| Revision as of 02:15, 7 October 2005 editNTBot~enwiki (talk | contribs)5,404 editsm robot Adding: pt← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:31, 14 November 2024 edit undoSpicemix (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users92,025 edits →Notable people from Takamatsu: MOS:ENDASH | ||
| (338 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{other uses}} | |||
| '''Takamatsu''' (高松市; -shi lit. high ]) is the capital ] of ] on ] island of ]. It is located on the northern border of Shikoku and faces the ]. | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | |||
| | name = | |||
| | official_name = | |||
| | native_name = {{nobold|高松市}} | |||
| | native_name_lang = ja | |||
| | settlement_type = ] | |||
| | other_name = | |||
| | image_skyline = Takamatsu montage.png | |||
| | image_caption = From top left: Central Takamatsu, ], ], Marugame-machi shopping mall, ] | |||
| | image_flag = Flag of Takamatsu, Kagawa.svg | |||
| | image_seal = Emblem of Takamatsu, Kagawa.svg | |||
| | image_map = {{maplink|frame=yes|plain=yes|frame-width=265|type=shape|stroke-width=2|stroke-color=#000000|zoom=8}} | |||
| | map_caption = Location of Takamatsu in Kagawa Prefecture | |||
| |image_map1 = Kagawa-takamatsu-city.svg | |||
| | map_caption1 = | |||
| | pushpin_map = Japan | |||
| | pushpin_map_caption = Location in Japan | |||
| | coordinates = {{coord|34|21|N|134|3|E|region:JP-37|display=it}} | |||
| | subdivision_type = Country | |||
| | subdivision_name = {{flag|Japan}} | |||
| | subdivision_type1 = ] | |||
| | subdivision_name1 = ] | |||
| | subdivision_type2 = ] | |||
| | subdivision_name2 = ] | |||
| | subdivision_type3 = ] | |||
| | subdivision_name3 = | |||
| | established_title = | |||
| | established_date = | |||
| | established_title2 = | |||
| | established_date2 = | |||
| | leader_title = Mayor | |||
| | leader_name = ] | |||
| | leader_title1 = Vice Mayor | |||
| | leader_name1 = | |||
| | unit_pref = Metric | |||
| | area_total_km2 = 375.41 | |||
| | population_total = 414,134 | |||
| | population_as_of = November 1, 2022 | |||
| | population_density_km2 = auto | |||
| | timezone1 = ] | |||
| | utc_offset1 = +09:00 | |||
| | postal_code_type = | |||
| | postal_code = | |||
| | blank_name_sec1 = City hall address | |||
| | blank_info_sec1 = 1-8-15 Banchō, Takamatsu-shi, Kagawa-ken 760-8571 | |||
| | blank_name_sec2 = ] | |||
| | blank_info_sec2 = ] | |||
| | website = {{Official website|1=www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/}} | |||
| | module = {{Infobox place symbols| embedded=yes | |||
| | tree = ] | |||
| | flower = ] | |||
| | bird = | |||
| | butterfly = | |||
| | fish = | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{nihongo|'''Takamatsu'''|高松市|Takamatsu-shi|extra={{IPA|ja|takaꜜmatsɯ|lang}}}} is a capital ] located in ], Japan. {{As of|2022|11|01}}, the city had an estimated ] of 414,134 in 190,120 households and a ] of 1,100 persons per km<sup>2</sup>.<ref name="Takamatsu-hp">{{cite web |url=https://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/kurashi/index.htmll|title= Takamatsu city official statistics|location= Japan|language= ja}}</ref> The total area of the city is {{convert|375.41|sqkm|sqmi}}. It is the capital city of the prefecture. | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| As of ], the city has an estimated ] of 334,397 with a population ] of 1,720.77 persons per ]. The total area is 194.33 km². | |||
| Takamatsu is located in central ] on the island of ]. The city is located in the Takamatsu Plain, which is part of the Sanuki Plain, and is occupied by a gentle slope as a whole. The northern part faces the ], forming a semicircular urban area centered on Takamatsu Port and Takamatsu New Port (commonly known as Shinminato).The western part of the city consists of an ] formed by the sedimentation of the Koto River. The eastern part is a flooded plain formed by the Kasuga River and Shinkawa River. In the northeastern part of the island, there is ], a table-shaped plateau protruding into the Seto Inland Sea, which was the site of the ] in the ], and Cape Takei, the northernmost tip of the main island of Shikoku. Parts of the city are located within the borders of the ]. The city area also includes a number of small inhabited islands in the Seto Inland Sea. | |||
| === Neighbouring municipalities === | |||
| The city was officially founded on ], ]. It had been a political and economic center in this area since the ] when the ] made Takamatsu the capital of their ]. | |||
| Kagawa Prefecture | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| Tokushima Prefecture | |||
| * ] | |||
| ===Climate=== | |||
| Since the opening of the ], trains ferry passengers between Takamatsu and Uno (]). | |||
| Takamatsu has a ] (] ''Cfa'') with hot, humid summers, and cool winters. Some rain falls throughout the year, but the months from May to September have the heaviest rain. | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| The city's major tourist attraction is ], a beautiful garden, created in the ]. | |||
| |width=auto | |||
| |collapsed = Y | |||
| |single line = Y | |||
| |metric first = Y | |||
| |location = Takamatsu (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1941−present) | |||
| |Jan record high C = 18.9 | |||
| |Feb record high C = 24.0 | |||
| |Mar record high C = 25.5 | |||
| |Apr record high C = 30.9 | |||
| |May record high C = 32.6 | |||
| |Jun record high C = 36.5 | |||
| |Jul record high C = 38.2 | |||
| |Aug record high C = 38.6 | |||
| |Sep record high C = 37.6 | |||
| |Oct record high C = 34.0 | |||
| |Nov record high C = 26.6 | |||
| |Dec record high C = 21.2 | |||
| |Jan record low C = -7.7 | |||
| |Feb record low C = -6.0 | |||
| |Mar record low C = -4.4 | |||
| |Apr record low C = -2.4 | |||
| |May record low C = 2.8 | |||
| |Jun record low C = 7.5 | |||
| |Jul record low C = 15.3 | |||
| |Aug record low C = 15.8 | |||
| |Sep record low C = 9.4 | |||
| |Oct record low C = 2.0 | |||
| |Nov record low C = -1.8 | |||
| |Dec record low C = -5.3 | |||
| |precipitation colour = green | |||
| |Jan precipitation mm = 39.4 | |||
| |Feb precipitation mm = 45.8 | |||
| |Mar precipitation mm = 81.4 | |||
| |Apr precipitation mm = 74.6 | |||
| |May precipitation mm = 100.9 | |||
| |Jun precipitation mm = 153.1 | |||
| |Jul precipitation mm = 159.8 | |||
| |Aug precipitation mm = 106.0 | |||
| |Sep precipitation mm = 167.4 | |||
| |Oct precipitation mm = 120.1 | |||
| |Nov precipitation mm = 55.0 | |||
| |Dec precipitation mm = 46.7 | |||
| |year precipitation mm = 1150.1 | |||
| |Jan mean C = 5.9 | |||
| |Feb mean C = 6.3 | |||
| |Mar mean C = 9.4 | |||
| |Apr mean C = 14.7 | |||
| |May mean C = 19.8 | |||
| |Jun mean C = 23.3 | |||
| |Jul mean C = 27.5 | |||
| |Aug mean C = 28.6 | |||
| |Sep mean C = 24.7 | |||
| |Oct mean C = 19.0 | |||
| |Nov mean C = 13.2 | |||
| |Dec mean C = 8.1 | |||
| |year mean C = 16.7 | |||
| |Jan high C = 9.7 | |||
| |Feb high C = 10.5 | |||
| |Mar high C = 14.1 | |||
| |Apr high C = 19.8 | |||
| |May high C = 24.8 | |||
| |Jun high C = 27.5 | |||
| |Jul high C = 31.7 | |||
| |Aug high C = 33.0 | |||
| |Sep high C = 28.8 | |||
| |Oct high C = 23.2 | |||
| |Nov high C = 17.5 | |||
| |Dec high C = 12.1 | |||
| |year high C = 21.1 | |||
| |Jan low C = 2.1 | |||
| |Feb low C = 2.2 | |||
| |Mar low C = 5.0 | |||
| |Apr low C = 9.9 | |||
| |May low C = 15.1 | |||
| |Jun low C = 19.8 | |||
| |Jul low C = 24.1 | |||
| |Aug low C = 25.1 | |||
| |Sep low C = 21.2 | |||
| |Oct low C = 15.1 | |||
| |Nov low C = 9.1 | |||
| |Dec low C = 4.3 | |||
| |year low C = 12.8 | |||
| |Jan humidity = 63 | |||
| |Feb humidity = 63 | |||
| |Mar humidity = 62 | |||
| |Apr humidity = 62 | |||
| |May humidity = 64 | |||
| |Jun humidity = 72 | |||
| |Jul humidity = 73 | |||
| |Aug humidity = 70 | |||
| |Sep humidity = 72 | |||
| |Oct humidity = 70 | |||
| |Nov humidity = 69 | |||
| |Dec humidity = 66 | |||
| |year humidity = 67 | |||
| |Jan sun = 141.4 | |||
| |Feb sun = 143.8 | |||
| |Mar sun = 175.0 | |||
| |Apr sun = 194.5 | |||
| |May sun = 210.1 | |||
| |Jun sun = 158.2 | |||
| |Jul sun = 191.8 | |||
| |Aug sun = 221.2 | |||
| |Sep sun = 159.6 | |||
| |Oct sun = 164.6 | |||
| |Nov sun = 145.5 | |||
| |Dec sun = 142.7 | |||
| |year sun = 2046.5 | |||
| |Jan snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Feb snow cm = 1 | |||
| |Mar snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Apr snow cm = 0 | |||
| |May snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Jun snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Jul snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Aug snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Sep snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Oct snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Nov snow cm = 0 | |||
| |Dec snow cm = 0 | |||
| |year snow cm = 1 | |||
| |unit precipitation days = 0.5 mm | |||
| |Jan precipitation days = 7.5 | |||
| |Feb precipitation days = 8.0 | |||
| |Mar precipitation days = 10.8 | |||
| |Apr precipitation days = 10.1 | |||
| |May precipitation days = 9.4 | |||
| |Jun precipitation days = 11.5 | |||
| |Jul precipitation days = 10.5 | |||
| |Aug precipitation days = 7.9 | |||
| |Sep precipitation days = 10.5 | |||
| |Oct precipitation days = 9.3 | |||
| |Nov precipitation days = 7.8 | |||
| |Dec precipitation days = 7.9 | |||
| |year precipitation days = 111.3 | |||
| |source 1 = Japan Meteorological Agency<ref>{{cite web | |||
| | url = https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/index.php?prec_no=72&block_no=47891&year=&month=&day=&view= | |||
| |script-title=ja:気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | access-date = May 19, 2021}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| |width=auto | |||
| |collapsed = Y | |||
| |location = ], Takamatsu (2003−2020 normals, extremes 2003−present) | |||
| |single line = Y | |||
| |metric first = Y | |||
| |Jan record high C = 16.6 | |||
| |Feb record high C = 22.8 | |||
| |Mar record high C = 25.2 | |||
| |Apr record high C = 29.6 | |||
| |May record high C = 31.9 | |||
| |Jun record high C = 34.8 | |||
| |Jul record high C = 36.0 | |||
| |Aug record high C = 37.8 | |||
| |Sep record high C = 35.5 | |||
| |Oct record high C = 31.9 | |||
| |Nov record high C = 26.1 | |||
| |Dec record high C = 19.4 | |||
| |Jan record low C = -5.6 | |||
| |Feb record low C = -5.5 | |||
| |Mar record low C = -3.6 | |||
| |Apr record low C = -1.1 | |||
| |May record low C = 2.9 | |||
| |Jun record low C = 9.7 | |||
| |Jul record low C = 16.3 | |||
| |Aug record low C = 15.9 | |||
| |Sep record low C = 11.0 | |||
| |Oct record low C = 4.6 | |||
| |Nov record low C = -0.4 | |||
| |Dec record low C = -4.9 | |||
| |Jan high C = 8.2 | |||
| |Feb high C = 9.3 | |||
| |Mar high C = 13.1 | |||
| |Apr high C = 18.8 | |||
| |May high C = 23.7 | |||
| |Jun high C = 26.4 | |||
| |Jul high C = 30.2 | |||
| |Aug high C = 31.7 | |||
| |Sep high C = 27.5 | |||
| |Oct high C = 21.9 | |||
| |Nov high C = 16.3 | |||
| |Dec high C = 10.5 | |||
| |Jan mean C = 4.1 | |||
| |Feb mean C = 4.9 | |||
| |Mar mean C = 8.0 | |||
| |Apr mean C = 13.3 | |||
| |May mean C = 18.3 | |||
| |Jun mean C = 21.8 | |||
| |Jul mean C = 25.6 | |||
| |Aug mean C = 26.7 | |||
| |Sep mean C = 22.8 | |||
| |Oct mean C = 17.3 | |||
| |Nov mean C = 11.8 | |||
| |Dec mean C = 6.5 | |||
| |Jan low C = 0.4 | |||
| |Feb low C = 0.7 | |||
| |Mar low C = 3.0 | |||
| |Apr low C = 7.9 | |||
| |May low C = 13.0 | |||
| |Jun low C = 17.7 | |||
| |Jul low C = 22.0 | |||
| |Aug low C = 22.8 | |||
| |Sep low C = 19.1 | |||
| |Oct low C = 13.3 | |||
| |Nov low C = 7.7 | |||
| |Dec low C = 2.7 | |||
| |precipitation colour = green | |||
| |Jan precipitation mm = 41.0 | |||
| |Feb precipitation mm = 54.8 | |||
| |Mar precipitation mm = 84.8 | |||
| |Apr precipitation mm = 77.8 | |||
| |May precipitation mm = 105.5 | |||
| |Jun precipitation mm = 160.7 | |||
| |Jul precipitation mm = 193.2 | |||
| |Aug precipitation mm = 150.1 | |||
| |Sep precipitation mm = 214.4 | |||
| |Oct precipitation mm = 148.4 | |||
| |Nov precipitation mm = 64.4 | |||
| |Dec precipitation mm = 59.0 | |||
| |year precipitation mm = 1353.9 | |||
| |unit precipitation days = 1.0 mm | |||
| |Jan precipitation days = 6.6 | |||
| |Feb precipitation days = 8.4 | |||
| |Mar precipitation days = 10.1 | |||
| |Apr precipitation days = 9.8 | |||
| |May precipitation days = 8.3 | |||
| |Jun precipitation days = 11.1 | |||
| |Jul precipitation days = 10.5 | |||
| |Aug precipitation days = 8.7 | |||
| |Sep precipitation days = 10.2 | |||
| |Oct precipitation days = 8.5 | |||
| |Nov precipitation days = 8.0 | |||
| |Dec precipitation days = 7.9 | |||
| |source 1 = ]<ref>{{cite web | |||
| | url = https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/view/rank_a.php?prec_no=72&block_no=1475&year=&month=&day=&view=h0 | |||
| |script-title=ja:観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値) | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | access-date = April 24, 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | |||
| | url = https://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/view/nml_amd_ym.php?prec_no=72&block_no=1475&year=&month=&day=&view=h0 | |||
| |script-title=ja:気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | access-date = April 24, 2022}}</ref>}} | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| These days, the city is getting more famous for its noodles:]. The noodles made in this city are called Sanuki Udon. They are widely considered to be inexpensive and delicious. | |||
| Per Japanese census data, the population of Takamatsu in 2020 is 417,496 people.<ref name=zensus/> Takamatsu has been conducting censuses since 1920. | |||
| {{Historical populations | |||
| | 1920 | 186,963 | |||
| | 1925 | 199,141 | |||
| | 1930 | 213,001 | |||
| | 1935 | 222,545 | |||
| | 1940 | 219,082 | |||
| | 1945 | 246,809 | |||
| | 1950 | 269,159 | |||
| | 1955 | 284,684 | |||
| | 1960 | 295,178 | |||
| | 1965 | 307,549 | |||
| | 1970 | 327,170 | |||
| | 1975 | 360,024 | |||
| | 1980 | 386,547 | |||
| | 1985 | 401,020 | |||
| | 1990 | 406,853 | |||
| | 1995 | 412,626 | |||
| | 2000 | 416,680 | |||
| | 2005 | 418,125 | |||
| | 2010 | 419,429 | |||
| | 2015 | 420,748 | |||
| | 2020 | 417,496 | |||
| |align = none | |||
| |cols = 1 | |||
| |footnote = Takamatsu population statistics<ref name=zensus></ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| == History == | |||
| The area of Takamatsu was part of ancient ]. During the ] and ], as the closest port to ] from Shikoku island, the area was a transportation center and gateway for pilgrims to the ]. During the ], ] suit the first ] in 1588. In 1642, ], the son of ] of ] and grandson of ], was awarded the 120,000 ''koku'' ], which his descendants would continue to rule until the ].<ref name="Nakayama">{{cite book |last1=Nakayama |first1=Yoshiaki |title=江戸三百藩大全 全藩藩主変遷表付 |date=2015 |publisher=Kosaido Publishing |isbn= 978-4331802946}}{{in lang|ja}}</ref> | |||
| Following the Meiji restoration, the city of Takamatsu was created with the establishment of the modern municipalities system on February 15, 1890. The ] formerly used as the symbol of the city was destroyed during the ]. The city borders expanded in several iterations by the annexation on neighboring villages and towns. During ], Takamatsu was selected as a target by the United States' ] because the city was an important focal point of Shikoku's rail and road transit systems, and containing some industry vital to supporting the war effort. On July 3, 1945, at 6:40 pm (]) 128 ] bombers dropped over 800 tons of incendiary bombs on Takamatsu, destroying 78% of the built-up areas of the city and killing 1359 people.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.scribd.com/doc/61702152/21st-Bomber-Command-Tactical-Mission-Report-247-250-Ocr|title = 21st Bomber Command Tactical Mission Report 247, 250, Ocr | Aviation | Armed Conflict}}</ref> | |||
| The city quickly recovered after the war, and its borders continued to expand. On April 1, 1999, it was designated a ] with increased local autonomy. | |||
| On September 26, 2005, the town of ] (from ]) was merged into Takamatsu. On January 10, 2006, Takamatsu absorbed the following towns: ] and ] (from ]), ] and ] (from ]), and ] (from ]). | |||
| ==Government== | |||
| Takamatsu has a ] form of government with a directly elected mayor and a ] city council of 40 members. Takamatsu contributes 15 members to the Kagawa Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is divided between Kagawa 1st district and Kagawa 2nd district of the ] of the ]. | |||
| ===Crime and safety=== | |||
| The ] ] syndicate is based in Takamatsu. The Shinwa-kai is the only ] based in the ] region.<ref name="PWP2010">, 2021, '']'' {{in lang|ja}}</ref> | |||
| In October 2017, '']'' reported five people received minor injuries when a ] entered a local ] mall.<ref name="JT2007">, 2007, '']'' {{in lang|en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| ] | |||
| Takamatsu is the largest municipality in Shikoku and is a city with a large concentration of nationwide companies' branch offices, which play a large role in its economy. It also contains most of the national government's branch offices for Shikoku. In 2004, construction of the Symbol Tower, the new symbol of Takamatsu, was completed. The Symbol Tower is in the ] area of the city. The Symbol Tower is the tallest building in Takamatsu, and is right next to another tall building The JR Clement Hotel (formerly the ANA Clement Hotel), which is also part of the Sunport complex. Sunport Takamatsu is also connected to the ports of Takamatsu. | |||
| Companies headquartered in the city include: | |||
| *]<ref>" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100324005655/http://www.jr-shikoku.co.jp/04_company/company/gaiyou.shtm |date=2010-03-24 }}." ]. Retrieved on March 27, 2010.</ref> | |||
| *Shikoku Shimbun | |||
| *]<ref>" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304000853/http://www.tadano.com/company/coprofile/index.html |date=2016-03-04 }}." ]. Retrieved on April 15, 2015.</ref> | |||
| ==Education== | |||
| Takamatsu has 48 public elementary schools, 22 public middle schools and one public high school operated by the city government. The city has eight public high schools and one combined middle/high school operated by the Kagawa Prefectural Board of Education. There are also two private combined middle/high schools, seven private high schools and one national elementary, one national middle and one national high school. The Kagawa Prefectural government also operates three special education schools for the handicapped. | |||
| ===Universities=== | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| == Transportation == | |||
| The main train station is ], operated by ]. Trains from here run to destinations around Shikoku, as well as ] on Honshū via the ]. The private ] railway connects much of Takamatsu, with a hub and department store at ], and Takamatsu-Chikko Station nearby Takamatsu Station. Buses and trains operated by Kotoden accept a ] card for travel called an IruCa.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.reviewmylife.co.uk/blog/2009/12/21/takamatsu-japan-what-to-do-there/ |title=Takamatsu Japan, what to do there |date=20 December 2009 |access-date=2010-03-13}}</ref> | |||
| ===Airports=== | |||
| *] | |||
| === Railways === | |||
| ] ] - ] | |||
| * {{STN|Takamatsu|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Kōzai}} - {{STN|Kinashi}} - {{STN|Hashioka}} - {{STN|Kokubu|Kagawa}} | |||
| ] ] - ] | |||
| * {{STN|Sanuki-Mure}} - {{STN|Yakuriguchi}} - {{STN|Furutakamatsu-Minami}} - {{STN|Yashima|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Kitachō}} - {{STN|Ritsurin}} - {{STN|Ritsurin-Kōen-Kitaguchi}} - {{STN|Shōwachō|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Takamatsu|Kagawa}} | |||
| ] ] - ] | |||
| * {{STN|Takamatsu-Chikkō}}- {{STN|Kataharamachi|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Kawaramachi|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Ritsurin-Kōen}} - {{STN|Sanjō|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Fuseishi}} - {{STN|Ōta|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Busshōzan}} - {{STN|Kūkō-dōri}} - {{STN|Ichinomiya}} - {{STN|Enza}} - {{STN|Okamoto|Kagawa}} | |||
| ] ] - ] | |||
| * ({{STN|Takamatsu-Chikkō}} - {{STN|Kataharamachi|Kagawa}}) - {{STN|Kawaramachi|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Hanazono|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Hayashimichi}} - {{STN|Kita-Higashiguchi}} - {{STN|Motoyama|Takamatsu}} - {{STN|Mizuta}} - {{STN|Nishi-Maeda}} -{{STN|Takata|Kagawa}} | |||
| ] ] - ] | |||
| * {{STN|Kawaramachi|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Imabashi}} - {{STN|Matsushima-Nichōme}} - {{STN|Oki-Matsushima}} - {{STN|Kasugagawa}} - {{STN|Katamoto}} - {{STN|Kotoden-Yashima}} - {{STN|Furu-Takamatsu}} - {{STN|Yakuri}} - {{STN|Rokumanji}} - {{STN|Ōmachi|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Yakuri-Shinmichi}} - {{STN|Shioya|Kagawa}} - {{STN|Fusazaki}} - {{STN|Hara|Kagawa}} | |||
| === Highways === | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|11}} | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|30}} | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|32}} | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|193}} | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|377}} | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|436}} | |||
| * {{jct|country=JPN|Route|492}} | |||
| ===Ports=== | |||
| *] | |||
| ==Local attractions== | |||
| *], a ] designated as a Special Place of Scenic Beauty by the Japanese government | |||
| *] is known for using seawater in its moat and recently the old keep of the castle was successfully restored and opened for public viewing.<ref>{{Cite web |script-title=ja:高松城天守閣復元|url = http://www.takamatsujyo.com/tensyukaku.htm|website = www.takamatsujyo.com|access-date = 2016-01-19}}</ref> | |||
| *] plateau which is home to various sightseeing spots. At the base of the mountain is the open air museum ] where aspects of regional history and culture are exhibited. On the mountain itself is ], number 84 of the ]. At the top of the mountain there is also an observation deck which offers views across the Seto Inland Sea. | |||
| *Takamatsu also acts as a hub to access various islands of the Seto Inland Sea. These include, ], ], ], ] and ]. Since 2010, Takamatsu, along with these islands and more, has been host to the ], a contemporary art festival with many outdoor exhibitions by prominent artists from across the world. | |||
| ===Sports teams=== | |||
| *] (Basketball, ]) | |||
| *Kagawa Ice Fellows (Ice Hockey) | |||
| *] (Baseball) | |||
| *] (Football) | |||
| ==International relations== | |||
| {{See also|List of twin towns and sister cities in Japan}} | |||
| ===Twin towns – sister cities=== | |||
| Takamatsu is ] with: | |||
| * {{flagicon|US}} ], United States<ref>{{cite web | title=St. Petersburg | url=http://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/english/profile/st-petersburg/ | publisher=Takamatsu city | access-date=2009-05-26 | url-status=dead | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090611035610/http://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/english/profile/st-petersburg/ | archive-date=2009-06-11 }}</ref> | |||
| * {{flagicon|FRA}} ], France<ref>{{cite web | title=Tours | url=http://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/english/profile/tours/ | publisher=Takamatsu city | access-date=2009-05-26 | url-status=dead | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090611035615/http://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/english/profile/tours/ | archive-date=2009-06-11 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Friendship cities=== | |||
| Takamatsu has friendship arrangements with: | |||
| * {{flagicon|PRC}} ], China, since 1990<ref>{{cite web | title=Nanchang | url=http://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/english/profile/nanchang/ | publisher=Takamatsu city | access-date=2009-05-26 | url-status=dead | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090611035555/http://www.city.takamatsu.kagawa.jp/english/profile/nanchang/ | archive-date=2009-06-11 }}</ref><ref name="Nanchang twinnings">{{cite web|url=http://english.nc.gov.cn/aboutnanchang/sistercity/|title=Nanchang City and Sister Cities Intercommunion|access-date=2013-11-05|work=Nanchang Municipal Party Committee of the CPC and Nanchang Municipal Government|publisher=Nanchang Economic Information Center|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130522211744/http://english.nc.gov.cn/aboutnanchang/sistercity/|archive-date=2013-05-22}}</ref> | |||
| ==In literature== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| *Takamatsu is the main setting for ]'s novel '']''. | |||
| *The naval commander ], born in Takamatsu in 1900, recounts his childhood there in the memoir ''Japanese Destroyer Captain''.<ref>{{cite book| last = Hara| first = Tameichi| author-link = Tameichi Hara| year = 1961| chapter = Born A Samurai| title = Japanese Destroyer Captain| publisher = ]| location = New York & Toronto| isbn = 978-1-59114-354-3| oclc = 255849609}}</ref> | |||
| *Takamatsu is the main setting for the manga and anime ]. | |||
| ==Notable people from Takamatsu== | |||
| The following politicians, celebrities, and other well-known people are from Takamatsu (listed alphabetically by surname):<!--only list people with articles here--> | |||
| *] (actor, born 1982) | |||
| *] (politician, born 1956) | |||
| *] (Olympic athlete, 1926–2011) | |||
| *] (politician, born 1958) | |||
| *] (musician and composer, born 1968) | |||
| *] (writer and publisher, 1888–1948) | |||
| *] (actor, born 1981) | |||
| *] (soccer player, born 1967) | |||
| *] (shogi player, born 1957) | |||
| *] (baseball player, 1938–2019) | |||
| *] (karateka, 1893–1983) | |||
| *] (politician, 1884–1956) | |||
| *] (tennis player, 1904–1967) | |||
| *] (golfer, born 1996) | |||
| *] (mixed martial artist, born 1981) | |||
| *] (baseball player, 1928–1984) | |||
| *] (baseball player, born 1994) | |||
| *] (sledge hockey coach, born 1963) | |||
| *] (baseball player, born 1933) | |||
| *] (comedian and TV personality, born 1965) | |||
| *] (violinist, born 1971) | |||
| *] (artist, born 1980) | |||
| *] (politician, born 1971) | |||
| *] (politician, born 1972) | |||
| *] (darts player, born 1982) | |||
| *] (singer and drummer, born 1977) | |||
| *] (pianist, born 1980) | |||
| *] (politician, born 1967) | |||
| *] (fencer, born 1991) | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Japan}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * {{in lang|ja}} | |||
| * - Official account of Takamatsu city about tourism. | |||
| *{{osmrelation-inline|4051287}} | |||
| *{{Wikivoyage inline|Takamatsu}} | |||
| *{{Commons category-inline|Takamatsu, Kagawa}} | |||
| == External link == | |||
| * in Japanese | |||
| {{Kagawa}} | {{Kagawa}} | ||
| {{Metropolitan cities of Japan}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Japan |
{{Most populous cities in Japan}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:31, 14 November 2024
For other uses, see Takamatsu (disambiguation). Core city in Shikoku, Japan| Takamatsu 高松市 | |
|---|---|
| Core city | |
 From top left: Central Takamatsu, Chūō dōri street, Takamatsu Castle, Marugame-machi shopping mall, Ritsurin Garden From top left: Central Takamatsu, Chūō dōri street, Takamatsu Castle, Marugame-machi shopping mall, Ritsurin Garden | |
 Flag Flag Seal Seal | |
| Location of Takamatsu in Kagawa Prefecture | |
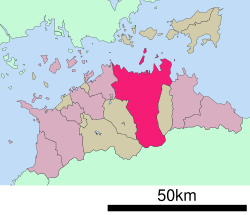 | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 34°21′N 134°3′E / 34.350°N 134.050°E / 34.350; 134.050 | |
| Country | |
| Region | Shikoku |
| Prefecture | Kagawa |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Hideto Ōnishi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 375.41 km (144.95 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 414,134 |
| • Density | 1,100/km (2,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) |
| City hall address | 1-8-15 Banchō, Takamatsu-shi, Kagawa-ken 760-8571 |
| Climate | Cfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Flower | Azalea |
| Tree | Pine |



Takamatsu (高松市, Takamatsu-shi, Japanese: [takaꜜmatsɯ]) is a capital city located in Kagawa Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 November 2022, the city had an estimated population of 414,134 in 190,120 households and a population density of 1,100 persons per km. The total area of the city is 375.41 square kilometres (144.95 sq mi). It is the capital city of the prefecture.
Geography
Takamatsu is located in central Kagawa Prefecture on the island of Shikoku. The city is located in the Takamatsu Plain, which is part of the Sanuki Plain, and is occupied by a gentle slope as a whole. The northern part faces the Seto Inland Sea, forming a semicircular urban area centered on Takamatsu Port and Takamatsu New Port (commonly known as Shinminato).The western part of the city consists of an alluvial fan formed by the sedimentation of the Koto River. The eastern part is a flooded plain formed by the Kasuga River and Shinkawa River. In the northeastern part of the island, there is Yashima, a table-shaped plateau protruding into the Seto Inland Sea, which was the site of the Battle of Yashima in the Genpei War, and Cape Takei, the northernmost tip of the main island of Shikoku. Parts of the city are located within the borders of the Setonaikai National Park. The city area also includes a number of small inhabited islands in the Seto Inland Sea.
Neighbouring municipalities
Kagawa Prefecture
Tokushima Prefecture
Climate
Takamatsu has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with hot, humid summers, and cool winters. Some rain falls throughout the year, but the months from May to September have the heaviest rain.
| Climate data for Takamatsu (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1941−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.9 (66.0) |
24.0 (75.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
30.9 (87.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
36.5 (97.7) |
38.2 (100.8) |
38.6 (101.5) |
37.6 (99.7) |
34.0 (93.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
21.2 (70.2) |
38.6 (101.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
10.5 (50.9) |
14.1 (57.4) |
19.8 (67.6) |
24.8 (76.6) |
27.5 (81.5) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
28.8 (83.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
17.5 (63.5) |
12.1 (53.8) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.9 (42.6) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.7 (58.5) |
19.8 (67.6) |
23.3 (73.9) |
27.5 (81.5) |
28.6 (83.5) |
24.7 (76.5) |
19.0 (66.2) |
13.2 (55.8) |
8.1 (46.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
2.2 (36.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
9.9 (49.8) |
15.1 (59.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.1 (77.2) |
21.2 (70.2) |
15.1 (59.2) |
9.1 (48.4) |
4.3 (39.7) |
12.8 (55.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.7 (18.1) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
7.5 (45.5) |
15.3 (59.5) |
15.8 (60.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 39.4 (1.55) |
45.8 (1.80) |
81.4 (3.20) |
74.6 (2.94) |
100.9 (3.97) |
153.1 (6.03) |
159.8 (6.29) |
106.0 (4.17) |
167.4 (6.59) |
120.1 (4.73) |
55.0 (2.17) |
46.7 (1.84) |
1,150.1 (45.28) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 0 (0) |
1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1 (0.4) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 7.5 | 8.0 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 9.4 | 11.5 | 10.5 | 7.9 | 10.5 | 9.3 | 7.8 | 7.9 | 111.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 63 | 63 | 62 | 62 | 64 | 72 | 73 | 70 | 72 | 70 | 69 | 66 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 141.4 | 143.8 | 175.0 | 194.5 | 210.1 | 158.2 | 191.8 | 221.2 | 159.6 | 164.6 | 145.5 | 142.7 | 2,046.5 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kōnan, Takamatsu (2003−2020 normals, extremes 2003−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.6 (61.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
25.2 (77.4) |
29.6 (85.3) |
31.9 (89.4) |
34.8 (94.6) |
36.0 (96.8) |
37.8 (100.0) |
35.5 (95.9) |
31.9 (89.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
37.8 (100.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.2 (46.8) |
9.3 (48.7) |
13.1 (55.6) |
18.8 (65.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
30.2 (86.4) |
31.7 (89.1) |
27.5 (81.5) |
21.9 (71.4) |
16.3 (61.3) |
10.5 (50.9) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.1 (39.4) |
4.9 (40.8) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.3 (55.9) |
18.3 (64.9) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.7 (80.1) |
22.8 (73.0) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.8 (53.2) |
6.5 (43.7) |
15.1 (59.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0.4 (32.7) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.9 (46.2) |
13.0 (55.4) |
17.7 (63.9) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
19.1 (66.4) |
13.3 (55.9) |
7.7 (45.9) |
2.7 (36.9) |
10.9 (51.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
2.9 (37.2) |
9.7 (49.5) |
16.3 (61.3) |
15.9 (60.6) |
11.0 (51.8) |
4.6 (40.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 41.0 (1.61) |
54.8 (2.16) |
84.8 (3.34) |
77.8 (3.06) |
105.5 (4.15) |
160.7 (6.33) |
193.2 (7.61) |
150.1 (5.91) |
214.4 (8.44) |
148.4 (5.84) |
64.4 (2.54) |
59.0 (2.32) |
1,353.9 (53.30) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6.6 | 8.4 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 8.3 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 8.7 | 10.2 | 8.5 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 108.1 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Per Japanese census data, the population of Takamatsu in 2020 is 417,496 people. Takamatsu has been conducting censuses since 1920.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 186,963 | — |
| 1925 | 199,141 | +6.5% |
| 1930 | 213,001 | +7.0% |
| 1935 | 222,545 | +4.5% |
| 1940 | 219,082 | −1.6% |
| 1945 | 246,809 | +12.7% |
| 1950 | 269,159 | +9.1% |
| 1955 | 284,684 | +5.8% |
| 1960 | 295,178 | +3.7% |
| 1965 | 307,549 | +4.2% |
| 1970 | 327,170 | +6.4% |
| 1975 | 360,024 | +10.0% |
| 1980 | 386,547 | +7.4% |
| 1985 | 401,020 | +3.7% |
| 1990 | 406,853 | +1.5% |
| 1995 | 412,626 | +1.4% |
| 2000 | 416,680 | +1.0% |
| 2005 | 418,125 | +0.3% |
| 2010 | 419,429 | +0.3% |
| 2015 | 420,748 | +0.3% |
| 2020 | 417,496 | −0.8% |
| Takamatsu population statistics | ||
History
The area of Takamatsu was part of ancient Sanuki Province. During the Heian and Kamakura period, as the closest port to Honshu from Shikoku island, the area was a transportation center and gateway for pilgrims to the Kotohira Shrine. During the Sengoku period, Ikoma Chikamasa suit the first Takamatsu Castle in 1588. In 1642, Matsudaira Yorishige, the son of Tokugawa Yorifusa of Mito Domain and grandson of Tokugawa Ieyasu, was awarded the 120,000 koku Takamatsu Domain, which his descendants would continue to rule until the Meiji restoration.
Following the Meiji restoration, the city of Takamatsu was created with the establishment of the modern municipalities system on February 15, 1890. The castle tower formerly used as the symbol of the city was destroyed during the Meiji period. The city borders expanded in several iterations by the annexation on neighboring villages and towns. During World War II, Takamatsu was selected as a target by the United States' XXI Bomber Command because the city was an important focal point of Shikoku's rail and road transit systems, and containing some industry vital to supporting the war effort. On July 3, 1945, at 6:40 pm (JST) 128 B-29 Superfortress bombers dropped over 800 tons of incendiary bombs on Takamatsu, destroying 78% of the built-up areas of the city and killing 1359 people.
The city quickly recovered after the war, and its borders continued to expand. On April 1, 1999, it was designated a core city with increased local autonomy.
On September 26, 2005, the town of Shionoe (from Kagawa District) was merged into Takamatsu. On January 10, 2006, Takamatsu absorbed the following towns: Aji and Mure (from Kita District), Kagawa and Kōnan (from Kagawa District), and Kokubunji (from Ayauta District).
Government
Takamatsu has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 40 members. Takamatsu contributes 15 members to the Kagawa Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is divided between Kagawa 1st district and Kagawa 2nd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Crime and safety
The Shinwa-kai yakuza syndicate is based in Takamatsu. The Shinwa-kai is the only designated yakuza group based in the Shikoku region.
In October 2017, Japan Today reported five people received minor injuries when a wild boar entered a local Aeon mall.
Economy

Takamatsu is the largest municipality in Shikoku and is a city with a large concentration of nationwide companies' branch offices, which play a large role in its economy. It also contains most of the national government's branch offices for Shikoku. In 2004, construction of the Symbol Tower, the new symbol of Takamatsu, was completed. The Symbol Tower is in the Sunport area of the city. The Symbol Tower is the tallest building in Takamatsu, and is right next to another tall building The JR Clement Hotel (formerly the ANA Clement Hotel), which is also part of the Sunport complex. Sunport Takamatsu is also connected to the ports of Takamatsu.
Companies headquartered in the city include:
- Shikoku Railway Company
- Shikoku Shimbun
- Tadano Limited
Education
Takamatsu has 48 public elementary schools, 22 public middle schools and one public high school operated by the city government. The city has eight public high schools and one combined middle/high school operated by the Kagawa Prefectural Board of Education. There are also two private combined middle/high schools, seven private high schools and one national elementary, one national middle and one national high school. The Kagawa Prefectural government also operates three special education schools for the handicapped.
Universities
Transportation
The main train station is Takamatsu Station, operated by JR Shikoku. Trains from here run to destinations around Shikoku, as well as Okayama Station on Honshū via the Seto-Ōhashi Bridge. The private Kotoden railway connects much of Takamatsu, with a hub and department store at Kawaramachi Station, and Takamatsu-Chikko Station nearby Takamatsu Station. Buses and trains operated by Kotoden accept a contactless payment card for travel called an IruCa.
Airports
Railways
![]() Shikoku Railway Company - Yosan Line
Shikoku Railway Company - Yosan Line
![]() Shikoku Railway Company - Kōtoku Line
Shikoku Railway Company - Kōtoku Line
- Sanuki-Mure - Yakuriguchi - Furutakamatsu-Minami - Yashima - Kitachō - Ritsurin - Ritsurin-Kōen-Kitaguchi - Shōwachō - Takamatsu
![]() Takamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotoden Kotohira Line
Takamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotoden Kotohira Line
- Takamatsu-Chikkō- Kataharamachi - Kawaramachi - Ritsurin-Kōen - Sanjō - Fuseishi - Ōta - Busshōzan - Kūkō-dōri - Ichinomiya - Enza - Okamoto
![]() Takamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotoden Nagao Line
Takamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotoden Nagao Line
- (Takamatsu-Chikkō - Kataharamachi) - Kawaramachi - Hanazono - Hayashimichi - Kita-Higashiguchi - Motoyama - Mizuta - Nishi-Maeda -Takata
![]() Takamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotoden Shido Line
Takamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotoden Shido Line
- Kawaramachi - Imabashi - Matsushima-Nichōme - Oki-Matsushima - Kasugagawa - Katamoto - Kotoden-Yashima - Furu-Takamatsu - Yakuri - Rokumanji - Ōmachi - Yakuri-Shinmichi - Shioya - Fusazaki - Hara
Highways
 Takamatsu Expressway
Takamatsu Expressway National Route 11
National Route 11 National Route 30
National Route 30 National Route 32
National Route 32 National Route 193
National Route 193 National Route 377
National Route 377 National Route 436
National Route 436 National Route 492
National Route 492
Ports
Local attractions
- Ritsurin Garden, a Japanese garden designated as a Special Place of Scenic Beauty by the Japanese government
- Takamatsu Castle is known for using seawater in its moat and recently the old keep of the castle was successfully restored and opened for public viewing.
- Yashima plateau which is home to various sightseeing spots. At the base of the mountain is the open air museum Shikoku Mura where aspects of regional history and culture are exhibited. On the mountain itself is Yashima-ji, number 84 of the Shikoku pilgrimage. At the top of the mountain there is also an observation deck which offers views across the Seto Inland Sea.
- Takamatsu also acts as a hub to access various islands of the Seto Inland Sea. These include, Megijima, Ogijima, Naoshima, Teshima and Shōdoshima. Since 2010, Takamatsu, along with these islands and more, has been host to the Setouchi Triennale, a contemporary art festival with many outdoor exhibitions by prominent artists from across the world.
Sports teams
- Kagawa Five Arrows (Basketball, B.League)
- Kagawa Ice Fellows (Ice Hockey)
- Kagawa Olive Guyners (Baseball)
- Kamatamare Sanuki (Football)
International relations
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in JapanTwin towns – sister cities
Takamatsu is twinned with:
 St. Petersburg, United States
St. Petersburg, United States Tours, France
Tours, France
Friendship cities
Takamatsu has friendship arrangements with:
 Nanchang, China, since 1990
Nanchang, China, since 1990
In literature

- Takamatsu is the main setting for Haruki Murakami's novel Kafka on the Shore.
- The naval commander Tameichi Hara, born in Takamatsu in 1900, recounts his childhood there in the memoir Japanese Destroyer Captain.
- Takamatsu is the main setting for the manga and anime Poco's Udon World.
Notable people from Takamatsu
The following politicians, celebrities, and other well-known people are from Takamatsu (listed alphabetically by surname):
- Ema Fujisawa (actor, born 1982)
- Shinichiro Furumoto (politician, born 1956)
- Yoshihiro Hamaguchi (Olympic athlete, 1926–2011)
- Takuya Hirai (politician, born 1958)
- Ikuko Kawai (musician and composer, born 1968)
- Kan Kikuchi (writer and publisher, 1888–1948)
- Akiko Kinouchi (actor, born 1981)
- Makoto Kitano (soccer player, born 1967)
- Kenji Kobayashi (shogi player, born 1957)
- Akihito Kondo (baseball player, 1938–2019)
- Yasuhiro Konishi (karateka, 1893–1983)
- Bukichi Miki (politician, 1884–1956)
- Ryuki Miki (tennis player, 1904–1967)
- Lu Wanyao (golfer, born 1996)
- Yoshiro Maeda (mixed martial artist, born 1981)
- Shigeru Makino (baseball player, 1928–1984)
- Ryuya Matsumoto (baseball player, born 1994)
- Kojin Nakakita (sledge hockey coach, born 1963)
- Futoshi Nakanishi (baseball player, born 1933)
- Kiyotaka Nanbara (comedian and TV personality, born 1965)
- Ayano Ninomiya (violinist, born 1971)
- Tetsuya Noguchi (artist, born 1980)
- Junya Ogawa (politician, born 1971)
- Kentaro Sonoura (politician, born 1972)
- Mikuru Suzuki (darts player, born 1982)
- Daisuke Tsuda (singer and drummer, born 1977)
- Ayako Uehara (pianist, born 1980)
- Emiko Uematsu (politician, born 1967)
- Satoru Uyama (fencer, born 1991)
See also
References
- "Takamatsu city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved April 24, 2022.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved April 24, 2022.
- ^ Takamatsu population statistics
- Nakayama, Yoshiaki (2015). 江戸三百藩大全 全藩藩主変遷表付. Kosaido Publishing. ISBN 978-4331802946.(in Japanese)
- "21st Bomber Command Tactical Mission Report 247, 250, Ocr | Aviation | Armed Conflict".
- "2021 Police White Paper Chapter 2 : Furtherance of Organized Crime Countermeasures", 2021, National Police Agency (in Japanese)
- "5 injured after wild boar goes on rampage through Kagawa mall, 2007, Japan Today (in English)
- "Company Information Archived 2010-03-24 at the Wayback Machine." Shikoku Railway Company. Retrieved on March 27, 2010.
- "Corporate Profile Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine." Tadano Limited. Retrieved on April 15, 2015.
- "Takamatsu Japan, what to do there". 20 December 2009. Retrieved 2010-03-13.
- 高松城天守閣復元. www.takamatsujyo.com. Retrieved 2016-01-19.
- "St. Petersburg". Takamatsu city. Archived from the original on 2009-06-11. Retrieved 2009-05-26.
- "Tours". Takamatsu city. Archived from the original on 2009-06-11. Retrieved 2009-05-26.
- "Nanchang". Takamatsu city. Archived from the original on 2009-06-11. Retrieved 2009-05-26.
- "Nanchang City and Sister Cities Intercommunion". Nanchang Municipal Party Committee of the CPC and Nanchang Municipal Government. Nanchang Economic Information Center. Archived from the original on 2013-05-22. Retrieved 2013-11-05.
- Hara, Tameichi (1961). "Born A Samurai". Japanese Destroyer Captain. New York & Toronto: Ballantine Books. ISBN 978-1-59114-354-3. OCLC 255849609.
External links
- Takamatsu City official website (in Japanese)
- Experience Takamatsu-Sense of Wonder- - Official account of Takamatsu city about tourism.
 Geographic data related to Takamatsu at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Takamatsu at OpenStreetMap Takamatsu travel guide from Wikivoyage
Takamatsu travel guide from Wikivoyage Media related to Takamatsu, Kagawa at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Takamatsu, Kagawa at Wikimedia Commons
| Takamatsu (capital) | ||
| Core city | ||
| Cities | ||
| Districts | ||
| Others | ||
| List of mergers in Kagawa Prefecture | ||
| Metropolitan cities of Japan | |
|---|---|
| also a prefectural capital; eligible for core city status but not yet nominated; to become core cities |