| Revision as of 23:01, 13 February 2008 view sourceBriangotts (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users14,437 edits →Conversion to Judaism and relations with world Jewry← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:33, 10 January 2025 view source Don Stroud (talk | contribs)267 editsm removed Category:Barbarian kingdoms using HotCat | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Historical semi-nomadic Turkic ethnic group}} | |||
| {{History of Russia}} | |||
| {{Redirect2|Khazar|Kazar}} | |||
| {{History of Ukraine}} | |||
| {{Pp-semi-indef|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2017}} | |||
| {{EngvarB|date=April 2017}} | |||
| {{Infobox country | |||
| | conventional_long_name = Khazar Khaganate | |||
| | common_name = Khazaria | |||
| | era = Middle Ages | |||
| | status = ] | |||
| | year_start = {{c.}} 650 | |||
| | year_end = 969 | |||
| | p1 = Western Turkic Khaganate | |||
| | p2 = Old Great Bulgaria | |||
| | s1 = Cumania | |||
| | s2 = Pechenegs | |||
| | s3 = Kievan Rus' | |||
| | s4 = Durdzuks | |||
| | s5 = Volga Bulgaria | |||
| | s6 = Alania | |||
| | event_pre = | |||
| | date_pre = | |||
| | event_start = | |||
| | date_start = | |||
| | event_end = ]'s ] | |||
| | date_end = | |||
| | image_flag = | |||
| | image_coat = | |||
| | symbol_type_article = | |||
| | symbol_type = | |||
| | image_map = Chasaren.jpg | |||
| | image_map_caption = Khazar Khaganate, 650–850 | |||
| | capital = {{Plainlist| | |||
| * ] ({{circa}} 650 – {{circa}} 720) | |||
| * ] (720–750) | |||
| * ] (750 – c. 965–969) | |||
| }} | |||
| | national_motto = | |||
| | national_anthem = | |||
| | common_languages = {{Plainlist| | |||
| * ]{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=91}} (''lingua franca'') | |||
| * ]{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=91}} (dynastic, spoken) | |||
| * ]{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=91}} (spoken) | |||
| }} | |||
| | religion = {{Plainlist| | |||
| * ]{{sfn|Wexler|1996|p=50}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ]{{sfn|Brook|2010|p=107}} | |||
| }} | |||
| | currency = ] | |||
| | leader1 = ] | |||
| | year_leader1 = {{circa}} 650 | |||
| | leader2 = ] | |||
| | year_leader2 = 8th century | |||
| | leader3 = ] | |||
| | year_leader3 = 9th century | |||
| | leader4 = ] | |||
| | year_leader4 = 9th century | |||
| | leader5 = ] | |||
| | year_leader5 = 9th century | |||
| | leader6 = ] | |||
| | year_leader6 = 9th century | |||
| | leader7 = ] | |||
| | year_leader7 = 10th century | |||
| | leader8 = ] | |||
| | year_leader8 = 10th century | |||
| | leader9 = ] | |||
| | year_leader9 = 10th century | |||
| | leader10 = ] | |||
| | year_leader10 = 11th century | |||
| | title_leader = ] | |||
| | stat_year1 = 850 est. | |||
| | stat_area1 = 3000000 | |||
| | ref_area1 = {{sfn|Turchin|Adams|Hall|2006|p=222}} | |||
| | stat_year2 = 900 est. | |||
| | stat_area2 = 1000000 | |||
| | ref_area2 = {{sfn|Taagepera|1997|p=496}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{History of the Turkic peoples pre-14th century}} | |||
| {{History of Tatarstan}} | |||
| The '''Khazars'''{{efn|{{langx|el|Χάζαροι}} {{grc-transl|Χάζαροι}}; {{langx|he|כּוּזָרִים|Kūzārīm}};{{sfn|Luttwak|2009|p=152}} {{langx|orv|коꙁаре|kozare}}; {{langx|cu|коꙁари|kozari}}{{efn|group=note|name=Gazari}}; {{langx|la|Gazari}},{{sfn|Meserve|2009|p=294, n. 164}}{{efn|group=note|name=Gazari|"The ''Gazari'' are, presumably, the Khazars, although this term or the ''Kozary'' of the perhaps near contemporary ''Vita Constantini'' ... could have reflected any of a number of peoples within Khazaria." {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=139}}}} or {{lang|la|Gasani}};{{efn|group=note|"Somewhat later, however, in a letter to the Byzantine Emperor Basil I, dated to 871, Louis the German, clearly taking exception to what had apparently become Byzantine usage, declares that 'we have not found that the leader of the Avars, or Khazars (''Gasanorum'')'..." {{harv|Golden|2001a|p=33}}}}{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=255}} {{lang-zh|突厥曷薩}} {{lang|zh-Latn|Tūjué Hésà}}; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', {{lit|Türk Khazar}}{{sfn|Golden|2018|p=294}}}} ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|x|ɑː|z|ɑːr|z}}) were a ] ] that, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern ], ], ], and ].{{sfn|Encyclopedia Britannica: Khazar|2020}} They created what, for its duration, was the most powerful ] to emerge from the break-up of the ].{{sfn|Sneath|2007|p=25}} Astride a major artery of commerce between ] and ], Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the ] world, commanding the western ] of the ] and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between ], the ], and ].{{sfn|Noonan|1999|p=493}}{{sfn|Golden|2011a|p=65}} For some three centuries ({{circa|650}}–965), the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern ] and the northern ].{{sfn|Noonan|1999|p=498}} | |||
| The '''Khazars''' were a semi-]ic ] who dominated the ] and the North ] from the 7th to the 10th century CE. The name 'Khazar' (] ''sing.'' "{{lang|he-Latn|Kuzari}}" {{lang|he|כוזרי}} ''plur.'' "{{lang|he-Latn|Kuzarim}}" {{lang|he|כוזרים}}; ] ''sing.'' "{{lang|tr|Hazar}}" ''plur.'' {{lang|tr|Hazarlar}}; ] ''sing.'' {{lang|ru|Хазарин}} ''plur.'' {{lang|ru|Хазары}}; ] ''sing'' {{lang|tt|Xäzär}} ''plur.'' {{lang|tt|Xäzärlär}}; ] sing.{{lang|crh|Hazar}}, plur. {{lang|crh|Hazarlar}}; ] {{lang|el|Χαζάροι}}/{{lang|el|Χάζαροι}}; ]{{lang|fa|خزر}} ''khazar''; ] "{{lang|la|Gazari}}" or "{{lang|la|Cosri}}") seems to be tied to a ] verb form meaning "wandering" (cf. ] adjective 'gezer' = "mobile", verb 'gezmek' = "to walk around", 'gez-' being the root for the idea of "stroll"). In the ] CE they founded an independent ]ate in the Northern ] along the ]. Although the Khazars were initially ] ], many of them converted to ], ], and other religions. During the eighth or ninth century the ] became ], and the Jewish religion became widespread among the population. At their height, the Khazar khaganate and its tributaries controlled much of what is today southern ], western ], eastern ], ], large portions of the Caucasus (including ] and ], ]), and the ]. | |||
| Khazaria long served as a ] between the ], the nomads of the northern steppes, and the ] and ] Caliphates, having previously served as the Byzantine Empire's proxy against the ]. The alliance was dissolved around the year 900 when Byzantium began encouraging the ] to attack Khazaria. This move aimed to weaken Khazaria's control over Crimea and the Caucasus, for the Empire sought an ] with the rising power of the ] in the north—a region they hoped to convert to ].{{sfn|Noonan|1999|pp=499, 502–503}} Between 965 and 969, ] of Kiev, the ruler of Kievan Rus', along with his allies, conquered the capital, ], thus ending Khazaria's independence. | |||
| They were important allies of the ] against the ] and later the ], the ], and the ]. In later years, however, once Khazaria had become a significant regional power, the Byzantines abandoned the alliance and turned to the Rus' and ] against the Khazars. Between ] and ], their sovereignty was broken by ], and they became a subject people of ]. Gradually displaced by the Rus, the ], and later the conquering ] ], the Khazars largely disappeared as a culturally-distinct people. | |||
| Determining the origins and nature of the Khazars is closely bound with theories of ]. Still, it is a matter of intricate difficulty since no indigenous records in the Khazar language survived, and the state was ] and ]. The native religion of the Khazars is thought to have been ] like that of the ] and other ].{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=131}} The polyethnic populace of the Khazar Khaganate appears to have been a multiconfessional mosaic of ], Tengrist, ], Christian, and ] worshippers.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=28}} Some of the Khazars (namely, the ]s) joined the ancient Hungarians in the 9th century. The ruling elite of the Khazars was said by ] and ] to have converted to ] in the 8th century,{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=149}} but the scope of the ] within the Khazar Khanate remains uncertain.{{sfn|Behar|Metspalu|Baran|Kopelman|2013|pp=859–900}} | |||
| Today, various place names invoking ''Khazar'' persist. Indeed, the ], traditionally known as the '']'' and '']'' in ], came to be known to ]ians as the ''Khazar Sea'' as an alternative name. Many other cultures still call the Caspian Sea "Khazar Sea"; ''e.g.'' "Xəzər dənizi" in Azerbaijani, "Hazar Denizi" in Turkish, "Bahr ul-Khazar" in Arabic, "Darya-ye Khazar" in Persian. | |||
| Where the Khazars dispersed after the fall of the Khanate is subject to many conjectures. Proposals have been made regarding the possibility of a Khazar factor in the ] of numerous peoples, such as the ], ], the ], the ] region and ], the Muslim ], the Turkic-speaking ] and their Crimean neighbours the ], the ], the ], and even some ] (based on their Ukrainian and Cossack origin).{{sfn|Kizilov|2009|p=335}}{{sfn|Patai|Patai|1989|p=73}}{{sfn|Wexler|1987|p=70}} | |||
| ==Origins and prehistory== | |||
| [[Image:Sarkel.jpg|thumb|left|250px|The site of the Khazar fortress at Sarkel. Aerial photo from excavations | |||
| conducted by ] in the 1930s.]] | |||
| The late 19th century saw the ] that the core of today's ] are descended from a hypothetical Khazarian Jewish diaspora that migrated westward from modern-day Russia and Ukraine into modern-day France and Germany. Linguistic and genetic studies have not supported the theory of a Khazar connection to ]. The theory still finds occasional support, but most scholars view it with considerable scepticism.{{sfn|Wexler|2002|p=536}}{{sfn|Behar|Metspalu|Baran|Kopelman|2013|pp=859–900}} The theory is sometimes associated with ]{{sfn|Davies|1992|p=242}} and ].{{sfn|Vogt|1975}} | |||
| The origins of the Khazars are unclear. Following their ], the Khazars themselves traced their origins to ], a son of ]. Togarmah is mentioned in ] in the ] as a grandson of ]. | |||
| In ] ], the ] is still named the "]", an enduring legacy of the medieval Khazar state. | |||
| Scholars in the former ] considered the Khazars to be an ] of the ]. Some scholars, such as ], considered the Khazars to be connected with a ] or ] confederation tribe called ] in ] sources from the ] (Suishu, 84). However, the ] appears to have been an ] tongue, similar to that spoken by the early ].<ref>This Oghuric hypothesis has been disputed by recent scholarship; for a full discussion ''see'' Erdal 75-107.</ref> Therefore, a ] origin has also been postulated. Since the Turkic peoples were never ethnically homogenous, these ideas need not be deemed mutually exclusive. It is likely that the Khazar nation was made up of tribes from various ethnic backgrounds, as steppe nations traditionally absorbed those they conquered. Their name is accordingly derived from Turkic *''qaz-'', meaning "to wander, flee." | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| ]n chronicles contain references to the Khazars as early as the late ]. These are generally regarded as ]s, and most scholars believe that they actually refer to ]s or ]s. ] relates that one of the nations in the ]nish confederacy was called ]. Their king was named ] or Karidachus. Some, going on the similarity between Akatziroi and "Ak-Khazar" (see below), have speculated that the Akatziroi were early proto-Khazars. | |||
| ], following ], derived ''Khazar'' from a hypothetical *Qasar reflecting a Turkic ] ''qaz-'' ("to ramble, to roam") being an hypothetical ] of ] ''kez-'';{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=15}} however, ] objected that *''qaz-'' is a ].{{sfn|Zimonyi|1990|p=58}} In the fragmentary ] of the ] the form ''Qasar'' is attested, although uncertainty remains whether this represents a personal or tribal name, gradually other hypotheses emerged. ] derived it from Turkic ''qas-'' ("tyrannize, oppress, terrorize") on the basis of its phonetic similarity to the Uyğur tribal name, Qasar.{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Golden|2007a|p=16 and n.38}} citing L. Bazin, {{lang|fr|"Pour une nouvelle hypothèse sur l'origine des Khazar"}}, in ''Materialia Turcica,'' 7/8 (1981–1982): 51–71.}} Róna-Tas connects ''qasar'' with ''Kesar'', the ] transcription of the ].{{efn|group=note|Compare ] ''dru-gu Ge-sar'' (the Turk Gesar){{harv|Golden|2007a|p=16}} or ''Phrom Ge-sar'', who was possibly inspired by ] (拂菻罽娑 ]: ''Fúlǐn Jìsuō'' < ]: *''pʰɨut̚ -liɪm<sup>X</sup> kˠiᴇi<sup>H</sup>-sɑ''), a king of the ] of mixed ]-] origins ({{harvnb|Rezakhani|2017}}, {{harvnb|Kim|2016|pp=58–59}}, {{harvnb|Inaba|Balogh|2020|p=106}}, {{harvnb|Kordosis|2017|pp=183–192}}).}} | |||
| ] tried to link the Chinese term for "Khazars" to one of the tribal names of the Uyğur, or ], namely the ''Qasar'' (] 葛薩 ''Gésà'').{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|pp=34–40}}{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=16}} The objections are that Uyğur 葛薩 ''Gésà''/''Qasar'' was not a tribal name but rather the surname of the chief of the 思结 ''Sijie'' tribe (]: ''Sikari'') of the Toquz Oğuz (Ch. 九姓 ''jĭu xìng''),{{efn|group=note|''Sijie'' 思結 (also 斯結{{sfn|Wei Zheng, vol. 84}}{{sfn|Golden|1992}}) was mentioned as a 鐵勒 ], later Toquz Oghuz tribe, and distinguished from 突厥 ''Tujue'' in Chinese sources such as ],{{sfn|Jiu Tangshu, Vol. 199b Tiele}} ]{{sfn|Xin Tangshu, vol 217a Huihe}} or ].{{sfn|Wang Pu, vol 98}} However, in other sources ''Sijie'' were also associated with ''Tujue'' (] ''Ttrūka''): ] mentioned the ''Tujue Sijie'' 突厥思結{{sfn|Sima Guang, vol. 196}} and Tang Huiyao also counted 思結 ''Sijie'' (rendered as 恩結 ''Enjie'') among the ] living south of the ].{{sfn|Wang Pu, vol. 72}}{{sfn|Dobrovits|2004|p=259}} A ''saikairä ttūrkä chārä'' (< *''sïqïr türk čor'') was also mentioned in a Khotanese Saka text about Turks in ].{{sfn|Bailey|1949|p=50}}{{sfn|Bailey|1951|p=19}}}} and that in ] the ethnonym "Khazars" was always prefaced with ''Tūjué'', then still reserved for ] and their splinter groups,{{sfn|Lee|2016|pp=103–105}} (''Tūjué Kěsà bù'':突厥可薩部; ''Tūjué Hésà'':突厥曷薩) and "Khazar's" first syllable is transcribed with different characters (可 and 曷) than 葛, which is used to render the syllable ''Qa-'' in the Uyğur word ''Qasar''.{{efn|group=note|Kěsà (可薩) would have been pronounced something like ''k<sup>h</sup>a'sat'' in both ] and ], while Hésà 葛 (曷薩) would yield ''ɣat-sat'' in (]) and ''xɦat sat'' (]) respectively, where final "t" often transcribes –r- in foreign words. Thus, while these Chinese forms could transcribe a foreign word of the type *Kasar/*Kazar, *Ġatsar, *Ġazar, *Ġasar, there is a problem phonetically with assimilating these to the Uyğur word ''Qasar'' 葛薩 (] ''Gesa'' < EMC/LMC *''Kat-sat''{{=}} *''Kar sar''{{=}} *''Kasar'').{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=17}}}}{{sfn|Shirota|2005|pp=235, 248}}{{sfn|Brook|2010|p=5}} While it is far from given that the Khazars are not signifying a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual cluster of peoples and clans, some more nomadic, some less, it doesn't exclude that some clans, or splintergroups, or even rulers has identified with the name(s) of the Khazars, in the variety of ways it has been expressed. | |||
| Dmitri Vasil'ev of ] recently hypothesized that the Khazars moved in to the Pontic steppe region only in the late ], and originally lived in ]. According to Vasil'ev, Khazar populations remained behind in Transoxiana under ] and ] ], possibly remaining in contact with the main body of their people. | |||
| After their conversion it is reported that they adopted the Hebrew script,{{efn|group=note|] commenting on script systems in 987–88 recorded that the Khazars wrote in ] {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=148}}.}} and it is likely that, although speaking a Turkic language, the Khazar ] under Judaism probably corresponded in ].{{efn|group=note|"The chancellery of the Jewish state of the Khazars is therefore also likely to have used Hebrew writing even if the official language was a Turkic one." {{harv|Erdal|2007|pp=98–99}}}} | |||
| ==Tribes== | |||
| The Khazars' tribal structure is not well understood. They were divided between Ak-Khazars ("White Khazars") and Kara-Khazars ("Black Khazars"). The Arab Geographer al-] claimed that the White Khazars were strikingly handsome with reddish hair, white skin and blue eyes while the Black Khazars were swarthy verging on deep black as if they were "some kind of ]n".<ref>Dunlop, ''History'' 96.</ref> However, many Turkic nations had a similar (political, not racial) division between a "white" ruling warrior caste and a "black" class of commoners; the consensus among mainstream scholars is that Istakhri was himself confused by the name given to the two groups.<ref>Brook 3-4.</ref> | |||
| == |
== Linguistics == | ||
| {{Main|Khazar language}} | |||
| ===Formation of the Khazar state=== | |||
| ]ates at their height, c. 600 CE. Lighter areas show direct rule; darker areas show spheres of influence.]] | |||
| Early Khazar history is intimately tied with that of the ] empire, founded when the ] clan overthrew the ] in ] CE. With the collapse of the Göktürk empire due to internal conflict in the ], the western half of the Turk empire split into a number of tribal confederations, among whom were the ], led by the ], and the Khazars, led by the ] clan, the traditional rulers of the Gok Turk empire. By ], the Khazars had broken the Bulgar confederation, causing various tribal groups to migrate and leaving two remnants of Bulgar rule - ], and the ]n khanate on the ] River. | |||
| Determining the origins and nature of the Khazars is closely bound with theories of ], but analysis of their languages' origins is difficult, since no indigenous records in the Khazar language survive, and the state was ] and ].{{efn|group=note|"there must have been many different ethnic groups within the Khazar realm ... These groups spoke different languages, some of them no doubt belonging to the Indo-European or different Caucasian language families." {{harv|Erdal|2007|p=75, n.2}}}}{{efn|group=note|The high chancery official of the ] under ], Sallām the interpreter (''Sallam al-tardjuman''), famous for his reputed mastery of thirty languages, might have been both Jewish and a Khazar {{harvnb|Wasserstein|2007|pp=376, and n.2}}, referring to {{harvnb|Dunlop|1954|pp=190–193}}.}} Whereas the royal or ruling elite probably spoke an eastern variety of ], the subject tribes appear to have spoken varieties of ], such as ], a language variously identified with ], ], and ]. | |||
| The first significant appearance of the Khazars in history is their aid to the campaign of the ] emperor ] against the ] ]ns. The Khazar ruler Ziebel (sometimes identified as ] of the West Turks) aided the Byzantines in overrunning ]. A marriage was even contemplated between Ziebel's son and Heraclius' daughter, but never took place. During these campaigns, the Khazars may have been ruled by ] and their forces may have been under the command of his son ].<ref>Pletneva 15-16.</ref> | |||
| ], c. 650, showing the early territory of the Khazars and their neighbors.]] | |||
| During the ] and ] the Khazar fought a series of wars against the ] ], which was attempting simultaneously to expand its influence into ] and the ]. The first war was fought in the early ] and ended with the defeat of an Arab force led by ] outside the Khazar town of ], after a battle in which both sides used ]s on the others' troops. | |||
| ] | |||
| A number of Russian sources give the name of a Khazar khagan, ], from this period, and describe him as a scion of the Göktürk royal house, the Ashina. Whether Irbis ever existed is open to debate, as is the issue of whether he can be identified with one of the many ] rulers of the same name. | |||
| The latter based upon the assertion of the Persian historian ] the Khazar language was different from any other known tongue. Alano-As was also widely spoken. Eastern Common Turkic, the language of the royal house and its core tribes, in all likelihood remained the language of the ruling elite in the same way that Mongol continued to be used by the rulers of the Golden Horde, alongside of the ] speech spoken by the bulk of the Turkic tribesmen that constituted the military force of this part of the ] empire. Similarity, Oğuric, like Qipčaq Turkic in the Jočid realm, functioned as one of the languages of government.{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=91}}{{efn|group=note|al-Iṣṭakhrī's account however then contradicts itself by likening the language to ] {{harv|Golden|2007a|pp=13–14, 14 n.28}}.}} One method for tracing their origins consists in the analysis of the possible etymologies behind the ] "Khazar". | |||
| Several further conflicts erupted in the decades that followed, with Arab attacks and Khazar raids into ] and ]. There is evidence from the account of al-Tabari that the Khazars formed a united front with the remnants of the Gok Turks in Transoxiana. | |||
| == History == | |||
| ===Khazars and Byzantium=== | |||
| === Tribal origins and early history === | |||
| Khazar overlordship over most of the ] dates back to the late 7th century. In the mid-8th century the rebellious ] were put down and their city, ] (modern Mangup) occupied. A Khazar tudun was resident at ] in the ], despite the fact that this town was nominally subject to the ]. | |||
| The tribes{{efn|group=note|"The word ''tribe'' is as troublesome as the term ''clan''. It is commonly held to denote a group, like the clan, claiming descent from a common (in some culture zones eponymous) ancestor, possessing a common territory, economy, language, culture, religion, and sense of identity. In reality, tribes were often highly fluid sociopolitical structures, arising as 'ad hoc responses to ephemeral situations of competition,' as Morton H. Fried has noted." {{harv|Golden|2001b|p=78}}}} that were to comprise the Khazar empire were not an ethnic union, but a congeries of steppe nomads and peoples who came to be subordinated, and subscribed to a core Turkic leadership.{{sfn|Whittow|1996|pp=220–223}} Many Turkic groups, such as the ], including ], Oğurs, ], and ] who earlier formed part of the ], are attested quite early, having been driven West by the ], who in turn fled the ], and began to flow into the ]–]–] zone from as early as the 4th century CE and are recorded by ] to reside in the Western Eurasian steppe lands as early as 463.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=14}}{{sfn|Szádeczky-Kardoss|1994|p=206}} They appear to stem from Mongolia and South Siberia in the aftermath of the fall of the ]/] nomadic polities. A variegated tribal federation led by these Turks, probably comprising a complex assortment of ],{{efn|group=note|Dieter Ludwig, in his doctoral thesis {{lang|de|Struktur und Gesellschaft des Chazaren-Reiches im Licht der schriftlichen Quellen}}, (Münster, 1982) suggested that the Khazars were Turkic members of the ], where the lingua franca was a variety of Iranian ({{harvnb|Golden|2007a|pp=40–41}}; {{harvnb|Brook|2010|p=4}}).}} ], ], and ] clans, vanquished the ] of the hegemonic central Asian Avars in 552 and swept westwards, taking in their train other steppe nomads and peoples from ].{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=86}} | |||
| The ruling family of this confederation may have hailed from the ] of the ],{{sfn|Pritsak|1978|p=261}}{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=53}}{{sfn|Golden|2007c|p=165}} although ] regards Ashina and their pivotal role in the formation of the Khazars with scepticism.{{efn|group=note|"The reader should be warned that the A-shih-na link of the Khazar dynasty, an old phantom of ... Khazarology, will ... lose its last claim to reality" {{harv|Zuckerman|2007|p=404}}.}} Golden notes that Chinese and Arabic reports are almost identical, making the connection a strong one, and conjectures that their leader may have been ] ({{lang|zh|乙毗射匱}}), who lost power or was killed around 651.{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=89}} Moving west, the confederation reached the land of the ],{{efn|group=note|In this view, the name Khazar would derive from a hypothetical *Aq Qasar {{harv|Golden|2006|pp=89–90}}: e.g. Pritsak (1978) links ''Ak-Katzirs'' (< {{lang|grc|Άκατζίροι}}) to the name ], though he explains that the polity was named Khazar because the Ashina-ruled ], after ], took over the territory formerly occupied by the Akatziri ({{harvnb|Pritsak|1978|p=261}}). However, the hypothesized link between the Akatizoi and the Khazars was not solid, being based on mere phonetic resemblance ({{harvnb|Golden|2011b|p=136}}, {{harvnb|Brook|2006|p=10}}).}} who had been important allies of Byzantium in fighting off ]'s army. | |||
| They are also known to have been allied with the ] during at least part of the eighth century. In ]/] ], exiled in ], escaped into Khazar territory and married ], the sister of the Khagan ]. With the aid of his wife, he escaped from Busir, who was intriguing against him with the usurper ], murdering two Khazar officials in the process. He fled to ], whose Khan ] helped him regain the throne. The Khazars later provided aid to the rebel general ], who seized the throne in ] as Emperor ]. | |||
| === Rise of the Khazar state === | |||
| The Byzantine emperor ] married his son Constantine (later ] Kopronymous) to the Khazar princess ] (daughter of the Khagan ]) as part of the alliance between the two empires. Tzitzak, who was baptized as ], became famous for her wedding gown, which started a fashion craze in Constantinople for a type of robe (for men) called ''tzitzakion''. Their son Leo (]) would be better known as "Leo the Khazar". | |||
| {{Continental Asia in 800 CE|right|The Khazar Khaganate and contemporary polities circa 800.}} | |||
| An embryonic state of Khazaria began to form sometime after 630,{{sfn|Kaegi|2003|p=143, n.115}}{{sfn|Golden|1992|pp=127–136, 234–237}} when it emerged from the breakdown of the larger ]. Göktürk armies had penetrated the Volga by 549, ejecting the Avars, who were then forced to flee to the sanctuary of the ]. The Ashina clan appeared on the scene by 552, when they overthrew the Rourans and established the ] ], whose self designation was ''Tür(ü)k''.{{efn|group=note|Whittow states that the word Türk had no strict ethnic meaning at the time: "Throughout the early middle ages on the Eurasian steppes, the term 'Turk' may or may not imply membership of the ethnic group of Turkic peoples, but it does always mean at least some awareness and acceptance of the traditions and ideology of the Gök Türk empire, and a share, however distant, in the political and cultural inheritance of that state." {{harv|Whittow|1996|p=221}}}} By 568, these Göktürks were probing for an alliance with Byzantium to attack ]. An ] broke out between the senior eastern Göktürks and the junior West Turkic Khaganate some decades later, when on the death of ], a ] between Taspar's chosen heir, the ], and the ruler appointed by the tribal high council, Āshǐnà Shètú (阿史那摄图), the ]. | |||
| By the first decades of the 7th century, the Ashina ] ] managed to stabilise the Western division, but upon his death, after providing crucial military assistance to Byzantium in routing the Sasanian army in the Persian heartland,{{sfn|Kaegi|2003|pp=154–186}}{{sfn|Whittow|1996|p=222}} the Western Turkic Qağanate dissolved under pressure from the ] and split into two competing federations, each consisting of five tribes, collectively known as the "Ten Arrows" (''On Oq''). Both briefly challenged Tang hegemony in eastern Turkestan. To the West, two new nomadic states arose in the meantime, ] under ], the Duōlù clan leader, and the Nǔshībì subconfederation, also consisting of five tribes.{{efn|group=note|The ] were the left wing of the ''On Oq'', the ], and together they were registered in Chinese sources as the "ten names" (shí míng:十名) {{harv|Golden|2010|pp=54–55}}.}} The Duōlù challenged the Avars in the ]-] area while the Khazar Qağanate consolidated further westwards, led apparently by an Ashina dynasty. With a resounding victory over the tribes in 657, engineered by ], Chinese overlordship was imposed to their East after a final mop-up operation in 659, but the two confederations of Bulğars and Khazars fought for supremacy on the western steppeland, and with the ascendency of the latter, the former either succumbed to Khazar rule or, as under ], Kubrat's son, shifted even further west across the Danube to lay the foundations of the ] in the Balkans ({{circa|679}}).{{sfn|Golden|2001b|pp=94–95}}{{sfn|Somogyi|2008|p=128}} | |||
| ===Second Khazar-Arab war=== | |||
| ] to 750 CE.<br> From The Historical Atlas by William R. Shepherd, 1923 <br> Courtesy of The General Libraries, The University of Texas at Austin]] | |||
| The Qağanate of the Khazars thus took shape out of the ruins of this nomadic empire as it broke up under pressure from the Tang dynasty armies to the east sometime between 630 and 650.{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=89}} After their conquest of the lower Volga region to the East and an area westwards between the ] and the ], and their subjugation of the ]-] union, sometime around 670, a properly constituted Khazar Qağanate emerges,{{sfn|Zuckerman|2007|p=417}} becoming the westernmost ] of the formidable Göktürk Qağanate after its disintegration. According to ], the language of the Onoğur-Bulğar federation was to become the ] of Khazaria{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=90}} as it developed into what ] called a "steppe Atlantis" (''stepnaja Atlantida''/ Степная Атлантида).{{sfn|Golden|2007a|pp=11–13}} Historians have often referred to this period of Khazar domination as the ] since the state became an international trading hub permitting Western Eurasian merchants safe transit across it to pursue their business without interference.{{sfn|Noonan|2001|p=91}} The high status soon to be accorded this empire to the north is attested by ]'s ''Fârsnâma'' (c. 1100), which relates that the ] Shah, ], placed three thrones by his own, one for the King of China, a second for the King of Byzantium, and a third for the king of the Khazars. Although anachronistic in retrodating the Khazars to this period, the legend, in placing the Khazar qağan on a throne with equal status to kings of the other two superpowers, bears witness to the reputation won by the Khazars from early times.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|pp=7–8}}{{sfn|Golden|2001b|p=73}} | |||
| Hostilities broke out again with the Caliphate in the ], with raids back and forth across the Caucasus but few decisive battles. The Khazars, led by a prince named ], invaded northwestern ] and defeated the ] forces at ] in ], killing the Arab warlord ] and briefly occupying the town. They were defeated the next year at ], where Barjik directed Khazar forces from a throne mounted with al-Djarrah's severed head, and Barjik was killed. Arab armies led first by the Arab prince ] and then by Marwan ibn Muhammad (later Caliph ]) poured across the Caucasus and eventually (in ]) defeated a Khazar army led by ], briefly occupying ] itself and possibly forcing the Khagan to convert to Islam. The instability of the Umayyad regime made a permanent occupation impossible; the Arab armies withdrew and Khazar independence was re-asserted. It has been speculated that the adoption of ] (which in this theory would have taken place around ]) was part of this re-assertion of ]. | |||
| === Khazar state: culture and institutions === | |||
| It is worth noting that around ], Arab sources give the name of the ruler of the Khazars as ] or Barsbek, a woman who appears to have directed military operations against them. This suggests that women could have very high positions within the Khazar state, possibly even as a stand-in for the khagan. | |||
| ==== Royal Diarchy with sacral Qağanate ==== | |||
| Khazaria developed a ] governance structure,{{efn|group=note|Several scholars connect it to Judaization, with ] linking its introduction to Obadiyah's reforms and the imposition of full Rabbinical Judaism and ] to the same period (799–833), arguing that the ], a majordomo from the Iranian *''Barč/Warâ Bolčan'' clan, identified with Obadiyah, compelled the Qağanal clan to convert, an event which putatively caused the Qabar revolt. Golden comments: "There is nothing but conjecture to connect it with the reforms of Obadiyah, the further evolution of Khazar Judaism or the ] ... The fact is we do not know when, precisely, the Khazar system of dual kingship emerged. It could not have come ''ex nihilo''. It was not present in the early stages of Khazar history. Given the Old Türk traditions of the Khazar state ... and the overall institutional conservation of steppe society, one must exercise great caution here. Clear evidence for it is relatively late (the latter part of the ninth century perhaps and more probably the tenth century)- although it was probably present by the first third of the ninth century. Iranian influences via the ] guard of the Qağans may have also been a factor" {{harv|Golden|2007b|pp=155–156}}}} typical among Turkic nomads, consisting of a ''shad/bäk'' and a ''qağan''.{{sfn|Noonan|1999|p=500}} The emergence of this system may be deeply entwined with the conversion to Judaism.{{sfn|Olsson|2013|p=496}} According to Arabic sources, the lesser king was called '']'' and the greater king ''Khazar ]''; the former managed and commanded the military, while the greater king's role was primarily sacral, less concerned with daily affairs. The greater king was recruited from the Khazar house of notables (''ahl bait ma'rûfīn'') and, in an initiation ritual, was nearly strangled until he declared the number of years he wished to reign, on the expiration of which he would be ].{{efn|group=note|There was a maximum limit on the number of years of a king's reign, according to ]; if a Qağan had reigned for at least forty years, his courtiers and subjects felt his ability to reason would become impaired by old age. They would then kill the Qağan {{harv|Dunlop|1954|pp=97, 112}}.}}{{sfn|Noonan|2001|p=77}}{{sfn|Golden|2006|pp=81–82}}{{efn|group=note|Petrukhin notes that Ibn Fadlan's description of a Rus' prince (''malik'') and his lieutenant ('']'') mirrored the Khazarian diarchy, but the comparison was flawed, as there was no sacral kingship among the Rus' {{harv|Petrukhin|2007|pp=256–257}}.}} The deputy ruler would enter the presence of the reclusive greater king only with great ceremony, approaching him barefoot to prostrate himself in the dust and then light a piece of wood as a purifying fire, while waiting humbly and calmly to be summoned.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|pp=133–134}} Particularly elaborate rituals accompanied a ]. At one period, travellers had to dismount, bow before the ruler's tomb, and then walk away on foot.{{sfn|Shingiray|2012|p=212}} Subsequently, the charismatic sovereign's burial place was hidden from view, with a palatial structure ("Paradise") constructed and then ] under rerouted river water to avoid disturbance by evil spirits and later generations. Such a royal burial ground ('']'') is typical of inner Asian peoples.{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|p=181}} Both the îšâ and the xâqân converted to Judaism sometime in the 8th century, while the rest, according to the Persian traveller ], probably followed the old Tūrkic religion.{{sfn|Golden|2006|pp=79–81}}{{efn|group=note|"the rest of the Khazars profess a religion similar to that of the Turks." {{harv|Golden|2007b|pp=130–131}}}} | |||
| ==== Ruling elite ==== | |||
| Although they stopped the ] expansion into ] for some time after these wars, the Khazars were forced to withdraw behind the Caucasus. In the ensuing decades they extended their territories from the ] in the east (many cultures still call the Caspian Sea "Khazar Sea"; e.g. "Xəzər dənizi" in ], "Hazar Denizi" in Turkish, "Bahr ul-Khazar" in Arabic, "Darya-ye Khazar" in Persian) to the steppe region north of ] in the west, as far west at least as the ] River. | |||
| The ruling stratum, like that of the later ] within the ], was a relatively small group that differed ethnically and linguistically from its subject peoples, meaning the ] and Oğuric Turkic tribes, who were numerically superior within Khazaria.{{sfn|Golden|2006|p=88}} The Khazar Qağans, while taking wives and concubines from the subject populations, were protected by a ] guard corps, or '']'', called the ].{{efn|group=note|This regiment was exempt from campaigning against fellow Muslims, evidence that non-Judaic beliefs were no obstacle to access to the highest levels of government. They had abandoned their homeland and sought service with the Khazars in exchange for the right to exercise their religious freedom, according to al-Masudi {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=138}}.}}{{efn|group=note|Olsson writes that there is no evidence for this Islamic guard for the 9th century, but that its existence is attested for 913 {{harv|Olsson|2013|p=507}}.}} But unlike many other local polities, they hired soldiers (mercenaries) (the ''junûd murtazîqa'' in ]).{{sfn|Golden|2006|pp=79–80, 88}} At the peak of their empire, the Khazars ran a centralised fiscal administration, with a standing army of some 7–12,000 men, which could, at need, be multiplied two or three times that number by inducting reserves from their nobles' retinues.{{sfn|Olsson|2013|p=495}}{{efn|group=note|Noonan gives the lower figure for the Muslim contingents, but adds that the army could draw on other mercenaries stationed in the capital, Rūs, ] and pagans. Olsson's 10,000 refers to the spring-summer horsemen in the nomadic king's retinue {{harv|Noonan|2007|pp=211, 217}}.}} Other figures for the permanent standing army indicate that it numbered as many as one hundred thousand. They controlled and exacted tribute from 25 to 30 different nations and tribes inhabiting the vast territories between the Caucasus, the Aral Sea, the Ural Mountains, and the Ukrainian steppes.{{sfn|Koestler|1977|p=18}} Khazar armies were led by the Qağan Bek (pronounced as Kagan Bek) and commanded by subordinate ] known as ]s. When the bek sent out a body of troops, they would not retreat under any circumstances. If they were defeated, every one who returned was killed.{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|p=113}} | |||
| Settlements were governed by administrative officials known as '']s''. In some cases, such as the Byzantine settlements in southern ], a ''tudun'' would be appointed for a town nominally within another polity's ]. Other officials in the Khazar government included dignitaries referred to by ] as '']'' and '']'', but their responsibilities are unknown. | |||
| In ], the ] ] Abdullah ] ordered ], one of his nobles and military governor of ], to take a royal Khazar bride and make peace. Yazid took home a daughter of Khagan ], the Khazar leader. Unfortunately, the girl died inexplicably, possibly in childbirth. Her attendants returned home, convinced that some Arab faction had poisoned her, and her father was enraged. A Khazar general named ] invaded what is now northwestern Iran, plundering and raiding for several months. Thereafter relations between the Khazars and the ] (whose foreign policies were generally less expansionist than its Umayyad predecessor) became increasingly cordial. | |||
| ==== Demographics ==== | |||
| ==Khazar religion== | |||
| It has been estimated that 25 to 28 distinct ethnic groups made up the population of the Khazar Qağanate, aside from the ethnic elite. The ruling elite seems to have been constituted out of nine tribes/clans, themselves ethnically heterogeneous, spread over perhaps nine provinces or principalities, each of which would have been allocated to a clan.{{sfn|Noonan|2001|p=77}} In terms of caste or class, some evidence suggests that there was a distinction, whether racial or social is unclear, between "White Khazars" (ak-Khazars) and "Black Khazars" (qara-Khazars).{{sfn|Noonan|2001|p=77}} The 10th-century Muslim geographer ] claimed that the White Khazars were strikingly handsome with reddish hair, white skin, and blue eyes, while the Black Khazars were swarthy, verging on deep black as if they were "some kind of ]n".{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|p=96}} Many Turkic nations had a similar (political, not racial) division between a "white" ruling warrior caste and a "black" class of commoners; the consensus among mainstream scholars is that Istakhri was confused by the names given to the two groups.{{sfn|Brook|2010|pp=3–4}} However, Khazars are generally described by early Arab sources as having a white complexion, blue eyes, and reddish hair.{{sfn|Patai|Patai|1989|p=70}}{{sfn|Brook|2010|p=3}} The ethnonym in the Tang Chinese annals, Ashina, often accorded a key role in the Khazar leadership, may reflect an Eastern Iranian or ] word (] ''âşşeina-āššsena'' "blue"): ] ''axšaêna'' ("dark-coloured"): ] ''âśna'' ("blue", "dark").{{sfn|Luttwak|2009|p=152}} The distinction appears to have survived the collapse of the Khazarian empire. Later Russian chronicles, commenting on the role of the Khazars in the magyarisation of Hungary, refer to them as "White ]" and ] as "]".{{sfn|Oppenheim|1994|p=312}} Studies of the physical remains, such as skulls at ], have revealed individuals belonging to the Slavic, other European, and a few Mongolian types.{{sfn|Brook|2010|pp=3–4}} | |||
| ===Turkic shamanism=== | |||
| {{main|Shamanism}} | |||
| Originally, the Khazars practiced traditional Turkic ]ism, focused on the sky ] ], but were heavily influenced by ] ideas imported from ], notably that of the ]. The ] clan were considered to be the chosen of Tengri and the kaghan was the incarnation of the favor the sky-god bestowed on the Turks. A kaghan who failed had clearly lost the god's favor and was typically ]. Historians have sometimes wondered, only half in jest, whether the Khazar tendency to occasionally execute their rulers on religious grounds led those rulers to seek out other religions. | |||
| ==== Economy ==== | |||
| The Khazars worshipped a number of deities subordinate to Tengri, including the fertility ] ], ], a thunder god, and ], the god of death. | |||
| The import and export of foreign wares, and the revenues derived from taxing their transit, was a hallmark of the Khazar economy, although it is said also to have produced ].{{sfn|Barthold|1993|p=936}} Distinctively among the nomadic steppe polities, the Khazar Qağanate developed a self-sufficient domestic ]{{sfn|Zhivkov|2015|p=173}} economy, a combination of traditional pastoralism – allowing sheep and cattle to be exported – extensive agriculture, abundant use of the Volga's rich fishing stocks, together with craft manufacture, with diversification in lucrative returns from taxing international trade given its pivotal control of major trade routes. | |||
| The ] constituted one of the two great furnishers of slaves to ] to ] (the other being the ]), supplying it with captured Slavs and tribesmen from the Eurasian northlands.{{sfn|Golden|2011a|p=64}} It profited from the latter which enabled it to maintain a standing army of Khwarezm Muslim troops. The capital Atil reflected the division: Kharazān on the western bank where the king and his Khazar elite, with a retinue of some 4,000 attendants, dwelt, and Itil proper to the East, inhabited by Jews, Christians, Muslims and slaves and by craftsmen and foreign merchants.{{efn|group=note|A third division may have contained the dwellings of the tsarina. The dimensions of the western part were 3x3, as opposed to the eastern part's 8 x 8 ''farsakhs'' {{harv|Noonan|2007|pp=208–209, 216–219}}.}} | |||
| ===Conversion to Judaism and relations with world Jewry=== | |||
| {{Jew}} | |||
| ] communities had existed in the Greek cities of the ] coast since late classical times. ], ], ] and other Crimean cities possessed Jewish communities, as did ], and ] / ] was said to have had a Jewish majority as early as the ]. There is evidence that Jews from Byzantium immigrated to Khazaria as a consequence of persecution under ], ] and other emperors. | |||
| <ref> Golden, "conversion" 141, 161; Brook ''passim''; Graetz 139; ''for general information on the status of Jews in the Byzantine Empire see'' e.g. Ostrogorski 161; Cohen 112; Norwich 89; | |||
| Geanakoplos 268; ''The Oxford History of Byzantium'' 13.; Browning 54; Cameron 272-274.</ref> | |||
| These were joined by other Jews fleeing from ] ] (particularly during the ] revolts),<ref>Levy ch. 4 ''passim''.</ref> and, later, the ] world. | |||
| Jewish merchants such as the ]s regularly traded in Khazar territory, and may have wielded significant economic and political influence. Though their origins and history are somewhat unclear, the ] also lived in or near Khazar territory and may have been allied with or subject to Khazar overlordship; it is conceivable that they too played a role in the conversion. | |||
| The Khazar Khaghanate played a key role in the trade between Europe and the Muslim world in the early middle ages. People taken captive during the viking raids in Europe, such as Ireland, could be transported to ] or ] in Scandinavia and from there via the ] to Russia, where slaves and furs were sold to Muslim merchants in exchange for Arab silver '']'' and ], which have been found in ], ] and ];{{sfn|Reuter|1999|p=91}} during the 8th- and 9th-century this trade route between Europe and the ] passed via the Khazar Kaghanate,{{sfn|Noonan|2007|p=232}} until it was supplanted in the 10th-century by the route of ], ], and the ].{{sfn|Reuter|1999|p=504}} | |||
| At some point in the last decades of the ] or the early ], the Khazar ] and ] converted to ], and part of the general population followed.<ref>''E.g.'', Brook; Dunlop; Golden, ''Khazar Studies''; ''passim'', and Christian 282-300.</ref> The extent of the conversion is debated. ] reported in the 10th century that "all the Khazars are Jews." Notwithstanding this statement, some scholars believe that only the upper classes converted to Judaism; there is some support for this in contemporary Muslim texts.<ref>Dunlop; Pritsak, "Conversion"; and Barthold ''passim''.</ref> However, recent archeological excavations have uncovered widespread shifts in burial practices. Around the mid-800s burials in Khazaria began to take on a decidedly Jewish flavor. Grave goods disappeared almost altogether. Judging by interment evidence, by ] Judaism had become widespread among all classes of Khazar society. | |||
| The ruling elite wintered in the city and spent from spring to late autumn in their fields. A large irrigated greenbelt, drawing on channels from the Volga river, lay outside the capital, where meadows and vineyards extended for some 20 ''farsakhs'' (c. 60 miles).{{sfn|Noonan|2007|p=214}} While customs duties were imposed on traders, and tribute and tithes were exacted from 25 to 30 tribes, with a levy of one sable skin, squirrel pelt, sword, dirham per hearth or ploughshare, or hides, wax, honey and livestock, depending on the zone. Trade disputes were handled by a commercial tribunal in Atil consisting of seven judges, two for each of the monotheistic inhabitants (Jews, Muslims, Christians) and one for the pagans.{{efn|group=note|Outside Muslim traders were under the jurisdiction of a special royal official (''ghulām'') {{harv|Noonan|2007|pp=211–214}}.}} | |||
| Essays in the '']'', written by ], detail a moral liturgical reason for the conversion which some consider a moral tale. Some researchers have suggested part of the reason for this mass conversion was political expediency to maintain a degree of ]: the Khazar empire was between growing populations, ]s to the east and ]s to the west. Both religions recognized Judaism as a forebear and worthy of some respect. The exact date of the conversion is hotly contested. It may have occurred as early as 740 or as late as the mid-]. Recently discovered ] evidence suggests that Judaism was the established state religion by c. ], and though ] (who visited Khazaria in ]) did not identify the Khazars as Jews, the khagan of that period, ], had a biblical Hebrew name. Some medieval sources give the name of the ] who oversaw the conversion of the Khazars as ] or ]. | |||
| === Khazars and Byzantium === | |||
| The first Jewish Khazar king was named ] which means "]", though some sources give him the Hebrew name ]. A later king, ], strengthened Judaism, inviting ]s into the kingdom and built ]s. Jewish figures such as ] made positive references to the Khazars, and they are excoriated in contemporary ] writings as "bastards"; it is therefore unlikely that they adopted Karaism as some (such as ]) have proposed. | |||
| {{see also|Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628|Third Perso-Turkic War}} | |||
| Byzantine diplomatic policy towards the steppe peoples generally consisted of encouraging them to fight among themselves. The ] provided great assistance to the Byzantines in the 9th century in exchange for regular payments.{{sfn|Luttwak|2009|p=52}} Byzantium also sought alliances with the ] against common enemies: in the early 7th century, one such alliance was brokered with the Western Tűrks against the Persian ] in the ]. The Byzantines called Khazaria ''Tourkía'', and by the 9th century referred to the Khazars as "Turks".{{efn|group=note|] around 813 defined them as ''Eastern Turks''. The designation is complex and Róna-Tas writes: "The ''Georgian Chronicle'' refers to the Khazars in 626–628 as the 'West Turks' who were then opposed to the East Turks of Central Asia. Shortly after 679 the ''Armenian Geography'' mentions the Turks together with the Khazars; this may be the first record of the Magyars. Around 813, Theophanes uses – alongside the generic name ''Turk'' – 'East Turk' for the designation of the Khazars, and in context, the 'West Turks' may actually have meant the Magyars. We know that Nicholas Misticus referred to the Magyars as 'West Turks' in 924/925. In the 9th century the name ''Turk'' was mainly used to designate the Khazars." {{harv|Róna-Tas|1999|p=282}}}} During the period leading up to and after the ] in 626, ] sought help via emissaries, and eventually personally, from a Göktürk chieftain{{efn|group=note|Many sources identify the Göktürks in this alliance as Khazars--for example, Beckwith writes recently: "The alliance sealed by Heraclius with the Khazars in 627 was of seminal importance to the Byzantine Empire through the Early Middle Ages, and helped assure its long-term survival."{{sfn|Beckwith|2011|pp=120, 122}} Early sources such as the almost contemporary ] history, ''Patmutʿiwn Ałuanicʿ Ašxarhi'', attributed to Movsēs Dasxurancʿ, and the Chronicle attributed to Theophanes identify these Turks as Khazars (Theophanes has: "Turks, who are called Khazars"). Both Zuckerman and Golden reject the identification.{{sfn|Zuckerman|2007|pp=403–404}}}} of the Western Turkic Khaganate, ], in ], plying him with gifts and the promise of marriage to his daughter, ].{{sfn|Kaegi|2003|pp=143–145}} Tong Yabghu responded by sending a large force to ravage the Persian empire, marking the start of the ].{{sfn|Róna-Tas|1999|p=230}} A joint Byzantine-Tűrk operation breached the ] and sacked ] in 627. Together they then besieged ], where the Byzantines may have deployed an early variety of ] (]) to breach the walls. After the campaign, Tong Yabghu is reported, perhaps with some exaggeration, to have left some 40,000 troops behind with Heraclius.{{sfn|Kaegi|2003|p=145}} Although occasionally identified with Khazars, the Göktürk identification is more probable since the Khazars only emerged from that group after the fragmentation of the former sometime after 630.{{sfn|Kaegi|2003|p=143, n.115}}{{sfn|Golden|1992|pp=127–136, 234–237}} Some scholars argued that Sasanian Persia never recovered from the devastating defeat wrought by this invasion.{{efn|group=note|Scholars dismiss Chinese annals which, reporting the events from Turkic sources, attribute the destruction of Persia and its leader ] personally to Tong Yabghu. Zuckerman argues instead that the account is correct in its essentials {{harv|Zuckerman|2007|p=417}}.}} | |||
| ] | |||
| According to the ], early Khazar Judaism was centered on a ] similar to that mentioned in the ]. Archaeologists at ] have tentatively identified a folding altar unearthed at ] as part of such a construct. | |||
| Once the Khazars emerged as a power, the Byzantines also began to form alliances with them, dynastic and military. In 695, the last ], ], nicknamed "the slit-nosed" (ὁ ῥινότμητος) after he was mutilated and deposed, was exiled to ] in the ], where a Khazar governor (''tudun'') presided. He escaped into Khazar territory in 704 or 705 and was given asylum by qağan ] (Ἰβουζῆρος Γλιαβάνος), who gave him his sister in marriage, perhaps in response to an offer by Justinian, who may have thought a dynastic marriage would seal by kinship a powerful tribal support for his attempts to regain the throne.{{sfn|Bauer|2010|p=341}} The Khazarian spouse thereupon changed her name to ].{{sfn|Ostrogorski|1969|pp=124–126}} Busir was offered a bribe by the Byzantine usurper, ], to kill Justinian. Warned by Theodora, Justinian escaped, murdering two Khazar officials in the process. He fled to Bulgaria, whose Khan ] helped him regain the throne. Upon his reinstalment, and despite Busir's treachery during his exile, he sent for Theodora; Busir complied, and she was crowned as Augusta, suggesting that both prized the alliance.{{sfn|Cameron|Herrin|1984|p=212}}{{sfn|Bauer|2010|pp=341–342}} | |||
| Decades later, ] (ruled 717–741) made a similar alliance to co-ordinate strategy against a common enemy, the ]. He sent an embassy to the Khazar qağan ] and married his son, the future ] (ruled 741–775), to Bihar's daughter, a princess referred to as ], in 732. On converting to Christianity, she took the name Irene. Constantine and Irene had a son, the future ], who thereafter bore the sobriquet, "the Khazar".{{sfn|Luttwak|2009|pp=137–138}}{{sfn|Piltz|2004|p=42}} Leo died in mysterious circumstances after his Athenian wife bore him a son, ], who on his majority co-ruled with his mother, the dowager. He proved unpopular, and his death ended the dynastic link of the Khazars to the Byzantine throne.{{sfn|Schwartzwald|2015|p=26}}{{sfn|Luttwak|2009|pp=137–138}} By the 8th century, Khazars ] (650–c. 950), and even extended their influence into the Byzantine peninsula of Cherson until it was wrested back in the 10th century.{{sfn|Noonan|2007|p=220}} Khazar and ] mercenaries constituted part of the imperial Byzantine '']'' bodyguard after its formation in 840, a position that could openly be purchased by a payment of seven pounds of gold.{{sfn|Beckwith|2011|p=392, n.22}}{{sfn|Heath|1979|p=14}} | |||
| The Khazars enjoyed close relations with the Jews of the ] and ]. The Persian Jews, for example, hoped that the Khazars might succeed in conquering the Caliphate.<ref>], in Kohut Memorial Volume, p. 244.</ref> The high esteem in which the Khazars were held among the Jews of the Orient may be seen in the application to them, in an ] commentary on ] ascribed by some to Saadia Gaon, and by others to ], of ] 48:14: "The Lord hath loved him." "This," says the commentary, "refers to the Khazars, who will go and destroy ]" (i.e., ]ia), a name used to designate the country of the Arabs.<ref>Harkavy in "Ha-Maggid." 1877, p. 357.</ref> From the ] it is apparent that two Spanish Jews, Judah ben Meir ben Nathan and Joseph Gagris, had succeeded in settling in the land of the Khazars. Saadia, who had a fair knowledge of the kingdom of the Khazars, mentions a certain Isaac ben Abraham who had removed from ] to Khazaria.<ref>Harkavy, in Kohut Memorial Volume, p. 244.</ref> | |||
| === {{anchor|Second Khazar-Arab war}}Arab–Khazar wars === | |||
| Likewise, the Khazar rulers viewed themselves as the protectors of international ], and corresponded with foreign Jewish leaders (] exchanged between the Khazar ruler ] and the Spanish rabbi ] have been preserved). They were known to retaliate against Muslim or Christian interests in Khazaria for persecution of Jews abroad. ] relates that around ] the Khazar ruler received information that Muslims had destroyed a synagogue in the land of ], in ]; he gave orders that the ] of the ] in his capital should be broken off, and the ] executed. He further declared that he would have destroyed all the mosques in the country had he not been afraid that the Muslims would in turn destroy all the synagogues in their lands. | |||
| {{Main|Arab–Khazar wars}} | |||
| During the 7th and 8th centuries, the Khazars fought a series of wars against the ] and its ] successor. The First Arab-Khazar War began during the first phase of ]. By 640, Muslim forces had reached Armenia; in 642 they launched their first raid across the Caucasus under ]. In 652 Arab forces advanced on the Khazar capital, ], but were ], suffering heavy losses; according to Persian historians such as ], both sides in the battle used ]s against the opposing troops. A number of Russian sources give the name of a Khazar khagan from this period as ] and describe him as a scion of the Göktürk royal house, the Ashina. Whether Irbis ever existed is open to debate, as is whether he can be identified with one of the many Göktürk rulers of the same name. | |||
| The theory that the majority of ] Jews are the descendants of the non-Semitic converted Khazars was advocated by various ] and otherwise ] circles towards the end of the 20th century, especially following the publication of Arthur Koestler's ]. Since Ashkenazi Jews make up the majority of world Jewry, such speculation is often held in conjunction with the belief that modern-day Jews are not the true descendants of the Ancient ], and that contemporary Jewry has no rightful claim to the land of the ]. This thesis is usually advanced in the context of the political conflict between ] and ] to promote Muslim claims to Israeli territory. Despite recent contrary genetic evidence,<ref name="behar">{{cite journal| url=http://www.ftdna.com/pdf/43026_Doron.pdf| title=The Matrilineal Ancestry of Ashkenazi Jewry: Portrait of a Recent Founder Event| first=Doron M.| last=Behar| coauthors=Ene Metspalu, Toomas Kivisild, Alessandro Achilli, Yarin Hadid, Shay Tzur, Luisa Pereira, Antonio Amorim, Lluı's Quintana-Murci, Kari Majamaa, Corinna Herrnstadt, Neil Howell, Oleg Balanovsky, Ildus Kutuev, Andrey Pshenichnov, David Gurwitz, Batsheva Bonne-Tamir, Antonio Torroni, Richard Villems, and Karl Skorecki| journal=The American Journal of Human Genetics| month=March| year=2006| volume=78| issue=3| pages=487-97| id=PMID 16404693}}</ref> and a lack of any real mainstream scholarly support, this belief is still popular among groups such as the ], ], ] and others who claim that they are the descendants of Israel instead of the Jews and seek to downplay the connection between the Jewish people and their Israelite ancestors. | |||
| For more detail on this controversy, ]. | |||
| Due to the outbreak of the ] and other priorities, the Arabs refrained from repeating an attack on the Khazars until the early 8th century.{{sfn|Mako|2010|p=45}} The Khazars launched a few raids into Transcaucasian principalities under Muslim dominion, including a large-scale raid in 683–685 during the ] that rendered much booty and many prisoners.{{sfn|Brook|2010|pp=126–127}} There is evidence from the account of al-Tabari that the Khazars formed a united front with the remnants of the Göktürks in Transoxiana. | |||
| ===Other religions=== | |||
| Besides ], other religions probably practiced in areas ruled by the Khazars included ], ], and ] Christianity, ] as well as ], ], and ] cults. The Khazar government tolerated a wide array of religious practices within the Khaganate. Many Khazars reportedly were converts to Christianity and Islam. (See "Judiciary", below.) | |||
| ] | |||
| A ] bishop was resident at Atil and was subject to the authority of the ] of ]. The "apostle of the Slavs", ], is said to have attempted the conversion of Khazars without enduring results. Khazaran had a sizable Muslim quarter with a number of ]s. A Muslim officer, the '']'', represented the Muslim community in the royal court. | |||
| The Second Arab-Khazar War began with a series of raids across the Caucasus in the early 8th century. The Umayyads tightened their grip on Armenia in 705 after suppressing a large-scale rebellion. In 713 or 714, the Umayyad general ] conquered Derbent and drove deeper into Khazar territory. The Khazars launched raids in response into ] and ] but were driven back by the Arabs under ].{{sfn|Brook|2010|p=127}} The conflict escalated in 722 with an invasion by 30,000 Khazars into Armenia inflicting a crushing defeat. Caliph ] responded, sending 25,000 Arab troops north, swiftly driving the Khazars back across the Caucasus, recovering Derbent, and advancing on Balanjar. The Arabs ] and stormed the city; most of its inhabitants were killed or enslaved, but a few of them managed to flee north.{{sfn|Brook|2010|pp=126–127}} Despite their success, the Arabs had not yet defeated the Khazar army, and they retreated south of the Caucasus. | |||
| In 724, the Arab general ] inflicted a crushing defeat on the Khazars in a long battle between the rivers ] and ], then moved on to capture ], bringing ] under Muslim suzerainty. The Khazars struck back in 726, led by a prince named ], launching a major invasion of Albania and Azerbaijan; by 729, the Arabs had lost control of northeastern Transcaucasia and were thrust again into the defensive. In 730, Barjik invaded Iranian Azerbaijan and ] Arab forces at ], killing the general ] and briefly occupying the town. Barjik was defeated and killed the next year at ], where he directed Khazar forces from a throne mounted with al-Djarrah's severed head {{citation needed|date=November 2016}}. In 737, Marwan Ibn Muhammad entered Khazar territory under the guise of seeking a truce. He then launched a surprise attack in which The Qaghan fled north and the Khazars surrendered.{{sfn|Golden|1980|p=64}} The Arabs did not have enough resources to influence the affairs of Transcaucasia.{{sfn|Golden|1980|p=64}} The Qağan was forced to accept terms involving his conversion to Islam, and subject himself to the rule of the Caliphate, but the accommodation was short-lived because a combination of internal instability among the Umayyads and Byzantine support undid the agreement within three years, and the Khazars re-asserted their independence.{{sfn|Wasserstein|2007|pp=375–376}} The suggestion that the Khazars adopted ] as early as 740 is based on the idea that, in part, it was, a re-assertion of their independence from the rule of both regional powers, Byzantium and the Caliphate, while it also conformed to a general Eurasian trend to embrace a ].{{efn|group=note|"The Khazars, the close allies of the Byzantines, adopted Judaism, as their official religion, apparently by 740, three years after an invasion by the Arabs under Marwan ibn Muhammad. Marwan had used treachery against a Khazar envoy in order to gain peaceful entrance into Khazar territory. He then declared his dishonourable intentions and pressed deep into Khazar territory, subsequently, he released the envoy. The Arabs devastated the horse herds, seized many Khazars and others as captives, and forced much of the population to flee into the Ural Mountains. Marwan's terms dictated that the kaghan and his Khazars should convert to Islam. Having no choice, the kaghan accepted Marwan's terms, and the Arabs returned home in triumph. As soon as the Arabs were gone, the kaghan renounced Islam – with, one may assume, great vehemence. The Khazar Dynasty's conversion to Judaism is best explained by this specific historical background, together with the fact that the mid-eighth century was an age in which the major Eurasian states proclaimed their adherence to distinctive world religions. Adopting Judaism also was politically astute: it meant that the Khazars did not have to accept the overlordship (however theoretical) of the Arab caliph or the Byzantine emperor." {{harv|Beckwith|2011|p=149}}}} | |||
| ==Government== | |||
| ===Khazar kingship=== | |||
| {{main|Khagan|Khagan Bek|List of Khazar rulers}} | |||
| Whatever the impact of Marwan's campaigns was, warfare between the Khazars and the Arabs ceased for more than two decades after 737. Arab raids continued to occur until 741, but their control of the region was limited because maintaining a large garrison at Derbent further depleted their already overstretched army. A ] soon broke out, leading to the Abbasid Revolution and the fall of the Umayyad dynasty in 750. | |||
| )</ref>]] | |||
| In 758, the ] ] ] attempted to strengthen diplomatic ties with the Khazars, ordering ], one of his nobles and the ], to take a royal Khazar bride.{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|p=179}} Yazid married a daughter of Khazar Khagan ], but she died inexplicably, possibly during childbirth. Her attendants returned home, convinced that some members of another Arab faction had poisoned her, and her father was enraged. The Khazar general ] invaded regions which were located south of the Caucasus in 762–764, devastating Albania, Armenia, and Iberia, and capturing Tiflis.{{sfn|Brook|2018|p=115}} Thereafter, relations between the Khazars and the Abbasids became increasingly cordial, because the foreign policies of the Abbasids were generally less expansionist than the foreign policies of the Umayyads, relations between the Khazars and the Abbasids were ultimately broken by a series of raids which occurred in 799, the raids occurred after another marriage alliance failed.{{sfn|Brook|2018|p=115}} | |||
| Khazar kingship was divided between the ] and the ] or ]. Contemporary Arab historians related that the Khagan was purely a spiritual ruler or figurehead with limited powers, while the Bek was responsible for administration and military affairs. | |||
| === Khazars and Hungarians === | |||
| Both the Khagan and the Khagan Bek lived in Itil. The Khagan's palace, according to Arab sources, was on an island in the Volga River. He was reported to have 25 wives, each the daughter of a client ruler; this may, however, have been an exaggeration. | |||
| Around 830, a rebellion broke out in the Khazar khaganate. As a result, three ] tribes{{sfn|Makkai|1994|p=11}} of the Khazars (probably the majority of ethnic Khazars) joined the Hungarians and moved through ] to what the Hungarians call the ], the territory between the ] and the ]. The Hungarians faced their first attack by the ] around 854,{{sfn|Country Study: Hungary|1989}} though other sources state that an attack by Pechenegs was the reason for their departure to Etelköz. The new neighbours of the Hungarians were the ] and the eastern ]. From 862 onwards, the Hungarians (already referred to as the ''Ungri'') along with their allies, the Kabars, started a series of raids from the Etelköz into the Carpathian Basin, mostly against the ] (Germany) and ], but also against the ] and ]. Then they together ended up at the outer slopes of Carpathians, and settled there. | |||
| === Rise of the Rus' and the collapse of the Khazarian state === | |||
| ] | |||
| By the 9th century, groups of ], developing a powerful warrior-merchant system, began probing south down the waterways controlled by the Khazars and their protectorate, the ]ns, partially in pursuit of the Arab silver that flowed north for hoarding through the Khazarian-Volga Bulgarian trading zones,{{efn|group=note|Over 520 separate hoards of such silver have been uncovered in Sweden and ] {{harv|Moss|2002|p=16}}.}} partially to trade in furs and ironwork.{{efn|group=note|The Volga Bulgarian state was converted to Islam in the 10th century, and wrested liberty from its Khazarian suzerains when ] razed Atil {{harv|Abulafia|1987|pp=419, 480–483}}.}} Northern mercantile fleets passing Atil were tithed, as they were at Byzantine ].{{sfn|Shepard|2006|p=19}} Their presence may have prompted the formation of a Rus' state by convincing the ], ] and the ]' to unite to protect common interests against Khazarian exactions of tribute. It is often argued that a ] modelled on the Khazarian state had formed to the east and that the Varangian chieftain of the coalition appropriated the title of qağan (''khagan'') as early as the 830s: the title survived to denote the princes of ], whose capital, ], is often associated with a Khazarian foundation.{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=245}}{{sfn|Noonan|2001|p=81}}{{efn|group=note|Whittow argues however that: "The title of qaghan, with its claims to lordship over the steppe world, is likely to be no more than ideological booty from the 965 victory." {{harv|Whittow|1996|pp=243–252}}}}{{efn|group=note|Korobkin citing Golb & Pritsak notes that Khazars have often been connected with Kiev's foundations.{{sfn|Korobkin|1998|p=xxvii}} Pritsak and Golb state that children in ] were being given a mixture of ] and ] names by c. 930.{{sfn|Golb|Pritsak|1982|p=15}} Toch on the other hand is sceptical, and argues that "a significant Jewish presence in early medieval Kiev or indeed in Russia at large remains much in doubt".{{sfn|Toch|2012|p=166}}}} The construction of the ], with technical assistance from Khazaria's Byzantine ally at the time, together with the minting of an autonomous Khazar coinage around the 830s, may have been a defensive measure against emerging threats from Varangians to the north and from the ] on the eastern steppe.{{efn|group=note|The '']'' based on the Arab '']'' was perhaps issued in reaction to fall-off in Muslim minting in the 820s, and to a felt need in the turbulent upheavals of the 830s to assert a new religious profile, with the Jewish legends stamped on them {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=156}}.}}{{efn|group=note|Scholars are divided as to whether the fortification of Sarkel represents a defensive bulwark against a growing Magyar or Varangian threat {{harv|Petrukhin|2007|pp=247, and n.1}}.}} By 860, the Rus' had penetrated as far as Kiev and, via the ], ].{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=257}} | |||
| In the ], ] identifies himself as the ruler of the Khazars and makes no reference to a colleague. It has been disputed whether Joseph was a Khagan or a Bek; his description of his military campaigns make the latter probable. A third option is that by the time of the Correspondence (c. 950-]) the Khazars had merged the two positions into a single ruler, or that the Beks had somehow supplanted the Khagans or vice versa. | |||
| ] in the 1950s).]] | |||
| The Khazar dual kingship may have influenced other people; power was similarly divided among the early ] between the sacral king, or ], and the military king, or ]. Similarly, according to ], the early ] had a warlord, the ], who was subordinate to the reigning ]. | |||
| Alliances often shifted. Byzantium, threatened by Varangian Rus' raiders, would assist Khazaria, and Khazaria at times allowed the northerners to pass through their territory in exchange for a portion of the booty.{{sfn|Kohen|2007|p=107}} From the beginning of the 10th century, the Khazars found themselves fighting on multiple fronts as nomadic incursions were exacerbated by uprisings by former clients and invasions from former allies. The ] was caught in a pincer movement between steppe Pechenegs and the strengthening of an emergent Rus' power to the north, both undermining Khazaria's tributary empire.{{sfn|Noonan|1999|pp=502–503}} According to the ], the Khazar ruler ] (ca.880–890) fought a battle against the allied forces of five lands whose moves were perhaps encouraged by Byzantium.{{efn|group=note|''MQDWN'' or the ]; ''SY'', perhaps a central Volga statelet, ], Asya; ''PYYNYL'' denoting the ]; ''BM'', perhaps indicating the ], and ''TWRQY'' or ]. The provisory identifications are those of Pritsak {{harv|Kohen|2007|p=106}}.}} Although Benjamin was victorious, his son ] faced another invasion, this time led by the ], whose leader had converted to Christianity and entered into an alliance with Byzantium, which, under ], encouraged them to fight against the Khazars. | |||
| By the 880s, Khazar control of the Middle ] from Kiev, where they collected tribute from Eastern Slavic tribes, began to wane as ] wrested control of the city from the Varangian warlords ], and embarked on what was to prove to be the foundation of a Rus' empire.{{sfn|Noonan|1999|p=508}} The Khazars had initially allowed the Rus' to use the ] along the Volga River, and raid southwards. See ]. According to ], the qağan is said to have given his assent on the condition that the Rus' give him half of the booty.{{sfn|Kohen|2007|p=107}} In 913, however, two years after Byzantium concluded a peace treaty with the Rus' in 911, a ] foray, with Khazar connivance, through Arab lands led to a request to the Khazar throne by the Khwârazmian Islamic guard for permission to retaliate against the large Rus' contingent on its return. The purpose was to revenge the violence the Rus' ] had inflicted on their fellow Muslim believers.{{efn|group=note|Al-Mas'udi says the king secretly tipped off the Rus' of the attack but was unable to oppose the request of his guards {{harv|Olsson|2013|p=507}}.}} The Rus' force was thoroughly routed and massacred.{{sfn|Kohen|2007|p=107}} The Khazar rulers closed the passage down the Volga to the Rus', sparking a war. In the early 960s, Khazar ruler ] wrote to ] about the deterioration of Khazar relations with the Rus': "I protect the mouth of the river (Itil-Volga) and prevent the Rus arriving in their ships from setting off by sea against the ] and (equally) all (their) enemies from setting off by land to ]."{{efn|group=note|The letter continues: "I wage war with them. If I left them (in peace) for a single hour they would crush the whole land of the Ishmaelites up to ]." {{harv|Petrukhin|2007|p=257}}}} | |||
| ===Army=== | |||
| ] (in boat), destroyer of the Khazar Khaganate.{{efn|group=note|From Klavdiy Lebedev (1852–1916), ''Svyatoslav's meeting with ], as described by Leo the Deacon.''}}]] | |||
| Khazar armies were led by the ] and commanded by subordinate ]s known as ]s. A famous tarkhan referred to in ] sources as ] led an invasion of ] in ]. The army included regiments of ] auxiliaries known as ], of ]ian or ] extraction, who were quite influential. These regiments were exempt from campaigning against their fellow Muslims. Early ]n sources sometimes referred to the city of ] (across the ] from ]) as ] and the Khazar (]) sea as ]. According to some scholars such as ], these terms were ] versions of "Khwarezmian" and referred to these ]. | |||
| The Rus' warlords launched several wars against the Khazar Qağanate, and raided down to ]. The ] relates the story of a campaign against Khazaria by ''HLGW'' (recently identified as Oleg of Chernigov) around 941 in which Oleg was defeated by the Khazar general ].{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=259}} The Khazar alliance with the Byzantine empire began to collapse in the early 10th century. Byzantine and Khazar forces may have clashed in the Crimea, and by the 940s emperor ] was speculating in '']'' about ways in which the Khazars could be isolated and attacked. The Byzantines during the same period began to attempt alliances with the Pechenegs and the Rus', with varying degrees of success. A further factor undermining the Khazar Qağanate was a shift in Islamic routes at this time, as Muslims in Khwarazmia forged trade links with the recently converted Volga Bulgarian Muslims, a move which may have caused a drastic drop, perhaps up to 80%, in the revenue base of Khazaria, and consequently, a crisis in its ability to pay for its defence.{{sfn|Feldman|2022a|pp=75–84}} | |||
| ] finally succeeded in destroying Khazar imperial power in the 960s, in a circular sweep that overwhelmed Khazar fortresses like ] and ], and reached as far as the Caucasian Kassogians/]{{efn|group=note|] argued that the Khazars were the ancestors of contemporary Circassians {{harv|Howorth|1870|pp=182–192}}.}} and then back to Kiev.{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=262}} Sarkel fell in 965, with the capital city of ] following, c. 968 or 969. | |||
| In addition to the Bek's standing army, the Khazars could call upon tribal levies in times of danger and were often joined by ] from subject nations. | |||
| In the Russian chronicle, the vanquishing of the Khazar traditions is associated with Vladimir's conversion in 986.{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|pp=262–263}} According to the '']'', in 986, Khazar Jews were present at ]'s ] to decide on the prospective religion of the Kievan Rus'.{{sfn|''Russian Primary Chronicle''}} Whether these were Jews who had settled in Kiev or emissaries from some Jewish Khazar remnant state is unclear. Conversion to one of the faiths of the people of Scripture was a precondition to any peace treaty with the Arabs, whose Bulgar envoys had arrived in Kiev after 985.{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=263}} | |||
| ===Other officials=== | |||
| Settlements were governed by administrative officials known as ]s. In some cases (such as the Byzantine settlements in southern ]), a tudun would be appointed for a town nominally within another polity's ]. | |||
| A visitor to Atil wrote soon after the sacking of the city that its vineyards and garden had been razed, that not a grape or raisin remained in the land, and not even alms for the poor were available.{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|p=242}} An attempt to rebuild may have been undertaken, since ] and ] refer to it after that date, but by ]'s time (1048) it was in ruins.{{efn|group=note|Dunlop thought the later city of ] lay on or near Atil {{harv|Dunlop|1954|p=248}}.}} | |||
| Other officials in the Khazar government included dignitaries referred to by ] as '']'' and '']'', but their responsibilities are unknown. | |||
| === Aftermath: impact, decline and dispersion === | |||
| ===Judiciary=== | |||
| Although Poliak argued that the Khazar kingdom did not wholly succumb to Sviatoslav's campaign, but lingered on until 1224, when the ],{{sfn|Gow|1995|p=31, n.28}}{{sfn|Sand|2010|p=229}} by most accounts, the Rus'-Oghuz campaigns left Khazaria devastated, with perhaps many Khazarian Jews in flight,{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=148}} and leaving behind at best a minor ]. It left little trace, except for some placenames,{{efn|group=note|The ] is still known to Arabs, and many peoples of the region, as the "Khazar Sea" (Arabic ''Bahr ul-Khazar'') {{harv|Brook|2010|p=156}}}} and much of its population was undoubtedly absorbed in successor hordes.{{sfn|Noonan|1999|p=503}} ], writing ca.985, mentions Khazar beyond the Caspian sea as a district of "woe and squalor", with honey, many sheep and Jews.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|pp=147–148}} ] mentions a joint Rus'-Byzantine attack on Khazaria in 1016, which defeated its ruler ]. The name suggests Christian affiliations. The account concludes by saying, that after Tzul's defeat, the Khazar ruler of "upper Media", Senaccherib, had to sue for peace and submission.{{sfn|Kohen|2007|p=109}} In 1024 ] (one of Vladimir's sons) marched against his brother Yaroslav with an army that included "Khazars and Kassogians" in a repulsed attempt to restore a kind of "Khazarian"-type dominion over Kiev.{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=262}} ]'s mention of a "raid of Faḍlūn the Kurd against the Khazars" in 1030 CE, in which 10,000 of his men were vanquished by the latter, has been taken as a reference to such a Khazar remnant, but ] identified this Faḍlūn as ] and the "Khazars" as either ] or ].{{sfn|Shapira|2007a|p=305}}{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|p=253}} A Kievian prince named ] was reportedly kidnapped by "Khazars" in 1079 and shipped off to ], although most scholars believe that this is a reference to the ]-] or other steppe peoples then dominant in the Pontic region. Upon his conquest of ] in the 1080s Oleg gave himself the title "] of Khazaria".{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=262}} In 1083 Oleg is said to have exacted revenge on the Khazars after his brother Roman was killed by their allies, the ]. After one more conflict with these Polovtsi in 1106, the Khazars fade from history.{{sfn|Kohen|2007|p=109}} By the 13th century they survived in Russian folklore only as "Jewish heroes" in the "land of the Jews". (''zemlya Jidovskaya'').{{sfn|Falk|2017|p=102}} | |||
| Muslim sources report that the Khazar supreme court consisted of two ], two ], two ], and a "heathen" (whether this is a Turkic shaman or a priest of Slavic or Norse religion is unclear), and a citizen had the right to be judged according to the laws of his religion. Some have argued that this configuration is unlikely, as a Beit Din, or rabbinical court, requires three members. It is therefore possible that as practitioners of the state religion, the Jews had three judges on the Supreme Court rather than two, and that the Muslim sources were attempting to downplay their influence. A ] or ] court can function with only one or two judges. | |||
| By the end of the 12th century, ] reported travelling through what he called "Khazaria", and had little to remark on other than describing its ''minim'' (sectaries) living amidst desolation in perpetual mourning.{{sfn|Sand|2010|p=227}} The reference seems to be to Karaites.{{sfn|Dubnov|1980|p=792}} The Franciscan missionary ] likewise found only impoverished pastures in the lower Volga area where Ital once lay.{{sfn|Noonan|2007|p=214}} ], the papal legate to the court of the ] Khan ] at that time, mentioned an otherwise unattested Jewish tribe, the ], perhaps in the Volga region. Although connections are made to the Khazars, the link is based merely on a common attribution of Judaism.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=45, n.157}} | |||
| ==Economic position== | |||
| ===Trade=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The Khazars occupied a prime ] nexus. Goods from western Europe travelled east to Central Asia and China and vice versa, and the Muslim world could only interact with northern Europe via Khazar intermediaries. The ], a guild of medieval Jewish merchants, had a trade route that ran through Khazaria, and may have been instrumental in the Khazars' conversion to Judaism. | |||
| ]s, c. 1015 (areas in blue possibly still under Khazar control).]] | |||
| No Khazar paid taxes to the central government. Revenue came from a 10% levy on goods transiting through the region, and from tribute paid by subject nations. The Khazars exported ], ]s, ], ] and other ]s, ], and ]. D.M. Dunlop and Artamanov asserted that the Khazars produced no material goods themselves, living solely on trade. This theory has been refuted by discoveries over the last half-century, which include pottery and glass factories. | |||
| The 10th century ] ] registered the collapse of Khazar power in attributing its eclipse to the enfeebling effects of "false" religion.{{efn|group=note|"thus it is clear that the false doctrine of Yišô in Rome (Hrôm) and that of Môsê among the Khazars and that of Mânî in Turkistan took away their might and the valor that they once possessed and made them feeble and decadent among their rivals" {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=130}}.}} The decline was contemporary to that suffered by the ] ] empire to the east, both events paving the way for the rise of the ], whose founding traditions mention Khazar connections.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=159}}{{efn|group=note|Some sources claim that the father of ], the eponymous progenitor of the ], namely Toqaq Temür Yalığ, began his career as an Oghuz soldier in Khazar service in the early and mid-10th century, and rose to high rank before he fell out with the Khazar rulers and departed for ]. Seljuk's sons, significantly, all bear names from the ]: Mîkâ"il, Isrâ"îl, Mûsâ, Yûnus. Peacock argues that early traditions attesting a Seljuk origin within the Khazar empire when it was powerful, were later rewritten, after Khazaria fell from power in the 11th century, to blank out the connection {{harv|Peacock|2010|pp=27–35}}.}} Whatever successor entity survived, it could no longer function as a bulwark against the pressure east and south of nomad expansions. By 1043, ] and ], thrusting westwards, pressured the ], who in turn pushed the ] west towards Byzantium's Balkan provinces.{{sfn|Peacock|2010|p=35}} | |||
| Khazaria nonetheless left its mark on the rising states and some of their traditions and institutions. Much earlier, ], the Khazar wife of ], introduced into the Byzantine court the distinctive kaftan or riding habit of the nomadic Khazars, the tzitzakion (τζιτζάκιον), and this was adopted as a solemn element of imperial dress.{{efn|group=note|Tzitzak is often treated as her original ], with a Turkic etymology ''čiček'' ("flower"). Erdal, however, citing the Byzantine work on court ceremony ], authored by ], argues that the word referred only to the dress Irene wore at court, perhaps denoting its colourfulness, and compares it to the Hebrew '']'', the knotted fringes of a ceremonial shawl, or ] ({{harvnb|Erdal|2007|p=80, n.22}}; {{harvnb|Wexler|1987|p=72}}).}} The orderly hierarchical system of succession by "scales" (''lestvichnaia sistema'':лествичная система) to the ] was arguably modelled on Khazar institutions, via the example of the ].{{sfn|Golden|2001a|pp=28–29, 37}} | |||
| ===Khazar coinage=== | |||
| ''See also: ]'' | |||
| The proto-Hungarian Pontic tribe, while perhaps threatening Khazaria as early as 839 (Sarkel), practiced their institutional model, such as the dual rule of a ceremonial ''kende-kündü'' and a ''gyula'' administering practical and military administration, as tributaries of the Khazars. A dissident group of Khazars, the ], joined the Hungarians in their migration westwards as they moved into ]. Elements within the Hungarian population can be viewed as perpetuating Khazar traditions as a successor state. Byzantine sources refer to Hungary as ] in contrast to Khazaria, Eastern Tourkia. The gyula line produced the kings of medieval Hungary through descent from ], while the Qabars retained their traditions longer, and were known as "black Hungarians" (''fekete magyarság''). Some archaeological evidence from ] suggests the Qabars practised Judaism{{sfn|Golden|1994b|pp=247–248}}{{sfn|Róna-Tas|1999|p=56}}{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=33}} since warrior graves with Jewish symbols were found there, including ], ]s, ]s, ]s, candlesnuffers, ash collectors, inscriptions in Hebrew, and a six-pointed star identical to the ].{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=150}}{{sfn|Brook|2010|p=167}} | |||
| The Khazars are known to have minted silver coins, called '']s''. Many of these were imitations of Arab ]s with corrupted Arabic letters. Coins of the Caliphate were in widespread use due to their reliable silver content. Merchants from as far away as ], ], and ] accepted them regardless of their inability to read the Arab writing. Thus issuing imitation dirhems was a way to ensure acceptance of Khazar coinage in foreign lands. | |||
| ] | |||
| The Khazar state was not the only Jewish state to rise between the ] (67–70 CE) and the ] (1948). A ] also adopted Judaism in the 4th century, lasting until the rise of Islam.{{sfn|Bowersock|2013|pp=85ff.}} | |||
| Some surviving examples bear the legend "Ard al-Khazar" (Arabic for "land of the Khazars"). In 1999 a hoard of ] coins was discovered on the property of the Spillings farm in the ] island of ]. Among the coins were several dated 837/8 CE and bearing the legend, in ], "] is the Prophet of God" (a modification of the Muslim coin inscription "] is the Prophet of God").<ref>Brook ch. 5.</ref> In "Creating Khazar Identity through Coins", Roman Kovalev postulated that these dirhems were a special ] issue celebrating the adoption of Judaism by the Khazar ruler Bulan.<ref>Kovalev, "Creating Khazar Identity" 220-253.</ref> | |||
| The Khazar kingdom is said to have stimulated messianic aspirations for a return to Israel as early as ].{{sfn|Schweid|2007|p=286}} In the time of the Egyptian vizier ] (d. 1121), one Solomon ben Duji, often identified as a Khazarian Jew,{{efn|group=note|Brook says this thesis was developed by Jacob Mann, based on a reading of the word "Khazaria" in the Cairo Geniza fragment. Bernard Lewis, he adds, challenged the assumption by noting that the original text reads ''Hakkâri'' and refers to the Kurds of the ] in south-east Turkey {{harv|Brook|2010|pp=191–192, n.72}}.}} attempted to advocate for a messianic effort for the liberation of, and return of all Jews to, Palestine. He wrote to many Jewish communities to enlist support. He eventually moved to ] where his son ] some decades later assumed the title of ] and, raising an army for this purpose, took the fortress of ] north of ]. His project was opposed by the rabbinical authorities and he was poisoned in his sleep. One theory maintains that the Star of David, until then a decorative motif or magical emblem, began to assume its national value in late Jewish tradition from its earlier symbolic use by Menachem.{{sfn|Baron|1957|pp=202–204 }} | |||
| ==Extent of influence== | |||
| The Khazar Khaganate was, at its height, an immensely powerful state. The Khazar heartland was on the lower Volga and the Caspian coast as far south as ]. In addition, from the late 600s the Khazars controlled most of the ] and the northeast littoral of the ]. By 800 Khazar holdings included most of the Pontic steppe as far west as the Dneiper and as far east as the Aral Sea (some Turkic history atlases show the Khazar sphere of influence extending well east of the Aral). During the Khazar-Arab war of the early 700s, some Khazars evacuated to the ] foothills, and some settlements may have remained. | |||
| The word Khazar, as an ethnonym, was last used in the 13th century by people in the North Caucasus believed to practice Judaism.{{sfn|Wexler|2002|p=514}} The nature of a hypothetical Khazar ], Jewish or otherwise, is disputed. ] mentions encountering rabbinical students descended from Khazars as far away as ] in the 1160s.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=149}} Khazar communities persisted here and there. Many Khazar mercenaries served in the armies of the Islamic Caliphates and other states. Documents from medieval Constantinople attest to a Khazar community mingled with the Jews of the suburb of ].{{sfn|Brook|2010|pp=177–178}} Khazar merchants were active in both Constantinople and Alexandria in the 12th century.{{sfn|Noonan|2007|p=229}} | |||
| ===Khazar towns=== | |||
| ] ] and surrounding states, c. 820 CE. Area of direct Khazar control shown in dark blue, sphere of influence in purple. Other boundaries shown in dark red.]] | |||
| Khazar towns included: | |||
| *Along the Caspian coast and Volga delta: | |||
| :]; ]; ] | |||
| *In the ]: | |||
| :]; ]; ]; ] | |||
| *In ] and ] region: | |||
| :] (also called Bospor); ]; Güzliev (modern ]); ] (also called ], Tamatarkha); ] (also called Sugdaia) | |||
| *In the ] valley: | |||
| :] | |||
| *A number of Khazar settlements have been discovered in the ] region. On the ], the Khazars founded a settlement called Sambat, which was part of what would become the city of ]. ] is also thought to have started as a Khazar settlement. | |||
| == Religion == | |||
| ===Tributary and subject nations=== | |||
| === Tengrism === | |||
| ] ] and surrounding states, c. 820 CE. ]] | |||
| {{Main|Tengrism}} | |||
| Many nations were tributaries of the Khazars. A ] subject to Khazar overlordship was called an "]". At various times, Khazar vassals included: | |||
| Direct sources for the Khazar religion are not many, but in all likelihood they originally engaged in a traditional Turkic form of religious practices known as ], which focused on the ] ]. Something of its nature may be deduced from what we know of the rites and beliefs of contiguous tribes, such as the North Caucasian Huns. ]s were made to this supreme deity. Rites involved offerings to fire, water, and the moon, to remarkable creatures, and to "gods of the road" (cf. Old Türk ''yol tengri'', perhaps a god of fortune). Sun amulets were widespread as cultic ornaments. A tree cult was also maintained. Whatever was struck by lightning, man or object, was considered a sacrifice to the high god of heaven. The afterlife, to judge from excavations of aristocratic tumuli, was much a continuation of life on earth, warriors being interred with their weapons, horses, and sometimes with human sacrifices: the funeral of one ''tudrun'' in 711-12 saw 300 soldiers killed to accompany him to the otherworld. ] was observed. The key religious figure appears to have been a ]-like ''qam'',{{sfn|Golden|2007b|pp=131–133}} and it was these (''qozmím'') that were, according to the Khazar Hebrew conversion stories, driven out. | |||
| '''In the Pontic steppes, Crimea and Turkestan''' | |||
| :The ] ; the ]; the ]; the Crimean ] (]?); the early ] | |||
| Many sources suggest, and a notable number of scholars have argued, that the charismatic Ashina clan played a germinal role in the early Khazar state, although Zuckerman dismisses the widespread notion of their pivotal role as a "phantom". The Ashina were closely associated with the Tengri cult, whose practices involved rites performed to assure a tribe of heaven's protective providence.{{sfn|Whittow|1996|p=220}} The qağan was deemed to rule by virtue of ], "the heavenly mandate/good fortune to rule."{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=133}}{{efn|group=note|Whittow notes that this native institution, given the constant, lengthy, military and acculturating pressures on the tribes from China to the East, was influenced also by the ] doctrine of the ], which signaled legitimacy of rule {{harv|Whittow|1996|p=220}}.}} | |||
| '''In the Caucasus''' | |||
| :]; ]; various ]n principalities; ]; the ]; ]; the ]; the ]; and the ]. | |||
| === Christianity === | |||
| '''On the Upper Don and Dneiper''' | |||
| Khazaria long served as a ] between the ] and both the nomads of the northern steppes and the ], after serving as Byzantium's proxy against the ]. The alliance was dropped around 900. Byzantium began to encourage the ] to attack Khazaria and weaken its hold on Crimea and the Caucasus, while seeking to obtain an entente with the rising Rus' power to the north, which it aspired to convert to Christianity.{{sfn|Noonan|1999|pp=499, 502–503}} | |||
| :Various ] tribes such as the ] and the ]; various early ] polities | |||
| On Khazaria's southern flank, both Islam and Byzantine Christianity were proselytising great powers. Byzantine success in the north was sporadic, although Armenian and Albanian missions from ] built churches extensively in maritime ], then a Khazar district.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|pp=124, 135}} ] also had exercised an attraction on leaders of both the Eastern (552–742) and Western Qağanates (552–659), the latter being the progenitor of the Khazar state.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=125}} In 682, according to the Armenian chronicle of ], the king of ], ], dispatched a bishop, Israyêl, to convert Caucasian "Huns" who were subject to the Khazars, and managed to convince Alp Ilut'uêr, a son-in-law of the Khazar qağan, and his army, to abandon their shamanising cults and join the Christian fold.{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|pp=292–293}}{{efn|group=note|Alp Ilut'uêr is a Turkish subordinate title {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=124}}.}} | |||
| '''On the Volga''' | |||
| :]; the ]; various ] forest tribes such as the ] and ]; the ]; the ] | |||
| The Arab Georgian martyr ], who converted to Christianity within the Khazar kingdom around 779–80, describes local Khazars as irreligious.{{efn|group=note|Golden and Shapira thinks the evidence from such Georgian sources renders suspect a conversion prior to this date ({{harvnb|Golden|2007b|pp=135–136}}; {{harvnb|Shapira|2007b|pp=347–348}}).}} Some reports register a Christian majority at ],{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Golden|2007b|pp=135–136}}, reporting on ].}} or Muslim majorities.{{efn|group=note|During Islamic invasions, some groups of Khazars who suffered defeat, including a qağan, were converted to Islam {{harv|DeWeese|1994|p=73}}.}} | |||
| ==Decline and fall== | |||
| The ninth century is sometimes known as the '']'', a period of Khazar ] over the ] that allowed trade to flourish and facilitated trans-Eurasian contacts. However, in the early 10th century the empire began to decline due to the attacks of both ]s from ] and various Turkic tribes. It enjoyed a brief revival under the strong rulers ] and ], who subdued rebellious client states such as the ] and led victorious wars against Rus invaders. | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Kabar rebellion and the departure of the Magyars=== | |||
| {{main|Kabar}} | |||
| At some point in the ninth century (as reported by ]) a group of three Khazar clans called the ] revolted against the Khazar government. ] and others have speculated that the revolt had something to do with a rejection of rabbinic Judaism; this is unlikely as it is believed that both the Kabars and mainstream Khazars had pagan, Jewish, Christian, and Muslim members. Pritsak maintained that the Kabars were led by the Khagan Khan-Tuvan Dyggvi in a war against the Bek. In any event Pritsak cited no primary source for his propositions in this matter. The Kabars were defeated and joined a confederacy led by the Magyars. It has been speculated that "Hungarian" derives from the Turkic word "Onogur", or "Ten Arrows", referring to seven ] tribes and the three tribes of the Kabars. | |||
| === Judaism === | |||
| In the closing years of the ninth century the Khazars and Oghuz allied to attack the Pechenegs, who had been attacking both nations. The Pechenegs were driven westward, where they forced out the Magyars (]) who had previously inhabited the Don-Dnieper basin in vassalage to Khazaria. Under the leadership of the chieftain ] and later ], the Hungarians moved west into modern-day ]. The departure of the Hungarians led to an unstable power vacuum and the loss of Khazar control over the steppes north of the Black Sea. | |||
| ] and dated c. 837/8 CE (223 ]). It is inscribed with "Moses is the messenger of God" instead of the usual Muslim text "Muhammad is the messenger of God".{{sfn|Kovalev|2005|pp=226–228, 252}}]] | |||
| Conversion to Judaism is mentioned in the ] and medieval external sources. The authenticity of the former was long doubted and challenged,{{efn|group=note|] first published the letters around 1660. Controversy arose over their authenticity; it was even argued that the letters represented "no more than Jewish self-consolation and fantasmagory over the lost dreams of statehood" {{harv|Kohen|2007|p=112}}.}} but the documents are now widely accepted by specialists as either authentic or as reflecting internal Khazar traditions.{{efn|group=note|"If anyone thinks that the Khazar correspondence was first composed in 1577 and published in ''Qol Mebasser'', the onus of proof is certainly on him. He must show that a number of ancient manuscripts, which appear to contain references to the correspondence, have all been interpolated since the end of the sixteenth century. This will prove a very difficult or rather an impossible task." {{harv|Dunlop|1954|p=130}}}}{{efn|group=note|"The issue of the authenticity of the Correspondence has a long and mottled history which need not detain us here. Dunlop and most recently Golb have demonstrated that Hasdai's letter, Joseph's response (dating perhaps from the 950s) and the 'Cambridge Document' are, indeed, authentic." {{harv|Golden|2007b|pp=145–146}}}}{{efn|group=note|"(a court debate on conversion) appears in accounts of Khazar Judaism in two Hebrew accounts, as well as in one eleventh-century Arabic account. These widespread and evidently independent attestations would seem to support the historicity of some kind of court debate, but, more important, clearly suggest the currency of tales recounting the conversion and originating among the Khazar Jewish community itself" ... "the 'authenticity' of the Khazar correspondence is hardly relevant"{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|p=171}} "The wider issue of the 'authenticity' of the 'Khazar correspondence', and of the significance of this tale's parallels with the equally controversial Cambridge document /Schechter text, has been discussed extensively in the literature on Khazar Judaism; much of the debate loses significance if, as Pritsak has recently suggested, the accounts are approached as 'epic' narratives rather than evaluated from the standpoint of their 'historicity'."{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|p=305}}}}{{sfn|Szpiech|2012|p=102}} Archaeological evidence for conversion, on the other hand, remains elusive,{{efn|group=note|"Of the intensive archaeological study of Khazar sites (over a thousand burial sites have been investigated!), not one has yet yielded finds that yet fit in some way the material legacy of antique European or Middle Eastern Jewry." {{harv|Toch|2012|pp=162–163}}}}{{efn|group=note|Shingiray noting the widespread lack of artifacts of wealth in Khazar burials, arguing that nomads used few materials to express their personal attributes: "The SMC assemblages-even if they were not entirely missing from the Khazar imperial center - presented an outstanding instance of archaeological material minimalism in this region." {{harv|Shingiray|2012|pp=209–211}}}} and may reflect either the incompleteness of excavations, or that the stratum of actual adherents was thin.{{efn|group=note|"But, one must ask, are we to expect much religious paraphernalia in a recently converted steppe society? Do the Oğuz, in the century or so after their Islamization, present much physical evidence in the steppe for their new faith? These conclusions must be considered preliminary." {{harv|Golden|2007b|pp=150–151, and note 137}}}} Conversion of steppe or peripheral tribes to a ] is a fairly well attested phenomenon,{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Golden|2007b|pp=128–129}} compares ]'s conversions of the ] to ]; Al-Masudi records a conversion of the ] to Christianity during the Abbasid period; the Volga Bulğars adopted Islam after their leader converted in the 10th century; the Uyğur Qağan accepted Manichaeism in 762.}} and the Khazar conversion to Judaism, although unusual, would not have been without precedent.{{efn|group=note|Golden takes exception to ]'s claim (1912) that it was "unique in history".{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=123}}{{sfn|Koestler|1977|p=52}} Golden also cites from Jewish history the conversion of ] under ]; of the ]ns under ]; of the kingdom of ] under ]; the ], and ] assimilations into North African Jewry.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=153}}}} | |||
| ===Diplomatic isolation and military threats=== | |||
| ] (seated in the boat), the destroyer of the Khazar Khaganate. <br>From Klavdiy Lebedev (1852–1916), ''Svyatoslav's meeting with ], as described by Leo the Deacon.'']] | |||
| Jews from both the Islamic world and Byzantium are known to have migrated to Khazaria during periods of persecution under ], ], ], and ].{{sfn|Golden|2007b|pp=141–145, 161}}{{sfn|Noonan|2001|pp=77–78}} For ], Jewish communities from the Balkans and the Bosphoran Crimea, especially from ], began migrating to the more hospitable climate of pagan Khazaria in the wake of these persecutions, and were joined there by Jews from Armenia. The ], he argues, make it clear the Judaising reforms sent roots down into the whole of the population.{{sfn|Schama|2013|p=266}} The pattern is one of an elite conversion preceding large-scale adoption of the new religion by the general population, which often resisted the imposition.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=125}} One important condition for mass conversion was a settled urban state, where churches, synagogues or mosques provided a focus for religion, as opposed to the free nomadic lifestyle of life on the open steppes.{{efn|group=note|"The ] wandering out into the steppe was far more effective in bringing Islam to the Turkic nomads than the learned ] of the cities." {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=126}}}} A tradition of the Iranian ] claims that their ancestors were responsible for the Khazar conversion.{{sfn|Wexler|1987|p=61}} A legend traceable to the 16th-century Italian rabbi ] attributed it to ].{{sfn|Szyszman|1980|pp=71, 73}}{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|pp=122–124}}{{sfn|Brook|2010|pp=95, 117 n.51,52}} | |||
| The alliance with the Byzantines began to collapse in the early ]. Byzantine and Khazar forces may have clashed in the Crimea, and by the ] ] Porphyrogentius was speculating in '']'' about ways in which the Khazars could be isolated and attacked. The Byzantines during the same period began to attempt alliances with the Pechenegs and the Rus, with varying degrees of success. | |||
| Both the date of the conversion, and the extent of its influence beyond the elite,{{efn|group=note|"the Khazars (most of whom did not convert to Judaism, but remained animists, or adopted Islam and Christianity)" {{harv|Wexler|2002|p=514}}}} often minimised in some scholarship,{{efn|group=note|"In much of the literature on conversions of Inner Asian peoples, attempts are made, 'to minimize the impact' ... This has certainly been true of some of the scholarship regarding the Khazars." {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=127}}}} are a matter of dispute,{{efn|group=note|"scholars who have contributed to the subject of the Khazars' conversion, have based their arguments on a limited corpus of textual, and more recently, numismatic evidence ... Taken together these sources offer a cacophony of distortions, contradictions, vested interests, and anomalies in some areas, and nothing but silence in others." {{harv|Olsson|2013|p=496}}}} but at some point between 740 and 920 CE, the Khazar ] and ] appear to have converted to ], in part, it is argued, perhaps to deflect competing pressures from Arabs and Byzantines to accept either Islam or Christianity.{{efn|group=note|"Judaism was apparently chosen because it was a religion of the book without being the faith of a neighbouring state which had designs on Khazar lands." {{harv|Noonan|1999|p=502}}}}{{efn|group=note|"Their conversion to Judaism was the equivalent of a declaration of neutrality between the two rival powers." {{harv|Baron|1957|p=198}}}} | |||
| From the beginning of the tenth century, the Khazars found themselves fighting on multiple fronts as nomadic incursions were exacerbated by uprisings by former clients and invasions from former allies. According to the ], the Khazar ruler ] fought a war against a coalition of "'SY, TWRQY, 'BM, and PYYNYL," who were instigated and aided by "MQDWN". MQDWN or ] refers to the Byzantine Empire in many medieval Jewish writings; the other entities named have been tenuously identified by scholars including Omeljan Pritsak with the ], ], ] and ], respectively. Though Benjamin was victorious, his son ] had to face another invasion, this time led by the ]. Aaron defeated the Alans with Oghuz help, yet within a few years the Oghuz and Khazars were enemies. | |||
| The conversion of the Khazars to Judaism is an emotionally charged topic in Israel,{{efn|group=note|"in Israel, emotions are still high when it comes to the history of the Khazars, as I witnessed in a symposium on the issue at the Israeli Academy of Sciences in Jerusalem (May 24, 2011). Whereas Prof. Shaul Stampfer believed the story of the Khazars' conversion to Judaism was a collection of stories or legends that have no historical foundation, (and insisted that the Ashkenazi of Eastern Europe of today stem from Jews in Central Europe who emigrated eastwards), Prof. Dan Shapiro believed that the conversion of the Khazars to Judaism was part of the history of Russia at the time it established itself as a kingdom." {{harv|Falk|2017|p=101, n. 9}}}} and two scholars, ] (2011) and ], (2013) have challenged the authenticity of the medieval Hebrew documents and argue that the conversion of the Khazar elite to Judaism never happened.{{sfn|Stampfer|2013|pp=1–72}}{{sfn|Gil|2011|pp=429–441}} Alex M. Feldman is critical of Stampfer and Gil's dismissal of "overwhelming textual and archaeological evidence" of Khazarian Judaism, though agrees it is unlikely that Ashkenazim are descended from Khazarian Jews, he posits "a middle ground which can simultaneously accept Khazarian Judaism and doubt the Khazar-Ashkenazi descent theory advanced in dubious genetic studies."{{sfn|Feldman|2022b|pp=193–205}} | |||
| ] reported Oghuz hostility to the Khazars during his journey c. 921. Some sources, discussed by Tamara Rice, claim that ], the eponymous progenitor of the ], began his career as an Oghuz soldier in Khazar service in the early and mid-tenth century, rising to high rank before he fell out with the Khazar rulers and departed for ]. | |||
| ==== History of discussions about Khazar Jewishness ==== | |||
| ===Rise of Rus=== | |||
| The earliest surviving Arabic text that refers to Khazar Jewishness appears to be that which was written by ], a Persian scholar who wrote an encyclopedic work on geography in the early tenth century.{{sfn|Stampfer|2013|p=17}} It is believed that ibn Rustah derived much of his information from the works of his contemporary ] based in Central Asia. | |||
| ] | |||
| Originally the Khazars were probably allied with various ] factions who controlled the region around ]. The ], an early Rus polity in northwestern Russia, was probably heavily influenced by the Khazars. The Rus' regularly travelled through Khazar-held territory to attack territories around the Black and Caspian Seas; in one such raid, the Khagan is said to have given his assent on the condition that the Rus' give him half of the booty. In addition, the Khazars allowed the Rus to use the ] along the Volga River. This alliance was apparently fostered by the hostility between the Khazars and Arabs. At a certain point, however, the Khazar connivance to the sacking of the Muslim lands by the ] led to a backlash against the Norsemen from the Muslim population of the Khaganate. The Khazar rulers closed the passage down the Volga for the Rus', sparking a war. In the early 960s, Khazar ruler ] wrote to ] about the deterioration of Khazar relations with the Rus: "I have to wage war with them, for if I would give them any chance at all they would lay waste the whole land of the Muslims as far as ]." | |||
| ] (in red) and the ] (in purple). Other trade routes of the ]-] shown in orange.]] | |||
| ] has ] (Orkhon) inscription word-phrase ''OKHQURÜM'', "I read (this or it)".]] | |||
| The Rus warlords ] and ] launched several wars against the Khazar khaganate, often with Byzantine connivance. The Schechter Letter relates the story of a campaign against Khazaria by HLGW (Oleg) around ] (in which Oleg was defeated by the Khazar general ]; this calls into question the timeline of the ] and other related works on the history of the Eastern Slavs. | |||
| ] in his ] (c. 860–870s) refers to ''Gazari'', presumably Khazars, as living in the lands of ], who were circumcised and ''omnem Judaismum observat''—observing all the laws of Judaism.{{efn|group=note|"We are not aware of any nation under the sky that would not have Christians among them. For even in Gog and Magog, the Hunnic people who call themselves Gazari, those whom Alexander confined, there was a tribe more brave than the others. This tribe had already been circumcised and they profess all dogmata of Judaism (''omnem Judaismum observat'')." {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=139}}}} New numismatic evidence of coins dated 837/8 bearing the inscriptions ''arḍ al-ḫazar'' (Land of the Khazars), or ''Mûsâ rasûl Allâh'' (], in imitation of the Islamic coin phrase: ''Muḥammad rasûl Allâh'') suggest to many the conversion took place in that decade.{{efn|group=note|The idea of a forced general conversion imposed on the Qağanal dynasty in the 830s was advanced by Omeljian Pritsak, and is now supported by Roman Kovalev and Peter Golden {{harv|Olsson|2013|p=497}}.}} Olsson argues that the 837/8 evidence marks only the beginning of a long and difficult official ] that concluded some decades later.{{efn|group=note|Olsson identifies this with the onset of Magyar invasions of the Pontic steppe in the 830s, the construction of Sarkel, and the Schechter letter's reference to Bulan, converted to his Jewish wife Serakh's faith, wresting power, in a period of famine, elements which undermined the qağan, and allowed the creation of the royal diarchy {{harv|Olsson|2013|pp=507, 513ff}}.}} A 9th-century Jewish traveller, ], is said to have informed Spanish Jews in 883 that there was a Jewish polity in the East, and that fragments of the legendary ], part of the line of ] and half-line of ], dwelt in "the land of the Khazars", receiving tribute from some 25 to 28 kingdoms.{{sfn|Brook|2018|p=6}}{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|pp=140–142}}{{sfn|Zhivkov|2015|p=42}} Another view holds that by the 10th century, while the royal clan officially claimed Judaism, a non-normative variety of Islamisation took place among the majority of Khazars.{{sfn|Shingiray|2012|pp=212–214}} | |||
| By the 10th century, the ] asserts that, after the royal conversion, "Israel returned (''yashuvu yisra'el'') with the people of Qazaria (to Judaism) in complete repentance (''bi-teshuvah shelemah'')."{{sfn|Szpiech|2012|pp=92–117 }} ] ] wrote that "all the Khazars are Jews, but they have been Judaized recently". ], based on his Caliphal mission (921–922) to the Volga Bulğars, also reported that "the core element of the state, the Khazars, were Judaized",{{efn|group=note|''wa al-ḥazarwa malikuhum kulluhum yahûd'' ("The Khazars and their king are all Jews") {{harv|Golden|2007b|pp=143, 159}}}} something underwritten by the ] scholar ] around 937.{{efn|group=note|Golden, citing his comment on ] 9:27: "some other commentators are of the opinion that this verse alludes to the Khazars who accepted Judaism", with Golden's comment: "Certainly, by this time, the association of Khazaria and Judaism in the Jewish world was an established fact" {{harv|Golden|2007b|p=143}}.}} The conversion appears to have occurred against a background of frictions arising from both an intensification of Byzantine missionary activity from the Crimea to the Caucasus, and Arab attempts to wrest control over the latter in the 8th century CE,{{sfn|Golden|2007b|pp=137–138}} and a revolt, put down, by the ] around the mid-9th century is often invoked as in part influenced by their refusal to accept Judaism.{{sfn|Spinei|2009|p=50}} Modern scholars generally{{efn|group=note|Shapira and Zuckerman disagree, positing only one stage and placing it later. Shapira takes stage 1 as a Jewish-Khazar reinterpretation of the Tengri-cult in terms of a monotheism similar to Judaism's; Zuckerman thinks Judaisation took place, just once, after 861 ({{harvnb|Shapira|2007b|pp=349, and n.178}}; {{harvnb|Zuckerman|1995|p=250}}).}} see the conversion as a slow process through three stages, which accords with Richard Eaton's model of syncretic ''inclusion'', gradual ''identification'' and, finally, ''displacement'' of the older tradition.{{efn|group=note|Dunlop thought the first stage occurred with the king's conversion c. 740; the second with the installation of Rabbinical Judaism c. 800 ({{harvnb|Golden|2007b|pp=127–128, 151–153}}; {{harvnb|Dunlop|1954|p=170}}).}}{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|pp=300–308}} | |||
| Sviatoslav finally succeeded in destroying Khazar imperial power in the ]. The Khazar fortresses of ] and ] fell to the Rus in ], with the capital city of ] following circa ] or ]. A visitor to Atil wrote soon after the sacking of the city: "The Rus attacked, and no grape or raisin remained, not a leaf on a branch." | |||
| Sometime between 954 and 961, ], from ] (Muslim Spain), wrote a letter of inquiry addressed to the ruler of Khazaria, and received a reply from ]. The exchanges of this ], together with the ] discovered in the ] and the famous ] nizing dialogue{{sfn|Melamed|2003|pp=24–26}} by ], '']'' ("Book (of) The Khazari"), which plausibly drew on such sources,{{efn|group=note|Arabic original: ''Kitâb al-ḥuyya wa'l-dalîl fi naṣr al-din al-dhalîl'' (Book of the Argument and Demonstration in Aid of the Despised Faith) {{harv|Schweid|2007|p=279}}.}} provide us with the only direct evidence of the indigenous traditions{{efn|group=note|Brook mentions also a letter in Hebrew, the ], dated 985–986, which refers to "our lord David, the Khazar prince" who lived in ]. As Brook notes, both ] and Dan Shapira dismiss it as a forgery {{harv|Brook|2010|pp=30; 41, n.75}}.}} concerning the conversion. ]{{efn|group=note|The name is commonly etymologized as meaning "elk" in Türkic. Shapira identifies him with the Sabriel of the Schechter letter, and suggests, since Sabriel is unattested as a Jewish name, although the root is "hope, believe, find out, understand" that it is a calque on the Oğuz Türkic ''bulan'' (one who finds out) or ''bilen'' (one who knows) {{harv|Shapira|2009|p=1102}}.}} is said to have driven out the sorcerers,{{efn|group=note|Szpiech, citing the ]: ''et ha-qosmim ve-et'ovdei avodah zarah'' ("expelled the wizards and idolators") {{harv|Szpiech|2012|pp=93–117 }}.}} and to have received angelic visitations exhorting him to find the true religion, upon which, accompanied by his vizier, he travelled to desert mountains of Warsān on a seashore, where he came across a cave rising from the plain of Tiyul in which Jews used to celebrate the Sabbath. Here he was circumcised.{{efn|group=note|This detail is in Halevi's ''Sefer Ha-Kusari''.{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|p=302}} Golden has identified Warsān as Transcaucasian Varaˇc'an.{{sfn|Olsson|2013|p=512}} Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ's letter also mentions a legend that the Chaldaeans, under persecution, hid the Scriptures in a cave, and taught their sons to pray there, which they did until their descendants forgot the custom. Much later, a tradition has it, a man of Israel entered the cave and, retrieving the books, taught the descendants how to learn the Law.{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|pp=304–305}}}} Bulan is then said to have convened a royal debate between exponents of the three ]. He decided to convert when he was convinced of Judaism's superiority. Many scholars situate this c. 740, a date supported by Halevi's own account.{{sfn|Korobkin|1998|p=352, n.8}}{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|p=170}} The details are both Judaic{{efn|group=note|The Schechter document has officers during the religious debate speak of a cave in a certain plain (''TYZWL'') where books are to be retrieved. They turn out to be the books of the ] ({{harvnb|DeWeese|1994|p=303}}; {{harvnb|Golb|Pritsak|1982|p=111}}).}} and Türkic: a Türkic ethnogonic myth speaks of an ancestral cave in which the Ashina were conceived from the mating of their human ancestor and a wolf ancestress.{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=157}}{{efn|group=note|The original ancestral cavern of the Türks, according to Chinese sources, was called ''Ötüken'', and the tribal leaders would travel there annually to conduct sacrificial rites {{harv|DeWeese|1994|pp=276, 300–304}}.}}{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|pp=117–118}} These accounts suggest that there was a rationalising syncretism of native pagan traditions with Jewish law, by melding through the motif of the cave, a site of ancestral ritual and repository of forgotten sacred texts, Türkic myths of origin and Jewish notions of redemption of Israel's fallen people.{{sfn|DeWeese|1994|pp=304–305}} It is generally agreed they adopted Rabbinical rather than ].{{sfn|Róna-Tas|1999|p=232}} | |||
| ==Khazars outside Khazaria== | |||
| Khazar communities existed outside those areas under Khazar overlordship. Many Khazar ] served in the armies of the ] and other ] states. Documents from medieval ] attest to a Khazar community mingled with the Jews of the suburb of ]. Christian Khazars also lived in Constantinople, and some served in its armies. The ] ] was once angrily referred to by the Emperor as "Khazar-face", though whether this refers to his actual lineage or is a generic insult is unclear. | |||
| ] reports that the settlement of disputes in Khazaria was adjudicated by judges hailing each from his community, be it Christian, Jewish, Muslim, or Pagan.{{sfn|Maroney|2010|p=72}} Some evidence suggests that the Khazar king saw himself as a defender of Jews even beyond the kingdom's frontiers, retaliating against Muslim or Christian interests in Khazaria in the wake of Islamic and Byzantine persecutions of Jews abroad.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=34}}{{efn|group=note|Kohen refers to Khazar killings of Christians or the uncircumcized in retaliation for persecutions of Jews in Byzantium, and Khazar reprisals against Muslims for persecutions of Jews in ], perhaps under Emir Nasr {{harv|Kohen|2007|pp=107–108}}.}} Ibn Fadlan recounts specifically an incident in which the king of Khazaria destroyed the minaret of a mosque in Atil as revenge for the destruction of a synagogue in Dâr al-Bâbûnaj, and allegedly said he would have done worse were it not for a fear that the Muslims might retaliate in turn against Jews.{{sfn|Róna-Tas|1999|p=232}}{{sfn|Golden|2007b|p=161}} Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ sought information on Khazaria in the hope he might discover "a place on this earth where harassed Israel can rule itself" and wrote that, were it to prove true that Khazaria had such a king, he would not hesitate to forsake his high office and his family in order to emigrate there.{{efn|group=note|"If indeed I could learn that this was the case, then, despising all my glory, abandoning my high estate, leaving my family, I would go over mountains and hills, through seas and lands, till I should arrive at the place where my Lord the King resides, that I might see not only his glory and magnificence, and that of his servants and ministers, but also the tranquillity of the Israelites. On beholding this my eyes would brighten, my reins would exult, my lips would pour forth praises to God, who has not withdrawn his favour from his afflicted ones." ({{harvnb|Koestler|1977|p=63}}; {{harvnb|Leviant|2008|pp=159–162}})}} | |||
| ] reported Khazar ]nical students, or rabbinical students who were the descendants of Khazars, in 12th century ]. Jews from Kiev and elsewhere in Russia, who may or may not have been Khazars, were reported in France, Germany and England. | |||
| ] noted in 1877 that an ] commentary on ] | |||
| The ]s who settled in ] in the late ninth and early tenth centuries may have included Jews among their number. Many Khazar Jews probably fled foreign conquest into Hungary and elsewhere in ]. There they likely merged with local Jews and ensuing waves of Jewish immigration from Germany and Western Europe. They most likely did not constitute the dominant group within Eastern European Jewry, as ] maintained (see below). | |||
| ascribed to ] or to the Karaite scholar ], interpreted "The Lord hath loved him" as a reference "to the Khazars, who will go and destroy ]" (i.e., ]ia), a name used to designate the country of the Arabs. This has been taken as an indication of hopes by Jews that the Khazars might succeed in destroying the ].{{sfn|Szyszman|1980|pp=71, 73}} | |||
| === Islam === | |||
| ] legends speak of Jews being present in ] before the establishment of the Polish monarchy. Polish coins from the 12th and 13th centuries sometimes bore Slavic inscriptions written in the ]<ref name = "JE">.</ref><ref name = "JE2">.</ref> though connecting these coins to Khazar influence is purely a matter of speculation. | |||
| In 965, as the Qağanate was struggling against the victorious campaign of the Rus' prince Sviatoslav, the Islamic historian ] mentions that Khazaria, attacked by ], sought help from ], but their appeal was rejected because they were regarded as "infidels" (''al-kuffâr''; pagans). Save for the king, the Khazarians are said to have converted to Islam in order to secure an alliance, and the Turks were, with Khwarezm's military assistance, repelled. It was this that, according to Ibn al-Athîr, led the Jewish king of Khazar to convert to Islam.{{sfn|Petrukhin|2007|p=263}} | |||
| == Genetics == | |||
| ==Late references to the Khazars== | |||
| Nine skeletons dating to the 7th–9th centuries excavated from elite military burial mounds of the Khazar Khaganate (in the modern ] region) were analyzed in two genetic studies (from 2019 and 2021). According to the 2019 study, the results "confirm the Turkic roots of the Khazars, but also highlight their ethnic diversity and some integration of conquered populations". The samples did not show a genetic connection to Ashkenazi Jews, and the results do not support the hypothesis of Ashkenazi Jews being descendants of the Khazars.{{sfn|Mikheyev|Qiu|Zarubin|Moshkov|2019}} In the 2021 study the results showed both European and East Asian paternal haplogroups in the samples: three individuals carried ] Y-haplogroup, two had ], and the rest carried haplogroups ], ], ], and ], respectively. According to the authors, "The Y-chromosome data are consistent with the results of the craniological study and genome-wide analysis of the same individuals in the sense that they show mixed genetic origins for the early medieval Khazar nobility".{{sfn|Kornienko|Faleeva|Schurr|Aramova|2021|pp=477–488}} Their facial features were of mix of East Asian and European, with East Asian type dominating (70%) in the early Khazars.{{sfn|Kornienko|Faleeva|Schurr|Aramova|2021|p=478}} | |||
| ]s, c.1015. The areas in blue are those possibly still under Khazar control.]] | |||
| There is debate as to the temporal and geographic extent of Khazar polities following ]'s sack of Atil in 967/9, or even whether any such states existed. The Khazars may have retained control over some areas in the Caucasus for another two centuries, but sparse historical records make this difficult to confirm. | |||
| == Claims of Khazar ancestry == | |||
| The evidence of later Khazar polities includes the fact that Sviatoslav did not occupy the Volga basin after he destroyed Atil, and departed relatively quickly to embark on his campaign in ]. The permanent conquest of the Volga basin seems to have been left to later waves of steppe peoples like the ]. | |||
| Claims of Khazar origins of peoples, or suggestions that the Khazars were absorbed by them, have been made with regard to the ], the ], the ] ] ], the Muslim ], the ], the ], the ] and the ] (see ]), the Turkic-speaking ] and their Crimean neighbours the ], ],{{sfn|Who are the Mishars?|2016}} the Moldavian ] and others.{{sfn|Kizilov|2009|p=335}}{{sfn|Brook|2018|pp=145, 149–151, 162–163, 164}}{{sfn|Patai|Patai|1989|p=73}}{{sfn|Wexler|1987|p=70}} ]-speaking ] (known in the ] as ''Qaraylar''), some of whom migrated in the 19th century from the ] to Poland and Lithuania have claimed Khazar origins. Specialists in Khazar history question the connection.{{sfn|Brook|2018|pp=210–216}}{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=9}}{{efn|group=note|name=Rabinnic|Rabbinic Judaism rather than Qaraism was the form adopted. Small ] communities may have existed, but the linguistic and historical evidence suggests that the ] in Poland and Lithuania, of which one branch also existed in the Crimea, descend from the Khazars. "At most, it is conceivable that the smaller Karaite community which lived in Khazaria gained the Kipchak type Turkic language, that they speak today, through an exchange of language." Khazars probably converted to ], whereas in ] only the ] is accepted, the ] being ignored {{harv|Róna-Tas|1999|p=232}}.}} Scholarship is likewise sceptical of claims that the ] of the Crimea descend from Khazars.{{sfn|Brook|2018|pp=208–209}} | |||
| === Crimean Karaites and Krymchaks === | |||
| ===Jewish sources=== | |||
| {{Main|Crimean Karaites|Krymchaks}} | |||
| A letter in Hebrew dated ] ] (]–]) refers to "our lord David, the Khazar prince" who lived in ]. The letter said that this David was visited by envoys from Kievan Rus to ask about religious matters — this could be connected to the Vladimir conversion which took place during the same time period. Taman was a principality of Kievan Rus around ], so this ] (if that is what it was) may have been conquered altogether. The authenticity of this letter, the ], has however been questioned by such scholars as ]. | |||
| ], c. 1870.]] | |||
| Abraham ibn Daud, a twelfth-century Spanish rabbi, reported meeting Khazar rabbinical students in ], and that they informed him that the "remnant of them is of the rabbinic faith." This reference indicates that some Khazars maintained ethnic, if not political, autonomy at least two centuries after the sack of Atil. | |||
| In 1839, the ] scholar ] was appointed by the Russian government as a researcher into the origins of the Jewish sect known as the ].{{sfn|Goldstein|2011|p=9}} In 1846, one of his acquaintances, the Russian orientalist Vasilii Vasil'evich Grigor'ev (1816–1881), theorised that the Crimean Karaites were of Khazar stock. Firkovich vehemently rejected the idea,{{sfn|Shapira|2006|p=166}} a position seconded by Firkovich,{{clarify inline|reason=He seconded his own position?|date=October 2024}} who hoped that by "proving" his people were of Turkic origin, he would secure them exception from Russian anti-Jewish laws, since they bore no responsibility for Christ's crucifixion.{{sfnp|Blady|2000|p=125}} This idea has a notable impact in Crimean Karaite circles.{{efn|group=note|"At a time when Russia masked imperialist goals by pretending to be the protector of Slavic peoples and the Orthodox faith, Crimean Karism was exercising its own version of cultural imperialism. It is clear that the Crimean Karaites intended to expand their dominion to include Cairo, Jerusalem, and Damascus, basing their pre-eminence on the claim that Karaism, an ancient, pre-Talmudic form of Judaism, had been brought to the Middle East by the Khazars. Such an allegation would, however, have been much more difficult, if not impossible, to maintain.{{pb}}To summarize the Khazar-Karaite nexus commonly accepted in the Russian Empire during the last century: the Khazars, who were of pagan Turkic origin, were supposedly brought to Judaism by Karaites, descendants of Jews who had lived in the Black Sea areas since biblical times and whose Judaism was, therefore, pre-Talmudic and nonrabbinic. As a result, the Khazars' Judaism was Karaite, and later Karaites, who spoken a Turkic language, must have descended from the Khazars, with whom the ancient Jews had assimilated. The circularity of the argument aside, modern historians have concluded that the Khazars were converted by Rabbanite Jews and that they and their descendants observed rabbinic law and traditions. Indeed, recent scholarship has demonstrated that Khazaria was altogether unrepresented in the Karaite literature of the ninth and early tenth centuries, as well as that written during its Golden Age – when Karaism had a militant and missionary influence."{{sfn|Miller|1993|pp=7–9}}}} It is now believed that he forged much of this material on Khazars and Karaites.{{sfn|Weinryb|1973a|pp=21–22}} Specialists in Khazar history also question the connection.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=9}}{{efn|group=note|name=Rabinnic}} A genetic study of European Karaites by ] found no evidence of a Khazar or Turkic origin for any uniparental lineage but did reveal the European Karaites' links to Egyptian Karaites and to Rabbinical Jewish communities.{{sfn|Brook|2018|pp=213–215}}{{sfn|Brook|2014|pp=69–84}} | |||
| ], a thirteenth-century rabbi and traveler, reported traveling through "Khazaria", though he gave few details of its inhabitants except to say that they lived amidst desolation in perpetual mourning. | |||
| Another Turkic Crimean group, the ] had retained very simple Jewish traditions, mostly devoid of ], and very much taken with magical superstitions which, in the wake of the enduring educational efforts of the great Sephardi scholar ], came to conform with traditional Judaism.{{sfnp|Blady|2000|p=122}} | |||
| He further related: | |||
| Though the assertion they were not of Jewish stock enabled many Crimean Karaites to survive the Holocaust, which led to the murder of 6,000 Krymchaks, after the war, many of the latter, somewhat indifferent to their Jewish heritage, took a cue from the Crimean Karaites, and denied this connection in order to avoid the antisemitic effects of the stigma attached to Jews.{{sfnp|Blady|2000|p=126}} | |||
| <blockquote>''Whilst at Baghdad saw ambassadors from the kings of ], for Magog'' (medieval Christian writers said that the Khazars lived in the land of ]) ''is about ten days' journey from thence. The land extends as far as the Mountains of Darkness'' (a term often used to describe the ]). ''Beyond the Mountains of Darkness are the sons of ], son of Rechab'' (an official in the court of King ] of ]). ''To the seven kings of Meshech an angel appeared in a dream, bidding them to give up the laws and statutes, and to embrace the laws of ], son of Amram. If not, he threatened to lay waste their country. However, they delayed until the ] commenced to lay waste their country, when the kings of Meshech and all the inhabitants of their countries became proselytes, and they sent to the head of the academy'' (i.e., the ] of Sura or Pumbedita) ''a request to send them some disciples of the wise. Every disciple that is poor goes there to teach them the law and Babylonian Talmud. From the land of Egypt the disciples go there to study. He saw the ambassadors visit the grave of ]…"''</blockquote> | |||
| === Ashkenazi-Khazar theories === | |||
| The account of the conversion of the "seven kings of Meshech" is extremely similar to the accounts of the Khazar conversion given in the ], and in ]. It is possible that Meshech refers to the Khazars, or to some Judaized polity influenced by them. Arguments against this possibility include the reference to "seven kings" (though this, in turn, could refer to seven successor tribes or state micropolities). | |||
| {{Main|Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestry}} | |||
| Several scholars have suggested that instead of disappearing after the dissolution of their Empire, the Khazars migrated westward and eventually, they formed part of the core of the later ] population of Europe. This hypothesis is greeted with scepticism or caution by most scholars.{{efn|group=note|"Most scholars are skeptical of the hypothesis".{{sfn|Wexler|2002|p=536}} Wexler, who proposes a variation of the idea, argues that a combination of three reasons accounts for scholarly aversion to the concept: a desire not to get mixed up in controversy, ideological insecurities, and the incompetence of much earlier work in favor of that hypothesis.}}{{efn|group=note|"Methodologically, Wexler has opened up some new areas, taking elements of folk culture into account. I think that his conclusions have gone well beyond the evidence. Nonetheless, these are themes that should be pursued further." {{harv|Golden|2007a|p=56}}}}{{efn|group=note|"]'s book '']'' which claimed that the converted Khazars were the progenitors of today's ], has largely been rejected by serious scholars. However, the disputed theory that the stereotypical European Jew is descended from an ]an nation of Jewish converts, has been sufficiently unwelcome as to render study of the Khazars an area of research largely off limits for Jewish as well as Russian archaeologists, the Russians being unhappy with the prospect that their empire was initially ruled by Jewish kings, and the Jews being unhappy with the prospect that the Ashkenazim might not have a genetic connection to the freed slaves who met with God at Sinai." {{harv|Mariner|1999|pp=95–96}}}} | |||
| ===Muslim sources=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] and ] refer to Atil after 969, indicating that it may have been rebuilt. Al-Biruni (mid-]) reported that Atil was in ruins, and did not mention the later city of ] which was built nearby, so it is possible that this new Atil was only destroyed in the middle of the eleventh century. Even assuming al-Biruni's report was not an anachronism, there is no evidence that this "new" Atil was populated by Khazars rather than by ] or a different tribe. | |||
| The German Orientalist ], in the context of an earlier controversy about possible connections between the Khazars and the ancestors of the ], suggested as early as 1847 that emigrant Khazars might have influenced the core population of Eastern European Jews.{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Kizilov|2014|p=389}} citing ], (1847) 2nd ed. Teubner 1855 pp. 125–126.}} | |||
| ], who wrote around ], described "the raid of Fadhlun the Kurd against the Khazars". Fadhlun the Kurd has been identified as ] ], who ruled ] and other parts of ] in the 1030s. According to the account he attacked the Khazars but had to flee when they ambushed his army and killed 10,000 of his men. Two of the great early 20th century scholars on Eurasian nomads, ]<!--name spelling changed in 1922--> and ], disagreed about this account. Marquart believed that this incident refers to some Khazar remnant that had reverted to paganism and nomadic life. Barthold, (and more recently, Kevin Brook), took a much more skeptical approach and said that ibn al-Athir must have been referring to Georgians or Abkhazians. There is no evidence to decide the issue one way or the other. | |||
| The theory was then taken up by ] in 1869, when he also claimed that a possible link existed between the Khazars and the Ashkenazim,{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Rossman|2002|p=98}}: Abraham Harkavy, ''O yazykye evreyev, zhivshikh v drevneye vremya na Rusi i o slavianskikh slovakh, vstrechaiuschikhsia u evreiskikh pisatelei,'' St. Petersburg.}} but the theory that Khazar converts formed a major proportion of the Ashkenazim was first proposed to the Western public in a lecture which was delivered by ] in 1883.{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Barkun|1997|p=137}}: Ernest Renan, "Judaism as a Race and as Religion." Delivered on 27 January 1883.}}{{sfn|Rossman|2002|p=98}} Occasional suggestions that there was a small Khazar component in East European Jews emerged in works by ] (1886), ], a critic of antisemitism (1893),<ref>{{harvnb|Singerman|2004|pp=3–4}}, ''Israël chez les nations'' (1893)</ref> ],{{efn|group=note|The source is Maksymilian Ernest Gumplowicz, ''Początki religii żydowskiej w Polsce,'' Warsaw: E. Wende i S-ka, 1903 {{harv|Polonsky|Basista|Link-Lenczowski|1993|p=120}}}} and by the Russian-Jewish anthropologist ].{{efn|group=note|Goldstein writes "The theory that Eastern European Jews are descended from the Khazars was originally proposed by Samuel Weissenberg in an attempt to show that Jews were deeply rooted on Russian soil and the cradle of ] was the Caucasus".{{sfn|Goldstein|2006|p=131}} Weissenberg's book ''Die Südrussischen Juden'', was published in 1895.}} In 1909, ] developed the notion into a book-length study,{{sfn|Koestler|1977|pp=134, 150}}{{sfn|von Kutschera|1909}} arguing that the Khazars formed the foundational core of the modern Ashkenazim.{{sfn|Koestler|1977|pp=134, 150}} ] introduced the notion to American audiences in 1911.{{sfn|Goldstein|2006|p=131}}{{sfn|Fishberg|1911}} The idea was also taken up by the Polish-Jewish economic historian and ] ] in 1918.{{efn|group=note|Schipper's first monograph on this was published in the ''Almanach Žydowski'' (Vienna) in 1918. While in the ] before falling victim to the Holocaust at ], Schipper (1884–1943) was working on the Khazar hypothesis {{harv|Litman|1984|pp=85–110 }}.}}{{sfn|Brook|2010|p=210}} ] has suggested that from the ] onwards, polemical pamphlets against the Khazars were inspired by ] organizations which opposed the Khazaro-Ashkenazim.{{sfn|Falk|2017|p=101, n.9}} | |||
| ===Kievan Rus sources=== | |||
| According to the ], in 986 Khazar Jews were present at ]'s ] to decide on the prospective religion of the Kievian Rus. Whether these were Jews who had settled in Kiev or emissaries from some Jewish Khazar remnant state is unclear. The whole incident is regarded by a few radical scholars as a fabrication, but the reference to Khazar Jews (after the destruction of the Khaganate) is still relevant. ] alleged that these were Jewish missionaries from the Crimea, but provided no reference to primary sources for his allegation. | |||
| Scholarly anthropologists, such as ] (1923), and writers such as ] (1920) used it to argue that "The main part of Jewry never was in ]",{{efn|group=note|"There were Arab tribes who were Jews in the time of Muhammad, and a Turkic people who were mainly Jews in South Russia in the ninth century. Judaism is indeed the reconstructed political ideal of many shattered peoples-mainly semitic. As a result of these coalescences and assimilations, almost everywhere in the towns throughout the ], and far beyond it in the east, Jewish communities traded and flourished, and they were kept in touch through the ], and through a religious and educational organization. The main part of Jewry never was in Judea and it had never come out of Judea." {{harv|Wells|1920|p=570}}}}{{sfn|Singerman|2004|p=4}} a thesis that was to have a political echo in later opinion.{{efn|group=note|] held that Russian Jews "have considerably less Middle Eastern blood, consisting largely of pagan Slav proselytes or of Khazar Turks." For Glubb, they were not "descendants of the Judeans ...The Arabs of Palestine are probably more closely related to the Judeans (genetically) than are modern Russian or German Jews.... Of course, an anti-Zionist (as well as an anti-Semitic) point is being made here: The Palestinians have a greater political right to Palestine than the Jews do, as they, not the modern-day Jews, are the true descendants of the land's Jewish inhabitants/owners" {{harv|Morris|2003|p=22}}.}}{{sfn|Burrage Dixon|1923}}{{sfn|Wells|1920|p=?}} | |||
| In ] the ] reports that ] (one of Vladimir's sons) marched against his brother Yaroslav with an army that included "Khazars and Kasogs". Kasogs were an early ] people. "Khazars" in this reference is considered by most to be intended in the generic sense, but some have questioned why the reference reads "Khazars and Kasogs", when "Khazars" as a generic would have been sufficient. Even if the reference is to Khazars, of course, it does not follow that there was a Khazar state in this period. They could have been Khazars under the rule of the Rus. | |||
| In 1932, ] ventured the theory that the biblical Ashkenaz referred to northern ], and he identified it as the ancestral homeland of the Khazars, a position which was immediately disputed by Jacob Mann.{{sfn|Malkiel|2008|p=263, n.1}} Ten years later, in 1942, ] (sometimes referred to as ''Poliak''), later professor for the history of the Middle Ages at ], published a Hebrew monograph in which he concluded that the East European Jews came from Khazaria.{{efn|group=note|First written as an article in 1941 – "The Khazars' Conversion to Judaism", then written as a monograph (1943), it was revised twice, first, it was revised in 1944, and in 1951, it was revised again and it was also retitled ''Kazariyah: Toldot mamlacha yehudit'' be'Eropa (Khazaria: History of a Jewish Kingdom in Europe) Mosad Bialik, Tel Aviv, 1951.}}{{efn|group=note|"Poliak sought the origins of Eastern European Jewry in Khazaria" {{harv|Golden|2007a|p=29}}.}}{{sfn|Sand|2010|p=234}} ], writing in 1954, thought that very little evidence supported what he considered a mere assumption, and he also argued that the Ashkenazi-Khazar descent theory went far beyond what "our imperfect records" permit.{{sfn|Dunlop|1954|pp=261, 263}} In 1955, ], who assumed that the Jews of Western Europe resulted from a "panmixia" in the first millennium, asserted that it was widely assumed that Europe's Eastern Jews were descended from a mixture of Khazarian and German Jews.{{efn|group=note|"As for the Jews of Eastern Europe (Poles, Russians, etc.), it has always been assumed that they descended from an amalgamation of Jews of Khazar stock from southern Russia and German Jews (the latter having imposed their superior culture)." {{harv|Poliakov|2005|p=285}}}} Poliak's work found some support in ] and ],{{efn|group=note|Sand{{sfn|Sand|2010|pp=241–242}} cites ], "before and after the Mongol upheaval the Khazars sent many offshoots into the unsubdued Slavonic lands, helping ultimately to build up the great Jewish center of Eastern Europe";{{sfn|Baron|1957|pp=196–206 }} as well as ]: "The Russian conquests did not destroy the Khazar kingdom entirely, but they broke it up and diminished it. And this kingdom, which had absorbed Jewish immigration and refugees from many exiles, must itself have become a diaspora mother, the mother of one of the greatest of the diasporas (''Em-galuyot, em akhat hagaluyot hagdolot'')-of Israel in Russia, Lithuania and Poland."{{sfn|Dinur|1961|pp=2, 5}}}}{{efn|group=note|"Salo Baron, who incorrectly viewed them as Finno-Ugrians, believed that the Khazars 'sent many offshoots into the unsubdued Slavonic lands, helping ultimately to build up the great Jewish centers of eastern Europe'" {{harv|Golden|2007a|p=55}}}} but was dismissed by Bernard Weinryb as a fiction (1962).{{efn|group=note|"dismissed ... rather airily" {{harv|Golden|2007a|p=55}}.}} ] was of the opinion that the word in ] interpreted as Khazaria is actually ] and therefore it relates to the ] of the Hakkari mountains in southeast ].{{sfn|Brook|2006|p=192}} | |||
| A Kievian prince named ] (not to be confused with ]) was reportedly kidnapped by "Khazars" in ] and shipped off to ], although most scholars believe that this is a reference to the Kipchaks or other steppe peoples then dominant in the Pontic region. Upon his conquest of ] in the 1080s Oleg gave himself the title "] of Khazaria". | |||
| The Khazar-Ashkenazi hypothesis came to the attention of a much wider public with the publication of ]'s '']'' in 1976,{{sfn|Sand|2010|p=240}} which was both positively reviewed and dismissed as a fantasy, and a somewhat dangerous one. Israeli historian Zvi Ankori argued that Koestler had allowed his literary imagination to espouse Poliak's thesis, which most historians dismissed as speculative.{{sfn|Falk|2017|p=102}} Israel's ambassador to Britain branded it "an anti-Semitic action financed by the ]", while ] claimed that the idea was not supported by any evidence whatsoever, and it had been abandoned by all serious scholars.{{sfn|Sand|2010|p=240}}{{efn|group=note|"Some limit this denial to European Jews and make use of the theory that the Jews of Europe are not of Israelite descent at all but are the offspring of a tribe of Central Asian Turks converted to Judaism, called the Khazars. This theory, first put forward by an Austrian anthropologist in the early years of this century, is supported by no evidence whatsoever. It has long since been abandoned by all serious scholars in the field, including those in Arab countries, where Khazar theory is little used except in occasional political polemics."{{sfn|Lewis|1987|p=48}} Assertions of this kind have been challenged by Paul Wexler{{sfn|Wexler|2002|p=538}} who also notes that the arguments on this issue are riven by contrasting ideological investments: "Most writers who have supported the Ashkenazi-Khazar hypothesis have not argued their claims in a convincing manner ... The opponents of the Khazar-Ashkenazi nexus are no less guilty of empty polemics and unconvincing arguments."{{sfn|Wexler|2002|p=537}}}} ], however, registered some support for the idea that Khazar remnants had played a role in the growth of Eastern European Jewish communities,{{efn|group=note|"it is assumed by all historians that those Jewish Khazars who survived the last fateful decades sought and found refuge in the bosom of Jewish communities in the Christian countries to the west, and especially in Russia and Poland, on the one hand, and in the Muslim countries to the east and the south, on the other. Some historians and anthropologists go so far as to consider the modern Jews of East Europe, and more particularly of Poland, the descendants of the medieval Khazars." {{harv|Patai|Patai|1989|p=71}}}} and several amateur researchers, such as ] (1994),{{sfn|Golden|2007a|p=9}} kept the thesis in the public eye. The theory has been occasionally manipulated to deny Jewish nationhood.{{sfn|Sand|2010|p=240}}{{sfn|Toch|2012|p=155, n.4}} Recently, a variety of approaches, from linguistics (]){{sfn|Wexler|2007|pp=387–398}} to historiography (]){{sfn|Sand|2010|pp=190–249}} and ] (], a geneticist from the ]){{sfn|Elhaik|2012|pp=61–74}} have emerged to keep the theory alive.{{sfn|Spolsky|2014|pp=174–177}} In a broad academic perspective, both the idea that the Khazars converted ''en masse'' to Judaism and the suggestion they emigrated to form the core population of Ashkenazi Jewry, remain highly polemical issues.{{sfn|Golden|2007a|pp=9–10}} One thesis held that the Khazar Jewish population went into a northern diaspora and had a significant impact on the rise of ]. Connected to this thesis is the theory, expounded by Paul Wexler, dissenting from the majority of Yiddish linguists, that the grammar of ] contains a Khazar substrate.{{sfn|Wexler|2002|pp=513–541}} | |||
| ===Byzantine, Georgian and Armenian sources=== | |||
| ] documented a joint attack on the Khazar state in ], ruled by ], by the Byzantines and Russians in ]. Following 1016, there are more ambiguous references in Eastern Christian sources to Khazars that may or may not be using "Khazars" in a general sense (the Byzantines and Arabs, for example, called all steppe people "]"; before them the ] had called them all "]"). Jewish Khazars were also mentioned in a Georgian chronicle as a group that inhabited ] in the late ]. | |||
| ==== Use in antisemitic polemic ==== | |||
| At least one 12th-century Byzantine source refers to tribes practicing ] law and living in the ]; see ]. The connection between this group and the Khazars is rejected by most modern Khazar scholars. | |||
| According to ], while the Khazar hypothesis generally never played any major role in the development of ],{{sfn|Barkun|1997|pp=136–137}} it has exercised a noticeable influence on American antisemites since the ].{{efn|group=note|"The Khazar theory never figured as a major component of antisemitism. The connection receives only scant attention in ]'s monumental history of the subject. It did however come to exercise a particular attraction for advocates of immigration restriction in America." {{harv|Barkun|1997|pp=136–137}}}}{{efn|group=note|"Although the Khazar theory gets surprisingly little attention in scholarly histories of anti-Semitism, it has been an influential theme among American anti-Semites since the immigration restrictionists of the 1920s" {{harv|Barkun|2012|p=165}}.}} Maurice Fishberg and Roland B. Dixon's works were later exploited in ] and religious polemical literature, particularly in literature which advocated ], both in Britain and the United States.{{sfn|Goldstein|2006|p=131}}{{efn|group=note|"By the 1960s, when ] was established as a force on the ], the Khazar ancestry of the Jews was a firm article of faith. Two books, written in this milieu and widely read, came to exercise a strong influence in this regard. John Beaty's ''Iron Curtain over America'' (1951) and Wilmot Robertson's ''Dispossessed Majority'' (1972) repeated the Khazar thesis of Stoddard. Christian identity teachings readily seized on this negative reference to Russian Jewry, however, it backdated the history of intermarriage between Jews and Khazars to biblical times. In ''A Short History of Esau-Edom in Jewry'' (1948), the Vancouver-based writer C.F. Parker claimed that a tiny remnant of 'true Judah' was pitted against a large group of Idumean-Hittites who masqueraded as the true seed of Abraham and sought to expel the descendants of Jacob. These Esau-Hittites are the Ashkenazim, concentrated in Eastern and Central Europe and America." {{harv|Goodrick-Clarke|2003|p=237}}}} Particularly after the publication of ]'s ''The Jews in America'', (1923){{sfn|Singerman|2004|pp=4–5}} it began to enjoy a vogue among advocates of immigration restriction in the 1920s; racial theorists{{sfn|Goodrick-Clarke|2003|p=237}} such as ]; antisemitic conspiracy-theorists such as the ]'s ]; and some anti-communist polemicists such as ]{{efn|group=note|Beaty was an antisemitic, ] professor of Old English at ], author of ''The Iron Curtain over America'' (Dallas 1952). According to him, "the Khazar Jews ... were responsible for all of America's – and the world's ills, beginning with World War 1." The book "had little impact" until the former Wall Street broker and oil tycoon J. Russell Maguire promoted it ({{harvnb|Boller|1992|pp=2, 6–7}}; {{harvnb|Barkun|1997|pp=141–142}}).}} and ], whose views influenced ].<ref>{{harvnb|Barkun|1997|pp=140–141}}. Cf. Wilmot Robertson ''Dispossessed Majority''(1972)</ref> | |||
| According to ] (1968) and others,{{efn|group=note|{{harvnb|Wexler|2002|p=514}} has a more detailed bibliography.}} it played a role in Arab ] polemics, and took on an antisemitic edge. ], noting in 1987 that Arab scholars had dropped it, remarked that it only occasionally emerged in Arab political discourse.{{efn|group=note|"Arab anti-Semitism might have been expected to be free from the idea of racial odium, since Jews and Arabs are both regarded by race theory as Semites, but the odium is directed, not against the Semitic race, but against the Jews as a historical group. The main idea is that the Jews, racially, are a mongrel community, most of them being not Semites, but of Khazar and European origin."{{sfn|Harkabi|1987|p=424}} This essay was translated from Harkabi Hebrew text "Arab Antisemitism" in Shmuel Ettinger, ''Continuity and Discontinuity in Antisemitism,'' (Hebrew) 1968 (p.50).}} It has also played some role in Soviet antisemitic ]{{efn|group=note|"in the very late 1980s Russian nationalists were fixated on the 'Khazar episode.' For them the Khazar issue seemed to be a crucial one. They treated it as the first historically documented case of the imposition of a foreign yoke on the Slavs, ... In this context the term 'Khazars' became popular as a euphemism for the so-called 'Jewish occupation regime'." {{harv|Shnirelman|2007|pp=353–372}}}} and Slavic Eurasian historiography; particularly, in the works of scholars like ],{{sfn|Rossman|2007|pp=121–188}} it came to be exploited by the ] ]{{sfn|Barkun|1997|pp=142–144}} and even by terrorist esoteric cults like ].{{sfn|Goodman|Miyazawa|2000|pp=263–264}} The Kazar hypothesis was further exploited by esoteric fascists such as ], referring to a lost '']'' by the German Nazi-scholar ], who claimed to have proven that the Jews descended from a prehistoric migrant group parasiting on the Great Civilizations.{{sfn|Serrano|2011|pp=79, 295}} The phrase "Khazar kaghanate" gained new traction in 2000s among antisemitic nationalists in Russia, such as ].{{sfn|Meduza|2022}} | |||
| === |
==== Genetic studies ==== | ||
| {{See also|Ashkenazi Jews#Genetic origins|Genetic studies on Jews|Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestry#Genetics and the Khazar theory}} | |||
| ], a thirteenth century Papal legate to the court of the ] Khan ], gave a list of the nations the Mongols had conquered in his account. One of them, listed among tribes of the Caucasus, Pontic steppe and the Caspian region, was the "], who are Jews." The identity of the Brutakhi is unclear. Giovanni later refers to the Brutakhi as shaving their heads. Though Giovanni refers to them as Kipchaks, they may have been a remnant of the Khazar people. Alternatively, they may have been Kipchak converts to Judaism (possibly connected to the ]s or the ]). | |||
| The hypothesis of Khazarian ancestry in Ashkenazi has also been a subject of vehement disagreements in the field of ],{{efn|group=note|"The Khazar king and part of his court allegedly adopted the Jewish religion ... The truth of such a conversion and its extent has been the topic of many discussions, and the topic of vehement disagreements in our age of genomic DNA analyses." {{harv|Falk|2017|p=100}}}} wherein claims have been made concerning evidence both for and against it. Eran Elhaik argued in 2012 for a significant Khazar component in the admixture of Ashkenazi Jews using Caucasian populations—Georgians, Armenians and ]—as proxies.{{efn|group=note|"Strong evidence for the Khazarian hypothesis is the clustering of European Jews with the populations that reside on opposite ends of ancient Khazaria: Armenians, Georgians, and Azerbaijani Jews" {{harv|Elhaik|2012|pp=61–74}}.}} The evidence from historians he used has been criticised by ]{{sfn|Stampfer|2013}} and the technical response to such a position from geneticists is mostly dismissive, arguing that, if traces of descent from Khazars exist in the Ashkenazi gene pool, the contribution would be quite minor,{{sfn|Ostrer|2012|pp=24–27, 93–95, 124–125}}{{sfn|Nebel|Filon|Brinkmann|2001|pp=1095–1112}}{{sfn|Behar|Thomas|Skorecki|Hammer|2003|pp=769–779}}{{sfn|Nebel|Filon|Faerman|2005|pp=388–391}}{{efn|group=note|"During Greco-Roman times, recorded mass conversions led to 6 million people practicing Judaism in Roman times or up to 10% of the population of the Roman Empire. Thus, the genetic proximity of these European/Syrian Jewish populations, including Ashkenazi Jews, to each other and to French, Northern Italian, and Sardinian populations favors the idea of non-Semitic Mediterranean ancestry in the formation of the European/Syrian Jewish groups and is incompatible with theories that Ashkenazi Jews are for the most part the direct lineal descendants of converted Khazars or Slavs. The genetic proximity of Ashkenazi Jews to southern European populations has been observed in several other recent studies.. Admixture with local populations, including Khazars and Slavs, may have occurred subsequently during the 1000 year (2nd millennium) history of the European Jews. Based on analysis of Y chromosomal polymorphisms, Hammer estimated that the rate might have been as high as 0.5% per generation or 12.5% cumulatively (a figure derived from Motulsky), although this calculation might have underestimated the influx of European Y chromosomes during the initial formation of European Jewry.15 Notably, up to 50% of Ashkenazi Jewish Y chromosomal haplogroups (E3b, G, J1, and Q) are of Middle Eastern origin, 15 whereas the other prevalent haplogroups (J2, R1a1, R1b) may be representative of the early European admixture.20 The 7.5% prevalence of the R1a1 haplogroup among Ashkenazi Jews has been interpreted as a possible marker for Slavic or Khazar admixture because this haplogroup is very common among Ukrainians (where it was thought to have originated), Russians, and Sorbs, as well as among Central Asian populations, although the admixture may have occurred with Ukrainians, Poles, or Russians, rather than Khazars." {{harv|Atzmon|Ostrer|2010|pp=850–859}}}} or insignificant.{{sfn|Costa|Pereira|Richards|2013|pp=1–10}}{{sfn|Behar|Metspalu|Baran|Kopelman|2013}} One geneticist, ], has argued that "national and ethnic prejudices play a central role in the controversy."{{efn|group=note|"The extent to which the Khazars contributed to the Jewish gene-pool, and more specifically to the Ashkenazi ethnic-group(s), has become a charged issue among expert scientists as well as nonprofessionals. National and ethnic prejudices play a central role in the controversy." {{harv|Falk|2017|p=100}}}} | |||
| According to ], the issues of origins are generally complicated by the difficulties of writing history via genome studies and the biases of emotional investments in different narratives, depending on whether the emphasis lies on direct descent or on conversion within Jewish history. At the time of her writing, the lack of Khazar DNA samples that might allow verification also presented difficulties.{{efn|group=note|"if the genome does not prove Sand wrong, neither can it prove him right. It is the wrong kind of evidence and the wrong style of reasoning for the task at hand."{{sfn|Abu El-Haj|2012|p=28}} "They (researchers) will never be able to prove descent from Khazars: there are no 'verification' samples."{{sfn|Abu El-Haj|2012|p=133}}}} | |||
| == |
== In literature == | ||
| The '']'' is an influential work written by the medieval ] ]ish philosopher and poet Rabbi ] (c. 1075–1141). Divided into five essays (''ma'amarim''), it takes the form of a fictional dialogue between the pagan king of the Khazars and a ] who was invited to instruct him in the tenets of the ]. The intent of the work, although based on Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ's correspondence with the Khazar king, was not historical, but rather to defend Judaism as a revealed religion, written in the context, firstly of Karaite challenges to the Spanish rabbinical intelligentsia, and then against temptations to adapt ] and Islamic philosophy to the Jewish faith.{{sfn|Lobel|2000|pp=2–4}} Originally written in ], it was translated into Hebrew by ].{{sfn|Melamed|2003|pp=24–26}} | |||
| {{Turkic topics}} | |||
| ===Date and extent of the conversion=== | |||
| The date of the conversion, and whether it occurred as one event or as a sequence of events over time, is widely disputed. The issues surrounding this controversy are discussed above. | |||
| ]'s early novel ''Alroy'' (1833) draws on Menachem ben Solomon's story.{{sfn|Baron|1957|p=204}} The question of mass religious conversion and the indeterminability of the truth of stories about identity and conversion are central themes of ]'s best-selling mystery story '']''.{{sfn|Wachtel|1998|pp=210–215}} | |||
| The number of Khazars who converted to Judaism is also hotly contested. ] was of the opinion that only the upper class converted; this was the majority view until relatively recently. Analysis of recent archaeological grave evidence by such scholars as ] asserts that the sudden shift in burial customs, with the abandonment of pagan-style burial with grave goods and the adoption of simple shroud burials during the mid-800s suggests a more widespread conversion.<ref>Brook, ch. 4 ''passim''.</ref> | |||
| ]'s ''Justinian'', ]'s ''Book of Abraham'' and ''Wind of the Khazars'', and ]'s '']'' allude to or feature elements of Khazar history or create fictional Khazar characters.{{sfn|Cokal|2007}} | |||
| ===Alleged Khazar ancestry of Ashkenazim=== | |||
| The theory that all or most ] ("European") Jews might be descended from Khazars (rather than Semitic groups in the Middle East) dates back to the late nineteenth century, and is frequently cited to malign modern Jews as not actually being Israelites and/or to undermine Israeli claims to territory also sought by Palestinians. It was first publicly proposed in lecture given by ] on January 27, 1883, titled "Judaism as a Race and as Religion."<ref>Michael Barkun, ''Religion and the Racist Right: The Origins of the Christian Identity Movement'', UNC Press, ISBN 0807846384, p. 137.</ref> It was repeated in articles in '']'' in 1923 and 1925, and popularized by racial theorist ] in a 1926 article in the ''Forum'' titled "The Pedigree of Judah", where he argued that Ashkenazi Jews were a mix of people, of which the Khazars were a primary element.<ref name=Goodrick-Clarke>Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke, ''Black Sun: Aryan cults, esoteric nazism, and the politics of identity'', NYU Press, 2002, ISBN 0814731554, p. 237.</ref><ref>Barkun, pp. 138-139.</ref> Stoddard's views were "based on nineteenth and twentieth-century concepts of race, in which small variations on facial features as well as presumed accompanying character traits were deemed to pass from generation to generation, subject only to the corrupting effects of marriage with members of other groups, the result of which would lower the superior stock without raising the inferior partners."<ref>Barkun, p. 139.</ref> This theory was adopted by ], who saw it as a means of invalidating the claims of Jews (rather than themselves) to be the true descendants of the ancient Israelites, and was supported by early anti-Zionists.<ref name=Goodrick-Clarke/><ref>Barkun, pp. 138-139.</ref> | |||
| == Cities associated with the Khazars == | |||
| In 1951 ] professor John O. Beaty published ''The Iron Curtain over America'', a work which claimed that "Khazar Jews" were "responsible for all of America's - and the world's - ills beginning with World War I". The book repeated a number of familiar antisemitic claims, placing responsibility for U.S. involvement in World Wars I and II and the Bolshevik revolution on these Khazars, and insisting that Khazar Jews were attempting to subvert Western Christianity and establish communism throughout the world. The American millionaire J. Russell Maguire gave money towards its promotion, and it was met with enthusiasm by hate groups and the extreme right.<ref>Paul F. Boller, ''Memoirs of an Obscure Professor and Other Essays'', TCU Press, 1992, pp. 5-6.</ref><ref>Barkun, pp.140-141.</ref> By the 1960s the Khazar theory had become a "firm article of faith" amongst ] groups.<ref name=Goodrick-Clarke/><ref>Barkun, p. 142.</ref> In 1971 ] also took up this theme, insisting that Palestinians were more closely related to the ancient Judeans than were Jews. According to ]: | |||
| Cities associated with the Khazars include ], ], ]; in the ], ], ], ], and ]; in ] and the ] region, ], ], ] (]), ] (also called ], Tamatarkha), and ]; and in the ] valley, ]. A number of Khazar settlements have been discovered in the ] region. Some scholars suppose that the Khazar settlement of Sambat on the ] refers to the later ].{{efn|group=note|"Kiev in Khazar is Sambat, the same as the Hungarian word ''szombat'', 'Saturday', which is likely to have been derived from the Khazar Jews living in Kyiv." {{harv|Róna-Tas|1999|p=152}}}} | |||
| <blockquote>Of course an anti-Zionist (as well as an anti-Semitic) point is being made here: The Palestinians have a greater political right to Palestine than the Jews do, as they, not the modern-day Jews, are the true descendants of the land's Jewish inhabitants\owners.<ref>], ''The Road to Jerusalem: Glubb Pasha, Palestine and the Jews'', I.B.Tauris, 2003, ISBN 1860649890, p. 22.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| The theory gained further support when the novelist ] devoted his popular book '']'' (1976) to the topic. Koestler's historiography has been attacked as highly questionable by many historians; it has also been pointed out that his discussion of theories about Ashkenazi descent is largely unsupported; to the extent that Koestler referred to place-names and documentary evidence his analysis has been described as a mixture of flawed etymologies and misinterpreted primary sources.<ref>''E.g.'', Abramsky, Chimen. "The Khazar Myth." ''Jewish Chronicle'' (April 9, 1976): 19; Maccoby, Hyam. "Koestler's Racism." ''Midstream'' 23 (March 1977).</ref> Commentors have also noted that Koestler mischaracterized the sources he cited, particularly ]'s ''History of the Jewish Khazars'' (1954).<ref>McInnes, Neil. ''National Interest''. Fall 1999.</ref> | |||
| Koestler himself was emphatically pro-] based on ] considerations, and did not see alleged Khazar ancestry as diminishing the claim of Jews to Israel, which he felt was based on the United Nations mandate, and not on Biblical covenants or genetic inheritance. In his view, "The problem of the Khazar infusion a thousand years ago ... is irrelevant to modern Israel". In addition, he was apparently "either unaware of or oblivious to the use anti-Semites had made to the Khazar theory since its introduction at the turn of the century."<ref>Barkun, pp. 144-145.</ref> | |||
| Nevertheless, in the Arab world the Khazar theory has been adopted by anti-Zionists<ref name=Lewis/> and anti-Semites;<ref>Arab anti-Semitism might have been expected to be free from the idea of racial odium, since Jews and Arabs are both regarded by race theory as Semites, but the odium is directed, not against the Semitic race, but against the Jews as a historical group. The main idea is that the Jews, racially, are a mongrel community, most of them being not Semites, but of Khazar and European origin." Yehoshafat Harkabi, "Contemporary Arab Anti-Semitism: its Causes and Roots", in Helen Fein, ''The Persisting Question: Sociological Perspectives and Social Contexts of Modern Antisemitism'', Walter de Gruyter, 1987, ISBN 311010170X, p. 424.</ref> such proponents argue that if Ashkenazi Jews are primarily Khazar and not Semitic in origin, they would have no historical claim to Israel, nor would they be the subject of the ]'s ] promise of ] to the ]s, thus undermining the theological basis of both ] and ]. In the 1970s and 80s the Khazar theory was also advanced used by some Russian ] antisemites, particularly the historian ], who portrayed "Judeo-Khazars" as having repeatedly sabotaged Russia's development since the 7th century.<ref name = "CDI">.</ref> | |||
| According to ]: | |||
| <blockquote>This theory… is supported by no evidence whatsoever. It has long since been abandoned by all serious scholars in the field, including those in Arab countries, where the Khazar theory is little used except in occasional political polemics.<ref name=Lewis>]. "Semites and Anti-Semites", W.W. Norton and Company, ISBN 0-393-31839-7, p. 48.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| ====DNA Evidence==== | |||
| Most Jews, including Ashkenazi Jews, do not exhibit the oriental features of the Khazars, who were likely of Central Asian Turkish origin. Modern DNA studies on the ] of Jews worldwide have also discredited the Khazar origin theory for the vast majority of Jews, including the Ashkenazi. | |||
| A study published by the ] found that "The results support the hypothesis that the paternal gene pools of Jewish communities from Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East descended from a common Middle Eastern ancestral population, and suggest that most Jewish communities have remained relatively isolated from neighboring non-Jewish communities during and after the Diaspora." | |||
| . Researchers express surprise at the remarkable genetic uniformity they found among modern Jews, no matter where the ] has become dispersed around the world. Contradicting the "mongrel" theory, DNA demonstrated substantially less inter-marriage among Jews over the last 3000 years than found in other populations. | |||
| "The results accord with Jewish history and tradition and refute theories like those holding that Jewish communities consist mostly of converts from other faiths, or that they are descended from the Khazars, a medieval Turkish tribe that adopted Judaism." | |||
| <ref name="New York Times">{{cite journal| title=Y Chromosome Bears Witness to Story of the Jewish Diaspora | journal=New York Times | month=May 9 | year=2000}}</ref> | |||
| Morever, "The analysis provides genetic witness that these communities have, to a remarkable extent, retained their biological identity separate from their host populations, evidence of relatively little intermarriage or conversion into Judaism over the centuries." ''Id.'' And "Another finding, paradoxical but unsurprising, is that by the yardstick of the Y chromosome, the world's Jewish communities closely resemble not only each other but also Palestinians, Syrians and Lebanese, suggesting that all are descended from a common ancestral population that inhabited the Middle East some four thousand years ago. ''Id.'' | |||
| This study found that both Sephardi and Ashkenazi Jews showed they had an "extremely close affinity non-Jewish Middle Eastern populations", indicating "a common Middle Eastern origin",<ref name="hammer">{{cite journal| title=Jewish and Middle Eastern non-Jewish populations share a common pool of Y-chromosome biallelic haplotypes| first=M. F.| last=Hammer| coauthors=A. J. Redd, E. T. Wood, M. R. Bonner, H. Jarjanazi, T. Karafet, S. Santachiara-Benerecetti, A. Oppenheim, M. A. Jobling, T. Jenkins, H. Ostrer, and B. Bonné-Tamir| journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences| month=May 9| year=2000}}</ref> as does the ] (mtDNA) of at least 40% of the current Ashkenazi population.<ref name="behar">{{cite journal| url=http://www.ftdna.com/pdf/43026_Doron.pdf| title=The Matrilineal Ancestry of Ashkenazi Jewry: Portrait of a Recent Founder Event| first=Doron M.| last=Behar| coauthors=Ene Metspalu, Toomas Kivisild, Alessandro Achilli, Yarin Hadid, Shay Tzur, Luisa Pereira, Antonio Amorim, Lluı's Quintana-Murci, Kari Majamaa, Corinna Herrnstadt, Neil Howell, Oleg Balanovsky, Ildus Kutuev, Andrey Pshenichnov, David Gurwitz, Batsheva Bonne-Tamir, Antonio Torroni, Richard Villems, and Karl Skorecki| journal=The American Journal of Human Genetics| month=March| year=2006| volume=78| issue=3| pages=487–97| id=PMID 16404693}}</ref> So although Khazars could possibly have been absorbed into the modern Jewish population as we know it today, it is unlikely that they formed a large percentage of the ancestors of modern Jews.<ref>'''', Almut Nebel, Dvora Filon, Bernd Brinkmann, Partha P. Majumder, Marina Faerman, Ariella Oppenheim (''The American Journal of Human Genetics'', Volume 69, number 5. pp. 1095–112).</ref> | |||
| DNA analysis further determined that modern Jews of the priesthood tribe -- or "Cohanim" -- share a common ancestor in Israel dating back about 3000 years, 1700 years older than the Khazar conversion to Judaism. This result is consistent for all Jewish populations around the world.<ref name="hammer">{{cite journal| title=Y Chromosomes of Jewish Priests| first=M. F.| last=Hammer| coauthors=Karl Skorecki, Sara Selig, Shraga Blazer, Bruce Rappaport, Robert Bradman, Neil Bradman, P.J. Waburton, Monic Ismajlowicz | journal=NATURE, Volume 385| month=January 2| year=1997}}</ref> | |||
| "Using a combination of molecular genetics and mathematical analysis, the scientists arrived an an estimated date for the most recent common ancestor of contemporary Cohanim. According to this analysis, the common ancestor lived between the Exodus (approx. 1000 B.C.E) and the destruction of the first Temple (586 B.C.E.), consistent with the biblical account. Similar results were obtained based on analysis of either Sephardi or Ashkenzi communities, confirming the ancestral link of the two communities which had ben separated for more than 500 years." | |||
| <ref name="American Society For Technion">{{cite journal| title=Priestly Gene Shared By Widely Dispersed Jews | journal=American Society For Technion, Israel Institute Of Technology | month=July 14| year=1998}}</ref> "To date the original high priest, the research team used a formula based on a commonly accepted mutation rate. This formula yieded some 106 generations for both Ashkenazi and Sephardi Jews, or between 2,650 and 3,180 years, depending on whether a generation is counted as 25 or 30 years." | |||
| ===Other claims of descent=== | |||
| Others have claimed Khazar origins for such groups as the ], ]s, ], and ]. There is little evidence to support any of these theories, although it is possible that some Khazar descendants found their way into these communities. Non-Jewish groups who claim at least partial descent from the Khazars include the ] and ]; as with the above-mentioned Jewish groups, these claims are subject to a great deal of controversy and debate. | |||
| ==In fiction== | |||
| {{main|Khazars in fiction}} | |||
| The question of mass religious conversion is a central theme in ]'s international bestselling novel '']''. The novel, however, contained many invented elements and had little to do with actual Khazar history. More recently, several novels, including ]'s ''Justinian'' (about the life of Justinian II) and ]'s ''Book of Abraham'' and ''Wind of the Khazars'' have dealt either directly or indirectly with the topic of the Khazars and their role in history. | |||
| In 2007, the '']'' serialized a novel by ] entitled '']'' which features 10th century Khazar characters. | |||
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| {{colbegin}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] his mother was a Khazar princess. | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] (] ], r. 775–780, born in 750 to Emperor ] and Empress ], a Khazar Turkic princess, daughter of ] ]) | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{colend}} | |||
| *] | |||
| == Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| === Footnotes === | |||
| <!-- Dead note "<Hammer>": ''Jewish and Middle Eastern non-Jewish populations share a common pool of Y-chromosome biallelic haplotypes.'' M. F. Hammer, A. J. Redd, E. T. Wood, M. R. Bonner, H. Jarjanazi, T. Karafet, S. Santachiara-Benerecetti, A. Oppenheim, M. A. Jobling, T. Jenkins, H. Ostrer, and B. Bonné-Tamir. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'', May 9, 2000. --> | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| <!-- Dead note "Goldstein": http://www.humanitas-international.org/perezites/news/jewish-dna-nytimes.htm --> | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| === Resource notes === | |||
| ==Resources== | |||
| {{Reflist|group=note}} | |||
| * ]. (1996). "Khazar". '']'' (Brill Online). Eds.: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill. | |||
| *." ''The American Journal of Human Genetics'', March, 2006. | |||
| *Bowman, Stephen B., Ankori, Zvi ''The Jews of Byzantium 1204-1453'' Bloch Pub Co (December 2001). | |||
| *]. ''The Jews of Khazaria.'' 2nd ed. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc, 2006. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| *Browning, Robert. ''The Byzantine Empire''. Catholic University of America Press, 1992. | |||
| *Cameron, Averil, ''Byzantines and Jews: some recent work on early Byzantium'', Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies 20 (1996): 249-274. | |||
| *Cohen, M. R. ''The Voice of the Poor in the Middle Ages: An Anthology of Documents from the Cairo Geniza, Princeton University Press (2005). | |||
| *]. ''The History of the Jewish Khazars,'' Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1954. | |||
| *Douglas M. Dunlop. "The Khazars." ''The ]: Jews in Christian Europe, 711-1096''. 1966. | |||
| *Geanakoplos, D. J. ''Byzantium: Church, Society, and Civilization Seen through Contemporary Eyes'' University Of Chicago Press; New Ed edition (1986). | |||
| *]. ''Khazar Studies: An Historio-Philological Inquiry into the Origins of the Khazars.'' Budapest: Akademia Kiado, 1980. | |||
| *Peter B. Golden. "Khazar Turkic Ghulâms in Caliphal Service" (Journal Article in ''Journal Asiatique'', 2004.) | |||
| *Peter B. Golden. "Khazar Turkic Ghulâms in Caliphal Service: Onomastic Notes" (Journal Article in ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'', 1993.) | |||
| *Peter B. Golden. "Khazars" (Book Chapter in ''Turkish-Jewish Encounters: Studies on Turkish-Jewish Relations through the Ages'', 2001.) | |||
| *Peter B. Golden, ''et al.'', eds. ''The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives: Selected Papers from the Jerusalem 1999 International Khazar Colloquium''(Handbook of Oriental Studies/Handbuch Der Orientalistik). Brill: 2007; contains, ''inter alia'', | |||
| **Peter B. Golden. "The Conversion of the Khazars to Judaism." ''The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives''. Brill, 2007. pp. 123-162. | |||
| **]. "The Khazar Language". ''The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives''. Brill, 2007. pp. 75-107. | |||
| *] and ], ''Khazarian Hebrew Documents of the Tenth Century.'' Ithaca: Cornell Univ. Press, 1982. | |||
| *]. ''History of the Jews'', Vol. III. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1902. | |||
| *]. (1976): ''The Thirteenth Tribe: The Khazar Empire and Its Heritage''. Random House. ISBN 0-394-40284-7 | |||
| *Elli Kohen. History of the Byzantine Jews: A Microcosmos in the Thousand Year Empire. ''University Press of America'', 2007. | |||
| *]. "What Does Historical Numismatics Suggest About the Monetary History of Khazaria in the Ninth Century? – Question Revisited." ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 13 (2004): 97–129. | |||
| *Roman K. Kovalev. "Creating Khazar Identity through Coins: The Special Issue Dirhams of 837/8." ''East Central and Eastern Europe in the Early Middle Ages'', ed. Florin Curta, pp. 220–253. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press, 2005. | |||
| *Habib Levy, ''et al.'' ''Comprehensive History of the Jews of Iran: The Outset of the Diaspora''. George W. Maschke, trans. Mazda Publishers, 1999. | |||
| * Logan, Donald F. (1992). ''The Vikings in History'' 2nd ed. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-08396-6 | |||
| * Mango, Cyril (Ed) ''The Oxford History of Byzantium'' Oxford University Press, USA (December 5, 2002). | |||
| *Timothy S. Miller, "The Legend of Saint Zotikos According to Constantine Akropolites." ''Analecta Bollandiana'' vol. 112, 1994, pp. 339-376. | |||
| *]. "Did the Khazars Possess a Monetary Economy? An Analysis of the Numismatic Evidence." ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 2 (1982): 219-267. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "What Does Historical Numismatics Suggest About the History of Khazaria in the Ninth Century?" ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 3 (1983): 265-281. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "Why ]s First Reached Russia: The Role of Arab-Khazar Relations in the Development of the Earliest Islamic Trade with ]." ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 4 (1984): 151-282. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "Khazaria as an Intermediary between Islam and Eastern Europe in the Second Half of the Ninth Century: The Numismatic Perspective." ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 5 (1985): 179-204. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "Byzantium and the Khazars: a special relationship?" ''Byzantine Diplomacy: Papers from the Twenty-fourth Spring Symposium of Byzantine Studies'', Cambridge, March 1990, ed. ] and Simon Franklin, pp. 109-132. Aldershot, England: Variorium, 1992. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "What Can Archaeology Tell Us About the Economy of Khazaria?" ''The Archaeology of the Steppes: Methods and Strategies - Papers from the International Symposium held in Naples 9-12 November 1992'', ed. Bruno Genito, pp. 331-345. Napoli, Italy: Istituto Universitario Orientale, 1994. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "The Khazar Economy." ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 9 (1995-1997): 253-318. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "The Khazar-Byzantine World of the Crimea in the Early Middle Ages: The Religious Dimension." ''Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi'' 10 (1998-1999): 207-230. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "Les Khazars et le commerce oriental." ''Les Échanges au Moyen Age: Justinien, Mahomet, Charlemagne: trois empires dans l'économie médiévale'', pp. 82-85. Dijon: Editions Faton S.A., 2000. | |||
| *Thomas S. Noonan. "The Khazar Qaghanate and its Impact on the Early Rus' State: The translatio imperii from Itil to Kiev." ''Nomads in the Sedentary World'', eds. ] and André Wink, pp. 76-102. Richmond, England: Curzon Press, 2001. | |||
| *John Julius Norwich. ''A Short History of Byzantium''. Vintage, 1998. | |||
| *George Ostrogorski. ''History of the Byzantine State'', Rutgers University Press (July 1986). | |||
| *]. ''Khazary'', 2nd ed. Moscow: Nauka, 1986. | |||
| *Omeljan Pritsak. "The Khazar Kingdom's Conversion to ]." (Journal Article in ''Harvard Ukrainian Studies'', 1978) | |||
| *Omeljan Pritsak. "The Pre-Ashkenazic Jews of Eastern Europe in Relation to the Khazars, the Rus', and the Lithuanians". ''Ukrainian-Jewish Relations in HIstorical Perspective'', ed. Howard Aster and Peter J. Potichnyj. Edmonton, Alberta: Canadian Institute of Ukrainian Studies Press, 1990. p. 7. | |||
| *Starr, Joshua, ''The Jews in the Byzantine Empire 641-1204'' Burt Franklin (1970). | |||
| *Tamara Talbot Rice. The ] in ]. Thames and Hudson, London, 1961. pp.18-19. | |||
| *Zolitor, Jeff, Wolfe, Peter "The Khazars" Philadelphia: Conference of the Congress of Secular Jewish Organizations, (2002), Canadian Jewish Outlook (Sept/Oct 2002) /www.csjo.org/pages/essays/essaykhazars.htm | |||
| * Vital, David (1999): ''A People Apart: A History of the Jews in Europe''. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-821980-6 | |||
| == Citations == | |||
| ===Works written before 1915=== | |||
| {{Reflist|22em}} | |||
| *Blind, Karl. "A Forgotten Turkish Nation in Europe". ''The Gentleman's Quarterly''. Vol. CCXLI, No. 19. London: Chatto & Windus, 1877. pp. 439-460. | |||
| *''Itinéraires de la Terre Sainte'', Carmody, (Brussels, 1847) | |||
| *''Sur le Khazars''. Vivien St. Martin. (Paris, 1851) | |||
| *'']'', translated by ], (St. Petersburg, 1869) | |||
| *''Der khazarische Königsbrief'', Cassel, (Berlin, 1877) | |||
| *''Der Ursprung der Magyaren'', Vambéry, (Leipzig, 1882) | |||
| *''Das Buch se-Chazari'', Hirschfield, (Breslau, 1885) | |||
| *''Pre- and Proto-historic Finns'', Abercromby, (London, 1898) | |||
| *''Osteuropäische und Ostasiatische Streifzüge'', Marquart, (Leipzig, 1903) | |||
| *''Jewish Quarterly Review'', Volume iii, Pages 181–219, "An Unknown Khazar Document," (n.s., Philadelphia, 1913) | |||
| *Accounts of Oriental writers were published at St. Petersburg by Fraehn, (1821), and by Harkavy, (1874 et seq.) | |||
| == Bibliography == | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Genealogical Science: The Search for Jewish Origins and the Politics of Epistemology | |||
| * The Jewish History Resource Center, Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem | |||
| | last = Abu El-Haj | first = Nadia | year = 2012 | |||
| * by Yair Davidiy | |||
| | author-link = Nadia Abu El-Haj | |||
| * | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = Chicago, IL | |||
| * | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=8DDXi4kWW4cC&pg=26 | via = ] | |||
| * | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-226-20142-9 | |||
| * | |||
| }} | |||
| * | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = Asia, Africa and the Trade of Medieval Europe | |||
| * | |||
| | last = Abulafia | first = David | year = 1987 | |||
| * | |||
| | author-link = David Abulafia | |||
| * by ] | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1952 | |||
| *{{ru icon}} ''(660 Years Together and 50 Years of Lies)'' by Semyon Charny. Lechaim magazine, March 2003. | |||
| | title = The Cambridge Economic History of Europe: Trade and industry in the Middle Ages | |||
| | editor1-last = Postan | editor1-first = Michael Moïssey | editor1-link = Michael Postan | |||
| | editor2-last = Habakkuk | editor2-first = H.J. | editor2-link = John Habakkuk | |||
| | editor3-last = Miller | editor3-first = Edward | editor3-link = Edward Miller (historian) | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 2 | pages = 402–473 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=cHRvtwTLcMAC&pg=PA421 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-521-08709-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Geheimbericht aus der Grossen Steppe. Die Wahrheit über das Reich der Russen | |||
| | trans-title = Secret report from the Great Steppe. The truth about the empire of the Russians | |||
| | last = Altschüler | first = Boris | year = 1994 | |||
| | publisher = Altschüler | location = Saarbrücken | |||
| | language = de | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=G2DZAQAACAAJ&q=Altsch%C3%BCler%2BGeheimbericht+auf+der+Grossen+Steppe | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-9803917-0-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = Abraham's children in the genome era: major Jewish diaspora populations comprise distinct genetic clusters with shared Middle Eastern Ancestry | |||
| | vauthors = Atzmon G, Hao L, Pe'er I, Velez C, Pearlman A, Palamara PF, Morrow B, Friedman E, Oddoux C, Burns E, Ostrer H | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | date = June 2010 | volume = 86 | issue = 6 | pages = 850–859 | |||
| | doi = 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.04.015 | pmc = 3032072 | pmid = 20560205 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Atzmon|Ostrer|2010}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = A Khotanese text concerning the Turks in Kanṭṣou | |||
| | last = Bailey | first = H.W. | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 1949 | pages = 28–52 | |||
| | series = New Series 1.1 | |||
| | url = https://www2.ihp.sinica.edu.tw/file/1335WFtDneU.pdf | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210126063237/https://www2.ihp.sinica.edu.tw/file/1335WFtDneU.pdf | |||
| | archive-date = 26 January 2021 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Staël-Holstein Miscellany | |||
| | last = Bailey | first = H.W. | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 1951 | pages = 1–45 | |||
| | series = New Series 2.1 | |||
| | url = https://www2.ihp.sinica.edu.tw/file/1355ixUQunJ.pdf | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210126060310/https://www2.ihp.sinica.edu.tw/file/1355ixUQunJ.pdf | |||
| | archive-date = 26 January 2021 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Religion and the Racist Right: The Origins of the Christian Identity Movement | |||
| | last = Barkun | first = Michael | year = 1997 | |||
| | author-link = Michael Barkun | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/details/religionracistri0000bark | url-access = registration | via = ] | |||
| | page = | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8078-4638-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = Anti-Semitism from Outer Space: The Protocols in the UFO Subculture | |||
| | last = Barkun | first = Michael | year = 2012 | |||
| | author-link = Michael Barkun | |||
| | title = The Paranoid Apocalypse: A Hundred-year Retrospective on the Protocols of the Elders of Zion | |||
| | editor1-last = Landes | editor1-first = Richard Allen | editor1-link = Richard Landes | |||
| | editor2-last = Katz | editor2-first = Steven T. | editor2-link = Steven T. Katz | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=DV1S9dpW2aQC&pg=PA163 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 163–171 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8147-4945-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = A Social and Religious History of the Jews | |||
| | last = Baron | first = Salo Wittmayer | year = 1957 | |||
| | author-link = Salo Wittmayer Baron | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 3 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=tPwuH_KLAScC | via = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite encyclopedia| title = Khazar | |||
| | last = Barthold | first = Vasili | year = 1993 | |||
| | author-link = Vasili Barthold | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1936 | |||
| | encyclopedia = First Encyclopedia of Islam, 1913–1936 | |||
| | editor1-last = Houtsma | editor1-first = Martijn Theodoor | editor1-link = Martijn Theodoor Houtsma | |||
| | editor2-last = Bosworth | editor2-first = C.E. | editor2-link = Clifford Edmund Bosworth | |||
| | editor3-last = van Donzel | editor3-first = E. | |||
| | editor4-last = Heinrichs | editor4-first = W.P. | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 4 | pages = 935–937 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=7CP7fYghBFQC&pg=PA936 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-09790-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The History of the Medieval World: From the Conversion of Constantine to the First Crusade | |||
| | last = Bauer | first = Susan Wise | year = 2010 | |||
| | author-link = Susan Wise Bauer | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = New York, NY | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=1u2oP2RihIgC&pg=PA341 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-393-07817-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present | |||
| | last = Beckwith | first = Christopher I. | year = 2011 | |||
| | author-link = Christopher I. Beckwith | |||
| | orig-year = First published 2009 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = Princeton, NJ | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=5jG1eHe3y4EC&pg=PA149 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-691-15034-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = No Evidence of a Khazar origin for the Ashkenazi Jews | |||
| | last1 = Behar | first1 = D. M. | |||
| | last2 = Metspalu | first2 = M. | |||
| | last3 = Baran | first3 = Y. | |||
| | last4 = Kopelman | first4 = N. M. | |||
| | last5 = Yunusbayev | first5 = B. | |||
| | last6 = Gladstein | first6 = A. | |||
| | last7 = Tzur | first7 = S. | |||
| | last8 = Sahakyan | first8 = H. | |||
| | last9 = Bahmanimehr | first9 = A. | |||
| | last10 = Yepiskoposyan | first10 = L. | |||
| | last11 = Tambets | first11 = K. | |||
| | last12 = Khusnutdinova | first12 = E. K. | |||
| | last13 = Kushniarevich | first13 = A. | |||
| | last14 = Balanovsky | first14 = O. | |||
| | last15 = Balanovsky | first15 = E. | |||
| | last16 = Kovacevic | first16 = L. | |||
| | last17 = Marjanovic | first17 = D. | |||
| | last18 = Mihailov | first18 = E. | |||
| | last19 = Kouvatsi | first19 = A. | |||
| | last20 = Triantaphyllidis | first20 = C. | |||
| | last21 = King | first21 = R. J. | |||
| | last22 = Semino | first22 = O. | |||
| | last23 = Torroni | first23 = A. | |||
| | last24 = Hammer | first24 = M. F. | |||
| | last25 = Metspalu | first25 = E. | |||
| | last26 = Skorecki | first26 = K. | |||
| | last27 = Rosset | first27 = S. | |||
| | last28 = Halperin | first28 = E. | |||
| | last29 = Villems | first29 = R. | |||
| | last30 = Rosenberg | first30 = N. A. | |||
| | display-authors = 6 | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 2013 | volume = 85 | issue = 6 | pages = 859–900 | |||
| | url = http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/humbiol/vol85/iss6/9/ | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20141014231218/http://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/humbiol/vol85/iss6/9/ | |||
| | archive-date = 14 October 2014 | |||
| | doi = 10.3378/027.085.0604 | pmid = 25079123 | s2cid = 2173604 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = Multiple Origins of Ashkenazi Levites: Y Chromosome Evidence for Both Near Eastern and European Ancestries | |||
| | last1 = Behar | first1 = Doron M | |||
| | last2 = Thomas | first2 = Mark G | |||
| | last3 = Skorecki | first3 = Karl | |||
| | last4 = Hammer | first4 = Michael F | |||
| | display-authors = etal | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | date = October 2003 | volume = 73 | issue = 4 | pages = 768–779 | |||
| | doi = 10.1086/378506 | pmc = 1180600 | pmid = 13680527 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Jewish Communities in Exotic Places | |||
| | last = Blady | first = Ken | year = 2000 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=yY0KQUVXw2MC&pg=PA124 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-765-76112-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Memoirs of an Obscure Professor: And Other Essays | |||
| | last = Boller | first = Paul F. | year = 1992 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=ycS5O-p4EzAC&pg=PA6 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-87565-097-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Throne of Adulis: Red Sea Wars on the Eve of Islam | |||
| | last = Bowersock | first = G.W. | year = 2013 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=X4BoAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA85 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-199-33384-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Jews of Byzantium 1204–1453 | |||
| | last1 = Bowman | first1 = Stephen B. | |||
| | last2 = Ankori | first2 = Zvi | |||
| | year = 2001 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=UnRGPQAACAAJ | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8197-0703-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Jews of Khazaria | |||
| | last = Brook | first = Kevin Alan | year = 2006 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = Lanham, Maryland | |||
| | page = 192 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-4422-0302-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Jews of Khazaria | edition = 2nd | |||
| | last = Brook | first = Kevin Alan | year = 2010 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1999 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=hEuIveNl9kcC | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230417104350/https://books.google.com/books?id=hEuIveNl9kcC | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 14 August 2015 | archive-date = 17 April 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7425-4982-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Genetics of Crimean Karaites | |||
| | last = Brook | first = Kevin Alan | |||
| | journal = Karadeniz Arastirmalari | |||
| | date = Summer 2014 | volume = 11 | issue = 42 | pages = 69–84 | |||
| | url = http://www.karam.org.tr/Makaleler/909058854_5-%20Brook.pdf | url-status = dead | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20190602032408/http://www.karam.org.tr/Makaleler/909058854_5-%20Brook.pdf | |||
| | archive-date = 2 June 2019 | |||
| | doi = 10.12787/KARAM859 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Jews of Khazaria | edition = 3rd | |||
| | last = Brook | first = Kevin Alan | year = 2018 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-5381-0342-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Maternal Genetic Lineages of Ashkenazic Jews | |||
| | last = Brook | first = Kevin Alan | year = 2022 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-64469-984-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Byzantine Empire | edition = 2nd | |||
| | last = Browning | first = Robert | year = 1992 | |||
| | author-link = Robert Browning (Byzantinist) # | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1980 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/details/byzantineempire0000brow | url-access = registration | via = ] | |||
| | page = | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8132-0754-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Racial History of Man | |||
| | last = Burrage Dixon | first = Roland | year = 1923 | |||
| | author-link = Roland Burrage Dixon | |||
| | publisher = C. Scribners sons | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = L'Islam, des origines au début de l'Empire ottoman | edition = 2nd | |||
| | trans-title = Islam, from its origins to the beginning of the Ottoman Empire | |||
| | last = Cahen | first = Claude | year = 2011 | |||
| | author-link = Claude Cahen | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1997 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | language = fr | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=OnRrzgAACAAJ&q=claude+cahen%2Bl'islam+des+origines | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-2-8185-0155-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = Byzantines and Jews: some recent work on early Byzantium | |||
| | last = Cameron | first = Averil | |||
| | author-link = Averil Cameron | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 1996 | volume = 20 | pages = 249–274 | |||
| | doi = 10.1179/byz.1996.20.1.249 | s2cid = 162277927 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Constantinople in the Early Eighth Century: The Parastaseis Syntomoi Chronikai: Introduction, Translation, and Commentary | |||
| | last1 = Cameron | first1 = Averil | |||
| | last2 = Herrin | first2 = Judith | |||
| | author1-link = Averil Cameron | |||
| | year = 1984 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 10 | series = Columbia Studies in the Classical Tradition | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=5ZM3AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA212 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-07010-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Voice of the Poor in the Middle Ages: An Anthology of Documents from the Cairo Geniza | |||
| | last = Cohen | first = Mark R. | year = 2005 | |||
| | author-link = Douglas Morton Dunlop | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | series = Jews, Christians, and Muslims from the Ancient to the Modern World Series | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-691-09271-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite news| title = Jews With Swords | |||
| | last = Cokal | first = Susann | |||
| | author-link = Susann Cokal | |||
| | newspaper = ] | |||
| | url = https://www.nytimes.com/2007/10/28/books/review/Cokal-t.html | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120414180701/http://www.nytimes.com/2007/10/28/books/review/Cokal-t.html | |||
| | date = 28 October 2007 | access-date = 5 August 2013 | archive-date = 14 April 2012 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = A substantial prehistoric European ancestry amongst Ashkenazi maternal lineages | |||
| | last1 = Costa | first1 = M. D. | |||
| | last2 = Pereira | first2 = Joana B. | |||
| | last3 = Richards | first3 = Martin B. | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | date = 8 October 2013 | volume = 4 | page = 2543 | |||
| | bibcode = 2013NatCo...4.2543C | doi = 10.1038/ncomms3543 | pmc = 3806353 | pmid = 24104924 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Russian Primary Chronicle (Laurentian text) | |||
| | translator1-last = Cross | translator1-first = Samuel Hazzard | |||
| | translator2-last = Sherbowitz-Wetzor | translator2-first = Olgerd P. | |||
| | editor1-last = Cross | editor1-first = Samuel Hazzard | |||
| | editor2-last = Sherbowitz-Wetzor | editor2-first = Olgerd P. | |||
| | year = 1953 | |||
| | publisher = The Mediaeval Academy of America | location = Cambridge, MA | |||
| | url = http://www.mgh-bibliothek.de/dokumente/a/a011458.pdf | url-status = dead | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131016005423/http://www.mgh-bibliothek.de/dokumente/a/a011458.pdf | |||
| | archive-date = 16 October 2013 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|''Russian Primary Chronicle''}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = The Keegstra Affair | |||
| | last = Davies | first = Alan | year = 1992 | |||
| | title = Antisemitism in Canada: History and Interpretation | |||
| | editor-last = Davies | editor-first = Alan | |||
| | publisher = Wilfrid Laurier University Press | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3kLgn7dIEwIC&pg=PA242 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 227–248 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-889-20216-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Islamization and Native Religion in the Golden Horde: Baba Tükles and Conversion to Islam in Historical and Epic Tradition | |||
| | last = DeWeese | first = Devin A. | year = 1994 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | series = Hermeneutics, Studies in the History of Religions | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=Ut77eAbMUHoC | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-271-04445-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Yisrael ba-gola | edition = 3rd | |||
| | last = Dinur | first = Ben-Zion | year = 1961 | |||
| | author-link = Ben-Zion Dinur | |||
| | publisher = Bialik Institute | |||
| | volume = 1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Thirty Tribes of the Turks | |||
| | last = Dobrovits | first = M. | |||
| | journal = Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae | |||
| | year = 2004 | volume = 57 | issue = 3 | page = 259 | |||
| | doi = 10.1556/aorient.57.2004.3.1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = History of the Jews: From the Roman Empire to the Early Medieval Period | |||
| | last = Dubnov | first = Simon | year = 1980 | |||
| | author-link = Simon Dubnov | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 2 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=MZ2MwNzB69IC&pg=PA792 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8453-6659-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = History of the Jewish Khazars | |||
| | last = Dunlop | first = Douglas Morton | year = 1954 | |||
| | author-link = Douglas Morton Dunlop | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = New York, NY | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=_YdAAAAAIAAJ&q=Dunlop%2BHistory+of+the+Jewish+Khazars | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = Early History | |||
| | title = A Country Study: Hungary | |||
| | publisher = Federal Research Division, ] | |||
| | series = Library of Congress Country Studies | |||
| | chapter-url = http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+hu0013) | |||
| | url-status = dead | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20041029114728/http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd%2Fcstdy%3A%40field%28DOCID+hu0013%29 | |||
| | date = September 1989 | archive-date = 29 October 2004 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Country Study: Hungary|1989}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Missing Link of Jewish European Ancestry: Contrasting the Rhineland and the Khazarian Hypotheses | |||
| | last = Elhaik | first = Eran | |||
| | journal = Genome Biology and Human Evolution | |||
| | date = December 2012 | volume = 5 | issue = 1 | pages = 61–74 | |||
| | arxiv = 1208.1092 | bibcode = 2012arXiv1208.1092E | doi = 10.1093/gbe/evs119 | pmc = 3595026 | pmid = 23241444 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = The Khazar Language | |||
| | last = Erdal | first = Marcel | year = 2007 | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = BRILL | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 75–108 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PA75 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Zionism and the Biology of Jews | |||
| | last = Falk | first = Raphael | year = 2017 | |||
| | author-link = Raphael Falk (geneticist) | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=s4otDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA102 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-319-57345-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Jew and Gentile in the Ancient World: Attitudes and Interactions from Alexander to Justinian | |||
| | last = Feldman | first = Louis H. | year = 1996 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=uuJasOSDTW0C&pg=PA413 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-4008-2080-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = The Decline and Fall of Khazaria – Might or Money? | |||
| | last = Feldman | first = Alex M. | |||
| | journal = Vostok (Oriens) | |||
| | year = 2022a | issue = 4 | pages = 75–84 | |||
| | url = https://vostokoriens.jes.su/s086919080021412-0-1/ | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20221013092512/https://vostokoriens.jes.su/s086919080021412-0-1/ | |||
| | archive-date = 13 October 2022 | |||
| | doi = 10.31857/S086919080021412-0 | s2cid = 253192191 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Monotheisation of Pontic-Caspian Eurasia From the Eighth to the Thirteenth Century | |||
| | last = Feldman | first = Alex M. | year = 2022b | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| |access-date=2024-09-23 | |||
| |series=Edinburgh Byzantine Studies | |||
| | url = https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/the-monotheisation-of-pontic-caspian-eurasia/9AE71976F642F43F6B982B29C67CADE7 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-474-47810-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Jews: A Study of Race and Environment | |||
| | last = Fishberg | first = Maurice | year = 1911 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3aB5AAAAMAAJ | via = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Byzantium: Church, Society, and Civilization Seen through Contemporary Eyes | edition = 2nd | |||
| | last = Geanakoplos | first = Deno John | year = 1984 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=bAfFzCT36ekC&q=Geanakoplos | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-226-28461-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Did the Khazars Convert to Judaism? | |||
| | last = Gil | first = Moshe | |||
| | author-link = Moshe Gil | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | date = July–December 2011 | volume = 170 | issue = 3–4 | pages = 429–441 | |||
| | doi = 10.2143/REJ.170.3.2141801 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Khazarian Hebrew Documents of the Tenth Century | |||
| | last1 = Golb | first1 = Norman | |||
| | last2 = Pritsak | first2 = Omeljan | |||
| | author1-link = Norman Golb | |||
| | author2-link = Omeljan Pritsak | |||
| | year = 1982 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=h-toAAAAMAAJ | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8014-1221-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Ethnogonic Tales of the Türks | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter B. | |||
| | journal = The Medieval History Journal | |||
| | date = July 2018 | volume = 21 | issue = 2 | page = 294 | |||
| | doi = 10.1177/0971945818775373 | s2cid = 166026934 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Khazar Studies: An Historio-Philological Inquiry into the Origins of the Khazars | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 1980 | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | publisher = Akademia Kiado | location = Budapest | |||
| | volume = 1,2 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=bAfFzCT36ekC&q=Geanakoplos | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-226-28461-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples: Ethnogenesis And State Formation in the Medieval and Early Modern Eurasia and the Middle East | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 1992 | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | publisher = O. Harrassowitz | location = Wiesbaden | |||
| | volume = 9 | series = Turcologica | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books/about/An_Introduction_to_the_History_of_the_Tu.html%3Fid%3D5B6xMQEACAAJ&sa | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-447-03274-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The peoples of the South Russian steppes | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 1994a | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1990 | |||
| | title = The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia | |||
| | editor-last = Sinor | editor-first = Denis | editor-link = Denis Sinor | |||
| | publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| | volume = 1 | pages = 256–283 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=ST6TRNuWmHsC&pg=PA264 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-521-24304-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The peoples of the Russian forest belt | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 1994b | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1990 | |||
| | title = The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia | |||
| | editor-last = Sinor | editor-first = Denis | editor-link = Denis Sinor | |||
| | publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| | volume = 1 | pages = 230–255 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=ST6TRNuWmHsC&pg=PA247 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-521-24304-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Nomads in the Sedentary World: The Case of Pre-Chinggisid Rus' and Georgia | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2001a | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | title = Nomads in the Sedentary World | |||
| | editor1-last = Khazanov | editor1-first = Anatoly M. | editor1-link = Anatoly Khazanov | |||
| | editor2-last = Wink | editor2-first = Andre | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | series = Curzon-IIAS Asian studies series | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=z96HrZh4_N4C&pg=PA24 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 24–74 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7007-1369-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Nomad and Sedentary societies in Eurasia | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2001b | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | title = Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History | |||
| | editor-last = Adas | editor-first = Michael | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 2 | series = Critical Perspectives on the Past Series. American Historical Association | |||
| | pages = 71–115 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=qcSsoJ0IXawC&pg=PA86 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-56639-832-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Nomads and their neighbours in the Russian steppe: Turks, Khazars and Qipchaqs | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2003 | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books/about/Nomads_and_their_neighbours_in_the_Russi.htm | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-86078-885-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Khazar Sacral Kingship | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2006 | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | title = Pre-modern Russia and its world: Essays in Honour of Thomas S. Noonan | |||
| | editor1-last = Reyerson | editor1-first = Kathryn Von | |||
| | editor2-last = Stavrou | editor2-first = Theofanis George | |||
| | editor3-last = Tracy | editor3-first = James Donald | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=LMwmcqwZUGcC&pg=PA79 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 79–102 | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-447-05425-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Khazar Studies: Achievements and Perspectives | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2007a | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | encyclopedia = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | pages = 7–57 | |||
| | series = Handbook of Oriental Studies | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PR2 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = The Conversion of the Khazars to Judaism | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2007b | |||
| | author-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | encyclopedia = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | pages = 123–161 | |||
| | series = Handbook of Oriental Studies | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PR2 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Irano-Turcica: The Khazar Sacral Kingship Revisited | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | |||
| | journal = Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae | via = ] | |||
| | year = 2007c | volume = 60 | issue = 2 | pages = 161–194 | |||
| | url = https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250979819 | |||
| | doi = 10.1556/AOrient.60.2007.2.2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Turks and Khazars: Origins, Institutions, and Interactions in Pre-Mongol Eurasia | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2010 | |||
| | author-link = Peter B. Golden | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 952 | series = Variorum Collected Studies Series | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=AOhIAQAAIAAJ | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-4094-0003-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Central Asia in World History | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2011a | |||
| | author-link = Peter B. Golden | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | series = New Oxford World History | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=PtT5p-6V5FcC&pg=PA65 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-19-979317-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Studies on the Peoples and Cultures of the Eurasian Steppes | |||
| | last = Golden | first = Peter Benjamin | year = 2011b | |||
| | author-link = Peter B. Golden | |||
| | publisher = Editura Academiei Române | |||
| | url = https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227466942 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-973-27-2152-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Price of Whiteness: Jews, Race, and American Identity | |||
| | last = Goldstein | first = Eric L. | year = 2006 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=qsvlFZ6rgpkC&pg=PA131 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-691-12105-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Karaite Exegesis in Medieval Jerusalem | |||
| | last = Goldstein | first = Miriam | year = 2011 | |||
| | publisher = Mohr Siebeck | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=F9pu1RJKbdkC&q=Abraham+Firkovich+1839&pg=PA9 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | page = 9 | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-16-150972-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Jews in the Japanese Mind: The History and Uses of a Cultural Stereotype | |||
| | last1 = Goodman | first1 = David G. | |||
| | last2 = Miyazawa | first2 = Masanori | |||
| | year = 2000 | orig-year = First published 1995 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=R_PQLj2D1DQC&pg=PA263 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7391-0167-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Black Sun: Aryan cults, esoteric nazism, and the politics of identity | |||
| | last = Goodrick-Clarke | first = Nicholas | year = 2003 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 2001 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=xaiaM77s6N4C&pg=PA237 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8147-3155-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The " Red Jews": Antisemitism in the Apocalyptic Age 1200–1600 | |||
| | last = Gow | first = Andrew Colin | year = 1995 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=Yp5O_rPI7nsC&pg=PA31 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-10255-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Kuzari: In Defense of the Despised Faith | |||
| | last = HaLevi | first = Yehuda | year = 1998 | |||
| | author-link = Judah Halevi | |||
| | editor-last = Korobkin | editor-first = Nissan Daniel | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = Northvale, New Jersey-Jerusalem | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=QKzXAAAAMAAJ | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7657-9970-8 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Korobkin|1998}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Kuzari. In Defense of the Despised Faith | edition = 2nd | |||
| | last = HaLevi | first = Yehudah | year = 2013 | |||
| | author-link = Judah Halevi | |||
| | editor-last = Korobkin | editor-first = N. Daniel | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=z7vDoAEACAAJ | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230603045239/https://books.google.com/books?id=z7vDoAEACAAJ | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 3 June 2023 | archive-date = 3 June 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-59826-961-1 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Korobkin|2013}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Contemporary Arab Anti-Semitism: its Causes and Roots | |||
| | last = Harkabi | first = Yehoshafat | year = 1987 | |||
| | author-link = Yehoshafat Harkabi | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1968 | |||
| | title = The Persisting Question: Sociological Perspectives and Social Contexts of Modern Antisemitism | |||
| | editor-last = Fein | editor-first = Helen | editor-link = Helen Fein | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=uHWG1pDCtNgC&pg=PA424 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 412–427 | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-11-010170-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Byzantine Armies 886-1118 | |||
| | last = Heath | first = Ian | year = 1979 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-85045306-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Demography | |||
| | last = Herlihy | first = David | year = 1984 | |||
| | author-link = David Herlihy | |||
| | encyclopedia = Dictionary of the Middle Ages | |||
| | editor-last = Strayer | editor-first = Joseph R. | editor-link = Joseph Strayer | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 4 | pages = 136–148 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-684-17024-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = On the Westerly Drifting of Nomades, from the Fifth to the Nineteenth Century. Part IV. The Circassians and White Khazars | |||
| | last = Howorth | first = H. H. | |||
| | author-link = Henry Hoyle Howorth | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 1870 | volume = 2 | issue = 2 | pages = 182–192 | |||
| | url = https://zenodo.org/record/2114761 | |||
| | doi = 10.2307/3014425 | jstor = 3014425 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = The legend of Xinnie in the seventh and eighth centuries | |||
| | last1 = Inaba | first1 = Minoru | |||
| | last2 = Balogh | first2 = Dániel | |||
| | year = 2020 | |||
| | title = Hunnic Peoples in Central and South Asia: Sources for their Origin and History | |||
| | editor-last = Balogh | editor-first = Dániel | |||
| | publisher = Barkhuis | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=frnVDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA106 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 103–107 | |||
| | isbn = 978-9-493-19401-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Heraclius, Emperor of Byzantium | edition = 2nd | |||
| | last = Kaegi | first = Walter Emil | year = 2003 | |||
| | author-link = Walter Kaegi | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=tlNlFZ_7UhoC&pg=PA142 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-521-81459-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Khazar | |||
| | encyclopedia = Encyclopedia Britannica | |||
| | url = https://www.britannica.com/topic/Khazar | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220302083101/https://www.britannica.com/topic/Khazar | |||
| | date = 29 March 2020 | access-date = 30 July 2018 | archive-date = 2 March 2022 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Encyclopedia Britannica: Khazar|2020}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Huns | |||
| | last = Kim | first = Hyun Jin | year = 2016 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=mcf4CgAAQBAJ&pg=PT61 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-317-34090-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Karaites of Galicia: An Ethnoreligious Minority Among the Ashkenazim, the Turks, and the Slavs, 1772–1945 | |||
| | last = Kizilov | first = Mikhail | year = 2009 | |||
| | author-link = Mikhail Kizilov | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=hGILHIgEl7cC&pg=PA335 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16602-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = National Inventions: The Imperial Emancipation of the Karaites from Jewishness | |||
| | last = Kizilov | first = Mikhail | year = 2014 | |||
| | author-link = Mikhail Kizilov | |||
| | title = An Empire of Others: Creating Ethnographic Knowledge in Imperial Russia and the USSR | |||
| | editor1-last = Cvetkovski | editor1-first = Roland | |||
| | editor2-last = Hofmeister | editor2-first = Alexis | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=36t_CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA388 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 369–393 | |||
| | isbn = 978-6-155-22576-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Thirteenth Tribe: The Khazar Empire and Its Heritage | |||
| | last = Koestler | first = Arthur | year = 1977 | |||
| | author-link = Arthur Koestler | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1976 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = London | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=IsbslAEACAAJ&q=The+Thirteenth+Tribe%2BKoestler | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-09-125550-3 | |||
| }}{{Dead link|date=May 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes}} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = History of the Byzantine Jews: A Microcosmos in the Thousand Year Empire | |||
| | last = Kohen | first = Elli | year = 2007 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=r-9qJRP20MIC&pg=PA103 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7618-3623-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Barbarian Emperors? Aspects of the Byzantine Perception of the qaghan (chaganos) in the Earlier Middle Ages | |||
| | last = Kolditz | first = Sebastian | year = 2017 | |||
| | title = Transcultural Approaches to the Concept of Imperial Rule in the Middle Ages | |||
| | editor1-last = Scholl | editor1-first = Christian | |||
| | editor2-last = Gebhardt | editor2-first = Torben R. | |||
| | editor3-last = Clauß | editor3-first = Jan | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | pages = 41–76 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://www.peterlang.com/view/9783631706244/chapter-003.xhtml | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210421140030/https://www.peterlang.com/view/9783631706244/chapter-003.xhtml | |||
| | archive-date = 21 April 2021 | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-631-70624-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = The Tibetan Title Dru gu Gesar (Turk Caesar / Caesar of the Turks) in the Northern Branch of the Silk Route and the Role of the Khazars | |||
| | last = Kordosis | first = Stefanos | |||
| | journal = ΘΗΣΑΥΡΙΣΜΑΤΑ | |||
| | year = 2017 | issue = 47 | pages = 183–192 | |||
| | url = https://www.academia.edu/39530827 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211223203830/https://www.academia.edu/39530827 | |||
| | archive-date = 23 December 2021 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Y-Chromosome Haplogroup Diversity in Khazar Burials from Southern Russia | |||
| | last1 = Kornienko | first1 = I. V. | |||
| | last2 = Faleeva | first2 = T. G. | |||
| | last3 = Schurr | first3 = T. G. | |||
| | last4 = Aramova | first4 = O. Yu | |||
| | last5 = Ochir-Goryaeva | first5 = M. A. | |||
| | last6 = Batieva | first6 = E. F. | |||
| | last7 = Vdovchenkov | first7 = E. V. | |||
| | last8 = Moshkov | first8 = N. E. | |||
| | last9 = Kukanova | first9 = V. V. | |||
| | last10 = Ivanov | first10 = I. N. | |||
| | last11 = Sidorenko | first11 = Yu S. | |||
| | journal = ] | via = ] | |||
| | date = 1 April 2021 | volume = 57 | issue = 4 | pages = 477–488 | |||
| | url = https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351294127 | |||
| | doi = 10.1134/S1022795421040049 | issn = 1608-3369 | s2cid = 233479468 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = Creating Khazar Identity through Coins: the Special Issue Dirhams of 837/838 | |||
| | last = Kovalev | first = R.K. | year = 2005 | |||
| | title = East Central and Eastern Europe in the Early Middle Ages | |||
| | editor-last = Curta | editor-first = Florin | |||
| | publisher = University of Michigan Press | location = Ann Arbor | |||
| | pages = 220–251 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-472-11498-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Die Chasaren; historische Studie | |||
| | trans-title = Those Khazars; historical Study | |||
| | last = von Kutschera | first = Hugo | year = 1909 | |||
| | publisher = A. Holzhauen | |||
| | language = de | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=G_zEugEACAAJ | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-274-47307-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Historical Meaning of the Term Turk and the Nature of the Turkic Identity of the Chinggisid and Timurid Elites in Post-Mongol Central Asia | |||
| | last = Lee | first = Joo-Yup | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 2016 | volume = 59 | issue = 1–2 | pages = 101–132 | |||
| | url = https://www.academia.edu/35007944 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211223203830/https://www.academia.edu/35007944 | |||
| | archive-date = 23 December 2021 | |||
| | doi = 10.13173/centasiaj.59.1-2.0101 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Masterpieces of Hebrew Literature: Selections from 2000 Years of Jewish Creativity | |||
| | last = Leviant | first = Curt | year = 2008 | |||
| | author-link = Curt Leviant | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1969 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=1jT7jD1t8jAC&pg=PA159 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8276-0954-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Semites and Anti-Semites: An Inquiry Into Conflict and Prejudice | |||
| | last = Lewis | first = Bernard | year = 1987 | |||
| | author-link = Bernard Lewis | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1986 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = New York | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/details/semitesantisemit00bern | url-access = registration | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-393-30420-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Jews of Islam | |||
| | last = Lewis | first = Bernard | year = 2013 | |||
| | author-link = Bernard Lewis | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=nmBUKnFfgvcC&pg=PP61 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-135-03021-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Economic Role of Jews in Medieval Poland: The Contribution of Yitzhak Schipper | |||
| | last = Litman | first = Jacob | year = 1984 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books/about/The_economic_role_of_Jews_in_Medieval_Po.html%3Fid%3DIJ9tAAAAMAAJ | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8191-4244-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Between Mysticism and Philosophy: Sufi Language of Religious Experience in Experience in Judah Ha-Levi's Kuzari | |||
| | last = Lobel | first = Diana | year = 2000 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=V8DbnUcf6QUC&pg=PA3 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7914-4451-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Vikings in History | edition = 2nd | |||
| | last = Logan | first = F. Donald | year = 1992 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1983 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=jsp-whocldIC&pg=PA201 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-415-08396-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire | |||
| | last = Luttwak | first = Edward N. | year = 2009 | |||
| | author-link = Edward N. Luttwak | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=cUVJKJejPY8C&pg=PA448 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-674-03519-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite web| title = Magyars | |||
| | website = WebChron: The Web Chronology Project | |||
| | url = http://www.thenagain.info/WebChron/EastEurope/Magyars.html | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200411024439/http://www.thenagain.info/WebChron/EastEurope/Magyars.html | |||
| | access-date = 22 August 2013 | archive-date = 11 April 2020 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|WebChron: Magyars}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Hungarians' Prehistory, Their Conquest of Hungary and their raids to the West | |||
| | last = Makkai | first = László | year = 1994 | |||
| | title = A History of Hungary | |||
| | editor1-last = Sugar | editor1-first = Peter F. | |||
| | editor2-last = Hanák | editor2-first = Péter | |||
| | editor3-last = Frank | editor3-first = Tibor | editor3-link = Tibor Frank | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=SKwmGQCT0MAC&q=Hungarian+conquest&pg=PA1 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | page = 11 | |||
| | isbn = 0-253-35578-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = The Possible Reasons for the Arab-Khazar Wars | |||
| | last = Mako | first = Gerald | |||
| | journal = Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi | |||
| | year = 2010 | volume = 17 | pages = 45–57 | |||
| | url = https://www.academia.edu/638371 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210823211652/https://www.academia.edu/638371 | |||
| | archive-date = 23 August 2021 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Reconstructing Ashkenaz: The Human Face of Franco-German Jewry, 1000–1250 | |||
| | last = Malkiel | first = David | year = 2008 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=XNJRKSk6gS4C&pg=PA263 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8047-8684-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Oxford History of Byzantium | |||
| | editor-last = Mango | editor-first = Cyril | editor-link = Cyril Mango | |||
| | year = 2002 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-19-814098-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Conversion to Judaism: a tale of the good, the bad and the ungrateful | |||
| | last = Mariner | first = Rodney | year = 1999 | |||
| | title = Religious Conversion: Contemporary Practices and Controversies | |||
| | editor1-last = Lamb | editor1-first = Christopher | |||
| | editor2-last = Bryant | editor2-first = M. Darroll | |||
| | publisher = A&C Black | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=shdQ-QSZMdIC&pg=PA95 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 89–101 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-826-43713-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Other Zions: The Lost Histories of Jewish Nations | |||
| | last = Maroney | first = Eric | year = 2010 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/details/otherzionslosthi0000maro | url-access = registration | via = ] | |||
| | page = | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-4422-0045-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite web| script-title = ru:Мы хотим убивать "Медуза" рассказывает, как (и зачем) неонацисты из России отправились "денацифицировать" Украину | |||
| | trans-title = We want to kill "Meduza" tells how (and why) neo-Nazis from Russia set out to "denazify" Ukraine | |||
| | author = ((Meduza)) | |||
| | website = Meduza | |||
| | language = ru | |||
| | url = https://meduza.io/feature/2022/07/08/my-hotim-ubivat | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220708054523/https://meduza.io/feature/2022/07/08/my-hotim-ubivat | |||
| | date = 8 July 2022 | access-date = 26 August 2023 | archive-date = 8 July 2022 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Philosopher-King in Medieval and Renaissance Jewish Political Thought | |||
| | last = Melamed | first = Avraham | year = 2003 | |||
| | editor-last = Goodman | editor-first = Lenn Evan | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=CarNyTThFqYC&pg=PA24 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7914-8770-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Empires of Islam in Renaissance Historical Thought | |||
| | last = Meserve | first = Margaret | year = 2009 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 158 | series = Harvard Historical Series | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=XDmZXIDiZG8C&pg=PA295 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-674-02656-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite bioRxiv| title = Diverse genetic origins of medieval steppe nomad conquerors | |||
| | last1 = Mikheyev | first1 = Alexander S. | |||
| | last2 = Qiu | first2 = Lijun | |||
| | last3 = Zarubin | first3 = Alexei | |||
| | last4 = Moshkov | first4 = Nikita | |||
| | last5 = Orlov | first5 = Yuri | |||
| | last6 = Chartier | first6 = Duane R. | |||
| | last7 = Kornienko | first7 = Igor V. | |||
| | last8 = Faleeva | first8 = Tatyana G. | |||
| | last9 = Klyuchnikov | first9 = Vladimir | |||
| | last10 = Batieva | first10 = Elena F. | |||
| | last11 = Tatarinova | first11 = Tatiana V. | |||
| | date = 16 December 2019 | |||
| | biorxiv = 10.1101/2019.12.15.876912 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Karaite Separatism in Nineteenth-Century Russia: Joseph Solomon Lutski's Epistle of Israel's Deliverance | |||
| | last = Miller | first = Philip E. | year = 1993 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = Cincinnati | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=WPaKDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA7 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-878-20137-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Road to Jerusalem: Glubb Pasha, Palestine and the Jews | |||
| | last = Morris | first = Benny | year = 2003 | |||
| | author-link = Benny Morris | |||
| | orig-year = First published 2002 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=zL_1icJwNP0C&pg=PA22 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-86064-989-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = A History of Russia: To 1917 | |||
| | last = Moss | first = Walter | year = 2002 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1997 | |||
| | publisher = Anthem Press | |||
| | volume = 1 | series = Anthem Russian and Slavonic studies | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=BXgNSFIEJ2QC&pg=PA16 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-85728-752-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = The Y chromosome pool of Jews as part of the genetic landscape of the Middle East | |||
| | last1 = Nebel | first1 = Almut | |||
| | last2 = Filon | first2 = Dvora | |||
| | last3 = Brinkmann | first3 = B | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 2001 | volume = 69 | issue = 5 | pages = 1095–1112 | |||
| | doi = 10.1086/324070 | pmc = 1274378 | pmid = 11573163 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Y chromosome evidence for a founder effect in Ashkenazi Jews | |||
| | last1 = Nebel | first1 = Almut | |||
| | last2 = Filon | first2 = Dvora | |||
| | last3 = Faerman | first3 = Marina | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | date = March 2005 | volume = 13 | issue = 3 | pages = 388–391 | |||
| | doi = 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201319 | pmid = 15523495 | s2cid = 1466556 | |||
| | doi-access = free | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = European Russia c500-c1050 | |||
| | last = Noonan | first = Thomas S. | year = 1999 | |||
| | author-link = Thomas S. Noonan | |||
| | title = The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 3, C.900-c.1024 | |||
| | editor1-last = Reuter | editor1-first = Timothy | editor1-link = Timothy Reuter | |||
| | editor2-last = McKitterick | editor2-first = Rosamond | editor2-link = Rosamond McKitterick | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 3 | pages = 485–534 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=u-SsbHs5zTAC&pg=PA508 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-521-36447-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Khazar Qaghanate and its impact on the early Rus' state: the Translatio Imperii from Itil to Kiev | |||
| | last = Noonan | first = Thomas S. | year = 2001 | |||
| | author-link = Thomas S. Noonan | |||
| | title = Nomads in the Sedentary World | |||
| | editor1-last = Khazanov | editor1-first = Anatoly M. | editor1-link = Anatoly Khazanov | |||
| | editor2-last = Wink | editor2-first = André | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | series = Curzon-IIAS Asian studies series | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=z96HrZh4_N4C&pg=PA76 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 76–102 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-7007-1369-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Economy of the Khazar Khaganate | |||
| | last = Noonan | first = Thomas S. | year = 2007 | |||
| | author-link = Thomas S. Noonan | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 207–244 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&dq=Noonan%2BThe+Economy+of+the+Khazar+Khaganate&pg=PA207 | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230415164821/https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&dq=Noonan+The+Economy+of+the+Khazar+Khaganate&pg=PA207 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 19 March 2023 | archive-date = 15 April 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Coup d'état, Coronation and Conversion: Some Reflections on the Adoption of Judaism by the Khazar Khaganate | |||
| | last = Olsson | first = Joshua T. | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 2013 | volume = 23 | issue = 4 | pages = 495–526 | |||
| | doi = 10.1017/S1356186313000266 | s2cid = 161833156 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Jews | |||
| | last = Oppenheim | first = Samuel A | year = 1994 | |||
| | dictionary = An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires | |||
| | editor1-last = Olson | editor1-first = James Stuart | |||
| | editor2-last = Pappas | editor2-first = Lee Brigance | |||
| | editor3-last = Pappas | editor3-first = Charles | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 305–328 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=CquTz6ps5YgC&pg=PA310 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-313-27497-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Legacy: A Genetic History of the Jewish People | |||
| | last = Ostrer | first = Harry | year = 2012 | |||
| | author-link = Harry Ostrer | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=RayZR3V1SFwC&pg=PA26 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-19-997638-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = History of the Byzantine State | |||
| | last = Ostrogorski | first = George | year = 1969 | |||
| | author-link = George Ostrogorski | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/details/historyofbyzanti00ostr | url-access = registration | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8135-0599-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Myth of the Jewish Race | |||
| | last1 = Patai | first1 = Raphael | |||
| | last2 = Patai | first2 = Jennifer | |||
| | author1-link = Raphael Patai | |||
| | year = 1989 | orig-year = First published 1975 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=Xt7f6WBEP0EC&pg=PA71 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8143-1948-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Early Seljūq History: A New Interpretation | |||
| | last = Peacock | first = Andrew C.S. | year = 2010 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=xj9haotAapcC&pg=PA27 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-415-54853-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Khazaria and Rus': An Examination of their Historical Relations | |||
| | last = Petrukhin | first = Vladimir | year = 2007 | |||
| | author-link = Vladimir Petrukhin | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = BRILL | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 245–268 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books/about/The_World_of_the_Khazars.html%3Fid%3D3ZzXjdyK-CEC | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Iudaizm v Khazarii po dannym arkheologii | |||
| | script-chapter = ru:Иудаизм в Хазарии по данным археологии | |||
| | trans-chapter = Judaism in Khazaria according to Archaeological Data | |||
| | last1 = Petrukhin | first1 = Vladimir | |||
| | last2 = Flyorov | first2 = Valeriy | |||
| | author1-link = Vladimir Petrukhin | |||
| | year = 2010 | |||
| | title = Istoriya yevreyskogo naroda v Rossii. Ot drevnosti do rannego Novogo vremeni | |||
| | script-title = ru:История еврейского народа в России. От древности до раннего Нового времени | |||
| | trans-title = History of Jewish People in Russia. From Antiquity to the Early Modern Period | |||
| | editor1-last = Bartal | editor1-first = Israel | |||
| | editor2-last = Kulik | editor2-first = Alexander | |||
| | publisher = Bridges of Culture; Gerashim | location = Moscow; Jerusalem | |||
| | volume = 1 | pages = 149–161 | |||
| | language = ru | |||
| | isbn = 978-5-457-51756-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Middle Byzantine Court Costume | |||
| | last = Piltz | first = Elisabeth | year = 2004 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1997 | |||
| | title = Byzantine Court Culture from 829 To 1204 | |||
| | editor-last = Maguire | editor-first = Henry | editor-link = Martijn Theodoor Houtsma | |||
| | publisher = Dumbarton Oaks | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=qjy2d8ExpTAC&pg=PA42 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 39–52 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-88402-308-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The History of Anti-semitism: From the time of Christ to the court Jews | |||
| | last = Poliakov | first = Léon | year = 2005 | |||
| | author-link = Léon Poliakov | |||
| | orig-year = 1955/1975 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=9uyoN09ZsHEC&pg=PA285 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8122-1863-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Jews in Old Poland: 1000–1795 | |||
| | editor1-last = Polonsky | editor1-first = Antony | editor1-link = Antony Polonsky | |||
| | editor2-last = Basista | editor2-first = Jakub | |||
| | editor3-last = Link-Lenczowski | editor3-first = Andrzej | |||
| | year = 1993 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=-LltAAAAMAAJ&q=Maksymilian+Gumplowicz+khazars | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-85043-342-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = The Khazar Kingdom's Conversion to Judaism | |||
| | last = Pritsak | first = Omeljan | |||
| | journal = Harvard Ukrainian Studies | |||
| | date = September 1978 | volume = II | number = 3 | pages = 261–281 | |||
| | url = https://diasporiana.org.ua/wp-content/uploads/books/14056/file.pdf | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220111190442/https://diasporiana.org.ua/wp-content/uploads/books/14056/file.pdf | |||
| | archive-date = 11 January 2022 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The New Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 3, c.900–c.1024 | |||
| | editor-last = Reuter | editor-first = Timothy | editor-link = Timothy Reuter | |||
| | year = 1999 | |||
| | publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| | doi = 10.1017/CHOL9780521364478 | isbn = 978-1-13905572-7 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = ReOrienting the Sasanians: East Iran in Late Antiquity | |||
| | last = Rezakhani | first = Khodadad | year = 2017 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=VjVYDwAAQBAJ&pg=PT233 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-474-40031-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Hungarians & Europe in the Early Middle Ages: An Introduction to Early Hungarian History | |||
| | last = Róna-Tas | first = András | year = 1999 | |||
| | author-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=I-RTt0Q6AcYC | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-963-9116-48-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Russian Intellectual Antisemitism in the Post-Communist Era | |||
| | last = Rossman | first = Vadim Joseph | year = 2002 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=pF-I25OC5ugC&pg=PA98 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8032-3948-7 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Anti-Semitism in Eurasian Historiography: The Caser of Lev Gumilev | |||
| | last = Rossman | first = Vadim Joseph | year = 2007 | |||
| | title = Russia Between East and West: Scholarly Debates on Eurasianism | |||
| | editor-last = Shlapentokh | editor-first = Dmitry | |||
| | publisher = BRILL | |||
| | volume = 102 | series = International Studies in Sociology and Social Anthropology | |||
| | pages = 121–188 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=EnsHyxPZfOIC&pg=PA134 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-15415-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite news| title = 'Jews a Race' Genetic Theory Comes Under Fierce Attack by DNA Expert | |||
| | last = Rubin | first = Rita | |||
| | magazine = ] | |||
| | url = http://forward.com/articles/175912/jews-a-race-genetic-theory-comes-under-fierce-atta/?p=all | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20140719154152/http://forward.com/articles/175912/jews-a-race-genetic-theory-comes-under-fierce-atta/?p=all | |||
| | date = 7 May 2013 | access-date = 9 June 2014 | archive-date = 19 July 2014 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Population in Europe | |||
| | last = Russell | first = Josiah C. | year = 1972 | |||
| | title = The Fontana Economic History of Europe: The Middle Ages | |||
| | editor-last = Cipolla | editor-first = Carlo M. | editor-link = Carlo M. Cipolla | |||
| | publisher = Collins/Fontana | |||
| | volume = 1 | pages = 25–71 | |||
| | chapter-url = http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/source/pop-in-eur.html | |||
| | url-status = dead | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20141029063430/http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/source/pop-in-eur.html | |||
| | archive-date = 29 October 2014 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Invention of the Jewish People | |||
| | last = Sand | first = Shlomo | year = 2010 | |||
| | author-link = Shlomo Sand | |||
| | orig-year = First published 2009 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = London | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/details/inventionofjewi00sand | url-access = registration | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-84467-623-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Story of the Jews: Finding the Words (1000 BCE – 1492) | |||
| | last = Schama | first = Simon | year = 2013 | |||
| | author-link = Simon Schama | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=yLdkwBPMLaQC&pg=PA266 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-409-04004-0 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Collapse and Recovery of Europe, AD 476-1648 | |||
| | last = Schwartzwald | first = Jack L. | year = 2015 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=bqgHCwAAQBAJ&dq=Constantine+VI%2Bdowager%2Bunpopular&pg=PA26 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20230415192801/https://books.google.com/books?id=bqgHCwAAQBAJ&dq=Constantine+VI+dowager+unpopular&pg=PA26 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 19 March 2023 | archive-date = 15 April 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-476-66230-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Khazar motif in Judah Halevi's ''Sefer ha-Kuzari'' | |||
| | last = Schweid | first = Eliezer | year = 2007 | |||
| | author-link = Eliezer Schweid | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 279–290 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=yO-vCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA279 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Adolf Hitler, the Ultimate Avatar | |||
| | last = Serrano | first = Miguel | year = 2011 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1984 | |||
| | publisher = Editorial Solar | |||
| | url = https://archive.org/stream/serranomigueladolfhitlertheultimateavatar2000#page/n77/mode/1up | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 79, 295 | |||
| | isbn = <!-- not printed in the book --> | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Jews in Khazaria | |||
| | last = Shapira | first = Dan D. Y. | year = 2009 | |||
| | encyclopedia = Encyclopedia of the Jewish Diaspora: Origins, Experiences, and Culture | |||
| | editor-last = Ehrlich | editor-first = Mark Avrum | |||
| | publisher = ABC-CLIO | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 3: (Countries, Regions, and Communities) | pages = 1097–1104 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=NoPZu79hqaEC&pg=PA1097 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-85109-873-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Remarks on Avraham Firkovicz and the Hebrew Mejelis "Document" | |||
| | last = Shapira | first = Dan D.Y. | |||
| | journal = Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae | |||
| | year = 2006 | volume = 59 | issue = 2 | pages = 131–180 | |||
| | doi = 10.1556/AOrient.59.2006.2.1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Iranian Sources on the Khazars | |||
| | last = Shapira | first = Dan D.Y. | year = 2007a | |||
| | encyclopedia = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | pages = 291–305 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PR2 | |||
| | access-date = 13 February 2013 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = Armenian and Georgian Sources on the Khazars – A Re-Evaluation | |||
| | last = Shapira | first = Dan D.Y. | year = 2007b | |||
| | encyclopedia = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | pages = 307–351 | |||
| | series = Handbook of Oriental Studies | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PR2 | |||
| | access-date = 13 February 2013 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Closer Encounters with the Byzantine World: The Rus at the Straits of Kerch | |||
| | last = Shepard | first = Jonathan | year = 2006 | |||
| | title = Pre-modern Russia and its world: Essays in Honour of Thomas S. Noonan | |||
| | editor1-last = Reyerson | editor1-first = Kathryn Von | |||
| | editor2-last = Stavrou | editor2-first = Theofanis George | |||
| | editor3-last = Tracy | editor3-first = James Donald | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=LMwmcqwZUGcC&pg=PA35 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 15–77 | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-447-05425-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Ethos, Materiality and Paradigms of Political Action in Early Medieval Communities of the Northwestern Caspian Region | |||
| | last = Shingiray | first = Irina Lita | year = 2012 | |||
| | title = The Archaeology of Power and Politics in Eurasia: Regimes and Revolutions | |||
| | editor1-last = Hartley | editor1-first = Charles W. | |||
| | editor2-last = Yazicioğlu | editor2-first = G. Bike | |||
| | editor3-last = Smith | editor3-first = Adam T. | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=UstGrkGNNQcC&pg=PA208 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 188–216 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-107-01652-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = The Chinese Chroniclers of the Khazars: Notes on Khazaria in Tang Period Texts | |||
| | last = Shirota | first = Shun (城田俊) | |||
| | editor1-last = Woods | editor1-first = John E. | |||
| | editor2-last = Pfeiffer | editor2-first = Judith | |||
| | editor3-last = Tucker | editor3-first = Ernest | |||
| | journal = Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi | |||
| | year = 2005 | volume = 14 | pages = 231–261 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Story of an Euphemism: The Khazars in Russian Nationalist Literature | |||
| | last = Shnirelman | first = Victor A | year = 2007 | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 353–372 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PA360 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = vol. 196 | |||
| | author = ((Sima Guang)) | |||
| | author-link = Sima Guang | |||
| | display-authors = etal | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://ctext.org/wiki.pl?if=gb&chapter=579709 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20201113152318/https://ctext.org/wiki.pl?if=gb&chapter=579709 | |||
| | archive-date = 13 November 2020 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Sima Guang, vol. 196}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite web| title = Contemporary Racist and Judeophobic Ideology Discovers the Khazars, or, Who Really Are the Jews? | |||
| | last = Singerman | first = Robert | year = 2004 | |||
| | series = Rosaline and Myer Feinstein Lecture Series | |||
| | url = http://www.jewishlibraries.org/main/Portals/0/AJL_Assets/documents/Feinstein/Robert%20Singerman.pdf | url-status = dead | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20140305220540/http://www.jewishlibraries.org/main/Portals/0/AJL_Assets/documents/Feinstein/Robert%20Singerman.pdf | |||
| | access-date = 1 March 2014 | archive-date = 5 March 2014 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Headless State: Aristocratic Orders, Kinship Society, and Misrepresentations of Nomadic Inner Asia | |||
| | last = Sneath | first = David | year = 2007 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=OR14qaApQbgC&pg=PA25 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-231-51167-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = New remarks on the flow of Byzantine coins in Avaria and Walachia during the second half of the seventh century | |||
| | last = Somogyi | first = Péter | year = 2008 | |||
| | title = The "Other" Europe in the Middle Ages: Avars, Bulgars, Khazars and Cumans | |||
| | editor1-last = Curta | editor1-first = Florin | |||
| | editor2-last = Kovalev | editor2-first = Roman | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 2 | series = East Central and Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 450–1450 | |||
| | pages = 83–149 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=_-G1L-9Zec0C&pg=PA125 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16389-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Romanians and the Turkic Nomads North of the Danube Delta from the Tenth to the Mid-Thirteenth Century | |||
| | last = Spinei | first = Victor | year = 2009 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=Q9KwCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA50 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-9-004-17536-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Languages of the Jews: A Sociolinguistic History | |||
| | last = Spolsky | first = Bernard | year = 2014 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=nl72AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA177 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-107-05544-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Did the Khazars Convert to Judaism? | |||
| | last = Stampfer | first = Shaul | |||
| | author-link = Shaul Stampfer | |||
| | journal = Jewish Social Studies | via = ] | |||
| | year = 2013 | volume = 19 | issue = 3 | pages = 1–72 | |||
| | url = http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/jewish_social_studies/v019/19.3.stampfer.pdf | |||
| | doi = 10.2979/jewisocistud.19.3.1 | s2cid = 161320785 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite magazine| title = Are We All Khazars Now? | |||
| | last = Stampfer | first = Shaul | year = 2014 | |||
| | author-link = Shaul Stampfer | |||
| | magazine = ] | |||
| | pages = 1–72 | |||
| | url = http://jewishreviewofbooks.com/articles/802/are-we-all-khazars-now/ | url-access = limited | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160501183726/http://jewishreviewofbooks.com/articles/802/are-we-all-khazars-now/ | |||
| | access-date = 3 May 2016 | archive-date = 1 May 2016 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia| title = The Avars | |||
| | last = Szádeczky-Kardoss | first = Samuel | year = 1994 | |||
| | orig-year = First published 1990 | |||
| | encyclopedia = The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia | |||
| | editor-last = Sinor | editor-first = Denis | editor-link = Denis Sinor | |||
| | publisher = ] | via = ] | |||
| | volume = 1 | pages = 206–228 | |||
| | series = Handbook of Oriental Studies | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=ST6TRNuWmHsC&pg=PR5 | |||
| | access-date = 13 February 2013 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-521-24304-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Conversion and Narrative: Reading and Religious Authority in Medieval Polemic | |||
| | last = Szpiech | first = Ryan | year = 2012 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=JDWq_qDnAqAC&pg=PA102 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8122-0761-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Le karaïsme: ses doctrines et son histoire | |||
| | trans-title = Karaism: its doctrines and its history | |||
| | last = Szyszman | first = Simon | year = 1980 | |||
| | author-link = :fr:Simon Szyszman | |||
| | publisher = Éditions L'Âge d'Homme | |||
| | language = fr | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=1UEavztCkKIC&pg=PA71 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-2-8251-3088-9 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia | |||
| | last = Taagepera | first = Rein | |||
| | author-link = Rein Taagepera | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | date = September 1997 | volume = 41 | issue = 3 | page = 496 | |||
| | url = http://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/3cn68807 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20181119114740/https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3cn68807 | |||
| | archive-date = 19 November 2018 | |||
| | doi = 10.1111/0020-8833.00053 | jstor = 2600793 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Vol. 199b Tiele | |||
| | last1 = Tangshu | first1 = Jiu | |||
| | author1-link = Jiu Tangshu | |||
| | author2 = ((Jiu Tangshu)) | |||
| | language = zh | |||
| | url = https://zh.wikisource.org/%E8%88%8A%E5%94%90%E6%9B%B8/%E5%8D%B7199%E4%B8%8B#%E9%90%B5%E5%8B%92 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110516124654/https://zh.wikisource.org/%E8%88%8A%E5%94%90%E6%9B%B8/%E5%8D%B7199%E4%B8%8B#%E9%90%B5%E5%8B%92 | |||
| | archive-date = 16 May 2011 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Jiu Tangshu, Vol. 199b Tiele}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Economic History of European Jews: Late Antiquity and Early Middle Ages | |||
| | last = Toch | first = Michael | year = 2012 | |||
| | publisher = ] | location = Leiden | |||
| | volume = 56 | series = Études sur le Judaïsme Médiéval | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=M5oNKrvYWZAC&pg=PA155 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-23534-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = ] | |||
| | last = Toynbee | first = Arnold | year = 1962 | |||
| | author-link = Arnold J. Toynbee | |||
| | orig-year = 1934–1961 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 1–12 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = East-West Orientation of Historical Empires | |||
| | last1 = Turchin | first1 = Peter | |||
| | last2 = Adams | first2 = Jonathan M. | |||
| | last3 = Hall | first3 = Thomas D | |||
| | journal = Journal of World-Systems Research | |||
| | date = December 2006 | volume = 12 | issue = 2 | page = 222 | |||
| | url = http://jwsr.pitt.edu/ojs/index.php/jwsr/article/view/369/381 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20190520161830/http://jwsr.pitt.edu/ojs/index.php/jwsr/article/view/369/381 | |||
| | archive-date = 20 May 2019 | |||
| | issn = 1076-156X | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite journal | title = Left-wing 'anti-Zionism' in Norway | |||
| | last = Vogt | first = Judith | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 1975 | volume = 9 | issue = 6 | pages = 15–q8 | |||
| | doi = 10.1080/0031322X.1975.9969275 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Making a Nation, Breaking a Nation: Literature and Cultural Politics in Yugoslavia | |||
| | last = Wachtel | first = Andrew | year = 1998 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=cnISZNM6X6EC&pg=PA210 | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 210–215 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8047-3181-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Tang Huiyao | |||
| | last = Wang | first = Pu | |||
| | display-authors = etal | |||
| | volume = 98 | |||
| | language = zh | |||
| | url = https://zh.wikisource.org/%E5%94%90%E6%9C%83%E8%A6%81/%E5%8D%B7098 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20210119092204/https://zh.wikisource.org/%E5%94%90%E6%9C%83%E8%A6%81/%E5%8D%B7098 | |||
| | archive-date = 19 January 2021 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Wang Pu, vol 98}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = Tang Huiyao | |||
| | last = Wang | first = Pu | |||
| | display-authors = etal | |||
| | volume = 72 | |||
| | language = zh | |||
| | url = https://zh.wikisource.org/%E5%94%90%E6%9C%83%E8%A6%81/%E5%8D%B7072 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20201104005510/https://zh.wikisource.org/%E5%94%90%E6%9C%83%E8%A6%81/%E5%8D%B7072 | |||
| | archive-date = 4 November 2020 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Wang Pu, vol. 72}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = The Khazars and the World of Islam | |||
| | last = Wasserstein | first = David | year = 2007 | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 373–386 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books/about/The_World_of_the_Khazars.html%3Fid%3D3ZzXjdyK-CEC | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = vol. 84 | |||
| | last = Wei | first = Zheng | |||
| | display-authors = etal | |||
| | title = ] | |||
| | language = zh | |||
| | chapter-url = https://zh.wikisource.org/%E9%9A%8B%E6%9B%B8/%E5%8D%B784#%E9%90%B5%E5%8B%92 | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20221211133548/https://zh.wikisource.org/%E9%9A%8B%E6%9B%B8/%E5%8D%B784#%E9%90%B5%E5%8B%92 | |||
| | archive-date = 11 December 2022 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Wei Zheng, vol. 84}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Jews of Poland: A Social and Economic History of the Jewish Community in Poland from 1100 to 1800 | |||
| | last = Weinryb | first = Bernard Dov | year = 1973a | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=K2DgBdSCQnsC&q=Abraham+Firkovich+khazars&pg=PA21 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | pages = 21–22 | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8276-0016-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Jews of Poland: A Social and Economic History of the Jewish Community in Poland from 1100 to 1800 he non-Jewish origins of the Sephardic Jews | |||
| | last = Weinryb | first = Bernard Dov | year = 1973b | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=K2DgBdSCQnsC&pg=PA20 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-8276-0016-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Outline of History: Being a Plain History of Life and Mankind | |||
| | last = Wells | first = H. G. | year = 1920 | |||
| | author-link = Herbert George Wells | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 1 | |||
| | url = https://en.wikisource.org/Page:The_Outline_of_History_Vol_1.djvu/594 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20200713075456/https://en.wikisource.org/Page:The_Outline_of_History_Vol_1.djvu/594 | |||
| | archive-date = 13 July 2020 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Explorations in Judeo-Slavic Linguistics | |||
| | last = Wexler | first = Paul | year = 1987 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 2 | series = Contributions to the sociology of Jewish languages | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=FfYUAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA72 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-07656-3 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The non-Jewish origins of the Sephardic Jews | |||
| | last = Wexler | first = Paul | year = 1996 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=XZwO2TX8EOcC&pg=PA25 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20231117073550/https://books.google.com/books?id=XZwO2TX8EOcC&pg=PA25 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 12 December 2015 | archive-date = 17 November 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-1-4384-2393-7 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Two-Tiered Relexification in Yiddish: Jews, Sorbs, Khazars and the Kiev-Polessian Dialect | |||
| | last = Wexler | first = Paul | year = 2002 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 136 | series = Trends in linguistics / Studies and monographs: Studies and monographs | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=JL7CY2MW63gC&pg=PA537 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20231117073549/https://books.google.com/books?id=JL7CY2MW63gC&pg=PA537 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 14 August 2015 | archive-date = 17 November 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-3-11-017258-4 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| chapter = Yiddish Evidence for the Khazar Component in the Ashkenazic ethnogenesis | |||
| | last = Wexler | first = Paul | year = 2007 | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 387–398 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PA387 | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20231117073542/https://books.google.com/books?id=3ZzXjdyK-CEC&pg=PA387 | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | access-date = 14 August 2015 | archive-date = 17 November 2023 | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = The Making of Byzantium, 600–1025 | |||
| | last = Whittow | first = David | year = 1996 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=22NNIjrpd20C&pg=PA226 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-0-520-20496-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = New Book of Tang | |||
| | last = Xin | first = Tangshu | |||
| | volume = 217a Huihe | |||
| | language = zh | |||
| | url = https://zh.wikisource.org/%E6%96%B0%E5%94%90%E6%9B%B8/%E5%8D%B7217%E4%B8%8A | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20190504083529/https://zh.wikisource.org/%E6%96%B0%E5%94%90%E6%9B%B8/%E5%8D%B7217%E4%B8%8A | |||
| | archive-date = 4 May 2019 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Xin Tangshu, vol 217a Huihe}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite book| title = Khazaria in the Ninth and Tenth Centuries | |||
| | last = Zhivkov | first = Boris | year = 2015 | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=7Du2CAAAQBAJ&pg=PA173 | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-9-004-29448-6 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| title = The Origins of the Volga Bulghars | |||
| | last = Zimonyi | first = István | year = 1990 | |||
| | editor-last = Szõnyi-Sándor | editor-first = Klára | |||
| | series = Studia Uralo-Altaica, 32 | |||
| | isbn = 978-963-481-839-7 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite journal | title = On the date of the Khazars' Conversion to Judaism and the Chronology of the Kings of the Rus' Oleg and Igor | |||
| | last = Zuckerman | first = Constantine | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | year = 1995 | volume = 53 | pages = 237–270 | |||
| | url = https://www.persee.fr/doc/rebyz_0766-5598_1995_num_53_1_1906 | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20221129134425/https://www.persee.fr/doc/rebyz_0766-5598_1995_num_53_1_1906 | |||
| | archive-date = 29 November 2022 | |||
| | doi = 10.3406/rebyz.1995.1906 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite book| chapter = The Khazars and Byzantium –The First Encounter | |||
| | last = Zuckerman | first = Constantine | year = 2007 | |||
| | title = The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives | |||
| | editor1-last = Golden | editor1-first = Peter B. | editor1-link = Peter Benjamin Golden | |||
| | editor2-last = Ben-Shammai | editor2-first = Haggai | |||
| | editor3-last = Róna-Tas | editor3-first = András | editor3-link = András Róna-Tas | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 17 | series = Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies | |||
| | pages = 399–431 | |||
| | chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books/about/The_World_of_the_Khazars.html%3Fid%3D3ZzXjdyK-CEC | |||
| | via = ] | |||
| | isbn = 978-90-04-16042-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{cite encyclopedia| entry = КАСПИЙСКОЕ МОРЕ перевод | |||
| | dictionary = Русско-крымскотатарский словарь (кириллица) | |||
| | lang = ru | |||
| | entry-url = http://www.classes.ru/all-crtatar/dictionary-russian-crtatar-cyr-term-3892.htm | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20211026015642/http://www.classes.ru/all-crtatar/dictionary-russian-crtatar-cyr-term-3892.htm | |||
| | access-date = 12 February 2021 | archive-date = 26 October 2021 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Caspian Sea translation}} | |||
| }} | |||
| *{{Cite magazine| title = Ясно-понятно. Кто такие мишари? | |||
| | trans-title = Clearly understood: Who are the Mishars? | |||
| | magazine = Инде (inde.io) | |||
| | language = ru | |||
| | url = https://inde.io/article/2207-yasno-ponyatno-kto-takie-mishari | url-status = live | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20221108191102/https://inde.io/article/2207-yasno-ponyatno-kto-takie-mishari | |||
| | date = 2016 | access-date = 23 May 2024 | archive-date = 8 November 2022 | |||
| | ref = {{harvid|Who are the Mishars?|2016}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * in the ] collection. | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/19971221083021/http://khazaria.com/ |date=21 December 1997}} | |||
| * The Jewish History Resource Center, Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem | |||
| * {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091026233731/http://geocities.com/ayatoles/ |date=26 October 2009 |title=Khazar Historic Maps}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100106005357/http://www.sacred-texts.com/jud/khz/index.htm |date=6 January 2010}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170810091901/http://www.haaretz.com/jewish/2.209/ancient-lost-capital-of-the-jewish-khazar-kingdom-found-1.254377 |date=10 August 2017}} | |||
| {{Turkic topics}} | |||
| {{Khazaria}} | {{Khazaria}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Turkic peoples}} | ||
| {{Crimea topics}} | |||
| {{Barbarian kingdoms}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Khazar}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ]<!--please leave the empty space as standard--> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:33, 10 January 2025
Historical semi-nomadic Turkic ethnic group "Khazar" and "Kazar" redirect here. For other uses, see Khazar (disambiguation).
| Khazar Khaganate | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 650–969 | |||||||||||||||||||||
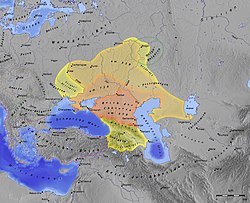 Khazar Khaganate, 650–850 Khazar Khaganate, 650–850 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Khaganate | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Qaghan | |||||||||||||||||||||
| • c. 650 | Irbis | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 8th century | Bulan | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 9th century | Obadiah | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 9th century | Zachariah | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 9th century | Manasseh | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 9th century | Benjamin | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 10th century | Aaron | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 10th century | Joseph | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 10th century | David | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • 11th century | Georgios | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • Established | c. 650 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • Sviatoslav's sacking and razing of Atil | 969 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 850 est. | 3,000,000 km (1,200,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 900 est. | 1,000,000 km (390,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Yarmaq | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Tatarstan |
 |
The Khazars (/ˈxɑːzɑːrz/) were a nomadic Turkic people that, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what, for its duration, was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East, and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (c. 650–965), the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus.
Khazaria long served as a buffer state between the Byzantine Empire, the nomads of the northern steppes, and the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates, having previously served as the Byzantine Empire's proxy against the Sasanian Empire. The alliance was dissolved around the year 900 when Byzantium began encouraging the Alans to attack Khazaria. This move aimed to weaken Khazaria's control over Crimea and the Caucasus, for the Empire sought an entente with the rising power of the Kievan Rus’ in the north—a region they hoped to convert to Eastern Christianity. Between 965 and 969, Sviatoslav I of Kiev, the ruler of Kievan Rus', along with his allies, conquered the capital, Atil, thus ending Khazaria's independence.
Determining the origins and nature of the Khazars is closely bound with theories of their languages. Still, it is a matter of intricate difficulty since no indigenous records in the Khazar language survived, and the state was polyglot and polyethnic. The native religion of the Khazars is thought to have been Tengrism like that of the North Caucasian Huns and other Turkic peoples. The polyethnic populace of the Khazar Khaganate appears to have been a multiconfessional mosaic of pagan, Tengrist, Jewish, Christian, and Muslim worshippers. Some of the Khazars (namely, the Kabars) joined the ancient Hungarians in the 9th century. The ruling elite of the Khazars was said by Judah Halevi and Abraham ibn Daud to have converted to Rabbinic Judaism in the 8th century, but the scope of the conversion to Judaism within the Khazar Khanate remains uncertain.
Where the Khazars dispersed after the fall of the Khanate is subject to many conjectures. Proposals have been made regarding the possibility of a Khazar factor in the ethnogenesis of numerous peoples, such as the Hazaras, Hungarians, the Kazakhs, the Cossacks of the Don region and of Ukraine, the Muslim Kumyks, the Turkic-speaking Krymchaks and their Crimean neighbours the Crimean Karaites, the Moldavian Csángós, the Mountain Jews, and even some Subbotniks (based on their Ukrainian and Cossack origin).
The late 19th century saw the emergence of a theory that the core of today's Ashkenazi Jews are descended from a hypothetical Khazarian Jewish diaspora that migrated westward from modern-day Russia and Ukraine into modern-day France and Germany. Linguistic and genetic studies have not supported the theory of a Khazar connection to Ashkenazi Jewry. The theory still finds occasional support, but most scholars view it with considerable scepticism. The theory is sometimes associated with antisemitism and anti-Zionism.
In Oghuz Turkic languages, the Caspian Sea is still named the "Khazar Sea", an enduring legacy of the medieval Khazar state.
Etymology
Gyula Németh, following Zoltán Gombocz, derived Khazar from a hypothetical *Qasar reflecting a Turkic root qaz- ("to ramble, to roam") being an hypothetical retracted variant of Common Turkic kez-; however, András Róna-Tas objected that *qaz- is a ghost word. In the fragmentary Tes and Terkhin inscriptions of the Uyğur empire (744–840) the form Qasar is attested, although uncertainty remains whether this represents a personal or tribal name, gradually other hypotheses emerged. Louis Bazin derived it from Turkic qas- ("tyrannize, oppress, terrorize") on the basis of its phonetic similarity to the Uyğur tribal name, Qasar. Róna-Tas connects qasar with Kesar, the Pahlavi transcription of the Roman title Caesar.
D. M. Dunlop tried to link the Chinese term for "Khazars" to one of the tribal names of the Uyğur, or Toquz Oğuz, namely the Qasar (Ch. 葛薩 Gésà). The objections are that Uyğur 葛薩 Gésà/Qasar was not a tribal name but rather the surname of the chief of the 思结 Sijie tribe (Sogdian: Sikari) of the Toquz Oğuz (Ch. 九姓 jĭu xìng), and that in Middle Chinese the ethnonym "Khazars" was always prefaced with Tūjué, then still reserved for Göktürks and their splinter groups, (Tūjué Kěsà bù:突厥可薩部; Tūjué Hésà:突厥曷薩) and "Khazar's" first syllable is transcribed with different characters (可 and 曷) than 葛, which is used to render the syllable Qa- in the Uyğur word Qasar. While it is far from given that the Khazars are not signifying a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual cluster of peoples and clans, some more nomadic, some less, it doesn't exclude that some clans, or splintergroups, or even rulers has identified with the name(s) of the Khazars, in the variety of ways it has been expressed.
After their conversion it is reported that they adopted the Hebrew script, and it is likely that, although speaking a Turkic language, the Khazar chancellery under Judaism probably corresponded in Hebrew.
Linguistics
Main article: Khazar languageDetermining the origins and nature of the Khazars is closely bound with theories of their languages, but analysis of their languages' origins is difficult, since no indigenous records in the Khazar language survive, and the state was polyglot and polyethnic. Whereas the royal or ruling elite probably spoke an eastern variety of Shaz Turkic, the subject tribes appear to have spoken varieties of Lir Turkic, such as Oğuric, a language variously identified with Bulğaric, Chuvash, and Hunnish.
The latter based upon the assertion of the Persian historian Istakhri the Khazar language was different from any other known tongue. Alano-As was also widely spoken. Eastern Common Turkic, the language of the royal house and its core tribes, in all likelihood remained the language of the ruling elite in the same way that Mongol continued to be used by the rulers of the Golden Horde, alongside of the Qipčaq Turkic speech spoken by the bulk of the Turkic tribesmen that constituted the military force of this part of the Činggisid empire. Similarity, Oğuric, like Qipčaq Turkic in the Jočid realm, functioned as one of the languages of government. One method for tracing their origins consists in the analysis of the possible etymologies behind the ethnonym "Khazar".
History
Tribal origins and early history
The tribes that were to comprise the Khazar empire were not an ethnic union, but a congeries of steppe nomads and peoples who came to be subordinated, and subscribed to a core Turkic leadership. Many Turkic groups, such as the Oğuric peoples, including Šarağurs, Oğurs, Onoğurs, and Bulğars who earlier formed part of the Tiele (Tiělè) confederation, are attested quite early, having been driven West by the Sabirs, who in turn fled the Asian Avars, and began to flow into the Volga–Caspian–Pontic zone from as early as the 4th century CE and are recorded by Priscus to reside in the Western Eurasian steppe lands as early as 463. They appear to stem from Mongolia and South Siberia in the aftermath of the fall of the Hunnic/Xiōngnú nomadic polities. A variegated tribal federation led by these Turks, probably comprising a complex assortment of Iranian, proto-Mongolic, Uralic, and Palaeo-Siberian clans, vanquished the Rouran Khaganate of the hegemonic central Asian Avars in 552 and swept westwards, taking in their train other steppe nomads and peoples from Sogdiana.
The ruling family of this confederation may have hailed from the Āshǐnà (阿史那) clan of the Western Turkic Khaganate, although Constantine Zuckerman regards Ashina and their pivotal role in the formation of the Khazars with scepticism. Golden notes that Chinese and Arabic reports are almost identical, making the connection a strong one, and conjectures that their leader may have been Yǐpíshèkuì (乙毗射匱), who lost power or was killed around 651. Moving west, the confederation reached the land of the Akatziroi, who had been important allies of Byzantium in fighting off Attila's army.
Rise of the Khazar state
 SIND800UYGHUR KHAGANATEGURJARA-
SIND800UYGHUR KHAGANATEGURJARA-PRATIHARASRASHTRA-
KUTASPALA
EMPIRECHAM-
PANAN-
ZHAOTURK
SHAHISTANG
DYNASTYSILLAKhitansJurchensTungusKARLUK
YABGHUTatarsCHENLADVARA-
VATISRIVIJAYAKyrgyzsPaleo-SiberiansSamoyedsKimeksTangutsShatuosABBASID CALIPHATEKHAZAR
KHAGANATEBYZANTINE
EMPIREOGHUZ-
YABGUSTIBETAN
EMPIREclass=notpageimage| The Khazar Khaganate and contemporary polities circa 800.
An embryonic state of Khazaria began to form sometime after 630, when it emerged from the breakdown of the larger Göktürk Khaganate. Göktürk armies had penetrated the Volga by 549, ejecting the Avars, who were then forced to flee to the sanctuary of the Hungarian plain. The Ashina clan appeared on the scene by 552, when they overthrew the Rourans and established the Göktürk Qağanate, whose self designation was Tür(ü)k. By 568, these Göktürks were probing for an alliance with Byzantium to attack Persia. An internecine war broke out between the senior eastern Göktürks and the junior West Turkic Khaganate some decades later, when on the death of Taspar Qağan, a succession dispute led to a dynastic crisis between Taspar's chosen heir, the Apa Qağan, and the ruler appointed by the tribal high council, Āshǐnà Shètú (阿史那摄图), the Ishbara Qağan.
By the first decades of the 7th century, the Ashina yabgu Tong managed to stabilise the Western division, but upon his death, after providing crucial military assistance to Byzantium in routing the Sasanian army in the Persian heartland, the Western Turkic Qağanate dissolved under pressure from the encroaching Tang dynasty armies and split into two competing federations, each consisting of five tribes, collectively known as the "Ten Arrows" (On Oq). Both briefly challenged Tang hegemony in eastern Turkestan. To the West, two new nomadic states arose in the meantime, Old Great Bulgaria under Kubrat, the Duōlù clan leader, and the Nǔshībì subconfederation, also consisting of five tribes. The Duōlù challenged the Avars in the Kuban River-Sea of Azov area while the Khazar Qağanate consolidated further westwards, led apparently by an Ashina dynasty. With a resounding victory over the tribes in 657, engineered by General Sū Dìngfāng (蘇定方), Chinese overlordship was imposed to their East after a final mop-up operation in 659, but the two confederations of Bulğars and Khazars fought for supremacy on the western steppeland, and with the ascendency of the latter, the former either succumbed to Khazar rule or, as under Asparukh, Kubrat's son, shifted even further west across the Danube to lay the foundations of the First Bulgarian Empire in the Balkans (c. 679).
The Qağanate of the Khazars thus took shape out of the ruins of this nomadic empire as it broke up under pressure from the Tang dynasty armies to the east sometime between 630 and 650. After their conquest of the lower Volga region to the East and an area westwards between the Danube and the Dniepr, and their subjugation of the Onoğur-Bulğar union, sometime around 670, a properly constituted Khazar Qağanate emerges, becoming the westernmost successor state of the formidable Göktürk Qağanate after its disintegration. According to Omeljan Pritsak, the language of the Onoğur-Bulğar federation was to become the lingua franca of Khazaria as it developed into what Lev Gumilev called a "steppe Atlantis" (stepnaja Atlantida/ Степная Атлантида). Historians have often referred to this period of Khazar domination as the Pax Khazarica since the state became an international trading hub permitting Western Eurasian merchants safe transit across it to pursue their business without interference. The high status soon to be accorded this empire to the north is attested by Ibn al-Balḫî's Fârsnâma (c. 1100), which relates that the Sasanian Shah, Ḫusraw 1, Anûsîrvân, placed three thrones by his own, one for the King of China, a second for the King of Byzantium, and a third for the king of the Khazars. Although anachronistic in retrodating the Khazars to this period, the legend, in placing the Khazar qağan on a throne with equal status to kings of the other two superpowers, bears witness to the reputation won by the Khazars from early times.
Khazar state: culture and institutions
Royal Diarchy with sacral Qağanate
Khazaria developed a dual kingship governance structure, typical among Turkic nomads, consisting of a shad/bäk and a qağan. The emergence of this system may be deeply entwined with the conversion to Judaism. According to Arabic sources, the lesser king was called îšâ and the greater king Khazar xâqân; the former managed and commanded the military, while the greater king's role was primarily sacral, less concerned with daily affairs. The greater king was recruited from the Khazar house of notables (ahl bait ma'rûfīn) and, in an initiation ritual, was nearly strangled until he declared the number of years he wished to reign, on the expiration of which he would be killed by the nobles. The deputy ruler would enter the presence of the reclusive greater king only with great ceremony, approaching him barefoot to prostrate himself in the dust and then light a piece of wood as a purifying fire, while waiting humbly and calmly to be summoned. Particularly elaborate rituals accompanied a royal burial. At one period, travellers had to dismount, bow before the ruler's tomb, and then walk away on foot. Subsequently, the charismatic sovereign's burial place was hidden from view, with a palatial structure ("Paradise") constructed and then hidden under rerouted river water to avoid disturbance by evil spirits and later generations. Such a royal burial ground (qoruq) is typical of inner Asian peoples. Both the îšâ and the xâqân converted to Judaism sometime in the 8th century, while the rest, according to the Persian traveller Ahmad ibn Rustah, probably followed the old Tūrkic religion.
Ruling elite
The ruling stratum, like that of the later Činggisids within the Golden Horde, was a relatively small group that differed ethnically and linguistically from its subject peoples, meaning the Alano-As and Oğuric Turkic tribes, who were numerically superior within Khazaria. The Khazar Qağans, while taking wives and concubines from the subject populations, were protected by a Khwârazmian guard corps, or comitatus, called the Ursiyya. But unlike many other local polities, they hired soldiers (mercenaries) (the junûd murtazîqa in al-Mas'ûdî). At the peak of their empire, the Khazars ran a centralised fiscal administration, with a standing army of some 7–12,000 men, which could, at need, be multiplied two or three times that number by inducting reserves from their nobles' retinues. Other figures for the permanent standing army indicate that it numbered as many as one hundred thousand. They controlled and exacted tribute from 25 to 30 different nations and tribes inhabiting the vast territories between the Caucasus, the Aral Sea, the Ural Mountains, and the Ukrainian steppes. Khazar armies were led by the Qağan Bek (pronounced as Kagan Bek) and commanded by subordinate officers known as tarkhans. When the bek sent out a body of troops, they would not retreat under any circumstances. If they were defeated, every one who returned was killed.
Settlements were governed by administrative officials known as tuduns. In some cases, such as the Byzantine settlements in southern Crimea, a tudun would be appointed for a town nominally within another polity's sphere of influence. Other officials in the Khazar government included dignitaries referred to by ibn Fadlan as Jawyshyghr and Kündür, but their responsibilities are unknown.
Demographics
It has been estimated that 25 to 28 distinct ethnic groups made up the population of the Khazar Qağanate, aside from the ethnic elite. The ruling elite seems to have been constituted out of nine tribes/clans, themselves ethnically heterogeneous, spread over perhaps nine provinces or principalities, each of which would have been allocated to a clan. In terms of caste or class, some evidence suggests that there was a distinction, whether racial or social is unclear, between "White Khazars" (ak-Khazars) and "Black Khazars" (qara-Khazars). The 10th-century Muslim geographer al-Iṣṭakhrī claimed that the White Khazars were strikingly handsome with reddish hair, white skin, and blue eyes, while the Black Khazars were swarthy, verging on deep black as if they were "some kind of Indian". Many Turkic nations had a similar (political, not racial) division between a "white" ruling warrior caste and a "black" class of commoners; the consensus among mainstream scholars is that Istakhri was confused by the names given to the two groups. However, Khazars are generally described by early Arab sources as having a white complexion, blue eyes, and reddish hair. The ethnonym in the Tang Chinese annals, Ashina, often accorded a key role in the Khazar leadership, may reflect an Eastern Iranian or Tokharian word (Khotanese Saka âşşeina-āššsena "blue"): Middle Persian axšaêna ("dark-coloured"): Tokharian A âśna ("blue", "dark"). The distinction appears to have survived the collapse of the Khazarian empire. Later Russian chronicles, commenting on the role of the Khazars in the magyarisation of Hungary, refer to them as "White Oghurs" and Magyars as "Black Oghurs". Studies of the physical remains, such as skulls at Sarkel, have revealed individuals belonging to the Slavic, other European, and a few Mongolian types.
Economy
The import and export of foreign wares, and the revenues derived from taxing their transit, was a hallmark of the Khazar economy, although it is said also to have produced isinglass. Distinctively among the nomadic steppe polities, the Khazar Qağanate developed a self-sufficient domestic Saltovo economy, a combination of traditional pastoralism – allowing sheep and cattle to be exported – extensive agriculture, abundant use of the Volga's rich fishing stocks, together with craft manufacture, with diversification in lucrative returns from taxing international trade given its pivotal control of major trade routes.
The Khazar slave trade constituted one of the two great furnishers of slaves to the Muslim market to slavery in the Abbasid Caliphate (the other being the Iranian Sâmânid amîrs), supplying it with captured Slavs and tribesmen from the Eurasian northlands. It profited from the latter which enabled it to maintain a standing army of Khwarezm Muslim troops. The capital Atil reflected the division: Kharazān on the western bank where the king and his Khazar elite, with a retinue of some 4,000 attendants, dwelt, and Itil proper to the East, inhabited by Jews, Christians, Muslims and slaves and by craftsmen and foreign merchants.
The Khazar Khaghanate played a key role in the trade between Europe and the Muslim world in the early middle ages. People taken captive during the viking raids in Europe, such as Ireland, could be transported to Hedeby or Brännö in Scandinavia and from there via the Volga trade route to Russia, where slaves and furs were sold to Muslim merchants in exchange for Arab silver dirham and silk, which have been found in Birka, Wollin and Dublin; during the 8th- and 9th-century this trade route between Europe and the Abbasid Caliphate passed via the Khazar Kaghanate, until it was supplanted in the 10th-century by the route of Volga Bulgaria, Khwarazm, and the Samanid slave trade.
The ruling elite wintered in the city and spent from spring to late autumn in their fields. A large irrigated greenbelt, drawing on channels from the Volga river, lay outside the capital, where meadows and vineyards extended for some 20 farsakhs (c. 60 miles). While customs duties were imposed on traders, and tribute and tithes were exacted from 25 to 30 tribes, with a levy of one sable skin, squirrel pelt, sword, dirham per hearth or ploughshare, or hides, wax, honey and livestock, depending on the zone. Trade disputes were handled by a commercial tribunal in Atil consisting of seven judges, two for each of the monotheistic inhabitants (Jews, Muslims, Christians) and one for the pagans.
Khazars and Byzantium
See also: Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628 and Third Perso-Turkic WarByzantine diplomatic policy towards the steppe peoples generally consisted of encouraging them to fight among themselves. The Pechenegs provided great assistance to the Byzantines in the 9th century in exchange for regular payments. Byzantium also sought alliances with the Göktürks against common enemies: in the early 7th century, one such alliance was brokered with the Western Tűrks against the Persian Sasanians in the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. The Byzantines called Khazaria Tourkía, and by the 9th century referred to the Khazars as "Turks". During the period leading up to and after the siege of Constantinople in 626, Heraclius sought help via emissaries, and eventually personally, from a Göktürk chieftain of the Western Turkic Khaganate, Tong Yabghu Qağan, in Tiflis, plying him with gifts and the promise of marriage to his daughter, Epiphania. Tong Yabghu responded by sending a large force to ravage the Persian empire, marking the start of the Third Perso-Turkic War. A joint Byzantine-Tűrk operation breached the Caspian gates and sacked Derbent in 627. Together they then besieged Tiflis, where the Byzantines may have deployed an early variety of traction trebuchets (ἑλέπόλεις) to breach the walls. After the campaign, Tong Yabghu is reported, perhaps with some exaggeration, to have left some 40,000 troops behind with Heraclius. Although occasionally identified with Khazars, the Göktürk identification is more probable since the Khazars only emerged from that group after the fragmentation of the former sometime after 630. Some scholars argued that Sasanian Persia never recovered from the devastating defeat wrought by this invasion.

Once the Khazars emerged as a power, the Byzantines also began to form alliances with them, dynastic and military. In 695, the last Heraclian emperor, Justinian II, nicknamed "the slit-nosed" (ὁ ῥινότμητος) after he was mutilated and deposed, was exiled to Cherson in the Crimea, where a Khazar governor (tudun) presided. He escaped into Khazar territory in 704 or 705 and was given asylum by qağan Busir Glavan (Ἰβουζῆρος Γλιαβάνος), who gave him his sister in marriage, perhaps in response to an offer by Justinian, who may have thought a dynastic marriage would seal by kinship a powerful tribal support for his attempts to regain the throne. The Khazarian spouse thereupon changed her name to Theodora. Busir was offered a bribe by the Byzantine usurper, Tiberius III, to kill Justinian. Warned by Theodora, Justinian escaped, murdering two Khazar officials in the process. He fled to Bulgaria, whose Khan Tervel helped him regain the throne. Upon his reinstalment, and despite Busir's treachery during his exile, he sent for Theodora; Busir complied, and she was crowned as Augusta, suggesting that both prized the alliance.
Decades later, Leo III (ruled 717–741) made a similar alliance to co-ordinate strategy against a common enemy, the Muslim Arabs. He sent an embassy to the Khazar qağan Bihar and married his son, the future Constantine V (ruled 741–775), to Bihar's daughter, a princess referred to as Tzitzak, in 732. On converting to Christianity, she took the name Irene. Constantine and Irene had a son, the future Leo IV (775–780), who thereafter bore the sobriquet, "the Khazar". Leo died in mysterious circumstances after his Athenian wife bore him a son, Constantine VI, who on his majority co-ruled with his mother, the dowager. He proved unpopular, and his death ended the dynastic link of the Khazars to the Byzantine throne. By the 8th century, Khazars dominated the Crimea (650–c. 950), and even extended their influence into the Byzantine peninsula of Cherson until it was wrested back in the 10th century. Khazar and Farghânian (Φάργανοι) mercenaries constituted part of the imperial Byzantine Hetaireia bodyguard after its formation in 840, a position that could openly be purchased by a payment of seven pounds of gold.
Arab–Khazar wars
Main article: Arab–Khazar warsDuring the 7th and 8th centuries, the Khazars fought a series of wars against the Umayyad Caliphate and its Abbasid successor. The First Arab-Khazar War began during the first phase of Muslim expansion. By 640, Muslim forces had reached Armenia; in 642 they launched their first raid across the Caucasus under Abd ar-Rahman ibn Rabiah. In 652 Arab forces advanced on the Khazar capital, Balanjar, but were defeated, suffering heavy losses; according to Persian historians such as al-Tabari, both sides in the battle used catapults against the opposing troops. A number of Russian sources give the name of a Khazar khagan from this period as Irbis and describe him as a scion of the Göktürk royal house, the Ashina. Whether Irbis ever existed is open to debate, as is whether he can be identified with one of the many Göktürk rulers of the same name.
Due to the outbreak of the First Muslim Civil War and other priorities, the Arabs refrained from repeating an attack on the Khazars until the early 8th century. The Khazars launched a few raids into Transcaucasian principalities under Muslim dominion, including a large-scale raid in 683–685 during the Second Muslim Civil War that rendered much booty and many prisoners. There is evidence from the account of al-Tabari that the Khazars formed a united front with the remnants of the Göktürks in Transoxiana.
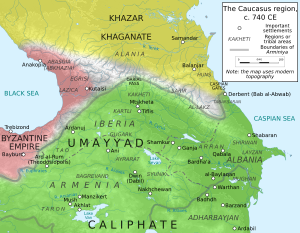
The Second Arab-Khazar War began with a series of raids across the Caucasus in the early 8th century. The Umayyads tightened their grip on Armenia in 705 after suppressing a large-scale rebellion. In 713 or 714, the Umayyad general Maslamah conquered Derbent and drove deeper into Khazar territory. The Khazars launched raids in response into Albania and Iranian Azerbaijan but were driven back by the Arabs under Hasan ibn al-Nu'man. The conflict escalated in 722 with an invasion by 30,000 Khazars into Armenia inflicting a crushing defeat. Caliph Yazid II responded, sending 25,000 Arab troops north, swiftly driving the Khazars back across the Caucasus, recovering Derbent, and advancing on Balanjar. The Arabs broke through the Khazar defence and stormed the city; most of its inhabitants were killed or enslaved, but a few of them managed to flee north. Despite their success, the Arabs had not yet defeated the Khazar army, and they retreated south of the Caucasus.
In 724, the Arab general al-Jarrah ibn Abdallah al-Hakami inflicted a crushing defeat on the Khazars in a long battle between the rivers Cyrus and Araxes, then moved on to capture Tiflis, bringing Caucasian Iberia under Muslim suzerainty. The Khazars struck back in 726, led by a prince named Barjik, launching a major invasion of Albania and Azerbaijan; by 729, the Arabs had lost control of northeastern Transcaucasia and were thrust again into the defensive. In 730, Barjik invaded Iranian Azerbaijan and defeated Arab forces at Ardabil, killing the general al-Djarrah al-Hakami and briefly occupying the town. Barjik was defeated and killed the next year at Mosul, where he directed Khazar forces from a throne mounted with al-Djarrah's severed head . In 737, Marwan Ibn Muhammad entered Khazar territory under the guise of seeking a truce. He then launched a surprise attack in which The Qaghan fled north and the Khazars surrendered. The Arabs did not have enough resources to influence the affairs of Transcaucasia. The Qağan was forced to accept terms involving his conversion to Islam, and subject himself to the rule of the Caliphate, but the accommodation was short-lived because a combination of internal instability among the Umayyads and Byzantine support undid the agreement within three years, and the Khazars re-asserted their independence. The suggestion that the Khazars adopted Judaism as early as 740 is based on the idea that, in part, it was, a re-assertion of their independence from the rule of both regional powers, Byzantium and the Caliphate, while it also conformed to a general Eurasian trend to embrace a world religion.
Whatever the impact of Marwan's campaigns was, warfare between the Khazars and the Arabs ceased for more than two decades after 737. Arab raids continued to occur until 741, but their control of the region was limited because maintaining a large garrison at Derbent further depleted their already overstretched army. A third Muslim civil war soon broke out, leading to the Abbasid Revolution and the fall of the Umayyad dynasty in 750.
In 758, the Abbasid Caliph al-Mansur attempted to strengthen diplomatic ties with the Khazars, ordering Yazid ibn Usayd al-Sulami, one of his nobles and the military governor of Armenia, to take a royal Khazar bride. Yazid married a daughter of Khazar Khagan Baghatur, but she died inexplicably, possibly during childbirth. Her attendants returned home, convinced that some members of another Arab faction had poisoned her, and her father was enraged. The Khazar general Ras Tarkhan invaded regions which were located south of the Caucasus in 762–764, devastating Albania, Armenia, and Iberia, and capturing Tiflis. Thereafter, relations between the Khazars and the Abbasids became increasingly cordial, because the foreign policies of the Abbasids were generally less expansionist than the foreign policies of the Umayyads, relations between the Khazars and the Abbasids were ultimately broken by a series of raids which occurred in 799, the raids occurred after another marriage alliance failed.
Khazars and Hungarians
Around 830, a rebellion broke out in the Khazar khaganate. As a result, three Kabar tribes of the Khazars (probably the majority of ethnic Khazars) joined the Hungarians and moved through Levedia to what the Hungarians call the Etelköz, the territory between the Carpathians and the Dnieper River. The Hungarians faced their first attack by the Pechenegs around 854, though other sources state that an attack by Pechenegs was the reason for their departure to Etelköz. The new neighbours of the Hungarians were the Varangians and the eastern Slavs. From 862 onwards, the Hungarians (already referred to as the Ungri) along with their allies, the Kabars, started a series of raids from the Etelköz into the Carpathian Basin, mostly against the Eastern Frankish Empire (Germany) and Great Moravia, but also against the Lower Pannonian principality and Bulgaria. Then they together ended up at the outer slopes of Carpathians, and settled there.
Rise of the Rus' and the collapse of the Khazarian state

By the 9th century, groups of Varangian Rus', developing a powerful warrior-merchant system, began probing south down the waterways controlled by the Khazars and their protectorate, the Volga Bulgarians, partially in pursuit of the Arab silver that flowed north for hoarding through the Khazarian-Volga Bulgarian trading zones, partially to trade in furs and ironwork. Northern mercantile fleets passing Atil were tithed, as they were at Byzantine Cherson. Their presence may have prompted the formation of a Rus' state by convincing the Slavs, Merja and the Chud' to unite to protect common interests against Khazarian exactions of tribute. It is often argued that a Rus' Khaganate modelled on the Khazarian state had formed to the east and that the Varangian chieftain of the coalition appropriated the title of qağan (khagan) as early as the 830s: the title survived to denote the princes of Kievan Rus', whose capital, Kiev, is often associated with a Khazarian foundation. The construction of the Sarkel fortress, with technical assistance from Khazaria's Byzantine ally at the time, together with the minting of an autonomous Khazar coinage around the 830s, may have been a defensive measure against emerging threats from Varangians to the north and from the Magyars on the eastern steppe. By 860, the Rus' had penetrated as far as Kiev and, via the Dnieper, Constantinople.

Alliances often shifted. Byzantium, threatened by Varangian Rus' raiders, would assist Khazaria, and Khazaria at times allowed the northerners to pass through their territory in exchange for a portion of the booty. From the beginning of the 10th century, the Khazars found themselves fighting on multiple fronts as nomadic incursions were exacerbated by uprisings by former clients and invasions from former allies. The pax Khazarica was caught in a pincer movement between steppe Pechenegs and the strengthening of an emergent Rus' power to the north, both undermining Khazaria's tributary empire. According to the Schechter Text, the Khazar ruler King Benjamin (ca.880–890) fought a battle against the allied forces of five lands whose moves were perhaps encouraged by Byzantium. Although Benjamin was victorious, his son Aaron II faced another invasion, this time led by the Alans, whose leader had converted to Christianity and entered into an alliance with Byzantium, which, under Leo VI the Wise, encouraged them to fight against the Khazars.
By the 880s, Khazar control of the Middle Dnieper from Kiev, where they collected tribute from Eastern Slavic tribes, began to wane as Oleg of Novgorod wrested control of the city from the Varangian warlords Askold and Dir, and embarked on what was to prove to be the foundation of a Rus' empire. The Khazars had initially allowed the Rus' to use the trade route along the Volga River, and raid southwards. See Caspian expeditions of the Rus'. According to Al-Mas'udi, the qağan is said to have given his assent on the condition that the Rus' give him half of the booty. In 913, however, two years after Byzantium concluded a peace treaty with the Rus' in 911, a Varangian foray, with Khazar connivance, through Arab lands led to a request to the Khazar throne by the Khwârazmian Islamic guard for permission to retaliate against the large Rus' contingent on its return. The purpose was to revenge the violence the Rus' razzias had inflicted on their fellow Muslim believers. The Rus' force was thoroughly routed and massacred. The Khazar rulers closed the passage down the Volga to the Rus', sparking a war. In the early 960s, Khazar ruler Joseph wrote to Hasdai ibn Shaprut about the deterioration of Khazar relations with the Rus': "I protect the mouth of the river (Itil-Volga) and prevent the Rus arriving in their ships from setting off by sea against the Ishmaelites and (equally) all (their) enemies from setting off by land to Bab."

The Rus' warlords launched several wars against the Khazar Qağanate, and raided down to the Caspian sea. The Schechter Letter relates the story of a campaign against Khazaria by HLGW (recently identified as Oleg of Chernigov) around 941 in which Oleg was defeated by the Khazar general Pesakh. The Khazar alliance with the Byzantine empire began to collapse in the early 10th century. Byzantine and Khazar forces may have clashed in the Crimea, and by the 940s emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus was speculating in De Administrando Imperio about ways in which the Khazars could be isolated and attacked. The Byzantines during the same period began to attempt alliances with the Pechenegs and the Rus', with varying degrees of success. A further factor undermining the Khazar Qağanate was a shift in Islamic routes at this time, as Muslims in Khwarazmia forged trade links with the recently converted Volga Bulgarian Muslims, a move which may have caused a drastic drop, perhaps up to 80%, in the revenue base of Khazaria, and consequently, a crisis in its ability to pay for its defence.
Sviatoslav I finally succeeded in destroying Khazar imperial power in the 960s, in a circular sweep that overwhelmed Khazar fortresses like Sarkel and Tamatarkha, and reached as far as the Caucasian Kassogians/Circassians and then back to Kiev. Sarkel fell in 965, with the capital city of Atil following, c. 968 or 969.
In the Russian chronicle, the vanquishing of the Khazar traditions is associated with Vladimir's conversion in 986. According to the Primary Chronicle, in 986, Khazar Jews were present at Vladimir's disputation to decide on the prospective religion of the Kievan Rus'. Whether these were Jews who had settled in Kiev or emissaries from some Jewish Khazar remnant state is unclear. Conversion to one of the faiths of the people of Scripture was a precondition to any peace treaty with the Arabs, whose Bulgar envoys had arrived in Kiev after 985.
A visitor to Atil wrote soon after the sacking of the city that its vineyards and garden had been razed, that not a grape or raisin remained in the land, and not even alms for the poor were available. An attempt to rebuild may have been undertaken, since Ibn Hawqal and al-Muqaddasi refer to it after that date, but by Al-Biruni's time (1048) it was in ruins.
Aftermath: impact, decline and dispersion
Although Poliak argued that the Khazar kingdom did not wholly succumb to Sviatoslav's campaign, but lingered on until 1224, when the Mongols invaded Rus', by most accounts, the Rus'-Oghuz campaigns left Khazaria devastated, with perhaps many Khazarian Jews in flight, and leaving behind at best a minor rump state. It left little trace, except for some placenames, and much of its population was undoubtedly absorbed in successor hordes. Al-Muqaddasi, writing ca.985, mentions Khazar beyond the Caspian sea as a district of "woe and squalor", with honey, many sheep and Jews. Kedrenos mentions a joint Rus'-Byzantine attack on Khazaria in 1016, which defeated its ruler Georgius Tzul. The name suggests Christian affiliations. The account concludes by saying, that after Tzul's defeat, the Khazar ruler of "upper Media", Senaccherib, had to sue for peace and submission. In 1024 Mstislav of Chernigov (one of Vladimir's sons) marched against his brother Yaroslav with an army that included "Khazars and Kassogians" in a repulsed attempt to restore a kind of "Khazarian"-type dominion over Kiev. Ibn al-Athir's mention of a "raid of Faḍlūn the Kurd against the Khazars" in 1030 CE, in which 10,000 of his men were vanquished by the latter, has been taken as a reference to such a Khazar remnant, but Barthold identified this Faḍlūn as Faḍl ibn Muḥammad and the "Khazars" as either Georgians or Abkhazians. A Kievian prince named Oleg, grandson of Jaroslav was reportedly kidnapped by "Khazars" in 1079 and shipped off to Constantinople, although most scholars believe that this is a reference to the Cumans-Kipchaks or other steppe peoples then dominant in the Pontic region. Upon his conquest of Tmutarakan in the 1080s Oleg gave himself the title "archon of Khazaria". In 1083 Oleg is said to have exacted revenge on the Khazars after his brother Roman was killed by their allies, the Polovtsi. After one more conflict with these Polovtsi in 1106, the Khazars fade from history. By the 13th century they survived in Russian folklore only as "Jewish heroes" in the "land of the Jews". (zemlya Jidovskaya).
By the end of the 12th century, Petachiah of Ratisbon reported travelling through what he called "Khazaria", and had little to remark on other than describing its minim (sectaries) living amidst desolation in perpetual mourning. The reference seems to be to Karaites. The Franciscan missionary William of Rubruck likewise found only impoverished pastures in the lower Volga area where Ital once lay. Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, the papal legate to the court of the Mongol Khan Guyuk at that time, mentioned an otherwise unattested Jewish tribe, the Brutakhi, perhaps in the Volga region. Although connections are made to the Khazars, the link is based merely on a common attribution of Judaism.
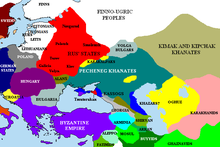
The 10th century Zoroastrian Dênkart registered the collapse of Khazar power in attributing its eclipse to the enfeebling effects of "false" religion. The decline was contemporary to that suffered by the Transoxiana Sāmānid empire to the east, both events paving the way for the rise of the Great Seljuq Empire, whose founding traditions mention Khazar connections. Whatever successor entity survived, it could no longer function as a bulwark against the pressure east and south of nomad expansions. By 1043, Kimeks and Qipchaqs, thrusting westwards, pressured the Oğuz, who in turn pushed the Pechenegs west towards Byzantium's Balkan provinces.
Khazaria nonetheless left its mark on the rising states and some of their traditions and institutions. Much earlier, Tzitzak, the Khazar wife of Leo III, introduced into the Byzantine court the distinctive kaftan or riding habit of the nomadic Khazars, the tzitzakion (τζιτζάκιον), and this was adopted as a solemn element of imperial dress. The orderly hierarchical system of succession by "scales" (lestvichnaia sistema:лествичная система) to the Grand Principate of Kiev was arguably modelled on Khazar institutions, via the example of the Rus' Khaganate.
The proto-Hungarian Pontic tribe, while perhaps threatening Khazaria as early as 839 (Sarkel), practiced their institutional model, such as the dual rule of a ceremonial kende-kündü and a gyula administering practical and military administration, as tributaries of the Khazars. A dissident group of Khazars, the Qabars, joined the Hungarians in their migration westwards as they moved into Pannonia. Elements within the Hungarian population can be viewed as perpetuating Khazar traditions as a successor state. Byzantine sources refer to Hungary as Western Tourkia in contrast to Khazaria, Eastern Tourkia. The gyula line produced the kings of medieval Hungary through descent from Árpád, while the Qabars retained their traditions longer, and were known as "black Hungarians" (fekete magyarság). Some archaeological evidence from Čelarevo suggests the Qabars practised Judaism since warrior graves with Jewish symbols were found there, including menorahs, shofars, etrogs, lulavs, candlesnuffers, ash collectors, inscriptions in Hebrew, and a six-pointed star identical to the Star of David.

The Khazar state was not the only Jewish state to rise between the fall of the Second Temple (67–70 CE) and the establishment of Israel (1948). A state in Yemen also adopted Judaism in the 4th century, lasting until the rise of Islam.
The Khazar kingdom is said to have stimulated messianic aspirations for a return to Israel as early as Judah Halevi. In the time of the Egyptian vizier Al-Afdal Shahanshah (d. 1121), one Solomon ben Duji, often identified as a Khazarian Jew, attempted to advocate for a messianic effort for the liberation of, and return of all Jews to, Palestine. He wrote to many Jewish communities to enlist support. He eventually moved to Kurdistan where his son Menachem some decades later assumed the title of Messiah and, raising an army for this purpose, took the fortress of Amadiya north of Mosul. His project was opposed by the rabbinical authorities and he was poisoned in his sleep. One theory maintains that the Star of David, until then a decorative motif or magical emblem, began to assume its national value in late Jewish tradition from its earlier symbolic use by Menachem.
The word Khazar, as an ethnonym, was last used in the 13th century by people in the North Caucasus believed to practice Judaism. The nature of a hypothetical Khazar diaspora, Jewish or otherwise, is disputed. Avraham ibn Daud mentions encountering rabbinical students descended from Khazars as far away as Toledo, Spain in the 1160s. Khazar communities persisted here and there. Many Khazar mercenaries served in the armies of the Islamic Caliphates and other states. Documents from medieval Constantinople attest to a Khazar community mingled with the Jews of the suburb of Pera. Khazar merchants were active in both Constantinople and Alexandria in the 12th century.
Religion
Tengrism
Main article: TengrismDirect sources for the Khazar religion are not many, but in all likelihood they originally engaged in a traditional Turkic form of religious practices known as Tengrism, which focused on the sky god Tengri. Something of its nature may be deduced from what we know of the rites and beliefs of contiguous tribes, such as the North Caucasian Huns. Horse sacrifices were made to this supreme deity. Rites involved offerings to fire, water, and the moon, to remarkable creatures, and to "gods of the road" (cf. Old Türk yol tengri, perhaps a god of fortune). Sun amulets were widespread as cultic ornaments. A tree cult was also maintained. Whatever was struck by lightning, man or object, was considered a sacrifice to the high god of heaven. The afterlife, to judge from excavations of aristocratic tumuli, was much a continuation of life on earth, warriors being interred with their weapons, horses, and sometimes with human sacrifices: the funeral of one tudrun in 711-12 saw 300 soldiers killed to accompany him to the otherworld. Ancestor worship was observed. The key religious figure appears to have been a shaman-like qam, and it was these (qozmím) that were, according to the Khazar Hebrew conversion stories, driven out.
Many sources suggest, and a notable number of scholars have argued, that the charismatic Ashina clan played a germinal role in the early Khazar state, although Zuckerman dismisses the widespread notion of their pivotal role as a "phantom". The Ashina were closely associated with the Tengri cult, whose practices involved rites performed to assure a tribe of heaven's protective providence. The qağan was deemed to rule by virtue of qut, "the heavenly mandate/good fortune to rule."
Christianity
Khazaria long served as a buffer state between the Byzantine empire and both the nomads of the northern steppes and the Umayyad empire, after serving as Byzantium's proxy against the Sasanian Persian empire. The alliance was dropped around 900. Byzantium began to encourage the Alans to attack Khazaria and weaken its hold on Crimea and the Caucasus, while seeking to obtain an entente with the rising Rus' power to the north, which it aspired to convert to Christianity.
On Khazaria's southern flank, both Islam and Byzantine Christianity were proselytising great powers. Byzantine success in the north was sporadic, although Armenian and Albanian missions from Derbend built churches extensively in maritime Daghestan, then a Khazar district. Buddhism also had exercised an attraction on leaders of both the Eastern (552–742) and Western Qağanates (552–659), the latter being the progenitor of the Khazar state. In 682, according to the Armenian chronicle of Movsês Dasxuranc'i, the king of Caucasian Albania, Varaz Trdat, dispatched a bishop, Israyêl, to convert Caucasian "Huns" who were subject to the Khazars, and managed to convince Alp Ilut'uêr, a son-in-law of the Khazar qağan, and his army, to abandon their shamanising cults and join the Christian fold.
The Arab Georgian martyr St Abo, who converted to Christianity within the Khazar kingdom around 779–80, describes local Khazars as irreligious. Some reports register a Christian majority at Samandar, or Muslim majorities.
Judaism

Conversion to Judaism is mentioned in the Khazar Correspondence and medieval external sources. The authenticity of the former was long doubted and challenged, but the documents are now widely accepted by specialists as either authentic or as reflecting internal Khazar traditions. Archaeological evidence for conversion, on the other hand, remains elusive, and may reflect either the incompleteness of excavations, or that the stratum of actual adherents was thin. Conversion of steppe or peripheral tribes to a universal religion is a fairly well attested phenomenon, and the Khazar conversion to Judaism, although unusual, would not have been without precedent.
Jews from both the Islamic world and Byzantium are known to have migrated to Khazaria during periods of persecution under Heraclius, Justinian II, Leo III, and Romanus Lakapēnos. For Simon Schama, Jewish communities from the Balkans and the Bosphoran Crimea, especially from Panticapaeum, began migrating to the more hospitable climate of pagan Khazaria in the wake of these persecutions, and were joined there by Jews from Armenia. The Geniza fragments, he argues, make it clear the Judaising reforms sent roots down into the whole of the population. The pattern is one of an elite conversion preceding large-scale adoption of the new religion by the general population, which often resisted the imposition. One important condition for mass conversion was a settled urban state, where churches, synagogues or mosques provided a focus for religion, as opposed to the free nomadic lifestyle of life on the open steppes. A tradition of the Iranian Judeo-Tats claims that their ancestors were responsible for the Khazar conversion. A legend traceable to the 16th-century Italian rabbi Judah Moscato attributed it to Yitzhak ha-Sangari.
Both the date of the conversion, and the extent of its influence beyond the elite, often minimised in some scholarship, are a matter of dispute, but at some point between 740 and 920 CE, the Khazar royalty and nobility appear to have converted to Judaism, in part, it is argued, perhaps to deflect competing pressures from Arabs and Byzantines to accept either Islam or Christianity.
The conversion of the Khazars to Judaism is an emotionally charged topic in Israel, and two scholars, Moshe Gil (2011) and Shaul Stampfer, (2013) have challenged the authenticity of the medieval Hebrew documents and argue that the conversion of the Khazar elite to Judaism never happened. Alex M. Feldman is critical of Stampfer and Gil's dismissal of "overwhelming textual and archaeological evidence" of Khazarian Judaism, though agrees it is unlikely that Ashkenazim are descended from Khazarian Jews, he posits "a middle ground which can simultaneously accept Khazarian Judaism and doubt the Khazar-Ashkenazi descent theory advanced in dubious genetic studies."
History of discussions about Khazar Jewishness
The earliest surviving Arabic text that refers to Khazar Jewishness appears to be that which was written by ibn Rustah, a Persian scholar who wrote an encyclopedic work on geography in the early tenth century. It is believed that ibn Rustah derived much of his information from the works of his contemporary Abu al Jayhani based in Central Asia.

Christian of Stavelot in his Expositio in Matthaeum Evangelistam (c. 860–870s) refers to Gazari, presumably Khazars, as living in the lands of Gog and Magog, who were circumcised and omnem Judaismum observat—observing all the laws of Judaism. New numismatic evidence of coins dated 837/8 bearing the inscriptions arḍ al-ḫazar (Land of the Khazars), or Mûsâ rasûl Allâh (Moses is the messenger of God, in imitation of the Islamic coin phrase: Muḥammad rasûl Allâh) suggest to many the conversion took place in that decade. Olsson argues that the 837/8 evidence marks only the beginning of a long and difficult official Judaization that concluded some decades later. A 9th-century Jewish traveller, Eldad ha-Dani, is said to have informed Spanish Jews in 883 that there was a Jewish polity in the East, and that fragments of the legendary Ten Lost Tribes, part of the line of Simeon and half-line of Manasseh, dwelt in "the land of the Khazars", receiving tribute from some 25 to 28 kingdoms. Another view holds that by the 10th century, while the royal clan officially claimed Judaism, a non-normative variety of Islamisation took place among the majority of Khazars.
By the 10th century, the letter of King Joseph asserts that, after the royal conversion, "Israel returned (yashuvu yisra'el) with the people of Qazaria (to Judaism) in complete repentance (bi-teshuvah shelemah)." Persian historian Ibn al-Faqîh wrote that "all the Khazars are Jews, but they have been Judaized recently". Ibn Fadlân, based on his Caliphal mission (921–922) to the Volga Bulğars, also reported that "the core element of the state, the Khazars, were Judaized", something underwritten by the Qaraite scholar Ya'kub Qirqisânî around 937. The conversion appears to have occurred against a background of frictions arising from both an intensification of Byzantine missionary activity from the Crimea to the Caucasus, and Arab attempts to wrest control over the latter in the 8th century CE, and a revolt, put down, by the Khavars around the mid-9th century is often invoked as in part influenced by their refusal to accept Judaism. Modern scholars generally see the conversion as a slow process through three stages, which accords with Richard Eaton's model of syncretic inclusion, gradual identification and, finally, displacement of the older tradition.
Sometime between 954 and 961, Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ, from al-Andalus (Muslim Spain), wrote a letter of inquiry addressed to the ruler of Khazaria, and received a reply from Joseph of Khazaria. The exchanges of this Khazar Correspondence, together with the Schechter Letter discovered in the Cairo Geniza and the famous plato nizing dialogue by Judah Halevi, Sefer ha-Kuzari ("Book (of) The Khazari"), which plausibly drew on such sources, provide us with the only direct evidence of the indigenous traditions concerning the conversion. King Bulan is said to have driven out the sorcerers, and to have received angelic visitations exhorting him to find the true religion, upon which, accompanied by his vizier, he travelled to desert mountains of Warsān on a seashore, where he came across a cave rising from the plain of Tiyul in which Jews used to celebrate the Sabbath. Here he was circumcised. Bulan is then said to have convened a royal debate between exponents of the three Abrahamic religions. He decided to convert when he was convinced of Judaism's superiority. Many scholars situate this c. 740, a date supported by Halevi's own account. The details are both Judaic and Türkic: a Türkic ethnogonic myth speaks of an ancestral cave in which the Ashina were conceived from the mating of their human ancestor and a wolf ancestress. These accounts suggest that there was a rationalising syncretism of native pagan traditions with Jewish law, by melding through the motif of the cave, a site of ancestral ritual and repository of forgotten sacred texts, Türkic myths of origin and Jewish notions of redemption of Israel's fallen people. It is generally agreed they adopted Rabbinical rather than Qaraite Judaism.
Ibn Fadlan reports that the settlement of disputes in Khazaria was adjudicated by judges hailing each from his community, be it Christian, Jewish, Muslim, or Pagan. Some evidence suggests that the Khazar king saw himself as a defender of Jews even beyond the kingdom's frontiers, retaliating against Muslim or Christian interests in Khazaria in the wake of Islamic and Byzantine persecutions of Jews abroad. Ibn Fadlan recounts specifically an incident in which the king of Khazaria destroyed the minaret of a mosque in Atil as revenge for the destruction of a synagogue in Dâr al-Bâbûnaj, and allegedly said he would have done worse were it not for a fear that the Muslims might retaliate in turn against Jews. Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ sought information on Khazaria in the hope he might discover "a place on this earth where harassed Israel can rule itself" and wrote that, were it to prove true that Khazaria had such a king, he would not hesitate to forsake his high office and his family in order to emigrate there.
Albert Harkavy noted in 1877 that an Arabic commentary on Isaiah 48:14 ascribed to Saadia Gaon or to the Karaite scholar Benjamin Nahâwandî, interpreted "The Lord hath loved him" as a reference "to the Khazars, who will go and destroy Babel" (i.e., Babylonia), a name used to designate the country of the Arabs. This has been taken as an indication of hopes by Jews that the Khazars might succeed in destroying the Caliphate.
Islam
In 965, as the Qağanate was struggling against the victorious campaign of the Rus' prince Sviatoslav, the Islamic historian Ibn al-Athîr mentions that Khazaria, attacked by the Oğuz, sought help from Khwarezm, but their appeal was rejected because they were regarded as "infidels" (al-kuffâr; pagans). Save for the king, the Khazarians are said to have converted to Islam in order to secure an alliance, and the Turks were, with Khwarezm's military assistance, repelled. It was this that, according to Ibn al-Athîr, led the Jewish king of Khazar to convert to Islam.
Genetics
Nine skeletons dating to the 7th–9th centuries excavated from elite military burial mounds of the Khazar Khaganate (in the modern Rostov region) were analyzed in two genetic studies (from 2019 and 2021). According to the 2019 study, the results "confirm the Turkic roots of the Khazars, but also highlight their ethnic diversity and some integration of conquered populations". The samples did not show a genetic connection to Ashkenazi Jews, and the results do not support the hypothesis of Ashkenazi Jews being descendants of the Khazars. In the 2021 study the results showed both European and East Asian paternal haplogroups in the samples: three individuals carried R1a Y-haplogroup, two had C2b, and the rest carried haplogroups G2a, N1a, Q, and R1b, respectively. According to the authors, "The Y-chromosome data are consistent with the results of the craniological study and genome-wide analysis of the same individuals in the sense that they show mixed genetic origins for the early medieval Khazar nobility". Their facial features were of mix of East Asian and European, with East Asian type dominating (70%) in the early Khazars.
Claims of Khazar ancestry
Claims of Khazar origins of peoples, or suggestions that the Khazars were absorbed by them, have been made with regard to the Kazakhs, the Hungarians, the Judaizing Slavic Subbotniks, the Muslim Karachays, the Kumyks, the Avars, the Cossacks of the Don and the Ukrainian Cossacks (see Khazar hypothesis of Cossack ancestry), the Turkic-speaking Krymchaks and their Crimean neighbours the Karaites, Mishar Tatars, the Moldavian Csángós and others. Turkic-speaking Crimean Karaites (known in the Crimean Tatar language as Qaraylar), some of whom migrated in the 19th century from the Crimea to Poland and Lithuania have claimed Khazar origins. Specialists in Khazar history question the connection. Scholarship is likewise sceptical of claims that the Tatar-speaking Krymchak Jews of the Crimea descend from Khazars.
Crimean Karaites and Krymchaks
Main articles: Crimean Karaites and KrymchaksIn 1839, the Karaim scholar Abraham Firkovich was appointed by the Russian government as a researcher into the origins of the Jewish sect known as the Karaites. In 1846, one of his acquaintances, the Russian orientalist Vasilii Vasil'evich Grigor'ev (1816–1881), theorised that the Crimean Karaites were of Khazar stock. Firkovich vehemently rejected the idea, a position seconded by Firkovich, who hoped that by "proving" his people were of Turkic origin, he would secure them exception from Russian anti-Jewish laws, since they bore no responsibility for Christ's crucifixion. This idea has a notable impact in Crimean Karaite circles. It is now believed that he forged much of this material on Khazars and Karaites. Specialists in Khazar history also question the connection. A genetic study of European Karaites by Kevin Alan Brook found no evidence of a Khazar or Turkic origin for any uniparental lineage but did reveal the European Karaites' links to Egyptian Karaites and to Rabbinical Jewish communities.
Another Turkic Crimean group, the Krymchaks had retained very simple Jewish traditions, mostly devoid of halakhic content, and very much taken with magical superstitions which, in the wake of the enduring educational efforts of the great Sephardi scholar Chaim Hezekiah Medini, came to conform with traditional Judaism.
Though the assertion they were not of Jewish stock enabled many Crimean Karaites to survive the Holocaust, which led to the murder of 6,000 Krymchaks, after the war, many of the latter, somewhat indifferent to their Jewish heritage, took a cue from the Crimean Karaites, and denied this connection in order to avoid the antisemitic effects of the stigma attached to Jews.
Ashkenazi-Khazar theories
Main article: Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestrySeveral scholars have suggested that instead of disappearing after the dissolution of their Empire, the Khazars migrated westward and eventually, they formed part of the core of the later Ashkenazi Jewish population of Europe. This hypothesis is greeted with scepticism or caution by most scholars.
The German Orientalist Karl Neumann, in the context of an earlier controversy about possible connections between the Khazars and the ancestors of the Slavic peoples, suggested as early as 1847 that emigrant Khazars might have influenced the core population of Eastern European Jews.
The theory was then taken up by Albert Harkavi in 1869, when he also claimed that a possible link existed between the Khazars and the Ashkenazim, but the theory that Khazar converts formed a major proportion of the Ashkenazim was first proposed to the Western public in a lecture which was delivered by Ernest Renan in 1883. Occasional suggestions that there was a small Khazar component in East European Jews emerged in works by Joseph Jacobs (1886), Anatole Leroy-Beaulieu, a critic of antisemitism (1893), Maksymilian Ernest Gumplowicz, and by the Russian-Jewish anthropologist Samuel Weissenberg. In 1909, Hugo von Kutschera developed the notion into a book-length study, arguing that the Khazars formed the foundational core of the modern Ashkenazim. Maurice Fishberg introduced the notion to American audiences in 1911. The idea was also taken up by the Polish-Jewish economic historian and General Zionist Yitzhak Schipper in 1918. Israel Bartal has suggested that from the Haskalah onwards, polemical pamphlets against the Khazars were inspired by Sephardi organizations which opposed the Khazaro-Ashkenazim.
Scholarly anthropologists, such as Roland B. Dixon (1923), and writers such as H. G. Wells (1920) used it to argue that "The main part of Jewry never was in Judea", a thesis that was to have a political echo in later opinion.
In 1932, Samuel Krauss ventured the theory that the biblical Ashkenaz referred to northern Asia Minor, and he identified it as the ancestral homeland of the Khazars, a position which was immediately disputed by Jacob Mann. Ten years later, in 1942, Abraham N. Polak (sometimes referred to as Poliak), later professor for the history of the Middle Ages at Tel Aviv University, published a Hebrew monograph in which he concluded that the East European Jews came from Khazaria. D.M. Dunlop, writing in 1954, thought that very little evidence supported what he considered a mere assumption, and he also argued that the Ashkenazi-Khazar descent theory went far beyond what "our imperfect records" permit. In 1955, Léon Poliakov, who assumed that the Jews of Western Europe resulted from a "panmixia" in the first millennium, asserted that it was widely assumed that Europe's Eastern Jews were descended from a mixture of Khazarian and German Jews. Poliak's work found some support in Salo Wittmayer Baron and Ben-Zion Dinur, but was dismissed by Bernard Weinryb as a fiction (1962). Bernard Lewis was of the opinion that the word in Cairo Geniza interpreted as Khazaria is actually Hakkari and therefore it relates to the Kurds of the Hakkari mountains in southeast Turkey.
The Khazar-Ashkenazi hypothesis came to the attention of a much wider public with the publication of Arthur Koestler's The Thirteenth Tribe in 1976, which was both positively reviewed and dismissed as a fantasy, and a somewhat dangerous one. Israeli historian Zvi Ankori argued that Koestler had allowed his literary imagination to espouse Poliak's thesis, which most historians dismissed as speculative. Israel's ambassador to Britain branded it "an anti-Semitic action financed by the Palestinians", while Bernard Lewis claimed that the idea was not supported by any evidence whatsoever, and it had been abandoned by all serious scholars. Raphael Patai, however, registered some support for the idea that Khazar remnants had played a role in the growth of Eastern European Jewish communities, and several amateur researchers, such as Boris Altschüler (1994), kept the thesis in the public eye. The theory has been occasionally manipulated to deny Jewish nationhood. Recently, a variety of approaches, from linguistics (Paul Wexler) to historiography (Shlomo Sand) and population genetics (Eran Elhaik, a geneticist from the University of Sheffield) have emerged to keep the theory alive. In a broad academic perspective, both the idea that the Khazars converted en masse to Judaism and the suggestion they emigrated to form the core population of Ashkenazi Jewry, remain highly polemical issues. One thesis held that the Khazar Jewish population went into a northern diaspora and had a significant impact on the rise of Ashkenazi Jews. Connected to this thesis is the theory, expounded by Paul Wexler, dissenting from the majority of Yiddish linguists, that the grammar of Yiddish contains a Khazar substrate.
Use in antisemitic polemic
According to Michael Barkun, while the Khazar hypothesis generally never played any major role in the development of anti-Semitism, it has exercised a noticeable influence on American antisemites since the restrictions on immigration were imposed in the 1920s. Maurice Fishberg and Roland B. Dixon's works were later exploited in racist and religious polemical literature, particularly in literature which advocated British Israelism, both in Britain and the United States. Particularly after the publication of Burton J. Hendrick's The Jews in America, (1923) it began to enjoy a vogue among advocates of immigration restriction in the 1920s; racial theorists such as Lothrop Stoddard; antisemitic conspiracy-theorists such as the Ku Klux Klan's Hiram Wesley Evans; and some anti-communist polemicists such as John O. Beaty and Wilmot Robertson, whose views influenced David Duke. According to Yehoshafat Harkabi (1968) and others, it played a role in Arab anti-Zionist polemics, and took on an antisemitic edge. Bernard Lewis, noting in 1987 that Arab scholars had dropped it, remarked that it only occasionally emerged in Arab political discourse. It has also played some role in Soviet antisemitic chauvinism and Slavic Eurasian historiography; particularly, in the works of scholars like Lev Gumilev, it came to be exploited by the white supremacist Christian Identity movement and even by terrorist esoteric cults like Aum Shinrikyō. The Kazar hypothesis was further exploited by esoteric fascists such as Miguel Serrano, referring to a lost Palestinabuch by the German Nazi-scholar Herman Wirth, who claimed to have proven that the Jews descended from a prehistoric migrant group parasiting on the Great Civilizations. The phrase "Khazar kaghanate" gained new traction in 2000s among antisemitic nationalists in Russia, such as Yan Petrovsky.
Genetic studies
See also: Ashkenazi Jews § Genetic origins, Genetic studies on Jews, and Khazar hypothesis of Ashkenazi ancestry § Genetics and the Khazar theoryThe hypothesis of Khazarian ancestry in Ashkenazi has also been a subject of vehement disagreements in the field of population genetics, wherein claims have been made concerning evidence both for and against it. Eran Elhaik argued in 2012 for a significant Khazar component in the admixture of Ashkenazi Jews using Caucasian populations—Georgians, Armenians and Azerbaijani Jews—as proxies. The evidence from historians he used has been criticised by Shaul Stampfer and the technical response to such a position from geneticists is mostly dismissive, arguing that, if traces of descent from Khazars exist in the Ashkenazi gene pool, the contribution would be quite minor, or insignificant. One geneticist, Raphael Falk, has argued that "national and ethnic prejudices play a central role in the controversy." According to Nadia Abu El-Haj, the issues of origins are generally complicated by the difficulties of writing history via genome studies and the biases of emotional investments in different narratives, depending on whether the emphasis lies on direct descent or on conversion within Jewish history. At the time of her writing, the lack of Khazar DNA samples that might allow verification also presented difficulties.
In literature
The Kuzari is an influential work written by the medieval Spanish Jewish philosopher and poet Rabbi Yehuda Halevi (c. 1075–1141). Divided into five essays (ma'amarim), it takes the form of a fictional dialogue between the pagan king of the Khazars and a Jew who was invited to instruct him in the tenets of the Jewish religion. The intent of the work, although based on Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ's correspondence with the Khazar king, was not historical, but rather to defend Judaism as a revealed religion, written in the context, firstly of Karaite challenges to the Spanish rabbinical intelligentsia, and then against temptations to adapt Aristotelianism and Islamic philosophy to the Jewish faith. Originally written in Arabic, it was translated into Hebrew by Judah ibn Tibbon.
Benjamin Disraeli's early novel Alroy (1833) draws on Menachem ben Solomon's story. The question of mass religious conversion and the indeterminability of the truth of stories about identity and conversion are central themes of Milorad Pavić's best-selling mystery story Dictionary of the Khazars.
H.N. Turteltaub's Justinian, Marek Halter's Book of Abraham and Wind of the Khazars, and Michael Chabon's Gentlemen of the Road allude to or feature elements of Khazar history or create fictional Khazar characters.
Cities associated with the Khazars
Cities associated with the Khazars include Atil, Khazaran, Samandar; in the Caucasus, Balanjar, Kazarki, Sambalut, and Samiran; in Crimea and the Taman region, Kerch, Theodosia, Yevpatoria (Güzliev), Samkarsh (also called Tmutarakan, Tamatarkha), and Sudak; and in the Don valley, Sarkel. A number of Khazar settlements have been discovered in the Mayaki-Saltovo region. Some scholars suppose that the Khazar settlement of Sambat on the Dnieper refers to the later Kiev.
See also
- List of Khazar rulers
- Hormizd IV his mother was a Khazar princess.
- Leo IV the Khazar (Byzantine emperor, r. 775–780, born in 750 to Emperor Constantine V and Empress Tzitzak, a Khazar Turkic princess, daughter of Bihar Khagan)
- Leon II of Abkhazia
- List of Turkic Khaganates
- List of Jewish states and dynasties
- History of the Jews in Central Asia
- Turkish Jews
- Red Jews
- History of Kyiv
- Grand Prince of Kiev
- Rus' Khaganate
- Rus'–Byzantine War (860)
- Rus'–Byzantine War (907)
- Rus'–Byzantine War (941)
- Rus'–Byzantine War (968-971)
Notes
Footnotes
- Greek: Χάζαροι Kházaroi; Hebrew: כּוּזָרִים, romanized: Kūzārīm; Old East Slavic: коꙁаре, romanized: kozare; Church Slavonic: коꙁари, romanized: kozari; Latin: Gazari, or Gasani; Chinese: 突厥曷薩 Tūjué Hésà; 突厥可薩 Tūjué Kěsà, lit. 'Türk Khazar'
Resource notes
- ^ "The Gazari are, presumably, the Khazars, although this term or the Kozary of the perhaps near contemporary Vita Constantini ... could have reflected any of a number of peoples within Khazaria." (Golden 2007b, p. 139)
- "Somewhat later, however, in a letter to the Byzantine Emperor Basil I, dated to 871, Louis the German, clearly taking exception to what had apparently become Byzantine usage, declares that 'we have not found that the leader of the Avars, or Khazars (Gasanorum)'..." (Golden 2001a, p. 33)
- Golden 2007a, p. 16 and n.38 citing L. Bazin, "Pour une nouvelle hypothèse sur l'origine des Khazar", in Materialia Turcica, 7/8 (1981–1982): 51–71.
- Compare Tibetan dru-gu Ge-sar (the Turk Gesar)(Golden 2007a, p. 16) or Phrom Ge-sar, who was possibly inspired by Fromo Kesaro (拂菻罽娑 standard Chinese: Fúlǐn Jìsuō < Middle Chinese: *pʰɨut̚ -liɪm kˠiᴇi-sɑ), a king of the Turk Shahis of mixed Hephthalite-Western Turkic origins (Rezakhani 2017, Kim 2016, pp. 58–59, Inaba & Balogh 2020, p. 106, Kordosis 2017, pp. 183–192).
- Sijie 思結 (also 斯結) was mentioned as a 鐵勒 Tiele, later Toquz Oghuz tribe, and distinguished from 突厥 Tujue in Chinese sources such as Old Book of Tang, New Book of Tang or Tang Huiyao. However, in other sources Sijie were also associated with Tujue (Saka Ttrūka): Zizhi Tongjian mentioned the Tujue Sijie 突厥思結 and Tang Huiyao also counted 思結 Sijie (rendered as 恩結 Enjie) among the Eastern Turkic tribes living south of the Gobi desert. A saikairä ttūrkä chārä (< *sïqïr türk čor) was also mentioned in a Khotanese Saka text about Turks in Ganzhou.
- Kěsà (可薩) would have been pronounced something like ka'sat in both Early Middle Chinese/EMC and Late Middle Chinese/LMC, while Hésà 葛 (曷薩) would yield ɣat-sat in (EMC) and xɦat sat (LMC) respectively, where final "t" often transcribes –r- in foreign words. Thus, while these Chinese forms could transcribe a foreign word of the type *Kasar/*Kazar, *Ġatsar, *Ġazar, *Ġasar, there is a problem phonetically with assimilating these to the Uyğur word Qasar 葛薩 (Standard Chinese Gesa < EMC/LMC *Kat-sat= *Kar sar= *Kasar).
- Ibn al-Nadīm commenting on script systems in 987–88 recorded that the Khazars wrote in Hebrew (Golden 2007b, p. 148).
- "The chancellery of the Jewish state of the Khazars is therefore also likely to have used Hebrew writing even if the official language was a Turkic one." (Erdal 2007, pp. 98–99)
- "there must have been many different ethnic groups within the Khazar realm ... These groups spoke different languages, some of them no doubt belonging to the Indo-European or different Caucasian language families." (Erdal 2007, p. 75, n.2)
- The high chancery official of the Abbasid Caliphate under Al-Wathiq, Sallām the interpreter (Sallam al-tardjuman), famous for his reputed mastery of thirty languages, might have been both Jewish and a Khazar Wasserstein 2007, pp. 376, and n.2, referring to Dunlop 1954, pp. 190–193.
- al-Iṣṭakhrī's account however then contradicts itself by likening the language to Bulğaric (Golden 2007a, pp. 13–14, 14 n.28).
- "The word tribe is as troublesome as the term clan. It is commonly held to denote a group, like the clan, claiming descent from a common (in some culture zones eponymous) ancestor, possessing a common territory, economy, language, culture, religion, and sense of identity. In reality, tribes were often highly fluid sociopolitical structures, arising as 'ad hoc responses to ephemeral situations of competition,' as Morton H. Fried has noted." (Golden 2001b, p. 78)
- Dieter Ludwig, in his doctoral thesis Struktur und Gesellschaft des Chazaren-Reiches im Licht der schriftlichen Quellen, (Münster, 1982) suggested that the Khazars were Turkic members of the Hephthalite Empire, where the lingua franca was a variety of Iranian (Golden 2007a, pp. 40–41; Brook 2010, p. 4).
- "The reader should be warned that the A-shih-na link of the Khazar dynasty, an old phantom of ... Khazarology, will ... lose its last claim to reality" (Zuckerman 2007, p. 404).
- In this view, the name Khazar would derive from a hypothetical *Aq Qasar (Golden 2006, pp. 89–90): e.g. Pritsak (1978) links Ak-Katzirs (< Άκατζίροι) to the name Khazar, though he explains that the polity was named Khazar because the Ashina-ruled Western Turks, after losing their territories to Tang Chinese, took over the territory formerly occupied by the Akatziri (Pritsak 1978, p. 261). However, the hypothesized link between the Akatizoi and the Khazars was not solid, being based on mere phonetic resemblance (Golden 2011b, p. 136, Brook 2006, p. 10).
- Whittow states that the word Türk had no strict ethnic meaning at the time: "Throughout the early middle ages on the Eurasian steppes, the term 'Turk' may or may not imply membership of the ethnic group of Turkic peoples, but it does always mean at least some awareness and acceptance of the traditions and ideology of the Gök Türk empire, and a share, however distant, in the political and cultural inheritance of that state." (Whittow 1996, p. 221)
- The Duōlù (咄陆) were the left wing of the On Oq, the Nǔshībì (弩失畢: *Nu Šad(a)pit), and together they were registered in Chinese sources as the "ten names" (shí míng:十名) (Golden 2010, pp. 54–55).
- Several scholars connect it to Judaization, with Artamonov linking its introduction to Obadiyah's reforms and the imposition of full Rabbinical Judaism and Pritsak to the same period (799–833), arguing that the Beg, a majordomo from the Iranian *Barč/Warâ Bolčan clan, identified with Obadiyah, compelled the Qağanal clan to convert, an event which putatively caused the Qabar revolt. Golden comments: "There is nothing but conjecture to connect it with the reforms of Obadiyah, the further evolution of Khazar Judaism or the Qabars ... The fact is we do not know when, precisely, the Khazar system of dual kingship emerged. It could not have come ex nihilo. It was not present in the early stages of Khazar history. Given the Old Türk traditions of the Khazar state ... and the overall institutional conservation of steppe society, one must exercise great caution here. Clear evidence for it is relatively late (the latter part of the ninth century perhaps and more probably the tenth century)- although it was probably present by the first third of the ninth century. Iranian influences via the Ors guard of the Qağans may have also been a factor" (Golden 2007b, pp. 155–156)
- There was a maximum limit on the number of years of a king's reign, according to Ibn Fadlan; if a Qağan had reigned for at least forty years, his courtiers and subjects felt his ability to reason would become impaired by old age. They would then kill the Qağan (Dunlop 1954, pp. 97, 112).
- Petrukhin notes that Ibn Fadlan's description of a Rus' prince (malik) and his lieutenant (khalifa) mirrored the Khazarian diarchy, but the comparison was flawed, as there was no sacral kingship among the Rus' (Petrukhin 2007, pp. 256–257).
- "the rest of the Khazars profess a religion similar to that of the Turks." (Golden 2007b, pp. 130–131)
- This regiment was exempt from campaigning against fellow Muslims, evidence that non-Judaic beliefs were no obstacle to access to the highest levels of government. They had abandoned their homeland and sought service with the Khazars in exchange for the right to exercise their religious freedom, according to al-Masudi (Golden 2007b, p. 138).
- Olsson writes that there is no evidence for this Islamic guard for the 9th century, but that its existence is attested for 913 (Olsson 2013, p. 507).
- Noonan gives the lower figure for the Muslim contingents, but adds that the army could draw on other mercenaries stationed in the capital, Rūs, Ṣaqāliba and pagans. Olsson's 10,000 refers to the spring-summer horsemen in the nomadic king's retinue (Noonan 2007, pp. 211, 217).
- A third division may have contained the dwellings of the tsarina. The dimensions of the western part were 3x3, as opposed to the eastern part's 8 x 8 farsakhs (Noonan 2007, pp. 208–209, 216–219).
- Outside Muslim traders were under the jurisdiction of a special royal official (ghulām) (Noonan 2007, pp. 211–214).
- Theophanes the Confessor around 813 defined them as Eastern Turks. The designation is complex and Róna-Tas writes: "The Georgian Chronicle refers to the Khazars in 626–628 as the 'West Turks' who were then opposed to the East Turks of Central Asia. Shortly after 679 the Armenian Geography mentions the Turks together with the Khazars; this may be the first record of the Magyars. Around 813, Theophanes uses – alongside the generic name Turk – 'East Turk' for the designation of the Khazars, and in context, the 'West Turks' may actually have meant the Magyars. We know that Nicholas Misticus referred to the Magyars as 'West Turks' in 924/925. In the 9th century the name Turk was mainly used to designate the Khazars." (Róna-Tas 1999, p. 282)
- Many sources identify the Göktürks in this alliance as Khazars--for example, Beckwith writes recently: "The alliance sealed by Heraclius with the Khazars in 627 was of seminal importance to the Byzantine Empire through the Early Middle Ages, and helped assure its long-term survival." Early sources such as the almost contemporary Armenian history, Patmutʿiwn Ałuanicʿ Ašxarhi, attributed to Movsēs Dasxurancʿ, and the Chronicle attributed to Theophanes identify these Turks as Khazars (Theophanes has: "Turks, who are called Khazars"). Both Zuckerman and Golden reject the identification.
- Scholars dismiss Chinese annals which, reporting the events from Turkic sources, attribute the destruction of Persia and its leader Shah Khusrau II personally to Tong Yabghu. Zuckerman argues instead that the account is correct in its essentials (Zuckerman 2007, p. 417).
- "The Khazars, the close allies of the Byzantines, adopted Judaism, as their official religion, apparently by 740, three years after an invasion by the Arabs under Marwan ibn Muhammad. Marwan had used treachery against a Khazar envoy in order to gain peaceful entrance into Khazar territory. He then declared his dishonourable intentions and pressed deep into Khazar territory, subsequently, he released the envoy. The Arabs devastated the horse herds, seized many Khazars and others as captives, and forced much of the population to flee into the Ural Mountains. Marwan's terms dictated that the kaghan and his Khazars should convert to Islam. Having no choice, the kaghan accepted Marwan's terms, and the Arabs returned home in triumph. As soon as the Arabs were gone, the kaghan renounced Islam – with, one may assume, great vehemence. The Khazar Dynasty's conversion to Judaism is best explained by this specific historical background, together with the fact that the mid-eighth century was an age in which the major Eurasian states proclaimed their adherence to distinctive world religions. Adopting Judaism also was politically astute: it meant that the Khazars did not have to accept the overlordship (however theoretical) of the Arab caliph or the Byzantine emperor." (Beckwith 2011, p. 149)
- Over 520 separate hoards of such silver have been uncovered in Sweden and Gotland (Moss 2002, p. 16).
- The Volga Bulgarian state was converted to Islam in the 10th century, and wrested liberty from its Khazarian suzerains when Svyatislav razed Atil (Abulafia 1987, pp. 419, 480–483).
- Whittow argues however that: "The title of qaghan, with its claims to lordship over the steppe world, is likely to be no more than ideological booty from the 965 victory." (Whittow 1996, pp. 243–252)
- Korobkin citing Golb & Pritsak notes that Khazars have often been connected with Kiev's foundations. Pritsak and Golb state that children in Kiev were being given a mixture of Hebrew and Slavic names by c. 930. Toch on the other hand is sceptical, and argues that "a significant Jewish presence in early medieval Kiev or indeed in Russia at large remains much in doubt".
- The yarmaq based on the Arab dirhem was perhaps issued in reaction to fall-off in Muslim minting in the 820s, and to a felt need in the turbulent upheavals of the 830s to assert a new religious profile, with the Jewish legends stamped on them (Golden 2007b, p. 156).
- Scholars are divided as to whether the fortification of Sarkel represents a defensive bulwark against a growing Magyar or Varangian threat (Petrukhin 2007, pp. 247, and n.1).
- MQDWN or the Macedon dynasty of Byzantium; SY, perhaps a central Volga statelet, Burtas, Asya; PYYNYL denoting the Danube-Don Pechnegs; BM, perhaps indicating the Volga Bulgars, and TWRQY or Oghuz Turks. The provisory identifications are those of Pritsak (Kohen 2007, p. 106).
- Al-Mas'udi says the king secretly tipped off the Rus' of the attack but was unable to oppose the request of his guards (Olsson 2013, p. 507).
- The letter continues: "I wage war with them. If I left them (in peace) for a single hour they would crush the whole land of the Ishmaelites up to Baghdad." (Petrukhin 2007, p. 257)
- From Klavdiy Lebedev (1852–1916), Svyatoslav's meeting with Emperor John, as described by Leo the Deacon.
- H. H. Howorth argued that the Khazars were the ancestors of contemporary Circassians (Howorth 1870, pp. 182–192).
- Dunlop thought the later city of Saqsin lay on or near Atil (Dunlop 1954, p. 248).
- The Caspian Sea is still known to Arabs, and many peoples of the region, as the "Khazar Sea" (Arabic Bahr ul-Khazar) (Brook 2010, p. 156)
- "thus it is clear that the false doctrine of Yišô in Rome (Hrôm) and that of Môsê among the Khazars and that of Mânî in Turkistan took away their might and the valor that they once possessed and made them feeble and decadent among their rivals" (Golden 2007b, p. 130).
- Some sources claim that the father of Seljuk, the eponymous progenitor of the Seljuk Turks, namely Toqaq Temür Yalığ, began his career as an Oghuz soldier in Khazar service in the early and mid-10th century, and rose to high rank before he fell out with the Khazar rulers and departed for Khwarazm. Seljuk's sons, significantly, all bear names from the Jewish scriptures: Mîkâ"il, Isrâ"îl, Mûsâ, Yûnus. Peacock argues that early traditions attesting a Seljuk origin within the Khazar empire when it was powerful, were later rewritten, after Khazaria fell from power in the 11th century, to blank out the connection (Peacock 2010, pp. 27–35).
- Tzitzak is often treated as her original proper name, with a Turkic etymology čiček ("flower"). Erdal, however, citing the Byzantine work on court ceremony De Ceremoniis, authored by Constantine Porphyrogennetos, argues that the word referred only to the dress Irene wore at court, perhaps denoting its colourfulness, and compares it to the Hebrew ciciot, the knotted fringes of a ceremonial shawl, or tallit (Erdal 2007, p. 80, n.22; Wexler 1987, p. 72).
- "Engravings that resemble the six-pointed Star of David were found on circular Khazar relics and bronze mirrors from Sarkel and Khazarian grave fields in Upper Saltov. However, rather than having been made by Jews, these appear to be shamanistic sun discs." (Brook 2010, pp. 113, 122–123 n.148)
- Brook says this thesis was developed by Jacob Mann, based on a reading of the word "Khazaria" in the Cairo Geniza fragment. Bernard Lewis, he adds, challenged the assumption by noting that the original text reads Hakkâri and refers to the Kurds of the Hakkâri mountains in south-east Turkey (Brook 2010, pp. 191–192, n.72).
- Whittow notes that this native institution, given the constant, lengthy, military and acculturating pressures on the tribes from China to the East, was influenced also by the sinocentric doctrine of the Mandate of Heaven (Tiānmìng:天命), which signaled legitimacy of rule (Whittow 1996, p. 220).
- Alp Ilut'uêr is a Turkish subordinate title (Golden 2007b, p. 124).
- Golden and Shapira thinks the evidence from such Georgian sources renders suspect a conversion prior to this date (Golden 2007b, pp. 135–136; Shapira 2007b, pp. 347–348).
- Golden 2007b, pp. 135–136, reporting on al-Muqaddasi.
- During Islamic invasions, some groups of Khazars who suffered defeat, including a qağan, were converted to Islam (DeWeese 1994, p. 73).
- Johannes Buxtorf first published the letters around 1660. Controversy arose over their authenticity; it was even argued that the letters represented "no more than Jewish self-consolation and fantasmagory over the lost dreams of statehood" (Kohen 2007, p. 112).
- "If anyone thinks that the Khazar correspondence was first composed in 1577 and published in Qol Mebasser, the onus of proof is certainly on him. He must show that a number of ancient manuscripts, which appear to contain references to the correspondence, have all been interpolated since the end of the sixteenth century. This will prove a very difficult or rather an impossible task." (Dunlop 1954, p. 130)
- "The issue of the authenticity of the Correspondence has a long and mottled history which need not detain us here. Dunlop and most recently Golb have demonstrated that Hasdai's letter, Joseph's response (dating perhaps from the 950s) and the 'Cambridge Document' are, indeed, authentic." (Golden 2007b, pp. 145–146)
- "(a court debate on conversion) appears in accounts of Khazar Judaism in two Hebrew accounts, as well as in one eleventh-century Arabic account. These widespread and evidently independent attestations would seem to support the historicity of some kind of court debate, but, more important, clearly suggest the currency of tales recounting the conversion and originating among the Khazar Jewish community itself" ... "the 'authenticity' of the Khazar correspondence is hardly relevant" "The wider issue of the 'authenticity' of the 'Khazar correspondence', and of the significance of this tale's parallels with the equally controversial Cambridge document /Schechter text, has been discussed extensively in the literature on Khazar Judaism; much of the debate loses significance if, as Pritsak has recently suggested, the accounts are approached as 'epic' narratives rather than evaluated from the standpoint of their 'historicity'."
- "Of the intensive archaeological study of Khazar sites (over a thousand burial sites have been investigated!), not one has yet yielded finds that yet fit in some way the material legacy of antique European or Middle Eastern Jewry." (Toch 2012, pp. 162–163)
- Shingiray noting the widespread lack of artifacts of wealth in Khazar burials, arguing that nomads used few materials to express their personal attributes: "The SMC assemblages-even if they were not entirely missing from the Khazar imperial center - presented an outstanding instance of archaeological material minimalism in this region." (Shingiray 2012, pp. 209–211)
- "But, one must ask, are we to expect much religious paraphernalia in a recently converted steppe society? Do the Oğuz, in the century or so after their Islamization, present much physical evidence in the steppe for their new faith? These conclusions must be considered preliminary." (Golden 2007b, pp. 150–151, and note 137)
- Golden 2007b, pp. 128–129 compares Ulfilas's conversions of the Goths to Arianism; Al-Masudi records a conversion of the Alans to Christianity during the Abbasid period; the Volga Bulğars adopted Islam after their leader converted in the 10th century; the Uyğur Qağan accepted Manichaeism in 762.
- Golden takes exception to J. B. Bury's claim (1912) that it was "unique in history". Golden also cites from Jewish history the conversion of Idumeans under John Hyrcanus; of the Itureans under Aristobulus I; of the kingdom of Adiabene under Queen Helena; the Ḥimyârî kings in Yemen, and Berber assimilations into North African Jewry.
- "The Șûfî wandering out into the steppe was far more effective in bringing Islam to the Turkic nomads than the learned 'ulamâ of the cities." (Golden 2007b, p. 126)
- "the Khazars (most of whom did not convert to Judaism, but remained animists, or adopted Islam and Christianity)" (Wexler 2002, p. 514)
- "In much of the literature on conversions of Inner Asian peoples, attempts are made, 'to minimize the impact' ... This has certainly been true of some of the scholarship regarding the Khazars." (Golden 2007b, p. 127)
- "scholars who have contributed to the subject of the Khazars' conversion, have based their arguments on a limited corpus of textual, and more recently, numismatic evidence ... Taken together these sources offer a cacophony of distortions, contradictions, vested interests, and anomalies in some areas, and nothing but silence in others." (Olsson 2013, p. 496)
- "Judaism was apparently chosen because it was a religion of the book without being the faith of a neighbouring state which had designs on Khazar lands." (Noonan 1999, p. 502)
- "Their conversion to Judaism was the equivalent of a declaration of neutrality between the two rival powers." (Baron 1957, p. 198)
- "in Israel, emotions are still high when it comes to the history of the Khazars, as I witnessed in a symposium on the issue at the Israeli Academy of Sciences in Jerusalem (May 24, 2011). Whereas Prof. Shaul Stampfer believed the story of the Khazars' conversion to Judaism was a collection of stories or legends that have no historical foundation, (and insisted that the Ashkenazi of Eastern Europe of today stem from Jews in Central Europe who emigrated eastwards), Prof. Dan Shapiro believed that the conversion of the Khazars to Judaism was part of the history of Russia at the time it established itself as a kingdom." (Falk 2017, p. 101, n. 9)
- "We are not aware of any nation under the sky that would not have Christians among them. For even in Gog and Magog, the Hunnic people who call themselves Gazari, those whom Alexander confined, there was a tribe more brave than the others. This tribe had already been circumcised and they profess all dogmata of Judaism (omnem Judaismum observat)." (Golden 2007b, p. 139)
- The idea of a forced general conversion imposed on the Qağanal dynasty in the 830s was advanced by Omeljian Pritsak, and is now supported by Roman Kovalev and Peter Golden (Olsson 2013, p. 497).
- Olsson identifies this with the onset of Magyar invasions of the Pontic steppe in the 830s, the construction of Sarkel, and the Schechter letter's reference to Bulan, converted to his Jewish wife Serakh's faith, wresting power, in a period of famine, elements which undermined the qağan, and allowed the creation of the royal diarchy (Olsson 2013, pp. 507, 513ff).
- wa al-ḥazarwa malikuhum kulluhum yahûd ("The Khazars and their king are all Jews") (Golden 2007b, pp. 143, 159)
- Golden, citing his comment on Genesis 9:27: "some other commentators are of the opinion that this verse alludes to the Khazars who accepted Judaism", with Golden's comment: "Certainly, by this time, the association of Khazaria and Judaism in the Jewish world was an established fact" (Golden 2007b, p. 143).
- Shapira and Zuckerman disagree, positing only one stage and placing it later. Shapira takes stage 1 as a Jewish-Khazar reinterpretation of the Tengri-cult in terms of a monotheism similar to Judaism's; Zuckerman thinks Judaisation took place, just once, after 861 (Shapira 2007b, pp. 349, and n.178; Zuckerman 1995, p. 250).
- Dunlop thought the first stage occurred with the king's conversion c. 740; the second with the installation of Rabbinical Judaism c. 800 (Golden 2007b, pp. 127–128, 151–153; Dunlop 1954, p. 170).
- Arabic original: Kitâb al-ḥuyya wa'l-dalîl fi naṣr al-din al-dhalîl (Book of the Argument and Demonstration in Aid of the Despised Faith) (Schweid 2007, p. 279).
- Brook mentions also a letter in Hebrew, the Mejelis document, dated 985–986, which refers to "our lord David, the Khazar prince" who lived in Taman. As Brook notes, both D. M. Dunlop and Dan Shapira dismiss it as a forgery (Brook 2010, pp. 30, 41, n.75).
- The name is commonly etymologized as meaning "elk" in Türkic. Shapira identifies him with the Sabriel of the Schechter letter, and suggests, since Sabriel is unattested as a Jewish name, although the root is "hope, believe, find out, understand" that it is a calque on the Oğuz Türkic bulan (one who finds out) or bilen (one who knows) (Shapira 2009, p. 1102).
- Szpiech, citing the Letter of King Joseph: et ha-qosmim ve-et'ovdei avodah zarah ("expelled the wizards and idolators") (Szpiech 2012, pp. 93–117 ).
- This detail is in Halevi's Sefer Ha-Kusari. Golden has identified Warsān as Transcaucasian Varaˇc'an. Ḥasdai ibn Shaprūṭ's letter also mentions a legend that the Chaldaeans, under persecution, hid the Scriptures in a cave, and taught their sons to pray there, which they did until their descendants forgot the custom. Much later, a tradition has it, a man of Israel entered the cave and, retrieving the books, taught the descendants how to learn the Law.
- The Schechter document has officers during the religious debate speak of a cave in a certain plain (TYZWL) where books are to be retrieved. They turn out to be the books of the Torah (DeWeese 1994, p. 303; Golb & Pritsak 1982, p. 111).
- The original ancestral cavern of the Türks, according to Chinese sources, was called Ötüken, and the tribal leaders would travel there annually to conduct sacrificial rites (DeWeese 1994, pp. 276, 300–304).
- Kohen refers to Khazar killings of Christians or the uncircumcized in retaliation for persecutions of Jews in Byzantium, and Khazar reprisals against Muslims for persecutions of Jews in Caucasian Albania, perhaps under Emir Nasr (Kohen 2007, pp. 107–108).
- "If indeed I could learn that this was the case, then, despising all my glory, abandoning my high estate, leaving my family, I would go over mountains and hills, through seas and lands, till I should arrive at the place where my Lord the King resides, that I might see not only his glory and magnificence, and that of his servants and ministers, but also the tranquillity of the Israelites. On beholding this my eyes would brighten, my reins would exult, my lips would pour forth praises to God, who has not withdrawn his favour from his afflicted ones." (Koestler 1977, p. 63; Leviant 2008, pp. 159–162)
- ^ Rabbinic Judaism rather than Qaraism was the form adopted. Small Karaim communities may have existed, but the linguistic and historical evidence suggests that the Turkic-speaking Karaim Jews in Poland and Lithuania, of which one branch also existed in the Crimea, descend from the Khazars. "At most, it is conceivable that the smaller Karaite community which lived in Khazaria gained the Kipchak type Turkic language, that they speak today, through an exchange of language." Khazars probably converted to Rabbinic Judaism, whereas in Karaism only the Torah is accepted, the Talmud being ignored (Róna-Tas 1999, p. 232).
- "At a time when Russia masked imperialist goals by pretending to be the protector of Slavic peoples and the Orthodox faith, Crimean Karism was exercising its own version of cultural imperialism. It is clear that the Crimean Karaites intended to expand their dominion to include Cairo, Jerusalem, and Damascus, basing their pre-eminence on the claim that Karaism, an ancient, pre-Talmudic form of Judaism, had been brought to the Middle East by the Khazars. Such an allegation would, however, have been much more difficult, if not impossible, to maintain.To summarize the Khazar-Karaite nexus commonly accepted in the Russian Empire during the last century: the Khazars, who were of pagan Turkic origin, were supposedly brought to Judaism by Karaites, descendants of Jews who had lived in the Black Sea areas since biblical times and whose Judaism was, therefore, pre-Talmudic and nonrabbinic. As a result, the Khazars' Judaism was Karaite, and later Karaites, who spoken a Turkic language, must have descended from the Khazars, with whom the ancient Jews had assimilated. The circularity of the argument aside, modern historians have concluded that the Khazars were converted by Rabbanite Jews and that they and their descendants observed rabbinic law and traditions. Indeed, recent scholarship has demonstrated that Khazaria was altogether unrepresented in the Karaite literature of the ninth and early tenth centuries, as well as that written during its Golden Age – when Karaism had a militant and missionary influence."
- "Most scholars are skeptical of the hypothesis". Wexler, who proposes a variation of the idea, argues that a combination of three reasons accounts for scholarly aversion to the concept: a desire not to get mixed up in controversy, ideological insecurities, and the incompetence of much earlier work in favor of that hypothesis.
- "Methodologically, Wexler has opened up some new areas, taking elements of folk culture into account. I think that his conclusions have gone well beyond the evidence. Nonetheless, these are themes that should be pursued further." (Golden 2007a, p. 56)
- "Arthur Koestler's book The Thirteenth Tribe which claimed that the converted Khazars were the progenitors of today's Ashkenazi Jews, has largely been rejected by serious scholars. However, the disputed theory that the stereotypical European Jew is descended from an Eastern European nation of Jewish converts, has been sufficiently unwelcome as to render study of the Khazars an area of research largely off limits for Jewish as well as Russian archaeologists, the Russians being unhappy with the prospect that their empire was initially ruled by Jewish kings, and the Jews being unhappy with the prospect that the Ashkenazim might not have a genetic connection to the freed slaves who met with God at Sinai." (Mariner 1999, pp. 95–96)
- Kizilov 2014, p. 389 citing Karl Neumann, Die Völker des südlichen Russlands in ihrer geschichtlichen Entwicklung, (1847) 2nd ed. Teubner 1855 pp. 125–126.
- Rossman 2002, p. 98: Abraham Harkavy, O yazykye evreyev, zhivshikh v drevneye vremya na Rusi i o slavianskikh slovakh, vstrechaiuschikhsia u evreiskikh pisatelei, St. Petersburg.
- Barkun 1997, p. 137: Ernest Renan, "Judaism as a Race and as Religion." Delivered on 27 January 1883.
- The source is Maksymilian Ernest Gumplowicz, Początki religii żydowskiej w Polsce, Warsaw: E. Wende i S-ka, 1903 (Polonsky, Basista & Link-Lenczowski 1993, p. 120)
- Goldstein writes "The theory that Eastern European Jews are descended from the Khazars was originally proposed by Samuel Weissenberg in an attempt to show that Jews were deeply rooted on Russian soil and the cradle of Jewish civilization was the Caucasus". Weissenberg's book Die Südrussischen Juden, was published in 1895.
- Schipper's first monograph on this was published in the Almanach Žydowski (Vienna) in 1918. While in the Warsaw ghetto before falling victim to the Holocaust at Majdanek, Schipper (1884–1943) was working on the Khazar hypothesis (Litman 1984, pp. 85–110 ).
- "There were Arab tribes who were Jews in the time of Muhammad, and a Turkic people who were mainly Jews in South Russia in the ninth century. Judaism is indeed the reconstructed political ideal of many shattered peoples-mainly semitic. As a result of these coalescences and assimilations, almost everywhere in the towns throughout the Roman Empire, and far beyond it in the east, Jewish communities traded and flourished, and they were kept in touch through the Bible, and through a religious and educational organization. The main part of Jewry never was in Judea and it had never come out of Judea." (Wells 1920, p. 570)
- John Bagot Glubb held that Russian Jews "have considerably less Middle Eastern blood, consisting largely of pagan Slav proselytes or of Khazar Turks." For Glubb, they were not "descendants of the Judeans ...The Arabs of Palestine are probably more closely related to the Judeans (genetically) than are modern Russian or German Jews.... Of course, an anti-Zionist (as well as an anti-Semitic) point is being made here: The Palestinians have a greater political right to Palestine than the Jews do, as they, not the modern-day Jews, are the true descendants of the land's Jewish inhabitants/owners" (Morris 2003, p. 22).
- First written as an article in 1941 – "The Khazars' Conversion to Judaism", then written as a monograph (1943), it was revised twice, first, it was revised in 1944, and in 1951, it was revised again and it was also retitled Kazariyah: Toldot mamlacha yehudit be'Eropa (Khazaria: History of a Jewish Kingdom in Europe) Mosad Bialik, Tel Aviv, 1951.
- "Poliak sought the origins of Eastern European Jewry in Khazaria" (Golden 2007a, p. 29).
- "As for the Jews of Eastern Europe (Poles, Russians, etc.), it has always been assumed that they descended from an amalgamation of Jews of Khazar stock from southern Russia and German Jews (the latter having imposed their superior culture)." (Poliakov 2005, p. 285)
- Sand cites Salo Wittmayer Baron, "before and after the Mongol upheaval the Khazars sent many offshoots into the unsubdued Slavonic lands, helping ultimately to build up the great Jewish center of Eastern Europe"; as well as Ben-Zion Dinur: "The Russian conquests did not destroy the Khazar kingdom entirely, but they broke it up and diminished it. And this kingdom, which had absorbed Jewish immigration and refugees from many exiles, must itself have become a diaspora mother, the mother of one of the greatest of the diasporas (Em-galuyot, em akhat hagaluyot hagdolot)-of Israel in Russia, Lithuania and Poland."
- "Salo Baron, who incorrectly viewed them as Finno-Ugrians, believed that the Khazars 'sent many offshoots into the unsubdued Slavonic lands, helping ultimately to build up the great Jewish centers of eastern Europe'" (Golden 2007a, p. 55)
- "dismissed ... rather airily" (Golden 2007a, p. 55).
- "Some limit this denial to European Jews and make use of the theory that the Jews of Europe are not of Israelite descent at all but are the offspring of a tribe of Central Asian Turks converted to Judaism, called the Khazars. This theory, first put forward by an Austrian anthropologist in the early years of this century, is supported by no evidence whatsoever. It has long since been abandoned by all serious scholars in the field, including those in Arab countries, where Khazar theory is little used except in occasional political polemics." Assertions of this kind have been challenged by Paul Wexler who also notes that the arguments on this issue are riven by contrasting ideological investments: "Most writers who have supported the Ashkenazi-Khazar hypothesis have not argued their claims in a convincing manner ... The opponents of the Khazar-Ashkenazi nexus are no less guilty of empty polemics and unconvincing arguments."
- "it is assumed by all historians that those Jewish Khazars who survived the last fateful decades sought and found refuge in the bosom of Jewish communities in the Christian countries to the west, and especially in Russia and Poland, on the one hand, and in the Muslim countries to the east and the south, on the other. Some historians and anthropologists go so far as to consider the modern Jews of East Europe, and more particularly of Poland, the descendants of the medieval Khazars." (Patai & Patai 1989, p. 71)
- "The Khazar theory never figured as a major component of antisemitism. The connection receives only scant attention in Léon Poliakov's monumental history of the subject. It did however come to exercise a particular attraction for advocates of immigration restriction in America." (Barkun 1997, pp. 136–137)
- "Although the Khazar theory gets surprisingly little attention in scholarly histories of anti-Semitism, it has been an influential theme among American anti-Semites since the immigration restrictionists of the 1920s" (Barkun 2012, p. 165).
- "By the 1960s, when Christian identity was established as a force on the extreme right, the Khazar ancestry of the Jews was a firm article of faith. Two books, written in this milieu and widely read, came to exercise a strong influence in this regard. John Beaty's Iron Curtain over America (1951) and Wilmot Robertson's Dispossessed Majority (1972) repeated the Khazar thesis of Stoddard. Christian identity teachings readily seized on this negative reference to Russian Jewry, however, it backdated the history of intermarriage between Jews and Khazars to biblical times. In A Short History of Esau-Edom in Jewry (1948), the Vancouver-based writer C.F. Parker claimed that a tiny remnant of 'true Judah' was pitted against a large group of Idumean-Hittites who masqueraded as the true seed of Abraham and sought to expel the descendants of Jacob. These Esau-Hittites are the Ashkenazim, concentrated in Eastern and Central Europe and America." (Goodrick-Clarke 2003, p. 237)
- Beaty was an antisemitic, McCarthyite professor of Old English at SMU, author of The Iron Curtain over America (Dallas 1952). According to him, "the Khazar Jews ... were responsible for all of America's – and the world's ills, beginning with World War 1." The book "had little impact" until the former Wall Street broker and oil tycoon J. Russell Maguire promoted it (Boller 1992, pp. 2, 6–7; Barkun 1997, pp. 141–142).
- Wexler 2002, p. 514 has a more detailed bibliography.
- "Arab anti-Semitism might have been expected to be free from the idea of racial odium, since Jews and Arabs are both regarded by race theory as Semites, but the odium is directed, not against the Semitic race, but against the Jews as a historical group. The main idea is that the Jews, racially, are a mongrel community, most of them being not Semites, but of Khazar and European origin." This essay was translated from Harkabi Hebrew text "Arab Antisemitism" in Shmuel Ettinger, Continuity and Discontinuity in Antisemitism, (Hebrew) 1968 (p.50).
- "in the very late 1980s Russian nationalists were fixated on the 'Khazar episode.' For them the Khazar issue seemed to be a crucial one. They treated it as the first historically documented case of the imposition of a foreign yoke on the Slavs, ... In this context the term 'Khazars' became popular as a euphemism for the so-called 'Jewish occupation regime'." (Shnirelman 2007, pp. 353–372)
- "The Khazar king and part of his court allegedly adopted the Jewish religion ... The truth of such a conversion and its extent has been the topic of many discussions, and the topic of vehement disagreements in our age of genomic DNA analyses." (Falk 2017, p. 100)
- "Strong evidence for the Khazarian hypothesis is the clustering of European Jews with the populations that reside on opposite ends of ancient Khazaria: Armenians, Georgians, and Azerbaijani Jews" (Elhaik 2012, pp. 61–74).
- "During Greco-Roman times, recorded mass conversions led to 6 million people practicing Judaism in Roman times or up to 10% of the population of the Roman Empire. Thus, the genetic proximity of these European/Syrian Jewish populations, including Ashkenazi Jews, to each other and to French, Northern Italian, and Sardinian populations favors the idea of non-Semitic Mediterranean ancestry in the formation of the European/Syrian Jewish groups and is incompatible with theories that Ashkenazi Jews are for the most part the direct lineal descendants of converted Khazars or Slavs. The genetic proximity of Ashkenazi Jews to southern European populations has been observed in several other recent studies.. Admixture with local populations, including Khazars and Slavs, may have occurred subsequently during the 1000 year (2nd millennium) history of the European Jews. Based on analysis of Y chromosomal polymorphisms, Hammer estimated that the rate might have been as high as 0.5% per generation or 12.5% cumulatively (a figure derived from Motulsky), although this calculation might have underestimated the influx of European Y chromosomes during the initial formation of European Jewry.15 Notably, up to 50% of Ashkenazi Jewish Y chromosomal haplogroups (E3b, G, J1, and Q) are of Middle Eastern origin, 15 whereas the other prevalent haplogroups (J2, R1a1, R1b) may be representative of the early European admixture.20 The 7.5% prevalence of the R1a1 haplogroup among Ashkenazi Jews has been interpreted as a possible marker for Slavic or Khazar admixture because this haplogroup is very common among Ukrainians (where it was thought to have originated), Russians, and Sorbs, as well as among Central Asian populations, although the admixture may have occurred with Ukrainians, Poles, or Russians, rather than Khazars." (Atzmon & Ostrer 2010, pp. 850–859)
- "The extent to which the Khazars contributed to the Jewish gene-pool, and more specifically to the Ashkenazi ethnic-group(s), has become a charged issue among expert scientists as well as nonprofessionals. National and ethnic prejudices play a central role in the controversy." (Falk 2017, p. 100)
- "if the genome does not prove Sand wrong, neither can it prove him right. It is the wrong kind of evidence and the wrong style of reasoning for the task at hand." "They (researchers) will never be able to prove descent from Khazars: there are no 'verification' samples."
- "Kiev in Khazar is Sambat, the same as the Hungarian word szombat, 'Saturday', which is likely to have been derived from the Khazar Jews living in Kyiv." (Róna-Tas 1999, p. 152)
Citations
- ^ Golden 2006, p. 91.
- Wexler 1996, p. 50.
- Brook 2010, p. 107.
- Turchin, Adams & Hall 2006, p. 222.
- Taagepera 1997, p. 496.
- ^ Luttwak 2009, p. 152.
- Meserve 2009, p. 294, n. 164.
- Petrukhin 2007, p. 255.
- Golden 2018, p. 294.
- Encyclopedia Britannica: Khazar 2020.
- Sneath 2007, p. 25.
- Noonan 1999, p. 493.
- Golden 2011a, p. 65.
- Noonan 1999, p. 498.
- ^ Noonan 1999, pp. 499, 502–503.
- Golden 2007a, p. 131.
- Golden 2007a, p. 28.
- Golden 2007a, p. 149.
- ^ Behar et al. 2013, pp. 859–900.
- ^ Kizilov 2009, p. 335.
- ^ Patai & Patai 1989, p. 73.
- ^ Wexler 1987, p. 70.
- ^ Wexler 2002, p. 536.
- Davies 1992, p. 242.
- Vogt 1975.
- Golden 2007a, p. 15.
- Zimonyi 1990, p. 58.
- Dunlop 1954, pp. 34–40.
- Golden 2007a, p. 16.
- Wei Zheng, vol. 84.
- Golden 1992.
- Jiu Tangshu, Vol. 199b Tiele.
- Xin Tangshu, vol 217a Huihe.
- Wang Pu, vol 98.
- Sima Guang, vol. 196.
- Wang Pu, vol. 72.
- Dobrovits 2004, p. 259.
- Bailey 1949, p. 50.
- Bailey 1951, p. 19.
- Lee 2016, pp. 103–105.
- Golden 2007a, p. 17.
- Shirota 2005, pp. 235, 248.
- Brook 2010, p. 5.
- Whittow 1996, pp. 220–223.
- Golden 2007a, p. 14.
- Szádeczky-Kardoss 1994, p. 206.
- Golden 2006, p. 86.
- Pritsak 1978, p. 261.
- Golden 2007a, p. 53.
- Golden 2007c, p. 165.
- ^ Golden 2006, p. 89.
- ^ Kaegi 2003, p. 143, n.115.
- ^ Golden 1992, pp. 127–136, 234–237.
- Kaegi 2003, pp. 154–186.
- Whittow 1996, p. 222.
- Golden 2001b, pp. 94–95.
- Somogyi 2008, p. 128.
- Zuckerman 2007, p. 417.
- Golden 2006, p. 90.
- Golden 2007a, pp. 11–13.
- Noonan 2001, p. 91.
- Golden 2007a, pp. 7–8.
- Golden 2001b, p. 73.
- Noonan 1999, p. 500.
- Olsson 2013, p. 496.
- ^ Noonan 2001, p. 77.
- Golden 2006, pp. 81–82.
- Golden 2007b, pp. 133–134.
- Shingiray 2012, p. 212.
- DeWeese 1994, p. 181.
- Golden 2006, pp. 79–81.
- Golden 2006, p. 88.
- Golden 2006, pp. 79–80, 88.
- Olsson 2013, p. 495.
- Koestler 1977, p. 18.
- Dunlop 1954, p. 113.
- Dunlop 1954, p. 96.
- ^ Brook 2010, pp. 3–4.
- Patai & Patai 1989, p. 70.
- Brook 2010, p. 3.
- Oppenheim 1994, p. 312.
- Barthold 1993, p. 936.
- Zhivkov 2015, p. 173.
- Golden 2011a, p. 64.
- Reuter 1999, p. 91.
- Noonan 2007, p. 232.
- Reuter 1999, p. 504.
- ^ Noonan 2007, p. 214.
- Luttwak 2009, p. 52.
- Beckwith 2011, pp. 120, 122.
- Zuckerman 2007, pp. 403–404.
- Kaegi 2003, pp. 143–145.
- Róna-Tas 1999, p. 230.
- Kaegi 2003, p. 145.
- Bauer 2010, p. 341.
- Ostrogorski 1969, pp. 124–126.
- Cameron & Herrin 1984, p. 212.
- Bauer 2010, pp. 341–342.
- ^ Luttwak 2009, pp. 137–138.
- Piltz 2004, p. 42.
- Schwartzwald 2015, p. 26.
- Noonan 2007, p. 220.
- Beckwith 2011, p. 392, n.22.
- Heath 1979, p. 14.
- Mako 2010, p. 45.
- ^ Brook 2010, pp. 126–127.
- Brook 2010, p. 127.
- ^ Golden 1980, p. 64.
- Wasserstein 2007, pp. 375–376.
- Dunlop 1954, p. 179.
- ^ Brook 2018, p. 115.
- Makkai 1994, p. 11.
- Country Study: Hungary 1989.
- Shepard 2006, p. 19.
- Petrukhin 2007, p. 245.
- Noonan 2001, p. 81.
- Korobkin 1998, p. xxvii.
- Golb & Pritsak 1982, p. 15.
- Toch 2012, p. 166.
- Petrukhin 2007, p. 257.
- ^ Kohen 2007, p. 107.
- Noonan 1999, pp. 502–503.
- Noonan 1999, p. 508.
- Petrukhin 2007, p. 259.
- Feldman 2022a, pp. 75–84.
- ^ Petrukhin 2007, p. 262.
- Petrukhin 2007, pp. 262–263.
- Russian Primary Chronicle.
- ^ Petrukhin 2007, p. 263.
- Dunlop 1954, p. 242.
- Gow 1995, p. 31, n.28.
- Sand 2010, p. 229.
- Golden 2007b, p. 148.
- Noonan 1999, p. 503.
- Golden 2007b, pp. 147–148.
- ^ Kohen 2007, p. 109.
- Shapira 2007a, p. 305.
- Dunlop 1954, p. 253.
- ^ Falk 2017, p. 102.
- Sand 2010, p. 227.
- Dubnov 1980, p. 792.
- Golden 2007a, p. 45, n.157.
- Golden 2007b, p. 159.
- Peacock 2010, p. 35.
- Golden 2001a, pp. 28–29, 37.
- Golden 1994b, pp. 247–248.
- Róna-Tas 1999, p. 56.
- Golden 2007a, p. 33.
- Golden 2007b, p. 150.
- Brook 2010, p. 167.
- Bowersock 2013, pp. 85ff..
- Schweid 2007, p. 286.
- Baron 1957, pp. 202–204 .
- Wexler 2002, p. 514.
- Golden 2007b, p. 149.
- Brook 2010, pp. 177–178.
- Noonan 2007, p. 229.
- Golden 2007b, pp. 131–133.
- Whittow 1996, p. 220.
- Golden 2007b, p. 133.
- Golden 2007b, pp. 124, 135.
- ^ Golden 2007b, p. 125.
- DeWeese 1994, pp. 292–293.
- Kovalev 2005, pp. 226–228, 252.
- DeWeese 1994, p. 171.
- DeWeese 1994, p. 305.
- Szpiech 2012, p. 102.
- Golden 2007b, p. 123.
- Koestler 1977, p. 52.
- Golden 2007b, p. 153.
- Golden 2007b, pp. 141–145, 161.
- Noonan 2001, pp. 77–78.
- Schama 2013, p. 266.
- Wexler 1987, p. 61.
- ^ Szyszman 1980, pp. 71, 73.
- Dunlop 1954, pp. 122–124.
- Brook 2010, pp. 95, 117 n.51, 52.
- Stampfer 2013, pp. 1–72.
- Gil 2011, pp. 429–441.
- Feldman 2022b, pp. 193–205.
- Stampfer 2013, p. 17.
- Brook 2018, p. 6.
- Dunlop 1954, pp. 140–142.
- Zhivkov 2015, p. 42.
- Shingiray 2012, pp. 212–214.
- Szpiech 2012, pp. 92–117 .
- Golden 2007b, pp. 137–138.
- Spinei 2009, p. 50.
- DeWeese 1994, pp. 300–308.
- ^ Melamed 2003, pp. 24–26.
- DeWeese 1994, p. 302.
- Olsson 2013, p. 512.
- ^ DeWeese 1994, pp. 304–305.
- Korobkin 1998, p. 352, n.8.
- Dunlop 1954, p. 170.
- Golden 2007b, p. 157.
- Dunlop 1954, pp. 117–118.
- ^ Róna-Tas 1999, p. 232.
- Maroney 2010, p. 72.
- Golden 2007a, p. 34.
- Golden 2007b, p. 161.
- Mikheyev et al. 2019.
- Kornienko et al. 2021, pp. 477–488.
- Kornienko et al. 2021, p. 478.
- Who are the Mishars? 2016.
- Brook 2018, pp. 145, 149–151, 162–163, 164.
- Brook 2018, pp. 210–216.
- ^ Golden 2007a, p. 9.
- Brook 2018, pp. 208–209.
- Goldstein 2011, p. 9.
- Shapira 2006, p. 166.
- Blady (2000), p. 125.
- Miller 1993, pp. 7–9.
- Weinryb 1973a, pp. 21–22.
- Brook 2018, pp. 213–215.
- Brook 2014, pp. 69–84.
- Blady (2000), p. 122.
- Blady (2000), p. 126.
- Rossman 2002, p. 98.
- Singerman 2004, pp. 3–4, Israël chez les nations (1893)
- ^ Goldstein 2006, p. 131.
- ^ Koestler 1977, pp. 134, 150.
- von Kutschera 1909.
- Fishberg 1911.
- Brook 2010, p. 210.
- Falk 2017, p. 101, n.9.
- Singerman 2004, p. 4.
- Burrage Dixon 1923.
- Wells 1920, p. ?.
- Malkiel 2008, p. 263, n.1.
- Sand 2010, p. 234.
- Dunlop 1954, pp. 261, 263.
- Sand 2010, pp. 241–242.
- Baron 1957, pp. 196–206 .
- Dinur 1961, pp. 2, 5.
- Brook 2006, p. 192.
- ^ Sand 2010, p. 240.
- Lewis 1987, p. 48.
- Wexler 2002, p. 538.
- Wexler 2002, p. 537.
- Toch 2012, p. 155, n.4.
- Wexler 2007, pp. 387–398.
- Sand 2010, pp. 190–249.
- Elhaik 2012, pp. 61–74.
- Spolsky 2014, pp. 174–177.
- Golden 2007a, pp. 9–10.
- Wexler 2002, pp. 513–541.
- Barkun 1997, pp. 136–137.
- Singerman 2004, pp. 4–5.
- Goodrick-Clarke 2003, p. 237.
- Barkun 1997, pp. 140–141. Cf. Wilmot Robertson Dispossessed Majority(1972)
- Harkabi 1987, p. 424.
- Rossman 2007, pp. 121–188.
- Barkun 1997, pp. 142–144.
- Goodman & Miyazawa 2000, pp. 263–264.
- Serrano 2011, pp. 79, 295.
- Meduza 2022.
- Stampfer 2013.
- Ostrer 2012, pp. 24–27, 93–95, 124–125.
- Nebel, Filon & Brinkmann 2001, pp. 1095–1112.
- Behar et al. 2003, pp. 769–779.
- Nebel, Filon & Faerman 2005, pp. 388–391.
- Costa, Pereira & Richards 2013, pp. 1–10.
- Behar et al. 2013.
- Abu El-Haj 2012, p. 28.
- Abu El-Haj 2012, p. 133.
- Lobel 2000, pp. 2–4.
- Baron 1957, p. 204.
- Wachtel 1998, pp. 210–215.
- Cokal 2007.
Bibliography
- Abu El-Haj, Nadia (2012). The Genealogical Science: The Search for Jewish Origins and the Politics of Epistemology. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-20142-9 – via Google Books.
- Abulafia, David (1987) . "Asia, Africa and the Trade of Medieval Europe". In Postan, Michael Moïssey; Habakkuk, H.J.; Miller, Edward (eds.). The Cambridge Economic History of Europe: Trade and industry in the Middle Ages. Vol. 2. Cambridge University Press. pp. 402–473. ISBN 978-0-521-08709-4 – via Google Books.
- Altschüler, Boris (1994). Geheimbericht aus der Grossen Steppe. Die Wahrheit über das Reich der Russen [Secret report from the Great Steppe. The truth about the empire of the Russians] (in German). Saarbrücken: Altschüler. ISBN 978-3-9803917-0-2 – via Google Books.
- Atzmon G, Hao L, Pe'er I, Velez C, Pearlman A, Palamara PF, Morrow B, Friedman E, Oddoux C, Burns E, Ostrer H (June 2010). "Abraham's children in the genome era: major Jewish diaspora populations comprise distinct genetic clusters with shared Middle Eastern Ancestry". American Journal of Human Genetics. 86 (6): 850–859. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.04.015. PMC 3032072. PMID 20560205.
- Bailey, H.W. (1949). "A Khotanese text concerning the Turks in Kanṭṣou" (PDF). Asia Major. New Series 1.1: 28–52. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2021.
- Bailey, H.W. (1951). "The Staël-Holstein Miscellany" (PDF). Asia Major. New Series 2.1: 1–45. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2021.
- Barkun, Michael (1997). Religion and the Racist Right: The Origins of the Christian Identity Movement. University of North Carolina Press. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-8078-4638-4 – via Internet Archive.
- Barkun, Michael (2012). "Anti-Semitism from Outer Space: The Protocols in the UFO Subculture". In Landes, Richard Allen; Katz, Steven T. (eds.). The Paranoid Apocalypse: A Hundred-year Retrospective on the Protocols of the Elders of Zion. New York University Press. pp. 163–171. ISBN 978-0-8147-4945-6 – via Google Books.
- Baron, Salo Wittmayer (1957). A Social and Religious History of the Jews. Vol. 3. Columbia University Press – via Google Books.
- Barthold, Vasili (1993) . "Khazar". In Houtsma, Martijn Theodoor; Bosworth, C.E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W.P. (eds.). First Encyclopedia of Islam, 1913–1936. Vol. 4. Brill. pp. 935–937. ISBN 978-90-04-09790-2 – via Google Books.
- Bauer, Susan Wise (2010). The History of the Medieval World: From the Conversion of Constantine to the First Crusade. New York, NY: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-07817-6 – via Google Books.
- Beckwith, Christopher I. (2011) . Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-15034-5 – via Google Books.
- Behar, D. M.; Metspalu, M.; Baran, Y.; Kopelman, N. M.; Yunusbayev, B.; Gladstein, A.; et al. (2013). "No Evidence of a Khazar origin for the Ashkenazi Jews". Human Biology. 85 (6): 859–900. doi:10.3378/027.085.0604. PMID 25079123. S2CID 2173604. Archived from the original on 14 October 2014.
- Behar, Doron M; Thomas, Mark G; Skorecki, Karl; Hammer, Michael F; et al. (October 2003). "Multiple Origins of Ashkenazi Levites: Y Chromosome Evidence for Both Near Eastern and European Ancestries". American Journal of Human Genetics. 73 (4): 768–779. doi:10.1086/378506. PMC 1180600. PMID 13680527.
- Blady, Ken (2000). Jewish Communities in Exotic Places. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-765-76112-5 – via Google Books.
- Boller, Paul F. (1992). Memoirs of an Obscure Professor: And Other Essays. TCU Press. ISBN 978-0-87565-097-5 – via Google Books.
- Bowersock, G.W. (2013). The Throne of Adulis: Red Sea Wars on the Eve of Islam. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-199-33384-4 – via Google Books.
- Bowman, Stephen B.; Ankori, Zvi (2001). The Jews of Byzantium 1204–1453. Bloch Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-8197-0703-1 – via Google Books.
- Brook, Kevin Alan (2006). The Jews of Khazaria. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 192. ISBN 978-1-4422-0302-0.
- Brook, Kevin Alan (2010) . The Jews of Khazaria (2nd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-7425-4982-1. Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2015 – via Google Books.
- Brook, Kevin Alan (Summer 2014). "The Genetics of Crimean Karaites" (PDF). Karadeniz Arastirmalari. 11 (42): 69–84. doi:10.12787/KARAM859. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 June 2019.
- Brook, Kevin Alan (2018). The Jews of Khazaria (3rd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-5381-0342-5.
- Brook, Kevin Alan (2022). The Maternal Genetic Lineages of Ashkenazic Jews. Academic Studies Press. ISBN 978-1-64469-984-3.
- Browning, Robert (1992) . The Byzantine Empire (2nd ed.). Catholic University of America Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-8132-0754-4 – via Internet Archive.
- Burrage Dixon, Roland (1923). The Racial History of Man. C. Scribners sons.
- Cahen, Claude (2011) . L'Islam, des origines au début de l'Empire ottoman [Islam, from its origins to the beginning of the Ottoman Empire] (in French) (2nd ed.). Hachette. ISBN 978-2-8185-0155-9 – via Google Books.
- Cameron, Averil (1996). "Byzantines and Jews: some recent work on early Byzantium". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies. 20: 249–274. doi:10.1179/byz.1996.20.1.249. S2CID 162277927.
- Cameron, Averil; Herrin, Judith (1984). Constantinople in the Early Eighth Century: The Parastaseis Syntomoi Chronikai: Introduction, Translation, and Commentary. Columbia Studies in the Classical Tradition. Vol. 10. Brill Archive. ISBN 978-90-04-07010-3 – via Google Books.
- Cohen, Mark R. (2005). The Voice of the Poor in the Middle Ages: An Anthology of Documents from the Cairo Geniza. Jews, Christians, and Muslims from the Ancient to the Modern World Series. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-09271-3.
- Cokal, Susann (28 October 2007). "Jews With Swords". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 14 April 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
- Costa, M. D.; Pereira, Joana B.; Richards, Martin B. (8 October 2013). "A substantial prehistoric European ancestry amongst Ashkenazi maternal lineages". Nature Communications. 4: 2543. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.2543C. doi:10.1038/ncomms3543. PMC 3806353. PMID 24104924.
- Cross, Samuel Hazzard; Sherbowitz-Wetzor, Olgerd P., eds. (1953). The Russian Primary Chronicle (Laurentian text) (PDF). Translated by Cross, Samuel Hazzard; Sherbowitz-Wetzor, Olgerd P. Cambridge, MA: The Mediaeval Academy of America. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 October 2013.
- Davies, Alan (1992). "The Keegstra Affair". In Davies, Alan (ed.). Antisemitism in Canada: History and Interpretation. Wilfrid Laurier University Press. pp. 227–248. ISBN 978-0-889-20216-0 – via Google Books.
- DeWeese, Devin A. (1994). Islamization and Native Religion in the Golden Horde: Baba Tükles and Conversion to Islam in Historical and Epic Tradition. Hermeneutics, Studies in the History of Religions. Penn State Press. ISBN 978-0-271-04445-3 – via Google Books.
- Dinur, Ben-Zion (1961). Yisrael ba-gola. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Bialik Institute.
- Dobrovits, M. (2004). "The Thirty Tribes of the Turks". Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae. 57 (3): 259. doi:10.1556/aorient.57.2004.3.1.
- Dubnov, Simon (1980). History of the Jews: From the Roman Empire to the Early Medieval Period. Vol. 2. Associated University Presses. ISBN 978-0-8453-6659-2 – via Google Books.
- Dunlop, Douglas Morton (1954). History of the Jewish Khazars. New York, NY: Schocken Books – via Google Books.
- "Early History". A Country Study: Hungary. Library of Congress Country Studies. Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. September 1989. Archived from the original on 29 October 2004.
- Elhaik, Eran (December 2012). "The Missing Link of Jewish European Ancestry: Contrasting the Rhineland and the Khazarian Hypotheses". Genome Biology and Human Evolution. 5 (1): 61–74. arXiv:1208.1092. Bibcode:2012arXiv1208.1092E. doi:10.1093/gbe/evs119. PMC 3595026. PMID 23241444.
- Erdal, Marcel (2007). "The Khazar Language". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. BRILL. pp. 75–108. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Falk, Raphael (2017). Zionism and the Biology of Jews. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-57345-8 – via Google Books.
- Feldman, Louis H. (1996). Jew and Gentile in the Ancient World: Attitudes and Interactions from Alexander to Justinian. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-2080-1 – via Google Books.
- Feldman, Alex M. (2022a). "The Decline and Fall of Khazaria – Might or Money?". Vostok (Oriens) (4): 75–84. doi:10.31857/S086919080021412-0. S2CID 253192191. Archived from the original on 13 October 2022.
- Feldman, Alex M. (2022b). The Monotheisation of Pontic-Caspian Eurasia From the Eighth to the Thirteenth Century. Edinburgh Byzantine Studies. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-1-474-47810-6. Retrieved 23 September 2024.
- Fishberg, Maurice (1911). The Jews: A Study of Race and Environment. Scribner's – via Google Books.
- Geanakoplos, Deno John (1984). Byzantium: Church, Society, and Civilization Seen through Contemporary Eyes (2nd ed.). University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-28461-3 – via Google Books.
- Gil, Moshe (July–December 2011). "Did the Khazars Convert to Judaism?". Revue des Études Juives. 170 (3–4): 429–441. doi:10.2143/REJ.170.3.2141801.
- Golb, Norman; Pritsak, Omeljan (1982). Khazarian Hebrew Documents of the Tenth Century. Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-1221-9 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter B. (July 2018). "The Ethnogonic Tales of the Türks". The Medieval History Journal. 21 (2): 294. doi:10.1177/0971945818775373. S2CID 166026934.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (1980). Khazar Studies: An Historio-Philological Inquiry into the Origins of the Khazars. Vol. 1, 2. Budapest: Akademia Kiado. ISBN 978-0-226-28461-3 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples: Ethnogenesis And State Formation in the Medieval and Early Modern Eurasia and the Middle East. Turcologica. Vol. 9. Wiesbaden: O. Harrassowitz. ISBN 978-3-447-03274-2 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (1994a) . "The peoples of the South Russian steppes". In Sinor, Denis (ed.). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. pp. 256–283. ISBN 978-0-521-24304-9 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (1994b) . "The peoples of the Russian forest belt". In Sinor, Denis (ed.). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. pp. 230–255. ISBN 978-0-521-24304-9 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2001a). "Nomads in the Sedentary World: The Case of Pre-Chinggisid Rus' and Georgia". In Khazanov, Anatoly M.; Wink, Andre (eds.). Nomads in the Sedentary World. Curzon-IIAS Asian studies series. Routledge. pp. 24–74. ISBN 978-0-7007-1369-1 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2001b). "Nomad and Sedentary societies in Eurasia". In Adas, Michael (ed.). Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History. Critical Perspectives on the Past Series. American Historical Association. Vol. 2. Temple University Press. pp. 71–115. ISBN 978-1-56639-832-9 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2003). Nomads and their neighbours in the Russian steppe: Turks, Khazars and Qipchaqs. Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-86078-885-0 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2006). "The Khazar Sacral Kingship". In Reyerson, Kathryn Von; Stavrou, Theofanis George; Tracy, James Donald (eds.). Pre-modern Russia and its world: Essays in Honour of Thomas S. Noonan. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 79–102. ISBN 978-3-447-05425-6 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2007a). "Khazar Studies: Achievements and Perspectives". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbook of Oriental Studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 7–57. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2007b). "The Conversion of the Khazars to Judaism". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbook of Oriental Studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 123–161. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2007c). "Irano-Turcica: The Khazar Sacral Kingship Revisited". Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae. 60 (2): 161–194. doi:10.1556/AOrient.60.2007.2.2 – via ResearchGate.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2010). Turks and Khazars: Origins, Institutions, and Interactions in Pre-Mongol Eurasia. Variorum Collected Studies Series. Vol. 952. Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4094-0003-5 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2011a). Central Asia in World History. New Oxford World History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-979317-4 – via Google Books.
- Golden, Peter Benjamin (2011b). Studies on the Peoples and Cultures of the Eurasian Steppes. Editura Academiei Române. ISBN 978-973-27-2152-0 – via ResearchGate.
- Goldstein, Eric L. (2006). The Price of Whiteness: Jews, Race, and American Identity. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-12105-5 – via Google Books.
- Goldstein, Miriam (2011). Karaite Exegesis in Medieval Jerusalem. Mohr Siebeck. p. 9. ISBN 978-3-16-150972-8 – via Google Books.
- Goodman, David G.; Miyazawa, Masanori (2000) . Jews in the Japanese Mind: The History and Uses of a Cultural Stereotype. Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0-7391-0167-4 – via Google Books.
- Goodrick-Clarke, Nicholas (2003) . Black Sun: Aryan cults, esoteric nazism, and the politics of identity. NYU Press. ISBN 978-0-8147-3155-0 – via Google Books.
- Gow, Andrew Colin (1995). The " Red Jews": Antisemitism in the Apocalyptic Age 1200–1600. Brill Publishers. ISBN 978-90-04-10255-2 – via Google Books.
- HaLevi, Yehuda (1998). Korobkin, Nissan Daniel (ed.). The Kuzari: In Defense of the Despised Faith. Northvale, New Jersey-Jerusalem: Jason Aronson. ISBN 978-0-7657-9970-8 – via Google Books.
- HaLevi, Yehudah (2013). Korobkin, N. Daniel (ed.). The Kuzari. In Defense of the Despised Faith (2nd ed.). Feldheim Publishers. ISBN 978-1-59826-961-1. Archived from the original on 3 June 2023. Retrieved 3 June 2023 – via Google Books.
- Harkabi, Yehoshafat (1987) . "Contemporary Arab Anti-Semitism: its Causes and Roots". In Fein, Helen (ed.). The Persisting Question: Sociological Perspectives and Social Contexts of Modern Antisemitism. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 412–427. ISBN 978-3-11-010170-6 – via Google Books.
- Heath, Ian (1979). Byzantine Armies 886-1118. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85045306-5.
- Herlihy, David (1984). "Demography". In Strayer, Joseph R. (ed.). Dictionary of the Middle Ages. Vol. 4. Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 136–148. ISBN 978-0-684-17024-4.
- Howorth, H. H. (1870). "On the Westerly Drifting of Nomades, from the Fifth to the Nineteenth Century. Part IV. The Circassians and White Khazars". The Journal of the Ethnological Society of London. 2 (2): 182–192. doi:10.2307/3014425. JSTOR 3014425.
- Inaba, Minoru; Balogh, Dániel (2020). "The legend of Xinnie in the seventh and eighth centuries". In Balogh, Dániel (ed.). Hunnic Peoples in Central and South Asia: Sources for their Origin and History. Barkhuis. pp. 103–107. ISBN 978-9-493-19401-4 – via Google Books.
- Kaegi, Walter Emil (2003). Heraclius, Emperor of Byzantium (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81459-1 – via Google Books.
- "Khazar". Encyclopedia Britannica. 29 March 2020. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- Kim, Hyun Jin (2016). The Huns. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-34090-4 – via Google Books.
- Kizilov, Mikhail (2009). The Karaites of Galicia: An Ethnoreligious Minority Among the Ashkenazim, the Turks, and the Slavs, 1772–1945. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-16602-8 – via Google Books.
- Kizilov, Mikhail (2014). "National Inventions: The Imperial Emancipation of the Karaites from Jewishness". In Cvetkovski, Roland; Hofmeister, Alexis (eds.). An Empire of Others: Creating Ethnographic Knowledge in Imperial Russia and the USSR. Central European University Press. pp. 369–393. ISBN 978-6-155-22576-5 – via Google Books.
- Koestler, Arthur (1977) . The Thirteenth Tribe: The Khazar Empire and Its Heritage. London: Pan Books. ISBN 978-0-09-125550-3 – via Google Books.
- Kohen, Elli (2007). History of the Byzantine Jews: A Microcosmos in the Thousand Year Empire. University Press of America. ISBN 978-0-7618-3623-0 – via Google Books.
- Kolditz, Sebastian (2017). "Barbarian Emperors? Aspects of the Byzantine Perception of the qaghan (chaganos) in the Earlier Middle Ages". In Scholl, Christian; Gebhardt, Torben R.; Clauß, Jan (eds.). Transcultural Approaches to the Concept of Imperial Rule in the Middle Ages. Peter Lang. pp. 41–76. ISBN 978-3-631-70624-4. Archived from the original on 21 April 2021.
- Kordosis, Stefanos (2017). "The Tibetan Title Dru gu Gesar (Turk Caesar / Caesar of the Turks) in the Northern Branch of the Silk Route and the Role of the Khazars". ΘΗΣΑΥΡΙΣΜΑΤΑ (47): 183–192. Archived from the original on 23 December 2021.
- Kornienko, I. V.; Faleeva, T. G.; Schurr, T. G.; Aramova, O. Yu; Ochir-Goryaeva, M. A.; Batieva, E. F.; Vdovchenkov, E. V.; Moshkov, N. E.; Kukanova, V. V.; Ivanov, I. N.; Sidorenko, Yu S. (1 April 2021). "Y-Chromosome Haplogroup Diversity in Khazar Burials from Southern Russia". Russian Journal of Genetics. 57 (4): 477–488. doi:10.1134/S1022795421040049. ISSN 1608-3369. S2CID 233479468 – via ResearchGate.
- Kovalev, R.K. (2005). "Creating Khazar Identity through Coins: the Special Issue Dirhams of 837/838". In Curta, Florin (ed.). East Central and Eastern Europe in the Early Middle Ages. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. pp. 220–251. ISBN 978-0-472-11498-6.
- von Kutschera, Hugo (1909). Die Chasaren; historische Studie [Those Khazars; historical Study] (in German). A. Holzhauen. ISBN 978-0-274-47307-6 – via Google Books.
- Lee, Joo-Yup (2016). "The Historical Meaning of the Term Turk and the Nature of the Turkic Identity of the Chinggisid and Timurid Elites in Post-Mongol Central Asia". Central Asiatic Journal. 59 (1–2): 101–132. doi:10.13173/centasiaj.59.1-2.0101. Archived from the original on 23 December 2021.
- Leviant, Curt (2008) . Masterpieces of Hebrew Literature: Selections from 2000 Years of Jewish Creativity. Jewish Publication Society. ISBN 978-0-8276-0954-9 – via Google Books.
- Lewis, Bernard (1987) . Semites and Anti-Semites: An Inquiry Into Conflict and Prejudice. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-30420-6 – via Internet Archive.
- Lewis, Bernard (2013). The Jews of Islam. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-03021-6 – via Google Books.
- Litman, Jacob (1984). The Economic Role of Jews in Medieval Poland: The Contribution of Yitzhak Schipper. University Press of America. ISBN 978-0-8191-4244-3 – via Google Books.
- Lobel, Diana (2000). Between Mysticism and Philosophy: Sufi Language of Religious Experience in Experience in Judah Ha-Levi's Kuzari. SUNY Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-4451-1 – via Google Books.
- Logan, F. Donald (1992) . The Vikings in History (2nd ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-08396-6 – via Google Books.
- Luttwak, Edward N. (2009). The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03519-5 – via Google Books.
- "Magyars". WebChron: The Web Chronology Project. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- Makkai, László (1994). "The Hungarians' Prehistory, Their Conquest of Hungary and their raids to the West". In Sugar, Peter F.; Hanák, Péter; Frank, Tibor (eds.). A History of Hungary. Indiana University Press. p. 11. ISBN 0-253-35578-8 – via Google Books.
- Mako, Gerald (2010). "The Possible Reasons for the Arab-Khazar Wars". Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi. 17: 45–57. Archived from the original on 23 August 2021.
- Malkiel, David (2008). Reconstructing Ashkenaz: The Human Face of Franco-German Jewry, 1000–1250. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-8684-3 – via Google Books.
- Mango, Cyril, ed. (2002). The Oxford History of Byzantium. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-814098-6.
- Mariner, Rodney (1999). "Conversion to Judaism: a tale of the good, the bad and the ungrateful". In Lamb, Christopher; Bryant, M. Darroll (eds.). Religious Conversion: Contemporary Practices and Controversies. A&C Black. pp. 89–101. ISBN 978-0-826-43713-6 – via Google Books.
- Maroney, Eric (2010). The Other Zions: The Lost Histories of Jewish Nations. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 55. ISBN 978-1-4422-0045-6 – via Internet Archive.
- Meduza (8 July 2022). Мы хотим убивать "Медуза" рассказывает, как (и зачем) неонацисты из России отправились "денацифицировать" Украину [We want to kill "Meduza" tells how (and why) neo-Nazis from Russia set out to "denazify" Ukraine]. Meduza (in Russian). Archived from the original on 8 July 2022. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- Melamed, Avraham (2003). Goodman, Lenn Evan (ed.). The Philosopher-King in Medieval and Renaissance Jewish Political Thought. SUNY Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-8770-9 – via Google Books.
- Meserve, Margaret (2009). Empires of Islam in Renaissance Historical Thought. Harvard Historical Series. Vol. 158. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-02656-8 – via Google Books.
- Mikheyev, Alexander S.; Qiu, Lijun; Zarubin, Alexei; Moshkov, Nikita; Orlov, Yuri; Chartier, Duane R.; Kornienko, Igor V.; Faleeva, Tatyana G.; Klyuchnikov, Vladimir; Batieva, Elena F.; Tatarinova, Tatiana V. (16 December 2019). "Diverse genetic origins of medieval steppe nomad conquerors". bioRxiv 10.1101/2019.12.15.876912.
- Miller, Philip E. (1993). Karaite Separatism in Nineteenth-Century Russia: Joseph Solomon Lutski's Epistle of Israel's Deliverance. Cincinnati: Hebrew Union College Press. ISBN 978-0-878-20137-2 – via Google Books.
- Morris, Benny (2003) . The Road to Jerusalem: Glubb Pasha, Palestine and the Jews. I. B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-86064-989-9 – via Google Books.
- Moss, Walter (2002) . A History of Russia: To 1917. Anthem Russian and Slavonic studies. Vol. 1. Anthem Press. ISBN 978-0-85728-752-6 – via Google Books.
- Nebel, Almut; Filon, Dvora; Brinkmann, B (2001). "The Y chromosome pool of Jews as part of the genetic landscape of the Middle East". American Journal of Human Genetics. 69 (5): 1095–1112. doi:10.1086/324070. PMC 1274378. PMID 11573163.
- Nebel, Almut; Filon, Dvora; Faerman, Marina (March 2005). "Y chromosome evidence for a founder effect in Ashkenazi Jews". European Journal of Human Genetics. 13 (3): 388–391. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201319. PMID 15523495. S2CID 1466556.
- Noonan, Thomas S. (1999). "European Russia c500-c1050". In Reuter, Timothy; McKitterick, Rosamond (eds.). The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 3, C.900-c.1024. Vol. 3. Cambridge University Press. pp. 485–534. ISBN 978-0-521-36447-8 – via Google Books.
- Noonan, Thomas S. (2001). "The Khazar Qaghanate and its impact on the early Rus' state: the Translatio Imperii from Itil to Kiev". In Khazanov, Anatoly M.; Wink, André (eds.). Nomads in the Sedentary World. Curzon-IIAS Asian studies series. Routledge. pp. 76–102. ISBN 978-0-7007-1369-1 – via Google Books.
- Noonan, Thomas S. (2007). "The Economy of the Khazar Khaganate". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 207–244. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2. Archived from the original on 15 April 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023 – via Google Books.
- Olsson, Joshua T. (2013). "Coup d'état, Coronation and Conversion: Some Reflections on the Adoption of Judaism by the Khazar Khaganate". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society. 23 (4): 495–526. doi:10.1017/S1356186313000266. S2CID 161833156.
- Oppenheim, Samuel A (1994). "Jews". In Olson, James Stuart; Pappas, Lee Brigance; Pappas, Charles (eds.). An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 305–328. ISBN 978-0-313-27497-8 – via Google Books.
- Ostrer, Harry (2012). Legacy: A Genetic History of the Jewish People. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-997638-6 – via Google Books.
- Ostrogorski, George (1969). History of the Byzantine State. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0-8135-0599-2 – via Internet Archive.
- Patai, Raphael; Patai, Jennifer (1989) . The Myth of the Jewish Race. Wayne State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8143-1948-2 – via Google Books.
- Peacock, Andrew C.S. (2010). Early Seljūq History: A New Interpretation. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-54853-3 – via Google Books.
- Petrukhin, Vladimir (2007). "Khazaria and Rus': An Examination of their Historical Relations". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. BRILL. pp. 245–268. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Petrukhin, Vladimir; Flyorov, Valeriy (2010). "Iudaizm v Khazarii po dannym arkheologii" Иудаизм в Хазарии по данным археологии [Judaism in Khazaria according to Archaeological Data]. In Bartal, Israel; Kulik, Alexander (eds.). Istoriya yevreyskogo naroda v Rossii. Ot drevnosti do rannego Novogo vremeni История еврейского народа в России. От древности до раннего Нового времени [History of Jewish People in Russia. From Antiquity to the Early Modern Period] (in Russian). Vol. 1. Moscow; Jerusalem: Bridges of Culture; Gerashim. pp. 149–161. ISBN 978-5-457-51756-1.
- Piltz, Elisabeth (2004) . "Middle Byzantine Court Costume". In Maguire, Henry (ed.). Byzantine Court Culture from 829 To 1204. Dumbarton Oaks. pp. 39–52. ISBN 978-0-88402-308-1 – via Google Books.
- Poliakov, Léon (2005) . The History of Anti-semitism: From the time of Christ to the court Jews. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-1863-3 – via Google Books.
- Polonsky, Antony; Basista, Jakub; Link-Lenczowski, Andrzej, eds. (1993). The Jews in Old Poland: 1000–1795. I. B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-85043-342-2 – via Google Books.
- Pritsak, Omeljan (September 1978). "The Khazar Kingdom's Conversion to Judaism" (PDF). Harvard Ukrainian Studies. II (3): 261–281. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 January 2022.
- Reuter, Timothy, ed. (1999). The New Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 3, c.900–c.1024. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CHOL9780521364478. ISBN 978-1-13905572-7.
- Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017). ReOrienting the Sasanians: East Iran in Late Antiquity. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 978-1-474-40031-2 – via Google Books.
- Róna-Tas, András (1999). Hungarians & Europe in the Early Middle Ages: An Introduction to Early Hungarian History. Central European University Press. ISBN 978-963-9116-48-1 – via Google Books.
- Rossman, Vadim Joseph (2002). Russian Intellectual Antisemitism in the Post-Communist Era. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-3948-7 – via Google Books.
- Rossman, Vadim Joseph (2007). "Anti-Semitism in Eurasian Historiography: The Caser of Lev Gumilev". In Shlapentokh, Dmitry (ed.). Russia Between East and West: Scholarly Debates on Eurasianism. International Studies in Sociology and Social Anthropology. Vol. 102. BRILL. pp. 121–188. ISBN 978-90-04-15415-5 – via Google Books.
- Rubin, Rita (7 May 2013). "'Jews a Race' Genetic Theory Comes Under Fierce Attack by DNA Expert". The Forward. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- Russell, Josiah C. (1972). "The Population in Europe". In Cipolla, Carlo M. (ed.). The Fontana Economic History of Europe: The Middle Ages. Vol. 1. Collins/Fontana. pp. 25–71. Archived from the original on 29 October 2014.
- Sand, Shlomo (2010) . The Invention of the Jewish People. London: Verso Books. ISBN 978-1-84467-623-1 – via Internet Archive.
- Schama, Simon (2013). The Story of the Jews: Finding the Words (1000 BCE – 1492). Random House. ISBN 978-1-409-04004-0 – via Google Books.
- Schwartzwald, Jack L. (2015). The Collapse and Recovery of Europe, AD 476-1648. McFarland. ISBN 978-1-476-66230-5. Archived from the original on 15 April 2023. Retrieved 19 March 2023 – via Google Books.
- Schweid, Eliezer (2007). "The Khazar motif in Judah Halevi's Sefer ha-Kuzari". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 279–290. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Serrano, Miguel (2011) . Adolf Hitler, the Ultimate Avatar. Editorial Solar. pp. 79, 295 – via Internet Archive.
- Shapira, Dan D. Y. (2009). "Jews in Khazaria". In Ehrlich, Mark Avrum (ed.). Encyclopedia of the Jewish Diaspora: Origins, Experiences, and Culture. Vol. 3: (Countries, Regions, and Communities). ABC-CLIO. pp. 1097–1104. ISBN 978-1-85109-873-6 – via Google Books.
- Shapira, Dan D.Y. (2006). "Remarks on Avraham Firkovicz and the Hebrew Mejelis "Document"". Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae. 59 (2): 131–180. doi:10.1556/AOrient.59.2006.2.1.
- Shapira, Dan D.Y. (2007a). "Iranian Sources on the Khazars". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 291–305. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2. Retrieved 13 February 2013 – via Google Books.
- Shapira, Dan D.Y. (2007b). "Armenian and Georgian Sources on the Khazars – A Re-Evaluation". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbook of Oriental Studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 307–351. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2. Retrieved 13 February 2013 – via Google Books.
- Shepard, Jonathan (2006). "Closer Encounters with the Byzantine World: The Rus at the Straits of Kerch". In Reyerson, Kathryn Von; Stavrou, Theofanis George; Tracy, James Donald (eds.). Pre-modern Russia and its world: Essays in Honour of Thomas S. Noonan. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 15–77. ISBN 978-3-447-05425-6 – via Google Books.
- Shingiray, Irina Lita (2012). "Ethos, Materiality and Paradigms of Political Action in Early Medieval Communities of the Northwestern Caspian Region". In Hartley, Charles W.; Yazicioğlu, G. Bike; Smith, Adam T. (eds.). The Archaeology of Power and Politics in Eurasia: Regimes and Revolutions. Cambridge University Press. pp. 188–216. ISBN 978-1-107-01652-1 – via Google Books.
- Shirota, Shun (城田俊) (2005). Woods, John E.; Pfeiffer, Judith; Tucker, Ernest (eds.). "The Chinese Chroniclers of the Khazars: Notes on Khazaria in Tang Period Texts". Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi. 14: 231–261.
- Shnirelman, Victor A (2007). "The Story of an Euphemism: The Khazars in Russian Nationalist Literature". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 353–372. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Sima Guang; et al. vol. 196. Chinese Text Project. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020.
- Singerman, Robert (2004). "Contemporary Racist and Judeophobic Ideology Discovers the Khazars, or, Who Really Are the Jews?" (PDF). Rosaline and Myer Feinstein Lecture Series. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 March 2014. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- Sneath, David (2007). The Headless State: Aristocratic Orders, Kinship Society, and Misrepresentations of Nomadic Inner Asia. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-51167-4 – via Google Books.
- Somogyi, Péter (2008). "New remarks on the flow of Byzantine coins in Avaria and Walachia during the second half of the seventh century". In Curta, Florin; Kovalev, Roman (eds.). The "Other" Europe in the Middle Ages: Avars, Bulgars, Khazars and Cumans. East Central and Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 450–1450. Vol. 2. Brill. pp. 83–149. ISBN 978-90-04-16389-8 – via Google Books.
- Spinei, Victor (2009). The Romanians and the Turkic Nomads North of the Danube Delta from the Tenth to the Mid-Thirteenth Century. BRILL. ISBN 978-9-004-17536-5 – via Google Books.
- Spolsky, Bernard (2014). The Languages of the Jews: A Sociolinguistic History. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-05544-5 – via Google Books.
- Stampfer, Shaul (2013). "Did the Khazars Convert to Judaism?" (PDF). Jewish Social Studies. 19 (3): 1–72. doi:10.2979/jewisocistud.19.3.1. S2CID 161320785 – via Project MUSE.
- Stampfer, Shaul (2014). "Are We All Khazars Now?". Jewish Review of Books. pp. 1–72. Archived from the original on 1 May 2016. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- Szádeczky-Kardoss, Samuel (1994) . "The Avars". In Sinor, Denis (ed.). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia. Handbook of Oriental Studies. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. pp. 206–228. ISBN 978-0-521-24304-9. Retrieved 13 February 2013 – via Google Books.
- Szpiech, Ryan (2012). Conversion and Narrative: Reading and Religious Authority in Medieval Polemic. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-0761-3 – via Google Books.
- Szyszman, Simon (1980). Le karaïsme: ses doctrines et son histoire [Karaism: its doctrines and its history] (in French). Éditions L'Âge d'Homme. ISBN 978-2-8251-3088-9 – via Google Books.
- Taagepera, Rein (September 1997). "Expansion and Contraction Patterns of Large Polities: Context for Russia". International Studies Quarterly. 41 (3): 496. doi:10.1111/0020-8833.00053. JSTOR 2600793. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018.
- Tangshu, Jiu; Jiu Tangshu. Vol. 199b Tiele (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 16 May 2011.
- Toch, Michael (2012). The Economic History of European Jews: Late Antiquity and Early Middle Ages. Études sur le Judaïsme Médiéval. Vol. 56. Leiden: Brill Publishers. ISBN 978-90-04-23534-2 – via Google Books.
- Toynbee, Arnold (1962) . A Study of History. Vol. 1–12. Oxford University Press.
- Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires". Journal of World-Systems Research. 12 (2): 222. ISSN 1076-156X. Archived from the original on 20 May 2019.
- Vogt, Judith (1975). "Left-wing 'anti-Zionism' in Norway". Patterns of Prejudice. 9 (6): 15–q8. doi:10.1080/0031322X.1975.9969275.
- Wachtel, Andrew (1998). Making a Nation, Breaking a Nation: Literature and Cultural Politics in Yugoslavia. Stanford University Press. pp. 210–215. ISBN 978-0-8047-3181-2 – via Google Books.
- Wang, Pu; et al. Tang Huiyao (in Chinese). Vol. 98. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021.
- Wang, Pu; et al. Tang Huiyao (in Chinese). Vol. 72. Archived from the original on 4 November 2020.
- Wasserstein, David (2007). "The Khazars and the World of Islam". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 373–386. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- Wei, Zheng; et al. "vol. 84". Book of Sui (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 11 December 2022.
- Weinryb, Bernard Dov (1973a). The Jews of Poland: A Social and Economic History of the Jewish Community in Poland from 1100 to 1800. Jewish Publication Society. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-0-8276-0016-4 – via Google Books.
- Weinryb, Bernard Dov (1973b). The Jews of Poland: A Social and Economic History of the Jewish Community in Poland from 1100 to 1800 he non-Jewish origins of the Sephardic Jews. Jewish Publication Society. ISBN 978-0-8276-0016-4 – via Google Books.
- Wells, H. G. (1920). The Outline of History: Being a Plain History of Life and Mankind. Vol. 1. Macmillan. Archived from the original on 13 July 2020.
- Wexler, Paul (1987). Explorations in Judeo-Slavic Linguistics. Contributions to the sociology of Jewish languages. Vol. 2. Brill Archive. ISBN 978-90-04-07656-3 – via Google Books.
- Wexler, Paul (1996). The non-Jewish origins of the Sephardic Jews. SUNY. ISBN 978-1-4384-2393-7. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 12 December 2015 – via Google Books.
- Wexler, Paul (2002). Two-Tiered Relexification in Yiddish: Jews, Sorbs, Khazars and the Kiev-Polessian Dialect. Trends in linguistics / Studies and monographs: Studies and monographs. Vol. 136. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-017258-4. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2015 – via Google Books.
- Wexler, Paul (2007). "Yiddish Evidence for the Khazar Component in the Ashkenazic ethnogenesis". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 387–398. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2. Archived from the original on 17 November 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2015 – via Google Books.
- Whittow, David (1996). The Making of Byzantium, 600–1025. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-20496-6 – via Google Books.
- Xin, Tangshu. New Book of Tang (in Chinese). Vol. 217a Huihe. Archived from the original on 4 May 2019.
- Zhivkov, Boris (2015). Khazaria in the Ninth and Tenth Centuries. BRILL. ISBN 978-9-004-29448-6 – via Google Books.
- Zimonyi, István (1990). Szõnyi-Sándor, Klára (ed.). The Origins of the Volga Bulghars. Studia Uralo-Altaica, 32. ISBN 978-963-481-839-7.
- Zuckerman, Constantine (1995). "On the date of the Khazars' Conversion to Judaism and the Chronology of the Kings of the Rus' Oleg and Igor". Revue des études byzantines. 53: 237–270. doi:10.3406/rebyz.1995.1906. Archived from the original on 29 November 2022.
- Zuckerman, Constantine (2007). "The Khazars and Byzantium –The First Encounter". In Golden, Peter B.; Ben-Shammai, Haggai; Róna-Tas, András (eds.). The World of the Khazars: New Perspectives. Handbuch der Orientalistik: Handbook of Uralic studies. Vol. 17. Brill. pp. 399–431. ISBN 978-90-04-16042-2 – via Google Books.
- "КАСПИЙСКОЕ МОРЕ перевод [CASPIAN SEA translation]". Русско-крымскотатарский словарь (кириллица) (in Russian). Archived from the original on 26 October 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- "Ясно-понятно. Кто такие мишари?" [Clearly understood: Who are the Mishars?]. Инде (inde.io) (in Russian). 2016. Archived from the original on 8 November 2022. Retrieved 23 May 2024.
External links
- The Kievan Letter scan in the Cambridge University Library collection.
- Khazaria.com Archived 21 December 1997 at the Wayback Machine
- Resources – Medieval Jewish History – The Khazars The Jewish History Resource Center, Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- Khazar Historic Maps at the Wayback Machine (archived 26 October 2009)
- The Kitab al-Khazari of Judah Hallevi, full English translation at sacred-texts.com Archived 6 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Ancient lost capital of the Khazar kingdom found Archived 10 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine
| Languages |
|  | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peoples |
| ||||
| Politics | |||||
| Origins | |||||
| Locations |
| ||||
| Studies | |||||
| Religions | |||||
| Traditional sports | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| These are traditional areas of settlement; the Turkic group has been living in the listed country/region for centuries and should not be confused with modern diasporas. State with limited international recognition. | |||||
| Khazaria | ||
|---|---|---|
| Khazar rulers | 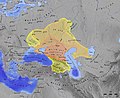 | |
| Other figures | ||
| Places | ||
| Tributaries | ||
| Scholars | ||
| Legacy | ||
| Turkic peoples | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peoples |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diasporas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Asian (i.e. Turkmeni, Afghani and Iranian) Turkmens, distinct from Levantine (i.e. Iraqi and Syrian) Turkmen/Turkoman minorities, who mostly adhere to an Ottoman-Turkish heritage and identity. In traditional areas of Turkish settlement (i.e. former Ottoman territories). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crimea articles | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
|  | |||||||||||
| Geography |
| ||||||||||||
| Politics | |||||||||||||
| Economy | |||||||||||||
| Society |
| ||||||||||||
| Barbarian kingdoms established around the Migration Period | |
|---|---|
|
