen by one congregation or organized as parachurch enterprises, but many congregations hold themselves apart from such cooperative projects." Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, page 206, entry on Church, Doctrine of the
- "It is nothing less than phenomenal that the Churches of Christ get so much done without any centralized planning or structure. Everything is ad hoc. Most programs emerge from the inspiration and commitment of a single congregation or even a single person. Worthwhile projects survive and prosper by the voluntary cooperation of other individuals and congregations." Page 449, Leroy Garrett, The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement, College Press, 2002, ISBN 0-89900-909-3, ISBN 978-0-89900-909-4, 573 pages
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Ministry
- Everett Ferguson, "Authority and Tenure of Elders", Archived 2008-05-16 at the Wayback Machine Restoration Quarterly, Vol. 18 No. 3 (1975): 142–150
- ^ Everett Ferguson, The Church of Christ: A Biblical Ecclesiology for Today, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 1996, ISBN 0-8028-4189-9, ISBN 978-0-8028-4189-6, 443 pages
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Elders, Eldership
- "Where elderships do not exist, most congregations function through a 'business meeting' system that may include any member of the congregation or, in other cases, the men of the church." Page 531, Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Ministry
- Roberts, Price (1979). Studies for New Converts. Cincinnati: The Standard Publishing Company. pp. 53–56.
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Preaching
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Schools of Preaching
- R. B. Sweet, Now That I'm a Christian, Sweet Publishing, 1948 (revised 2003), ISBN 0-8344-0129-0
- Jeffery S. Stevenson, All People, All Times Rethinking Biblical Authority in Churches of Christ, Xulon Press, 2009, ISBN 1-60791-539-1, ISBN 978-1-60791-539-3
- ^ Richard Thomas Hughes and R. L. Roberts, The Churches of Christ, 2nd Edition, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2001, ISBN 0-313-23312-8, ISBN 978-0-313-23312-8, 345 pages
- ^ Ralph K. Hawkins, A Heritage in Crisis: Where We've Been, Where We Are, and Where We're Going in the Churches of Christ, University Press of America, 2008, 147 pages, ISBN 0-7618-4080-X, 9780761840800
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Instrumental Music
- Ross, Bobby Jr (January 2007). "Nation's largest Church of Christ adding instrumental service". christianchronicle.org. The Christian Chronicle. Archived from the original on May 16, 2013. Retrieved September 19, 2008.
- Ross, Bobby Jr. "Who are we?". Features. The Christian Chronicle. Archived from the original on December 19, 2011. Retrieved August 26, 2020.
- "Whenever there are disagreements in the Churches of Christ, a 'reference to the scriptures is made in settling every religious question. A pronouncement from the scripture is considered the final word.'" page 240, Carmen Renee Berry, The Unauthorized Guide to Choosing a Church, Brazos Press, 2003
- See F. LaGard Smith, "The Cultural Church", 20th Century Christian, 1992, 237 pages, ISBN 978-0-89098-131-3
- ^ Thomas H. Olbricht, "Hermeneutics in the Churches of Christ," Archived 2008-09-22 at the Wayback Machine Restoration Quarterly, Vol. 37/No. 1 (1995)
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, page 219
- ^ Tom J. Nettles, Richard L. Pratt, Jr., John H. Armstrong, Robert Kolb, Understanding Four Views on Baptism, Zondervan, 2007, ISBN 0-310-26267-4, ISBN 978-0-310-26267-1, 222 pages
- ^ Rees Bryant, Baptism, Why Wait?: Faith's Response in Conversion, College Press, 1999, ISBN 0-89900-858-5, ISBN 978-0-89900-858-5, 224 pages
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Baptism
- ^ Harold Hazelip, Gary Holloway, Randall J. Harris, Mark C. Black, Theology Matters: In Honor of Harold Hazelip: Answers for the Church Today, College Press, 1998, ISBN 0-89900-813-5, ISBN 978-0-89900-813-4, 368 pages
- ^ Douglas A. Foster, "Churches of Christ and Baptism: An Historical and Theological Overview," Archived May 20, 2010, at the Wayback Machine Restoration Quarterly, Volume 43/Number 2 (2001)
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Regeneration
- ^ Wakefield, John C. (January 31, 2014). "Stone-Campbell tradition, the". The Grove Dictionary of American Music, 2nd edition. Grove Music Online.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - Ross, Bobby Jr (January 2007). "Nation's largest Church of Christ adding instrumental service". christianchronicle.org. The Christian Chronicle. Archived from the original on May 16, 2013. Retrieved September 19, 2008.
- De Gennaro, Nancy (April 16, 2015). "Local Church of Christ adds Instruments to Worship". Daily News Journal. Murfreesboro. Retrieved January 6, 2017.
- Hall, Heidi (March 6, 2015). "Church of Christ opens door to musical instruments". USA Today. The Tennessean. Retrieved January 6, 2017.
About 20 of 12,000 Church of Christ congregations nationwide offer instrumental music
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Theology
- "Creeds are rejected because they are believed to generate schisms in the body of Christ. As well, theological paradigms (such as Calvinism and Arminianism) are avoided because the New Testament alone is the proper guide to doctrinal belief." Ron Rhodes, The Complete Guide to Christian Denominations, Harvest House Publishers, 2005, ISBN 0-7369-1289-4, page 123.
- Dispensational premillennialism is characterized by an emphasis on the rapture, the restoration of Israel, Armageddon and related ideas.
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Boll, Robert Henry
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Eschatology
- Robert E. Hooper, A Distinct People: A History of the Churches of Christ in the 20th Century (West Monroe, LA: Howard Publishing, 1994), pp. 131–180 et passim, ISBN 1-878990-26-8.
- Mac Lynn, Churches of Christ in the United States: inclusive of her commonwealth and territories, Twentieth Century Christian Books, 2000, ISBN 0-89098-172-8, ISBN 978-0-89098-172-6, 682 pages
- ^ Douglas A. Foster, "Waves of the Spirit Against a Rational Rock: The Impact of the Pentecostal, Charismatic and Third Wave Movements on American Churches of Christ," Archived 2011-09-27 at the Wayback Machine Restoration Quarterly, 45:1, 2003
- See for example, Harvey Floyd, Is the Holy Spirit for me?: A search for the meaning of the Spirit in today's church, 20th Century Christian, 1981, ISBN 978-0-89098-446-8, 128 pages
- Olbricht, Thomas H (January 1, 2004). "Barton W. Stone and Walter Scott on the Holy Spirit and Ministry". Leaven. 12 (3): 1–6 – via Google Scholar.
- "An Address to the Christian Churches, Second Edition (1821)". webfiles.acu.edu. Retrieved July 5, 2024.
- "Alexander Campbell on Trinity and Christology". John Mark Hicks. March 18, 2013. Retrieved July 5, 2024.
- Demmitt, Greg. "The Christologies of Barton Stone and Alexander Campbell" (PDF). Restoration Fellowship. Retrieved July 5, 2024.
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, 9780802838988, 854 pages, entry on Restoration, Historical Models of
- ^ Roy B. Ward, "The Restoration Principle": A Critical Analysis," Archived 2013-12-11 at the Wayback Machine Restoration Quarterly, Vol. 8, No. 4, 1965
- ^ Leroy Garrett (editor), "Restoration or Reformation?," Restoration Review, Volume 22, Number 4, April 1980
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, 9780802838988, 854 pages, entry on "Restoration," Meanings of Within the Movement
- Leroy Garrett (editor), "Why Church of Christ Exclusivism Must Go," Restoration Review, Volume 26, Number 8, October 1984
- Leroy Garrett (editor), "What We've Been Saying (2)," Restoration Review, Volume 34, Number 9, November 1992
- For example:
- History, Church of Christ of Genesee County website, (accessed 12/04/2013);
- A Missing Chapter in Church History Archived 2014-12-05 at the Wayback Machine, West End Church of Christ website Archived 2014-12-05 at the Wayback Machine (accessed 12/04/2013);
- What is the church of Christ? Archived December 10, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, Woodbridge Church of Christ website Archived December 10, 2013, at the Wayback Machine (accessed 12/04/2013);
- John Telgren, Some More About Us Archived 2015-04-03 at the Wayback Machine, Leavenworth Church of Christ website Archived 2015-04-03 at the Wayback Machine (accessed 12/04/2013);
- A History of the Church of Christ!, Glendale church of Christ website (accessed 12/04/2013).
- Mack Lyon, Churches of Christ: Who Are They?, Publishing Designs, Inc., Huntsville, Alabama, 2006
- Hans Godwin Grimm. (1963). Tradition and History of the Early Churches of Christ In Central Europe. Translated by H.L. Schug. Firm Foundation Publishing House. ASIN B0006WF106.
- Keith Sisman, Traces of the Kingdom, 2nd edition, self-published under the imprint "Forbidden Books," 2011, ISBN 978-0-9564937-1-2.
- Jeff. W. Childers, Douglas A. Foster and Jack R. Reese, The Crux of the Matter, ACU Press, 2002, ISBN 0-89112-036-X
- "U.S. religious groups and their political leanings". Pew Research Center. February 23, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- bobbyross (February 25, 2016). "Elephant in the pews: Is the GOP the party of Churches of Christ?". The Christian Chronicle. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- "Political ideology among members of the Churches of Christ - Religion in America: U.S. Religious Data, Demographics and Statistics". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- "Homosexuality and Transgenderism: The Science Supports the Bible". apologeticspress.org. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- "Straight Talk About Homosexuality". Christian Courier. Archived from the original on March 20, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- Hans Rollmann, "In Essentials Unity: The Pre-history of a Restoration Movement Slogan," Restoration Quarterly, Volume 39/Number 3 (1997)
- Garrison, Winfred Earnest and DeGroot, Alfred T. (1948). The Disciples of Christ, A History, St Louis, Missouri: The Bethany Press
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, Introductory section entitled Stone-Campbell History Over Three Centuries: A Survey and Analysis
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, Introductory Chronology
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Great Awakenings
- ^ McAlister, Lester G. and Tucker, William E. (1975), Journey in Faith: A History of the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) – St. Louis, Chalice Press, ISBN 978-0-8272-1703-4
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Missionary Societies, Controversy Over, pp. 534-537
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on American Christian Missionary Society, pages 24-26
- Reid, D. G., Linder, R. D., Shelley, B. L., & Stout, H. S. (1990). Dictionary of Christianity in America. Downers Grove, IL: InterVarsity Press. Entry on Churches of Christ (Non-Instrumental)
- David Lipscomb, 1899, as quoted by Leroy Garrett on page 104 of The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement, College Press, 2002, ISBN 0-89900-909-3, ISBN 978-0-89900-909-4, 573 pages
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Race Relations
- David Lipscomb, Gospel Advocate, 49 (1 August 1907): 488–489.
- Brown, Michael D (June 6, 2012). "Despite school sentiment, Harding's leader said no to integration". Arkansas Times. Retrieved December 29, 2018.
- ^ "The manner in which the brethren in some quarters are going in for the negro meetings leads one to wonder whether they are trying to make white folks out of the negroes or negroes out of the white folks. The trend of the general mix-up seems to be toward the latter. Reliable reports have come to me of white women, members of the church, becoming so animated over a certain colored preacher as to go up to him after a sermon and shake hands with him holding his hand in both of theirs. That kind of thing will turn the head of most white preachers, and sometimes affect their conduct, and anybody ought to know that it will make fools out of the negroes. For any woman in the church to so far forget her dignity, and lower herself so, just because a negro has learned enough about the gospel to preach it to his race, is pitiable indeed. Her husband should take her in charge unless he has gone crazy, too. In that case somebody ought to take both of them in charge." Foy E. Wallace, Vol. 3, No. 8 March 1941, "Negro Meetings for White People," in the Bible Banner.
- Don Haymes (June 9, 1961). "Abilene Christian College Desegregates its Graduate School". The Christian Chronicle. 18: 1, 6.
- Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Southwestern Christian College
- Randy Harshbarger, "A history of the institutional controversy among Texas Churches of Christ: 1945 to the present," M.A. thesis, Stephen F. Austin State University, 2007, 149 pages; AAT 1452110
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on International Churches of Christ
- ^ Paden, Russell (July 1995). "The Boston Church of Christ". In Timothy Miller (ed.). America's Alternative Religions. Albany: State University of New York Press. pp. 133–36. ISBN 978-0-7914-2397-4. Retrieved August 7, 2007.
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Africa, Missions in
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Asia, Missions in
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Australia, The Movement in
- Wayne Turner, "The Strangers Among Us," Archived March 1, 2010, at the Wayback Machine Gospel Herald, February 2007
- "Church of Christ Directory," Archived 2013-09-27 at the Wayback Machine Gospel Herald website (accessed December 6, 2013)
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Great Britain and Ireland, Churches of Christ in
- ^ Douglas Allen Foster and Anthony L. Dunnavant, The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-8028-3898-7, ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8, 854 pages, entry on Europe, Missions in
- David M. Thompson, Let Sects and Parties Fall: A Short History of the Association of Churches of Christ in Great Britain and Ireland, Berean Publishing Trust (January 1980), ISBN 978-0-85050-012-7, 160 pages
- Joe Nisbet, gen. ed. Historical Survey of Churches of Christ in the British Isles. Aberdeen, Scotland, 1995. 580 pages
- "As Igrejas de Cristo / Cristās e o Movimento de Restauroção" [The Churches of Christ / Christians and the Restoration Movement]. www.movimentoderestauracao.com (in Portuguese). Movimento de Restauração. Archived from the original on April 29, 2018. Retrieved June 17, 2019. (English and various other translations available)
Sources
- Allen, Crawford Leonard (1988). Discovering Our Roots: The Ancestry of Churches of Christ. Abilene, Texas: Abilene Christian University Press. p. 161. ISBN 0-89112-008-4.
- Brownlow, Leroy (1973). Why I Am a Member of the Church of Christ. Fort Worth, Texas: L. Brownlow Publishing Co. p. 192. OCLC 213866131.
- Cartwright, Colbert S. (1987). People of the Chalice. St, Louis, Missouri: Chalice Press. ISBN 978-0-8272-2938-9.
- Ferguson, Everett (1996). The Church of Christ: A Biblical Ecclesiology for Today. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 443. ISBN 978-0-8028-4189-6.
- Foster, Douglas Allen; Dunnavant, Anthony L. (2004). The Encyclopedia of the Stone-Campbell Movement: Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), Christian Churches/Churches of Christ, Churches of Christ. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 854. ISBN 978-0-8028-3898-8.
- Garrett, Leroy (1983). The Stone-Campbell Movement. Joplin: College Press. ISBN 0-89900-059-2.
- Garrett, Leroy (2002). The Stone-Campbell Movement: The Story of the American Restoration Movement. College Press. p. 573. ISBN 978-0-89900-909-4.
- Hawley, Monroe E. (1976). Redigging the Wells: Seeking Undenominational Christianity. Abilene, Texas: Quality Publications. ISBN 978-0-89137-513-5.
- Holloway, Gary; Foster, Douglas A. (2001). Renewing God's People. Abilene, TX: Abilene Christian University Press. p. 151. ISBN 978-0-89112-010-0.
- Hughes, Richard T. (1996). Reviving the Ancient Faith: The Story of Churches of Christ in America. Abilene, Texas: Abilene Christian University Press. p. 448. ISBN 978-0-8028-4086-8.
- Hughes, Richard; Hatch, Nathan O.; Harrell, David Edwin Jr. (2000). American Origins of the Churches of Christ. Abilene, Texas: Abilene Christian University Press. p. 118. ISBN 978-0-89112-009-4.
- McMillon, Lynn A. (1983). Restoration Roots. Dallas: Gospel Teachers Publications, Inc. p. 97. OCLC 10950221.
- Murch, James DeForest (1962). Christians Only, A history of the Restoration Movement. Cincinnati: The Standard Publishing Company. OCLC 3047672.
- Shelly, Rubel (1984). I Just Want to Be a Christian. Nashville, Tennessee: 20th Century Christian. ISBN 978-0-89098-021-7.
External links
- Church of Christ Internet Ministries
- Brotherhood News – Online news source of the Churches of Christ
- The Christian Chronicle – A newspaper of the Churches of Christ.
- Christian Courier Archived July 17, 2016, at the Wayback Machine – A religious journal associated with the Churches of Christ.
- HisLoveforme.com – A Church of Christ Ministry Website, providing Sound Doctrine Teaching Content from Sound Churches of Christ.
- Fellowship of Churches of Christ in Great Britain & Ireland
- Restoration Movement Texts at the Wayback Machine (archived June 15, 2012)
- The Restoration Movement Pages (historical texts, images, biographies and other resources), Abilene Christian University, archived from the original on November 23, 2013
- SOAS Special Collections Archived October 22, 2021, at the Wayback Machine – archive papers of the Missionary Committee of Churches of Christ Great Britain and Ireland
| Universities and colleges affiliated with the Churches of Christ | |
|---|---|
|
| Evangelicalism in the United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Churches |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thought | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Practices | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forms | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Movements | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Institutions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major figures | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Presbyterian Church in the United States of America | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||||||||||
| Derivatives |
| ||||||||||||