| Revision as of 10:57, 12 November 2007 editHellobeto (talk | contribs)2 edits →See also: →Other links← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:10, 2 December 2024 edit undoCipherRephic (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,091 edits Reverting edit(s) by 199.243.245.162 (talk) to rev. 1259963795 by Gelasin: Vandalism (RW 16.1)Tags: RW Undo | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Presentation application, part of Microsoft 365}} | |||
| {{redirect|Power point}} | |||
| {{About|the presentation software program by Microsoft Corporation|other uses|Power point (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Infobox Software | | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=July 2017}} | |||
| name = Microsoft PowerPoint (Windows) | | |||
| {{Infobox software | |||
| logo = ] | | |||
| | name = Microsoft PowerPoint | |||
| | logo = Microsoft Office PowerPoint (2018–present).svg | |||
| | screenshot = Microsoft PowerPoint.png | |||
| | caption = A photo presentation being created and edited in PowerPoint, running on ] | |||
| latest_release_version = 12.0.4518.1014 (2007) | | |||
| | developer = ] | |||
| latest_release_date = ], ] | | |||
| | released = {{start date and age|1987|4|20}} | |||
| operating_system = ] | | |||
| | latest release version = 2312 (Build 17126.20132) | |||
| genre = ] | | |||
| | latest release date = {{Start date and age|2024|01|09}}<ref>{{cite web|website=]|url=https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/officeupdates/current-channel|title=Release notes for Current Channel releases - Office release notes|access-date=2024-01-10|archive-date=2024-01-10|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240110150723/https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/officeupdates/current-channel|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| license = ] | | |||
| | operating_system = ] | |||
| website = | | |||
| | language count = 102 | |||
| | language footnote = <ref>{{cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Language-Accessory-Pack-for-Office-82ee1236-0f9a-45ee-9c72-05b026ee809f |last=Microsoft Corp. |title=Language Accessory Pack for Office |date=2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170828200853/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Language-Accessory-Pack-for-Office-82ee1236-0f9a-45ee-9c72-05b026ee809f |url-status=live |archive-date=August 28, 2017 |access-date=August 28, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| | language = Afrikaans, Albanian, Amharic, Arabic, Armenian, Assamese, Azerbaijani (Latin), Bangla (Bangladesh), Bangla (Bengali India), Basque, Belarusian, Bosnian (Latin), Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dari, Dutch, English, Estonian, Filipino, Finnish, French, Galician, Georgian, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hausa, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Icelandic, Igbo, Indonesian, Irish, isiXhosa, isiZulu, Italian, Japanese, Kannada, Kazakh, Khmer, Kinyarwanda, Kiswahili, Konkani, Korean, Kyrgyz, Latvian, Lithuanian, Luxembourgish, Macedonian (Macedonia), Malay (Latin), Malayalam, Maltese, Maori, Marathi, Mongolian (Cyrillic), Nepali, Norwegian (Bokmål), Norwegian (Nynorsk), Odia, Pashto, Persian (Farsi), Polish, Portuguese (Portugal), Portuguese (Brazil), Punjabi (India), Quechua, Romanian, Romansh, Russian, Scottish Gaelic, Serbian (Cyrillic, Serbia), Serbian (Latin, Serbia), Serbian (Cyrillic, Bosnia and Herzegovina), Sesotho sa Leboa, Setswana, Sindhi (Arabic), Sinhala, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Tamil, Tatar (Cyrillic), Telugu, Thai, Turkish, Turkmen (Latin), Ukrainian, Urdu, Uyghur, Uzbek (Latin), Valencian, Vietnamese, Welsh, Wolof, Yoruba | |||
| | genre = ] | |||
| | replaces = Forethought Powerpoint | |||
| | license = ] | |||
| | programming language = ] (back-end)<ref name="C++ in MS Office">{{Cite web |date=July 17, 2014 |title=C++ in MS Office |url=https://cppcon.org/bonus-talk-cxx-in-ms-office-2014/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191107064047/https://cppcon.org/bonus-talk-cxx-in-ms-office-2014/ |archive-date=November 7, 2019 |access-date=June 25, 2019 |publisher=cppcon}}</ref> | |||
| | website = {{URL|microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/powerpoint}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Infobox software | |||
| | name = Microsoft PowerPoint for Android OS | |||
| | screenshot = ] | |||
| | caption = PowerPoint for Android running on ] | |||
| | developer = ] | |||
| | latest_release_version = 16.0.16501.20160 | |||
| | latest_release_date = {{Start date and age|2023|05|26}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.apkmirror.com/apk/microsoft-corporation/powerpoint/|title=Microsoft PowerPoint: Slideshows and Presentations APKs|website=APKMirror}}</ref> | |||
| | operating_system = ] or later | |||
| | genre = ] | |||
| | license = ] ] | |||
| | website = {{URL|https://products.office.com/en-us/powerpoint}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Infobox software | |||
| | name = Microsoft PowerPoint for Mac | |||
| | logo = <!--For 2016, it is the same as above--> | |||
| | screenshot = PowerPoint for Mac screenshot.png | |||
| | caption = PowerPoint for Mac (version 16.69.1), running on ] (13.2) | |||
| | developer = ] | |||
| | released = {{Start date and age|1987|4|20}} | |||
| | latest release version = 16.70 (Build 23021201) | |||
| | latest release date = {{Start date and age|2023|02|14}}<ref>{{cite web|website=]|url=https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/officeupdates/update-history-office-for-mac|title=Update history for Office for Mac|date=June 13, 2023 }}</ref> | |||
| | latest_preview_version = | |||
| | programming language = ] (back-end), ] (API/UI)<ref name="C++ in MS Office" /> <!-- Don't forget your source please --> | |||
| | operating_system = ] or later | |||
| | language = English, Arabic, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Norwegian Bokmål, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Slovak, Spanish, Swedish, Thai, Traditional Chinese, Turkish | |||
| | language count = 26 | |||
| | language footnote = <ref>{{cite web |url=https://apps.apple.com/gb/app/microsoft-powerpoint/id462062816 |title=Microsoft Powerpoint on the Mac App Store |access-date=March 2, 2023}}</ref> | |||
| | genre = ] | |||
| | license = ] ] | |||
| | website = hide | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Infobox |
{{Infobox software | ||
| | name = Microsoft PowerPoint for iOS | |||
| | screenshot = | |||
| logo = <!-- Deleted image removed: ] -->| | |||
| | caption = | |||
| logo = ] | | |||
| | developer = ] | |||
| screenshot = ] | | |||
| | latest_release_version = 2.73 | |||
| caption = Microsoft PowerPoint 2004 running on ]. | | |||
| | latest_release_date = {{Start date and age|2023|05|15}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://apps.apple.com/app/id586449534|title=Microsoft PowerPoint|website=App Store|date=June 12, 2023 |language=en-us}}</ref> | |||
| developer = ] | | |||
| | operating_system = ] or later {{break}} ] or later {{break}} ] or later | |||
| latest_release_version = 11.3.5 (2004) | | |||
| | language = English, Arabic, Catalan, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Malay, Norwegian Bokmål, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Slovak, Spanish, Swedish, Thai, Traditional Chinese, Turkish, Ukrainian, Vietnamese | |||
| latest_release_date = ], ] | | |||
| | language count = 33 | |||
| latest_preview_version = 2008 v12.x | |||
| | genre = ] | |||
| | latest_preview_date = | | |||
| | license = ] ] | |||
| operating_system = ] | | |||
| | website = {{URL|https://products.office.com/en-us/powerpoint}} | |||
| genre = ] | license = ] | | |||
| }} | |||
| website = | | |||
| {{Infobox software | |||
| | name = PowerPoint Mobile for Windows 10 | |||
| | logo = | |||
| | screenshot = | |||
| | caption = | |||
| | developer = ] | |||
| | released = | |||
| | discontinued = Yes | |||
| | latest release version = 16002.12325.20032.0 | |||
| | latest release date = {{Start date and age|2019|12|10}} | |||
| | latest_preview_version = | |||
| | operating_system = ], ] | |||
| | language = | |||
| | language count = | |||
| | language footnote = | |||
| | genre = ] | |||
| | license = ] | |||
| | website = {{URL|https://www.microsoft.com/store/productid/9WZDNCRFJB5Q}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Microsoft PowerPoint''' is a ],<ref name="Britannica-lead">{{Cite encyclopedia |encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Britannica |title=Microsoft PowerPoint |url=https://www.britannica.com/technology/Microsoft-PowerPoint |date=November 25, 2013 |access-date=August 25, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151008163642/https://www.britannica.com/technology/Microsoft-PowerPoint |url-status=live |archive-date=October 8, 2015 |quote=Microsoft PowerPoint, virtual presentation software developed by Robert Gaskins, Tom Rudkin and Dennis Austin for the American computer software company Forethought, Inc. The program, initially named Presenter, was released for the Apple Macintosh in 1987.}}</ref> created by ], Tom Rudkin, and ]<ref name="Britannica-lead" /> at a software company named ]<ref name="Britannica-lead"/> It was released on April 20, 1987,<ref>{{Cite news |last=Mace |first=Scott |date=March 2, 1969 |title=Presentation Package Lets Users Control Look |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1TAEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA5 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=9 |issue=9 |page=5 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085435/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym2krMYP?url=https://filetea.me/t1sKNh0ZTl2S8xyckHWoi2ywg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 25, 2017 |quote=The $395 program will be shipped to dealers on April 20, Forethought said.}}</ref> initially for ] computers only.<ref name="Britannica-lead" /> ] acquired PowerPoint for about $14 million three months after it appeared.<ref name="Britannica-acquisition-lead">{{cite encyclopedia |encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Britannica |title=Microsoft PowerPoint |url=https://www.britannica.com/technology/Microsoft-PowerPoint |date=November 25, 2013 |access-date=August 25, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151008163642/https://www.britannica.com/technology/Microsoft-PowerPoint |url-status=live |archive-date=October 8, 2015 |quote= ... in 1987 ... n July of that year, the Microsoft Corporation, in its first significant software acquisition, purchased the rights to PowerPoint for $14 million.}}</ref> This was Microsoft's first significant acquisition,<ref name="NYT-lead">{{cite news |last=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=July 31, 1987 |title=Microsoft Buys Software Unit |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/31/business/company-news-microsoft-buys-software-unit.html <!-- full URL required --> |department=Company News |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |volume=CXXXV |issue=46,717 |publication-date=July 31, 1987 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150524214338/http://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/31/business/company-news-microsoft-buys-software-unit.html |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=August 25, 2017 |quote= ... the acquisition of Forethought is the first significant one for Microsoft, which is based in Redmond, Wash. Forethought would remain in Sunnyvale, giving Microsoft a Silicon Valley presence.}}</ref> and Microsoft set up a new business unit for PowerPoint in ] where Forethought had been located.<ref name="NYT-lead"/> | |||
| '''Microsoft PowerPoint''' is a ] developed by ]. It is part of the ] system. Microsoft PowerPoint runs on ] and the ] computer operating systems. | |||
| PowerPoint became a component of the ] suite, first offered in 1989 for Macintosh<ref>{{Cite news |last=Flynn |first=Laurie |date=June 19, 1989 |title=The Microsoft Office Bundles 4 Programs |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lzAEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA17 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=11 |issue=25 |page=37 <!-- Note pg in URL is correctly off by 20, PA37 doesn't work --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085716/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym7SWz2j?url=https://filetea.me/t1s8ljg1ymETEWjSQxw5r2mMQ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 25, 2017}}</ref> and in 1990 for ],<ref>{{Cite news |last=Johnston |first=Stuart J. |date=October 1, 1990 |title=Office for Windows Bundles Popular Microsoft Applications |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VTwEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PT17 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=12 |issue=40 |page=16 <!-- Note pg in URL is correctly off by 1 and PT, PA17 doesn't work --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085840/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym8WVBD3?url=https://filetea.me/t1s24zfAGB3Qm6bLZB2JeRKdg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 25, 2017}}</ref> which bundled several Microsoft apps. Beginning with PowerPoint 4.0 (1994), PowerPoint was integrated into Microsoft Office development, and adopted shared common components and a converged user interface.<ref name="austin-timeline-2001-lead">{{Cite web |url=http://www.gbuwizards.com/files/powerpoint-timeline-to-1995-dennis-austin.pdf |title=PowerPoint Version Timeline (to PowerPoint 7.0, 1995) |last=Austin |first=Dennis |date=2001 |website=GBU Wizards of Menlo Park |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528055458/https://www.webcitation.org/6sWbRP9tx?url=https://filetea.me/n3wNc4xaoNgRPCO0cpdXD8mng |url-status=live |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| It is widely used by business people, educators, students, and trainers and is among the most prevalent forms of ]. Beginning with Microsoft Office 2003, Microsoft revised branding to emphasize PowerPoint's identity as a component within the Office suite: Microsoft began calling it Microsoft Office PowerPoint instead of merely Microsoft PowerPoint. The current version of Microsoft Office PowerPoint is Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007. As a part of Microsoft Office, Microsoft Office PowerPoint has become the world's most widely used presentation program. | |||
| PowerPoint's market share was very small at first, prior to introducing a version for Microsoft Windows, but grew rapidly with the growth of Windows and of Office.<ref>{{cite book |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |title=Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint |year=2012 |publisher=Vinland Books |isbn=978-0-9851424-0-7 <!-- hardcover ed --> |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RC_5OCQQJ7YC |access-date=August 12, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624031005/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/sweating-bullets/gaskins-sweating-bullets-webpdf-isbn-9780985142414.pdf <!-- webpdf ed --> |url-status=live |archive-date=June 24, 2017}}</ref>{{Rp|pages=402–404}} Since the late 1990s, PowerPoint's worldwide market share of presentation software has been estimated at 95 percent.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Thielsch |first1=Meinald T. |last2=Perabo |first2=Isabel |date=May 2012 |title=Use and Evaluation of Presentation Software |url=http://www.thielsch.org/download/paper/Thielsch_Perabo_2012.pdf |journal=Technical Communication |volume=59 |issue=2 |pages=112–123 |issn=0049-3155 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160809191010/http://www.thielsch.org/download/paper/Thielsch_Perabo_2012.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=August 9, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=For many years, Microsoft has led the market with its program PowerPoint. Zongker and Salesin (2003) estimated a market share of 95% in 2003, and a Forrester study (Montalbano, 2009) widely confirmed this number, stating that only 8% of enterprise customers use alternative products.}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| The original Microsoft Office PowerPoint was developed by ] and software developer ] as '''Presenter''' for ]. <ref></ref>. | |||
| PowerPoint was originally designed to provide visuals for group presentations within business organizations, but has come to be widely used in other communication situations in business and beyond.<ref name="Britannica-uses-lead">{{Cite encyclopedia |encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Britannica |title=Microsoft PowerPoint |url=https://www.britannica.com/technology/Microsoft-PowerPoint |date=November 25, 2013 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint was developed for business use but has wide applications elsewhere such as for schools and community organizations |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170828152107/https://www.britannica.com/technology/Microsoft-PowerPoint |archive-date=August 28, 2017 |url-status=dead |df=mdy-all }}</ref> The wider use led to the development of the PowerPoint presentation as a new form of communication,<ref name="Davies">{{Cite magazine |last=Davies |first=Russell |date=May 26, 2016 |title=29 Reasons to Love PowerPoint |url=https://www.wired.co.uk/article/powerpoint-birthday-defence |magazine=Wired UK |issn=1758-8332 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170815170737/http://www.wired.co.uk/article/powerpoint-birthday-defence |url-status=live |archive-date=August 15, 2017 |access-date=September 6, 2017}} {{Cite web |url=http://www.russelldavies.com/writing/tuftepowerpoint/tuftepoint.html |title=29 Bullets |access-date=October 26, 2017 |archive-date=September 11, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170911084850/http://www.russelldavies.com/writing/tuftepowerpoint/tuftepoint.html |url-status=bot: unknown }}</ref> with strong reactions including advice that it should be used less,<ref name="Tufte-2003-2006">{{Cite book |last=Tufte |first=Edward |author-link=Edward Tufte |year=2006 |orig-year=1st ed. 2003, 24 pg. |title=The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint: Pitching Out Corrupts Within |edition=2nd |location=Cheshire, Connecticut |publisher=Graphics Press LLC |pages=32 |isbn=978-0-9613921-6-1}}</ref> differently,<ref name="Mayer-Atkinson-2004">{{Cite web |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228893840 |title=Five ways to reduce PowerPoint overload |last1=Atkinson |first1=Cliff |last2=Mayer |first2=Richard E. |author-link2=Richard E. Mayer |date=April 23, 2004 |version=Revision 1.1 |website=ResearchGate |format=PDF |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZMK2qMHz?url=https://filetea.me/t1sWlhUAjlwTqxmEj6Ds9ZT4Q |url-status=live |archive-date=June 17, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017 }}</ref> or better.<ref name="Kosslyn-2007">{{Cite book |last=Kosslyn |first=Stephen M. |author-link=Stephen Kosslyn |year=2007 |pages=222 |title=Clear and to the Point: Eight Psychological Principles for Compelling PowerPoint Presentations |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-532069-5}}</ref> | |||
| Forethought released PowerPoint 1.0 in April ] for the ]. It ran in black and white, generating text-and-graphics pages for overhead transparencies. A new full color version of PowerPoint shipped a year later after the first color Macintosh came to market. | |||
| The first PowerPoint version (Macintosh 1987) was used to produce overhead transparencies,<ref name="CACM-Gaskins-2007-lead">{{Cite journal |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=December 2007 |title=PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics |url=https://www.academia.edu/1866305 |department=Viewpoint |journal=] |publication-date=December 2007 |volume=50 |issue=12 |page=17 |issn=0001-0782 |doi=10.1145/1323688.1323710 |s2cid=48306 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107161639/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-at-20-cacm-vol50-no12-dec-2007-p15-p17.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=May 27, 2015 }}</ref> the second (Macintosh 1988, Windows 1990) could also produce color 35 mm slides.<ref name="CACM-Gaskins-2007-lead" /> The third version (Windows and Macintosh 1992) introduced video output of virtual slideshows to digital projectors, which would over time replace physical transparencies and slides.<ref name="CACM-Gaskins-2007-lead" /> A dozen major versions since then have added additional features and modes of operation<ref name="austin-timeline-2001-lead" /> and have made PowerPoint available beyond Apple Macintosh and Microsoft Windows, adding versions for ], ], and web access.<ref>{{Cite web |date=April 19, 2022 |title=Compare PowerPoint features on different platforms |url=https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/compare-powerpoint-features-on-different-platforms-90986850-227c-4b25-938e-1c5838166b8b |access-date=October 23, 2022 |website=Microsoft Support}}</ref> | |||
| Microsoft Corporation purchased Forethought and its PowerPoint software product for $14 million on July 31, ].<ref>{{cite news | url=http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9B0DE7DD1530F932A05754C0A961948260 | title=COMPANY NEWS; Microsoft Buys Software Unit | date=July 31, 1987 | work=New York Times | accessdate=2006-12-02}}</ref> In ] the first ] versions were produced for ]. Since ], PowerPoint is included in ] suite of applications -- except for the Basic Editions of the suite. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| The ] version, part of the Microsoft Office XP suite and also available as a stand-alone product, provided features such as comparing and merging changes in presentations, the ability to define ] paths for individual shapes, pyramid/radial/target and ]s, multiple slide masters, a "task pane" to view and select text and objects on the ], ] protection for presentations, automatic "photo album" generation, and the use of "smart tags" allowing people to quickly select the format of text copied into the presentation. | |||
| ===Creation at Forethought (1984–1987)=== | |||
| PowerPoint was created by ] and ] at a software ] in ] named ]<ref>{{Cite news |last=Gomes |first=Lee |date=June 20, 2007 |title=PowerPoint Turns 20, As Its Creators Ponder A Dark Side to Success |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB118228116940840904 |url-access=subscription <!-- but archive is ungated --> |department=Portals |newspaper=Wall Street Journal |issn=0099-9660 |edition=US |volume=CCXLIX |issue=143 |page=B1 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528060821/https://www.webcitation.org/6sthPU4jp?url=https://filetea.me/n3wpdnAIxrfQpWtQBrQFab9sg |url-status=live | archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 22, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint's two creators ... Robert Gaskins was the visionary entrepreneur ... with major programming done by Dennis Austin, an old chum ... .}}</ref> Forethought had been founded in 1983 to create an integrated environment and applications for future personal computers that would provide a graphical user interface, but it had run into difficulties requiring a "restart" and new plan.<ref name="Brock-2017-re-Forethought">{{Cite journal |last=Brock |first=David C. |date=October 31, 2017 |title=The Improbable Origins of PowerPoint |url= https://spectrum.ieee.org/the-improbable-origins-of-powerpoint |department=History |journal=] |publication-date=November 2, 2017 |volume=54 |issue=11 |pages=42–49 |issn=0018-9235 |doi=10.1109/MSPEC.2017.8093800 |s2cid=27013411 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171102205858/https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-history/cyberspace/the-improbable-origins-of-powerpoint |url-status=live |archive-date=November 2, 2017 |access-date=November 2, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint was not at all in their original plan. ... Pohlman and Campbell's idea was to bring a graphical-software environment like the Xerox Alto's to the hugely popular but graphically challenged PC. ... Rather than liquidate the firm, management and investors decided to "restart" Forethought ... .}}</ref> | |||
| On July 5, 1984, Forethought hired Robert Gaskins as its vice president of product development<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history">{{Cite book |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |title=Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint |year=2012 |publisher=Vinland Books |isbn=978-0-9851424-0-7 <!-- hardcover ed --> |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RC_5OCQQJ7YC |access-date=August 12, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624031005/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/sweating-bullets/gaskins-sweating-bullets-webpdf-isbn-9780985142414.pdf <!-- webpdf ed --> |url-status=live |archive-date=June 24, 2017}}</ref>{{Rp|page=51}} to create a new application that would be especially suited to the new ] personal computers, such as the ] and later ].<ref name="Brock-2017-re-PowerPoint">{{Cite journal |last=Brock |first=David C. |date=October 31, 2017 |title=The Improbable Origins of PowerPoint |url= https://spectrum.ieee.org/the-improbable-origins-of-powerpoint |department=History |journal=] |publication-date=November 2, 2017 |volume=54 |issue=11 |pages=42–49 |issn=0018-9235 |doi=10.1109/MSPEC.2017.8093800 |s2cid=27013411 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171102205858/https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-history/cyberspace/the-improbable-origins-of-powerpoint |url-status=live |archive-date=November 2, 2017 |access-date=November 2, 2017 |quote= ... Forethought began to develop a software product of its own. This new effort was the brainchild of Robert Gaskins, an accomplished computer scientist who'd been hired to lead Forethought's product development.}}</ref> Gaskins produced his initial description of PowerPoint about a month later (August 14, 1984) in the form of a 2-page document titled "Presentation Graphics for Overhead Projection."<ref name="presenter-proposal">{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-original-proposal-1984-aug-14.pdf |title=Presentation Graphics for Overhead Projection |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=August 14, 1984 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151106153939/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-original-proposal-1984-aug-14.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=November 6, 2015 |access-date=August 21, 2017}}</ref> By October 1984, Gaskins had selected Dennis Austin to be the developer for PowerPoint.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/access/text/2012/06/102745695-01-acc.pdf |title=Beginnings of PowerPoint: A Personal Technical Story |last=Austin |first=Dennis |date=2009 |website=Computer History Museum, Archive |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141112105359/http://archive.computerhistory.org/resources/access/text/2012/06/102745695-01-acc.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=November 12, 2014 |access-date=August 21, 2017 |quote=In October ...I joined Forethought ... . }}</ref> Gaskins and Austin worked together on the definition and design of the new product for nearly a year, and produced the first specification document dated August 21, 1985.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/austin-gaskins-powerpoint-design-1985-aug-21.pdf |title=Presenter Design |last1=Austin |first1=Dennis |last2=Gaskins |first2=Robert |author-link2=Robert Gaskins |date=August 21, 1985 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107153656/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/austin-gaskins-powerpoint-design-1985-aug-21.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=April 22, 2015}}</ref> This first design document showed a product as it would look in Microsoft ],<ref>{{Cite news |last=Foster |first=Edward |date=July 1, 1985 |title=Microsoft Ships Windows: Once Written Off Because of Delays, Windows Now Seen as a Contender Against Topview |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EC8EAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA17 |department=News, Software |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=7 |issue=26 |page=17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170824182047/https://books.google.com/books?id=EC8EAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA17#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live |archive-date=August 24, 2017 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote='We're quite happy to have people know our plan is to leverage our Mac experience with Microsoft Windows,' says Robert Gaskins, vice president of development.}}</ref> which at that time had not been released.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.technologizer.com/2010/11/20/the-secret-origin-of-windows |title=The Secret Origin of Windows |last=Trower |first=Tandy |author-link=Tandy Trower |date=November 20, 2010 |website=Technologizer |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110123114439/http://technologizer.com/2010/11/20/the-secret-origin-of-windows-2/comment-page-1/ |url-status=live |archive-date=January 23, 2011 |access-date=August 23, 2017 |quote=Windows 1.0 shipped on November 20th, 1985 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| Microsoft Office PowerPoint ] did not differ much from the ]/XP version. It enhanced collaboration between co-workers and featured "Package for CD", which makes it easy to burn presentations with ] content and the viewer on ] for distribution. It also improved support for graphics and multimedia. | |||
| Development from that spec was begun by Austin in November 1985, for Macintosh first.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history" />{{Rp|page=104}} About six months later, on May 1, 1986, Gaskins and Austin chose a second developer to join the project, Thomas Rudkin.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history" />{{Rp|page=149}} Gaskins prepared two final product specification marketing documents in June 1986; these described a product for both Macintosh and Windows.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-marketing-analysis-1986-jun-27.pdf |title=Presenter Product Marketing Analysis |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=June 27, 1986 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107154620/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-marketing-analysis-1986-jun-27.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-summary-and-review-1986-jul-15.pdf |title=Presenter New Product Summary and Review |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=July 15, 1986 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107161645/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-summary-and-review-1986-jul-15.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> At about the same time, Austin, Rudkin, and Gaskins produced a second and final major design specification document, this time showing a Macintosh look.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/austin-rudkin-gaskins-powerpoint-spec-1986-may-22.pdf |title=Presenter Specification |last1=Austin |first1=Dennis |last2=Rudkin |first2=Thomas |last3=Gaskins |first3=Robert |author-link3=Robert Gaskins |date=May 22, 1986 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107154652/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/austin-rudkin-gaskins-powerpoint-spec-1986-may-22.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| The current version, ], released in ] ], brought major changes of the ] and enhanced graphic capabilities. <ref>http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/powerpoint/HA100742261033.aspx</ref> | |||
| Throughout this development period, the product was called "Presenter". Then, just before release, there was a last-minute check with Forethought's lawyers to register the name as a trademark, and "Presenter" was unexpectedly rejected because it had already been used by someone else. Gaskins says that he thought of "PowerPoint", based on the product's goal of "empowering" individual presenters, and sent that name to the lawyers for clearance, while all the documentation was hastily revised.<ref name="Indezine-2012">{{cite interview |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |subject-link=Robert Gaskins |interviewer=Geetesh Bajaj |title=PowerPoint at 25: Conversation with Robert Gaskins |url=http://blog.indezine.com/2012/08/powerpoint-at-25-conversation-with.html#Named |date=August 13, 2012 |access-date=August 21, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150404114624/http://blog.indezine.com/2012/08/powerpoint-at-25-conversation-with.html |url-status=live |archive-date=April 4, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| == Operation == | |||
| In PowerPoint, as in most other presentation software, text, graphics, movies, and other objects are positioned on individual pages or "slides". The "slide" analogy is a reference to the ], a device which has become somewhat ] due to the use of PowerPoint and other presentation software. Slides can be printed, or (more often) displayed on-screen and navigated through at the command of the presenter. Slides can also form the basis of ]. | |||
| Funding to complete development of PowerPoint was assured in mid-January 1987, when a new Apple Computer venture capital fund, called Apple's Strategic Investment Group,<ref>{{Cite news |last=Ranney |first=Elizabeth |date=May 5, 1986 |title=Apple Proceeding With Strategic Investment Plans |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Qi8EAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA3 |department="Just Heard" column |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=8 |issue=18 |page=3 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085758/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym7tmtXq?url=https://filetea.me/t1swkwPNQcNT1OVxxWVGlbCeA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote= Eilers stressed ... 'we are going to make minority investments in companies that add value to Apple computers and thereby increase the sales of Apple computers over time.' }}</ref> selected PowerPoint to be its first investment.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history" />{{Rp|pages=169–171}} A month later, on February 22, 1987, Forethought announced PowerPoint at the Personal Computer Forum in ]; ], the CEO of Apple, appeared at the announcement and said "We see desktop presentation as potentially a bigger market for Apple than desktop publishing."<ref>{{Cite news |last=Mace |first=Scott |date=March 2, 1987 |title=Presentation Package Lets Users Control Look |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1TAEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA5 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=9 |issue=9 |page=5 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085435/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym2krMYP?url=https://filetea.me/t1sKNh0ZTl2S8xyckHWoi2ywg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| PowerPoint provides three types of movements. Entrance, emphasis, and exit of elements on a slide itself are controlled by what PowerPoint calls ]. Transitions, on the other hand are movements between slides. These can be animated in a variety of ways. The overall design of a presentation can be controlled with a master slide; and the overall structure, extending to the text on each slide, can be edited using a primitive ]. | |||
| Presentations can be saved and run in any of the ]s: the default ''.ppt'' (presentation), ''.pps'' (PowerPoint Show) or ''.pot'' (template). In PowerPoint 2007 the XML-based file formats ''.pptx'', ''.ppsx'' and ''.potx'' have been introduced. | |||
| PowerPoint 1.0 for Macintosh shipped from manufacturing on April 20, 1987, and the first production run of 10,000 units was sold out.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-history-of-forethought-1987-may-25.pdf |title=Forethought Restart Completed (A Brief History) |page=9 |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=May 25, 1987 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107154610/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-history-of-forethought-1987-may-25.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=We completed PowerPoint so as to ship it on schedule on April 20. By early May, we had shipped about $1,000,000 worth of PowerPoint and exhausted the first printing of 10,000 copies.}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Acquisition by Microsoft (1987–1992)=== | |||
| ==Compatibility== | |||
| By early 1987, Microsoft was starting to plan a new application to create presentations, an activity led by ], who was head of marketing for the Applications Division.<ref name="raikes-history-pt2-2010-hist">{{Cite web |last=Microsoft Corporation |title=The History of Microsoft—The Jeff Raikes Story, Part Two |website=Channel9 videos, Microsoft Developer Network |date=April 8, 2010 |url=https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/shows/history/history-of-microsoft-jeff-raikes-story-part-two |at=05:42 to 07:18 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170824185801/https://channel9.msdn.com/Series/History/The-History-of-Microsoft-The-Jeff-Raikes-Story-Part-Two |url-status=live |archive-date=August 24, 2017 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=Jeff Raikes talks ... about having an idea in 1987 for a presentation product before discovering Forethought, which had a product called PowerPoint.}} A of the relevant section is also available. <!--backup: Archived at {{cbignore}} and the {{cbignore}}: {{webarchive|format=addlarchives|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TCpcI_WCiI8 |date=February 25, 2011 |title=The History of Microsoft—The Jeff Raikes Story (Part 2 of 2)}}{{cbignore}} --></ref> Microsoft assigned an internal group to write a specification and plan for a new presentation product.<ref>{{Cite news |last=May |first=Trish |date=January 17, 2010 |title=The Road to the Cure |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/17/jobs/17boss.html |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |page=BU7 |edition=New York |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220620033145/https://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/17/jobs/17boss.html?_r=0 |url-status=live |archive-date=June 20, 2022 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=I wrote and presented a proposal to Bill Gates for a new piece of software for the personal computer, specifically to help people create presentations ... .}}</ref> They contemplated an acquisition to speed up development, and in early 1987 Microsoft sent a letter of intent to acquire ]'s product called ], an outlining program that could print its outlines as bullet charts.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Swaine |first=Michael |title=Calling Apple's Bluff |website=Dr. Dobb's Journal |date=September 1, 1991 |url=http://www.drdobbs.com/calling-apples-bluff/184408623 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6Zba5qXQj?url=https://filetea.me/t1sWOUvVIUxQ1q3s2Yn7UdfxA |url-status=live |archive-date=June 27, 2015 |quote=I had a meeting with Bill Gates in, I guess it was February of '87 ... We worked out a letter of intent.}}</ref> During this preparatory activity Raikes discovered that a program specifically to make overhead presentations was already being developed by Forethought, Inc., and that it was nearly completed.<ref name="raikes-history-pt2-2010-hist" /> Raikes and others visited Forethought on February 6, 1987, for a confidential demonstration.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history" />{{Rp|page=173}} | |||
| As Microsoft Office files are often sent from one computer user to another, arguably the most important feature of any presentation software—such as ]'s ], or ]—has become the ability to open Microsoft Office PowerPoint files. However, because of PowerPoint's ability to embed content from other applications through ], some kinds of presentations become highly tied to the ] platform, meaning that even PowerPoint on ] cannot always successfully open its own files originating in the Windows version. This has led to a movement towards ]s, such as ] and ] ]. | |||
| Raikes later recounted his reaction to seeing PowerPoint and his report about it to ], who was initially skeptical:<ref name="raikes-history-pt2-2010-hist" /> | |||
| == Cultural effects == | |||
| {{Blockquote|I thought, "software to do overheads—that's a great idea." I came back to see Bill. I said, "Bill, I think we really ought to do this;" and Bill said, "No, no, no, no, no, that's just a feature of Microsoft Word, just put it into Word." ... And I kept saying, "Bill, no, it's not just a feature of Microsoft Word, it's a whole genre of how people do these presentations." And, to his credit, he listened to me and ultimately allowed me to go forward and ... buy this company in Silicon Valley called Forethought, for the product known as PowerPoint.}} | |||
| Supporters and critics generally agree<ref>http://www.shkaminski.com/Classes/Handouts/powerpoint.htm</ref><ref>http://www.bioscience.heacademy.ac.uk/journal/vol2/beej-2-3.htm</ref><ref>http://technologysource.org/article/use_of_powerpoint_in_teaching_comparative_politics/</ref> that the ease of use of presentation software can save a lot of time for people who otherwise would have used other types of visual aid—hand-drawn or mechanically typeset slides, blackboards or whiteboards, or overhead projections. Ease of use also encourages those who otherwise would not have used visual aids, or would not have given a presentation at all, to make presentations. As PowerPoint's style, ], and ] abilities have become more sophisticated, and as PowerPoint has become generally easier to produce presentations with (even to the point of having an "AutoContent Wizard" suggesting a structure for a presentation—initially started as a joke by the Microsoft engineers but later included as a serious feature in the ]s), the difference in needs and desires of presenters and audiences has become more noticeable. | |||
| When PowerPoint was released by Forethought, its initial press was favorable; the ''Wall Street Journal'' reported on early reactions: {{" '}}I see about one product a year I get this excited about,' says Amy hora, a consultant in Bala Cynwyd, Pa. 'People will ].{{' "}}<ref>{{Cite news |last=Carroll |first=Paul B. |date=March 6, 1987 |title=New Software Simplifies Show and Tell |url=https://secure.pqarchiver.com/wsj/doc/135282891.html |url-access=subscription <!-- but archive is ungated --> |department=Technology |newspaper=Wall Street Journal |issn=0099-9660 |page=33 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528060702/https://www.webcitation.org/6stGJoV2i?url=https://filetea.me/n3wkyU6jExiTquT65RsohieMQ |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 21, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ==Criticism== | |||
| On April 28, 1987, a week after shipment, a group of Microsoft's senior executives spent another day at Forethought to hear about initial PowerPoint sales on Macintosh and plans for Windows.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history" />{{Rp|page=191}} The following day, Microsoft sent a letter to Dave Winer withdrawing its earlier letter of intent to acquire his company,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Winer |first=Dave |author-link=Dave Winer |title=Microsoft rejection letter, 1987 |website=Scripting News |date=April 10, 2010 |url=http://scripting.com/stories/2010/04/10/microsoftRejectionLetter19.html |access-date=August 21, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150907205437/http://scripting.com/stories/2010/04/10/microsoftRejectionLetter19.html |url-status=live |archive-date=September 7, 2015}}</ref> and in mid-May 1987 Microsoft sent a letter of intent to acquire Forethought.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/microsoft-letter-of-intent-for-forethought-1987-may-13.pdf |title= Letter of Intent |last=Shirley |first=Jon |author-link=Jon Shirley |date=May 13, 1987 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140517183105/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/microsoft-letter-of-intent-for-forethought-1987-may-13.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=May 17, 2014 |access-date=August 21, 2017}}</ref> As requested in that letter of intent, Robert Gaskins from Forethought went to Redmond for a one-on-one meeting with Bill Gates in early June 1987,<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-history" />{{Rp|page=197}} and by the end of July an agreement was concluded for an acquisition. The ''New York Times'' reported:<ref>{{Cite news |last=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=July 31, 1987 |title=Microsoft Buys Software Unit |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/31/business/company-news-microsoft-buys-software-unit.html <!-- full URL required --> |department=Company News |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |volume=CXXXV |issue=46,717 |publication-date=July 31, 1987 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150524214338/http://www.nytimes.com/1987/07/31/business/company-news-microsoft-buys-software-unit.html |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=August 21, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| One major source of criticism of PowerPoint comes from Yale University professor emeritus of statistics and graphic design ], who criticizes many ] of the software:<ref>Edward Tufte. ''The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint: Pitching Out Corrupts Within'' (Second edition). Graphics Press, 2006. ISBN 0961392169</ref> | |||
| * It is used to guide and reassure a presenter, rather than to enlighten the audience; | |||
| * Unhelpfully simplistic tables and charts, resulting from the low resolution of computer displays; | |||
| * The outliner causing ideas to be arranged in an unnecessarily deep hierarchy, itself subverted by the need to restate the hierarchy on each slide; | |||
| * Enforcement of the audience's linear progression through that hierarchy (whereas with handouts, readers could browse and relate items at their leisure); | |||
| * Poor typography and chart layout, from presenters who are poor designers and who use poorly designed templates and default settings; | |||
| * Simplistic thinking, from ideas being squashed into bulleted lists, and stories with beginning, middle, and end being turned into a collection of disparate, loosely disguised points. This may present a kind of image of objectivity and neutrality that people associate with science, technology, and "bullet points". | |||
| * Every slideshow made usually ends up looking like everybody elses due to the provided templates for slideshows. | |||
| Tufte's criticism of the use of PowerPoint has extended to its use by NASA engineers in the events leading to the ]. Tufte's analysis of a representative NASA PowerPoint slide is included in a full page sidebar entitled "Engineering by Viewgraphs" <ref></ref> in Volume 1 of the ] report. | |||
| {{Blockquote| ... July 30, 1987— The Microsoft Corporation announced its first significant software acquisition today, paying $14 million for Forethought Inc. of Sunnyvale, Calif. Forethought makes a program called PowerPoint that allows users of Apple Macintosh computers to make overhead transparencies or flip charts. ... he acquisition of Forethought is the first significant one for Microsoft, which is based in Redmond, Wash. Forethought would remain in Sunnyvale, giving Microsoft a Silicon Valley presence. The unit will be headed by Robert Gaskins, Forethought's vice president of product development.}} | |||
| Research has show that far from helping the audience follow the presentation, Presenter Focused slideware reduces audience engagement, they actually switch off when they have finished reading the slide and wait for the next one, only really paying attention when they see something interesting. This can have a detrimental effect on a presentation. {{Fact|date=October 2007}} | |||
| Microsoft's president ] offered his company's motivation for the acquisition: {{" '}}We made this deal primarily because of our belief in desktop presentations as a product category. ... Forethought was first to market with a product in this category.{{' "}}<ref name="Shirley-comments">{{Cite news |last1=Parker |first1=Rachel |date=August 3, 1987 |title=Microsoft Acquires Forethought, Publisher of PowerPoint Package |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1zsEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA8 |department=News |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=9 |issue=31 |page=8 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZVlHDCYN?url=https://filetea.me/t1sZ0YKQbIxQxKUb7kT6fp3Xw |url-status=live |archive-date=June 23, 2015 |access-date=August 22, 2017 |quote=The Forethought group will become Microsoft's Graphics Business Unit, forming a permanent Microsoft development and marketing facility in Sunnyvale, California. With a site in California, Microsoft hopes to recruit programmers who might not want to relocate to Washington, Shirley said.}}</ref> Microsoft had 50% market share in Macintosh applications, and led in three categories; Raikes said that after the acquisition it would lead in five categories. (Forethought distributed the database ], which Microsoft wanted to continue marketing.) The company intended for Forethought to be its Silicon Valley base to develop and market future graphics software,<ref name="keefe19870803">{{Cite magazine |last=Keefe |first=Patricia |date=1987-08-03 |title=Microsoft buys Forethought |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oNqVCaMq9mUC&lpg=PP101&pg=PP101#v=onepage&q&f=false |access-date=2024-11-01 |magazine=Computerworld |page=81}}</ref> so set up within its Applications Division, an independent "Graphics Business Unit" for PowerPoint, the first Microsoft application group distant from the main Redmond location. The company hoped to hire employees uninterested in living in Washington state.<ref name="Shirley-comments" /> All the PowerPoint people from Forethought joined Microsoft, and the new location was headed by Robert Gaskins, with Dennis Austin and Thomas Rudkin leading development. PowerPoint 1.0 for Macintosh was modified to indicate the new Microsoft ownership and continued to be sold. A year after the acquisition, Gaskins reported that all seven Forethought PowerPoint employees had stayed with Microsoft, and the Graphics Business Unit had hired 12 employees, many of whom did not want to move to Redmond. The GBU had moved to a new location on ] in ]; it was much larger than needed for 19 people, but Gaskins wrote that he and Microsoft wanted future capacity as the company grew in Silicon Valley.<ref name="GBU-first-year-1988">{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-gbu-first-year-report-to-microsoft-1988-aug-08.pdf |title=Results of Microsoft's Graphics Business Unit after Our First Year |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=August 8, 1988 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |type=Microsoft Memo |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107153728/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-gbu-first-year-report-to-microsoft-1988-aug-08.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 23, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| == Versions == | |||
| Versions for the ] include: | |||
| A new PowerPoint 2.0 for Macintosh, adding color 35 mm slides, shipped in May 1988,<ref name="GBU-first-year-1988" /> and again received good reviews.<ref name="pournelle198901">{{Cite magazine |last=Pournelle |first=Jerry |author-link=Jerry Pournelle |date=January 1989 |title=To the Stars |url=https://archive.org/stream/byte-magazine-1989-01/1989_01_BYTE_14-01_PC_Communications_and_Annual_Awards_and_Digitizing_Tablets#page/n151/mode/2up <!-- adjusted URL and page number to exact ref, not article beginning --> |magazine=BYTE |issn=0360-5280 |volume=14 |issue=1 |page=120 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20170930222615/https://archive.org/stream/byte-magazine-1989-01/1989_01_BYTE_14-01_PC_Communications_and_Annual_Awards_and_Digitizing_Tablets%23page/n151/mode/2up |url-status=live |archive-date=September 30, 2017 |access-date=September 30, 2017 |quote=I'll just say that if you're in the business of putting on briefings and otherwise making presentations, you might want to seriously contemplate getting a Mac II just so you can use this program; it's that good. Highly recommended. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> The same PowerPoint 2.0 product re-developed for Windows was shipped two years later, in mid-1990, at the same time as ].<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XlEEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA15 |last=Borzo |first=Jeanette |title=PowerPoint users pleased by changes |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=14 |issue=20 |date=May 18, 1992 |page=15 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090441/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnF6x0m9?url=https://filetea.me/t1s93DMYfS1T7Gs3VyxWzxRZw |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> Much of the color technology was the result of a joint development partnership with ], the dominant presentation services company.<ref name="GBU-first-year-genigraphics">{{cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-gbu-first-year-report-to-microsoft-1988-aug-08.pdf |title=Results of Microsoft's Graphics Business Unit after Our First Year |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=August 8, 1988 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |type=Microsoft Memo |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107153728/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-gbu-first-year-report-to-microsoft-1988-aug-08.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 23, 2017 |quote=We have learned a tremendous number of technical insights through working with the Genigraphics engineering group ... .}}</ref> | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 1.0 for Mac OS classic | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2.0 for Mac OS classic | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 3.0 for Mac OS classic | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 4.0 for Mac OS classic | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 98 (8.0) for Mac OS classic (Office 1998 for mac) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2001 (9.0) for ] (Office 2001 for mac) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint v. X (10.0) for ] (Office:mac v. X) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2004 (11.0) for ] ] | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2008 (12.0) for ] ] | |||
| PowerPoint 3.0, which was shipped in 1992 for both Windows and Mac, added live video for projectors and monitors, with the result that PowerPoint was thereafter used for delivering presentations as well as for preparing them. This was at first an alternative to overhead transparencies and 35 mm slides, but over time would come to replace them.<ref name="CACM-2007-Gaskins-history">{{Cite journal |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=December 2007 |title=PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics |url=https://www.academia.edu/1866305 |department=Viewpoint |journal=] |publication-date=December 2007 |volume=50 |issue=12 |pages=15–17 |issn=0001-0782 |doi=10.1145/1323688.1323710 |s2cid=48306 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107161639/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-at-20-cacm-vol50-no12-dec-2007-p15-p17.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017 }} The first three versions are described in the sidebar, "Presentation Formats and PowerPoint," p. 17.</ref> | |||
| ''Note: There is no PowerPoint 5.0 , 6.0 or 7.0 for Mac. There is no version 5.0 or 6.0 because the Windows 95 version was launched with Word 7. All of the Office 95 products have ] 2 capacity - moving data automatically from various programs - and PowerPoint '''7''' shows that it was contemporary with Word '''7'''. There was no version 7.0 made for mac to coincide with either version 7.0 for windows or PowerPoint 97.''<ref>http://www.bitbetter.com/powertips.htm</ref>.<ref>http://www.microsoft.com/mac/otherproducts/otherproducts.aspx?pid=otherproducts</ref>. | |||
| ] | |||
| Versions for ] include: | |||
| ===Part of Microsoft Office (since 1993)=== | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2.0 for Windows 3.0 | |||
| {{See also|History of Microsoft Office}} | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 3.0 for Windows 3.1 | |||
| PowerPoint had been included in ] from the beginning. PowerPoint 2.0 for Macintosh was part of the first Office bundle for Macintosh which was offered in mid-1989.<ref name="mac-office-1989">{{Cite news |last=Flynn |first=Laurie |date=June 19, 1989 |title=The Microsoft Office Bundles 4 Programs |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lzAEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA17 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=11 |issue=25 |page=37 <!-- Note pg in URL is correctly off by 20, PA37 doesn't work --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085716/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym7SWz2j?url=https://filetea.me/t1s8ljg1ymETEWjSQxw5r2mMQ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=A special promotion announced last week by Microsoft Corp. enables Macintosh customers to buy four of the company's business applications at a 35 percent discount. The special edition, called The Microsoft Office, includes Word 4.0, Excel 2.2, PowerPoint 2.01, and Mail 1.37. The package sells for $849; if purchased separately, the programs would cost $1,310, the company said. The promotion is available until the end of the year.}}</ref> When PowerPoint 2.0 for Windows appeared, a year later, it was part of a similar Office bundle for Windows, which was offered in late 1990.<ref name="win-office-1990">{{Cite news |last=Johnston |first=Stuart J. |date=October 1, 1990 |title=Office for Windows Bundles Popular Microsoft Applications |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VTwEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PT17 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=12 |issue=40 |page=16 <!-- Note pg in URL is correctly off by 1 and PT, PA17 doesn't work --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085840/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym8WVBD3?url=https://filetea.me/t1s24zfAGB3Qm6bLZB2JeRKdg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=Microsoft last week announced the release of The Microsoft Office for Windows, which bundles three of the company's popular Windows applications—Word, Excel, and PowerPoint—for significantly less than they would cost separately. The product brings to the Windows environment basically the equivalent of The Microsoft Office for Macintosh, which was announced a year ago.}}</ref> Both of these were bundling promotions, in which the independent applications were packaged together and offered for a lower total price.<ref name="mac-office-1989" /><ref name="win-office-1990"/> | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 4.0 (Office 4.x) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint for Windows 95 (version 7.0) — (Office 95) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 97 — (Office '97) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2000 (version 9.0) — (Office 2000) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2002 (version 10) — (Office XP) | |||
| * ] PowerPoint 2003 (version 11) — (Office 2003) | |||
| * ]-] PowerPoint 2007 (version 12) — (Office 2007) | |||
| PowerPoint 3.0 (1992) was again separately specified and developed,<ref name="austin-timeline-2001-lead" /> and was advertised and sold separately from Office.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Microsoft Corporation|date=March 1993 |title=New PowerPoint 3.0. Because powerful tools make powerful presentations |url=https://archive.org/stream/MacWorld_9303_March_1993#page/n1/mode/2up |type=advertisement |newspaper=MacWorld |issn=0741-8647 |volume=10 |issue=3 |pages=BA1–BA2 (inside front cover spread) |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528061023/https://www.webcitation.org/6sxzJkfQc?url=https://filetea.me/n3wgT51xEYjRt6alx4riYE5fg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> It was, as before, included in ], both for Windows and the corresponding version for Macintosh.<ref>{{Cite news |last=<!-- no byline --> |date=August 31, 1992 |title=Microsoft Office now has Mail, PowerPoint |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EVEEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA15 |department=Pipeline |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=14 |issue=35 |page=15 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161221124333/https://books.google.com/books/content?id=EVEEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA15&img=1&zoom=3&hl=en&sig=ACfU3U0RcN93Pp_McbAK0yCLoIO3niurMw |url-status=live |archive-date=December 21, 2016 |access-date=August 23, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ''Note: There is no PowerPoint version 5.0 or 6.0, because the Windows 95 version was launched with Word 7.0. All Office 95 products have ] 2 capacity - moving data automatically from various programs - and PowerPoint '''7.0''' shows that it was contemporary with Word '''7.0'''.'' | |||
| A plan to integrate the applications themselves more tightly had been indicated as early as February 1991, toward the end of PowerPoint 3.0 development, in an internal memo by Bill Gates:<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://antitrust.slated.org/www.iowaconsumercase.org/011607/0000/PX00577.pdf |title=Market Share of Applications in the United States |last=Gates |first=Bill |author-link=Bill Gates |date=February 19, 1991 |type=Microsoft Memo |website=Slated Antitrust (scanned court evidence files) |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170828062531/http://antitrust.slated.org/www.iowaconsumercase.org/011607/0000/PX00577.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=August 28, 2017 |access-date=August 22, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ==Other links== | |||
| {{wikibooks|Microsoft Office PowerPoint}} | |||
| {{Blockquote|Another important question is what portion of our applications sales over time will be a set of applications versus a single product. ... Please assume that we stay ahead in integrating our family together in evaluating our future strategies—the product teams WILL deliver on this. ... I believe that we should position the "OFFICE" as our most important application.}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| The move from bundling separate products to integrated development began with PowerPoint 4.0, developed in 1993–1994 under new management from Redmond.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/research/stocks/private/person.asp?personId=1123010&privcapId=1217370 |title=Executive Profile: Vijay R. Vashee |last=S&P Global Market Intelligence |date=2017 |website=Bloomberg.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170822230747/https://www.bloomberg.com/research/stocks/private/person.asp?personId=1123010&privcapId=1217370 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 22, 2017 |access-date=August 22, 2017 |quote=From 1982 ... Mr. Vashee served in various senior marketing, product management and executive positions at Microsoft. ... and as the General Manager for PowerPoint from 1992 to 1997 ... played a key role in the integration of PowerPoint into the Microsoft Office suite.}}</ref> The PowerPoint group in Silicon Valley was reorganized from the independent "Graphics Business Unit" (GBU) to become the "Graphics Product Unit" (GPU) for Office, and PowerPoint 4.0 changed to adopt a converged user interface and other components shared with the other apps in Office.<ref name="austin-timeline-2001-lead" /> | |||
| When it was released, the computer press reported on the change approvingly: "PowerPoint 4.0 has been re-engineered from the ground up to resemble and work with the latest applications in Office: Word 6.0, Excel 5.0, and Access 2.0. The integration is so good, you'll have to look twice to make sure you're running PowerPoint and not Word or Excel."<ref>{{Cite news |last=Fridlund |first=Alan |date=June 6, 1994 |title=PowerPoint 4.0 makes it into the big time |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hzgEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA95 |department=Reviews |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=16 |issue=23 |pages=95–98 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YmAg2aM9?url=https://filetea.me/t1sdT1vnOdpQOqyCVTgHxyljA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> Office integration was further underscored in the following version, PowerPoint 95, which was given the version number PowerPoint 7.0 (skipping 5.0 and 6.0) so that all the components of Office would share the same major version number.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.lassesen.com/msdn/using%20microsoft%20ole%20automation%20servers%20to%20develop%20solutions.pdf |title=Using Microsoft OLE Automation Servers to Develop Solutions |last=Lassesen |first=Ken |date=October 17, 1995 |website=Archive of Articles from MSDN Technology Group |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807073017/http://www.lassesen.com/msdn/using%20microsoft%20ole%20automation%20servers%20to%20develop%20solutions.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=Note that version 7.0 of a product is the same as a '95' designation, for example, Microsoft Excel 95 is the same as Microsoft Excel version 7.0.}}</ref> | |||
| Although PowerPoint by this point had become part of the integrated Microsoft Office product, its development remained in Silicon Valley. Succeeding versions of PowerPoint introduced important changes, particularly version 12.0 (2007) which had a very different shared Office "]" user interface, and a new shared ].<ref>{{cite web | url=https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa338198(v=office.12).aspx |last=Microsoft |title=Developer Overview of the User Interface for the 2007 Microsoft Office System |date=May 2006 |website=Microsoft Developer Network |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170707194202/https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa338198(v=office.12).aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=July 7, 2017 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> This marked the 20th anniversary of PowerPoint, and Microsoft held an event to commemorate that anniversary at its Silicon Valley Campus for the PowerPoint team there. Special guests were Robert Gaskins, Dennis Austin, and Thomas Rudkin, and the featured speaker was Jeff Raikes, all from PowerPoint 1.0 days, 20 years before.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/ |title=Microsoft's 20-year PPT party |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=August 17, 2007 |website=Robert Gaskins Home Page |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170824202650/http://www.robertgaskins.com/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 24, 2017 |access-date=August 24, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Since then major development of PowerPoint as part of Office has continued. New development techniques (shared across Office) for PowerPoint 2016 have made it possible to ship versions of PowerPoint 2016 for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and web access nearly simultaneously,{{citation needed|date=July 2018}} and to release new features on an almost monthly schedule.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/What-s-new-in-PowerPoint-2016-for-Windows-e8ef980c-5b12-4fff-ae3f-0819e6a21a1f |last=Microsoft |title=What's New in PowerPoint 2016 for Windows |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170731220459/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/What-s-new-in-PowerPoint-2016-for-Windows-e8ef980c-5b12-4fff-ae3f-0819e6a21a1f |url-status=live |archive-date=July 31, 2017 |access-date=August 26, 2017}}</ref> PowerPoint development is still carried out in Silicon Valley {{As of|2017|lc=y}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://careers.microsoft.com/jobdetails.aspx?ss=&pg=0&so=&rw=1&jid=305962&jlang=EN&pp=SS |title=Microsoft Careers: Senior Software Engineer (Job #1064262) |website=Microsoft Silicon Valley |date=August 17, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170821205245/https://careers.microsoft.com/jobdetails.aspx?ss=&pg=0&so=&rw=1&jid=305962&jlang=en&pp=ss |url-status=live |archive-date=August 21, 2017 |access-date=August 21, 2017 |quote=Come join the PowerPoint team ... in the heart of the Silicon Valley in Mountain View, CA. The PowerPoint team has the responsibility for the design, implementation, and testing ... .}}</ref> | |||
| In 2010, Jeff Raikes, who had most recently been President of the Business Division of Microsoft (including responsibility for Office),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://news.microsoft.com/2008/01/10/microsoft-announces-retirement-and-transition-plan-for-jeff-raikes-president-of-the-microsoft-business-division/ |title=Microsoft Announces Retirement and Transition Plan for Jeff Raikes, President of the Microsoft Business Division |last=Microsoft Corp. |date=January 10, 2008 |website=Microsoft News Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141128004953/http://news.microsoft.com/2008/01/10/microsoft-announces-retirement-and-transition-plan-for-jeff-raikes-president-of-the-microsoft-business-division/ |archive-date=November 28, 2014 |url-status=live |access-date=August 25, 2017 |quote=MBD has grown to include ... the Microsoft Office system ... .}}</ref> observed: "of course, today we know that PowerPoint is oftentimes the number two—or in some cases even the number one—most-used tool" among the applications in Office.<ref name="raikes-history-pt2-2010-hist" /> | |||
| ===Sales and market share=== | |||
| PowerPoint's initial sales were about 40,000 copies sold in 1987 (nine months), about 85,000 copies in 1988, and about 100,000 copies in 1989, all for Macintosh.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums">{{Cite book |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |title=Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint |year=2012 |publisher=Vinland Books |isbn=978-0-9851424-0-7 <!-- hardcover ed --> |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RC_5OCQQJ7YC |access-date=August 12, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624031005/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/sweating-bullets/gaskins-sweating-bullets-webpdf-isbn-9780985142414.pdf <!-- webpdf ed --> |url-status=live |archive-date=June 24, 2017}} Rounded unit sales figures are from the revenue tables (p. 403) adjusted to calendar years (p. 170) with the transfer pricing indicated (p. 182).</ref> PowerPoint's market share in its first three years was a tiny part of the total presentation market, which was very heavily dominated by ] applications on PCs.<ref name="PC-market-share-2005">{{cite web |url=https://arstechnica.com/features/2005/12/total-share |title=Total share: 30 years of personal computer market share figures |last=Reimer |first=Jeremy |date=December 14, 2005 |website=Ars Technica |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150512015006/http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0124/10/28217_181627497.shtml |url-status=live |archive-date=May 12, 2015 |access-date=August 25, 2017 |quote= ... the IBM PC platform ... an 84% share in 1990. The Macintosh stabilized at about 6% market share ... .}}</ref> The market leaders on MS-DOS in 1988–1989<ref>{{cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uzsEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PT33 <!-- URL is correctly off by 1 --> |last= <!-- table, no author --> |title=Egghead Software Sales: ... Graphics/DOS |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=11 |issue=1 |date=January 2, 1989 |page=32 <!-- URL is correctly off by one --> |access-date=September 9, 2017 |quote= Graphics/DOS ... 1 Harvard Graphics (Software Publishing), 2 Freelance + (Lotus) ... .}} </ref> were ] (introduced by ] in 1986<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=33QfOHT69aMC&pg=PA10 |last=Watt |first=Peggy |title=Software Publishing adds graphic package to Harvard line |newspaper=Computerworld |publisher=IDG Communications |issn=0010-4841 |volume=XX |issue=4 |date=January 27, 1986 |page=10 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6tM1bxeaU?url=https://filetea.me/n3wKciph2t9QxChZDY7ePKACg |url-status=live |archive-date=September 9, 2017 |access-date=September 9, 2017 |quote=... graphics presentation program, Harvard Presentation Graphics, introduced last week. ... will be available in March ... . |df=mdy-all }}</ref>) in first place, and ] (also introduced in 1986<ref>{{cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mTwEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA3 |last=Schemenaur |first=PJ |title=Lotus to Unveil Revision of Freelance |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=8 |issue=43 |date=October 27, 1986 |page=3 <!-- URL is correctly off by 2 --> |access-date=September 9, 2017 |quote= ... Freelance Plus, the first new release of Freelance since Lotus acquired the graphics package from Graphics Communications Inc. in June.}} </ref>) as a strong second.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UenCawr7OowC&pg=PA95 |last1=Howard |first1=Bill |last2=Kunkel |first2=Gerard |title=More Than Meets the Eye: Designing Great Graphics |newspaper=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |volume=7 |issue=16 |date=September 27, 1988 |page=95 |access-date=September 8, 2017 |quote=''Harvard Graphics'' gained the top spot this year, and now outsells ''Freelance Plus'' by a three-to-two margin.}} </ref> They were competing with more than a dozen other MS-DOS presentation products,<ref>{{cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UenCawr7OowC&pg=PA109 |last=<!-- 19 contributing authors --> |title=Designing Great Graphics: Desktop Solutions |newspaper=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |volume=7 |issue=16 |date=September 27, 1988 |pages=109–179 |access-date=September 8, 2017 |quote= 18 ... software packages reviewed ... .}} </ref> and Microsoft did not develop a PowerPoint version for MS-DOS.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Parker |first=Rachel |date=August 3, 1987 |title=Microsoft Acquires Forethought, Publisher of PowerPoint Package |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1zsEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA8 |department=News |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=9 |issue=31 |page=8 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZVlHDCYN?url=https://filetea.me/t1sZ0YKQbIxQxKUb7kT6fp3Xw |url-status=live |archive-date=June 23, 2015 |access-date=August 25, 2017 |quote= Shirley ... said that Microsoft has no firm plans currently to develop an MS-DOS version of PowerPoint.}}</ref> After three years, PowerPoint sales were disappointing. Jeff Raikes, who had bought PowerPoint for Microsoft, later recalled: "By 1990, it looked like it wasn't a very smart idea , because not very many people were using PowerPoint."<ref name="raikes-history-pt2-2010-hist" /> | |||
| This began to change when the first version for Windows, PowerPoint 2.0, brought sales up to about 200,000 copies in 1990 and to about 375,000 copies in 1991, with Windows units outselling Macintosh.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=403}} PowerPoint sold about 1 million copies in 1992, of which about 80 percent were for Windows and about 20 percent for Macintosh,<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=403}} and in 1992 PowerPoint's market share of worldwide presentation graphics software sales was reported as 63 percent.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=404}} By the last six months of 1992, PowerPoint revenue was running at a rate of over $100 million annually (${{Formatprice|{{Inflation|US|100000000|1987|r=1}}}} in present-day terms{{Inflation-fn|US}}).<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=405}}<ref>{{Cite news |last=Gates |first=Bill |author-link=Bill Gates |date=August 16, 1993 |title=Free market economics—not intervention—drives innovation |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qjsEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA44 |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=15 |issue=33 |department=Letters to the Editor |page=44 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085959/https://www.webcitation.org/6YmBkekB0?url=https://filetea.me/t1sRyyL0aAKRemuy8x8TwCfww |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 26, 2017 |quote=Data from the Software Publishers Association and other sources show that in 1992, while overall sales of application products grew only 12 percent, sales of Windows-based applications grew by nearly 100 percent. At least a dozen companies besides Microsoft have sold more than 1 million units of Windows applications.}}</ref> | |||
| Sales of PowerPoint 3.0 doubled to about 2 million copies in 1993, of which about 90 percent were for Windows and about 10 percent for Macintosh,<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=403}} and in 1993 PowerPoint's market share of worldwide presentation graphics software sales was reported as 78 percent.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=404}} In both years, about half of total revenue came from sales outside the U.S.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" />{{Rp|page=404}} | |||
| By 1997 PowerPoint sales had doubled again, to more than 4 million copies annually, representing 85 percent of the world market.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Ziff Davis Market Intelligence |date=September 1998 |title=The 800-Pound Gorilla of the Presentation Market |journal=Mobile Computing and Communications |page=95 |volume=9 |issue=9 |issn=1047-1952 |quote=... in 1997, without question the market leader was Microsoft Corp.'s PowerPoint, which sold more than 4 million copies and controls 85 percent of the market. |url=https://filetea.me/t1sEVBHlotISPCAVUKpeg2F5A |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6bxj2eryp?url=https://filetea.me/t1sEVBHlotISPCAVUKpeg2F5A |archive-date=October 1, 2015 |df=mdy-all }} {{webarchive|format=addlarchives|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170826204750/https://filetea.me/n3wiYbSzCLuStyw3hl7fDW0dA |date=August 26, 2017}}</ref> Also in 1997, an internal publication from the PowerPoint group said that by then over 20 million copies of PowerPoint were in use, and that total revenues from PowerPoint over its first ten years (1987 to 1996) had already exceeded $1 billion.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/belleville-peterson-somogyi-gbu-10-year-reunion-1997-apr.pdf |title=PowerPoint: The First Ten Years |last1=Belleville |first1=Catherine |last2=Peterson |first2=Lucy |last3=Somogyi |first3=Aniko |date=April 1997 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |pages=2, 8 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107153706/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/belleville-peterson-somogyi-gbu-10-year-reunion-1997-apr.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 25, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Since the late 1990s, PowerPoint's market share of total world presentation software has been estimated at 95 percent by both industry and academic sources.<ref name="Thielsch-Perabo-2012-history">{{Cite journal |last1=Thielsch |first1=Meinald T. |last2=Perabo |first2=Isabel |date=May 2012 |title=Use and Evaluation of Presentation Software |url=http://www.thielsch.org/download/paper/Thielsch_Perabo_2012.pdf |journal=Technical Communication |volume=59 |issue=2 |pages=112–123 |issn=0049-3155 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6bk3O2vuL?url=http://www.thielsch.org/download/paper/Thielsch_Perabo_2012.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=September 22, 2015 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |quote=For many years, Microsoft has led the market with its program PowerPoint. Zongker and Salesin (2003) estimated a market share of 95% in 2003, and a Forrester study (Montalbano, 2009) widely confirmed this number, stating that only 8% of enterprise customers use alternative products. ... we confirm the prior estimates ... . }} Embedded citations: (1) {{Cite conference |url=http://grail.cs.washington.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/zongker-2003-oca.pdf |title=On Creating Animated Presentations |last1=Zongker |first1=Douglas E. |last2=Salesin |first2=David H. |year=2003 |conference=Eurographics/SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation, San Diego, CA, July 26–27, 2003 |conference-url=http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=846276 |book-title=SCA '03 Symposium on Computer Animation 2003 |publisher=Eurographics Association |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6bk2fHC1g?url=http://grail.cs.washington.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/zongker-2003-oca.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=September 22, 2015 |location=Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland |pages=298–308 |isbn=978-1-58113-659-3 |access-date=August 24, 2017 }} (2) {{Cite news |last=Montalbano |first=Elizabeth |date=June 4, 2009 |title=Forrester: Microsoft Office in No Danger From Competitors |url=http://www.pcworld.com/article/166123 |newspaper=PC World |issn=0737-8939 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160816143250/http://www.pcworld.com/article/166123/article.html |url-status=live |archive-date=August 16, 2016 |access-date=August 24, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ==Operation== | |||
| The earliest version of PowerPoint (1987 for Macintosh) could be used to print black and white pages to be photocopied onto ] for projection from ]s, and to print speaker's notes and audience handouts; the next version (1988 for Macintosh, 1990 for Windows) was extended to also produce ] by communicating a file over a modem to a ] imaging center with slides returned by overnight delivery for projection from ]s. PowerPoint was used for planning and preparing a presentation, but not for delivering it (apart from previewing it on a computer screen, or distributing printed paper copies).<ref name="CACM-2007-Gaskins-operation">{{Cite journal |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=December 2007 |title=PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics |url=https://www.academia.edu/1866305 |department=Viewpoint |journal=] |publication-date=December 2007 |volume=50 |issue=12 |pages=15–17 |issn=0001-0782 |doi=10.1145/1323688.1323710 |s2cid=48306 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107161639/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-at-20-cacm-vol50-no12-dec-2007-p15-p17.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 12, 2017 }} The first three versions are described in the sidebar, "Presentation Formats and PowerPoint," p. 17.</ref> The operation of PowerPoint changed substantially in its third version (1992 for Windows and Macintosh), when PowerPoint was extended to also deliver a presentation by producing direct video output to ] or large monitors.<ref name="CACM-2007-Gaskins-operation" /> In 1992 video projection of presentations was rare and expensive, and practically unknown from a laptop computer. Robert Gaskins, one of the creators of PowerPoint, says he publicly demonstrated that use for the first time at a large Microsoft meeting held in Paris on February 25, 1992, by using an unreleased development build of PowerPoint 3.0 running on an early pre-production sample of a powerful new color laptop and feeding a ].<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-Gaskins-operation">{{Cite book |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |title=Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint |year=2012 |publisher=Vinland Books |isbn=978-0-9851424-0-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RC_5OCQQJ7YC |access-date=August 12, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624031005/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/sweating-bullets/gaskins-sweating-bullets-webpdf-isbn-9780985142414.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=June 24, 2017}}</ref>{{Rp|pages=373–375}} | |||
| By about 2003, ten years later, digital projection had become the dominant mode of use, replacing transparencies and 35mm slides and their projectors.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-Gaskins-operation" />{{Rp|pages=410–414}}<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.edwardtufte.com/bboard/q-and-a-fetch-msg?msg_id=0000n8 |title=The End of the Carousel Slide Projector? |last=<!-- corporate announcement, no author listed> --> |date=July 14, 2003 |website=Edward Tufte Forum |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111103030333/http://www.edwardtufte.com/bboard/q-and-a-fetch-msg?msg_id=0000n8 |url-status=live |archive-date=November 3, 2011 |access-date=August 20, 2017 |quote=Eastman Kodak Company has confirmed plans to discontinue the manufacture and sales of slide projection products and accessories in June of 2004.}}</ref> As a result, the meaning of "PowerPoint presentation" narrowed to mean specifically digital projection:<ref name="Yates-and-Orlikowski-2007">{{Cite book |last1=Yates |first1=JoAnne |author1-link=JoAnne Yates |last2=Orlikowski |first2=Wanda |author2-link=Wanda Orlikowski |year=2007 |chapter=Chapter 4: The PowerPoint Presentation and Its Corollaries: How Genres Shape Communicative Action in Organizations |pages=67–91 |editor1-last=Zachry |editor1-first=Mark |editor2-last=Thralls |editor2-first=Charlotte |title=Communicative Practices in Workplaces and the Professions: Cultural Perspectives on the Regulation of Discourse and Organizations |chapter-url=http://seeit.mit.edu/publications/yatesorlikowski_powerpoint_2006.pdf |location=Amityville, N.Y. |publisher=Baywood Publishing Co. |isbn=978-0-89503-372-7 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YIufUdMc?url=http://seeit.mit.edu/publications/yatesorlikowski_powerpoint_2006.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=May 5, 2015 |access-date=August 19, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote| ... in the business lexicon, "PowerPoint presentation" had come to refer to a presentation made using a PowerPoint slideshow projected from a computer. Although the PowerPoint software had been used to generate transparencies for over a decade, this usage was not typically encompassed by a common understanding of the term.}} | |||
| In contemporary operation, PowerPoint is used to create a file (called a "presentation" or "deck") containing a sequence of pages (called "slides" in the app) which usually have a consistent style (from template masters), and which may contain information imported from other apps or created in PowerPoint, including text, bullet lists, tables, charts, drawn shapes, images, audio clips, video clips, animations of elements, and animated transitions between slides, plus attached notes for each slide.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Basic-tasks-for-creating-a-PowerPoint-presentation-efbbc1cd-c5f1-4264-b48e-c8a7b0334e36 |title=Basic tasks for creating a PowerPoint presentation |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170709192522/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Basic-tasks-for-creating-a-PowerPoint-presentation-efbbc1cd-c5f1-4264-b48e-c8a7b0334e36 |url-status=live |archive-date=July 9, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| After such a file is created, typical operation is to present it as a ] using a portable computer, where the presentation file is stored on the computer or available from a network, and the computer's screen shows a "presenter view" with current slide, next slide, speaker's notes for the current slide, and other information.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Start-the-presentation-and-see-your-notes-in-Presenter-view-4de90e28-487e-435c-9401-eb49a3801257 |title=Start the presentation and see your notes in Presenter view |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818222229/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Start-the-presentation-and-see-your-notes-in-Presenter-view-4de90e28-487e-435c-9401-eb49a3801257 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> Video is sent from the computer to one or more external digital projectors or monitors, showing only the current slide to the audience, with sequencing controlled by the speaker at the computer. A smartphone remote control built in to PowerPoint for iOS (optionally controlled from Apple Watch)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/microsoft-powerpoint/id586449534 |title=Microsoft PowerPoint, Version 2.4 |date=August 14, 2017 |website=Apple iTunes Store |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818182030/https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/microsoft-powerpoint/id586449534 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017 |quote=Start the slide show with your Apple Watch and easily navigate to the next and previous slides.}}</ref> and for Android<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.microsoft.office.powerpoint |title=Microsoft PowerPoint |date=August 14, 2017 |website=Google Play Store |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818181821/https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.microsoft.office.powerpoint |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> allows the presenter to control the show from elsewhere in the room. | |||
| In addition to a computer slide show projected to a live audience by a speaker, PowerPoint can be used to deliver a presentation in a number of other ways: | |||
| * Displayed on the screen of the presentation computer or tablet (for a very small group)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Choose-the-right-view-for-the-task-in-PowerPoint-21332d8d-adbc-4717-a2c6-e25a697b40e9 |title=Choose the right view for the task in PowerPoint |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818223414/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Choose-the-right-view-for-the-task-in-PowerPoint-21332d8d-adbc-4717-a2c6-e25a697b40e9 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}} (This mode of operation was available since version 1.0.)</ref> | |||
| * Printed for distribution as paper documents (in several formats)<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Print-your-handouts-notes-or-slides-91c62c83-9032-497c-ab76-cae8f3e1a402 |title=Print your handouts, notes, or slides |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818223841/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Print-your-handouts-notes-or-slides-91c62c83-9032-497c-ab76-cae8f3e1a402 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}} (This mode of operation was available since version 1.0.)</ref> | |||
| * Distributed as files for private viewing, even on computers without PowerPoint<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/View-a-presentation-without-PowerPoint-2f1077ab-9a4e-41ba-9f75-d55bd9b231a6 |title=View a presentation without PowerPoint |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818224151/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/View-a-presentation-without-PowerPoint-2f1077ab-9a4e-41ba-9f75-d55bd9b231a6 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * Packaged for distribution on CD or a network, including linked and embedded data<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Package-a-presentation-for-CD-52d431bf-01e2-44db-bc40-49777b7cf55a |title=Package a presentation for CD |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818232256/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Package-a-presentation-for-CD-52d431bf-01e2-44db-bc40-49777b7cf55a |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * Transmitted as a live broadcast presentation over the web<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Present-online-using-the-Office-Presentation-Service-c1fd3f16-97c0-4f96-91c3-79e147e7e574 |title=Present online using the Office Presentation Service |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818225610/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Present-online-using-the-Office-Presentation-Service-c1fd3f16-97c0-4f96-91c3-79e147e7e574 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017 |quote=This feature was known as the 'presentation broadcast service' in previous versions of PowerPoint.}}</ref> | |||
| * Embedded in a web page or blog<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Embed-a-presentation-in-a-web-page-or-blog-19668a1d-2299-4af3-91e1-ae57af723a60 |title=Embed a presentation in a web page or blog |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818225838/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Embed-a-presentation-in-a-web-page-or-blog-19668a1d-2299-4af3-91e1-ae57af723a60 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * Shared on social networks such as ] or ]<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Post-a-presentation-to-Facebook-Twitter-or-other-social-network-d0692c2c-5154-43df-994e-9455c1ad69dd |title=Post a presentation to Facebook, Twitter, or other social network |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818230412/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Post-a-presentation-to-Facebook-Twitter-or-other-social-network-d0692c2c-5154-43df-994e-9455c1ad69dd |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * Set up as a self-running unattended display<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Create-a-self-running-presentation-57fc41ae-f36a-4fb5-94a3-52d5bc466037 |title=Create a self-running presentation |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818230619/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Create-a-self-running-presentation-57fc41ae-f36a-4fb5-94a3-52d5bc466037 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * Recorded as video/audio (]/]), to be distributed as for any other video<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Turn-your-presentation-into-a-video-c140551f-cb37-4818-b5d4-3e30815c3e83 |title=Turn your presentation into a video |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170818230906/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Turn-your-presentation-into-a-video-c140551f-cb37-4818-b5d4-3e30815c3e83 |url-status=live |archive-date=August 18, 2017 |access-date=August 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Some of these ways of using PowerPoint have been studied by ] and ] of the ]:<ref name="Yates-and-Orlikowski-2007" /> | |||
| {{Blockquote|The standard form of such presentations involves a single person standing before a group of people, talking and using the PowerPoint slideshow to project visual aids onto a screen. ... In practice, however, presentations are not always delivered in this mode. In our studies, we often found that the presenter sat at a table with a small group of people and walked them through a "deck", composed of paper copies of the slides. In some cases, decks were simply distributed to individuals, without even a walk-through or discussion. ... Other variations in the form included sending the PowerPoint file electronically to another site and talking through the slides over an audio or video channel (e.g., telephone or video conference) as both parties viewed the slides. ... Another common variation was placing a PowerPoint file on a web site for people to view at different times.}} | |||
| They found that some of these ways of using PowerPoint could influence the content of presentations, for example when "the slides themselves have to carry more of the substance of the presentation, and thus need considerably more content than they would have if they were intended for projection by a speaker who would orally provide additional details and nuance about content and context."<ref name="Yates-and-Orlikowski-2007" /> | |||
| == Other platforms == | |||
| ===PowerPoint for mobile=== | |||
| PowerPoint Mobile is included with ]. It is a ] capable of reading and editing Microsoft PowerPoint presentations, although authoring abilities are limited to adding notes, editing text, and rearranging slides. It can't create new presentations.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Ralph|first1=Nate|title=Office for Windows Phone 8: Your handy starter guide|url=http://www.techhive.com/article/2025977/office-for-windows-phone-8-your-handy-starter-guide.html|website=TechHive|accessdate=August 30, 2014|archive-date=October 15, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141015060254/http://www.techhive.com/article/2025977/office-for-windows-phone-8-your-handy-starter-guide.html|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>. Microsoft. Retrieved September 14, 2007.</ref> Versions of PowerPoint Mobile for Windows Phone 7 can also watch presentation broadcasts streamed from the Internet.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.windowsphone.com/en-us/how-to/wp7/office/use-office-powerpoint-mobile |title=Use Microsoft PowerPoint Mobile |work=Windows Phone How-to (United States) |publisher=] |date= |accessdate=April 28, 2014}}</ref> In 2015, Microsoft released PowerPoint Mobile for Windows 10 as a ]. In this version of PowerPoint users can create and edit new presentations, present, and share their PowerPoint documents.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/store/apps/powerpoint-mobile/9wzdncrfjb5q|title=PowerPoint Mobile|last=|first=|date=|website=]|publisher=]|access-date=June 26, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| ===PowerPoint for the web=== | |||
| {{Further|Microsoft Office#Office on the web}} | |||
| PowerPoint for the web is a free lightweight version of Microsoft PowerPoint available as part of Office on the web, which also includes web versions of Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Word. | |||
| PowerPoint for the web does not support inserting or editing charts, equations, or audio or video stored on your PC, but they are all displayed in the presentation if they were added in using a desktop app. Some elements, like WordArt effects or more advanced animations and transitions, are not displayed at all, although they are preserved in the document. PowerPoint for the web also lacks the Outline, Master, Slide Sorter, and Presenter views present in the desktop app, as well as having limited printing options.<ref name="osupport-ppt">{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/how-certain-features-behave-in-web-based-powerpoint-a931f0c8-1305-4428-8f7c-9cfa00ef28c5 |title=How certain features behave in web-based PowerPoint |website=Office Support |publisher=] |access-date=October 31, 2019 |df=dmy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ==Cultural impact== | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Business uses=== | |||
| PowerPoint was originally targeted just for business presentations. Robert Gaskins, who was responsible for its design, has written about his intended customers: "... I did not target other existing large groups of users of presentations, such as school teachers or military officers. ... I also did not plan to target people who were not existing users of presentations ... such as clergy and school children ... . Our focus was purely on business users, in small and large companies, from one person to the largest multinationals."<ref name="Gaskins-Sweating-Bullets-2012-cultural">{{Cite book |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |title=Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint |year=2012 |publisher=Vinland Books |isbn=978-0-9851424-0-7 <!-- hardcover ed -->|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RC_5OCQQJ7YC |access-date=September 5, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624031005/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/sweating-bullets/gaskins-sweating-bullets-webpdf-isbn-9780985142414.pdf <!-- webpdf ed --> |url-status=live |archive-date=June 24, 2017}}</ref>{{Rp|pages=76–77}} Business people had for a long time made presentations for sales calls and for internal company communications, and PowerPoint produced the same formats in the same style and for the same purposes.<ref name="Gaskins-Sweating-Bullets-2012-cultural" />{{Rp|page=420}} | |||
| PowerPoint use in business grew over its first five years (1987–1992) to sales of about 1 million copies annually, for worldwide market share of 63 percent.<ref name="Sweating-Bullets-2012-salesnums" /> Over the following five years (1992–1997) PowerPoint sales accelerated, to a rate of about 4 million copies annually, for worldwide market share of 85 percent.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Ziff Davis Market Intelligence |date=September 1998 |title=The 800-Pound Gorilla of the Presentation Market |journal=Mobile Computing and Communications |page=95 |volume=9 |issue=9 |issn=1047-1952 |quote=... in 1997, without question the market leader was Microsoft Corp.'s PowerPoint, which sold more than 4 million copies and controls 85 percent of the market. |url=https://filetea.me/t1sEVBHlotISPCAVUKpeg2F5A |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6bxj2eryp?url=https://filetea.me/t1sEVBHlotISPCAVUKpeg2F5A |archive-date=October 1, 2015 |access-date=September 29, 2017 |df=mdy-all }} {{webarchive|format=addlarchives|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170826204750/https://filetea.me/n3wiYbSzCLuStyw3hl7fDW0dA |date=August 26, 2017}}</ref> The increase in business use has been attributed to "]s", whereby additional users of PowerPoint in a company or an industry increased its salience and value to other users.<ref>{{Cite interview |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |subject-link=Robert Gaskins |interviewer=Clay Chandler |title=The Man Who Invented PowerPoint |publisher=] |journal=Bento |number=7 |url=http://bento.hult.edu/the-man-who-dreamed-of-powerpoint/ <!-- URL is correctly different from title --> |date=October 2016 |access-date=September 22, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170922214245/http://bento.hult.edu/the-man-who-dreamed-of-powerpoint/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 22, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint succeeded so quickly because it spread rapidly by viral transmission from user to user ... every time early adopters used our product effectively, they demonstrated its value to other potential customers. PowerPoint made it especially easy for colleagues within the same company to share materials and incorporate one another's slides into their presentations with automatic formatting. This created networks of cooperation that benefited everyone.}}</ref> | |||
| Not everyone immediately approved of the greater use of PowerPoint for presentations, even in business. CEOs who very early were reported to discourage or ban PowerPoint presentations at internal business meetings included ] (at IBM, in 1993),<ref>{{cite book |last=Gerstner | first=Louis V. Jr. |author-link=Louis V. Gerstner Jr. |date=2002 |title=Who Says Elephants Can't Dance? Inside IBM's Historic Turnaround |publisher=HarperCollins |page= |isbn=978-0060523794 |quote= By that afternoon an email about my hitting the Off button on the overhead projector was crisscrossing the world. Talk about consternation! It was as if the President of the United States had banned the use of English at White House meetings. |url=https://archive.org/details/whosayselephants00gers/page/43 }}</ref> ] (at Sun Microsystems, in 1996),<ref>{{cite news |editor-last=Rae-Dupree |editor-first=Janet |date=January 27, 1997 |title=Sun Microsystems' Chief: A Mission Against 'Dark Side' (Q & A With Scott McNealy) |newspaper=San Jose Mercury News |issn=0747-2099 |department=Business Monday |edition=Morning Final |page=8E |url=http://www.mercurynews.com/archive-search/ |url-access=subscription <!-- but archive is ungated --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20170923220156/https://filetea.me/n3wHzDE7FZKSFqqS6e5Vl8ICw |archive-date=September 23, 2017 |url-status=live |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote= ' ... we've had three unbelievable record-breaking fiscal quarters since we banned PowerPoint. Now, I would argue that every company in the world, if they would just ban PowerPoint, would see their earnings skyrocket. Employees would stand around going, "What do I do? Guess I've got to go to work.{{Double single}} |df=mdy-all }} {{webarchive|format=addlarchives|url=https://archive.today/20170923220156/https://filetea.me/n3wHzDE7FZKSFqqS6e5Vl8ICw |date=September 23, 2017}}</ref> and ] (at Apple, in 1997).<ref>{{cite book |last=Isaacson |first=Walter |author-link=Walter Isaacson |date=2011 |title=Steve Jobs |publisher=Simon and Schuster |page= |isbn=978-1-4516-4853-9 |quote= 'People would confront a problem by creating a presentation. I wanted them to engage, to hash things out at the table, rather than show a bunch of slides. People who know what they're talking about don't need PowerPoint.' |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/stevejobs00isaa/page/337 }}</ref> But even so, Rich Gold, a scholar who studied corporate presentation use at ], could write in 1999: "Within today's corporation, if you want to communicate an idea ... you use PowerPoint."<ref>{{Cite book |chapter-url=https://faculty.washington.edu/farkas/TC510-Fall2011/GoldReadingPowerpoint.pdf |last=Gold |first=Rich |orig-year=Syposium paper 1999 |chapter=Chapter 14: Reading PowerPoint |pages=256–270 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170923165414/https://faculty.washington.edu/farkas/TC510-Fall2011/GoldReadingPowerpoint.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=September 23, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |editor-last=Allen |editor-first=Nancy |title=Working with Words and Images: New Steps in an Old Dance |location=Westport, Conn. |publisher=Ablex Publishing |isbn=978-1-56750-608-2 |date=2002 |series=New Directions in Computers and Composition Studies}}</ref> | |||
| ===Uses beyond business=== | |||
| At the same time that PowerPoint was becoming dominant in business settings, it was also being adopted for uses beyond business: "Personal computing ... scaled up the production of presentations. ... The result has been the rise of presentation culture. In an information society, nearly everyone presents."<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Robles-Anderson |first1=Erica |last2=Svensson |first2=Patrik |date=January 15, 2016 |title='One Damn Slide After Another': PowerPoint at Every Occasion for Speech |url=http://computationalculture.net/article/one-damn-slide-after-another-powerpoint-at-every-occasion-for-speech |journal=Computational Culture |issn=2047-2390 |volume=1 |issue=5 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170906030606/http://computationalculture.net/article/one-damn-slide-after-another-powerpoint-at-every-occasion-for-speech |url-status=live |archive-date=September 6, 2017 |access-date=September 6, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| In 1998, at about the same time that Gold was pronouncing PowerPoint's ubiquity in business, the influential ] engineer ] could already write about broader uses:<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Lucky |first=Robert W. |author-link=Robert W. Lucky |date=January 1998 |title=The World According to PowerPoint |department=Reflections |journal=] |publication-date=January 1998 |volume=35 |issue=1 |page=17 |issn=0018-9235 |doi=10.1109/MSPEC.1998.646010 }}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote|... the world has run amok with the giddy power of presentation graphics. A new language is in the air, and it is codified in PowerPoint. ... In a family discussion about what to do on a given evening, for example, I feel like pulling out my laptop and giving a ] presentation... In church, I am surprised that the preachers haven't caught on yet. ... How have we gotten on so long without PowerPoint?}} | |||
| Over a decade or so, beginning in the mid 1990s, PowerPoint began to be used in many communication situations, well beyond its original business presentation uses, to include teaching in schools<ref>{{Cite news |last=Guernsey |first=Lisa |date=May 31, 2001 |title=PowerPoint Invades the Classroom |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2001/05/31/technology/31POWE.html |department=Technology |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170606211756/http://www.nytimes.com/2001/05/31/technology/powerpoint-invades-the-classroom.html |url-status=live |archive-date=June 6, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint—the must-have presentation software of the corporate world—has infiltrated the schoolhouse. In the coming weeks, students from 12th grade to, yes, kindergarten will finish science projects and polish end-of-the-year presentations on computerized slide shows ... . Software designed for business people has found an audience among the spiral notebook set.}}</ref> and in universities,<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Levasseur |first1=David G. |last2=Sawyer |first2=J. Kanan |date=August 19, 2006 |title=Pedagogy Meets PowerPoint: A Research Review of the Effects of Computer-Generated Slides in the Classroom |journal=Review of Communication |issn=1535-8593 |volume=6 |issue=1–2 |pages=101–123 |doi=10.1080/15358590600763383 |s2cid=144022054 |quote=Higher education has certainly not been immune from the growing influence of presentation software. ... Five years ago, none of our department's classrooms were equipped to show multimedia slides. At present, all of our classrooms have been upgraded with such technology, and faculty are actively encouraged to incorporate slides into their lectures. Our institution is certainly not alone in this trend. A large number of educators in the United States use PowerPoint in their classrooms ... .}}</ref> lecturing in scientific meetings<ref>{{Cite news |last=Pinker |first=Steven |author-link=Steven Pinker |date=June 10, 2010 |title=Mind Over Mass Media |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/11/opinion/11Pinker.html |department=Opinion Pages |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |page=A31 |edition=New York |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170910050739/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/06/11/opinion/11Pinker.html |url-status=live |archive-date=September 10, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=These days scientists ... cannot lecture without PowerPoint.}}</ref> (and preparing their related poster sessions<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.umt.edu/ugresearch/documents/make_posters.pdf |title=Making a Large Format Scientific Poster Using PowerPoint |last=<!-- no author attribution --> |date=February 1, 2001 |website=University of Montana |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131231122843/http://www.umt.edu/ugresearch/documents/make_posters.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=December 31, 2013 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint ... can do all the basics .}}</ref>), worshipping in churches,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Watson |first=Jeremy |date=August 12, 2005 |title=Presentation software—worship at the click of a mouse |url=http://www.brnow.org/Resources/Archives-2000-2007/August-2005/Presentation-software-worship-at-the-click-of-a-mo |website=BRNow.org |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170923182647/https://brnow.org/Resources/Archives-2000-2007/August-2005/Presentation-software-worship-at-the-click-of-a-mo |url-status=live |archive-date=September 23, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=According to LifeWay, 'Statistics show that around 90 percent of churches that show multimedia during worship use Microsoft PowerPoint.' }}</ref> making legal arguments in courtrooms,<ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Armstrong |first=Ken |date=December 23, 2014 |title=The Sneakiest Way Prosecutors Get a Guilty Verdict: PowerPoint |url=https://www.wired.com/2014/12/prosecutors-powerpoint-presentations/ |magazine=Wired |issn=1059-1028 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141223195616/http://www.wired.com/2014/12/prosecutors-powerpoint-presentations |url-status=live |archive-date=December 23, 2014 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=The use of sophisticated visuals in the courtroom has boomed in recent years, thanks to research on the power of show-and-tell. ... In one civil case in Los Angeles County, a plaintiff spent $60,000 on a PowerPoint slide show. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> displaying supertitles in theaters,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.gordonsupertitles.com/tech.html |title=David Gordon Choral Supertitles |last=Gordon |first=David |author-link=David Gordon (tenor) |date=2015 |website=David Gordon Supertitles |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161023022014/http://gordonsupertitles.com/tech.html |url-status=live |archive-date=October 23, 2016 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote= ... supertitles are simple PowerPoint presentations, completely compatible with PCs or Macs.}}</ref> driving helmet-mounted displays in spacesuits for NASA astronauts,<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.astrobio.net/moon-to-mars/making-a-list-checking-it-twice/ |title=Making a List, Checking It Twice |last=Bortman |first=Henry |date=October 13, 2005 |website=Astrobiology Magazine | publisher=] |issn=2152-1239 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170923193329/https://www.astrobio.net/moon-to-mars/making-a-list-checking-it-twice/ |url-status=usurped |archive-date=September 23, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote= ... They're mounted in the helmet so that when you turn and look, there's this little screen that shows the checklist. Now in this case, I've written the checklists and put them in PowerPoint, so we just launch a PowerPoint slide show. ... It's a real treat to use.}}</ref> giving military briefings,<ref>{{Cite news |last=Jaffe |first=Greg |date=April 26, 2000 |title=What's Your Point, Lieutenant? Please, Just Cut to the Pie Charts |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB956703757412556977 |url-access=subscription <!-- but archive is ungated --> |department=A-Hed |newspaper=Wall Street Journal |issn=0099-9660 |edition=US |page=A1 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ta1rPrxK?url=https://filetea.me/n3wWd80E7jUQBunx1dNjWUTBg |url-status=live |archive-date=September 18, 2017 |access-date=September 18, 2017 |quote=Old-fashioned slide briefings, designed to update generals on troop movements, have been a staple of the military since World War II. But in only a few short years PowerPoint has altered the landscape. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> issuing governmental reports,<ref>{{Cite thesis |last=Pece |first=Gregory S. |title=The PowerPoint Society: The Influence of PowerPoint in the U.S. Government and Bureaucracy |type=M.A. Thesis |url=http://hdl.handle.net/10919/33029 |date=May 10, 2005 |publisher=Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University |hdl=10919/33029 |place=Blacksburg, Virginia |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151025221506/http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-05202005-065041/unrestricted/PecePPthesis.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=October 25, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=The standard method for presenting information in the military and political establishments of the US government is through the projection of data in bullet style and/or graphical formats onto an illuminated screen, using some sort of first analogue, or now, digital media. Since the late 1990s, the most common and expected form of presentation is via the most commonly pre-installed software of presentation genre: Microsoft PowerPoint. This style of presentation has become the norm of communication ... .}}</ref> undertaking diplomatic negotiations,<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://nsarchive.gwu.edu/NSAEBB/NSAEBB234/Powell_slides.pdf |title=Iraq: Failing to Disarm (U.S. Secretary of State Powell's Presentation to the UN Security Council) |last=Powell |first=Colin |author-link=Colin Powell |date=February 5, 2003 |website=The National Security Archive (George Washington University) |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150505133227/http://nsarchive.gwu.edu/NSAEBB/NSAEBB234/Powell_slides.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=May 5, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Peterson |first=Scott |date=July 9, 2012 |title=Iran makes its nuclear case—with PowerPoint |url=https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Middle-East/2012/0709/Iran-makes-its-nuclear-case-with-PowerPoint |newspaper=Christian Science Monitor |issn=0882-7729 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170923225938/https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Middle-East/2012/0709/Iran-makes-its-nuclear-case-with-PowerPoint |url-status=live |archive-date=September 23, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=The complete set of PowerPoint slides that Iran used during a meeting with world powers are now public.}}</ref> writing novels,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Egan |first=Jennifer |author-link=Jennifer Egan |title=A Visit from the Goon Squad |year=2010 |publisher=Alfred A. Knopf |isbn=978-0-307-59283-5 |pages=176–251|title-link=A Visit from the Goon Squad }}</ref> giving architectural demonstrations,<ref>{{Cite report |last1=Stark |first1=David |last2=Paravel |first2=Verena |date=February 2007 |title=PowerPoint Demonstrations: Digital Technologies of Persuasion (Working Paper 07-04) |publisher=Institute for Social and Economic Research and Policy, Columbia University |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237291359 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6bt9xmP7K?url=https://filetea.me/t1shl0UDrmOR925XRRrRzWB6w |url-status=live |archive-date=September 28, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017 }}</ref> prototyping website designs,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://boxesandarrows.com/interactive-prototypes-with-powerpoint/ |title=Interactive Prototypes with PowerPoint |last=Kelly |first=Maureen |date=August 7, 2007 |website=Boxes and Arrows |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150905092717/http://boxesandarrows.com/interactive-prototypes-with-powerpoint/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 5, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote= ... many designers ... use PowerPoint for blocking out screens without ever discovering the interactive features for creating hyperlinks, buttons, and dynamic mouseover effects. Yes, PowerPoint can do all that.}}</ref> creating animated video games,<ref>{{Cite news |last=Greenberg |first=Andy |author-link=Andy Greenberg |date=May 11, 2010 |title=The Underground Art Of PowerPoint |url=https://www.forbes.com/2010/05/10/microsoft-software-iphone-technology-powerpoint.html |newspaper=Forbes |issn=0015-6914 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170630132845/https://www.forbes.com/2010/05/10/microsoft-software-iphone-technology-powerpoint.html |url-status=live |archive-date=June 30, 2017 |access-date=September 15, 2017 |quote= ... a subculture of PowerPoint enthusiasts is teaching the old application new tricks, and may even be turning a dry presentation format into a full-fledged artistic medium.}}</ref> editing images,<ref>{{cite web | url=https://blogs.articulate.com/rapid-elearning/5-ways-to-use-powerpoint-as-an-image-editor/ | title=5 Ways to Use PowerPoint as an Image Editor | date=February 27, 2018 }}</ref> creating art projects,<ref name="Vienne">{{Cite news |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2003/08/17/books/art-architecture-david-byrne-s-alternate-powerpoint-universe.html |last=Vienne |first=Veronique |date=August 17, 2003 |title=David Byrne's Alternate PowerPoint Universe |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |department=Art/Architecture |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121114105710/http://www.nytimes.com/2003/08/17/books/art-architecture-david-byrne-s-alternate-powerpoint-universe.html |url-status=live |archive-date=November 14, 2012 |access-date=September 15, 2017 |quote=With his newest project, David Byrne has tried not only to see it anew, but also to use it in the least likely of all applications: a medium for creative expression.}}</ref> and even as a substitute for writing engineering technical reports,<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Columbia Accident Investigation Board |author-link1=Columbia Accident Investigation Board |last2=National Aeronautics and Space Administration | author-link2=NASA |year=2003 |title=Report Volume I |url=https://www.nasa.gov/columbia/home/CAIB_Vol1.html |chapter=7. The Accident's Organizational Causes |chapter-url=https://s3.amazonaws.com/akamai.netstorage/anon.nasa-global/CAIB/CAIB_lowres_chapter7.pdf |page=191 |isbn=978-0-16-067904-9 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161202012844/http://s3.amazonaws.com/akamai.netstorage/anon.nasa-global/CAIB/CAIB_lowres_chapter7.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=December 2, 2016 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=At many points during its investigation, the Board was surprised to receive similar presentation slides from NASA officials in place of technical reports. The Board views the endemic use of PowerPoint briefing slides instead of technical papers as an illustration of the problematic methods of technical communication at NASA.}}</ref> and as an organizing tool for writing general business documents.<ref>{{Cite journal |url=https://hbr.org/2015/07/why-i-write-in-powerpoint |title=Why I Write in PowerPoint |last=Duarte |first=Nancy |author-link=Nancy Duarte |date=July 27, 2015 |journal=Harvard Business Review |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305000950/https://hbr.org/2015/07/why-i-write-in-powerpoint |url-status=live |archive-date=March 5, 2016 |access-date=September 21, 2017 |quote=Because PowerPoint is so modular, it allows me to block out major themes (potential sections or chapters) and quickly see if I can generate ample ideas to support them. ... Working in slides, as opposed to one long document, helps me focus on organizing before I really begin writing. I think of the slides as index cards or sticky notes that can be arranged and rearranged until I'm sure my thoughts are in the right order. As I write, I can easily toggle back and forth from 'Slide View' to 'Slide Sorter' to get a sense of the whole and the parts.}}</ref> | |||
| By 2003, it seemed that PowerPoint was being used everywhere. Julia Keller reported for the ''Chicago Tribune'':<ref>{{Cite news |last=Keller |first=Julia |date=January 22, 2003 |title=Is PowerPoint the Devil? |url=http://www.rasmusen.org/g751/06d-readings/Keller_%20Is%20PowerPoint%20the%20devil_.pdf |newspaper=Chicago Tribune |issn=1085-6706 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170904163317/http://www.rasmusen.org/g751/06d-readings/Keller_%20Is%20PowerPoint%20the%20devil_.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=September 4, 2017 |access-date=September 6, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote |PowerPoint ... is one of the most pervasive and ubiquitous technological tools ever concocted. In less than a decade, it has revolutionized the worlds of business, education, science, and communications, swiftly becoming the standard for just about anybody who wants to explain just about anything to just about anybody else. From corporate middle managers reporting on production goals to 4th-graders fashioning a show-and-tell on the French and Indian War to church pastors explicating the seven deadly sins ... PowerPoint seems poised for world domination.}} | |||
| ===Cultural reactions=== | |||
| As uses broadened, cultural awareness of PowerPoint grew and commentary about it began to appear. "With the widespread adoption of PowerPoint came complaints ... often very general statements reflecting dissatisfaction with modern media and communication practices as well as the dysfunctions of organizational culture."<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Farkas |first=David K. |date=2006 |title=Toward a better understanding of PowerPoint deck design |url=https://faculty.washington.edu/farkas/FarkasTowardUnderstandingPPT.pdf |journal= Information Design Journal|issn=0142-5471 |volume=14 |issue=2 |pages=162–171 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130830020920/http://faculty.washington.edu/farkas/FarkasTowardUnderstandingPPT.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=August 30, 2013 |access-date=September 23, 2017|doi=10.1075/idj.14.2.08far }}</ref> Indications of this awareness included increasing mentions of PowerPoint use in the '']'' comic strips of ],<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-comments-on-dilbert-history-of-powerpoint.pdf |title=Comments on Dilbert's History of PowerPoint |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |date=April 20, 2012 |website=PowerPoint History Documents |type=Draft |pages=59 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140517154506/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-comments-on-dilbert-history-of-powerpoint.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=May 17, 2014 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=It took ten to fifteen years for PowerPoint to become an everyday topic of popular discourse.}}</ref> comic parodies of poor or inappropriate use such as the ] in PowerPoint<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://norvig.com/Gettysburg/ |title=The Gettysburg PowerPoint Presentation |last=Norvig |first=Peter |author-link=Peter Norvig |date=January 2000 |website=Peter Norvig personal website |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20001109193600/http://www.norvig.com/Gettysburg/ |url-status=live |archive-date=November 9, 2000 |access-date=September 22, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://norvig.com/Gettysburg/making.html |title=The Making of the Gettysburg PowerPoint Presentation |last=Norvig |first=Peter |author-link=Peter Norvig |date=2008 |website=Peter Norvig personal website |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081230051340/http://www.norvig.com/Gettysburg/making.html |url-status=live |archive-date=December 30, 2008 |access-date=September 22, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> or summaries of Shakespeare's ''Hamlet'' and Nabokov's ''Lolita'' in PowerPoint,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.radosh.net/writing/ppaol.html |title=The PowerPoint Anthology of Literature |last=Radosh |first=Daniel |author-link=Daniel Radosh |date=2003 |website=Daniel Radosh personal website |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060710004518/http://www.radosh.net/writing/ppaol.html |url-status=live |archive-date=July 10, 2006 |access-date=September 22, 2017}}</ref> and a vast number of publications on the general subject of PowerPoint, especially about how to use it.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.worldcat.org/search?q=kw%3Apowerpoint&fq=yr%3A1987..2017+%3E&dblist=638 |title=Search Results for 'kw:powerpoint' > '1987..2017' |date=September 29, 2017 |website=OCLC WorldCat Global Catalog |archive-url=https://archive.today/20170929193106/https://www.worldcat.org/search?q=kw:powerpoint&fq=yr:1987..2017+%3E&dblist=638 |url-status=live |archive-date=September 29, 2017 |access-date=September 29, 2017 |quote=All Formats (66,169) ... Print book (23,696), eBook (3,475), Thesis/dissertation (1,078) ... Article (18,085) ... Video (3,537) ... |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Kaplan|first=Sarah|date=2011|title=Strategy and PowerPoint: An Inquiry into the Epistemic Culture and Machinery of Strategy Making|journal=Organization Science|language=en|volume=22|issue=2|pages=320–346|doi=10.1287/orsc.1100.0531|s2cid=37755593 |issn=1047-7039}}</ref> | |||
| Out of all the analyses of PowerPoint over a quarter of a century, at least three general themes emerged as categories of reaction to its broader use: (1) "Use it less": avoid PowerPoint in favor of alternatives, such as using more-complex graphics and written prose, or using nothing;<ref name="Tufte-2003-2006" /> (2) "Use it differently": make a major change to a PowerPoint style that is simpler and pictorial, turning the presentation toward a performance, more like a Steve Jobs keynote;<ref name="Mayer-Atkinson-2004" /> and (3) "Use it better": retain much of the conventional PowerPoint style but learn to avoid making many kinds of mistakes that can interfere with communication.<ref name="Kosslyn-2007" /> | |||
| ====Use it less==== | |||
| {{See also |Edward Tufte|Anti-PowerPoint Party}} | |||
| An early reaction was that the broader use of PowerPoint was a mistake, and should be reversed. An influential example of this came from ], an authority on information design, who has been a professor of political science, statistics, and computer science at Princeton and Yale, but is best known for his self-published books on data visualization, which have sold nearly 2 million copies as of 2014.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.edwardtufte.com/files/ETresume.pdf |title=Edward R. Tufte, Resume |last1=Tufte |first1=Edward |author-link1=Edward Tufte |date=December 2014 |website=Edward Tufte personal website |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161009173114/http://www.edwardtufte.com/files/ETresume.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=October 9, 2016 |access-date=September 20, 2017 |quote=1.9 million copies of 4 books and 422,000 copies of 4 booklets printed from 1983–2014, and continuing.}}</ref> | |||
| In 2003, he published a widely-read booklet titled ''The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint,'' revised in 2006.<ref name="Tufte-2003-2006" /> Tufte found a number of problems with the "cognitive style" of PowerPoint, many of which he attributed to the standard default style templates:<ref name="Tufte-2003-2006" /> | |||
| {{Blockquote|PowerPoint's convenience for some presenters is costly to the content and the audience. These costs arise from the ''cognitive style characteristics of the standard default PP presentation:'' foreshortening of evidence and thought, low spatial resolution, an intensely hierarchical single-path structure as the model for organizing every type of content, breaking up narratives and data into slides and minimal fragments, rapid temporal sequencing of thin information rather than focused spatial analysis, conspicuous chartjunk and PP Phluff, branding of slides with logotypes, a preoccupation with format not content, incompetent designs for data graphics and tables, and a smirky commercialism that turns information into a sales pitch and presenters into marketeers ''''.}} | |||
| Tufte particularly advised against using PowerPoint for reporting scientific analyses, using as a dramatic example some slides made during the flight of the space shuttle ''Columbia'' after it had been damaged by an accident at liftoff, slides which poorly communicated the engineers' limited understanding of what had happened.<ref name="Tufte-2003-2006" />{{Rp|pages=8–14}} For such technical presentations, and for most occasions apart from its initial domain of sales presentations, Tufte advised against using PowerPoint at all; in many situations, according to Tufte, it would be better to substitute high-resolution graphics or concise prose documents as handouts for the audience to study and discuss, providing a great deal more detail.<ref name="Tufte-2003-2006" /> | |||
| Many commentators enthusiastically joined in Tufte's vivid criticism of PowerPoint uses,<ref>{{Cite news |last=Parks |first=Bob |date=August 30, 2012 |title=Death to PowerPoint! |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2012-08-30/death-to-powerpoint |url-access=subscription |newspaper=] |issn=0007-7135 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150312035814/http://www.bloomberg.com/bw/articles/2012-08-30/death-to-powerpoint |url-status=live |archive-date=March 12, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017}}</ref> and at a conference held in 2013 (a decade after Tufte's booklet appeared) one paper claimed that "Despite all the criticism about his work, Tufte can be considered as the single most influential author in the discourse on PowerPoint. ... While his approach was not rigorous from a research perspective, his articles received wide resonance with the public at large ... ."<ref>{{Cite conference |title=10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of PowerPoint": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities |url=https://filetea.me/t1szChzbSBbQkuvlhlAXqxljg |last1=Kernbach |first1=Sebastian |last2=Bresciani |first2=Sabrina |chapter=10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of Power ''Point''": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities |date=July 16–18, 2013 |conference=Information Visualisation (IV), 2013 17th International Conference |location=London |pages=345–350 |doi=10.1109/IV.2013.44 |isbn=978-1-4799-0834-9 |publisher=IEEE |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6Y8PV6QHI?url=https://filetea.me/t1szChzbSBbQkuvlhlAXqxljg |url-status=dead |archive-date=April 28, 2015 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> There were also others who disagreed with Tufte's assertion that the PowerPoint program reduces the quality of presenters' thoughts: ], professor of psychology at MIT and later Harvard, had earlier argued that "If anything, PowerPoint, if used well, would ideally reflect the way we think."<ref>{{Cite news |last=Zuckerman |first=Laurence |date=April 17, 1999 |title=Words Go Right to the Brain, But Can They Stir the Heart?; Some Say Popular Software Debases Public Speaking |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1999/04/17/arts/words-go-right-brain-but-can-they-stir-heart-some-say-popular-software-debases.html |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |access-date=September 23, 2017}}</ref> Pinker later reinforced this opinion: "Any general opposition to PowerPoint is just dumb, ... It's like denouncing lectures—before there were awful PowerPoint presentations, there were awful scripted lectures, unscripted lectures, slide shows, chalk talks, and so on."<ref>{{Cite news |last=Feith |first=David |date=July 31, 2009 |title=Speaking Truth to PowerPoint |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10001424052970204619004574318473921093400 |url-access=subscription |newspaper=Wall Street Journal |issn=0099-9660 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZSdhYhA9?url=https://filetea.me/t1sq7c2KUvATqeAdKcx5xc1gQ |url-status=live |archive-date=June 21, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Much of the early commentary, on all sides, was "informal" and "anecdotal", because empirical research had been limited.<ref>{{Cite conference |title=10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of PowerPoint": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities |url=https://filetea.me/t1szChzbSBbQkuvlhlAXqxljg |last1=Kernbach |first1=Sebastian |last2=Bresciani |first2=Sabrina |chapter=10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of Power ''Point''": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities |date=July 16–18, 2013 |conference=Information Visualisation (IV), 2013 17th International Conference |location=London |pages=345–350 |doi=10.1109/IV.2013.44 |isbn=978-1-4799-0834-9 |publisher=IEEE |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6Y8PV6QHI?url=https://filetea.me/t1szChzbSBbQkuvlhlAXqxljg |url-status=dead |archive-date=April 28, 2015 |quote=Because every day a huge number of people meet to exchange ideas and make decisions with PowerPoint slides being displayed on the wall, investigating the tool is enormously important ... . Despite the pervasiveness of PowerPoint in our culture there have been few empirical studies and most of the non-empirical work is based on casual essays and informal anecdotal reviews which very often take a polemic and overall negative position on PowerPoint, rather than conducting formal scholarship. This lack of rigorous studies and empirical research is surprising given the enormous complexity and importance of the PowerPoint tool. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ====Use it differently==== | |||
| {{See also|Richard E. Mayer |Stevenote |label 2=Steve Jobs Keynotes}} | |||
| A second reaction to PowerPoint use was to say that PowerPoint can be used well, but only by substantially changing its style of use. This reaction is exemplified by ], a professor of psychology at the University of California, Santa Barbara, who has studied cognition and learning, particularly the design of educational multimedia, and who has published more than 500 publications, including over 30 books.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.psych.ucsb.edu/people/faculty/mayer |title=Richard Mayer |date=2017 |website=Department of Psychological & Brain Sciences, University of California at Santa Barbara, faculty directory |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170617030504/https://www.psych.ucsb.edu/people/faculty/mayer |url-status=dead |archive-date=June 17, 2017 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=Dr. Mayer is concerned with how to present information in ways that help people understand, including how to use words and pictures to explain scientific and mathematical concepts.}}</ref> Mayer's theme has been that "In light of the science, it is up to us to make a fundamental shift in our thinking—we can no longer expect people to struggle to try to adapt to our PowerPoint habits. Instead, we have to change our PowerPoint habits to align with the way people learn."<ref name="Mayer-Atkinson-2004" /> | |||
| Tufte had argued his judgment that the information density of text on PowerPoint slides was too low, perhaps only 40 words on a slide, leading to over-simplified messages;<ref>{{Cite book |last=Tufte |first=Edward |author-link=Edward Tufte |year=2006 |orig-year=1st ed. 2003, 24 pg. |title=The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint: Pitching Out Corrupts Within |edition=2nd |location=Cheshire, Connecticut |publisher=Graphics Press LLC |isbn=978-0-9613921-6-1 |pages=4, 15 |quote=very little information per slide ... the text is grossly impoverished .. the PowerPoint slide typically shows 40 words ... .}}</ref> Mayer responded that his empirical research showed exactly the opposite, that the amount of text on PowerPoint slides was usually too high, and that even fewer than 40 words on a slide resulted in "PowerPoint overload" that impeded understanding during presentations.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228893840 |title=Five ways to reduce PowerPoint overload |last1=Atkinson |first1=Cliff |last2=Mayer |first2=Richard E. |author-link2=Richard E. Mayer |date=April 23, 2004 |version=Revision 1.1 |website=ResearchGate |format=PDF |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZMK2qMHz?url=https://filetea.me/t1sWlhUAjlwTqxmEj6Ds9ZT4Q |url-status=live |archive-date=June 17, 2015 |access-date=September 23, 2017 |quote=... it is conventional wisdom to put no more than six lines of text on a PowerPoint slide, six words per line. But that convention is no longer wise in the light of research that shows that even that amount of text on a slide can be a recipe for information overload.}}</ref> | |||
| Mayer suggested a few major changes from traditional PowerPoint formats:<ref name="Mayer-Atkinson-2004" /> | |||
| * replacing brief slide titles with longer "headlines" expressing complete ideas; | |||
| * showing more slides but simpler ones; | |||
| * removing almost all text including nearly all bullet lists (reserving the text for the spoken narration); | |||
| * using larger, higher-quality, and more important graphics and photographs; | |||
| * removing all extraneous decoration, backgrounds, logos and identifications, everything but the essential message. | |||
| Mayer's ideas are claimed by ] to have been reflected in Steve Jobs's presentations: "Mayer outlined fundamental principles of multimedia design based on what scientists know about cognitive functioning. Steve Jobs's slides adhere to each of Mayer's principles ... ."<ref name="Gallo-2009">{{Cite book |last=Gallo |first=Carmine |author-link=Carmine Gallo |year=2009 |title=The Presentation Secrets of Steve Jobs |publisher=McGraw-Hill |isbn=978-0-07-163608-7}}</ref>{{Rp|page=92}} Though not unique to Jobs, many people saw the style for the first time in Jobs's famous product introductions.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Gallo |first=Carmine |author-link=Carmine Gallo |date=September 7, 2012 |title=Jeff Bezos and The End of PowerPoint As We Know It |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/carminegallo/2012/09/07/jeff-bezos-and-the-end-of-powerpoint-as-we-know-it/ |newspaper=Forbes |issn=0015-6914 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150325150413/http://www.forbes.com/sites/carminegallo/2012/09/07/jeff-bezos-and-the-end-of-powerpoint-as-we-know-it/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=March 25, 2015 |access-date=September 24, 2017 |quote=And no, Steve Jobs did not invent the style. He just happened to use it very effectively.}}</ref> Steve Jobs would have been using Apple's ], which was designed for Jobs's own slide shows beginning in 2003, but Gallo says that "speaking like Jobs has little to do with the type of presentation software you use (PowerPoint, Keynote, etc.) ... all the techniques apply equally to PowerPoint and Keynote."<ref name="Gallo-2009" />{{Rp|pages=14,46}} Gallo adds that "Microsoft's PowerPoint has one big advantage over Apple's Keynote presentation software—it's everywhere ... it's safe to say that the number of Keynote presentations is minuscule in comparison with PowerPoint. Although most presentation designers who are familiar with both formats prefer to work in the more elegant Keynote system, those same designers will tell you that the majority of their client work is done in PowerPoint."<ref name="Gallo-2009" />{{Rp|page=44}} | |||
| Consistent with its association with Steve Jobs's keynotes, a response to this style has been that it is particularly effective for "ballroom-style presentations" (as often given in conference center ballrooms) where a celebrated and practiced speaker addresses a large passive audience, but less appropriate for "conference room-style presentations" which are often recurring internal business meetings for in-depth discussion with motivated counterparts.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Gabrielle |first=Bruce R. |year=2010 |title=Speaking PowerPoint: The New Language of Business |publisher=Insights Publishing |isbn=978-0-9842360-4-6 |pages=16–17}}</ref> | |||
| ====Use it better==== | |||
| {{See also |Stephen Kosslyn}} | |||
| A third reaction to PowerPoint use was to conclude that the standard style is capable of being used well, but that many small points need to be executed carefully, to avoid impeding understanding. This kind of analysis is particularly associated with ], a cognitive neuroscientist who specializes in the psychology of learning and visual communication, and who has been head of the department of psychology at Harvard, has been Director of Stanford's Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences, and has published some 300 papers and 14 books.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.minerva.kgi.edu/people/stephen-kosslyn/ |title=Stephen M. Kosslyn, Ph.D., Dean of Arts and Sciences |date=2017 |website=Minerva Schools at Keck Graduate Institute (Claremont Colleges) |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160301232956/https://www.minerva.kgi.edu/people/stephen-kosslyn/ |url-status=live |archive-date=March 1, 2016 |access-date=September 24, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Kosslyn presented a set of psychological principles of "human perception, memory, and comprehension" that "appears to capture the major points of agreement among researchers."<ref name="Kosslyn-et-al=2012">{{Cite journal |last1=Kosslyn |first1=Stephen M. |author-link1=Stephen Kosslyn |last2=Kievit |first2=Rogier A. |last3=Russell |first3=Alexandra G. |last4=Shephard |first4=Jennifer M. |date=July 17, 2012 |title=PowerPoint Presentation Flaws and Failures: A Psychological Analysis |journal=Frontiers in Psychology |issn=1664-1078 |volume=3 |issue=230 |pages=230 |doi=10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00230 |pmid=22822402 |pmc=3398435 |df=mdy-all |doi-access=free }}</ref> He reports that his experiments support the idea that it is not intuitive or obvious how to create effective PowerPoint presentations that conform to those agreed principles, and that even small differences that might not seem significant to a presenter can produce very different results in audiences' understanding. For this reason, Kosslyn says, users need specific education to be able to identify best ways to avoid "flaws and failures":<ref name="Kosslyn-et-al=2012" /> | |||
| {{Blockquote|Specifically, we hypothesized and found that the psychological principles are often violated in PowerPoint slideshows across different fields ..., that some types of presentation flaws are noticeable and annoying to audience members ..., and that observers have difficulty identifying many violations in graphical displays in individual slides ... . These studies converge in painting the following picture: PowerPoint presentations are commonly flawed; some types of flaws are more common than others; flaws are not isolated to one domain or context; and, although some types of flaws annoy the audience, flaws at the level of slide design are not always obvious to an untrained observer ... .}} | |||
| The many "flaws and failures" identified were those "likely to disrupt the comprehension or memory of the material." Among the most common examples were "Bulleted items are not presented individually, growing the list from the top to the bottom," "More than four bulleted items appear in a single list," "More than two lines are used per bulleted sentence," and "Words are not large enough (i.e., greater than 20 point) to be easily seen." Among audience reactions common problems reported were "Speakers read word-for-word from notes or from the slides themselves," "The slides contained too much material to absorb before the next slide was presented," and "The main point was obscured by lots of irrelevant detail."<ref name="Kosslyn-et-al=2012" /> | |||
| Kosslyn observes that these findings could help to explain why the many studies of the instructional effectiveness of PowerPoint have been inconclusive and conflicting, if there were differences in the quality of the presentations tested in different studies that went unobserved because "many may feel that 'good design' is intuitively clear."<ref name="Kosslyn-et-al=2012" /> | |||
| In 2007 Kosslyn wrote a book about PowerPoint, in which he suggested a very large number of fairly modest changes to PowerPoint styles and gave advice on recommended ways of using PowerPoint.<ref name="Kosslyn-2007" /> In a later second book about PowerPoint he suggested nearly 150 clarifying style changes (in fewer than 150 pages).<ref>{{Cite book |last=Kosslyn |first=Stephen M. |author-link=Stephen Kosslyn |year=2010 |title=Better PowerPoint: Quick Fixes Based on How Your Audience Thinks |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-537675-3}}</ref> Kosslyn summarizes:<ref name="Kosslyn-2007" />{{Rp|pages=2–3,200}} | |||
| {{Blockquote| ... there's nothing fundamentally wrong with the PowerPoint program as a medium; rather, I claim that the problem lies in how it is used. ... In fact, this medium is a remarkably versatile tool that can be extraordinarily effective. ... For many purposes, PowerPoint presentations are a superior medium of communication, which is why they have become standard in so many fields.}} | |||
| In 2017, an online poll of social media users in the UK was reported to show that PowerPoint "remains as popular with young tech-savvy users as it is with the Baby Boomers," with about four out of five saying that "PowerPoint was a great tool for making presentations," in part because "PowerPoint, with its capacity to be highly visual, bridges the wordy world of yesterday with the visual future of tomorrow."<ref>{{Cite news |last=Burn-Callander |first=Rebecca |date=April 24, 2017 |title=Your attention, please, for the software we love to hate: PowerPoint celebrates its 30th birthday |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/business/2017/04/23/powerpoint-celebrates-30th-birthday/ |newspaper=The Daily Telegraph |issn=0307-1235 |department=Business |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6rrW6PL5n?url=https://filetea.me/n3wt2GSIIdrSaG4OKObsDPCbw |url-access=subscription <!-- but archive is ungated --> |url-status=live |archive-date=July 10, 2017 |access-date=July 10, 2017 |quote=... with new research showing that it remains as popular with young tech-savvy users as it is with the Baby Boomers. An online poll by YouGov showed that 81 per cent of UK Snapchat users agreed that PowerPoint was a great tool for making presentations. ... long -form prose has become increasingly unpopular with modern users. PowerPoint, with its capacity to be highly visual, bridges the wordy world of yesterday with the visual future of tomorrow. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| Also in 2017, the Managerial Communication Group of ] polled their incoming MBA students, finding that "results underscore just how differently this generation communicates as compared with older workers."<ref name="mit-sloan-2017">{{Cite web |url=http://mitsloan.mit.edu/newsroom/articles/3-surprising-ways-that-millennials-communicate/ |title=How millennials approach writing, giving presentations, and data visualization diverges from previous generations |last=Baskin |first=Kara |date=October 4, 2017 |website=MIT Sloan School of Management |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171004150949/http://mitsloan.mit.edu/newsroom/articles/3-surprising-ways-that-millennials-communicate/ |archive-date=October 4, 2017 |url-status=live |access-date=October 7, 2017 |quote=""Communication is part of everyone's job, but millennials do it differently," said MIT Sloan lecturer Miro Kazakoff, who co-authored the study with MIT Sloan senior lecturer Kara Blackburn."}}</ref> Fewer than half of respondents reported doing any meaningful, longer-form writing at work, and even that minority mostly did so very infrequently, but "85 percent of students named producing presentations as a meaningful part of their job responsibilities. Two-thirds report that they present on a daily or weekly basis—so it's no surprise that in-person presentations is the top skill they hope to improve."<ref name="mit-sloan-2017" /> One of the researchers concluded: "We're not likely to see future workplaces with long-form writing. The trend is toward presentations and slides, and we don't see any sign of that slowing down."<ref name="mit-sloan-2017" /> | |||
| ===U.S. military excess=== | |||
| Use of PowerPoint by the U.S. military services began slowly, because they were invested in mainframe computers, MS-DOS PCs and specialized military-specification graphic output devices, all of which PowerPoint did not support.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Gaskins |first=Robert |author-link=Robert Gaskins |title=Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint |year=2012 |publisher=Vinland Books |isbn=978-0-9851424-0-7 <!-- hardcover ed -->|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RC_5OCQQJ7YC |access-date=September 5, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624031005/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/sweating-bullets/gaskins-sweating-bullets-webpdf-isbn-9780985142414.pdf <!-- webpdf ed --> |url-status=live |archive-date=June 24, 2017 |pages=428–433 |quote=PowerPoint got off to a very slow start in infiltrating the military forces of the world ... .}}</ref> But because of the strong military tradition of presenting ], as soon as they acquired the computers needed to run it, PowerPoint became part of the U.S. military.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Gole |first=Henry G. |date=1999 |title=Leadership in Literature |url=http://ssi.armywarcollege.edu/pubs/parameters/articles/99autumn/autessay.htm |journal=] |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=134–150 |issn=0031-1723 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170918224109/http://ssi.armywarcollege.edu/pubs/parameters/articles/99autumn/autessay.htm |url-status=live |archive-date=September 18, 2017 |access-date=September 18, 2017 |quote=In the 1990s, the outward signs of form over substance are field grade officers grinding out slick PowerPoint briefing charts ... .}}</ref> | |||
| By 2000, ten years after PowerPoint for Windows appeared, it was already identified as an important feature of U.S. armed forces culture, in a front-page story in the ''Wall Street Journal'':<ref name="WSJ-Jaffe-2000">{{Cite news |last=Jaffe |first=Greg |date=April 26, 2000 |title=What's Your Point, Lieutenant? Please, Just Cut to the Pie Charts |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB956703757412556977 |url-access=subscription <!-- but archive is ungated --> |department=A-Hed |newspaper=Wall Street Journal |issn=0099-9660 |edition=US |page=A1 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ta1rPrxK?url=https://filetea.me/n3wWd80E7jUQBunx1dNjWUTBg |url-status=live |archive-date=September 18, 2017 |access-date=September 18, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote|Old-fashioned slide briefings, designed to update generals on troop movements, have been a staple of the military since World War II. But in only a few short years PowerPoint has altered the landscape. Just as word processing made it easier to produce long, meandering memos, the spread of PowerPoint has unleashed a blizzard of jazzy but often incoherent visuals. Instead of drawing up a dozen slides on a legal pad and running them over to the graphics department, captains and colonels now can create hundreds of slides in a few hours without ever leaving their desks. If the spirit moves them they can build in gunfire sound effects and images that explode like land mines. ... PowerPoint has become such an ingrained part of the defense culture that it has seeped into the military lexicon. "PowerPoint Ranger" is a derogatory term for a desk-bound bureaucrat more adept at making slides than tossing grenades.}} | |||
| U.S. military use of PowerPoint may have influenced its use by armed forces of other countries: "Foreign armed services also are beginning to get in on the act. 'You can't speak with the U.S. military without knowing PowerPoint,' says Margaret Hayes, an instructor at National Defense University in Washington D.C., who teaches Latin American military officers how to use the software."<ref name="WSJ-Jaffe-2000" /> | |||
| After another 10 years, in 2010 (and again on its front page) the ''New York Times'' reported that PowerPoint use in the military was then "a military tool that has spun out of control":<ref name="NYT-Bumiller-2010">{{Cite news |last=Bumiller |first=Elisabeth |date=April 27, 2010 |title=We Have Met the Enemy and He Is PowerPoint |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/04/27/world/27powerpoint.html |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |page=A1 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100427191554/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/04/27/world/27powerpoint.html |url-status=live |archive-date=April 27, 2010 |access-date=September 19, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote|Like an insurgency, PowerPoint has crept into the daily lives of military commanders and reached the level of near obsession. The amount of time expended on PowerPoint, the Microsoft presentation program of computer-generated charts, graphs and bullet points, has made it a running joke in the Pentagon and in Iraq and Afghanistan. ... Commanders say that behind all the PowerPoint jokes are serious concerns that the program stifles discussion, critical thinking and thoughtful decision-making. Not least, it ties up junior officers ... in the daily preparation of slides, be it for a Joint Staff meeting in Washington or for a platoon leader's pre-mission combat briefing in a remote pocket of Afghanistan.}} | |||
| The ''New York Times'' account went on to say that as a result some U.S. generals had banned the use of PowerPoint in their operations:<ref name="NYT-Bumiller-2010" /> | |||
| {{Blockquote|"PowerPoint makes us stupid," Gen. ] of the Marine Corps, the Joint Forces commander, said this month at a military conference in North Carolina. (He spoke without PowerPoint.) Brig. Gen. ], who banned PowerPoint presentations when he led the successful effort to secure the northern Iraqi city of Tal Afar in 2005, followed up at the same conference by likening PowerPoint to an internal threat. "It's dangerous because it can create the illusion of understanding and the illusion of control," General McMaster said in a telephone interview afterward. "Some problems in the world are not bullet-izable."}} | |||
| Several incidents, about the same time, gave wide currency to discussions by serving military officers describing excessive PowerPoint use and the organizational culture that encouraged it.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.armedforcesjournal.com/essay-dumb-dumb-bullets/ |title=Dumb-dumb Bullets |last=Hammes |first=Thomas X. |author-link=Thomas Hammes |date=July 1, 2009 |website=Armed Forces Journal |issn=0196-3597 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YlvTTCxK?url=https://filetea.me/t1s4y7by8yxTcuTjnsQfO5ZRA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=September 18, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://smallwarsjournal.com/blog/the-tx-hammes-powerpoint-challenge-essay-contest |title=The T. X. Hammes PowerPoint Challenge |last=Burke |first=Crispin |date=July 24, 2009 |website=Small Wars Journal |issn=2156-227X |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6Ylw4vDnF?url=https://filetea.me/t1sZXwaBBkaTwx02K12wmPwCA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=September 19, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130117031309/http://www.armytimes.com/news/2010/09/army-colonel-fired-for-powerpoint-rant-090210w/ |archive-date=January 17, 2013 |title=The PowerPoint rant that got a colonel fired |last=Sellin |first=Lawrence |date=September 2, 2010 |website=] |issn=0004-2595 |url=http://www.armytimes.com/news/2010/09/army-colonel-fired-for-powerpoint-rant-090210w/ |url-status=dead |access-date=September 19, 2017}} {{webarchive|format=addlarchives|url=https://archive.today/20150524000432/http://archive.armytimes.com/article/20100902/NEWS/9020339/The-PowerPoint-rant-that-got-a-colonel-fired |date=May 24, 2015}}</ref> In response to the ''New York Times'' story, ] and ] sent a joint letter to the editor stressing the institutional culture of the military: "... many military personnel bemoan the overuse and misuse of PowerPoint. ... The problem is not in the tool itself, but in the way that people use it—which is partly a result of how institutions promote misuse."<ref>{{Cite news |last1=Norvig |first1=Peter |author-link1=Peter Norvig |last2=Kosslyn |first2=Stephen M. |author-link2=Stephen Kosslyn |date=April 29, 2010 |title=A Tool Only as Good as the User |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/04/30/opinion/l30power.html |department=Letters to the Editor |newspaper=New York Times |issn=0362-4331 |edition=New York |publication-date=April 29, 2010 |page=A24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100503115425/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/04/30/opinion/l30power.html |url-status=live |archive-date=May 3, 2010 |access-date=September 19, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| The two generals who had been mentioned in 2010 as opposing the institutional culture of excessive PowerPoint use were both in the news again in 2017, when ] became U.S. Secretary of Defense,<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.military.com/daily-news/2017/01/20/senate-confirms-mattis-secretary-of-defense.html |last=Sisk |first=Richard |date=January 20, 2017 |title=Senate Confirms Mattis as Secretary of Defense |website=Military.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170122191417/http://www.military.com/daily-news/2017/01/20/senate-confirms-mattis-secretary-of-defense.html |url-status=live |archive-date=January 22, 2017 |access-date=September 18, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> and ] was appointed as U.S. National Security Advisor.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.military.com/daily-news/2017/02/20/trump-picks-army-lt-gen-mcmaster-national-security-adviser.html |last=McGarry |first=Brendan |date=February 20, 2017 |title=Trump Picks Army Lt. Gen. McMaster as National Security Adviser |website=Military.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222001809/http://www.military.com/daily-news/2017/02/20/trump-picks-army-lt-gen-mcmaster-national-security-adviser.html |url-status=live |archive-date=February 22, 2017 |access-date=September 18, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ===Artistic medium=== | |||
| Musician ] has been using PowerPoint as a medium for art for years, producing a book and DVD and showing at galleries his PowerPoint-based artwork.<ref name="Vienne"/> Byrne has written: "I have been working with PowerPoint, the ubiquitous presentation software, as an art medium for a number of years. It started off as a joke (this software is a symbol of corporate salesmanship, or lack thereof) but then the work took on a life of its own as I realized I could create pieces that were moving, despite the limitations of the 'medium.{{Single double}}<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://216.92.211.74/art/eeei/ |title=Envisioning Emotional Epistemological Information |last=Byrne |first=David |author-link=David Byrne |date=2003 |website=David Byrne Archive |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170916033800/http://216.92.211.74/art/eeei/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 16, 2017 |access-date=September 16, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| In 2005 Byrne toured with a theater piece styled as a PowerPoint presentation. When he presented it in Berkeley, on March 8, 2005, the University of California news service reported: "Byrne also defended appeal as more than just a business tool—as a medium for art and theater. His talk was titled 'I ♥ PowerPoint'. Berkeley alumnus ] and ] were in the audience. Eventually, Byrne said, PowerPoint could be the foundation for 'presentational theater,' with roots in Brechtian drama and Asian puppet theater."<ref>{{Cite web |last=Powell |first=Bonnie Azab |date=March 8, 2005 |title=David Byrne really does ♥ PowerPoint, Berkeley presentation shows |url=http://www.berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2005/03/08_byrne.shtml |website=UC Berkeley News Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050311025730/http://www.berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2005/03/08_byrne.shtml |url-status=live |archive-date=March 11, 2005 |access-date=September 15, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> After that performance, Byrne described it in his own online journal: "Did the PowerPoint talk in Berkeley for an audience of IT legends and academics. I was terrified. The guys that originally turned PowerPoint into a program were there, what were THEY gonna think? ... did tell me afterwards that he liked the PowerPoint as theater idea, which was a relief."<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://davidbyrne.typepad.com/db/page/49/ |title=Journal: 3.8.05: San Francisco |last=Byrne |first=David |author-link=David Byrne |date=2005 |website=David Byrne Journal |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170916033610/http://davidbyrne.typepad.com/db/page/49/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 16, 2017 |access-date=September 16, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| The expressions "PowerPoint Art" or "]" are used to define a contemporary Italian artistic movement which believes that the corporate world can be a unique and exceptional source of inspiration for the artist.<ref>{{cite web|last=Nastro |first=Santa |title=Arte e aziende. Nasce il Manifesto della Corporate Art: lo firmano Ugo Nespolo, Alexander Ponomarev e Fernando De Filippi |url=http://www.artribune.com/tribnews/2016/11/arte-aziende-nasce-manifesto-corporate-art-lo-firmano-ugo-nespolo-alexander-ponomarev-fernando-de-filippi/ |newspaper=Artribune |location=Rome |issn=2280-8817 |date=November 21, 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170916172548/http://www.artribune.com/tribnews/2016/11/arte-aziende-nasce-manifesto-corporate-art-lo-firmano-ugo-nespolo-alexander-ponomarev-fernando-de-filippi/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 16, 2017 |access-date=September 16, 2017 |quote= The corporate world can be an art object. }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.pptart.net/manifesto |title=pptArt Manifesto |last=pptArt |author-link=pptArt |date=2014 |website=pptArt.net |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YkPnogNv?url=https://filetea.me/t1siHirAq8GRca1nkAALDtJ0A |url-status=live |archive-date=May 23, 2015 |access-date=September 15, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> They say: "The pptArt name refers to PowerPoint, the symbolic and abstract language developed by the corporate world which has become a universal and highly symbolic communication system beyond cultures and borders."<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.pptart.net/corporate |title=Our Services for Corporate Clients |last=pptArt |author-link=pptArt |date=2014 |website=pptArt.net |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YkPuCnUs?url=https://filetea.me/t1s0zwT0tUpSD2uctnVellocg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 23, 2015 |access-date=September 15, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| The wide use of PowerPoint had, by 2010, given rise to " ... a subculture of PowerPoint enthusiasts is teaching the old application new tricks, and may even be turning a dry presentation format into a full-fledged artistic medium,"<ref>{{Cite news |last=Greenberg |first=Andy |author-link=Andy Greenberg |date=May 11, 2010 |title=The Underground Art Of PowerPoint |url=https://www.forbes.com/2010/05/10/microsoft-software-iphone-technology-powerpoint.html |newspaper=Forbes |issn=0015-6914 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170630132845/https://www.forbes.com/2010/05/10/microsoft-software-iphone-technology-powerpoint.html |url-status=live |archive-date=June 30, 2017 |access-date=September 15, 2017}}</ref> by using ] to create "games, artworks, anime, and movies."<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://pptheaven.mvps.org/ |title=PowerPoint Heaven: The Power to Animate |last=Toh |first=Shawn |date=2014 |website=PowerPoint Heaven |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170606041637/http://pptheaven.mvps.org/index.html |url-status=live |archive-date=June 6, 2017 |access-date=September 15, 2017 |quote= Our goal is to show users that PowerPoint is not simply a presentation tool, but is also capable on leveraging into other areas such as creating games, artworks and animations.}}</ref> | |||
| ==PowerPoint Viewer== | |||
| PowerPoint Viewer is the name for a series of small free application programs to be used on computers without PowerPoint installed, to view, project, or print (but not create or edit) presentations.<ref name="view-presentation-without-ppt">{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/View-a-presentation-without-PowerPoint-2f1077ab-9a4e-41ba-9f75-d55bd9b231a6 |title=View a presentation without PowerPoint |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170901170528/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/View-a-presentation-without-PowerPoint-2f1077ab-9a4e-41ba-9f75-d55bd9b231a6 |url-status=live |archive-date=September 1, 2017 |access-date=September 1, 2017 |quote=If you do not have PowerPoint installed on your computer, you can still open and view PowerPoint presentations by using PowerPoint Viewer, PowerPoint Mobile, or PowerPoint Online.}}</ref> | |||
| The first version was introduced with PowerPoint 3.0 in 1992, to enable electronic presentations to be projected using conference-room computers and to be freely distributed; on Windows, it took advantage of the new feature of embedding ] fonts within PowerPoint presentation files to make such distribution easier.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Fridlund |first=Alan |date=August 24, 1992 |title=PowerPoint 3.0 catches up with the best |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5VIEAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA62 |department=Reviews |newspaper=InfoWorld |issn=0199-6649 |volume=14 |issue=34|pages=61–63 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YmCLOu27?url=https://filetea.me/t1sUVQhKWxnSoqiAjX7Sd2Org |url-status=live |archive-date=May 25, 2015 |access-date=September 1, 2017 |quote=Version 3.0 now includes a PowerPoint Viewer that runs on any Windows 3.1 machine and can be distributed freely with your presentation files. ... A major advance ... is the use of embedded TrueType fonts ... ensuring that the appearance of your presentation is completely repeatable on any machine equipped with the viewer.}}</ref> The same kind of viewer app was shipped with PowerPoint 3.0 for Macintosh, also in 1992.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ebay.com/itm/262748389649 |title=Microsoft PowerPoint 3.0 for Macintosh |date=April 22, 2017 |website=eBay |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170902180732/http://www.ebay.com/itm/262748389649 |url-status=live |archive-date=September 2, 2017 |access-date=September 2, 2017 |quote=Includes ... 1 PowerPoint Viewer disk.}}</ref> | |||
| Beginning with PowerPoint 2003, a feature called "Package for CD" automatically managed all linked video and audio files plus needed fonts when exporting a presentation to a disk or flash drive or network location,<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/828504/description-of-how-to-use-the-package-for-cd-feature-in-powerpoint-200 |title=Description of how to use the Package for CD feature in PowerPoint 2003 and in PowerPoint 2007 |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=September 12, 2011 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528061629/https://www.webcitation.org/6t9ssO7Gj?url=https://filetea.me/n3wXFenSmHQRUSTK5pMr1NUbQ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=September 1, 2017}}</ref> and also included a copy of a revised PowerPoint Viewer application so that the result could be presented on other PCs without installing anything.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://blogs.msdn.com/b/waynekao/archive/2004/04/01/105381.aspx |title=New PowerPoint Viewer |last=Kao |first=Wayne |date=April 1, 2004 |website=Wayne's Microsoft Blog |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140516150318/http://blogs.msdn.com/b/waynekao/archive/2004/04/01/105381.aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=May 16, 2014 |access-date=September 3, 2017 |quote=... 2003 ... a brand new PowerPoint Viewer. The previous viewer had been written for the PowerPoint 97 release ... can be run without any installation or setup, which means it can be run directly off your USB keychain or even off write-protected media like a CD orDVD. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| The latest version that runs on Windows "was created in conjunction with PowerPoint 2010, but it can also be used to view newer presentations created in PowerPoint 2013 and PowerPoint 2016. ... All transitions, videos and effects appear and behave the same when viewed using PowerPoint Viewer as they do when viewed in PowerPoint 2010." It supports presentations created using PowerPoint 97 and later.<ref name="view-presentation-without-ppt" /> The latest version that runs on Macintosh is PowerPoint 98 Viewer for the ] and ], for Macs supporting System 7.5 to ] (10.4).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.microsoft.com/mac/products/office/98/updates/powerpoint98_viewer/default.asp |title=PowerPoint 98 Viewer |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=1998 |website=Microsoft Mac Office |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20001217103900/http://www.microsoft.com/MAC/products/office/98/updates/powerpoint98_viewer/default.asp |archive-date=December 17, 2000 |url-status=dead |access-date=September 3, 2017 <!-- dead --> |df=mdy-all }}</ref> It can open presentations only from PowerPoint 3.0, 4.0, and 8.0 (PowerPoint 98), although presentations created on Mac can be opened in PowerPoint Viewer on Windows.<ref>{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130510103008/http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm <!-- long URL needed --> |title=PowerPoint FAQ: Versions |last=<!-- author not given --> |date=May 10, 2013 |website=A Bit Better Corporation |url=http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 10, 2013 |access-date=August 4, 2017}} A diagram shows "which versions of PowerPoint can open/save which other versions" up to version 9.0 for Windows ("PowerPoint 2000").</ref> | |||
| {{As of|May 2018}}, the last versions of PowerPoint Viewer for all platforms have been retired by Microsoft; they are no longer available for download and no longer receive security updates.<ref name="PPT-Viewer-retired">{{Cite web |url= https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/office_sustained_engineering/2017/11/16/end-of-support-for-the-excel-and-powerpoint-Viewers-and-the-office-compatibility-pack/ |title=End of support for the Excel and PowerPoint viewers and the Office Compatibility Pack |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=November 16, 2017 |website=Microsoft Office Sustained Engineering Team Blog |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171118072211/https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/office_sustained_engineering/2017/11/16/end-of-support-for-the-excel-and-powerpoint-viewers-and-the-office-compatibility-pack/ |url-status=live |archive-date=November 18, 2017 |access-date=January 25, 2018}}</ref> The final PowerPoint Viewer for Windows (2010)<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=13 |title=PowerPoint Viewer |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=October 25, 2011 |website=Microsoft Download Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120712230357/http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=13 |url-status=dead |archive-date=July 12, 2012 |access-date=January 25, 2018 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> and the final PowerPoint Viewer for ] (1998)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.microsoft.com/mac/products/office/98/updates/powerpoint98_viewer/default.asp |title=Microsoft PowerPoint 98 Viewer |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=1998 |website=Microsoft MacTopia |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20000816202129/http://www.microsoft.com/mac/products/office/98/updates/powerpoint98_viewer/default.asp |archive-date=August 16, 2000 <!-- earliest archive of doc -->|url-status=dead |access-date=January 25, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://download.microsoft.com/download/office98mac/Update/98/MacOS/EN-US/PPT98VW.hqx |title=Download Mac PowerPoint 98 Viewer |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2017 |website=Microsoft Download Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170202011407/http://download.microsoft.com/download/office98mac/Update/98/MacOS/EN-US/PPT98VW.hqx |archive-date=February 2, 2017 <!-- latest archive of code, 6808 KB. Beware, archive of this code linked from from August 16, 2000 IA archive of its doc (preceding ref) is corrupt (silently truncated at 1024 KB). Can not use one ref for both, because ALL archives of the doc at IA (last in 2001) have links to truncated code. -->|url-status=dead |access-date=January 25, 2018}}</ref> are available only from archives. The recommended replacements for PowerPoint Viewer: "On Windows 10 PCs, download the free ... PowerPoint Mobile application from the Windows Store,"<ref name="PPT-Viewer-retired" /> and "On Windows 7 or Windows 8/8.1 PCs, upload the file to OneDrive and view it for free using ... PowerPoint Online."<ref name="PPT-Viewer-retired" /> | |||
| ==Versions== | |||
| {{Version |t |show=11110}} | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
| |+ PowerPoint release history | |||
| |- | |||
| ! <!-- type from Dts --> |Date | |||
| ! class="unsortable" |Name | |||
| ! data-sort-type="number" |Version | |||
| ! data-sort-type="text" |System | |||
| ! class="unsortable" |Comments | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |April 1987}}<ref name="ppt-1-mac-apr-1987"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1TAEAAAAMBAJ |last=Mace |first=Scott |title= Presentation Package Lets Users Control Look |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=9 |issue=9 |date=March 2, 1987 |page=5 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085435/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym2krMYP?url=https://filetea.me/t1sKNh0ZTl2S8xyckHWoi2ywg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |1.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |Shipped by Forethought, Inc. | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |October 1987}}<ref name="ppt-1-01-mac-oct-1987"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sTsEAAAAMBAJ |last=Flynn |first=Laurie |title=Apple Sets Its Sights on Desktop Presentations |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=9 |issue=37 |date=September 14, 1987 |page=35 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YnD6swM3?url=https://filetea.me/t1syOlJ9TLtQJaV9bSFaDul7Q |url-status=live |archive-date=May 25, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}} Report of Seybold conference in late September 1987 where Microsoft introduced relabeled PowerPoint. ''Macworld'' magazine carried its first Microsoft advertisement for PowerPoint in its November 1987 issue, with the initial subhead "Introducing Microsoft PowerPoint." | |||
| {{cite magazine |url=https://archive.org/stream/MacWorld_8711_November_1987#page/n43/ |author=Microsoft Corporation |type=advertisement |title=Everything you need to make a great presentation, just add water. |magazine=MacWorld |issn=0741-8647 |volume=4 |issue=11 |publisher=IDG |date=November 1987 |pages=40–41 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6s0euEfcJ?url=https://dropfile.to/AKrOGPD |url-status=live |archive-date=July 16, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |1.01}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |Relabeled and shipped by Microsoft | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |May 1988}}<ref name="ppt-2-mac-may-1988"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mz0EAAAAMBAJ |last=Flynn |first=Laurie |title=Updated PowerPoint Supports Mac II Colors |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=10 |issue=18 |date=May 2, 1988 |page=27 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090241/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnELZSzx?url=https://filetea.me/t1sZzVDo8j6QrWRoxZrPTJyaA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |2.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |December 1988}}<ref name="ppt-2-01-mac-dec-1988"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CjoEAAAAMBAJ |last=Flynn |first=Laurie |title=Driver Sends PowerPoint Files Out for Conversion |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=10 |issue=50 |date=December 12, 1988 |page=33 <!-- note pg in url is off by 1, PT (PA33 does not work) --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090322/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnEcUWhh?url=https://filetea.me/t1sgBV6VhYjSRebuDNtTzr4JQ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |2.01}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |Added Genigraphics software and services | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |May 1990}}<ref name="ppt-2-win-may-1990"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nzsEAAAAMBAJ | last=Coale |first=Kristi |title=PowerPoint to Challenge PC Presentation Market |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=12 |issue=22 |date=May 28, 1990 |page=13 <!-- note pg in url is off by 1, PT (PA13 does not work) --> |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090400/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnEtn33t?url=https://filetea.me/t1sx0ZdfHKRStiWtmXVAukXxA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |2.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Announced with Windows 3.0, numbered to match contemporary Macintosh version | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |May 1992}}<ref name="ppt-3-win-may-1992"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XlEEAAAAMBAJ |last=Borzo |first=Jeanette |title=PowerPoint users pleased by changes |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=14 |issue=20 |date=May 18, 1992 |page=15 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090441/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnF6x0m9?url=https://filetea.me/t1s93DMYfS1T7Gs3VyxWzxRZw |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |3.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Announced with Windows 3.1 | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |September 1992}}<ref name="ppt-3-mac-sep-1992"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=n1EEAAAAMBAJ |last=Damore |first=Kelley |title=PowerPoint 3.0 for the Mac mirrors version for Windows |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=14 |issue=41 |date=October 12, 1992 |page=151 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090521/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnFN9lh9?url=https://filetea.me/t1sBdIbxLvYTQuc167ruzsQRg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |3.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |February 1994}}<ref name="ppt-4-win-feb-1994"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7DoEAAAAMBAJ |last= <!-- staff writer(s), no byline --> |title=Microsoft Corp. will start shipping PowerPoint 4.0 |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=16 |issue=7 |date=February 14, 1994 |page=19 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090600/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnFcG8UW?url=https://filetea.me/t1sxxgKgmolQxy8ZI6wU4RI8Q |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |4.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |October 1994}}<ref name="ppt-4-mac-oct-1994"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mEU4Qex5594C |last=Halper |first=Mark |title=Native Microsoft suite coming for Power Mac |newspaper=Computerworld |publisher=IDG |issn=0010-4841 |volume=28 |issue=31 |date=August 1, 1994 |page=15 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085638/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym5o22HM?url=https://filetea.me/t1sLY5ExbkxTXal3ry6EGMQGw |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote= ... the forthcoming version of PowerPoint 4.0, which is part of Office 4.2. ... Microsoft said it is packaging separate ... versions for 68000-based Macintoshes and for newer PowerPC-based Power Macintoshes, all in one shrink-wrapped box.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint | |||
| |{{Version |o |4.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |Native for Power Mac | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |July 1995}}<ref name="ppt-7-win-jul-1995"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3joEAAAAMBAJ |last=Grace |first=Rich |title=PowerPoint gains multimedia strength |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=17 |issue=30 |date=July 24, 1995 |page=98 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090640/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnFte6IK?url=https://filetea.me/t1sZKPjFhhWSVCLyAgg9cG1lQ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 95 | |||
| |{{Version |o |7.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Versions 5.0 and 6.0 were skipped on Windows, so all apps in Office 95 were 7.0<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.lassesen.com/msdn/using%20microsoft%20ole%20automation%20servers%20to%20develop%20solutions.pdf |title=Using Microsoft OLE Automation Servers to Develop Solutions |last=Lassesen |first=Ken |date=October 17, 1995 |website=Archive of Articles from MSDN Technology Group |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807073017/http://www.lassesen.com/msdn/using%20microsoft%20ole%20automation%20servers%20to%20develop%20solutions.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=Note that version 7.0 of a product is the same as a '95' designation ... .}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |January 1997}}<ref name="ppt-8-win-jan-1997"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bjoEAAAAMBAJ |last=Vadlamudi |first=Pardhu |title=Office 97 now open for business |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=19 |issue=3 |date=January 20, 1997 |page=6 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090722/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnG82A7W?url=https://filetea.me/t1sMjetlKKHTLms7retG5461Q |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 97 | |||
| |{{Version |o |8.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Support ended on February 28, 2002<ref name="support.microsoft.com">{{Cite web |date=2014-03-29 |title=Microsoft Office Products Support Lifecycle FAQ |url=http://support.microsoft.com/gp/lifeoffice |access-date=2023-12-13 |archive-date=March 29, 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140329171056/http://support.microsoft.com/gp/lifeoffice |url-status=bot: unknown }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |March 1998}}<ref name="ppt-8-mac-mar-1998"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DFEEAAAAMBAJ |last=Senna |first=Jeff |title=Office 98 boasts cross-platform parity |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=20 |issue=9 |date=March 2, 1998 |page=113 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090802/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnGRAExl?url=https://filetea.me/t1siW4z1qGuQ5ygpYZc40xgiQ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 98 | |||
| |{{Version |o |8.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |Versions 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0 were skipped on Macintosh, to match Windows<ref>{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130510103008/http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm |title=PowerPoint FAQ: Unsolved Mysteries |last=<!-- author not listed --> |date=May 10, 2013 |website=A Bit Better Corporation |url=http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 10, 2013 |access-date=August 4, 2017}} | |||
| <!-- backup archive at: https://www.webcitation.org/6s6Trrd1t?url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130510103008/http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm --></ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 1999}}<ref name="ppt-9-win-jun-1999"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EVAEAAAAMBAJ |last=Railsback |first=Kevin |title=Office 2000: making life easier for IT and end-users alike |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=21 |issue=15 |date=April 12, 1999 |page=10 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090842/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnGfc70d?url=https://filetea.me/t1sxZiF8w6SRx6Vz01udAoBUg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2000 | |||
| |{{Version |o |9.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Support ended on July 14, 2009<ref name="support.microsoft.com"/> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |August 2000}}<ref name="ppt-9-mac-aug-2000"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.cnet.com/products/microsoft-office-2001-macos/ |title=Microsoft Office 2001: MacOS review |last=Steinberg |first=Gene |date=September 14, 2000 |website=CNET Review |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140925070802/http://www.cnet.com/products/microsoft-office-2001-macos/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 25, 2014 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2001 | |||
| |{{Version |o |9.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |May 2001}}<ref name="ppt-10-win-may-2001"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qzgEAAAAMBAJ |last=Yager |first=Tom |title=Office spruced with surprising subtlety |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=23 |issue=12 |date=March 19, 2001 |page=53 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527090924/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnGuiBvl?url=https://filetea.me/t1sKhsdOVPTRvWMX8uSxNpUpw |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint XP | |||
| |{{Version |o |10.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Support ended on July 12, 2011<ref>{{Cite web |last=GitHub-Name |title=Office XP - Microsoft Lifecycle |url=https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/office-xp |access-date=2023-12-13 |website=learn.microsoft.com |language=en-us}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |November 2001}}<ref name="ppt-10-mac-nov-2001"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=http://www.macworld.com/article/1019797/office.html |last=Dalrymple |first=Jim |title=Microsoft sets date for Office v. X release |date=October 24, 2001 |website=Macworld |publisher=IDG |issn=0741-8647 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170718034148/http://www.macworld.com/article/1019797/office.html <!-- webcitation has bugs when archiving this URL --> |url-status=live |archive-date=July 18, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=Microsoft's Macintosh Business Unit (MacBU) today announced that Office v. X would be available to the public on November 19. ... Office v. X runs natively on OS X – it will not run under OS 9.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint v. X | |||
| |{{Version |o |10.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |October 2003}}<ref name="ppt-11-win-oct-2003"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=http://www.cbsnews.com/news/microsoft-revamps-office-software/ |last=Cosgrove-Mather |first=Bootie |title=Microsoft Revamps Office Software |website=CBS News |date=October 22, 2003 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170806194509/http://www.cbsnews.com/news/microsoft-revamps-office-software/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 6, 2017 |access-date=August 6, 2017 |quote=... Bill Gates introduces Microsoft Office 2003 in New York Tuesday, Oct. 21, 2003.}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6zkEAAAAMBAJ |last= <!-- staff writer(s), no byline --> |title=Microsft Issues Critical Office Patch |newspaper=InfoWorld |publisher=IDG |issn=0199-6649 |volume=25 |issue=44 |date=November 10, 2003 |page=18 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527091003/https://www.webcitation.org/6YnH7aIgW?url=https://filetea.me/t1sxXGOv7Z4RhOJIvz08MUW8Q |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=... less than a month after the software officially launched.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2003 | |||
| |{{Version |o |11.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Support ended on April 8, 2014<ref>{{Cite web |last=GitHub-Name |title=Microsoft Office 2003 - Microsoft Lifecycle |url=https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/microsoft-office-2003 |access-date=2023-12-13 |website=learn.microsoft.com |language=en-us}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 2004}}<ref name="ppt-11-mac-jun-2004"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZVxJ-vb1jzAC |last=Dreier |first=Troy |title=Office 2004 for Mac: An Essential Upgrade |newspaper=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |volume=23 |issue=12 |date=July 2004 |page=53 |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240527085515/https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym4GgvHs?url=https://filetea.me/t1swe0LQEPWTKxqLrrOo1OpfA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 27, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2004 | |||
| |{{Version |o |11.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |May 2005}}<ref name="ppt-11-mob-may-2005"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qwIAAAAAMBAJ |last= <!-- staff writer(s), no byline --> |title=Windows Mobile 5.0 Comes to PDAs and Smartphones |page=16 |date=August 2005 |newspaper=Maximum PC |issn=1522-4279 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZpUPtNl5?url=https://filetea.me/t1sx3vdYBUkRfud0VK6YIgRCg |url-status=live |archive-date=July 6, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=PowerPoint Mobile—a new addition to the suite—doubles as a powerful sleep-aid.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile | |||
| |{{Version |o | 11.0 }} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |January 2007}}<ref name="ppt-12-win-jan-2007"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Vi8LZRM6MlcC |last=<!-- staff writer(s), no byline --> |title=Microsoft Office 2007: Worth the Wait |newspaper=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |volume=26 |issue=1/2 <!-- combined issue --> |date=January 2007 |page=48 |archive-url= https://www.webcitation.org/6YnCoYrqc?url=https://filetea.me/t1sx7AmJ1moTxSnb6J2i1TQEw |url-status=live |archive-date=May 25, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2007 | |||
| |{{Version |o |12.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |End of support October 10, 2017<ref name="ppt-12-win-eos">{{Cite web |url=https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/3198497/office-2007-approaching-end-of-extended-support |title=Office 2007 approaching end of extended support |website=Microsoft Support |date=February 6, 2017 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6uDe33MUQ?url=https://filetea.me/n3wPnyIxgosRPmAaLvaLqCx1A |url-status=live |archive-date=October 15, 2017 |access-date=October 14, 2017 |quote=Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 ... PowerPoint 2007 (Home and Student version) ... no new security updates, non-security updates, free or paid assisted support options, or online technical content updates ... 10/10/2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |September 2007}}<ref name="ppt-12-mob-sep-2007"> | |||
| {{Cite news |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KmFF_zr-HVgC |last=<!-- staff writer(s), no byline --> |title=Windows Mobile 6: Make Your Smartphone Smarter |newspaper=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |volume=26 |issue=12 |date=June 5, 2007 |page=44 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6Ym4qp14n?url=https://filetea.me/t1sqxsHYJbvRGSjNYKWIpVlBg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 }} PowerPoint was updated in November 2007: {{Cite web |url=https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=10555 |last=Microsoft |title=Microsoft Office Mobile 6.1: Upgrade for Microsoft Office 2007 file formats |date=November 28, 2007 |website=Microsoft Download Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120427074505/http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=10555 |url-status=live |archive-date=April 27, 2012 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile | |||
| |{{Version |o | 12.0 }} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |January 2008}}<ref name="ppt-12-mac-jan-2008"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=http://www.macworld.com/article/1131597 |last=Tessler |first=Franklin N. |title=Microsoft PowerPoint 2008 At a Glance |date=January 18, 2008 |website=Macworld |publisher=IDG |issn=0741-8647 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZpSDQXNx?url=https://filetea.me/t1srxIXa4lbRPWAZ9k87vpKRw |url-status=live |archive-date=July 6, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2008 | |||
| |{{Version |o |12.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 2010 |addkey=1}}<ref name="ppt-14-win-jun-2010"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://news.microsoft.com/2010/06/15/microsoft-office-2010-now-available-for-consumers-worldwide/ |title=Microsoft Office 2010 Now Available for Consumers Worldwide |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=June 15, 2010 |website=Microsoft News Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160629195435/http://news.microsoft.com/2010/06/15/microsoft-office-2010-now-available-for-consumers-worldwide/ |url-status=live |archive-date=June 29, 2016 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2010 | |||
| |{{Version|o|14.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| |Version 13.0 was skipped for ] concerns.<ref name="why-no-13">{{Cite web |url=http://channel9.msdn.com/Shows/ButWhy/There-is-no-Office-13-But-Why |title=There is no Office 13, but why? |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=February 25, 2010 |website= Channel9 videos, Microsoft Developer Network |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140807115109/http://channel9.msdn.com/Shows/ButWhy/There-is-no-Office-13-But-Why |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2014 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> Support ended on October 13, 2020<ref>{{Cite web |last=GitHub-Name |title=Microsoft Office 2010 - Microsoft Lifecycle |url=https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/microsoft-office-2010 |access-date=2023-12-13 |website=learn.microsoft.com |language=en-us}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 2010 |addkey=2}}<ref name="ppt-14-web-jun-2010">{{Cite web |url=https://www.pcmag.com/article2/0%2C2817%2C2365016%2C00.asp/ |last=Mendelson |first=Edward |author-link=Edward Mendelson |title=Microsoft Office Web Apps |date=June 14, 2010 |website=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YQPuWqxx?url=https://filetea.me/t1smEpx9l31SGyZLqmUg2HZ2A |url-status=live |archive-date=May 10, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2010 Web App | |||
| |{{Version |o |14.0}} | |||
| |Web | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 2010 |addkey=3}}<ref name="ppt-14-mob-jun-2010"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2364654,00.asp/ |last=Lendino |first=Jamie |title=Microsoft Office Mobile 2010 (Windows Phone) |date=June 4, 2010 |website=PC Magazine |publisher=Ziff Davis |issn=0888-8507 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YQQM1oQN?url=https://filetea.me/t1sqLezurqlTRWMio25wxvtKA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 10, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2010 | |||
| |{{Version |o | 14.0 }} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |November 2010}}<ref name="ppt-14-mac-nov-2010"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://news.microsoft.com/2010/10/26/mac-meets-pc-with-new-office-release/ |title=Mac Meets PC with New Office Release |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=October 26, 2010 |website=Microsoft News Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807071358/https://news.microsoft.com/2010/10/26/mac-meets-pc-with-new-office-release/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2011 | |||
| |{{Version |o |14.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |Version 13.0 was skipped for ] concerns<ref name="why-no-13" /> End of support October 10, 2017<ref name="ppt-14-mac-eos">{{Cite web |url=https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4001737/products-reaching-end-of-support-for-2017 |title=Products Reaching End of Support for 2017 |website=Microsoft Support |date=September 7, 2017 |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6uDeGX6f8?url=https://filetea.me/n3wHtYaSifRQdCvzqlvQhxmgQ |url-status=live |archive-date=October 15, 2017 |access-date=October 14, 2017 |quote=Microsoft PowerPoint for Mac 2011 ... no new security updates, non-security updates, free or paid assisted support options or online technical content updates ... October 10, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |April 2012}}<ref name="ppt-14-symbian-apr-2012"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.zdnet.com/article/full-microsoft-office-mobile-now-available-on-select-nokia-symbian-phones/ |last=Foley |first=Mary Jo |title=Full Microsoft Office Mobile now available on select Nokia Symbian phones |date=April 10, 2012 |website=ZDnet.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150715053728/http://www.zdnet.com/article/full-microsoft-office-mobile-now-available-on-select-nokia-symbian-phones/ |url-status=live |archive-date=July 15, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2010 | |||
| |{{Version |o | 14.0 }} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |October 2012}}<ref name="ppt-15-web-oct-2012"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.zdnet.com/article/microsofts-new-office-web-apps-to-roll-out-to-office-365-users-in-late-october/ |last=Foley |first=Mary Jo |title=Microsoft's new Office Web Apps to roll out to Office 365 users in late October |date=October 10, 2012 |website=ZDnet.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150921141756/http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsofts-new-office-web-apps-to-roll-out-to-office-365-users-in-late-october/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 21, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Web App 2013 | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |Web | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |November 2012 |addkey=1}}<ref name="ppt-15-mob-nov-2012"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://rcpmag.com/articles/2012/10/31/windows-phone-8-new-office.aspx |last=Mackie |first=Kurt |title=Windows Phone 8 to Include 'New Office' Version for Mobile |date=October 31, 2012 |website=Redmond Channel Partner Magazine |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150425172915/http://rcpmag.com/articles/2012/10/31/windows-phone-8-new-office.aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=April 25, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2013 | |||
| |{{Version |o | 15.0 }} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |November 2012 |addkey=2}}<ref name="ppt-15-winrt-nov-2012"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-to-deliver-final-version-of-office-2013-rt-starting-in-early-november/ |last=Foley |first=Mary Jo |title=Microsoft to deliver final version of Office 2013 RT starting in early November |date=September 14, 2012 |website=ZDnet.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150123192314/http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-to-deliver-final-version-of-office-2013-rt-starting-in-early-november/ |url-status=live |archive-date=January 23, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint RT 2013 | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |January 2013}}<ref name="ppt-15-win-jan-2013"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=http://bgr.com/2013/01/28/microsoft-office-2013-set-for-january-29th-debut-309767/ |last=Graziano |first=Dan |title=Microsoft Office 2013 set for January 29th debut |date=January 28, 2013 |website=BGR.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150427071140/http://bgr.com/2013/01/28/microsoft-office-2013-set-for-january-29th-debut-309767/ |url-status=live |archive-date=April 27, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2013 | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 2013}}<ref name="ppt-15-iphone-jun-2013"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://blogs.office.com/2013/06/14/office-mobile-for-iphone/ |last=O'Donald |first=Andy |title=Office Mobile for iPhone |date=June 14, 2013 |website=Microsoft Office Blogs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150424030048/http://blogs.office.com/2013/06/14/office-mobile-for-iphone/ |url-status=live |archive-date=April 24, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2013 for iPhone | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |iPhone | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |July 2013}}<ref name="ppt-15-android-jul-2013"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://blogs.office.com/2013/07/31/office-mobile-for-android-phones/ |last=Office 365 Team |title=Office Mobile for Android phones |date=July 31, 2013 |website=Microsoft Office Blogs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150510114812/http://blogs.office.com/2013/07/31/office-mobile-for-android-phones/ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 10, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2013 for Android | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |Android | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |February 2014}}<ref name="ppt-15-online-feb-2014"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=http://www.pcworld.com/article/2099502 |last=Paul |first=Ian |title=Meet Office Online, Microsoft's slightly tweaked Office Web Apps replacement |date=February 20, 2014 |website=PCWorld |publisher=IDG |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6ZUCkbom9?url=https://filetea.me/t1sYd9NCeSIRKmG4c4p7WNALg |url-status=live |archive-date=June 22, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2013 Online | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |Web | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |March 2014}}<ref name="ppt-15-ipad-mar-2014"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://blogs.office.com/2014/03/27/announcing-the-office-you-love-now-on-the-ipad/ |last=Case |first=John |title= Announcing the Office you love, now on the iPad |date=March 27, 2014 |website=Microsoft Office Blogs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150510213134/http://blogs.office.com/2014/03/27/announcing-the-office-you-love-now-on-the-ipad/ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 10, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2013 for iPad | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |iPad | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |November 2014}}<ref name="ppt-15-ios-nov-2014"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://redmondmag.com/articles/2014/11/06/office-ipad-and-iphone.aspx |last=Mackie |first=Kurt |title= Office iPad and iPhone Users Can Now Create and Edit Docs for Free |date=November 6, 2014 |website=Redmond Magazine |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807073724/https://redmondmag.com/articles/2014/11/06/office-ipad-and-iphone.aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2013 for iOS | |||
| |{{Version |co |15.0}} | |||
| |iOS | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |June 2015}}<ref name="ppt-16-android-jun-2015"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.thurrott.com/mobile/android/4296/office-apps-for-android-handsets-exit-preview |last=Thurrott |first=Paul |title=Office Apps for Android Handsets Exit Preview |date=June 24, 2015 |website=Thurrott.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150626143645/https://www.thurrott.com/mobile/android/4296/office-apps-for-android-handsets-exit-preview |url-status=live |archive-date=June 26, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2016 for Android | |||
| |{{Version |c |16.0}} | |||
| |Android | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |July 2015 |addkey=1}}<ref name="ppt-15-mac-jul-2015"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://blogs.office.com/en-us/2015/07/09/office-2016-for-mac-is-here/ |last=Koenigsbauer |first=Kirk |title=Office 2016 for Mac is here! |date=July 9, 2015 |website=Microsoft Office Blogs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150926024835/https://blogs.office.com/2015/07/09/office-2016-for-mac-is-here/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 26, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=Office 2016 for Mac is now available in 139 countries and 16 languages.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2016 for Macintosh | |||
| |{{Version |c |16.0}} | |||
| |Macintosh | |||
| |There had been no PowerPoint 2013 for Mac.<ref name="ppt-2013-mac-none"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.cultofmac.com/179541/microsoft-wont-bring-office-2013-to-mac-but-it-will-add-skydrive-integration-to-office-2011/ |last=Bell |first=Killian |title=Microsoft Won't Bring Office 2013 To Mac ... |date=July 18, 2012 |website=Cult of Mac |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807073303/https://www.cultofmac.com/179541/microsoft-wont-bring-office-2013-to-mac-but-it-will-add-skydrive-integration-to-office-2011/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=Microsoft confirmed to us that there is no Office for Mac 2013 release planned.}}</ref> Was version 15.0 from July 2015 to January 2018.<ref name="ppt-2016-mac-ver16"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Update-history-for-Office-2016-for-Mac-700cab62-0d67-4f23-947b-3686cb1a8eb7 |last=Microsoft Corp. |title=Update history for Office 2016 for Mac |date=January 18, 2018 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://archive.today/20180119001050/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Update-history-for-Office-2016-for-Mac-700cab62-0d67-4f23-947b-3686cb1a8eb7 |url-status=live |archive-date=January 19, 2018 |access-date=January 18, 2018 |quote=PowerPoint 16.9.0 (18011602). |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |July 2015 |addkey=2}}<ref name="ppt-16-mob-jul-2015"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.thurrott.com/windows/windows-10/4661/office-mobile-apps-for-windows-10-are-now-generally-available |last=Thurrott |first=Paul |title=Office Mobile Apps for Windows 10 are Now Generally Available |date=July 16, 2015 |website=Thurrott.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150717045623/https://www.thurrott.com/windows/windows-10/4661/office-mobile-apps-for-windows-10-are-now-generally-available |url-status=live |archive-date=July 17, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=Microsoft noted that it has added 'Mobile' to the app names on PCs and big tablets to help distinguish them from the desktop-based Office application suite ... . On phones and small tablets—i.e. on ]—these apps will simply retain their normal names (Word, Excel and PowerPoint), with no Mobile added.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2016 | |||
| |{{Version |c |16.0}} | |||
| |] | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |July 2015 |addkey=3}}<ref name="ppt-16-ios-jul-2015"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=http://techview.me/2015/07/microsoft-launches-arabic-version-of-office-2016-for-mac/ |last=Gupta |first=Nakul |title=News: Microsoft updates Office apps for iPhone and iPad |date=July 27, 2015 |website=TechView |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807072959/http://techview.me/2015/07/microsoft-launches-arabic-version-of-office-2016-for-mac/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint Mobile 2016 for iOS | |||
| |{{Version |c |16.0}} | |||
| |iOS | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |September 2015}}<ref name="ppt-16-win-sep-2015"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://blogs.office.com/en-us/2015/09/22/thenewoffice/ |last=Koenigsbauer |first=Kirk |title=The new Office is here |date=September 22, 2015 |website=Microsoft Office Blogs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150923015853/https://blogs.office.com/2015/09/22/thenewoffice/ |url-status=live |archive-date=September 23, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |quote=Today is the worldwide release of Office 2016 for Windows.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2016 for Windows | |||
| |{{Version |c |16.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{dts |January 2018}}<ref name="ppt-16-winstore-jan-2018"> | |||
| {{Cite web |url=https://www.zdnet.com/home-and-office/work-life/microsoft-brings-its-core-office-apps-to-the-microsoft-store/ |last=Foley |first=Mary Jo |title=Microsoft brings its core Office apps to the Microsoft Store |date=January 24, 2018 |website=ZDnet.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180125015332/http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-brings-its-core-office-apps-to-the-microsoft-store/ |url-status=live |archive-date=January 25, 2018 |access-date=January 25, 2018 |quote=Microsoft made these Desktop Bridge apps—which company officials previously referred to as the "Office in the Windows Store apps"—available to Windows 10 S users in preview form last Summer.}}</ref> | |||
| |PowerPoint 2016 for Windows Store | |||
| |{{Version |c |16.0}} | |||
| |Windows | |||
| | | |||
| |- | |||
| |2018 | |||
| |PowerPoint 2019 | |||
| |{{Version|c|16.0}} | |||
| |Windows and other OS | |||
| |This and subsequent versions (PowerPoint 2021 and Office 365 PowerPoint) are all internally version 16.0 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Date | |||
| ! Name | |||
| ! Version | |||
| ! System | |||
| ! Comments | |||
| |} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ;PowerPoint 1.0 | |||
| :For Macintosh: April 1987<ref name="ppt-1-mac-apr-1987" /> | |||
| :Innovations included: multiple slides in a single file, organizing slides with a slide sorter view and a title view (precursor of outline view), speakers' notes pages attached to each slide, printing of audience handouts with multiple slides per page, text with outlining styles and full word-processor formatting, graphic shapes with attached text for drawing diagrams and tables.<ref name="austin-timeline-2001">{{Cite web |url=http://www.gbuwizards.com/files/powerpoint-timeline-to-1995-dennis-austin.pdf |title=PowerPoint Version Timeline (to PowerPoint 7.0, 1995) |last=Austin |first=Dennis |date=2001 |website=GBU Wizards of Menlo Park |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528055458/https://www.webcitation.org/6sWbRP9tx?url=https://filetea.me/n3wNc4xaoNgRPCO0cpdXD8mng |url-status=live |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 6, 2017}}</ref> It also shipped with a hardbound book as its manual.<ref name="belleville-ppthistory-2000">{{Cite web |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528054138/https://www.webcitation.org/6sTSdansK?url=https://filetea.me/n3wRMyjrmLfTJCb6c5kzbN8Pg |title=PowerPoint Historical Review |last=Belleville |first=Cathleen |date=August 24, 2000 |website=A Bit Better Corporation |url=http://www.bitbetter.com:80/downloads/belleville_ppthistory.ppt |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 28, 2024 <!-- latest copy at Internet Archive is March 24, 2016 --> |access-date=August 4, 2017}}{{webarchive|format=addlarchives|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160324163116/http://www.bitbetter.com/downloads/belleville_ppthistory.ppt |date=March 24, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| :"It produced overhead transparencies on a black-and-white Macintosh for laser printing. Presenters could now directly control their own overheads and would no longer have to work through the person with the typewriter. PowerPoint handled the task of making the overheads all look alike; one change reformats them all. Typographic fonts were better than an Orator typeball, and charts and diagrams could be imported from MacDraw, MacPaint, and Excel, thanks to the new Mac clipboard."<ref name="gaskins-cacm-2007">{{Cite journal |last1=Gaskins |first1=Robert |author-link1=Robert Gaskins |date=December 2007 |title=PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics |department=Viewpoint |journal=] |publication-date=December 2007 |volume=50 |issue=12 |pages=15–17 |issn=0001-0782 |doi=10.1145/1323688.1323710 |s2cid=48306 |url=https://www.academia.edu/1866305 |format=PDF |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160107161639/http://www.robertgaskins.com/powerpoint-history/documents/gaskins-powerpoint-at-20-cacm-vol50-no12-dec-2007-p15-p17.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=January 7, 2016 |access-date=August 4, 2017 }} These versions are described in the sidebar, "Presentation Formats and PowerPoint," p. 17.</ref> | |||
| :System requirements: (Mac) Original Macintosh or better, System 1.0 or higher, 512K RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013">{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130424125125/http://www.bitbetter.com/powertips.htm <!-- long URL needed --> |title=PowerPoint Tips & Tricks: PowerPoint System Requirements |last=<!-- author not given --> |date=April 24, 2013 |website=A Bit Better Corporation |url=http://www.bitbetter.com/powertips.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=April 24, 2013 |access-date=August 4, 2017}} System requirements are in a table at the very end of this document.</ref> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 2.0 | |||
| :For Macintosh: May 1988;<ref name="ppt-2-mac-may-1988" /> for Windows: May 1990<ref name="ppt-2-win-may-1990" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: color, more word processing features, find and replace, spell checking, color schemes for presentations, guide to color selection, ability to change color scheme retrospectively, shaded coloring for fills.<ref name="austin-timeline-2001" /> | |||
| :"It added color 35 mm slides, transmitting the resulting file over a modem to Genigraphics for imaging on Genigraphics' film recorders and photo processing in Genigraphics' labs overnight. Genigraphics was the leading professional service bureau, having developed its own Digital Equipment Corp. PDP-11-based computer systems for its artists. After a short time, though, Genigraphics itself switched to PowerPoint."<ref name="gaskins-cacm-2007" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Mac) Original Macintosh or better, System 4.1 or higher, 1 MB RAM. (Windows) 286 PC or higher, Windows 3.0, 1 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013"/> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 3.0 | |||
| :For Windows, May 1992;<ref name="ppt-3-win-may-1992" /> for Mac: September 1992<ref name="ppt-3-mac-sep-1992" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: the first application designed exclusively for the new Windows 3.1 platform, full support for TrueType fonts (new in Windows 3.1), presentation templates, editing in outline view, new drawing, including freeform tool, autoshapes, flip, rotate, scale, align, and transforming imported pictures into their drawing primitives to make them editable, transitions between slides in slide show, progressive builds, incorporating sound and video.<ref name="austin-timeline-2001" /> Animations included "flying bullets" where bullet points "flew" into the slide one by one, and some degree of Pen Computing support was included.<ref name="belleville-ppthistory-2000" /> | |||
| :"It added video-out to feed the new video projectors, with effects that could replace a bank of synchronized slide projectors. This version added fades, dissolves, and other transitions, as well as animation of text and pictures, and could incorporate video clips with synchronized audio."<ref name="gaskins-cacm-2007" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 286 PC or higher, Windows 3.1, 2 MB RAM. (Mac) Macintosh Plus or better, System 7 or higher, 4 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013" /> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 4.0 | |||
| :For Windows: February 1994;<ref name="ppt-4-win-feb-1994" /> for Mac: October 1994<ref name="ppt-4-mac-oct-1994" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: autolayouts, Word tables, rehearsal mode, hidden slides, and the "AutoContent Wizard".<ref name="belleville-ppthistory-2000" /> | |||
| :Introduced a standard "Microsoft Office" look and feel (shared with Word and Excel), with status bar, toolbars, tooltips. Full ] 2.0 with in-place activation.<ref name="austin-timeline-2001" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 386 PC or higher, Windows 3.1, 8 MB RAM. (Mac) 68020 Mac or better, System 7 or higher, 8 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013" /> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 7.0 | |||
| :For Windows: July 1995<ref name="ppt-7-win-jul-1995" /> | |||
| :Part of ]. Innovations included: new animation effects, real curves and textures, black and white view, autocorrect, insert symbol, meeting support features such as "Meeting Minder".<ref name="belleville-ppthistory-2000" /> | |||
| :"A complete rewrite of the product from the ground up in C++, full object model with internal ] programmability".<ref name="austin-timeline-2001" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 386 DX PC or higher, Windows 95, 6 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013" /> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 8.0 | |||
| :For Windows: January 1997;<ref name="ppt-8-win-jan-1997" /> for Mac: March 1998<ref name="ppt-8-mac-mar-1998" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: "Office Assistant", file compression, save to HTML, "Pack and Go", "AutoClipArt", transparent GIFs.<ref name="belleville-ppthistory-2000" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 486 PC or higher, 8 MB RAM. (Mac) PowerPC Mac or better, 16 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013" /> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 9.0 | |||
| :For Windows: June 1999;<ref name="ppt-9-win-jun-1999" /> for Mac: August 2000<ref name="ppt-9-mac-aug-2000" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: three-pane "browser" view (selectable list of slide miniatures or titles, large single slide, notes), autofit text, real tables, presentation conferencing, save to web, picture bullets, animated GIFs, aliased fonts.<ref name="belleville-ppthistory-2000" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) Pentium 75MHz+, Windows 95 or higher, 20 MB RAM. (Mac) PowerPC Mac 120MHz+ or better, MacOS 8.5 or higher, minimum 48 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013" /> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 10.0 | |||
| :For Windows: May 2001;<ref name="ppt-10-win-may-2001" /> for Mac: November 2001<ref name="ppt-10-mac-nov-2001" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: install from web, most clipart on web, use of Exchange and SharePoint for storage and collaboration.<ref name="ppt-10-win-may-2001" /> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) Pentium III, Windows 98 or higher, 40 MB RAM.<ref name="bitbetter-pptsystemreq-2013" /> (Mac) OS X 10.1 ("Puma") or later (will not run under OS 9).<ref name="ppt-10-mac-nov-2001-os-x-version">{{Cite web |url=https://www.macworld.com/article/1001393/office.html |title=Capsule Review: Microsoft Office v. X |website=Macworld |publisher=IDG |issn=0741-8647 |date=February 1, 2002 |last=Negrino |first=Tom |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121210231150/http://www.macworld.com/article/1001393/office.html |url-status=live |archive-date=December 10, 2012 |access-date=September 29, 2017 |quote=Office v. X requires OS X 10.1 or later to run ... PowerPoint X ... benefit from OS X technologies ... . |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 11.0 | |||
| :For Windows: October 2003;<ref name="ppt-11-win-oct-2003" /> for Mac: June 2004;<ref name="ppt-11-mac-jun-2004" /> for Mobile: May 2005<ref name="ppt-11-mob-may-2005" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: tools visible to presenter during slide show (notes, thumbnails, time clock, re-order and edit slides), "Package for CD" to write presentation and viewer app to CD.<ref name="ppt-11-mac-jun-2004" /> "Microsoft Producer for PowerPoint 2003" was a free plug-in from Microsoft, using a video camera, "that creates Web page presentations, with talking head narration, coordinated and timed to your existing PowerPoint presentation" for delivery over the web.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.videomaker.com/article/c5/9821-microsoft-producer-for-powerpoint-2003-review |last=Muratore |first=Stephen |title=Microsoft Producer for PowerPoint 2003 Review |date=March 1, 2004 |website=Videomaker Magazine |publisher=York Publishing |issn=0889-4973 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170729195751/https://www.videomaker.com/article/c5/9821-microsoft-producer-for-powerpoint-2003-review |url-status=live |archive-date=July 29, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> The Genigraphics software to send a presentation for imaging as 35mm slides was removed from this version.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc178951(v=office.12).aspx |last=Microsoft |title=Differences between Office XP and Office 2003 |date=August 13, 2007 |website=Microsoft TechNet |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807073435/https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc178951(v=office.12).aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) Pentium 233Mhz+, Windows 2000 with SP3 or later, 128 MB RAM.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/822129/list-of-system-requirements-for-microsoft-office-2003 |last=Microsoft |title=List of system requirements for Microsoft Office 2003 |date=March 29, 2017 |website=Microsoft Support |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528053331/https://www.webcitation.org/6sLpwpdXu?url=https://filetea.me/n3wqNbjtczRQWCnYrQTJ0xilg |url-status=live |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> (Mac) Power Mac G3 or better, OS X 10.2.8 or later, 256 MB RAM.<ref name="ppt-11-mac-jun-2004" /> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 12.0 | |||
| :For Windows: January 2007;<ref name="ppt-12-win-jan-2007" /> for Mobile: September 2007;<ref name="ppt-12-mob-sep-2007" /> for Mac: January 2008<ref name="ppt-12-mac-jan-2008" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: new user interface ("Office Fluent") employing a changeable "ribbon" of tools across the top to replace menus and toolbars, SmartArt graphics, many graphical improvements in text and drawing, improved "Presenter View" (from 2003), widescreen slide formats. The "AutoContent Wizard" was removed from this version.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://echosvoice.com/powerpoint-2007/ |last=Swinford |first=Echo |title=PPT 2007 |date=January 1, 2009 |website=Echo's Voice |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140813014809/http://www.echosvoice.com/powerpoint-2007/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 13, 2014 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| :A major change in PowerPoint 2007 was from a binary file format, used from 1997 to 2003, to a new XML file format which evolved over further versions. | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 500 MHz processor or higher, Windows XP with SP2 or later, 256 MB RAM.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd188670(office.12).aspx#BKMK_SysReqs |last=Microsoft |title=Getting started with the 2007 Office system |date=April 28, 2009 |website=Microsoft TechNet |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170730023318/https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd188670(office.12).aspx#BKMK_SysReqs |url-status=live |archive-date=July 30, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> (Mac) 500 MHz processor or higher, MacOS X 10.4.9 or later, 512 MB RAM.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.cnet.com/products/microsoft-office-2008-for-mac/specs/ |last=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |title=Microsoft Office 2008 for Mac, Specifications |date=January 15, 2008 |website=CNET |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150529065528/http://www.cnet.com/products/microsoft-office-2008-for-mac/specs/ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 29, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 14.0<ref name="why-no-13" /> | |||
| :For Windows: June 2010;<ref name="ppt-14-win-jun-2010" /> for Web: June 2010;<ref name="ppt-14-web-jun-2010" /> for Mobile: June 2010;<ref name="ppt-14-mob-jun-2010" /> for Mac: November 2010,<ref name="ppt-14-mac-nov-2010" /> for Symbian: April 2012<ref name="ppt-14-symbian-apr-2012" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: Single document interface (SDI), sections within presentations, reading view, redesign of "Backstage" functions (under File menu), save as video, insert video from web, embed video and audio, enhanced editing for video and for pictures, broadcast slideshow.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://echosvoice.com/powerpoint-2010/ |last=Swinford |first=Echo |title=PPT 2010 new stuff |date=March 26, 2011 |website=Echo's Voice |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140813014858/http://echosvoice.com/powerpoint-2010/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 13, 2014 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 500 MHz processor or higher, Windows XP with SP3 or later, 256 MB RAM, 512 MB RAM recommended for video.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee624351%28v=office.14%29.aspx#section11 |last=Microsoft |title=System requirements for Office 2010: Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 |date=February 15, 2013 |website=Microsoft TechNet |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120325002713/http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee624351(v=office.14).aspx#section11 |url-status=live |archive-date=March 25, 2012 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> (Mac) Intel processor, Mac OS X 10.5.8 or later, 1 GB RAM.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2581812/microsoft-office-for-mac-2011-system-requirements |last=Microsoft |title=Microsoft Office for Mac 2011 system requirements |date=June 16, 2017 |website=Microsoft Support |archive-url=https://archive.today/20240528053412/https://www.webcitation.org/6sNDTK89f?url=https://filetea.me/n3wdNxkNxfbRty9qlbOYKtYbA |url-status=live |archive-date=May 28, 2024 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 15.0 | |||
| :For Web: October 2012;<ref name="ppt-15-web-oct-2012" /> for Mobile: November 2012;<ref name="ppt-15-mob-nov-2012" /> for Windows RT: November 2012;<ref name="ppt-15-winrt-nov-2012" /> for Windows: January 2013;<ref name="ppt-15-win-jan-2013" /> for iPhone: June 2013;<ref name="ppt-15-iphone-jun-2013" /> for Android: July 2013;<ref name="ppt-15-android-jul-2013" /> for Web: February 2014;<ref name="ppt-15-online-feb-2014" /> for iPad: March 2014;<ref name="ppt-15-ipad-mar-2014" /> for iOS: November 2014;<ref name="ppt-15-ios-nov-2014" /> for Mac: July 2015<ref name="ppt-15-mac-jul-2015" /> | |||
| :Part of ] and ]. Innovations included: Change default slide shape to 16:9 aspect ratio, online collaboration by multiple authors, user interface redesigned for multi-touch screens, improved audio, video, animations, and transitions, further changes to Presenter View. Clipart collections (and insertion tool) were removed, but available online.<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/What-s-new-in-PowerPoint-2013-1c38822e-0284-4acb-8099-23dc6f3207c5 |last=Microsoft |title=What's New in PowerPoint 2013 <!-- |date=no date on page --> |website=Microsoft Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141209202036/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Whats-new-in-PowerPoint-2013-1c38822e-0284-4acb-8099-23dc6f3207c5?ui=en-US&rs=en-US&ad=US |url-status=live |archive-date=December 9, 2014 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref>{{Thinsp}}<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://echosvoice.com/big-list-o-new-features-in-powerpoint-2013/ |last=Swinford |first=Echo |title=Big list o' new features in powerpoint 2013 |date=November 5, 2012 |website=Echo's Voice |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121108020220/http://echosvoice.com/big-list-o-new-features-in-powerpoint-2013/ |url-status=live |archive-date=November 8, 2012 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 1 GHz processor or faster, x86- or x64-bit processor with SSE2 instruction set, Windows 7 or later, 1 GB RAM (32-bit), 2 GB RAM (64-bit).<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee624351.aspx |last=Microsoft |title=System requirements for Office 2013 |date=December 16, 2016 |website=Microsoft TechNet |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130119020642/https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee624351.aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=January 19, 2013 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> (Mac) Intel processor, Mac OS X 10.10 or later, 4 GB RAM.<ref name="ppt-2016-15-mac-sys-req">{{Cite web |url=https://products.office.com/en-us/office-system-requirements |last=Microsoft |title=System requirements for Office <!-- |date=no date on page --> |website=Microsoft Office |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150925115345/http://products.office.com/en-us/office-system-requirements |url-status=live |archive-date=September 25, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ;PowerPoint 16.0 | |||
| :For Android: June 2015;<ref name="ppt-16-android-jun-2015" /> for Mobile: July 2015;<ref name="ppt-16-mob-jul-2015" /> for iOS: July 2015;<ref name="ppt-16-ios-jul-2015" /> for Windows: September 2015;<ref name="ppt-16-win-sep-2015" /> and Windows Store: January 2018<ref name="ppt-16-winstore-jan-2018" /> | |||
| :Part of ]. Innovations included: "Tell me" to search for program controls, "PowerPoint Designer" pane, Morph transition, real-time collaboration, "Zoom" to slides or sections in slideshow,<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/What-s-new-in-PowerPoint-2016-for-Windows-e8ef980c-5b12-4fff-ae3f-0819e6a21a1f |last=Microsoft |title=What's New in PowerPoint 2016 for Windows <!-- |date=no date on page --> |website=Microsoft Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170731220459/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/What-s-new-in-PowerPoint-2016-for-Windows-e8ef980c-5b12-4fff-ae3f-0819e6a21a1f |url-status=live |archive-date=July 31, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}} This webpage contains dated feature updates listed separately for each nearly-monthly update since the original release.</ref> and "Presentation Translator" for real-time translation of a presenter's spoken words to on-screen captions in any of 60+ languages, with the system analyzing the text of the PowerPoint presentation as context to increase the accuracy and relevance of the translations.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-delivers-ai-powered-presentation-translator-add-in-for-powerpoint/ |last=Foley |first=Mary Jo |title=Microsoft delivers 'AI-powered' Presentation Translator add-in for PowerPoint |date=July 12, 2017 |website=ZDnet.com |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170720142802/http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-delivers-ai-powered-presentation-translator-add-in-for-powerpoint/ |url-status=live |archive-date=July 20, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref>{{Thinsp}}<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/garage/profiles/presentation-translator/ |last=Microsoft |title=Presentation Translator: an Office add-in for PowerPoint <!-- |date=no date on page --> |website=Microsoft Garage |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170801211429/https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/garage/profiles/presentation-translator/ |url-status=live |archive-date=August 1, 2017 |access-date=August 4, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| :System requirements: (Windows) 1 GHz processor or faster, x86- or x64-bit processor with SSE2 instruction set, Windows 7 with SP 1 or later, 2 GB RAM.<ref name="ppt-2016-16-win-sys-req">{{Cite web |url=https://products.office.com/en-us/office-system-requirements#Office-standalone-applications-section |last=Microsoft |title=System requirements for Office <!-- |date=no date on page --> |website=Microsoft Office |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150925115345/http://products.office.com/en-us/office-system-requirements#Office-standalone-applications-section |url-status=live |archive-date=September 25, 2015 |access-date=August 4, 2017 |df=mdy-all }}</ref> | |||
| ==File formats== | |||
| <!--] redirects directly here.--> | |||
| {{Infobox file format | |||
| | name=PowerPoint Presentation | |||
| | icon = ] ] | |||
| | extensions=.pptx, .ppt<ref name="file-formats">{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/File-formats-that-are-supported-in-PowerPoint-252c6fa0-a4bc-41be-ac82-b77c9773f9dc |title=File formats that are supported in PowerPoint |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2016 |website=Microsoft Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807213337/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/File-formats-that-are-supported-in-PowerPoint-252c6fa0-a4bc-41be-ac82-b77c9773f9dc |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 7, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| | mime=application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint<ref name="mime-types">{{Cite web |url=http://referencesource.microsoft.com/#System.Web/MimeMapping.cs.html |title=MimeMapping.cs |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=February 22, 2014 |website=Microsoft Reference Source |archive-url=https://www.webcitation.org/6YlfhuoTj?url=https://filetea.me/t1sQXwolO3LRPaK1USdCYKg2A |url-status=live |archive-date=May 24, 2015 |access-date=August 10, 2017 |quote=This module maps document extensions to Content Mime Type.}}</ref> | |||
| | uniform_type=com.microsoft.powerpoint.ppt<ref name="type-codes">{{Cite web |url=https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/Miscellaneous/Reference/UTIRef/Articles/System-DeclaredUniformTypeIdentifiers.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40009259-SW1 |title=System-Declared Uniform Type Identifiers |date=November 17, 2009 |website=developer.apple.com |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080724151058/http://developer.apple.com/documentation/Carbon/Conceptual/understanding_utis/utilist/chapter_4_section_1.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40001319-CH205-CHDIJFGJ |archive-date=July 24, 2008 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | owner=] | |||
| | genre=] | |||
| }} | |||
| === Binary (1987–2007) === | |||
| Early versions of PowerPoint, from 1987 through 1995 (versions 1.0 through 7.0), evolved through a sequence of binary file formats, different in each version, as functionality was added.<ref name="early-file-compatibility">{{Cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130510103008/http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm <!-- long URL needed --> |title=PowerPoint FAQ: Versions |last=<!-- author not given --> |date=May 10, 2013 |website=A Bit Better Corporation |url=http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 10, 2013 |access-date=August 4, 2017}} A diagram shows "which versions of PowerPoint can open/save which other versions" up to version 9.0 for Windows ("PowerPoint 2000"). <!-- backup archive at: https://www.webcitation.org/6s6Trrd1t?url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130510103008/http://www.bitbetter.com/powerfaq.htm --></ref> This set of formats were never documented, but an open-source ''libmwaw'' (used by ]) exists to read them.<ref>{{cite web |title=libmwaw |url=https://sourceforge.net/projects/libmwaw/ |website=SourceForge |date=April 30, 2023 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| A stable binary format (called a .ppt file, like all earlier binary formats) that was shared as the default in PowerPoint 97 through PowerPoint 2003 for Windows, and in PowerPoint 98 through PowerPoint 2004 for Mac (that is, in PowerPoint versions 8.0 through 11.0) was finally created. It was based on the ].<ref name="ppt-binary-doc">{{Cite web |url=https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc313106(v=office.12).aspx |title=: PowerPoint (.ppt) Binary File Format (Protocol Revision 4.1) |date=June 20, 2017 |website=Microsoft Developer Network |author=Microsoft Corporation |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170807204504/https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc313106(v=office.12).aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=August 7, 2017 |access-date=August 7, 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/intro/specifications.shtml |title=Specifications for Digital Formats: Microsoft Office Binary (doc, xls, ppt) File Formats |last=Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |author-link=National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |date=March 2, 2017 |website=Digital Preservation, Library of Congress |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170813223732/https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/intro/specifications.shtml |url-status=live |archive-date=August 13, 2017 |access-date=August 13, 2017}}</ref> The specification document is actively maintained and can be freely downloaded,<ref name="ppt-binary-doc" /> because, although no longer the default, that binary format can be read and written by some later versions of PowerPoint, including PowerPoint 2016.<ref name="file-formats" /> After the stable binary format was adopted, versions of PowerPoint continued to be able to read and write differing file formats from earlier versions.<ref name="early-file-compatibility" /> But beginning with PowerPoint 2007 and PowerPoint 2008 for Mac (PowerPoint version 12.0), this was the only binary format available for saving; PowerPoint 2007 (version 12.0) no longer supported saving to binary file formats used earlier than PowerPoint 97 (version 8.0), ten years before.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-ca/article/Use-PowerPoint-2007-to-open-or-save-a-presentation-in-another-file-format-50e447ac-7475-4853-b709-7e1c3e20860e |title=Use PowerPoint 2007 to open or save a presentation in another file format |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2015 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170814173954/https://support.office.com/en-ca/article/Use-PowerPoint-2007-to-open-or-save-a-presentation-in-another-file-format-50e447ac-7475-4853-b709-7e1c3e20860e |url-status=live |archive-date=August 14, 2017 |access-date=May 23, 2015 |quote=... PowerPoint 2007 does not support saving to PowerPoint 95 and earlier file formats.}}</ref> | |||
| The ".pps" and ".ppsx" file extensions are technically the same as ".ppt" and ".pptx", except they are launched as presentation instead of for editing by default.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://notes.indezine.com/2004/08/ppt-vs-pps.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211004121853/https://notes.indezine.com/2004/08/ppt-vs-pps.html|archive-date=October 4, 2021|title=PPTX vs. PPSX (Or PPT vs. PPS)}}</ref> | |||
| '''Binary ]s'''<ref name="file-formats" /> | |||
| * .ppt, PowerPoint 97–2003 binary presentation | |||
| * .pps, PowerPoint 97–2003 binary slide show | |||
| * .pot, PowerPoint 97–2003 binary template | |||
| '''Binary ]s'''<ref name="mime-types" /> | |||
| * .ppt, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint | |||
| * .pps, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint | |||
| * .pot, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint | |||
| === Office Open XML (since 2007) === | |||
| The big change in PowerPoint 2007 and PowerPoint 2008 for Mac (PowerPoint version 12.0) was that the stable binary file format of 97–2003 was replaced as the default by a new ] ]-based ] format (.pptx files).<ref name="open-xml-formats">{{Cite web |url=https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Open-XML-Formats-and-file-name-extensions-5200d93c-3449-4380-8e11-31ef14555b18 |title=Open XML Formats and file name extensions |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=2015 |website=Microsoft Office Support |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170430175040/https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Open-XML-Formats-and-file-name-extensions-5200d93c-3449-4380-8e11-31ef14555b18 |url-status=live |archive-date=April 30, 2017 |access-date=August 11, 2017 |quote=Starting with the 2007 Microsoft Office system, Microsoft Office uses the XML-based file formats, such as .docx, .xlsx, and .pptx. These formats and file name extensions apply to ... Microsoft PowerPoint.}}</ref> Microsoft's explanation of the benefits of the change included: smaller file sizes, up to 75% smaller than comparable binary documents; security, through being able to identify and exclude executable macros and personal data; less chance to be corrupted than binary formats; and easier interoperability for exchanging data among Microsoft and other business applications, all while maintaining backward compatibility.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa338205%28v=office.12%29.aspx |title=Introducing the Office (2007) Open XML File Formats |date=May 2006 |website=Microsoft Developer Network |last=Rice |first=Frank |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161228063121/https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa338205(v=office.12).aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=December 28, 2016 |access-date=August 12, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| '''XML ]s'''<ref name="file-formats" /> | |||
| * .pptx, PowerPoint 2007 XML presentation | |||
| * .pptm, PowerPoint 2007 XML macro-enabled presentation | |||
| * .ppsx, PowerPoint 2007 XML slide show | |||
| * .ppsm, PowerPoint 2007 XML macro-enabled slide show | |||
| * .ppam, PowerPoint 2007 XML add-in | |||
| * .potx, PowerPoint 2007 XML template | |||
| * .potm, PowerPoint 2007 XML macro-enabled template | |||
| '''XML ]s'''<ref name="mime-types" /> | |||
| * .pptx, application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation | |||
| * .pptm, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.presentation.macroEnabled.12 | |||
| * .ppsx, application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slideshow | |||
| * .ppsm, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.slideshow.macroEnabled.12 | |||
| * .ppam, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.addin.macroEnabled.12 | |||
| * .potx, application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.template | |||
| * .potm, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.template.macroEnabled.12 | |||
| The specification for the new format was published as an ], ],<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-376.htm |title=Standard ECMA-376: Office Open XML File Formats |last=Ecma Technical Committee 45 |date=2016 |website=Ecma International |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170714033758/http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/standards/Ecma-376.htm |url-status=live |archive-date=July 14, 2017 |access-date=August 12, 2017}}</ref> through ] Technical Committee 45 (TC45).<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ecma-international.org/news/TC45_current_work/OpenXML%20White%20Paper.pdf |title=Office Open XML Overview |editor-last=Ngo |editor-first=Tom |author-last=Ecma Technical Committee 45 |date=2012 |website=Ecma International |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150412160349/http://www.ecma-international.org/news/TC45_current_work/OpenXML%20White%20Paper.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=April 12, 2015 |access-date=August 12, 2017 |quote=OpenXML was designed from the start to be capable of faithfully representing the pre-existing corpus of word-processing documents, presentations, and spreadsheets that are encoded in binary formats defined by Microsoft Corporation. ... The original binary formats for these files were based on direct serialization of in-memory data structures ... . Technical Committee 45 (TC45) ... includes representatives from Apple, Barclays Capital, BP, The British Library, Essilor, Intel, Microsoft, NextPage, Novell, Statoil, Toshiba, and the United States Library of Congress. |df=mdy-all }}</ref> The Ecma 376 standard was approved in December 2006, and was submitted for standardization through ] WG4 in early 2007. The ] was contentious.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Magee |first1=Liam |last2=Thom |first2=James A. |date=2014 |title=What's in a Word? When one electronic document format standard is not enough |journal=Information Technology & People |volume=27 |issue=4 |pages=482–511 |issn=0959-3845 |doi=10.1108/ITP-09-2012-0096 |url=https://researchbank.rmit.edu.au/eserv/rmit:29076/n2006050256.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170813152222/https://researchbank.rmit.edu.au/eserv/rmit:29076/n2006050256.pdf |url-status=live |archive-date=August 13, 2017 |access-date=August 13, 2017 |quote=The case of the standardisation of two ISO electronic document formats, the ''OpenDocument Format'' (ODF) and ''Office Open XML'' (OOXML) ... In this case, the attempt to design a ''de jure'' standard in fact produced even greater entrenchment of the existing ''de facto'' standard it was designed to replace.}}</ref> It was approved as ] in early 2008.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/fdd/fdd000395.shtml |title=OOXML Format Family—ISO/IEC 29500 and ECMA 376 |last=Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |author-link=National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |date=February 21, 2017 |website=Digital Preservation, Library of Congress |type=Format Description ID:fdd000395 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170811221108/https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/fdd/fdd000395.shtml |url-status=live |archive-date=August 11, 2017 |access-date=August 11, 2017}}</ref> Copies of the ISO/IEC standard specification are freely available, in two parts.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/c071691_ISO_IEC_29500-1_2016.zip |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170811222524/http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/c071691_ISO_IEC_29500-1_2016.zip |url-status=dead |archive-date=2017-08-11 |title=ISO/IEC 29500-1:2016, Fundamentals and Markup Language Reference |last= ISO/IEC JTC 1 |author-link= ISO/IEC JTC 1 |date=2016 |website=International Organization for Standardization |access-date=August 9, 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/c071692_ISO_IEC_29500-4_2016.zip |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170811222524/http://standards.iso.org/ittf/PubliclyAvailableStandards/c071692_ISO_IEC_29500-4_2016.zip |url-status=dead |archive-date=2017-08-11 |title=ISO/IEC 29500-4:2016, Transitional Migration Features |last= ISO/IEC JTC 1 |author-link= ISO/IEC JTC 1 |date=2016 |website=International Organization for Standardization |access-date=August 9, 2017}}</ref> These define two related standards known as "Transitional" and "Strict". The two standards were progressively adopted by PowerPoint: PowerPoint version 12.0 (2007, 2008 for Mac) could read and write Transitional format, but could neither read nor write Strict format. PowerPoint version 14.0 (2010, 2011 for Mac) could read and write Transitional, and also read but not write Strict. PowerPoint version 15.0 and later (beginning 2013, 2016 for Mac) can read and write both Transitional and Strict formats. The reason for the two variants was explained by Microsoft:<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://blogs.office.com/2012/08/13/new-file-format-options-in-the-new-office/ |title=New file format options in the new Office |last=Knowlton |first=Gray |date=August 13, 2012 |website=Microsoft Office Blogs |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150512003108/http://blogs.office.com/2012/08/13/new-file-format-options-in-the-new-office/ |url-status=live |archive-date=May 12, 2015 |access-date=August 11, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| {{Blockquote| ... the participants in the ISO/IEC standardization process recognized two objectives with competing requirements. The first objective was for the Open XML standard to provide an XML-based file format that could fully support conversion of the billions of existing Office documents without any loss of features, content, text, layout, or other information, including embedded data. The second was to specify a file format that did not rely on Microsoft-specific data types. They created two variants of Open XML—Transitional, which supports previously-defined Microsoft-specific data types, and Strict, which does not rely on them. Prior versions of Office have supported reading and writing Transitional Open XML, and Office 2010 can read Strict Open XML documents. With the addition of write support for Strict Open XML, Office 2013 provides full support for both variants of Open XML.}} | |||
| The PowerPoint .pptx file format (called "]" for Presentation Markup Language) contains separate structures for all the complex parts of a PowerPoint presentation.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://msdn.microsoft.com/EN-US/library/office/gg278335.aspx |title=Structure of a PresentationML document (Open XML SDK) |last=Microsoft Corporation |date=July 27, 2012 |website=Microsoft Developer Network, Office Dev Center |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170814062849/https://msdn.microsoft.com/EN-US/library/office/gg278335.aspx |url-status=live |archive-date=August 14, 2017 |access-date=August 10, 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://officeopenxml.com/anatomyofOOXML-pptx.php |title=Presentation ML (pptx) |last=Office Open XML Consortium |date=2012 |website=Office Open XML |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150508143517/http://officeopenxml.com/anatomyofOOXML-pptx.php |url-status=live |archive-date=May 8, 2015 |access-date=August 10, 2017}}</ref> The specification documents run to over six thousand pages.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/fdd/fdd000399.shtml |title=PPTX Transitional (Office Open XML), ISO 29500:2008–2016, ECMA-376, Editions 1–5 |last=Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |author-link=National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |date=January 1, 2017 |website=Digital Preservation, Library of Congress |type=Format Description ID: fdd000399 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170811222524/https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/fdd/fdd000399.shtml |url-status=live |archive-date=August 11, 2017 |access-date=August 11, 2017 |quote=The standards documents that specify this format run to over six thousand pages.}}</ref> Because of the widespread use of PowerPoint, the standardized file formats are considered important for the long-term access to digital documents in library collections and archives, according to the U.S. Library of Congress.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.digitalpreservation.gov/series/challenge/formats_challenge.html |title=Setting Standards (Office Open XML and PDF/A) |last=Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |author-link=National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program |date=2008 |website=Digital Preservation, Library of Congress |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170220030311/http://www.digitalpreservation.gov//series/challenge/formats_challenge.html |url-status=live |archive-date=February 20, 2017 |access-date=August 13, 2017 |quote=Library staff have participated in a technical committee working toward the standardization of the Office Open XML specifications, which ... will make it easier for libraries and archives to preserve a large body of digital material by ensuring that the content is generated in formats for which the specifications are published and will be maintained under the auspices of a standards organization. Specifically, this standard is based on the formats used by the latest version of Microsoft Office and supports all features in the various versions of Microsoft Office since 1997.}}</ref> | |||
| PowerPoint 2013 and PowerPoint 2016 provide options to set default saving to ISO/IEC 29500 Strict format, but the initial default setting remains Transitional, for compatibility with legacy features incorporating binary data in existing documents.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/e969fc0a-9fcd-4efe-bf6d-79ea8c34360f |title=What is the default file format for saving in MS Office 2013? |last=Meng |first=Max |date=May 20, 2013 |website=Microsoft Technet Forums |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190921163748/https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/e969fc0a-9fcd-4efe-bf6d-79ea8c34360f/what-is-the-default-file-format-for-saving-in-ms-office-2013-is-it-still-the-transitional-ooxml-or |url-status=live |archive-date=September 21, 2019 |access-date=August 10, 2017}}</ref> PowerPoint 2013 or PowerPoint 2016 will both open and save files in the former binary format (.ppt), for compatibility with older versions of the program (but not versions older than PowerPoint 97).<ref name="file-formats" /><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://blog.zamzar.com/2012/04/17/open-old-powerpoint-presentations-in-office-2007-and-office2010/ |title=Open Old Powerpoint Presentations in Office 2007 and Office 2010 |last=Zamzar |author-link=Zamzar |date=April 17, 2012 |website=Zamzar Blog |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170606185325/https://blog.zamzar.com/2012/04/17/open-old-powerpoint-presentations-in-office-2007-and-office2010/ |url-status=live |archive-date=June 6, 2017 |access-date=August 7, 2017}}</ref> In saving to older formats, these versions of PowerPoint will check to assure that no features have been introduced into the presentation which are incompatible with the older formats.<ref name="open-xml-formats" /> | |||
| PowerPoint 2013 and 2016 will also save a presentation in many other file formats, including ] format, ] or ] video, as a sequence of single-picture files (using image formats including ], ], ], ], and some older formats), and as a single presentation file in which all slides are replaced with pictures. PowerPoint will both open and save files in ] format (ODP) for compatibility.<ref name="file-formats" /> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| <!--See http://en.wikipedia.org/Wikipedia:Footnotes for an explanation of how to generate footnotes using the <ref(erences/)> tags--> | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Reuss |first1=Elke I. |last2=Signer |first2=Beat |last3=Norrie |first3=Moira C. |date=2008 |chapter-url=https://www.academia.edu/175414 |chapter=PowerPoint Multimedia Presentations in Computer Science Education: What do Users Need? |title=Proceedings of the 4th Symposium on Usability & HCI for Education and Work (USAB 2008) |pages=281–298 |location=Graz, Austria |chapter-url-access=registration }} | |||
| * | |||
| ** Also available at: | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Lowenthal |first=Patrick R. |date=2009 |chapter-url=http://www.ucdenver.edu/academics/CUOnline/FacultySupport/Handbook/Documents/Chapter_12.pdf |chapter=Improving the Design of PowerPoint Presentations |editor-first1=Patrick R. |editor-last1=Lowenthal |editor-first2=David |editor-last2=Thomas |editor-first3=Anna |editor-last3=Thai |editor-first4=Brian |editor-last4=Yuhnke |title=The CU Online Handbook 2009 |pages=61–66 |publisher=University of Colorado Denver}} | |||
| * Tutorials and animations in regards to using PowerPoint. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Kalyuga |first1=Slava |last2=Chandler |first2=Paul |last3=Sweller |first3=John |title=When Redundant On-Screen Text in Multimedia Technical Instruction Can Interfere With Learning |journal=Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society |date=2004 |volume=46 |issue=3 |pages=567–581 |doi=10.1518/hfes.46.3.567.50405 |pmid=15573552 |s2cid=6992108 }} | |||
| * Frequently Asked Questions on PowerPoint. | |||
| ** Also available at: {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201028120546/https://www.it.iitb.ac.in/~s1000brains/rswork/dokuwiki/media/redundant_on_screen_text_in_multimedia_instruction_can_interfere_with_learning.pdf |date=October 28, 2020 }} (Feb 2015). | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{wikibooks|Microsoft Office/Creating and Editing a Presentation}} | |||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| {{wikiquote}} | |||
| * {{Official website}} | |||
| {{Presentation software}} | |||
| {{Microsoft Office}} | {{Microsoft Office}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:10, 2 December 2024
Presentation application, part of Microsoft 365 This article is about the presentation software program by Microsoft Corporation. For other uses, see Power point (disambiguation).
 | |
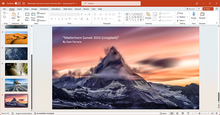 A photo presentation being created and edited in PowerPoint, running on Windows 11 A photo presentation being created and edited in PowerPoint, running on Windows 11 | |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 20, 1987; 37 years ago (1987-04-20) |
| Stable release | 2312 (Build 17126.20132) / January 9, 2024; 11 months ago (2024-01-09) |
| Written in | C++ (back-end) |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Predecessor | Forethought Powerpoint |
| Available in | 102 languages |
| List of languagesAfrikaans, Albanian, Amharic, Arabic, Armenian, Assamese, Azerbaijani (Latin), Bangla (Bangladesh), Bangla (Bengali India), Basque, Belarusian, Bosnian (Latin), Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dari, Dutch, English, Estonian, Filipino, Finnish, French, Galician, Georgian, German, Greek, Gujarati, Hausa, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Icelandic, Igbo, Indonesian, Irish, isiXhosa, isiZulu, Italian, Japanese, Kannada, Kazakh, Khmer, Kinyarwanda, Kiswahili, Konkani, Korean, Kyrgyz, Latvian, Lithuanian, Luxembourgish, Macedonian (Macedonia), Malay (Latin), Malayalam, Maltese, Maori, Marathi, Mongolian (Cyrillic), Nepali, Norwegian (Bokmål), Norwegian (Nynorsk), Odia, Pashto, Persian (Farsi), Polish, Portuguese (Portugal), Portuguese (Brazil), Punjabi (India), Quechua, Romanian, Romansh, Russian, Scottish Gaelic, Serbian (Cyrillic, Serbia), Serbian (Latin, Serbia), Serbian (Cyrillic, Bosnia and Herzegovina), Sesotho sa Leboa, Setswana, Sindhi (Arabic), Sinhala, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Tamil, Tatar (Cyrillic), Telugu, Thai, Turkish, Turkmen (Latin), Ukrainian, Urdu, Uyghur, Uzbek (Latin), Valencian, Vietnamese, Welsh, Wolof, Yoruba | |
| Type | Presentation program |
| License | Trialware |
| Website | microsoft |
 PowerPoint for Android running on Android 13 PowerPoint for Android running on Android 13 | |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 16.0.16501.20160 / May 26, 2023; 19 months ago (2023-05-26) |
| Operating system | Android Pie or later |
| Type | Presentation program |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products |
 PowerPoint for Mac (version 16.69.1), running on macOS Ventura (13.2) PowerPoint for Mac (version 16.69.1), running on macOS Ventura (13.2) | |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 20, 1987; 37 years ago (1987-04-20) |
| Stable release | 16.70 (Build 23021201) / February 14, 2023; 22 months ago (2023-02-14) |
| Written in | C++ (back-end), Objective-C (API/UI) |
| Operating system | macOS 11 or later |
| Available in | 26 languages |
| List of languagesEnglish, Arabic, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Norwegian Bokmål, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Slovak, Spanish, Swedish, Thai, Traditional Chinese, Turkish | |
| Type | Presentation program |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2.73 / May 15, 2023; 19 months ago (2023-05-15) |
| Operating system | iOS 15 or later IPadOS 15 or later watchOS 8 or later |
| Available in | 33 languages |
| List of languagesEnglish, Arabic, Catalan, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Malay, Norwegian Bokmål, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Simplified Chinese, Slovak, Spanish, Swedish, Thai, Traditional Chinese, Turkish, Ukrainian, Vietnamese | |
| Type | Presentation program |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Final release | 16002.12325.20032.0 / December 10, 2019; 5 years ago (2019-12-10) |
| Operating system | Windows 10, Windows 10 Mobile |
| Type | Presentation program |
| License | Trialware |
| Website | www |
Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation program, created by Robert Gaskins, Tom Rudkin, and Dennis Austin at a software company named Forethought, Inc. It was released on April 20, 1987, initially for Macintosh computers only. Microsoft acquired PowerPoint for about $14 million three months after it appeared. This was Microsoft's first significant acquisition, and Microsoft set up a new business unit for PowerPoint in Silicon Valley where Forethought had been located.
PowerPoint became a component of the Microsoft Office suite, first offered in 1989 for Macintosh and in 1990 for Windows, which bundled several Microsoft apps. Beginning with PowerPoint 4.0 (1994), PowerPoint was integrated into Microsoft Office development, and adopted shared common components and a converged user interface.
PowerPoint's market share was very small at first, prior to introducing a version for Microsoft Windows, but grew rapidly with the growth of Windows and of Office. Since the late 1990s, PowerPoint's worldwide market share of presentation software has been estimated at 95 percent.
PowerPoint was originally designed to provide visuals for group presentations within business organizations, but has come to be widely used in other communication situations in business and beyond. The wider use led to the development of the PowerPoint presentation as a new form of communication, with strong reactions including advice that it should be used less, differently, or better.
The first PowerPoint version (Macintosh 1987) was used to produce overhead transparencies, the second (Macintosh 1988, Windows 1990) could also produce color 35 mm slides. The third version (Windows and Macintosh 1992) introduced video output of virtual slideshows to digital projectors, which would over time replace physical transparencies and slides. A dozen major versions since then have added additional features and modes of operation and have made PowerPoint available beyond Apple Macintosh and Microsoft Windows, adding versions for iOS, Android, and web access.
History
Creation at Forethought (1984–1987)
PowerPoint was created by Robert Gaskins and Dennis Austin at a software startup in Silicon Valley named Forethought, Inc. Forethought had been founded in 1983 to create an integrated environment and applications for future personal computers that would provide a graphical user interface, but it had run into difficulties requiring a "restart" and new plan.
On July 5, 1984, Forethought hired Robert Gaskins as its vice president of product development to create a new application that would be especially suited to the new graphical personal computers, such as the Apple Macintosh and later Microsoft Windows. Gaskins produced his initial description of PowerPoint about a month later (August 14, 1984) in the form of a 2-page document titled "Presentation Graphics for Overhead Projection." By October 1984, Gaskins had selected Dennis Austin to be the developer for PowerPoint. Gaskins and Austin worked together on the definition and design of the new product for nearly a year, and produced the first specification document dated August 21, 1985. This first design document showed a product as it would look in Microsoft Windows 1.0, which at that time had not been released.
Development from that spec was begun by Austin in November 1985, for Macintosh first. About six months later, on May 1, 1986, Gaskins and Austin chose a second developer to join the project, Thomas Rudkin. Gaskins prepared two final product specification marketing documents in June 1986; these described a product for both Macintosh and Windows. At about the same time, Austin, Rudkin, and Gaskins produced a second and final major design specification document, this time showing a Macintosh look.
Throughout this development period, the product was called "Presenter". Then, just before release, there was a last-minute check with Forethought's lawyers to register the name as a trademark, and "Presenter" was unexpectedly rejected because it had already been used by someone else. Gaskins says that he thought of "PowerPoint", based on the product's goal of "empowering" individual presenters, and sent that name to the lawyers for clearance, while all the documentation was hastily revised.
Funding to complete development of PowerPoint was assured in mid-January 1987, when a new Apple Computer venture capital fund, called Apple's Strategic Investment Group, selected PowerPoint to be its first investment. A month later, on February 22, 1987, Forethought announced PowerPoint at the Personal Computer Forum in Phoenix; John Sculley, the CEO of Apple, appeared at the announcement and said "We see desktop presentation as potentially a bigger market for Apple than desktop publishing."
PowerPoint 1.0 for Macintosh shipped from manufacturing on April 20, 1987, and the first production run of 10,000 units was sold out.
Acquisition by Microsoft (1987–1992)
By early 1987, Microsoft was starting to plan a new application to create presentations, an activity led by Jeff Raikes, who was head of marketing for the Applications Division. Microsoft assigned an internal group to write a specification and plan for a new presentation product. They contemplated an acquisition to speed up development, and in early 1987 Microsoft sent a letter of intent to acquire Dave Winer's product called MORE, an outlining program that could print its outlines as bullet charts. During this preparatory activity Raikes discovered that a program specifically to make overhead presentations was already being developed by Forethought, Inc., and that it was nearly completed. Raikes and others visited Forethought on February 6, 1987, for a confidential demonstration.
Raikes later recounted his reaction to seeing PowerPoint and his report about it to Bill Gates, who was initially skeptical:
I thought, "software to do overheads—that's a great idea." I came back to see Bill. I said, "Bill, I think we really ought to do this;" and Bill said, "No, no, no, no, no, that's just a feature of Microsoft Word, just put it into Word." ... And I kept saying, "Bill, no, it's not just a feature of Microsoft Word, it's a whole genre of how people do these presentations." And, to his credit, he listened to me and ultimately allowed me to go forward and ... buy this company in Silicon Valley called Forethought, for the product known as PowerPoint.
When PowerPoint was released by Forethought, its initial press was favorable; the Wall Street Journal reported on early reactions: "'I see about one product a year I get this excited about,' says Amy hora, a consultant in Bala Cynwyd, Pa. 'People will buy a Macintosh just to get access to this product.'"
On April 28, 1987, a week after shipment, a group of Microsoft's senior executives spent another day at Forethought to hear about initial PowerPoint sales on Macintosh and plans for Windows. The following day, Microsoft sent a letter to Dave Winer withdrawing its earlier letter of intent to acquire his company, and in mid-May 1987 Microsoft sent a letter of intent to acquire Forethought. As requested in that letter of intent, Robert Gaskins from Forethought went to Redmond for a one-on-one meeting with Bill Gates in early June 1987, and by the end of July an agreement was concluded for an acquisition. The New York Times reported:
... July 30, 1987— The Microsoft Corporation announced its first significant software acquisition today, paying $14 million for Forethought Inc. of Sunnyvale, Calif. Forethought makes a program called PowerPoint that allows users of Apple Macintosh computers to make overhead transparencies or flip charts. ... he acquisition of Forethought is the first significant one for Microsoft, which is based in Redmond, Wash. Forethought would remain in Sunnyvale, giving Microsoft a Silicon Valley presence. The unit will be headed by Robert Gaskins, Forethought's vice president of product development.
Microsoft's president Jon Shirley offered his company's motivation for the acquisition: "'We made this deal primarily because of our belief in desktop presentations as a product category. ... Forethought was first to market with a product in this category.'" Microsoft had 50% market share in Macintosh applications, and led in three categories; Raikes said that after the acquisition it would lead in five categories. (Forethought distributed the database Filemaker, which Microsoft wanted to continue marketing.) The company intended for Forethought to be its Silicon Valley base to develop and market future graphics software, so set up within its Applications Division, an independent "Graphics Business Unit" for PowerPoint, the first Microsoft application group distant from the main Redmond location. The company hoped to hire employees uninterested in living in Washington state. All the PowerPoint people from Forethought joined Microsoft, and the new location was headed by Robert Gaskins, with Dennis Austin and Thomas Rudkin leading development. PowerPoint 1.0 for Macintosh was modified to indicate the new Microsoft ownership and continued to be sold. A year after the acquisition, Gaskins reported that all seven Forethought PowerPoint employees had stayed with Microsoft, and the Graphics Business Unit had hired 12 employees, many of whom did not want to move to Redmond. The GBU had moved to a new location on Sand Hill Road in Menlo Park, California; it was much larger than needed for 19 people, but Gaskins wrote that he and Microsoft wanted future capacity as the company grew in Silicon Valley.
A new PowerPoint 2.0 for Macintosh, adding color 35 mm slides, shipped in May 1988, and again received good reviews. The same PowerPoint 2.0 product re-developed for Windows was shipped two years later, in mid-1990, at the same time as Windows 3.0. Much of the color technology was the result of a joint development partnership with Genigraphics, the dominant presentation services company.
PowerPoint 3.0, which was shipped in 1992 for both Windows and Mac, added live video for projectors and monitors, with the result that PowerPoint was thereafter used for delivering presentations as well as for preparing them. This was at first an alternative to overhead transparencies and 35 mm slides, but over time would come to replace them.
Part of Microsoft Office (since 1993)
See also: History of Microsoft OfficePowerPoint had been included in Microsoft Office from the beginning. PowerPoint 2.0 for Macintosh was part of the first Office bundle for Macintosh which was offered in mid-1989. When PowerPoint 2.0 for Windows appeared, a year later, it was part of a similar Office bundle for Windows, which was offered in late 1990. Both of these were bundling promotions, in which the independent applications were packaged together and offered for a lower total price.
PowerPoint 3.0 (1992) was again separately specified and developed, and was advertised and sold separately from Office. It was, as before, included in Microsoft Office 3.0, both for Windows and the corresponding version for Macintosh.
A plan to integrate the applications themselves more tightly had been indicated as early as February 1991, toward the end of PowerPoint 3.0 development, in an internal memo by Bill Gates:
Another important question is what portion of our applications sales over time will be a set of applications versus a single product. ... Please assume that we stay ahead in integrating our family together in evaluating our future strategies—the product teams WILL deliver on this. ... I believe that we should position the "OFFICE" as our most important application.
The move from bundling separate products to integrated development began with PowerPoint 4.0, developed in 1993–1994 under new management from Redmond. The PowerPoint group in Silicon Valley was reorganized from the independent "Graphics Business Unit" (GBU) to become the "Graphics Product Unit" (GPU) for Office, and PowerPoint 4.0 changed to adopt a converged user interface and other components shared with the other apps in Office.
When it was released, the computer press reported on the change approvingly: "PowerPoint 4.0 has been re-engineered from the ground up to resemble and work with the latest applications in Office: Word 6.0, Excel 5.0, and Access 2.0. The integration is so good, you'll have to look twice to make sure you're running PowerPoint and not Word or Excel." Office integration was further underscored in the following version, PowerPoint 95, which was given the version number PowerPoint 7.0 (skipping 5.0 and 6.0) so that all the components of Office would share the same major version number.
Although PowerPoint by this point had become part of the integrated Microsoft Office product, its development remained in Silicon Valley. Succeeding versions of PowerPoint introduced important changes, particularly version 12.0 (2007) which had a very different shared Office "ribbon" user interface, and a new shared Office XML-based file format. This marked the 20th anniversary of PowerPoint, and Microsoft held an event to commemorate that anniversary at its Silicon Valley Campus for the PowerPoint team there. Special guests were Robert Gaskins, Dennis Austin, and Thomas Rudkin, and the featured speaker was Jeff Raikes, all from PowerPoint 1.0 days, 20 years before.
Since then major development of PowerPoint as part of Office has continued. New development techniques (shared across Office) for PowerPoint 2016 have made it possible to ship versions of PowerPoint 2016 for Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and web access nearly simultaneously, and to release new features on an almost monthly schedule. PowerPoint development is still carried out in Silicon Valley as of 2017.
In 2010, Jeff Raikes, who had most recently been President of the Business Division of Microsoft (including responsibility for Office), observed: "of course, today we know that PowerPoint is oftentimes the number two—or in some cases even the number one—most-used tool" among the applications in Office.
Sales and market share
PowerPoint's initial sales were about 40,000 copies sold in 1987 (nine months), about 85,000 copies in 1988, and about 100,000 copies in 1989, all for Macintosh. PowerPoint's market share in its first three years was a tiny part of the total presentation market, which was very heavily dominated by MS-DOS applications on PCs. The market leaders on MS-DOS in 1988–1989 were Harvard Graphics (introduced by Software Publishing in 1986) in first place, and Lotus Freelance Plus (also introduced in 1986) as a strong second. They were competing with more than a dozen other MS-DOS presentation products, and Microsoft did not develop a PowerPoint version for MS-DOS. After three years, PowerPoint sales were disappointing. Jeff Raikes, who had bought PowerPoint for Microsoft, later recalled: "By 1990, it looked like it wasn't a very smart idea , because not very many people were using PowerPoint."
This began to change when the first version for Windows, PowerPoint 2.0, brought sales up to about 200,000 copies in 1990 and to about 375,000 copies in 1991, with Windows units outselling Macintosh. PowerPoint sold about 1 million copies in 1992, of which about 80 percent were for Windows and about 20 percent for Macintosh, and in 1992 PowerPoint's market share of worldwide presentation graphics software sales was reported as 63 percent. By the last six months of 1992, PowerPoint revenue was running at a rate of over $100 million annually ($268 million in present-day terms).
Sales of PowerPoint 3.0 doubled to about 2 million copies in 1993, of which about 90 percent were for Windows and about 10 percent for Macintosh, and in 1993 PowerPoint's market share of worldwide presentation graphics software sales was reported as 78 percent. In both years, about half of total revenue came from sales outside the U.S.
By 1997 PowerPoint sales had doubled again, to more than 4 million copies annually, representing 85 percent of the world market. Also in 1997, an internal publication from the PowerPoint group said that by then over 20 million copies of PowerPoint were in use, and that total revenues from PowerPoint over its first ten years (1987 to 1996) had already exceeded $1 billion.
Since the late 1990s, PowerPoint's market share of total world presentation software has been estimated at 95 percent by both industry and academic sources.
Operation
The earliest version of PowerPoint (1987 for Macintosh) could be used to print black and white pages to be photocopied onto sheets of transparent film for projection from overhead projectors, and to print speaker's notes and audience handouts; the next version (1988 for Macintosh, 1990 for Windows) was extended to also produce color 35mm slides by communicating a file over a modem to a Genigraphics imaging center with slides returned by overnight delivery for projection from slide projectors. PowerPoint was used for planning and preparing a presentation, but not for delivering it (apart from previewing it on a computer screen, or distributing printed paper copies). The operation of PowerPoint changed substantially in its third version (1992 for Windows and Macintosh), when PowerPoint was extended to also deliver a presentation by producing direct video output to digital projectors or large monitors. In 1992 video projection of presentations was rare and expensive, and practically unknown from a laptop computer. Robert Gaskins, one of the creators of PowerPoint, says he publicly demonstrated that use for the first time at a large Microsoft meeting held in Paris on February 25, 1992, by using an unreleased development build of PowerPoint 3.0 running on an early pre-production sample of a powerful new color laptop and feeding a professional auditorium video projector.
By about 2003, ten years later, digital projection had become the dominant mode of use, replacing transparencies and 35mm slides and their projectors. As a result, the meaning of "PowerPoint presentation" narrowed to mean specifically digital projection:
... in the business lexicon, "PowerPoint presentation" had come to refer to a presentation made using a PowerPoint slideshow projected from a computer. Although the PowerPoint software had been used to generate transparencies for over a decade, this usage was not typically encompassed by a common understanding of the term.
In contemporary operation, PowerPoint is used to create a file (called a "presentation" or "deck") containing a sequence of pages (called "slides" in the app) which usually have a consistent style (from template masters), and which may contain information imported from other apps or created in PowerPoint, including text, bullet lists, tables, charts, drawn shapes, images, audio clips, video clips, animations of elements, and animated transitions between slides, plus attached notes for each slide.
After such a file is created, typical operation is to present it as a slide show using a portable computer, where the presentation file is stored on the computer or available from a network, and the computer's screen shows a "presenter view" with current slide, next slide, speaker's notes for the current slide, and other information. Video is sent from the computer to one or more external digital projectors or monitors, showing only the current slide to the audience, with sequencing controlled by the speaker at the computer. A smartphone remote control built in to PowerPoint for iOS (optionally controlled from Apple Watch) and for Android allows the presenter to control the show from elsewhere in the room.
In addition to a computer slide show projected to a live audience by a speaker, PowerPoint can be used to deliver a presentation in a number of other ways:
- Displayed on the screen of the presentation computer or tablet (for a very small group)
- Printed for distribution as paper documents (in several formats)
- Distributed as files for private viewing, even on computers without PowerPoint
- Packaged for distribution on CD or a network, including linked and embedded data
- Transmitted as a live broadcast presentation over the web
- Embedded in a web page or blog
- Shared on social networks such as Facebook or Twitter
- Set up as a self-running unattended display
- Recorded as video/audio (H.264/AAC), to be distributed as for any other video
Some of these ways of using PowerPoint have been studied by JoAnne Yates and Wanda Orlikowski of the MIT Sloan School of Management:
The standard form of such presentations involves a single person standing before a group of people, talking and using the PowerPoint slideshow to project visual aids onto a screen. ... In practice, however, presentations are not always delivered in this mode. In our studies, we often found that the presenter sat at a table with a small group of people and walked them through a "deck", composed of paper copies of the slides. In some cases, decks were simply distributed to individuals, without even a walk-through or discussion. ... Other variations in the form included sending the PowerPoint file electronically to another site and talking through the slides over an audio or video channel (e.g., telephone or video conference) as both parties viewed the slides. ... Another common variation was placing a PowerPoint file on a web site for people to view at different times.
They found that some of these ways of using PowerPoint could influence the content of presentations, for example when "the slides themselves have to carry more of the substance of the presentation, and thus need considerably more content than they would have if they were intended for projection by a speaker who would orally provide additional details and nuance about content and context."
Other platforms
PowerPoint for mobile
PowerPoint Mobile is included with Windows Mobile 5.0. It is a presentation program capable of reading and editing Microsoft PowerPoint presentations, although authoring abilities are limited to adding notes, editing text, and rearranging slides. It can't create new presentations. Versions of PowerPoint Mobile for Windows Phone 7 can also watch presentation broadcasts streamed from the Internet. In 2015, Microsoft released PowerPoint Mobile for Windows 10 as a universal app. In this version of PowerPoint users can create and edit new presentations, present, and share their PowerPoint documents.
PowerPoint for the web
Further information: Microsoft Office § Office on the webPowerPoint for the web is a free lightweight version of Microsoft PowerPoint available as part of Office on the web, which also includes web versions of Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Word.
PowerPoint for the web does not support inserting or editing charts, equations, or audio or video stored on your PC, but they are all displayed in the presentation if they were added in using a desktop app. Some elements, like WordArt effects or more advanced animations and transitions, are not displayed at all, although they are preserved in the document. PowerPoint for the web also lacks the Outline, Master, Slide Sorter, and Presenter views present in the desktop app, as well as having limited printing options.
Cultural impact

Business uses
PowerPoint was originally targeted just for business presentations. Robert Gaskins, who was responsible for its design, has written about his intended customers: "... I did not target other existing large groups of users of presentations, such as school teachers or military officers. ... I also did not plan to target people who were not existing users of presentations ... such as clergy and school children ... . Our focus was purely on business users, in small and large companies, from one person to the largest multinationals." Business people had for a long time made presentations for sales calls and for internal company communications, and PowerPoint produced the same formats in the same style and for the same purposes.
PowerPoint use in business grew over its first five years (1987–1992) to sales of about 1 million copies annually, for worldwide market share of 63 percent. Over the following five years (1992–1997) PowerPoint sales accelerated, to a rate of about 4 million copies annually, for worldwide market share of 85 percent. The increase in business use has been attributed to "network effects", whereby additional users of PowerPoint in a company or an industry increased its salience and value to other users.
Not everyone immediately approved of the greater use of PowerPoint for presentations, even in business. CEOs who very early were reported to discourage or ban PowerPoint presentations at internal business meetings included Lou Gerstner (at IBM, in 1993), Scott McNealy (at Sun Microsystems, in 1996), and Steve Jobs (at Apple, in 1997). But even so, Rich Gold, a scholar who studied corporate presentation use at Xerox PARC, could write in 1999: "Within today's corporation, if you want to communicate an idea ... you use PowerPoint."
Uses beyond business
At the same time that PowerPoint was becoming dominant in business settings, it was also being adopted for uses beyond business: "Personal computing ... scaled up the production of presentations. ... The result has been the rise of presentation culture. In an information society, nearly everyone presents."
In 1998, at about the same time that Gold was pronouncing PowerPoint's ubiquity in business, the influential Bell Labs engineer Robert W. Lucky could already write about broader uses:
... the world has run amok with the giddy power of presentation graphics. A new language is in the air, and it is codified in PowerPoint. ... In a family discussion about what to do on a given evening, for example, I feel like pulling out my laptop and giving a Vugraph presentation... In church, I am surprised that the preachers haven't caught on yet. ... How have we gotten on so long without PowerPoint?
Over a decade or so, beginning in the mid 1990s, PowerPoint began to be used in many communication situations, well beyond its original business presentation uses, to include teaching in schools and in universities, lecturing in scientific meetings (and preparing their related poster sessions), worshipping in churches, making legal arguments in courtrooms, displaying supertitles in theaters, driving helmet-mounted displays in spacesuits for NASA astronauts, giving military briefings, issuing governmental reports, undertaking diplomatic negotiations, writing novels, giving architectural demonstrations, prototyping website designs, creating animated video games, editing images, creating art projects, and even as a substitute for writing engineering technical reports, and as an organizing tool for writing general business documents.
By 2003, it seemed that PowerPoint was being used everywhere. Julia Keller reported for the Chicago Tribune:
PowerPoint ... is one of the most pervasive and ubiquitous technological tools ever concocted. In less than a decade, it has revolutionized the worlds of business, education, science, and communications, swiftly becoming the standard for just about anybody who wants to explain just about anything to just about anybody else. From corporate middle managers reporting on production goals to 4th-graders fashioning a show-and-tell on the French and Indian War to church pastors explicating the seven deadly sins ... PowerPoint seems poised for world domination.
Cultural reactions
As uses broadened, cultural awareness of PowerPoint grew and commentary about it began to appear. "With the widespread adoption of PowerPoint came complaints ... often very general statements reflecting dissatisfaction with modern media and communication practices as well as the dysfunctions of organizational culture." Indications of this awareness included increasing mentions of PowerPoint use in the Dilbert comic strips of Scott Adams, comic parodies of poor or inappropriate use such as the Gettysburg Address in PowerPoint or summaries of Shakespeare's Hamlet and Nabokov's Lolita in PowerPoint, and a vast number of publications on the general subject of PowerPoint, especially about how to use it.
Out of all the analyses of PowerPoint over a quarter of a century, at least three general themes emerged as categories of reaction to its broader use: (1) "Use it less": avoid PowerPoint in favor of alternatives, such as using more-complex graphics and written prose, or using nothing; (2) "Use it differently": make a major change to a PowerPoint style that is simpler and pictorial, turning the presentation toward a performance, more like a Steve Jobs keynote; and (3) "Use it better": retain much of the conventional PowerPoint style but learn to avoid making many kinds of mistakes that can interfere with communication.
Use it less
See also: Edward Tufte and Anti-PowerPoint PartyAn early reaction was that the broader use of PowerPoint was a mistake, and should be reversed. An influential example of this came from Edward Tufte, an authority on information design, who has been a professor of political science, statistics, and computer science at Princeton and Yale, but is best known for his self-published books on data visualization, which have sold nearly 2 million copies as of 2014.
In 2003, he published a widely-read booklet titled The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint, revised in 2006. Tufte found a number of problems with the "cognitive style" of PowerPoint, many of which he attributed to the standard default style templates:
PowerPoint's convenience for some presenters is costly to the content and the audience. These costs arise from the cognitive style characteristics of the standard default PP presentation: foreshortening of evidence and thought, low spatial resolution, an intensely hierarchical single-path structure as the model for organizing every type of content, breaking up narratives and data into slides and minimal fragments, rapid temporal sequencing of thin information rather than focused spatial analysis, conspicuous chartjunk and PP Phluff, branding of slides with logotypes, a preoccupation with format not content, incompetent designs for data graphics and tables, and a smirky commercialism that turns information into a sales pitch and presenters into marketeers .
Tufte particularly advised against using PowerPoint for reporting scientific analyses, using as a dramatic example some slides made during the flight of the space shuttle Columbia after it had been damaged by an accident at liftoff, slides which poorly communicated the engineers' limited understanding of what had happened. For such technical presentations, and for most occasions apart from its initial domain of sales presentations, Tufte advised against using PowerPoint at all; in many situations, according to Tufte, it would be better to substitute high-resolution graphics or concise prose documents as handouts for the audience to study and discuss, providing a great deal more detail.
Many commentators enthusiastically joined in Tufte's vivid criticism of PowerPoint uses, and at a conference held in 2013 (a decade after Tufte's booklet appeared) one paper claimed that "Despite all the criticism about his work, Tufte can be considered as the single most influential author in the discourse on PowerPoint. ... While his approach was not rigorous from a research perspective, his articles received wide resonance with the public at large ... ." There were also others who disagreed with Tufte's assertion that the PowerPoint program reduces the quality of presenters' thoughts: Steven Pinker, professor of psychology at MIT and later Harvard, had earlier argued that "If anything, PowerPoint, if used well, would ideally reflect the way we think." Pinker later reinforced this opinion: "Any general opposition to PowerPoint is just dumb, ... It's like denouncing lectures—before there were awful PowerPoint presentations, there were awful scripted lectures, unscripted lectures, slide shows, chalk talks, and so on."
Much of the early commentary, on all sides, was "informal" and "anecdotal", because empirical research had been limited.
Use it differently
See also: Richard E. Mayer and Steve Jobs KeynotesA second reaction to PowerPoint use was to say that PowerPoint can be used well, but only by substantially changing its style of use. This reaction is exemplified by Richard E. Mayer, a professor of psychology at the University of California, Santa Barbara, who has studied cognition and learning, particularly the design of educational multimedia, and who has published more than 500 publications, including over 30 books. Mayer's theme has been that "In light of the science, it is up to us to make a fundamental shift in our thinking—we can no longer expect people to struggle to try to adapt to our PowerPoint habits. Instead, we have to change our PowerPoint habits to align with the way people learn."
Tufte had argued his judgment that the information density of text on PowerPoint slides was too low, perhaps only 40 words on a slide, leading to over-simplified messages; Mayer responded that his empirical research showed exactly the opposite, that the amount of text on PowerPoint slides was usually too high, and that even fewer than 40 words on a slide resulted in "PowerPoint overload" that impeded understanding during presentations.
Mayer suggested a few major changes from traditional PowerPoint formats:
- replacing brief slide titles with longer "headlines" expressing complete ideas;
- showing more slides but simpler ones;
- removing almost all text including nearly all bullet lists (reserving the text for the spoken narration);
- using larger, higher-quality, and more important graphics and photographs;
- removing all extraneous decoration, backgrounds, logos and identifications, everything but the essential message.
Mayer's ideas are claimed by Carmine Gallo to have been reflected in Steve Jobs's presentations: "Mayer outlined fundamental principles of multimedia design based on what scientists know about cognitive functioning. Steve Jobs's slides adhere to each of Mayer's principles ... ." Though not unique to Jobs, many people saw the style for the first time in Jobs's famous product introductions. Steve Jobs would have been using Apple's Keynote, which was designed for Jobs's own slide shows beginning in 2003, but Gallo says that "speaking like Jobs has little to do with the type of presentation software you use (PowerPoint, Keynote, etc.) ... all the techniques apply equally to PowerPoint and Keynote." Gallo adds that "Microsoft's PowerPoint has one big advantage over Apple's Keynote presentation software—it's everywhere ... it's safe to say that the number of Keynote presentations is minuscule in comparison with PowerPoint. Although most presentation designers who are familiar with both formats prefer to work in the more elegant Keynote system, those same designers will tell you that the majority of their client work is done in PowerPoint."
Consistent with its association with Steve Jobs's keynotes, a response to this style has been that it is particularly effective for "ballroom-style presentations" (as often given in conference center ballrooms) where a celebrated and practiced speaker addresses a large passive audience, but less appropriate for "conference room-style presentations" which are often recurring internal business meetings for in-depth discussion with motivated counterparts.
Use it better
See also: Stephen KosslynA third reaction to PowerPoint use was to conclude that the standard style is capable of being used well, but that many small points need to be executed carefully, to avoid impeding understanding. This kind of analysis is particularly associated with Stephen Kosslyn, a cognitive neuroscientist who specializes in the psychology of learning and visual communication, and who has been head of the department of psychology at Harvard, has been Director of Stanford's Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences, and has published some 300 papers and 14 books.
Kosslyn presented a set of psychological principles of "human perception, memory, and comprehension" that "appears to capture the major points of agreement among researchers." He reports that his experiments support the idea that it is not intuitive or obvious how to create effective PowerPoint presentations that conform to those agreed principles, and that even small differences that might not seem significant to a presenter can produce very different results in audiences' understanding. For this reason, Kosslyn says, users need specific education to be able to identify best ways to avoid "flaws and failures":
Specifically, we hypothesized and found that the psychological principles are often violated in PowerPoint slideshows across different fields ..., that some types of presentation flaws are noticeable and annoying to audience members ..., and that observers have difficulty identifying many violations in graphical displays in individual slides ... . These studies converge in painting the following picture: PowerPoint presentations are commonly flawed; some types of flaws are more common than others; flaws are not isolated to one domain or context; and, although some types of flaws annoy the audience, flaws at the level of slide design are not always obvious to an untrained observer ... .
The many "flaws and failures" identified were those "likely to disrupt the comprehension or memory of the material." Among the most common examples were "Bulleted items are not presented individually, growing the list from the top to the bottom," "More than four bulleted items appear in a single list," "More than two lines are used per bulleted sentence," and "Words are not large enough (i.e., greater than 20 point) to be easily seen." Among audience reactions common problems reported were "Speakers read word-for-word from notes or from the slides themselves," "The slides contained too much material to absorb before the next slide was presented," and "The main point was obscured by lots of irrelevant detail."
Kosslyn observes that these findings could help to explain why the many studies of the instructional effectiveness of PowerPoint have been inconclusive and conflicting, if there were differences in the quality of the presentations tested in different studies that went unobserved because "many may feel that 'good design' is intuitively clear."
In 2007 Kosslyn wrote a book about PowerPoint, in which he suggested a very large number of fairly modest changes to PowerPoint styles and gave advice on recommended ways of using PowerPoint. In a later second book about PowerPoint he suggested nearly 150 clarifying style changes (in fewer than 150 pages). Kosslyn summarizes:
... there's nothing fundamentally wrong with the PowerPoint program as a medium; rather, I claim that the problem lies in how it is used. ... In fact, this medium is a remarkably versatile tool that can be extraordinarily effective. ... For many purposes, PowerPoint presentations are a superior medium of communication, which is why they have become standard in so many fields.
In 2017, an online poll of social media users in the UK was reported to show that PowerPoint "remains as popular with young tech-savvy users as it is with the Baby Boomers," with about four out of five saying that "PowerPoint was a great tool for making presentations," in part because "PowerPoint, with its capacity to be highly visual, bridges the wordy world of yesterday with the visual future of tomorrow."
Also in 2017, the Managerial Communication Group of MIT Sloan School of Management polled their incoming MBA students, finding that "results underscore just how differently this generation communicates as compared with older workers." Fewer than half of respondents reported doing any meaningful, longer-form writing at work, and even that minority mostly did so very infrequently, but "85 percent of students named producing presentations as a meaningful part of their job responsibilities. Two-thirds report that they present on a daily or weekly basis—so it's no surprise that in-person presentations is the top skill they hope to improve." One of the researchers concluded: "We're not likely to see future workplaces with long-form writing. The trend is toward presentations and slides, and we don't see any sign of that slowing down."
U.S. military excess
Use of PowerPoint by the U.S. military services began slowly, because they were invested in mainframe computers, MS-DOS PCs and specialized military-specification graphic output devices, all of which PowerPoint did not support. But because of the strong military tradition of presenting briefings, as soon as they acquired the computers needed to run it, PowerPoint became part of the U.S. military.
By 2000, ten years after PowerPoint for Windows appeared, it was already identified as an important feature of U.S. armed forces culture, in a front-page story in the Wall Street Journal:
Old-fashioned slide briefings, designed to update generals on troop movements, have been a staple of the military since World War II. But in only a few short years PowerPoint has altered the landscape. Just as word processing made it easier to produce long, meandering memos, the spread of PowerPoint has unleashed a blizzard of jazzy but often incoherent visuals. Instead of drawing up a dozen slides on a legal pad and running them over to the graphics department, captains and colonels now can create hundreds of slides in a few hours without ever leaving their desks. If the spirit moves them they can build in gunfire sound effects and images that explode like land mines. ... PowerPoint has become such an ingrained part of the defense culture that it has seeped into the military lexicon. "PowerPoint Ranger" is a derogatory term for a desk-bound bureaucrat more adept at making slides than tossing grenades.
U.S. military use of PowerPoint may have influenced its use by armed forces of other countries: "Foreign armed services also are beginning to get in on the act. 'You can't speak with the U.S. military without knowing PowerPoint,' says Margaret Hayes, an instructor at National Defense University in Washington D.C., who teaches Latin American military officers how to use the software."
After another 10 years, in 2010 (and again on its front page) the New York Times reported that PowerPoint use in the military was then "a military tool that has spun out of control":
Like an insurgency, PowerPoint has crept into the daily lives of military commanders and reached the level of near obsession. The amount of time expended on PowerPoint, the Microsoft presentation program of computer-generated charts, graphs and bullet points, has made it a running joke in the Pentagon and in Iraq and Afghanistan. ... Commanders say that behind all the PowerPoint jokes are serious concerns that the program stifles discussion, critical thinking and thoughtful decision-making. Not least, it ties up junior officers ... in the daily preparation of slides, be it for a Joint Staff meeting in Washington or for a platoon leader's pre-mission combat briefing in a remote pocket of Afghanistan.
The New York Times account went on to say that as a result some U.S. generals had banned the use of PowerPoint in their operations:
"PowerPoint makes us stupid," Gen. James N. Mattis of the Marine Corps, the Joint Forces commander, said this month at a military conference in North Carolina. (He spoke without PowerPoint.) Brig. Gen. H. R. McMaster, who banned PowerPoint presentations when he led the successful effort to secure the northern Iraqi city of Tal Afar in 2005, followed up at the same conference by likening PowerPoint to an internal threat. "It's dangerous because it can create the illusion of understanding and the illusion of control," General McMaster said in a telephone interview afterward. "Some problems in the world are not bullet-izable."
Several incidents, about the same time, gave wide currency to discussions by serving military officers describing excessive PowerPoint use and the organizational culture that encouraged it. In response to the New York Times story, Peter Norvig and Stephen M. Kosslyn sent a joint letter to the editor stressing the institutional culture of the military: "... many military personnel bemoan the overuse and misuse of PowerPoint. ... The problem is not in the tool itself, but in the way that people use it—which is partly a result of how institutions promote misuse."
The two generals who had been mentioned in 2010 as opposing the institutional culture of excessive PowerPoint use were both in the news again in 2017, when James N. Mattis became U.S. Secretary of Defense, and H. R. McMaster was appointed as U.S. National Security Advisor.
Artistic medium
Musician David Byrne has been using PowerPoint as a medium for art for years, producing a book and DVD and showing at galleries his PowerPoint-based artwork. Byrne has written: "I have been working with PowerPoint, the ubiquitous presentation software, as an art medium for a number of years. It started off as a joke (this software is a symbol of corporate salesmanship, or lack thereof) but then the work took on a life of its own as I realized I could create pieces that were moving, despite the limitations of the 'medium.'"
In 2005 Byrne toured with a theater piece styled as a PowerPoint presentation. When he presented it in Berkeley, on March 8, 2005, the University of California news service reported: "Byrne also defended appeal as more than just a business tool—as a medium for art and theater. His talk was titled 'I ♥ PowerPoint'. Berkeley alumnus Bob Gaskins and Dennis Austin were in the audience. Eventually, Byrne said, PowerPoint could be the foundation for 'presentational theater,' with roots in Brechtian drama and Asian puppet theater." After that performance, Byrne described it in his own online journal: "Did the PowerPoint talk in Berkeley for an audience of IT legends and academics. I was terrified. The guys that originally turned PowerPoint into a program were there, what were THEY gonna think? ... did tell me afterwards that he liked the PowerPoint as theater idea, which was a relief."
The expressions "PowerPoint Art" or "pptArt" are used to define a contemporary Italian artistic movement which believes that the corporate world can be a unique and exceptional source of inspiration for the artist. They say: "The pptArt name refers to PowerPoint, the symbolic and abstract language developed by the corporate world which has become a universal and highly symbolic communication system beyond cultures and borders."
The wide use of PowerPoint had, by 2010, given rise to " ... a subculture of PowerPoint enthusiasts is teaching the old application new tricks, and may even be turning a dry presentation format into a full-fledged artistic medium," by using PowerPoint animation to create "games, artworks, anime, and movies."
PowerPoint Viewer
PowerPoint Viewer is the name for a series of small free application programs to be used on computers without PowerPoint installed, to view, project, or print (but not create or edit) presentations.
The first version was introduced with PowerPoint 3.0 in 1992, to enable electronic presentations to be projected using conference-room computers and to be freely distributed; on Windows, it took advantage of the new feature of embedding TrueType fonts within PowerPoint presentation files to make such distribution easier. The same kind of viewer app was shipped with PowerPoint 3.0 for Macintosh, also in 1992.
Beginning with PowerPoint 2003, a feature called "Package for CD" automatically managed all linked video and audio files plus needed fonts when exporting a presentation to a disk or flash drive or network location, and also included a copy of a revised PowerPoint Viewer application so that the result could be presented on other PCs without installing anything.
The latest version that runs on Windows "was created in conjunction with PowerPoint 2010, but it can also be used to view newer presentations created in PowerPoint 2013 and PowerPoint 2016. ... All transitions, videos and effects appear and behave the same when viewed using PowerPoint Viewer as they do when viewed in PowerPoint 2010." It supports presentations created using PowerPoint 97 and later. The latest version that runs on Macintosh is PowerPoint 98 Viewer for the Classic Mac OS and Classic Environment, for Macs supporting System 7.5 to Mac OS X Tiger (10.4). It can open presentations only from PowerPoint 3.0, 4.0, and 8.0 (PowerPoint 98), although presentations created on Mac can be opened in PowerPoint Viewer on Windows.
As of May 2018, the last versions of PowerPoint Viewer for all platforms have been retired by Microsoft; they are no longer available for download and no longer receive security updates. The final PowerPoint Viewer for Windows (2010) and the final PowerPoint Viewer for Classic Mac OS (1998) are available only from archives. The recommended replacements for PowerPoint Viewer: "On Windows 10 PCs, download the free ... PowerPoint Mobile application from the Windows Store," and "On Windows 7 or Windows 8/8.1 PCs, upload the file to OneDrive and view it for free using ... PowerPoint Online."
Versions
| Legend: | Old version, not maintained | Old version, still maintained | Current stable version | Latest preview version | Future release |
|---|
| Date | Name | Version | System | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| April 1987 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 1.0 | Macintosh | Shipped by Forethought, Inc. |
| October 1987 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 1.01 | Macintosh | Relabeled and shipped by Microsoft |
| May 1988 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 2.0 | Macintosh | |
| December 1988 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 2.01 | Macintosh | Added Genigraphics software and services |
| May 1990 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 2.0 | Windows | Announced with Windows 3.0, numbered to match contemporary Macintosh version |
| May 1992 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 3.0 | Windows | Announced with Windows 3.1 |
| September 1992 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 3.0 | Macintosh | |
| February 1994 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 4.0 | Windows | |
| October 1994 | PowerPoint | Old version, no longer maintained: 4.0 | Macintosh | Native for Power Mac |
| July 1995 | PowerPoint 95 | Old version, no longer maintained: 7.0 | Windows | Versions 5.0 and 6.0 were skipped on Windows, so all apps in Office 95 were 7.0 |
| January 1997 | PowerPoint 97 | Old version, no longer maintained: 8.0 | Windows | Support ended on February 28, 2002 |
| March 1998 | PowerPoint 98 | Old version, no longer maintained: 8.0 | Macintosh | Versions 5.0, 6.0, and 7.0 were skipped on Macintosh, to match Windows |
| June 1999 | PowerPoint 2000 | Old version, no longer maintained: 9.0 | Windows | Support ended on July 14, 2009 |
| August 2000 | PowerPoint 2001 | Old version, no longer maintained: 9.0 | Macintosh | |
| May 2001 | PowerPoint XP | Old version, no longer maintained: 10.0 | Windows | Support ended on July 12, 2011 |
| November 2001 | PowerPoint v. X | Old version, no longer maintained: 10.0 | Macintosh | |
| October 2003 | PowerPoint 2003 | Old version, no longer maintained: 11.0 | Windows | Support ended on April 8, 2014 |
| June 2004 | PowerPoint 2004 | Old version, no longer maintained: 11.0 | Macintosh | |
| May 2005 | PowerPoint Mobile | Old version, no longer maintained: 11.0 | Windows Mobile 5 | |
| January 2007 | PowerPoint 2007 | Old version, no longer maintained: 12.0 | Windows | End of support October 10, 2017 |
| September 2007 | PowerPoint Mobile | Old version, no longer maintained: 12.0 | Windows Mobile 6 | |
| January 2008 | PowerPoint 2008 | Old version, no longer maintained: 12.0 | Macintosh | |
| June 2010 | PowerPoint 2010 | Old version, no longer maintained: 14.0 | Windows | Version 13.0 was skipped for triskaidekaphobia concerns. Support ended on October 13, 2020 |
| June 2010 | PowerPoint 2010 Web App | Old version, no longer maintained: 14.0 | Web | |
| June 2010 | PowerPoint Mobile 2010 | Old version, no longer maintained: 14.0 | Windows Phone 7 | |
| November 2010 | PowerPoint 2011 | Old version, no longer maintained: 14.0 | Macintosh | Version 13.0 was skipped for triskaidekaphobia concerns End of support October 10, 2017 |
| April 2012 | PowerPoint Mobile 2010 | Old version, no longer maintained: 14.0 | Nokia Symbian | |
| October 2012 | PowerPoint Web App 2013 | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | Web | |
| November 2012 | PowerPoint Mobile 2013 | Old version, no longer maintained: 15.0 | Windows Phone 8 | |
| November 2012 | PowerPoint RT 2013 | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | Windows RT | |
| January 2013 | PowerPoint 2013 | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | Windows | |
| June 2013 | PowerPoint Mobile 2013 for iPhone | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | iPhone | |
| July 2013 | PowerPoint Mobile 2013 for Android | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | Android | |
| February 2014 | PowerPoint 2013 Online | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | Web | |
| March 2014 | PowerPoint 2013 for iPad | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | iPad | |
| November 2014 | PowerPoint Mobile 2013 for iOS | Old version, yet still maintained: 15.0 | iOS | |
| June 2015 | PowerPoint Mobile 2016 for Android | Current stable version: 16.0 | Android | |
| July 2015 | PowerPoint 2016 for Macintosh | Current stable version: 16.0 | Macintosh | There had been no PowerPoint 2013 for Mac. Was version 15.0 from July 2015 to January 2018. |
| July 2015 | PowerPoint Mobile 2016 | Current stable version: 16.0 | Windows 10 Mobile | |
| July 2015 | PowerPoint Mobile 2016 for iOS | Current stable version: 16.0 | iOS | |
| September 2015 | PowerPoint 2016 for Windows | Current stable version: 16.0 | Windows | |
| January 2018 | PowerPoint 2016 for Windows Store | Current stable version: 16.0 | Windows | |
| 2018 | PowerPoint 2019 | Current stable version: 16.0 | Windows and other OS | This and subsequent versions (PowerPoint 2021 and Office 365 PowerPoint) are all internally version 16.0 |
| Date | Name | Version | System | Comments |

- PowerPoint 1.0
- For Macintosh: April 1987
- Innovations included: multiple slides in a single file, organizing slides with a slide sorter view and a title view (precursor of outline view), speakers' notes pages attached to each slide, printing of audience handouts with multiple slides per page, text with outlining styles and full word-processor formatting, graphic shapes with attached text for drawing diagrams and tables. It also shipped with a hardbound book as its manual.
- "It produced overhead transparencies on a black-and-white Macintosh for laser printing. Presenters could now directly control their own overheads and would no longer have to work through the person with the typewriter. PowerPoint handled the task of making the overheads all look alike; one change reformats them all. Typographic fonts were better than an Orator typeball, and charts and diagrams could be imported from MacDraw, MacPaint, and Excel, thanks to the new Mac clipboard."
- System requirements: (Mac) Original Macintosh or better, System 1.0 or higher, 512K RAM.
- PowerPoint 2.0
- For Macintosh: May 1988; for Windows: May 1990
- Part of Microsoft Office for Mac and Microsoft Office for Windows. Innovations included: color, more word processing features, find and replace, spell checking, color schemes for presentations, guide to color selection, ability to change color scheme retrospectively, shaded coloring for fills.
- "It added color 35 mm slides, transmitting the resulting file over a modem to Genigraphics for imaging on Genigraphics' film recorders and photo processing in Genigraphics' labs overnight. Genigraphics was the leading professional service bureau, having developed its own Digital Equipment Corp. PDP-11-based computer systems for its artists. After a short time, though, Genigraphics itself switched to PowerPoint."
- System requirements: (Mac) Original Macintosh or better, System 4.1 or higher, 1 MB RAM. (Windows) 286 PC or higher, Windows 3.0, 1 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 3.0
- For Windows, May 1992; for Mac: September 1992
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 3.0 and Microsoft Office for Mac 3.0. Innovations included: the first application designed exclusively for the new Windows 3.1 platform, full support for TrueType fonts (new in Windows 3.1), presentation templates, editing in outline view, new drawing, including freeform tool, autoshapes, flip, rotate, scale, align, and transforming imported pictures into their drawing primitives to make them editable, transitions between slides in slide show, progressive builds, incorporating sound and video. Animations included "flying bullets" where bullet points "flew" into the slide one by one, and some degree of Pen Computing support was included.
- "It added video-out to feed the new video projectors, with effects that could replace a bank of synchronized slide projectors. This version added fades, dissolves, and other transitions, as well as animation of text and pictures, and could incorporate video clips with synchronized audio."
- System requirements: (Windows) 286 PC or higher, Windows 3.1, 2 MB RAM. (Mac) Macintosh Plus or better, System 7 or higher, 4 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 4.0
- For Windows: February 1994; for Mac: October 1994
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 4.0 and Microsoft Office for Mac 4.2. Innovations included: autolayouts, Word tables, rehearsal mode, hidden slides, and the "AutoContent Wizard".
- Introduced a standard "Microsoft Office" look and feel (shared with Word and Excel), with status bar, toolbars, tooltips. Full OLE 2.0 with in-place activation.
- System requirements: (Windows) 386 PC or higher, Windows 3.1, 8 MB RAM. (Mac) 68020 Mac or better, System 7 or higher, 8 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 7.0
- For Windows: July 1995
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 95. Innovations included: new animation effects, real curves and textures, black and white view, autocorrect, insert symbol, meeting support features such as "Meeting Minder".
- "A complete rewrite of the product from the ground up in C++, full object model with internal VBA programmability".
- System requirements: (Windows) 386 DX PC or higher, Windows 95, 6 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 8.0
- For Windows: January 1997; for Mac: March 1998
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 97 and Microsoft Office 98 Macintosh Edition. Innovations included: "Office Assistant", file compression, save to HTML, "Pack and Go", "AutoClipArt", transparent GIFs.
- System requirements: (Windows) 486 PC or higher, 8 MB RAM. (Mac) PowerPC Mac or better, 16 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 9.0
- For Windows: June 1999; for Mac: August 2000
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 2000 and Microsoft Office for Mac 2001. Innovations included: three-pane "browser" view (selectable list of slide miniatures or titles, large single slide, notes), autofit text, real tables, presentation conferencing, save to web, picture bullets, animated GIFs, aliased fonts.
- System requirements: (Windows) Pentium 75MHz+, Windows 95 or higher, 20 MB RAM. (Mac) PowerPC Mac 120MHz+ or better, MacOS 8.5 or higher, minimum 48 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 10.0
- For Windows: May 2001; for Mac: November 2001
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows XP and Microsoft Office for Mac v.X. Innovations included: install from web, most clipart on web, use of Exchange and SharePoint for storage and collaboration.
- System requirements: (Windows) Pentium III, Windows 98 or higher, 40 MB RAM. (Mac) OS X 10.1 ("Puma") or later (will not run under OS 9).
- PowerPoint 11.0
- For Windows: October 2003; for Mac: June 2004; for Mobile: May 2005
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 2003 and Microsoft Office for Mac 2004. Innovations included: tools visible to presenter during slide show (notes, thumbnails, time clock, re-order and edit slides), "Package for CD" to write presentation and viewer app to CD. "Microsoft Producer for PowerPoint 2003" was a free plug-in from Microsoft, using a video camera, "that creates Web page presentations, with talking head narration, coordinated and timed to your existing PowerPoint presentation" for delivery over the web. The Genigraphics software to send a presentation for imaging as 35mm slides was removed from this version.
- System requirements: (Windows) Pentium 233Mhz+, Windows 2000 with SP3 or later, 128 MB RAM. (Mac) Power Mac G3 or better, OS X 10.2.8 or later, 256 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 12.0
- For Windows: January 2007; for Mobile: September 2007; for Mac: January 2008
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 2007 and Microsoft Office for Mac 2008. Innovations included: new user interface ("Office Fluent") employing a changeable "ribbon" of tools across the top to replace menus and toolbars, SmartArt graphics, many graphical improvements in text and drawing, improved "Presenter View" (from 2003), widescreen slide formats. The "AutoContent Wizard" was removed from this version.
- A major change in PowerPoint 2007 was from a binary file format, used from 1997 to 2003, to a new XML file format which evolved over further versions.
- System requirements: (Windows) 500 MHz processor or higher, Windows XP with SP2 or later, 256 MB RAM. (Mac) 500 MHz processor or higher, MacOS X 10.4.9 or later, 512 MB RAM.
- PowerPoint 14.0
- For Windows: June 2010; for Web: June 2010; for Mobile: June 2010; for Mac: November 2010, for Symbian: April 2012
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 2010 and Microsoft Office for Mac 2011. Innovations included: Single document interface (SDI), sections within presentations, reading view, redesign of "Backstage" functions (under File menu), save as video, insert video from web, embed video and audio, enhanced editing for video and for pictures, broadcast slideshow.
- System requirements: (Windows) 500 MHz processor or higher, Windows XP with SP3 or later, 256 MB RAM, 512 MB RAM recommended for video. (Mac) Intel processor, Mac OS X 10.5.8 or later, 1 GB RAM.
- PowerPoint 15.0
- For Web: October 2012; for Mobile: November 2012; for Windows RT: November 2012; for Windows: January 2013; for iPhone: June 2013; for Android: July 2013; for Web: February 2014; for iPad: March 2014; for iOS: November 2014; for Mac: July 2015
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 2013 and Microsoft Office for Mac 2016. Innovations included: Change default slide shape to 16:9 aspect ratio, online collaboration by multiple authors, user interface redesigned for multi-touch screens, improved audio, video, animations, and transitions, further changes to Presenter View. Clipart collections (and insertion tool) were removed, but available online.
- System requirements: (Windows) 1 GHz processor or faster, x86- or x64-bit processor with SSE2 instruction set, Windows 7 or later, 1 GB RAM (32-bit), 2 GB RAM (64-bit). (Mac) Intel processor, Mac OS X 10.10 or later, 4 GB RAM.
- PowerPoint 16.0
- For Android: June 2015; for Mobile: July 2015; for iOS: July 2015; for Windows: September 2015; and Windows Store: January 2018
- Part of Microsoft Office for Windows 2016. Innovations included: "Tell me" to search for program controls, "PowerPoint Designer" pane, Morph transition, real-time collaboration, "Zoom" to slides or sections in slideshow, and "Presentation Translator" for real-time translation of a presenter's spoken words to on-screen captions in any of 60+ languages, with the system analyzing the text of the PowerPoint presentation as context to increase the accuracy and relevance of the translations.
- System requirements: (Windows) 1 GHz processor or faster, x86- or x64-bit processor with SSE2 instruction set, Windows 7 with SP 1 or later, 2 GB RAM.
File formats
| Filename extensions | .pptx, .ppt |
|---|---|
| Internet media type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint |
| Uniform Type Identifier (UTI) | com.microsoft.powerpoint.ppt |
| Developed by | Microsoft |
| Type of format | Presentation |
Binary (1987–2007)
Early versions of PowerPoint, from 1987 through 1995 (versions 1.0 through 7.0), evolved through a sequence of binary file formats, different in each version, as functionality was added. This set of formats were never documented, but an open-source libmwaw (used by LibreOffice) exists to read them.
A stable binary format (called a .ppt file, like all earlier binary formats) that was shared as the default in PowerPoint 97 through PowerPoint 2003 for Windows, and in PowerPoint 98 through PowerPoint 2004 for Mac (that is, in PowerPoint versions 8.0 through 11.0) was finally created. It was based on the Compound File Binary Format. The specification document is actively maintained and can be freely downloaded, because, although no longer the default, that binary format can be read and written by some later versions of PowerPoint, including PowerPoint 2016. After the stable binary format was adopted, versions of PowerPoint continued to be able to read and write differing file formats from earlier versions. But beginning with PowerPoint 2007 and PowerPoint 2008 for Mac (PowerPoint version 12.0), this was the only binary format available for saving; PowerPoint 2007 (version 12.0) no longer supported saving to binary file formats used earlier than PowerPoint 97 (version 8.0), ten years before.
The ".pps" and ".ppsx" file extensions are technically the same as ".ppt" and ".pptx", except they are launched as presentation instead of for editing by default.
Binary filename extensions
- .ppt, PowerPoint 97–2003 binary presentation
- .pps, PowerPoint 97–2003 binary slide show
- .pot, PowerPoint 97–2003 binary template
Binary media types
- .ppt, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint
- .pps, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint
- .pot, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint
Office Open XML (since 2007)
The big change in PowerPoint 2007 and PowerPoint 2008 for Mac (PowerPoint version 12.0) was that the stable binary file format of 97–2003 was replaced as the default by a new zipped XML-based Office Open XML format (.pptx files). Microsoft's explanation of the benefits of the change included: smaller file sizes, up to 75% smaller than comparable binary documents; security, through being able to identify and exclude executable macros and personal data; less chance to be corrupted than binary formats; and easier interoperability for exchanging data among Microsoft and other business applications, all while maintaining backward compatibility.
- .pptx, PowerPoint 2007 XML presentation
- .pptm, PowerPoint 2007 XML macro-enabled presentation
- .ppsx, PowerPoint 2007 XML slide show
- .ppsm, PowerPoint 2007 XML macro-enabled slide show
- .ppam, PowerPoint 2007 XML add-in
- .potx, PowerPoint 2007 XML template
- .potm, PowerPoint 2007 XML macro-enabled template
XML media types
- .pptx, application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation
- .pptm, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.presentation.macroEnabled.12
- .ppsx, application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.slideshow
- .ppsm, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.slideshow.macroEnabled.12
- .ppam, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.addin.macroEnabled.12
- .potx, application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.template
- .potm, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint.template.macroEnabled.12
The specification for the new format was published as an open standard, ECMA-376, through Ecma International Technical Committee 45 (TC45). The Ecma 376 standard was approved in December 2006, and was submitted for standardization through ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 34 WG4 in early 2007. The standardization process was contentious. It was approved as ISO/IEC 29500 in early 2008. Copies of the ISO/IEC standard specification are freely available, in two parts. These define two related standards known as "Transitional" and "Strict". The two standards were progressively adopted by PowerPoint: PowerPoint version 12.0 (2007, 2008 for Mac) could read and write Transitional format, but could neither read nor write Strict format. PowerPoint version 14.0 (2010, 2011 for Mac) could read and write Transitional, and also read but not write Strict. PowerPoint version 15.0 and later (beginning 2013, 2016 for Mac) can read and write both Transitional and Strict formats. The reason for the two variants was explained by Microsoft:
... the participants in the ISO/IEC standardization process recognized two objectives with competing requirements. The first objective was for the Open XML standard to provide an XML-based file format that could fully support conversion of the billions of existing Office documents without any loss of features, content, text, layout, or other information, including embedded data. The second was to specify a file format that did not rely on Microsoft-specific data types. They created two variants of Open XML—Transitional, which supports previously-defined Microsoft-specific data types, and Strict, which does not rely on them. Prior versions of Office have supported reading and writing Transitional Open XML, and Office 2010 can read Strict Open XML documents. With the addition of write support for Strict Open XML, Office 2013 provides full support for both variants of Open XML.
The PowerPoint .pptx file format (called "PresentationML" for Presentation Markup Language) contains separate structures for all the complex parts of a PowerPoint presentation. The specification documents run to over six thousand pages. Because of the widespread use of PowerPoint, the standardized file formats are considered important for the long-term access to digital documents in library collections and archives, according to the U.S. Library of Congress.
PowerPoint 2013 and PowerPoint 2016 provide options to set default saving to ISO/IEC 29500 Strict format, but the initial default setting remains Transitional, for compatibility with legacy features incorporating binary data in existing documents. PowerPoint 2013 or PowerPoint 2016 will both open and save files in the former binary format (.ppt), for compatibility with older versions of the program (but not versions older than PowerPoint 97). In saving to older formats, these versions of PowerPoint will check to assure that no features have been introduced into the presentation which are incompatible with the older formats.
PowerPoint 2013 and 2016 will also save a presentation in many other file formats, including PDF format, MPEG-4 or WMV video, as a sequence of single-picture files (using image formats including GIF, JPEG, PNG, TIFF, and some older formats), and as a single presentation file in which all slides are replaced with pictures. PowerPoint will both open and save files in OpenDocument Presentation format (ODP) for compatibility.
See also
References
- "Release notes for Current Channel releases - Office release notes". Microsoft Learn. Archived from the original on January 10, 2024. Retrieved January 10, 2024.
- ^ "C++ in MS Office". cppcon. July 17, 2014. Archived from the original on November 7, 2019. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- Microsoft Corp. (2017). "Language Accessory Pack for Office". Archived from the original on August 28, 2017. Retrieved August 28, 2017.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint: Slideshows and Presentations APKs". APKMirror.
- "Update history for Office for Mac". Microsoft Docs. June 13, 2023.
- "Microsoft Powerpoint on the Mac App Store". Retrieved March 2, 2023.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint". App Store. June 12, 2023.
- ^ "Microsoft PowerPoint". Encyclopaedia Britannica. November 25, 2013. Archived from the original on October 8, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
Microsoft PowerPoint, virtual presentation software developed by Robert Gaskins, Tom Rudkin and Dennis Austin for the American computer software company Forethought, Inc. The program, initially named Presenter, was released for the Apple Macintosh in 1987.
- Mace, Scott (March 2, 1969). "Presentation Package Lets Users Control Look". InfoWorld. Vol. 9, no. 9. p. 5. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
The $395 program will be shipped to dealers on April 20, Forethought said.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint". Encyclopaedia Britannica. November 25, 2013. Archived from the original on October 8, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
... in 1987 ... n July of that year, the Microsoft Corporation, in its first significant software acquisition, purchased the rights to PowerPoint for $14 million.
- ^ "Microsoft Buys Software Unit". Company News. New York Times. Vol. CXXXV, no. 46, 717. July 31, 1987. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
... the acquisition of Forethought is the first significant one for Microsoft, which is based in Redmond, Wash. Forethought would remain in Sunnyvale, giving Microsoft a Silicon Valley presence.
- Flynn, Laurie (June 19, 1989). "The Microsoft Office Bundles 4 Programs". InfoWorld. Vol. 11, no. 25. p. 37. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- Johnston, Stuart J. (October 1, 1990). "Office for Windows Bundles Popular Microsoft Applications". InfoWorld. Vol. 12, no. 40. p. 16. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- ^ Austin, Dennis (2001). "PowerPoint Version Timeline (to PowerPoint 7.0, 1995)" (PDF). GBU Wizards of Menlo Park. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (2012). Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint. Vinland Books. ISBN 978-0-9851424-0-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- Thielsch, Meinald T.; Perabo, Isabel (May 2012). "Use and Evaluation of Presentation Software" (PDF). Technical Communication. 59 (2): 112–123. ISSN 0049-3155. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 9, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
For many years, Microsoft has led the market with its program PowerPoint. Zongker and Salesin (2003) estimated a market share of 95% in 2003, and a Forrester study (Montalbano, 2009) widely confirmed this number, stating that only 8% of enterprise customers use alternative products.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint". Encyclopaedia Britannica. November 25, 2013. Archived from the original on August 28, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
PowerPoint was developed for business use but has wide applications elsewhere such as for schools and community organizations
- Davies, Russell (May 26, 2016). "29 Reasons to Love PowerPoint". Wired UK. ISSN 1758-8332. Archived from the original on August 15, 2017. Retrieved September 6, 2017. "29 Bullets". Archived from the original on September 11, 2017. Retrieved October 26, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Tufte, Edward (2006) . The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint: Pitching Out Corrupts Within (2nd ed.). Cheshire, Connecticut: Graphics Press LLC. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-9613921-6-1.
- ^ Atkinson, Cliff; Mayer, Richard E. (April 23, 2004). "Five ways to reduce PowerPoint overload" (PDF). ResearchGate. Revision 1.1. Archived from the original on June 17, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- ^ Kosslyn, Stephen M. (2007). Clear and to the Point: Eight Psychological Principles for Compelling PowerPoint Presentations. Oxford University Press. p. 222. ISBN 978-0-19-532069-5.
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (December 2007). "PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics". Viewpoint. Communications of the ACM. 50 (12): 17. doi:10.1145/1323688.1323710. ISSN 0001-0782. S2CID 48306. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved May 27, 2015.
- "Compare PowerPoint features on different platforms". Microsoft Support. April 19, 2022. Retrieved October 23, 2022.
- Gomes, Lee (June 20, 2007). "PowerPoint Turns 20, As Its Creators Ponder A Dark Side to Success". Portals. Wall Street Journal. Vol. CCXLIX, no. 143 (US ed.). p. B1. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
PowerPoint's two creators ... Robert Gaskins was the visionary entrepreneur ... with major programming done by Dennis Austin, an old chum ... .
- Brock, David C. (October 31, 2017). "The Improbable Origins of PowerPoint". History. IEEE Spectrum. 54 (11) (published November 2, 2017): 42–49. doi:10.1109/MSPEC.2017.8093800. ISSN 0018-9235. S2CID 27013411. Archived from the original on November 2, 2017. Retrieved November 2, 2017.
PowerPoint was not at all in their original plan. ... Pohlman and Campbell's idea was to bring a graphical-software environment like the Xerox Alto's to the hugely popular but graphically challenged PC. ... Rather than liquidate the firm, management and investors decided to "restart" Forethought ... .
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (2012). Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint. Vinland Books. ISBN 978-0-9851424-0-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- Brock, David C. (October 31, 2017). "The Improbable Origins of PowerPoint". History. IEEE Spectrum. 54 (11) (published November 2, 2017): 42–49. doi:10.1109/MSPEC.2017.8093800. ISSN 0018-9235. S2CID 27013411. Archived from the original on November 2, 2017. Retrieved November 2, 2017.
... Forethought began to develop a software product of its own. This new effort was the brainchild of Robert Gaskins, an accomplished computer scientist who'd been hired to lead Forethought's product development.
- Gaskins, Robert (August 14, 1984). "Presentation Graphics for Overhead Projection" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 6, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- Austin, Dennis (2009). "Beginnings of PowerPoint: A Personal Technical Story" (PDF). Computer History Museum, Archive. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 12, 2014. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
In October ...I joined Forethought ... .
- Austin, Dennis; Gaskins, Robert (August 21, 1985). "Presenter [PowerPoint] Design" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved April 22, 2015.
- Foster, Edward (July 1, 1985). "Microsoft Ships Windows: Once Written Off Because of Delays, Windows Now Seen as a Contender Against Topview". News, Software. InfoWorld. Vol. 7, no. 26. p. 17. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on August 24, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
'We're quite happy to have people know our plan is to leverage our Mac experience with Microsoft Windows,' says Robert Gaskins, vice president of development.
- Trower, Tandy (November 20, 2010). "The Secret Origin of Windows". Technologizer. Archived from the original on January 23, 2011. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
Windows 1.0 shipped on November 20th, 1985
- Gaskins, Robert (June 27, 1986). "Presenter [PowerPoint] Product Marketing Analysis" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (July 15, 1986). "Presenter [PowerPoint] New Product Summary and Review" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Austin, Dennis; Rudkin, Thomas; Gaskins, Robert (May 22, 1986). "Presenter [PowerPoint] Specification" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (August 13, 2012). "PowerPoint at 25: Conversation with Robert Gaskins" (Interview). Interviewed by Geetesh Bajaj. Archived from the original on April 4, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- Ranney, Elizabeth (May 5, 1986). "Apple Proceeding With Strategic Investment Plans". "Just Heard" column. InfoWorld. Vol. 8, no. 18. p. 3. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
Eilers stressed ... 'we are going to make minority investments in companies that add value to Apple computers and thereby increase the sales of Apple computers over time.'
- Mace, Scott (March 2, 1987). "Presentation Package Lets Users Control Look". InfoWorld. Vol. 9, no. 9. p. 5. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (May 25, 1987). "Forethought Restart Completed (A Brief History)" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. p. 9. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
We completed PowerPoint so as to ship it on schedule on April 20. By early May, we had shipped about $1,000,000 worth of PowerPoint and exhausted the first printing of 10,000 copies.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (April 8, 2010). "The History of Microsoft—The Jeff Raikes Story, Part Two". Channel9 videos, Microsoft Developer Network. 05:42 to 07:18. Archived from the original on August 24, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
Jeff Raikes talks ... about having an idea in 1987 for a presentation product before discovering Forethought, which had a product called PowerPoint.
A transcript of the relevant section is also available. - May, Trish (January 17, 2010). "The Road to the Cure". New York Times (New York ed.). p. BU7. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on June 20, 2022. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
I wrote and presented a proposal to Bill Gates for a new piece of software for the personal computer, specifically to help people create presentations ... .
- Swaine, Michael (September 1, 1991). "Calling Apple's Bluff". Dr. Dobb's Journal. Archived from the original on June 27, 2015. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
I had a meeting with Bill Gates in, I guess it was February of '87 ... We worked out a letter of intent.
- Carroll, Paul B. (March 6, 1987). "New Software Simplifies Show and Tell". Technology. Wall Street Journal. p. 33. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- Winer, Dave (April 10, 2010). "Microsoft rejection letter, 1987". Scripting News. Archived from the original on September 7, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- Shirley, Jon (May 13, 1987). "[Microsoft] Letter of Intent [to acquire Forethought]" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 17, 2014. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- "Microsoft Buys Software Unit". Company News. New York Times. Vol. CXXXV, no. 46, 717. July 31, 1987. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- ^ 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. "Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–". Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- ^ Parker, Rachel (August 3, 1987). "Microsoft Acquires Forethought, Publisher of PowerPoint Package". News. InfoWorld. Vol. 9, no. 31. p. 8. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on June 23, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
The Forethought group will become Microsoft's Graphics Business Unit, forming a permanent Microsoft development and marketing facility in Sunnyvale, California. With a site in California, Microsoft hopes to recruit programmers who might not want to relocate to Washington, Shirley said.
- Keefe, Patricia (August 3, 1987). "Microsoft buys Forethought". Computerworld. p. 81. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (August 8, 1988). "Results of Microsoft's Graphics Business Unit after Our First Year" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents (Microsoft Memo). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
- Pournelle, Jerry (January 1989). "To the Stars". BYTE. Vol. 14, no. 1. p. 120. ISSN 0360-5280. Archived from the original on September 30, 2017. Retrieved September 30, 2017.
I'll just say that if you're in the business of putting on briefings and otherwise making presentations, you might want to seriously contemplate getting a Mac II just so you can use this program; it's that good. Highly recommended.
- Borzo, Jeanette (May 18, 1992). "PowerPoint users pleased by changes". InfoWorld. Vol. 14, no. 20. IDG. p. 15. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (August 8, 1988). "Results of Microsoft's Graphics Business Unit after Our First Year" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents (Microsoft Memo). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
We have learned a tremendous number of technical insights through working with the Genigraphics engineering group ... .
- Gaskins, Robert (December 2007). "PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics". Viewpoint. Communications of the ACM. 50 (12): 15–17. doi:10.1145/1323688.1323710. ISSN 0001-0782. S2CID 48306. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017. The first three versions are described in the sidebar, "Presentation Formats and PowerPoint," p. 17.
- ^ Flynn, Laurie (June 19, 1989). "The Microsoft Office Bundles 4 Programs". InfoWorld. Vol. 11, no. 25. p. 37. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
A special promotion announced last week by Microsoft Corp. enables Macintosh customers to buy four of the company's business applications at a 35 percent discount. The special edition, called The Microsoft Office, includes Word 4.0, Excel 2.2, PowerPoint 2.01, and Mail 1.37. The package sells for $849; if purchased separately, the programs would cost $1,310, the company said. The promotion is available until the end of the year.
- ^ Johnston, Stuart J. (October 1, 1990). "Office for Windows Bundles Popular Microsoft Applications". InfoWorld. Vol. 12, no. 40. p. 16. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
Microsoft last week announced the release of The Microsoft Office for Windows, which bundles three of the company's popular Windows applications—Word, Excel, and PowerPoint—for significantly less than they would cost separately. The product brings to the Windows environment basically the equivalent of The Microsoft Office for Macintosh, which was announced a year ago.
- Microsoft Corporation (March 1993). "New PowerPoint 3.0. Because powerful tools make powerful presentations". MacWorld (advertisement). Vol. 10, no. 3. pp. BA1–BA2 (inside front cover spread). ISSN 0741-8647. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- "Microsoft Office now has Mail, PowerPoint". Pipeline. InfoWorld. Vol. 14, no. 35. August 31, 1992. p. 15. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on December 21, 2016. Retrieved August 23, 2017.
- Gates, Bill (February 19, 1991). "Market Share of Applications in the United States" (PDF). Slated Antitrust (scanned court evidence files) (Microsoft Memo). Archived (PDF) from the original on August 28, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- S&P Global Market Intelligence (2017). "Executive Profile: Vijay R. Vashee". Bloomberg.com. Archived from the original on August 22, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
From 1982 ... Mr. Vashee served in various senior marketing, product management and executive positions at Microsoft. ... and as the General Manager for PowerPoint from 1992 to 1997 ... played a key role in the integration of PowerPoint into the Microsoft Office suite.
- Fridlund, Alan (June 6, 1994). "PowerPoint 4.0 makes it into the big time". Reviews. InfoWorld. Vol. 16, no. 23. pp. 95–98. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Lassesen, Ken (October 17, 1995). "Using Microsoft OLE Automation Servers to Develop Solutions" (PDF). Archive of Articles from MSDN Technology Group. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
Note that version 7.0 of a product is the same as a '95' designation, for example, Microsoft Excel 95 is the same as Microsoft Excel version 7.0.
- Microsoft (May 2006). "Developer Overview of the User Interface for the 2007 Microsoft Office System". Microsoft Developer Network. Archived from the original on July 7, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (August 17, 2007). "Microsoft's 20-year PPT party". Robert Gaskins Home Page. Archived from the original on August 24, 2017. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
- Microsoft (2017). "What's New in PowerPoint 2016 for Windows". Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on July 31, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
- "Microsoft Careers: Senior Software Engineer (Job #1064262)". Microsoft Silicon Valley. August 17, 2017. Archived from the original on August 21, 2017. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
Come join the PowerPoint team ... in the heart of the Silicon Valley in Mountain View, CA. The PowerPoint team has the responsibility for the design, implementation, and testing ... .
- Microsoft Corp. (January 10, 2008). "Microsoft Announces Retirement and Transition Plan for Jeff Raikes, President of the Microsoft Business Division". Microsoft News Center. Archived from the original on November 28, 2014. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
MBD has grown to include ... the Microsoft Office system ... .
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (2012). Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint. Vinland Books. ISBN 978-0-9851424-0-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017. Rounded unit sales figures are from the revenue tables (p. 403) adjusted to calendar years (p. 170) with the transfer pricing indicated (p. 182).
- Reimer, Jeremy (December 14, 2005). "Total share: 30 years of personal computer market share figures". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
... the IBM PC platform ... an 84% share in 1990. The Macintosh stabilized at about 6% market share ... .
- "Egghead Software Sales: ... Graphics/DOS". InfoWorld. Vol. 11, no. 1. January 2, 1989. p. 32. ISSN 0199-6649. Retrieved September 9, 2017.
Graphics/DOS ... 1 Harvard Graphics (Software Publishing), 2 Freelance + (Lotus) ... .
Alt URL - Watt, Peggy (January 27, 1986). "Software Publishing adds graphic package to Harvard line". Computerworld. Vol. XX, no. 4. IDG Communications. p. 10. ISSN 0010-4841. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017. Retrieved September 9, 2017.
... graphics presentation program, Harvard Presentation Graphics, introduced last week. ... will be available in March ... .
- Schemenaur, PJ (October 27, 1986). "Lotus to Unveil Revision of Freelance". InfoWorld. Vol. 8, no. 43. p. 3. ISSN 0199-6649. Retrieved September 9, 2017.
... Freelance Plus, the first new release of Freelance since Lotus acquired the graphics package from Graphics Communications Inc. in June.
Alt URL - Howard, Bill; Kunkel, Gerard (September 27, 1988). "More Than Meets the Eye: Designing Great Graphics". PC Magazine. Vol. 7, no. 16. Ziff Davis. p. 95. ISSN 0888-8507. Retrieved September 8, 2017.
Harvard Graphics gained the top spot this year, and now outsells Freelance Plus by a three-to-two margin.
Alt URL - "Designing Great Graphics: Desktop Solutions". PC Magazine. Vol. 7, no. 16. Ziff Davis. September 27, 1988. pp. 109–179. ISSN 0888-8507. Retrieved September 8, 2017.
18 ... software packages reviewed ... .
Alt URL - Parker, Rachel (August 3, 1987). "Microsoft Acquires Forethought, Publisher of PowerPoint Package". News. InfoWorld. Vol. 9, no. 31. p. 8. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on June 23, 2015. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
Shirley ... said that Microsoft has no firm plans currently to develop an MS-DOS version of PowerPoint.
- Gates, Bill (August 16, 1993). "Free market economics—not intervention—drives innovation". Letters to the Editor. InfoWorld. Vol. 15, no. 33. p. 44. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 26, 2017.
Data from the Software Publishers Association and other sources show that in 1992, while overall sales of application products grew only 12 percent, sales of Windows-based applications grew by nearly 100 percent. At least a dozen companies besides Microsoft have sold more than 1 million units of Windows applications.
- Ziff Davis Market Intelligence (September 1998). "The 800-Pound Gorilla of the Presentation Market". Mobile Computing and Communications. 9 (9): 95. ISSN 1047-1952. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015.
... in 1997, without question the market leader was Microsoft Corp.'s PowerPoint, which sold more than 4 million copies and controls 85 percent of the market.
Additional archives: August 26, 2017. - Belleville, Catherine; Peterson, Lucy; Somogyi, Aniko (April 1997). "PowerPoint: The First Ten Years" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents. pp. 2, 8. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
- Thielsch, Meinald T.; Perabo, Isabel (May 2012). "Use and Evaluation of Presentation Software" (PDF). Technical Communication. 59 (2): 112–123. ISSN 0049-3155. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 22, 2015. Retrieved August 24, 2017.
For many years, Microsoft has led the market with its program PowerPoint. Zongker and Salesin (2003) estimated a market share of 95% in 2003, and a Forrester study (Montalbano, 2009) widely confirmed this number, stating that only 8% of enterprise customers use alternative products. ... we confirm the prior estimates ... .
Embedded citations: (1) Zongker, Douglas E.; Salesin, David H. (2003). "On Creating Animated Presentations" (PDF). SCA '03 Symposium on Computer Animation 2003. Eurographics/SIGGRAPH Symposium on Computer Animation, San Diego, CA, July 26–27, 2003. Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland: Eurographics Association. pp. 298–308. ISBN 978-1-58113-659-3. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 22, 2015. Retrieved August 24, 2017. (2) Montalbano, Elizabeth (June 4, 2009). "Forrester: Microsoft Office in No Danger From Competitors". PC World. ISSN 0737-8939. Archived from the original on August 16, 2016. Retrieved August 24, 2017. - ^ Gaskins, Robert (December 2007). "PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics". Viewpoint. Communications of the ACM. 50 (12): 15–17. doi:10.1145/1323688.1323710. ISSN 0001-0782. S2CID 48306. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 12, 2017. The first three versions are described in the sidebar, "Presentation Formats and PowerPoint," p. 17.
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (2012). Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint. Vinland Books. ISBN 978-0-9851424-0-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- "The End of the Carousel Slide Projector?". Edward Tufte Forum. July 14, 2003. Archived from the original on November 3, 2011. Retrieved August 20, 2017.
Eastman Kodak Company has confirmed plans to discontinue the manufacture and sales of slide projection products and accessories in June of 2004.
- ^ Yates, JoAnne; Orlikowski, Wanda (2007). "Chapter 4: The PowerPoint Presentation and Its Corollaries: How Genres Shape Communicative Action in Organizations" (PDF). In Zachry, Mark; Thralls, Charlotte (eds.). Communicative Practices in Workplaces and the Professions: Cultural Perspectives on the Regulation of Discourse and Organizations. Amityville, N.Y.: Baywood Publishing Co. pp. 67–91. ISBN 978-0-89503-372-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 5, 2015. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Basic tasks for creating a PowerPoint presentation". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on July 9, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Start the presentation and see your notes in Presenter view". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint, Version 2.4". Apple iTunes Store. August 14, 2017. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
Start the slide show with your Apple Watch and easily navigate to the next and previous slides.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint". Google Play Store. August 14, 2017. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Choose the right view for the task in PowerPoint". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017. (This mode of operation was available since version 1.0.)
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Print your handouts, notes, or slides". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017. (This mode of operation was available since version 1.0.)
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "View a presentation without PowerPoint". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Package a presentation for CD". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Present online using the Office Presentation Service". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
This feature was known as the 'presentation broadcast service' in previous versions of PowerPoint.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Embed a presentation in a web page or blog". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Post a presentation to Facebook, Twitter, or other social network". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Create a self-running presentation". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Turn your presentation into a video". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 18, 2017. Retrieved August 18, 2017.
- Ralph, Nate. "Office for Windows Phone 8: Your handy starter guide". TechHive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2014. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- Use PowerPoint Mobile. Microsoft. Retrieved September 14, 2007.
- "Use Microsoft PowerPoint Mobile". Windows Phone How-to (United States). Microsoft. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- "PowerPoint Mobile". Windows Store. Microsoft. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- "How certain features behave in web-based PowerPoint". Office Support. Microsoft. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (2012). Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint. Vinland Books. ISBN 978-0-9851424-0-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2017. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
- Ziff Davis Market Intelligence (September 1998). "The 800-Pound Gorilla of the Presentation Market". Mobile Computing and Communications. 9 (9): 95. ISSN 1047-1952. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015. Retrieved September 29, 2017.
... in 1997, without question the market leader was Microsoft Corp.'s PowerPoint, which sold more than 4 million copies and controls 85 percent of the market.
Additional archives: August 26, 2017. - Gaskins, Robert (October 2016). "The Man Who Invented PowerPoint". Bento (Interview) (7). Interviewed by Clay Chandler. Hult International Business School. Archived from the original on September 22, 2017. Retrieved September 22, 2017.
PowerPoint succeeded so quickly because it spread rapidly by viral transmission from user to user ... every time early adopters used our product effectively, they demonstrated its value to other potential customers. PowerPoint made it especially easy for colleagues within the same company to share materials and incorporate one another's slides into their presentations with automatic formatting. This created networks of cooperation that benefited everyone.
- Gerstner, Louis V. Jr. (2002). Who Says Elephants Can't Dance? Inside IBM's Historic Turnaround. HarperCollins. p. 43. ISBN 978-0060523794.
By that afternoon an email about my hitting the Off button on the overhead projector was crisscrossing the world. Talk about consternation! It was as if the President of the United States had banned the use of English at White House meetings.
- Rae-Dupree, Janet, ed. (January 27, 1997). "Sun Microsystems' Chief: A Mission Against 'Dark Side' (Q & A With Scott McNealy)". Business Monday. San Jose Mercury News (Morning Final ed.). p. 8E. ISSN 0747-2099. Archived from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
' ... we've had three unbelievable record-breaking fiscal quarters since we banned PowerPoint. Now, I would argue that every company in the world, if they would just ban PowerPoint, would see their earnings skyrocket. Employees would stand around going, "What do I do? Guess I've got to go to work."'
Additional archives: September 23, 2017. - Isaacson, Walter (2011). Steve Jobs. Simon and Schuster. p. 337. ISBN 978-1-4516-4853-9.
'People would confront a problem by creating a presentation. I wanted them to engage, to hash things out at the table, rather than show a bunch of slides. People who know what they're talking about don't need PowerPoint.'
- Gold, Rich (2002) . "Chapter 14: Reading PowerPoint" (PDF). In Allen, Nancy (ed.). Working with Words and Images: New Steps in an Old Dance. New Directions in Computers and Composition Studies. Westport, Conn.: Ablex Publishing. pp. 256–270. ISBN 978-1-56750-608-2. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Robles-Anderson, Erica; Svensson, Patrik (January 15, 2016). "'One Damn Slide After Another': PowerPoint at Every Occasion for Speech". Computational Culture. 1 (5). ISSN 2047-2390. Archived from the original on September 6, 2017. Retrieved September 6, 2017.
- Lucky, Robert W. (January 1998). "The World According to PowerPoint". Reflections. IEEE Spectrum. 35 (1): 17. doi:10.1109/MSPEC.1998.646010. ISSN 0018-9235.
- Guernsey, Lisa (May 31, 2001). "PowerPoint Invades the Classroom". Technology. New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on June 6, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
PowerPoint—the must-have presentation software of the corporate world—has infiltrated the schoolhouse. In the coming weeks, students from 12th grade to, yes, kindergarten will finish science projects and polish end-of-the-year presentations on computerized slide shows ... . Software designed for business people has found an audience among the spiral notebook set.
- Levasseur, David G.; Sawyer, J. Kanan (August 19, 2006). "Pedagogy Meets PowerPoint: A Research Review of the Effects of Computer-Generated Slides in the Classroom". Review of Communication. 6 (1–2): 101–123. doi:10.1080/15358590600763383. ISSN 1535-8593. S2CID 144022054.
Higher education has certainly not been immune from the growing influence of presentation software. ... Five years ago, none of our department's classrooms were equipped to show multimedia slides. At present, all of our classrooms have been upgraded with such technology, and faculty are actively encouraged to incorporate slides into their lectures. Our institution is certainly not alone in this trend. A large number of educators in the United States use PowerPoint in their classrooms ... .
- Pinker, Steven (June 10, 2010). "Mind Over Mass Media". Opinion Pages. New York Times (New York ed.). p. A31. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on September 10, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
These days scientists ... cannot lecture without PowerPoint.
- "Making a Large Format Scientific Poster Using PowerPoint" (PDF). University of Montana. February 1, 2001. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 31, 2013. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
PowerPoint ... can do all the basics .
- Watson, Jeremy (August 12, 2005). "Presentation software—worship at the click of a mouse". BRNow.org. Archived from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
According to LifeWay, 'Statistics show that around 90 percent of churches that show multimedia during worship use Microsoft PowerPoint.'
- Armstrong, Ken (December 23, 2014). "The Sneakiest Way Prosecutors Get a Guilty Verdict: PowerPoint". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Archived from the original on December 23, 2014. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
The use of sophisticated visuals in the courtroom has boomed in recent years, thanks to research on the power of show-and-tell. ... In one civil case in Los Angeles County, a plaintiff spent $60,000 on a PowerPoint slide show.
- Gordon, David (2015). "David Gordon Choral Supertitles". David Gordon Supertitles. Archived from the original on October 23, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
... supertitles are simple PowerPoint presentations, completely compatible with PCs or Macs.
- Bortman, Henry (October 13, 2005). "Making a List, Checking It Twice". Astrobiology Magazine. NASA. ISSN 2152-1239. Archived from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
... They're mounted in the helmet so that when you turn and look, there's this little screen that shows the checklist. Now in this case, I've written the checklists and put them in PowerPoint, so we just launch a PowerPoint slide show. ... It's a real treat to use.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - Jaffe, Greg (April 26, 2000). "What's Your Point, Lieutenant? Please, Just Cut to the Pie Charts". A-Hed. Wall Street Journal (US ed.). p. A1. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on September 18, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
Old-fashioned slide briefings, designed to update generals on troop movements, have been a staple of the military since World War II. But in only a few short years PowerPoint has altered the landscape.
- Pece, Gregory S. (May 10, 2005). The PowerPoint Society: The Influence of PowerPoint in the U.S. Government and Bureaucracy (M.A. Thesis). Blacksburg, Virginia: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. hdl:10919/33029. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
The standard method for presenting information in the military and political establishments of the US government is through the projection of data in bullet style and/or graphical formats onto an illuminated screen, using some sort of first analogue, or now, digital media. Since the late 1990s, the most common and expected form of presentation is via the most commonly pre-installed software of presentation genre: Microsoft PowerPoint. This style of presentation has become the norm of communication ... .
- Powell, Colin (February 5, 2003). "Iraq: Failing to Disarm (U.S. Secretary of State Powell's Presentation to the UN Security Council)" (PDF). The National Security Archive (George Washington University). Archived (PDF) from the original on May 5, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Peterson, Scott (July 9, 2012). "Iran makes its nuclear case—with PowerPoint". Christian Science Monitor. ISSN 0882-7729. Archived from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
The complete set of PowerPoint slides that Iran used during a meeting with world powers are now public.
- Egan, Jennifer (2010). A Visit from the Goon Squad. Alfred A. Knopf. pp. 176–251. ISBN 978-0-307-59283-5.
- Stark, David; Paravel, Verena (February 2007). PowerPoint Demonstrations: Digital Technologies of Persuasion (Working Paper 07-04) (Report). Institute for Social and Economic Research and Policy, Columbia University. Archived from the original on September 28, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Kelly, Maureen (August 7, 2007). "Interactive Prototypes with PowerPoint". Boxes and Arrows. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
... many designers ... use PowerPoint for blocking out screens without ever discovering the interactive features for creating hyperlinks, buttons, and dynamic mouseover effects. Yes, PowerPoint can do all that.
- Greenberg, Andy (May 11, 2010). "The Underground Art Of PowerPoint". Forbes. ISSN 0015-6914. Archived from the original on June 30, 2017. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
... a subculture of PowerPoint enthusiasts is teaching the old application new tricks, and may even be turning a dry presentation format into a full-fledged artistic medium.
- "5 Ways to Use PowerPoint as an Image Editor". February 27, 2018.
- ^ Vienne, Veronique (August 17, 2003). "David Byrne's Alternate PowerPoint Universe". Art/Architecture. New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on November 14, 2012. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
With his newest project, David Byrne has tried not only to see it anew, but also to use it in the least likely of all applications: a medium for creative expression.
- Columbia Accident Investigation Board; National Aeronautics and Space Administration (2003). "7. The Accident's Organizational Causes" (PDF). Report Volume I. p. 191. ISBN 978-0-16-067904-9. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 2, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
At many points during its investigation, the Board was surprised to receive similar presentation slides from NASA officials in place of technical reports. The Board views the endemic use of PowerPoint briefing slides instead of technical papers as an illustration of the problematic methods of technical communication at NASA.
- Duarte, Nancy (July 27, 2015). "Why I Write in PowerPoint". Harvard Business Review. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
Because PowerPoint is so modular, it allows me to block out major themes (potential sections or chapters) and quickly see if I can generate ample ideas to support them. ... Working in slides, as opposed to one long document, helps me focus on organizing before I really begin writing. I think of the slides as index cards or sticky notes that can be arranged and rearranged until I'm sure my thoughts are in the right order. As I write, I can easily toggle back and forth from 'Slide View' to 'Slide Sorter' to get a sense of the whole and the parts.
- Keller, Julia (January 22, 2003). "Is PowerPoint the Devil?" (PDF). Chicago Tribune. ISSN 1085-6706. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 4, 2017. Retrieved September 6, 2017.
- Farkas, David K. (2006). "Toward a better understanding of PowerPoint deck design" (PDF). Information Design Journal. 14 (2): 162–171. doi:10.1075/idj.14.2.08far. ISSN 0142-5471. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 30, 2013. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Gaskins, Robert (April 20, 2012). "Comments on Dilbert's History of PowerPoint" (PDF). PowerPoint History Documents (Draft). p. 59. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 17, 2014. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
It took ten to fifteen years for PowerPoint to become an everyday topic of popular discourse.
- Norvig, Peter (January 2000). "The Gettysburg PowerPoint Presentation". Peter Norvig personal website. Archived from the original on November 9, 2000. Retrieved September 22, 2017.
- Norvig, Peter (2008). "The Making of the Gettysburg PowerPoint Presentation". Peter Norvig personal website. Archived from the original on December 30, 2008. Retrieved September 22, 2017.
- Radosh, Daniel (2003). "The PowerPoint Anthology of Literature". Daniel Radosh personal website. Archived from the original on July 10, 2006. Retrieved September 22, 2017.
- "Search Results for 'kw:powerpoint' > '1987..2017' [WorldCat.org]". OCLC WorldCat Global Catalog. September 29, 2017. Archived from the original on September 29, 2017. Retrieved September 29, 2017.
All Formats (66,169) ... Print book (23,696), eBook (3,475), Thesis/dissertation (1,078) ... Article (18,085) ... Video (3,537) ...
- Kaplan, Sarah (2011). "Strategy and PowerPoint: An Inquiry into the Epistemic Culture and Machinery of Strategy Making". Organization Science. 22 (2): 320–346. doi:10.1287/orsc.1100.0531. ISSN 1047-7039. S2CID 37755593.
- Tufte, Edward (December 2014). "Edward R. Tufte, Resume" (PDF). Edward Tufte personal website. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2016. Retrieved September 20, 2017.
1.9 million copies of 4 books and 422,000 copies of 4 booklets printed from 1983–2014, and continuing.
- Parks, Bob (August 30, 2012). "Death to PowerPoint!". Bloomberg Businessweek. ISSN 0007-7135. Archived from the original on March 12, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Kernbach, Sebastian; Bresciani, Sabrina (July 16–18, 2013). "10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of Power Point": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities". 10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of PowerPoint": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities. Information Visualisation (IV), 2013 17th International Conference. London: IEEE. pp. 345–350. doi:10.1109/IV.2013.44. ISBN 978-1-4799-0834-9. Archived from the original on April 28, 2015.
- Zuckerman, Laurence (April 17, 1999). "Words Go Right to the Brain, But Can They Stir the Heart?; Some Say Popular Software Debases Public Speaking". New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Feith, David (July 31, 2009). "Speaking Truth to PowerPoint". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on June 21, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- Kernbach, Sebastian; Bresciani, Sabrina (July 16–18, 2013). "10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of Power Point": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities". 10 Years after Tufte's "Cognitive Style of PowerPoint": Synthesizing its Constraining Qualities. Information Visualisation (IV), 2013 17th International Conference. London: IEEE. pp. 345–350. doi:10.1109/IV.2013.44. ISBN 978-1-4799-0834-9. Archived from the original on April 28, 2015.
Because every day a huge number of people meet to exchange ideas and make decisions with PowerPoint slides being displayed on the wall, investigating the tool is enormously important ... . Despite the pervasiveness of PowerPoint in our culture there have been few empirical studies and most of the non-empirical work is based on casual essays and informal anecdotal reviews which very often take a polemic and overall negative position on PowerPoint, rather than conducting formal scholarship. This lack of rigorous studies and empirical research is surprising given the enormous complexity and importance of the PowerPoint tool.
- "Richard Mayer". Department of Psychological & Brain Sciences, University of California at Santa Barbara, faculty directory. 2017. Archived from the original on June 17, 2017. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
Dr. Mayer is concerned with how to present information in ways that help people understand, including how to use words and pictures to explain scientific and mathematical concepts.
- Tufte, Edward (2006) . The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint: Pitching Out Corrupts Within (2nd ed.). Cheshire, Connecticut: Graphics Press LLC. pp. 4, 15. ISBN 978-0-9613921-6-1.
very little information per slide ... the text is grossly impoverished .. the PowerPoint slide typically shows 40 words ... .
- Atkinson, Cliff; Mayer, Richard E. (April 23, 2004). "Five ways to reduce PowerPoint overload" (PDF). ResearchGate. Revision 1.1. Archived from the original on June 17, 2015. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
... it is conventional wisdom to put no more than six lines of text on a PowerPoint slide, six words per line. But that convention is no longer wise in the light of research that shows that even that amount of text on a slide can be a recipe for information overload.
- ^ Gallo, Carmine (2009). The Presentation Secrets of Steve Jobs. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-163608-7.
- Gallo, Carmine (September 7, 2012). "Jeff Bezos and The End of PowerPoint As We Know It". Forbes. ISSN 0015-6914. Archived from the original on March 25, 2015. Retrieved September 24, 2017.
And no, Steve Jobs did not invent the style. He just happened to use it very effectively.
- Gabrielle, Bruce R. (2010). Speaking PowerPoint: The New Language of Business. Insights Publishing. pp. 16–17. ISBN 978-0-9842360-4-6.
- "Stephen M. Kosslyn, Ph.D., Dean of Arts and Sciences". Minerva Schools at Keck Graduate Institute (Claremont Colleges). 2017. Archived from the original on March 1, 2016. Retrieved September 24, 2017.
- ^ Kosslyn, Stephen M.; Kievit, Rogier A.; Russell, Alexandra G.; Shephard, Jennifer M. (July 17, 2012). "PowerPoint Presentation Flaws and Failures: A Psychological Analysis". Frontiers in Psychology. 3 (230): 230. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00230. ISSN 1664-1078. PMC 3398435. PMID 22822402.
- Kosslyn, Stephen M. (2010). Better PowerPoint: Quick Fixes Based on How Your Audience Thinks. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-537675-3.
- Burn-Callander, Rebecca (April 24, 2017). "Your attention, please, for the software we love to hate: PowerPoint celebrates its 30th birthday". Business. The Daily Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on July 10, 2017. Retrieved July 10, 2017.
... with new research showing that it remains as popular with young tech-savvy users as it is with the Baby Boomers. An online poll by YouGov showed that 81 per cent of UK Snapchat users agreed that PowerPoint was a great tool for making presentations. ... long -form prose has become increasingly unpopular with modern users. PowerPoint, with its capacity to be highly visual, bridges the wordy world of yesterday with the visual future of tomorrow.
- ^ Baskin, Kara (October 4, 2017). "How millennials approach writing, giving presentations, and data visualization diverges from previous generations". MIT Sloan School of Management. Archived from the original on October 4, 2017. Retrieved October 7, 2017.
"Communication is part of everyone's job, but millennials do it differently," said MIT Sloan lecturer Miro Kazakoff, who co-authored the study with MIT Sloan senior lecturer Kara Blackburn.
- Gaskins, Robert (2012). Sweating Bullets: Notes about Inventing PowerPoint. Vinland Books. pp. 428–433. ISBN 978-0-9851424-0-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2017. Retrieved September 5, 2017.
PowerPoint got off to a very slow start in infiltrating the military forces of the world ... .
- Gole, Henry G. (1999). "Leadership in Literature". Parameters. 29 (3): 134–150. ISSN 0031-1723. Archived from the original on September 18, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
In the 1990s, the outward signs of form over substance are field grade officers grinding out slick PowerPoint briefing charts ... .
- ^ Jaffe, Greg (April 26, 2000). "What's Your Point, Lieutenant? Please, Just Cut to the Pie Charts". A-Hed. Wall Street Journal (US ed.). p. A1. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on September 18, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ Bumiller, Elisabeth (April 27, 2010). "We Have Met the Enemy and He Is PowerPoint". New York Times. p. A1. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on April 27, 2010. Retrieved September 19, 2017.
- Hammes, Thomas X. (July 1, 2009). "Dumb-dumb Bullets". Armed Forces Journal. ISSN 0196-3597. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- Burke, Crispin (July 24, 2009). "The T. X. Hammes PowerPoint Challenge". Small Wars Journal. ISSN 2156-227X. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2017.
- Sellin, Lawrence (September 2, 2010). "The PowerPoint rant that got a colonel fired". Army Times. ISSN 0004-2595. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved September 19, 2017. Additional archives: May 24, 2015.
- Norvig, Peter; Kosslyn, Stephen M. (April 29, 2010). "A Tool Only as Good as the User". Letters to the Editor. New York Times (New York ed.). p. A24. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on May 3, 2010. Retrieved September 19, 2017.
- Sisk, Richard (January 20, 2017). "Senate Confirms Mattis as Secretary of Defense". Military.com. Archived from the original on January 22, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- McGarry, Brendan (February 20, 2017). "Trump Picks Army Lt. Gen. McMaster as National Security Adviser". Military.com. Archived from the original on February 22, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- Byrne, David (2003). "Envisioning Emotional Epistemological Information". David Byrne Archive. Archived from the original on September 16, 2017. Retrieved September 16, 2017.
- Powell, Bonnie Azab (March 8, 2005). "David Byrne really does ♥ PowerPoint, Berkeley presentation shows". UC Berkeley News Center. Archived from the original on March 11, 2005. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
- Byrne, David (2005). "Journal: 3.8.05: San Francisco". David Byrne Journal. Archived from the original on September 16, 2017. Retrieved September 16, 2017.
- Nastro, Santa (November 21, 2016). "Arte e aziende. Nasce il Manifesto della Corporate Art: lo firmano Ugo Nespolo, Alexander Ponomarev e Fernando De Filippi". Artribune. Rome. ISSN 2280-8817. Archived from the original on September 16, 2017. Retrieved September 16, 2017.
The corporate world can be an art object.
- pptArt (2014). "pptArt Manifesto". pptArt.net. Archived from the original on May 23, 2015. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
- pptArt (2014). "Our Services for Corporate Clients". pptArt.net. Archived from the original on May 23, 2015. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
- Greenberg, Andy (May 11, 2010). "The Underground Art Of PowerPoint". Forbes. ISSN 0015-6914. Archived from the original on June 30, 2017. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
- Toh, Shawn (2014). "PowerPoint Heaven: The Power to Animate". PowerPoint Heaven. Archived from the original on June 6, 2017. Retrieved September 15, 2017.
Our goal is to show users that PowerPoint is not simply a presentation tool, but is also capable on leveraging into other areas such as creating games, artworks and animations.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (2017). "View a presentation without PowerPoint". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on September 1, 2017. Retrieved September 1, 2017.
If you do not have PowerPoint installed on your computer, you can still open and view PowerPoint presentations by using PowerPoint Viewer, PowerPoint Mobile, or PowerPoint Online.
- Fridlund, Alan (August 24, 1992). "PowerPoint 3.0 catches up with the best". Reviews. InfoWorld. Vol. 14, no. 34. pp. 61–63. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 25, 2015. Retrieved September 1, 2017.
Version 3.0 now includes a PowerPoint Viewer that runs on any Windows 3.1 machine and can be distributed freely with your presentation files. ... A major advance ... is the use of embedded TrueType fonts ... ensuring that the appearance of your presentation is completely repeatable on any machine equipped with the viewer.
- "Microsoft PowerPoint 3.0 for Macintosh". eBay. April 22, 2017. Archived from the original on September 2, 2017. Retrieved September 2, 2017.
Includes ... 1 PowerPoint Viewer disk.
- Microsoft Corporation (September 12, 2011). "Description of how to use the Package for CD feature in PowerPoint 2003 and in PowerPoint 2007". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved September 1, 2017.
- Kao, Wayne (April 1, 2004). "New PowerPoint Viewer". Wayne's Microsoft Blog. Archived from the original on May 16, 2014. Retrieved September 3, 2017.
... 2003 ... a brand new PowerPoint Viewer. The previous viewer had been written for the PowerPoint 97 release ... can be run without any installation or setup, which means it can be run directly off your USB keychain or even off write-protected media like a CD orDVD.
- Microsoft Corporation (1998). "PowerPoint 98 Viewer". Microsoft Mac Office. Archived from the original on December 17, 2000. Retrieved September 3, 2017.
- "PowerPoint FAQ: Versions". A Bit Better Corporation. May 10, 2013. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013. Retrieved August 4, 2017. A diagram shows "which versions of PowerPoint can open/save which other versions" up to version 9.0 for Windows ("PowerPoint 2000").
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (November 16, 2017). "End of support for the Excel and PowerPoint viewers and the Office Compatibility Pack". Microsoft Office Sustained Engineering Team Blog. Archived from the original on November 18, 2017. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- Microsoft Corporation (October 25, 2011). "PowerPoint Viewer". Microsoft Download Center. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- Microsoft Corporation (1998). "Microsoft PowerPoint 98 Viewer [Documentation]". Microsoft MacTopia. Archived from the original on August 16, 2000. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- Microsoft Corporation (2017). "Download Mac PowerPoint 98 Viewer [Code]". Microsoft Download Center. Archived from the original on February 2, 2017. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- ^ Mace, Scott (March 2, 1987). "Presentation Package Lets Users Control Look". InfoWorld. Vol. 9, no. 9. IDG. p. 5. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Flynn, Laurie (September 14, 1987). "Apple Sets Its Sights on Desktop Presentations". InfoWorld. Vol. 9, no. 37. IDG. p. 35. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 25, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017. Report of Seybold conference in late September 1987 where Microsoft introduced relabeled PowerPoint. Macworld magazine carried its first Microsoft advertisement for PowerPoint in its November 1987 issue, with the initial subhead "Introducing Microsoft PowerPoint." Microsoft Corporation (November 1987). "Everything you need to make a great presentation, just add water". MacWorld (advertisement). Vol. 4, no. 11. IDG. pp. 40–41. ISSN 0741-8647. Archived from the original on July 16, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Flynn, Laurie (May 2, 1988). "Updated PowerPoint Supports Mac II Colors". InfoWorld. Vol. 10, no. 18. IDG. p. 27. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Flynn, Laurie (December 12, 1988). "Driver Sends PowerPoint Files Out for Conversion". InfoWorld. Vol. 10, no. 50. IDG. p. 33. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Coale, Kristi (May 28, 1990). "PowerPoint to Challenge PC Presentation Market". InfoWorld. Vol. 12, no. 22. IDG. p. 13. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Borzo, Jeanette (May 18, 1992). "PowerPoint users pleased by changes". InfoWorld. Vol. 14, no. 20. IDG. p. 15. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Damore, Kelley (October 12, 1992). "PowerPoint 3.0 for the Mac mirrors version for Windows". InfoWorld. Vol. 14, no. 41. IDG. p. 151. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ "Microsoft Corp. will start shipping PowerPoint 4.0". InfoWorld. Vol. 16, no. 7. IDG. February 14, 1994. p. 19. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^
Halper, Mark (August 1, 1994). "Native Microsoft suite coming for Power Mac". Computerworld. Vol. 28, no. 31. IDG. p. 15. ISSN 0010-4841. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
... the forthcoming version of PowerPoint 4.0, which is part of Office 4.2. ... Microsoft said it is packaging separate ... versions for 68000-based Macintoshes and for newer PowerPC-based Power Macintoshes, all in one shrink-wrapped box.
- ^ Grace, Rich (July 24, 1995). "PowerPoint gains multimedia strength". InfoWorld. Vol. 17, no. 30. IDG. p. 98. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Lassesen, Ken (October 17, 1995). "Using Microsoft OLE Automation Servers to Develop Solutions" (PDF). Archive of Articles from MSDN Technology Group. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
Note that version 7.0 of a product is the same as a '95' designation ... .
- ^ Vadlamudi, Pardhu (January 20, 1997). "Office 97 now open for business". InfoWorld. Vol. 19, no. 3. IDG. p. 6. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ "Microsoft Office Products Support Lifecycle FAQ". March 29, 2014. Archived from the original on March 29, 2014. Retrieved December 13, 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Senna, Jeff (March 2, 1998). "Office 98 boasts cross-platform parity". InfoWorld. Vol. 20, no. 9. IDG. p. 113. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- "PowerPoint FAQ: Unsolved Mysteries". A Bit Better Corporation. May 10, 2013. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Railsback, Kevin (April 12, 1999). "Office 2000: making life easier for IT and end-users alike". InfoWorld. Vol. 21, no. 15. IDG. p. 10. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Steinberg, Gene (September 14, 2000). "Microsoft Office 2001: MacOS review". CNET Review. Archived from the original on September 25, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Yager, Tom (March 19, 2001). "Office spruced with surprising subtlety". InfoWorld. Vol. 23, no. 12. IDG. p. 53. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- GitHub-Name. "Office XP - Microsoft Lifecycle". learn.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 13, 2023.
- ^
Dalrymple, Jim (October 24, 2001). "Microsoft sets date for Office v. X release". Macworld. IDG. ISSN 0741-8647. Archived from the original on July 18, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
Microsoft's Macintosh Business Unit (MacBU) today announced that Office v. X would be available to the public on November 19. ... Office v. X runs natively on OS X – it will not run under OS 9.
- ^
Cosgrove-Mather, Bootie (October 22, 2003). "Microsoft Revamps Office Software". CBS News. Archived from the original on August 6, 2017. Retrieved August 6, 2017.
... Bill Gates introduces Microsoft Office 2003 in New York Tuesday, Oct. 21, 2003.
- "Microsft Issues Critical Office Patch [for Office 2003]". InfoWorld. Vol. 25, no. 44. IDG. November 10, 2003. p. 18. ISSN 0199-6649. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
... less than a month after the software officially launched.
- GitHub-Name. "Microsoft Office 2003 - Microsoft Lifecycle". learn.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 13, 2023.
- ^ Dreier, Troy (July 2004). "Office 2004 for Mac: An Essential Upgrade". PC Magazine. Vol. 23, no. 12. Ziff Davis. p. 53. ISSN 0888-8507. Archived from the original on May 27, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^
"Windows Mobile 5.0 Comes to PDAs and Smartphones". Maximum PC. August 2005. p. 16. ISSN 1522-4279. Archived from the original on July 6, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
PowerPoint Mobile—a new addition to the suite—doubles as a powerful sleep-aid.
- ^ "Microsoft Office 2007: Worth the Wait". PC Magazine. Vol. 26, no. 1/2. Ziff Davis. January 2007. p. 48. ISSN 0888-8507. Archived from the original on May 25, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- "Office 2007 approaching end of extended support". Microsoft Support. February 6, 2017. Archived from the original on October 15, 2017. Retrieved October 14, 2017.
Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2007 ... PowerPoint 2007 (Home and Student version) ... no new security updates, non-security updates, free or paid assisted support options, or online technical content updates ... 10/10/2017
- ^ "Windows Mobile 6: Make Your Smartphone Smarter". PC Magazine. Vol. 26, no. 12. Ziff Davis. June 5, 2007. p. 44. ISSN 0888-8507. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017. PowerPoint was updated in November 2007: Microsoft (November 28, 2007). "Microsoft Office Mobile 6.1: Upgrade for Microsoft Office 2007 file formats". Microsoft Download Center. Archived from the original on April 27, 2012. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Tessler, Franklin N. (January 18, 2008). "Microsoft PowerPoint 2008 At a Glance". Macworld. IDG. ISSN 0741-8647. Archived from the original on July 6, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (June 15, 2010). "Microsoft Office 2010 Now Available for Consumers Worldwide". Microsoft News Center. Archived from the original on June 29, 2016. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (February 25, 2010). "There is no Office 13, but why?". Channel9 videos, Microsoft Developer Network. Archived from the original on August 7, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- GitHub-Name. "Microsoft Office 2010 - Microsoft Lifecycle". learn.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 13, 2023.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (June 14, 2010). "Microsoft Office Web Apps". PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. ISSN 0888-8507. Archived from the original on May 10, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Lendino, Jamie (June 4, 2010). "Microsoft Office Mobile 2010 (Windows Phone)". PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. ISSN 0888-8507. Archived from the original on May 10, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (October 26, 2010). "Mac Meets PC with New Office Release". Microsoft News Center. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- "Products Reaching End of Support for 2017". Microsoft Support. September 7, 2017. Archived from the original on October 15, 2017. Retrieved October 14, 2017.
Microsoft PowerPoint for Mac 2011 ... no new security updates, non-security updates, free or paid assisted support options or online technical content updates ... October 10, 2017
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (April 10, 2012). "Full Microsoft Office Mobile now available on select Nokia Symbian phones". ZDnet.com. Archived from the original on July 15, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (October 10, 2012). "Microsoft's new Office Web Apps to roll out to Office 365 users in late October". ZDnet.com. Archived from the original on September 21, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Mackie, Kurt (October 31, 2012). "Windows Phone 8 to Include 'New Office' Version for Mobile". Redmond Channel Partner Magazine. Archived from the original on April 25, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (September 14, 2012). "Microsoft to deliver final version of Office 2013 RT starting in early November". ZDnet.com. Archived from the original on January 23, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Graziano, Dan (January 28, 2013). "Microsoft Office 2013 set for January 29th debut". BGR.com. Archived from the original on April 27, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ O'Donald, Andy (June 14, 2013). "Office Mobile for iPhone". Microsoft Office Blogs. Archived from the original on April 24, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^
Office 365 Team (July 31, 2013). "Office Mobile for Android phones". Microsoft Office Blogs. Archived from the original on May 10, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Paul, Ian (February 20, 2014). "Meet Office Online, Microsoft's slightly tweaked Office Web Apps replacement". PCWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on June 22, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Case, John (March 27, 2014). "Announcing the Office you love, now on the iPad". Microsoft Office Blogs. Archived from the original on May 10, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Mackie, Kurt (November 6, 2014). "Office iPad and iPhone Users Can Now Create and Edit Docs for Free". Redmond Magazine. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (June 24, 2015). "Office Apps for Android Handsets Exit Preview". Thurrott.com. Archived from the original on June 26, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^
Koenigsbauer, Kirk (July 9, 2015). "Office 2016 for Mac is here!". Microsoft Office Blogs. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
Office 2016 for Mac is now available in 139 countries and 16 languages.
-
Bell, Killian (July 18, 2012). "Microsoft Won't Bring Office 2013 To Mac ..." Cult of Mac. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
Microsoft confirmed to us that there is no Office for Mac 2013 release planned.
-
Microsoft Corp. (January 18, 2018). "Update history for Office 2016 for Mac". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on January 19, 2018. Retrieved January 18, 2018.
PowerPoint 16.9.0 (18011602).
- ^
Thurrott, Paul (July 16, 2015). "Office Mobile Apps for Windows 10 are Now Generally Available". Thurrott.com. Archived from the original on July 17, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
Microsoft noted that it has added 'Mobile' to the app names on PCs and big tablets to help distinguish them from the desktop-based Office application suite ... . On phones and small tablets—i.e. on Windows 10 Mobile—these apps will simply retain their normal names (Word, Excel and PowerPoint), with no Mobile added.
- ^ Gupta, Nakul (July 27, 2015). "News: Microsoft updates Office apps for iPhone and iPad". TechView. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^
Koenigsbauer, Kirk (September 22, 2015). "The new Office is here". Microsoft Office Blogs. Archived from the original on September 23, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
Today is the worldwide release of Office 2016 for Windows.
- ^
Foley, Mary Jo (January 24, 2018). "Microsoft brings its core Office apps to the Microsoft Store". ZDnet.com. Archived from the original on January 25, 2018. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
Microsoft made these Desktop Bridge apps—which company officials previously referred to as the "Office in the Windows Store apps"—available to Windows 10 S users in preview form last Summer.
- ^ Austin, Dennis (2001). "PowerPoint Version Timeline (to PowerPoint 7.0, 1995)" (PDF). GBU Wizards of Menlo Park. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 6, 2017.
- ^ Belleville, Cathleen (August 24, 2000). "PowerPoint Historical Review". A Bit Better Corporation. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.Additional archives: March 24, 2016.
- ^ Gaskins, Robert (December 2007). "PowerPoint at 20: Back to Basics" (PDF). Viewpoint. Communications of the ACM. 50 (12): 15–17. doi:10.1145/1323688.1323710. ISSN 0001-0782. S2CID 48306. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 7, 2016. Retrieved August 4, 2017. These versions are described in the sidebar, "Presentation Formats and PowerPoint," p. 17.
- ^ "PowerPoint Tips & Tricks: PowerPoint System Requirements". A Bit Better Corporation. April 24, 2013. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved August 4, 2017. System requirements are in a table at the very end of this document.
- Negrino, Tom (February 1, 2002). "Capsule Review: Microsoft Office v. X". Macworld. IDG. ISSN 0741-8647. Archived from the original on December 10, 2012. Retrieved September 29, 2017.
Office v. X requires OS X 10.1 or later to run ... PowerPoint X ... benefit from OS X technologies ... .
- Muratore, Stephen (March 1, 2004). "Microsoft Producer for PowerPoint 2003 Review". Videomaker Magazine. York Publishing. ISSN 0889-4973. Archived from the original on July 29, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft (August 13, 2007). "Differences between Office XP and Office 2003". Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft (March 29, 2017). "List of system requirements for Microsoft Office 2003". Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Swinford, Echo (January 1, 2009). "PPT 2007". Echo's Voice. Archived from the original on August 13, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft (April 28, 2009). "Getting started with the 2007 Office system". Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on July 30, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- "Microsoft Office 2008 for Mac, Specifications". CNET. January 15, 2008. Archived from the original on May 29, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Swinford, Echo (March 26, 2011). "PPT 2010 new stuff". Echo's Voice. Archived from the original on August 13, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft (February 15, 2013). "System requirements for Office 2010: Microsoft PowerPoint 2010". Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on March 25, 2012. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft (June 16, 2017). "Microsoft Office for Mac 2011 system requirements". Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on May 28, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft. "What's New in PowerPoint 2013". Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on December 9, 2014. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Swinford, Echo (November 5, 2012). "Big list o' new features in powerpoint 2013". Echo's Voice. Archived from the original on November 8, 2012. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft (December 16, 2016). "System requirements for Office 2013". Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft. "System requirements for Office". Microsoft Office. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft. "What's New in PowerPoint 2016 for Windows". Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on July 31, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017. This webpage contains dated feature updates listed separately for each nearly-monthly update since the original release.
- Foley, Mary Jo (July 12, 2017). "Microsoft delivers 'AI-powered' Presentation Translator add-in for PowerPoint". ZDnet.com. Archived from the original on July 20, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft. "Presentation Translator: an Office add-in for PowerPoint". Microsoft Garage. Archived from the original on August 1, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- Microsoft. "System requirements for Office". Microsoft Office. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2017.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (2016). "File formats that are supported in PowerPoint". Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 7, 2017.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (February 22, 2014). "MimeMapping.cs". Microsoft Reference Source. Archived from the original on May 24, 2015. Retrieved August 10, 2017.
This module maps document extensions to Content Mime Type.
- "System-Declared Uniform Type Identifiers". developer.apple.com. Apple. November 17, 2009. Archived from the original on July 24, 2008.
- ^ "PowerPoint FAQ: Versions". A Bit Better Corporation. May 10, 2013. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013. Retrieved August 4, 2017. A diagram shows "which versions of PowerPoint can open/save which other versions" up to version 9.0 for Windows ("PowerPoint 2000").
- "libmwaw". SourceForge. April 30, 2023.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (June 20, 2017). "[MS-PPT]: PowerPoint (.ppt) Binary File Format (Protocol Revision 4.1)". Microsoft Developer Network. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 7, 2017.
- Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program (March 2, 2017). "Specifications for Digital Formats: Microsoft Office Binary (doc, xls, ppt) File Formats". Digital Preservation, Library of Congress. Archived from the original on August 13, 2017. Retrieved August 13, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (2015). "Use PowerPoint 2007 to open or save a presentation in another file format". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on August 14, 2017. Retrieved May 23, 2015.
... PowerPoint 2007 does not support saving to PowerPoint 95 and earlier file formats.
- "PPTX vs. PPSX (Or PPT vs. PPS)". Archived from the original on October 4, 2021.
- ^ Microsoft Corporation (2015). "Open XML Formats and file name extensions". Microsoft Office Support. Archived from the original on April 30, 2017. Retrieved August 11, 2017.
Starting with the 2007 Microsoft Office system, Microsoft Office uses the XML-based file formats, such as .docx, .xlsx, and .pptx. These formats and file name extensions apply to ... Microsoft PowerPoint.
- Rice, Frank (May 2006). "Introducing the Office (2007) Open XML File Formats". Microsoft Developer Network. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- Ecma Technical Committee 45 (2016). "Standard ECMA-376: Office Open XML File Formats". Ecma International. Archived from the original on July 14, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Ecma Technical Committee 45 (2012). Ngo, Tom (ed.). "Office Open XML Overview" (PDF). Ecma International. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 12, 2015. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
OpenXML was designed from the start to be capable of faithfully representing the pre-existing corpus of word-processing documents, presentations, and spreadsheets that are encoded in binary formats defined by Microsoft Corporation. ... The original binary formats for these files were based on direct serialization of in-memory data structures ... . Technical Committee 45 (TC45) ... includes representatives from Apple, Barclays Capital, BP, The British Library, Essilor, Intel, Microsoft, NextPage, Novell, Statoil, Toshiba, and the United States Library of Congress.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Magee, Liam; Thom, James A. (2014). "What's in a Word? When one electronic document format standard is not enough [pre-print]" (PDF). Information Technology & People. 27 (4): 482–511. doi:10.1108/ITP-09-2012-0096. ISSN 0959-3845. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 13, 2017. Retrieved August 13, 2017.
The case of the standardisation of two ISO electronic document formats, the OpenDocument Format (ODF) and Office Open XML (OOXML) ... In this case, the attempt to design a de jure standard in fact produced even greater entrenchment of the existing de facto standard it was designed to replace.
- Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program (February 21, 2017). "OOXML Format Family—ISO/IEC 29500 and ECMA 376". Digital Preservation, Library of Congress (Format Description ID:fdd000395). Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 11, 2017.
- ISO/IEC JTC 1 (2016). "ISO/IEC 29500-1:2016, Fundamentals and Markup Language Reference". International Organization for Standardization. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 9, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ISO/IEC JTC 1 (2016). "ISO/IEC 29500-4:2016, Transitional Migration Features". International Organization for Standardization. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 9, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Knowlton, Gray (August 13, 2012). "New file format options in the new Office". Microsoft Office Blogs. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved August 11, 2017.
- Microsoft Corporation (July 27, 2012). "Structure of a PresentationML document (Open XML SDK)". Microsoft Developer Network, Office Dev Center. Archived from the original on August 14, 2017. Retrieved August 10, 2017.
- Office Open XML Consortium (2012). "Presentation ML (pptx)". Office Open XML. Archived from the original on May 8, 2015. Retrieved August 10, 2017.
- Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program (January 1, 2017). "PPTX Transitional (Office Open XML), ISO 29500:2008–2016, ECMA-376, Editions 1–5". Digital Preservation, Library of Congress (Format Description ID: fdd000399). Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 11, 2017.
The standards documents that specify this format run to over six thousand pages.
- Library of Congress, National Digital Information Infrastructure and Preservation Program (2008). "Setting Standards (Office Open XML and PDF/A)". Digital Preservation, Library of Congress. Archived from the original on February 20, 2017. Retrieved August 13, 2017.
Library staff have participated in a technical committee working toward the standardization of the Office Open XML specifications, which ... will make it easier for libraries and archives to preserve a large body of digital material by ensuring that the content is generated in formats for which the specifications are published and will be maintained under the auspices of a standards organization. Specifically, this standard is based on the formats used by the latest version of Microsoft Office and supports all features in the various versions of Microsoft Office since 1997.
- Meng, Max (May 20, 2013). "What is the default file format for saving in MS Office 2013?". Microsoft Technet Forums. Archived from the original on September 21, 2019. Retrieved August 10, 2017.
- Zamzar (April 17, 2012). "Open Old Powerpoint Presentations in Office 2007 and Office 2010". Zamzar Blog. Archived from the original on June 6, 2017. Retrieved August 7, 2017.
Further reading
- Reuss, Elke I.; Signer, Beat; Norrie, Moira C. (2008). "PowerPoint Multimedia Presentations in Computer Science Education: What do Users Need?". Proceedings of the 4th Symposium on Usability & HCI for Education and Work (USAB 2008). Graz, Austria. pp. 281–298.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lowenthal, Patrick R. (2009). "Improving the Design of PowerPoint Presentations" (PDF). In Lowenthal, Patrick R.; Thomas, David; Thai, Anna; Yuhnke, Brian (eds.). The CU Online Handbook 2009. University of Colorado Denver. pp. 61–66.
- Kalyuga, Slava; Chandler, Paul; Sweller, John (2004). "When Redundant On-Screen Text in Multimedia Technical Instruction Can Interfere With Learning". Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society. 46 (3): 567–581. doi:10.1518/hfes.46.3.567.50405. PMID 15573552. S2CID 6992108.
- Also available at: Archived October 28, 2020, at the Wayback Machine (Feb 2015).
External links
| Presentation software | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software |
| ||||||||||
| Formats | |||||||||||
| Microsoft 365 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Office |
| ||||
| Applications (list) | |||||
| Technologies | |||||
| Related | |||||