| Revision as of 19:09, 1 December 2007 editRex Germanus (talk | contribs)11,278 edits no linguistic experience. Discuss on talk or I'm reporting you.← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 10:25, 27 November 2024 edit undoSpamHunters (talk | contribs)263 edits zero added value | ||
| (303 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Germanic language}} | |||
| {{Template:Dutch dialects}} | |||
| {{cleanup reorganize|date=August 2017}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{expand Dutch|topic=cult|otherarticle=West-Vlaams|date=November 2012}} | |||
| '''West Flemish''' (West Flemish: ''Vlaemsch'', ]: ''West-Vlaams'', ]: ''Flamand occidental'') is a group of dialects spoken in parts of the ], ], and ]. | |||
| {{Infobox language | |||
| | name = West Flemish | |||
| | altname = | |||
| | nativename = ''West-Vlaams'' | |||
| | states = Belgium, Netherlands, France | |||
| | region = ] | |||
| | speakers = {{sigfig|1.424|2}} million | |||
| | date = 1998 | |||
| | ref = e18 | |||
| | familycolor = Indo-European | |||
| | fam2 = ] | |||
| | fam3 = ] | |||
| | fam4 = ] | |||
| | fam5 = ] | |||
| | fam6 = ] | |||
| | dia1 = ] | |||
| | dia2 = ] | |||
| | lc1 = vls | |||
| | ld1 = (West) Vlaams | |||
| | lc2 = zea | |||
| | ld2 = ] (Zeeuws) | |||
| | lingua = 52-ACB-ag | |||
| | glotto = sout3292 | |||
| | glottoname = Southwestern Dutch | |||
| | glotto2 = vlaa1240 | |||
| | glottoname2 = Western Flemish | |||
| | map2 = Lang Status 80-VU.svg | |||
| | mapcaption2 = {{center|{{small|West Flemish is classified as Vulnerable by the ] ]}}}} | |||
| }} | |||
| '''West Flemish''' (''West-Vlams'' or ''West-Vloams'' or ''Vlaemsch'' (in ]), {{langx|nl|West-Vlaams}}, {{langx|fr|link=no|flamand occidental}}) is a collection of ] varieties spoken in western Belgium and the neighbouring areas of France and the Netherlands. | |||
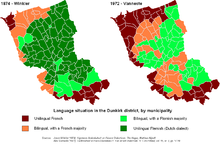
| The West Flemish dialect is spoken by around 1.05 million people in ] (in Belgium), 90,000 in the neighboring ] coastal district of ], and approximately 20,000 in the northern part of the ] '']'' of ] where it is classified as one of the ]. | |||
| West Flemish is spoken by about a million people in the Belgian province of ], and a further 50,000 in the neighbouring Dutch coastal district of ] (200,000 if including the closely related dialects of ]) and 10-20,000 in the northern part of the French department of ].<ref name="e18" /> Some of the main cities where West Flemish is widely spoken are ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| The dialects of the Dutch province of ], ], are sometimes also classified under ''West Flemish'' ] Dutch but this is sometimes disputed. The dialects of Zeelandic Flanders however ''do'' count as West Flemish variants. In fact, both dialects are linked by a ] which proceeds further north into Hollandic. | |||
| West Flemish is listed as a "vulnerable" language in ]'s online ].<ref>{{Cite web | |||
| West Flemish is very different from standard Dutch in pronunciation as well as vocabulary and grammar, to the extent that it's quite unintelligible to Dutch speakers unaccustomed to the dialect. A simple phrase like "''Ik ben gisteren nog bij hen geweest''" (I was at their place only yesterday) will be pronounced as "'' 'k zijn histern no(g) toet ulders (h)ewist''". <div style="margin-bottom:-.5em;">{{clear}}</div> | |||
| | title = UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |||
| | archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20101030021439/http://www.unesco.org/culture/ich/index.php?pg=00206 | |||
| | archive-date= 30 October 2010 | |||
| | url-status= dead | |||
| |url=https://ich.unesco.org/en/home|access-date=2023-02-07 | |||
| | publisher= United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization }}</ref> | |||
| {{Dutch dialects}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] in France, in 1874 and 1972]] | |||
| {{clear left}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Phonology== | |||
| West Flemish has a phonology that differs significantly from that of Standard Dutch, being similar to ] in the case of long E, O and A. Also where Standard Dutch has ''sch'', in some parts of West Flanders, West-Flemish, like Afrikaans, has ''sk''. However, the best known traits are the replacement of Standard Dutch (pre-)velar fricatives ''g'' and ''ch'' in Dutch ({{IPA|/x, ɣ/}}) with glottal ''h'' {{IPA|}},. The following differences are listed by their Dutch spelling, as some different letters have merged their sounds in Standard Dutch but remained separate sounds in West Flemish. Pronunciations can also differ slightly from region to region. | |||
| * ''sch'' - {{IPA|/sx/}} is realised as {{IPA|}}, {{IPA|}} or {{IPA|}} (''sh'' or ''sk''). | |||
| * ''ei'' - {{IPA|/ɛi/}} is realised as {{IPA|}} or {{IPA|}} (''è'' or ''jè''). | |||
| * ''ij '' - {{IPA|/ɛi/}} is realised as {{IPA|}} (short ''ie'', also written as ''y'') and in some words as {{IPA|}}. | |||
| * ''ui '' - {{IPA|/œy/}} is realised as {{IPA|}} (short ''u'') and in some words as {{IPA|}}. | |||
| * ''au'' - {{IPA|/ʌu/}} is realised as {{IPA|}} (''ow'') | |||
| * ''ou'' - {{IPA|/ʌu/}} is realised as {{IPA|}} (short ''oe''), it is very similar to the long "oe" that is also used in Standard Dutch ({{IPA|}}), which can cause confusion | |||
| * ''e'' - {{IPA|/ɛ/}} is realised as {{IPA|}} or {{IPA|}}. | |||
| * ''i'' - {{IPA|/ɪ/}} is realised as {{IPA|}}. | |||
| * ''ie'' - {{IPA|/i/}} is longer {{IPA|}} | |||
| * ''aa'' - {{IPA|/aː/}} is realised as {{IPA|}}. | |||
| The absence of {{IPA|/x/}} and {{IPA|/ɣ/}} in West Flemish makes pronouncing them very difficult for native speakers. That often causes ] of the {{IPA|/h/}} sounds to a {{IPA|/x/}} or {{IPA|/ɣ/}}. | |||
| Standard Dutch also has many words with an ''-en'' ({{IPA|/ən/}}) suffix (mostly plural forms of verbs and nouns). While Standard Dutch and most dialects do not pronounce the final ''n'', West Flemish typically drops the ''e'' and pronounces the ''n'' inside the base word. For base words already ending with ''n'', the final ''n'' sound is often lengthened to clarify the suffix. That makes many words become similar to those of English: ''beaten'', ''listen'' etc. | |||
| The short ''o'' ({{IPA|}}) can also be pronounced as a short ''u'' ({{IPA|}}), a phenomenon also occurring in ] and some other ], called ]. That happens spontaneously to some words, but other words keep their original short ''o'' sounds. Similarly, the short ''a'' ({{IPA|}}) can turn into a short ''o'' ({{IPA|}}) in some words spontaneously. | |||
| The diphthong ''ui'' ({{IPA|/œy/}}) does not exist in West Flemish and is replaced by a long ''u'' ({{IPA|}}) or a long ''ie'' ({{IPA|}}). Like for the ''ui'', the long ''o'' ({{IPA|}}) can be replaced by an {{IPA|}} (''eu'') for some words but a {{IPA|}} for others. That often causes similarities to ranchers English. {{clarification needed|reason=what is “ranchers English”?|date=January 2022}} | |||
| Here are some examples showing the sound shifts that are part of the vocabulary: | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Dutch !! West Flemish !! English | |||
| |- | |||
| | vol (short ''o'') || vul {{IPA|}}|| full | |||
| |- | |||
| | zon (short ''o'') || zunne {{IPA|}}|| sun | |||
| |- | |||
| | boter (long ''o'') || beuter {{IPA|}}|| butter | |||
| |- | |||
| | boot (long ''o'') || boot {{IPA|}} || boat | |||
| |- | |||
| | kuiken || kiek'n {{IPA|}} || chick | |||
| |- | |||
| | bruin || brun {{IPA|}} || brown | |||
| |} | |||
| == Grammar == | |||
| === Plural form === | |||
| Plural forms in Standard Dutch most often add ''-en'', but West Flemish usually uses ''-s'', like the Low Saxon dialects and even more prominently in English in which ''-en'' has become very rare. Under the influence of Standard Dutch, ''-s'' is being used by fewer people, and younger speakers tend to use ''-en''. | |||
| === Verb conjugation === | |||
| The verbs ''zijn'' ("to be") and ''hebben'' ("to have") are also conjugated differently. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Dutch !! West Flemish !! English !! Dutch !! West Flemish !! English | |||
| |- | |||
| | zijn || zyn || to be || hebben || èn || to have | |||
| |- | |||
| | ik ben || 'k zyn || I am || ik heb || 'k è || I have | |||
| |- | |||
| | jij bent || gy zyt || you are || jij hebt || gy èt || you have | |||
| |- | |||
| | hij is || ie is || he is || hij heeft || ie èt || he has | |||
| |- | |||
| | wij zijn || wydder zyn || we are || wij hebben || wydder èn || we have | |||
| |- | |||
| | jullie zijn || gydder zyt || you are || jullie hebben || gydder èt || you have | |||
| |- | |||
| | zij zijn || zydder zyn || they are || zij hebben || zydder èn || they have | |||
| |} | |||
| === Double subject === | |||
| West Flemish often has a double subject. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Dutch !! West Flemish !! English | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{lang|nl|Jij hebt dat gedaan.}} || {{lang|vls|'''G{{'}}''' èt '''gy''' da gedoan.}} || You have done that. | |||
| |- | |||
| | {{lang|nl|Ik heb dat niet gedaan.}} || {{lang|vls|'''{{'}}K''' èn '''ekik''' da nie gedoan.}} || I didn't do that. | |||
| |} | |||
| === Articles === | |||
| Standard Dutch has an indefinite article that does not depend on gender, unlike in West Flemish. However, a gender-independent article is increasingly used. Like in English, ''n'' is pronounced only if the next word begins with a vowel sound. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Dutch !! West Flemish !! English | |||
| |- | |||
| | een stier (m) || ne stier || a bull | |||
| |- | |||
| | een koe (f) || e koeje || a cow | |||
| |- | |||
| | een kalf (o) || e kolf || a calf | |||
| |- | |||
| | een aap (m) || nen oap || an ape | |||
| |- | |||
| | een huis (o) || en 'us || a house | |||
| |} | |||
| === Conjugation of ''yes'' and ''no'' === | |||
| Another feature of West Flemish is the conjugation of ''ja'' and ''nee'' ("yes" and "no") to the subject of the sentence. That is somewhat related to the double subject, but even when the rest of the sentence is not pronounced, ''ja'' and ''nee'' are generally used with the first part of the double subject. | |||
| This conjugation can be negated with the extra word, ''toet'' ({{IPA|}}), or strenght strengthened by adding mo- or ba- (or both). | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! Dutch !! West Flemish !! English | |||
| |- | |||
| | Heb jij dat gedaan? - Ja / Nee || Èj gy da gedoan? - Joak / Nink|| Did you do that? - Yes / No | |||
| |- | |||
| | Je hebt dat niet gedaan, hé? - Maar jawel || G'èt da nie gedoan, é? - Bajoak (ja'k en doe 't) || You didn't do that, eh? - On the contrary (But yes I did). | |||
| |- | |||
| | Heeft hij dat gedaan? - Ja / Nee || Èt ie (ne) da gedoan? - Joaj/Nij (Joan / Nin)|| Did he do that? - Yes / No | |||
| |- | |||
| | Gaan we verder? - Ja / Nee || Zyn me? - Joam / Nim || Can we go? - Yes / No | |||
| |} | |||
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] - i.e. ''Flemings'' | |||
| * ] (''Flemings'' or ''Vlamingen'') | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * {{citation | |||
| |last=Debrabandere | |||
| |first=Frans | |||
| |chapter=Kortrijk | |||
| |editor-last1=Kruijsen | |||
| |editor-first1=Joep | |||
| |editor-last2=van der Sijs | |||
| |editor-first2=Nicoline | |||
| |title=Honderd Jaar Stadstaal | |||
| |publisher=Uitgeverij Contact | |||
| |date=1999 | |||
| |pages=289–299 | |||
| |chapter-url=http://dbnl.org/arch/sijs002hond01_01/pag/sijs002hond01_01.pdf | |||
| }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| {{commons category|West Flemish language}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | * | ||
| {{InterWiki|code=vls}} | {{InterWiki|code=vls}} | ||
| {{Languages of Belgium}} | |||
| {{Languages of the Benelux}} | |||
| {{Germanic languages}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:25, 27 November 2024
Germanic language| This article may be in need of reorganization to comply with Misplaced Pages's layout guidelines. Please help by editing the article to make improvements to the overall structure. (August 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Dutch. (November 2012) Click for important translation instructions.
|
| West Flemish | |
|---|---|
| West-Vlaams | |
| Native to | Belgium, Netherlands, France |
| Region | West Flanders |
| Native speakers | (1.4 million cited 1998) |
| Language family | Indo-European |
| Dialects | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:vls – (West) Vlaamszea – Zeelandic (Zeeuws) |
| Glottolog | sout3292 Southwestern Dutchvlaa1240 Western Flemish |
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB-ag |
 West Flemish is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger West Flemish is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
West Flemish (West-Vlams or West-Vloams or Vlaemsch (in French Flanders), Dutch: West-Vlaams, French: flamand occidental) is a collection of Low Franconian varieties spoken in western Belgium and the neighbouring areas of France and the Netherlands.
West Flemish is spoken by about a million people in the Belgian province of West Flanders, and a further 50,000 in the neighbouring Dutch coastal district of Zeelandic Flanders (200,000 if including the closely related dialects of Zeelandic) and 10-20,000 in the northern part of the French department of Nord. Some of the main cities where West Flemish is widely spoken are Bruges, Dunkirk, Kortrijk, Ostend, Roeselare and Ypres.
West Flemish is listed as a "vulnerable" language in UNESCO's online Red Book of Endangered Languages.
| This article is a part of a series on |
| Dutch |
|---|
| Low Saxon dialects |
| West Low Franconian dialects |
| East Low Franconian dialects |


Phonology
West Flemish has a phonology that differs significantly from that of Standard Dutch, being similar to Afrikaans in the case of long E, O and A. Also where Standard Dutch has sch, in some parts of West Flanders, West-Flemish, like Afrikaans, has sk. However, the best known traits are the replacement of Standard Dutch (pre-)velar fricatives g and ch in Dutch (/x, ɣ/) with glottal h ,. The following differences are listed by their Dutch spelling, as some different letters have merged their sounds in Standard Dutch but remained separate sounds in West Flemish. Pronunciations can also differ slightly from region to region.
- sch - /sx/ is realised as , or (sh or sk).
- ei - /ɛi/ is realised as or (è or jè).
- ij - /ɛi/ is realised as (short ie, also written as y) and in some words as .
- ui - /œy/ is realised as (short u) and in some words as .
- au - /ʌu/ is realised as (ow)
- ou - /ʌu/ is realised as (short oe), it is very similar to the long "oe" that is also used in Standard Dutch (), which can cause confusion
- e - /ɛ/ is realised as or .
- i - /ɪ/ is realised as .
- ie - /i/ is longer
- aa - /aː/ is realised as .
The absence of /x/ and /ɣ/ in West Flemish makes pronouncing them very difficult for native speakers. That often causes hypercorrection of the /h/ sounds to a /x/ or /ɣ/.
Standard Dutch also has many words with an -en (/ən/) suffix (mostly plural forms of verbs and nouns). While Standard Dutch and most dialects do not pronounce the final n, West Flemish typically drops the e and pronounces the n inside the base word. For base words already ending with n, the final n sound is often lengthened to clarify the suffix. That makes many words become similar to those of English: beaten, listen etc.
The short o () can also be pronounced as a short u (), a phenomenon also occurring in Russian and some other Slavic languages, called akanye. That happens spontaneously to some words, but other words keep their original short o sounds. Similarly, the short a () can turn into a short o () in some words spontaneously.
The diphthong ui (/œy/) does not exist in West Flemish and is replaced by a long u () or a long ie (). Like for the ui, the long o () can be replaced by an (eu) for some words but a for others. That often causes similarities to ranchers English.
Here are some examples showing the sound shifts that are part of the vocabulary:
| Dutch | West Flemish | English |
|---|---|---|
| vol (short o) | vul | full |
| zon (short o) | zunne | sun |
| boter (long o) | beuter | butter |
| boot (long o) | boot | boat |
| kuiken | kiek'n | chick |
| bruin | brun | brown |
Grammar
Plural form
Plural forms in Standard Dutch most often add -en, but West Flemish usually uses -s, like the Low Saxon dialects and even more prominently in English in which -en has become very rare. Under the influence of Standard Dutch, -s is being used by fewer people, and younger speakers tend to use -en.
Verb conjugation
The verbs zijn ("to be") and hebben ("to have") are also conjugated differently.
| Dutch | West Flemish | English | Dutch | West Flemish | English |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zijn | zyn | to be | hebben | èn | to have |
| ik ben | 'k zyn | I am | ik heb | 'k è | I have |
| jij bent | gy zyt | you are | jij hebt | gy èt | you have |
| hij is | ie is | he is | hij heeft | ie èt | he has |
| wij zijn | wydder zyn | we are | wij hebben | wydder èn | we have |
| jullie zijn | gydder zyt | you are | jullie hebben | gydder èt | you have |
| zij zijn | zydder zyn | they are | zij hebben | zydder èn | they have |
Double subject
West Flemish often has a double subject.
| Dutch | West Flemish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Jij hebt dat gedaan. | G' èt gy da gedoan. | You have done that. |
| Ik heb dat niet gedaan. | 'K èn ekik da nie gedoan. | I didn't do that. |
Articles
Standard Dutch has an indefinite article that does not depend on gender, unlike in West Flemish. However, a gender-independent article is increasingly used. Like in English, n is pronounced only if the next word begins with a vowel sound.
| Dutch | West Flemish | English |
|---|---|---|
| een stier (m) | ne stier | a bull |
| een koe (f) | e koeje | a cow |
| een kalf (o) | e kolf | a calf |
| een aap (m) | nen oap | an ape |
| een huis (o) | en 'us | a house |
Conjugation of yes and no
Another feature of West Flemish is the conjugation of ja and nee ("yes" and "no") to the subject of the sentence. That is somewhat related to the double subject, but even when the rest of the sentence is not pronounced, ja and nee are generally used with the first part of the double subject.
This conjugation can be negated with the extra word, toet (), or strenght strengthened by adding mo- or ba- (or both).
| Dutch | West Flemish | English |
|---|---|---|
| Heb jij dat gedaan? - Ja / Nee | Èj gy da gedoan? - Joak / Nink | Did you do that? - Yes / No |
| Je hebt dat niet gedaan, hé? - Maar jawel | G'èt da nie gedoan, é? - Bajoak (ja'k en doe 't) | You didn't do that, eh? - On the contrary (But yes I did). |
| Heeft hij dat gedaan? - Ja / Nee | Èt ie (ne) da gedoan? - Joaj/Nij (Joan / Nin) | Did he do that? - Yes / No |
| Gaan we verder? - Ja / Nee | Zyn me? - Joam / Nim | Can we go? - Yes / No |
See also
- Flemish dialects
- Dutch dialects
- Flemish people (Flemings or Vlamingen)
- French Flemish
- Hebban olla vogala
- Westhoek
References
- ^ (West) Vlaams at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Zeelandic (Zeeuws) at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) - "UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger". United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. Archived from the original on 30 October 2010. Retrieved 2023-02-07.
Further reading
- Debrabandere, Frans (1999), "Kortrijk" (PDF), in Kruijsen, Joep; van der Sijs, Nicoline (eds.), Honderd Jaar Stadstaal, Uitgeverij Contact, pp. 289–299
External links
| Languages of Belgium | |
|---|---|
| Official languages | |
| Germanic | |
| Romance | |
| Francosign | |
| Germanosign | |
| Indo-Aryan | |
| Languages and dialects of Benelux | |
|---|---|
| Sign languages | |