| Revision as of 11:52, 23 December 2009 editDouglasdzone (talk | contribs)42 edits →History← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:35, 6 August 2024 edit undoJoeNMLC (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users114,592 edits Successfully de-orphaned!♦ Wikiproject Orphanage: You can help!♦; add link at Business model article | ||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Context|date=November 2023}} | |||
| {{Article issues|orphan =November 2009|wikify =November 2009|date=December 2009}} | |||
| '''Dynamic Business Modeling''' ("DBM") describes the ability to automate ]s within an open framework. The |
'''Dynamic Business Modeling''' ("DBM") describes the ability to automate ]s within an open framework. The independent analyst firm ] has recently called Dynamic Business Modeling "critical for ] solutions to succeed". | ||
| Dynamic Business Modeling is based on principles wherein the ] of an ] is managed independently from the ]s that automate the services and processes defined in the business logic. Business modeling and integration (which itself is defined as part of the business model) are defined in |
Dynamic Business Modeling is based on principles wherein the ] of an ] is managed independently from the ]s that automate the services and processes defined in the business logic. Business modeling and integration (which itself is defined as part of the business model) are defined in a business logic layer, allowing underlying application servers to be business logic agnostic and therefore need no business driven customization. DBM applied correctly should reduce both the cost and risk in the initial implementation and its future evolution of systems. | ||
| Previous generations of IT systems (from 1990 to approximately 2001) were designed to address specific business models and regulatory practices and no value was given to ]–] segregation. These systems provided value by automating predefined business models (commonly referred to as "off-the-shelf"). As a result, they implicitly drove ] where DBM states that they should be driven by it. By being "predefined" they do not: | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | * openly incorporate business changes in the business landscape of an industry | ||
| ⚫ | Dynamic Business modeling is suited for open automation of strategy-driven business models. By removing the need for |
||
| ⚫ | * leverage potential business models that new technologies allow | ||
| ⚫ | Dynamic Business modeling is suited for open automation of strategy-driven business models. By removing the need for customization of core application servers it is postulated as more ], rapidly deployed and evolveable. Dynamic Business Modeling was initially described (though applied much earlier in practice) by Doug Zone at MetraTech Corp. in reference to the billing segment of the enterprise software market. "Service Oriented Applications" (also known as "service based applications") coined by IBM describe potential methodologies to achieve DBM. | ||
| "Service Oriented Applications" coined by IBM would implicitly be compliant with DBM. | |||
| ==Technical definition == | ==Technical definition == | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
| ==Business definition == | ==Business definition == | ||
| Dynamic Business Modeling is defined as the enabler of a strategic advantage achieved by focused ] in any aspect of business (from marketing to finance to operations). This differentiation is achieved through how business is conducted: openly and dynamically defining the business model. ] – human, physical and intellectual – must be aimed at allowing the definition of the business model to be dynamic. | Dynamic Business Modeling is defined as the enabler of a strategic advantage achieved by focused ] in any aspect of business (from marketing to finance to operations). This differentiation is achieved through how business is conducted: openly and dynamically defining the business model. ] – human, physical and intellectual – must be aimed at allowing the definition of the business model to be dynamic. | ||
| Dynamic Business Modeling recognises that businesses dynamically evolve, |
Dynamic Business Modeling recognises that businesses dynamically evolve, re-inventing their (business) models to achieve strategic advantage. DBM posits that the role of ] (CRM, billing, ERP) is to dynamically automate and advance the business processes and services that lie behind these Business models. | ||
| ⚫ | ==History== | ||
| ⚫ | ==Core principles == | ||
| The term was first used to describe the architecture of MetraNet, a ], ]ing, ] and ] from MetraTech Corp. | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | ==Core principles == | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | # Business strategy drives selection of business models. | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | # These business models drive the design of underlying processes and services. | ||
| ⚫ | #* ''Business Analysis is critical: Any number of models can address a strategic imperative. But the best models, services and processes will exploit existing business capabilities (human, IT and physical), the areas where change is possible and the areas where ] will make most change possible at the lowest cost.'' | ||
| # Enterprise software automates these services and processes. | |||
| # DBM enables change: Strategic adeptness requires tuning and/or the re-definition of the present Business Model. | |||
| ⚫ | #* ''The business must begin with the principle that allows rapid tuning and/or re-definition of the underlying services and processes. This must apply at human and technological levels''. | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ==Key success criteria == | ==Key success criteria == | ||
| # Open modeling capabilities: | |||
| ⚫ | #* ''Dynamic Business Modeling requires ] and ]s that automate the business model – not just a business model.'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Ease of modeling: | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | #* ''Definition and ] of new and evolved business services and processes must be accessible at the ] level. Ideally the models and its services and processes are defined and stored in open ] oriented data (for example ].)'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Open integration: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | #* ''Dynamic Business Modeling must work with processes and services (both automated and human) that are NOT dynamic. These fixed constraints are not external to the new business model but are part of its fabric. IT Architecture and Enterprise applications must be able to incorporate, embed and/or build upon these existing processes and services.'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Robustness: | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | #* ''Regardless of the dynamism of the business model. The automated and human-based business processes and services must have all the robustness of long standing static processes and services. Dynamic IT automation must have a full ] capability, reprocessing ability and standards compliance (i.e. PCI).'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Perpetual dynamism: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | #* ''Automation is never finished. Processes and services change and are added constantly. IT Architecture and Enterprise applications must be designed to prevent “lock down” where the service and process automation on “Day One” is so tightly coupled that only minor evolution is economic. SOA principles of openness and loss coupling must be applied inside business applications.'' | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ==Best practice == | ==Best practice == | ||
| # DBM is service-based: | |||
| ⚫ | #* '' The application should be based on the principle that processes and integration can be de-constructed internally into services.'' | ||
| # Services and processes are loosely coupled: | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | #* ''Changing one should not impact the others.'' | ||
| # Services and process definitions are open: | |||
| ⚫ | #* ''And accessible to a business analyst. Ideally definitions are kept in metadata.'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Application servers must be free of embedded business logic: | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | #* ''For services, processes, data, workflows alike.'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Dynamic documentation is a feature: | ||
| 3. Services and process definitions are open: | |||
| ⚫ | #* ''As the model evolves the documentation must evolve as well. The application should allow the business analyst to document at service level and then generate a cohesive document that encompasses entire model.'' | ||
| ⚫ | # Business Analyst Interface is friendly and flexible: | ||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | #* ''The application must provide a way to put the definition of services and processes in analyst terms – using universal concepts such as flows and tables. The interface should encourage documentation, warn on inconsistencies, and allow testing.'' | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | * |
||
| ⚫ | ==History== | ||
| ⚫ | ==Graphics== | ||
| The term was first used to describe the functionality of MetraNet, a fourth-generation ] and ] product offered by ] Corp. MetraNet addresses DBM by service orientation, and unlike traditional charging and billing systems, it is not hard-coded to particular charging schemes or measurement technologies. | |||
| ⚫ | <gallery> | ||
| ⚫ | ==Graphics== |
||
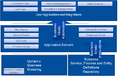
| ⚫ | File:Dynamic Business Modeling.png|Dynamic Business Modeling | ||
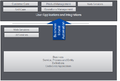
| ⚫ | File:Non Dynamic Business Modeling.png|Non-Dynamic Business Modeling | ||
| ⚫ | <gallery> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| </gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| <references /> | <references /> | ||
| http://ralyx.inria.fr/2008/Raweb/triskell/triskell.pdf | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| *Gartner Dataquest Insight: Telecommunications BSS Software Solutions Can Help Other Industries Improve Efficiency | *Gartner Dataquest Insight: Telecommunications BSS Software Solutions Can Help Other Industries Improve Efficiency {{dead link|date=December 2021|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:35, 6 August 2024
| This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. Please help improve the article by providing more context for the reader. (November 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Dynamic Business Modeling ("DBM") describes the ability to automate business models within an open framework. The independent analyst firm Gartner has recently called Dynamic Business Modeling "critical for BSS solutions to succeed".
Dynamic Business Modeling is based on principles wherein the business logic of an application is managed independently from the application servers that automate the services and processes defined in the business logic. Business modeling and integration (which itself is defined as part of the business model) are defined in a business logic layer, allowing underlying application servers to be business logic agnostic and therefore need no business driven customization. DBM applied correctly should reduce both the cost and risk in the initial implementation and its future evolution of systems.
Previous generations of IT systems (from 1990 to approximately 2001) were designed to address specific business models and regulatory practices and no value was given to logic–infrastructure segregation. These systems provided value by automating predefined business models (commonly referred to as "off-the-shelf"). As a result, they implicitly drove business strategy where DBM states that they should be driven by it. By being "predefined" they do not:
- openly incorporate business changes in the business landscape of an industry
- leverage potential business models that new technologies allow
Dynamic Business modeling is suited for open automation of strategy-driven business models. By removing the need for customization of core application servers it is postulated as more cost efficient, rapidly deployed and evolveable. Dynamic Business Modeling was initially described (though applied much earlier in practice) by Doug Zone at MetraTech Corp. in reference to the billing segment of the enterprise software market. "Service Oriented Applications" (also known as "service based applications") coined by IBM describe potential methodologies to achieve DBM.
Technical definition
Dynamic Business Modeling is defined as the automation of Enterprise Business Models based on the principle that the model's underlying business processes and business services need to be dynamically and openly definable and re-definable.
Business definition
Dynamic Business Modeling is defined as the enabler of a strategic advantage achieved by focused differentiation in any aspect of business (from marketing to finance to operations). This differentiation is achieved through how business is conducted: openly and dynamically defining the business model. Capital investment – human, physical and intellectual – must be aimed at allowing the definition of the business model to be dynamic.
Dynamic Business Modeling recognises that businesses dynamically evolve, re-inventing their (business) models to achieve strategic advantage. DBM posits that the role of enterprise software (CRM, billing, ERP) is to dynamically automate and advance the business processes and services that lie behind these Business models.
History
The term was first used to describe the architecture of MetraNet, a charging, billing, settlement and customer care from MetraTech Corp.
Core principles
- Business strategy drives selection of business models.
- These business models drive the design of underlying processes and services.
- Business Analysis is critical: Any number of models can address a strategic imperative. But the best models, services and processes will exploit existing business capabilities (human, IT and physical), the areas where change is possible and the areas where investment will make most change possible at the lowest cost.
- Enterprise software automates these services and processes.
- DBM enables change: Strategic adeptness requires tuning and/or the re-definition of the present Business Model.
- The business must begin with the principle that allows rapid tuning and/or re-definition of the underlying services and processes. This must apply at human and technological levels.
Key success criteria
- Open modeling capabilities:
- Dynamic Business Modeling requires IT architecture and enterprise applications that automate the business model – not just a business model.
- Ease of modeling:
- Definition and automation of new and evolved business services and processes must be accessible at the business analysis level. Ideally the models and its services and processes are defined and stored in open business analyst oriented data (for example metadata.)
- Open integration:
- Dynamic Business Modeling must work with processes and services (both automated and human) that are NOT dynamic. These fixed constraints are not external to the new business model but are part of its fabric. IT Architecture and Enterprise applications must be able to incorporate, embed and/or build upon these existing processes and services.
- Robustness:
- Regardless of the dynamism of the business model. The automated and human-based business processes and services must have all the robustness of long standing static processes and services. Dynamic IT automation must have a full audit capability, reprocessing ability and standards compliance (i.e. PCI).
- Perpetual dynamism:
- Automation is never finished. Processes and services change and are added constantly. IT Architecture and Enterprise applications must be designed to prevent “lock down” where the service and process automation on “Day One” is so tightly coupled that only minor evolution is economic. SOA principles of openness and loss coupling must be applied inside business applications.
Best practice
- DBM is service-based:
- The application should be based on the principle that processes and integration can be de-constructed internally into services.
- Services and processes are loosely coupled:
- Changing one should not impact the others.
- Services and process definitions are open:
- And accessible to a business analyst. Ideally definitions are kept in metadata.
- Application servers must be free of embedded business logic:
- For services, processes, data, workflows alike.
- Dynamic documentation is a feature:
- As the model evolves the documentation must evolve as well. The application should allow the business analyst to document at service level and then generate a cohesive document that encompasses entire model.
- Business Analyst Interface is friendly and flexible:
- The application must provide a way to put the definition of services and processes in analyst terms – using universal concepts such as flows and tables. The interface should encourage documentation, warn on inconsistencies, and allow testing.
Graphics
References
http://ralyx.inria.fr/2008/Raweb/triskell/triskell.pdf
External links
- Gartner Dataquest Insight: Telecommunications BSS Software Solutions Can Help Other Industries Improve Efficiency