| Revision as of 00:40, 6 February 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{drugbox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 18:04, 21 October 2024 edit undoJWBE (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users10,111 edits removed Category:Phenols; added Category:Hydroxyarenes using HotCat | ||
| (43 intermediate revisions by 33 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Chemical compound}} | |||
| {{drugbox | verifiedrevid = 410808162 | |||
| {{Drugbox | |||
| | | |||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | IUPAC_name = 3,6α-dihydroxy- 4,5α-epoxy- 7,8-didehydromorphinan | |||
| | |
| Watchedfields = changed | ||
| | |
| verifiedrevid = 412254473 | ||
| | |
| IUPAC_name = 3,6α-Dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-7,8-didehydromorphinan | ||
| | |
| image = Normorphine.svg | ||
| | |
| width = 180 | ||
| | |
<!--Clinical data-->| tradename = | ||
| | |
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | ||
| ⚫ | | pregnancy_US = <!-- A / B / C / D / X --> | ||
| ⚫ | | IUPHAR_ligand = 1630 | ||
| | |
| pregnancy_category = | ||
| | |
| legal_AU = S9 | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_BR = A1 | ||
| | molecular_weight = 271.311 g/mol | |||
| | legal_BR_comment = <ref>{{Cite web |author=Anvisa |author-link=Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency |date=2023-03-31 |title=RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial |trans-title=Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control|url=https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-rdc-n-784-de-31-de-marco-de-2023-474904992 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803143925/https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-rdc-n-784-de-31-de-marco-de-2023-474904992 |archive-date=2023-08-03 |access-date=2023-08-16 |publisher=] |language=pt-BR |publication-date=2023-04-04}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | | bioavailability = | ||
| | |
| legal_CA = Schedule I | ||
| ⚫ | | legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD / Class A, B, C --> | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | legal_US = Schedule I | |||
| | legal_DE = Anlage I | |||
| | dependency_liability = High | |||
| ⚫ | | routes_of_administration = <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | ||
| ⚫ | | bioavailability = | ||
| ⚫ | | protein_bound = | ||
| | metabolism = | |||
| | elimination_half-life = | | elimination_half-life = | ||
| | excretion = | | excretion = <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | |
| CAS_number = 466-97-7 | ||
| | ATC_prefix = none | |||
| | pregnancy_category= | |||
| | ATC_suffix = | |||
| | legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S3 / S4 / S5 / S6 / S7 / S8 / S9 --> | |||
| | PubChem = 5462508 | |||
| | legal_CA = <!-- / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| | DrugBank = | |||
| ⚫ | | legal_UK |
||
| | |
| KEGG = C11785 | ||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | ChemSpiderID = 4575435 | |||
| ⚫ | | routes_of_administration = | ||
| ⚫ | | IUPHAR_ligand = 1630 | ||
| | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|changed|FDA}} | |||
| | UNII = XUI1Y24IMI | |||
| <!--Chemical data-->| C = 16 | |||
| | H = 17 | |||
| | N = 1 | |||
| | O = 3 | |||
| | ChEMBL = 1227 | |||
| | synonyms = Normorphine | |||
| | smiles = c1cc(c2c3c1C453(CCN4)(O2)(C=C5)O)O | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C16H17NO3/c18-11-3-1-8-7-10-9-2-4-12(19)15-16(9,5-6-17-10)13(8)14(11)20-15/h1-4,9-10,12,15,17-19H,5-7H2/t9-,10+,12-,15-,16-/m0/s1 | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChIKey = ONBWJWYUHXVEJS-ZTYRTETDSA-N | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | '''Normorphine''' is an ] analogue, the N-demethylated derivative of ], that was first described in the 1950s<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Clark RL, Pessolano AA, Weijlard J, Pfister K | title = N-Substituted epoxymorphinans | journal = Journal of the American Chemical Society | date = October 1953 | volume = 75 | issue = 20 | pages = 4963–7 | doi = 10.1021/ja01116a024 }}</ref> when a large group of N-substituted morphine analogues were characterized for activity. The compound has relatively little opioid activity in its own right,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fraser HF, Wikler A, Van Horn GD, Eisenman AJ, Isbell H | title = Human pharmacology and addiction liability of normorphine | journal = The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics | volume = 122 | issue = 3 | pages = 359–69 | date = March 1958 | pmid = 13539761 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lasagna L, De Kornfeld TJ | title = Analgesic potency of normorphine in patients with postoperative pain | journal = The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics | volume = 124 | issue = 3 | pages = 260–3 | date = November 1958 | pmid = 13588540 }}</ref> but is a useful intermediate which can be used to produce both ]s such as ], and also potent opioid agonists such as ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Yeh SY | title = Urinary excretion of morphine and its metabolites in morphine-dependent subjects | journal = The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics | volume = 192 | issue = 1 | pages = 201–10 | date = January 1975 | pmid = 235634 }}</ref> with its formation from morphine catalyzed by the ] ]s ] and ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Projean D, Morin PE, Tu TM, Ducharme J | title = Identification of CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 as the major cytochrome P450 s responsible for morphine N-demethylation in human liver microsomes | journal = Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems | volume = 33 | issue = 8 | pages = 841–54 | date = August 2003 | pmid = 12936704 | doi = 10.1080/0049825031000121608 | s2cid = 41467595 }}</ref> | ||
| '''Normorphine''' is an ] analogue that is the N-demethylated derivative of ]. | |||
| Normorphine is a controlled substance listed under the Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961 and the laws in various states implementing it; for example, in the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance, with an ACSCN of 9313 and an annual aggregate manufacturing quota of 18 grams in 2014, unchanged from the prior year. The salts in use are the free base hexahydrate (free base conversion ratio 0.715), and hydrochloride (0.833).<ref>{{Cite web | url=http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/quotas/2014/fr0825.htm | title = Quotas - 2014 | work = DEA Diversion Control Division}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | Normorphine has relatively little opioid activity in its own right,<ref>Fraser HF, Wikler A, Van Horn GD, Eisenman AJ, Isbell H |
||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| {{Opioidergics}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:04, 21 October 2024
Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound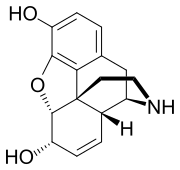 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Normorphine |
| Dependence liability | High |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.712 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 271.316 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Normorphine is an opiate analogue, the N-demethylated derivative of morphine, that was first described in the 1950s when a large group of N-substituted morphine analogues were characterized for activity. The compound has relatively little opioid activity in its own right, but is a useful intermediate which can be used to produce both opioid antagonists such as nalorphine, and also potent opioid agonists such as N-phenethylnormorphine. with its formation from morphine catalyzed by the liver enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2C8.
Normorphine is a controlled substance listed under the Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961 and the laws in various states implementing it; for example, in the United States it is a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance, with an ACSCN of 9313 and an annual aggregate manufacturing quota of 18 grams in 2014, unchanged from the prior year. The salts in use are the free base hexahydrate (free base conversion ratio 0.715), and hydrochloride (0.833).
References
- Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- Clark RL, Pessolano AA, Weijlard J, Pfister K (October 1953). "N-Substituted epoxymorphinans". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 75 (20): 4963–7. doi:10.1021/ja01116a024.
- Fraser HF, Wikler A, Van Horn GD, Eisenman AJ, Isbell H (March 1958). "Human pharmacology and addiction liability of normorphine". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 122 (3): 359–69. PMID 13539761.
- Lasagna L, De Kornfeld TJ (November 1958). "Analgesic potency of normorphine in patients with postoperative pain". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 124 (3): 260–3. PMID 13588540.
- Yeh SY (January 1975). "Urinary excretion of morphine and its metabolites in morphine-dependent subjects". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 192 (1): 201–10. PMID 235634.
- Projean D, Morin PE, Tu TM, Ducharme J (August 2003). "Identification of CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 as the major cytochrome P450 s responsible for morphine N-demethylation in human liver microsomes". Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems. 33 (8): 841–54. doi:10.1080/0049825031000121608. PMID 12936704. S2CID 41467595.
- "Quotas - 2014". DEA Diversion Control Division.