| Revision as of 02:21, 18 December 2008 editPvkeller (talk | contribs)389 editsmNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:34, 19 November 2024 edit undoSnowFire (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers26,359 edits partially undo old, non-standard change from 2021 to reference headings.. although separating out the long citations is still a little odd. | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Hypothetical type of nuclear reaction}} | |||
| {{articleissues|pov = October 2008|rewrite=October 2008|citationstyle=November 2008|weasel = November 2008}} | |||
| {{Hatnote group|{{About|the Fleischmann–Pons claims of nuclear fusion at room temperature, and subsequent research|the original use of the term "cold fusion"|muon-catalyzed fusion|all other definitions|Cold fusion (disambiguation)}} | |||
| ] (2005)]] | |||
| {{Distinguish|cold welding}} | |||
| {{dablink|This article refers to a purported type of nuclear fusion. For the programming language, see ] . Also see ].}} | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Cold fusion''' is a purported type of ] in which fusion reactions occur at room temperature under special conditions. Whereas typical reactions require high temperatures or a ] in order to overcome the repulsive forces that inhibit fusion, cold fusion is hypothesized to occur without these by use of special apparatus. The field is also known as '''low energy nuclear reactions''' (LENR) or '''condensed matter nuclear science'''. | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2019}} | |||
| ] used at the New Hydrogen Energy Institute in Japan]] | |||
| '''Cold fusion''' is a hypothesized type of ] that would occur at, or near, ]. It would contrast starkly with the ] that is known to take place naturally within ] and artificially in ] and prototype ] under immense pressure and at temperatures of millions of degrees, and be distinguished from ]. There is currently no accepted theoretical model that would allow cold fusion to occur. | |||
| The field gained attention in 1989, when ] and ] reported producing a tabletop nuclear fusion reaction at the University of Utah.<ref name="FleischmannPons_1989_301">{{harvnb|Fleischmann|Pons|1989|p=301}}</ref> In their press conferences and papers, they reported the observation of anomalous heating ("excess heat") of an electrolytic cell during ] of ] using ] (Pd) electrodes, and proposed that this heating was caused by ] of ] (D). Their report raised hopes of a cheap and abundant source of energy.<ref name="Browne_1989_para1">{{harvnb|Browne|1989|loc=para. 1}}</ref> | |||
| In 1989, two ] at the University of Utah, ] and ], reported that their apparatus had produced anomalous heat ("excess heat") of a magnitude they asserted would defy explanation except in terms of nuclear processes.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| Cold fusion gained a reputation as ] after several researchers presented reports of failed replication attempts at conferences and in journals, and because of the known difficulty of overcoming nuclear repulsion forces.<ref>{{harvnb|Voss|1999}}, {{harvnb|Platt|1998}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993}}, {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}</ref> Cold fusion research continues,<ref>{{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004}},{{harvnb|Van Noorden|2007}}</ref> but most scientists remain skeptical.<ref>{{harvnb|Beaudette|2002}}, {{harvnb|Feder|2005}}, {{harvnb|Hutchinson|2006}}, {{harvnb|Kruglinksi|2006}}, {{harvnb|Biberian|2007}}</ref> | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |title = 60 Minutes: Once Considered Junk Science, Cold Fusion Gets A Second Look By Researchers | |||
| |url = https://www.cbsnews.com/news/cold-fusion-is-hot-again/ | |||
| |publisher = ] | |||
| |date = 17 April 2009 | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120212001503/http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2009/04/17/60minutes/main4952167.shtml | |||
| |archive-date = 12 February 2012 | |||
| }}</ref> They further reported measuring small amounts of nuclear reaction byproducts, including ] and ].<ref name=FP1989>{{harvnb|Fleischmann|Pons|1989|p=301}} ("It is inconceivable that this could be due to anything but nuclear processes... We realise that the results reported here raise more questions than they provide answers...")</ref> The small tabletop experiment involved ] of ] on the surface of a ] (Pd) electrode.{{sfn|ps=|Voss|1999a}} The reported results received wide media attention{{sfn|ps=|Voss|1999a}} and raised hopes of a cheap and abundant source of energy.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989|loc=para. 1}} | |||
| Many scientists tried to ] the experiment with the few details available. Expectations diminished as a result of numerous failed replications, the retraction of several previously reported positive replications, the identification of methodological flaws and experimental errors in the original study, and, ultimately, the confirmation that Fleischmann and Pons had not observed the expected nuclear reaction byproducts.<ref>{{harvnb|Browne|1989}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993}}</ref> By late 1989, most scientists considered cold fusion claims dead,{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}}<ref name="most scientists">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=262, 265–266, 269–270, 273, 285, 289, 293, 313, 326, 340–344, 364, 366, 404–406}}, {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}, {{harvnb|Van Noorden|2007}}, {{harvnb|Kean|2010}}</ref> and cold fusion subsequently gained a reputation as ].<ref name="nytdoe"> | |||
| The majority of a review panel organized by the ] (DOE) in 1989 found that the evidence for the discovery of a new nuclear process was not persuasive. In 2004, the DOE convened a second cold fusion review panel which reached conclusions that were similar to those of the 1989 panel.<ref>{{harvnb|Choi|2005}}, {{harvnb|Feder|2005}}, {{harvnb|US DOE|2004|Ref=DOE2004r}}</ref> | |||
| {{cite news|mode=cs2 | |||
| |date=25 March 2004 | |||
| |title=US will give cold fusion a second look | |||
| |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2004/03/25/us/us-will-give-cold-fusion-second-look-after-15-years.html | |||
| |newspaper=The New York Times | |||
| |access-date=8 February 2009 | |||
| | first=Kenneth | |||
| | last=Chang | |||
| }}</ref><ref name="Ouellette"> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |date = 23 December 2011 | |||
| |title = Could Starships Use Cold Fusion Propulsion? | |||
| |url = http://news.discovery.com/space/could-interstellar-starships-use-cold-fusion-propulsion-111223.html | |||
| |work = Discovery News | |||
| |first = Jennifer | |||
| |last = Ouellette | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120107185538/http://news.discovery.com/space/could-interstellar-starships-use-cold-fusion-propulsion-111223.html | |||
| |archive-date = 7 January 2012 | |||
| }}</ref> In 1989 the ] (DOE) concluded that the reported results of excess heat did not present convincing evidence of a useful source of energy and decided against allocating funding specifically for cold fusion. A second DOE review in 2004, which looked at new research, reached similar conclusions and did not result in DOE funding of cold fusion.<ref>{{harvnb|US DOE|2004}}, {{harvnb|Choi|2005}}, {{harvnb|Feder|2005}}</ref> Presently, since articles about cold fusion are rarely published in ] mainstream ]s, they do not attract the level of scrutiny expected for mainstream ].<ref>{{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}, {{harvnb|Labinger|Weininger|2005|p=1919}}</ref> | |||
| Nevertheless, some interest in cold fusion has continued through the decades—for example, a Google-funded failed replication attempt was published in a 2019 issue of ].<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|last=Koziol|first=Michael|date=22 March 2021|title=Whether Cold Fusion or Low-Energy Nuclear Reactions, U.S. Navy Researchers Reopen Case|url=https://spectrum.ieee.org/cold-fusion-or-low-energy-nuclear-reactions-us-navy-researchers-reopen-case|access-date=2021-03-23|website=IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Berlinguette | first1 = C.P. | last2 = Chiang | first2 = YM. | last3 = Munday | first3 = J.N. | display-authors = etal | year = 2019| title = Revisiting the cold case of cold fusion | url = | journal = Nature | volume = 570 | issue = 7759| pages = 45–51 | doi = 10.1038/s41586-019-1256-6 | pmid = 31133686 | bibcode = 2019Natur.570...45B | s2cid = 167208748 }}</ref> A small community of researchers continues to investigate it,{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}}<ref name=Broad1989b/><ref name="small community">{{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}, {{harvnb|Platt|1998}}, {{harvnb|Voss|1999a}}, {{harvnb|Beaudette|2002}}, {{harvnb|Feder|2005}}, {{harvnb|Adam|2005}} "Advocates insist that there is just too much evidence of unusual effects in the thousands of experiments since Pons and Fleischmann to be ignored", {{harvnb|Kruglinski|2006}}, {{harvnb|Van Noorden|2007}}, {{harvnb|Alfred|2009}}. {{harvnb|Daley|2004}} calculates between 100 and 200 researchers, with damage to their careers.</ref> often under the alternative designations ''low-energy nuclear reactions'' (''LENR'') or ''condensed matter nuclear science'' (''CMNS'').<ref name="ACS Press Release"> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |url = http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2009-03/acs-fr031709.php | |||
| |title = 'Cold fusion' rebirth? New evidence for existence of controversial energy source | |||
| |publisher = ] | |||
| |url-status = live | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20141221073942/http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2009-03/acs-fr031709.php | |||
| |archive-date = 21 December 2014 | |||
| }}</ref>{{sfn|ps=|Hagelstein|McKubre|Nagel|Chubb|2004}}<ref>{{cite web |title=ICMNS FAQ |url=http://www.iscmns.org/FAQ.HTM#ref2 |publisher=International Society of Condensed Matter Nuclear Science |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20151103020057/http://iscmns.org/FAQ.HTM#ref2 |archive-date=3 November 2015}}</ref>{{sfn|ps=|Biberian|2007}} | |||
| == |
==History== | ||
| ] is normally understood to occur at temperatures in the tens of millions of degrees. This is called "]". Since the 1920s, there has been speculation that nuclear fusion might be possible at much lower temperatures by ] fusing hydrogen absorbed in a metal catalyst. In 1989, a claim by Stanley Pons and Martin Fleischmann (then one of the world's leading ]) that such cold fusion had been observed caused a brief ] before the majority of scientists criticized their claim as incorrect after many found they could not replicate the excess heat. Since the initial announcement, cold fusion research has continued by a small community of researchers who believe that such reactions happen and hope to gain wider recognition for their experimental evidence. | |||
| === Early work === | |||
| The special ability of palladium to absorb hydrogen was recognized as early as the nineteenth century by ].<ref name="DOE_1989_7">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|p=7}}</ref> In the late nineteen-twenties, two ]n born scientists, ] and ], originally reported the transformation of hydrogen into helium by spontaneous nuclear catalysis when hydrogen was absorbed by finely divided palladium at room temperature. However, the authors later acknowledged that the helium they measured was due to background from the air.<ref>{{harvnb|Paneth and Peters|1926|Ref=CITEREFPanethPeters1926}}</ref><ref name="DOE_1989_7" /> | |||
| ===Early research=== | |||
| In 1927, ] scientist J. Tandberg stated that he had fused hydrogen into helium in an ] with palladium electrodes.<ref name="DOE_1989_7"/> On the basis of his work, he applied for a Swedish patent for "a method to produce helium and useful reaction energy". After deuterium was discovered in 1932, Tandberg continued his experiments with ]. Due to Paneth and Peters' retraction, Tandberg's patent application was eventually denied.<ref name="DOE_1989_7"/> | |||
| The ability of ] was recognized as early as the nineteenth century by ].{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=7}}<ref>{{Cite journal|title = On the Absorption and Dialytic Separation of Gases by Colloid Septa|journal = Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London|date = 1 January 1866|issn = 0261-0523|pages = 399–439|volume = 156|doi = 10.1098/rstl.1866.0018|first = Thomas|last = Graham|doi-access = free}}</ref> In the late 1920s, two Austrian-born scientists, ] and ], originally reported the transformation of hydrogen into helium by nuclear catalysis when hydrogen was absorbed by finely divided palladium at room temperature. However, the authors later retracted that report, saying that the helium they measured was due to background from the air.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=7}}{{sfn|ps=|Paneth|Peters|1926}} | |||
| In 1927, Swedish scientist John Tandberg reported that he had fused hydrogen into helium in an ] with palladium electrodes.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=7}} On the basis of his work, he applied for a Swedish patent for "a method to produce helium and useful reaction energy".{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=7}} Due to Paneth and Peters's retraction and his inability to explain the physical process, his patent application was denied.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=7}}<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303210020/http://www.nyteknik.se/popular_teknik/smatt_gott/article3092779.ece |date=3 March 2016 }}, Ny Teknik, Kaianders Sempler, 9 February 2011</ref> After ] was discovered in 1932, Tandberg continued his experiments with ].{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=7}} The final experiments made by Tandberg with heavy water were similar to the original experiment by Fleischmann and Pons.<ref name="similar_to_tandberg">{{harvnb|Pool|1989}}, {{harvnb|Wilner|1989}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=19–21}} {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=13–14, 271}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993|p=214}}</ref> Fleischmann and Pons were not aware of Tandberg's work.<ref>{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=13–14}}</ref><ref group="text" name="tandberg_not_known_by_FP" /><ref group="text" name="tandberg_not_known_by_FP2" /> | |||
| The term "cold fusion" was coined by ] of ] in 1986 in an investigation of "geo-fusion", or the possible existence of fusion in a ].<ref name="Kowalski_2004_IIA2">{{harvnb|Kowalski|2004|loc=II.A2}}</ref> | |||
| The term "cold fusion" was used as early as 1956 in an article in ''The New York Times'' about ]'s work on ].{{sfn|ps=|Laurence|1956}} ] and then ] of ] used the term "cold fusion" in 1986 in an investigation of "geo-fusion", the possible existence of fusion involving hydrogen isotopes in a ].{{sfn|ps=|Kowalski|2004|loc=II.A2}} In his original paper on this subject with Clinton Van Siclen, submitted in 1985, Jones had coined the term "piezonuclear fusion".{{sfn|ps=|Kowalski|2004|loc=II.A2}}<ref>C. DeW. Van Siclen and S. E. Jones, "Piezonuclear fusion in isotopic hydrogen molecules," J. Phys. G: Nucl. Phys. 12: 213–221 (March 1986).</ref> | |||
| === Fleischmann-Pons announcement === | |||
| {{Main|Fleischmann-Pons experiment}} | |||
| Fleischmann and Pons were invesitgating a hypothesis that collective effects in ], which would require ] to calculate, might influence nuclear processes more than predicted by ] calculations.<ref>{{harvnb|Leggett|1989}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Fleischmann–Pons experiment=== | |||
| Their experimental apparatus was a calorimeter, an insulated vessel used for measuring process heat. Within the vessel was a palladium catchode which they used for ] of heavy water to produce deuterium and oxygen, which were allowed to leave the cell carrying along some heat. It was necessary to replenish the cell with ] at regular intervals.<ref name="FleischmannPons_1989_301"/> A current was applied to the cell continuously for many weeks. For most of the time, the power input to the cell was equal to the energy leaving the cell within measurement accuracy, and the cell temperature was stable at around 30 °C. But then, at some point (and in some of the experiments), the temperature rose suddenly to about 50 °C without changes in the input power, for durations of 2 days or more. The generated power was signifanclty higher the input power during these power bursts. Eventually the power bursts in any one cell would no longer occur and the cell was turned off.<ref name="FleischmannPons_1989_301"/> | |||
| The most famous cold fusion claims were made by Stanley Pons and Martin Fleischmann in 1989. After a brief period of interest by the wider scientific community, their reports were called into question by nuclear physicists. Pons and Fleischmann never retracted their claims, but moved their research program from the US to France after the controversy erupted. | |||
| ====Events preceding announcement==== | |||
| In 1988, Fleischmann and Pons applied to the ] for funding towards a larger series of experiments. Up to this point they had been funding their experiments using a small device built with $100,000 ].<ref name="LADN_092489">{{harvnb|Crease|Samios|1989|p=V1}}</ref> The grant proposal was turned over for ], and one of the reviewers was ] of ].<ref name="LADN_092489"/> Jones had worked on ] for some time, and had written an article on the topic entitled "Cold nuclear fusion" that had been published in '']'' in July 1987. Fleischmann and Pons and co-workers met with Jones and co-workers on occasion in ] to share research and techniques. During this time, Fleischmann and Pons described their experiments as generating considerable "excess energy", in the sense that it could not be explained by ]s alone.<ref name = "vxuvtq">{{harvnb|Fleischmann et al.|1990|Ref=Fleischmann1990|p=293}}</ref> They felt that such a discovery could bear significant commercial value and would be entitled to ]. Jones, however, was measuring neutron flux, which was not of commercial interest.<ref name="LADN_092489"/> In order to avoid problems in the future, the teams appeared to agree to simultaneously publish their results, although their accounts of their ] meeting differ.<ref name="Lewenstein-1994_8">{{harvnb|Lewenstein|1994|p=8}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] of the ] and ] of the ] hypothesized that the high compression ratio and mobility of ] that could be achieved within palladium metal using electrolysis might result in nuclear fusion.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|1989|p=301}} To investigate, they conducted electrolysis experiments using a palladium cathode and heavy water within a ], an insulated vessel designed to measure process heat. Current was applied continuously for many weeks, with the ] being renewed at intervals.{{sfn |ps= |Fleischmann |Pons |1989 |p=301}} Some deuterium was thought to be accumulating within the cathode, but most was allowed to bubble out of the cell, joining oxygen produced at the anode.{{sfn |ps= |Fleischmann |Pons |Anderson |Li |1990}} For most of the time, the power input to the cell was equal to the calculated power leaving the cell within measurement accuracy, and the cell temperature was stable at around 30 °C. But then, at some point (in some of the experiments), the temperature rose suddenly to about 50 °C without changes in the input power. These high temperature phases would last for two days or more and would repeat several times in any given experiment once they had occurred. The calculated power leaving the cell was significantly higher than the input power during these high temperature phases. Eventually the high temperature phases would no longer occur within a particular cell.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990}} | |||
| In 1988, Fleischmann and Pons applied to the ] for funding towards a larger series of experiments. Up to this point they had been funding their experiments using a small device built with $100,000 ].{{sfn|ps=|Crease|Samios|1989|p=V1}} The grant proposal was turned over for ], and one of the reviewers was ] of ].{{sfn|ps=|Crease|Samios|1989|p=V1}} Jones had worked for some time on ], a known method of inducing nuclear fusion without high temperatures, and had written an article on the topic entitled "Cold nuclear fusion" that had been published in '']'' in July 1987. Fleischmann and Pons and co-workers met with Jones and co-workers on occasion in ] to share research and techniques. During this time, Fleischmann and Pons described their experiments as generating considerable "excess energy", in the sense that it could not be explained by ]s alone.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990}} They felt that such a discovery could bear significant commercial value and would be entitled to ] protection. Jones, however, was measuring neutron flux, which was not of commercial interest.{{sfn|ps=|Crease|Samios|1989|p=V1}}{{clarify|date=November 2015}} To avoid future problems, the teams appeared to agree to publish their results simultaneously, though their accounts of their 6 March meeting differ.{{sfn|ps=|Lewenstein|1994|pp=8–9}} | |||
| In mid-March, both research teams were ready to publish their findings, and Fleischmann and Jones had agreed to meet at an airport on ] to send their papers to '']'' via ].<ref name="Lewenstein-1994_8"/> Fleischmann and Pons, however, broke their apparent agreement, submitting their paper to the ''Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry'' on ], and disclosing their work via a press conference on March 23.<ref name="LADN_092489"/> Jones, upset, faxed in his paper to ''Nature'' after the press conference.<ref name="Lewenstein-1994_8"/> | |||
| ====Announcement==== | |||
| === Reaction to the announcement === | |||
| In mid-March 1989, both research teams were ready to publish their findings, and Fleischmann and Jones had agreed to meet at an airport on 24 March to send their papers to '']'' via ].{{sfn|ps=|Lewenstein|1994|pp=8–9}} Fleischmann and Pons, however, pressured by the University of Utah, which wanted to establish priority on the discovery,<ref name="utah patent"/> broke their apparent agreement, disclosing their work at a press conference on 23 March<ref name="nature-lessons">{{Cite journal |last=Ball |first=Philip |date=2019-05-27 |title=Lessons from cold fusion, 30 years on |journal=Nature |language=EN |volume=569 |issue=7758 |pages=601 |doi=10.1038/d41586-019-01673-x|pmid=31133704 |bibcode=2019Natur.569..601B |doi-access=free }}</ref> (they claimed in the press release that it would be published in ''Nature''<ref name="nature-lessons" /> but instead submitted their paper to the ''Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry'').{{sfn|ps=|Crease|Samios|1989|p=V1}} Jones, upset, faxed in his paper to '']'' after the press conference.{{sfn|ps=|Lewenstein|1994|pp=8–9}} | |||
| Fleischmann and Pons' anouncement drew wide media attention. Scores of laboratories in the United States and abroad attempted to repeat the experiments.<ref name="Browne_1989"/> A few reported success, many others failure.<ref name="Browne_1989"/> Even those reporting success had difficulty reproducing Fleischmann and Pons' results.<ref name="Kee_1999_1">{{harvnb|Kee|1999|p=1}}</ref> One of the more promonent reports of success came from a group at the ], which observed neutron production.<ref name="Broad_1989">{{harvnb|Broad|1989}}</ref>. The Georgia Institute of Technology group later retracted their announcement.<ref name="Wilford_1989">{{harvnb|Wilford|1989}}</ref> For weeks, competing claims, counterclaims and suggested explanations kept what was referred to as "cold fusion" or "fusion confusion" in the news.<ref>{{harvnb|Bowen|1989}}</ref> | |||
| Fleischmann and Pons' announcement drew wide media attention,{{refn|group="notes"|name=Brooks|For example, in 1989, the ''Economist'' editorialized that the cold fusion "affair" was "exactly what science should be about."<ref>{{Cite book|mode=cs2|first=J. K.|last=Footlick|title=Truth and Consequences: how colleges and universities meet public crises|isbn=978-0-89774-970-1|page= |location=Phoenix|publisher=Oryx Press |year=1997 |url=https://archive.org/details/truthconsequence0000foot/page/51}} as cited in {{Cite book|mode=cs2 |first=M|last=Brooks|title=13 Things That Don't Make Sense|isbn=978-1-60751-666-8 |page=67|location=New York|publisher=]|year=2008|title-link=13 Things That Don't Make Sense}}</ref>}} as well as attention from the scientific community. The 1986 discovery of ] had made scientists more open to revelations of unexpected but potentially momentous scientific results that could be replicated reliably even if they could not be explained by established theories.<ref>{{harvnb|Simon|2002|pp=57–60}}, {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}</ref> Many scientists were also reminded of the ], a process involving ] in a solid. Its discovery 30 years earlier had also been unexpected, though it was quickly replicated and explained within the existing physics framework.{{sfn|ps=|Goodstein|1994}} | |||
| In May 1989, the ] held a session on cold fusion, at which were heard many reports of experiments that failed to produce evidence of cold fusion. At the end of the session, eight of the nine leading speakers stated they considered the initial Fleischmann and Pons' claim dead.<ref name="Browne_1989">{{harvnb|Browne|1989}}</ref>. | |||
| The announcement of a new purported clean source of energy came at a crucial time: adults still remembered the ] and the problems caused by oil dependence, anthropogenic ] was starting to become notorious, the ] was labeling nuclear power plants as dangerous and getting them closed, people had in mind the consequences of ], ], the ] and the ], which happened the day after the announcement.<ref>{{harvnb|Petit|2009}}, {{harvnb|Park|2000|p=16}}</ref> In the press conference, ], Fleischmann and Pons, backed by the solidity of their scientific credentials, repeatedly assured the journalists that cold fusion would solve environmental problems, and would provide a limitless inexhaustible source of clean energy, using only seawater as fuel.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=xviii–xx}}, {{harvnb|Park|2000|p=16}}</ref> They said the results had been confirmed dozens of times and they had no doubts about them.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=xx–xxi}} In the accompanying press release Fleischmann was quoted saying: "What we have done is to open the door of a new research area, our indications are that the discovery will be relatively easy to make into a usable technology for generating heat and power, but continued work is needed, first, to further understand the science and secondly, to determine its value to energy economics."{{sfn|ps=|Scanlon|Hill|1999|p=212}} | |||
| In April 1989, Fleischmann and Pons published a "preliminary note" in the ''Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry''.<ref name="FleischmannPons_1989_301"/> This paper notably showed a gamma peak without its corresponding ], which indicated a mistake indicating they had not detected gamma radiation as they had claimed.<ref>{{harvnb|Tate|1989|p=1}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Platt|1998}}</ref> The "preliminary note" was followed up a year later with a much longer paper that went into details of calorimetry but did not include any nuclear measurements.<ref name = "vxuvtq"/> | |||
| ====Response and fallout==== | |||
| In July and November 1989, ''Nature'' published papers critical of cold fusion claims.<ref>{{harvnb|Gai et al.|Ref=Gai1989|1989|pp=29-34}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Williams et al.|1989|Ref=Williams1989|pp=375-384}}</ref> | |||
| Although the experimental protocol had not been published, physicists in several countries attempted, and failed, to replicate the excess heat phenomenon. The first paper submitted to ''Nature'' reproducing excess heat, although it passed peer review, was rejected because most similar experiments were negative and there were no theories that could explain a positive result;<ref group="notes" name="Beaudette rejection"/>{{sfn|ps=|Beaudette|2002|pp=183, 313}} this paper was later accepted for publication by the journal ''Fusion Technology''. | |||
| ], professor of chemistry at the ], led one of the most ambitious validation efforts, trying many variations on the experiment without success,<ref name="CAB">{{cite web |last=Aspaturian |first=Heidi |date=14 December 2012<!-- pdf metadata, archive record page updated 2012-12-26 --> |title=Interview with Charles A. Barnes on 13 and 26 June 1989 |publisher=The Caltech Institute Archives |url=http://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechOH:OH_Barnes_C_coldfusion |access-date=22 August 2014}}</ref> while ] physicist Douglas R. O. Morrison said that "essentially all" attempts in Western Europe had failed.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}} Even those reporting success had difficulty reproducing Fleischmann and Pons' results.{{sfn|ps=|Schaffer|1999|p=2}} On 10 April 1989, a group at ] published results of excess heat and later that day a group at the ] announced neutron production—the strongest replication announced up to that point due to the detection of neutrons and the reputation of the lab.<ref name=Broad1989a/> On 12 April Pons was acclaimed at an ACS meeting.<ref name=Broad1989a/> But Georgia Tech retracted their announcement on 13 April, explaining that their neutron detectors gave false positives when exposed to heat.<ref name=Broad1989a/>{{sfn|ps=|Wilford|1989}} | |||
| Nevetherless, Fleischmann and Pons', Steven E. Jones, and others who found positive results stood by their experimental findings.<ref name="Browne_1989"/> In August of 1989, the state of Utah invested $4.5 million to create the National Cold Fusion Institute.<ref>{{harvnb|Joyce|1990}}</ref> | |||
| Another attempt at independent replication, headed by ] at ], which also reported early success with a light water control,<ref>Broad, William J. 19 April 1989. , '']''.</ref> became the only scientific support for cold fusion in 26 April US Congress hearings.<ref group="text" name="only-support"/> But when he finally presented his results he reported an excess heat of only one degree ], a result that could be explained by chemical differences between heavy and light water in the presence of lithium.<ref group="notes" name="differences"/> He had not tried to measure any radiation<ref>{{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=184}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|p=56}}</ref> and his research was derided by scientists who saw it later.<ref>{{harvnb|Browne|1989}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=253–255, 339–340, 250}}</ref> For the next six weeks, competing claims, counterclaims, and suggested explanations kept what was referred to as "cold fusion" or "fusion confusion" in the news.{{sfn|ps=|Lewenstein|1994|pp=8–9}}<ref>{{harvnb|Bowen|1989}}, {{harvnb|Crease|Samios|1989}}</ref> | |||
| === 1989 DOE panel === | |||
| The ] organized a special panel to review cold fusion theory and research.<ref name="DOE_1989_39">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|p=39}}</ref> In November of 1989, the panel issued its report, concluding that results as of that date did not present convincing evidence that useful sources of energy would result from phenomena attributed to cold fusion.<ref name="DOE_1989_36">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|p=36}}</ref> The panel noted the inconsistency of reports of excess heat and the greater inconsistency of reports of nuclear reaction byproducts. Nuclear fusion of the type postulated would be inconsistent with current understanding and would require the invention of an entirely new nuclear process. The panel was against special funding for cold fusion research, but supported modest funding of focused experiments within the general funding system."<ref name="DOE_1989_37">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|p=37}}</ref> | |||
| In April 1989, Fleischmann and Pons published a "preliminary note" in the '']''.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|1989|p=301}} This paper notably showed a gamma peak without its corresponding ], which indicated they had made a mistake in claiming evidence of fusion byproducts.<ref>{{harvnb|Tate|1989|p=1}}, {{harvnb|Platt|1998}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=277–288, 362–363}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=141, 147, 167–171, 243–248, 271–272, 288}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=63, 138–139}}</ref> Fleischmann and Pons replied to this critique,<ref>{{cite journal|mode=cs2 |title=Measurement of gamma-rays from cold fusion (letter by Fleischmann et al. and reply by Petrasso et al.) |journal=Nature |volume=339 |issue=6227 |date=29 June 1989 |doi=10.1038/339667a0 |bibcode=1989Natur.339..667F |page=667 |last1=Fleischmann |first1=Martin |last2=Pons |first2=Stanley |last3=Hawkins |first3=Marvin |last4=Hoffman |first4=R. J |s2cid=4274005 |doi-access=free }}</ref> but the only thing left clear was that no gamma ray had been registered and that Fleischmann refused to recognize any mistakes in the data.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=310–314}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=286–287}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=63, 138–139}}</ref> A much longer paper published a year later went into details of calorimetry but did not include any nuclear measurements.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990}} | |||
| === Further developments (1989-2004) === | |||
| After the 1989 review by the DOE, cold fusion was generally seen as an example of pathological science. Science writers ] and ] have published books criticizing cold fusion experiments and researchers.<ref name="Taubes_1993">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993}}</ref><ref name="Park_2000">{{harvnb|Park|2000}}</ref> | |||
| Nevertheless, Fleischmann and Pons and a number of other researchers who found positive results remained convinced of their findings.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}} The University of Utah asked Congress to provide $25 million to pursue the research, and Pons was scheduled to meet with representatives of President Bush in early May.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}} | |||
| In June 1990, Gary Taubes wrote an editorial in ] suggesting that Texas A&M cells might have been spiked with tritiated water.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1990}}</ref> A 3-professor panel of Texas A&M later found that none of the experiments were fraudulently conducted, saying that spiking was unlikely because scientists got different results when they tested the spiking theory by intentionally putting tritium in water.<ref>{{harvnb|New York Times|1990}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Storms|1990}}</ref> John Bockris later published his side of the controversy and a defense of academic freedom in "Accountability in Research".<ref>{{harvnb|Bockris|2000}}</ref> | |||
| On 30 April 1989, cold fusion was declared dead by ''The New York Times''. The ''Times'' called it a circus the same day, and the ''Boston Herald'' attacked cold fusion the following day.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|p=242}} (Boston Herald's is {{harvnb|Tate|1989}}).</ref> | |||
| In 1991, ] stated that the negative report issued by the ] in 1989, which was highly influential in the controversy, was inaccurate. After lodging an official complaint, Mallove resigned from his post as chief science writer at the MIT news office on ], ].<ref>{{harvnb|Brooks|2008|p=65}}</ref> | |||
| On 1 May 1989, the ] held a session on cold fusion in Baltimore, including many reports of experiments that failed to produce evidence of cold fusion. At the end of the session, eight of the nine leading speakers stated that they considered the initial Fleischmann and Pons claim dead, with the ninth, ], abstaining.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}} ] of ] called the Utah report a result of "''the incompetence and delusion of Pons and Fleischmann,''" which was met with a standing ovation.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|p=266}} ], a physicist representing ], was the first to call the episode an example of ].{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}}<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/pub/academic/physics/Cold-fusion/vince-cate/aps.ascii|title=APS Special Session on Cold Fusion, May 1–2, 1989|website=ibiblio.org|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080726071304/http://www.ibiblio.org/pub/academic/physics/Cold-fusion/vince-cate/aps.ascii|archive-date=26 July 2008}}</ref> On 4 May, due to all this new criticism, the meetings with various representatives from Washington were cancelled.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=267–268}} | |||
| In 1991, researcher ] was killed when a cold fusion cell exploded, possibly due to accumulation of deuterium gas and the failure of a safety valve.<ref name="Charles_1992">{{harvnb|Charles|1992}}</ref> | |||
| From 8 May, only the A&M tritium results kept cold fusion afloat.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=275, 326}} | |||
| In September 1990, ], Director of the ], compiled a list 92 groups of researchers from 10 different countries that had reported excess heat, tritium, helium4, neutrons or other nuclear effects.<ref>{{harvnb|Mallove|1991|p=246-248}}</ref> Proponents estimate that 3,000 cold fusion papers have been published, <ref>{{harvnb|Anderson|2007}}</ref> including over 1,000 journal papers and books, where the latter number includes both pro and con articles.{{Ref label|Britz|α|2}} | |||
| In July and November 1989, ''Nature'' published papers critical of cold fusion claims.{{sfn|ps=|Gai|Rugari|France|Lund|1989|pp=29–34}}{{sfn|ps=|Williams|Findlay|Craston|Sené|1989|pp=375–384}} Negative results were also published in several other ]s including '']'', '']'', and '']'' (nuclear physics).<ref group="notes" name="nature critical papers"/> In August 1989, in spite of this trend, the state of ] invested $4.5 million to create the National Cold Fusion Institute.{{sfn|ps=|Joyce|1990}} | |||
| Fleischmann and Pons relocated their laboratory to France under a grant from the ]. The laboratory, IMRA, was closed in 1998 after spending £12 million on cold fusion work.<ref>{{harvnb|Voss|1999}}</ref> | |||
| ] of the open type, used at the New Hydrogen Energy Institute in Japan. ''Source: SPAWAR/US Navy TR1862'']] | |||
| The ] organized a special panel to review cold fusion theory and research.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=39}} The panel issued its report in November 1989, concluding that results as of that date did not present convincing evidence that useful sources of energy would result from the phenomena attributed to cold fusion.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=36}} The panel noted the large number of failures to replicate excess heat and the greater inconsistency of reports of nuclear reaction byproducts expected by established ]. Nuclear fusion of the type postulated would be inconsistent with current understanding and, if verified, would require established conjecture, perhaps even theory itself, to be extended in an unexpected way. The panel was against special funding for cold fusion research, but supported modest funding of "focused experiments within the general funding system".{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|1989|p=37}} | |||
| Between 1992 and 1997, Japan's ] sponsored a "New Hydrogen Energy Program" of US$20 million to research cold fusion. Announcing the end of the program, ] stated in 1997 "We couldn't achieve what was first claimed in terms of cold fusion." He added, "We can't find any reason to propose more money for the coming year or for the future."<ref>{{harvnb|Pollack|1997|p=C4}}</ref> | |||
| Cold fusion supporters continued to argue that the evidence for excess heat was strong, and in September 1990 the National Cold Fusion Institute listed 92 groups of researchers from 10 countries that had reported corroborating evidence of excess heat, but they refused to provide any evidence of their own arguing that it could endanger their patents.<ref>{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|p=165}}</ref> However, no further DOE nor NSF funding resulted from the panel's recommendation.{{sfn|ps=|Mallove|1991|pp=246–248}} By this point, however, academic consensus had moved decidedly toward labeling cold fusion as a kind of "pathological science".<ref name="nytdoe"/>{{sfn|Rousseau|1992}} | |||
| In 1994, ] described cold fusion as "a pariah field, cast out by the scientific establishment. Between and respectable science there is virtually no communication at all. Cold fusion papers are almost never published in refereed scientific journals, with the result that those works don't receive the normal critical scrutiny that science requires. On the other hand, because the Cold-Fusioners see themselves as a community under siege, there is little internal criticism. Experiments and theories tend to be accepted at face value, for fear of providing even more fuel for external critics, if anyone outside the group was bothering to listen. In these circumstances, crackpots flourish, making matters worse for those who believe that there is serious science going on here."<ref name="Goodstein_1994">{{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}</ref> | |||
| In March 1990, Michael H. Salamon, a physicist from the ], and nine co-authors reported negative results.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Salamon|first1=M. H.|last2=Wrenn|first2=M. E.|last3=Bergeson|first3=H. E.|last4=Crawford|first4=H. C.|last5=Delaney|first5=W. H.|last6=Henderson|first6=C. L.|last7=Li|first7=Y. Q.|last8=Rusho|first8=J. A.|last9=Sandquist|first9=G. M.|last10=Seltzer|first10=S. M. |s2cid=4369849|display-authors= 4|title=Limits on the emission of neutrons, γ-rays, electrons and protons from Pons/Fleischmann electrolytic cells|journal=Nature|date=29 March 1990|volume=344|issue=6265|pages=401–405|doi=10.1038/344401a0|bibcode=1990Natur.344..401S}}</ref> University faculty were then "stunned" when a lawyer representing Pons and Fleischmann demanded the Salamon paper be retracted under threat of a lawsuit. The lawyer later apologized; Fleischmann defended the threat as a legitimate reaction to alleged bias displayed by cold-fusion critics.<ref name="nytimes escapes">{{cite news|last=Broad|first=William J.|title=Cold Fusion Still Escapes Usual Checks Of Science|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1990/10/30/science/cold-fusion-still-escapes-usual-checks-of-science.html?pagewanted=all&src=pm|access-date=27 November 2013|newspaper=The New York Times|date=30 October 1990|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131219181647/http://www.nytimes.com/1990/10/30/science/cold-fusion-still-escapes-usual-checks-of-science.html?pagewanted=all&src=pm|archive-date=19 December 2013}}</ref> | |||
| Most people attempting to publish anything about the subject faced rejection of their papers.{{Fact|date=November 2008}} The late ] ] (1918 - 1994) was so outraged by the way the ] treated his papers that he resigned from that body in protest.<ref>{{harvnb|Storms|2007|P=12}}</ref> Cold fusion researchers said that cold fusion was being suppressed, and that skeptics suffered from "]".<ref>{{harvnb|Josephson|2004}}</ref> They said that there was virtually no possibility for funding in cold fusion in the United States, and no possibility of getting published.<ref name="Feder_2004_27">{{harvnb|Feder|2004|p=27}}</ref> They said that people in universities refused to work on it because they would be ridiculed by their colleagues.<ref>{{harvnb|Rusbringer|2005}}</ref> | |||
| In early May 1990, one of the two A&M researchers, ], acknowledged the possibility of spiking, but said that the most likely explanation was tritium contamination in the palladium electrodes or simply contamination due to sloppy work.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=410–411}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=270, 322}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=118–119, 121–122}}</ref> In June 1990 an article in ''Science'' by science writer ] destroyed the public credibility of the A&M tritium results when it accused its group leader ] and one of his graduate students of spiking the cells with tritium.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=410–411, 412, 420}}, the Science article was {{harvnb|Taubes|1990}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=122, 127–128}}.</ref> In October 1990 Wolf finally said that the results were explained by tritium contamination in the rods.{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|pp=122–123}} An A&M cold fusion review panel found that the tritium evidence was not convincing and that, while they couldn't rule out spiking, contamination and measurements problems were more likely explanations,<ref group="text" name="spiking"/> and Bockris never got support from his faculty to resume his research. | |||
| To provide a forum for researchers to share their results, the first International Conference on Cold Fusion was held in 1990. The conference, recently renamed the International Conference on Condensed Matter Nuclear Science, is held every 12 to 18 months in various countries around the world. The periodicals ''Fusion Facts'', ''Cold Fusion Magazine'', ''Infinite Energy Magazine'', and ''New Energy Times'' were established in the 1990s to cover developments in cold fusion and related new energy sciences. In 2004 was formed "To promote the understanding, development and application of Condensed Matter Nuclear Science for the benefit of the public." | |||
| On 30 June 1991, the National Cold Fusion Institute closed after it ran out of funds;<ref>{{cite web|mode=cs2 |title=National Cold Fusion Institute Records, 1988–1991 |url=http://content.lib.utah.edu/cdm4/item_viewer.php?CISOROOT=/UU_EAD&CISOPTR=160 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120717185323/http://content.lib.utah.edu/cdm4/item_viewer.php?CISOROOT=/UU_EAD&CISOPTR=160 |archive-date=17 July 2012 }}</ref> it found no excess heat, and its reports of tritium production were met with indifference.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|p=424}} | |||
| In February 2002, the U.S. Navy revealed that its researchers had been studying cold fusion on the quiet more or less continuously since 1989. Researchers at their ] in ] released a two-volume report, entitled "Thermal and nuclear aspects of the Pd/D<sub>2</sub>O system," with a plea for proper funding.<ref>{{harvnb|Mullins|2004}}</ref> | |||
| On 1 January 1991, Pons left the University of Utah and went to Europe.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|p=424}}{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|p=184}} In 1992, Pons and Fleischmann resumed research with ]'s IMRA lab in France.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|p=424}} Fleischmann left for England in 1995, and the contract with Pons was not renewed in 1998 after spending $40 million with no tangible results.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=136–138}} The IMRA laboratory stopped cold fusion research in 1998 after spending £12 million.{{sfn|ps=|Voss|1999a}} Pons has made no public declarations since, and only Fleischmann continued giving talks and publishing papers.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=136–138}} | |||
| === 2004 DOE panel === | |||
| In 2004, the DOE organized another panel to take a look at cold fusion developments since 1989 to determine if their policies towards cold fusion should be altered.<ref name="DOEr_2004_3">{{harvnb|US DOE|2004|Ref=DOE2004r|p=3}}</ref> The resulting report stated, among other things, that: "Two-thirds of the reviewers ... did not feel the evidence was conclusive for low energy nuclear reactions, one found the evidence convincing, and the remainder indicated they were somewhat convinced." It also stated: "The nearly unanimous opinion of the reviewers in the 2004 review was that funding agencies should entertain individual, well-designed proposals for experiments that address specific scientific issues relevant to the question of whether or not there is anomalous energy production in Pd/D systems, or whether or not D-D fusion reactions occur at energies on the order of a few ]s (eV). These proposals should meet accepted scientific standards and undergo the rigors of peer review. No reviewer recommended a focused federally funded program for low energy nuclear reactions." | |||
| Mostly in the 1990s, several books were published that were critical of cold fusion research methods and the conduct of cold fusion researchers.<ref>{{harvnb|Close|1992}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993}}, and {{harvnb|Park|2000}}</ref> Over the years, several books have appeared that defended them.<ref>{{harvnb|Mallove|1991}}, {{harvnb|Beaudette|2002}}, {{harvnb|Simon|2002}}, {{harvnb|Kozima|2006}}</ref> Around 1998, the University of Utah had already dropped its research after spending over $1 million, and in the summer of 1997, Japan cut off research and closed its own lab after spending $20 million.<ref name="wired steam"/> | |||
| In its conclusion, the report stated: "While significant progress has been made in the sophistication of calorimeters since the review of this subject in 1989, the conclusions reached by the reviewers today are similar to those found in the 1989 review." <ref name="DOEr_2004_5">{{harvnb|US DOE|2004|Ref=DOE2004r|p=5}}</ref> | |||
| == Later research == | |||
| The reports of excess heat and anomalous tritium production{{Ref label|Britz|α|3}} have been met by most scientists with ],<ref>{{harvnb|Feder|2005}}</ref> although discussion in professional settings still continues. The American Chemical Society's (ACS) 2007 conference in Chicago held an "invited symposium" on cold fusion and low-energy nuclear reactions, and thirteen papers were presented at the "Cold Fusion" session of the March 2006 American Physical Society (APS) Meeting in Baltimore.<ref>{{harvnb|Van Noorden|2007|loc=para. 2}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Chubb et al.|2006|Ref=APS2006}}</ref> Articles supporting cold fusion have been published in ]ed journals such as ''], ], ] A, European Physical Journal C, ], Journal of Solid State Phenomena, Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry'', and ''Journal of Fusion Energy''.<ref>Krivit, S. </ref><ref>{{harvnb|Di Giulio|2002}}</ref> | |||
| A 1991 review by a cold fusion proponent had calculated "about 600 scientists" were still conducting research.<ref name="small community 600">{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=210–211}} citing {{cite journal|mode=cs2 |title=Nuclear Fusion in an Atomic Lattice: An Update on the International Status of Cold Fusion Research |last=Srinivisan |first=M.|journal=Current Science |volume=60 |page=471}}</ref> After 1991, cold fusion research only continued in relative obscurity, conducted by groups that had increasing difficulty securing public funding and keeping programs open. These small but committed groups of cold fusion researchers have continued to conduct experiments using Fleischmann and Pons electrolysis setups in spite of the rejection by the mainstream community.<ref name=Broad1989b/><ref name="small community" />{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=131–133, 218}} ''The Boston Globe'' estimated in 2004 that there were only 100 to 200 researchers working in the field, most suffering damage to their reputation and career.{{sfn|ps=|Daley|2004}} Since the main controversy over Pons and Fleischmann had ended, cold fusion research has been funded by private and small governmental scientific investment funds in the United States, Italy, Japan, and India. For example, it was reported in ], in May, 2019, that ] had spent approximately $10 million on cold fusion research. A group of scientists at well-known research labs (e.g., ], ], and others) worked for several years to establish experimental protocols and measurement techniques in an effort to re-evaluate cold fusion to a high standard of scientific rigor. Their reported conclusion: no cold fusion.<ref>{{cite magazine |last=Ball |first=David |date= September 2019 |title= Google funds cold fusion research: Results still negative|magazine=] |location=Amherst, NY |publisher=Center for Inquiry}}</ref> | |||
| In 2007, a ] researcher with no previous experience with cold fusion wrote a review of experiments with solid ] cathodes and electrolytes with ], or with D<sub>2</sub> gas loaded in palladium powders. The author said that more than 10 groups worldwide have reported the measurement of excess heat in 1/3 of their experiments and that most of the research groups have reported occasionally seeing 50-200% excess heat for hours to days. The positive results were difficult to reproduce, which the author attributed to variations in the loading ratios of deuterium to palladium achieved by different research teams.<ref name="Hubler_2007"/> | |||
| In 2021, following ''Nature's'' 2019 publication of anomalous findings that might only be explained by some localized fusion, scientists at the ] announced that they had assembled a group of scientists from the Navy, Army and ] to undertake a new, coordinated study.<ref name=":0" /> With few exceptions, researchers have had difficulty publishing in mainstream journals.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}}<ref name=Broad1989b/><ref name="most scientists" /><ref name="small community" /> The remaining researchers often term their field Low Energy Nuclear Reactions (LENR), Chemically Assisted Nuclear Reactions (CANR),{{sfn|ps=|Mullins|2004}} Lattice Assisted Nuclear Reactions (LANR), Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (CMNS) or Lattice Enabled Nuclear Reactions; one of the reasons being to ] associated with "cold fusion".{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=131–133, 218}}{{sfn|ps=|Seife|2008|pp=154–155}} The new names avoid making bold implications, like implying that fusion is actually occurring.<ref>{{harvnb|Simon|2002|pp=131}}, citing {{harvnb|Collins|Pinch|1993|loc=p. 77 in first edition}}</ref> | |||
| In 2008, the government of India reviewed the field.<ref>{{harvnb|Jayaraman|2008}}</ref> M. R. Srinivasan, former chairman of the ] said: "There is some science here that needs to be understood. We should set some people to investigate these experiments. There is much to be commended for the progress in the work. The neglect should come to an end".<ref>{{harvnb|Srinivasan|2008}}</ref> | |||
| The researchers who continue their investigations acknowledge that the flaws in the original announcement are the main cause of the subject's marginalization, and they complain of a chronic lack of funding<ref name="bbc march 2009">{{cite web| mode=cs2 | title=Cold fusion debate heats up again | publisher=] | date=23 March 2009 | url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7959183.stm | url-status=live | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160111172930/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7959183.stm | archive-date=11 January 2016 }}</ref> and no possibilities of getting their work published in the highest impact journals.{{sfn|ps=|Feder|2004|p=27}} University researchers are often unwilling to investigate cold fusion because they would be ridiculed by their colleagues and their professional careers would be at risk.<ref>{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=292, 352, 358}}, {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}, {{harvnb|Adam|2005}} (comment attributed to George Miley of the University of Illinois)</ref> In 1994, ], a professor of physics at ], advocated increased attention from mainstream researchers and described cold fusion as: | |||
| == Field overview == | |||
| {{Weasel|date=November 2008}} | |||
| {{NPOV-section|date=November 2008}} | |||
| An experimental cold device usually includes: | |||
| {{blockquote|1=A pariah field, cast out by the scientific establishment. Between cold fusion and respectable science there is virtually no communication at all. Cold fusion papers are almost never published in refereed scientific journals, with the result that those works don't receive the normal critical scrutiny that science requires. On the other hand, because the Cold-Fusioners see themselves as a community under siege, there is little internal criticism. Experiments and theories tend to be accepted at face value, for fear of providing even more fuel for external critics, if anyone outside the group was bothering to listen. In these circumstances, crackpots flourish, making matters worse for those who believe that there is serious science going on here.{{sfn|ps=|Goodstein|1994}}}} | |||
| * a metal, such as ] or ], in bulk, thin films or powder; | |||
| * ] and/or ], in the form of water, gas or plasma; and | |||
| * an excitation in the form of ], ], ], ], ] beam(s), or of ].<ref>{{harvnb|Storms|2007|p=144-150}}</ref> | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| Cold fusion researchers have reported observing excess heat, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]-4, helium-3, and/or "anomalous" isotopic distributions.<ref name="Biberian_2007_?"/><ref>{{Ref label|Britz|α|4}}</ref>, although many of the findings are not published in reputable journals or subjected to mainstream scrutiny. No experiment has unequivocally produced a particle emission spectrum matching that predicted by nuclear science. There is still no theory explaining cold fusion that has been accepted by the scientific community, but many explanations have been proposed. <ref name="Biberian_2007_?">{{harvnb|Biberian|2007}}</ref> | |||
| ] (2005)]] | |||
| United States Navy researchers at the ] (SPAWAR) in San Diego have been studying cold fusion since 1989.{{sfn|ps=|Mullins|2004}}<ref name=MosierBoss2009 /> In 2002 they released a two-volume report, "Thermal and nuclear aspects of the Pd/D<sub>2</sub>O system", with a plea for funding.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130216190531/http://www.spawar.navy.mil/sti/publications/pubs/tr/1862/tr1862-vol1.pdf |date=16 February 2013 }}, Feb 2002. Reported by {{harvnb|Mullins|2004}}</ref> This and other published papers prompted a 2004 ] (DOE) review.{{sfn|ps=|Mullins|2004}} | |||
| === Excess heat === | |||
| The excess power observed in some experiments is theorized to be beyond that attributable to ordinary chemical or solid state sources, or measurement error. Proponents attribute this excess power to nuclear fusion reactions.<ref name="DOEr_2004_3"/><ref name="Hubler_2007">{{harvnb|Hubler|2007}}</ref> In addition to Fleischmann and Pons, the generation of excess heat has been reported by others in various venues.<ref>{{harvnb|Oriani|Nelson|Lee|Broadhurst|1990|pp=652-662}}, cited by {{harvnb|Storms|2007|p=61}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Bush|Lagowski|Miles|Ostrom|1991}}, cited by {{harvnb|Biberian|2007}}</ref><ref>e.g. {{harvnb|Storms|1993}}, {{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Miles et al.|1993|Ref=MilesE}}</ref><ref>e.g. {{harvnb|Arata|Zhang|1998}}, {{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Gozzi|1998|Ref=GozziEtAl1998}}, cited by {{harvnb|Biberian|2007}}</ref> | |||
| ==== 2004 DOE panel ==== | |||
| In 1993, Fleischmann reported "heat-after-death" experiments: he observed the continuing generation of excess heat after the electric current supplied to the electrolytic cell was turned off.<ref>{{harvnb|Fleischmann|1993}}</ref> Such observations have been reported by others.<ref>{{harvnb|Mengoli|1998}}</ref><ref name=Szpak2004>{{harvnb|Szpak|2004|Ref=Szpak2004}}</ref> | |||
| In August 2003, the ], ], ordered the DOE to organize a second review of the field.{{sfn|ps=|Brumfiel|2004}} This was thanks to an April 2003 letter sent by MIT's ],<ref name="Weinberger2004" />{{rp|3}} and the publication of many new papers, including the Italian ENEA and other researchers in the 2003 International Cold Fusion Conference,<ref name="ENEA_Magazin" /> and a two-volume book by U.S. ] in 2002.{{sfn|ps=|Mullins|2004}} Cold fusion researchers were asked to present a review document of all the evidence since the 1989 review. The report was released in 2004. The reviewers were "split approximately evenly" on whether the experiments had produced energy in the form of heat, but "most reviewers, even those who accepted the evidence for excess power production, 'stated that the effects are not repeatable, the magnitude of the effect has not increased in over a decade of work, and that many of the reported experiments were not well documented'". {{sfn|ps=|Brumfiel|2004}}{{sfn|ps=|Feder|2005}} In summary, reviewers found that cold fusion evidence was still not convincing 15 years later, and they did not recommend a federal research program.{{sfn|ps=|Brumfiel|2004}}{{sfn|ps=|Feder|2005}} They only recommended that agencies consider funding individual well-thought studies in specific areas where research "could be helpful in resolving some of the controversies in the field".{{sfn|ps=|Brumfiel|2004}}{{sfn|ps=|Feder|2005}} They summarized its conclusions thus: | |||
| {{poemquote|While significant progress has been made in the sophistication of calorimeters since the review of this subject in 1989, the conclusions reached by the reviewers today are similar to those found in the 1989 review. | |||
| The cold fusion researchers who presented their review document to the 2004 DOE panel said that "the hypothesis that the excess heat effect arises only as a consequence of errors in calorimetry was considered, studied, tested, and ultimately rejected".<ref name="DOE_2004_1">{{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004|p=1}}</ref> | |||
| The current reviewers identified a number of basic science research areas that could be helpful in resolving some of the controversies in the field, two of which were: 1) material science aspects of deuterated metals using modern characterization techniques, and 2) the study of particles reportedly emitted from deuterated foils using state-of-the-art apparatus and methods. The reviewers believed that this field would benefit from the peer-review processes associated with proposal submission to agencies and paper submission to archival journals. |Report of the Review of Low Energy Nuclear Reactions, US Department of Energy, December 2004{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004}}}} | |||
| === Nuclear products === | |||
| ] detector showing possible nuclear activity in cold fusion experiments at ].<ref>{{harvnb|Mosier-Boss|Szpak|Gordon|2007|loc=slide 7}}<br />reported in {{harvnb|Krivit|2007|p=2}}</ref>]] The cold fusion researchers who presented their review document to the 2004 DOE panel on cold fusion proposed that there were insufficient chemical reaction products to account for the excess heat.<ref name="DOE_2004_7">{{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004|p=7}}</ref>However, the amount of helium in the gas stream was about half of what would be expected for a heat source of the type D + D → <sup>4</sup>He. | |||
| Cold fusion researchers placed a "rosier spin"{{sfn|ps=|Feder|2005}} on the report, noting that they were finally being treated like normal scientists, and that the report had increased interest in the field and caused "a huge upswing in interest in funding cold fusion research".{{sfn|ps=|Feder|2005}} However, in a 2009 BBC article on an American Chemical Society's meeting on cold fusion, particle physicist ] was quoted stating that the problems that plagued the original cold fusion announcement were still happening: results from studies are still not being independently verified and inexplicable phenomena encountered are being labelled as "cold fusion" even if they are not, in order to attract the attention of journalists.<ref name="bbc march 2009"/> | |||
| Cold fusion researchers have also reported detection of many kinds of radiation: alpha, beta, gamma, proton, and ]. However, ] and other energetic emissions were never found in quantities commensurate with the excess heat, as would be expected by established theories of nuclear physics. This has led some cold fusion proponents to conjecture that new processes may be converting nuclear energy directly to heat.<ref name="DOE_2004_7"/> | |||
| In February 2012, millionaire ], convinced that cold fusion was worth investing in by a 19 April 2009 interview with physicist ] on the US news show '']'',<ref name=Columbia_Tribune_SKINR /> made a grant of $5.5 million to the ] to establish the Sidney Kimmel Institute for Nuclear Renaissance (SKINR). The grant was intended to support research into the interactions of hydrogen with palladium, nickel or platinum under extreme conditions.<ref name=Columbia_Tribune_SKINR>Janese Silvey, {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121215042347/http://www.columbiatribune.com/news/2012/feb/10/billionaire-helps-fund-mu-energy-research/ |date=15 December 2012 }}, Columbia Daily Tribune, 10 February 2012</ref><ref name=Press_Release_Kimmel>University of Missouri-Columbia {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305011010/http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2012-02/uom-mg021012.php |date=5 March 2016 }}, 10 February 2012, (press release), </ref><ref name=Missourian_SKINR> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120305101814/http://www.columbiamissourian.com/stories/2012/02/10/sidney-kimmel-foundation-awards-55-million-mu-scientists/ |date=5 March 2012 }} Allison Pohle, Missourian, 10 February 2012</ref> In March 2013 Graham K. Hubler, a nuclear physicist who worked for the Naval Research Laboratory for 40 years, was named director.<ref>Christian Basi, {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304023438/http://munews.missouri.edu/news-releases/2013/0308-hubler-named-director-of-nuclear-renaissance-institute-at-mu/ |date=4 March 2016}}, (press release) Missouri University News Bureau, 8 March 2013</ref> One of the SKINR projects is to replicate a 1991 experiment in which a professor associated with the project, Mark Prelas, says bursts of millions of neutrons a second were recorded, which was stopped because "his research account had been frozen". He claims that the new experiment has already seen "neutron emissions at similar levels to the 1991 observation".<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121102004909/http://www.columbiatribune.com/news/2012/oct/28/professor-revisits-fusion-work-from-two-decades/ |date=2 November 2012 }} Columbia Daily Tribune, 28 October 2012</ref><ref>Mark A. Prelas, Eric Lukosi. {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130116205612/http://prelas.nuclear.missouri.edu/Publications/LENR%20Korea%20ICCF-17%20Proceedings%20Titanium%20Thermal%20Shock%20v3.pdf |date=16 January 2013 }} (self published)</ref> | |||
| In 2007, the ] reported their observation of pits in ] detectors during D/Pd co-deposition experiments in the '']''. They said that those pits have features consistent with those observed for nuclear-generated tracks, that the Pd cathode is the source of those pits, and that they are not due to contamination or chemical reactions. They attributed some pits to knock-ons due to neutrons, and said that other pits are consistent with those obtained for ]s.<ref>{{harvnb|Mosier-Boss|Szpak|Gordon|Forsley|2007}}</ref> Further analysis of "triple pits" suggests that Deuterium-Tritium reactions occurring inside the Pd lattice produce neutrons with an energy above 9.6 MeV.<ref>{{harvnb|Mosier-Boss|Szpak|Gordon|Forsley|2008}}</ref> | |||
| In May 2016, the ], in its report on the 2017 National Defense Authorization Act, directed the ] to "provide a briefing on the military utility of recent U.S. industrial base LENR advancements to the House Committee on Armed Services by September 22, 2016".<ref>{{cite web |last=Hambling |first=David |date=May 13, 2016 |work=Popular Mechanics |url=http://www.popularmechanics.com/science/energy/a20874/us-house-cold-fusion/ |access-date=18 May 2016 |title=Congress Is Suddenly Interested in Cold Fusion |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160518221421/http://www.popularmechanics.com/science/energy/a20874/us-house-cold-fusion/ |archive-date=18 May 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.congress.gov/114/crpt/hrpt537/CRPT-114hrpt537.pdf#page=123 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160516124400/https://www.congress.gov/114/crpt/hrpt537/CRPT-114hrpt537.pdf |archive-date=16 May 2016 |title=Committee on Armed Services, House of Representatives Report 114-537 |page=87}}</ref> | |||
| === Nuclear transmutations === | |||
| There have been reports that small amounts of copper and other metals can appear within Pd electrodes.<ref name="Storms_2007_93_95">{{harvnb|Storms|2007|p=93-95}}</ref> Iwamura et al. report transmuting Cs to Pr and Sr to Mo, with the mass number increasing by 8, and the atomic number by 4 in either case.<ref name="IwamuraSakanoItoh_2002_full">{{harvnb|Iwamura|Sakano|Itoh|2002|pp=4642-4650}}</ref>. Cs or Sr was applied to the surface of a Pd complex consisting of a thin Pd layer, alternating CaO and Pd layers, and bulk Pd. Deuterium was diffused through this complex. The surface was analyzed periodically with ] and at the end of the experiment with glow discharge mass spectrometry.<ref name="IwamuraSakanoItoh_2002_full">{{harvnb|Iwamura|Sakano|Itoh|2002|pp=4642-4650}}</ref> | |||
| == |
===Italy=== | ||
| {{criticism-section}} | |||
| Since the Fleischmann and Pons announcement, the Italian national agency for new technologies, energy and sustainable economic development (]) has funded Franco Scaramuzzi's research into whether excess heat can be measured from metals loaded with deuterium gas.{{sfn|ps=|Goodstein|2010|pp=87–94}} Such research is distributed across ENEA departments, ] laboratories, ], universities and industrial laboratories in Italy, where the group continues to try to achieve reliable reproducibility (i.e. getting the phenomenon to happen in every cell, and inside a certain frame of time). In 2006–2007, the ENEA started a research program which claimed to have found excess power of up to 500 percent, and in 2009, ENEA hosted the 15th cold fusion conference.<ref name=ENEA_Magazin>{{cite journal|mode= cs2 |title= Effetto Fleischmann e Pons: il punto della situazione |journal= Energia Ambiente e Innovazione |issue= 3 |date= May–June 2011 |language= it |url= http://www.enea.it/it/produzione-scientifica/energia-ambiente-e-innovazione-1/anno-2011/indice-world-view-3-2011/fusione-fredda |url-status= live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120808194206/http://www.enea.it/it/produzione-scientifica/energia-ambiente-e-innovazione-1/anno-2011/indice-world-view-3-2011/fusione-fredda |archive-date= 8 August 2012 }}</ref>{{sfn|ps=|Martellucci |Rosati |Scaramuzzi |Violante |2009}} | |||
| In the original 1989 DOE review,<ref name="DOE_1989_6_8">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|pp=6-8}}</ref> skepticism towards cold fusion focused on four issues: the precision of calorimetry, the lack of consistently reproducible results, the absence of nuclear products in quantities consistent with the excess heat, and the lack of a mainstream theoretical mechanism. In the subsequent years considerable efforts have been made on these fronts. Today these issues still remain the focus of criticisms. | |||
| ===Japan=== | |||
| === Precision and accuracy of calorimetry === | |||
| {{main|Calorimetry in cold fusion experiments}} | |||
| In the first years after the Fleishmann-Pons announcement various challenges were put forth. The efficacy of the stirring method in the Fleischmann-Pons experiment, and thus the validity of the temperature measurements was disputed by Browne.<ref name="Browne_1989_para16">{{harvnb|Browne|1989|loc=para. 16}}</ref> The experiment has also been criticized by Wilson.<ref name="Wilson_1992">{{harvnb|Wilson|1992}}</ref> The possibility that electrochemically mediated deuterium-oxygen recombination can cause the appearance of excess heat was discussed by Shkedi<ref name="ShkediMcDonaldBreenMaguireVeranth_1995_?">{{harvnb|Shkedi et al.|1995|Ref=Shkedi1995}}</ref> and Jones.<ref name="JonesHansenJonesSheltonThorne_1995_1">{{harvnb|Jones et al.|1995|Ref=Jones1995|p=1}}</ref> | |||
| Between 1992 and 1997, Japan's ] sponsored a "New Hydrogen Energy (NHE)" program of US$20 million to research cold fusion.<ref name="pollack" /> Announcing the end of the program in 1997, the director and one-time proponent of cold fusion research Hideo Ikegami stated "We couldn't achieve what was first claimed in terms of cold fusion. (...) We can't find any reason to propose more money for the coming year or for the future."<ref name="pollack">{{harvnb|Pollack|1992}}, {{harvnb|Pollack|1997|p=C4}}</ref> In 1999 the Japan C-F Research Society was established to promote the independent research into cold fusion that continued in Japan.<ref name=JCFRS>{{cite web|url=http://jcfrs.org/indexe.html|title=Japan CF-research Society|website=jcfrs.org|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160121185606/http://jcfrs.org/indexe.html|archive-date=21 January 2016}}</ref> The society holds annual meetings.<ref name=JCFRS2011> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160312140405/http://jcfrs.org/JCF12/jcf12-abstracts.pdf |date=12 March 2016 }}</ref> Perhaps the most famous Japanese cold fusion researcher was ], from Osaka University, who claimed in a demonstration to produce excess heat when deuterium gas was introduced into a cell containing a mixture of palladium and zirconium oxide,<ref group="text" name="mixture"/> a claim supported by fellow Japanese researcher Akira Kitamura of Kobe University{{sfn|ps=|Kitamura|Nohmi|Sasaki|Taniike|2009}} and ] at SRI. | |||
| The 2004 DOE panel noted that "significant progress has been made in the sophistication of calorimeters since ... 1989", and summarized that "Evaluations by the reviewers ranged from: 1) evidence for excess power is compelling, to 2) there is no convincing evidence that excess power is produced when integrated over the life of an experiment. The reviewers were split approximately evenly on this topic."<ref name="DOEr_2004_3"/> | |||
| ===India=== | |||
| The panel continued, "Many reviewers noted that poor experiment design, documentation, background control and other similar issues hampered the understanding and interpretation of the results presented". The reviewers who did not find the production of excess power convincing said that excess power in the short term is not the same as net energy production over the entire time of an experiment, that such short-term excess power is only a few percent of the total external power applied and hence ] and systematic effects could account for the purported effect, that all possible chemical and solid state causes of excess heat had not been investigated and eliminated as an explanation, that the ] of the effect had not increased after over a decade of work. | |||
| In the 1990s, India stopped its research in cold fusion at the ] because of the lack of consensus among mainstream scientists and the US denunciation of the research.{{sfn|ps=|Jayaraman|2008}} Yet, in 2008, the ] recommended that the Indian government revive this research. Projects were commenced at ]'s ], the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre and the ].{{sfn|ps=|Jayaraman|2008}} However, there is still skepticism among scientists and, for all practical purposes, research has stalled since the 1990s.<ref>{{cite news|mode= cs2 |title= Our dream is a small fusion power generator in each house |date= 4 February 2011 |url= https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/home/opinion/interviews/Our-dream-is-a-small-fusion-power-generator-in-each-house/articleshow/7419731.cms |url-status= live |archive-url= http://archive.wikiwix.com/cache/20110826044622/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-02-04/interviews/28358904_1_cold-fusion-hydrogen-and-nickel-scientists |work= ] |archive-date= 26 August 2011 }}</ref> A special section in the Indian multidisciplinary journal '']'' published 33 cold fusion papers in 2015 by major cold fusion researchers including several Indian researchers.<ref name="currentscience.ac.in">{{cite web |url=http://www.currentscience.ac.in/php/feat.php?feature=Special+Section:+Low+Energy+Nuclear+Reactions&featid=10094 |title=Category: Special Section: Low Energy Nuclear Reactions |work=Current Science |date=25 Feb 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20170805185756/http://www.currentscience.ac.in/php/feat.php?feature=Special+Section:+Low+Energy+Nuclear+Reactions&featid=10094 |archive-date=2017-08-05}}</ref> | |||
| Kirk Shanahan suggested that a calibration constant shift could explain apparent excess heat signals, and that such a shift could occur by a redistribution of heat in a F&P cell. He further speculated that such a redistribution would occur if recombination at the electrode became active, but acknowledged that this is not experimentally proven.<ref name="Shanahan 2002"/><ref name="Shanahan 2006">{{harvnb|Shanahan|2006}}</ref> Cold fusion proponents say that such speculations are not supported by experimental results (in particular, that the measured volume of recombined output evolved gases does not allow for recombination within the cell)<ref name=Szpak2004/> a statement that Shanahan's papers dispute.<ref name="Shanahan 2002">{{harvnb|Shanahan|2002}}</ref><ref name="Shanahan 2005">{{harvnb|Shanahan|2005}}</ref><ref name="Shanahan 2006">{{harvnb|Shanahan|2006}}</ref> | |||
| ==Reported results== | |||
| === Lack of reproducibility of excess heat === | |||
| A cold fusion experiment usually includes: | |||
| In 1989, the DOE panel noted that "Even a single short but valid cold fusion period would be revolutionary. As a result, it is difficult convincingly to resolve all cold fusion claims since, for example, any good experiment that fails to find cold fusion can be discounted as merely not working for unknown reasons." <ref name="DOE_1989_36"/>. | |||
| * a metal, such as ] or ], in bulk, thin films or powder; and | |||
| * ], ], or both, in the form of water, gas or plasma. | |||
| Electrolysis cells can be either open cell or closed cell. In open cell systems, the electrolysis products, which are gaseous, are allowed to leave the cell. In closed cell experiments, the products are captured, for example by catalytically recombining the products in a separate part of the experimental system. These experiments generally strive for a steady state condition, with the electrolyte being replaced periodically. There are also "heat-after-death" experiments, where the evolution of heat is monitored after the electric current is turned off. | |||
| The cold fusion researchers who presented their review document to the 2004 DOE panel on cold fusion said that the observation of excess heat has been reproduced, that it can be reproduced at will under the proper conditions, and that many of the reasons for failure to reproduce it have been discovered.<ref name="DOE_2004_14">{{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004|p=14}}</ref> Contrary to these assertions, most reviewers stated that the effects are not repeatable, the magnitude of the effect has not increased in over a decade of work, and that many of the reported experiments were not well documented. <ref name="DOE_2004_3">{{harvnb|US DOE|2004|Ref=DOE2004r|p=3}}</ref> | |||
| The most basic setup of a cold fusion cell consists of two electrodes submerged in a solution containing palladium and heavy water. The electrodes are then connected to a power source to transmit electricity from one electrode to the other through the solution.<ref name="reignites">{{cite journal | |||
| === Missing nuclear products === | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| The fusion of two ] nuclei usually produces either a ] nucleus and a ], or a ] (<sup>3</sup>He) nucleus and a ]. The level of neutrons, tritium and <sup>3</sup>He actually observed in the Fleischmann-Pons experiments have been well below the level expected in view of the heat generated, implying that these fusion reactions cannot explain it. If the excess heat were generated by the fusion of two deuterium nuclei into helium (<sup>4</sup>He), a reaction which is normally extremely rare, ]s and helium (alpha particles) would be expected. In 1989, insufficient levels of helium (alpha particles) and gamma rays were observed to explain the excess heat.<ref name="DOE_1989_5_6">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|pp=5-6}}</ref> | |||
| |journal = ] | |||
| |author = Mark Anderson | |||
| |date = March 2009 | |||
| |title = New Cold Fusion Evidence Reignites Hot Debate | |||
| |url = http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/energy/nuclear/new-cold-fusion-evidence-reignites-hot-debate | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20090710014539/http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/energy/nuclear/new-cold-fusion-evidence-reignites-hot-debate | |||
| |archive-date = 10 July 2009 | |||
| |access-date = 13 June 2009 | |||
| }}</ref> Even when anomalous heat is reported, it can take weeks for it to begin to appear—this is known as the "loading time," the time required to saturate the palladium electrode with hydrogen (see "Loading ratio" section). | |||
| The Fleischmann and Pons early findings regarding helium, neutron radiation and tritium were never replicated satisfactorily, and its levels were too low for the claimed heat production and inconsistent with each other.<ref>{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|p=29}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993}}{{Page needed|date=March 2012}}</ref> Neutron radiation has been reported in cold fusion experiments at very low levels using different kinds of detectors, but levels were too low, close to background, and found too infrequently to provide useful information about possible nuclear processes.<ref>{{harvnb|Hoffman|1995|pp=111–112}}</ref> | |||
| New information was presented in 2004 to the DOE review panel regarding the production of <sup>4</sup>He.<ref name="DOE_2004">{{harvnb|Hagelstein et al.|2004|Ref=DOE2004}}</ref> When members of the panel were asked about the evidence of low energy nuclear reactions, twelve of the eighteen did not feel that there was any conclusive evidence, five found the evidence "somewhat convincing", and one was entirely convinced. The evidence of D+D fusion was taken as convincing or somewhat convincing by some reviewers; for others the lack of consistency was an indication that the overall hypothesis was not justified. Contamination of apparatus or samples by air containing 4He was cited as one possible cause for false positive results in some measurements.<ref name="DOE_2004_3"/> | |||
| ===Excess heat and energy production=== | |||
| An example of this was published by Clarke et al. in 2003.<ref>{{harvnb|Clarke|2003}}</ref> Their paper reported on the analysis of gases found in four ‘Case-type’ cells obtained from the McKubre group at SRI International, a primary cold fusion research group. The Abstract states: “One sample appears to be identical in composition to air, and the other three have been seriously affected by leak(s) into and from the SRI cells.” The Conclusions states: "The samples of gas from Case-type cells provided to us by the SRI workers do not show any evidence of production of <sup>4</sup>He via cold fusion. Our analytical results can be explained by a combination of two factors: (a) severe leak(s) that allowed air into the cells, and also caused removal of gases including hydrogen from the cells to the atmosphere, and (b) the action of the Pd/C catalyst on O2 in the incoming air, which resulted in high CO and CO2 concentrations—telltale fingerprints of chemical combination of atmospheric O2 and C in the catalyst." | |||
| An excess heat observation is based on an ]. Various sources of energy input and output are continuously measured. Under normal conditions, the energy input can be matched to the energy output to within experimental error. In experiments such as those run by Fleischmann and Pons, an electrolysis cell operating steadily at one temperature transitions to operating at a higher temperature with no increase in applied current.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990}} If the higher temperatures were real, and not an experimental artifact, the energy balance would show an unaccounted term. In the Fleischmann and Pons experiments, the rate of inferred excess heat generation was in the range of 10–20% of total input, though this could not be reliably replicated by most researchers.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004|p=3}} Researcher ] discovered that the excess heat in Fleischmann and Pons's original paper was not measured, but estimated from measurements that didn't have any excess heat.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=256–259}} | |||
| Unable to produce excess heat or neutrons, and with positive experiments being plagued by errors and giving disparate results, most researchers declared that heat production was not a real effect and ceased working on the experiments.<ref>{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=x, 22–40, 70–72, 75–78, 97, 222–223}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=211–214, 230–232, 254–271}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=264–266, 270–271}} {{harvnb|Choi|2005}}</ref> In 1993, after their original report, Fleischmann reported "heat-after-death" experiments—where excess heat was measured after the electric current supplied to the electrolytic cell was turned off.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|1993}} This type of report has also become part of subsequent cold fusion claims.<ref>{{harvnb|Mengoli|Bernardini|Manduchi|Zannoni|1998}}, {{harvnb|Szpak|Mosier-Boss|Miles|Fleischmann|2004}}</ref> | |||
| === Insufficient theoretical explanations === | |||
| Nuclear fusion in the laboratory normally requires temperatures of tens of millions of degrees. The 1989 DOE panel said that such "nuclear fusion at room temperature would be contrary to all understanding gained of nuclear reactions in the last half century" and "it would require the invention of an entirely new nuclear process." <ref name="DOE_1989_37"/> but it also recognized that "the failure of a theory to account for cold fusion can be discounted on the grounds that the correct explanation and theory has not been provided",<ref name="DOE_1989_36"/> that is, the lack of a satisfactory explanation could not be used to dismiss experimental evidence. | |||
| ===Helium, heavy elements, and neutrons=== | |||
| Cold fusion observations are contrary to the conventional physics of nuclear fusion in several ways : | |||
| ] plastic radiation detector claimed as evidence for neutron emission from palladium deuteride]] | |||
| * Nuclear reactions would occur at low temperatures if the nuclei could be forced close enough together. The average density of deuterium atoms that can be obtained in palladium is vastly insufficient for fusion to occur according to known mechanisms. The average distance is approximately 0.17 ]s, which is too far apart to allow a significant rate of fusion through quantum mechanical tunneling. In fact, this distance is farther than the separation of nuclei in D<sub>2</sub> gas molecules, which do not exhibit fusion.<ref name="DOE_1989_6_7">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|Ref=DOE1989|pp=6-7}}</ref> | |||
| Known instances of nuclear reactions, aside from producing energy, also produce ]s and particles on readily observable ballistic trajectories. In support of their claim that nuclear reactions took place in their electrolytic cells, Fleischmann and Pons reported a ] of 4,000 neutrons per second, as well as detection of tritium. The classical ] for previously known fusion reactions that produce tritium would predict, with 1 ] of power, the production of 10<sup>12</sup> neutrons per second, levels that would have been fatal to the researchers.<ref>{{harvnb|Simon|2002|p=}}, {{harvnb|Park|2000|pp=}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=7}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=306–307}}</ref> In 2009, ] et al. reported what they called the first scientific report of highly energetic neutrons, using ] plastic radiation detectors,<ref name=MosierBoss2009>{{harvnb|Mosier-Boss|Szpak|Gordon|Forsley|2009}}, {{harvnb|Sampson|2009}}</ref> but the claims cannot be validated without a ] of neutrons.{{sfn|ps=|Barras|2009}}{{sfn|ps=|Berger|2009}} | |||
| * There is no known mechanism that would release fusion energy as heat instead of radiation within the relatively small metal lattice.<ref name="Goodstein_1994_528">{{harvnb|Goodstein|1994|p=528}}</ref> The direct conversion of fusion energy into heat is not possible because of energy and ] conservation and the laws of ].<ref name="Kee_1999_5">{{harvnb|Kee|1999|p=5}}</ref> | |||
| Several medium and heavy elements like calcium, titanium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, copper and zinc have been reported as detected by several researchers, like ] or ]. The report presented to the ] in 2004 indicated that deuterium-loaded foils could be used to detect fusion reaction products and, although the reviewers found the evidence presented to them as inconclusive, they indicated that those experiments did not use state-of-the-art techniques.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004|pp=3, 4, 5}} | |||
| Cold fusion researchers acknowledge these issues and have proposed various speculative theories (for a full review, see {{harvnb|Storms|2007}}) to explain the reported observations, but none has received mainstream acceptance.<ref name="Biberian_2007">{{harvnb|Biberian|2007}}</ref> | |||
| In response to doubts about the lack of nuclear products, cold fusion researchers have tried to capture and measure nuclear products correlated with excess heat.{{sfn|ps=|Hagelstein|2010}} Considerable attention has been given to measuring <sup>4</sup>He production.{{sfn|ps=|Hagelstein|McKubre|Nagel|Chubb|2004}} However, the reported levels are very near to background, so contamination by trace amounts of helium normally present in the air cannot be ruled out. In the report presented to the DOE in 2004, the reviewers' opinion was divided on the evidence for <sup>4</sup>He, with the most negative reviews concluding that although the amounts detected were above background levels, they were very close to them and therefore could be caused by contamination from air.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004|pp=3,4}} | |||
| One of the main criticisms of cold fusion was that deuteron-deuteron fusion into helium was expected to result in the production of ]—which were not observed and were not observed in subsequent cold fusion experiments.{{sfn|ps=|Schaffer|1999|p=2}}{{sfn|ps=|Rogers|Sandquist|1990}} Cold fusion researchers have since claimed to find X-rays, helium, neutrons{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|p=215}} and ]s.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=150–153, 162}} Some researchers also claim to have found them using only light water and nickel cathodes.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|p=215}} The 2004 DOE panel expressed concerns about the poor quality of the theoretical framework cold fusion proponents presented to account for the lack of gamma rays.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004|pp=3,4}} | |||
| ==Proposed mechanisms== | |||
| Researchers in the field do not agree on a theory for cold fusion.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=153, 214–216}} One proposal considers that hydrogen and its ] can be absorbed in certain solids, including ], at high densities. This creates a high partial pressure, reducing the average separation of hydrogen isotopes. However, the reduction in separation is not enough to create the fusion rates claimed in the original experiment, by a factor of ten.<ref name="distance" /> It was also proposed that a higher density of hydrogen inside the palladium and a lower potential barrier could raise the possibility of fusion at lower temperatures than expected from a simple application of ]. ] of the positive hydrogen nuclei by the negative electrons in the palladium lattice was suggested to the 2004 DOE commission,{{sfn|ps=|Hagelstein|McKubre|Nagel|Chubb|2004|pp=14–15}} but the panel found the theoretical explanations not convincing and inconsistent with current physics theories.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004}} | |||
| ==Criticism== | |||
| Criticism of cold fusion claims generally take one of two forms: either pointing out the theoretical implausibility that fusion reactions have occurred in electrolysis setups or criticizing the excess heat measurements as being spurious, erroneous, or due to poor methodology or controls. There are several reasons why known fusion reactions are an unlikely explanation for the excess heat and associated cold fusion claims.<ref group="text" name="branching_and_gamma" /> | |||
| ===Repulsion forces=== | |||
| Because nuclei are all positively charged, they strongly repel one another.{{sfn|ps=|Schaffer|1999|p=2}} Normally, in the absence of a catalyst such as a ], very high ] are required to overcome this ].{{sfn|ps=|Schaffer|1999|p=1}}{{sfn|ps=|Morrison|1999|pp=3–5}} Extrapolating from known fusion rates, the rate for uncatalyzed fusion at room-temperature energy would be 50 orders of magnitude lower than needed to account for the reported excess heat.<ref>{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|p=viii}} "''Enhancing the probability of a nuclear reaction by 50 orders of magnitude (...) via the chemical environment of a metallic lattice, contradicted the very foundation of nuclear science.''", {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}, {{harvnb|Scaramuzzi|2000|p=4}}</ref> In muon-catalyzed fusion there are more fusions because the presence of the muon causes deuterium nuclei to be 207 times closer than in ordinary deuterium gas.<ref>{{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=32, 54}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|p=112}}</ref> But deuterium nuclei inside a palladium lattice are further apart than in deuterium gas, and there should be fewer fusion reactions, not more.<ref name="distance">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|pp=7–8, 33, 53–58 (appendix 4.A)}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=257–258}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|p=112}}, {{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=253–254}} quoting ] in the special cold fusion session of the 1989 spring meeting of the Materials Research Society, {{harvnb|Park|2000|pp=17–18, 122}}, {{harvnb|Simon|2002|p=50}} citing {{cite journal|mode=cs2 |author1=Koonin S.E. |author2=M Nauenberg |s2cid=4335882 |year= 1989 |title= Calculated Fusion Rates in Isotopic Hydrogen Molecules |journal= Nature |issue= 6227|pages= 690–692 |doi= 10.1038/339690a0 |bibcode = 1989Natur.339..690K |volume=339}}</ref> | |||
| Paneth and Peters in the 1920s already knew that palladium can absorb up to 900 times its own volume of hydrogen gas, storing it at several thousands of times the ].{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=19–20}} This led them to believe that they could increase the nuclear fusion rate by simply loading palladium rods with hydrogen gas.{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=19–20}} Tandberg then tried the same experiment but used electrolysis to make palladium absorb more deuterium and force the deuterium further together inside the rods, thus anticipating the main elements of Fleischmann and Pons' experiment.{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=19–20}}<ref name="similar_to_tandberg" /> They all hoped that pairs of hydrogen nuclei would fuse together to form helium, which at the time was needed in Germany to fill ]s, but no evidence of helium or of increased fusion rate was ever found.{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=19–20}} | |||
| This was also the belief of geologist Palmer, who convinced Steven Jones that the helium-3 occurring naturally in Earth perhaps came from fusion involving hydrogen isotopes inside catalysts like nickel and palladium.{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=63–64}} This led their team in 1986 to independently make the same experimental setup as Fleischmann and Pons (a palladium cathode submerged in heavy water, absorbing deuterium via electrolysis).{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=64–66}} Fleischmann and Pons had much the same belief,{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=32–33}} but they calculated the pressure to be of 10<sup>27</sup> ], when cold fusion experiments achieve a loading ratio of only one to one, which has only between 10,000 and 20,000 atmospheres.<ref group="text" name="pressure" /> ] says they had misinterpreted the ], leading them to believe that there was enough pressure to bring deuterons so close to each other that there would be spontaneous fusions.{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|pp=33, 47}} | |||
| ===Lack of expected reaction products=== | |||
| Conventional deuteron fusion is a two-step process,<ref group="text" name="branching_and_gamma" /> in which an unstable high-energy ] is formed: | |||
| :] + {{sup|2}}H → ]] + 24 ] | |||
| Experiments have shown only three decay pathways for this excited-state nucleus, with the ] showing the probability that any given intermediate follows a particular pathway.<ref group="text" name="branching_and_gamma"/> The products formed via these decay pathways are: | |||
| :{{sup|4}}He{{sup|*}} → ] + ] + 3.3 MeV (]=50%) | |||
| :{{sup|4}}He{{sup|*}} → ] + ] + 4.0 MeV (ratio=50%) | |||
| :] + ] + 24 MeV (ratio=10{{sup|−6}}) | |||
| Only about one in a million of the intermediaries take the third pathway, making its products very rare compared to the other paths.{{sfn|ps=|Schaffer|1999|p=2}} This result is consistent with the predictions of the ].<ref group="text" name="consistent"/> If 1 watt (6.242 × 10{{sup|18}} eV/s){{refn|group="notes"|name=watt-ev|refn=1 W = 1 J/s ; 1 J = 6.242 × 10{{sup|18}} eV since 1 eV = 1.602 × 10{{sup|−19}} joule}} were produced from ~2.2575 × 10{{sup|11}} deuteron fusions per second, with the known branching ratios, the resulting neutrons and tritium ({{sup|3}}H) would be easily measured.{{sfn|ps=|Schaffer|1999|p=2}}{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|pp=7}} Some researchers reported detecting {{sup|4}}He but without the expected neutron or tritium production; such a result would require branching ratios strongly favouring the third pathway, with the actual rates of the first two pathways lower by at least five orders of magnitude than observations from other experiments, directly contradicting both theoretically predicted and observed branching probabilities.<ref group="text" name="branching_and_gamma" /> Those reports of {{sup|4}}He production did not include detection of ]s, which would require the third pathway to have been changed somehow so that gamma rays are no longer emitted.<ref group="text" name="branching_and_gamma" /> | |||
| The known rate of the decay process together with the inter-atomic spacing in a ] makes heat transfer of the 24 MeV excess energy into the host metal lattice prior to the intermediary's decay inexplicable by conventional understandings of ] and energy transfer,<ref>{{harvnb|Scaramuzzi|2000|p=4}}, {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=207–208, 218}}</ref> and even then there would be measurable levels of radiation.<ref>{{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=308–309}} "Some radiation would emerge, either electrons ejected from atoms or X-rays as the atoms are disturbed, but none were seen."</ref> Also, experiments indicate that the ratios of deuterium fusion remain constant at different energies.<ref name="Huizenga_chemical_environment">{{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=268}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=112–113}}</ref> In general, pressure and chemical environment cause only small changes to fusion ratios.<ref name="Huizenga_chemical_environment" /> An early explanation invoked the ] at low energies, but its magnitude was too small to explain the altered ratios.{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|pp=75–76, 113}} | |||
| ===Setup of experiments=== | |||
| Cold fusion setups utilize an input power source (to ostensibly provide ]), a ] ], a deuterium or hydrogen source, a ], and, at times, detectors to look for byproducts such as helium or neutrons. Critics have variously taken issue with each of these aspects and have asserted that there has not yet been a consistent reproduction of claimed cold fusion results in either energy output or byproducts. Some cold fusion researchers who claim that they can consistently measure an excess heat effect have argued that the apparent lack of reproducibility might be attributable to a lack of quality control in the electrode metal or the amount of hydrogen or deuterium loaded in the system. Critics have further taken issue with what they describe as mistakes or errors of interpretation that cold fusion researchers have made in calorimetry analyses and energy budgets.{{citation needed|date=March 2021}} | |||
| ====Reproducibility==== | |||
| In 1989, after Fleischmann and Pons had made their claims, many research groups tried to reproduce the Fleischmann-Pons experiment, without success. A few other research groups, however, reported successful reproductions of cold fusion during this time. In July 1989, an Indian group from the ] (] and M. Srinivasan) and in October 1989, ]' group from ] reported on the creation of tritium. In December 1990, professor ] of the ] reported excess heat.{{sfn|ps=|Taubes|1993|pp=364–365}} | |||
| Groups that did report successes found that some of their cells were producing the effect, while other cells that were built exactly the same and used the same materials were not producing the effect.{{sfn|ps=|Platt|1998}} Researchers that continued to work on the topic have claimed that over the years many successful replications have been made, but still have problems getting reliable replications.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} ] is one of the main principles of the scientific method, and its lack led most physicists to believe that the few positive reports could be attributed to experimental error.{{sfn|ps=|Platt|1998}}<ref group="text" name="reger"/> The DOE 2004 report said among its conclusions and recommendations: | |||
| {{blockquote|text=Ordinarily, new scientific discoveries are claimed to be consistent and reproducible; as a result, if the experiments are not complicated, the discovery can usually be confirmed or disproved in a few months. The claims of cold fusion, however, are unusual in that even the strongest proponents of cold fusion assert that the experiments, for unknown reasons, are not consistent and reproducible at the present time. (...) Internal inconsistencies and lack of predictability and reproducibility remain serious concerns. (...) The Panel recommends that the cold fusion research efforts in the area of heat production focus primarily on confirming or disproving reports of excess heat.{{sfn|ps=|US DOE|2004}}}} | |||
| =====Loading ratio===== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Cold fusion researchers (] since 1994,{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} ] in 2011<ref name=ENEA_Magazin/>) have speculated that a cell that is loaded with a deuterium/palladium ratio lower than 100% (or 1:1) will not produce excess heat.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} Since most of the negative replications from 1989 to 1990 did not report their ratios, this has been proposed as an explanation for failed reproducibility.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} This loading ratio is hard to obtain, and some batches of palladium never reach it because the pressure causes cracks in the palladium, allowing the deuterium to escape.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} Fleischmann and Pons never disclosed the deuterium/palladium ratio achieved in their cells;{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|p=82}} there are no longer any batches of the palladium used by Fleischmann and Pons (because the supplier now uses a different manufacturing process),{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} and researchers still have problems finding batches of palladium that achieve heat production reliably.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=145–148}} | |||
| ====Misinterpretation of data==== | |||
| Some research groups initially reported that they had replicated the Fleischmann and Pons results but later retracted their reports and offered an alternative explanation for their original positive results. A group at ] found problems with their neutron detector, and Texas A&M discovered bad wiring in their thermometers.{{sfn|ps=|Bird|1998|pp=261–262}} These retractions, combined with negative results from some famous laboratories,{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989}} led most scientists to conclude, as early as 1989, that no positive result should be attributed to cold fusion.{{sfn|ps=|Bird|1998|pp=261–262}}{{sfn|ps=|Saeta|1999|loc= (pages 5–6; "Response"; Heeter, Robert F.)}} | |||
| ====Calorimetry errors==== | |||
| The calculation of excess heat in electrochemical cells involves certain assumptions.<ref>{{harvnb|Biberian|2007}} "Input power is calculated by multiplying current and voltage, and output power is deduced from the measurement of the temperature of the cell and that of the bath"</ref> Errors in these assumptions have been offered as non-nuclear explanations for excess heat. | |||
| One assumption made by Fleischmann and Pons is that the efficiency of electrolysis is nearly 100%, meaning nearly all the electricity applied to the cell resulted in electrolysis of water, with negligible ] and substantially all the electrolysis product leaving the cell unchanged.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990}} This assumption gives the amount of energy expended converting liquid D<sub>2</sub>O into gaseous D<sub>2</sub> and O<sub>2</sub>.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990|loc=Appendix}} The efficiency of electrolysis is less than one if hydrogen and oxygen recombine to a significant extent within the calorimeter. Several researchers have described potential mechanisms by which this process could occur and thereby account for excess heat in electrolysis experiments.{{sfn|ps=|Shkedi|McDonald|Breen|Maguire|1995}}{{sfn|ps=|Jones|Hansen|Jones|Shelton|1995|p=1}}{{sfn|ps=|Shanahan|2002}} | |||
| Another assumption is that heat loss from the calorimeter maintains the same relationship with measured temperature as found when calibrating the calorimeter.{{sfn|ps=|Fleischmann|Pons|Anderson|Li|1990}} This assumption ceases to be accurate if the temperature distribution within the cell becomes significantly altered from the condition under which calibration measurements were made.<ref>{{harvnb|Biberian|2007}} "Almost all the heat is dissipated by radiation and follows the temperature fourth power law. The cell is calibrated ..."</ref> This can happen, for example, if fluid circulation within the cell becomes significantly altered.{{sfn|ps=|Browne|1989|loc=para. 16}}{{sfn|ps=|Wilson|Bray|Kosky|Vakil|1992}} Recombination of hydrogen and oxygen within the calorimeter would also alter the heat distribution and invalidate the calibration.{{sfn|ps=|Shanahan|2002}}{{sfn|ps=|Shanahan|2005}}{{sfn|ps=|Shanahan|2006}} | |||
| == Publications == | |||
| The ] identified cold fusion as the scientific topic with the largest number of published papers in 1989, of all scientific disciplines.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=180–183, 209}} The ] ] declared himself a supporter of cold fusion in the fall of 1989, after much of the response to the initial reports had turned negative. He tried to publish his theoretical paper "Cold Fusion: A Hypothesis" in '']'', but the peer reviewers rejected it so harshly that he felt deeply insulted, and he resigned from the ] (publisher of ''PRL'') in protest.{{sfn|ps=|Mehra |Milton |Schwinger |2000|p=}}{{sfn|ps=|Close|1992|pp=197–198}} | |||
| The number of papers sharply declined after 1990 because of two simultaneous phenomena: first, scientists abandoned the field; second, journal editors declined to review new papers. Consequently, cold fusion fell off the ISI charts.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=180–183, 209}}{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=180–183}} Researchers who got negative results turned their backs on the field; those who continued to publish were simply ignored.{{sfn|ps=|Huizenga|1993|pp=208}} A 1993 paper in ''Physics Letters A'' was the last paper published by Fleischmann, and "one of the last reports to be formally challenged on technical grounds by a cold fusion skeptic."<ref group="text" name="last_challenged" /> | |||
| The ''Journal of Fusion Technology'' (FT) established a permanent feature in 1990 for cold fusion papers, publishing over a dozen papers per year and giving a mainstream outlet for cold fusion researchers. When editor-in-chief ] retired in 2001, the journal stopped accepting new cold fusion papers.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=180–183}} This has been cited as an example of the importance of sympathetic influential individuals to the publication of cold fusion papers in certain journals.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=180–183}} | |||
| The decline of publications in cold fusion has been described as a "failed information epidemic".<ref group="text" name="fie" /> The sudden surge of supporters until roughly 50% of scientists support the theory, followed by a decline until there is only a very small number of supporters, has been described as a characteristic of ].<ref group="text" name="pathological" /><ref group="notes" name="Langmuir" /> The lack of a shared set of unifying concepts and techniques has prevented the creation of a dense network of collaboration in the field; researchers perform efforts in their own and in disparate directions, making the transition to "normal" science more difficult.{{sfn|ps=|Bettencourt|Kaiser|Kaur|2009}} | |||
| Cold fusion reports continued to be published in a few journals like '']'' and '']''. Some papers also appeared in '']'', '']'', '']'', and a number of Japanese and Russian journals of physics, chemistry, and engineering.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=180–183}} Since 2005, '']'' has published cold fusion papers; in 2009, the journal named a cold fusion researcher to its editorial board. In 2015 the Indian multidisciplinary journal '']'' published a special section devoted entirely to cold fusion related papers.<ref name="currentscience.ac.in"/> | |||
| In the 1990s, the groups that continued to research cold fusion and their supporters established (non-peer-reviewed) periodicals such as ''Fusion Facts'', ''Cold Fusion Magazine'', '']'' and ''New Energy Times'' to cover developments in cold fusion and other fringe claims in energy production that were ignored in other venues. The internet has also become a major means of communication and self-publication for CF researchers.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=183–187}} | |||
| == Conferences == | |||
| Cold fusion researchers were for many years unable to get papers accepted at scientific meetings, prompting the creation of their own conferences. The ] (ICCF) was first held in 1990 and has met every 12 to 18 months since. Attendees at some of the early conferences were described as offering no criticism to papers and presentations for fear of giving ammunition to external critics,{{sfn|ps=|Park|2000|pp=12–13}} thus allowing the proliferation of ] and hampering the conduct of serious science.{{sfn|ps=|Goodstein|1994}}<ref group="notes">The first three conferences are commented in detail in {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993 |pp=237–247, 274–285}}, specially 240, 275–277</ref> Critics and skeptics stopped attending these conferences, with the notable exception of Douglas Morrison,<ref>{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=276}}, {{harvnb|Park|2000|pp=12–13}}, {{harvnb|Simon|2002|p=108}}</ref> who died in 2001. With the founding in 2004 of the International Society for Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (ISCMNS),<ref>{{cite web|url=https://iscmns.org/mission/faq/#ref1|title=ISCMNS FAQ|website=iscmns.org|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111223114431/http://www.iscmns.org/faq.htm#ref1|archive-date=23 December 2011}}</ref> the conference was renamed the International Conference on Condensed Matter Nuclear Science{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=131–133, 218}}{{sfn|ps=|Seife|2008|pp=154–155}}<ref name="taubes378">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=378, 427}} ''anomalous effects in deuterated metals,'' which was the new, preferred, politically palatable nom de science for cold fusion ."</ref>—for reasons that are detailed in the ] above—but reverted to the old name in 2008.<ref>{{cite book |url=http://www.iscmns.org/iccf14/ProcICCF14b.pdf |title=Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Condensed Matter Nuclear Science and the 14th International Conference on Cold Fusion (ICCF-14) – 10–15 August 2008 Washington DC |year=2008 |volume=2 |publisher=New Energy Foundation |editor-last1=Nagel |editor-first1=David J. |editor-last2=Melich |editor-first2=Michael E. |isbn=978-0-578-06694-3 |access-date=31 October 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120731065530/http://www.iscmns.org/iccf14/ProcICCF14b.pdf |archive-date=31 July 2012}}</ref> Cold fusion research is often referenced by proponents as "low-energy nuclear reactions", or LENR,<ref name="bbc march 2009" /> but according to sociologist ] the "cold fusion" label continues to serve a social function in creating a ] for the field.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=131–133, 218}} | |||
| Since 2006, the ] (APS) has included cold fusion sessions at their semiannual meetings, clarifying that this does not imply a softening of skepticism.<ref name="aps meeting">{{harvnb|Chubb|McKubre|Krivit|Chubb|2006}}, {{harvnb|Adam|2005}} (". Anyone can deliver a paper. We defend the openness of science" – Bob Park of APS, when asked if hosting the meeting showed a softening of scepticism)</ref>{{sfn|ps=|Van Noorden|2007}} Since 2007, the ] (ACS) meetings also include "invited symposium(s)" on cold fusion.{{sfn|ps=|Van Noorden|2007|loc=para. 2}} An ACS program chair, Gopal Coimbatore, said that without a proper forum the matter would never be discussed and, "with the world facing an energy crisis, it is worth exploring all possibilities."{{sfn|ps=|Van Noorden|2007}} | |||
| On 22–25 March 2009, the American Chemical Society meeting included a four-day symposium in conjunction with the 20th anniversary of the announcement of cold fusion. Researchers working at the U.S. Navy's ] (SPAWAR) reported detection of energetic ] using a heavy water electrolysis setup and a ] detector,<ref name="ACS Press Release" /><ref name="reignites" /> a result previously published in '']''.{{sfn|ps=|Barras|2009}} The authors claim that these neutrons are indicative of nuclear reactions.<ref name="afp march 2009">{{cite web|mode=cs2 |url=https://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5j2QobOQnlULUZ7oalSRUVjnlHjng |title=Scientists in possible cold fusion breakthrough |access-date=24 March 2009 |publisher=] |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090327020127/http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5j2QobOQnlULUZ7oalSRUVjnlHjng |archive-date=27 March 2009 }}</ref> Without quantitative analysis of the number, energy, and timing of the neutrons and exclusion of other potential sources, this interpretation is unlikely to find acceptance by the wider scientific community.{{sfn|ps=|Barras|2009}}{{sfn|ps=|Berger|2009}} | |||
| ==Patents== | |||
| Although details have not surfaced, it appears that the University of Utah forced the 23 March 1989 Fleischmann and Pons announcement to establish priority over the discovery and its patents before the joint publication with Jones.<ref name="utah patent"/> The ] (MIT) announced on 12 April 1989 that it had applied for its own patents based on theoretical work of one of its researchers, ], who had been sending papers to journals from 5 to 12 April.<ref name=Broad1989/> An MIT graduate student applied for a patent but was reportedly rejected by the USPTO in part by the citation of the "negative" MIT Plasma Fusion Center's cold fusion experiment of 1989. On 2 December 1993 the University of Utah licensed all its cold fusion patents to ENECO, a new company created to profit from cold fusion discoveries,{{sfn|ps=|Lewenstein|1994|p=43}} and in March 1998 it said that it would no longer defend its patents.<ref name="wired steam">{{cite magazine|mode= cs2 |title= Cold Fusion Patents Run Out of Steam |author= Wired News Staff Email |date= 24 March 1998 |magazine= ] |url= https://www.wired.com/science/discoveries/news/1998/03/11179 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20140104170533/http://www.wired.com/science/discoveries/news/1998/03/11179 |archive-date= 4 January 2014 |url-status= live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] (USPTO) now rejects patents claiming cold fusion.<ref name="Weinberger2004"/> Esther Kepplinger, the deputy commissioner of patents in 2004, said that this was done using the same argument as with ]s: that they do not work.<ref name="Weinberger2004"/> Patent applications are required to show that the invention is "useful", and this ] is dependent on the invention's ability to function.<ref name="incredible"/> In general USPTO rejections on the sole grounds of the invention's being "inoperative" are rare, since such rejections need to demonstrate "proof of total incapacity",<ref name="incredible"/> and cases where those rejections are upheld in a Federal Court are even rarer: nevertheless, in 2000, a rejection of a cold fusion patent was appealed in a Federal Court and it was upheld, in part on the grounds that the inventor was unable to establish the utility of the invention.<ref name="incredible"/><ref group="notes" name="patent case"/> | |||
| A U.S. patent might still be granted when given a different name to disassociate it from cold fusion,{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=193, 233}} though this strategy has had little success in the US: the same claims that need to be patented can identify it with cold fusion, and most of these patents cannot avoid mentioning Fleischmann and Pons' research due to legal constraints, thus alerting the patent reviewer that it is a cold-fusion-related patent.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=193, 233}} David Voss said in 1999 that some patents that closely resemble cold fusion processes, and that use materials used in cold fusion, have been granted by the USPTO.<ref name="voss-science"/> The inventor of three such patents had his applications initially rejected when they were reviewed by experts in nuclear science; but then he rewrote the patents to focus more on the electrochemical parts so they would be reviewed instead by experts in electrochemistry, who approved them.<ref name="voss-science"/><ref>{{cite journal|mode=cs2 |title=A Case Study of Inoperable Inventions: Why Is the USPTO Patenting Pseudoscience? |author=Daniel C. Rislove |journal=Wisconsin Law Review |year=2006 |volume=2006 |issue=4 |pages=1302–1304, footnote 269 in page 1307 |url=http://hosted.law.wisc.edu/lawreview/issues/2006-4/rislove.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150925131935/http://hosted.law.wisc.edu/lawreview/issues/2006-4/rislove.pdf |archive-date=25 September 2015 }}</ref> When asked about the resemblance to cold fusion, the patent holder said that it used nuclear processes involving "new nuclear physics" unrelated to cold fusion.<ref name="voss-science"/> Melvin Miles was granted in 2004 a patent for a cold fusion device, and in 2007 he described his efforts to remove all instances of "cold fusion" from the patent description to avoid having it rejected outright.<ref name=Sanderson2007/> | |||
| At least one patent related to cold fusion has been granted by the ].<ref name=Fox1994a/> | |||
| A patent only legally prevents others from using or benefiting from one's invention. However, the general public perceives a patent as a stamp of approval, and a holder of three cold fusion patents said the patents were very valuable and had helped in getting investments.<ref name="voss-science"/> | |||
| ==Cultural references== | |||
| A 1990 ] film '']'', starring ] and ], referenced the Fleischmann and Pons experiment. The film – a comedy – concerned conmen trying to steal scientists' purported findings. However, the film had a poor reception, described as "appallingly unfunny".{{sfn|ps=|Radio Times Film Unit|2013|pp=181–182}} | |||
| In ''Undead Science'', sociologist Bart Simon gives some examples of cold fusion in popular culture, saying that some scientists use cold fusion as a synonym for outrageous claims made with no supporting proof,{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} and courses of ethics in science give it as an example of pathological science.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} It has appeared as a joke in '']'' and '']''.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} It was adopted as a software product name ] and a brand of protein bars (Cold Fusion Foods).{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} It has also appeared in advertising as a synonym for impossible science, for example a 1995 advertisement for ].{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} | |||
| The plot of '']'', a 1997 action-adventure film, parallels the story of Fleischmann and Pons, although with a different ending.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} In ''Undead Science'', Simon posits that film might have affected the public perception of cold fusion, pushing it further into the science fiction realm.{{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=91–95, 116–118}} | |||
| Similarly, the tenth episode of 2000 science fiction TV drama '']'' ("Paradise Island") is also based around cold fusion, specifically the efforts of eccentric scientist Hepzibah McKinley (]), who is convinced she has perfected it based on her father's incomplete research into the subject.<ref name = "The Hill and Beyond" >{{cite book |last=McGown |first=Alistair |author-link= |date=2003 |title=The Hill and Beyond: Children's Television Drama – An Encyclopedia |url=https://archive.org/details/hillbeyondchildr0000mcgo |publisher=BFI |page=266 |isbn=0851708781}}</ref> The episode explores its potential benefits and viability within the ongoing post-apocalyptic ] scenario of the series.<ref name = "The Hill and Beyond" ></ref> | |||
| In the 2023 video game '']'', cold fusion is responsible for nearly all of the technological advances.<ref>{{cite web |title=Atomic Heart – Everything You Need to Know |url=https://nexushub.co.za/nexus/atomic-heart-everything-you-need-to-know.html |website=Nexus Hub}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{Div col|colwidth=22em}} | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (E-cat) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (patent concept) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| == |
== Notes== | ||
| {{Reflist|group="notes"|refs= | |||
| {{reflist|3}} | |||
| <ref group="notes" name="differences">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=228–229, 255}} "(...) there are indeed chemical differences between heavy and light water, especially once lithium is added, as it was in the Pons-Fleischmann electrolyte. This had been in the scientific literature since 1958. It seems that the electrical conductivity of heavy water with lithium is considerably less than that of light water with lithium. And this difference is more than enough to account for the heavy water cell running hotter (...) (quoting a member of the A&M group) 'they're making the same mistake we did'"</ref> | |||
| <ref group="notes" name="nature critical papers">E.g.: | |||
| * {{cite journal |mode=cs2 | vauthors= Miskelly GM, Heben MJ, Kumar A, Penner RM, Sailor MJ, Lewis NL | s2cid = 42943868 | title = Analysis of the Published Calorimetric Evidence for Electrochemical Fusion of Deuterium in Palladium | journal = ] | volume = 246 | issue = 4931 | year = 1989 | doi = 10.1126/science.246.4931.793 | pages = 793–796 | pmid = 17748706 |bibcode = 1989Sci...246..793M |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |mode=cs2 | vauthors= Aberdam D, Avenier M, Bagieu G, Bouchez J, Cavaignac JF, Collot J | doi = 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.1196 | title = Limits on neutron emission following deuterium absorption into palladium and titanium | journal = Phys. Rev. Lett. | volume = 65 | issue = 10 | pages = 1196–1199 | year = 1990 | bibcode=1990PhRvL..65.1196A |ref=none|display-authors=etal | pmid=10042199}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |mode=cs2 | vauthors= Price PB, Barwick SW, Williams WT, Porter JD | title = Search for energetic-charged-particle emission from deuterated Ti and Pd foils | volume = 63 | issue = 18 | pages = 1926–1929 | journal = Phys. Rev. Lett. | year = 1989 | doi = 10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.1926 | bibcode=1989PhRvL..63.1926P |ref=none | pmid=10040716 | url = https://zenodo.org/record/1233870 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |mode=cs2 | vauthors= Roberts DA, Becchetti FD, Ben-Jacob E, Garik P, Musser J, Orr B, Tarlé G, Tomasch A, Holder JS, Redina D, Heuser B, Wicker G | title = Energy and flux limits of cold-fusion neutrons using a deuterated liquid scintillator | journal = Phys. Rev. C | volume = 42 | issue = 5 | pages = R1809–R1812 | doi = 10.1103/PhysRevC.42.R1809 | pmid = 9966919 | year = 1990 |bibcode = 1990PhRvC..42.1809R |ref=none|display-authors=4}} | |||
| * {{harvnb|Lewis|Barnes|Heben|Kumar|1989}}</ref> | |||
| <!-- Not in use | |||
| <ref group="notes" name="watt-ev">1 W = 1 J/s ; 1 J = 6.242 × 10<sup>18</sup> eV = 6.242 × 10<sup>12</sup> MeV since 1 eV = 1.602 × 10<sup>−19</sup> joule</ref> | |||
| Not in use--> | |||
| <ref group="notes" name="Langmuir">Sixth criterion of Langmuir: "During the course of the controversy the ratio of supporters to critics rises to near 50% and then falls gradually to oblivion. {{harvnb|Langmuir|Hall|1989|pp=43–44}}", quoted in {{harvnb|Simon|2002|p=104}}, paraphrased in {{harvnb|Ball|2001|p=308}}. It has also been applied to the number of published results, in {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=xi, 207–209}} "The ratio of the worldwide positive results on cold fusion to negative results peaked at approximately 50% (...) qualitatively in agreement with Langmuir's sixth criteria."</ref> | |||
| <ref group="notes" name="Beaudette rejection">On 26 January 1990, journal ''Nature'' rejected Oriani's paper, citing the lack of nuclear ash and the general difficulty that others had in replication.{{harvnb|Beaudette|2002|p=183}} It was later published in ''Fusion Technology''.{{harvnb|Oriani|Nelson|Lee|Broadhurst|1990|pp=652–662}}</ref> | |||
| <ref group="notes" name="patent case">Swartz, 232 F.3d 862, 56 USPQ2d 1703, (Fed. Cir. 2000). {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080312055400/http://www.ll.georgetown.edu/FEDERAL/judicial/fed/opinions/00opinions/00-1108.html |date=12 March 2008 }}. Sources: | |||
| * {{cite web|mode=cs2 |title=2164.07 Relationship of Enablement Requirement to Utility Requirement of 35 U.S.C. 101 – 2100 Patentability. B. Burden on the Examiner. Examiner Has Initial Burden To Show That One of Ordinary Skill in the Art Would Reasonably Doubt the Asserted Utility |publisher=U.S. Patent and Trademark Office |url=http://www.uspto.gov/web/offices/pac/mpep/documents/2100_2164_07.htm |ref=none |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120912152657/http://www.uspto.gov/web/offices/pac/mpep/documents/2100_2164_07.htm |archive-date=12 September 2012 |url-status=live}} Manual of Patent Examining Procedure, in reference to {{usc|35|101}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2|title=Patent law essentials: a concise guide |author=Alan L. Durham |edition=2nd, illustrated |publisher=] |year=2004 |isbn=9780275982058 |page=72 (footnote 30) |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RzZydAHtUoIC&q=patent+cold+fusion&pg=PA72 |ref=none}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2|title=How to write a patent application |author=Jeffrey G. Sheldon |edition=illustrated |publisher=] |year=1992 |isbn=978-0-87224-044-5 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=aIFyzuKs6q0C&q=patent+cold+fusion&pg=RA1-PT332 |ref=none}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| === Citations === | |||
| {{Reflist|30em|refs= | |||
| <ref name="utah patent">{{harvnb|Shamoo|Resnik|2003|p=86}}, {{harvnb|Simon|2002|pp=28–36}}</ref> | |||
| {{sfn|ps=|Simon|2002|pp=193, 233}} | |||
| <ref name="voss-science">{{harvnb|Voss|1999b}}, in reference to US patents {{Patent|US|5,616,219}}, {{Patent|US|5,628,886}} and {{Patent|US|5,672,259}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Sanderson2007>{{harvnb|Sanderson|2007}}, in reference to US patent {{Patent|US|6,764,561}}</ref> | |||
| {{sfn|ps=|Lewenstein|1994|p=43}} | |||
| <ref name=Fox1994a>{{harvnb|Fox|1994}} in reference to Canon's {{patent|EP|568118}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Broad1989>{{cite news |mode=cs2 |title='Cold Fusion' Patents Sought |author=Broad, William J. |author-link=William J. Broad |date=13 April 1989 |newspaper=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1989/04/13/us/cold-fusion-patents-sought.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170129235214/http://www.nytimes.com/1989/04/13/us/cold-fusion-patents-sought.html |archive-date=29 January 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Broad1989a>{{cite news |mode=cs2 |last=Broad |first=William J. |author-link=William J. Broad |date=14 April 1989 |title=Georgia Tech Team Reports Flaw In Critical Experiment on Fusion |newspaper=The New York Times |url= https://www.nytimes.com/1989/04/14/us/georgia-tech-team-reports-flaw-in-critical-experiment-on-fusion.html |access-date=25 May 2008}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name=Broad1989b>{{cite news |mode=cs2 |last=Broad |first=William J. |author-link=William J. Broad |date=31 October 1989 |title=Despite Scorn, Team in Utah Still Seeks Cold-Fusion Clues |newspaper=The New York Times |page=C1 |url= https://www.nytimes.com/1989/10/31/science/despite-scorn-team-in-utah-still-seeks-cold-fusion-clues.html?pagewanted=all}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="Weinberger2004">{{cite news|mode=cs2|newspaper=]|title=Warming Up to Cold Fusion|first=Sharon|last=Weinberger|date=21 November 2004|page=W22|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A54964-2004Nov16.html|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161119053757/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A54964-2004Nov16.html|archive-date=19 November 2016}} (page 2 in online version)</ref> | |||
| <ref name="incredible">{{cite web|mode=cs2|title=2107.01 General Principles Governing Utility Rejections (R-5) – 2100 Patentability. II. Wholly inoperative inventions; "incredible" utility |publisher=] |url=http://www.uspto.gov/web/offices/pac/mpep/documents/2100_2107_01.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120827184025/http://www.uspto.gov/web/offices/pac/mpep/documents/2100_2107_01.htm |archive-date=27 August 2012|url-status=live}} ]</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| === Citations of quotations === | |||
| {{reflist|group=text|35em|refs= | |||
| <ref name="only-support">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=225–226, 229–231}} " Like those of MIT or Harvard or Caltech, and official Stanford University announcement is not something to be taken lightly. (...) With the news out of Stanford, the situation, as one Department of Energy official put it, 'had come to a head'. The department had had its laboratory administrators send emissaries to Washington immediately. (...) the secretary of energy, had made the pursuit of cold fusion the department's highest priority (...) The government laboratories had free {{sic|rei|gn}} to pursue their cold fusion research, Ianniello said, to use whatever resources they needed, and DOE would cover the expenses. (...) While Huggins may have appeared to be the savior of cold fusion, his results also made him, and Stanford, a prime competitor for patents and rights.", {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=184, 250}} " The only support for Fleischmann and Pons came from Robert Huggins (...) The British Embassy in Washington rushed news of the proceedings to the Cabinet Office and Department of Energy in London. (...) noting that Huggin's heat measurements lent some support but that he had not checked for radiation, and also emphasizing that none of the US government laboratories had yet managed to replicate the effect.", {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|p=56}} "Of the above speakers (in the US Congress hearings) only Huggins supported the Fleischmann-Pons claim of excess heat."</ref> | |||
| <ref name="spiking">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|pp=418–420}} "While it is not possible for us to categorically exclude spiking as a possibility, it is our opinion, that possibility is much less probable than that of inadvertent contamination or other explained factors in the measurements.", {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=128–129}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="mixture">{{cite web|mode=cs2|title=Physicist Claims First Real Demonstration of Cold Fusion|date=27 May 2008|website=Physorg.com|url=http://www.physorg.com/news131101595.html|url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120315124847/http://www.physorg.com/news131101595.html|archive-date=15 March 2012}}. The peer reviewed papers referenced at the end of the article are "The Establishment of Solid Nuclear Fusion Reactor" – Journal of High Temperature Society, Vol. 34 (2008), No. 2, pp.85–93 and "Atomic Structure Analysis of Pd Nano-Cluster in Nano-Composite Pd⁄ZrO2 Absorbing Deuterium" – Journal of High Temperature Society, Vol. 33 (2007), No. 3, pp.142–156</ref> | |||
| <ref name="fie">{{harvnb|Ackermann|2006}} "(p. 11) Both the Polywater and Cold Nuclear Fusion journal literatures exhibit episodes of epidemic growth and decline."</ref> | |||
| <ref name="pathological">{{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=254–255, 329}} " The usual cycle in such cases, he notes, is that interest suddenly erupts (...) The phenomenon then separates the scientists in two camps, believers and skeptics. Interest dies as only a small band of believers is able to 'produce the phenomenon' (...) even in the face of overwhelming evidence to the contrary, the original practitioners may continue to believe in it for the rest of the careers.", {{harvnb|Ball|2001|p=308}}, {{harvnb|Simon|2002|pp=104}}, {{harvnb|Bettencourt|Kaiser|Kaur|2009}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="branching_and_gamma">{{harvnb|US DOE|1989|p=29}}, {{harvnb|Schaffer|1999|pp=1, 2}}, {{harvnb|Scaramuzzi|2000|p=4}}, {{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=265–268}} "(...) the equality of the two channels is known to be preserved from high energy through 20 keV and down to about 5 keV. A reason that it is not as well known below this energy because the individual rates are so low. However, the rate is known at room temperature from muon catalysed fusion experiments. (...) theory can even accommodate the subtle variations in the ratio at these low temperatures ", {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=6–7, 35–36, 75, 108–109, 112–114, 118–125, 130, 139, 173, 183, 217–218, 243–245}} " have been studied over a range of deuteron kinetic energies down to a few kiloelectron volts (keV). (...) appear to be essentially constant at low energies. There is no reason to think that these branching ratios would be measurably altered for cold fusion. The near equality of has been verified also for muon-catalyzed fusion. ", {{harvnb|Goodstein|1994}} (explaining Pons and Fleischmann would both be dead if they had produced neutrons in proportion to their measurements of excess heat) ("It has been said . . . three 'miracles' are necessary ")</ref> | |||
| <ref name="pressure">{{harvnb|Close|1992|pp=257–258}}, {{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=33, 47–48, 79, 99–100, 207, 216}} "By comparing cathode charging of deuterium into palladium with gas charging for a D7Pd ratio of unity, one obtains an equivalent pressure of 1.5x10<sup>4</sup> atmospheres, a value more than 20 orders of magnitude (10<sup>20</sup>) less than the Fleischmann-Pons claimed pressure.", Huizenga also cites {{harvnb|US DOE|2004|pp=33–34}} in chapter ''IV. Materials Characterization: D. 'Relevant' Materials Parameters: 2. Confinement Pressure,'' which has a similar explanation.</ref> | |||
| <ref name="consistent">{{harvnb|Huizenga|1993|pp=6–7, 35–36}} " This well established experimental result is consistent with the Bohr model, which predicts that the compound nucleus decays predominantly by particle emission , as opposed to radioactive capture , whenever it is energetically possible."</ref> | |||
| <ref name="reger">{{harvnb|Reger|Goode|Ball|2009|pp=814–815}} "After several years and multiple experiments by numerous investigators, most of the scientific community now considers the original claims unsupported by the evidence. Virtually every experiment that tried to replicate their claims failed. Electrochemical cold fusion is widely considered to be discredited."</ref> | |||
| <ref name="tandberg_not_known_by_FP">{{harvnb|Taubes|1993|p=214}} says the similarity was discovered on 13 April 1991, by a computer scientist and disseminated via the Internet. Another computer scientist translated an old article in the Swedish technical journal '']''. Taubes says: "''Ny Teknika'' seemed to believe that Tandberg had missed on the discovery of the century, done in by an ignorant patent bureau. When Pons heard the story, he agreed."</ref> | |||
| <ref name="tandberg_not_known_by_FP2">Brigham Young University discovered Tandberg's 1927 patent application, and showed it as proof that Utah University didn't have priority for the discovery of cold fusion, cited in {{harvnb|Wilford|1989}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="last_challenged">{{harvnb|Labinger|Weininger|2005|p=1919}} Fleischmann's paper was challenged in {{cite journal|last=Morrison |first=R.O. Douglas |title=Comments on claims of excess enthalpy by Fleischmann and Pons using simple cells made to boil |doi=10.1016/0375-9601(94)91133-9 |journal=Phys. Lett. A |volume=185 |issue=5–6 |date=28 February 1994 |pages=498–502 |bibcode=1994PhLA..185..498M |citeseerx=10.1.1.380.7178 }}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| == Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
| {{ |
{{Refbegin|30em}} | ||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Adam |first=David | |||
| | last=Ackermann | first=Eric | |||
| |s2cid=29197941 | |||
| |title=In from the cold | |||
| | date=February 2006 | |||
| |newspaper=The Guardian | |||
| | title=Indicators of failed information epidemics in the scientific journal literature: A publication analysis of Polywater and Cold Nuclear Fusion | |||
| |date=24 March 2005 | |||
| | journal=Scientometrics | |||
| |url=http://education.guardian.co.uk/higher/research/story/0,9865,1444306,00.html | |||
| | volume=66 | issue=3 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 | |||
| | pages=451–466 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | doi=10.1007/s11192-006-0033-0 | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Anderson |first=Mark | |||
| |title=Cold-Fusion Graybeards Keep the Research Coming | |||
| |periodical=Wired Magazine | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| |month=August | |||
| |url=http://www.wired.com/science/discoveries/news/2007/08/cold_fusion | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Arata |first=Yoshiaki | |||
| |last2=Zhang |first2=Yue-Chang | |||
| |title=Anomalous difference between reaction energies generated within D<sub>2</sub>0-cell and H<sub>2</sub>0 Cell | |||
| |journal=Japanese Journal of Applied Physics | |||
| |volume=37 | |||
| |issue=11A | |||
| |year=1998 | |||
| |pages=L1274–L1276 | |||
| |doi=10.1143/JJAP.37.L1274}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Beaudette |first=Charles G. | |||
| |title=Excess Heat & Why Cold Fusion Research Prevailed | |||
| |year=2002 | |||
| |location=New York | |||
| |publisher=Oak Grove Press | |||
| |isbn=9-9678548-2-2}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Biberian |first=Jean-Paul | |||
| |title=Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (Cold Fusion): An Update | |||
| |journal=International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Technology | |||
| |volume=3 | |||
| |issue=1 | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| |pages=31–43 | |||
| |doi=10.1504/IJNEST.2007.012439 | |||
| |url=http://www.jeanpaulbiberian.net/Download/Paper%2056.pdf | |||
| |format=PDF}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Bockris |first=John | |||
| |title=Accountability and academic freedom: The battle concerning research on cold fusion at Texas A&M University | |||
| |journal=Accountability Res. | |||
| |volume=8 | |||
| |year=2000 | |||
| |pages=103 | |||
| |doi=10.1080/08989620008573968}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Bowen |first=Jerry | |||
| |title=Science: Nuclear Fusion | |||
| |periodical=CBS Evening News | |||
| |date=April 10, 1989 | |||
| |url=http://openweb.tvnews.vanderbilt.edu/1989-4/1989-04-10-CBS-7.html | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25}} | |||
| *{{citation |last=Broad |first=William J. | |||
| |title=Georgia Tech Team Reports Flaw In Critical Experiment on Fusion | |||
| |newspaper=New York Times | |||
| |date=April 14, 1989 | |||
| |url=http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=950DE7DE1130F937A25757C0A96F948260 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Brooks|first=Michael | |||
| |title=13 things that don't make sense | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| |location=New York | |||
| |publisher=Doubleday | |||
| |isbn=978-0-385-52068-3}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Britz |first=Dieter | |||
| |title=Book review:The Science of Low Energy Nuclear Reaction | |||
| |journal=Journal of Scientific Exploration | |||
| |url=http://www.scientificexploration.org/jse/abstracts.php | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| |volume=21 | |||
| |issue=4 | |||
| |pages=801 | |||
| |issn=0892-3310 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Browne |first=M. | |||
| |title=Physicists Debunk Claim Of a New Kind of Fusion | |||
| |newspaper=New York Times | |||
| |date=May 3, 1989 | |||
| |url=http://partners.nytimes.com/library/national/science/050399sci-cold-fusion.html | |||
| |accessdate=2008-05-25}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Bush |first=Ben F. | |||
| |last2=Lagowski |first2=J. J. | |||
| |last3=Miles |first3=M. H. | |||
| |last4=Ostrom |first4=Greg S. | |||
| |year=1991 | |||
| |title=Helium Production During the Electrolysis of D<sub>2</sub>O in Cold Fusion | |||
| |journal=] | |||
| |volume=304 | |||
| |pages=271–278 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(91)85510-V}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Charles |first=Dan | |||
| |title=Fatal explosion closes cold fusion laboratory | |||
| |journal=New Scientist | |||
| |year=1992 | |||
| |url=http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg13318030.600-fatal-explosion-closes-cold-fusion-laboratory-.html | |||
| |accessdate=2008-08-29 | |||
| |issn=0262-4079 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Choi |first=Charles | |||
| |title=Back to Square One | |||
| |periodical=Scientific American | |||
| |year=2005 | |||
| |url=http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=back-to-square-one | |||
| |accessdate=2008-11-25 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Chubb |first=Scott et al. | |||
| |ref=APS2006 | |||
| |title=Session W41: Cold Fusion | |||
| |publisher=American Physical Society | |||
| |year=2006 | |||
| |url=http://meetings.aps.org/Meeting/MAR06/SessionIndex2/?SessionEventID=45597 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Clarke |first=W. Brian | |||
| |last2=Bos |first2=Stanley J. | |||
| |last3=Oliver |first3=Brian M. | |||
| |title=Production of <sup>4</sup>He in D<sub>2</sub>-loaded palladium-carbon catalyst II | |||
| |journal=] | |||
| |publisher=American Nuclear Society | |||
| |year=2003 | |||
| |volume=43 | |||
| |issue=2 | |||
| |pages=250–255 | |||
| |url=http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=14591064 | |||
| |accessdate=2008-08-31 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Close |first=Frank E. | |||
| |authorlink=Frank Close | |||
| |title=Too Hot to Handle: The Race for Cold Fusion | |||
| |edition=2 | |||
| |location=London | |||
| |publisher=Penguin | |||
| |year=1992 | |||
| |isbn=0-14-015926-6}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Crease |first=Robert | |||
| |last2=Samios |first2=N. P. | |||
| |title=Cold Fusion confusion | |||
| |periodical=New York Times Magazine | |||
| |page=34-38 | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| |issue=September 24, 1989 | |||
| |accessdate=2008-02-02 | |||
| |issn=0028-7822 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Di Giulio |first=M. | |||
| |last2=Filippoa |first2=E. | |||
| |last3=Mannoa |first3=D. | |||
| |last4=Nassisi |first4=V. | |||
| |title=Analysis of nuclear transmutations observed in D- and H-loaded Pd films | |||
| |journal=International Journal of Hydrogen Energy | |||
| |volume=27 | |||
| |issue=5 | |||
| |pages=527–531 | |||
| |year=2002 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/S0360-3199(01)00168-9 }} | |||
| * {{citation|last=Feder|first=Toni | |||
| |title=DOE Warms to Cold Fusion | |||
| |journal=Physics Today | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |volume=57 | |||
| |issue=4 | |||
| |pages=27–28 | |||
| |url=http://scitation.aip.org/journals/doc/PHTOAD-ft/vol_57/iss_4/27_1.shtml | |||
| |doi=10.1063/1.1752414}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Feder |first=Toni | |||
| |title=Cold Fusion Gets Chilly Encore | |||
| |journal=Physics Today | |||
| |year=2005 | |||
| |month=January | |||
| |page=31 | |||
| |url=http://scitation.aip.org/journals/doc/PHTOAD-ft/vol_58/iss_1/31_1.shtml | |||
| |doi=10.1063/1.1881896 | |||
| |volume=58 | |||
| |pages=31}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Fleischmann |first=Martin | |||
| |authorlink=Martin Fleischmann | |||
| |last2=Pons |first2=Stanley | |||
| |title=Electrochemically induced nuclear fusion of deuterium | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |volume=261 | |||
| |issue=2A | |||
| |pages=301–308 | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(89)80006-3}} | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Fleischmann1990 | |||
| |last=Fleischmann |first=Martin | |||
| |last2=Pons |first2=Stanley | |||
| |last3=Anderson |first3=Mark W. | |||
| |last4=Li |first4=Lian Jun | |||
| |last5=Hawkins |first5=Marvin | |||
| |title=Calorimetry of the palladium-deuterium-heavy water system | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |volume=287 | |||
| |year=1990 | |||
| |pages=293–348 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(90)80009-U}} | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Fleischmann1992 | |||
| |last=Fleischmann |first=Martin | |||
| |last2=Pons |first2=Stanley | |||
| |title=Some Comments on The Paper 'Analysis of Experiments on The Calorimetry of LiOD-D<sub>2</sub>O Electrochemical Cells,' R.H. Wilson et al., Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Vol. 332, (1992) | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |volume=332 | |||
| |year=1992 | |||
| |pages=33 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(92)80339-6}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Fleischmann |first=Martin | |||
| |year=1993 | |||
| |title=Calorimetry of the Pd-D2O system: from simplicity via complications to simplicity | |||
| |journal=Physics Letters A | |||
| |volume=176 | |||
| |issue=1-2 | |||
| |pages=118–129 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0375-9601(93)90327-V}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Fleischmann |first=Martin | |||
| |year=2002 | |||
| |chapter=Searching for the consequences of many-body effects in condensed phase systems | |||
| |url=http://lenr-canr.org/acrobat/Fleischmansearchingf.pdf | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |title=The 9th International Conference on Cold Fusion, Condensed Matter Nuclear Science | |||
| |location=Tsinghua University, Beijing | |||
| |publisher=Tsinghua University Press | |||
| |isbn=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Fleischmann |first=Martin | |||
| |year=2003 | |||
| |chapter=Background to cold fusion: the genesis of a concept | |||
| |title=Tenth International Conference on Cold Fusion | |||
| |location=Cambridge, MA | |||
| |publisher=World Scientific Publishing | |||
| |isbn=978-9812565648}} | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Gai1989 | |||
| |last=Gai |first=M. | |||
| |first2=S. L. |last2=Rugari | |||
| |first3=R. H. |last3=France | |||
| |first4=B. J. |last4=Lund | |||
| |first5=Z. |last5=Zhao | |||
| |first6=A. J. |last6=Davenport | |||
| |first7=H. S. |last7=Isaacs | |||
| |first8=K. G. |last8=Lynn | |||
| |title=Upper limits on neutron and big gamma-ray emission from cold fusion | |||
| |journal=Nature | |||
| |volume=340 | |||
| |pages=29–34 | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| |doi=10.1038/340029a0}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Good II |first=W.R. | |||
| |title=Comments on 'Calorimetry, excess heat, and Faraday efficiency in Ni-H<sub>2</sub>O electrolytic cells' | |||
| |journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| |volume=30 | |||
| |issue=1 | |||
| |pages=132–133 | |||
| |year=1996 | |||
| |issn=0748-1896 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Goodstein |first=David | |||
| |title=Whatever happened to cold fusion? | |||
| |journal=American Scholar | |||
| |publisher=Phi Beta Kappa Society | |||
| |volume=63 | |||
| |issue=4 | |||
| |year=1994 | |||
| |pages=527–541 | |||
| |url=http://www.its.caltech.edu/~dg/fusion_art.html | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 | |||
| |issn=0003-0937 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Gozzi |first=D. | |||
| |last2=Cellucci |first2=F. | |||
| |last3=Cignini |first3=P.L. | |||
| |last4=Gigli |first4=G. | |||
| |last5=Tomellini |first5=M. | |||
| |ref=GozziEtAl1998 | |||
| |title=X-ray, heat excess and <sup>4</sup>He in the D:Pd system | |||
| |publisher=Elsevier | |||
| |date=30 September 1997 | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |volume=435 | |||
| |issue=1-2 | |||
| |pages=113–136 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/S0022-0728(97)00297-0}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Hagelstein |first=Peter | |||
| |authorlink=Peter L. Hagelstein | |||
| |last2=Michael |first2=McKubre | |||
| |last3=Nagel|first3=David | |||
| |last4=Chubb |first4=Talbot | |||
| |last5=Hekman |first5=Randall | |||
| |ref=DOE2004 | |||
| |title=New Physical Effects in Metal Deuterides | |||
| |location=Washington | |||
| |publisher=US Department of Energy | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20070106185101/www.science.doe.gov/Sub/Newsroom/News_Releases/DOE-SC/2004/low_energy/Appendix_1.pdf | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Hubler |first=G. K. | |||
| |title=Anomalous Effects in Hydrogen-Charged Palladium - A Review | |||
| |journal=Surface and Coatings Technology | |||
| |url=http://www.newenergytimes.com/Library/2007HublerG-AnomalousEffects.pdf | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |volume=201 | |||
| |issue=19-20 | |||
| |date=5 August 2007 | |||
| |pages=8568–8573; () | |||
| |doi=10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.03.062}}<nowiki>from SMMIB 2005, 14th International Conference on Surface Modification of Materials by Ion Beams</nowiki> | |||
| * {{citation |last=Huizenga |first=John R. | |||
| |title=Cold Fusion: The Scientific Fiasco of the Century | |||
| |edition=2 | |||
| |location=Oxford and New York | |||
| |publisher=Oxford University Press | |||
| |year=1993 | |||
| |isbn=0-19-855817-1}} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Hutchinson |first=Alex | |||
| |title=The Year in Science: Physics | |||
| |periodical=Discover Magazine (online) | |||
| |date=January 8, 2006 | |||
| |url=http://discovermagazine.com/2006/jan/physics | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-06-20 | |||
| |issn=0274-7529 | |||
| |doi= | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{cite news | |||
| * {{citation |last=Iwamura |first=Yasuhiro | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |first2=Mitsuru |last2=Sakano | |||
| |last = Adam | |||
| |first3=Takehiko |last3=Itoh | |||
| |first = David | |||
| |title=Elemental Analysis of Pd Complexes: Effects of D<sub>2</sub> Gas Permeation | |||
| |editor-last = Rusbringer | |||
| |journal=Japanese Journal of Applied Physics | |||
| |editor-first = Alan | |||
| |year=2002 | |||
| |title = In from the cold | |||
| |volume=41 | |||
| |newspaper = The Guardian | |||
| |issue=7A | |||
| |date = 24 March 2005 | |||
| |pages=4642–4650 | |||
| |url = https://www.theguardian.com/education/2005/mar/24/research.highereducation2 | |||
| |doi=10.1143/JJAP.41.4642}} | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Jayaraman|first=K. S. | |||
| |location = London | |||
| |title=Cold fusion hot again | |||
| }} | |||
| |journal=Nature India | |||
| * {{cite magazine | |||
| |date=January 17, 2008 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |doi=10.1038/nindia.2008.77 | |||
| |last = Alfred | |||
| |url=http://www.nature.com/nindia/2008/080117/full/nindia.2008.77.html | |||
| |first = Randy | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-12-07}} | |||
| |title = March 23, 1989: Cold Fusion Gets Cold Shoulder | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Jones1995 | |||
| |magazine= ] | |||
| |last=Jones |first=J. E. | |||
| |date = 23 March 2009 | |||
| |last2=Hansen |first2=L. D. | |||
| |url = https://www.wired.com/science/discoveries/news/2009/03/dayintech_0323 | |||
| |last3=Jones |first3=S. E. | |||
| }} | |||
| |last4=Shelton |first4=D. S. | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |last5=Thorne |first5=J. M. | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |title=Faradaic efficiencies less than 100% during electrolysis of water can account for reports of excess heat in `cold fusion` cells | |||
| |last = Ball | |||
| |journal=Journal of Physical Chemistry | |||
| |first = Phillip | |||
| |year=1995 | |||
| |title = Life's matrix: a biography of water | |||
| |volume=99 | |||
| |edition = illustrated, reprinted | |||
| |issue=18 | |||
| |publisher = University of California Press | |||
| |pages=6973–6979 | |||
| |year = 2001 | |||
| |doi=10.1021/j100018a033}} | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-520-23008-8 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Josephson |first=Brian. D. | |||
| |url-access = registration | |||
| |authorlink=Brian David Josephson | |||
| |url = https://archive.org/details/lifesmatrixbiogr0000ball | |||
| |title=Pathological Disbelief | |||
| }} | |||
| |series=Lecture given at the Nobel Laureates’ meeting Lindau, June 30th., 2004 | |||
| * {{cite magazine | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |url=http://www.lenr-canr.org/acrobat/JosephsonBpathologic.pdf | |||
| |last = Barras | |||
| |publisher=LENR-CANR | |||
| |first = Collin | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |title = Neutron tracks revive hopes for cold fusion | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-07-17}} | |||
| |date = 23 March 2009 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Joyce |first=Christopher | |||
| |magazine = ] | |||
| |title=Gunfight at the cold fusion corral | |||
| |url = https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn16820-neutron-tracks-revive-hopes-for-cold-fusion.html | |||
| |periodical=New Scientist | |||
| }} | |||
| |issue=1721 | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| |date=16 June 1990 | |||
| | last=Beaudette | first=Charles G. | |||
| |page=22 | |||
| | title=Excess Heat & Why Cold Fusion Research Prevailed | |||
| |url=http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg12617210.700-gunfight-at-the-cold-fusion-corral-.html | |||
| | year=2002 | |||
| |accessdate = 2009-10-01 | |||
| | location=South Bristol, Maine | |||
| |issn=0262-4079 | |||
| | publisher=Oak Grove Press | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| | isbn=978-0-9678548-3-0 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Kainthla |first=R.C. | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Sporadic observation of the Fleischmann-Pons heat effect | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |journal=Electrochimica Acta | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |volume=34 | |||
| |last = Berger | |||
| |issue=9 | |||
| |first = Eric | |||
| |pages=1315–1318 | |||
| |title = Navy scientist announces possible cold fusion reactions | |||
| |month=September | |||
| |newspaper = ] | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| |date = 23 March 2009 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0013-4686(89)85026-1}} | |||
| |url = http://www.chron.com/disp/story.mpl/front/6333164.html | |||
| * {{citation |last=Kee |first=B | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=What is the current scientific thinking on cold fusion? Is there any possible validity to this phenomenon? | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |periodical=Scientific American | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |date=October 21, 1999 | |||
| |last1 = Bettencourt | |||
| |series=Ask the Experts | |||
| |first1 = Luís M.A. | |||
| |url=http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=what-is-the-current-scien | |||
| |last2 = Kaiser | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-12-17 | |||
| |first2 = David I. | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| |last3 = Kaur | |||
| * {{citation |last=Kozima |first=Hideo | |||
| |first3 = Jasleen | |||
| |title=The Science of the Cold Fusion phenomenon | |||
| |date = July 2009 | |||
| |publisher=Elsevier Science | |||
| |title = Scientific discovery and topological transitions in collaboration networks | |||
| |location=New York | |||
| |journal = ] | |||
| |year=2006 | |||
| |volume = 3 | |||
| |isbn=0-08-045110-1}} | |||
| |issue = 3 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Krivit |first=Steven B. | |||
| |pages = 210–221 | |||
| |title=Extraordinary Courage: Report on Some LENR Presentations at the 2007 American Physical Society Meeting | |||
| |doi = 10.1016/j.joi.2009.03.001 | |||
| |journal=New Energy Times | |||
| |postscript = , | |||
| |issue=21 | |||
| |hdl = 1721.1/50230 | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| |url=http:// |
|url = http://web.mit.edu/dikaiser/www/BKK.Topological.pdf | ||
| |citeseerx = 10.1.1.570.8621 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 | |||
| |s2cid = 1914074 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| }} . | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| * {{citation |last=Krivit |first=Steven B. | |||
| | mode=cs2 | |||
| |title=Low Energy Nuclear Reaction Research – Global Scenario | |||
| | last=Biberian | |||
| |journal=Current Science | |||
| | first=Jean-Paul | |||
| |date=10 April 2008 | |||
| | title=Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (Cold Fusion): An Update | |||
| |volume=94 | |||
| | journal=International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Technology | |||
| |issue=7 | |||
| | volume=3 | |||
| |pages=854–857 | |||
| | issue=1 | |||
| |url=http://www.ias.ac.in/currsci/apr102008/854.pdf | |||
| | year=2007 | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| | pages=31–42 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-07-19 | |||
| | doi=10.1504/IJNEST.2007.012439 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | url=http://www.jeanpaulbiberian.net/Download/Paper%2056.pdf | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| | citeseerx=10.1.1.618.6441 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Krivit |first=Steven | |||
| |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20080530160253/http://www.jeanpaulbiberian.net/Download/Paper%2056.pdf |archive-date=30 May 2008 |url-status=live | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| }} | |||
| |ref=Krivit2008b | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |chapter=Low Energy Nuclear Reactions: The Emergence of Condensed Matter Nuclear Science | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |chapterurl=http://newenergytimes.com/Library2/2008/2008KrivitS-ACS-LENR-Sourcebook-Intro.pdf | |||
| |last = Bird | |||
| |editor=Marwan, Jan and Krivit, Steven B., editors | |||
| |first = Alexander | |||
| |title=Low energy nuclear reactions sourcebook | |||
| |title = Philosophy of Science: Alexander Bird | |||
| |publisher=]/] | |||
| |edition = illustrated, reprint | |||
| |isbn=978-0-8412-6966-8}} | |||
| |editor = ] | |||
| * {{citation |last=Kruglinksi |first=Susan | |||
| |year = 1998 | |||
| |title=Whatever Happened To... Cold Fusion? | |||
| |isbn = 978-1-85728-504-8 | |||
| |periodical=Discover Magazine | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=czUjWnpAnUQC&pg=PA261 | |||
| |date=2006-03-03 | |||
| |publisher = UCL Press | |||
| |url=http://discovermagazine.com/2006/mar/cold-fusion | |||
| |location = London | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-06-20 | |||
| }} | |||
| |issn=0274-7529 | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Kowalski |first=Ludwik | |||
| |last = Bowen | |||
| |title=Jones’s manuscript on History of Cold Fusion at BYU | |||
| |first = Jerry | |||
| |location=Upper Montclair, New Jersey | |||
| |title = Science: Nuclear Fusion | |||
| |publisher=csam.montclair.edu | |||
| |work = CBS Evening News | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |date = 10 April 1989 | |||
| |url=http://pages.csam.montclair.edu/~kowalski/cf/131history.html | |||
| |url = http://tvnews.vanderbilt.edu/program.pl?ID=326384 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25}} | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Leggett |first=A.J. | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Exact upper bound on barrier penetration probabilities in many-body systems: Application to ‘‘cold fusion’’ | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |journal=Phys. Rev. Lett. | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |volume=63 | |||
| |last = Browne | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| |first = M. | |||
| |pages=191–194 | |||
| |title = Physicists Debunk Claim Of a New Kind of Fusion | |||
| |doi=10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.191}} | |||
| |newspaper =The New York Times | |||
| * {{citation |last=Lewenstein |first=Bruce V. | |||
| |date = 3 May 1989 | |||
| |title=Cornell cold fusion archive | |||
| |url = http://partners.nytimes.com/library/national/science/050399sci-cold-fusion.html | |||
| |location=collection n°4451, Division of Rare and Manuscript Collections, Cornell University Library | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| |year=1994 | |||
| }} | |||
| |url=http://rmc.library.cornell.edu/EAD/pdf_guides/RMM04451.pdf | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 | |||
| |last = Brumfiel | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| |first = Geoff | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Lewis1989 | |||
| |title = US review rekindles cold fusion debate. Energy panel split over whether experiments produced power | |||
| |last=Lewis |first=N. S. | |||
| |date = 2 December 2004 | |||
| |last2=Barnes† |first2=C. A. | |||
| |journal = Nature News | |||
| |last3=Heben |first3=M. J. | |||
| |url = http://www.nature.com/news/2004/041129/full/news041129-11.html | |||
| |last4=Kumar |first4=A. | |||
| |doi = 10.1038/news041129-11 | |||
| |last5=Lunt |first5=S. R. | |||
| |doi-access= free | |||
| |last6=McManis |first6=G. E. | |||
| }} | |||
| |last7=Miskelly |first7=S. R. | |||
| * {{cite magazine | |||
| |last8=Penner |first8=G. M. | |||
| | mode=cs2 | |||
| |last9=Sailor|first9=M. J. | |||
| | last=Choi | |||
| |last10=Santangelo |first10=P. G. | |||
| | first=Charles | |||
| |last11=Shreve |first11=G. A. | |||
| | title=Back to Square One | |||
| |last12=Tufts |first12=B. J. | |||
| | magazine=Scientific American | |||
| |last13=Youngquist |first13=M. G. | |||
| | year=2005 | |||
| |last14=Kavanagh |first14=R. W. | |||
| | url=http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=back-to-square-one | |||
| |last15=Kellogg |first15=S. E. | |||
| | access-date=25 November 2008 | |||
| |last16=Vogelaar |first16=R. B. | |||
| }} | |||
| |last17=Wang |first17=T. R. | |||
| * {{cite conference | |||
| |last18=Kondrat |first18=R. | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last19=New |first19=R. | |||
| |last1 = Chubb | |||
| |title=Searches for low-temperature nuclear fusion of deuterium in palladium | |||
| |first1 = Scott | |||
| |journal=Nature | |||
| |last2 = McKubre | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| |first2 = Michael C. H. | |||
| |volume=340 | |||
| |last3 = Krivit | |||
| |pages=525-530 | |||
| |first3 = Steve B. | |||
| |doi:10.1038/340525a0}} | |||
| |last4 = Chubb | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mallove |first=Eugene | |||
| |first4 = Talbot | |||
| |authorlink=Eugene Mallove | |||
| |last5 = Miley | |||
| |title=Fire from Ice: Searching for the Truth Behind the Cold Fusion Furor | |||
| |first5 = George H. | |||
| |location=London | |||
| |last6 = Swartz | |||
| |publisher=Wiley | |||
| |first6 = Mitchell | |||
| |year=1991 | |||
| |last7 = Violante | |||
| |isbn=0-471-53139-1}} | |||
| |first7 = V. | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mengoli |first=G | |||
| |last8 = Stringham | |||
| |year=1998 | |||
| |first8 = Roger | |||
| |title=Calorimetry close to the boiling temperature of the D<sub>2</sub>O/Pd electrolytic system | |||
| |last9 = Fleischmann | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |first9 = Martin | |||
| |volume=444 | |||
| |last10 = Li | |||
| |pages=155–167 | |||
| |first10 = Zing Z. | |||
| |doi=10.1016/S0022-0728(97)00634-7 }} | |||
| |last11 = Biberian | |||
| * {{citation |last=McKubre |first=M.C.H | |||
| |first11 = J.P. | |||
| |title=Isothermal Flow Calorimetric Investigations of the D/Pd and H/Pd Systems | |||
| |last12 = Collis | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |first12 = William | |||
| |year=1994 | |||
| |title = Session W41: Cold Fusion | |||
| |volume=368 | |||
| |publisher = American Physical Society | |||
| |pages=55 | |||
| |year = 2006 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |url = http://meetings.aps.org/Meeting/MAR06/SessionIndex2/?SessionEventID=45597 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(93)03070-6}} | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Miles |first=Melvin H. | |||
| }} | |||
| |last2=Hollins |first2=R. A. | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| |last3=Bush |first3=Ben F. | |||
| | last=Close | first=Frank E. | |||
| | author-link=Frank Close | |||
| |last5=Miles |first5=R. E. | |||
| | title=Too Hot to Handle: The Race for Cold Fusion | |||
| |ref=MilesEtAl1993 | |||
| | edition=2 | |||
| |title=Correlation of excess power and helium production during D<sub>2</sub>O and H<sub>2</sub>0 electrolysis using Palladium cathodes | |||
| | location=London | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| | publisher=Penguin | |||
| |year=1993 | |||
| | year=1992 | |||
| |volume=346 | |||
| | isbn=978-0-14-015926-4 | |||
| |issue=1-2 | |||
| }} | |||
| |pages=99–117 | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(93)85006-3}} | |||
| |last1 = Collins | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mizuno |first=Tadahiko | |||
| |first1 = Harry | |||
| |title=Analysis of Elements for Solid State Electrolyte in Deuterium Atmosphere during Applied Field | |||
| |author-link = Harry Collins | |||
| |journal=J. New Energy | |||
| |last2 = Pinch | |||
| |year=1996 | |||
| |first2 = Trevor | |||
| |volume=1 | |||
| |author-link2 = Trevor Pinch | |||
| |issue=2 | |||
| |title = The Golem: What Everyone Should Know About Science | |||
| |pages=37 | |||
| |edition = 1st | |||
| |url=http://iccf9.global.tsinghua.edu.cn/lenr%20home%20page/acrobat/MizunoTanalysisof.pdf | |||
| |publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |year = 1993 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |url =https://archive.org/details/golemwhateveryon00harr | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| |url-access=registration | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mizuno |first=Tadahiko | |||
| |isbn=0521477360 | |||
| |last2=Rothwell |first2=Jed (translator) | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Nuclear Transmutation: The Reality of Cold Fusion | |||
| * {{cite magazine|mode=cs2 | |||
| |year=1998 | |||
| | last1=Crease | first1=Robert | |||
| |location=Concord, New Hampshire | |||
| | last2=Samios | first2=N.P. | |||
| |publisher=Infinite Energy Press | |||
| | title=Cold Fusion confusion | |||
| |url=http://iccf9.global.tsinghua.edu.cn/LENR%20home%20page/acrobat/MizunoTnucleartra.pdf | |||
| | periodical=The New York Times Magazine | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| | pages=34–38 | |||
| |isbn=1-892925-00-1}} | |||
| | year=1989 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mullins |first=Justin | |||
| | issue=24 September 1989 | |||
| |title=Cold Fusion Back From the Dead | |||
| }} | |||
| |journal=IEEE Spectrum | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |volume=41 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |pages=22 | |||
| |last = Daley | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |first = Beth | |||
| |month=September | |||
| |title = Heating up a cold theory. MIT professor risks career to reenergize discredited idea | |||
| |doi=10.1109/MSPEC.2004.1330805}} | |||
| |newspaper= The Boston Globe | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mosier-Boss |first=Pamela A. | |||
| |date = 27 July 2004 | |||
| |last2=Szpak |first2=Stanislaw | |||
| |url = https://www.boston.com/news/globe/health_science/articles/2004/07/27/heating_up_a_cold_theory/ | |||
| |last3=Gordon |first3=Frank E. | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Production of High Energy Particles Using the Pd/D Co-Deposition Process | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |journal=Proceedings of the 2007 APS March Meeting, March 5–9, 2007 in Denver | |||
| | mode=cs2 | |||
| |location=College Park, Maryland | |||
| | title=What Science Is and How It Works | |||
| |publisher=American Physical Society | |||
| | last=Derry | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| | first=Gregory Neil | |||
| |url=http://meetings.aps.org/link/BAPS.2007.MAR.A31.2 | |||
| | edition=reprint, illustrated | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25}}. retrieved on ], 2008 | |||
| | publisher=] | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mosier-Boss |first=Pamela A. | |||
| | place=Princeton, New Jersey; Oxford | |||
| |last2=Szpak |first2=Stanislaw | |||
| | year=2002 | |||
| |last3=Gordon |first3=Frank E. | |||
| | isbn=978-0-691-09550-9 | |||
| |last4=Forsley |first4=L. P. G. | |||
| | oclc=40693869 | |||
| |title=Use of CR-39 in Pd/D co-deposition experiments | |||
| | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=H7gjz-b7S9IC&pg=PA179 | |||
| |journal=European Physical Journal Applied Physics | |||
| }} | |||
| |volume=40 | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |pages=293–303 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| |last = Feder | |||
| |doi=10.1051/epjap:2007152}} | |||
| |first = Toni | |||
| * {{citation |last=Mosier-Boss |first=Pamela A. | |||
| |title = DOE Warms to Cold Fusion | |||
| |last2=Szpak |first2=Stanislaw | |||
| |journal = Physics Today | |||
| |last3=Gordon |first3=Frank E. | |||
| |year = 2004 | |||
| |last4=Forsley |first4=L. P. G. | |||
| |volume = 57 | |||
| |title=Triple tracks in CR-39 as the result of Pd–D Co-deposition: evidence of energetic neutrons | |||
| |issue = 4 | |||
| |journal=Naturwissenschaften | |||
| |pages = 27–28 | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| |url = http://scitation.aip.org/journals/doc/PHTOAD-ft/vol_57/iss_4/27_1.shtml | |||
| |doi=10.1007/s00114-008-0449-x}} | |||
| |doi = 10.1063/1.1752414 | |||
| * {{citation |last= |first= | |||
| |bibcode = 2004PhT....57d..27F | |||
| |title=Texas Panel Finds No Fraud In Cold Fusion Experiments | |||
| }} | |||
| |newspaper=New York Times | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |date=November 20, 1990 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |url=http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?sec=health&res=9C0CE1DA143EF933A15752C1A966958260 | |||
| |last = Feder | |||
| |accessdate = 2009-09-24 }} | |||
| |first = Toni | |||
| * {{citation |last=Oriani |first=Richard A. | |||
| |title = Cold Fusion Gets Chilly Encore | |||
| |first2=John C. |last2=Nelson | |||
| |journal = Physics Today | |||
| |first3=Sung-Kyu |last3=Lee | |||
| |date = January 2005 | |||
| |first4=J. H. |last4=Broadhurst | |||
| |url = http://scitation.aip.org/journals/doc/PHTOAD-ft/vol_58/iss_1/31_1.shtml | |||
| |title=Calorimetric Measurements of Excess Power Output During the Cathodic Charging of Deuterium into Palladium | |||
| |doi = 10.1063/1.1881896 | |||
| |journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| |volume= |
|volume = 58 | ||
| |issue = 1 | |||
| |year=1990 | |||
| |page = 31 | |||
| |pages=652–662 | |||
| |bibcode = 2005PhT....58a..31F | |||
| |issn=0748-1896 | |||
| |doi-access= free | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Packham |first=Richard A. | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |title=Production of tritium from D<sub>2</sub>O electrolysis at a palladium cathode | |||
| | last1=Fleischmann | first1=Martin | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| | last2=Pons | first2=Stanley | |||
| |volume=270 | |||
| | title=Electrochemically induced nuclear fusion of deuterium | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| | journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |pages=451 | |||
| | volume=261 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | issue=2A | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(89)85059-4}} | |||
| | pages=301–308 | |||
| * {{citation | |||
| | year=1989 | |||
| |title=Über die Verwandlung von Wasserstoff in Helium | |||
| | doi=10.1016/0022-0728(89)80006-3 | |||
| |first=Fritz |last=Paneth | |||
| }} | |||
| |first2=Kurt |last2=Peters | |||
| * {{cite journal |mode=cs2 | |||
| |journal=] | |||
| | last1=Fleischmann | first1=Martin | |||
| |language=German | |||
| | last2=Pons | first2=Stanley | |||
| |volume=14 | |||
| | last3=Anderson | first3=Mark W. | |||
| |issue=43 | |||
| | last4=Li | first4=Lian Jun | |||
| |pages= 956–962 | |||
| | last5=Hawkins | first5=Marvin | |||
| |year=1926 | |||
| | title=Calorimetry of the palladium-deuterium-heavy water system | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |doi=10.1007/BF01579126 }} | |||
| | volume=287 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Park |first=Robert |authorlink=Robert L. Park | |||
| | year=1990 | |||
| |title=Voodoo Science: The Road from Foolishness to Fraud | |||
| | pages=293–348 | |||
| |url=http://en.wikipedia.org/Voodoo_science | |||
| | doi=10.1016/0022-0728(90)80009-U | |||
| |location=New York | |||
| | issue=2 | |||
| |publisher=Oxford University Press | |||
| }} | |||
| |year=2000 | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |isbn=0-19-513515-6}} | |||
| | last1=Fleischmann | first1=Martin | |||
| * {{citation |last=Platt |first=Charles | |||
| | last2=Pons | first2=S. | |||
| |title=What if Cold Fusion is Real? | |||
| | year=1993 | |||
| |periodical=] | |||
| | title=Calorimetry of the Pd-D2O system: from simplicity via complications to simplicity | |||
| |year=1998 | |||
| | journal=Physics Letters A | |||
| |issue=6.11 | |||
| | volume=176 | |||
| |url=http://www.wired.com/wired/archive/6.11/coldfusion.html?pg=1&topic=&topic_set= | |||
| | issue=1–2 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | pages=118–129 | |||
| |doi= | |||
| | doi=10.1016/0375-9601(93)90327-V | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25}} | |||
| | bibcode = 1993PhLA..176..118F | |||
| * {{citation |last=Pollack |first=A. | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Japan, Long a Holdout, is Ending its Quest for Cold Fusion | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |newspaper=New York Times | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |date=August 26, 1997 | |||
| |last = Fox | |||
| |volume=79 | |||
| |first = Barry | |||
| |pages=243, C4 | |||
| |title = Patents: Cold fusion rides again | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| |url = https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg14219314.000-patents-cold-fusion-rides-again.html | |||
| *{{citation| last=Seife |first=Charles |authorlink=Charles Seife | |||
| |journal = New Scientist | |||
| |title=Sun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful Thinking | |||
| |date = 25 June 1994 | |||
| |location=New York | |||
| |issue = 1931 | |||
| |publisher=Viking | |||
| |issn = 0262-4079 | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| }} | |||
| |isbn=0670020338}} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| *{{citation| last=Seife |first=Charles |authorlink=Charles Seife | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |title=Department of Energy: Outlook for Cold Fusion Is Still Chilly | |||
| |last1 = Gai | |||
| |periodical=Science | |||
| |first1 = M. | |||
| |date=10 December 2004 | |||
| |last2 = Rugari | |||
| |url=http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/306/5703/1873a | |||
| |first2 = S.L. | |||
| |accessdate=2008-10-28 | |||
| |last3 = France | |||
| |page=1834 | |||
| |first3 = R.H. | |||
| |volume=306 | |||
| |last4 = Lund | |||
| |issue=5703 | |||
| |first4 = B.J. | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |last5 = Zhao | |||
| |doi=10.1126/science.306.5703.1873a| pages=1873a| pmid=15591169}} | |||
| |first5 = Z. | |||
| * {{citation |last=Shanahan |first=Kirk L. | |||
| |last6 = Davenport | |||
| |title=A systematic error in mass flow calorimetry demonstrated | |||
| |first6 = A.J. | |||
| |journal=Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |last7 = Isaacs | |||
| |volume=382 | |||
| |first7 = H.S. | |||
| |issue=2 | |||
| |last8 = Lynn | |||
| |date=23 May 2002 | |||
| |first8 = K.G. | |||
| |pages=95–100 | |||
| |s2cid = 4331780 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |title = Upper limits on neutron and big gamma-ray emission from cold fusion | |||
| |doi=10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00832-2}} | |||
| |journal = Nature | |||
| * {{citation |last=Shanahan |first=Kirk L. | |||
| |volume = 340 | |||
| |url=http://sti.srs.gov/fulltext/ms2004528/ms2004528.pdf | |||
| |pages = 29–34 | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |year = 1989 | |||
| |title=Comments on "Thermal behavior of polarized Pd/D electrodes prepared by co-deposition" | |||
| |doi = 10.1038/340029a0 | |||
| |journal=Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |bibcode = 1989Natur.340...29G | |||
| |volume=428 | |||
| |issue= |
|issue = 6228 | ||
| |url = https://zenodo.org/record/1233083 | |||
| |year=2005 | |||
| }} | |||
| |month=April | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |pages=207–212 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/j.tca.2004.11.007}} | |||
| |last = Goodstein | |||
| * {{citation |last=Shanahan |first=Kirk L. | |||
| |first = David | |||
| |url=http://sti.srs.gov/fulltext/2005/ms2005556.pdf | |||
| |title = Whatever happened to cold fusion? | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| |journal = American Scholar | |||
| |title=Reply to 'Comment on papers by K. Shanahan that propose to explain anomalous heat generated by cold fusion', E. Storms, Thermochim. Acta, 2006 | |||
| |volume = 63 | |||
| |journal=Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |issue = 4 | |||
| |volume=441 | |||
| |year = 1994 | |||
| |issue=2 | |||
| |pages = 527–541 | |||
| |date=15 February 2006 | |||
| |url = http://www.its.caltech.edu/~dg/fusion_art.html | |||
| |pages=210–214 | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |issn = 0003-0937 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/j.tca.2005.11.029}} | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080516200325/http://www.its.caltech.edu/%7Edg/fusion_art.html | |||
| *{{citation |ref=Shkedi1995 | |||
| |archive-date = 16 May 2008 | |||
| |last=Shkedi |first=Zvi | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| |first2=Robert C. |last2=McDonald | |||
| }} | |||
| |first3=John J. |last3=Breen | |||
| * {{Cite book |mode=cs2 |title=On Fact and Fraud:Cautionary Tales from the Front Lines of Science |last=Goodstein |first=David L. |author-link=David Goodstein |year=2010 |publisher=Princeton University Press |location=Princeton |isbn=978-0691139661}} | |||
| |first4=Stephen J. |last4=Maguire | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 |last1=Hagelstein |first1=Peter L. |author-link=Peter L. Hagelstein |last2=McKubre |first2=Michael |last3=Nagel |first3=David |last4=Chubb |first4=Talbot |last5=Hekman |first5=Randall |chapter=New Physical Effects in Metal Deuterides |title=Condensed Matter Nuclear Science. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Cold Fusion. Held 31 October–5 November 2004 in Marseilles |journal=11th Condensed Matter Nuclear Science |volume=11 |pages=23 |year=2004 |chapter-url=http://www.science.doe.gov/Sub/Newsroom/News_Releases/DOE-SC/2004/low_energy/Appendix_1.pdf |bibcode=2006cmns...11...23H |doi=10.1142/9789812774354_0003 |citeseerx=10.1.1.233.5518 |isbn=9789812566409 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070106185101/http://www.science.doe.gov/Sub/Newsroom/News_Releases/DOE-SC/2004/low_energy/Appendix_1.pdf |archive-date=6 January 2007 |url-status=dead |postscript=,}} (manuscript). | |||
| |first5=Joe |last5=Veranth | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |title=Calorimetry, Excess Heat, and Faraday Efficiency in Ni-H<sub>2</sub>O Electrolytic Cells | |||
| | doi=10.1007/s00114-009-0644-4 | |||
| |journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| | last=Hagelstein | first=Peter L. | |||
| |volume=28 | |||
| |s2cid=9496513 | |||
| |issue=4 | |||
| | title=Constraints on energetic particles in the Fleischmann–Pons experiment | |||
| |year=1995 | |||
| | year=2010 | |||
| |pages=1720–1731 | |||
| | journal=Naturwissenschaften | |||
| |issn=0748-1896 | |||
| | volume=97 | |||
| |doi=}} | |||
| | issue=4 | pages=345–352 | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Shkedi1996 | |||
| | pmid=20143040 | bibcode = 2010NW.....97..345H | |||
| |last=Shkedi |first=Zvi | |||
| | hdl=1721.1/71631| hdl-access=free | |||
| |title=Response to Comments on 'Calorimetry, Excess Heat, and Faraday Efficiency in Ni-H<sub>2</sub>O Electrolytic Cells' | |||
| }} | |||
| |journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| |volume=30 | |||
| | last=Hoffman | first=Nate | |||
| |issue=1 | |||
| | title=A Dialogue on Chemically Induced Nuclear Effects: A Guide for the Perplexed About Cold Fusion | |||
| |date=1996-10-26 | |||
| | location=La Grange Park, Illinois | |||
| |page=133 | |||
| | publisher=American Nuclear Society | |||
| |issn=0748-1896 | |||
| | year=1995 | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| | isbn=978-0-89448-558-9 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Srinivasan |first=M. | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Meeting report: Energy concepts for the 21st century | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| |journal=Current Science | |||
| | last=Huizenga | first=John R. | |||
| |volume=94 | |||
| | author-link=John R. Huizenga | |||
| |issue=7 | |||
| | title=Cold Fusion: The Scientific Fiasco of the Century | |||
| |year=2008 | |||
| | edition=2 | |||
| |pages=842–843 | |||
| | location=Oxford and New York | |||
| |url=http://www.ias.ac.in/currsci/apr102008/842.pdf | |||
| | publisher=Oxford University Press | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| | year=1993 | |||
| |accessdate=10 April 2008 | |||
| | isbn=978-0-19-855817-0 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| * {{citation |last=Storms |first=Edmund | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |title=Storms' letter to Science | |||
| |last = Jayaraman | |||
| |journal=New Energy Times | |||
| |first = K.S. | |||
| |year=1990 | |||
| |title = Cold fusion hot again | |||
| |url=http://newenergytimes.com/Bockris/StormsLetterToScience.htm | |||
| |journal = Nature India | |||
| |accessdate = 2009-09-29 | |||
| |date = 17 January 2008 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |doi = 10.1038/nindia.2008.77 | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| |url = http://www.nature.com/nindia/2008/080117/full/nindia.2008.77.html | |||
| * {{citation |last=Storms |first=Edmund | |||
| |access-date = 7 December 2008 | |||
| |title=Measurements of excess heat from a Pons-Fleischmann-type electrolytic cell using palladium sheet | |||
| }} | |||
| |journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |issue=23 | |||
| | last1=Jones | first1=J.E. | |||
| |year=1993 | |||
| | last2=Hansen | first2=L.D. | |||
| |pages=230 | |||
| | last3=Jones | first3=S.E. | |||
| |issn=0748-1896 | |||
| | last4=Shelton | first4=D.S. | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| | last5=Thorne | first5=J.M. | |||
| * {{citation |last=Storms |first=Edmund | |||
| | title=Faradaic efficiencies less than 100% during electrolysis of water can account for reports of excess heat in 'cold fusion' cells | |||
| | journal=Journal of Physical Chemistry | |||
| | year=1995 | |||
| |volume=441 | |||
| | volume=99 | |||
| |issue=2 | |||
| | issue=18 | |||
| |year=2006 | |||
| | pages=6973–6979 | |||
| | doi=10.1021/j100018a033 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Storms |first=Edmund | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |title=Science of Low Energy Nuclear Reaction: A Comprehensive Compilation of Evidence and Explanations | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |location=Singapore | |||
| |last = Joyce | |||
| |publisher=World Scientific | |||
| |first = Christopher | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| |title = Gunfight at the cold fusion corral | |||
| |isbn=9-8127062-0-8 }} | |||
| |periodical = New Scientist | |||
| * {{citation |last=Szpak |first=Stanislaw | |||
| |issue = 1721 | |||
| |ref=Szpak2004 | |||
| |date = 16 June 1990 | |||
| |last2=Mosier-Boss |first2=Pamela A. | |||
| |page = 22 | |||
| |last3=Miles |first3=Melvin H. | |||
| |url = https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg12617210.700-gunfight-at-the-cold-fusion-corral-.html | |||
| |last4=Fleischmann |first4=Martin | |||
| |access-date = 1 October 2009 | |||
| |title=Thermal behavior of polarized Pd/D electrodes prepared by co-deposition. | |||
| |issn = 0262-4079 | |||
| |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20080308175946/lenr-canr.org/acrobat/SzpakSthermalbeh.pdf | |||
| }} | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| * {{cite magazine | |||
| |journal=Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |volume=410 | |||
| |last = Kean | |||
| |pages=101 | |||
| |first = Sam | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |title = Palladium: The Cold Fusion Fanatics Can't Get Enough of the Stuff | |||
| |doi=10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00401-5 }} | |||
| |magazine = Slate | |||
| * {{citation |last=Szpak |first=Stanislaw | |||
| |date = 26 July 2010 | |||
| |last2=Mosier-Boss |first2=Pamela A. | |||
| |url = http://www.slate.com/id/2258112/entry/2258878/ | |||
| |last3=Young |first3=Charles | |||
| |access-date = 31 July 2011 | |||
| |last4=Gordon |first4=Frank E. | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=Evidence of nuclear reactions in the Pd lattice | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |journal=] | |||
| | last1=Kitamura | first1=Akira | |||
| |volume=92 | |||
| | last2=Nohmi | first2=Takayoshi | |||
| |issue=8 | |||
| | last3=Sasaki | first3=Yu | |||
| |year=2005 | |||
| | last4=Taniike | first4=Akira | |||
| |pages=394–397 | |||
| | last5=Takahashi | first5=Akito | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | last6=Seto | first6=Reiko | |||
| |doi=10.1007/s00114-005-0008-7 }} | |||
| | last7=Fujita | first7=Yushi | |||
| * {{citation |last=Tate |first=N. | |||
| | title=Anomalous Effects in Charging of Pd Powders with High Density Hydrogen Isotopes | |||
| |title=MIT bombshell knocks fusion ‘breakthrough’ cold | |||
| | journal=Physics Letters A | |||
| |newspaper=Boston Herald | |||
| | volume=373 | |||
| |issue=May 1, 1989 | |||
| | issue=35 | |||
| |page=1 | |||
| | pages=3109–3112 | |||
| |issn=0738-5854 | |||
| | year=2009 | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| | doi=10.1016/j.physleta.2009.06.061 | bibcode = 2009PhLA..373.3109K | |||
| * {{citation |last=Taubes |first=Gary | |||
| | citeseerx=10.1.1.380.6124 | |||
| |title=Cold fusion conundrum at Texas A&M | |||
| }} | |||
| |periodical=] | |||
| * {{cite web | |||
| |volume=248 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |date=15 June 1990 | |||
| |last = Kowalski | |||
| |pages=1299-1304 | |||
| |first = Ludwik | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |title = Jones's manuscript on History of Cold Fusion at BYU | |||
| |doi=10.1126/science.248.4961.1299 | |||
| |location = Upper Montclair, New Jersey | |||
| |pmid=17735269 }} | |||
| |publisher = csam.montclair.edu | |||
| * {{citation |last=Taubes |first=Gary | |||
| |year = 2004 | |||
| |authorlink=Gary Taubes | |||
| |url = http://pages.csam.montclair.edu/~kowalski/cf/131history.html | |||
| |title=] | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| |location=New York | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080506023241/http://pages.csam.montclair.edu/~kowalski/cf/131history.html | |||
| |publisher=Random House | |||
| |archive-date = 6 May 2008 | |||
| |year=1993 | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| |isbn=0-394-58456-2 }} | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{citation | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| |author=U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| | last=Kozima | first=Hideo | |||
| |ref=DOE1989 | |||
| | title=The Science of the Cold Fusion phenomenon | |||
| |title=A Report of the Energy Research Advisory Board to the United States Department of Energy | |||
| | publisher=Elsevier Science | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| | location=New York | |||
| |publisher=U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| | year=2006 | |||
| |location=Washington, DC | |||
| | isbn=978-0-08-045110-7}} | |||
| |url=http://www.ncas.org/erab/ | |||
| * {{cite magazine | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-05-25 }} {{doubtful}} | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| * {{citation |author=U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| |last = Kruglinski | |||
| |ref=DOE2004r | |||
| |first = Susan | |||
| |year=2004 | |||
| |title = Whatever Happened To... Cold Fusion? | |||
| |title=Report of the Review of Low Energy Nuclear Reactions | |||
| |periodical = Discover Magazine | |||
| |location=Washington, DC | |||
| |date = 3 March 2006 | |||
| |publisher=U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| |url = http://discovermagazine.com/2006/mar/cold-fusion | |||
| |url=http://web.archive.org/web/20070114122346/http://www.science.doe.gov/Sub/Newsroom/News_Releases/DOE-SC/2004/low_energy/CF_Final_120104.pdf | |||
| |access-date = 20 June 2008 | |||
| |format=PDF | |||
| | |
|issn = 0274-7529 | ||
| }} | |||
| * {{citation |last=Van Noorden |first= R. | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |title=Cold fusion back on the menu | |||
| | title= Controversy in chemistry: how do you prove a negative? – the cases of phlogiston and cold fusion | |||
| |journal=Chemistry World | |||
| | last1=Labinger | first1=JA | |||
| |year=2007 | |||
| | last2=Weininger | first2=SJ | |||
| |month=April | |||
| | journal= Angew Chem Int Ed Engl | |||
| |url=http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/News/2007/March/22030701.asp | |||
| | year=2005 | |||
| |format=ASP | |||
| | volume=44 | issue=13 | pages=1916–1922 | |||
| |accessdate=2008-05-25 | |||
| | doi=10.1002/anie.200462084 | |||
| |issn=1473-7604 | |||
| | pmid= 15770617 | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| | quote= So there matters stand: no cold fusion researcher has been able to dispel the stigma of 'pathological science' by rigorously and reproducibly demonstrating effects sufficiently large to exclude the possibility of error (for example, by constructing a working power generator), nor does it seem possible to conclude unequivocally that all the apparently anomalous behavior can be attributed to error. | |||
| * {{citation |last=Voss |first=David | |||
| }} | |||
| |title=What Ever Happened to Cold Fusion | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |periodical=Physics World | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |date=March 1, 1999 | |||
| |last = Laurence | |||
| |url=http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/print/1258 | |||
| |first = William L. | |||
| |accessdate=2008-05-01 | |||
| |newspaper =The New York Times | |||
| |issn=0953-8585 | |||
| |title = Cold Fusion of Hydrogen Atoms; A Fourth Method Pulling Together | |||
| |doi= }} | |||
| |date = 30 December 1956 | |||
| *{{citation |last=Wilford |first=John Noble | |||
| |page = E7 | |||
| |title=Fusion Furor: Science's Human Face | |||
| |url = https://www.nytimes.com/1956/12/30/archives/cold-fusion-of-hydrogen-atoms-a-fourth-method-pulling-together.html?sq=%2522Cold%2520Fusion&scp=11&st=cse | |||
| |newspaper=New York Times | |||
| }} | |||
| |date=April 24, 1989 | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Langmuir |first1=Irving |first2=Robert N. |last2=Hall |title=Pathological science |journal=] |volume=42 |issue=10 |pages=36–48 |date=1989|doi=10.1063/1.881205 |bibcode=1989PhT....42j..36L }} | |||
| |url=http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=950DE7DF133CF937A15757C0A96F948260&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=all | |||
| * {{cite web | |||
| |issn=0362-4331 | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |doi= | |||
| |last = Lewenstein | |||
| |accessdate = 2008-09-23}} | |||
| |first = Bruce V. | |||
| * {{citation |last=Will |first=F.G. | |||
| |title = Cornell cold fusion archive | |||
| |title=Hydrogen + oxygen recombination and related heat generation in undivided electrolysis cells | |||
| |work = Collection n°4451, Division of Rare and Manuscript Collections, Cornell University Library | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| |year = 1994 | |||
| |volume=426 | |||
| |url = http://rmc.library.cornell.edu/EAD/pdf_guides/RMM04451.pdf | |||
| |issue=1 | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| |year=1997 | |||
| }} | |||
| |pages=177–184 | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/S0022-0728(96)04972-8}} | |||
| | last1=Lewis | first1=N.S. | |||
| * {{citation |ref=Williams1989 | |||
| | last2=Barnes | first2=C.A. | |||
| | last3=Heben | first3=M.J. | |||
| |first2=D.J.S. |last2=Findlay | |||
| | last4=Kumar | first4=A. | |||
| |first3=D.H. |last3=Craston | |||
| | last5=Lunt | first5=S.R. | |||
| |first4=M.R. |last4=Sené | |||
| | last6=McManis | first6=G.E. | |||
| |first5=M. |last5=Bailey | |||
| | last7=Miskelly | first7=S.R. | |||
| |first6=S. |last6=Croft | |||
| | last8=Penner | first8=G.M. | |||
| |first7=B.W. |last7=Hooton | |||
| | last9=Sailor | first9=M.J. | |||
| |first8=C.P. |last8=Jones | |||
| | last10=Santangelo | first10=P.G. | |||
| |first9=A.R.J. |last9=Kucernak | |||
| | last11=Shreve | first11=G. A. | |||
| |first10=J.A. |last10=Mason | |||
| | last12=Tufts | first12=B. J. | |||
| |first11=R.I. |last11=Taylor | |||
| | last13=Youngquist | first13=M.G. | |||
| |title=Upper bounds on 'cold fusion' in electrolytic cells | |||
| | last14=Kavanagh | first14=R.W. | |||
| |journal=Nature | |||
| | last15=Kellogg | first15=S.E. | |||
| |volume=342 | |||
| | last16=Vogelaar | first16=R.B. | |||
| |pages=375–384 | |||
| | last17=Wang | first17=T. R. | |||
| |year=1989 | |||
| | last18=Kondrat | first18=R. | |||
| |issn= | |||
| | last19=New | first19=R. | |||
| |doi=10.1038/342375a0}} | |||
| |s2cid=4359244 | |||
| * {{citation |last=Wilson |first=R.H. | |||
| | title=Searches for low-temperature nuclear fusion of deuterium in palladium | |||
| |title=Analysis of experiments on the calorimetry of LiOD-D<sub>2</sub>O electrochemical cells | |||
| | journal=Nature | |||
| |journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| | year=1989 | |||
| | volume=340 | |||
| | pages=525–530 | |||
| | doi=10.1038/340525a0 | bibcode = 1989Natur.340..525L | issue=6234 | |||
| |issn= | |||
| |display-authors=8 | |||
| |doi=10.1016/0022-0728(92)80338-5 }} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Mallove | |||
| |first = Eugene | |||
| |author-link = Eugene Mallove | |||
| |title = Fire from Ice: Searching for the Truth Behind the Cold Fusion Furor | |||
| |location = London | |||
| |publisher = Wiley | |||
| |year = 1991 | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-471-53139-5 | |||
| |url = https://archive.org/details/firefromicesearc00mall_0 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Cold Fusion: The history of research in Italy |year=2009 |editor-first1=Sergio |editor-last1=Martellucci |editor-first2=Angela |editor-last2=Rosati |editor-first3=Francesco |editor-last3=Scaramuzzi |editor-first4=Vittorio |editor-last4=Violante |translator-first=Chiara Maria |translator-last=Costigliola |url=http://www.enea.it/en/publications/volume-pdf/Cold_Fusion_Italy.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160313124607/http://www.enea.it/en/publications/volume-pdf/Cold_Fusion_Italy.pdf |archive-date=13 March 2016}} In the foreword by the president of ENEA the belief is expressed that the cold fusion phenomenon is proved. | |||
| * {{Cite book |mode=cs2 |last1=Mehra |first1=Jagdish |last2=Milton |first2=K. A. |last3=Schwinger |first3=Julian Seymour |title=Climbing the Mountain: The Scientific Biography of Julian Schwinger |edition=illustrated |location=New York |publisher=] |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-19-850658-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9SmZSN8F164C}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Mengoli | first1=G. | |||
| | last2=Bernardini | first2=M. | |||
| | last3=Manduchi | first3=C. | |||
| | last4=Zannoni | first4=G. | |||
| | year=1998 | |||
| | title=Calorimetry close to the boiling temperature of the D<sub>2</sub>O/Pd electrolytic system | |||
| | journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| | volume=444 | |||
| | pages=155–167 | |||
| | doi=10.1016/S0022-0728(97)00634-7 | |||
| | issue=2 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{harvc |last=Morrison |first=Douglas R.O. |c=Assessment |pp=3–5 |in=Saeta |year=1999}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Mosier-Boss | first1=Pamela A. | |||
| | last2=Szpak | first2=Stanislaw | |||
| | last3=Gordon | first3=Frank E. | |||
| | last4=Forsley | first4=L.P.G. | |||
| |s2cid=11044813 | |||
| | title=Triple tracks in CR-39 as the result of Pd–D Co-deposition: evidence of energetic neutrons | |||
| | journal=Naturwissenschaften | |||
| | year=2009 | |||
| | volume=96 | |||
| | issue=1 | |||
| | pages=135–142 | |||
| | doi=10.1007/s00114-008-0449-x | |||
| | pmid=18828003 | bibcode = 2009NW.....96..135M | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Mullins | |||
| |first = Justin | |||
| |s2cid = 7170843 | |||
| |title = Cold Fusion Back From the Dead | |||
| |journal = IEEE Spectrum | |||
| |volume = 41 | |||
| |page = 22 | |||
| |date = September 2004 | |||
| |doi = 10.1109/MSPEC.2004.1330805 | |||
| |issue = 9 | |||
| |url = https://spectrum.ieee.org/cold-fusion-back-from-the-dead | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Oriani | first1=Richard A. | |||
| | last2=Nelson | first2=John C. | |||
| | last3=Lee | first3=Sung-Kyu | |||
| | last4=Broadhurst | first4=J. H. | |||
| |s2cid=118860562 | |||
| | title=Calorimetric Measurements of Excess Power Output During the Cathodic Charging of Deuterium into Palladium | |||
| | journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| | volume=18 | |||
| |issue=4 | |||
| | year=1990 | |||
| | pages=652–662 | |||
| | issn=0748-1896 | |||
| | doi=10.13182/FST90-A29259 | |||
| | bibcode=1990FuTec..18..652O }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | title=Über die Verwandlung von Wasserstoff in Helium | |||
| | last1=Paneth | first1=Fritz | |||
| | last2=Peters | first2=Kurt | |||
| |s2cid=43265081 | |||
| | journal=] | |||
| | language=de | |||
| | volume=14 | |||
| | issue=43 | |||
| | pages=956–962 | |||
| | year=1926 | |||
| | doi=10.1007/BF01579126 | bibcode = 1926NW.....14..956P | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| | mode=cs2 | |||
| | year=2000 | |||
| | last=Park | |||
| | first=Robert L | |||
| | author-link=Robert L. Park | |||
| | title=Voodoo Science: The road from foolishness to fraud | |||
| | place=Oxford, U.K. & New York | |||
| | publisher=] | |||
| | isbn=978-0-19-860443-3 | |||
| | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xzCK6-Kqs6QC&q=%22voodoo+science%22 | |||
| | access-date=14 November 2010 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Petit | first=Charles | |||
| | title=Cold panacea: two researchers proclaimed 20 years ago that they'd achieved cold fusion, the ultimate energy solution. The workwent nowhere, but the hope remains | |||
| | periodical=Science News | |||
| | date=14 March 2009 | |||
| | doi=10.1002/scin.2009.5591750622 | |||
| | volume=175 | issue=6 | pages=20–24 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Platt | |||
| |first = Charles | |||
| |title = What if Cold Fusion is Real? | |||
| |volume = 6 | |||
| |periodical = ] | |||
| |year = 1998 | |||
| |issue = 11 | |||
| |url = https://www.wired.com/wired/archive/6.11/coldfusion.html?pg=1&topic=&topic_set= | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |title = Cold Fusion, Derided in U.S., Is Hot In Japan | |||
| |last = Pollack | |||
| |first = A. | |||
| |newspaper =The New York Times | |||
| |date = 17 November 1992 | |||
| |url = https://www.nytimes.com/1992/11/17/science/cold-fusion-derided-in-us-is-hot-in-japan.html | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Pollack | |||
| |first = A. | |||
| |title = Japan, Long a Holdout, is Ending its Quest for Cold Fusion | |||
| |newspaper =The New York Times | |||
| |date = 26 August 1997 | |||
| |volume = 79 | |||
| |pages = 243, C4 | |||
| |url = https://www.nytimes.com/1997/08/26/science/japan-long-a-holdout-is-ending-its-quest-for-cold-fusion.html?n=Top%2FNews%2FScience%2FTopics%2FResearch | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Pool | |||
| |first = Robert | |||
| |journal = Science | |||
| |title = How cold fusion happened – twice! | |||
| |date = 28 April 1989 | |||
| |volume = 244 | |||
| |issue = 4903 | |||
| |pages = 420–423 | |||
| |doi = 10.1126/science.244.4903.420 | |||
| |pmid = 17807604 | |||
| |url = http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-7597573.html | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20130602212724/http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-7597573.html | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| |archive-date = 2 June 2013 | |||
| |bibcode = 1989Sci...244..420P | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=Radio Times Guide to Films 2014 |author=Radio Times Film Unit |author-link=Radio Times |year=2013 |publisher=Immediate Media Company |isbn=978-0956752369}} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |title = Chemistry: Principles and Practice | |||
| |last1 = Reger | |||
| |first1 = Daniel L. | |||
| |last2 = Goode | |||
| |first2 = Scott R. | |||
| |last3 = Ball | |||
| |first3 = David W. | |||
| |edition = 3rd revised | |||
| |publisher = Cengage Learning | |||
| |year = 2009 | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-534-42012-3 | |||
| |pages = 814–815 | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=OUIaM1V3ThsC | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | title= Case Studies in Pathological Science: How the Loss of Objectivity Led to False Conclusions in Studies of Polywater, Infinite Dilution and Cold Fusion | |||
| | journal= ] | |||
| | last= Rousseau | first=D. L. |author-link = Denis Rousseau | |||
| | date= January–February 1992 | |||
| | volume= 80 | |||
| |issue=1 | |||
| | pages= 54–63 | |||
| | bibcode = 1992AmSci..80...54R | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite magazine | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |editor-last = Saeta | |||
| |editor-first = Peter N. | |||
| |title = What is the current scientific thinking on cold fusion? Is there any possible validity to this phenomenon? | |||
| |periodical = Scientific American | |||
| |pages = 1–6 | |||
| |date = 21 October 1999 | |||
| |series = Ask the Experts | |||
| |url = http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=what-is-the-current-scien | |||
| |access-date = 17 December 2008 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite web|mode=cs2 |last=Sampson |first=Mark T. |year=2009 |title='Cold fusion' rebirth? New evidence for existence of controversial energy source |publisher=] |url=http://portal.acs.org/portal/acs/corg/content?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=PP_ARTICLEMAIN&node_id=222&content_id=WPCP_012362&use_sec=true&sec_url_var=region1&__uuid=5885551e-7f60-4185-a6f1-c4bfe8d5e26d |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111002143748/http://portal.acs.org/portal/acs/corg/content?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=PP_ARTICLEMAIN&node_id=222&content_id=WPCP_012362&use_sec=true&sec_url_var=region1&__uuid=5885551e-7f60-4185-a6f1-c4bfe8d5e26d |archive-date=2 October 2011 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Sanderson | |||
| |first = Katharine | |||
| |title = Cold fusion is back at the American Chemical Society | |||
| |periodical = Nature News | |||
| |date = 29 March 2007 | |||
| |url = http://www.bioedonline.org/news/news.cfm?art=3234 | |||
| |access-date = 18 July 2009 | |||
| |issn = 0028-0836 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20090827033736/http://www.bioedonline.org/news/news.cfm?art=3234 | |||
| |archive-date = 27 August 2009 | |||
| |url-status = dead | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Scanlon |first1=Eileen |last2=Hill |first2=Roger |date=1999 |title=Communicating science: contexts and channels |publisher=Routledge |isbn=041519752X |location=London |oclc=39180844}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Scaramuzzi | first=F. | |||
| |s2cid=6158268 | |||
| | title=Ten years of cold fusion: an eye-witness account | |||
| | periodical=] | |||
| | year=2000 | |||
| | issue=1&2 | |||
| | volume=8 | |||
| | pages=77–101 | |||
| | issn=0898-9621 | |||
| | oclc=17959730 | |||
| | doi=10.1080/08989620008573967 | |||
| |citeseerx=10.1.1.380.8109 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{harvc |last=Schaffer |first=Michael J. |c=Historical overview, assessment |pp=1–3 |in=Saeta |year=1999}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Seife | first=Charles | author-link=Charles Seife | |||
| | title=Sun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful Thinking | |||
| | location=New York | |||
| | publisher=Viking | |||
| | year=2008 | |||
| | isbn=978-0-670-02033-1 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last1 = Shamoo | |||
| |first1 = Adil E. | |||
| |author-link = Adil E. Shamoo | |||
| |last2 = Resnik | |||
| |first2 = David B. | |||
| |title = Responsible Conduct of Research | |||
| |edition = 2nd illustrated | |||
| |editor = ] US | |||
| |year = 2003 | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=RLZin-f9eooC&q=announcement&pg=PA86 | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-19-514846-6 | |||
| |publisher = Oxford University Press | |||
| |location = Oxford | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Shanahan | |||
| |first = Kirk L. | |||
| |title = A systematic error in mass flow calorimetry demonstrated | |||
| |journal = Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |volume = 382 | |||
| |issue = 2 | |||
| |date = 23 May 2002 | |||
| |pages = 95–100 | |||
| |doi = 10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00832-2 | |||
| |url = https://zenodo.org/record/1259723 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Shanahan | |||
| |first = Kirk L. | |||
| |url = http://sti.srs.gov/fulltext/ms2004528/ms2004528.pdf | |||
| |title = Comments on "Thermal behavior of polarized Pd/D electrodes prepared by co-deposition" | |||
| |journal = Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |volume = 428 | |||
| |issue = 1–2 | |||
| |date = April 2005 | |||
| |pages = 207–212 | |||
| |doi = 10.1016/j.tca.2004.11.007 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Shanahan | |||
| |first = Kirk L. | |||
| |title = Reply to 'Comment on papers by K. Shanahan that propose to explain anomalous heat generated by cold fusion', E. Storms | |||
| |journal = Thermochimica Acta | |||
| |department = Short communication | |||
| |volume = 441 | |||
| |issue = 2 | |||
| |date = February 2006 | |||
| |pages = 210–214 | |||
| |doi = 10.1016/j.tca.2005.11.029 | |||
| |url = https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc874672/ | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Shkedi | first1=Zvi | |||
| | last2=McDonald | first2=Robert C. | |||
| | last3=Breen | first3=John J. | |||
| | last4=Maguire | first4=Stephen J. | |||
| | last5=Veranth | first5=Joe | |||
| | title=Calorimetry, Excess Heat, and Faraday Efficiency in Ni-H<sub>2</sub>O Electrolytic Cells | |||
| | journal=Fusion Technology | |||
| | volume=28 | |||
| | issue=4 | |||
| | year=1995 | |||
| | pages=1720–1731 | |||
| | issn=0748-1896 | |||
| | doi=10.13182/FST95-A30436 | |||
| | bibcode=1995FuTec..28.1720S }} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Simon | |||
| |first = Bart | |||
| |title = Undead Science: Science studies and the afterlife of cold fusion | |||
| |publisher = Rutgers University Press | |||
| |edition = illustrated | |||
| |year = 2002 | |||
| |page = | |||
| |isbn = 978-0-8135-3154-0 | |||
| |url = https://archive.org/details/undeadsciencesci0000simo | |||
| |url-access = registration | |||
| |bibcode = 2002usss.book.....S | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Szpak | first1=Stanislaw | |||
| | last2=Mosier-Boss | first2=Pamela A. | |||
| | last3=Miles | first3=Melvin H. | |||
| | last4=Fleischmann | first4=Martin | |||
| | title=Thermal behavior of polarized Pd/D electrodes prepared by co-deposition | |||
| | journal=Thermochimica Acta | |||
| | volume=410 | |||
| |issue=1–2 | |||
| | pages=101–107 | |||
| | year=2004 | |||
| | doi=10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00401-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite news|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Tate | first=N. | |||
| | title=MIT bombshell knocks fusion 'breakthrough' cold | |||
| | newspaper=Boston Herald | |||
| | year=1989 | |||
| | issue=1 May 1989 | |||
| | page=1 | |||
| | issn=0738-5854 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Taubes | first=Gary | |||
| |s2cid=9602261 | |||
| | title=Cold fusion conundrum at Texas A&M | |||
| | periodical=] | |||
| | volume=248 | |||
| | date=15 June 1990 | |||
| | pages=1299–1304 | |||
| | doi=10.1126/science.248.4961.1299 | |||
| | pmid=17747511 | |||
| | issue=4961 | |||
| | bibcode=1990Sci...248.1299T | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Taubes | first=Gary | |||
| | author-link=Gary Taubes | |||
| | title=Bad Science: The Short Life and Weird Times of Cold Fusion | |||
| | location=New York | |||
| | publisher=Random House | |||
| | year=1993 | |||
| | isbn=978-0-394-58456-0 | |||
| |title-link=Bad Science: The Short Life and Weird Times of Cold Fusion | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite report | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = US DOE | |||
| |first = U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| |title = A Report of the Energy Research Advisory Board to the United States Department of Energy | |||
| |year = 1989 | |||
| |publisher = U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| |location = Washington, DC | |||
| |url = http://files.ncas.org/erab/ | |||
| |access-date = 25 May 2008 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite report | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = US DOE | |||
| |first = U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| |year = 2004 | |||
| |title = Report of the Review of Low Energy Nuclear Reactions | |||
| |location = Washington, DC | |||
| |publisher = U.S. Department of Energy | |||
| |url = http://www.science.doe.gov/Sub/Newsroom/News_Releases/DOE-SC/2004/low_energy/CF_Final_120104.pdf | |||
| |access-date = 19 July 2008 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20080226210800/http://www.science.doe.gov/Sub/Newsroom/News_Releases/DOE-SC/2004/low_energy/CF_Final_120104.pdf | |||
| |archive-date = 26 February 2008 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal| mode=cs2 | last=Van Noorden | first=R. | title=Cold fusion back on the menu | journal=Chemistry World | date=April 2007 | url=http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/News/2007/March/22030701.asp | access-date=25 May 2008 | issn=1473-7604 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Rogers | first1=Vern C. | |||
| | last2=Sandquist | first2=Gary M. | |||
| |s2cid=120196723 | |||
| | title=Cold fusion reaction products and their measurement | |||
| | journal=Journal of Fusion Energy | |||
| | date=December 1990 | |||
| | volume=9 | issue=4 | pages=483–485 | doi=10.1007/BF01588284 | |||
| |bibcode=1990JFuE....9..483R | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Voss | |||
| |first = David | |||
| |title = What Ever Happened to Cold Fusion | |||
| |volume = 12 | |||
| |issue = 3 | |||
| |pages = 12–14 | |||
| |periodical = Physics World | |||
| |date = 1 March 1999a | |||
| |url = http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/print/1258 | |||
| |access-date = 1 May 2008 | |||
| |issn = 0953-8585 | |||
| |doi = 10.1088/2058-7058/12/3/14 | |||
| |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080701133103/http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/print/1258|archive-date=2008-07-01|url-status=dead | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| |last=Voss | first=David | |||
| |s2cid=108860158 | |||
| |title='New Physics' Finds a Haven at the Patent Office | |||
| |periodical=Science |date=21 May 1999b | |||
| |issn=0036-8075 | |||
| |doi=10.1126/science.284.5418.1252 |volume=284 |pages=1252–1254 |issue=5418 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite news | |||
| |mode = cs2 | |||
| |last = Wilford | |||
| |first = John Noble | |||
| |title = Fusion Furor: Science's Human Face | |||
| |newspaper =The New York Times | |||
| |date = 24 April 1989 | |||
| |url = https://www.nytimes.com/1989/04/24/us/fusion-furor-science-s-human-face.html?pagewanted=all | |||
| |issn = 0362-4331 | |||
| |access-date = 23 September 2008 | |||
| |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20170625044413/http://www.nytimes.com/1989/04/24/us/fusion-furor-science-s-human-face.html?pagewanted=all&src=pm |archive-date=25 June 2017 |url-status=live | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Williams | first1=D.E. | |||
| | last2=Findlay | first2=D.J.S. | |||
| | last3=Craston | first3=D.H. | |||
| | last4=Sené | first4=M.R. | |||
| | last5=Bailey | first5=M. | |||
| | last6=Croft | first6=S. | |||
| | last7=Hooton | first7=B.W. | |||
| | last8=Jones | first8=C.P. | |||
| | last9=Kucernak | first9=A.R.J. | |||
| | last10=Mason | first10=J.A. | |||
| | last11=Taylor | first11=R.I. | |||
| |s2cid=4347251 | |||
| | title=Upper bounds on 'cold fusion' in electrolytic cells | |||
| | journal=Nature | volume=342 | issue=6248 | pages=375–384 | year=1989 | |||
| | doi=10.1038/342375a0 | bibcode = 1989Natur.342..375W | |||
| |name-list-style=vanc |display-authors=4 | |||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last=Wilner | |||
| | first=Bertil | |||
| |s2cid=26487447 | |||
| | title=No new fusion under the Sun | |||
| | journal=Nature | volume=339 | issue=6221 | page=180 |date=May 1989 | doi =10.1038/339180a0 | |||
| |bibcode = 1989Natur.339..180W | doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|mode=cs2 | |||
| | last1=Wilson | first1=R.H. | |||
| | last2=Bray | first2=J.W. | |||
| | last3=Kosky | first3=P.G. | |||
| | last4=Vakil | first4=H.B. | |||
| | last5=Will | first5=F.G. | |||
| | title=Analysis of experiments on the calorimetry of LiOD-D<sub>2</sub>O electrochemical cells | |||
| | journal=Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry | |||
| | year=1992 | volume=332 |issue=1–2 | |||
| | pages=1–31 | |||
| | doi=10.1016/0022-0728(92)80338-5 | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| ] | |||
| * (iscmns.org), organizes the ICCF conferences and publishes the ''Journal of Condensed Matter Nuclear Science''. See: of published papers and proceedings. | |||
| ] | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151007025026/http://www.lenr-forum.com/forum/index.php/Attachment/386-IEEE-brief-DeChiaro-9-2015-pdf/ |date=7 October 2015 }}: ] report NSWCDD-PN-15-0040 by Louis F. DeChiaro, PhD, 23 September 2015 | |||
| {{authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Cold Fusion}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:34, 19 November 2024
Hypothetical type of nuclear reaction This article is about the Fleischmann–Pons claims of nuclear fusion at room temperature, and subsequent research. For the original use of the term "cold fusion", see muon-catalyzed fusion. For all other definitions, see Cold fusion (disambiguation). Not to be confused with cold welding.
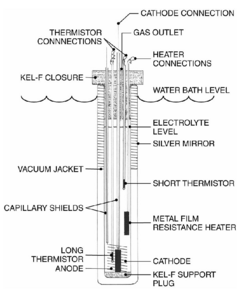
Cold fusion is a hypothesized type of nuclear reaction that would occur at, or near, room temperature. It would contrast starkly with the "hot" fusion that is known to take place naturally within stars and artificially in hydrogen bombs and prototype fusion reactors under immense pressure and at temperatures of millions of degrees, and be distinguished from muon-catalyzed fusion. There is currently no accepted theoretical model that would allow cold fusion to occur.
In 1989, two electrochemists at the University of Utah, Martin Fleischmann and Stanley Pons, reported that their apparatus had produced anomalous heat ("excess heat") of a magnitude they asserted would defy explanation except in terms of nuclear processes. They further reported measuring small amounts of nuclear reaction byproducts, including neutrons and tritium. The small tabletop experiment involved electrolysis of heavy water on the surface of a palladium (Pd) electrode. The reported results received wide media attention and raised hopes of a cheap and abundant source of energy.
Many scientists tried to replicate the experiment with the few details available. Expectations diminished as a result of numerous failed replications, the retraction of several previously reported positive replications, the identification of methodological flaws and experimental errors in the original study, and, ultimately, the confirmation that Fleischmann and Pons had not observed the expected nuclear reaction byproducts. By late 1989, most scientists considered cold fusion claims dead, and cold fusion subsequently gained a reputation as pathological science. In 1989 the United States Department of Energy (DOE) concluded that the reported results of excess heat did not present convincing evidence of a useful source of energy and decided against allocating funding specifically for cold fusion. A second DOE review in 2004, which looked at new research, reached similar conclusions and did not result in DOE funding of cold fusion. Presently, since articles about cold fusion are rarely published in peer-reviewed mainstream scientific journals, they do not attract the level of scrutiny expected for mainstream scientific publications.
Nevertheless, some interest in cold fusion has continued through the decades—for example, a Google-funded failed replication attempt was published in a 2019 issue of Nature. A small community of researchers continues to investigate it, often under the alternative designations low-energy nuclear reactions (LENR) or condensed matter nuclear science (CMNS).
History
Nuclear fusion is normally understood to occur at temperatures in the tens of millions of degrees. This is called "thermonuclear fusion". Since the 1920s, there has been speculation that nuclear fusion might be possible at much lower temperatures by catalytically fusing hydrogen absorbed in a metal catalyst. In 1989, a claim by Stanley Pons and Martin Fleischmann (then one of the world's leading electrochemists) that such cold fusion had been observed caused a brief media sensation before the majority of scientists criticized their claim as incorrect after many found they could not replicate the excess heat. Since the initial announcement, cold fusion research has continued by a small community of researchers who believe that such reactions happen and hope to gain wider recognition for their experimental evidence.
Early research
The ability of palladium to absorb hydrogen was recognized as early as the nineteenth century by Thomas Graham. In the late 1920s, two Austrian-born scientists, Friedrich Paneth and Kurt Peters, originally reported the transformation of hydrogen into helium by nuclear catalysis when hydrogen was absorbed by finely divided palladium at room temperature. However, the authors later retracted that report, saying that the helium they measured was due to background from the air.
In 1927, Swedish scientist John Tandberg reported that he had fused hydrogen into helium in an electrolytic cell with palladium electrodes. On the basis of his work, he applied for a Swedish patent for "a method to produce helium and useful reaction energy". Due to Paneth and Peters's retraction and his inability to explain the physical process, his patent application was denied. After deuterium was discovered in 1932, Tandberg continued his experiments with heavy water. The final experiments made by Tandberg with heavy water were similar to the original experiment by Fleischmann and Pons. Fleischmann and Pons were not aware of Tandberg's work.
The term "cold fusion" was used as early as 1956 in an article in The New York Times about Luis Alvarez's work on muon-catalyzed fusion. Paul Palmer and then Steven Jones of Brigham Young University used the term "cold fusion" in 1986 in an investigation of "geo-fusion", the possible existence of fusion involving hydrogen isotopes in a planetary core. In his original paper on this subject with Clinton Van Siclen, submitted in 1985, Jones had coined the term "piezonuclear fusion".
Fleischmann–Pons experiment
The most famous cold fusion claims were made by Stanley Pons and Martin Fleischmann in 1989. After a brief period of interest by the wider scientific community, their reports were called into question by nuclear physicists. Pons and Fleischmann never retracted their claims, but moved their research program from the US to France after the controversy erupted.
Events preceding announcement

Martin Fleischmann of the University of Southampton and Stanley Pons of the University of Utah hypothesized that the high compression ratio and mobility of deuterium that could be achieved within palladium metal using electrolysis might result in nuclear fusion. To investigate, they conducted electrolysis experiments using a palladium cathode and heavy water within a calorimeter, an insulated vessel designed to measure process heat. Current was applied continuously for many weeks, with the heavy water being renewed at intervals. Some deuterium was thought to be accumulating within the cathode, but most was allowed to bubble out of the cell, joining oxygen produced at the anode. For most of the time, the power input to the cell was equal to the calculated power leaving the cell within measurement accuracy, and the cell temperature was stable at around 30 °C. But then, at some point (in some of the experiments), the temperature rose suddenly to about 50 °C without changes in the input power. These high temperature phases would last for two days or more and would repeat several times in any given experiment once they had occurred. The calculated power leaving the cell was significantly higher than the input power during these high temperature phases. Eventually the high temperature phases would no longer occur within a particular cell.
In 1988, Fleischmann and Pons applied to the United States Department of Energy for funding towards a larger series of experiments. Up to this point they had been funding their experiments using a small device built with $100,000 out-of-pocket. The grant proposal was turned over for peer review, and one of the reviewers was Steven Jones of Brigham Young University. Jones had worked for some time on muon-catalyzed fusion, a known method of inducing nuclear fusion without high temperatures, and had written an article on the topic entitled "Cold nuclear fusion" that had been published in Scientific American in July 1987. Fleischmann and Pons and co-workers met with Jones and co-workers on occasion in Utah to share research and techniques. During this time, Fleischmann and Pons described their experiments as generating considerable "excess energy", in the sense that it could not be explained by chemical reactions alone. They felt that such a discovery could bear significant commercial value and would be entitled to patent protection. Jones, however, was measuring neutron flux, which was not of commercial interest. To avoid future problems, the teams appeared to agree to publish their results simultaneously, though their accounts of their 6 March meeting differ.
Announcement
In mid-March 1989, both research teams were ready to publish their findings, and Fleischmann and Jones had agreed to meet at an airport on 24 March to send their papers to Nature via FedEx. Fleischmann and Pons, however, pressured by the University of Utah, which wanted to establish priority on the discovery, broke their apparent agreement, disclosing their work at a press conference on 23 March (they claimed in the press release that it would be published in Nature but instead submitted their paper to the Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry). Jones, upset, faxed in his paper to Nature after the press conference.
Fleischmann and Pons' announcement drew wide media attention, as well as attention from the scientific community. The 1986 discovery of high-temperature superconductivity had made scientists more open to revelations of unexpected but potentially momentous scientific results that could be replicated reliably even if they could not be explained by established theories. Many scientists were also reminded of the Mössbauer effect, a process involving nuclear transitions in a solid. Its discovery 30 years earlier had also been unexpected, though it was quickly replicated and explained within the existing physics framework.
The announcement of a new purported clean source of energy came at a crucial time: adults still remembered the 1973 oil crisis and the problems caused by oil dependence, anthropogenic global warming was starting to become notorious, the anti-nuclear movement was labeling nuclear power plants as dangerous and getting them closed, people had in mind the consequences of strip mining, acid rain, the greenhouse effect and the Exxon Valdez oil spill, which happened the day after the announcement. In the press conference, Chase N. Peterson, Fleischmann and Pons, backed by the solidity of their scientific credentials, repeatedly assured the journalists that cold fusion would solve environmental problems, and would provide a limitless inexhaustible source of clean energy, using only seawater as fuel. They said the results had been confirmed dozens of times and they had no doubts about them. In the accompanying press release Fleischmann was quoted saying: "What we have done is to open the door of a new research area, our indications are that the discovery will be relatively easy to make into a usable technology for generating heat and power, but continued work is needed, first, to further understand the science and secondly, to determine its value to energy economics."
Response and fallout
Although the experimental protocol had not been published, physicists in several countries attempted, and failed, to replicate the excess heat phenomenon. The first paper submitted to Nature reproducing excess heat, although it passed peer review, was rejected because most similar experiments were negative and there were no theories that could explain a positive result; this paper was later accepted for publication by the journal Fusion Technology.
Nathan Lewis, professor of chemistry at the California Institute of Technology, led one of the most ambitious validation efforts, trying many variations on the experiment without success, while CERN physicist Douglas R. O. Morrison said that "essentially all" attempts in Western Europe had failed. Even those reporting success had difficulty reproducing Fleischmann and Pons' results. On 10 April 1989, a group at Texas A&M University published results of excess heat and later that day a group at the Georgia Institute of Technology announced neutron production—the strongest replication announced up to that point due to the detection of neutrons and the reputation of the lab. On 12 April Pons was acclaimed at an ACS meeting. But Georgia Tech retracted their announcement on 13 April, explaining that their neutron detectors gave false positives when exposed to heat.
Another attempt at independent replication, headed by Robert Huggins at Stanford University, which also reported early success with a light water control, became the only scientific support for cold fusion in 26 April US Congress hearings. But when he finally presented his results he reported an excess heat of only one degree Celsius, a result that could be explained by chemical differences between heavy and light water in the presence of lithium. He had not tried to measure any radiation and his research was derided by scientists who saw it later. For the next six weeks, competing claims, counterclaims, and suggested explanations kept what was referred to as "cold fusion" or "fusion confusion" in the news.
In April 1989, Fleischmann and Pons published a "preliminary note" in the Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry. This paper notably showed a gamma peak without its corresponding Compton edge, which indicated they had made a mistake in claiming evidence of fusion byproducts. Fleischmann and Pons replied to this critique, but the only thing left clear was that no gamma ray had been registered and that Fleischmann refused to recognize any mistakes in the data. A much longer paper published a year later went into details of calorimetry but did not include any nuclear measurements.
Nevertheless, Fleischmann and Pons and a number of other researchers who found positive results remained convinced of their findings. The University of Utah asked Congress to provide $25 million to pursue the research, and Pons was scheduled to meet with representatives of President Bush in early May.
On 30 April 1989, cold fusion was declared dead by The New York Times. The Times called it a circus the same day, and the Boston Herald attacked cold fusion the following day.
On 1 May 1989, the American Physical Society held a session on cold fusion in Baltimore, including many reports of experiments that failed to produce evidence of cold fusion. At the end of the session, eight of the nine leading speakers stated that they considered the initial Fleischmann and Pons claim dead, with the ninth, Johann Rafelski, abstaining. Steven E. Koonin of Caltech called the Utah report a result of "the incompetence and delusion of Pons and Fleischmann," which was met with a standing ovation. Douglas R. O. Morrison, a physicist representing CERN, was the first to call the episode an example of pathological science. On 4 May, due to all this new criticism, the meetings with various representatives from Washington were cancelled.
From 8 May, only the A&M tritium results kept cold fusion afloat.
In July and November 1989, Nature published papers critical of cold fusion claims. Negative results were also published in several other scientific journals including Science, Physical Review Letters, and Physical Review C (nuclear physics). In August 1989, in spite of this trend, the state of Utah invested $4.5 million to create the National Cold Fusion Institute.
The United States Department of Energy organized a special panel to review cold fusion theory and research. The panel issued its report in November 1989, concluding that results as of that date did not present convincing evidence that useful sources of energy would result from the phenomena attributed to cold fusion. The panel noted the large number of failures to replicate excess heat and the greater inconsistency of reports of nuclear reaction byproducts expected by established conjecture. Nuclear fusion of the type postulated would be inconsistent with current understanding and, if verified, would require established conjecture, perhaps even theory itself, to be extended in an unexpected way. The panel was against special funding for cold fusion research, but supported modest funding of "focused experiments within the general funding system".
Cold fusion supporters continued to argue that the evidence for excess heat was strong, and in September 1990 the National Cold Fusion Institute listed 92 groups of researchers from 10 countries that had reported corroborating evidence of excess heat, but they refused to provide any evidence of their own arguing that it could endanger their patents. However, no further DOE nor NSF funding resulted from the panel's recommendation. By this point, however, academic consensus had moved decidedly toward labeling cold fusion as a kind of "pathological science".
In March 1990, Michael H. Salamon, a physicist from the University of Utah, and nine co-authors reported negative results. University faculty were then "stunned" when a lawyer representing Pons and Fleischmann demanded the Salamon paper be retracted under threat of a lawsuit. The lawyer later apologized; Fleischmann defended the threat as a legitimate reaction to alleged bias displayed by cold-fusion critics.
In early May 1990, one of the two A&M researchers, Kevin Wolf, acknowledged the possibility of spiking, but said that the most likely explanation was tritium contamination in the palladium electrodes or simply contamination due to sloppy work. In June 1990 an article in Science by science writer Gary Taubes destroyed the public credibility of the A&M tritium results when it accused its group leader John Bockris and one of his graduate students of spiking the cells with tritium. In October 1990 Wolf finally said that the results were explained by tritium contamination in the rods. An A&M cold fusion review panel found that the tritium evidence was not convincing and that, while they couldn't rule out spiking, contamination and measurements problems were more likely explanations, and Bockris never got support from his faculty to resume his research.
On 30 June 1991, the National Cold Fusion Institute closed after it ran out of funds; it found no excess heat, and its reports of tritium production were met with indifference.
On 1 January 1991, Pons left the University of Utah and went to Europe. In 1992, Pons and Fleischmann resumed research with Toyota Motor Corporation's IMRA lab in France. Fleischmann left for England in 1995, and the contract with Pons was not renewed in 1998 after spending $40 million with no tangible results. The IMRA laboratory stopped cold fusion research in 1998 after spending £12 million. Pons has made no public declarations since, and only Fleischmann continued giving talks and publishing papers.
Mostly in the 1990s, several books were published that were critical of cold fusion research methods and the conduct of cold fusion researchers. Over the years, several books have appeared that defended them. Around 1998, the University of Utah had already dropped its research after spending over $1 million, and in the summer of 1997, Japan cut off research and closed its own lab after spending $20 million.
Later research
A 1991 review by a cold fusion proponent had calculated "about 600 scientists" were still conducting research. After 1991, cold fusion research only continued in relative obscurity, conducted by groups that had increasing difficulty securing public funding and keeping programs open. These small but committed groups of cold fusion researchers have continued to conduct experiments using Fleischmann and Pons electrolysis setups in spite of the rejection by the mainstream community. The Boston Globe estimated in 2004 that there were only 100 to 200 researchers working in the field, most suffering damage to their reputation and career. Since the main controversy over Pons and Fleischmann had ended, cold fusion research has been funded by private and small governmental scientific investment funds in the United States, Italy, Japan, and India. For example, it was reported in Nature, in May, 2019, that Google had spent approximately $10 million on cold fusion research. A group of scientists at well-known research labs (e.g., MIT, Lawrence Berkeley National Lab, and others) worked for several years to establish experimental protocols and measurement techniques in an effort to re-evaluate cold fusion to a high standard of scientific rigor. Their reported conclusion: no cold fusion.
In 2021, following Nature's 2019 publication of anomalous findings that might only be explained by some localized fusion, scientists at the Naval Surface Warfare Center, Indian Head Division announced that they had assembled a group of scientists from the Navy, Army and National Institute of Standards and Technology to undertake a new, coordinated study. With few exceptions, researchers have had difficulty publishing in mainstream journals. The remaining researchers often term their field Low Energy Nuclear Reactions (LENR), Chemically Assisted Nuclear Reactions (CANR), Lattice Assisted Nuclear Reactions (LANR), Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (CMNS) or Lattice Enabled Nuclear Reactions; one of the reasons being to avoid the negative connotations associated with "cold fusion". The new names avoid making bold implications, like implying that fusion is actually occurring.
The researchers who continue their investigations acknowledge that the flaws in the original announcement are the main cause of the subject's marginalization, and they complain of a chronic lack of funding and no possibilities of getting their work published in the highest impact journals. University researchers are often unwilling to investigate cold fusion because they would be ridiculed by their colleagues and their professional careers would be at risk. In 1994, David Goodstein, a professor of physics at Caltech, advocated increased attention from mainstream researchers and described cold fusion as:
A pariah field, cast out by the scientific establishment. Between cold fusion and respectable science there is virtually no communication at all. Cold fusion papers are almost never published in refereed scientific journals, with the result that those works don't receive the normal critical scrutiny that science requires. On the other hand, because the Cold-Fusioners see themselves as a community under siege, there is little internal criticism. Experiments and theories tend to be accepted at face value, for fear of providing even more fuel for external critics, if anyone outside the group was bothering to listen. In these circumstances, crackpots flourish, making matters worse for those who believe that there is serious science going on here.
United States

United States Navy researchers at the Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center (SPAWAR) in San Diego have been studying cold fusion since 1989. In 2002 they released a two-volume report, "Thermal and nuclear aspects of the Pd/D2O system", with a plea for funding. This and other published papers prompted a 2004 Department of Energy (DOE) review.
2004 DOE panel
In August 2003, the U.S. Secretary of Energy, Spencer Abraham, ordered the DOE to organize a second review of the field. This was thanks to an April 2003 letter sent by MIT's Peter L. Hagelstein, and the publication of many new papers, including the Italian ENEA and other researchers in the 2003 International Cold Fusion Conference, and a two-volume book by U.S. SPAWAR in 2002. Cold fusion researchers were asked to present a review document of all the evidence since the 1989 review. The report was released in 2004. The reviewers were "split approximately evenly" on whether the experiments had produced energy in the form of heat, but "most reviewers, even those who accepted the evidence for excess power production, 'stated that the effects are not repeatable, the magnitude of the effect has not increased in over a decade of work, and that many of the reported experiments were not well documented'". In summary, reviewers found that cold fusion evidence was still not convincing 15 years later, and they did not recommend a federal research program. They only recommended that agencies consider funding individual well-thought studies in specific areas where research "could be helpful in resolving some of the controversies in the field". They summarized its conclusions thus:
While significant progress has been made in the sophistication of calorimeters since the review of this subject in 1989, the conclusions reached by the reviewers today are similar to those found in the 1989 review.
— Report of the Review of Low Energy Nuclear Reactions, US Department of Energy, December 2004
The current reviewers identified a number of basic science research areas that could be helpful in resolving some of the controversies in the field, two of which were: 1) material science aspects of deuterated metals using modern characterization techniques, and 2) the study of particles reportedly emitted from deuterated foils using state-of-the-art apparatus and methods. The reviewers believed that this field would benefit from the peer-review processes associated with proposal submission to agencies and paper submission to archival journals.
Cold fusion researchers placed a "rosier spin" on the report, noting that they were finally being treated like normal scientists, and that the report had increased interest in the field and caused "a huge upswing in interest in funding cold fusion research". However, in a 2009 BBC article on an American Chemical Society's meeting on cold fusion, particle physicist Frank Close was quoted stating that the problems that plagued the original cold fusion announcement were still happening: results from studies are still not being independently verified and inexplicable phenomena encountered are being labelled as "cold fusion" even if they are not, in order to attract the attention of journalists.
In February 2012, millionaire Sidney Kimmel, convinced that cold fusion was worth investing in by a 19 April 2009 interview with physicist Robert Duncan on the US news show 60 Minutes, made a grant of $5.5 million to the University of Missouri to establish the Sidney Kimmel Institute for Nuclear Renaissance (SKINR). The grant was intended to support research into the interactions of hydrogen with palladium, nickel or platinum under extreme conditions. In March 2013 Graham K. Hubler, a nuclear physicist who worked for the Naval Research Laboratory for 40 years, was named director. One of the SKINR projects is to replicate a 1991 experiment in which a professor associated with the project, Mark Prelas, says bursts of millions of neutrons a second were recorded, which was stopped because "his research account had been frozen". He claims that the new experiment has already seen "neutron emissions at similar levels to the 1991 observation".
In May 2016, the United States House Committee on Armed Services, in its report on the 2017 National Defense Authorization Act, directed the Secretary of Defense to "provide a briefing on the military utility of recent U.S. industrial base LENR advancements to the House Committee on Armed Services by September 22, 2016".
Italy
Since the Fleischmann and Pons announcement, the Italian national agency for new technologies, energy and sustainable economic development (ENEA) has funded Franco Scaramuzzi's research into whether excess heat can be measured from metals loaded with deuterium gas. Such research is distributed across ENEA departments, CNR laboratories, INFN, universities and industrial laboratories in Italy, where the group continues to try to achieve reliable reproducibility (i.e. getting the phenomenon to happen in every cell, and inside a certain frame of time). In 2006–2007, the ENEA started a research program which claimed to have found excess power of up to 500 percent, and in 2009, ENEA hosted the 15th cold fusion conference.
Japan
Between 1992 and 1997, Japan's Ministry of International Trade and Industry sponsored a "New Hydrogen Energy (NHE)" program of US$20 million to research cold fusion. Announcing the end of the program in 1997, the director and one-time proponent of cold fusion research Hideo Ikegami stated "We couldn't achieve what was first claimed in terms of cold fusion. (...) We can't find any reason to propose more money for the coming year or for the future." In 1999 the Japan C-F Research Society was established to promote the independent research into cold fusion that continued in Japan. The society holds annual meetings. Perhaps the most famous Japanese cold fusion researcher was Yoshiaki Arata, from Osaka University, who claimed in a demonstration to produce excess heat when deuterium gas was introduced into a cell containing a mixture of palladium and zirconium oxide, a claim supported by fellow Japanese researcher Akira Kitamura of Kobe University and Michael McKubre at SRI.
India
In the 1990s, India stopped its research in cold fusion at the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre because of the lack of consensus among mainstream scientists and the US denunciation of the research. Yet, in 2008, the National Institute of Advanced Studies recommended that the Indian government revive this research. Projects were commenced at Chennai's Indian Institute of Technology, the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre and the Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research. However, there is still skepticism among scientists and, for all practical purposes, research has stalled since the 1990s. A special section in the Indian multidisciplinary journal Current Science published 33 cold fusion papers in 2015 by major cold fusion researchers including several Indian researchers.
Reported results
A cold fusion experiment usually includes:
- a metal, such as palladium or nickel, in bulk, thin films or powder; and
- deuterium, hydrogen, or both, in the form of water, gas or plasma.
Electrolysis cells can be either open cell or closed cell. In open cell systems, the electrolysis products, which are gaseous, are allowed to leave the cell. In closed cell experiments, the products are captured, for example by catalytically recombining the products in a separate part of the experimental system. These experiments generally strive for a steady state condition, with the electrolyte being replaced periodically. There are also "heat-after-death" experiments, where the evolution of heat is monitored after the electric current is turned off.
The most basic setup of a cold fusion cell consists of two electrodes submerged in a solution containing palladium and heavy water. The electrodes are then connected to a power source to transmit electricity from one electrode to the other through the solution. Even when anomalous heat is reported, it can take weeks for it to begin to appear—this is known as the "loading time," the time required to saturate the palladium electrode with hydrogen (see "Loading ratio" section).
The Fleischmann and Pons early findings regarding helium, neutron radiation and tritium were never replicated satisfactorily, and its levels were too low for the claimed heat production and inconsistent with each other. Neutron radiation has been reported in cold fusion experiments at very low levels using different kinds of detectors, but levels were too low, close to background, and found too infrequently to provide useful information about possible nuclear processes.
Excess heat and energy production
An excess heat observation is based on an energy balance. Various sources of energy input and output are continuously measured. Under normal conditions, the energy input can be matched to the energy output to within experimental error. In experiments such as those run by Fleischmann and Pons, an electrolysis cell operating steadily at one temperature transitions to operating at a higher temperature with no increase in applied current. If the higher temperatures were real, and not an experimental artifact, the energy balance would show an unaccounted term. In the Fleischmann and Pons experiments, the rate of inferred excess heat generation was in the range of 10–20% of total input, though this could not be reliably replicated by most researchers. Researcher Nathan Lewis discovered that the excess heat in Fleischmann and Pons's original paper was not measured, but estimated from measurements that didn't have any excess heat.
Unable to produce excess heat or neutrons, and with positive experiments being plagued by errors and giving disparate results, most researchers declared that heat production was not a real effect and ceased working on the experiments. In 1993, after their original report, Fleischmann reported "heat-after-death" experiments—where excess heat was measured after the electric current supplied to the electrolytic cell was turned off. This type of report has also become part of subsequent cold fusion claims.
Helium, heavy elements, and neutrons

Known instances of nuclear reactions, aside from producing energy, also produce nucleons and particles on readily observable ballistic trajectories. In support of their claim that nuclear reactions took place in their electrolytic cells, Fleischmann and Pons reported a neutron flux of 4,000 neutrons per second, as well as detection of tritium. The classical branching ratio for previously known fusion reactions that produce tritium would predict, with 1 watt of power, the production of 10 neutrons per second, levels that would have been fatal to the researchers. In 2009, Mosier-Boss et al. reported what they called the first scientific report of highly energetic neutrons, using CR-39 plastic radiation detectors, but the claims cannot be validated without a quantitative analysis of neutrons.
Several medium and heavy elements like calcium, titanium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, copper and zinc have been reported as detected by several researchers, like Tadahiko Mizuno or George Miley. The report presented to the United States Department of Energy (DOE) in 2004 indicated that deuterium-loaded foils could be used to detect fusion reaction products and, although the reviewers found the evidence presented to them as inconclusive, they indicated that those experiments did not use state-of-the-art techniques.
In response to doubts about the lack of nuclear products, cold fusion researchers have tried to capture and measure nuclear products correlated with excess heat. Considerable attention has been given to measuring He production. However, the reported levels are very near to background, so contamination by trace amounts of helium normally present in the air cannot be ruled out. In the report presented to the DOE in 2004, the reviewers' opinion was divided on the evidence for He, with the most negative reviews concluding that although the amounts detected were above background levels, they were very close to them and therefore could be caused by contamination from air.
One of the main criticisms of cold fusion was that deuteron-deuteron fusion into helium was expected to result in the production of gamma rays—which were not observed and were not observed in subsequent cold fusion experiments. Cold fusion researchers have since claimed to find X-rays, helium, neutrons and nuclear transmutations. Some researchers also claim to have found them using only light water and nickel cathodes. The 2004 DOE panel expressed concerns about the poor quality of the theoretical framework cold fusion proponents presented to account for the lack of gamma rays.
Proposed mechanisms
Researchers in the field do not agree on a theory for cold fusion. One proposal considers that hydrogen and its isotopes can be absorbed in certain solids, including palladium hydride, at high densities. This creates a high partial pressure, reducing the average separation of hydrogen isotopes. However, the reduction in separation is not enough to create the fusion rates claimed in the original experiment, by a factor of ten. It was also proposed that a higher density of hydrogen inside the palladium and a lower potential barrier could raise the possibility of fusion at lower temperatures than expected from a simple application of Coulomb's law. Electron screening of the positive hydrogen nuclei by the negative electrons in the palladium lattice was suggested to the 2004 DOE commission, but the panel found the theoretical explanations not convincing and inconsistent with current physics theories.
Criticism
Criticism of cold fusion claims generally take one of two forms: either pointing out the theoretical implausibility that fusion reactions have occurred in electrolysis setups or criticizing the excess heat measurements as being spurious, erroneous, or due to poor methodology or controls. There are several reasons why known fusion reactions are an unlikely explanation for the excess heat and associated cold fusion claims.
Repulsion forces
Because nuclei are all positively charged, they strongly repel one another. Normally, in the absence of a catalyst such as a muon, very high kinetic energies are required to overcome this charged repulsion. Extrapolating from known fusion rates, the rate for uncatalyzed fusion at room-temperature energy would be 50 orders of magnitude lower than needed to account for the reported excess heat. In muon-catalyzed fusion there are more fusions because the presence of the muon causes deuterium nuclei to be 207 times closer than in ordinary deuterium gas. But deuterium nuclei inside a palladium lattice are further apart than in deuterium gas, and there should be fewer fusion reactions, not more.
Paneth and Peters in the 1920s already knew that palladium can absorb up to 900 times its own volume of hydrogen gas, storing it at several thousands of times the atmospheric pressure. This led them to believe that they could increase the nuclear fusion rate by simply loading palladium rods with hydrogen gas. Tandberg then tried the same experiment but used electrolysis to make palladium absorb more deuterium and force the deuterium further together inside the rods, thus anticipating the main elements of Fleischmann and Pons' experiment. They all hoped that pairs of hydrogen nuclei would fuse together to form helium, which at the time was needed in Germany to fill zeppelins, but no evidence of helium or of increased fusion rate was ever found.
This was also the belief of geologist Palmer, who convinced Steven Jones that the helium-3 occurring naturally in Earth perhaps came from fusion involving hydrogen isotopes inside catalysts like nickel and palladium. This led their team in 1986 to independently make the same experimental setup as Fleischmann and Pons (a palladium cathode submerged in heavy water, absorbing deuterium via electrolysis). Fleischmann and Pons had much the same belief, but they calculated the pressure to be of 10 atmospheres, when cold fusion experiments achieve a loading ratio of only one to one, which has only between 10,000 and 20,000 atmospheres. John R. Huizenga says they had misinterpreted the Nernst equation, leading them to believe that there was enough pressure to bring deuterons so close to each other that there would be spontaneous fusions.
Lack of expected reaction products
Conventional deuteron fusion is a two-step process, in which an unstable high-energy intermediary is formed:
Experiments have shown only three decay pathways for this excited-state nucleus, with the branching ratio showing the probability that any given intermediate follows a particular pathway. The products formed via these decay pathways are:
Only about one in a million of the intermediaries take the third pathway, making its products very rare compared to the other paths. This result is consistent with the predictions of the Bohr model. If 1 watt (6.242 × 10 eV/s) were produced from ~2.2575 × 10 deuteron fusions per second, with the known branching ratios, the resulting neutrons and tritium (H) would be easily measured. Some researchers reported detecting He but without the expected neutron or tritium production; such a result would require branching ratios strongly favouring the third pathway, with the actual rates of the first two pathways lower by at least five orders of magnitude than observations from other experiments, directly contradicting both theoretically predicted and observed branching probabilities. Those reports of He production did not include detection of gamma rays, which would require the third pathway to have been changed somehow so that gamma rays are no longer emitted.
The known rate of the decay process together with the inter-atomic spacing in a metallic crystal makes heat transfer of the 24 MeV excess energy into the host metal lattice prior to the intermediary's decay inexplicable by conventional understandings of momentum and energy transfer, and even then there would be measurable levels of radiation. Also, experiments indicate that the ratios of deuterium fusion remain constant at different energies. In general, pressure and chemical environment cause only small changes to fusion ratios. An early explanation invoked the Oppenheimer–Phillips process at low energies, but its magnitude was too small to explain the altered ratios.
Setup of experiments
Cold fusion setups utilize an input power source (to ostensibly provide activation energy), a platinum group electrode, a deuterium or hydrogen source, a calorimeter, and, at times, detectors to look for byproducts such as helium or neutrons. Critics have variously taken issue with each of these aspects and have asserted that there has not yet been a consistent reproduction of claimed cold fusion results in either energy output or byproducts. Some cold fusion researchers who claim that they can consistently measure an excess heat effect have argued that the apparent lack of reproducibility might be attributable to a lack of quality control in the electrode metal or the amount of hydrogen or deuterium loaded in the system. Critics have further taken issue with what they describe as mistakes or errors of interpretation that cold fusion researchers have made in calorimetry analyses and energy budgets.
Reproducibility
In 1989, after Fleischmann and Pons had made their claims, many research groups tried to reproduce the Fleischmann-Pons experiment, without success. A few other research groups, however, reported successful reproductions of cold fusion during this time. In July 1989, an Indian group from the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (P. K. Iyengar and M. Srinivasan) and in October 1989, John Bockris' group from Texas A&M University reported on the creation of tritium. In December 1990, professor Richard Oriani of the University of Minnesota reported excess heat.
Groups that did report successes found that some of their cells were producing the effect, while other cells that were built exactly the same and used the same materials were not producing the effect. Researchers that continued to work on the topic have claimed that over the years many successful replications have been made, but still have problems getting reliable replications. Reproducibility is one of the main principles of the scientific method, and its lack led most physicists to believe that the few positive reports could be attributed to experimental error. The DOE 2004 report said among its conclusions and recommendations:
Ordinarily, new scientific discoveries are claimed to be consistent and reproducible; as a result, if the experiments are not complicated, the discovery can usually be confirmed or disproved in a few months. The claims of cold fusion, however, are unusual in that even the strongest proponents of cold fusion assert that the experiments, for unknown reasons, are not consistent and reproducible at the present time. (...) Internal inconsistencies and lack of predictability and reproducibility remain serious concerns. (...) The Panel recommends that the cold fusion research efforts in the area of heat production focus primarily on confirming or disproving reports of excess heat.
Loading ratio

Cold fusion researchers (McKubre since 1994, ENEA in 2011) have speculated that a cell that is loaded with a deuterium/palladium ratio lower than 100% (or 1:1) will not produce excess heat. Since most of the negative replications from 1989 to 1990 did not report their ratios, this has been proposed as an explanation for failed reproducibility. This loading ratio is hard to obtain, and some batches of palladium never reach it because the pressure causes cracks in the palladium, allowing the deuterium to escape. Fleischmann and Pons never disclosed the deuterium/palladium ratio achieved in their cells; there are no longer any batches of the palladium used by Fleischmann and Pons (because the supplier now uses a different manufacturing process), and researchers still have problems finding batches of palladium that achieve heat production reliably.
Misinterpretation of data
Some research groups initially reported that they had replicated the Fleischmann and Pons results but later retracted their reports and offered an alternative explanation for their original positive results. A group at Georgia Tech found problems with their neutron detector, and Texas A&M discovered bad wiring in their thermometers. These retractions, combined with negative results from some famous laboratories, led most scientists to conclude, as early as 1989, that no positive result should be attributed to cold fusion.
Calorimetry errors
The calculation of excess heat in electrochemical cells involves certain assumptions. Errors in these assumptions have been offered as non-nuclear explanations for excess heat.
One assumption made by Fleischmann and Pons is that the efficiency of electrolysis is nearly 100%, meaning nearly all the electricity applied to the cell resulted in electrolysis of water, with negligible resistive heating and substantially all the electrolysis product leaving the cell unchanged. This assumption gives the amount of energy expended converting liquid D2O into gaseous D2 and O2. The efficiency of electrolysis is less than one if hydrogen and oxygen recombine to a significant extent within the calorimeter. Several researchers have described potential mechanisms by which this process could occur and thereby account for excess heat in electrolysis experiments.
Another assumption is that heat loss from the calorimeter maintains the same relationship with measured temperature as found when calibrating the calorimeter. This assumption ceases to be accurate if the temperature distribution within the cell becomes significantly altered from the condition under which calibration measurements were made. This can happen, for example, if fluid circulation within the cell becomes significantly altered. Recombination of hydrogen and oxygen within the calorimeter would also alter the heat distribution and invalidate the calibration.
Publications
The ISI identified cold fusion as the scientific topic with the largest number of published papers in 1989, of all scientific disciplines. The Nobel Laureate Julian Schwinger declared himself a supporter of cold fusion in the fall of 1989, after much of the response to the initial reports had turned negative. He tried to publish his theoretical paper "Cold Fusion: A Hypothesis" in Physical Review Letters, but the peer reviewers rejected it so harshly that he felt deeply insulted, and he resigned from the American Physical Society (publisher of PRL) in protest.
The number of papers sharply declined after 1990 because of two simultaneous phenomena: first, scientists abandoned the field; second, journal editors declined to review new papers. Consequently, cold fusion fell off the ISI charts. Researchers who got negative results turned their backs on the field; those who continued to publish were simply ignored. A 1993 paper in Physics Letters A was the last paper published by Fleischmann, and "one of the last reports to be formally challenged on technical grounds by a cold fusion skeptic."
The Journal of Fusion Technology (FT) established a permanent feature in 1990 for cold fusion papers, publishing over a dozen papers per year and giving a mainstream outlet for cold fusion researchers. When editor-in-chief George H. Miley retired in 2001, the journal stopped accepting new cold fusion papers. This has been cited as an example of the importance of sympathetic influential individuals to the publication of cold fusion papers in certain journals.
The decline of publications in cold fusion has been described as a "failed information epidemic". The sudden surge of supporters until roughly 50% of scientists support the theory, followed by a decline until there is only a very small number of supporters, has been described as a characteristic of pathological science. The lack of a shared set of unifying concepts and techniques has prevented the creation of a dense network of collaboration in the field; researchers perform efforts in their own and in disparate directions, making the transition to "normal" science more difficult.
Cold fusion reports continued to be published in a few journals like Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Il Nuovo Cimento. Some papers also appeared in Journal of Physical Chemistry, Physics Letters A, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, and a number of Japanese and Russian journals of physics, chemistry, and engineering. Since 2005, Naturwissenschaften has published cold fusion papers; in 2009, the journal named a cold fusion researcher to its editorial board. In 2015 the Indian multidisciplinary journal Current Science published a special section devoted entirely to cold fusion related papers.
In the 1990s, the groups that continued to research cold fusion and their supporters established (non-peer-reviewed) periodicals such as Fusion Facts, Cold Fusion Magazine, Infinite Energy Magazine and New Energy Times to cover developments in cold fusion and other fringe claims in energy production that were ignored in other venues. The internet has also become a major means of communication and self-publication for CF researchers.
Conferences
Cold fusion researchers were for many years unable to get papers accepted at scientific meetings, prompting the creation of their own conferences. The International Conference on Cold Fusion (ICCF) was first held in 1990 and has met every 12 to 18 months since. Attendees at some of the early conferences were described as offering no criticism to papers and presentations for fear of giving ammunition to external critics, thus allowing the proliferation of crackpots and hampering the conduct of serious science. Critics and skeptics stopped attending these conferences, with the notable exception of Douglas Morrison, who died in 2001. With the founding in 2004 of the International Society for Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (ISCMNS), the conference was renamed the International Conference on Condensed Matter Nuclear Science—for reasons that are detailed in the subsequent research section above—but reverted to the old name in 2008. Cold fusion research is often referenced by proponents as "low-energy nuclear reactions", or LENR, but according to sociologist Bart Simon the "cold fusion" label continues to serve a social function in creating a collective identity for the field.
Since 2006, the American Physical Society (APS) has included cold fusion sessions at their semiannual meetings, clarifying that this does not imply a softening of skepticism. Since 2007, the American Chemical Society (ACS) meetings also include "invited symposium(s)" on cold fusion. An ACS program chair, Gopal Coimbatore, said that without a proper forum the matter would never be discussed and, "with the world facing an energy crisis, it is worth exploring all possibilities."
On 22–25 March 2009, the American Chemical Society meeting included a four-day symposium in conjunction with the 20th anniversary of the announcement of cold fusion. Researchers working at the U.S. Navy's Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center (SPAWAR) reported detection of energetic neutrons using a heavy water electrolysis setup and a CR-39 detector, a result previously published in Naturwissenschaften. The authors claim that these neutrons are indicative of nuclear reactions. Without quantitative analysis of the number, energy, and timing of the neutrons and exclusion of other potential sources, this interpretation is unlikely to find acceptance by the wider scientific community.
Patents
Although details have not surfaced, it appears that the University of Utah forced the 23 March 1989 Fleischmann and Pons announcement to establish priority over the discovery and its patents before the joint publication with Jones. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) announced on 12 April 1989 that it had applied for its own patents based on theoretical work of one of its researchers, Peter L. Hagelstein, who had been sending papers to journals from 5 to 12 April. An MIT graduate student applied for a patent but was reportedly rejected by the USPTO in part by the citation of the "negative" MIT Plasma Fusion Center's cold fusion experiment of 1989. On 2 December 1993 the University of Utah licensed all its cold fusion patents to ENECO, a new company created to profit from cold fusion discoveries, and in March 1998 it said that it would no longer defend its patents.
The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) now rejects patents claiming cold fusion. Esther Kepplinger, the deputy commissioner of patents in 2004, said that this was done using the same argument as with perpetual motion machines: that they do not work. Patent applications are required to show that the invention is "useful", and this utility is dependent on the invention's ability to function. In general USPTO rejections on the sole grounds of the invention's being "inoperative" are rare, since such rejections need to demonstrate "proof of total incapacity", and cases where those rejections are upheld in a Federal Court are even rarer: nevertheless, in 2000, a rejection of a cold fusion patent was appealed in a Federal Court and it was upheld, in part on the grounds that the inventor was unable to establish the utility of the invention.
A U.S. patent might still be granted when given a different name to disassociate it from cold fusion, though this strategy has had little success in the US: the same claims that need to be patented can identify it with cold fusion, and most of these patents cannot avoid mentioning Fleischmann and Pons' research due to legal constraints, thus alerting the patent reviewer that it is a cold-fusion-related patent. David Voss said in 1999 that some patents that closely resemble cold fusion processes, and that use materials used in cold fusion, have been granted by the USPTO. The inventor of three such patents had his applications initially rejected when they were reviewed by experts in nuclear science; but then he rewrote the patents to focus more on the electrochemical parts so they would be reviewed instead by experts in electrochemistry, who approved them. When asked about the resemblance to cold fusion, the patent holder said that it used nuclear processes involving "new nuclear physics" unrelated to cold fusion. Melvin Miles was granted in 2004 a patent for a cold fusion device, and in 2007 he described his efforts to remove all instances of "cold fusion" from the patent description to avoid having it rejected outright.
At least one patent related to cold fusion has been granted by the European Patent Office.
A patent only legally prevents others from using or benefiting from one's invention. However, the general public perceives a patent as a stamp of approval, and a holder of three cold fusion patents said the patents were very valuable and had helped in getting investments.
Cultural references
A 1990 Michael Winner film Bullseye!, starring Michael Caine and Roger Moore, referenced the Fleischmann and Pons experiment. The film – a comedy – concerned conmen trying to steal scientists' purported findings. However, the film had a poor reception, described as "appallingly unfunny".
In Undead Science, sociologist Bart Simon gives some examples of cold fusion in popular culture, saying that some scientists use cold fusion as a synonym for outrageous claims made with no supporting proof, and courses of ethics in science give it as an example of pathological science. It has appeared as a joke in Murphy Brown and The Simpsons. It was adopted as a software product name Adobe ColdFusion and a brand of protein bars (Cold Fusion Foods). It has also appeared in advertising as a synonym for impossible science, for example a 1995 advertisement for Pepsi Max.
The plot of The Saint, a 1997 action-adventure film, parallels the story of Fleischmann and Pons, although with a different ending. In Undead Science, Simon posits that film might have affected the public perception of cold fusion, pushing it further into the science fiction realm.
Similarly, the tenth episode of 2000 science fiction TV drama Life Force ("Paradise Island") is also based around cold fusion, specifically the efforts of eccentric scientist Hepzibah McKinley (Amanda Walker), who is convinced she has perfected it based on her father's incomplete research into the subject. The episode explores its potential benefits and viability within the ongoing post-apocalyptic global warming scenario of the series.
In the 2023 video game Atomic Heart, cold fusion is responsible for nearly all of the technological advances.
See also
- Bubble fusion
- Cold fission
- Energy Catalyzer (E-cat)
- Faraday-efficiency effect
- Incredible utility (patent concept)
- Lattice confinement fusion
- Muon-catalyzed fusion
- Nuclear transmutation
- Patterson power cell
- Pyroelectric fusion
- Widom–Larsen theory
Notes
- For example, in 1989, the Economist editorialized that the cold fusion "affair" was "exactly what science should be about."
- On 26 January 1990, journal Nature rejected Oriani's paper, citing the lack of nuclear ash and the general difficulty that others had in replication.Beaudette 2002, p. 183 It was later published in Fusion Technology.Oriani et al. 1990, pp. 652–662
- Taubes 1993, pp. 228–229, 255 "(...) there are indeed chemical differences between heavy and light water, especially once lithium is added, as it was in the Pons-Fleischmann electrolyte. This had been in the scientific literature since 1958. It seems that the electrical conductivity of heavy water with lithium is considerably less than that of light water with lithium. And this difference is more than enough to account for the heavy water cell running hotter (...) (quoting a member of the A&M group) 'they're making the same mistake we did'"
- E.g.:
- Miskelly GM, Heben MJ, Kumar A, Penner RM, Sailor MJ, Lewis NL (1989), "Analysis of the Published Calorimetric Evidence for Electrochemical Fusion of Deuterium in Palladium", Science, 246 (4931): 793–796, Bibcode:1989Sci...246..793M, doi:10.1126/science.246.4931.793, PMID 17748706, S2CID 42943868
- Aberdam D, Avenier M, Bagieu G, Bouchez J, Cavaignac JF, Collot J, et al. (1990), "Limits on neutron emission following deuterium absorption into palladium and titanium", Phys. Rev. Lett., 65 (10): 1196–1199, Bibcode:1990PhRvL..65.1196A, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.1196, PMID 10042199
- Price PB, Barwick SW, Williams WT, Porter JD (1989), "Search for energetic-charged-particle emission from deuterated Ti and Pd foils", Phys. Rev. Lett., 63 (18): 1926–1929, Bibcode:1989PhRvL..63.1926P, doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.1926, PMID 10040716
- Roberts DA, Becchetti FD, Ben-Jacob E, Garik P, et al. (1990), "Energy and flux limits of cold-fusion neutrons using a deuterated liquid scintillator", Phys. Rev. C, 42 (5): R1809 – R1812, Bibcode:1990PhRvC..42.1809R, doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.42.R1809, PMID 9966919
- Lewis et al. 1989
- 1 W = 1 J/s ; 1 J = 6.242 × 10 eV since 1 eV = 1.602 × 10 joule
- Sixth criterion of Langmuir: "During the course of the controversy the ratio of supporters to critics rises to near 50% and then falls gradually to oblivion. Langmuir & Hall 1989, pp. 43–44", quoted in Simon 2002, p. 104, paraphrased in Ball 2001, p. 308. It has also been applied to the number of published results, in Huizenga 1993, pp. xi, 207–209 "The ratio of the worldwide positive results on cold fusion to negative results peaked at approximately 50% (...) qualitatively in agreement with Langmuir's sixth criteria."
- The first three conferences are commented in detail in Huizenga 1993, pp. 237–247, 274–285, specially 240, 275–277
- Swartz, 232 F.3d 862, 56 USPQ2d 1703, (Fed. Cir. 2000). decision Archived 12 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Sources:
- "2164.07 Relationship of Enablement Requirement to Utility Requirement of 35 U.S.C. 101 – 2100 Patentability. B. Burden on the Examiner. Examiner Has Initial Burden To Show That One of Ordinary Skill in the Art Would Reasonably Doubt the Asserted Utility", U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, archived from the original on 12 September 2012 Manual of Patent Examining Procedure, in reference to 35 U.S.C. § 101
- Alan L. Durham (2004), Patent law essentials: a concise guide (2nd, illustrated ed.), Greenwood Publishing Group, p. 72 (footnote 30), ISBN 9780275982058
- Jeffrey G. Sheldon (1992), How to write a patent application (illustrated ed.), Practising Law Institute, ISBN 978-0-87224-044-5
References
Citations
- "60 Minutes: Once Considered Junk Science, Cold Fusion Gets A Second Look By Researchers", CBS, 17 April 2009, archived from the original on 12 February 2012
- Fleischmann & Pons 1989, p. 301 ("It is inconceivable that this could be due to anything but nuclear processes... We realise that the results reported here raise more questions than they provide answers...")
- ^ Voss 1999a
- Browne 1989, para. 1
- Browne 1989, Close 1992, Huizenga 1993, Taubes 1993
- ^ Browne 1989
- ^ Taubes 1993, pp. 262, 265–266, 269–270, 273, 285, 289, 293, 313, 326, 340–344, 364, 366, 404–406, Goodstein 1994, Van Noorden 2007, Kean 2010
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (25 March 2004), "US will give cold fusion a second look", The New York Times, retrieved 8 February 2009
- Ouellette, Jennifer (23 December 2011), "Could Starships Use Cold Fusion Propulsion?", Discovery News, archived from the original on 7 January 2012
- US DOE 2004, Choi 2005, Feder 2005
- Goodstein 1994, Labinger & Weininger 2005, p. 1919
- ^ Koziol, Michael (22 March 2021). "Whether Cold Fusion or Low-Energy Nuclear Reactions, U.S. Navy Researchers Reopen Case". IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- Berlinguette, C.P.; Chiang, YM.; Munday, J.N.; et al. (2019). "Revisiting the cold case of cold fusion". Nature. 570 (7759): 45–51. Bibcode:2019Natur.570...45B. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1256-6. PMID 31133686. S2CID 167208748.
- ^ Broad, William J. (31 October 1989), "Despite Scorn, Team in Utah Still Seeks Cold-Fusion Clues", The New York Times, p. C1
- ^ Goodstein 1994, Platt 1998, Voss 1999a, Beaudette 2002, Feder 2005, Adam 2005 "Advocates insist that there is just too much evidence of unusual effects in the thousands of experiments since Pons and Fleischmann to be ignored", Kruglinski 2006, Van Noorden 2007, Alfred 2009. Daley 2004 calculates between 100 and 200 researchers, with damage to their careers.
- ^ "'Cold fusion' rebirth? New evidence for existence of controversial energy source", American Chemical Society, archived from the original on 21 December 2014
- ^ Hagelstein et al. 2004
- "ICMNS FAQ". International Society of Condensed Matter Nuclear Science. Archived from the original on 3 November 2015.
- Biberian 2007
- ^ US DOE 1989, p. 7
- Graham, Thomas (1 January 1866). "On the Absorption and Dialytic Separation of Gases by Colloid Septa". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 156: 399–439. doi:10.1098/rstl.1866.0018. ISSN 0261-0523.
- Paneth & Peters 1926
- Kall fusion redan på 1920-talet Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Ny Teknik, Kaianders Sempler, 9 February 2011
- ^ Pool 1989, Wilner 1989, Close 1992, pp. 19–21 Huizenga 1993, pp. 13–14, 271, Taubes 1993, p. 214
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 13–14
- Laurence 1956
- ^ Kowalski 2004, II.A2
- C. DeW. Van Siclen and S. E. Jones, "Piezonuclear fusion in isotopic hydrogen molecules," J. Phys. G: Nucl. Phys. 12: 213–221 (March 1986).
- ^ Fleischmann & Pons 1989, p. 301
- ^ Fleischmann et al. 1990
- ^ Crease & Samios 1989, p. V1
- ^ Lewenstein 1994, pp. 8–9
- ^ Shamoo & Resnik 2003, p. 86, Simon 2002, pp. 28–36
- ^ Ball, Philip (27 May 2019). "Lessons from cold fusion, 30 years on". Nature. 569 (7758): 601. Bibcode:2019Natur.569..601B. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-01673-x. PMID 31133704.
- Footlick, J. K. (1997), Truth and Consequences: how colleges and universities meet public crises, Phoenix: Oryx Press, p. 51, ISBN 978-0-89774-970-1 as cited in Brooks, M (2008), 13 Things That Don't Make Sense, New York: Doubleday, p. 67, ISBN 978-1-60751-666-8
- Simon 2002, pp. 57–60, Goodstein 1994
- ^ Goodstein 1994
- Petit 2009, Park 2000, p. 16
- Taubes 1993, pp. xviii–xx, Park 2000, p. 16
- Taubes 1993, pp. xx–xxi
- Scanlon & Hill 1999, p. 212
- Beaudette 2002, pp. 183, 313
- Aspaturian, Heidi (14 December 2012). "Interview with Charles A. Barnes on 13 and 26 June 1989". The Caltech Institute Archives. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ Schaffer 1999, p. 2
- ^ Broad, William J. (14 April 1989), "Georgia Tech Team Reports Flaw In Critical Experiment on Fusion", The New York Times, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Wilford 1989
- Broad, William J. 19 April 1989. Stanford Reports Success, The New York Times.
- Close 1992, pp. 184, Huizenga 1993, p. 56
- Browne 1989, Taubes 1993, pp. 253–255, 339–340, 250
- Bowen 1989, Crease & Samios 1989
- Tate 1989, p. 1, Platt 1998, Close 1992, pp. 277–288, 362–363, Taubes 1993, pp. 141, 147, 167–171, 243–248, 271–272, 288, Huizenga 1993, pp. 63, 138–139
- Fleischmann, Martin; Pons, Stanley; Hawkins, Marvin; Hoffman, R. J (29 June 1989), "Measurement of gamma-rays from cold fusion (letter by Fleischmann et al. and reply by Petrasso et al.)", Nature, 339 (6227): 667, Bibcode:1989Natur.339..667F, doi:10.1038/339667a0, S2CID 4274005
- Taubes 1993, pp. 310–314, Close 1992, pp. 286–287, Huizenga 1993, pp. 63, 138–139
- Taubes 1993, p. 242 (Boston Herald's is Tate 1989).
- Taubes 1993, p. 266
- "APS Special Session on Cold Fusion, May 1–2, 1989". ibiblio.org. Archived from the original on 26 July 2008.
- Taubes 1993, pp. 267–268
- Taubes 1993, pp. 275, 326
- Gai et al. 1989, pp. 29–34
- Williams et al. 1989, pp. 375–384
- Joyce 1990
- US DOE 1989, p. 39
- US DOE 1989, p. 36
- US DOE 1989, p. 37
- Huizenga 1993, p. 165
- Mallove 1991, pp. 246–248
- Rousseau 1992.
- Salamon, M. H.; Wrenn, M. E.; Bergeson, H. E.; Crawford, H. C.; et al. (29 March 1990). "Limits on the emission of neutrons, γ-rays, electrons and protons from Pons/Fleischmann electrolytic cells". Nature. 344 (6265): 401–405. Bibcode:1990Natur.344..401S. doi:10.1038/344401a0. S2CID 4369849.
- Broad, William J. (30 October 1990). "Cold Fusion Still Escapes Usual Checks Of Science". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 December 2013. Retrieved 27 November 2013.
- Taubes 1993, pp. 410–411, Close 1992, pp. 270, 322, Huizenga 1993, pp. 118–119, 121–122
- Taubes 1993, pp. 410–411, 412, 420, the Science article was Taubes 1990, Huizenga 1993, pp. 122, 127–128.
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 122–123
- "National Cold Fusion Institute Records, 1988–1991", archived from the original on 17 July 2012
- ^ Taubes 1993, p. 424
- Huizenga 1993, p. 184
- ^ Taubes 1993, pp. 136–138
- Close 1992, Taubes 1993, Huizenga 1993, and Park 2000
- Mallove 1991, Beaudette 2002, Simon 2002, Kozima 2006
- ^ Wired News Staff Email (24 March 1998), "Cold Fusion Patents Run Out of Steam", Wired, archived from the original on 4 January 2014
{{cite magazine}}:|author=has generic name (help) - Huizenga 1993, pp. 210–211 citing Srinivisan, M., "Nuclear Fusion in an Atomic Lattice: An Update on the International Status of Cold Fusion Research", Current Science, 60: 471
- ^ Simon 2002, pp. 131–133, 218
- Daley 2004
- Ball, David (September 2019). "Google funds cold fusion research: Results still negative". Skeptical Inquirer. Amherst, NY: Center for Inquiry.
- ^ Mullins 2004
- ^ Seife 2008, pp. 154–155
- Simon 2002, pp. 131, citing Collins & Pinch 1993, p. 77 in first edition
- ^ "Cold fusion debate heats up again", BBC, 23 March 2009, archived from the original on 11 January 2016
- Feder 2004, p. 27
- Taubes 1993, pp. 292, 352, 358, Goodstein 1994, Adam 2005 (comment attributed to George Miley of the University of Illinois)
- ^ Mosier-Boss et al. 2009, Sampson 2009
- Szpak, Masier-Boss: Thermal and nuclear aspects of the Pd/D2O system Archived 16 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Feb 2002. Reported by Mullins 2004
- ^ Brumfiel 2004
- ^ Weinberger, Sharon (21 November 2004), "Warming Up to Cold Fusion", The Washington Post, p. W22, archived from the original on 19 November 2016 (page 2 in online version)
- ^ "Effetto Fleischmann e Pons: il punto della situazione", Energia Ambiente e Innovazione (in Italian) (3), May–June 2011, archived from the original on 8 August 2012
- ^ Feder 2005
- ^ US DOE 2004
- ^ Janese Silvey, "Billionaire helps fund MU energy research" Archived 15 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Columbia Daily Tribune, 10 February 2012
- University of Missouri-Columbia "$5.5 million gift aids search for alternative energy. Gift given by Sidney Kimmel Foundation, created by founder of the Jones Group" Archived 5 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, 10 February 2012, (press release), alternative link
- "Sidney Kimmel Foundation awards $5.5 million to MU scientists" Archived 5 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine Allison Pohle, Missourian, 10 February 2012
- Christian Basi, Hubler Named Director of Nuclear Renaissance Institute at MU Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, (press release) Missouri University News Bureau, 8 March 2013
- Professor revisits fusion work from two decades ago Archived 2 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine Columbia Daily Tribune, 28 October 2012
- Mark A. Prelas, Eric Lukosi. Neutron Emission from Cryogenically Cooled Metals Under Thermal Shock Archived 16 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine (self published)
- Hambling, David (13 May 2016). "Congress Is Suddenly Interested in Cold Fusion". Popular Mechanics. Archived from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- "Committee on Armed Services, House of Representatives Report 114-537" (PDF). p. 87. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 May 2016.
- Goodstein 2010, pp. 87–94
- Martellucci et al. 2009
- ^ Pollack 1992, Pollack 1997, p. C4
- "Japan CF-research Society". jcfrs.org. Archived from the original on 21 January 2016.
- Japan CF research society meeting Dec 2011 Archived 12 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Kitamura et al. 2009
- ^ Jayaraman 2008
- "Our dream is a small fusion power generator in each house", The Times of India, 4 February 2011, archived from the original on 26 August 2011
- ^ "Category: Special Section: Low Energy Nuclear Reactions". Current Science. 25 February 2015. Archived from the original on 5 August 2017.
- ^ Mark Anderson (March 2009), "New Cold Fusion Evidence Reignites Hot Debate", IEEE Spectrum, archived from the original on 10 July 2009, retrieved 13 June 2009
- US DOE 1989, p. 29, Taubes 1993
- Hoffman 1995, pp. 111–112
- US DOE 2004, p. 3
- Taubes 1993, pp. 256–259
- Huizenga 1993, pp. x, 22–40, 70–72, 75–78, 97, 222–223, Close 1992, pp. 211–214, 230–232, 254–271, Taubes 1993, pp. 264–266, 270–271 Choi 2005
- Fleischmann & Pons 1993
- Mengoli et al. 1998, Szpak et al. 2004
- Simon 2002, p. 49, Park 2000, pp. 17–18, Huizenga 1993, pp. 7, Close 1992, pp. 306–307
- ^ Barras 2009
- ^ Berger 2009
- US DOE 2004, pp. 3, 4, 5
- Hagelstein 2010
- ^ US DOE 2004, pp. 3, 4
- Rogers & Sandquist 1990
- ^ Simon 2002, p. 215
- Simon 2002, pp. 150–153, 162
- Simon 2002, pp. 153, 214–216
- ^ US DOE 1989, pp. 7–8, 33, 53–58 (appendix 4.A), Close 1992, pp. 257–258, Huizenga 1993, p. 112, Taubes 1993, pp. 253–254 quoting Howard Kent Birnbaum in the special cold fusion session of the 1989 spring meeting of the Materials Research Society, Park 2000, pp. 17–18, 122, Simon 2002, p. 50 citing Koonin S.E.; M Nauenberg (1989), "Calculated Fusion Rates in Isotopic Hydrogen Molecules", Nature, 339 (6227): 690–692, Bibcode:1989Natur.339..690K, doi:10.1038/339690a0, S2CID 4335882
- Hagelstein et al. 2004, pp. 14–15
- Schaffer 1999, p. 1
- Morrison 1999, pp. 3–5
- Huizenga 1993, p. viii "Enhancing the probability of a nuclear reaction by 50 orders of magnitude (...) via the chemical environment of a metallic lattice, contradicted the very foundation of nuclear science.", Goodstein 1994, Scaramuzzi 2000, p. 4
- Close 1992, pp. 32, 54, Huizenga 1993, p. 112
- ^ Close 1992, pp. 19–20
- Close 1992, pp. 63–64
- Close 1992, pp. 64–66
- Close 1992, pp. 32–33
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 33, 47
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 7
- Scaramuzzi 2000, p. 4, Goodstein 1994, Huizenga 1993, pp. 207–208, 218
- Close 1992, pp. 308–309 "Some radiation would emerge, either electrons ejected from atoms or X-rays as the atoms are disturbed, but none were seen."
- ^ Close 1992, pp. 268, Huizenga 1993, pp. 112–113
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 75–76, 113
- Taubes 1993, pp. 364–365
- ^ Platt 1998
- ^ Simon 2002, pp. 145–148
- Huizenga 1993, p. 82
- ^ Bird 1998, pp. 261–262
- Saeta 1999, (pages 5–6; "Response"; Heeter, Robert F.)
- Biberian 2007 "Input power is calculated by multiplying current and voltage, and output power is deduced from the measurement of the temperature of the cell and that of the bath"
- Fleischmann et al. 1990, Appendix
- Shkedi et al. 1995
- Jones et al. 1995, p. 1
- ^ Shanahan 2002
- Biberian 2007 "Almost all the heat is dissipated by radiation and follows the temperature fourth power law. The cell is calibrated ..."
- Browne 1989, para. 16
- Wilson et al. 1992
- Shanahan 2005
- Shanahan 2006
- ^ Simon 2002, pp. 180–183, 209
- Mehra, Milton & Schwinger 2000, p. 550
- Close 1992, pp. 197–198
- ^ Simon 2002, pp. 180–183
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 208
- Bettencourt, Kaiser & Kaur 2009
- Simon 2002, pp. 183–187
- Park 2000, pp. 12–13
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 276, Park 2000, pp. 12–13, Simon 2002, p. 108
- "ISCMNS FAQ". iscmns.org. Archived from the original on 23 December 2011.
- Taubes 1993, pp. 378, 427 anomalous effects in deuterated metals, which was the new, preferred, politically palatable nom de science for cold fusion ."
- Nagel, David J.; Melich, Michael E., eds. (2008). Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Condensed Matter Nuclear Science and the 14th International Conference on Cold Fusion (ICCF-14) – 10–15 August 2008 Washington DC (PDF). Vol. 2. New Energy Foundation. ISBN 978-0-578-06694-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 July 2012. Retrieved 31 October 2012.
- Chubb et al. 2006, Adam 2005 (". Anyone can deliver a paper. We defend the openness of science" – Bob Park of APS, when asked if hosting the meeting showed a softening of scepticism)
- ^ Van Noorden 2007
- Van Noorden 2007, para. 2
- "Scientists in possible cold fusion breakthrough", AFP, archived from the original on 27 March 2009, retrieved 24 March 2009
- Broad, William J. (13 April 1989), "'Cold Fusion' Patents Sought", The New York Times, archived from the original on 29 January 2017
- Lewenstein 1994, p. 43
- ^ "2107.01 General Principles Governing Utility Rejections (R-5) – 2100 Patentability. II. Wholly inoperative inventions; "incredible" utility", U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, archived from the original on 27 August 2012 Manual of Patent Examining Procedure
- ^ Simon 2002, pp. 193, 233
- ^ Voss 1999b, in reference to US patents US 5,616,219 , US 5,628,886 and US 5,672,259
- Daniel C. Rislove (2006), "A Case Study of Inoperable Inventions: Why Is the USPTO Patenting Pseudoscience?" (PDF), Wisconsin Law Review, 2006 (4): 1302–1304, footnote 269 in page 1307, archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2015
- Sanderson 2007, in reference to US patent US 6,764,561
- Fox 1994 in reference to Canon's EP 568118
- Radio Times Film Unit 2013, pp. 181–182
- ^ Simon 2002, pp. 91–95, 116–118
- ^ McGown, Alistair (2003). The Hill and Beyond: Children's Television Drama – An Encyclopedia. BFI. p. 266. ISBN 0851708781.
- "Atomic Heart – Everything You Need to Know". Nexus Hub.
Citations of quotations
- Taubes 1993, p. 214 says the similarity was discovered on 13 April 1991, by a computer scientist and disseminated via the Internet. Another computer scientist translated an old article in the Swedish technical journal Ny Teknika. Taubes says: "Ny Teknika seemed to believe that Tandberg had missed on the discovery of the century, done in by an ignorant patent bureau. When Pons heard the story, he agreed."
- Brigham Young University discovered Tandberg's 1927 patent application, and showed it as proof that Utah University didn't have priority for the discovery of cold fusion, cited in Wilford 1989
- Taubes 1993, pp. 225–226, 229–231 " Like those of MIT or Harvard or Caltech, and official Stanford University announcement is not something to be taken lightly. (...) With the news out of Stanford, the situation, as one Department of Energy official put it, 'had come to a head'. The department had had its laboratory administrators send emissaries to Washington immediately. (...) the secretary of energy, had made the pursuit of cold fusion the department's highest priority (...) The government laboratories had free reign [sic] to pursue their cold fusion research, Ianniello said, to use whatever resources they needed, and DOE would cover the expenses. (...) While Huggins may have appeared to be the savior of cold fusion, his results also made him, and Stanford, a prime competitor for patents and rights.", Close 1992, pp. 184, 250 " The only support for Fleischmann and Pons came from Robert Huggins (...) The British Embassy in Washington rushed news of the proceedings to the Cabinet Office and Department of Energy in London. (...) noting that Huggin's heat measurements lent some support but that he had not checked for radiation, and also emphasizing that none of the US government laboratories had yet managed to replicate the effect.", Huizenga 1993, p. 56 "Of the above speakers (in the US Congress hearings) only Huggins supported the Fleischmann-Pons claim of excess heat."
- Taubes 1993, pp. 418–420 "While it is not possible for us to categorically exclude spiking as a possibility, it is our opinion, that possibility is much less probable than that of inadvertent contamination or other explained factors in the measurements.", Huizenga 1993, pp. 128–129
- "Physicist Claims First Real Demonstration of Cold Fusion", Physorg.com, 27 May 2008, archived from the original on 15 March 2012. The peer reviewed papers referenced at the end of the article are "The Establishment of Solid Nuclear Fusion Reactor" – Journal of High Temperature Society, Vol. 34 (2008), No. 2, pp.85–93 and "Atomic Structure Analysis of Pd Nano-Cluster in Nano-Composite Pd⁄ZrO2 Absorbing Deuterium" – Journal of High Temperature Society, Vol. 33 (2007), No. 3, pp.142–156
- ^ US DOE 1989, p. 29, Schaffer 1999, pp. 1, 2, Scaramuzzi 2000, p. 4, Close 1992, pp. 265–268 "(...) the equality of the two channels is known to be preserved from high energy through 20 keV and down to about 5 keV. A reason that it is not as well known below this energy because the individual rates are so low. However, the rate is known at room temperature from muon catalysed fusion experiments. (...) theory can even accommodate the subtle variations in the ratio at these low temperatures ", Huizenga 1993, pp. 6–7, 35–36, 75, 108–109, 112–114, 118–125, 130, 139, 173, 183, 217–218, 243–245 " have been studied over a range of deuteron kinetic energies down to a few kiloelectron volts (keV). (...) appear to be essentially constant at low energies. There is no reason to think that these branching ratios would be measurably altered for cold fusion. The near equality of has been verified also for muon-catalyzed fusion. ", Goodstein 1994 (explaining Pons and Fleischmann would both be dead if they had produced neutrons in proportion to their measurements of excess heat) ("It has been said . . . three 'miracles' are necessary ")
- Close 1992, pp. 257–258, Huizenga 1993, pp. 33, 47–48, 79, 99–100, 207, 216 "By comparing cathode charging of deuterium into palladium with gas charging for a D7Pd ratio of unity, one obtains an equivalent pressure of 1.5x10 atmospheres, a value more than 20 orders of magnitude (10) less than the Fleischmann-Pons claimed pressure.", Huizenga also cites US DOE 2004, pp. 33–34 in chapter IV. Materials Characterization: D. 'Relevant' Materials Parameters: 2. Confinement Pressure, which has a similar explanation.
- Huizenga 1993, pp. 6–7, 35–36 " This well established experimental result is consistent with the Bohr model, which predicts that the compound nucleus decays predominantly by particle emission , as opposed to radioactive capture , whenever it is energetically possible."
- Reger, Goode & Ball 2009, pp. 814–815 "After several years and multiple experiments by numerous investigators, most of the scientific community now considers the original claims unsupported by the evidence. Virtually every experiment that tried to replicate their claims failed. Electrochemical cold fusion is widely considered to be discredited."
- Labinger & Weininger 2005, p. 1919 Fleischmann's paper was challenged in Morrison, R.O. Douglas (28 February 1994). "Comments on claims of excess enthalpy by Fleischmann and Pons using simple cells made to boil". Phys. Lett. A. 185 (5–6): 498–502. Bibcode:1994PhLA..185..498M. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.380.7178. doi:10.1016/0375-9601(94)91133-9.
- Ackermann 2006 "(p. 11) Both the Polywater and Cold Nuclear Fusion journal literatures exhibit episodes of epidemic growth and decline."
- Close 1992, pp. 254–255, 329 " The usual cycle in such cases, he notes, is that interest suddenly erupts (...) The phenomenon then separates the scientists in two camps, believers and skeptics. Interest dies as only a small band of believers is able to 'produce the phenomenon' (...) even in the face of overwhelming evidence to the contrary, the original practitioners may continue to believe in it for the rest of the careers.", Ball 2001, p. 308, Simon 2002, pp. 104, Bettencourt, Kaiser & Kaur 2009
Bibliography
- Ackermann, Eric (February 2006), "Indicators of failed information epidemics in the scientific journal literature: A publication analysis of Polywater and Cold Nuclear Fusion", Scientometrics, 66 (3): 451–466, doi:10.1007/s11192-006-0033-0, S2CID 29197941
- Adam, David (24 March 2005), Rusbringer, Alan (ed.), "In from the cold", The Guardian, London, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Alfred, Randy (23 March 2009), "March 23, 1989: Cold Fusion Gets Cold Shoulder", Wired
- Ball, Phillip (2001), Life's matrix: a biography of water (illustrated, reprinted ed.), University of California Press, ISBN 978-0-520-23008-8
- Barras, Collin (23 March 2009), "Neutron tracks revive hopes for cold fusion", New Scientist
- Beaudette, Charles G. (2002), Excess Heat & Why Cold Fusion Research Prevailed, South Bristol, Maine: Oak Grove Press, ISBN 978-0-9678548-3-0
- Berger, Eric (23 March 2009), "Navy scientist announces possible cold fusion reactions", Houston Chronicle
- Bettencourt, Luís M.A.; Kaiser, David I.; Kaur, Jasleen (July 2009), "Scientific discovery and topological transitions in collaboration networks" (PDF), Journal of Informetrics, 3 (3): 210–221, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.570.8621, doi:10.1016/j.joi.2009.03.001, hdl:1721.1/50230, S2CID 1914074, MIT Open Access Articles.
- Biberian, Jean-Paul (2007), "Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (Cold Fusion): An Update" (PDF), International Journal of Nuclear Energy Science and Technology, 3 (1): 31–42, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.618.6441, doi:10.1504/IJNEST.2007.012439, archived (PDF) from the original on 30 May 2008
- Bird, Alexander (1998), Routledge (ed.), Philosophy of Science: Alexander Bird (illustrated, reprint ed.), London: UCL Press, ISBN 978-1-85728-504-8
- Bowen, Jerry (10 April 1989), "Science: Nuclear Fusion", CBS Evening News, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Browne, M. (3 May 1989), "Physicists Debunk Claim Of a New Kind of Fusion", The New York Times, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Brumfiel, Geoff (2 December 2004), "US review rekindles cold fusion debate. Energy panel split over whether experiments produced power", Nature News, doi:10.1038/news041129-11
- Choi, Charles (2005), "Back to Square One", Scientific American, retrieved 25 November 2008
- Chubb, Scott; McKubre, Michael C. H.; Krivit, Steve B.; Chubb, Talbot; Miley, George H.; Swartz, Mitchell; Violante, V.; Stringham, Roger; Fleischmann, Martin; Li, Zing Z.; Biberian, J.P.; Collis, William (2006), Session W41: Cold Fusion, American Physical Society, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Close, Frank E. (1992), Too Hot to Handle: The Race for Cold Fusion (2 ed.), London: Penguin, ISBN 978-0-14-015926-4
- Collins, Harry; Pinch, Trevor (1993), The Golem: What Everyone Should Know About Science (1st ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521477360
- Crease, Robert; Samios, N.P. (1989), "Cold Fusion confusion", The New York Times Magazine, no. 24 September 1989, pp. 34–38
- Daley, Beth (27 July 2004), "Heating up a cold theory. MIT professor risks career to reenergize discredited idea", The Boston Globe
- Derry, Gregory Neil (2002), What Science Is and How It Works (reprint, illustrated ed.), Princeton, New Jersey; Oxford: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-09550-9, OCLC 40693869
- Feder, Toni (2004), "DOE Warms to Cold Fusion", Physics Today, 57 (4): 27–28, Bibcode:2004PhT....57d..27F, doi:10.1063/1.1752414
- Feder, Toni (January 2005), "Cold Fusion Gets Chilly Encore", Physics Today, 58 (1): 31, Bibcode:2005PhT....58a..31F, doi:10.1063/1.1881896
- Fleischmann, Martin; Pons, Stanley (1989), "Electrochemically induced nuclear fusion of deuterium", Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 261 (2A): 301–308, doi:10.1016/0022-0728(89)80006-3
- Fleischmann, Martin; Pons, Stanley; Anderson, Mark W.; Li, Lian Jun; Hawkins, Marvin (1990), "Calorimetry of the palladium-deuterium-heavy water system", Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 287 (2): 293–348, doi:10.1016/0022-0728(90)80009-U
- Fleischmann, Martin; Pons, S. (1993), "Calorimetry of the Pd-D2O system: from simplicity via complications to simplicity", Physics Letters A, 176 (1–2): 118–129, Bibcode:1993PhLA..176..118F, doi:10.1016/0375-9601(93)90327-V
- Fox, Barry (25 June 1994), "Patents: Cold fusion rides again", New Scientist (1931), ISSN 0262-4079
- Gai, M.; Rugari, S.L.; France, R.H.; Lund, B.J.; Zhao, Z.; Davenport, A.J.; Isaacs, H.S.; Lynn, K.G. (1989), "Upper limits on neutron and big gamma-ray emission from cold fusion", Nature, 340 (6228): 29–34, Bibcode:1989Natur.340...29G, doi:10.1038/340029a0, S2CID 4331780
- Goodstein, David (1994), "Whatever happened to cold fusion?", American Scholar, 63 (4): 527–541, ISSN 0003-0937, archived from the original on 16 May 2008, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Goodstein, David L. (2010), On Fact and Fraud:Cautionary Tales from the Front Lines of Science, Princeton: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691139661
- Hagelstein, Peter L.; McKubre, Michael; Nagel, David; Chubb, Talbot; Hekman, Randall (2004), "New Physical Effects in Metal Deuterides" (PDF), Condensed Matter Nuclear Science. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Cold Fusion. Held 31 October–5 November 2004 in Marseilles, vol. 11, p. 23, Bibcode:2006cmns...11...23H, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.233.5518, doi:10.1142/9789812774354_0003, ISBN 9789812566409, archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2007,
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) (manuscript). - Hagelstein, Peter L. (2010), "Constraints on energetic particles in the Fleischmann–Pons experiment", Naturwissenschaften, 97 (4): 345–352, Bibcode:2010NW.....97..345H, doi:10.1007/s00114-009-0644-4, hdl:1721.1/71631, PMID 20143040, S2CID 9496513
- Hoffman, Nate (1995), A Dialogue on Chemically Induced Nuclear Effects: A Guide for the Perplexed About Cold Fusion, La Grange Park, Illinois: American Nuclear Society, ISBN 978-0-89448-558-9
- Huizenga, John R. (1993), Cold Fusion: The Scientific Fiasco of the Century (2 ed.), Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-855817-0
- Jayaraman, K.S. (17 January 2008), "Cold fusion hot again", Nature India, doi:10.1038/nindia.2008.77, retrieved 7 December 2008
- Jones, J.E.; Hansen, L.D.; Jones, S.E.; Shelton, D.S.; Thorne, J.M. (1995), "Faradaic efficiencies less than 100% during electrolysis of water can account for reports of excess heat in 'cold fusion' cells", Journal of Physical Chemistry, 99 (18): 6973–6979, doi:10.1021/j100018a033
- Joyce, Christopher (16 June 1990), "Gunfight at the cold fusion corral", New Scientist (1721): 22, ISSN 0262-4079, retrieved 1 October 2009
- Kean, Sam (26 July 2010), "Palladium: The Cold Fusion Fanatics Can't Get Enough of the Stuff", Slate, retrieved 31 July 2011
- Kitamura, Akira; Nohmi, Takayoshi; Sasaki, Yu; Taniike, Akira; Takahashi, Akito; Seto, Reiko; Fujita, Yushi (2009), "Anomalous Effects in Charging of Pd Powders with High Density Hydrogen Isotopes", Physics Letters A, 373 (35): 3109–3112, Bibcode:2009PhLA..373.3109K, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.380.6124, doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2009.06.061
- Kowalski, Ludwik (2004), "Jones's manuscript on History of Cold Fusion at BYU", Upper Montclair, New Jersey: csam.montclair.edu, archived from the original on 6 May 2008, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Kozima, Hideo (2006), The Science of the Cold Fusion phenomenon, New York: Elsevier Science, ISBN 978-0-08-045110-7
- Kruglinski, Susan (3 March 2006), "Whatever Happened To... Cold Fusion?", Discover Magazine, ISSN 0274-7529, retrieved 20 June 2008
- Labinger, JA; Weininger, SJ (2005), "Controversy in chemistry: how do you prove a negative? – the cases of phlogiston and cold fusion", Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 44 (13): 1916–1922, doi:10.1002/anie.200462084, PMID 15770617,
So there matters stand: no cold fusion researcher has been able to dispel the stigma of 'pathological science' by rigorously and reproducibly demonstrating effects sufficiently large to exclude the possibility of error (for example, by constructing a working power generator), nor does it seem possible to conclude unequivocally that all the apparently anomalous behavior can be attributed to error.
- Laurence, William L. (30 December 1956), "Cold Fusion of Hydrogen Atoms; A Fourth Method Pulling Together", The New York Times, p. E7
- Langmuir, Irving; Hall, Robert N. (1989). "Pathological science". Physics Today. 42 (10): 36–48. Bibcode:1989PhT....42j..36L. doi:10.1063/1.881205.
- Lewenstein, Bruce V. (1994), "Cornell cold fusion archive" (PDF), Collection n°4451, Division of Rare and Manuscript Collections, Cornell University Library, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Lewis, N.S.; Barnes, C.A.; Heben, M.J.; Kumar, A.; Lunt, S.R.; McManis, G.E.; Miskelly, S.R.; Penner, G.M.; et al. (1989), "Searches for low-temperature nuclear fusion of deuterium in palladium", Nature, 340 (6234): 525–530, Bibcode:1989Natur.340..525L, doi:10.1038/340525a0, S2CID 4359244
- Mallove, Eugene (1991), Fire from Ice: Searching for the Truth Behind the Cold Fusion Furor, London: Wiley, ISBN 978-0-471-53139-5
- Martellucci, Sergio; Rosati, Angela; Scaramuzzi, Francesco; Violante, Vittorio, eds. (2009). Cold Fusion: The history of research in Italy (PDF). Translated by Costigliola, Chiara Maria. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2016. In the foreword by the president of ENEA the belief is expressed that the cold fusion phenomenon is proved.
- Mehra, Jagdish; Milton, K. A.; Schwinger, Julian Seymour (2000), Climbing the Mountain: The Scientific Biography of Julian Schwinger (illustrated ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-850658-4
- Mengoli, G.; Bernardini, M.; Manduchi, C.; Zannoni, G. (1998), "Calorimetry close to the boiling temperature of the D2O/Pd electrolytic system", Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 444 (2): 155–167, doi:10.1016/S0022-0728(97)00634-7
- Morrison, Douglas R.O. "Assessment". In Saeta (1999), pp. 3–5.
- Mosier-Boss, Pamela A.; Szpak, Stanislaw; Gordon, Frank E.; Forsley, L.P.G. (2009), "Triple tracks in CR-39 as the result of Pd–D Co-deposition: evidence of energetic neutrons", Naturwissenschaften, 96 (1): 135–142, Bibcode:2009NW.....96..135M, doi:10.1007/s00114-008-0449-x, PMID 18828003, S2CID 11044813
- Mullins, Justin (September 2004), "Cold Fusion Back From the Dead", IEEE Spectrum, 41 (9): 22, doi:10.1109/MSPEC.2004.1330805, S2CID 7170843
- Oriani, Richard A.; Nelson, John C.; Lee, Sung-Kyu; Broadhurst, J. H. (1990), "Calorimetric Measurements of Excess Power Output During the Cathodic Charging of Deuterium into Palladium", Fusion Technology, 18 (4): 652–662, Bibcode:1990FuTec..18..652O, doi:10.13182/FST90-A29259, ISSN 0748-1896, S2CID 118860562
- Paneth, Fritz; Peters, Kurt (1926), "Über die Verwandlung von Wasserstoff in Helium", Naturwissenschaften (in German), 14 (43): 956–962, Bibcode:1926NW.....14..956P, doi:10.1007/BF01579126, S2CID 43265081
- Park, Robert L (2000), Voodoo Science: The road from foolishness to fraud, Oxford, U.K. & New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-860443-3, retrieved 14 November 2010
- Petit, Charles (14 March 2009), "Cold panacea: two researchers proclaimed 20 years ago that they'd achieved cold fusion, the ultimate energy solution. The workwent nowhere, but the hope remains", Science News, 175 (6): 20–24, doi:10.1002/scin.2009.5591750622
- Platt, Charles (1998), "What if Cold Fusion is Real?", Wired Magazine, 6 (11), retrieved 25 May 2008
- Pollack, A. (17 November 1992), "Cold Fusion, Derided in U.S., Is Hot In Japan", The New York Times
- Pollack, A. (26 August 1997), "Japan, Long a Holdout, is Ending its Quest for Cold Fusion", The New York Times, vol. 79, pp. 243, C4
- Pool, Robert (28 April 1989), "How cold fusion happened – twice!", Science, 244 (4903): 420–423, Bibcode:1989Sci...244..420P, doi:10.1126/science.244.4903.420, PMID 17807604, archived from the original on 2 June 2013
- Radio Times Film Unit (2013). Radio Times Guide to Films 2014. Immediate Media Company. ISBN 978-0956752369.
- Reger, Daniel L.; Goode, Scott R.; Ball, David W. (2009), Chemistry: Principles and Practice (3rd revised ed.), Cengage Learning, pp. 814–815, ISBN 978-0-534-42012-3
- Rousseau, D. L. (January–February 1992), "Case Studies in Pathological Science: How the Loss of Objectivity Led to False Conclusions in Studies of Polywater, Infinite Dilution and Cold Fusion", American Scientist, 80 (1): 54–63, Bibcode:1992AmSci..80...54R
- Saeta, Peter N., ed. (21 October 1999), "What is the current scientific thinking on cold fusion? Is there any possible validity to this phenomenon?", Scientific American, Ask the Experts, pp. 1–6, retrieved 17 December 2008
- Sampson, Mark T. (2009), "'Cold fusion' rebirth? New evidence for existence of controversial energy source", ACS, archived from the original on 2 October 2011
- Sanderson, Katharine (29 March 2007), "Cold fusion is back at the American Chemical Society", Nature News, ISSN 0028-0836, archived from the original on 27 August 2009, retrieved 18 July 2009
- Scanlon, Eileen; Hill, Roger (1999). Communicating science: contexts and channels. London: Routledge. ISBN 041519752X. OCLC 39180844.
- Scaramuzzi, F. (2000), "Ten years of cold fusion: an eye-witness account", Accountability in Research, 8 (1&2): 77–101, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.380.8109, doi:10.1080/08989620008573967, ISSN 0898-9621, OCLC 17959730, S2CID 6158268
- Schaffer, Michael J. "Historical overview, assessment". In Saeta (1999), pp. 1–3.
- Seife, Charles (2008), Sun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful Thinking, New York: Viking, ISBN 978-0-670-02033-1
- Shamoo, Adil E.; Resnik, David B. (2003), Oxford University Press US (ed.), Responsible Conduct of Research (2nd illustrated ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-514846-6
- Shanahan, Kirk L. (23 May 2002), "A systematic error in mass flow calorimetry demonstrated", Thermochimica Acta, 382 (2): 95–100, doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(01)00832-2
- Shanahan, Kirk L. (April 2005), "Comments on "Thermal behavior of polarized Pd/D electrodes prepared by co-deposition"" (PDF), Thermochimica Acta, 428 (1–2): 207–212, doi:10.1016/j.tca.2004.11.007
- Shanahan, Kirk L. (February 2006), "Reply to 'Comment on papers by K. Shanahan that propose to explain anomalous heat generated by cold fusion', E. Storms", Short communication, Thermochimica Acta, 441 (2): 210–214, doi:10.1016/j.tca.2005.11.029
- Shkedi, Zvi; McDonald, Robert C.; Breen, John J.; Maguire, Stephen J.; Veranth, Joe (1995), "Calorimetry, Excess Heat, and Faraday Efficiency in Ni-H2O Electrolytic Cells", Fusion Technology, 28 (4): 1720–1731, Bibcode:1995FuTec..28.1720S, doi:10.13182/FST95-A30436, ISSN 0748-1896
- Simon, Bart (2002), Undead Science: Science studies and the afterlife of cold fusion (illustrated ed.), Rutgers University Press, p. 49, Bibcode:2002usss.book.....S, ISBN 978-0-8135-3154-0
- Szpak, Stanislaw; Mosier-Boss, Pamela A.; Miles, Melvin H.; Fleischmann, Martin (2004), "Thermal behavior of polarized Pd/D electrodes prepared by co-deposition", Thermochimica Acta, 410 (1–2): 101–107, doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00401-5
- Tate, N. (1989), "MIT bombshell knocks fusion 'breakthrough' cold", Boston Herald, no. 1 May 1989, p. 1, ISSN 0738-5854
- Taubes, Gary (15 June 1990), "Cold fusion conundrum at Texas A&M", Science, 248 (4961): 1299–1304, Bibcode:1990Sci...248.1299T, doi:10.1126/science.248.4961.1299, PMID 17747511, S2CID 9602261
- Taubes, Gary (1993), Bad Science: The Short Life and Weird Times of Cold Fusion, New York: Random House, ISBN 978-0-394-58456-0
- US DOE, U.S. Department of Energy (1989), A Report of the Energy Research Advisory Board to the United States Department of Energy (Report), Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Energy, retrieved 25 May 2008
- US DOE, U.S. Department of Energy (2004), Report of the Review of Low Energy Nuclear Reactions (PDF) (Report), Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Energy, archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2008, retrieved 19 July 2008
- Van Noorden, R. (April 2007), "Cold fusion back on the menu", Chemistry World, ISSN 1473-7604, retrieved 25 May 2008
- Rogers, Vern C.; Sandquist, Gary M. (December 1990), "Cold fusion reaction products and their measurement", Journal of Fusion Energy, 9 (4): 483–485, Bibcode:1990JFuE....9..483R, doi:10.1007/BF01588284, S2CID 120196723
- Voss, David (1 March 1999a), "What Ever Happened to Cold Fusion", Physics World, 12 (3): 12–14, doi:10.1088/2058-7058/12/3/14, ISSN 0953-8585, archived from the original on 1 July 2008, retrieved 1 May 2008
- Voss, David (21 May 1999b), "'New Physics' Finds a Haven at the Patent Office", Science, 284 (5418): 1252–1254, doi:10.1126/science.284.5418.1252, ISSN 0036-8075, S2CID 108860158
- Wilford, John Noble (24 April 1989), "Fusion Furor: Science's Human Face", The New York Times, ISSN 0362-4331, archived from the original on 25 June 2017, retrieved 23 September 2008
- Williams D, Findlay D, Craston D, Sené M, et al. (1989), "Upper bounds on 'cold fusion' in electrolytic cells", Nature, 342 (6248): 375–384, Bibcode:1989Natur.342..375W, doi:10.1038/342375a0, S2CID 4347251
- Wilner, Bertil (May 1989), "No new fusion under the Sun", Nature, 339 (6221): 180, Bibcode:1989Natur.339..180W, doi:10.1038/339180a0, S2CID 26487447
- Wilson, R.H.; Bray, J.W.; Kosky, P.G.; Vakil, H.B.; Will, F.G. (1992), "Analysis of experiments on the calorimetry of LiOD-D2O electrochemical cells", Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 332 (1–2): 1–31, doi:10.1016/0022-0728(92)80338-5
External links
- International Society for Condensed Matter Nuclear Science (iscmns.org), organizes the ICCF conferences and publishes the Journal of Condensed Matter Nuclear Science. See: library.htm of published papers and proceedings.
- Low Energy Nuclear Reactions (LENR) Phenomena and Potential Applications Archived 7 October 2015 at the Wayback Machine: Naval Surface Warfare Center report NSWCDD-PN-15-0040 by Louis F. DeChiaro, PhD, 23 September 2015