| Revision as of 23:35, 24 October 2005 view source72.235.86.15 (talk) →Historical maps and studies← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 04:46, 15 November 2024 view source Dracofulmen (talk | contribs)36 edits →International Hydrographic Organization: Typo fixTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Korea–Japan conflict}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{pp-semi|small=yes}} | |||
| There is a long-running '''dispute over the name of the ]''' (East Sea) between Japan and Korea. The two countries disagree over the sea's international name. The ]ese government insist that it be called "Sea of Japan", which they claim has been the international de facto standard since the ]. The ]n government challenge this name, contending that it is a symbol of Japan's imperialistic past, and want the name "East Sea" to be used. It points to its own tally of historic maps referring to the sea as "Sea of Korea/Corea/Chosen" or "East/Oriental Sea". The ]n government use "East Sea of Korea" in their English publications. | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2022}} | |||
| {{good article}} | |||
| ] | |||
| A dispute exists over the international name for the body of water which is bordered by ], ] (] and ]) and ]. In 1992, objections to the name ] were first raised by North Korea and South Korea at the Sixth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names.<ref name="MOFAJ">{{cite web|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/index.html|title=The Issue of the Name of the Sea of Japan|publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan}}</ref> The Japanese government supports the exclusive use of the name {{Nihongo|"Sea of Japan"|日本海|lead=yes}}, while South Korea supports the alternative name "East Sea" ({{Korean|hangul=동해|hanja=東海}}), and North Korea supports the name "Korean East Sea" ({{Korean|hangul=조선동해|hanja=朝鮮東海|labels=no|context=north}}). Currently, most international maps and documents use either the name Sea of Japan (or equivalent translation) by itself, or include both the name Sea of Japan and East Sea, often with East Sea listed in parentheses or otherwise marked as a secondary name. The ], the governing body for the naming of bodies of water around the world, in 2012 decided it was still unable to revise the 1953 version of its publication S-23 – Limits of Oceans and Seas, which includes only the single name "Sea of Japan", to include "East Sea" together with "Sea of Japan".<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160305024259/http://english.yonhapnews.co.kr/national/2012/04/26/69/0301000000AEN20120426001300315F.HTML |date=5 March 2016 }}, ''Yonhap News Agency'', 26 April 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2013.</ref><ref name="Sea of Japan name dispute rolls on">], " {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160910180939/http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2012/05/03/national/sea-of-japan-name-dispute-rolls-on/ |date=10 September 2016 }}", '']'', 3 May 2012, p. 3; ], "IHO nixes 'East Sea' name bid", '']'', 28 April 2012, p. 2; Rabiroff, Jon, and Yoo Kyong Chang, " {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160920033907/http://www.stripes.com/news/pacific/korea/agency-rejects-south-korea-s-request-to-rename-sea-of-japan-1.175687 |date=20 September 2016 }}", '']'', 28 April 2012, p. 5.</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20120426001355 |title=IHO delays decision on Korea's request for East Sea name to 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161011185743/http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20120426001355 |archive-date=11 October 2016 |work=] |date=26 April 2012 |access-date=26 July 2013}}</ref><ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924102524/http://english.chosun.com/site/data/html_dir/2012/04/27/2012042700597.html |date=24 September 2015 }}, ''The Chosun Ilbo'', 26 April 2012, Retrieved 26 July 2013.</ref> | |||
| The involved countries (especially Japan and South Korea) have advanced a variety of arguments to support their preferred name(s). Many of the arguments revolve around determining when the name Sea of Japan became the common name. South Korea argues that historically the more common name was East Sea, Sea of Korea, or another similar variant. South Korea further argues that the name Sea of Japan did not become common until ], at which time it had no ability to influence international affairs. Japan argues that the name Sea of Japan has been the most common international name since at least the beginning of the 19th century, long before its annexation of Korea. Both sides have conducted studies of antiquarian maps, but the two countries have produced divergent research results. Additional arguments have been raised regarding the underlying geography of the sea as well as potential problems regarding the ambiguity of one name or the other. | |||
| * The Japanese call it the "Sea of Japan" or sometimes "Japan Sea". | |||
| * North Koreans call it the "East Sea of Korea". | |||
| * South Koreans call it the "East Sea". | |||
| ==Arguments== | |||
| The South Korean government and media use "East Sea" consistently in their publications. Since the ], South Korea have increased their campaign efforts to change the sea's official international name. The ] (UNCSGN) and the ] (IHO) have so far neither accepted nor denied Korea's claims, but left the issue open to discussion while continuing to use "Sea of Japan". | |||
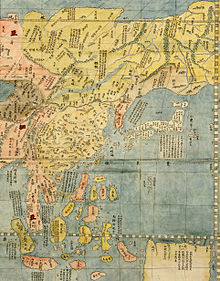
| ]'' by ] in 1602 describing the sea as the Sea of Japan]] | |||
| Both sides in the dispute have put forward a number of arguments to support their claims. | |||
| The dispute does not attempt to get the respective countries to adopt each other's preferred terms in their own languages. South Koreans generally do not object to Japanese maps calling the sea 日本海 (which translates as ''Japan Sea''), and Japanese do not object to Korean maps calling it 동해 (which translates as ''East Sea''). | |||
| ===Arguments based on historical maps=== | |||
| ==Historical developments of the dispute== | |||
| According to Japan's count, this sea is mainly called "Sea of Japan" on most maps earlier than the ], but some maps call it by various names including "Bay of Korea", "Chinese Ocean", "Sea of Corea", "Oriental Sea", or "Sea of Korea". According to South Korea's count, it is mainly called "Sea of Korea/Corea" or "East/Oriental Sea" on most maps of the same period. | |||
| ====Arguments from South Korea==== | |||
| At the ] meeting of the ] (IHB) to officially determine internationally acceptable names of bodies of water, Japanese delegates submitted the name "Sea of Japan" as the official name of the sea. At the time, "Sea of Japan" had been used almost exclusively on international maps, although the parties disagree on which name was previously prevalent. Korea could not participate during these talks because it was under Japanese colonial rule. | |||
| According to South Korea's Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the name East Sea(Donghae(동해)) can be found in various historical records produced in the span of over 2,000 years, including the '']'' (1145),<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.koreaworldtimes.com/topics/news/8195/|script-title=ja:トンヘ(東海)の呼称歴史は2000年? 2千年前発祥説が多い韓国|newspaper=KoreaWorldTimes |date=2020-11-23|language=ja|access-date=2021-09-27}}</ref> the monument of ] (414), and "Map of Eight Provinces of Korea" ({{Langx|ko|八道總圖|label=none}}, 1530).<ref name="km1">{{cite web|title=East Sea|url=http://www.mofat.go.kr/english/political/hotissues/eastsea/index.jsp | |||
| |publisher=]|year=2010 |access-date=21 November 2010}}</ref> According to such records, the name East Sea(동해(Donghae)) is almost 1700 years older than the first documented world map to name the area the Sea of Japan, named '']'' (坤輿萬國全圖), which was drawn by the Italian missionary ] in China (1602). No Japanese record published up to the late-18th century indicated any name for the body of water.<ref name="NEHF">{{cite web|title=Naming of the East Sea|url=http://english.historyfoundation.or.kr/?sub_num=160|publisher=Northeast Asian History Foundation|year=2007|access-date=22 November 2010|archive-date=15 August 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110815174553/http://english.historyfoundation.or.kr/?sub_num=160|url-status=dead}}</ref> Furthermore, South Korea has pointed out that Japan itself recognized the sea as Sea of Joseon (Korea) not Sea of Japan since some 18th and 19th-century Japanese maps referred to the sea as Chōsenkai( 朝鮮海, literally Sea of Joseon), including the {{Nihongo|Simplified Map of Japan's Periphery|日本邊界略圖|4=1809}}, Map of Asia (亞細亞全圖, 1794) which was drawn by Katsuragawa Hoshu (桂川甫周) and the {{Nihongo|New World Map|新製輿地全圖|4=1844}}.<ref name = km1/> Additionally, it specifically states that the name Sea of Japan was not widely used, even in Japan, as late as the mid 19th century.<ref name="legitimacy">{{cite web|title=Legitimacy for Restoring the Name East Sea|url=http://www.mofat.go.kr/english/political/images/res/east_sea.pdf|publisher=]|date=May 2009 |access-date=28 September 2010}}</ref> Moreover, South Korea argues that it was unable to present its case for the name 'East Sea' internationally beause it was under Japan's colonial rule and in the midst of the Korean War.<ref name="WorkingPaper48">{{cite web|title=Recent Changes in Geographical Names of Korean Cities and other Developments|url=https://www.un.org/depts/dhl/maplib/ungegn/session-20/working-papers/working-paper-48.pdf|work=Working Paper 48 of the UNGEGN Twentieth Session|publisher=]|date=17–28 January 2000|access-date=22 November 2010}}</ref> In 1992, the name "East Sea" was agreed upon as English name for the sea in South Korea and claimed by the country for the sea during its participation in the U.N. Conference on Standardization of Geographical Names.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2010-05-23|title= East Sea/Sea of Japan, what is the problem?|url=http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20100520000904|access-date=2021-03-29|website=]|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Korea's argument is, however, not to replace 'Sea of Japan' with 'East Sea' but rather to use the name 'East Sea' alongside 'Sea of Japan'. Since 1992, the Korean government has maintained the position that as Korea does not oppose the continuous use of the name 'Sea of Japan' in the international community, Japan should honour the name 'East Sea' that the Korean people have been using for a long time and agree on the dual names for that specific sea area. | |||
| In ], ''Limits of Oceans and Seas'', the first edition of the guideline by the IHB adopted "Japan Sea" with many other geographical names. | |||
| In fact, the concurrent use of the name East Sea and Sea of Japan conforms to the general naming principles in the international community. Moreover, when countries are unable to reach an agreement on the name of a feature, it is recommended to accept all names used by each of the countries concerned. This general rule of international cartography is confirmed by the relevant resolutions: the International Hydrographic Organization Resolution 1/1972 and the United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names Resolution III/20. | |||
| ====Arguments from Japan==== | |||
| In ] the ] (IHO) released technical resolution A.4.2.6 independently of this dispute. This resolution is frequently referred to, although it only gives general guidance. It endorses the principle that when the sharing countries of a geographical feature do not agree on a common name, the different names should be recognized simultaneously. | |||
| The Japanese government claims that the name Sea of Japan had been internationally used since the 17th century and established by the early 19th century, during which Japan was under an isolationist policy (]) of the ] that restricted cultural exchange and commerce with foreign countries except China and the Netherlands until 1854.<ref name="MOFARussianFederationstudy">{{cite web|title=Issue of naming of the Sea of Japan (Study in the Russian Federation) Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) of Japan|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/study-6.html|publisher=]|year=2010 |access-date=22 November 2010}}</ref><ref name="Basic Position">{{cite web | url = http://www1.kaiho.mlit.go.jp/GIJUTSUKOKUSAI/nihonkai/position_eng.htm | title = Japanese Basic Position on the Naming of the "Japan Sea" | publisher = ] | date = 1 March 2005 | access-date = 22 November 2010 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20110524092704/http://www1.kaiho.mlit.go.jp/GIJUTSUKOKUSAI/nihonkai/position_eng.htm | archive-date = 24 May 2011 | df = dmy-all }}</ref> Accordingly, they state, Japan could not have, at that time, had an influence on the international community regarding the naming of the sea.<ref name="Basic Position"/> | |||
| The invention of the ] in the late 18th century enabled Western explorers, such as ] from France, ] from Britain, and ] (Ivan Fyodorovich Kruzenshtern) from Russia, to measure time and longitudes on the sea precisely and map the detailed shape of the Sea of Japan.<ref name="Basic Position"/> Krusenstern was an ] and ], who led the ] of the ].<ref>{{cite book |author=Adam Johann von Krusenstern |title=Voyage Round the World |year=1813 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SgXVHAAACAAJ }}{{Dead link|date=August 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> According to Japanese records, it was Krusenstern who popularized the name "Mer du Japon" (Sea of Japan) in the West. In his work "Reise um die Welt in den Jahren" (1812), he wrote, "People also call this sea area the Sea of Korea, but because only a small part of this sea touches the Korean coast, it is better to name it the Sea of Japan."<ref name="Basic Position"/> The original book was published in ] in German and Russian, translated into Dutch, French, Swedish, Italian and English, and distributed widely among Europe.<ref name="Basic Position"/> As a result, the international name of the sea changed from no name to the Sea of Japan, on the maps drawn by countries other than Japan or Korea during the 17th to 20th centuries.<ref name="Basic Position"/> Thus, the Japanese side argues that the South Koreans misunderstand the history of the name. | |||
| In ], the third UN Conference on the Standardization of Geographic Names (]) adopted resolution III/20 entitled "Names of Features beyond a Single Sovereignty". The resolution recommended: | |||
| <blockquote>"when countries sharing a given geographical feature do not agree on a common name, it should be a general rule of cartography that the name used by each of the countries concerned will be accepted. A policy of accepting only one or some of such names while excluding the rest would be inconsistent as well as inexpedient in practice."</blockquote> | |||
| ====Surveys of antiquarian maps==== | |||
| In ], South Korea raised the issue at the sixth UNCSGN. Japan objected and the issue was not addressed. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center; font-size:85%" | |||
| |+ <big>The comparison of surveys of antiquarian maps by the government of Japan and South Korea</big><ref>{{cite web|title=A survey of historical maps from around the world |publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/#5}}</ref> | |||
| !Century ||colspan=5| 16th century ||colspan=5| 17th century ||colspan=6| 18th century ||colspan=7| 19th century || nowrap| Unknown ||colspan=7| Total | |||
| |- | |||
| ! nowrap |Surveyed by | |||
| !colspan=4 style="background:#A8D3FF"| Japan | |||
| ! style="white-space:nowrap; background:#ffb6b6;"| Korea | |||
| !colspan=4 style="background:#A8D3FF"| Japan | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Korea | |||
| !colspan=5 style="background:#A8D3FF"| Japan | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Korea | |||
| !colspan=6 style="background:#A8D3FF"| Japan | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Korea | |||
| ! style="background:#A8D3FF"| Japan | |||
| !colspan=6 style="background:#A8D3FF"| Japan | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Korea | |||
| |- style="background:#A8D3FF" | |||
| ! Surveyed in | |||
| | ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || '''Total''' | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Total | |||
| | ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || '''Total''' | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Total | |||
| | ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || '''Total''' | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Total | |||
| | ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || '''Total''' | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Total | |||
| | ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || ''']''' || '''Total''' | |||
| ! style="background:#FFB6B6"| Total | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! style="white-space:nowrap; color:red;"|Sea of Japan | |||
| | 1 || 0 || 1 || '''2''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''-''' | |||
| | 3 || 14 || 5 || '''22''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''17''' | |||
| | 47 || 24 || 23 || 2 || '''96''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''36''' | |||
| | 1059 || 206 || 487 || 27 || 50 || '''1829''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''69''' | |||
| | 10 || 1110 || 254 || 516 || 29 || 50 || '''1959''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''122''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! style="color:red;"|East Sea | |||
| | 0 || 0 || 3 || '''3''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=3| '''-''' | |||
| | 0 || 0 || 0 || '''0''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=3| '''39''' | |||
| | 5 || 0 || 7 || 1 || '''13''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=3| '''341''' | |||
| | 1 || 0 || 3 || 0 || 0 || '''4''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=3| '''60''' | |||
| | 0 || 6 || 0 || 13 || 1 || 0 || '''20''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=3| '''440''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| !Sea of Korea | |||
| | 0 || 2 || 0 || '''2''' | |||
| | 2 || 4 || 2 || '''8''' | |||
| | 94 || 49 || 159 || 5 || '''307''' | |||
| | 92 || 6 || 37 || 4 || 8 || '''147''' | |||
| | 7 || 188 || 68 || 198 || 9 || 8 || '''471''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! Oriental Sea | |||
| | 0 || 0 || 3 || '''3''' || 4 || 20 || 14 || '''38''' || 14 || 4 || 57 || – || '''75''' || 2 || 0 || 3 || – || – || '''5''' || 8 || 20 || 32 || 77 || – || – || '''129''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! nowrap |Sea of China | |||
| | 3 ||rowspan=2| 5 || 12 ||rowspan=2| '''25''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''16''' | |||
| | 11 ||rowspan=2| 36 || 18 ||rowspan=2| '''86''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''28''' | |||
| | 8 ||rowspan=2| 6 || 8 || 1 ||rowspan=2| '''56''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''10''' | |||
| | 0 ||rowspan=2| 5 || 1 || 0 || – ||rowspan=2| '''32''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''-''' | |||
| |rowspan=2| 4 || 22 ||rowspan=2| 56 || 39 || 1 || – ||rowspan=2| '''203''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''54''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! Others | |||
| | 0 || 5 | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=2 | '''13''' | |||
| | 3 || 18 | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=2 | '''41''' | |||
| | 17 || 16 || – | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=2 | '''80''' | |||
| | 22 || 4 || – || – | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=2 | '''12''' | |||
| | 42 || 43 || – || – | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" rowspan=2 | '''146''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! No entry<br />and not<br />determined | |||
| | 32 || – || 44 || '''76''' || 83 || – || 83 || '''166''' || 116 || – || 152 || 4 || '''272''' || 109 || – || 120 || 5 || – || '''234''' || – || 340 || – || 399 || 9 || – || '''748''' | |||
| |- style="background:#def;" | |||
| ! Total | |||
| | 36 || 7 || 68 || '''111''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''29''' | |||
| | 106 || 74 || 140 || '''320''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''125''' | |||
| | 301 || 83 || 422 || 13 || '''819''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''467''' | |||
| | 1285 || 217 || 655 || 36 || 58 || '''2251''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''141''' | |||
| | 29 || 1728 || 410 || 1285 || 49 || 58 || '''3530''' | |||
| | style="background:#ffe1e1" | '''762''' | |||
| |} | |||
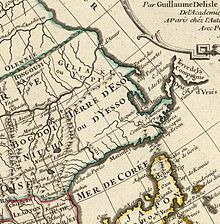
| ] | |||
| In ], South Korea deleted "Japan Sea" from its official nautical charts. Before then, South Korea's nautical charts showed both "Japan Sea" and "Tong Hae" (the then used romanization of "Donghae"), out of respect for international conventions. | |||
| ]. The sea is described as "Inland Sea of Japan" (日本内海) and the Pacific Ocean is described as "East Sea of Japan" (日本東海)]] | |||
| ] | |||
| To provide evidence for the date when Sea of Japan came to be used internationally, both South Korea and Japan have undertaken surveys of various historical maps. | |||
| In ], South Korea raised the issue again at the seventh UNCSGN and Japan opposed. The issue was not addressed but the resolution III/20 was recollected, which urges Japan and South Korea to reach a consensus. To date, however, neither country is willing to compromise their position, although Korea suggests that both names be used until the dispute is resolved. | |||
| In 2004, South Korea surveyed ancient maps archived in the British Library, the Cambridge University Library, the University of Southern California (USC) East Asian Map Collection, the U.S. Library of Congress, the National Library of Russia, and the French National Library. South Korean researchers examined 762 maps. They found that 440 maps had used Sea of Korea (Corea), Oriental Sea/East Sea, 122 had used Sea of Japan, and 200 had used other terms.<ref name="NAHF">{{cite web|title=Naming of the East Sea|url=http://english.historyfoundation.or.kr/?sub_num=160|publisher=Northeast Asian History Foundation|year=2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110815174553/http://english.historyfoundation.or.kr/?sub_num=160|archive-date=15 August 2011|access-date=2 September 2013}}</ref> In the ], the word ''orientale'' includes both the meaning of "eastern" related to compass direction and the meaning of "oriental", the Asiatic region. The same ambiguity is present in the ], with both "eastern" and "oriental" indicated by one word. | |||
| In ], South Korea raised the issue again at the eighth UNCSGN. Japan objected again and the issue was not addressed. | |||
| From 2003 to 2008, Japan conducted a number of surveys of different collections. In 2010, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan published their conclusions; they found that among 1,332 maps from the Berlin Library, 279 used Sea of Korea, Oriental Sea, or East Sea (or some combination thereof), 579 used Sea of Japan exclusively, 47 used China Sea (with or without other names), 33 used other term, and 384 used no term.<ref name="MOFAstudy7f">{{cite web|title=The Issue of the Naming of the Sea of Japan (Study in Germany)|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/study-7f.html|work=SEA OF JAPAN|publisher=]|year=2010|access-date=15 October 2010}}</ref> The ministry said the Struck collection (a collection of antiquarian maps owned by a European map collector) showed that out of 79 maps, 35 used Sea of Japan, 9 used the Sea of Korea, 2 used Oriental Sea, and 33 were unmarked.<ref name= MOFAstudy7f/> It also reported that among four Russian libraries and document archives holding 51 maps, 29 used Sea of Japan, 8 used Sea of Korea, 1 used Korea Strait, 1 used East Sea, 1 used Sea of China, and 11 used no name.<ref name="MOFAstudy6">{{cite web|title=Issue of naming of the Sea of Japan (Study in the Russian Federation)|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/study-6.html|publisher=]|year=2010|access-date=15 October 2010}}</ref> Among 1,213 maps from the U.S. Library of Congress, the ministry said, ones that gave a name for this body of water showed that 87 percent used Sea of Japan, 8 percent used Sea of Korea, 5 percent used other terms, and none used Oriental Sea or East Sea.<ref name="MOFApamphlet2003">{{cite web|title=Sea of Japan|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/pamph0903.pdf|publisher=]|date=February 2009|access-date=24 August 2010}}</ref> Similarly, the ministry said that 58 maps from the British Library and the University of Cambridge showed 86 percent used Sea of Japan, 14 percent used Sea of Korea, and none used Oriental Sea, East Sea, or other terms.<ref name=MOFApamphlet2003/> The ministry said that they looked at 1,485 maps in the French National Library. They reported that 95 percent of 215 French maps used Sea of Japan.<ref name=MOFApamphlet2003/> | |||
| In 2002, the ] (IHO) distributed a circular letter asking for a vote for omitting pages containing the Sea of Japan from the fourth edition of ''Limits of Oceans and Seas''. After Japan's objection, the IHO withdrew the letter. | |||
| ===Geographical arguments=== | |||
| On ] ], the ] affirmed in a written document to the Japanese government that it will continue using the name "Sea of Japan" in its official documents. However, it has agreed to leave the topic open for further discussion. In a letter to South Korea, it was explained that the UN was not determining the validity of either name, but using the currently most widely used term until the parties resolved the disagreement. | |||
| Japan argues that, the name Sea of Japan has been and should be used because the ] is separated from the Pacific Ocean by the ].<ref name="mofapamph0208">{{cite web|title=Sea of Japan|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/pamph0208.pdf|publisher=]|date=August 2002|access-date=21 November 2010}}</ref> Korea argues that the adjective "East" describes its geographical position east of the Asian continent, although it is west of Japan and south of Russia. It states that this is analogous to the ], which lies north of the European continent, but west of Scandinavian countries and east of Great Britain.<ref name = "WorkingPaper48"/> | |||
| ===Arguments relating to ambiguity=== | |||
| ==Response by media and publishers== | |||
| ] | |||
| Some publishers and media outlets have responded to the dispute by either adopting both names on maps, or—in very rare cases—leaving the area blank, until a consensus can be reached between Japan and Korea. Though some have adopted the usage of both names or just "East Sea", most publishers and media outlets still use "Sea of Japan" alone. | |||
| The Japanese Hydrographic and Oceanographic Department of the Japanese Coast Guard has claimed that the name East Sea is confusing and unsuitable as an international geographic name, because the local name for a variety of seas can be translated into English as East Sea. Examples include Dōng Hǎi (东海), the Chinese name for the ]; ''Biển Đông'', the Vietnamese name for the ]; and the ], whose name is equivalent to East Sea in several European languages such as German (''Ostsee''), Swedish (''Östersjön'') and Finnish (''Itämeri'').<ref name="Basic Position"/> East Sea is officially used as an English name for the body of water by the Government of Vietnam<ref name="Basic Position"/> and the Government of Vietnam thusly uses East Sea for South China Sea in its English-language publications;<ref>{{cite web|title=VN, China pledge to solve East Sea issue|date=20 April 2011|publisher=Socialist Republic of Việt Nam|url=http://thutuong.chinhphu.vn:2012/Home/VN-China-pledge-to-solve-East-Sea-issue/20114/1040.vgp}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=VN asserts sea and island sovereignty |date=2011-06-09|publisher=Socialist Republic of Việt Nam|url=http://thutuong.chinhphu.vn:2012/Home/VN-asserts-sea-and-island-sovereignty/20116/1025.vgp}}</ref> | |||
| likewise, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of China uses 'East Sea' for the East China Sea in its English-language publications.<ref>{{cite web|title=The Fourth Round of Consultation on East Sea between China and Japan to Be Held |publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of People's Republic of China|date=2 March 2006|url=http://www.fmprc.gov.cn/eng/wjdt/wsrc/t238013.htm}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Chinese Premier Meets with Japanese Prime Minister Taro Aso |publisher=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of People's Republic of China|date=24 October 2008|url=http://www.fmprc.gov.cn/eng/zxxx/t519594.htm}}</ref> | |||
| Even within Japan itself the term {{nihongo|East Sea|]|'']''}} is already used to refer to the parts of the ] east of middle and upper ], as can be seen in the naming of the ] and the ]. | |||
| The Japanese government is concerned that the name change could set a bad precedent and cause more naming disputes worldwide.<ref name="Basic Position"/> | |||
| The Korean side counters that all these problems are irrelevant as Korea's argument is not to replace 'Sea of Japan' with 'East Sea' but rather to use the name 'East Sea' alongside 'sea of Japan'. | |||
| ==Position of international bodies== | |||
| In ], ], one of the largest mapmakers in the United States, adopted a policy of concurrent use of both names, "East Sea" and "Sea of Japan". The Times (of London), Financial Times, Microsoft Encarta 97 World Atlas, Encyclopedia Britannica, MSN Expedia, Columbia Encyclopedia, About.com, and others have responded similarly, usually including "East Sea" as the secondary label. | |||
| The main two international organizations which have been involved in the naming dispute are the ] and the ]. | |||
| ===International Hydrographic Organization=== | |||
| In ], the ] recognized that the name was legitimately disputed by South Korea. Under its policy (if a geographical feature is shared by more than one nation, and its name is disputed, use the most commonly recognized form of the name first and label the disputed name in parentheses), "Sea of Japan" appears as the primary label and "East Sea" appears below in parentheses. | |||
| The International Hydrographic Organization is an organization that coordinates with member countries over ] issues. One of the organization's functions is to standardise the delineation of nautical regions. In 1929, the organization (then called the International Hydrographic Bureau) published edition 1 of "IHO Special Publication 23" (IHO SP 23) – Limits of Oceans and Seas, which included the limits of the sea area between the Korean Peninsula and Japan and the name Sea of Japan; however, at that time, Korea could not participate in the IHO because it was under Japanese rule. The name Sea of Japan remains in the current edition 3 of S-23, which was published in 1953.<ref name="KHOA">{{cite web|title=IHO Special Publication 23|url=http://eastsea.nori.go.kr/eng/open_content/iho/magazine.asp|publisher=Korean Hydrographic and Oceanographic Administration|year=2004|access-date=10 September 2010|archive-date=30 December 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121230120242/http://eastsea.nori.go.kr/eng/open_content/iho/magazine.asp|url-status=dead}}</ref> South Korea officially joined the IHO in 1957.<ref name="JCGchronology">{{cite web|title=Major Historical Background Information|url=http://www1.kaiho.mlit.go.jp/GIJUTSUKOKUSAI/nihonkai/keii_eng.htm|publisher=]|date=29 January 2009|access-date=21 November 2010|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110524121526/http://www1.kaiho.mlit.go.jp/GIJUTSUKOKUSAI/nihonkai/keii_eng.htm|archive-date=24 May 2011|df=dmy-all}}</ref> | |||
| In 1974, IHO released Technical Resolution A.4.2.6. This resolution stated that: | |||
| ==Arguments== | |||
| <blockquote>It is recommended that where two or more countries share a given geographical feature (such as a bay, a strait, channel or archipelago) under different names, they should endeavour to reach agreement on a single name for the feature concerned. If they have different official languages and cannot agree on a common name form, it is recommended that the name forms of each of the languages in question should be accepted for charts and publications unless technical reasons prevent this practice on small scale charts.</blockquote> | |||
| Both sides in the dispute have put forward a number of arguments to support their claim, either for a change, or against it. It is worth noting that many of these arguments are not supported by the respective governments, but rather by nationalist organizations. Around ], the volunteer Korean cyber-organization ] began an aggressive ] targeting webmasters, with some success but also backlash from supporters of Japan's position. | |||
| South Korea has argued that this resolution is relevant to the debate about the Sea of Japan and implies that both names should be used; Japan, however, argues that the resolution does not apply to the Sea of Japan, because it does not specify this body of water and only applies to geographical features for which sovereignty is shared between two or more countries and not applicable to high seas like the sea area between the Korean Peninsula and the Japanese Archipelago.<ref name = MOFApamphlet2003/> Contrary to Japan's claim, there are no high seas in accordance with UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea) in the sea area between the Korean Peninsula and the Japanese Archipelago. Even if Japan's usage of the term "high seas" includes exclusive economic zones, there are no grounds in international law for Japan's claim that these resolutions are not applicable to the case of East Sea/Sea of Japan. The English Channel/La Manche, which is referred to in the IHO Resolution 1/1972 as an example of concurrent usage, is composed of only the territorial seas and the exclusive economic zones of the UK and France. The East Sea/Sea of Japan is also composed of only territorial seas and exclusive economic zones of its coastal states, which is no different from the case of English Channel/La Manche. Therefore, this resolution should be applicable to the case of East Sea/Sea of Japan. | |||
| In 2017, the IHO's 1st Sesseion of the Assembly was held and the member states decided to discuss the future of S-23, taking into account the growing need to modernize the publication, the latest edition of which was published in 1953. | |||
| ===Geographical reasons=== | |||
| Japanese groups argue that as a ] of the ], the sea should be named for Japan. South Korean groups take a different point of view and argue that the sea is really located at the eastern end of the Asian continent, and thus should be called ''East Sea''. Korea argues that similar name for a body of water can be found in the example of the ], which derives its name from its location relative to the European continent. | |||
| At the 2nd Session of the Assembly in 2020, the member states decided to replace the sea area names in S-23 with unique numerical identifiers and to develop a new digital standard (S-130) that meets the requirements of contemporary geographic information systems. While developing a data-set to designate geographic sea areas by a system of unique numerical identifiers only, S-23 is kept publicly available as it is, as part of existing IHO publication, to demonstrate the evolutionary process from the analogue to the digital era. The IHO currently has a project team working to release S-130 by 2026.<ref name="Second Session of the IHO Assembly (A-2)">{{cite web|title=Second Session of the IHO Assembly (A-2)|url=https://iho.int/uploads/user/About%20IHO/Assembly/Assembly2/A-2_Final_Summary_Records_EN.pdf|publisher=]|access-date=23 August 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ===Historical reasons=== | |||
| Both sides use a selective sample of old maps to support their claim. South Koreans use old maps that show names other than "Sea of Japan", whereas the Japanese use maps to demonstrate that the said name was in use before their imperial time. Many old maps are ambiguous and some even do not include Korea or Japan. | |||
| ===United Nations=== | |||
| Japanese groups argue that the term "Sea of Japan" was originally named by Westerners and became the de-facto standard before Japan gained commercial and political influence in the region. Part of the dispute boils down to the disagreement over when "Sea of Japan" became the de facto standard. Japanese groups claim dates in the early 19th century, whereas Korean groups claim dates in the early 20th century when Korea was colonized by Japan. | |||
| While the United Nations has never directly addressed the issue of establishing an official, standardized name for the sea, several resolutions and statements by the UN have had relevance to the topic. Japan joined the United Nations in 1956, while South Korea and North Korea both joined in 1991.<ref name="UN members">{{cite web|title=Member States of the United Nations|url=https://www.un.org/en/members|publisher=]|date=3 July 2006|access-date=10 September 2010}}</ref> | |||
| In 1977, the Third U.N. Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names (UNCSGN) adopted Resolution III/20, entitled "Names of Features beyond a Single Sovereignty". The resolution recommended that "when countries sharing a given geographical feature do not agree on a common name, it should be a general rule of cartography that the name used by each of the countries concerned will be accepted. A policy of accepting only one or some of such names while excluding the rest would be inconsistent as well as inexpedient in practice." As with IHO Technical Resolution A.4.2.6, South Korea and Japan disagree about whether or not this policy applies to the East Sea/Sea of Japan.<ref name = MOFApamphlet2003/> | |||
| South Korean groups claim historical precedence of the names "Sea of Korea" and "East Sea", and argue that "East Sea" is a more neutral name that should be restored. They regard the dominance of the name "Sea of Japan" a reflection of Japan's imperial past. Korea even points out that a select few 19th century Japanese maps referred to the sea as the "Sea of Joseon (Korea)", including the ] Matsuda Rokuzan's Chikyubankoku zenzu, and the ] Meizi kaiteibankoku yochibunzu. | |||
| In 1992, during the 1992 Sixth UNCSGN, the South Korean government, in their first time participating in the UNCSGN, requested that the name the sea be determined through consultation, which the North Korean representative concurred with. The Japanese representative stated that the name of the Sea of Japan had already been accepted worldwide and that any change would introduce confusion. The conference recommended that the parties work together on the issue outside of the conference.<ref>{{citation|title=Report of the Sixth UNCSGN Conference|id=United Nations Publication E.93.I.23|pages=21–22|publisher=]|year=1993}}</ref> | |||
| ====Historical maps and studies==== | |||
| In July ], Korea produced a report on the names used on maps published in Europe, mostly in the 18th century, possessed by the ], claiming that of 377 maps which name the sea, 72 refer to it as "Sea of Korea" and/or "East Sea", and 10 use "Sea of Japan". However, upon close examination of this report, one finds that the figures have been manipulated and flawed. The most direct proof of this is that somehow they purport to have found 72 maps using "East Sea" whereas there are only 10 such maps according to their own data. | |||
| In 1998, South Korea raised the issue again at the Seventh UNCSGN. Japan, however, opposed the method by which the South Korean government proposed the issue, arguing that they had not followed the proper procedure for doing so. Following some debate, South Korea withdrew the issue, and instead recommended that the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names work so that a resolution could be submitted to the Eighth UNSCGN conference. The president of the conference urged that Japan, South Korea, and North Korea work towards a mutually acceptable agreement.<ref name="UNSCGN7">{{cite web|title=Report of the Seventh UNCSGN Conference|url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/geoinfo/UNGEGN/docs/7th-uncsgn-docs/7thUNCSGN-Report_E-.pdf|page = 18|publisher=]|date=13–22 January 1998|access-date=30 March 2011}}</ref> | |||
| In 2002, the ] published their Sea of Korea maps digital archive on the Internet, consisting of 172 maps made between 17th and 19th centuries. The names of seas begin to appear on maps beginning in the 18th century, 95 of which called the sea "Sea of Korea" or "East Sea" while "Sea of Japan" is found only on one map. Of the 19th century maps, "Sea of Japan" is found on 9, "Sea of Korea" is found on 30. Among all 165 maps in the collection, 135 used "Sea of Korea" or "East Sea" while only 10 used "Sea of Japan". | |||
| At the Eighth UNCSGN in 2002, South Korea and Japan presented a number of papers to the conference regarding their positions on the naming issue. South Korea asked for a resolution to adjudicate the name, while Japan asked that the name be decided through resolution outside of the conference. No resolution was passed, and the Committee again urged the countries to develop a mutually agreeable solution. The chairman further noted that standardization could only occur after consensus had been reached.<ref name="UNCSGN8">{{cite web|title=Eighth UNCSGN Conference Report|url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/geoinfo/UNGEGN/docs/8th-uncsgn-docs/8th_UNCSGN-E.pdf|publisher=]|pages = 29–30|date=27 August – 5 September 2002|access-date=30 March 2011}}</ref> The same situation occurred at the Ninth Conference in 2007. South Korea and North Korea both proposed a resolution by the UNCSGN, while Japan expressed a desire to settle the matter outside of the conference, and the Committee urged the members to seek a mutual agreement.<ref>{{cite web|title=Ninth UNCSGN Conference Report|url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/geoinfo/UNGEGN/docs/9th-uncsgn-docs/report%20of%209th%20uncsgn%20n0750902%20en.pdf|pages = 29–30|publisher=]|date=21–30 August 2007| access-date=23 September 2010}}</ref> | |||
| In December 2002, South Korea produced a report on the names used on 228 maps published prior to 1800 that are held by the U.S. ], claiming that two-thirds of the maps naming the sea used "East Sea", "Sea of Korea", or variants. Of the 103 maps that named the sea, the report claims 66 percent named it "Sea of Korea" and/or "East Sea" or variants. | |||
| On 23 April 2004, the United Nations affirmed in a written document to the Japanese government that it will continue using the name Sea of Japan in its official documents.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/un0406.html | title = The Policy of the United Nations Concerning the Naming of {{'}}Sea of Japan{{'}} | publisher = ] |date=June 2004|access-date=22 November 2010}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=UN and U.S. use "Sea of Japan"|url=https://www.mofa.go.jp/a_o/na/page1we_000112.html|access-date=2021-03-29|website=Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan|language=en}}</ref> However, it agreed to leave the topic open for further discussion. In a letter to South Korea, it was explained that the UN was not determining the validity of either name, but wished to use the term that is most widely used until the parties resolved the disagreement. The letter further stated, "The use of an appellation by the Secretariat based on the practice is without prejudice to any negotiations or agreements between the interested parties and should not be interpreted as advocating or endorsing any party's position, and can in no way be invoked by any party in support of a particular position in the matter."<ref>{{cite web| url = http://www.mofat.go.kr/pdffiles/en_Eastsea_1.htm| title = The Practice of the Secretariat of the United Nations Concerning the Naming of the Sea Area between Korea and Japan, The Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade of South Korea| access-date = 22 November 2010| publisher = ]| url-status = dead| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120806062346/http://www.mofat.go.kr/pdffiles/en_Eastsea_1.htm| archive-date = 6 August 2012| df = dmy-all}}</ref> | |||
| In September 2003, Japan produced a report on the names used on maps published in Europe between 1801 and 1861 possessed by the ] and the ], claiming that in the ], of 37 maps containing the areas surrounding the sea, 32 or 86.5% used "Sea of Japan" and 5 used "Sea of Korea". In the ], it found 21 maps containing the areas surrounding the sea, of which 18 or 85.7% used "Sea of Japan" and 3 used "Sea of Korea". | |||
| ] | |||
| In March 2004, the ] published a report with the list of maps it investigated on the investigation of maps at the ]. The study claims that from the 1,495 maps possessed by the Bibliotheque Nationale de France and published between the 16th and 19th century show that of 407 maps for which a name was recorded, 249, or 61% bore the name "Sea of Japan" and 60, or 15% bore the name "Sea of Korea". It found no maps that bore the name "East Sea". Furthermore, the report claims, of the maps published in the first half of the 19th century, 90.0% or 99 maps bore the name "Sea of Japan" and of the maps published in the latter half of the 19th century 100% or 105 maps bore the same name. | |||
| On 6 August 2012, representatives from South Korea and North Korea addressed an assembly at the ], asking that the names "East Sea" and "Sea of Japan" be used concurrently for the sea. ], chairman of the conference, responded that the organization had no authority to decide the issue and requested that the involved countries resolve the differences over the name amongst themselves.<ref>], " {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160104222924/http://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2012/08/08/national/genba-stands-firm-on-senkakus/ |date=4 January 2016 }}", '']'', 8 August 2012, p. 2</ref> | |||
| ==Other countries== | |||
| In July 2005, the ] published a report () of the investigation it conducted on the dispute. According to the report, the investigators from ] looked into maps published between 1300 and 1900 at the ], and from 1,435 maps which mention the disputed sea, 1,110 maps use "Sea of Japan". | |||
| Russia calls this sea "Япо́нское мо́ре" (Yapónskoye móre, Japanese Sea).<ref name="FEB_RAS">{{cite web|title=ATLAS OF OCEANOGRAPHY Bering Sea, Sea of Okhotsk and Sea of Japan|url=http://www.pacificinfo.ru/data/cdrom/2/HTML/4_00.htm|language=ru|publisher=Far East Branch of the ]|access-date=25 April 2011|archive-date=15 November 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091115073938/http://www.pacificinfo.ru/data/cdrom/2/HTML/4_00.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Univ.Press">{{cite web|title=Seas of the USSR|url=http://tapemark.narod.ru/more/20.html |language=ru |publisher=A. D. Dobrovolsky, BS Zalogin. Univ. Press, 1982. |access-date=25 April 2011}}</ref> Japan believes that Russia played a major role in establishing this name internationally, as mentioned above. Chinese government websites exclusively use the name ] (''rìběnhǎi'', 'Japan Sea').<ref>{{cite web |url =http://japanese.china.org.cn/politics/txt/2011-04/20/content_22403715.htm |script-title=ja:韓国国会議員、「日本海」呼称廃止を中国に求める |date=20 April 2011 |publisher = Japanese.China.org.cn |language = ja |trans-title=A South Korean lawmaker calls on China to abolish the name of the "Sea of Japan" |access-date=14 May 2011}}</ref> | |||
| In 2003, the French Defense Ministry issued nautical maps that included both terms Sea of Japan and East Sea.<ref name="mofqafeb2003">{{cite web|title=Q&A on the Issue of the Name "Sea of Japan"|url=http://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/q_a/faq14.html|publisher=]|access-date=22 November 2010|date=February 2003}}</ref> It reverted to Sea of Japan as a single name in the map issued in 2004.<ref>{{cite web | url =http://www.kaiho.mlit.go.jp/info/kouhou/h16/k20040713/0713kouhou.pdf | script-title=ja:フランス海軍海洋情報部刊行の海図目録 -「日本海」単独標記に- | publisher = ] |date=13 July 2004|access-date=22 November 2010|language = ja}}</ref> The United Kingdom and Germany officially use the Sea of Japan.<ref name="MOFAJ"/> | |||
| The ] (BGN) continues to advocate the use of Sea of Japan without qualification in ] publications. ] published by the ] follows the BGN's guidance.<ref>{{cite web|title=FAQ|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/docs/faqs.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070612214339/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/docs/faqs.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=12 June 2007|publisher=]|year=2010|access-date=8 November 2010}} Note: expand the "Policies" tab to see details.</ref> On 8 August 2011, a spokesman for the United States Department of State stated that the United States Board on Geographic Names considered the official name of the sea to be "Sea of Japan". | |||
| South Korea's ] website states that by its count, of 763 historic maps in various government and university libraries worldwide, 440 maps use "Sea of Korea", "East Sea", or variants, and 123 use "Sea of Japan" or variants. (retrieved September ]). | |||
| Despite the U.S. government's position for the single use of Sea of Japan, in 2011, ] state lawmaker ], acting on behalf of Korean-American voters, introduced a bill to the education panel of the ] that would have required public school textbooks to include both "Sea of Japan" and "East Sea" as names. The panel rejected the bill by an 8–7 vote on 26 January 2012.<ref>], "Virginia sinks sea-renaming plan", '']'', 31 January 2012, p. 2.</ref><ref>{{cite news | title='East Sea' textbook directive fails Senate panel | url=http://www.wtop.com/?sid=2722782&nid=120 | agency=Associated Press | access-date=28 April 2012}}</ref> The issue was revisited two years later on 3 February 2014, with the Education Committee of the ] passing legislation to use both "Sea of Japan" and "East Sea" in school textbooks.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://the-japan-news.com/news/article/0001001763 |title=Virginia nears law on Sea of Japan |publisher=The Japan News |access-date=24 February 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140307113844/http://the-japan-news.com/news/article/0001001763 |archive-date=7 March 2014 |df=dmy-all }}</ref> This bill, House Bill (BH) No. 11, was finally passed by the Virginia House of Delegates on 6 February 2014, signed by the Governor on 28 March and became effective on 1 Juy. The bill states that "all textbooks approved by the Board of Education pursuant to §22.1-238 of the Code of Virginia, when referring to the Sea of Japan, shall note that it is also referred to as the East Sea." | |||
| ===Ownership=== | |||
| Some Koreans argue that "Sea of Japan" implies ownership over an international body of water. Japanese counter by saying that the name of a body of water does not imply ownership. It is merely a name. Some Koreans argue that the name "Sea of Japan" is related to ownership because it was the Japanese delegates who submitted the name to the IHB when Korea was under Japanese colonial rule. | |||
| On 29 June 2012, Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs ] affirmed the BGN's position in his response, published on the White House website, to the ] concerning the usage of "Sea of Japan", in which he stated, "It is longstanding United States policy to refer to each sea or ocean by a single name. This policy applies to all seas, including those bordered by multiple countries that may each have their own names for such bodies of water. Concerning the body of water between the Japanese archipelago and the Korean Peninsula, longstanding U.S. policy is to refer to it as the "Sea of Japan".<ref>{{cite web | title=Response to We the People Petition on the Sea of Japan Naming Issue | url=https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/blog/2012/06/29/response-we-people-petition-sea-japan-naming-issue | via=] | work=] | date=29 June 2012 | access-date=3 July 2012}}</ref> He also stated, "We are aware the Republic of Korea refers to the body of water as the 'East Sea,' and the United States is not asking the Republic of Korea to change its nomenclature. U.S. usage of the 'Sea of Japan' in no way implies an opinion regarding any issue related to sovereignty."<ref>], " {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140222140447/http://info.japantimes.co.jp/text/nn20120704b3.html |date=22 February 2014 }}", '']'', 4 July 2012, p. 2</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=2012-06-29|title=Response to We the People Petition on the Sea of Japan Naming Issue|url=https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/blog/2012/06/29/response-we-people-petition-sea-japan-naming-issue|access-date=2021-03-29|website=whitehouse.gov|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ===Ambiguity=== | |||
| Japanese groups claim that the name "East Sea" is not suitable as an international geographic name, because it could refers to various places including the neighboring ]. Much of this argument is based on translations of local names into English. Commonly cited potential confusions are the ] name for the ], "Bien Dong", which literally means "East Sea", or the ] which in many European languages is called the equivalent of "East Sea". The Koreans state that this is irrelevant as there are other geographical places that share similar or the same name. It is sometimes also argued that "East Sea" is a mere translation of the local Korean name "Donghae", and thus not really an English name ''per se''. | |||
| Contrary to the position of a few major countries, a number of maps, encyclopedias, and other publications have switched to using both names. Today, it is easy to find examples of the concurrent use of the name "East Sea" and "Sea of Japan" on maps and in textbooks and prominent news media's articles both online and offline. For example, National Geographic Map Policy states that the sea between Japan and Korea is called the Sea of Japan by the Japanese and the East Sea by Koreans. | |||
| ===Precedence=== | |||
| Some Japanese groups insist that renaming or showing both simultaneously runs counter to the spirit of geographic standardization and will be a troubling precedent. Since the name "Sea of Japan" is the internationally established name, some people think renaming is an unnecessary complication. Koreans disagree stating that setting the name right is more important. | |||
| For example, the Manual of Style of the ] states that disputed place-names in international waters or jointly controlled by two or more countries should use the conventional name first with other names following in parentheses.<ref name="National Geographic Map Policy">{{cite web|title=National Geographic Map Policy|url=https://www.nationalgeographic.org/society/national-geographic-map-policy/|publisher=]|access-date=23 August 2024}}</ref> | |||
| In 2006, Google put both names on ], using East Sea near the Korean coast and Sea of Japan near the Japanese coast.<ref name="KoreaTimes2006">{{cite news|last=Cho|first=Jin-Seo|title=Google asked to identify Korea correctly|url=http://www.asiamedia.ucla.edu/article-eastasia.asp?parentid=50214|access-date=21 September 2010|newspaper=]|date=2 August 2006|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110520090640/http://www.asiamedia.ucla.edu/article-eastasia.asp?parentid=50214|archive-date=20 May 2011|df=dmy-all}}</ref> '']'' states that Sea of Japan is also known as and called by East Sea. On the encyclopedia's map, Sea of Japan and East Sea are used concurrently.<ref name="Britannica-Sea of Japan/East Sea">{{cite web|title=Britannica-Sea of Japan/East Sea|url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Sea-of-Japan|publisher=]|access-date=23 August 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{Portal bar|Geography|Oceans|Politics|Japan|China|Russia}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category|Sea of Japan naming dispute}} | |||
| * — by the Korean Overseas Information Service | |||
| '''Japan''' | |||
| * — Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs defends the use of "Sea of Japan". | |||
| * {{cite web|url=https://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/maritime/japan/index.html |title=The Issue of Name "Sea of Japan" |language=en |website=] }} | |||
| **{{cite web|author=MOFA, Japan |author-link=Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Japan) |title="Sea of Japan" - A globally established name |url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ac58ARaacAM&t=24s| archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211116/ac58ARaacAM| archive-date=2021-11-16 | url-status=live|date=4 April 2014 |language=en |via=YouTube }}{{cbignore}} | |||
| '''South Korea''' | |||
| ] | |||
| *{{cite web|author=대한민국외교부|author-link=Ministry of Foreign Affairs (South Korea)|title=East Sea, The Name from the Past, of the Present, and for the Future|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zmF2o3NEUd4| archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211116/zmF2o3NEUd4| archive-date=2021-11-16 | url-status=live|date=2017-02-20|language=en|via=YouTube}}{{cbignore}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Sea of Japan Naming Dispute}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] |
] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 04:46, 15 November 2024
Korea–Japan conflict

Japan's preference: Sea of Japan
North Korea's preference: Korean East Sea
South Korea's preference: East Sea
A dispute exists over the international name for the body of water which is bordered by Japan, Korea (North and South) and Russia. In 1992, objections to the name Sea of Japan were first raised by North Korea and South Korea at the Sixth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names. The Japanese government supports the exclusive use of the name "Sea of Japan" (Japanese: 日本海), while South Korea supports the alternative name "East Sea" (Korean: 동해; Hanja: 東海), and North Korea supports the name "Korean East Sea" (조선동해; 朝鮮東海). Currently, most international maps and documents use either the name Sea of Japan (or equivalent translation) by itself, or include both the name Sea of Japan and East Sea, often with East Sea listed in parentheses or otherwise marked as a secondary name. The International Hydrographic Organization, the governing body for the naming of bodies of water around the world, in 2012 decided it was still unable to revise the 1953 version of its publication S-23 – Limits of Oceans and Seas, which includes only the single name "Sea of Japan", to include "East Sea" together with "Sea of Japan".
The involved countries (especially Japan and South Korea) have advanced a variety of arguments to support their preferred name(s). Many of the arguments revolve around determining when the name Sea of Japan became the common name. South Korea argues that historically the more common name was East Sea, Sea of Korea, or another similar variant. South Korea further argues that the name Sea of Japan did not become common until Korea was under Japanese rule, at which time it had no ability to influence international affairs. Japan argues that the name Sea of Japan has been the most common international name since at least the beginning of the 19th century, long before its annexation of Korea. Both sides have conducted studies of antiquarian maps, but the two countries have produced divergent research results. Additional arguments have been raised regarding the underlying geography of the sea as well as potential problems regarding the ambiguity of one name or the other.
Arguments
Both sides in the dispute have put forward a number of arguments to support their claims.
Arguments based on historical maps
Arguments from South Korea
According to South Korea's Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the name East Sea(Donghae(동해)) can be found in various historical records produced in the span of over 2,000 years, including the History of the Three Kingdoms (1145), the monument of King Gwanggaeto (414), and "Map of Eight Provinces of Korea" (八道總圖, 1530). According to such records, the name East Sea(동해(Donghae)) is almost 1700 years older than the first documented world map to name the area the Sea of Japan, named Kunyu Wanguo Quantu (坤輿萬國全圖), which was drawn by the Italian missionary Matteo Ricci in China (1602). No Japanese record published up to the late-18th century indicated any name for the body of water. Furthermore, South Korea has pointed out that Japan itself recognized the sea as Sea of Joseon (Korea) not Sea of Japan since some 18th and 19th-century Japanese maps referred to the sea as Chōsenkai( 朝鮮海, literally Sea of Joseon), including the Simplified Map of Japan's Periphery (日本邊界略圖, 1809), Map of Asia (亞細亞全圖, 1794) which was drawn by Katsuragawa Hoshu (桂川甫周) and the New World Map (新製輿地全圖, 1844). Additionally, it specifically states that the name Sea of Japan was not widely used, even in Japan, as late as the mid 19th century. Moreover, South Korea argues that it was unable to present its case for the name 'East Sea' internationally beause it was under Japan's colonial rule and in the midst of the Korean War. In 1992, the name "East Sea" was agreed upon as English name for the sea in South Korea and claimed by the country for the sea during its participation in the U.N. Conference on Standardization of Geographical Names.
Korea's argument is, however, not to replace 'Sea of Japan' with 'East Sea' but rather to use the name 'East Sea' alongside 'Sea of Japan'. Since 1992, the Korean government has maintained the position that as Korea does not oppose the continuous use of the name 'Sea of Japan' in the international community, Japan should honour the name 'East Sea' that the Korean people have been using for a long time and agree on the dual names for that specific sea area. In fact, the concurrent use of the name East Sea and Sea of Japan conforms to the general naming principles in the international community. Moreover, when countries are unable to reach an agreement on the name of a feature, it is recommended to accept all names used by each of the countries concerned. This general rule of international cartography is confirmed by the relevant resolutions: the International Hydrographic Organization Resolution 1/1972 and the United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names Resolution III/20.
Arguments from Japan
The Japanese government claims that the name Sea of Japan had been internationally used since the 17th century and established by the early 19th century, during which Japan was under an isolationist policy (Sakoku) of the Tokugawa shogunate that restricted cultural exchange and commerce with foreign countries except China and the Netherlands until 1854. Accordingly, they state, Japan could not have, at that time, had an influence on the international community regarding the naming of the sea.
The invention of the marine chronometer in the late 18th century enabled Western explorers, such as Jean-François de Galaup from France, William Robert Broughton from Britain, and Adam Johann von Krusenstern (Ivan Fyodorovich Kruzenshtern) from Russia, to measure time and longitudes on the sea precisely and map the detailed shape of the Sea of Japan. Krusenstern was an admiral and explorer, who led the first Russian circumnavigation of the globe. According to Japanese records, it was Krusenstern who popularized the name "Mer du Japon" (Sea of Japan) in the West. In his work "Reise um die Welt in den Jahren" (1812), he wrote, "People also call this sea area the Sea of Korea, but because only a small part of this sea touches the Korean coast, it is better to name it the Sea of Japan." The original book was published in St. Petersburg in German and Russian, translated into Dutch, French, Swedish, Italian and English, and distributed widely among Europe. As a result, the international name of the sea changed from no name to the Sea of Japan, on the maps drawn by countries other than Japan or Korea during the 17th to 20th centuries. Thus, the Japanese side argues that the South Koreans misunderstand the history of the name.
Surveys of antiquarian maps
| Century | 16th century | 17th century | 18th century | 19th century | Unknown | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surveyed by | Japan | Korea | Japan | Korea | Japan | Korea | Japan | Korea | Japan | Japan | Korea | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Surveyed in | US | FR | DE | Total | Total | US | FR | DE | Total | Total | US | FR | DE | RU | Total | Total | US | FR | DE | RU | UK | Total | Total | FR | US | FR | DE | RU | UK | Total | Total |
| Sea of Japan | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | - | 3 | 14 | 5 | 22 | 17 | 47 | 24 | 23 | 2 | 96 | 36 | 1059 | 206 | 487 | 27 | 50 | 1829 | 69 | 10 | 1110 | 254 | 516 | 29 | 50 | 1959 | 122 |
| East Sea | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 5 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 13 | 341 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 60 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 20 | 440 |
| Sea of Korea | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 94 | 49 | 159 | 5 | 307 | 92 | 6 | 37 | 4 | 8 | 147 | 7 | 188 | 68 | 198 | 9 | 8 | 471 | |||||
| Oriental Sea | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 20 | 14 | 38 | 14 | 4 | 57 | – | 75 | 2 | 0 | 3 | – | – | 5 | 8 | 20 | 32 | 77 | – | – | 129 | |||||
| Sea of China | 3 | 5 | 12 | 25 | 16 | 11 | 36 | 18 | 86 | 28 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 56 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | – | 32 | - | 4 | 22 | 56 | 39 | 1 | – | 203 | 54 |
| Others | 0 | 5 | 13 | 3 | 18 | 41 | 17 | 16 | – | 80 | 22 | 4 | – | – | 12 | 42 | 43 | – | – | 146 | |||||||||||
| No entry and not determined |
32 | – | 44 | 76 | 83 | – | 83 | 166 | 116 | – | 152 | 4 | 272 | 109 | – | 120 | 5 | – | 234 | – | 340 | – | 399 | 9 | – | 748 | |||||
| Total | 36 | 7 | 68 | 111 | 29 | 106 | 74 | 140 | 320 | 125 | 301 | 83 | 422 | 13 | 819 | 467 | 1285 | 217 | 655 | 36 | 58 | 2251 | 141 | 29 | 1728 | 410 | 1285 | 49 | 58 | 3530 | 762 |


To provide evidence for the date when Sea of Japan came to be used internationally, both South Korea and Japan have undertaken surveys of various historical maps.
In 2004, South Korea surveyed ancient maps archived in the British Library, the Cambridge University Library, the University of Southern California (USC) East Asian Map Collection, the U.S. Library of Congress, the National Library of Russia, and the French National Library. South Korean researchers examined 762 maps. They found that 440 maps had used Sea of Korea (Corea), Oriental Sea/East Sea, 122 had used Sea of Japan, and 200 had used other terms. In the French language, the word orientale includes both the meaning of "eastern" related to compass direction and the meaning of "oriental", the Asiatic region. The same ambiguity is present in the Russian language, with both "eastern" and "oriental" indicated by one word.
From 2003 to 2008, Japan conducted a number of surveys of different collections. In 2010, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan published their conclusions; they found that among 1,332 maps from the Berlin Library, 279 used Sea of Korea, Oriental Sea, or East Sea (or some combination thereof), 579 used Sea of Japan exclusively, 47 used China Sea (with or without other names), 33 used other term, and 384 used no term. The ministry said the Struck collection (a collection of antiquarian maps owned by a European map collector) showed that out of 79 maps, 35 used Sea of Japan, 9 used the Sea of Korea, 2 used Oriental Sea, and 33 were unmarked. It also reported that among four Russian libraries and document archives holding 51 maps, 29 used Sea of Japan, 8 used Sea of Korea, 1 used Korea Strait, 1 used East Sea, 1 used Sea of China, and 11 used no name. Among 1,213 maps from the U.S. Library of Congress, the ministry said, ones that gave a name for this body of water showed that 87 percent used Sea of Japan, 8 percent used Sea of Korea, 5 percent used other terms, and none used Oriental Sea or East Sea. Similarly, the ministry said that 58 maps from the British Library and the University of Cambridge showed 86 percent used Sea of Japan, 14 percent used Sea of Korea, and none used Oriental Sea, East Sea, or other terms. The ministry said that they looked at 1,485 maps in the French National Library. They reported that 95 percent of 215 French maps used Sea of Japan.
Geographical arguments
Japan argues that, the name Sea of Japan has been and should be used because the marginal sea is separated from the Pacific Ocean by the Japanese Archipelago. Korea argues that the adjective "East" describes its geographical position east of the Asian continent, although it is west of Japan and south of Russia. It states that this is analogous to the North Sea, which lies north of the European continent, but west of Scandinavian countries and east of Great Britain.
Arguments relating to ambiguity

The Japanese Hydrographic and Oceanographic Department of the Japanese Coast Guard has claimed that the name East Sea is confusing and unsuitable as an international geographic name, because the local name for a variety of seas can be translated into English as East Sea. Examples include Dōng Hǎi (东海), the Chinese name for the East China Sea; Biển Đông, the Vietnamese name for the South China Sea; and the Baltic Sea, whose name is equivalent to East Sea in several European languages such as German (Ostsee), Swedish (Östersjön) and Finnish (Itämeri). East Sea is officially used as an English name for the body of water by the Government of Vietnam and the Government of Vietnam thusly uses East Sea for South China Sea in its English-language publications; likewise, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of China uses 'East Sea' for the East China Sea in its English-language publications. Even within Japan itself the term East Sea (東海, Tōkai) is already used to refer to the parts of the Pacific Ocean east of middle and upper Honshu, as can be seen in the naming of the Tōkaidō region and the Tōkai region. The Japanese government is concerned that the name change could set a bad precedent and cause more naming disputes worldwide. The Korean side counters that all these problems are irrelevant as Korea's argument is not to replace 'Sea of Japan' with 'East Sea' but rather to use the name 'East Sea' alongside 'sea of Japan'.
Position of international bodies
The main two international organizations which have been involved in the naming dispute are the International Hydrographic Organization and the United Nations.
International Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization is an organization that coordinates with member countries over hydrographic issues. One of the organization's functions is to standardise the delineation of nautical regions. In 1929, the organization (then called the International Hydrographic Bureau) published edition 1 of "IHO Special Publication 23" (IHO SP 23) – Limits of Oceans and Seas, which included the limits of the sea area between the Korean Peninsula and Japan and the name Sea of Japan; however, at that time, Korea could not participate in the IHO because it was under Japanese rule. The name Sea of Japan remains in the current edition 3 of S-23, which was published in 1953. South Korea officially joined the IHO in 1957.
In 1974, IHO released Technical Resolution A.4.2.6. This resolution stated that:
It is recommended that where two or more countries share a given geographical feature (such as a bay, a strait, channel or archipelago) under different names, they should endeavour to reach agreement on a single name for the feature concerned. If they have different official languages and cannot agree on a common name form, it is recommended that the name forms of each of the languages in question should be accepted for charts and publications unless technical reasons prevent this practice on small scale charts.
South Korea has argued that this resolution is relevant to the debate about the Sea of Japan and implies that both names should be used; Japan, however, argues that the resolution does not apply to the Sea of Japan, because it does not specify this body of water and only applies to geographical features for which sovereignty is shared between two or more countries and not applicable to high seas like the sea area between the Korean Peninsula and the Japanese Archipelago. Contrary to Japan's claim, there are no high seas in accordance with UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea) in the sea area between the Korean Peninsula and the Japanese Archipelago. Even if Japan's usage of the term "high seas" includes exclusive economic zones, there are no grounds in international law for Japan's claim that these resolutions are not applicable to the case of East Sea/Sea of Japan. The English Channel/La Manche, which is referred to in the IHO Resolution 1/1972 as an example of concurrent usage, is composed of only the territorial seas and the exclusive economic zones of the UK and France. The East Sea/Sea of Japan is also composed of only territorial seas and exclusive economic zones of its coastal states, which is no different from the case of English Channel/La Manche. Therefore, this resolution should be applicable to the case of East Sea/Sea of Japan.
In 2017, the IHO's 1st Sesseion of the Assembly was held and the member states decided to discuss the future of S-23, taking into account the growing need to modernize the publication, the latest edition of which was published in 1953.
At the 2nd Session of the Assembly in 2020, the member states decided to replace the sea area names in S-23 with unique numerical identifiers and to develop a new digital standard (S-130) that meets the requirements of contemporary geographic information systems. While developing a data-set to designate geographic sea areas by a system of unique numerical identifiers only, S-23 is kept publicly available as it is, as part of existing IHO publication, to demonstrate the evolutionary process from the analogue to the digital era. The IHO currently has a project team working to release S-130 by 2026.
United Nations
While the United Nations has never directly addressed the issue of establishing an official, standardized name for the sea, several resolutions and statements by the UN have had relevance to the topic. Japan joined the United Nations in 1956, while South Korea and North Korea both joined in 1991.
In 1977, the Third U.N. Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names (UNCSGN) adopted Resolution III/20, entitled "Names of Features beyond a Single Sovereignty". The resolution recommended that "when countries sharing a given geographical feature do not agree on a common name, it should be a general rule of cartography that the name used by each of the countries concerned will be accepted. A policy of accepting only one or some of such names while excluding the rest would be inconsistent as well as inexpedient in practice." As with IHO Technical Resolution A.4.2.6, South Korea and Japan disagree about whether or not this policy applies to the East Sea/Sea of Japan.
In 1992, during the 1992 Sixth UNCSGN, the South Korean government, in their first time participating in the UNCSGN, requested that the name the sea be determined through consultation, which the North Korean representative concurred with. The Japanese representative stated that the name of the Sea of Japan had already been accepted worldwide and that any change would introduce confusion. The conference recommended that the parties work together on the issue outside of the conference.
In 1998, South Korea raised the issue again at the Seventh UNCSGN. Japan, however, opposed the method by which the South Korean government proposed the issue, arguing that they had not followed the proper procedure for doing so. Following some debate, South Korea withdrew the issue, and instead recommended that the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names work so that a resolution could be submitted to the Eighth UNSCGN conference. The president of the conference urged that Japan, South Korea, and North Korea work towards a mutually acceptable agreement.
At the Eighth UNCSGN in 2002, South Korea and Japan presented a number of papers to the conference regarding their positions on the naming issue. South Korea asked for a resolution to adjudicate the name, while Japan asked that the name be decided through resolution outside of the conference. No resolution was passed, and the Committee again urged the countries to develop a mutually agreeable solution. The chairman further noted that standardization could only occur after consensus had been reached. The same situation occurred at the Ninth Conference in 2007. South Korea and North Korea both proposed a resolution by the UNCSGN, while Japan expressed a desire to settle the matter outside of the conference, and the Committee urged the members to seek a mutual agreement.
On 23 April 2004, the United Nations affirmed in a written document to the Japanese government that it will continue using the name Sea of Japan in its official documents. However, it agreed to leave the topic open for further discussion. In a letter to South Korea, it was explained that the UN was not determining the validity of either name, but wished to use the term that is most widely used until the parties resolved the disagreement. The letter further stated, "The use of an appellation by the Secretariat based on the practice is without prejudice to any negotiations or agreements between the interested parties and should not be interpreted as advocating or endorsing any party's position, and can in no way be invoked by any party in support of a particular position in the matter."

On 6 August 2012, representatives from South Korea and North Korea addressed an assembly at the United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names, asking that the names "East Sea" and "Sea of Japan" be used concurrently for the sea. Ferjan Ormeling Jr., chairman of the conference, responded that the organization had no authority to decide the issue and requested that the involved countries resolve the differences over the name amongst themselves.
Other countries
Russia calls this sea "Япо́нское мо́ре" (Yapónskoye móre, Japanese Sea). Japan believes that Russia played a major role in establishing this name internationally, as mentioned above. Chinese government websites exclusively use the name 日本海 (rìběnhǎi, 'Japan Sea'). In 2003, the French Defense Ministry issued nautical maps that included both terms Sea of Japan and East Sea. It reverted to Sea of Japan as a single name in the map issued in 2004. The United Kingdom and Germany officially use the Sea of Japan.
The United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) continues to advocate the use of Sea of Japan without qualification in U.S. government publications. The World Factbook published by the Central Intelligence Agency follows the BGN's guidance. On 8 August 2011, a spokesman for the United States Department of State stated that the United States Board on Geographic Names considered the official name of the sea to be "Sea of Japan".
Despite the U.S. government's position for the single use of Sea of Japan, in 2011, Virginia state lawmaker David W. Marsden, acting on behalf of Korean-American voters, introduced a bill to the education panel of the Senate of Virginia that would have required public school textbooks to include both "Sea of Japan" and "East Sea" as names. The panel rejected the bill by an 8–7 vote on 26 January 2012. The issue was revisited two years later on 3 February 2014, with the Education Committee of the Virginia House of Delegates passing legislation to use both "Sea of Japan" and "East Sea" in school textbooks. This bill, House Bill (BH) No. 11, was finally passed by the Virginia House of Delegates on 6 February 2014, signed by the Governor on 28 March and became effective on 1 Juy. The bill states that "all textbooks approved by the Board of Education pursuant to §22.1-238 of the Code of Virginia, when referring to the Sea of Japan, shall note that it is also referred to as the East Sea."
On 29 June 2012, Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs Kurt M. Campbell affirmed the BGN's position in his response, published on the White House website, to the We the People petition concerning the usage of "Sea of Japan", in which he stated, "It is longstanding United States policy to refer to each sea or ocean by a single name. This policy applies to all seas, including those bordered by multiple countries that may each have their own names for such bodies of water. Concerning the body of water between the Japanese archipelago and the Korean Peninsula, longstanding U.S. policy is to refer to it as the "Sea of Japan". He also stated, "We are aware the Republic of Korea refers to the body of water as the 'East Sea,' and the United States is not asking the Republic of Korea to change its nomenclature. U.S. usage of the 'Sea of Japan' in no way implies an opinion regarding any issue related to sovereignty."
Contrary to the position of a few major countries, a number of maps, encyclopedias, and other publications have switched to using both names. Today, it is easy to find examples of the concurrent use of the name "East Sea" and "Sea of Japan" on maps and in textbooks and prominent news media's articles both online and offline. For example, National Geographic Map Policy states that the sea between Japan and Korea is called the Sea of Japan by the Japanese and the East Sea by Koreans.
For example, the Manual of Style of the National Geographic Society states that disputed place-names in international waters or jointly controlled by two or more countries should use the conventional name first with other names following in parentheses.
In 2006, Google put both names on Google Earth, using East Sea near the Korean coast and Sea of Japan near the Japanese coast. Encyclopædia Britannica states that Sea of Japan is also known as and called by East Sea. On the encyclopedia's map, Sea of Japan and East Sea are used concurrently.
See also
- Anti-Japanese sentiment in Korea
- Anti-Korean sentiment in Japan
- Japanese-Korean disputes
- Geographical renaming
- Persian Gulf naming dispute
References
- ^ "The Issue of the Name of the Sea of Japan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan.
- "IHO rejects Japan's proposal to rule out East Sea name" Archived 5 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Yonhap News Agency, 26 April 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- Kyodo News, "Sea of Japan name dispute rolls on Archived 10 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine", Japan Times, 3 May 2012, p. 3; Kyodo News, "IHO nixes 'East Sea' name bid", Japan Times, 28 April 2012, p. 2; Rabiroff, Jon, and Yoo Kyong Chang, "Agency rejects South Korea's request to rename Sea of Japan Archived 20 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine", Stars and Stripes, 28 April 2012, p. 5.
- "IHO delays decision on Korea's request for East Sea name to 2017". The Korea Herald. 26 April 2012. Archived from the original on 11 October 2016. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- "IHO Puts Off East Sea Decision Until 2017" Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine, The Chosun Ilbo, 26 April 2012, Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- トンヘ(東海)の呼称歴史は2000年? 2千年前発祥説が多い韓国. KoreaWorldTimes (in Japanese). 23 November 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ "East Sea". South Korea Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. 2010. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- "Naming of the East Sea". Northeast Asian History Foundation. 2007. Archived from the original on 15 August 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- "Legitimacy for Restoring the Name East Sea" (PDF). South Korea Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. May 2009. Retrieved 28 September 2010.
- ^ "Recent Changes in Geographical Names of Korean Cities and other Developments" (PDF). Working Paper 48 of the UNGEGN Twentieth Session. United Nations. 17–28 January 2000. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- "[East Sea (1)] East Sea/Sea of Japan, what is the problem?". The Korea Herald. 23 May 2010. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- "Issue of naming of the Sea of Japan (Study in the Russian Federation) Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) of Japan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. 2010. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- ^ "Japanese Basic Position on the Naming of the "Japan Sea"". Japan Coast Guard. 1 March 2005. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- Adam Johann von Krusenstern (1813). Voyage Round the World.
- "A survey of historical maps from around the world". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan.
- "Naming of the East Sea". Northeast Asian History Foundation. 2007. Archived from the original on 15 August 2011. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ "The Issue of the Naming of the Sea of Japan (Study in Germany)". SEA OF JAPAN. Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. 2010. Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- "Issue of naming of the Sea of Japan (Study in the Russian Federation)". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. 2010. Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ^ "Sea of Japan" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. February 2009. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
- "Sea of Japan" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. August 2002. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- "VN, China pledge to solve East Sea issue". Socialist Republic of Việt Nam. 20 April 2011.
- "VN asserts sea and island sovereignty". Socialist Republic of Việt Nam. 9 June 2011.
- "The Fourth Round of Consultation on East Sea between China and Japan to Be Held". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of People's Republic of China. 2 March 2006.
- "Chinese Premier Meets with Japanese Prime Minister Taro Aso". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of People's Republic of China. 24 October 2008.
- "IHO Special Publication 23". Korean Hydrographic and Oceanographic Administration. 2004. Archived from the original on 30 December 2012. Retrieved 10 September 2010.
- "Major Historical Background Information". Japan Coast Guard. 29 January 2009. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- "Second Session of the IHO Assembly (A-2)" (PDF). IHO. Retrieved 23 August 2024.
- "Member States of the United Nations". United Nations. 3 July 2006. Retrieved 10 September 2010.
- Report of the Sixth UNCSGN Conference, United Nations, 1993, pp. 21–22, United Nations Publication E.93.I.23
- "Report of the Seventh UNCSGN Conference" (PDF). United Nations. 13–22 January 1998. p. 18. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- "Eighth UNCSGN Conference Report" (PDF). United Nations. 27 August – 5 September 2002. pp. 29–30. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- "Ninth UNCSGN Conference Report" (PDF). United Nations. 21–30 August 2007. pp. 29–30. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- "The Policy of the United Nations Concerning the Naming of 'Sea of Japan'". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. June 2004. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- "UN and U.S. use "Sea of Japan"". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- "The Practice of the Secretariat of the United Nations Concerning the Naming of the Sea Area between Korea and Japan, The Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade of South Korea". South Korea Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- Jiji Press, "Genba stands firm on Senkakus; Koreas in 'East Sea' push Archived 4 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine", Japan Times, 8 August 2012, p. 2
- "ATLAS OF OCEANOGRAPHY Bering Sea, Sea of Okhotsk and Sea of Japan" (in Russian). Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Archived from the original on 15 November 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- "Seas of the USSR" (in Russian). A. D. Dobrovolsky, BS Zalogin. Univ. Press, 1982. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- 韓国国会議員、「日本海」呼称廃止を中国に求める [A South Korean lawmaker calls on China to abolish the name of the "Sea of Japan"] (in Japanese). Japanese.China.org.cn. 20 April 2011. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- "Q&A on the Issue of the Name "Sea of Japan"". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. February 2003. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- フランス海軍海洋情報部刊行の海図目録 -「日本海」単独標記に- (PDF) (in Japanese). Japan Coast Guard. 13 July 2004. Retrieved 22 November 2010.
- "FAQ". Central Intelligence Agency. 2010. Archived from the original on 12 June 2007. Retrieved 8 November 2010. Note: expand the "Policies" tab to see details.
- Jiji Press, "Virginia sinks sea-renaming plan", Japan Times, 31 January 2012, p. 2.
- "'East Sea' textbook directive fails Senate panel". Associated Press. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- "Virginia nears law on Sea of Japan". The Japan News. Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 24 February 2014.
- "Response to We the People Petition on the Sea of Japan Naming Issue". whitehouse.gov. 29 June 2012. Retrieved 3 July 2012 – via National Archives.
- Kyodo News, "U.S. to keep Sea of Japan on books Archived 22 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine", Japan Times, 4 July 2012, p. 2
- "Response to We the People Petition on the Sea of Japan Naming Issue". whitehouse.gov. 29 June 2012. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- "National Geographic Map Policy". National Geographic Society. Retrieved 23 August 2024.
- Cho, Jin-Seo (2 August 2006). "Google asked to identify Korea correctly". The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 20 May 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- "Britannica-Sea of Japan/East Sea". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 23 August 2024.
External links
Japan
- "The Issue of Name "Sea of Japan"". MOFA, Japan.
- MOFA, Japan (4 April 2014). ""Sea of Japan" - A globally established name". Archived from the original on 16 November 2021 – via YouTube.
South Korea
- 대한민국외교부 (20 February 2017). "East Sea, The Name from the Past, of the Present, and for the Future". Archived from the original on 16 November 2021 – via YouTube.