| Revision as of 08:01, 12 January 2008 editCertified planner (talk | contribs)6 editsm →External links← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:49, 28 November 2024 edit undoNaturalisticFallacy (talk | contribs)32 editsm →Mixed scanning model: Clarity.Tag: Visual edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Body of knowledge of urban planning}} | |||
| ]'''Urban, city,''' or '''town planning''' is the discipline of ] which explores several aspects of the built and social environments of municipalities and communities. Other professions deal in more detail with a smaller scale of development, namely ], ] and ]. ] deals with a still larger environment, at a less detailed level. | |||
| {{Further|History of urban planning|Technical aspects of urban planning}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2019}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=April 2015}} | |||
| {{multiple issues| | |||
| {{weasel|date=November 2013}} | |||
| {{Globalize|article|Western culture|date=October 2013}} | |||
| {{essay-like|date=November 2013}} | |||
| }} | |||
| ] from Western District overlooking ], across ].]] | |||
| '''Planning theory''' is the body of scientific concepts, definitions, behavioral relationships, and assumptions that define the body of knowledge of ]. There is no one unified planning theory but various. Whittemore identifies nine procedural theories that dominated the field between 1959 and 1983: the Rational-Comprehensive approach, the Incremental approach, the Transformative Incremental (TI) approach, the Transactive approach, the Communicative approach, the Advocacy approach, the Equity approach, the Radical approach, and the Humanist or Phenomenological approach.<ref>{{Cite web | title = How Planners Use Planning Theory| url = http://www.planetizen.com/node/73570/how-planners-use-planning-theory |access-date= 24 April 2015}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Whittemore |first=Andrew H. |date=2015-03-01 |title=Practitioners Theorize, Too: Reaffirming Planning Theory in a Survey of Practitioners’ Theories |url=https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0739456X14563144 |journal=Journal of Planning Education and Research |language=en |volume=35 |issue=1 |pages=76–85 |doi=10.1177/0739456X14563144 |issn=0739-456X}}</ref> | |||
| Another key role of urban planning is ], and re-generation of inner cities by adapting urban planning methods to existing cities suffering from long-term infrastructural decay.<ref>Grogan, Paul, Proscio, Tony, ''Comeback Cities: A Blueprint for Urban Neighborhood Revival'', 2000. ISBN 0-8133-3952-9</ref> | |||
| == |
==Background== | ||
| Urban planning can include ], by adapting urban planning methods to existing cities suffering from decline. Alternatively, it can concern the massive challenges associated with urban growth, particularly in the ].<ref>{{Cite book|last1=James|first1=Paul|title=Institutional and Social Innovation for Sustainable Urban Development|last2=Holden|first2=Meg|last3=Lewin|first3=Mary|last4=Neilson|first4=Lyndsay|last5=Oakley|first5=Christine|last6=Truter|first6=Art|last7=Wilmoth|first7=David|publisher=Routledge|year=2013|editor1-last=Mieg|editor1-first=Harald|chapter=Managing Metropolises by Negotiating Mega-Urban Growth|author-link1=Paul James (academic)|editor2-last=Töpfer|editor2-first=Klaus|chapter-url=https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/rout/c3b5f/2013/00000001/00000001/art00015}}</ref> All in all, urban planning exists in various forms and addresses many different issues.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Van Assche|first1=Kristof|last2=Beunen|first2=Raoul|last3=Duineveld|first3=Martijn|last4=de Jong|first4=Harro|date=18 September 2012|title=Co-evolutions of planning and design: Risks and benefits of design perspectives in planning systems|journal=Planning Theory|volume=12|issue=2|pages=177–198|doi=10.1177/1473095212456771|s2cid=109970261}}</ref> The modern origins of urban planning lie in the movement for urban reform that arose as a reaction against the disorder of the ] in the mid-19th century. Many of the early influencers were inspired by ], which was popular in the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=3|language=en}}</ref> The new imagined urban form was meant to go hand-in-hand with a new society, based upon voluntary co-operation within self-governing communities.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| <!-- Image with unknown copyright status removed: ].]] --> | |||
| Urban planning as an organized profession has existed for less than a century; however, most settlements and cities have displayed various degrees of forethought and conscious design in their layout and functioning. | |||
| In the late 20th century, the term ] has come to represent an ideal outcome in the sum of all planning goals.<ref>Wheeler, Stephen (2004). "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", Routledge; 3rd edition.{{page needed|date=April 2019}}</ref> Sustainable architecture involves renewable materials and energy sources and is increasing in importance as an environmentally friendly solution<ref>{{Cite web|title=Why Sustainable Architecture Is Becoming more Important {{!}} CRL|url=https://c-r-l.com/content-hub/article/sustainable-architecture-designers/|website=c-r-l.com|language=en-US|access-date=2020-05-19}}</ref> | |||
| As ] replaced a ] existence, permanent human settlements, and larger settlements began to appear. These early ] became centres for trade, defense, and politics and as centers for distributing the agricultural surplus a settled farming society produces. | |||
| == Blueprint planning == | |||
| ] | |||
| Cities laid out with forethought and design permeate ]. Perhaps the earliest of these were those of the ancient ] and ] ] of the third century ]. | |||
| Since at least the ] and the ], urban planning had generally been assumed to be the physical planning and design of human communities.<ref name=":15">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=4|language=en}}</ref> Therefore, it was seen as related to architecture and civil engineering, and thereby to be carried out by such experts.<ref name=":15" /> This kind of planning was physicalist and design-orientated, and involved the production of masterplans and blueprints which would show precisely what the 'end-state' of land use should be, similar to architectural and engineering plans.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=4–5, 13|language=en}}</ref> Similarly, the theory of urban planning was mainly interested in visionary planning and design which would demonstrate how the ideal city should be organised spatially.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=15|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ] located near the ] and ] rivers in modern day ] and some ancient cities of the Indus Valley in modern day India are perhaps the earliest examples of deliberately planned and managed cities in history. The streets of these early cities were often paved and laid out at right angles in a ]. There was also with a hierarchy of streets (commercial boulevards to small residential alleyways). In Harrapan settlements, ] evidence suggests the houses were laid out to protect from noise, odors, and thieves, and had their own ], and sanitation. Ancient cities often had drainage, large ], and well-developed urban ]<ref>Eapen, Jacob. , 1997.</ref> | |||
| === Sanitary movement === | |||
| The Greek ] (c. 407 BC) is widely considered the father of city planning in the West, for his design of ]; Alexander commissioned him to lay out ], the grandest example of idealized urban planning of the Mediterranean world, where regularity was aided in large part by its level site near a mouth of the Nile. | |||
| Although it can be seen as an extension of the sort of civic pragmatism seen in ]'s plan for Savannah or ]'s plan for Philadelphia, the roots of the rational planning movement lie in Britain's ] (1800–1890).<ref>{{cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|title=The Cities of Tomorrow|year=2008|publisher=Blackwell|location=Publishing|isbn=978-0-631-23252-0|pages=13–47, 87–141}}</ref> During this period, advocates such as ] argued for central organized, top-down solutions to the problems of industrializing cities. In keeping with the rising power of industry, the source of the planning authority in the Sanitary movement included both traditional governmental offices and private development corporations. In London and its surrounding suburbs, cooperation between these two entities created a network of new communities clustered around the expanding rail system.<ref>{{cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|title=The Cities of Tomorrow|year=2008|publisher=Blackwell|location=Publishing|isbn=978-0-631-23252-0|pages=48–86}}</ref> | |||
| === Garden city movement === | |||
| The ] used a consolidated scheme for city planning, developed for military defense and civil convenience. The basic plan is a central ] with city services, surrounded by a compact rectilinear grid of streets and wrapped in a wall for defense. To reduce travel times, two diagonal streets cross the square grid corner-to-corner, passing through the central square. A river usually flows through the city, to provide water and transport, and carry away sewage, even in sieges.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} Effectively, many European towns still preserve the essence of these schemes, as in ].The Romans had a very logical way of designing their cities. They put all the streets at right angles, set up in a square grid. All the roads were equal in width and length except for two. These two roads formed the center of the grid and intersected in the middle. One went East/West, the other North/South. They were slightly wider than the others. All roads were made of carefully fitted stones and smaller hard packed stones. Bridges were also constructed where needed. Each square marked by four roads was called an insulae. An insulae was the Roman equivalent of a city block. Each insulae was 80 yards square. The land of each insulae was divided up. As the city developed, each insulae would eventually be filled with buildings of various shapes and sizes and would be crisscrossed with back roads and alleys. Most insulae were given to the first settlers of a budding new Roman city, but each person had to pay for the building of their own houses. The city was surrounded by a wall to protect the city from invaders and other enemies, and to mark the cities limits. Area outside of the walls and city limits was left for farmland. At the end of each main road, there was a large gateway with watchtowers. A portcullis covered the opening when the city was under siege. Other watchtowers were constructed around the rest of the city’s wall. An aqueduct was built outside of the cities walls. This brought in the water necessary for the cities functioning. | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] was founded by ] (1850-1928).<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=90|language=en}}</ref> His ideas were expressed in the book ] (1898).<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=91|language=en}}</ref> His influences included ], who had published a pamphlet in 1876 calling for low population density, good housing, wide roads, an underground railway and for open space; ] who had supported ] of land and the sharing of the rents it would produce; ] who had pioneered the idea of colonizing planned communities to house the poor in ] (including starting new cities separated by green belts at a certain point); ] who had designed a model town with a central place, radial avenues and industry in the periphery; as well as ], ] and the ], which had all called for the moving of masses to the countryside.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=92–96|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Howards' vision was to combine the best of both the countryside and the city in a new environment called Town-Country.<ref name=":1">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=96|language=en}}</ref> To make this happen, a group of individuals would establish a limited-dividend company to buy cheap agricultural land, which would then be developed with investment from manufacturers and housing for the workers.<ref name=":1" /> No more than 32,000 people would be housed in a settlement, spread over 1,000 acres.<ref name=":1" /> Around it would be a permanent green belt of 5,000 acres, with farms and institutions (such as mental institutions) which would benefit from the location.<ref name=":2">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=97|language=en}}</ref> After reaching the limit, a new settlement would be started, connected by an ], with the polycentric settlements together forming the "Social City".<ref name=":2" /> The lands of the settlements would be jointly owned by the inhabitants, who would use rents received from it to pay off the mortgage necessary to buy the land and then invest the rest in the community through ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=98|language=en}}</ref> Actual garden cities were built by Howard in ], ], and ]. The movement would also inspire the later ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=255|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| The idea of rational planning collapsed with the idea of the '']'' in the European ]. Round a fortress or fortified abbey or next to a Roman nucleus — sometimes itself abandoned— urban growth occurred "like the annular rings of a tree"<ref>], ''Space, Time and Architecture'' (1941) 1962, in reference to an air view (fig.8) of the medieval Italian town of Bagnocavallo. Giedion's source was Luigi Piccinati, "Urbanistica Medioevale" in ''Urbanistica deal Antichità ad Oggi'' (Florence 1943).</ref> whether in an extended village or the center of a larger city. Since the new center was often on high, defensible ground, the city plan took on an organic character, following the irregularities of ] like the shapes that result from ]. | |||
| === Linear city === | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The ideal city resurfaced in the ] in Florence, where the star-shaped city plan was adapted from the new cannon-resistant ]. The star-shaped fortification had a formative influence on the patterning of Renaissance urban planning: "The Renaissance was hypnotized by one city type which for a century and a half— from Filarete to ]— was impressed upon utopian schemes: this is the star-shaped city"<ref>], ''Space, Time and Architecture'' (1941) 1962 p 43.</ref> Radial streets extend outward from a defined center of military, communal or spiritual power. Only in ideal cities did a centrally-planned structure stand at the heart, as in ]'s ''Sposalizio'' of 1504 (''illustration''); as built, the unique example of a rationally-planned ''quattrocento'' new city center, that of ], 1493-95, resembles a closed space instead, surrounded by arcading. ]'s ideal city, building on hints in ]'s ''De re aedificatoria'', was named "]" in compliment to his patron; its twelve-pointed shape, circumscribable by a "perfect" ], the circle, takes no heed of its undulating terrain in Filarete's manuscript.<ref>The undulating terrace of housing makes its appearance surprisingly late: Giedion's example is ], 1794 (Giedion 1962:fig. 83</ref> | |||
| ] idea of the ] (1882)<ref>{{cite web|title=Arturo Soria y su proyecto Ciudad Lineal|url=http://www.alu.ua.es/a/arg18/Web/arturo_soria.html|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140604075645/http://www.alu.ua.es/a/arg18/Web/arturo_soria.html|archive-date=2014-06-04|access-date=2014-08-11}}</ref> replaced the traditional idea of the city as a centre and a periphery with the idea of constructing linear sections of infrastructure - roads, railways, gas, water, etc.- along an optimal line and then attaching the other components of the city along the length of this line. As compared to the concentric diagrams of ] and other in the same period, Soria's linear city creates the infrastructure for a controlled process of expansion that joins one growing city to the next in a rational way, instead of letting them both sprawl. The linear city was meant to ‘ruralize the city and urbanize the countryside’, and to be universally applicable as a ring around existing cities, as a strip connecting two cities, or as an entirely new linear town across an unurbanized region.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Caves|first=R. W.|url=https://archive.org/details/encyclopediacity00cave|title=Encyclopedia of the City|publisher=Routledge|year=2004|isbn=9780415252256|pages=|url-access=limited}}</ref> The idea was later taken up by ] in the ]. The ] was a practical application of the concept. | |||
| === Regional planning movement === | |||
| The true heirs of Greek rational planning were the ]s, who are thought to have originated the idea of formal ] (see ] and ] and the more general notion of ], or "stewardship" from which they arise),{{Fact|date=February 2007}} although modern usage in the West largely dates from the ideas of the ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] (1864-1932) was the founder of regional planning.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=150|language=en}}</ref> His main influences were the geographers ] and ], as well as the sociologist ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=152|language=en}}</ref> From these he received the idea of the ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=154|language=en}}</ref> According to Geddes, planning must start by surveying such a region by crafting a "Valley Section" which shows the general slope from mountains to the sea that can be identified across scale and place in the world, with the natural environment and the cultural environments produced by it included.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=154–155|language=en}}</ref> This was encapsulated in the motto "Survey before Plan".<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=155|language=en}}</ref> He saw cities as being changed by technology into more regional settlements, for which he coined the term '']''.<ref name=":3">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=161|language=en}}</ref> Similar to the garden city movement, he also believed in adding green areas to these urban regions.<ref name=":3" /> The ] advanced his ideas, coming up with the 'regional city' which would have a variety of urban communities across a green landscape of farms, parks and wilderness with the help of telecommunication and the automobile.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=165|language=en}}</ref> This had major influence on the ], 1944.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=196|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === City Beautiful movement === | |||
| Many cities in Central American civilizations also engineered urban planning in their cities including sewage systems and running water. Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was the capital of the Aztec empire, built on an island in Lake Texcoco in what is now the Federal District in central Mexico. At its height, Tenochtitlan was one of the largest cities in the world, with close to 250,000 inhabitants.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] was inspired by 19th century European capital cities such as ] ] or the ].<ref name=":4">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=203|language=en}}</ref> An influential figure was ] (1846-1912), who was the chief of construction of the ] in 1893.<ref name=":4" /> Urban problems such as the 1886 ] in ] had created a perceived need to reform the morality of the city among some of the elites.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=204|language=en}}</ref> Burnham's greatest achievement was the ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=204|language=en}}</ref> His aim was "to restore to the city a lost visual and aesthetic harmony, thereby creating the physical prerequisite for the emergence of a harmonious social order", essentially creating social reform through new ] and creating public space, which also endeared it the support of the ].<ref name=":5">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=207|language=en}}</ref> This was also believed to be economically advantageous by drawing in tourists and wealthy migrants.<ref name=":5" /> Because of this it has been referred to as "] urban development" and as "centrocentrist" for focusing only on the core of the city.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=210–211|language=en}}</ref> Other major cities planned according to the movement principles included British colonial capitals in ], ], ] ] and ],<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=212|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=218|language=en}}</ref> as well as that of ] in ],<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=223|language=en}}</ref> and ] plan for the Nazi capital ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=229|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Towers in the park === | |||
| In developed countries (], ], ] and ]) during the last two centuries, planning and architecture can be said to have gone through various stages of general consensus. Firstly there was the industrialised city of the 19th century, where control of building was largely held by businesses and the wealthy elite. Around the turn of the 20th century there began to be a movement for providing people, and factory workers in particular, with healthier environments. The concept of ] arose and some model towns were built, such as ] and ] the world's first garden cities, in ], UK. However, these were principally small scale in size, typically dealing with only a few thousand residents.<ref>] et al. ''Sociable Cities; the legacy of Ebeneezer Howard'', 1998, ISBN 0-471-98504-X, John Wiley & Sons, New York.</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] (1887–1965) pioneered a new urban form called ]. His approach was based on defining the house as 'a machine to live in'.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=238|language=en}}</ref> The ] he devised for ], which was never fulfilled, would have involved the demolition of much of historic Paris in favour of 18 uniform 700-foot tower blocks.<ref name=":6">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=241|language=en}}</ref> ] and the ] formulated his basic principles, including decongestion of the city by increased density and open space by building taller on a smaller footprint.<ref name=":6" /> Wide avenues should also be built to the city centre by demolishing old structures, which was criticized for lack of environmental awareness.<ref name=":6" /> His generic ethos of planning was based on the rule of experts who would "work out their plans in total freedom from partisan pressures and special interests" and that "once their plans are formulated, they must be implemented without opposition".<ref name=":7">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=244|language=en}}</ref> His ] helped inspire the 'urbanists' who wanted to build planned cities full of massive apartment blocks in Soviet countryside.<ref name=":7" /> The only city which he ever actually helped plan was ] in ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=245|language=en}}</ref> ], planned by ], also was heavily influenced by his thought.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=248–249|language=en}}</ref> Both cities suffered from the issue of unplanned settlements growing outside them.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=251|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Decentralised planning === | |||
| It wasn't until the 1920s when ] began to surface. Based on the ideas of ] and utilising new skyscraper building techniques, the modernist city stood for the elimination of disorder, congestion and the small scale, replacing them instead with preplanned and widely spaced freeways and tower blocks set within gardens. There were plans for large scale rebuilding of cities, such as the ''Plan Voisin'' (based on Le Corbusier's ]), which proposed clearing and rebuilding most of central Paris. No large scale plans were implemented until after ] however. Throughout the late 1940s and 1950s, housing shortages caused by war destructions led many cities around the world to build substantial amounts of government housing. Planners at the time used the opportunity to implement the modernist ideal of towers surrounded by gardens. The most prominent example of an entire modernist city is ], constructed between 1956 and 1960 in ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| In the United States, ] similarly identified vehicular mobility as a principal planning metric. Car-based suburbs had already been developed in the ] in 1907-1908 (including later the world's first car-based shopping centre of ]), as well as in ] in 1914 and ] in 1923.<ref name=":12">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=340–341|language=en}}</ref> Wright began to idealise this vision in his ] starting in 1924, with similarities to the garden city and regional planning movements.<ref name=":13">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=342|language=en}}</ref> The fundamental idea was for technology to liberate individuals.<ref name=":13" /> In his ], he described the city as<blockquote>"spacious, well-landscaped highways, grade crossings eliminated by a new kind of integrated by-passing or over- or under-passing all traffic in cultivated or living areas … Giant roads, themselves great architecture, pass public service stations . . . passing by farm units, roadside markets, garden schools, dwelling places, each on its acres of individually adorned and cultivated ground".<ref name=":14">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=344–345|language=en}}</ref></blockquote>This was justified as a ] ideal, as "“Democracy is the ideal of reintegrated decentralization … many free units developing strength as they learn by function and grow together in spacious mutual freedom.”<ref name=":14" /> This vision was however criticized by ] as being contradictory in its call for individualism while relying on the master-architect to design it all.<ref name=":14" /> | |||
| By the late 1960s and early 1970s, many planners were coming to realise that the imposition of modernist clean lines and a lack of human scale also tended to sap vitality from the community. This was expressed in high crime and social problems within these planned neighbourhoods. <ref>Smith Morris et al. ''British Town Planning and Urban Design'', 1997, ISBN 0-582-23496-4, Longman, Singapore.</ref> Modernism can be said to have ended in the 1970s when the construction of the cheap, uniform ]s ended in many countries, such as Britain and France. Since then many have been demolished and in their way more conventional housing has been built. Rather than attempting to eliminate all disorder, planning now concentrates on individualism and diversity in society and the economy. This is the post-modernist era.<ref>Smith Morris et al. ''British Town Planning and Urban Design'', 1997, ISBN 0-582-23496-4, Longman, Singapore.</ref> | |||
| After ], ]s similar to Broadacre City spread throughout the US, but without the social or economic aspects of his ideas.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=346|language=en}}</ref> A notable example was that of ], built 1947 to 1951.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=351|language=en}}</ref> The suburban design was criticized for their lack of form by ] as it lacked clear boundaries, and by ] because "Each building is treated in isolation, nothing binds it to the next one".<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=353–354|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Minimally-planned cities still exist. ] is an example of a large city (with a metropolitan population of 5.5 million) in a developed country, without a comprehensive zoning ordinance. Houston does, however, have many of the land use restrictions covered by traditional zoning regulations, such as restrictions on development density and parking requirements, even though specific land uses are not regulated. Moreover, private-sector developers have used subdivision covenants and deed restrictions effectively to create the same kinds of land use restrictions found in most municipal zoning laws. Houston voters have rejected proposals for a comprehensive zoning ordinance three times since 1948. Even without zoning in its traditional sense, metropolitan Houston displays similar land use patterns at the macro scale to regions comparable in age and population that do have zoning, such as Dallas. This suggests that factors outside the regulatory environment, such as the provision of urban infrastructure and methods of financing development, may play a greater role in the way American cities are developed than does zoning. | |||
| In the ] too, the so-called deurbanists (such as ] and ]) advocated for the use of electricity and new transportation technologies (especially the car) to disperse the population from the cities to the countryside, with the ultimate aim of a "townless, fully decentralized, and evenly populated country".<ref name=":12" /> However, in 1931 the ] ruled such views as forbidden.<ref name=":13" /> | |||
| ==Sustainable development and Sustainability== | |||
| ] and sustainability have become buzzwords in the planning industry, with the recognition that present ways of consumption and living have led to problems like the overuse of natural resources, ecosystem destruction, urban heat islands, pollution, growing inequality in cities, the degradation of human living conditions and human-induced climate change. Planners have, as a result, taken to advocating for the development of sustainable cities.<ref> Wheeler Stephen. "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", 1998, ISBN 0-415-27173-8, Routledge, New York.</ref> | |||
| === Opposition to blueprint planning === | |||
| However, the notion of sustainable development can be considered as rather recent and evolving, with many questions surrounding this concept.<ref>Wheeler Stephen. "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", 1998, ISBN 0-415-27173-8, Routledge, New York.</ref> That said, it is often not difficult to recognise what are 'unsustainable' forms of lifestyles, and urban planning is recognised to play a crucial position in the development of sustainable cities. | |||
| Throughout both the United States and Europe, the rational planning movement declined in the latter half of the 20th century.<ref>{{cite book|title=Planning Futures: New Directions for Planning Theory|url=https://archive.org/details/planningfuturesn00allm|url-access=limited|first=Philip|last=Allmendinger|year=2002|publisher=Routledge|pages=–25}}</ref> Key events in the United States include the demolition of the ] in ] and the national backlash against urban renewal projects, particularly urban expressway projects.<ref>{{cite book|title=Transportation: A Geographical Analysis|last=Black|first=William R.|page=29|publisher=The Guilford1 Press}}</ref> An influential critic of such planning was ], who wrote '']'' in 1961, claimed to be "one of the most influential books in the short history of city planning".<ref name=":8">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=282|language=en}}</ref> She attacked the garden city movement because its "prescription for saving the city was to do the city in" and because it "conceived of planning also as essentially paternalistic, if not authoritarian".<ref name=":8" /> The Corbusians on the other hand were claimed to be egoistic.<ref name=":8" /> In contrast, she defended the dense traditional inner-city neighborhoods like ] or ], and argued that an urban neighbourhood required about 200-300 people per acre, as well as a high net ground coverage at the expense of open space.<ref name=":9">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=283|language=en}}</ref> She also advocated for a diversity of land uses and building types, with the aim of having a constant churn of people throughout the neighbourhood across the times of the day.<ref name=":9" /> This essentially meant defending urban environments as they were before modern planning had aimed to start changing them.<ref name=":9" /> As she believed that such environments were essentially self-organizing, her approach was effectively one of ], and has been criticized for not being able to guarantee "the development of good neighbourhoods".<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=284|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| The most radical opposition to blueprint planning was declared in 1969 in a manifesto on the '']'', with the words that: <blockquote>The whole concept of planning (the town-and-country kind at least) has gone cockeyed … Somehow, everything must be watched; nothing must be allowed simply to “happen.” No house can be allowed to be commonplace in the way that things just are commonplace: each project must be weighed, and planned, and approved, and only then built, and only after that discovered to be commonplace after all.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=312|language=en}}</ref></blockquote>Another form of opposition came from the ] movement, opposes to traditional top-down and technical planning.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=315|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Stephen Wheeler, in his 1998 article, suggests a definition for sustainable urban development to be as "development that improves the long-term social and ecological health of cities and towns."<ref>Wheeler Stephen. "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", 1998, ISBN 0-415-27173-8, Routledge, New York.</ref> He goes on to suggest a framework that might help all to better understand what a 'sustainable' city might look like. These include compact, efficient land use; less automobile use yet with better access; efficient resource use, less pollution and waste; the restoration of natural systems; good housing and living environments; a healthy social ecology; sustainable economics; community participation and involvement; and preservation of local culture and wisdom.<ref>Wheeler Stephen. "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", 1998, ISBN 0-415-27173-8, Routledge, New York.</ref> | |||
| == Modernist planning == | |||
| The difficult challenge facing planners comes with the implementation of sustainability visions, policy and programmes, and in the midst of doing so, the need to modify institutions to achieve these goals. This is still being worked out by urban planners. | |||
| ] and ] inspired the related theories of rational process and systems approaches to urban planning in the 1960s.<ref name=":16">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=60|language=en}}</ref> They were imported into planning from other disciplines.<ref name=":16" /> The systems approach was a reaction to the issues associated with the traditional view of planning.<ref name=":19">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=64|language=en}}</ref> It did not understand the social and economic sides of cities, the complexity and interconnectedness of urban life, as well as lacking in flexibility.<ref name=":19" /> The 'quantitative revolution' of the 1960s also created a drive for more scientific and precise thinking, while the rise of ] made the approach more natural.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=65|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| == |
=== Systems theory === | ||
| ===]=== | |||
| ] | |||
| In developed countries there has been a backlash against excessive man-made clutter in the environment, such as signposts, signs, and hoardings.<ref>New Zealand Herald: </ref> Other issues that generate strong debate amongst urban designers are tensions between peripheral growth, increased housing density and planned new settlements. There are also unending debates about the benefits of mixing tenures and land uses, versus the benefits of distinguishing geographic zones where different uses predominate.<ref> Holm, Ivar (2006). ''Ideas and Beliefs in Architecture and Industrial design: How attitudes, orientations, and underlying assumptions shape the built environment''. Oslo School of Architecture and Design. ISBN 8254701741.</ref> | |||
| ] is based on the conception of phenomena as 'systems', which are themselves coherent entities composed of interconnected and interdependent parts.<ref name=":17">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=61|language=en}}</ref> A city can in this way be conceptualised as a system with interrelated parts of different land uses, connected by transport and other communications.<ref name=":17" /> The aim of urban planning thereby becomes that of planning and controlling the system.<ref name=":18">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=62|language=en}}</ref> Similar ideas had been put forward by Geddes, who had seen cities and their regions as analogous to organisms, though they did not receive much attention while planning was dominated by architects.<ref name=":18" /> | |||
| Successful urban planning considers character, of "home" and "sense of place", local identity, respect for natural, artistic and historic heritage, an understanding of the "urban grain" or "townscape," pedestrians and other modes of traffic, utilities and natural hazards, such as flood zones. | |||
| The idea of the city as a system meant that it became critical for planners to understand how cities functioned.<ref name=":18" /> It also meant that a change to one part in a city would have effects on others parts as well.<ref name=":18" /> There were also doubts raised about the goal of producing detailed blueprints of how cities should look like in the end, instead suggesting the need for more flexible plans with trajectories instead of fixed futures.<ref name=":20">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=63|language=en}}</ref> Planning should also be an ongoing process of monitoring and taking action in the city, rather than just producing the blueprint at one time.<ref name=":20" /> The systems approach also necessitated taking into account the economic and social aspects of cities, beyond just the aesthetic and physical ones.<ref name=":20" /> | |||
| Some argue that the medieval ] and arcade are the most widely appreciated elements of successful urban design, as demonstrated by the Italian cities of ] and ]{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. | |||
| === Rational process approach === | |||
| While it is rare that cities are planned from scratch, planners are important in managing the growth of cities, applying tools like ] to manage the uses of land, and ] to manage the pace of development. When examined historically, many of the cities now thought to be most beautiful are the result of dense, long lasting systems of prohibitions and guidance about building sizes, uses and features. These allowed substantial freedoms, yet enforce styles, safety, and often materials in practical ways. Many conventional planning techniques are being repackaged using the contemporary term, ]. | |||
| The focus on the procedural aspect of planning had already been pioneered by Geddes in his Survey-Analysis-Plan approach.<ref name=":21">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=66|language=en}}</ref> However, this approach had several shortfalls. It did not consider the reasons for doing a survey in the first place.<ref name=":21" /> It also suggested that there should be simply a single plan to be considered.<ref name=":21" /> Finally, it did not take into account the implementation stage of the plan.<ref name=":22">{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=67|language=en}}</ref> There should also be further action in monitoring the outcomes of the plan after that.<ref name=":22" /> The rational process, in contrast, identified five different stages: (1) the definition of problems and aims; (2) the identification of alternatives; (3) the evaluation of alternatives; (4) implementation: (5) monitoring.<ref name=":22" /> This new approach represented a rejection of blueprint planning.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=69|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Incrementalism === | |||
| There are some cities that have been planned from conception, and while the results often don't turn out quite as planned, evidence of the initial plan often remains. (''See ]'') | |||
| Beginning in the late 1950s and early 1960s, critiques of the rational paradigm began to emerge and formed into several different schools of planning thought. The first of these schools is Lindblom's ]. Lindblom describes planning as "muddling through" and thought that practical planning required decisions to be made incrementally. This incremental approach meant choosing from small number of policy approaches that can only have a small number consequences and are firmly bounded by reality, constantly adjusting the objectives of the planning process and using multiple analyses and evaluations.<ref name="Lindblom">{{cite journal|last1=Lindblom|first1=Charles E.|date=n.d.|title=The Science of 'Muddling Through'|journal=Public Administration Review|volume=19|issue=2|pages=79–88|doi=10.2307/973677|jstor=973677}}</ref> | |||
| ===Safety=== | |||
| ] in France is built upon high ground to provide maximum protection from attackers.]] | |||
| Historically within the Middle East, Europe and the rest of the ], settlements were located on higher ground (for defense) and close to fresh water sources{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. Cities have often grown onto coastal and flood plains at risk of floods and storm surges. Urban planners must consider these threats. If the dangers can be localised then the affected regions can be made into parkland or ], often with the added benefit of open space provision. | |||
| === Mixed scanning model === | |||
| Extreme ], ], or other emergencies can often be greatly mitigated with secure ] routes and emergency operations centres. These are relatively inexpensive and unintrusive, and many consider them a reasonable precaution for any urban space. Many cities will also have planned, built safety features, such as ]s, ]s, and shelters. | |||
| The mixed scanning model, developed by ], takes a similar approach to Lindblom. Etzioni (1968) suggested that organizations plan on two different levels: the tactical and the strategic. He posited that organizations could accomplish this by essentially scanning the environment on multiple levels and then choose different strategies and tactics to address what they found there. While Lindblom's approach only operated on the functional level Etzioni argued, the mixed scanning approach would allow planning organizations to work on both the functional and more big-picture oriented levels.<ref name="Etzioni">Etzioni, A. (1968). The active society: a theory of societal and political processes. New York: Free Press.</ref> | |||
| == Political planning == | |||
| In recent years, practitioners have also been expected to maximize the accessibility of an area to people with different abilities, practicing the notion of "inclusive design," to anticipate criminal behaviour and consequently to "design-out crime" and to consider "traffic calming" or "pedestrianisation" as ways of making urban life more pleasant. | |||
| In the 1960s, a view emerged of planning as an inherently normative and political activity.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=77|language=en}}</ref> Advocates of this approach included ], ], ], ], and ], the latter remarking that:<blockquote>Plans are policies and policies, in a democracy at any rate, spell politics. The question is not whether planning will reflect politics but whose politics it will reflect. What values and whose values will planners seek to implement? . . . No longer can the planner take refuge in the neutrality of the objectivity of the personally uninvolved scientist.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=83|language=en}}</ref></blockquote>The choices between alternative end points in planning was a key issue which was seen as political.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Taylor|first=Nigel|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cmYtMZhLtZUC&q=urban+planning+theory|title=Urban Planning Theory since 1945|date=1998-06-11|publisher=SAGE|isbn=978-1-84920-677-8|pages=83–84|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Participatory planning === | |||
| City planning tries to control ] with structures designed from theories such as ] or ]. These theories say that an urban environment can influence individuals' obedience to social rules. The theories often say that psychological pressure develops in more densely developed, unadorned areas. This stress causes some crimes and some use of illegal drugs. The antidote is usually more individual space and better, more beautiful design in place of ]. | |||
| {{main|Participatory planning}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Participatory planning is an urban planning ] that emphasizes involving the entire community in the strategic and management processes of urban planning; or, community-level planning processes, urban or rural. It is often considered as part of ].<ref name="REFALPHA">{{cite web|last1=Lefevre|first1=Pierre|last2=Kolsteren|first2=Patrick|last3=De Wael|first3=Marie-Paule|last4=Byekwaso|first4=Francis|last5=Beghin|first5=Ivan|date=December 2000|title=Comprehensive Participatory Planning and Evaluation|url=http://www.ifad.org/pub/bsf/cppe/cppe.pdf|access-date=2008-10-21|publisher=IFAD|location=Antwerp, Belgium|archive-date=3 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303200814/http://www.ifad.org/pub/bsf/cppe/cppe.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> Participatory planning aims to harmonize views among all of its participants as well as prevent conflict between opposing parties. In addition, marginalized groups have an opportunity to participate in the planning process.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=McTague|first1=Colleen|last2=Jakubowski|first2=Susan|date=October 2013|title=Marching to the beat of a silent drum: Wasted consensus-building and failed neighborhood participatory planning|journal=Applied Geography|volume=44|pages=182–191|doi=10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.07.019|bibcode=2013AppGe..44..182M }}</ref> | |||
| ] had first advocated for the "real and active participation" of citizens when working in the ], arguing against the "Dangers of Municipal Government from above" which would cause "detachment from public and popular feeling, and consequently, before long, from public and popular needs and usefulness".<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=299|language=en}}</ref> Further on, ] was researched by ] in the 1930s in his ''Town Planning in Practice''.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=300|language=en}}</ref> The Italian anarchist architect ] then argued in 1948 that "“The housing problem cannot be solved from above. It is a problem of the people, and it will not be solved, or even boldly faced, except by the concrete will and action of the people themselves", and that planning should exist "as the manifestation of communal collaboration".<ref name=":10">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=301|language=en}}</ref> Through the ], his ideas caught ], who started working in ] with Eduardo Neira.<ref name=":10" /> He would go on working in ] from the mid-'50s to the mid-'60s.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=302|language=en}}</ref> There he found that the ] were not ]s, but were rather highly organised and well-functioning.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=304|language=en}}</ref> As a result, he came to the conclusion that:<blockquote>"When dwellers control the major decisions and are free to make their own contributions in the design, construction or management of their housing, both this process and the environment produced stimulate individual and social well-being. When people have no control over nor responsibility for key decisions in the housing process, on the other hand, dwelling environments may instead become a barrier to personal fulfillment and a burden on the economy."<ref name=":11">{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=305–306|language=en}}</ref></blockquote>The role of the government was to provide a framework within which people would be able to work freely, for example by providing them the necessary resources, infrastructure and land.<ref name=":11" /> Self-build was later again taken up by ], who led a project called People Rebuild Berkeley in 1972, with the aim to create "self-sustaining, self-governing" communities, though it ended up being closer to traditional planning.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Peter|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0J1kAwAAQBAJ&q=cities+of+tomorrow|title=Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880|date=2014-04-17|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-118-45651-4|pages=311|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| '''Oscar Newman’s''' ] cites the modernist housing projects of the 1960s as an example of environmental determinism, where large blocks of flats are surrounded by shared and disassociated public areas, which are hard for residents to identify with. As those on lower incomes cannot hire others to maintain public space such as security guards or grounds keepers, and because no individual feels personally responsible, there was a general deterioration of public space leading to a sense of alienation and social disorder | |||
| === Synoptic planning === | |||
| ] is another notable environmental determinist and is associated with the "eyes on the street" concept. By improving ‘natural surveillance’ of shared land and facilities of nearby residents by literally increasing the number of people who can see it, and increasing the familiarity of residents, as a collective, residents can more easily detect undesirable or criminal behaviour. | |||
| After the "fall" of blueprint planning in the late 1950s and early 1960s, the synoptic model began to emerge as a dominant force in planning. Lane (2005) describes ] as having four central elements: | |||
| :"(1) an enhanced emphasis on the specification of goals and targets; (2) an emphasis on quantitative analysis and predication of the environment; (3) a concern to identify and evaluate alternative policy options; and (4) the evaluation of means against ends (page 289)."<ref name="Lane">{{cite journal |last1=Lane |first1=Marcus B. |title=Public Participation in Planning: an intellectual history |journal=Australian Geographer |date=November 2005 |volume=36 |issue=3 |pages=283–299 |doi=10.1080/00049180500325694 |bibcode=2005AuGeo..36..283L |s2cid=18008094 }}</ref> | |||
| The ] argues that small indicators of neglect, such as broken windows and unkempt lawns, promote a feeling that an area is in a state of decay. Anticipating decay, people likewise fail to maintain their own properties. The theory suggests that abandonment causes crime, rather than crime causing abandonment{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. | |||
| ] was first introduced into this model and it was generally integrated into the system process described above. However, the problem was that the idea of a single public interest still dominated attitudes, effectively devaluing the importance of participation because it suggests the idea that the public interest is relatively easy to find and only requires the most minimal form of participation.<ref name="Lane" /> | |||
| Some planning methods might help an elite group to control ordinary citizens. ] created a system of wide boulevards which prevented the construction of barricades in the streets and eased the movement of military troops. In ], the ] in the 1930s created ''ex novo'' many new ]s in order to concentrate ]s and poorer classes away from the elegant town. | |||
| ==== Transactive planning ==== | |||
| Other social theories point out that in Britain and most countries since the 18th century, the transformation of ] from rural agriculture to industry caused a difficult adaptation to urban living. These theories emphasize that many planning policies ignore personal tensions, forcing individuals to live in a condition of perpetual extraneity to their cities. Many people therefore lack the comfort of feeling "at home" when at home. Often these theorists seek a reconsideration of commonly used "standards" that rationalize the outcomes of a free (relatively unregulated) market. | |||
| Transactive planning was a radical break from previous models. Instead of considering public participation as a method that would be used in addition to the normal training planning process, participation was a central goal. For the first time, the public was encouraged to take on an active role in the policy-setting process, while the planner took on the role of a distributor of information and a feedback source.<ref name="Lane"/> Transactive planning focuses on interpersonal dialogue that develops ideas, which will be turned into action. One of the central goals is mutual learning where the planner gets more information on the community and citizens to become more educated about planning issues.<ref name="Friedman">Friedman, J. (1973). Retracking America: A Theory of Transactive Planning. Garden City, NJ: Anchor Press/Doubleday.</ref> | |||
| ===Slums=== | |||
| {{main|Slums}} | |||
| === Advocacy planning === | |||
| The rapid ] of the last century has resulted in a significant amount of slum habitation in the major cities of the world, particularly in the ]. There is significant demand for planning resources and strategies to address the issues that arise from slum development, and many planning theorists and practitioners are calling for increased attention and resources in this area, particularly the ].<ref>, Commonwealth Association of Planners</ref> When urban planners give their attention to slums, one also have to pay attention to the racial make - up of that area to ensure that ] does not occur. | |||
| Formulated in the 1960s by lawyer and planning scholar ], the advocacy planning model takes the perspective that there are large inequalities in the political system and in the bargaining process between groups that result in large numbers of people unorganized and unrepresented in the process. It concerns itself with ensuring that all people are equally represented in the planning process by advocating for the interests of the underprivileged and seeking social change.<ref name="Davidoff">Davidoff, P. (1965). Advocacy and Pluralism in Planning. Journal of the American Institute of Planners, 31 (4), 331–338.</ref><ref name="Maziotti">Mazziotti, D. F. (1982). The underlying assumptions of advocacy planning: pluralism and reform. In C. Paris (Ed.), Critical readings in planning theory (pp. 207–227) New York: Pergamon Press.</ref> Again, public participation is a central tenet of this model. A plurality of public interests is assumed, and the role of the planner is essentially the one as a facilitator who either advocates directly for underrepresented groups directly or encourages them to become part of the process.<ref name="Lane"/> | |||
| ===Radical planning=== | |||
| The issue of slum habitation has often been resolved via a simple policy of clearance, however more creative solutions are beginning to emerge such as ]'s "]" program, where established slum-dwellers have promised to build proper houses, schools, and community centers without any government money, in return for land they have been illegally squatting on for 30 years. The "Camp of Fire" program is one of many similar projects initiated by ], which has programs in ], ], and ].<ref>The Christian Science Monitor: , 26 May 2004</ref> | |||
| Radical planning is a stream of ] which seeks to manage development in an ] and ]-based manner. The seminal text to the radical planning movement is ''Foundations for a Radical Concept in Planning'' (1973), by ] and ]. Grabow and Heskin provided a critique of planning as elitist, centralizing and change-resistant, and proposed a new paradigm based upon systems change, decentralization, ], facilitation of human development and consideration of ecology. Grabow and Heskin were joined by ''Head of Department of Town Planning'' from the ] ], and his 1981 work ''Theories for Planning''. | |||
| In 1987 ] entered the fray with ''Planning in the Public Domain: From Knowledge to Action'', promoting a radical planning model based on "decolonization", "democratization", "self-empowerment" and "reaching out". Friedmann described this model as an "Agropolitan development" paradigm, emphasizing the re-localization of ] and ]. In "Toward a Non-] Mode of Planning" (1993) Friedmann further promoted the urgency of decentralizing planning, advocating a planning paradigm that is normative, innovative, political, transactive and based on a ] approach to knowledge and policy. | |||
| ===Urban decay=== | |||
| {{main|Urban decay}} | |||
| ] © 1980 Charlotte Street Stencils ], New York. ] and ] both came to this spot during their political careers to make promises.]] | |||
| === Bargaining model === | |||
| ] is a process by which a ], or a part of a city, falls into a state of disrepair. It is characterized by ], property abandonment, high ], fragmented families, political ], ], and desolate and unfriendly urban landscapes. | |||
| The bargaining model views planning as the result of giving and take on the part of a number of interests who are all involved in the process. It argues that this bargaining is the best way to conduct planning within the bounds of legal and political institutions.<ref name="McDonald">McDonald, G. T. (1989). Rural Land Use Planning Decisions by Bargaining. Journal of Rural Studies, 5 (4), 325–335.</ref> The most interesting part of this theory of planning is that it makes public participation the central dynamic in the decision-making process. Decisions are made first and foremost by the public, and the planner plays a more minor role.<ref name="Lane"/> | |||
| === Communicative approach === | |||
| Urban decay was associated with Western cities, especially ] and parts of ] during the ] and ]. During this time period major changes in global economies, ], and government policies created conditions that fostered urban decay<ref>'''' By Hans Skifter Andersen. ISBN 0754633055. 2003.</ref>. | |||
| {{Main|Communicative planning}} | |||
| The communicative approach to planning is perhaps the most difficult to explain. It focuses on using communication to help different interests in the process to understand each other. The idea is that each individual will approach a conversation with his or her own subjective experience in mind and that from that conversation shared goals and possibilities will emerge. Again, participation plays a central role in this model. The model seeks to include a broad range of voice to enhance the debate and negotiation that is supposed to form the core of actual plan making. In this model, participation is actually fundamental to the planning process happening. Without the involvement of concerned interests, there is no planning.<ref name="Lane"/> Looking at each of these models it becomes clear that participation is not only shaped by the public in a given area or by the attitude of the planning organization or planners that work for it. In fact, public participation is largely influenced by how planning is defined, how planning problems are defined, the kinds of knowledge that planners choose to employ and how the planning context is set.<ref name="Lane"/> Though some might argue that is too difficult to involve the public through transactive, advocacy, bargaining and communicative models because ] is some ways more technical than other fields, it is important to note that transportation is perhaps unique among planning fields in that its systems depend on the interaction of a number of individuals and organizations.<ref name="Wachs 2004">Wachs, M. (2004). Reflections on the planning process. In S. Hansen, & G. Guliano (Eds.), The Geography of Urban Transportation (3rd Edition ed., pp. 141–161). The Guilford Press.</ref> | |||
| == Process == | |||
| The effects of urban decay run counter to the development patterns found in most cities in ] and countries outside of ], where ]s are usually located on the outskirts of major metropolitan areas while the ] and ] retain high ] values and a steady or increasing population. In contrast, North American cities often experienced an outflux of population to city ] or ], as in the case of ].<ref name="crabgrass">'''' by Professor Kenneth T Jackson (1987)</ref>. | |||
| ] may sometimes cause communities to consider redeveloping and urban planning.]] | |||
| === Changes to the planning process === | |||
| There is no single cause of urban decay, though it may be triggered by a combination of interrelated factors, including urban planning decisions, the development of ]<ref name="power">'']: Robert Moses and the Fall of New York'' by ]. Page 522.<blockquote>The construction of the ], laying a concrete slab on top of lively, bustling Third Avenue, buried the avenue in shadow, and when the parkway was completed, the avenue was cast forever into darkness and gloom, and its bustle and life were forever gone.</blockquote></ref>, ], ]<ref> by Walter Thabit. ISBN 0814782671. Page 42.</ref>, immigration restrictions<ref name="comeback"> By Paul S. Grogan, Tony Proscio. ISBN 0813339529. Published 2002. Page 139-145.<blockquote>"The 1965 law brought an end to the lengthy and destructive -at least for cities- period of tightly restricted immigration a spell born of the ] and ] of the 1920s." Page 140</blockquote></ref> and ]. | |||
| ] over past decades have witnessed the metamorphosis of the role of the urban planner in the planning process. More citizens calling for ] planning & development processes have played a huge role in allowing the ] to make important decisions as part of the planning process. ] and ] are now very involved in planning from the grassroots level.<ref>Forester John. "Planning in the Face of Conflict", 1987, {{ISBN|0-415-27173-8}}, Routledge, New York.</ref> The term advocacy planning was coined by ] in his influential 1965 paper, "Advocacy and Pluralism in Planning" which acknowledged the political nature of planning and urged planners to acknowledge that their actions are not value-neutral and encouraged minority and underrepresented voices to be part of planning decisions.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.plannersnetwork.org/publications/2007_spring/angotti.htm |title=Advocacy and Community Planning: Past, Present, and Future |publisher=Planners Network |access-date=2014-08-11}}</ref> ] argued that planners had a political role to play and had to bend some truth to power if their plans were to be implemented.<ref>{{cite book|last=Benveniste|first=Guy|title=Mastering the Politics of Planning|year=1994|publisher=Jossey-Bass|location=San Francisco}}</ref> | |||
| ===Reconstruction and renewal=== | |||
| {{main|Urban Renewal}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Areas devastated by war or invasion represent a unique challenge to urban planners: the area of development is not one for simple modification, nor is it a "]". Buildings, roads, services and basic infrastructure like power, water and sewerage are often severely compromised and need to be evaluated to determine what, if anything, can be salvaged for re-incorporation. There is also the problem of population; more often than not, people are also still living in these areas, displaced but not removed, and their issues need to be addressed. Historic areas and religious or social centers also need to be preserved and re-integrated into the new city plan. A prime example of this is the capital city of ], ], which after decades of civil war and occupation has regions that have literally been reduced to rubble. Despite this, the indigenous population continues to live in the area, constructing makeshift homes and shops out of whatever can be salvaged. Any reconstruction plan proposed, such as ]'s ], needs to be sensitive to the needs of this community and its existing culture, businesses and needs. | |||
| ] have also played huge roles in development, particularly by planning projects. Many recent developments were results of large and small-scale developers who purchased land, designed the district and constructed the development from scratch. The ], for example, was largely an initiative pushed by private developers to redevelop the waterfront into a high-end residential and commercial district. | |||
| <!-- Unsourced image removed: ], designed by ] ] for central ].]] --> | |||
| Urban Reconstruction Development plans must also work with government agencies as well as private interests to develop workable designs. | |||
| Recent theories of urban planning, espoused, for example by ] see the city as an ] that grows according to process similar to those of ]. They say that urban planning should thus take its cues from such natural processes.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://zeta.math.utsa.edu/~yxk833/lifeandthegeometry.pdf |title="Life and the geometry of the environment", Nikos Salingaros, November 2010 |access-date=2014-08-11 |archive-date=9 October 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181009092225/http://zeta.math.utsa.edu/~yxk833/lifeandthegeometry.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> Such theories also advocate participation by inhabitants in the design of the urban environment, as opposed to simply leaving all development to large-scale construction firms.<ref>{{cite web| url = http://zeta.math.utsa.edu/~yxk833/P2PURBANISM.pdf| title = "P2P Urbanism", collection of articles by Nikos Salingaros and others| access-date = 26 November 2010| archive-date = 5 January 2017| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170105214519/http://zeta.math.utsa.edu/~yxk833/P2PURBANISM.pdf| url-status = dead}}</ref> | |||
| ===Transport=== | |||
| {{main|Transportation Planning}} | |||
| ]] | |||
| There is a direct, well-researched connection between the density of an urban environment, and the need to ] within it {{Fact|date=February 2007}}. Good quality transport is often followed by development. Development beyond a certain density can quickly overcrowd transport{{Fact|date=May 2007}}. | |||
| In the process of creating an urban plan or ], carrier-infill is one mechanism of spatial organization in which the city's figure and ground components are considered separately. The urban figure, namely buildings, is represented as total possible building volumes, which are left to be designed by architects in the following stages. The urban ground, namely in-between spaces and open areas, are designed to a higher level of detail. The carrier-infill approach is defined by an urban design performing as the carrying structure that creates the shape and scale of the spaces, including future building volumes that are then infilled by architects' designs. The contents of the carrier structure may include street pattern, ], open space, waterways, and other ]. The infill structure may contain ], ]s, quality guidelines, and ] based upon a ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Capeluto |first1=I.G. |last2=Shaviv |first2=E. |title=On the use of 'solar volume' for determining the urban fabric |journal=Solar Energy |date=2001 |volume=70 |issue=3 |pages=275–280 |doi=10.1016/S0038-092X(00)00088-8 |bibcode=2001SoEn...70..275C }}</ref><ref>Nelson, Nels O. , 2009, accessed 30 December 2010.</ref> Carrier-Infill urban design is differentiated from complete urban design, such as in the monumental axis of ], in which the urban design and architecture were created together. | |||
| Good planning attempts to place higher densities of jobs or residents near high-volume transportation. For example, some cities permit commerce and multi-story apartment buildings only within one block of train stations and four-lane boulevards, and accept single-family dwellings and parks further away{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. | |||
| In carrier-infill ] or urban planning, the negative space of the city, including landscape, open space, and infrastructure is designed in detail. The positive space, typically building a site for future construction, is only represented in unresolved volumes. The volumes are representative of the total possible building envelope, which can then be infilled by individual architects. | |||
| Densities can be measured in several ways{{Fact|date=May 2007}}. A common method, used is the ], using the floor area of buildings divided by the land area. Ratios below 1.5 could be considered low density, and plot ratios above five very high density. Most ] are below two, while most city centres are well above five. Walk-up apartments with basement garages can easily achieve a density of three. Skyscrapers easily achieve densities of thirty or more. | |||
| == See also == | |||
| City authorities may try to encourage lower densities to reduce infrastructure costs, though some observers note that low densities may not accommodate enough population to provide adequate demand or funding for that infrastructure. In the UK, recent years have seen a concerted effort to increase the density of residential development in order to better achieve sustainable development. Increasing development density has the advantage of making mass transport systems, district heating and other community facilities (schools, health centres, etc) more viable. However critics of this approach dub the densification of development as 'town cramming' and claim that it lowers quality of life and restricts market led choice{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=20em}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * Urban acupuncture | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| Problems can often occur at residential densities between about two and five{{Fact|date=May 2007}}. These densities can cause traffic jams for ], yet are too low to be commercially served by ]s or ] systems. The conventional solution is to use ]es, but these and light rail systems may fail where automobiles and excess road network capacity are both available, achieving less than 1% ridership{{Fact|date=May 2007}}. | |||
| '''Notes''' | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| <ref>{{cite journal |last1=Buchan |first1=Robert |title=Transformative Incrementalism: Planning for transformative change in local food systems. |journal=Progress in Planning |date=14 November 2019 |volume=134 |pages=100424 |doi=10.1016/j.progress.2018.07.002|s2cid=158726842 }}</ref> | |||
| '''Bibliography''' | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Allmendinger |first1=Phil |last2=Gunder |first2=Michael |title=Applying Lacanian Insight and a Dash of Derridean Deconstruction to Planning's 'Dark Side' |journal=Planning Theory |date=11 August 2016 |volume=4 |issue=1 |pages=87–112 |doi=10.1177/1473095205051444 |s2cid=145100234 }} | |||
| The ] claims that increasing road space is not an effective way of relieving traffic jams as ] invariably emerges to restore a socially-tolerable level of congestion. | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Bogo |first1=H. |last2=Gómez |first2=D.R. |last3=Reich |first3=S.L. |last4=Negri |first4=R.M. |last5=San Román |first5=E. |title=Traffic pollution in a downtown site of Buenos Aires City |journal=Atmospheric Environment |date=April 2001 |volume=35 |issue=10 |pages=1717–1727 |doi=10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00555-0 |bibcode=2001AtmEn..35.1717B }} | |||
| *{{cite book | author=Garvin, Alexander | title=The American City: What Works and What Doesn't | location=New York | publisher=McGraw Hill | year=2002 | isbn=978-0-07-137367-8}} (A standard text for many college and graduate courses in city planning in America) | |||
| Some theoreticians{{Fact|date=May 2007}} speculate that ] (PRT) might coax people from their automobiles, and yet effectively serve intermediate densities, but this has not been demonstrated. | |||
| * ], 1989, ''Myths from Mesopotamia: Creation, the Flood, Gilgamesh, and Others'', Oxford World's Classics, London, pp. 39–136 | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Gunder |first1=Michael |title=Passionate planning for the others' desire: an agonistic response to the dark side of planning |journal=Progress in Planning |date=October 2003 |volume=60 |issue=3 |pages=235–319 |doi=10.1016/S0305-9006(02)00115-0 }} | |||
| ====Addressing==== | |||
| * Hoch, Charles, Linda C. Dalton and Frank S. So, editors (2000). ''The Practice of Local Government Planning'', Intl City County Management Assn; 3rd edition. {{ISBN|0-87326-171-2}} (The "Green Book") | |||
| If ] is part of the plan, the risk that the | |||
| * {{Cite book | year=2013 | last1= James | first1= Paul | author-link1= Paul James (academic) | last2= Holden | first2=Meg | last3= Lewin | first3= Mary | last4= Neilson | first4= Lyndsay | last5= Oakley | first5= Christine | last6= Truter | first6= Art | last7= Wilmoth | first7= David | chapter= Managing Metropolises by Negotiating Mega-Urban Growth | title= Institutional and Social Innovation for Sustainable Urban Development | editor= Harald Mieg and Klaus Töpfer | chapter-url=https://www.academia.edu/7207756 | publisher= Routledge}} | |||
| numbering task will end up in the hands of non-professionals can be | |||
| * Kemp, Roger L. and Carl J. Stephani (2011). "Cities Going Green: A Handbook of Best Practices." McFarland and Co., Inc., Jefferson, NC, USA, and London, England, UK. {{ISBN|978-0-7864-5968-1}}. | |||
| reduced, saving citizens much lost time looking for addresses later. | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Oke |first1=T. R. |title=The energetic basis of the urban heat island |journal=Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society |date=January 1982 |volume=108 |issue=455 |pages=1–24 |doi=10.1002/qj.49710845502 |bibcode=1982QJRMS.108....1O |s2cid=120122894 }} | |||
| This is especially important for non ] areas with no city-wide | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Pløger |first1=John |title=Public Participation and the Art of Governance |journal=Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design |date=30 November 2016 |volume=28 |issue=2 |pages=219–241 |doi=10.1068/b2669 |s2cid=143996926 }} | |||
| addressing standard already in place. | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Roy |first1=Ananya |title=Post-Liberalism: On the Ethico-Politics of Planning |journal=Planning Theory |date=March 2008 |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=92–102 |doi=10.1177/1473095207087526 |s2cid=143458706 }} | |||
| * Santamouris, Matheos (2006). Environmental Design of Urban Buildings: An Integrated Approach. | |||
| ===Suburbanization=== | |||
| * Shrady, Nicholas, ''The Last Day: Wrath, Ruin & Reason in The Great Lisbon Earthquake of 1755'', Penguin, 2008, {{ISBN|978-0-14-311460-4}} | |||
| {{main|Suburbanization}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Tang |first1=Wing-Shing |title=Chinese Urban Planning at Fifty: An Assessment of the Planning Theory Literature |journal=Journal of Planning Literature |date=17 August 2016 |volume=14 |issue=3 |pages=347–366 |doi=10.1177/08854120022092700 |s2cid=154281106 }} | |||
| ], United States]] | |||
| * Tunnard, Christopher and Boris Pushkarev (1963). ''Man-Made America: Chaos or Control?: An Inquiry into Selected Problems of Design in the Urbanized Landscape'', ]: ] Press. (This book won the ], strictly America; a time capsule of photography and design approach.) | |||
| In some countries declining satisfaction with the urban environment is held to blame for continuing ] to smaller towns and rural areas (so-called ]). Successful urban planning supported ] can bring benefits to a much larger ] or ] and help to reduce both congestion along transport routes and the wastage of energy implied by excessive ]. Urban scholar N.J. Slabbert claims that the advent of the Internet has opened the way to "telecommunities" or populations of workers who will no longer commute physically, and that this will greatly revitalize small towns in the 21st century. <ref>Slabbert, N.J. "The Future of Urbanization: How Teletechnology is Shaping a New Urban Order", 2006, Harvard International Review, Cambridge, Mass.</ref> Yet, it is not completely without downsides toward "telecommunicating," such as lack of personal relationship/familiarity with the coworkers/supervisors if not the clients. This may lead to lower efficiency, less well coordination if not communication, and result in lower quality of products or services. | |||
| * Wheeler, Stephen (2004). "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", Routledge; 3rd edition. | |||
| * Yiftachel, Oren, 1995, "The Dark Side of Modernism: Planning as Control of an Ethnic Minority," in Sophie Watson and Katherine Gibson, eds., Postmodern Cities and Spaces (Oxford and Cambridge, MA: Blackwell), pp. 216–240. | |||
| ===Environmental factors=== | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Yiftachel |first1=Oren |title=Planning and Social Control: Exploring the Dark Side |journal=Journal of Planning Literature |date=6 November 2016 |volume=12 |issue=4 |pages=395–406 |doi=10.1177/088541229801200401 |s2cid=14859857 }} | |||
| {{main|Environmental planning}} | |||
| *{{cite journal |last1=Yiftachel |first1=Oren |title=Essay: Re-engaging Planning Theory? Towards 'South-Eastern' Perspectives |journal=Planning Theory |date=11 August 2016 |volume=5 |issue=3 |pages=211–22 |doi=10.1177/1473095206068627 |s2cid=145359885 }} | |||
| ] and conservation are of utmost importance to many planning systems across the world. Not only are the specific effects of development to be mitigated, but attempts are made to minimise the overall effect of development on the local and global environment. This is commonly done through the assessment of ]. In Europe this process is known as ]. | |||
| *, Doug Aberley Ph.D. MCIP, Winnipeg Inner City Research Alliance Summer Institute, June 2003 | |||
| *McConnell, Shean. ''Theories for Planning'', 1981, David & Charles, London. | |||
| ] seeks to unify the fields of ] and ], especially ], to achieve a harmonious environment for all living things. On a small scale, the ] theory has become popular, as it emphasizes a traditional 100-140 person scale for communities{{Fact|date=February 2007}}. | |||
| In most advanced urban or village planning models, local context is critical. In many, ] assumes a central role not only in ] but in the daily life of citizens. A series of related movements including ], ], ] and ] have put this in a ] as part of a focus on smaller systems of resource extraction, and waste disposal, ideally as part of ] which do such recycling automatically, just as nature does. The modern theory of ] emphasizes this as the primary difference between natural and ], and seeks ] for rationalizing a move back towards smaller village units. A common form of planning that leads to suburban sprawl is ]. | |||
| An urban planner is likely to use a number of Quantitative tools to forecast impacts of development on a variety of environmental concerns including ]s to predict air quality impacts of urban highways and ] models to predict ] effects of urban highways. As early as the 1960s, noise pollution was addressed in the design of urban highways as well as ]s.<ref></ref> The ] can be an important tool to the urban planner by identifying early in the planning process any geographic areas or parcels which have ] constraints. | |||
| ==Process== | |||
| ] | |||
| The traditional planning process focused on top-down processes where the ] created the plans. A planner is usually skilled in either surveying, engineering or architecture, bringing to the town planning process ideals based around these disciplines. They typically worked for national or local governments. {{Fact|date=November 2007}} | |||
| Changes to the planning process over past decades have witnessed the metamorphosis of the role of the urban planner in the planning process. Calls championing for more ] have played a huge role in allowing the ] to make important decisions as part of the planning process. ] and ] are now very involved in planning from the grassroots level.<ref>Forester John. "Planning in the Face of Conflict", 1987, ISBN 0-415-27173-8, Routledge, New York.</ref> | |||
| ]s too have played huge roles in influencing the way development occurs, particularly through project-based planning. Many recent developments were results of large and small-scale developers who purchased land, designed the district and constructed the development from scratch. The ], for example, was largely an initiative pushed by private developers who sought to redevelop the waterfront into a high-end residential and commercial district. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| * {{cite book | author=Garvin, Alexander | title=The American City: What Works and What Doesn't | location=New York | publisher=McGraw Hill | year=2002 | id=ISBN 0-07-137367-5}} (A standard text for many college and graduate courses in city planning in America) | |||
| * Hoch, Charles, Linda C. Dalton and Frank S. So, editors (2000). ''The Practice of Local Government Planning'', Intl City County Management Assn; 3rd edition. ISBN 0-87326-171-2 (The "Green Book") | |||
| *Tunnard, Christopher and Boris Pushkarev (1963). ''Man-Made America: Chaos or Control?: An Inquiry into Selected Problems of Design in the Urbanized Landscape'', ]: ] Press. (This book won the ], strictly America; a time capsule of photography and design approach.) | |||
| *Wheeler, Stephen (1998). "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", Routledge; 3rd edition. | |||
| == Further reading == | == Further reading == | ||
| * , Selected, Edited, and Provided with Headnotes by John W. Reps, Professor Emeritus, Cornell University. | |||
| * '']'', ], 1889 | |||
| * '' |
* ''City Planning According to Artistic Principles'', ], 1889 | ||
| * by Daniel Parolek of Opticos Design, Inc., 2012 | |||
| * '']'', ], 1901 | |||
| * Kemp, Roger L. and Carl J. Stephani (2011). "Cities Going Green: A Handbook of Best Practices." McFarland and Co., Inc., Jefferson, NC, USA, and London, England, UK. ({{ISBN|978-0-7864-5968-1}}). | |||
| * '']'', ], 1909 | |||
| * ''Tomorrow: A Peaceful Path to Real Reform'', ], 1898 | |||
| * ''The Improvement of Towns and Cities'', ], 1901 | |||
| * ''Town Planning in practice'', Raymond Unwin, 1909 | |||
| * '']'', ], 1911 | * '']'', ], 1911 | ||
| * '' |
* ''Cities in Evolution'', ], 1915 | ||
| * '' |
* ''The Image of the City'', ], 1960 | ||
| * '' |
* ''The Concise Townscape'', ], 1961 | ||
| * '']'', ], 1961 | * '']'', ], 1961 | ||
| * '']'', ], 1961 | * '']'', ], 1961 | ||
| * ''The City is the Frontier'', Charles Abrams, Harper & Row Publishing, New York, 1965. | |||
| * '']'', ], ] and ], 1977 | |||
| * '']'', ], Sara Ishikawa and ], 1977 | |||
| *, Selected, Edited, and Provided with Headnotes by John W. Reps, Professor Emeritus, Cornell University. | |||
| * , , American Planning Association, 1994. {{ISBN|978-0-918286-91-8}} | |||
| *, , Island Press, 2001. ISBN 1-55963-853-2 | |||
| * ''Planning the Twentieth-Century American City'', Christopher Silver and Mary Corbin Sies (Eds.), ], 1996 | |||
| *''The City is the Frontier'', Charles Abrams, Harper & Row Publishing, New York, 1965. | |||
| * "The City Shaped: Urban Patterns and Meanings Through History", ], 2nd Edition, Thames and Hudson Ltd, 1999 {{ISBN|978-0-500-28099-7}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * ''The American City: A Social and Cultural History'', Daniel J. Monti, Jr., Oxford, England and Malden, Massachusetts: ], 1999. 391 pp. {{ISBN|978-1-55786-918-0}}. | |||
| <!-- ==============================({{NoMoreLinks}})============================== --> | |||
| * , {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140615033738/http://www.urban.uiuc.edu/faculty/hopkins/ |date=15 June 2014 }}, Island Press, 2001. {{ISBN|1-55963-853-2}} | |||
| <!-- DO NOT ADD MORE LINKS TO THIS ARTICLE. WIKIPEDIA IS NOT A COLLECTION OF LINKS --> | |||
| * '''', ] and James DeFilippis, Oxford, England and Malden, Massachusetts: ], 2016. | |||
| <!-- If you think that your link might be useful, instead of placing it here, put --> | |||
| * Taylor, Nigel, (2007), ''Urban Planning Theory since 1945'', London, Sage. | |||
| <!-- it on this article's discussion page first. Links that have not been verified --> | |||
| * , by Aseem Inam (published by Routledge USA, 2005). | |||
| <!-- WILL BE DELETED --> | |||
| <!-- ============================================================================= --> | |||
| * {{Dmoz|Science/Social_Sciences/Urban_and_Regional_Planning/|Urban and Regional Planning }} | |||
| <!-- Refer to http://en.wikipedia.org/Talk:Urban_planning#External_links. I started that discussion on 6th January 2008 and now include the following links --> | |||
| * — A glossary of urban terms that have served to describe recent urban phenomena | |||
| * — Community for Urban Planners | |||
| * — Network for Urban Planning, Design and Development | |||
| * — News website for planning by planners | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Prone to spam|date=April 2015}} | |||
| {{Land-use planning|selected=branches}} | |||
| {{Environmental social science}} | |||
| {{Developments}} | {{Developments}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:49, 28 November 2024
Body of knowledge of urban planning Further information: History of urban planning and Technical aspects of urban planning
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

Planning theory is the body of scientific concepts, definitions, behavioral relationships, and assumptions that define the body of knowledge of urban planning. There is no one unified planning theory but various. Whittemore identifies nine procedural theories that dominated the field between 1959 and 1983: the Rational-Comprehensive approach, the Incremental approach, the Transformative Incremental (TI) approach, the Transactive approach, the Communicative approach, the Advocacy approach, the Equity approach, the Radical approach, and the Humanist or Phenomenological approach.
Background
Urban planning can include urban renewal, by adapting urban planning methods to existing cities suffering from decline. Alternatively, it can concern the massive challenges associated with urban growth, particularly in the Global South. All in all, urban planning exists in various forms and addresses many different issues. The modern origins of urban planning lie in the movement for urban reform that arose as a reaction against the disorder of the industrial city in the mid-19th century. Many of the early influencers were inspired by anarchism, which was popular in the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. The new imagined urban form was meant to go hand-in-hand with a new society, based upon voluntary co-operation within self-governing communities.
In the late 20th century, the term sustainable development has come to represent an ideal outcome in the sum of all planning goals. Sustainable architecture involves renewable materials and energy sources and is increasing in importance as an environmentally friendly solution
Blueprint planning
Since at least the Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment, urban planning had generally been assumed to be the physical planning and design of human communities. Therefore, it was seen as related to architecture and civil engineering, and thereby to be carried out by such experts. This kind of planning was physicalist and design-orientated, and involved the production of masterplans and blueprints which would show precisely what the 'end-state' of land use should be, similar to architectural and engineering plans. Similarly, the theory of urban planning was mainly interested in visionary planning and design which would demonstrate how the ideal city should be organised spatially.
Sanitary movement
Although it can be seen as an extension of the sort of civic pragmatism seen in Oglethorpe's plan for Savannah or William Penn's plan for Philadelphia, the roots of the rational planning movement lie in Britain's Sanitary movement (1800–1890). During this period, advocates such as Charles Booth argued for central organized, top-down solutions to the problems of industrializing cities. In keeping with the rising power of industry, the source of the planning authority in the Sanitary movement included both traditional governmental offices and private development corporations. In London and its surrounding suburbs, cooperation between these two entities created a network of new communities clustered around the expanding rail system.
Garden city movement

The Garden city movement was founded by Ebenezer Howard (1850-1928). His ideas were expressed in the book Garden Cities of To-morrow (1898). His influences included Benjamin Walter Richardson, who had published a pamphlet in 1876 calling for low population density, good housing, wide roads, an underground railway and for open space; Thomas Spence who had supported common ownership of land and the sharing of the rents it would produce; Edward Gibbon Wakefield who had pioneered the idea of colonizing planned communities to house the poor in Adelaide (including starting new cities separated by green belts at a certain point); James Silk Buckingham who had designed a model town with a central place, radial avenues and industry in the periphery; as well as Alfred Marshall, Peter Kropotkin and the back-to-the-land movement, which had all called for the moving of masses to the countryside.
Howards' vision was to combine the best of both the countryside and the city in a new environment called Town-Country. To make this happen, a group of individuals would establish a limited-dividend company to buy cheap agricultural land, which would then be developed with investment from manufacturers and housing for the workers. No more than 32,000 people would be housed in a settlement, spread over 1,000 acres. Around it would be a permanent green belt of 5,000 acres, with farms and institutions (such as mental institutions) which would benefit from the location. After reaching the limit, a new settlement would be started, connected by an inter-city rail, with the polycentric settlements together forming the "Social City". The lands of the settlements would be jointly owned by the inhabitants, who would use rents received from it to pay off the mortgage necessary to buy the land and then invest the rest in the community through social security. Actual garden cities were built by Howard in Letchworth, Brentham Garden Suburb, and Welwyn Garden City. The movement would also inspire the later New towns movement.
Linear city

Arturo Soria y Mata's idea of the Linear city (1882) replaced the traditional idea of the city as a centre and a periphery with the idea of constructing linear sections of infrastructure - roads, railways, gas, water, etc.- along an optimal line and then attaching the other components of the city along the length of this line. As compared to the concentric diagrams of Ebenezer Howard and other in the same period, Soria's linear city creates the infrastructure for a controlled process of expansion that joins one growing city to the next in a rational way, instead of letting them both sprawl. The linear city was meant to ‘ruralize the city and urbanize the countryside’, and to be universally applicable as a ring around existing cities, as a strip connecting two cities, or as an entirely new linear town across an unurbanized region. The idea was later taken up by Nikolay Alexandrovich Milyutin in the planning circles of the 1920s Soviet Union. The Ciudad Lineal was a practical application of the concept.
Regional planning movement
Patrick Geddes (1864-1932) was the founder of regional planning. His main influences were the geographers Élisée Reclus and Paul Vidal de La Blache, as well as the sociologist Pierre Guillaume Frédéric le Play. From these he received the idea of the natural region. According to Geddes, planning must start by surveying such a region by crafting a "Valley Section" which shows the general slope from mountains to the sea that can be identified across scale and place in the world, with the natural environment and the cultural environments produced by it included. This was encapsulated in the motto "Survey before Plan". He saw cities as being changed by technology into more regional settlements, for which he coined the term conurbation. Similar to the garden city movement, he also believed in adding green areas to these urban regions. The Regional Planning Association of America advanced his ideas, coming up with the 'regional city' which would have a variety of urban communities across a green landscape of farms, parks and wilderness with the help of telecommunication and the automobile. This had major influence on the County of London Plan, 1944.
City Beautiful movement

The City Beautiful movement was inspired by 19th century European capital cities such as Georges-Eugène Haussmann's Paris or the Vienna Ring Road. An influential figure was Daniel Burnham (1846-1912), who was the chief of construction of the World's Columbian Exposition in 1893. Urban problems such as the 1886 Haymarket affair in Chicago had created a perceived need to reform the morality of the city among some of the elites. Burnham's greatest achievement was the Chicago plan of 1909. His aim was "to restore to the city a lost visual and aesthetic harmony, thereby creating the physical prerequisite for the emergence of a harmonious social order", essentially creating social reform through new slum clearance and creating public space, which also endeared it the support of the Progressivist movement. This was also believed to be economically advantageous by drawing in tourists and wealthy migrants. Because of this it has been referred to as "trickle-down urban development" and as "centrocentrist" for focusing only on the core of the city. Other major cities planned according to the movement principles included British colonial capitals in New Delhi, Harare, Lusaka Nairobi and Kampala, as well as that of Canberra in Australia, and Albert Speer's plan for the Nazi capital Germania.
Towers in the park

Le Corbusier (1887–1965) pioneered a new urban form called towers in the park. His approach was based on defining the house as 'a machine to live in'. The Plan Voisin he devised for Paris, which was never fulfilled, would have involved the demolition of much of historic Paris in favour of 18 uniform 700-foot tower blocks. Ville Contemporaine and the Ville Radieuse formulated his basic principles, including decongestion of the city by increased density and open space by building taller on a smaller footprint. Wide avenues should also be built to the city centre by demolishing old structures, which was criticized for lack of environmental awareness. His generic ethos of planning was based on the rule of experts who would "work out their plans in total freedom from partisan pressures and special interests" and that "once their plans are formulated, they must be implemented without opposition". His influence on the Soviet Union helped inspire the 'urbanists' who wanted to build planned cities full of massive apartment blocks in Soviet countryside. The only city which he ever actually helped plan was Chandigarh in India. Brasília, planned by Oscar Niemeyer, also was heavily influenced by his thought. Both cities suffered from the issue of unplanned settlements growing outside them.
Decentralised planning

In the United States, Frank Lloyd Wright similarly identified vehicular mobility as a principal planning metric. Car-based suburbs had already been developed in the Country Club District in 1907-1908 (including later the world's first car-based shopping centre of Country Club Plaza), as well as in Beverly Hills in 1914 and Palos Verdes Estates in 1923. Wright began to idealise this vision in his Broadacre City starting in 1924, with similarities to the garden city and regional planning movements. The fundamental idea was for technology to liberate individuals. In his Usonian vision, he described the city as
"spacious, well-landscaped highways, grade crossings eliminated by a new kind of integrated by-passing or over- or under-passing all traffic in cultivated or living areas … Giant roads, themselves great architecture, pass public service stations . . . passing by farm units, roadside markets, garden schools, dwelling places, each on its acres of individually adorned and cultivated ground".
This was justified as a democratic ideal, as "“Democracy is the ideal of reintegrated decentralization … many free units developing strength as they learn by function and grow together in spacious mutual freedom.” This vision was however criticized by Herbert Muschamp as being contradictory in its call for individualism while relying on the master-architect to design it all.
After World War II, suburbs similar to Broadacre City spread throughout the US, but without the social or economic aspects of his ideas. A notable example was that of Levittown, built 1947 to 1951. The suburban design was criticized for their lack of form by Lewis Mumford as it lacked clear boundaries, and by Ian Nairn because "Each building is treated in isolation, nothing binds it to the next one".
In the Soviet Union too, the so-called deurbanists (such as Moisei Ginzburg and Mikhail Okhitovich) advocated for the use of electricity and new transportation technologies (especially the car) to disperse the population from the cities to the countryside, with the ultimate aim of a "townless, fully decentralized, and evenly populated country". However, in 1931 the Communist Party ruled such views as forbidden.
Opposition to blueprint planning
Throughout both the United States and Europe, the rational planning movement declined in the latter half of the 20th century. Key events in the United States include the demolition of the Pruitt-Igoe housing project in St. Louis and the national backlash against urban renewal projects, particularly urban expressway projects. An influential critic of such planning was Jane Jacobs, who wrote The Death and Life of Great American Cities in 1961, claimed to be "one of the most influential books in the short history of city planning". She attacked the garden city movement because its "prescription for saving the city was to do the city in" and because it "conceived of planning also as essentially paternalistic, if not authoritarian". The Corbusians on the other hand were claimed to be egoistic. In contrast, she defended the dense traditional inner-city neighborhoods like Brooklyn Heights or North Beach, San Francisco, and argued that an urban neighbourhood required about 200-300 people per acre, as well as a high net ground coverage at the expense of open space. She also advocated for a diversity of land uses and building types, with the aim of having a constant churn of people throughout the neighbourhood across the times of the day. This essentially meant defending urban environments as they were before modern planning had aimed to start changing them. As she believed that such environments were essentially self-organizing, her approach was effectively one of laissez-faire, and has been criticized for not being able to guarantee "the development of good neighbourhoods".
The most radical opposition to blueprint planning was declared in 1969 in a manifesto on the New Society, with the words that:
The whole concept of planning (the town-and-country kind at least) has gone cockeyed … Somehow, everything must be watched; nothing must be allowed simply to “happen.” No house can be allowed to be commonplace in the way that things just are commonplace: each project must be weighed, and planned, and approved, and only then built, and only after that discovered to be commonplace after all.
Another form of opposition came from the advocacy planning movement, opposes to traditional top-down and technical planning.
Modernist planning
Cybernetics and modernism inspired the related theories of rational process and systems approaches to urban planning in the 1960s. They were imported into planning from other disciplines. The systems approach was a reaction to the issues associated with the traditional view of planning. It did not understand the social and economic sides of cities, the complexity and interconnectedness of urban life, as well as lacking in flexibility. The 'quantitative revolution' of the 1960s also created a drive for more scientific and precise thinking, while the rise of ecology made the approach more natural.
Systems theory
Systems theory is based on the conception of phenomena as 'systems', which are themselves coherent entities composed of interconnected and interdependent parts. A city can in this way be conceptualised as a system with interrelated parts of different land uses, connected by transport and other communications. The aim of urban planning thereby becomes that of planning and controlling the system. Similar ideas had been put forward by Geddes, who had seen cities and their regions as analogous to organisms, though they did not receive much attention while planning was dominated by architects.
The idea of the city as a system meant that it became critical for planners to understand how cities functioned. It also meant that a change to one part in a city would have effects on others parts as well. There were also doubts raised about the goal of producing detailed blueprints of how cities should look like in the end, instead suggesting the need for more flexible plans with trajectories instead of fixed futures. Planning should also be an ongoing process of monitoring and taking action in the city, rather than just producing the blueprint at one time. The systems approach also necessitated taking into account the economic and social aspects of cities, beyond just the aesthetic and physical ones.
Rational process approach
The focus on the procedural aspect of planning had already been pioneered by Geddes in his Survey-Analysis-Plan approach. However, this approach had several shortfalls. It did not consider the reasons for doing a survey in the first place. It also suggested that there should be simply a single plan to be considered. Finally, it did not take into account the implementation stage of the plan. There should also be further action in monitoring the outcomes of the plan after that. The rational process, in contrast, identified five different stages: (1) the definition of problems and aims; (2) the identification of alternatives; (3) the evaluation of alternatives; (4) implementation: (5) monitoring. This new approach represented a rejection of blueprint planning.
Incrementalism
Beginning in the late 1950s and early 1960s, critiques of the rational paradigm began to emerge and formed into several different schools of planning thought. The first of these schools is Lindblom's incrementalism. Lindblom describes planning as "muddling through" and thought that practical planning required decisions to be made incrementally. This incremental approach meant choosing from small number of policy approaches that can only have a small number consequences and are firmly bounded by reality, constantly adjusting the objectives of the planning process and using multiple analyses and evaluations.
Mixed scanning model
The mixed scanning model, developed by Etzioni, takes a similar approach to Lindblom. Etzioni (1968) suggested that organizations plan on two different levels: the tactical and the strategic. He posited that organizations could accomplish this by essentially scanning the environment on multiple levels and then choose different strategies and tactics to address what they found there. While Lindblom's approach only operated on the functional level Etzioni argued, the mixed scanning approach would allow planning organizations to work on both the functional and more big-picture oriented levels.
Political planning
In the 1960s, a view emerged of planning as an inherently normative and political activity. Advocates of this approach included Norman Dennis, Martin Meyerson, Edward C. Banfield, Paul Davidoff, and Norton E. Long, the latter remarking that:
Plans are policies and policies, in a democracy at any rate, spell politics. The question is not whether planning will reflect politics but whose politics it will reflect. What values and whose values will planners seek to implement? . . . No longer can the planner take refuge in the neutrality of the objectivity of the personally uninvolved scientist.
The choices between alternative end points in planning was a key issue which was seen as political.
Participatory planning
Main article: Participatory planning
Participatory planning is an urban planning paradigm that emphasizes involving the entire community in the strategic and management processes of urban planning; or, community-level planning processes, urban or rural. It is often considered as part of community development. Participatory planning aims to harmonize views among all of its participants as well as prevent conflict between opposing parties. In addition, marginalized groups have an opportunity to participate in the planning process.
Patrick Geddes had first advocated for the "real and active participation" of citizens when working in the British Raj, arguing against the "Dangers of Municipal Government from above" which would cause "detachment from public and popular feeling, and consequently, before long, from public and popular needs and usefulness". Further on, self-build was researched by Raymond Unwin in the 1930s in his Town Planning in Practice. The Italian anarchist architect Giancarlo De Carlo then argued in 1948 that "“The housing problem cannot be solved from above. It is a problem of the people, and it will not be solved, or even boldly faced, except by the concrete will and action of the people themselves", and that planning should exist "as the manifestation of communal collaboration". Through the Architectural Association School of Architecture, his ideas caught John Turner, who started working in Peru with Eduardo Neira. He would go on working in Lima from the mid-'50s to the mid-'60s. There he found that the barrios were not slums, but were rather highly organised and well-functioning. As a result, he came to the conclusion that:
"When dwellers control the major decisions and are free to make their own contributions in the design, construction or management of their housing, both this process and the environment produced stimulate individual and social well-being. When people have no control over nor responsibility for key decisions in the housing process, on the other hand, dwelling environments may instead become a barrier to personal fulfillment and a burden on the economy."
The role of the government was to provide a framework within which people would be able to work freely, for example by providing them the necessary resources, infrastructure and land. Self-build was later again taken up by Christopher Alexander, who led a project called People Rebuild Berkeley in 1972, with the aim to create "self-sustaining, self-governing" communities, though it ended up being closer to traditional planning.
Synoptic planning
After the "fall" of blueprint planning in the late 1950s and early 1960s, the synoptic model began to emerge as a dominant force in planning. Lane (2005) describes synoptic planning as having four central elements:
- "(1) an enhanced emphasis on the specification of goals and targets; (2) an emphasis on quantitative analysis and predication of the environment; (3) a concern to identify and evaluate alternative policy options; and (4) the evaluation of means against ends (page 289)."
Public participation was first introduced into this model and it was generally integrated into the system process described above. However, the problem was that the idea of a single public interest still dominated attitudes, effectively devaluing the importance of participation because it suggests the idea that the public interest is relatively easy to find and only requires the most minimal form of participation.
Transactive planning
Transactive planning was a radical break from previous models. Instead of considering public participation as a method that would be used in addition to the normal training planning process, participation was a central goal. For the first time, the public was encouraged to take on an active role in the policy-setting process, while the planner took on the role of a distributor of information and a feedback source. Transactive planning focuses on interpersonal dialogue that develops ideas, which will be turned into action. One of the central goals is mutual learning where the planner gets more information on the community and citizens to become more educated about planning issues.
Advocacy planning
Formulated in the 1960s by lawyer and planning scholar Paul Davidoff, the advocacy planning model takes the perspective that there are large inequalities in the political system and in the bargaining process between groups that result in large numbers of people unorganized and unrepresented in the process. It concerns itself with ensuring that all people are equally represented in the planning process by advocating for the interests of the underprivileged and seeking social change. Again, public participation is a central tenet of this model. A plurality of public interests is assumed, and the role of the planner is essentially the one as a facilitator who either advocates directly for underrepresented groups directly or encourages them to become part of the process.
Radical planning
Radical planning is a stream of urban planning which seeks to manage development in an equitable and community-based manner. The seminal text to the radical planning movement is Foundations for a Radical Concept in Planning (1973), by Stephen Grabow and Allen Heskin. Grabow and Heskin provided a critique of planning as elitist, centralizing and change-resistant, and proposed a new paradigm based upon systems change, decentralization, communal society, facilitation of human development and consideration of ecology. Grabow and Heskin were joined by Head of Department of Town Planning from the Polytechnic of the South Bank Shean McConnell, and his 1981 work Theories for Planning.
In 1987 John Friedmann entered the fray with Planning in the Public Domain: From Knowledge to Action, promoting a radical planning model based on "decolonization", "democratization", "self-empowerment" and "reaching out". Friedmann described this model as an "Agropolitan development" paradigm, emphasizing the re-localization of primary production and manufacture. In "Toward a Non-Euclidian Mode of Planning" (1993) Friedmann further promoted the urgency of decentralizing planning, advocating a planning paradigm that is normative, innovative, political, transactive and based on a social learning approach to knowledge and policy.
Bargaining model
The bargaining model views planning as the result of giving and take on the part of a number of interests who are all involved in the process. It argues that this bargaining is the best way to conduct planning within the bounds of legal and political institutions. The most interesting part of this theory of planning is that it makes public participation the central dynamic in the decision-making process. Decisions are made first and foremost by the public, and the planner plays a more minor role.
Communicative approach
Main article: Communicative planningThe communicative approach to planning is perhaps the most difficult to explain. It focuses on using communication to help different interests in the process to understand each other. The idea is that each individual will approach a conversation with his or her own subjective experience in mind and that from that conversation shared goals and possibilities will emerge. Again, participation plays a central role in this model. The model seeks to include a broad range of voice to enhance the debate and negotiation that is supposed to form the core of actual plan making. In this model, participation is actually fundamental to the planning process happening. Without the involvement of concerned interests, there is no planning. Looking at each of these models it becomes clear that participation is not only shaped by the public in a given area or by the attitude of the planning organization or planners that work for it. In fact, public participation is largely influenced by how planning is defined, how planning problems are defined, the kinds of knowledge that planners choose to employ and how the planning context is set. Though some might argue that is too difficult to involve the public through transactive, advocacy, bargaining and communicative models because transportation is some ways more technical than other fields, it is important to note that transportation is perhaps unique among planning fields in that its systems depend on the interaction of a number of individuals and organizations.
Process

Changes to the planning process
Strategic Urban Planning over past decades have witnessed the metamorphosis of the role of the urban planner in the planning process. More citizens calling for democratic planning & development processes have played a huge role in allowing the public to make important decisions as part of the planning process. Community organizers and social workers are now very involved in planning from the grassroots level. The term advocacy planning was coined by Paul Davidoff in his influential 1965 paper, "Advocacy and Pluralism in Planning" which acknowledged the political nature of planning and urged planners to acknowledge that their actions are not value-neutral and encouraged minority and underrepresented voices to be part of planning decisions. Benveniste argued that planners had a political role to play and had to bend some truth to power if their plans were to be implemented.
Developers have also played huge roles in development, particularly by planning projects. Many recent developments were results of large and small-scale developers who purchased land, designed the district and constructed the development from scratch. The Melbourne Docklands, for example, was largely an initiative pushed by private developers to redevelop the waterfront into a high-end residential and commercial district.
Recent theories of urban planning, espoused, for example by Salingaros see the city as an adaptive system that grows according to process similar to those of plants. They say that urban planning should thus take its cues from such natural processes. Such theories also advocate participation by inhabitants in the design of the urban environment, as opposed to simply leaving all development to large-scale construction firms.
In the process of creating an urban plan or urban design, carrier-infill is one mechanism of spatial organization in which the city's figure and ground components are considered separately. The urban figure, namely buildings, is represented as total possible building volumes, which are left to be designed by architects in the following stages. The urban ground, namely in-between spaces and open areas, are designed to a higher level of detail. The carrier-infill approach is defined by an urban design performing as the carrying structure that creates the shape and scale of the spaces, including future building volumes that are then infilled by architects' designs. The contents of the carrier structure may include street pattern, landscape architecture, open space, waterways, and other infrastructure. The infill structure may contain zoning, building codes, quality guidelines, and Solar Access based upon a solar envelope. Carrier-Infill urban design is differentiated from complete urban design, such as in the monumental axis of Brasília, in which the urban design and architecture were created together.
In carrier-infill urban design or urban planning, the negative space of the city, including landscape, open space, and infrastructure is designed in detail. The positive space, typically building a site for future construction, is only represented in unresolved volumes. The volumes are representative of the total possible building envelope, which can then be infilled by individual architects.
See also
- Index of urban planning articles
- Index of urban studies articles
- List of planned cities
- List of planning journals
- List of urban planners
- List of urban theorists
- MONU – magazine on urbanism
- Planetizen
- Transition Towns (network)
- Transportation demand management
- Urban acupuncture
- Urban vitality
References
Notes
- "How Planners Use Planning Theory". Retrieved 24 April 2015.
- Whittemore, Andrew H. (1 March 2015). "Practitioners Theorize, Too: Reaffirming Planning Theory in a Survey of Practitioners' Theories". Journal of Planning Education and Research. 35 (1): 76–85. doi:10.1177/0739456X14563144. ISSN 0739-456X.
- James, Paul; Holden, Meg; Lewin, Mary; Neilson, Lyndsay; Oakley, Christine; Truter, Art; Wilmoth, David (2013). "Managing Metropolises by Negotiating Mega-Urban Growth". In Mieg, Harald; Töpfer, Klaus (eds.). Institutional and Social Innovation for Sustainable Urban Development. Routledge.
- Van Assche, Kristof; Beunen, Raoul; Duineveld, Martijn; de Jong, Harro (18 September 2012). "Co-evolutions of planning and design: Risks and benefits of design perspectives in planning systems". Planning Theory. 12 (2): 177–198. doi:10.1177/1473095212456771. S2CID 109970261.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Wheeler, Stephen (2004). "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", Routledge; 3rd edition.
- "Why Sustainable Architecture Is Becoming more Important | CRL". c-r-l.com. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. pp. 4–5, 13. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Hall, Peter (2008). The Cities of Tomorrow. Publishing: Blackwell. pp. 13–47, 87–141. ISBN 978-0-631-23252-0.
- Hall, Peter (2008). The Cities of Tomorrow. Publishing: Blackwell. pp. 48–86. ISBN 978-0-631-23252-0.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 90. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 91. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 92–96. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 97. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 98. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 255. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- "Arturo Soria y su proyecto Ciudad Lineal". Archived from the original on 4 June 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- Caves, R. W. (2004). Encyclopedia of the City. Routledge. pp. 621. ISBN 9780415252256.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 150. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 152. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 154. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 154–155. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 155. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 161. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 165. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 196. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 203. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 204. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 204. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 207. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 210–211. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 212. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 218. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 223. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 229. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 241. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 244. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 245. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 248–249. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 251. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 340–341. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 342. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 344–345. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 346. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 351. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 353–354. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Allmendinger, Philip (2002). Planning Futures: New Directions for Planning Theory. Routledge. pp. 20–25.
- Black, William R. Transportation: A Geographical Analysis. The Guilford1 Press. p. 29.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 282. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 283. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 284. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 312. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 315. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 60. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 64. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 65. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 61. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 63. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 66. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- ^ Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 67. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Lindblom, Charles E. (n.d.). "The Science of 'Muddling Through'". Public Administration Review. 19 (2): 79–88. doi:10.2307/973677. JSTOR 973677.
- Etzioni, A. (1968). The active society: a theory of societal and political processes. New York: Free Press.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 77. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. p. 83. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Taylor, Nigel (11 June 1998). Urban Planning Theory since 1945. SAGE. pp. 83–84. ISBN 978-1-84920-677-8.
- Lefevre, Pierre; Kolsteren, Patrick; De Wael, Marie-Paule; Byekwaso, Francis; Beghin, Ivan (December 2000). "Comprehensive Participatory Planning and Evaluation" (PDF). Antwerp, Belgium: IFAD. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- McTague, Colleen; Jakubowski, Susan (October 2013). "Marching to the beat of a silent drum: Wasted consensus-building and failed neighborhood participatory planning". Applied Geography. 44: 182–191. Bibcode:2013AppGe..44..182M. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.07.019.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 299. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 300. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 301. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 302. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 304. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 305–306. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- Hall, Peter (17 April 2014). Cities of Tomorrow: An Intellectual History of Urban Planning and Design Since 1880. John Wiley & Sons. p. 311. ISBN 978-1-118-45651-4.
- ^ Lane, Marcus B. (November 2005). "Public Participation in Planning: an intellectual history". Australian Geographer. 36 (3): 283–299. Bibcode:2005AuGeo..36..283L. doi:10.1080/00049180500325694. S2CID 18008094.
- Friedman, J. (1973). Retracking America: A Theory of Transactive Planning. Garden City, NJ: Anchor Press/Doubleday.
- Davidoff, P. (1965). Advocacy and Pluralism in Planning. Journal of the American Institute of Planners, 31 (4), 331–338.
- Mazziotti, D. F. (1982). The underlying assumptions of advocacy planning: pluralism and reform. In C. Paris (Ed.), Critical readings in planning theory (pp. 207–227) New York: Pergamon Press.
- McDonald, G. T. (1989). Rural Land Use Planning Decisions by Bargaining. Journal of Rural Studies, 5 (4), 325–335.
- Wachs, M. (2004). Reflections on the planning process. In S. Hansen, & G. Guliano (Eds.), The Geography of Urban Transportation (3rd Edition ed., pp. 141–161). The Guilford Press.
- Forester John. "Planning in the Face of Conflict", 1987, ISBN 0-415-27173-8, Routledge, New York.
- "Advocacy and Community Planning: Past, Present, and Future". Planners Network. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- Benveniste, Guy (1994). Mastering the Politics of Planning. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- ""Life and the geometry of the environment", Nikos Salingaros, November 2010" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 October 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ""P2P Urbanism", collection of articles by Nikos Salingaros and others" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- Capeluto, I.G.; Shaviv, E. (2001). "On the use of 'solar volume' for determining the urban fabric". Solar Energy. 70 (3): 275–280. Bibcode:2001SoEn...70..275C. doi:10.1016/S0038-092X(00)00088-8.
- Nelson, Nels O. Planning the Productive City, 2009, accessed 30 December 2010.
Bibliography
- Allmendinger, Phil; Gunder, Michael (11 August 2016). "Applying Lacanian Insight and a Dash of Derridean Deconstruction to Planning's 'Dark Side'". Planning Theory. 4 (1): 87–112. doi:10.1177/1473095205051444. S2CID 145100234.
- Bogo, H.; Gómez, D.R.; Reich, S.L.; Negri, R.M.; San Román, E. (April 2001). "Traffic pollution in a downtown site of Buenos Aires City". Atmospheric Environment. 35 (10): 1717–1727. Bibcode:2001AtmEn..35.1717B. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00555-0.
- Garvin, Alexander (2002). The American City: What Works and What Doesn't. New York: McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-137367-8. (A standard text for many college and graduate courses in city planning in America)
- Dalley, Stephanie, 1989, Myths from Mesopotamia: Creation, the Flood, Gilgamesh, and Others, Oxford World's Classics, London, pp. 39–136
- Gunder, Michael (October 2003). "Passionate planning for the others' desire: an agonistic response to the dark side of planning". Progress in Planning. 60 (3): 235–319. doi:10.1016/S0305-9006(02)00115-0.
- Hoch, Charles, Linda C. Dalton and Frank S. So, editors (2000). The Practice of Local Government Planning, Intl City County Management Assn; 3rd edition. ISBN 0-87326-171-2 (The "Green Book")
- James, Paul; Holden, Meg; Lewin, Mary; Neilson, Lyndsay; Oakley, Christine; Truter, Art; Wilmoth, David (2013). "Managing Metropolises by Negotiating Mega-Urban Growth". In Harald Mieg and Klaus Töpfer (ed.). Institutional and Social Innovation for Sustainable Urban Development. Routledge.
- Kemp, Roger L. and Carl J. Stephani (2011). "Cities Going Green: A Handbook of Best Practices." McFarland and Co., Inc., Jefferson, NC, USA, and London, England, UK. ISBN 978-0-7864-5968-1.
- Oke, T. R. (January 1982). "The energetic basis of the urban heat island". Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society. 108 (455): 1–24. Bibcode:1982QJRMS.108....1O. doi:10.1002/qj.49710845502. S2CID 120122894.
- Pløger, John (30 November 2016). "Public Participation and the Art of Governance". Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design. 28 (2): 219–241. doi:10.1068/b2669. S2CID 143996926.
- Roy, Ananya (March 2008). "Post-Liberalism: On the Ethico-Politics of Planning". Planning Theory. 7 (1): 92–102. doi:10.1177/1473095207087526. S2CID 143458706.
- Santamouris, Matheos (2006). Environmental Design of Urban Buildings: An Integrated Approach.
- Shrady, Nicholas, The Last Day: Wrath, Ruin & Reason in The Great Lisbon Earthquake of 1755, Penguin, 2008, ISBN 978-0-14-311460-4
- Tang, Wing-Shing (17 August 2016). "Chinese Urban Planning at Fifty: An Assessment of the Planning Theory Literature". Journal of Planning Literature. 14 (3): 347–366. doi:10.1177/08854120022092700. S2CID 154281106.
- Tunnard, Christopher and Boris Pushkarev (1963). Man-Made America: Chaos or Control?: An Inquiry into Selected Problems of Design in the Urbanized Landscape, New Haven: Yale University Press. (This book won the National Book Award, strictly America; a time capsule of photography and design approach.)
- Wheeler, Stephen (2004). "Planning Sustainable and Livable Cities", Routledge; 3rd edition.
- Yiftachel, Oren, 1995, "The Dark Side of Modernism: Planning as Control of an Ethnic Minority," in Sophie Watson and Katherine Gibson, eds., Postmodern Cities and Spaces (Oxford and Cambridge, MA: Blackwell), pp. 216–240.
- Yiftachel, Oren (6 November 2016). "Planning and Social Control: Exploring the Dark Side". Journal of Planning Literature. 12 (4): 395–406. doi:10.1177/088541229801200401. S2CID 14859857.
- Yiftachel, Oren (11 August 2016). "Essay: Re-engaging Planning Theory? Towards 'South-Eastern' Perspectives". Planning Theory. 5 (3): 211–22. doi:10.1177/1473095206068627. S2CID 145359885.
- A Short Introduction to Radical Planning Theory and Practice, Doug Aberley Ph.D. MCIP, Winnipeg Inner City Research Alliance Summer Institute, June 2003
- McConnell, Shean. Theories for Planning, 1981, David & Charles, London.
Further reading
- Urban Planning, 1794–1918: An International Anthology of Articles, Conference Papers, and Reports, Selected, Edited, and Provided with Headnotes by John W. Reps, Professor Emeritus, Cornell University.
- City Planning According to Artistic Principles, Camillo Sitte, 1889
- Missing Middle Housing: Responding to the Demand for Walkable Urban Living by Daniel Parolek of Opticos Design, Inc., 2012
- Kemp, Roger L. and Carl J. Stephani (2011). "Cities Going Green: A Handbook of Best Practices." McFarland and Co., Inc., Jefferson, NC, USA, and London, England, UK. (ISBN 978-0-7864-5968-1).
- Tomorrow: A Peaceful Path to Real Reform, Ebenezer Howard, 1898
- The Improvement of Towns and Cities, Charles Mulford Robinson, 1901
- Town Planning in practice, Raymond Unwin, 1909
- The Principles of Scientific Management, Frederick Winslow Taylor, 1911
- Cities in Evolution, Patrick Geddes, 1915
- The Image of the City, Kevin Lynch, 1960
- The Concise Townscape, Gordon Cullen, 1961
- The Death and Life of Great American Cities, Jane Jacobs, 1961
- The City in History, Lewis Mumford, 1961
- The City is the Frontier, Charles Abrams, Harper & Row Publishing, New York, 1965.
- A Pattern Language, Christopher Alexander, Sara Ishikawa and Murray Silverstein, 1977
- What Do Planners Do?: Power, Politics, and Persuasion, Charles Hoch, American Planning Association, 1994. ISBN 978-0-918286-91-8
- Planning the Twentieth-Century American City, Christopher Silver and Mary Corbin Sies (Eds.), Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996
- "The City Shaped: Urban Patterns and Meanings Through History", Spiro Kostof, 2nd Edition, Thames and Hudson Ltd, 1999 ISBN 978-0-500-28099-7
- The American City: A Social and Cultural History, Daniel J. Monti, Jr., Oxford, England and Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishers, 1999. 391 pp. ISBN 978-1-55786-918-0.
- Urban Development: The Logic Of Making Plans, Lewis D. Hopkins Archived 15 June 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Island Press, 2001. ISBN 1-55963-853-2
- 'Readings in Planning Theory, 4th edition, Susan Fainstein and James DeFilippis, Oxford, England and Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishers, 2016.
- Taylor, Nigel, (2007), Urban Planning Theory since 1945, London, Sage.
- Planning for the Unplanned: Recovering from Crises in Megacities, by Aseem Inam (published by Routledge USA, 2005).
References
- Buchan, Robert (14 November 2019). "Transformative Incrementalism: Planning for transformative change in local food systems". Progress in Planning. 134: 100424. doi:10.1016/j.progress.2018.07.002. S2CID 158726842.
External links
| Environmental social science | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fields |
| 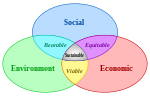 |
| Related |
| |
| Applied |
| |
| Real estate developments | |
|---|---|
| Commercial | |
| Industrial | |
| Residential |
|
| Science/education | |
| Municipal | |
| Buildings (types) | |
| Miscellaneous | |