| Revision as of 21:01, 22 January 2011 editSpace Cadet (talk | contribs)8,095 edits →Use← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 23:35, 26 July 2024 edit undoSmokefoot (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers74,208 edits →Synthesis and reactivity: reformat ref | ||
| (59 intermediate revisions by 35 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Redirect|Meerwein's salt||Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate}} | |||
| {{chembox | |||
| {{Chembox | |||
| | Reference = | |||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | Name = Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | ImageFile = Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate.png | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 409427530 | |||
| | ImageSize = 280px | |||
| | |
| ImageFile = Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate.png | ||
| | ImageFile_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | |||
| | ImageSizeL1 = 170px | |||
| | ImageSize = 210 | |||
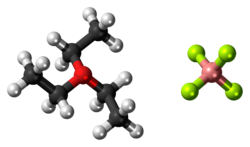
| | ImageNameL1 = Ball-and-stick model of the triethyloxonium cation | |||
| | ImageAlt = Skeletal formula of triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate | |||
| | ImageFileR1 = Tetrafluoroborate-ion-3D-balls.png | |||
| | ImageFile1 = Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate 3D ball.png | |||
| | ImageNameR1 = Ball-and-stick model of the tetrafluoroborate anion | |||
| | ImageFile1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | |||
| | IUPACName = Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate | |||
| | ImageSize1 = 250 | |||
| | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| | ImageAltL1 = Ball and stick models of the component ions of triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate | |||
| | CASNo = 368-39-8 | |||
| | IUPACName = Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate | |||
| | SMILES = | |||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| | RTECS = | |||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| | EINECS = | |||
| | CASNo = 368-39-8 | |||
| }} | |||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | |||
| | UNII = Z0B19DD36J | |||
| | Formula = C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>15</sub>BF<sub>4</sub>O | |||
| | PubChem = 2723982 | |||
| | MolarMass = 189,99 g/mol | |||
| | |
| ChemSpiderID = 2006158 | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | MeltingPt = 91–92 °C | |||
| | |
| UNNumber = 3261 | ||
| | |
| Beilstein = 3598090 | ||
| | SMILES = F(F)(F)F.CC(CC)CC | |||
| }} | |||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C6H15O.BF4/c1-4-7(5-2)6-3;2-1(3,4)5/h4-6H2,1-3H3;/q+1;-1 | |||
| | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | RPhrases = 34-40 | |||
| | StdInChIKey = IYDQMLLDOVRSJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| | SPhrases = 23-24/25-26-36/37/39-45 | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | |||
| | Formula = {{chem2|+−}} | |||
| | C=6 | H=15 | B=1 | F=4 | O=1 | |||
| | MeltingPtC = 91 to 92 | |||
| | Solubility = Reacts | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section3={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | Hazards_ref = <ref>{{cite web |title=Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate |url=https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/AU/en/product/SIAL/90520 |publisher=Sigma Aldrich}}</ref> | |||
| | GHSPictograms = {{GHS05}} | |||
| | GHSSignalWord = Danger | |||
| | HPhrases = {{H-phrases|314}} | |||
| | PPhrases = {{P-phrases|260|280|303+361+353|304+340+310|305+351+338|310|363}} | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate''' is the ] ] compound with the formula {{chem2|+−}}. It is often called '''Meerwein's reagent''' or '''Meerwein's salt''' after its discoverer ].<ref>{{cite journal | title = Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, I |author1=H. Meerwein |author2=G. Hinz |author3=P. Hofmann |author4=E. Kroning |author5=E. Pfeil |name-list-style=amp | journal = Journal für Praktische Chemie| volume = 147 | issue = 10–12| pages = 257 | year = 1937| doi = 10.1002/prac.19371471001}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | title = Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, II |author1=H. Meerwein |author2=E. Bettenberg |author3=H. Gold |author4=E. Pfeil |author5=G. Willfang |name-list-style=amp | journal = Journal für Praktische Chemie| volume = 154 | issue = 3–5| pages = 83 | year = 1940| doi = 10.1002/prac.19391540305}}</ref> Also well known and commercially available is the related ]. The compounds are white solids that dissolve in polar organic solvents. They are strong ]s. Aside from the ] salt, many related derivatives are available.<ref>Hartwig Perst, Dave G. Seapy "Triethyloxonium Tetrafluoroborate" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008. {{doi|10.1002/047084289X.rt223.pub2}}. Article Online Posting Date: March 14, 2008</ref> | |||
| '''Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate''' is the ] ] compound with the formula BF<sub>4</sub>. It is often called Meerwein's reagent after its discoverer ].<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| | title = Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, I | |||
| | author = H. Meerwein, G. Hinz, P. Hofmann, E. Kroning, and E. Pfeil | |||
| | journal = Journal für Praktische Chemie | |||
| | volume = 147 | |||
| | issue = 10-12 | |||
| | pages = 257 | |||
| | year = 1937 | |||
| | url = | |||
| | doi = 10.1002/prac.19371471001 }}{{cite journal | |||
| | title = Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, II | |||
| | author = H. Meerwein, E. Bettenberg, H. Gold, E. Pfeil, and G. Willfang | |||
| | journal = Journal für Praktische Chemie | |||
| | volume = 154 | |||
| | issue = 3-5 | |||
| | pages = 83 | |||
| | year = 1940 | |||
| | url = | |||
| | doi = 10.1002/prac.19391540305}}</ref> Also well known and commercially available is the related ]. The compounds are exceptionally strong ]s. Aside from the BF<sub>4</sub><sup>−</sup> salt, many related derivatives are available with varying solubilities and stabilities.<ref>Hartwig Perst, Dave G. Seapy "Triethyloxonium Tetrafluoroborate" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis | |||
| John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008. {{DOI|10.1002/047084289X.rt223.pub2}}. Article Online Posting Date: March 14, 2008</ref> | |||
| ==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis and reactivity== | ||
| Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is prepared from ], ], and ]:<ref>{{OrgSynth | author = H. Meerwein | |
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is prepared from ], ], and ]:<ref>{{OrgSynth | author = H. Meerwein | volume = 46 | year = 1966| page = 113 | doi = 10.15227/orgsyn.046.0113| title = Triethyloxonium fluoroborate}}</ref> | ||
| :{{chem2|4 Et2O*BF3 + 2 Et2O + 3 C2H3OCH2Cl → 3 +− + B(OCH(CH2Cl)CH2OEt)3}} | |||
| : 4 Et<sub>2</sub>O·BF<sub>3</sub> + 2 Et<sub>2</sub>O + 3 C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>3</sub>(O)CH<sub>2</sub>Cl → 3 Et<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>BF<sub>4</sub><sup>−</sup> + B<sub>3</sub> | |||
| The trimethyloxonium salt is available from ] via an analogous route.<ref>{{OrgSynth | author = T. J. Curphey | collvol = 6 | year = 1988| collvolpages = 1019 | prep = CV6P1019| title = Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate}}</ref> |
where the Et stands for ]. The trimethyloxonium salt is available from ] via an analogous route.<ref>{{OrgSynth | author = T. J. Curphey | collvol = 6 | year = 1988| collvolpages = 1019 | prep = CV6P1019| title = Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate}}</ref> These salts do not have long shelf-lives at room temperature. They degrade by hydrolysis: | ||
| :{{chem2|+− + H2O → Et2O + EtOH + −]]}} | |||
| :<sup>+</sup>BF<sub>4</sub><sup>−</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O → (CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>O + CH<sub>3</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>OH + ] | |||
| The propensity of |
The propensity of trialkyloxonium salts for alkyl-exchange can be advantageous. For example, trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate, which reacts sluggishly due to its low solubility in most compatible solvents, may be converted in situ to higher alkyl/more soluble oxoniums, thereby accelerating alkylation reactions.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Vartak A.P. |author2=Crooks P.A.|name-list-style=amp | title = A Scalable Enantioselective synthesis of the alpha2-adrenergic Agonist, Lofexidine | journal = ] | year = 2009 | volume = 13 | issue = 3 | pages = 415–419 | doi = 10.1021/op8002689}}</ref> | ||
| This reagent is useful for esterification of carboxylic acids under conditions where acid-catalyzed reactions are infeasible: <ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |first1=Douglas J.|last1=Raber|first2=Patrick |last2=Gariano, Jr|first3=Albert O. |last3=Brod|first4=Anne L. |last4=Gariano|first5=Wayne C.|last5=Guida|doi=10.15227/orgsyn.056.0059 |title=Esterification of Carboxylic Acids with Trialkyloxonium Salts: Ethyl and Methyl 4-Acetoxybenzoates |journal=Organic Syntheses |date=1977 |volume=56 |page=59 }}</ref> | |||
| :{{chem2|RCO2H + (C2H5)3OBF4 -> RCO2C2H5 + (C2H5)2O + HBF4}} | |||
| ==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| The structure of triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate has not been characterized by ], but the structure of triethyloxonium ] has been examined. The measurements confirm that the cation is pyramidal with C-O-C angles in the range 109.4°–115.5°. The average C–O distance is 1.49 Å.<ref>{{cite journal |doi=10.1021/ja00373a006|title=Structure of Oxonium Ions: An X-Ray Crystallographic Study of Triethyloxonium Hexafluorophosphate and Triphenyloxonium Tetraphenylborate|year=1982|last1=Watkins|first1=Michael I.|last2=Ip|first2=Wai Man|last3=Olah|first3=George A.|last4=Bau|first4=Robert|journal=Journal of the American Chemical Society|volume=104|issue=9|pages=2365–2372}}</ref> | |||
| The compound features pyramidal oxonium cation and a tetrahedral fluoroborate anion. Reflecting its ionic character, the salt dissolves in polar but inert solvents such as ], ], and ]. | |||
| ==Safety== | ==Safety== | ||
| Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is a strong alkylating agent, although the hazards are diminished because it is non-volatile. It releases strong acid upon contact with water. |
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is a very strong alkylating agent, although the hazards are diminished because it is non-volatile. It releases strong acid upon contact with water. The properties of the methyl derivative are similar. | ||
| ==Use== | |||
| Alkylating agent for nucleophilic functional groups in organic synthesis. | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| <references/> | <references/> | ||
| {{Tetrafluoroborates}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| {{chem-stub}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 23:35, 26 July 2024
"Meerwein's salt" redirects here. For other uses, see Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate.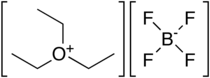
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 3598090 |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.096 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3261 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | [(CH3CH2)3O][BF4] |
| Molar mass | 189.99 g·mol |
| Melting point | 91 to 92 °C (196 to 198 °F; 364 to 365 K) |
| Solubility in water | Reacts |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338, P310, P363 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic oxonium compound with the formula [(CH3CH2)3O][BF4]. It is often called Meerwein's reagent or Meerwein's salt after its discoverer Hans Meerwein. Also well known and commercially available is the related trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. The compounds are white solids that dissolve in polar organic solvents. They are strong alkylating agents. Aside from the BF−4 salt, many related derivatives are available.
Synthesis and reactivity
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is prepared from boron trifluoride, diethyl ether, and epichlorohydrin:
- 4 Et2O·BF3 + 2 Et2O + 3 C2H3OCH2Cl → 3 [Et3O][BF4] + B(OCH(CH2Cl)CH2OEt)3
where the Et stands for ethyl. The trimethyloxonium salt is available from dimethyl ether via an analogous route. These salts do not have long shelf-lives at room temperature. They degrade by hydrolysis:
- [Et3O][BF4] + H2O → Et2O + EtOH + H[BF4]
The propensity of trialkyloxonium salts for alkyl-exchange can be advantageous. For example, trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate, which reacts sluggishly due to its low solubility in most compatible solvents, may be converted in situ to higher alkyl/more soluble oxoniums, thereby accelerating alkylation reactions.
This reagent is useful for esterification of carboxylic acids under conditions where acid-catalyzed reactions are infeasible:
- RCO2H + (C2H5)3OBF4 → RCO2C2H5 + (C2H5)2O + HBF4
Structure
The structure of triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate has not been characterized by X-ray crystallography, but the structure of triethyloxonium hexafluorophosphate has been examined. The measurements confirm that the cation is pyramidal with C-O-C angles in the range 109.4°–115.5°. The average C–O distance is 1.49 Å.
Safety
Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is a very strong alkylating agent, although the hazards are diminished because it is non-volatile. It releases strong acid upon contact with water. The properties of the methyl derivative are similar.
References
- "Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate". Sigma Aldrich.
- H. Meerwein; G. Hinz; P. Hofmann; E. Kroning & E. Pfeil (1937). "Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, I". Journal für Praktische Chemie. 147 (10–12): 257. doi:10.1002/prac.19371471001.
- H. Meerwein; E. Bettenberg; H. Gold; E. Pfeil & G. Willfang (1940). "Über Tertiäre Oxoniumsalze, II". Journal für Praktische Chemie. 154 (3–5): 83. doi:10.1002/prac.19391540305.
- Hartwig Perst, Dave G. Seapy "Triethyloxonium Tetrafluoroborate" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt223.pub2. Article Online Posting Date: March 14, 2008
- H. Meerwein (1966). "Triethyloxonium fluoroborate". Organic Syntheses. 46: 113. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.046.0113.
- T. J. Curphey (1988). "Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 6, p. 1019.
- Vartak A.P. & Crooks P.A. (2009). "A Scalable Enantioselective synthesis of the alpha2-adrenergic Agonist, Lofexidine". Org. Process Res. Dev. 13 (3): 415–419. doi:10.1021/op8002689.
- Raber, Douglas J.; Gariano, Jr, Patrick; Brod, Albert O.; Gariano, Anne L.; Guida, Wayne C. (1977). "Esterification of Carboxylic Acids with Trialkyloxonium Salts: Ethyl and Methyl 4-Acetoxybenzoates". Organic Syntheses. 56: 59. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.056.0059.
- Watkins, Michael I.; Ip, Wai Man; Olah, George A.; Bau, Robert (1982). "Structure of Oxonium Ions: An X-Ray Crystallographic Study of Triethyloxonium Hexafluorophosphate and Triphenyloxonium Tetraphenylborate". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 104 (9): 2365–2372. doi:10.1021/ja00373a006.
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the tetrafluoroborate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||